JP2004040726A - Optical cross connect apparatus - Google Patents
Optical cross connect apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2004040726A JP2004040726A JP2002198804A JP2002198804A JP2004040726A JP 2004040726 A JP2004040726 A JP 2004040726A JP 2002198804 A JP2002198804 A JP 2002198804A JP 2002198804 A JP2002198804 A JP 2002198804A JP 2004040726 A JP2004040726 A JP 2004040726A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- failure
- optical
- connect device
- path
- optical cross
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 112
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 30
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 claims description 23
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 16
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 14
- 230000002457 bidirectional effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000644 propagated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Use Of Switch Circuits For Exchanges And Methods Of Control Of Multiplex Exchanges (AREA)
- Optical Communication System (AREA)
Abstract
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は光通信ネットワークにおいて大容量の信号を切替るクロスコネクト装置やADM(Add/Drop Multiplexer)装置など光経路切替装置に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来、光通信ネットワークにおいて回線制御は光信号を電気信号に変換し、電気スイッチにより切替制御を行っていた。しかし、光信号を電気信号に変換する光/電気変換器は高価であり、ますます発展する光通信システムを顧みて、光信号を電気信号に変換することなく切替える方式も提案されており、障害回避策も検討されている。
【0003】
例えば、“特許公開平10−303814号公報”にて提案されている回避策を図9に示す。図において、現用光入力信号101と予備光入力信号102が、光信号切替部106にて切替えられ、光出力信号107に出力される。現用光入力信号101と予備光入力信号102は、それぞれ現用光レベル検出部103と予備光レベル検出部104にて光レベルを検出されており、検出された光レベルは光レベル識別部105に送信される。
現用光入力信号101に障害が発生した場合は、現用光レベル検出部103は現用光入力信号101の光レベルの低下を検出し、光レベル識別部105が光信号切替部106に対し切替信号を送信して、予備光入力信号102に切替える。これにより障害を回避している。
【0004】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、多ポートを有する光クロスコネクトによる光通信ネットワークにおいて、現用パス/予備パスの組合せは固定的なものではなく、柔軟に変化できるものでなければならない。必ずしも現用パスと予備パスが一対一に対応しているわけではなく、一予備対m現用と呼ばれるような予備パスを複数の現用パスで共用するケースにも対応する必要がある。更に、現用の入力(信号)線が増加し、しかも複数現用系に同時不具合が発生しても対処できる構成は、かなり複雑で大規模になるという課題がある。
これに加えて、障害が発生した場合に、迅速な障害検出及び障害復旧が要求される。パスを切替えると伝送路条件が異なることから伝送品質が変化するが、最悪ケースにあわせて障害検出の閾値を設定していたのでは、伝送品質の劣化判定が困難になる。また、迅速な障害復旧には、障害箇所の早急な特定が必須だが、パスが浮動的に変化するため、障害箇所の特定に時間を要するという課題もある。
また、パスは双方向に設定されるが、障害回避のための切替えが起きた時は、1つの双方向パスで現用系と予備系を共用するという状態になってしまい、パスの管理が複雑になるという課題もある。
【0005】
本発明は、このような課題を解決するためになされたものであり、先ずは、入力線数に関らず適切な予備パスの設定により規模を抑えて状態管理が行き届いたクロスコネクト装置を得る。
更に、障害発生時に発生理由に対応した個所を迅速に切り替えて、他への混乱波及がない切替を短時間に終える光クロスコネクト装置を得る。
【0006】
【課題を解決するための手段】
この発明に係る光クロスコネクト装置は、各入力毎に対応して設けた障害検出部と、
複数の入力を複数の出力に切替え選択出力する光信号切替部と、
各検出部対応に光信号切替部に切替え選択指示をするためのプロテクションテーブルと、
障害を検出すると、プロテクションテーブルを参照して光信号切替部を切替制御する判定部とを備えた。
【0007】
また更に、判定部は、他ノードからのパス状況を監視して、この監視したパスの状態に対応してプロテクションテーブルの設定を変更するようにした。
【0008】
また更に、光信号切替部は、1入力m(mは任意の整数)出力の切替器を複数集め、かつ出力側にも障害検出部を設けた構成とした。
【0009】
また更に、障害検出器を光信号切替部の入力側と、出力側に設けた。
【0010】
また更に、プロテクションテーブルは、障害検出時の復旧箇所を指定するようにしたした。
【0011】
また更に、プロテクションテーブルは、必要があれば関連する隣接ノード(隣接入力側、または隣接出力側)へ切替指示する欄を設けた。
【0012】
また更に、障害検出器は、障害判定用の閾値を設け、かつこの閾値を入力または出力毎に変更するようにした。
【0013】
また更に、プロテクションテーブルは、保持時間の設定欄を備え、障害検出時には上記保持時間経過して後、切替制御するようにした。
【0014】
また更に、予備系は、送信と受信の両方に対して用意し、障害検出時には、組となる送信と受信を共に予備系に切替えるようにした。
【0015】
【発明の実施の形態】
実施の形態1.
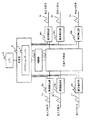
図1は本発明による実施の形態1を示す構成図である。本実施の形態における光クロスコネクト装置は、複数の光入力信号1と、複数の光出力信号2と、光信号を切替る光信号切替部3と、光信号切替部3の前後に配置された障害検出部4と、光信号切替部3の切替制御を行う制御部5と、障害検出部4からの障害情報をもとに障害を認識し障害復旧指示を行う判定部6と、判定部6内にあり障害情報及び復旧動作情報を保持するプロテクションテーブル7と、他の光クロスコネクト装置と制御信号のやりとりを行い、光クロスコネクト装置全体の制御を行うCPU(Central Processing Unit)8から構成される。
図2に本発明の主要要素であるプロテクションテーブル7の内容を示す。図において、障害検出部1〜nは、例えば図1の4aから4nを示していて、S1は障害検出部4aが検出した場合は、光入力信号1bを1aに替えて選択することを示している。本内容はCPU8によって設定されている。各障害検出部が障害を検出した時の復旧動作内容が示されており、複数の障害検出部が同時に障害を検出した場合にも対応している。
【0016】
次に本構成装置の動作について説明する。
伝送路を伝搬してきた光入力信号1は、障害検出部4にて伝送品質のモニタを行い、光信号切替部3に入力される。光信号切替部にて切替られた光信号は、障害検出部4を経て、光出力信号2として伝送路に出力される。各障害検出部4にて検出された障害情報は判定部6に送信される。各障害検出部4からあがってきた障害情報はプロテクションテーブル7上で一対一に対応しており、テーブルを参照することにより、ハードウェア上で復旧動作が決定される。復旧動作として光パスの切替を行う場合には、制御部5を介して、光信号切替部3に切替指示が伝達される。
【0017】
光信号切替部3の詳細構成例を図7に示す。m(現用)対1(予備)選択回路としては、図8(a)の構成でよく、逆に1入力対m出力構成には、図8(b)の構成でよい。従って図8(b)の各入力からの出力を、同一出力を合せることで、図8(c)のマトリックス構成が可能である。こうして少ない予備で多くの現用の不具合に対処することができる。即ちいわゆる1+1システム以外の、通常のシステムでも、少ない予備を共用して信頼性を向上できる。
なお、図2でS1の障害検出があると、単純に予備入力である入力ポート2が入力として選択されるが、図3の[テーブルB]の(パス2)に示すように、この場合は上流に対して現用の入力ポート1を入力ポート2側に切替えて出力することを要求して切り替わっている。
【0018】
以上のように、本実施の形態における光クロスコネクト装置は、予めCPU等で設定された、障害検出部切替え対象入力とを直接対応付けたプロテクションテーブル7を参照して、直ちに切替えを行うので、高速復旧が可能で、しかも事前に優先度等を考慮して信号線の選択を検討しているので、混乱が無い。またハードウェア規模も、入力側の障害検出のみで入力側の選択が可能で、管理が容易である。
以上のように、実施の形態1による光クロスコネクト装置は、ハードウェア的にプロテクションテーブル7を参照することで、復旧動作を決定することができるため、高速な復旧動作を実現することができる。
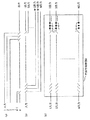
【0019】
本実施の形態における他のプロテクションテーブルを図3に示す。このプロテクションテーブルは、パス(経路)を決める[テーブルA]と、それらのパスに組み込まれた障害検出器の検出状態対応に動作を決める[テーブルB]とに分けてテーブルを持っている。後に述べるように、光信号切替部を含む内部回路の不具合を検出するための出力側検出器40aないし40nがあるが、光信号切替部3が図8(c)のように構成されているとすると、障害検出器は各パスにおいて入力側、出力側に各1ケある。
【0020】
従ってこの構成によると、障害検出器4aないし4nと、障害検出器40aないし40nの検出状況によって障害位置を確定できることにもなる。図3の[テーブルB]の障害箇所はこのことを示している。なお、この[テーブルB]はパスが変更されると、その変更時点で優先度等から次の処理が検討でき、従ってそれに伴って復旧動作指示が変更される。
こうしてパス変更に伴う管理と準備が容易になる。
【0021】
また、障害検出部は光強度の他に、波長、ビットエラーレートをモニタしてもよい。パス設定時におけるノード間のパス設定情報は障害検出部の判定閾値を含み、パス設定毎に判定閾値を変化させる。パス設定状況に応じた最適な判定閾値を設定することができるため、光学部品の劣化等に対する障害を迅速に検出することができる。
また、予めプロテクションテーブル内に設定してある障害位置情報から、障害検出と同時に障害位置を伝達することができるため、障害復旧時のCPUの処理を軽減することができる。
【0022】
復旧動作に他の光クロスコネクト装置の切替が必要になる場合は、CPUが他ノードに対して障害情報を送信しなければならない。図3におけるテーブルBの復旧動作の項目に示すように、プロテクションテーブルには、他ノードに切替指示を送信することという内容が設定されており、障害発生時に判定部からCPUへ障害検出と同時に他ノードへの切替指示を伝達することができるため、復旧動作に取り掛かる時間を短縮することができる。この図では、上流に切替指示しているが、下流に切替指示し、これに基いて下流が指示された予備系に切替るようにしてもよい。
c 光クロスコネクト装置による光通信ネットワークにおいて、パスは固定的なものではなく、クライアントの要求やシステムの稼動状態に従い柔軟に変更しなければならない。そして、パスを変更したときでも、高速なプロテクションを行えることを説明する。
図4は実施の形態1におけるプロテクションテーブルの更新を示す図である。ノード1からノード2にパスが設定されると、ノード1ではパスに障害が起きた時の復旧動作を示したプロテクションテーブル1−1が、ノード2ではプロテクションテーブル2−1が設定される。このパスが解除された時、光信号がなくなるため障害検出部で障害を検出することになるが、パスが解除されているため、ここで検出した障害は復旧動作を必要としないものである。解除前にプロテクションテーブルを、ノード1ではプロテクションテーブル1−2に、ノード2ではプロテクションテーブル2−2に更新しておくことにより、不要な切替動作を抑えることができる。
【0023】
また、新たにノード3からノード2にパスが設定された時は、プロテクションテーブルを、ノード2ではプロテクションテーブル2−3に更新、ノード3ではプロテクションテーブル3−1に設定することにより、新たなパスに対応したプロテクション動作を行うことができる。
このように、パス設定/解除時にプロテクションテーブルを更新することにより、不必要な切替を抑え、パス設定状況に応じた柔軟なプロテクション動作を実現することができる。
以上のように、本実施の形態における光クロスコネクト装置は、復旧動作を決定するプロテクションテーブルが光パスの設定毎に更新されるため、パスの変更に柔軟に対応することができる。また、障害検出を迅速に行い、CPUの処理を軽減することができるため、高速な復旧動作を実現することができる。
【0024】
実施の形態2.
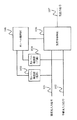
次に、光信号切替部3が多段構成となっている場合について説明する。図5は本実施の形態における光クロスコネクト装置の構成図である。複数の光信号分岐/切替部9、91、92から多段光信号切替部10が構成されており、光回路の中間部にも障害検出部4が配置されている。各障害検出部4、40、41、42で検出された障害は、判定部6内のプロテクションテーブル7に伝わり、障害情報と参照することにより、ハードウェア上で復旧動作が決定される。このように出力側にも障害検出部を設けると、入力側検出器までの間にある内部回路の不具合が検出できる。光クロスコネクト装置内部の障害であることが判定された場合は、制御部5を介して、障害が発生した光信号分岐/切替部9を回避するような切替指示を多段光信号切替部10に送信する。
【0025】
以上のように、本実施の形態による光クロスコネクト装置は、光信号切替部が多段構成になっている場合でも、プロテクションテーブルを各障害検出部に対応させることにより、高速な障害位置の特定及び復旧動作を行うことができる。
【0026】
実施の形態3.
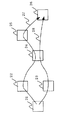
図6は本実施の形態における光ネットワークの構成を示す図である。起点ノード11から終点ノード13に対し、双方向パスが冗長系をもってはられている。現用系は現用送信パス14と現用受信パス15からなり、予備系は中間ノード12を介して予備送信パス16と予備受信パス17から構成される。ノードとしての光クロスコネクト装置は、そのプロテクションテーブルの復旧動作内に双方向パスの対応関係を有している。
【0027】
次に動作について説明する。終点ノード13にて現用送信パス14の障害を検出すると、終点ノード13は内部のプロテクションテーブルを参照し、予備送信パス16に切替る。同時に対応する双方向パスを読取り、終点ノード13からみると送信している現用受信パス15の送信を止める。起点ノード11は現用受信パスの障害を検出するため、予備受信パス17に切替る。
以上のように、実施の形態3による光クロスコネクト装置は、双方向パスを同時に切替ることができるため、現用系と予備系の混在を避けることができる。
【0028】
図7は本実施の形態における他のネットワーク構成を示す図である。この構成における光クロスコネクト装置の新しい部分は、プロテクションテーブルに図示していないが、保持時間の欄を設けたことである。そしてCPU8は、この欄の保持時間後に切り替え制御をする。
起点ノード21から終点ノード26に対し、現用パス27と予備パス28が冗長系をもってはられている。22〜25は中間ノードであり、中間ノード24は現用パス27と予備パス28が両方とも経由している。中間ノード24と終点ノード26ともプロテクションが設定されており、終点ノード26には障害検出時からプロテクション動作を起動するまでの適切な保持時間が設定されている。
【0029】
中間ノード22と中間ノード24間に障害が起きると、障害は中間ノード24と中間ノード25と終点ノード26にて検出される。中間ノード24は、中間ノード22を経由している現用パス27を、中間ノード23を経由する予備パス28に切替えようとする。同時に終点ノード26は中間ノード22、24、25を経由する現用パス27を、中間ノード23、24を経由する予備パス28に切替えようとする。終点ノード26は、プロテクションテーブルに保持時間が設定されているためすぐには切替えず、保持時間分だけ待機する。その間に中間ノード24にて予備パスに切替るため、終点ノード26では、現用パスが復旧し、切替を行わずに済む。そのため、不必要な切替動作を防ぎ、帯域を有効に活用することができる。
【0030】
保持時間をパス設定情報に含め、パス設定毎に設定すれば、柔軟なパス設定に対応させることができる。
伝送路上に起きた障害に対して説明したが、装置内に起きた障害でもよい。この場合、終点ノードは、障害がおきた装置が自身の装置内冗長系により復旧することを待ち、復旧しない場合に予備系に切替る。
以上のように、本実施の形態における他の光クロスコネクト装置は、保持時間を適切に設けることにより、障害復旧動作に優先順位を付け、一つの障害に対し複数の切替動作を起動させることなく、適切な復旧動作を行うことができる。
【0031】
【発明の効果】
以上のようにこの発明によれば、プロテクションテーブルを備えて、これに基づいて切替制御するので、装置規模を抑えて、しかも他への波及が無い切替を短時間に行える効果がある。
【0032】
また更に、光信号切替部は1入力多出力切替を複数集めた構成としたので、装置規模を抑える効果がある。
【0033】
また更に、障害検出器を光信号切替部の入力側と、出力側に設けたので、障害箇所の特定ができる効果がある。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】この発明の実施の形態1における光クロスコネクト装置の構成を示す図である。
【図2】実施の形態1におけるプロテクションテーブルの例を示す図である。
【図3】実施の形態1における他のプロテクションテーブルを示す図である。
【図4】実施の形態1におけるプロテクションテーブル更新トリガを説明する図である。
【図5】この発明の実施の形態2における光クロスコネクト装置の構成を示す図である。
【図6】この発明の実施の形態3における光ネットワークの構成を示す図である。
【図7】実施の形態3における他の光ネットワークの構成を示す図である。
【図8】この発明における光信号切替部の構成を説明する図である。
【図9】従来の光クロスコネクト装置の構成図である。
【符号の説明】
1a,1b,1n 光入力信号、2a,2b,2n 光出力信号、3 光信号切替部、4a,4b,4n,40a,40b,40n,41a,41b,41n,42a,42b,42n 障害検出器、5 制御部、6 判定部、7 プロテクションテーブル、8 CPU、9,91,92 光信号分岐/切替部、10 光信号多段切替部、11,12,13 ノード、14,15 現用パス、16,17 予備パス、21 起点ノード、22,23,24,25 中間ノード、26 終点ノード、27 現用パス、28 予備パス。[0001]
TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an optical path switching device such as a cross-connect device or an ADM (Add / Drop Multiplexer) device for switching large-capacity signals in an optical communication network.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Conventionally, line control in an optical communication network converts an optical signal into an electric signal and performs switching control by an electric switch. However, an optical / electrical converter that converts an optical signal into an electric signal is expensive, and in view of an increasingly developed optical communication system, a method of switching an optical signal without converting it into an electric signal has been proposed. Workarounds are also being considered.
[0003]
For example, FIG. 9 shows a workaround proposed in “Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 10-303814”. In the figure, an active
When a failure occurs in the active
[0004]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, in an optical communication network based on an optical cross-connect having multiple ports, the combination of the working path and the protection path must be not fixed but can be changed flexibly. The working path and the protection path do not necessarily correspond one-to-one, and it is necessary to cope with a case where a plurality of working paths share a protection path such as one protection-m working. Further, there is a problem that the configuration which can cope with an increase in the number of active input (signal) lines and a simultaneous failure in a plurality of active systems becomes considerably complicated and large-scale.
In addition, when a failure occurs, quick failure detection and recovery are required. When the path is switched, the transmission quality changes due to the different transmission path conditions. However, if the failure detection threshold is set according to the worst case, it becomes difficult to determine the deterioration of the transmission quality. In addition, although quick failure recovery requires quick identification of a failure location, there is also a problem that it takes time to identify the failure location because the path changes in a floating manner.
In addition, paths are set bidirectionally, but when switching to avoid a failure occurs, one bidirectional path shares the working system and the standby system, and path management becomes complicated. There is also a problem of becoming.
[0005]
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention has been made to solve such a problem. First, a cross-connect device in which the size is suppressed and the state management is well performed by setting an appropriate backup path regardless of the number of input lines is obtained. .
Furthermore, an optical cross-connect device is provided in which a portion corresponding to the reason for occurrence is quickly switched when a failure occurs, and the switching without disruption to others is completed in a short time.
[0006]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
An optical cross-connect device according to the present invention, a failure detection unit provided for each input,
An optical signal switching unit that switches a plurality of inputs to a plurality of outputs and selectively outputs the signals;
A protection table for instructing the optical signal switching unit to perform switching selection corresponding to each detection unit,
A determination unit configured to switch the optical signal switching unit by referring to the protection table when a failure is detected.
[0007]
Further, the determination unit monitors the status of the path from another node, and changes the setting of the protection table in accordance with the status of the monitored path.
[0008]
Further, the optical signal switching unit has a configuration in which a plurality of switches of 1 input m (m is an arbitrary integer) output are collected, and a failure detection unit is also provided on the output side.
[0009]
Further, a failure detector is provided on the input side and the output side of the optical signal switching unit.
[0010]
Further, the protection table is designed to specify a recovery point when a failure is detected.
[0011]
Further, the protection table is provided with a column for instructing switching to a related adjacent node (adjacent input side or adjacent output side) if necessary.
[0012]
Still further, the fault detector is provided with a threshold value for fault determination, and the threshold value is changed for each input or output.
[0013]
Further, the protection table has a holding time setting column, and when a failure is detected, switching is controlled after the holding time has elapsed.
[0014]
Further, a standby system is provided for both transmission and reception, and when a failure is detected, both transmission and reception forming a pair are switched to the standby system.
[0015]
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
FIG. 1 is a configuration
FIG. 2 shows the contents of the protection table 7 which is a main element of the present invention. In the figure, the
[0016]
Next, the operation of the configuration device will be described.
The
[0017]
FIG. 7 shows a detailed configuration example of the optical signal switching unit 3. The m (working) to 1 (spare) selection circuit may have the configuration shown in FIG. 8A, and the 1-input to m-output configuration may have the configuration shown in FIG. 8B. Therefore, by combining the outputs from the respective inputs in FIG. 8B with the same outputs, the matrix configuration in FIG. 8C is possible. In this manner, many current problems can be dealt with with a small number of spares. That is, even in a normal system other than the so-called 1 + 1 system, reliability can be improved by sharing a small number of spares.
When the failure is detected in S1 in FIG. 2, the
[0018]
As described above, the optical cross-connect device according to the present embodiment performs switching immediately by referring to the protection table 7 directly associated with the failure detection unit switching target input set in advance by the CPU or the like. High-speed recovery is possible, and there is no confusion because selection of signal lines is considered in advance in consideration of priorities and the like. Also, the hardware scale can be selected on the input side only by detecting the failure on the input side, and management is easy.
As described above, the optical cross-connect device according to the first embodiment can determine a restoration operation by referring to the protection table 7 in hardware, and thus can realize a high-speed restoration operation.
[0019]
FIG. 3 shows another protection table according to the present embodiment. The protection table has a table divided into [Table A] for determining a path (route) and [Table B] for determining an operation corresponding to a detection state of a failure detector incorporated in the path. As will be described later, there are
[0020]
Therefore, according to this configuration, it is also possible to determine the fault position based on the detection status of the fault detectors 4a to 4n and the
Thus, management and preparation for the path change are facilitated.
[0021]
Further, the failure detection unit may monitor the wavelength and the bit error rate in addition to the light intensity. The path setting information between nodes at the time of path setting includes a judgment threshold of the failure detection unit, and changes the judgment threshold for each path setting. Since it is possible to set an optimum determination threshold value according to the path setting situation, it is possible to quickly detect a failure due to deterioration of an optical component or the like.
Further, since the fault position can be transmitted simultaneously with the fault detection from the fault position information set in the protection table in advance, the processing of the CPU at the time of fault recovery can be reduced.
[0022]
If it is necessary to switch another optical cross-connect device for the recovery operation, the CPU must transmit failure information to another node. As shown in the item of the recovery operation of the table B in FIG. 3, the content of transmitting the switching instruction to another node is set in the protection table. Since the switching instruction can be transmitted to the node, the time required for the recovery operation can be reduced. In this figure, the switching instruction is given to the upstream, but the switching instruction may be given to the downstream, and based on the instruction, the switching may be made to the standby system designated to be downstream.
(c) In an optical communication network using an optical cross-connect device, a path is not fixed, and must be flexibly changed according to a client's request or an operating state of the system. Then, it will be described that high-speed protection can be performed even when the path is changed.
FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating updating of the protection table according to the first embodiment. When a path is set from the
[0023]
When a new path is set from the node 3 to the
As described above, by updating the protection table at the time of path setting / cancellation, unnecessary switching can be suppressed, and a flexible protection operation according to the path setting situation can be realized.
As described above, in the optical cross-connect device according to the present embodiment, the protection table for determining the recovery operation is updated each time an optical path is set, so that it is possible to flexibly cope with path changes. Further, since the failure detection can be performed quickly and the processing of the CPU can be reduced, a high-speed recovery operation can be realized.
[0024]
Next, a case where the optical signal switching unit 3 has a multi-stage configuration will be described. FIG. 5 is a configuration diagram of the optical cross-connect device according to the present embodiment. A multi-stage optical
[0025]
As described above, the optical cross-connect device according to the present embodiment enables high-speed fault location and identification by associating the protection table with each fault detection unit even when the optical signal switching unit has a multi-stage configuration. A recovery operation can be performed.
[0026]
Embodiment 3 FIG.
FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of an optical network according to the present embodiment. A bidirectional path is provided from the originating
[0027]
Next, the operation will be described. When the
As described above, the optical cross-connect device according to the third embodiment can simultaneously switch the bidirectional paths, so that it is possible to avoid a mixture of the active system and the standby system.
[0028]
FIG. 7 is a diagram showing another network configuration according to the present embodiment. A new part of the optical cross-connect device in this configuration is that a protection time column is provided, not shown in the protection table. Then, the
A working
[0029]
When a failure occurs between the
[0030]
If the holding time is included in the path setting information and is set for each path setting, flexible path setting can be supported.
Although a description has been given of a failure that has occurred on the transmission path, a failure that has occurred in the device may be performed. In this case, the end node waits for the failed device to be restored by its own redundant system, and switches to the standby system if the failed device is not restored.
As described above, the other optical cross-connect devices according to the present embodiment, by appropriately setting the holding time, prioritize the failure recovery operation without activating a plurality of switching operations for one failure. , An appropriate recovery operation can be performed.
[0031]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, a protection table is provided and switching control is performed based on the protection table. Therefore, there is an effect that switching can be performed in a short time while suppressing the size of the device and without affecting other devices.
[0032]
Furthermore, since the optical signal switching unit has a configuration in which a plurality of one-input / multiple-output switchings are collected, there is an effect of reducing the device scale.
[0033]
Further, since the fault detector is provided on the input side and the output side of the optical signal switching unit, there is an effect that a fault location can be specified.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a configuration of an optical cross-connect device according to
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating an example of a protection table according to the first embodiment.
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing another protection table in the first embodiment.
FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating a protection table update trigger according to the first embodiment.
FIG. 5 is a diagram showing a configuration of an optical cross-connect device according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 6 is a diagram showing a configuration of an optical network according to a third embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 7 is a diagram showing a configuration of another optical network according to the third embodiment.
FIG. 8 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of an optical signal switching unit according to the present invention.
FIG. 9 is a configuration diagram of a conventional optical cross-connect device.
[Explanation of symbols]
1a, 1b, 1n Optical input signal, 2a, 2b, 2n Optical output signal, 3 Optical signal switching unit, 4a, 4b, 4n, 40a, 40b, 40n, 41a, 41b, 41n, 42a, 42b, 42n Fault detector 5, control section, 6 determination section, 7 protection table, 8 CPU, 9, 91, 92 optical signal branching / switching section, 10 optical signal multi-stage switching section, 11, 12, 13 node, 14, 15 working path, 16, 17 backup path, 21 starting node, 22, 23, 24, 25 intermediate node, 26 end node, 27 working path, 28 backup path.
Claims (9)
複数の入力を複数の出力に切替え選択出力する光信号切替部と、
上記各検出部対応に上記光信号切替部に切替え選択指示をするためのプロテクションテーブルと、
障害を検出すると、上記プロテクションテーブルを参照して上記光信号切替部を切替制御する判定部とを備えたことを特徴とする光クロスコネクト装置。A failure detection unit provided for each input;
An optical signal switching unit that switches a plurality of inputs to a plurality of outputs and selectively outputs the signals;
A protection table for instructing the optical signal switching unit to perform switching selection corresponding to each of the detection units;
An optical cross-connect device comprising: a determination unit configured to switch the optical signal switching unit by referring to the protection table when a failure is detected.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002198804A JP4024607B2 (en) | 2002-07-08 | 2002-07-08 | Optical cross-connect device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002198804A JP4024607B2 (en) | 2002-07-08 | 2002-07-08 | Optical cross-connect device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004040726A true JP2004040726A (en) | 2004-02-05 |
| JP4024607B2 JP4024607B2 (en) | 2007-12-19 |
Family
ID=31706155
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002198804A Expired - Fee Related JP4024607B2 (en) | 2002-07-08 | 2002-07-08 | Optical cross-connect device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4024607B2 (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006079355A (en) * | 2004-09-09 | 2006-03-23 | Hitachi Ltd | Storage network management server, storage network management method, storage network management program, and storage network management system |
| WO2008000120A1 (en) * | 2006-06-20 | 2008-01-03 | Zte Corporation | A method and device for triggering the optical network protection under the configuration of sharing the receiving apparatus |
| US7447430B2 (en) | 2004-07-20 | 2008-11-04 | Hitachi Communications Technologies, Ltd. | Optical cross connect apparatus and optical transmission system |
| US7813640B2 (en) | 2004-03-30 | 2010-10-12 | Fujitsu Limited | Optical connection switching apparatus and management control unit thereof |
| WO2010148599A1 (en) * | 2009-06-26 | 2010-12-29 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Protection system, method and apparatus for optical network |
| JP2012015934A (en) * | 2010-07-05 | 2012-01-19 | Nec Corp | Optical transmission device and optical transmission method |
| WO2012124099A1 (en) * | 2011-03-17 | 2012-09-20 | 富士通株式会社 | Router device, and method for switching lines in router device |
| CN104243199A (en) * | 2013-11-29 | 2014-12-24 | 深圳市邦彦信息技术有限公司 | Data transmission method and protection device of packet transport network |
-
2002
- 2002-07-08 JP JP2002198804A patent/JP4024607B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7813640B2 (en) | 2004-03-30 | 2010-10-12 | Fujitsu Limited | Optical connection switching apparatus and management control unit thereof |
| US7447430B2 (en) | 2004-07-20 | 2008-11-04 | Hitachi Communications Technologies, Ltd. | Optical cross connect apparatus and optical transmission system |
| JP2006079355A (en) * | 2004-09-09 | 2006-03-23 | Hitachi Ltd | Storage network management server, storage network management method, storage network management program, and storage network management system |
| WO2008000120A1 (en) * | 2006-06-20 | 2008-01-03 | Zte Corporation | A method and device for triggering the optical network protection under the configuration of sharing the receiving apparatus |
| CN1874201B (en) * | 2006-06-20 | 2010-05-12 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method and equipment for triggering protection of optical network under shared configuration of receiving devices |
| US9008500B2 (en) | 2009-06-26 | 2015-04-14 | Zte Corporation | Protection system, method and apparatus for optical network |
| WO2010148599A1 (en) * | 2009-06-26 | 2010-12-29 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Protection system, method and apparatus for optical network |
| CN101605282B (en) * | 2009-06-26 | 2012-07-04 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | System, method and device for protecting optical network |
| EP2434662A4 (en) * | 2009-06-26 | 2016-01-06 | Zte Corp | Protection system, method and apparatus for optical network |
| JP2012015934A (en) * | 2010-07-05 | 2012-01-19 | Nec Corp | Optical transmission device and optical transmission method |
| JPWO2012124099A1 (en) * | 2011-03-17 | 2014-07-17 | 富士通株式会社 | Router device and line switching method in router device |
| WO2012124099A1 (en) * | 2011-03-17 | 2012-09-20 | 富士通株式会社 | Router device, and method for switching lines in router device |
| CN104243199A (en) * | 2013-11-29 | 2014-12-24 | 深圳市邦彦信息技术有限公司 | Data transmission method and protection device of packet transport network |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP4024607B2 (en) | 2007-12-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JPH0998181A (en) | Transmission equipment | |
| US20190158940A1 (en) | Procedures, apparatuses, systems, and computer programs for providing optical network channel protection | |
| US20080175587A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for network fault detection and protection switching using optical switches with integrated power detectors | |
| WO2014199471A1 (en) | Communication system, communication device, and protection method | |
| JP3740969B2 (en) | Optical cross-connect device | |
| US20140219080A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for interworking protection switching | |
| JP4024607B2 (en) | Optical cross-connect device | |
| JP3811007B2 (en) | Virtual connection protection switching | |
| JP2009105540A (en) | Method and device for high-speed switching of ring protocol | |
| US6993684B2 (en) | Ring control node | |
| US20030172315A1 (en) | Method of restoring a facility failure in a communication network, a communication network, a network element, a protocol, a program module and a communication interface module therefor | |
| US6526020B1 (en) | Ring network system, protection method therefor | |
| US6941486B1 (en) | Method and device for optimizing the transmission safety and the defect tolerance in high-bit-rate data networks | |
| JPH10190687A (en) | Path switching device | |
| JP2016086316A (en) | Transmission device and redundancy provision method | |
| JP6465627B2 (en) | Optical transmission system, management apparatus, optical transmission node, and optical transmission method | |
| JP4869983B2 (en) | Optical transmission system and optical transmission device | |
| JP5006342B2 (en) | Exchange system | |
| JP3674541B2 (en) | Method for detecting fault location in optical communication network and optical communication system | |
| JP2006165999A (en) | Layer 2 switching circuit, base station device, and layer 2 switching method | |
| JP2007027954A (en) | Packet network and layer 2 switch | |
| JP2007067612A (en) | Relaying apparatus and optical communication system | |
| JP2606130B2 (en) | Loop network | |
| JP6399312B2 (en) | Packet relay device, packet relay system, and packet relay method | |
| JP5176772B2 (en) | Transmission apparatus having load balancing configuration of protection line switching protocol processing CPU and CPU load balancing control method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20040519 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20041025 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20050607 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20070410 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20070424 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070620 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20070717 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070824 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20071002 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20071003 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101012 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111012 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121012 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131012 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |