JP2004019727A - Friction roller type transmission - Google Patents
Friction roller type transmission Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2004019727A JP2004019727A JP2002173091A JP2002173091A JP2004019727A JP 2004019727 A JP2004019727 A JP 2004019727A JP 2002173091 A JP2002173091 A JP 2002173091A JP 2002173091 A JP2002173091 A JP 2002173091A JP 2004019727 A JP2004019727 A JP 2004019727A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- speed
- side shaft
- roller
- outer ring
- speed side
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Pulleys (AREA)
- Friction Gearing (AREA)
Abstract
【課題】増速機への回転変動の伝達を低減して、高速回転機械へのねじり振動の伝達を抑制すること。
【解決手段】ハウジング1に低速側シャフト3を回転自在に支持し、この低速側シャフト3の一端部に外輪32を設ける一方、低速側シャフト3及び外輪32に対して偏心して、高速側シャフト17を回転自在に支持している。外輪32と高速側シャフト17の間に、2個のガイドローラ37a,37bと、トルク伝達時に移動する可動ローラ38とを介装している。くさびローラ式変速機Aの低速側シャフト3(入力側)に、ワンウェイクラッチYを内蔵したプーリPを使用している。
【選択図】 図1A transmission of torsional vibration to a high-speed rotating machine is suppressed by reducing the transmission of rotation fluctuation to a speed-increasing gear.
A low-speed side shaft is rotatably supported by a housing, and an outer ring is provided at one end of the low-speed side shaft, while the high-speed side shaft is eccentric to the low-speed side shaft and the outer ring. Is rotatably supported. Two guide rollers 37a and 37b and a movable roller 38 that moves during torque transmission are interposed between the outer ring 32 and the high-speed shaft 17. A pulley P incorporating a one-way clutch Y is used on the low-speed shaft 3 (input side) of the wedge roller type transmission A.
[Selection diagram] Fig. 1
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、高速側シャフトが高回転で回転する機械、例えば、ターボ機械、過給機、工作機械等の増速機に好適であるくさび作用を利用した摩擦ローラ式変速機に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
特開平4−203421号公報及び特開平11−294548号公報においては、車両用エンジンの過給機は、遠心式であって、エンジンの駆動軸から動力を直接ベルト伝動し、増速機により増速して、そのインペラーを回転駆動するようになっている。
【0003】
上記特開平4−203421号公報では、増速機として、高い増速比を得るため、遊星歯車機構を用いている。しかし、数万rpmから10万rpm以上にも及ぶ回転数では、ギアの振動や騒音とともに寿命にも大きな問題がある。
【0004】
また、上記特開平11−294548号公報では、摩擦ローラ機構の遊星ローラを用いた方式であるが、可撓性外側リングで遊星ローラと太陽軸を締め付けることにより、トラクションドライブで必要な押付力を得る構造となっている。そのため、高回転高トルク状態ですべりが発生し、駆動力をインペラに伝えることが出来ない。また、これを防止するためには、さらに大きな力で外側リングで遊星ローラを締め付ける必要があるが、そうすると、低回転低トルク状態では、過大な押付力で押し付けることになり、効率が低下してしまう。同時に常に大きな押付力が働くので、寿命的にも問題がある。
【0005】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
さらに、上述したように、エンジンの駆動軸(クランクシャフト)から動力を直接ベルト伝動により得る方式にあっては、エンジンのクランクシャフトの回転は、エンジンの点火・燃焼により気筒数に応じた回転変動を持っている。従って、エンジンのクランクシャフトから駆動される増速機のプーリには回転変動が入力される。増速機により回転は増速されるため、インペラ側ではエンジンの回転変動は増幅される。この増幅された回転変動(振動)により、インペラおよび出力軸に大きなねじり振動が加わるため、インペラおよび出力軸の強度が不足する虞れがある。
【0006】
このように、エンジンの点火・燃焼に起因する回転変動による問題は、増速機で数万rpmから10万rpm以上まで増速するがゆえ、その問題点がより顕著になる。
【0007】
なお、増速機のプーリには、一般にベルトにより増速された回転が入るので、ここでもエンジンの回転変動は増幅される。
【0008】
本発明は、上述したような事情に鑑みてなされたものであって、増速機への回転変動の伝達を低減して、高速回転機械へのねじり振動の伝達を抑制したくさび作用を利用した摩擦ローラ式変速機を提供することにある。
【0009】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記の目的を達成するため、本発明の請求項1に係るくさび作用を利用した摩擦ローラ式変速機は、ハウジングに低速側シャフトを回転自在に支持し、前記低速側シャフトの一端部に外輪を設ける一方、前記低速側シャフト及び前記外輪に対して偏心して、高速側シャフトを回転自在に支持し、
前記外輪と前記高速側シャフトの間に、少なくとも1個のガイドローラと、トルク伝達時に移動する少なくとも1個の可動ローラとを有し、
前記低速側シャフトは、ワンウェイクラッチを介してプーリを備えていることを特徴とする。
【0010】
また、請求項2に係るくさび作用を利用した摩擦ローラ式変速機は、ハウジングに低速側シャフトを回転自在に支持し、前記低速側シャフトの一端部に外輪を設ける一方、前記低速側シャフト及び前記外輪に対して偏心して、高速側シャフトを回転自在に支持し、
前記外輪と前記高速側シャフトの間に、少なくとも1個のガイドローラと、トルク伝達時に移動する少なくとも1個の可動ローラとを有し、
前記低速側シャフトは、トーショナルダンパを介してプーリを備えていることを特徴とする。
【0011】
このように、本発明によれば、くさび作用を利用した摩擦ローラ式変速機を高速回転機械の増速機として用いており、くさびローラ式変速機は、トラクションドライブであり、高速回転でも静かで滑らかな動力伝達が行えることから、振動や騒音の問題は全くない。さらに、トラクションドライブに必要な押付力は、くさび作用により得る機構であり、伝達トルクに比例した適正な押付力が常に得られるため、すべりが発生することはない。同時に、低回転低トルク領域から高回転高トルク領域まで高い効率が得られる。
【0012】
また、低速側シャフトは、ワンウェイクラッチを介してプーリを備えるか、又は、トーショナルダンパを介してプーリを備えている。
【0013】
従って、例えば、エンジン等からのからの回転変動は、くさびローラ式変速機に低減して入力することから、変速機での回転変動を低減して、高速回転機械に加わるねじり振動を抑制し、高速回転機械の出力軸が強度不足になる虞れをなくすことができる。なお、ディーゼルエンジンでは、エンジン回転変動が大きいので特に有効である。
【0014】
なお、トラクションドライブ式変速機は、静かで滑らかであることから産業上の各種用途に開発され、さらに近年は自動車や自転車といったパーソナルユースに応用する試みがなされ、次世代の動力伝達方式として注目されている。
【0015】
トラクションドライブ式変速機とは、歯車伝動とは異なり、滑らかな表面をもつ少なくとも2個の回転体を強く押し付け、これらの間に潤滑油膜(例えばEHL油膜)を介在させて、動力を伝達する機構であり、その基礎式は、Ft=μ・Fcという簡単な摩擦の式で表される(Ft:トラクション力)。ここで、Fcは、押し付け力と呼び、この発生に様々な方法が開発されている。
【0016】
このトラクションドライブ式変速機の一つとして、くさび作用を利用した摩擦ローラ式変速機(以後本明細書中では、くさびローラ式変速機と記す)がある。くさびローラ式変速機とは、高速側シャフトの先端部の周囲に、該高速側シャフトに対し偏心した状態で、回転自在に設けられた外輪と、該高速側シャフトの外周面である被駆動側円筒面と前記外輪の内周面である駆動側円筒面との間に存在して、径方向に関する幅が円周方向に関して不同である環状空間内に配置される、それぞれの外周面を動力伝達用円筒面とした、少なくとも1個のガイドローラおよび少なくとも1個の可動ローラとを備えた変速機のことを言う。又、可動ローラとは、くさび作用により押付け力を発生するローラであり、半径方向、円周方向に動くローラのことを言う。
【0017】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の実施の形態に係るくさびローラ式変速機を図面を参照しつつ説明する。
【0018】
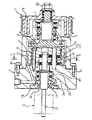
図1は、本発明の実施の形態に係るくさびローラ式変速機の断面図である。図2は図1のb−b線に沿ったワンウェイクラッチ機能を有するくさびローラ式変速機の断面図であり、図3はくさびローラ式変速機の作用を説明する図であり、図4は正逆両方向の回転時にトルクを伝達可能なくさびローラ式変速機の断面図である。
【0019】
くさびローラ式変速機Aは、本実施の形態では、低速側シャフト3(外輪側)を入力側とし、高速側シャフト17を出力側とした増速機として作用する。但し、本発明は、低速側シャフト(外輪側)を出力側とした減速機にも適用できる。
【0020】
また、図2に示すように、くさびローラ式変速機Aは、正転時には、トルクを伝達する一方、逆転時には、空転してトルクを伝達しないワンウェイクラッチ機能を有しているものや、図4に示すように、正逆両方の回転時にトルクを伝達するものであっても良い。
【0021】
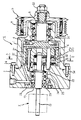
本発明の実施の形態に係るくさびローラ式変速機Aは、図1、図2において、略円筒状のハウジング1に、仕切板であるハウジング2が固定してある。ハウジング1には、低速側シャフト3が回転自在に支持してあり、ハウジング1内の低速側シャフト3の端部に、円盤状部材4が設けてあり、この円盤状部材4の外縁部に、外輪32が取付けてある。
【0022】
仕切板であるハウジング2には、高速側シャフト17が低速側シャフト3及び外輪32に対して偏心(オフセット)して回転自在に設けてある。
【0023】
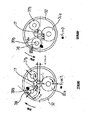
図2に示すように、外輪32と、高速側シャフト17との間には、大径のガイドローラ37aと、小径のガイドローラ37bと、トルク伝達時に移動する可動ローラ38とが介装してある。
【0024】
可動ローラ38を回転自在に支持する支持軸39bは、図3に示すように、高速側シャフト17と外輪32との間で「くさび」に食い込む方向に移動できるように構成してあり、また、この「くさび」に食い込む方向にシリンダ孔46に設置した圧縮ばね等の弾性材47(図2参照)により付勢してある。
【0025】
これにより、図3に示すように、正転時には、可動ローラ38は、高速側シャフト17と外輪32との間で「くさび」に食い込む方向に移動し、押し付け力Fcを発生する。このFcによりトラクション力が発生し、トルクを伝達することができる。
【0026】
一方、逆転時には、可動ローラ38は、「くさび」から離れる方向に移動し、押し付け力Fc=0となり、外輪32が空転し、高速側シャフト17にトルクを伝達できなくなる。
【0027】
図2に示すように、外輪32の内周面と高速側シャフト17の先端部外周面との間には、径方向に関する幅が円周方向に関して不同である環状空間36が設けられる。
【0028】
この様な環状空間36内には、2個のガイドローラ37a、37bと1個の可動ローラ38とを設置して、上記くさびローラ式変速機Aを構成している。図において、可動ローラ38は切欠いて部分的に示している。これら各ローラ37a、37b、38を設置する為に上記環状空間36部分には、3本の支持軸39a、39a、39bを設けている。これら3本の支持軸39a、39a、39bのうち、2本の支持軸39a,39aは、それぞれの両端部をハウジング2及び連結板14に形成した嵌合孔40、40に圧入固定している。従って、上記2本の支持軸39a,39aが、上記環状空間36内で円周方向或は直径方向に変位する事はない。これに対して、上記3本の支持軸39a、39a、39bのうち、図2の上部左側に位置する残り1本の支持軸39bは、両端部を上記ハウジング2及び連結板14に対し、上記外輪32の円周方向及び直径方向に関する若干の変位可能に支持している。この為に、上記ハウジング2及び連結板14の一部で上記1本の支持軸39bの両端部に整合する部分に、この支持軸39bの外径よりも大きな内径を有する支持孔41を形成し、これら各支持孔41に、上記支持軸39bの両端部を緩く係合させている。
【0029】
そして、上述の様に支持した各支持軸39a、39a、39bの中間部周囲に、それぞれ上記各ガイドローラ37a、37b及び可動ローラ38を、それぞれラジアルニードル軸受42、42等の軸受(可動ローラの軸受は図示省略)により、回転自在に支持している。尚、上記連結板14を上記ハウジング2に結合固定する為、この連結板14の片面に突設した、突部27、27は、それぞれこの連結板14の円周方向に関して、上記各ガイドローラ37a、37b及び可動ローラ38同士の間に存在する。言い換えれば、上記環状空間36内に上記各突部27、27と上記各ガイドローラ37a、37b又は可動ローラ38とが、上記環状空間36の円周方向に関して交互に存在する。又、これら各ガイドローラ37a、37b又は可動ローラ38の外周面と上記各突部27、27の円周方向側面とが干渉する(擦れ合う)事はない。
【0030】
この様にして、上記支持軸39a、39a、39bにより上記ハウジング2と連結板14との間にそれぞれ回転自在に支持した、上記ガイドローラ37a、37b及び可動ローラ38の外周面である、動力伝達用円筒面43a、43a、43bは、それぞれ前記高速側シャフト17の先端部の外周面である被駆動側円筒面44と前記外輪32の内周面である駆動側円筒面45とに当接させている。前述した通り、上記各ガイドローラ37a、37b及び可動ローラ38を設置した上記環状空間36の径方向に関する幅は、円周方向に関して不同である。この様に、この環状空間36の幅寸法を円周方向に関して不同にした分、上記ガイドローラ37a、37b及び可動ローラ38の外径を異ならせている。即ち、上記ガイドローラ37a、37b及び可動ローラ38のうち、それぞれ上記外輪32に対し高速側シャフト17の先端部が偏心している側(図2の上側)に位置する可動ローラ38及びガイドローラ37bの外径を、互いに同じにすると共に比較的小径にしている。これに対し、上記外輪32に対し高速側シャフト17の先端部が偏心しているのと反対側(図2の下側)に位置するガイドローラ37aの外径を、上記可動ローラ38及びガイドローラ37bの外径よりも大きくしている。そして、上記ガイドローラ37a、37b及び可動ローラ38の外周面である上記各動力伝達用円筒面43a、43a、43bを、それぞれ上記被駆動側、駆動側円筒面44、45に当接させている。
【0031】
尚、上記各ガイドローラ37a、37b及び可動ローラ38のうち、ガイドローラ37a、37bをそれぞれ支持した支持軸39a、39aの両端部は、前述の様に、前記ハウジング2及び連結板14に対し(環状空間36内に)固定している。これに対して、上記可動ローラ38を支持した支持軸39bは、やはり前述した様に上記ハウジング2及び連結板14に対し(環状空間36内に)、円周方向及び直径方向に関する若干の変位を可能に支持している。従って、上記可動ローラ38も、上記環状空間36内で円周方向及び直径方向に若干の変位可能である。そして、前記ハウジング2及び連結板14のシリンダ孔46内に設置した、圧縮ばね等の弾性材47により、上記可動ローラ38を支持した支持軸39bを、これら支持軸39bに回転自在に支持した可動ローラ38を前記環状空間36の幅の狭い部分に向け移動させるべく、弾性的に軽く押圧している。
【0032】
上述の様に構成する本発明に係るくさびローラ式変速機により回転軸を回転駆動する場合には、低速側シャフト3に駆動力を入力することにより外輪32を、図2の時計方向に回転させる。この外輪32の回転は、上記各ガイドローラ37a、37b及び可動ローラ38を介して前記高速側シャフト17に伝わり、高速側シャフト17を図2の反時計方向に回転させる。上記外輪32と上記ガイドローラ37a、37b及び可動ローラ38との間の動力伝達、並びに、これらガイドローラ37a、37b及び可動ローラ38と上記高速側シャフト17との間の動力伝達は、何れも摩擦伝達により行なわれる為、動力伝達時に発生する騒音並びに振動は低い。
【0033】
又、上記可動ローラ38は、上記外輪32から上記高速側シャフト17に伝達するトルクの大きさに応じた力で、前記環状空間36の幅が狭い部分(図2の上部中央部分)に食い込む傾向となる。この為、上記外輪32の内周面である駆動側円筒面45と上記ガイドローラ37a、37b及び可動ローラ38の外周面である動力伝達用円筒面43a、43a、43bとの当接部、並びに、これら各動力伝達用円筒面43a、43a、43bと上記高速側シャフト17の外周面である被駆動側円筒面44との当接部の面圧は、何れも、上記トルクが大きくなる程高くなる。逆に言えば、このトルクが小さい場合には、上記各当接部の面圧が低い状態となる。この為、これら各当接部の面圧を、伝達すべきトルクに合わせた適正値にして、トルク伝達を効率良く行なえる。
【0034】
即ち、上記外輪32が図2で時計方向に回転し、上記高速側シャフト17を同じく反時計方向に回転させる際には、上記可動ローラ38が、上記外輪32の内周面である駆動側円筒面45及び上記高速側シャフト17の外周面である被駆動側円筒面44から、前記弾性材47による押圧力と同方向の力を受けて、上記環状空間36の幅の狭い部分、即ち、図2の上部中央に向け移動する傾向となる。
【0035】
この結果、上記可動ローラ38の外周面である動力伝達用円筒面43bが、上記駆動側円筒面45と上記被駆動側円筒面44とを強く押圧する。そして、この動力伝達用円筒面43bと上記被駆動側円筒面44との当接部である内径側当接部48、及び、この動力伝達用円筒面43bと上記駆動側円筒面45との当接部である外径側当接部49の当接圧が高くなる。この様に上記可動ローラ38に関する内径側、外径側両当接部48、49の当接圧が高くなると、この可動ローラ38の外周面である動力伝達用円筒面43bにより押圧される、上記高速側シャフト17及び上記外輪32が、弾性変形や組み付け隙間により、直径方向に僅かに変位する。この結果、前記各ガイドローラ37a、37bに関する内径側、外径側両当接部48、49の当接圧が高くなる。そして、これら各内径側、外径側両当接部48、49での摩擦係合に基き、上記外輪32の回転力を、上記ガイドローラ37a、37b及び可動ローラ38を介して上記高速側シャフト17に伝達自在となる。
【0036】
上述の様にして、上記可動ローラ38を上記環状空間36の幅の狭い部分に向け移動させようとする力は、上記外輪32から上記高速側シャフト17に伝達する回転駆動力の大きさに応じて変化する。そして、この力が大きくなる程、上記内径側、外径側両当接部48、49の当接圧が高くなる。従って、この様な作用に基づき、上記伝達する回転駆動力に応じた当接圧を自動的に選定して、くさびローラ式変速機Aの伝達効率を確保できる。
【0037】
図2に示した例の場合には、くさびローラ式変速機Aは、ワンウェイクラッチ機能を備えており、上記高速側シャフト17の回転速度が上記外輪32の回転速度に見合う速度、即ち、この外輪32の回転速度にくさびローラ式変速機Aの増速比を掛けた速度よりも速くなった場合には、このくさびローラ式変速機Aの接続が断たれる。即ち、この場合には、上記可動ローラ38が、前記弾性材47の弾力に抗して、上記環状空間36の幅の広い側(図2の左下側)に変位する。この結果、上記内径側、外径側両当接部48、49の当接圧が低下若しくは喪失して、上記外輪32の回転が上記高速側シャフト17にまでは伝わらなくなる。
【0038】
次に、図4に示す、正逆両方向の回転時にトルクを伝達可能なくさびローラ式変速機について説明する。
【0039】
図4は、高速側シャフト17(図1参照)を時計、反時計の両方向に回転駆動自在な構造について示している。従って、本例の構造は、回転方向の変換自在な高速回転機械X(図1参照)と組み合わせて実施する。この様な本例の構造の揚合には、くさびローラ式変速機Aを構成する3個のローラとして、1個のガイドローラ37と2個の可動ローラ38a,38bとを便用している。このうち、環状空間36のうちで最も幅が広くなった部分に設置したローラを、比較的大径で設置位置が変化しないガイドローラ37としている。これに対して、上記環状空間36の幅が最も狭くなった部分を挟んで設けた1対のローラを、それぞれ比較的小径で円周方向及び直径方向に関する若干の変位を可能にした可動ローラ38a,38bとしている。そして、これら各可動ローラ38a,38bを支持した各支持軸39b,39bを、上記環状空間36の最も幅が狭くなった部分に向けそれぞれ弾性的に押圧している。
【0040】
上述の様に構成する本例の構造の場合には、外輪32が図4で時計方向に回転する場合には、同図で左側の可動ローラ38aが上記環状空間36の幅が狭くなった部分に食い込む。これに対して、上記外輪32が図4で反時計方向に回転する場合には、同図で右側の可動ローラ38bが上記環状空間36の幅が狭くなった部分に食い込む。又、本例の場合には、これら各可動ローラ38a,38bを支持した支持軸39b,39bの両端部を支持する為、ハウジング2及び連結板14に形成した支持孔41a,41aの、上記環状空間36の円周方向に関する長さを規制している。具体的には、これら各支持孔41a,41aのうち、上記環状空間36の幅が広い側(図4の下側)の端部の位置を、前述した図2で示した場合よりも、この環状空間36の最も幅が狭くなった位置に近づけている。そして、上記各可動ローラ38a,38bが、上記環状空間36の幅の広い側に過度に退避しない様にしている。
【0041】
上述の様に構成する本例の場合には、上記外輪32が時計、反時計の何れの方向に回転する場合でも、何れかの可動ローラ38a(38b)が上記環状空間36の幅の狭い部分に食い込み、当該可動ローラ38a(38b)に関する内径側、外径側各当接部48,49の当接圧を高める。一方、上記環状空間36の幅の狭い部分から退避する方向に変位する可動ローラ38b(38a)に関しても、その退避量は限られる。この結果、両可動ローラ38a,38b及び前記ガイドローラ37に関して、内径側、外径側各当接部48,49の当接圧が十分に上昇し、上記外輪32から高速側シャフト17にまで、動カを効率良く伝達できる。この様に、回転外輪32から高速側シャフト17への時計、反時計の両方向の動力伝達を可能にした点以外は、図2に前述した場合と同様であるから、同等部分に関する図示並びに説明は省略する。
【0042】
(第1実施の形態)
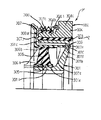
次に、第1実施の形態について説明する。図1は、本発明の第1実施の形態に係るくさびローラ式変速機の断面図である。図2は図1のb−b線に沿ったワンウェイクラッチ機能を有するくさびローラ式変速機の断面図であり、図3はくさびローラ式変速機の作用を説明する図であり、図4は正逆両方の回転時にトルクを伝達可能なくさびローラ式変速機の断面図である。図5は、アンギュラ玉軸受2個を正面組合せした例の拡大断面図である。
【0043】
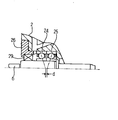
仕切板(ハウジング)2の孔23には、2個を正面組合せした1組のアンギュラ玉軸受24,25が介装してあり、予圧部材26により、シール部材29と共に堅固に固定してある。この予圧部材26は、軸受24,25の外輪を軸方向に押し付けて軸受内部隙間をなくすように予圧をかけている。
【0044】
また、高速回転機械X側では、軸受を設けていない。これは、高速側シャフト17を離れた2点で軸受支持すると、角度方向に微小に振れることができなくなるからである。
【0045】
このように、本実施の形態では、高速側シャフト17の軸受支持を、正面組合せした1組の2個のアンギュラ玉軸受24,25のみとしている。
【0046】
くさびローラ式変速機A側では、図5に示すように、アンギュラ玉軸受(24,25)2個を正面組合せしていることから高速側シャフト17の角度剛性を小さくでき、高速側シャフト17を角度方向に微小に振れることができ、加工誤差及び組立誤差、微小な移動を吸収することができる。
【0047】
また、高速側シャフト17は、これらアンギュラ玉軸受(24,25)2個により支持されるだけでなく、くさびローラ式変速機A側のローラ37a,37b,38によっても支持され、実質上2点で支持されている。そのため、高速側シャフト17は、ミソスリ運動等の不具合を生じることもなく、高速回転機械X側では、堅固に支持される。
【0048】
従って、本発明によれば、従来相容れなかったくさびローラ式変速機A側の要求と、高速回転機械X側の要求とを満足させることができ、高速回転機械Xに好適な増速機(または減速機)を提供することができる。
【0049】
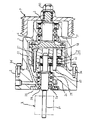
ところで、図9は、くさびローラ式変速機Aを増速機として用い、低速側シャフト3に通常のプーリPを装着した例の断面図である。この例のように、くさびローラ式変速機Aを高速回転機械の増速機として用いており、くさびローラ式変速機Aは、トラクションドライブであり、高速回転でも静かで滑らかな動力伝達が行えることから、振動や騒音の問題は全くない。さらに、トラクションドライブに必要な押付力は、くさび作用により得る機構であり、伝達トルクに比例した適正な押付力が常に得られるため、すべりが発生することはない。同時に、低回転低トルク領域から高回転高トルク領域まで高い効率が得られる。
【0050】
しかしながら、くさびローラ式変速機Aには、一方向のみ動力伝達タイプと両方向動力伝達タイプがあり、どちらでも適用でき、一方向のみ動力伝達タイプの場合には、ワンウェイクラッチ機能があるが、通常のプーリPを用いているため、空転時にも、与圧ばねによるドラグトルクがあり、エンジンの回転変動を取りきれない虞れがある。
【0051】
そこで、本実施の形態では、図1に示すように、くさびローラ式変速機Aの低速側シャフト3(入力側)に、ワンウェイクラッチYを内蔵したプーリPを使用している。なお、プーリPは、低速側シャフト3の端部にスプライン嵌合してあり、ナット50により固定してある。
【0052】
従って、エンジンからの回転変動は、くさびローラ式変速機Aに低減して入力することから、変速機Aでの回転変動を低減して、高速回転機械に加わるねじり振動を抑制し、高速回転機械の出力軸が強度不足になる虞れをなくすことができる。
【0053】
次に、ワンウェイクラッチYを内蔵したプーリPを、図6を参照しつつ説明する。図6は、ワンウェイクラッチを内蔵したプーリの断面図である。
【0054】
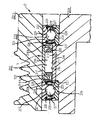
スリーブ208の周囲に従動プーリ207aを、スリーブ208と同心に配置している。スリーブ208の外周面と従動プーリ207aの内周面との間に、1対のサポート軸受209,209と、一方向クラッチであるローラクラッチ210(ワンウェイクラッチY)とを設けている。
【0055】
スリーブ208の外周面中央部には、この外周面から直径方向外方に突出する凸部213を、全周に亙り形成している。従動プーリ207aの外周面は、幅方向に亙る断面形状を波形として、ポリVベルトと呼ばれる無端ベルトの一部を掛け渡し自在としている。又、この従動プーリ207aの内周面は、単なる円筒面としている。そして、スリーブ208の外周面と従動プーリ207aの内周面との間に存在する空間の軸方向中間部に、ローラクラッチ210(ワンウェイクラッチY)を、同じくこの空間の軸方向両端部でこのローラクラッチ210を軸方向両側から挟む位置に、サポート軸受209、209をそれぞれ配置している。
【0056】
ローラクラッチ210は、従動プーリ207aがスリーブ208に対して所定方向に相対回転する傾向となる場合にのみ、これら従動プーリ207aとスリーブ208との間での回転力の伝達を自在とする。この様なローラクラッチ210を構成する為、スリーブ208の外周面に形成した凸部213に、ローラクラッチ用内輪214を、締り嵌めにより外嵌固定している。このローラクラッチ用内輪214は、浸炭鋼等の鋼板にプレス加工等の塑性加工を施して全体を円筒状に形成しており、外周面にカム面215を形成している。即ち、ローラクラッチ用内輪214の外周面に、ランプ部と呼ばれる複数の凹部216を、円周方向に亙って等間隔に形成する事により、外周面をカム面215としている。
【0057】
これに対して、従動プーリ207aの中間部内周面に締り嵌めにより内嵌固定したローラクラッチ用外輪217の内周面のうち、少なくとも次述するローラ219と当接する軸方向中間部は、単なる円筒面としている。この様なローラクラッチ用外輪217は、やはり浸炭鋼等の鋼板にプレス加工等の塑性加工を施して全体を円筒状に形成しており、軸方向両端部に内向フランジ状の鍔部218a、218bを形成している。尚、両鍔部218a、218bのうち、一方(図6の左方)の鍔部218aは、ローラクラッチ用外輪217の製造時に予め形成しておく為、このローラクラッチ用外輪217の円筒部と同等の肉厚にしている。これに対して、他方(図6の右方)の鍔部218bは、このローラクラッチ用外輪217の直径方向内側に、次述するローラ219やクラッチ用保持器220を組み込んでから形成する為、薄肉にしている。
【0058】
又、ローラクラッチ用内輪214及びローラクラッチ用外輪217と共にローラクラッチ210を構成する複数個のローラ219は、ローラクラッチ用内輪214に、このローラクラッチ用内輪214に対する回転を不能として外嵌した合成樹脂製のクラッチ用保持器220に、転動及び円周方向に亙る若干の変位自在に支持している。そして、このクラッチ用保持器220に設けた柱部と各ローラ219との間に、板ばね、或はこのクラッチ用保持器220と一体の合成樹脂ばね等のばねを設けて、これら各ローラ219を、円周方向に関して同方向に弾性的に押圧している。又、図示の状態で、クラッチ用保持器220の軸方向両端面は、ローラクラッチ用外輪217を構成する両鍔部218a、218bの内側面と近接対向させて、このクラッチ用保持器220が軸方向に変位する事を阻止している。尚、この様なローラクラッチ210の基本的な構造及び作用は、従来から周知であるから、これ以上の詳しい図示並びに説明は省略する。
【0059】
又、各サポート軸受209,209は、従動プーリ207aに加わるラジアル荷重を支承しつつ、この従動プーリ207aとスリーブ208との相対回転を自在とする。本例の場合、各サポート軸受209,209として、深溝型の玉軸受を使用している。即ち、これら各サポート軸受209,209は、それぞれ内周面に深溝型の外輪軌道221,221を有する軸受用外輪222,222と、それぞれの外周面に深溝型の内輪軌道223,223を有する軸受用内輪224,224と、外輪軌道221,221と内輪軌道223,223との間にそれぞれ複数個ずつ転動自在に設けた、転動体である玉225,225とから成る。又、軸受用外輪222,222の両端部内周面に形成した係止溝226,226に、それぞれシールリング227,227を装着する事により、各玉225,225を設置した空間228,228の両端開口を塞いでいる。
【0060】
(第2実施の形態)
次に、第2実施の形態について説明する。図7は、本発明の第2実施の形態に係るくさびローラ式変速機の断面図である。図8は、トーショナルダンパを内蔵したプーリの断面図である。
【0061】
本実施の形態では、ワンウェイクラッチYを内蔵したプーリPに代えて、トーショナルダンパZを内蔵したプーリPを用いている。なお、プーリPは、低速側シャフト3の端部にスプライン嵌合してあり、ナット50により固定してある。
【0062】
従って、エンジンからの回転変動は、くさびローラ式変速機Aに低減して入力することから、変速機Aでの回転変動を低減して、高速回転機械に加わるねじり振動を抑制し、高速回転機械の出力軸が強度不足になる虞れをなくすことができる。
【0063】
次に、トーショナルダンパZを内蔵したプーリPを、図8を参照しつつ説明する。図8は、トーショナルダンパを内蔵したプーリの断面図である。
【0064】
ハブ301が、シャフト(図示せず)に対する取付部301aと、径方向外方へ向けての立上がり部301bと、リム状の円筒部301cとを一体に備えており、円筒部301cの外周側に、弾性体303および質量体(振動リングとも称する)304を備えたトーショナルダンパ部302が設けられている。取付部301aの外周側に取付スリーブ305が嵌着されており、この取付スリーブ305の外周側にカップリングゴム306を介してプーリ307が接続され、このプーリ307が、円筒部301cの内周側に配置された円筒状部307aと、フランジ部307bと、質量体304の外周側に配置されたプーリ溝部307cとを一体に備えている。プーリ溝部307cは、小型のV溝を複数軸方向に並べたポリV状に成形されている。質量体304とプーリ溝部307cの間にベアリング308が介装され、このベアリング308に、質量体304とフランジ部307bの間に介装されたスラストベアリング部308aが一体に成形されている。円筒状部307aの、フランジ部307bとは反対側の軸方向端部(図上右端部)307dに、円周上一部の突起307eが軸方向一方(図上右方)へ向けて設けられ、この突起307eが、立上がり部301bに設けた円弧形の孔部301dに挿入され、この突起307eと孔部301dの組み合わせにより、円周方向に係合してハブ301とプーリ307の相対回転を所定角度までに制限するストッパ309が設けられている。
【0065】
ハブ301は所定の金属により環状に成形されている。孔部301dは、突起307eを相対回転自在とするとともに所定の角度で円周方向に係合することができれば、軸方向に貫通されていなくても良い。弾性体303は所定のゴム状弾性材により環状に成形され、円筒部301cと質量体304の間に軸方向一方から圧入されている。質量体304は所定の金属により環状に成形されている。この質量体304は外周面に段差304aを有して、この段差304aを境として小径部304bと大径部304cとを備えており、小径部304bの外周側にプーリ溝部307cが配置されている。大径部304cの外径寸法はプーリ溝部307cの外径寸法より大きく設定されている。弾性体303および質量体304を備えたトーショナルダンパ部302は、円筒部301cと質量体304の間に弾性体303を圧入した嵌合タイプのトーショナルダンパ部であるが、取付スリーブ(図示せず)と質量体304の間に弾性体303を加硫接着するとともに、この取付スリーブを円筒部301cに嵌着するブッシュタイプのトーショナルダンパ部であっても良い。取付スリーブ305およびプーリ307はそれぞれ所定の板金により環状に成形されている。ベアリング308は所定の樹脂により環状に成形されているが、その種類または材質は特に限定されない。カップリングゴム306は所定のゴム状弾性材により環状に成形され、成形と同時に取付スリーブ305およびプーリ307のそれぞれに加硫接着されている。
【0066】
またこのカップリングゴム306は、その内周端部306aと外周端部306bの軸方向相対位置が成形時とは異なるようにして、当該ダンパに組み込まれて、このカップリングゴム306に予圧縮が付与されている。すなわち、このカップリング306を成形するに際しては、取付スリーブ305のプーリ307に対する軸方向相対位置を図上鎖線で示す位置に設定し、このように取付スリーブ305とプーリ307を軸方向にずらした状態で、カップリングゴム306を成形するとともに取付スリーブ305およびプーリ307のそれぞれに加硫接着する。これによりカップリングゴム306は、図上鎖線で示した形状に成形され、この形状を原状(原形)として成形される。ゴム状弾性材(カップリングゴム306)を二つの剛材(取付スリーブ305およびプーリ307)の間に掛け渡すように成形接着した場合には、二つの剛材の相対位置が変わらない限り、ゴム状弾性材が成形後に熱収縮して、二つの剛材の間で引っ張られた状態となり、この状態のまま使用されると、負荷が大きいために、ゴム状弾性材が早期に劣化してしまう。これを防止するには、成形後にゴム状弾性材に予圧縮を付与して、引っ張り状態を圧縮状態に変更すれば良い訳で、そこで当該ダンパでは、破線の形状に成形したカップリングゴム306を実線の状態で当該ダンパに接着すべく、カップリングゴム306を、内周端部306aと外周端部306bの軸方向相対位置が成形時とは異なるようにして、当該ダンパに組み込むことにした。これにより内周端部306aと外周端部306bの距離が大きな比率をもって短くなるために、カップリングゴム306に大きな予圧縮が付与される。取付スリーブ305はこれを、取付部301aの外周面に設けた係合段部301eに当接するまで、圧入する。ここまで取付スリーブ305を圧入すると、プーリ7がカップリングゴム306の弾性により、スラストベアリング部308aを介して質量体304に押し付けられる。すなわち、スラストベアリング部308aが相対位置の変更状態を維持し、プーリ307がスラストベアリング部308aを介して質量体304に常に押し付けられることになる。
【0067】
上記構成を有するダンパは、取付部301aをもって低速側シャフト3の端部に取り付けられ、プーリ溝部307cに無端ベルト(図示せず)を巻架してトルクが伝達される際、クランクシャフトから伝達されるトルク変動を吸収することができる。
【0068】
なお、本発明は、上述した実施の形態に限定されず、種々変形可能である。
【0069】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように、本発明によれば、くさび作用を利用した摩擦ローラ式変速機を高速回転機械の増速機として用いており、くさびローラ式変速機は、トラクションドライブであり、高速回転でも静かで滑らかな動力伝達が行えることから、振動や騒音の問題は全くない。さらに、トラクションドライブに必要な押付力は、くさび作用により得る機構であり、伝達トルクに比例した適正な押付力が常に得られるため、すべりが発生することはない。同時に、低回転低トルク領域から高回転高トルク領域まで高い効率が得られる。
【0070】
また、低速側シャフトは、ワンウェイクラッチを介してプーリを備えるか、又は、トーショナルダンパを介してプーリを備えている。
【0071】
従って、エンジンからの回転変動は、くさびローラ式変速機に低減して入力することから、変速機での回転変動を低減して、高速回転機械に加わるねじり振動を抑制し、高速回転機械の出力軸が強度不足になる虞れをなくすことができる。なお、ディーゼルエンジンでは、エンジン回転変動が大きいので特に有効である。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の第1実施の形態に係るくさびローラ式変速機の内部構造を示す断面図。
【図2】図1のb−b線に沿った断面図。
【図3】くさびローラ式変速機の作用を説明する図。
【図4】本発明に係る、正逆両方向の回転時にトルク伝達可能なくさびローラ式変速機の断面図。
【図5】アンギュラ玉軸受2個を正面組合せした例の拡大断面図。
【図6】ワンウェイクラッチを内蔵したプーリの断面図である。
【図7】本発明の第2実施の形態に係るくさびローラ式変速機の断面図である。
【図8】トーショナルダンパを内蔵したプーリの断面図である。
【図9】くさびローラ式変速機を増速機として用い、低速側シャフトに通常のプーリを装着した例の断面図である。
【符号の説明】
1、101 ハウジング
2、102 ハウジング(仕切板)
3、103 低速側シャフト
4 円盤状部材
14 連結板
17、117 高速側シャフト
22 スラストニードル軸受
23、123 孔
24、25 アンギュラ玉軸受
26 予圧部材
27 突部
28 ボルト
29 シール部材
30 複列アンギュラ玉軸受
31、131a、131b 深溝玉軸受
32 外輪(低速側シャフト)
33 保持リング
34 ボルト
36 環状空間
37、37a、37b ガイドローラ
38、38a、38b 可動ローラ
39a、39b 支持軸
40 嵌合孔
41,41a 支持孔
42 ラジアルニードル軸受
43 動力伝達用円筒面
44 被駆動側円筒面
45 駆動側円筒面
46 シリンダ孔
47 弾性材
48 内径側当接部
49 外径側当接部
50 ナット
207a
A くさびローラ式変速機(増速機)
P プーリ
X 高速回転機械
Y ワンウェイクラッチ
Z トーショナルダンパ
207a 従動プーリ
208 スリーブ
209 サポート軸受
210 ローラクラッチ
213 凸部
214 ローラクラッチ用内輪
215 カム面
216 凹部
217 ローラクラッチ用外輪
218a,218b 鍔部
219 ローラ
220 クラッチ保持器
221 外輪軌道
222 軸受用外輪
223 内輪軌道
224 軸受用内輪
225 玉
226 係止溝
228 空間
301 ハブ
301a 取付部
301b 立ち上がり部
301c 円筒部
301d 孔部
301e 係合段部
302 トーショナルダンパ部
303 弾性体
304 質量体
304a 段差
304b 小径部
304c 大径部
305 取付スリーブ
306 カップリングゴム
306a 内周端部
306b 外周端部
307 プーリ
307a 円筒状部
307b フランジ部
307c プーリ溝部
307d 軸方向端部
307e 突起
308 ベアリング
308a スラストベアリング部
309 ストッパ[0001]
TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a friction roller type transmission utilizing a wedge effect which is suitable for a machine in which a high-speed side shaft rotates at a high speed, for example, a turbomachine, a supercharger, a speed increasing machine such as a machine tool.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In JP-A-4-203421 and JP-A-11-294548, a supercharger for a vehicle engine is of a centrifugal type, in which power is transmitted directly from an engine drive shaft to a belt, and is increased by a gearbox. At a high speed, the impeller is rotationally driven.
[0003]
In JP-A-4-203421, a planetary gear mechanism is used as a speed increasing device in order to obtain a high speed increasing ratio. However, at a rotational speed ranging from tens of thousands to more than 100,000 rpm, there is a serious problem in terms of life as well as gear vibration and noise.
[0004]
Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. H11-294548 discloses a method using a planetary roller of a friction roller mechanism. By tightening a planetary roller and a sun shaft with a flexible outer ring, a pressing force required by a traction drive is reduced. Structure. Therefore, slip occurs in a high rotation and high torque state, and the driving force cannot be transmitted to the impeller. In order to prevent this, it is necessary to tighten the planetary roller with the outer ring with a larger force, but in such a case, in a low rotation and low torque state, the pressing is performed with an excessive pressing force, and the efficiency is reduced. I will. At the same time, since a large pressing force always acts, there is a problem in terms of life.
[0005]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
Further, as described above, in the system in which power is directly obtained from the drive shaft (crankshaft) of the engine by belt transmission, the rotation of the crankshaft of the engine varies according to the number of cylinders due to ignition and combustion of the engine. have. Therefore, rotation fluctuations are input to the pulley of the gearbox driven from the crankshaft of the engine. Since the speed is increased by the speed increaser, the rotation fluctuation of the engine is amplified on the impeller side. Due to the amplified rotation fluctuation (vibration), a large torsional vibration is applied to the impeller and the output shaft, so that the strength of the impeller and the output shaft may be insufficient.
[0006]
As described above, the problem caused by the rotation fluctuation caused by the ignition and combustion of the engine is more remarkable because the speed increaser increases the speed from tens of thousands rpm to 100,000 rpm or more.
[0007]
In addition, since the rotation increased in speed by the belt enters the pulley of the speed increaser, the rotation fluctuation of the engine is also amplified here.
[0008]
The present invention has been made in view of the above-described circumstances, and utilizes a wedge effect that reduces transmission of rotational fluctuation to a speed-increasing gear and suppresses transmission of torsional vibration to a high-speed rotating machine. An object of the present invention is to provide a friction roller type transmission.
[0009]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to achieve the above object, a friction roller type transmission utilizing a wedge action according to claim 1 of the present invention rotatably supports a low speed side shaft in a housing, and has an outer ring at one end of the low speed side shaft. On the other hand, eccentric with respect to the low-speed side shaft and the outer ring, rotatably support the high-speed side shaft,
At least one guide roller and at least one movable roller that moves during torque transmission between the outer ring and the high-speed side shaft,
The low-speed side shaft is provided with a pulley via a one-way clutch.
[0010]
Further, the friction roller type transmission utilizing a wedge action according to
At least one guide roller and at least one movable roller that moves during torque transmission between the outer ring and the high-speed side shaft,
The low-speed side shaft is provided with a pulley via a torsional damper.
[0011]
As described above, according to the present invention, the friction roller type transmission utilizing the wedge action is used as a speed increasing device of a high-speed rotating machine, and the wedge roller type transmission is a traction drive, and is quiet even at high speed rotation. Since smooth power transmission can be performed, there is no problem of vibration and noise. Further, the pressing force required for the traction drive is a mechanism obtained by a wedge action, and an appropriate pressing force proportional to the transmission torque is always obtained, so that no slip occurs. At the same time, high efficiency is obtained from the low rotation and low torque region to the high rotation and high torque region.
[0012]
Further, the low-speed side shaft includes a pulley via a one-way clutch, or includes a pulley via a torsional damper.
[0013]
Therefore, for example, since the rotational fluctuation from the engine or the like is reduced and input to the wedge roller type transmission, the rotational fluctuation in the transmission is reduced, and the torsional vibration applied to the high-speed rotating machine is suppressed. The possibility that the output shaft of the high-speed rotating machine becomes insufficient in strength can be eliminated. Note that a diesel engine is particularly effective because the engine rotation fluctuation is large.
[0014]
The traction drive type transmission has been developed for various industrial uses because of its quietness and smoothness. In recent years, attempts have been made to apply it to personal use such as automobiles and bicycles, and it has attracted attention as a next-generation power transmission system. ing.
[0015]
A traction drive type transmission is different from a gear transmission in that at least two rotating bodies having a smooth surface are strongly pressed and a lubricating oil film (for example, an EHL oil film) is interposed therebetween to transmit power. The basic formula is represented by a simple friction formula of Ft = μ · Fc (Ft: traction force). Here, Fc is called a pressing force, and various methods have been developed for generating the pressing force.
[0016]
As one of the traction drive type transmissions, there is a friction roller type transmission utilizing a wedge action (hereinafter referred to as a wedge roller type transmission). The wedge roller type transmission includes an outer ring rotatably provided around an end of a high speed side shaft in an eccentric state with respect to the high speed side shaft, and a driven side which is an outer peripheral surface of the high speed side shaft. A power transmission is provided between the cylindrical surface and the drive-side cylindrical surface that is the inner peripheral surface of the outer ring, and is arranged in an annular space whose radial width is not uniform in the circumferential direction. A transmission having at least one guide roller and at least one movable roller as a cylindrical surface for use. The movable roller is a roller that generates a pressing force by a wedge action, and is a roller that moves in a radial direction and a circumferential direction.
[0017]
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, a wedge roller type transmission according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
[0018]
FIG. 1 is a sectional view of a wedge roller type transmission according to an embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of the wedge roller type transmission having a one-way clutch function along the line bb in FIG. 1, FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating the operation of the wedge roller type transmission, and FIG. It is sectional drawing of the wedge roller type transmission which can transmit a torque at the time of rotation of both reverse directions.
[0019]
In the present embodiment, the wedge roller type transmission A functions as a speed increase gear having the low speed side shaft 3 (outer ring side) as an input side and the high
[0020]
Also, as shown in FIG. 2, the wedge roller type transmission A has a one-way clutch function that transmits torque during forward rotation, but does not transmit torque when rotating reversely, As shown in FIG. 7, torque may be transmitted during both forward and reverse rotations.
[0021]
In a wedge roller type transmission A according to an embodiment of the present invention, a
[0022]
The high-
[0023]
As shown in FIG. 2, a large-
[0024]
As shown in FIG. 3, the
[0025]
As a result, as shown in FIG. 3, during normal rotation, the
[0026]
On the other hand, at the time of reverse rotation, the
[0027]
As shown in FIG. 2, between the inner peripheral surface of the
[0028]
In the
[0029]
The
[0030]
In this manner, the power transmission, which is the outer peripheral surfaces of the
[0031]
Note that, of the
[0032]
When the rotating shaft is rotationally driven by the wedge roller type transmission according to the present invention configured as described above, a driving force is input to the low-speed side shaft 3 to rotate the
[0033]
Further, the
[0034]
That is, when the
[0035]
As a result, the power transmission cylindrical surface 43b, which is the outer peripheral surface of the
[0036]
As described above, the force for moving the
[0037]
In the case of the example shown in FIG. 2, the wedge roller type transmission A has a one-way clutch function, and the rotation speed of the high-
[0038]
Next, a wedge roller type transmission shown in FIG. 4 that can transmit torque when rotating in both forward and reverse directions will be described.
[0039]
FIG. 4 shows a structure in which the high-speed shaft 17 (see FIG. 1) is rotatable in both clockwise and counterclockwise directions. Therefore, the structure of the present embodiment is implemented in combination with a high-speed rotating machine X (see FIG. 1) whose rotation direction can be freely changed. In such a configuration of the present example, one
[0040]
In the case of the structure of the present example configured as described above, when the
[0041]
In the case of the present embodiment configured as described above, even when the
[0042]
(1st Embodiment)
Next, a first embodiment will be described. FIG. 1 is a sectional view of a wedge roller type transmission according to a first embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of the wedge roller type transmission having a one-way clutch function along the line bb in FIG. 1, FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating the operation of the wedge roller type transmission, and FIG. It is sectional drawing of the wedge roller type transmission which can transmit a torque at the time of both reverse rotation. FIG. 5 is an enlarged sectional view of an example in which two angular ball bearings are combined in front.
[0043]
In the
[0044]
No bearing is provided on the high-speed rotating machine X side. This is because if the high-
[0045]
As described above, in the present embodiment, the bearing support of the high-
[0046]
On the wedge roller type transmission A side, as shown in FIG. 5, two angular ball bearings (24, 25) are combined in front, so that the angular rigidity of the high
[0047]
The high-
[0048]
Therefore, according to the present invention, the demands of the wedge roller type transmission A and the demands of the high-speed rotating machine X, which have conventionally been incompatible, can be satisfied. Machine) can be provided.
[0049]
FIG. 9 is a cross-sectional view of an example in which a wedge roller type transmission A is used as a speed increase gear and a normal pulley P is mounted on the low-speed side shaft 3. As in this example, the wedge roller type transmission A is used as a speed increaser of a high-speed rotating machine. The wedge roller type transmission A is a traction drive, and can perform quiet and smooth power transmission even at high speed rotation. Therefore, there is no problem of vibration and noise. Further, the pressing force required for the traction drive is a mechanism obtained by a wedge action, and an appropriate pressing force proportional to the transmission torque is always obtained, so that no slip occurs. At the same time, high efficiency is obtained from the low rotation and low torque region to the high rotation and high torque region.
[0050]
However, the wedge roller type transmission A has a one-way power transmission type and a two-way power transmission type, and can be applied to both. In the case of the one-way power transmission type, there is a one-way clutch function. Since the pulley P is used, there is a drag torque due to the pressurized spring even during idling, and there is a possibility that the rotation fluctuation of the engine cannot be completely removed.
[0051]
Therefore, in the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 1, a pulley P having a one-way clutch Y is used on the low-speed shaft 3 (input side) of the wedge roller type transmission A. The pulley P is spline-fitted to the end of the low-speed side shaft 3 and is fixed by a
[0052]
Therefore, the rotation fluctuation from the engine is reduced and input to the wedge roller type transmission A, so that the rotation fluctuation in the transmission A is reduced, torsional vibration applied to the high-speed rotation machine is suppressed, and the high-speed rotation machine is controlled. Can be prevented from becoming insufficient in strength.
[0053]
Next, the pulley P incorporating the one-way clutch Y will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 6 is a sectional view of a pulley incorporating a one-way clutch.
[0054]
A driven pulley 207a is arranged around the
[0055]
At the center of the outer peripheral surface of the
[0056]
The
[0057]
On the other hand, in the inner peripheral surface of the
[0058]
A plurality of
[0059]
The
[0060]
(2nd Embodiment)
Next, a second embodiment will be described. FIG. 7 is a cross-sectional view of a wedge roller type transmission according to a second embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 8 is a sectional view of a pulley incorporating a torsional damper.
[0061]
In the present embodiment, a pulley P containing a torsion damper Z is used instead of a pulley P containing a one-way clutch Y. The pulley P is spline-fitted to the end of the low-speed side shaft 3 and is fixed by a
[0062]
Therefore, the rotation fluctuation from the engine is reduced and input to the wedge roller type transmission A, so that the rotation fluctuation in the transmission A is reduced, torsional vibration applied to the high-speed rotation machine is suppressed, and the high-speed rotation machine is controlled. Can be prevented from becoming insufficient in strength.
[0063]
Next, a pulley P having a built-in torsional damper Z will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 8 is a sectional view of a pulley incorporating a torsional damper.
[0064]
The
[0065]
The
[0066]
The
[0067]
The damper having the above configuration is attached to the end of the low-speed side shaft 3 with the attachment portion 301a, and is transmitted from the crankshaft when torque is transmitted by winding an endless belt (not shown) around the pulley groove 307c. Torque fluctuations can be absorbed.
[0068]
The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, but can be variously modified.
[0069]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, a friction roller type transmission utilizing a wedge action is used as a speed increasing device of a high-speed rotating machine, and the wedge roller type transmission is a traction drive, Since the power can be transmitted quietly and smoothly, there is no problem of vibration or noise. Further, the pressing force required for the traction drive is a mechanism obtained by a wedge action, and an appropriate pressing force proportional to the transmission torque is always obtained, so that no slip occurs. At the same time, high efficiency is obtained from the low rotation and low torque region to the high rotation and high torque region.
[0070]
Further, the low-speed side shaft includes a pulley via a one-way clutch, or includes a pulley via a torsional damper.
[0071]
Therefore, the rotational fluctuation from the engine is reduced and input to the wedge roller type transmission, so that the rotational fluctuation in the transmission is reduced, torsional vibration applied to the high-speed rotating machine is suppressed, and the output of the high-speed rotating machine is reduced. It is possible to eliminate the possibility that the shaft has insufficient strength. Note that a diesel engine is particularly effective because the engine rotation fluctuation is large.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a sectional view showing an internal structure of a wedge roller type transmission according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a sectional view taken along the line bb in FIG. 1;
FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating the operation of a wedge roller type transmission.
FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view of a wedge roller type transmission capable of transmitting torque when rotating in both forward and reverse directions according to the present invention.
FIG. 5 is an enlarged cross-sectional view of an example in which two angular ball bearings are combined in front;
FIG. 6 is a sectional view of a pulley incorporating a one-way clutch.
FIG. 7 is a sectional view of a wedge roller type transmission according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 8 is a sectional view of a pulley incorporating a torsional damper.
FIG. 9 is a cross-sectional view of an example in which a wedge roller type transmission is used as a gearbox and a normal pulley is mounted on a low-speed side shaft.
[Explanation of symbols]
1, 101 housing
2,102 housing (partition plate)
3,103 Low speed shaft
4 Disc-shaped members
14 Connecting plate
17, 117 High speed side shaft
22 Thrust needle bearing
23,123 holes
24, 25 angular contact ball bearing
26 Preload member
27 Projection
28 volts
29 Sealing member
30 Double row angular contact ball bearing
31, 131a, 131b Deep groove ball bearing
32 Outer ring (low-speed side shaft)
33 Retaining ring
34 volts
36 Annular space
37, 37a, 37b Guide roller
38, 38a, 38b Movable roller
39a, 39b Support shaft
40 mating hole
41, 41a support holes
42 Radial needle bearing
43 Cylindrical surface for power transmission
44 Driven cylindrical surface
45 Drive side cylindrical surface
46 Cylinder hole
47 Elastic material
48 Inside contact part
49 Outer diameter side contact part
50 nuts
207a
A Wedge roller type transmission (speed increaser)
P pulley
X High-speed rotating machine
Y one way clutch
Z Torsional damper
207a driven pulley
208 sleeve
209 Support bearing
210 roller clutch
213 convex
214 Inner ring for roller clutch
215 Cam surface
216 recess
217 Outer ring for roller clutch
218a, 218b collar
219 Laura
220 clutch retainer
221 Outer ring track
222 Outer ring for bearing
223 Inner ring track
224 Inner ring for bearing
225 balls
226 Lock groove
228 space
301 hub
301a mounting part
301b rising part
301c cylindrical part
301d hole
301e engaging step
302 Torsional damper
303 elastic
304 mass
304a step
304b small diameter part
304c Large diameter part
305 Mounting sleeve
306 coupling rubber
306a Inner circumference end
306b Outer edge
307 pulley
307a cylindrical part
307b Flange part
307c Pulley groove
307d axial end
307e protrusion
308 bearing
308a Thrust bearing
309 Stopper
Claims (3)
前記外輪と前記高速側シャフトの間に、少なくとも1個のガイドローラと、トルク伝達時に移動する少なくとも1個の可動ローラとを有し、
前記低速側シャフトは、ワンウェイクラッチを介してプーリが具備されていることを特徴とするくさび作用を利用した摩擦ローラ式変速機。The low-speed side shaft is rotatably supported on the housing, and an outer ring is provided at one end of the low-speed side shaft, while the eccentricity is provided with respect to the low-speed side shaft and the outer ring, and the high-speed side shaft is rotatably supported,
At least one guide roller and at least one movable roller that moves during torque transmission between the outer ring and the high-speed side shaft,
The low-speed side shaft is provided with a pulley via a one-way clutch.
前記外輪と前記高速側シャフトの間に、少なくとも1個のガイドローラと、トルク伝達時に移動する少なくとも1個の可動ローラとを有し、
前記低速側シャフトは、トーショナルダンパを介してプーリが具備されていることを特徴とするくさび作用を利用した摩擦ローラ式変速機。The low-speed side shaft is rotatably supported on the housing, and an outer ring is provided at one end of the low-speed side shaft, while the eccentricity is provided with respect to the low-speed side shaft and the outer ring, and the high-speed side shaft is rotatably supported,
At least one guide roller and at least one movable roller that moves during torque transmission between the outer ring and the high-speed side shaft,
The low-speed side shaft is provided with a pulley via a torsional damper.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002173091A JP2004019727A (en) | 2002-06-13 | 2002-06-13 | Friction roller type transmission |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002173091A JP2004019727A (en) | 2002-06-13 | 2002-06-13 | Friction roller type transmission |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004019727A true JP2004019727A (en) | 2004-01-22 |
| JP2004019727A5 JP2004019727A5 (en) | 2005-09-22 |
Family
ID=31172480
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002173091A Withdrawn JP2004019727A (en) | 2002-06-13 | 2002-06-13 | Friction roller type transmission |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2004019727A (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009174580A (en) * | 2008-01-22 | 2009-08-06 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | Planetary roller type power transmission device |
| JP2012225480A (en) * | 2011-04-22 | 2012-11-15 | Nok Corp | Torsional damper |
| JP2016089886A (en) * | 2014-10-31 | 2016-05-23 | Ntn株式会社 | Power transmission roller |
-
2002
- 2002-06-13 JP JP2002173091A patent/JP2004019727A/en not_active Withdrawn
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009174580A (en) * | 2008-01-22 | 2009-08-06 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | Planetary roller type power transmission device |
| JP2012225480A (en) * | 2011-04-22 | 2012-11-15 | Nok Corp | Torsional damper |
| JP2016089886A (en) * | 2014-10-31 | 2016-05-23 | Ntn株式会社 | Power transmission roller |
| CN107076281A (en) * | 2014-10-31 | 2017-08-18 | Ntn株式会社 | Live-roller |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101369831B1 (en) | One-way clutch and off-axis coupling for an engine starting system | |
| US7108113B2 (en) | One-way clutch built-in type rotation transmission device | |
| WO2002002967A1 (en) | One-way clutch built-in type pulley device | |
| JP3652207B2 (en) | One-way clutch built-in type rotation transmission device | |
| JP2004019727A (en) | Friction roller type transmission | |
| JP2004092414A (en) | High-speed fluid device | |
| JP4103629B2 (en) | Power transmission device | |
| JP2010185547A (en) | One-way clutch built-in type pulley device | |
| JP2003301906A (en) | Friction roller type transmission | |
| JP2003314446A (en) | High-speed fluid device | |
| JP2002349677A (en) | Roller clutch and rotation transmission device with built-in roller clutch | |
| JP2000291785A (en) | Pulley device with built-in one-way clutch for alternator | |
| JP2001165201A (en) | Rotary transmission with built-in one-way clutch | |
| JP4306032B2 (en) | Pulley device with built-in one-way clutch for alternator | |
| JP2000240766A (en) | Pulley device with built-in one-way clutch | |
| JP2004270879A (en) | Friction roller type transmission | |
| JP2001099272A (en) | Pulley device with built-in one-way clutch | |
| JP2000320650A (en) | Pulley device with built-in one-way clutch for alternator | |
| JP2001012513A (en) | Pulley device with built-in one-way clutch for alternator | |
| JP2000337479A (en) | Pulley device with built-in roller clutch for alternator | |
| JP2000227151A5 (en) | ||
| JP2004347038A (en) | Friction roller type transmission | |
| JP2004239407A (en) | Friction roller type transmission and high speed fluid device | |
| JP2001032910A (en) | Pulley device with built-in one-way clutch for alternator | |
| JP2005140204A (en) | Friction roller type transmission |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050420 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20050420 |
|
| A761 | Written withdrawal of application |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A761 Effective date: 20060608 |