EP2777200B1 - Methods, radio base station and radio network controller - Google Patents
Methods, radio base station and radio network controller Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2777200B1 EP2777200B1 EP12790989.3A EP12790989A EP2777200B1 EP 2777200 B1 EP2777200 B1 EP 2777200B1 EP 12790989 A EP12790989 A EP 12790989A EP 2777200 B1 EP2777200 B1 EP 2777200B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- pdu
- information
- rbs
- loss
- rnc
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Not-in-force
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 69
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000004122 cyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 201000001718 Roberts syndrome Diseases 0.000 claims 21
- 208000012474 Roberts-SC phocomelia syndrome Diseases 0.000 claims 21
- 238000005001 rutherford backscattering spectroscopy Methods 0.000 claims 2
- 241001481828 Glyptocephalus cynoglossus Species 0.000 claims 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 12
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000001413 cellular effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000003111 delayed effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 101000741965 Homo sapiens Inactive tyrosine-protein kinase PRAG1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100038659 Inactive tyrosine-protein kinase PRAG1 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 230000010267 cellular communication Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010295 mobile communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000011664 signaling Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L43/00—Arrangements for monitoring or testing data switching networks
- H04L43/08—Monitoring or testing based on specific metrics, e.g. QoS, energy consumption or environmental parameters
- H04L43/0823—Errors, e.g. transmission errors
- H04L43/0829—Packet loss
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/12—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel
- H04L1/16—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel in which the return channel carries supervisory signals, e.g. repetition request signals
- H04L1/1607—Details of the supervisory signal
- H04L1/1621—Group acknowledgement, i.e. the acknowledgement message defining a range of identifiers, e.g. of sequence numbers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/08—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by repeating transmission, e.g. Verdan system
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/12—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel
- H04L1/16—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel in which the return channel carries supervisory signals, e.g. repetition request signals
- H04L1/1607—Details of the supervisory signal
- H04L1/1642—Formats specially adapted for sequence numbers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/12—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel
- H04L1/16—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel in which the return channel carries supervisory signals, e.g. repetition request signals
- H04L1/1607—Details of the supervisory signal
- H04L1/1671—Details of the supervisory signal the supervisory signal being transmitted together with control information
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/12—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel
- H04L1/16—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel in which the return channel carries supervisory signals, e.g. repetition request signals
- H04L1/18—Automatic repetition systems, e.g. Van Duuren systems
- H04L1/1829—Arrangements specially adapted for the receiver end
- H04L1/1835—Buffer management
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/12—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel
- H04L1/16—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel in which the return channel carries supervisory signals, e.g. repetition request signals
- H04L1/18—Automatic repetition systems, e.g. Van Duuren systems
- H04L1/1829—Arrangements specially adapted for the receiver end
- H04L1/1848—Time-out mechanisms
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/12—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel
- H04L1/16—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel in which the return channel carries supervisory signals, e.g. repetition request signals
- H04L1/18—Automatic repetition systems, e.g. Van Duuren systems
- H04L1/1867—Arrangements specially adapted for the transmitter end
- H04L1/1874—Buffer management
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L43/00—Arrangements for monitoring or testing data switching networks
- H04L43/04—Processing captured monitoring data, e.g. for logfile generation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W24/00—Supervisory, monitoring or testing arrangements
- H04W24/10—Scheduling measurement reports ; Arrangements for measurement reports
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L2001/0092—Error control systems characterised by the topology of the transmission link
- H04L2001/0097—Relays
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L47/00—Traffic control in data switching networks
- H04L47/10—Flow control; Congestion control
- H04L47/34—Flow control; Congestion control ensuring sequence integrity, e.g. using sequence numbers
Definitions
- the invention relates to multi-flow High-Speed Downlink Packet Access operation and particularly to drop and/or loss events in multi-flow operation.
- HSDPA High-Speed Downlink Packet Access
- the development includes several features in both UL (Uplink) and DL (Downlink) to enhance system performance and capacity as well as enabling a better user experience.
- Examples of developments are downlink MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) (3GPP TR (Third Generation Partnership Project Technical Report) 25.872 Release 7) and dual cell /dual band HSDPA (3GPP TR 25.872 Release 8 & 9).
- MF-HSDPA Multi-flow HSDPA
- MF-HSDPA Mobile Equipment nodes, also referred to as mobile/wireless terminals
- the cells can belong to the same Node B (intra site MF-HSDPA) or to different Node Bs (inter site MF-HSDPA).
- DC-HSDPA Dual Cell HSDPA, also known as Dual Carrier HSDPA
- the split may be in either the PDCP (Packet Data Convergence Protocol) or RLC (Radio Link Control) layer.
- a potential benefit of introducing MF-HSDPA is that cell edge users may suffer from bad coverage and/or low throughput which brings down the overall system capacity. If these users could use available resources from neighbouring cells, i.e. receive data also from the non-serving cell, their situation could be significantly improved. This would improve the overall system capacity and the user performance for cell edge users.
- HSDPA is described in further detail in HSDPA Multipoint Transmission, 3GPP TR 25.872.
- RLC transmissions When RLC transmissions get stuck on one link, it may be a good alternative to retransmit the RLC PDU(s) (Protocol Data Unit(s)) over the other link. If the retransmission cannot get through over the other link either, further retransmissions could be switched back to the original link. However, in this case there could be old copies existing at the link(s) besides the last retransmitted copy. Duplicate copies can result in lower application level throughputs.
- RLC PDU(s) Protocol Data Unit(s)
- the detected PDU drop event may correspond to a drop from a MAC-hs/ehs, Media Access Control - high speed/enhanced high speed, queue.
- the drop could be a deliberate drop by the RBS, which is then communicated to the RNC.
- the detected PDU loss event may correspond to a loss in a transport network interconnecting the RNC and at least one of the first RBS and the second RBS.
- the RBS detects an unintended loss of a packet in the transport network, this is communicated to the RBS.
- the loss in a transport network may be detected based on a sequence number. For example, if there is a gap in sequence numbers, this indicates a lost PDU.
- the sequence number may be a sequence number according to Iub FP, Frame Protocol.
- the loss in a transport network may be detected based on the sequence number and a delay reference time field of received Iub FP data frames.
- the information communicated from the RBS to the RNC, notifying of a detected PDU drop event and/or loss event may be configured to cause the RNC to retransmit a PDU associated with the detected PDU drop event and/or loss event.
- the communicating information from the RBS to the RNC, notifying of each detected PDU drop event and/or loss event may comprise: communicating the information including a sequence number and/or a DRT, Delay Reference Time and CRC, Cyclic Redundancy Check, of an Iub DF, Data Frame, in which the PDU was received by the RBS.
- the information may comprise the first two octets of the PDU associated with the respective drop event and/or loss event.
- the information may comprise a CRC of a DF related to the PDU associated with the respective drop event and/or loss event.
- the information may comprise a position of the MAC-d, Medium Access Control Dedicated Data, PDU in an Iub DF.
- the information may provide an indication of Iub frames received right before and right after a detected Iub frame loss.
- the information may comprise the first two octets of the PDUs that were received right before and right after a gap due to TN, Transport Network, loss of the PDU associated with the respective drop event and/or loss event.
- the information may comprise an RLC header associated with the dropped PDU.
- the information may comprise a header of the last PDU in a frame before a gap due to TN loss.
- the information may comprise the header of the first PDU in a frame after a gap due to TN loss.
- the information may comprise a DRT field, an FSN, Frame Sequence Number, field and a CRC of Iub Data Frames that were received right before and right after a gap due to TN loss.
- the information may comprise the following fields: drop reason, number of PDUs dropped, and identifiers of all PDUs dropped.
- the information may comprise the following fields: drop reason, identifier of the last PDU before the lost PDU and identifier of the first PDU after the lost PDU.
- a radio base station according to claim 19 product storing instructions that, when executed by the processor, causes the radio base station to: detect PDU drop events and/or loss events; and communicate information from the RBS to the RNC, notifying of each detected PDU drop event and/or loss event.
- the retransmitting may comprise retransmitting the PDU through a different route that includes a second RBS.
- the method may further comprise: storing second information at the RNC, including the sequence number and/or the DRT and CRC of the Iub DF in which the PDU was transmitted to the RBS; and comparing the first and second information to identify the PDU to be retransmitted.
- the method may further comprise receiving the second information.
- the storing second information may comprise storing a hash value in a hash repository representing the second information; and the comparing may comprise comparing the hash value representing the second information with a hash value representing the first information, to identify the PDU to be retransmitted.
- a radio network controller according to claim 25.
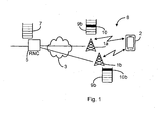
- Fig 1 is a schematic diagram illustrating a cellular network 8 where embodiments presented herein maybe applied.
- the cellular communications network 8 comprises a core network (not shown), a radio network controller (RNC) and two or more radio base stations (RBSs) 1a-b, here in the form of Node Bs, also known as NodeBs or NBs.
- the radio base stations 1a-b could also be in the form of evolved Node Bs, BTSs (Base Transceiver Stations) and/or BSSs (Base Station Subsystems), etc.
- the radio base stations 1a-b provide radio connectivity to a plurality of user equipment nodes (UEs) 2 (where one is shown in Fig 1 ).
- the term UE is also known as wireless terminal, mobile terminal, user terminal, user agent, etc.
- the radio base stations 1 are also connected via a transport network 3 to the radio network controller (RNC) 5 for radio network control, and connectivity to central functions and other networks.
- RNC radio network controller
- the cellular network 8 may e.g. comply with any one or a combination of W-CDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiplex), LTE (Long Term Evolution), EDGE (Enhanced Data Rates for GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) Evolution), GPRS (General Packet Radio Service), CDMA2000 (Code Division Multiple Access 2000), or any other current or future wireless network, as long as the principles described hereinafter are applicable.
- W-CDMA Wideband Code Division Multiplex
- LTE Long Term Evolution
- EDGE Enhanced Data Rates for GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) Evolution
- GPRS General Packet Radio Service
- CDMA2000 Code Division Multiple Access 2000
- the interface between each one of the RBSs 1a-b and the RNC 5 is called Iub and the interface between the RNC 5 and core network is called Iu.
- the RNC 5 has a PDCP PDU queue 7 and the two RBSs 1a-b have respective MAC-hs/ehs queues 9a-b.
- RBS Radio Base Station
- RLC PDU retransmission independently of whether that PDU was discarded or only delayed
- more than one copy of the same RLC PDU can exist in the system. Duplicate copies can result in lower application level throughputs.
- RBS that operates to inform the RLC protocol in the RNC about RLC PDU loss over the TN (Transport Network) and RLC PDU drop in the RBS.
- TN Transport Network
- RLC PDU drop in the RBS This allows faster reaction of RLC in RNC to packet loss and provides more efficient RLC PDU retransmission mechanism without redundant RLC PDUs.
- the RBS 1a-b informs the RNC 5 about PDU drop/loss events, e.g. loss in the TN (Transport Network) 3 and drop from a MAC-hs/ehs (Media Access Control - high speed/enhanced high speed) queue.
- PDU drop/loss events e.g. loss in the TN (Transport Network) 3 and drop from a MAC-hs/ehs (Media Access Control - high speed/enhanced high speed) queue.
- the RLC can make more efficient and faster RLC PDU retransmission mechanism and can also avoid redundant RLC PDUs.
- the RLC PDUs are transmitted over the TN using the Iub FP (Frame Protocol).
- the TN loss can be detected based on Iub FP sequence number.
- the RNC RLC Based on the sequence number and the DRT (delay reference time) field of the received Iub FP data frames, the RNC RLC can determine the missing RLC PDUs (lost over the TN).
- H-ARQ Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest
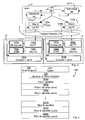
- Fig 2 is a schematic block diagram illustrating one embodiment of RNC and RBSs of Fig 1 .
- the block diagram illustrates modules (comprising hardware and/or software), of which some are used for embodiments presented herein.
- RLC control module 100 There is an RLC control module 100 and two respective MAC-d (Medium Access Control Dedicated Data) modules 102a-b for the two, via the transport network 3, connected radio base stations 1a-b.
- MAC-d Medium Access Control Dedicated Data
- Iub FP modules for incoming and outgoing frame protocol communication.
- the first base station 1a comprises its own Iub FP module 105a and a MAC-hs queue 106a.
- the MAC-hs queue could comprise a MAC-ehs queue.
- a TN loss detection module 107a is connected to the Iub FP module 105a.
- an Active Queue Manager (AQM) 108a is connected to the MAC-hs queue 106a for e.g. detecting dropped expired packets in the MAC-hs queue 106a.
- AQM Active Queue Manager
- a compile and send module 109a compiles information about lost or dropped packets from the AQM 108a and/or the TN loss detector module107a and sends this via the TN 3 to the first Iub FP module 103a of the RNC 5.
- a first determine list module 101a in the RNC determines a list of dropped or lost RLC PDUs and provides this data to the RLC control module 100.
- the first determine list module 101 also uses input from the RLC comprising information about sent RLC PDUs such as sequence number (SN), sending time, etc.
- the second radio base station 1b comprises modules corresponding to the first radio base station 1a and interacts with the RNC 3 in a corresponding way, whereby the RNC also comprises a second determine list module 101b.
- RBSs 1a-b relevant information is collected about lost/dropped PDUs and this information is thus sent back to the RNC 5. Based on this information the RLC 100 can retransmit these packets immediately without waiting for NACK for them from UE. Retransmission of these packets may be carried out on a different leg. These operations can provide more control over the RLC retransmission mechanism.
- the MAC-hs/ehs priority queue additional identification may be needed for each PDU (e.g. the sequence number, DRT and CRC of the Iub DF (Data Frame) in which the given PDU was received).
- the same information is stored for each RLC PDU transmitted in order to be able to identify the dropped PDU.
- a hash table is used for fast lookup. When an RLC PDU is acknowledged by the UE, it is removed from the hash table.
- Some embodiments may operate to:
- the DRT field may be included in all of the HS-DSCH (High-Speed Downlink Shared Channel) data frames.
- some embodiments time-stamp PDUs when they arrive to the MAC-hs/ehs buffer.
- an RBS When an RLC PDU is discarded, an RBS according to some embodiments communicates an indication of the discard and which PDUs were discarded to the RNC 5.
- DRT field the FSN field of the Iub Data Frame are sent back to the RNC, in which the PDUs were received.
- This optionally also includes the CRC of the DF to further enhance identification.
- the position of the RLC PDU in the Iub DF is included when it is a goal to be able to identify separate PDUs (e.g. 1 for the 1st RLC PDU in a DF, 2 for the 2nd etc.)
- an additional sequence number is included in the Iub FP or MAC-d layer for the purposes of these identifications.
- the additional sequence number is 15 bits long, allowing values between 0 and 32767 (decimal).
- the sequence number can be assigned to each frame by the RNC and is be used by the RBS to identify the set of MAC-d PDU's sent in frame. This can also be used by RNC to indicate the MAC-d PDU's that the Node B shall discard.
- the DRT field, the FSN field and CRC of the Iub Data Frame back that were received right before and right after the gap due to TN loss are sent back to the RNC.
- an addition sequence number in the Iub FP or MAC-d layer for the purposes of this identification is included.
- a HS-DSCH PDU Drop Indication control frame is communicated to allow the RBS to notify the RNC about the frame drop.
- the identifiers disclosed above can alternatively be used in signalling from the RNC to the RBS for an explicit drop request.
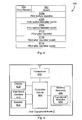
- Fig 3 is a schematic diagram illustrating the structure of a drop indication control frame 199 according to one embodiment, sent from the compile and send module (109a-b of Fig 2 ) of the RBS to the RNC.
- the fields shown in the control frame 199 of Fig 3 are provided in some embodiments for a HS-DSCH PDU Drop Indication control frame of Type 1, related to explicit drop.
- each row is an octet of data.
- This type of control frame is used when the content of the dropped PDU or Data Frame is available in the RBS. In this case, direct identification of the PDUs is possible.
- a drop reason field 200 indicates the reason for the drop. In this embodiment, there are the following possible values:
- a field 202 for number of PDUs dropped is an integer indicating the number of PDUs that have been identified as having been dropped.
- a field comprising several subfields 203a comprises the identifier of the first PDU that has been identified as being dropped. If there are more than one PDU that have been identified as being dropped, the identities of all dropped PDUs are included in the control frame, until an end identifier, each PDU corresponding to its own set of one or more subfields 203'a-c.
- Fig 4 is a schematic diagram illustrating the structure of a drop indication control frame 198 according to one embodiment, sent from the compile and send module (109a-b of Fig 2 ) of the RBS to the RNC.
- the fields shown in the control frame 198 of Fig 4 are provided in some embodiments for a HS-DSCH PDU Drop Indication control frame of Type 1, related to a detected drop.
- each row is an octet of data.
- This type of control frame is used when the content of the dropped PDU or Data Frame is not available in the RBS. In this case only indirect identification of the PDUs is possible.
- control frame 198 there is a set of subfields 210a-c comprising an identifier of the last PDU/DF before the lost PDU(s)/DF(s).
- subfields 211a-c comprising an identifier of the first PDU/DF after the lost PDU(s)/DF(s).
- Fig 5 is a schematic diagram illustrating some modules of a user equipment of Fig 1 .
- the UE is configured according to some embodiments of the present invention.
- the UE 2 includes a transceiver 602, a controller circuit 604, and a memory device(s) 606 containing functional modules 608.
- the UE 2 may further include other elements, such as a display 610, a user input interface 612, and a speaker 614.
- the transceiver 602 (e.g. 3GPP compliant or other RF (Radio Frequency) communication transceiver) is configured to communicate with a base station over a wireless communication interface.
- the controller circuit 604 may include one or more data processing circuits, such as a general purpose and/or special purpose processor (e.g., microprocessor and/or digital signal processor).
- the controller circuit 604 is configured to execute computer program instructions from the functional modules 608 of the memory device(s) 606, described below as a computer readable medium, to perform at least some of the operations and methods described herein as being performed by a UE in accordance with one or more embodiments of the present invention.
- the UE 2 maybe a mobile telephone ("cellular" telephone), a data terminal, and/or another processing device with wireless communication capability, such as, for example, a portable computer, a pocket computer, a hand-held computers, a laptop computers, an electronic book reader, and/or a video game console.
- cellular mobile telephone
- data terminal a data terminal
- processing device with wireless communication capability such as, for example, a portable computer, a pocket computer, a hand-held computers, a laptop computers, an electronic book reader, and/or a video game console.
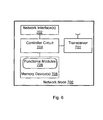
- Fig 6 is a block diagram of a network node 700 configured according to some embodiments of the present invention, and elements of which maybe included in the RBS, the RNC, and/or other nodes of the communications system of Figs 1-2 .
- the network node 700 can include a transceiver 701, a network interface(s) 702, a controller circuit 704, application specific integrated circuit etc.), and a memory device(s) 706 being a computer program product containing functional modules 708.
- the transceiver 701 (e.g., 3GPP compliant or other RF communication transceiver) is configured to communicate with one or more UEs or other nodes of the system.
- the controller circuit 704 may include one or more data processing circuits, such as a general purpose and/or special purpose processor (e.g., microprocessor and/or digital signal processor).
- the controller circuit 704 is configured to execute computer program instructions from the functional modules 708 of the memory device(s) 706, described below as a computer readable medium, to perform at least some of the operations and methods described herein as being performed by an RBS and/or RNC in accordance with one or more embodiments of the present invention.
- the network interface 702 communicates via a network with an RNC (when located in an RBS) or communicates via a network with an RBS and (when located in an RNC).
- Fig 7 is a flow chart illustrating a method according to one embodiment. The method is performed in the first RBS (1a of Fig 1 ), in communication with the RNC (5 of Fig 1 ).
- the RNC is configured for multi-flow HSDPA operation wherein PDUs are communicated toward the UE via the first RBS and at least one second RBS (1b of Fig 1 ).
- PDU drop events and/or loss events are detected, e.g. using the TN loss detector module and/or AQM of Fig 2 , as described above.
- the detected PDU drop event corresponds to a drop from a MAC-hs/ehs queue.
- the detected PDU loss event corresponds to a loss in the transport network interconnecting the RNC and the RBS.
- the loss in the transport network can e.g. be detected based on a sequence number, for instance in accordance with Iub FP.
- the loss in the transport network can also be detected based on the sequence number and a delay reference time field of received Iub FP data frames.
- a communicate to RNC step 22 information is communicated from the RBS to the RNC, notifying of each detected PDU drop event and/or loss event. This can e.g. be effected using the compile and send module of Fig 2 , as described above.
- the information communicated from the RBS to the RNC can be configured to cause the RNC to retransmit a PDU associated with the detected PDU drop event and/or loss event.
- the information communicated from the RBS to the RNC can include one or more of a sequence number, a DRT, a CRC of an Iub DF, in which the PDU was received by the RBS.
- the information communicated from the RBS to the RNC can comprise the first two octets of the PDU associated with the respective drop event and/or loss event.
- the PDU can e.g. be a MAC-d PDU.
- the information communicated from the RBS to the RNC can comprise can comprises a CRC of a DF related to the PDU associated with the respective drop event and/or loss event.
- the information communicated from the RBS to the RNC can comprise a position of the MAC-d, Medium Access Control Dedicated Data, PDU in an Iub DF.
- the information communicated from the RBS to the RNC can provide an indication of Iub frames received right before and right after a detected Iub frame loss.
- the RNC can, in at least some cases, determine which one or more Iub frames that have been lost and can retransmit that or those ones.
- the information communicated from the RBS to the RNC can comprise the first two octets of the PDUs that were received right before and right after a gap due to TN loss of the PDU.
- the PDU can be either a MAC-d or an RLC PDU.
- the information communicated from the RBS to the RNC can comprise an RLC header associated with the dropped PDU.
- the PDU can be either a MAC-d or an RLC PDU.
- the information communicated from the RBS to the RNC can comprise a header of the last PDU in a frame before a gap due to TN loss.
- the information communicated from the RBS to the RNC can comprise the header of the first PDU in a frame after a gap due to TN loss.
- the information communicated from the RBS to the RNC can comprise any one or more of a DRT field, an FSN (Frame Sequence Number) field and a CRC of Iub Data Frames that were received right before and right after a gap due to TN loss.
- a DRT field an FSN (Frame Sequence Number) field
- a CRC of Iub Data Frames that were received right before and right after a gap due to TN loss.
- the information communicated from the RBS to the RNC can comprise the following fields: drop reason, number of PDUs dropped, and identifiers of all PDUs dropped, as described with reference to Fig 3 above.
- the information communicated from the RBS to the RNC can comprise the following fields: drop reason, identifier of the last PDU before the lost PDU and identifier of the first PDU after the lost PDU, as described with reference to Fig 4 above.
- Figs 8A-B are flow charts illustrating methods performed in the RNC of Fig 1 .
- the RNC is configured for multi-flow HSDPA operation, wherein PDUs are communicated toward a the UE via at least the first and second RBSs (1a-b of Fig 1 ). The method illustrated by Fig 8A will be described first.
- a receive first information step 30 first information from the first RBS is received, notifying of a PDU drop event and/or loss event detected by the first RBS.
- a retransmit step 32 the PDU associated with the detected PDU drop event and/or loss event toward the UE is retransmitted in response to the received first information.
- the retransmit step 32 can comprise retransmitting the PDU through a different route that includes a second RBS, i.e. avoiding the first RBS, which reported the loss and/or drop.
- a receive second information step 34 second information is received from the RBS.
- the second information comprises the sequence number and/or the DRT and CRC of the Iub DF in which the PDU was transmitted to the RBS. This second information is used in conjunction with the first information of the receive first information step 30 to determine a dropped PDU.
- the second information is stored at the RNC.
- a compare step 38 the first and second information are compared to identify the PDU to be retransmitted.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
- Detection And Prevention Of Errors In Transmission (AREA)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP15169182.1A EP2938017B1 (en) | 2011-11-10 | 2012-11-08 | Methods, radio base station and radio network controller |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201161558174P | 2011-11-10 | 2011-11-10 | |
| PCT/SE2012/051218 WO2013070162A1 (en) | 2011-11-10 | 2012-11-08 | Methods, radio base station and radio network controller |
Related Child Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP15169182.1A Division EP2938017B1 (en) | 2011-11-10 | 2012-11-08 | Methods, radio base station and radio network controller |
| EP15169182.1A Division-Into EP2938017B1 (en) | 2011-11-10 | 2012-11-08 | Methods, radio base station and radio network controller |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2777200A1 EP2777200A1 (en) | 2014-09-17 |
| EP2777200B1 true EP2777200B1 (en) | 2015-07-01 |
Family
ID=47222269
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP15169182.1A Active EP2938017B1 (en) | 2011-11-10 | 2012-11-08 | Methods, radio base station and radio network controller |
| EP12790989.3A Not-in-force EP2777200B1 (en) | 2011-11-10 | 2012-11-08 | Methods, radio base station and radio network controller |
Family Applications Before (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP15169182.1A Active EP2938017B1 (en) | 2011-11-10 | 2012-11-08 | Methods, radio base station and radio network controller |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US9325594B2 (OSRAM) |
| EP (2) | EP2938017B1 (OSRAM) |
| JP (1) | JP6027622B2 (OSRAM) |
| KR (1) | KR20140098126A (OSRAM) |
| CN (1) | CN103918213B (OSRAM) |
| IN (1) | IN2014DN03308A (OSRAM) |
| MY (1) | MY168125A (OSRAM) |
| WO (1) | WO2013070162A1 (OSRAM) |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2587503Y2 (ja) | 1993-03-26 | 1998-12-16 | 株式会社鈴木製作所 | ミシンの糸案内 |
| WO2013066258A2 (en) * | 2011-11-04 | 2013-05-10 | Telefonaktiebolaget L M Ericsson (Publ) | Handling redundant data in a communication system |
| US9351201B2 (en) * | 2012-03-08 | 2016-05-24 | Qualcomm Incorporated | System and method for reducing data loss during a serving cell change in a multi-flow HSDPA communication network |
| CN106452681B (zh) * | 2013-09-23 | 2019-10-22 | 华为技术有限公司 | 信号处理方法及设备 |
| US20150089382A1 (en) * | 2013-09-26 | 2015-03-26 | Wu-chi Feng | Application context migration framework and protocol |
| WO2015053664A1 (en) | 2013-10-07 | 2015-04-16 | Telefonaktiebolaget L M Ericsson (Publ) | Congestion control in a transport network |
| CN111479330A (zh) * | 2019-01-24 | 2020-07-31 | 电信科学技术研究院有限公司 | 一种数据传输方法、装置、发送节点及接收节点 |
| US20220210693A1 (en) * | 2019-04-26 | 2022-06-30 | Ntt Docomo, Inc. | Communication equipment |
| EP4074131A4 (en) * | 2019-12-10 | 2023-09-06 | Qualcomm Incorporated | UE-BASED PAIR ID FOR REDUNDANT PDU SESSIONS |
| EP4515777A1 (en) * | 2022-08-10 | 2025-03-05 | ZTE Corporation | Method, device, and system for awareness based data transmission and reception in wireless networks |
| EP4591535A4 (en) * | 2022-11-04 | 2025-10-29 | Apple Inc | PDCP PROTOCOL REJECTION INDICATIONS FOR EXTENDED REALITY |
Family Cites Families (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100547871B1 (ko) * | 2001-11-08 | 2006-02-01 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 이동 통신시스템의 기지국 제어기와 기지국간 패킷 데이터재전송 방법 및 장치 |
| US7266130B2 (en) * | 2001-12-28 | 2007-09-04 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Apparatus and method for multiplexing multiple end-to-end transmission links in a communication system |
| SG143988A1 (en) * | 2002-05-10 | 2008-07-29 | Interdigital Tech Corp | System for permitting control of the purging of a node b by the serving radio network controller |
| US7706405B2 (en) * | 2002-09-12 | 2010-04-27 | Interdigital Technology Corporation | System for efficient recovery of Node-B buffered data following MAC layer reset |
| CN1788448B (zh) * | 2003-04-10 | 2011-09-14 | 艾利森电话股份有限公司 | 重传的方法和系统 |
| EP1745669B1 (en) * | 2004-05-05 | 2013-07-31 | Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson (Publ) | Hsdpa flow control |
| JP2006174279A (ja) * | 2004-12-17 | 2006-06-29 | Fujitsu Ltd | 無線基地局、移動局 |
| US7724656B2 (en) * | 2005-01-14 | 2010-05-25 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Uplink congestion detection and control between nodes in a radio access network |
| EP1689130A1 (en) * | 2005-02-07 | 2006-08-09 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method for settling an error in a radio link control |
| JP4859419B2 (ja) * | 2005-09-14 | 2012-01-25 | 株式会社エヌ・ティ・ティ・ドコモ | 無線基地局およびユーザ共通データ伝送方法 |
| WO2008136115A1 (ja) * | 2007-04-26 | 2008-11-13 | Fujitsu Limited | 基地局、移動局、通信システム、送信方法及びリオーダリング方法 |
| JP5235877B2 (ja) * | 2007-06-12 | 2013-07-10 | 富士通株式会社 | 移動通信システムにおける通信方法および無線網制御装置 |
| CN101849391B (zh) * | 2007-11-01 | 2012-10-10 | 艾利森电话股份有限公司 | 无线网络控制器rnc中的高效流控制 |
| EP2204016B1 (en) | 2007-11-01 | 2011-05-18 | Telefonaktiebolaget L M Ericsson (publ) | Efficient flow control in a radio network controller (rnc) |
| US8121128B2 (en) * | 2008-02-26 | 2012-02-21 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Method and apparatus for link control in a wireless communication system |
| WO2009116914A1 (en) * | 2008-03-20 | 2009-09-24 | Telefonaktiebolaget L M Ericsson (Publ) | A method and a transceiver for reducing retransmissions in a telecommunications system |
| WO2009133626A1 (ja) | 2008-05-02 | 2009-11-05 | 富士通株式会社 | 制御装置、無線通信装置、通信システムおよび制御方法 |
| EP2301180B1 (en) * | 2008-05-22 | 2013-03-06 | Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson (publ) | Enhanced recovery procedure |
| EP2378738A4 (en) * | 2008-12-17 | 2013-11-27 | Fujitsu Ltd | PACKET TRANSMITTER, PACKET RECEIVER, COMMUNICATION SYSTEM AND PACKAGE COMMUNICATION METHOD |
| WO2010075892A1 (en) * | 2008-12-30 | 2010-07-08 | Telefonaktiebolaget L M Ericsson (Publ) | Apparatus and method for improved handover performance |
| CN103797743B (zh) | 2011-11-04 | 2018-09-21 | 瑞典爱立信有限公司 | 在通信系统中处理冗余数据 |
| WO2013066258A2 (en) | 2011-11-04 | 2013-05-10 | Telefonaktiebolaget L M Ericsson (Publ) | Handling redundant data in a communication system |
-
2012
- 2012-11-08 EP EP15169182.1A patent/EP2938017B1/en active Active
- 2012-11-08 MY MYPI2014701116A patent/MY168125A/en unknown
- 2012-11-08 JP JP2014541005A patent/JP6027622B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2012-11-08 KR KR1020147015542A patent/KR20140098126A/ko not_active Ceased
- 2012-11-08 CN CN201280055363.4A patent/CN103918213B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2012-11-08 US US13/700,515 patent/US9325594B2/en active Active
- 2012-11-08 EP EP12790989.3A patent/EP2777200B1/en not_active Not-in-force
- 2012-11-08 IN IN3308DEN2014 patent/IN2014DN03308A/en unknown
- 2012-11-08 WO PCT/SE2012/051218 patent/WO2013070162A1/en not_active Ceased
-
2016
- 2016-03-28 US US15/082,609 patent/US9654362B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US9325594B2 (en) | 2016-04-26 |
| CN103918213B (zh) | 2018-04-03 |
| JP6027622B2 (ja) | 2016-11-16 |
| EP2777200A1 (en) | 2014-09-17 |
| EP2938017A1 (en) | 2015-10-28 |
| EP2938017B1 (en) | 2021-01-06 |
| WO2013070162A1 (en) | 2013-05-16 |
| US9654362B2 (en) | 2017-05-16 |
| MY168125A (en) | 2018-10-11 |
| CN103918213A (zh) | 2014-07-09 |
| US20140050145A1 (en) | 2014-02-20 |
| KR20140098126A (ko) | 2014-08-07 |
| JP2015502070A (ja) | 2015-01-19 |
| IN2014DN03308A (OSRAM) | 2015-06-26 |
| US20160212030A1 (en) | 2016-07-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2777200B1 (en) | Methods, radio base station and radio network controller | |
| JP6139490B2 (ja) | 複数の送信点からの受信を可能にするmacおよびrlcアーキテクチャならびに手順 | |
| US8413002B2 (en) | Method of performing ARQ procedure for transmitting high rate data | |
| JP4866431B2 (ja) | 無線通信システムのためのエラー処理装置及び方法 | |
| US10819416B2 (en) | Apparatuses and methods for using ARQ processes in a relay device | |
| US8953576B2 (en) | Handling redundant data in a communication system | |
| US20100067481A1 (en) | Data retransmission method, network controller, mobile station and base station | |
| US11240703B2 (en) | Communications devices, method and mobile communications system | |
| US9461782B2 (en) | Handling redundant data in a communication system | |
| US20100074178A1 (en) | Method for Indication of Consecutive Data Units in a RAN | |
| EP2521398B1 (en) | Method, device and system for processing user equipment handover in long term evolution (lte) system | |
| WO2019095228A1 (en) | Method, apparatus and computer program | |
| HK1186021A (en) | Mac and rlc architecture and procedures to enable reception from multiple transmission points | |
| NZ618590B2 (en) | Handling redundant data in a communication system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20140416 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R079 Ref document number: 602012008466 Country of ref document: DE Free format text: PREVIOUS MAIN CLASS: H04L0001160000 Ipc: H04L0001180000 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: H04L 12/26 20060101ALN20150225BHEP Ipc: H04L 1/00 20060101ALN20150225BHEP Ipc: H04L 1/16 20060101ALI20150225BHEP Ipc: H04W 24/10 20090101ALN20150225BHEP Ipc: H04L 1/18 20060101AFI20150225BHEP |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20150318 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 734500 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20150715 Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602012008466 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK05 Ref document number: 734500 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20150701 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20150701 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151002 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151001 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151102 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151101 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 602012008466 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20160404 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20151108 Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20151130 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20151130 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20160729 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20151108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20151130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20121108 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20150701 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20211129 Year of fee payment: 10 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20211126 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 602012008466 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20221108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20221108 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20230601 |