EP2672412A1 - Method and computer program product for task management on late clinical information - Google Patents
Method and computer program product for task management on late clinical information Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2672412A1 EP2672412A1 EP12170796.2A EP12170796A EP2672412A1 EP 2672412 A1 EP2672412 A1 EP 2672412A1 EP 12170796 A EP12170796 A EP 12170796A EP 2672412 A1 EP2672412 A1 EP 2672412A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- task
- report
- clinical information
- image
- additional
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/06—Resources, workflows, human or project management; Enterprise or organisation planning; Enterprise or organisation modelling
- G06Q10/063—Operations research, analysis or management
- G06Q10/0631—Resource planning, allocation, distributing or scheduling for enterprises or organisations
- G06Q10/06311—Scheduling, planning or task assignment for a person or group
- G06Q10/063114—Status monitoring or status determination for a person or group
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/06—Resources, workflows, human or project management; Enterprise or organisation planning; Enterprise or organisation modelling
- G06Q10/063—Operations research, analysis or management
- G06Q10/0633—Workflow analysis
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H15/00—ICT specially adapted for medical reports, e.g. generation or transmission thereof
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H30/00—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images
- G16H30/20—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images for handling medical images, e.g. DICOM, HL7 or PACS
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H40/00—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices
- G16H40/20—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities, e.g. managing hospital staff or surgery rooms
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L51/00—User-to-user messaging in packet-switching networks, transmitted according to store-and-forward or real-time protocols, e.g. e-mail
- H04L51/04—Real-time or near real-time messaging, e.g. instant messaging [IM]
Definitions
- the present invention generally relates to workflow management in clinical applications, e.g. management of the different tasks to be performed by an individual or a team of individuals in a medical imaging environment.
- Workflow management is for instance important in medical applications such as radiology, where a technician makes medical images of a patient (e.g. an x-ray scan, a CT scan, an MRI scan, an ultrasound scan, etc.), a radiologist interprets the medical images, a transcriptionist produces a report reflecting the radiologists' interpretation, and a clinician receives the report and advises the patient.
- the individuals involved in the entire workflow may be working at a single facility (e.g. a hospital or imaging centre) or may be working at different locations (e.g. a hospital or enterprise with multiple facilities).
- a workflow management tool In order to govern the different tasks to be performed, a workflow management tool will be deployed and made accessible to the involved individuals at different locations.
- the current invention in particular concerns a method and tool for workflow management in clinical applications where additional information, e.g. belated medical images, laboratory results, diagnostic information, post-operative information, etc. may arrive in the system at a point in time a report has been generated already for the medical procedure where the additional, belated information belongs to.
- the above defined objectives are realized by the method for operating a data processing system for task management on clinical information defined by claim 1, the method comprising:
- the invention consists in checking whether a report was already created for a medical procedure when belated information such as an additional scan arrives in the system. If a report already exists, the system shall automatically create a task for the author of that report to verify if the report is still valid or needs to be updated in view of the additional information. This way, unnecessary notifications are avoided, while it is ensured that the existing report will be reviewed by its author for correctness in view of of the newly available information.
- the method according to the present invention further comprises:
- the method according to the present invention further comprises:
- the users may be notified of creation of the task, e.g. through a pop-up window on their screens, and/or their task lists may be updated automatically to include the new task.
- the method according to the present invention may further comprise:
- the method according to the present invention may further comprise:
- the method according to the current invention comprises:
- the additional clinical information may be a belated medical image.
- the type of the belated image may be verified and the task for verification of the report may be generated only when the belated image is of a predefined type.
- the present invention may filter on the type of image such that only the arrival of real images leads to the creation of a verification task for existing reports. This way, verification tasks are avoided to be triggered by late arrival of derived images in the system. As a result, the number of unnecessary tasks created automatically is reduced, further increasing the efficiency of the system.
- the present invention relates to a corresponding data processing system as defined by claim 9, comprising means for carrying out the method.
- the current invention in addition also relates to a computer program as defined by claim 10 comprising software code adapted to perform the method.
- the invention further relates to a computer readable storage medium as defined by claim 11, comprising the computer program.
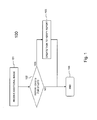
- Fig. 1 is a flow chart of a first embodiment of the method according to the present invention.
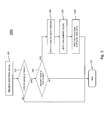
- Fig. 2 is a flow chart of a second embodiment of the method according to the present invention.
- Fig. 1-2 illustrate embodiments of the current invention implemented as part of a software application for workflow management in radiology.
- Such workflow management application typically has a client-server architecture.
- the server part of the application receives queries from the client part, runs these queries on a centralized or distributed database system wherein at least the medical images, medical reports, and tasks are stored and maintained.
- the server part also notifies the client part in case of changes in the database system that match with one of the queries received from that client, in order to enable the client part to update and refresh the information displayed to the user.
- the client part of the application enables the user to configure queries, and it generates the desktops for different types of users and the various screens according to the user's preferences and configuration settings.
- the desktops generated by the client part may for instance comprise a diagnostic desktop for radiologist users, a configuration desktop for administrator users, a transcriptionist desktop for the transcriptionist-user that uses the system to transfer speech recordings into text, a clinician desktop for the clinician-user that reads the medical reports from the radiologist(s) and advises the patient, a technologist desktop for the technician-user that makes the medical images.
- Each of these users makes use of one or more task lists accessible through his/her desktop for workflow management. Each such task list can be configured, i.e.
- the data fields to be displayed in a screen as part of the task list can be selected by the user, filtering criteria enabling selection of the relevant tasks for that task list are configurable by the user, and the criteria to be applied for sorting the tasks within the task list can be configured by the user.
- filtering criteria enabling selection of the relevant tasks for that task list are configurable by the user
- the criteria to be applied for sorting the tasks within the task list can be configured by the user.
- a radiologist user is assumed to have authored a report.
- additional images are uploaded in the database system by a technician.
- Fig. 1 illustrates a basic implementation of the method according to the invention.
- step 101 one or several additional medical images are received by the system that is used for workflow management in a medical imaging environment.
- the additional image(s) may for instance be images resulting from an additional scan, e.g. an x-ray scan, a CT scan, an MRI scan, an ultrasound scan, etc., or they may be processed images, e.g. a 3D reconstruction, an image supplemented with data, etc.
- the system automatically verifies if the additional images belong to a medical procedure for which a report has been produced already. If no report is existing in the system for that medical procedure, the method shall end, as is indicated by 104 in Fig. 1 .
- the received additional images shall be stored together with earlier stored images in order to be processed and/or studied later.
- the existing report may be inaccurate or incomplete because it was produced without considering the additional images.
- the system shall automatically create a task for the author of the existing report to verify the existing report in view of the additional images. This is indicated by step 103 in Fig. 1 .
- the automatically generated task shall be added to the overall task list in the system and be treated, i.e. notified to the author, escalated, etc. in a manner similar to other tasks.
- the method again ends at step 104.
- Fig. 2 illustrates a more advanced implementation of the method according to the invention.
- the system again receives one or several additional, belated medical images in relation to a medical procedure for which the system performs task management.
- the system in step 202 first verifies the type of the additional image(s). If the DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) standard is used to transfer the additional images to the system, the DICOM metadata may be consulted by the system in order to determine if an additional image is a "real" image, i.e. a first capture, or a processed image, i.e. a second capture that contains for instance data, parameter values, a 3D reconstruction, etc.
- DICOM Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine
- the system shall assume that it is not necessary to generate additional tasks and immediately terminate at step 207. If the additional image is a first capture, the system shall automatically verify in step 203 if a report is already existing for the medical procedure where the additional image relates to. In case no report exists in the system for that medical procedure, the method shall again terminate at step 207. The additional image(s) shall then be stored in the system for later evaluation. If however one or several reports exist already for the medical procedure where the additional image belongs to, the system will automatically create a task for the author(s) of each of these reports to verify the existing reports in view of the additional image.
- step 204 in Fig. 2 The system thereupon automatically assigns the created task to the person or group of persons that authored the existing report(s). This is done in step 205.
- the verification task shall be assigned to another responsible for the medical procedure according to assignment rules that are predefined in the system. This way, it is avoided that a newly created task will be assigned to a person or team that is no longer using the system.
- step 206 the system automatically notifies the user(s) whereto the verification task is assigned.
- the system automatically updates all task lists of these user(s) whose query matches with the newly created task.
- a radiologist shall typically maintain different task lists, like for instance high priority tasks that need to be completed by a close deadline, reading tasks like the interpretation of certain medical images as soon as these images have become available in the system, and sign-off tasks.
- the high priority task list is empty, the radiologist shall start to work on the reading tasks.
- both the high priority task list and the reading task list are empty, the radiologist will switch to sign-off tasks.
- tasks may appear in multiple individual lists, or dynamically move from one list to another.
- a reading task or sign-off task may for instance become a high priority task when its deadline is nearing.
- Each task list is defined by a query. Tasks that match with the query appear in the task list. Thanks to the current invention, the task for verification of an existing report that is automatically created by the system upon arrival of an additional "real" image, shall appear in the task lists of the assigned persons whose queries match with the created task.
- Comments could for instance be attached to the created verification task to explain why the task was created. Such comments could contain a reference or link to the additional image(s) received by the system.
- the system may also implement escalation rules that define which responsible or supervisor needs to be informed when the task for verification of the existing report is not completed by the assigned person(s) within a given time frame.
- the system may also automatically trigger a distribution flow as soon as the existing report has been reviewed and eventually has been updated by the person(s) to whom this task was assigned. This way, it is ensured that all persons making use of the report become aware of the existence of a new version of the report that also considers the additional images arrived late in the system.
- DICOM DICOM standard
- Alternative protocols for formatting and reporting medical images like for instance HL7 or EDIFACT-EDI standards may be used.
- the present invention may take benefit of the protocol for filtering if the metadata contain an indication of the type of image, as is the case for DICOM.
- the invention illustrated here above with two embodiments in the field of medical imaging may be applied more widely to late arrival of any type of clinical information in a task management system.
- clinical information may include laboratory results, diagnostic information, post-operative information, etc.
- a task for verification of the existing report(s) can be generated automatically with same advantages as described here above in relation to medical images.
- the method according to the invention shall typically be computer-implemented on a system or platform with client-server architecture.
- the images and tasks are maintained centrally or distributed on one or more servers. Users access their task lists and consult images stored in the system via a client device.
- a data processing system or computing device that is operated according to the present invention can include a workstation, a server, a laptop, a desktop, a hand-held device, a mobile device, a tablet computer, or other computing devices, as would be understood by those of skill in the art.
- the data processing system or computing device can include a bus or network for connectivity between several components, directly or indirectly: a memory or database, one or more processors, input/output ports, a power supply, etc.
- the bus or network can include one or more busses, such as an address bus, a data bus, or any combination thereof, or can include one or more network links.
- multiple of these components can be implemented by a single device. Similarly, in some instances, a single component can be implemented by multiple devices.
- the data processing system or computing device can include or interact with a variety of computer-readable media.
- computer-readable media can include Random Access Memory (RAM), Read Only Memory (ROM), Electronically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM), flash memory or other memory technologies, CDROM, digital versatile disks (DVD) or other optical or holographic media, magnetic cassettes, magnetic tape, magnetic disk storage or other magnetic storage devices that can be used to encode information and can be accessed by the data processing system or computing device.
- the memory can include computer-storage media in the form of volatile and/or nonvolatile memory.
- the memory may be removable, non-removable, or any combination thereof.
- Exemplary hardware devices are devices such as hard drives, solid-state memory, optical-disc drives, or the like.
- the data processing system or computing device can include one or more processors that read data from components such as the memory, the various I/O components, etc.
- the I/O ports can allow the data processing system or computing device to be logically coupled to other devices, such as I/O components.
- I/O components can be built into the computing device. Examples of such I/O components include a microphone, joystick, recording device, game pad, satellite dish, scanner, printer, wireless device, networking device, or the like.
- top, bottom, over, under, and the like are introduced for descriptive purposes and not necessarily to denote relative positions. It is to be understood that the terms so used are interchangeable under appropriate circumstances and embodiments of the invention are capable of operating according to the present invention in other sequences, or in orientations different from the one(s) described or illustrated above.
Landscapes
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Human Resources & Organizations (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Tourism & Hospitality (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Operations Research (AREA)
- Game Theory and Decision Science (AREA)
- Educational Administration (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Development Economics (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Medical Treatment And Welfare Office Work (AREA)
- Measuring And Recording Apparatus For Diagnosis (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
- Child & Adolescent Psychology (AREA)
- Information Transfer Between Computers (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP12170796.2A EP2672412A1 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2012-06-05 | Method and computer program product for task management on late clinical information |
| CN201380029544.4A CN104364786A (zh) | 2012-06-05 | 2013-06-03 | 用于关于迟到临床信息的任务管理的方法和计算机程序产品 |
| BR112014030290A BR112014030290A2 (pt) | 2012-06-05 | 2013-06-03 | um método e produto de programa de computador para gerenciamento de tarefa sobre informações clínicas atrasadas |
| US14/405,514 US20150154530A1 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2013-06-03 | Method and computer program product for task management on late clinical information |
| IN9526DEN2014 IN2014DN09526A (enExample) | 2012-06-05 | 2013-06-03 | |
| PCT/EP2013/061393 WO2013182526A1 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2013-06-03 | A method and computer program product for task management on late clinical information |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP12170796.2A EP2672412A1 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2012-06-05 | Method and computer program product for task management on late clinical information |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2672412A1 true EP2672412A1 (en) | 2013-12-11 |
Family
ID=46229287
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP12170796.2A Withdrawn EP2672412A1 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2012-06-05 | Method and computer program product for task management on late clinical information |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20150154530A1 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP2672412A1 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN104364786A (enExample) |
| BR (1) | BR112014030290A2 (enExample) |
| IN (1) | IN2014DN09526A (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2013182526A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107863140A (zh) * | 2017-11-06 | 2018-03-30 | 贵阳朗玛信息技术股份有限公司 | Dicom文件的处理方法及装置 |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11604823B2 (en) | 2016-01-26 | 2023-03-14 | Envision Healthcare Corporation | Medical imaging distribution system and device |
| US10678850B2 (en) | 2016-04-18 | 2020-06-09 | Imaging Advantage Llc | System and device for pre-caching of related medical imaging |
| US11488698B2 (en) * | 2016-06-23 | 2022-11-01 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Facilitated structured measurement management tool progress and compliance analytics solution |
| US10997567B2 (en) * | 2016-07-14 | 2021-05-04 | Casio Computer Co., Ltd | Work support device, work support method and computer readable storage medium |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7693917B2 (en) * | 2001-11-30 | 2010-04-06 | Intelligent Medical Objects, Inc. | Method for adaptive data management |
| US9070095B2 (en) * | 2008-04-01 | 2015-06-30 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Ensuring referential integrity of medical image data |
| US20090287504A1 (en) * | 2008-05-14 | 2009-11-19 | Algotec Systems Ltd. | Methods, systems and a platform for managing medical data records |
| US8571884B2 (en) * | 2008-06-13 | 2013-10-29 | Aionex, Inc. | Healthcare communication and workflow management system and method |
| EP2169577A1 (en) * | 2008-09-25 | 2010-03-31 | Algotec Systems Ltd. | Method and system for medical imaging reporting |
| EP2411931A1 (en) * | 2009-03-26 | 2012-02-01 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | A system that automatically retrieves report templates based on diagnostic information |
| EP2531944A1 (en) * | 2010-02-05 | 2012-12-12 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | Treatment plan creation workflow tracking |
-
2012
- 2012-06-05 EP EP12170796.2A patent/EP2672412A1/en not_active Withdrawn
-
2013
- 2013-06-03 WO PCT/EP2013/061393 patent/WO2013182526A1/en not_active Ceased
- 2013-06-03 IN IN9526DEN2014 patent/IN2014DN09526A/en unknown
- 2013-06-03 US US14/405,514 patent/US20150154530A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2013-06-03 BR BR112014030290A patent/BR112014030290A2/pt not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2013-06-03 CN CN201380029544.4A patent/CN104364786A/zh active Pending
Non-Patent Citations (4)
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107863140A (zh) * | 2017-11-06 | 2018-03-30 | 贵阳朗玛信息技术股份有限公司 | Dicom文件的处理方法及装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| IN2014DN09526A (enExample) | 2015-07-17 |
| BR112014030290A2 (pt) | 2017-06-27 |
| WO2013182526A1 (en) | 2013-12-12 |
| US20150154530A1 (en) | 2015-06-04 |
| CN104364786A (zh) | 2015-02-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9542481B2 (en) | Radiology data processing and standardization techniques | |
| RU2554522C2 (ru) | Рабочий процесс с обратной связью | |
| CN114787934B (zh) | 有助于医疗保健成像诊断的工作流的算法编配 | |
| CN102859527B (zh) | 处置计划创建工作流程跟踪 | |
| US8719046B2 (en) | Systems and methods for interruption workflow management | |
| US7664659B2 (en) | Displaying clinical predicted length of stay of patients for workload balancing in a healthcare environment | |
| US20090138318A1 (en) | Systems and methods for adaptive workflow and resource prioritization | |
| US9734476B2 (en) | Dynamically allocating data processing components | |
| US20150019252A1 (en) | Dental implant management system and method | |
| Schreiweis et al. | Comparison of electronic health record system functionalities to support the patient recruitment process in clinical trials | |
| US11989878B2 (en) | Enhancing medical imaging workflows using artificial intelligence | |
| US20120221346A1 (en) | Administering Medical Digital Images In A Distributed Medical Digital Image Computing Environment | |
| US20200311938A1 (en) | Platform for evaluating medical information and method for using the same | |
| CN110223739A (zh) | 临床发现的主动追踪观察 | |
| KR102130098B1 (ko) | 의료 영상과 관련된 장치들 간에 송수신되는 의료 데이터를 생성하는 방법 및 장치. | |
| US20150154530A1 (en) | Method and computer program product for task management on late clinical information | |
| US20140058740A1 (en) | Method and system for pre-operative document management | |
| Boland | Enhancing CT productivity: strategies for increasing capacity | |
| US20140278579A1 (en) | Medical Form Generation, Customization and Management | |
| US20150294071A1 (en) | Method and computer program for resource scheduling | |
| US11087862B2 (en) | Clinical case creation and routing automation | |
| US20200126646A1 (en) | System and Method for Processing Healthcare Information | |
| US20230187059A1 (en) | Automated ticket attachment creation | |
| US20150142503A1 (en) | Method and computer program product for workflow management | |
| Caforio et al. | HINT project: A BPM teleconsultation and telemonitoring platform |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20140611 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20170331 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 20170811 |