EP2369801A2 - Datenempfänger mit verbesserter Antwort auf lang- und kurzfristige Datensignalausblendung - Google Patents
Datenempfänger mit verbesserter Antwort auf lang- und kurzfristige Datensignalausblendung Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2369801A2 EP2369801A2 EP11159476A EP11159476A EP2369801A2 EP 2369801 A2 EP2369801 A2 EP 2369801A2 EP 11159476 A EP11159476 A EP 11159476A EP 11159476 A EP11159476 A EP 11159476A EP 2369801 A2 EP2369801 A2 EP 2369801A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- data signal
- decision metric
- receiver
- receiver according
- broadcast receiver
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000005562 fading Methods 0.000 title claims description 15
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 title description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 230000001427 coherent effect Effects 0.000 claims description 26
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 25
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 claims description 23
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 230000006735 deficit Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 abstract description 38
- 230000001934 delay Effects 0.000 description 26
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000007476 Maximum Likelihood Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000006978 adaptation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003044 adaptive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012512 characterization method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001143 conditioned effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000593 degrading effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009795 derivation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012938 design process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013507 mapping Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010363 phase shift Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000644 propagated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003595 spectral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L25/00—Baseband systems
- H04L25/02—Details ; arrangements for supplying electrical power along data transmission lines
- H04L25/03—Shaping networks in transmitter or receiver, e.g. adaptive shaping networks
- H04L25/03006—Arrangements for removing intersymbol interference
- H04L25/03178—Arrangements involving sequence estimation techniques
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L25/00—Baseband systems
- H04L25/02—Details ; arrangements for supplying electrical power along data transmission lines
- H04L25/06—DC level restoring means; Bias distortion correction ; Decision circuits providing symbol by symbol detection
- H04L25/067—DC level restoring means; Bias distortion correction ; Decision circuits providing symbol by symbol detection providing soft decisions, i.e. decisions together with an estimate of reliability
Definitions
- the invention to which this application relates is a broadcast data receiver apparatus which is provided in a form so as to have an improved response to long and short term fading of the data channels.
- Broadcast signals which are transmitted are typically distorted by atmospheric and environmental impairments, thereby degrading the quality of the signal which is subsequently received.
- one form of deterioration is fading which is typically caused by physical phenomena such as reflection, diffraction and scattering.
- the effect of these phenomena is either rich or poor. This is the case in the occurrence of multipath and shadowing fading, respectively.
- Suzuki statistical distribution Another known distribution known as the Suzuki statistical distribution has the advantage that it is a composite Rayleigh/Lognormal distribution. As a consequence, it is capable of describing at once both the multipath and the shadowing of communication signals which occur simultaneously during wireless propagation.
- PDF probability density function
- An existing method of compensating for shadowing is by providing the receiver with empirical data, i.e. actual data, relating to the geographical area in which the receiver is to be used.
- empirical data i.e. actual data
- the data is not always specific enough to the receiver location, and if the receiver is moved to a new location, new empirical data has to be obtained.
- An aim of the present invention is to provide a receiver which can characterise accurately the signal degradation caused by the presence of multipath fading and shadowing. Another aim is to provide a method whereby the characterisation of the signal degradation can be accurately determined.
- ⁇ and ⁇ denote the variance and mean value respectively of the Lognormal distribution, in order to take into account potential impairment of the said data signal.
- the receiver can be optimised in a number of conditions such that the requirement for empirically modelling the channel before deploying a new network is removed.
- the receiver has improved performance over fading channels and is adaptive to the location of the receiver.
- s k t , ⁇ l l 1 Lp
- This decision metric allows implementation of a receiver configuration design in the case of known delays but unknown phases and amplitudes.
- s k t is:
- This decision metric allows implementation of a receiver configuration design for the case of unknown delays, phases and amplitudes.
- the design or configuration of the receiving apparatus include details of coherent detection as well as non-coherent detection.
- the designs include details of the possible modulation schemes, typically M-PSK, M-QAM, ASK/PAM, FSK, MSK and OFDM.
- the designs include a plurality of shaping pulses, typically square, sinusoidal and cosine.
- the broadcast receiver characterises signal impairment optimally by utilising any, or any combination of, the decision metrics described herein.
- the decision metric allows optimisation of the signal reception parameters or design.
- a method of configuring receiving and/or processing apparatus for at least one data signal received from a remote transmitting location including the steps of:
- a real bandpass signal which can be represented as :
- S ⁇ k is the k th complex bandpass signal
- S ⁇ k (t) is the corresponding k th complex baseband signal chosen from the set of M equi-probable message waveforms which represents the transmitted information.
- the above signal (1) is transmitted over the fading channel which is characterized by L p independent diversity paths. Each of these paths is a time varying channel that attenuates, delays, phase-shifts the signal while it also adds an AWGN source.
- the received data signal at the receiving apparatus is in fact a set of "noisy" replicas of the transmitted signal.
- the optimum receiver computes the set of a posteriori probabilities p s k t
- the receiver is assumed to be time - synchronised to the transmitted signal.
- s k t , k 1 , 2 , ... , M which is the Maximum - Likelihood (ML) decision rule.
- Receivers that make use of CSI have been termed self-adaptive in that the estimates of the system parameters are utilized to adjust the decision structure, thereby, improving the system performance by adaptation to variation of the channel changes.
- Example 1 Known amplitudes, phases and delays; non-coherent detection
- the conditional probability p r l t l 1 Lp
- Example 2 Known phases and delays, unknown amplitudes; non-coherent detection
- ⁇ the variance of Lognormal distribution
- ⁇ mean value of lognormal distribution
- s k t ⁇ l l 1 Lp
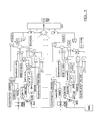
- the receiver apparatus configuration design illustrated in Figure 1 can be implemented for the case of known delay and phase values but unknown amplitude values for the data signal to be received.
- This design contains a block that theoretically includes the modulation schemes that can be possibly used. It also contains three different shaping pulses. Furthermore, non - coherent detection as well as uniform PDP are assumed.
- Example 3 Known data signal phase value, unknown data signal delay and amplitude values; non-coherent detection
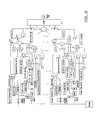
- the receiver design illustrated in Figure 2 can be implemented for the case of known phases but unknown delays and amplitudes. As in the above case, this design contains a block that theoretically includes the modulation schemes that can be possibly used together with the shaping pulses. Furthermore, non-coherent detection as well as uniform power decay profile (PDP) have been assumed.
- PDP uniform power decay profile
- Example 4 known delay and amplitude values, unknown phase value; non-coherent detection
- conditional probability p r l t l 1 Lp
- JPDF joint probability density function
- Example 5 Known delay values, unknown phase and amplitude values for a received data signal; non-coherent detection
- Equation (33) cannot be solved in closed-form as currently expressed.
- the additional factor of complexity in this case is the modified Bessel function.
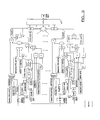
- the receiver design illustrated in Figure 3 can be implemented for the case of known delays but unknown phases and amplitudes.
- this design contains a block that theoretically includes the modulation schemes that can be possibly used together with shaping pulses.
- coherent detection as well as uniform PDP have been selected in this design.
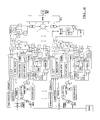
- Example 6 Unknown phase, delay and amplitude values for a received data signal; non-coherent detection
- this design contains a block that theoretically includes the modulation schemes that can be possibly used together with the shaping pulses. Furthermore, coherent detection as well as uniform PDP have been selected in this design.
- the Power Decay Profile critically affects the performance of wireless communications systems and it is always considered as a factor of significant importance during the system design process.
- the PDP is considered to be of the same nature in all diversity paths between transmitter and receiver.
- Uniform PDP indicates the uniform rate of variation of the power of the signal while Exponential PDP indicates its exponential variation.
- the nature of the PDP determines the degree of optimisation of a receiver design. For uniform PDP, the receiver design is considered optimum, while, for non-uniform PDP (exponential in our case), the receiver design is considered suboptimum.
- the data signal which is transmitted can be shaped in a desired waveform which will make it relatively easier for the receiver to filter the received signals effectively and extract the information included in it.
- the typical shaping pulses that are used are the square, sinusoidal and cosine.
- Digital modulation techniques can be an important factor in the transmission of digital data in order to achieve the highest possible data transmission rates.
- the higher the order of the modulation the higher the spectral efficiency i.e. the higher the number of bits per transmitted symbol.
- the complexity, and hence, the cost increase dramatically.
- the information symbols are located very close to each other which results in inter symbol interference (ISI). This increases the error rate and raises the need for more sophisticated, complex and costly receiver designs. Therefore, the choice of the appropriate modulation scheme for each system is relative to the performance requirements of it.
- Six types of digital modulations namely, M-PSK, M-QAM, ASK/PAM, FSK, MSK and OFDM can be expressed mathematically as follows:
- the configuration design of the receiving apparatus can be achieved by referring to the appropriate decision metric.
- four basic receiver designs are produced directly from the four different derived decision metrics in equations (20), (24), (37), (40).
- the PDP was considered uniform in the four initial designs.
- receiver designs with coherent and non-coherent detection under exponential PDP can be produced in a straightforward manner.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Digital Transmission Methods That Use Modulated Carrier Waves (AREA)
- Radio Transmission System (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| GBGB1004946.8A GB201004946D0 (en) | 2010-03-24 | 2010-03-24 | Receiver with improved response to long and short term fading |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2369801A2 true EP2369801A2 (de) | 2011-09-28 |
| EP2369801A3 EP2369801A3 (de) | 2012-10-24 |
| EP2369801B1 EP2369801B1 (de) | 2017-11-22 |
Family
ID=42228269
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP11159476.8A Active EP2369801B1 (de) | 2010-03-24 | 2011-03-23 | Datenempfänger mit verbesserter Antwort auf lang- und kurzfristige Datensignalausblendung |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8654907B2 (de) |
| EP (1) | EP2369801B1 (de) |
| GB (1) | GB201004946D0 (de) |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7280942B2 (en) * | 2005-08-15 | 2007-10-09 | Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories, Inc. | Method for representing a combination of signals with a distribution of a single lognormal random variable |
-
2010
- 2010-03-24 GB GBGB1004946.8A patent/GB201004946D0/en not_active Ceased
-
2011
- 2011-03-23 EP EP11159476.8A patent/EP2369801B1/de active Active
- 2011-03-24 US US13/070,587 patent/US8654907B2/en active Active
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| None |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| GB201004946D0 (en) | 2010-05-12 |
| US20120014481A1 (en) | 2012-01-19 |
| EP2369801B1 (de) | 2017-11-22 |
| US8654907B2 (en) | 2014-02-18 |
| EP2369801A3 (de) | 2012-10-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Ye et al. | Adaptive modulation for variable-rate OFDM systems with imperfect channel information | |
| EP1611723B1 (de) | Positionskorrigiertes schutzzeitintervall für ein ofdm-kommunikationssystem | |
| Polprasert et al. | Capacity of OFDM systems over fading underwater acoustic channels | |
| US10644904B2 (en) | System and method for channel estimation | |
| Hebley et al. | The effect of diversity on a burst-mode carrier-frequency estimator in the frequency-selective multipath channel | |
| CA2695642A1 (en) | System and method for automated link quality measurement for adaptive modulation systems using noise level estimates | |
| Baas et al. | Pulse shaping for wireless communication over time-or frequency-selective channels | |
| Tarchi et al. | Adaptive coding and modulation techniques for next generation hand-held mobile satellite communications | |
| US7366232B2 (en) | Method and device for the automatic selection of the bit rate in high frequency transmissions | |
| Srinivas | OFDM system implementation, channel estimation and performance comparison of OFDM signal | |
| Samara et al. | Adapt and aggregate: Adaptive OFDM numerology and carrier aggregation for high data rate terahertz communications | |
| CN103532881B (zh) | 一种自适应调整单载波水声相干通信制式的方法 | |
| EP2369801B1 (de) | Datenempfänger mit verbesserter Antwort auf lang- und kurzfristige Datensignalausblendung | |
| Nissel et al. | Closed-form capacity expression for low complexity BICM with uniform inputs | |
| Uryvsky et al. | Applied research of modulation-coding schemes selection algorithms effectiveness in 802.11 equipment | |
| Araújo et al. | A Spectral Efficiency Enhancement for Chirp Spread Spectrum Downlink Communications | |
| EP1983708A1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Erzeugung von Trainingssequenzcodes in einem Kommunikationssystem | |
| Zhang et al. | Symbol estimation algorithm for MIMO underwater acoustic communication system based on multiplicative noise model | |
| Mahal et al. | The closed-form BER expressions of PSK modulation for OFDM and SC-FDMA under jamming and imperfect channel estimation | |
| Poikonen | Efficient channel modeling methods for mobile communication systems | |
| Chen et al. | Effect of channel estimation error onto the BER performance of PSAM-OFDM in Rayleigh fading | |
| Jia et al. | Integrated Multimode Adaptive CSS Modulation Based on OCDM-IM for UWA Communication | |
| Zhang et al. | Flexible FTN-OTFS for High-Mobility LEO Satellite-to-Ground Communication | |
| Salim et al. | New adaptive data transmission scheme over HF radio | |
| CN102404083A (zh) | 空时分组码正交频分复用链路的功率分配方法及装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: H04L 25/06 20060101ALI20120920BHEP Ipc: H04L 25/03 20060101AFI20120920BHEP |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20130326 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20170620 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 949361 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20171215 |
|
| RAP2 | Party data changed (patent owner data changed or rights of a patent transferred) |
Owner name: ARRIS GLOBAL LTD. |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602011043512 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 602011043512 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: KASTEL PATENTANWAELTE, DE Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R081 Ref document number: 602011043512 Country of ref document: DE Owner name: ARRIS GLOBAL LTD, GB Free format text: FORMER OWNER: PACE PLC, SHIPLEY, WEST YORKSHIRE, GB Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 602011043512 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: KASTEL PATENTANWAELTE PARTG MBB, DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20171122 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK05 Ref document number: 949361 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20171122 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180222 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180223 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180222 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 602011043512 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20180823 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20180331 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180323 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180323 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180331 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180331 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180323 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20110323 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20171122 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20171122 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20180322 |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230530 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R081 Ref document number: 602011043512 Country of ref document: DE Owner name: ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC (N. D. GES. D. STAATES D, US Free format text: FORMER OWNER: ARRIS GLOBAL LTD, SHIPLEY, GB Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R081 Ref document number: 602011043512 Country of ref document: DE Owner name: ANDREW WIRELESS SYSTEMS UK LTD., GB Free format text: FORMER OWNER: ARRIS GLOBAL LTD, SHIPLEY, GB |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R081 Ref document number: 602011043512 Country of ref document: DE Owner name: ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC (N. D. GES. D. STAATES D, US Free format text: FORMER OWNER: ANDREW WIRELESS SYSTEMS UK LTD., LONDON, GB |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: 732E Free format text: REGISTERED BETWEEN 20250213 AND 20250219 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20250327 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20250327 Year of fee payment: 15 |