EP1322091B1 - Communication system, server device, client device and method for controlling the same - Google Patents
Communication system, server device, client device and method for controlling the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1322091B1 EP1322091B1 EP02258074A EP02258074A EP1322091B1 EP 1322091 B1 EP1322091 B1 EP 1322091B1 EP 02258074 A EP02258074 A EP 02258074A EP 02258074 A EP02258074 A EP 02258074A EP 1322091 B1 EP1322091 B1 EP 1322091B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- access point
- communication apparatus
- authentication
- informing
- client terminal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W12/00—Security arrangements; Authentication; Protecting privacy or anonymity
- H04W12/06—Authentication
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0816—Key establishment, i.e. cryptographic processes or cryptographic protocols whereby a shared secret becomes available to two or more parties, for subsequent use
- H04L9/0819—Key transport or distribution, i.e. key establishment techniques where one party creates or otherwise obtains a secret value, and securely transfers it to the other(s)
- H04L9/0822—Key transport or distribution, i.e. key establishment techniques where one party creates or otherwise obtains a secret value, and securely transfers it to the other(s) using key encryption key
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W12/00—Security arrangements; Authentication; Protecting privacy or anonymity
- H04W12/04—Key management, e.g. using generic bootstrapping architecture [GBA]
- H04W12/043—Key management, e.g. using generic bootstrapping architecture [GBA] using a trusted network node as an anchor
- H04W12/0431—Key distribution or pre-distribution; Key agreement
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/0005—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off
- H04W36/0011—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off for data sessions of end-to-end connection
- H04W36/0033—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off for data sessions of end-to-end connection with transfer of context information
- H04W36/0038—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off for data sessions of end-to-end connection with transfer of context information of security context information
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W84/00—Network topologies
- H04W84/02—Hierarchically pre-organised networks, e.g. paging networks, cellular networks, WLAN [Wireless Local Area Network] or WLL [Wireless Local Loop]
- H04W84/10—Small scale networks; Flat hierarchical networks
- H04W84/12—WLAN [Wireless Local Area Networks]
Definitions
- the present invention concerns a server device which informs an access point in a communication system of an encipher key used when a client terminal (i.e. a communication apparatus) initiates a communication through the access point. It also concerns a method for controlling the same, and a computer-readable storage medium storing instructions to carry out such a method.
- a client terminal has been connected to a network through wireless communication with an access point on the network.
- a wireless LAN system in which a client terminal receives authentication of connection to a network through an access point from an authentication server on a network.
- the client terminal when the client terminal receives authentication from the authentication server, the client terminal and the authentication server create an encipher key of a wired equivalent privacy (WEP) encipher system, and the authentication server informs the access point of the created encipher key. Then, the client terminal transfers enciphered data with the access point by using the encipher key of the WEP encipher system to perform secure wireless communication.
- WEP wired equivalent privacy
- a communicable range of the access point is limited to a range reached by electric waves.
- the client terminal can be freely moved. Accordingly, the client terminal may be moved from a communicable range of an access point 1 to a communicable range of an access point 2.
- the client terminal must receive authentication of connection to the network from the authentication server again through wireless communication with the access point 2, the client terminal and the authentication server must create a new WEP key, and the authentication server must inform the access point 2 of the new WEP key.
- a server device with authentication means to authenticate a communication apparatus connected to a first access point and informing means to inform said access point of an enciphar key when a valid authentication occurs is known from WO 0124560 A and WO 0296151 A .
- a server device comprising: authentication means for authenticating a communication apparatus which is connected to a network through a first access point;
- the present invention provides a server device as set out in claim 1.
- the present invention also provides a control method for the server device as set out in claim 4 and a computer readable storage medium as set out in claim 5.
- Advantageous embodiments thereof are disclosed in corresponding dependent claims.
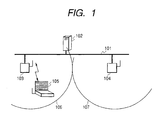
- FIG. 1 is a configuration view of a system according to the embodiment of the invention.
- a reference numeral 101 denotes a network, to which an access point A103, and an access point B104 are connected.
- the two access points are shown in FIG. 1, but the number of installed points is not limited to two.
- Each of the access points A103 and B104 can perform wireless communication with a client terminal 105 present in communicable ranges 106, 107.
- a wireless local area network based on a standard such as IEEE 802. 11, IEEE 802. 11b, or IEEE 802. 11a is used as a wireless local area network (LAN) based on a standard such as IEEE 802. 11, IEEE 802. 11b, or IEEE 802. 11a is used.
- the reference numeral 105 is the client terminal, which is connected to the network 101 through wireless communication with the access point A103 or B104. Though not shown in FIG. 1, a plurality of client terminals 105 may be present.
- a reference numeral 102 denotes an authentication server, which authenticates the client terminal 105 connected to the network 101, and creates an encipher key used in a wired equivalency privacy (WEP) encipher system.
- WEP wired equivalency privacy
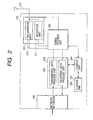
- FIG. 2 is a block diagram of the access point A103.
- a case of the access point B104 is similar.
- a reference numeral 201 denotes a wireless unit, which transfers wireless data.
- the wireless unit 201 is constituted of a transmission unit 210, a reception unit 211, and an antenna 212.
- a reference numeral 202 denotes a signal process unit, which detects a signal received by the reception unit 211 to convert it into a digital signal, and modulates the signal in order to transmit a digital signal sent from a data process unit 203 by wireless.
- the signal process unit 202 has a function of adding a header or the like in order to use data sent from the data process unit 203 for wireless transmission, and removing a header or the like from received data to send it to the data process unit 203.
- the reference numeral 203 is the data process unit, which is constituted of a transmission data process unit 205 for enciphering data from a network interface 208 by a WEP encipher system, and a reception data process unit 206 for decoding enciphered data.
- a reference numeral 204 denotes a control unit, which executes determination of presence of a new client terminal 105, control of the entire access point A103, and the like.
- a reference numeral 207 denotes a storage unit, which stores an encipher key for WEP enciphering, and information regarding an ID or the like of the client terminal 105.
- the reference numeral 208 is the network interface, which is an interface between the access point A103 and the network 101.
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram of the client terminal 105.
- the client terminal 105 of the embodiment is constituted of a wireless communication card.
- a reference numeral 301 denotes a data communication interface, which is connected to an information processor such as a personal computer to perform data communication.
- a reference numeral 302 denotes a storage unit, which stores an encipher key for WEP enciphering, and information regarding an ID or the like of the client terminal 105 necessary for wireless communication with the access point A103 or the access point B104.
- a media access control (MAC) address is used as an ID of the client terminal 105.
- the client terminal 105 executes open authentication in the wireless LAN to be connected to the access point A103 (5401).
- the access point A103 obtains an ID of the client terminal 105 (S402).
- the access point A103 informs the authentication server 102 of the ID of the client terminal 105 (S403).
- the authentication server 102 determines whether authentication for the connection of the client terminal 105 to the network 101 has been finished or not, based on the ID informed from the access point A103 (S404).
- the client terminal 105 makes the connection for the first time, and the authentication has not been finished. Thus, it is determined that the authentication has not been finished.
- the authentication server 102 requests the client terminal 105 to input a user name and a password (S405).
- the client terminal 105 inputs the user name and the password (S406).
- the client terminal 105 executes irreversible numerical value processing called one-way hash, and informs the authentication server 102 of its one-way hash data (S407).
- the authentication server 102 collates the one-way hash data informed in step S407 with a data group regarding a user for permitting connection to the network 101, which is saved in a database in the authentication server 102. If a result of the collation shows coincident data, the connection to the network 101 is permitted to the client terminal 105, and the ID of the client terminal 105 is stored (step S408).
- the client terminal 105 and the authentication server 102 create an encipher key called a WEP session key (S409).
- the WEP session key is an encipher key, which is used in the WEP encipher system, and valid only for enciphering traffic of the client terminal 105.
- the authentication server 102 stores the created WEP session key in association with the ID of the client terminal 105, and informs it to the access point A103 (S410).
- the access point A103 enciphers a broadcast key with the WEP session key (S411), and sends the enciphered broadcast key to the client terminal 105 (S412).
- the broadcast key is an encipher key, which is used when data broadcast from the access point A130 to a plurality of client terminals 105 is enciphered.
- the client terminal 105 decodes the enciphered broadcast key by using the WEP session key created in step S409 to obtain a broadcast key (S413).
- the access point A103 and the client terminal 105 start WEP encipher sequences (S414, S415).
- the access point A103 transfers data enciphered with the WEP session key to perform secure wireless communication (S416).
- the access point A103 transfers data enciphered with the broadcast key to perform secure wireless communication (S416).
- Fig. 5 shows a sequential view of an operation when the client terminal 105, for which authentication of its connection to the network 101 through the access point A103 has been finished, is moved from the communicable range 106 of the access point A103 to the communicable range 107 of the access point B104 to be connected to the network 101 through the access point B104.
- the client terminal. 105 is moved out of the communicable range 106 of the access point A103 to be incommunicable with the access point A103 (5501). Then, the client terminal 105 is moved into the communicable range 107 of the access point B104 to be communicable with the access point B104.
- the client terminal 105 executes open authentication to be connected to the access point B104 (S502).
- the access point B104 obtains an ID of the client terminal 105 (S503).
- the access point B104 informs the authentication server 102 of the ID of the client terminal 105 (S504).
- the authentication server 102 determines whether authentication for the connection of the client terminal 105 to the network 101 has been finished or not, based on the ID informed in step S504, and the stored ID of the client terminal 105, for which the authentication has been finished (S505).
- the authentication of its connection to the network 101 through the access point A103 was finished in step S408 (FIG. 4), and the ID of the client terminal has been stored. Thus, it is determined that the authentication has been finished.
- the authentication server 102 instructs the access point A103 to delete the WEP session key stored in the storage unit 207 to be used for wireless communication with the client terminal 105 (S506).
- the authentication server 102 informs the access point B104 of the WEP session key stored in association with the ID of the client terminal 105 in step S410 (FIG. 4) (S507).
- the access point B104 enciphers a broadcast key with the WEP session key informed in step S507 (S508), and sends the enciphered broadcast key to the client terminal 105 (S509).
- the client terminal 105 decodes the enciphered broadcast key by the WEP session key created in step S409 (FIG. 4) to obtain a broadcast key (S510).
- the access point B104 and the client terminal 105 start WEP encipher sequences (S511, S512).
- the access point B104 transfers data enciphered with the same WEP session key as that used for the communication between the client terminal 105 and the access point A103 to perform secure wireless communication (S513).
- the access point B104 transfers data enciphered with the broadcast key to perform secure wireless communication (S513).
- step S507 the WEP session key stored in the authentication server 102 is informed to the access point B104.
- the WEP session key stored in the access point A103 may be informed through the authentication server 102 to the access point B104:
- the client terminal 105 was the wireless communication card.
- a function similar to the wireless communication card may be incorporated in a personal computer or personal digital assistants (PDA).
- PDA personal digital assistants
- the present invention can be implimented by supplying a computer-readable storage medium, in which software program codes for realizing the functions of the client terminal, the access points, and the authentication server are stored, to a system or a device, and causing the system or a computer (alternatively CPU or MPU) of the device to read and execute the program codes stored in the storage medium.
- a computer alternatively CPU or MPU
- the program codes read from the storage medium realize the functions of the embodiment themselves, and the storage medium, in which the program codes are stored, constitutes the present invention.
- a ROM, a floppy disk, a hard disk, an optical disk, a magneto-optical disk, a CD-ROM, a CD-R, a magnetic tape, a nonvolatile memory card or the like can be used as the storage medium for supplying the program codes.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
- Small-Scale Networks (AREA)
- Information Transfer Between Computers (AREA)
Description
- The present invention concerns a server device which informs an access point in a communication system of an encipher key used when a client terminal (i.e. a communication apparatus) initiates a communication through the access point. It also concerns a method for controlling the same, and a computer-readable storage medium storing instructions to carry out such a method.
- Conventionally, in a wireless LAN system, a client terminal has been connected to a network through wireless communication with an access point on the network.
- There is also a wireless LAN system, in which a client terminal receives authentication of connection to a network through an access point from an authentication server on a network.
- In such a system, when the client terminal receives authentication from the authentication server, the client terminal and the authentication server create an encipher key of a wired equivalent privacy (WEP) encipher system, and the authentication server informs the access point of the created encipher key. Then, the client terminal transfers enciphered data with the access point by using the encipher key of the WEP encipher system to perform secure wireless communication.
- Incidentally, a communicable range of the access point is limited to a range reached by electric waves. On the other hand, the client terminal can be freely moved. Accordingly, the client terminal may be moved from a communicable range of an access point 1 to a communicable range of an access point 2. In this case, the client terminal must receive authentication of connection to the network from the authentication server again through wireless communication with the access point 2, the client terminal and the authentication server must create a new WEP key, and the authentication server must inform the access point 2 of the new WEP key.
- That is, when the client terminal changed the access point, re-authentication from the authentication server, creation of a new WEP key, informing of a WEP key, and the like prolonged the process until communication became possible. Consequently the process took time.
- In addition, in a system of many client terminals, since authentication and creation of a WEP key prolonged a process, a load on an authentication server inevitably became large.
- Furthermore, since the process took time when the access point was changed, usability was reduced.
- A server device with authentication means to authenticate a communication apparatus connected to a first access point and informing means to inform said access point of an enciphar key when a valid authentication occurs, is known from
WO 0124560 A WO 0296151 A - With a view of overcoming the problems discussed hereinabove, a server device is disclosed in
International Patent Application WO 0221768 A2 - informing means for informing said first access point, to which said communication apparatus is connected, of an encipher key, in accordance with the result of the authentication by said authentication means;
- determination means for determining whether or not said communication apparatus has been authenticated on the basis of identification information of said communication apparatus informed from an access point; and
- control means for i) requesting said informing means to inform a second access point, to which the identification information is notified, of the encipher key informed to said first access point when said determination means determines that said communication apparatus has been authenticated by said authentication means via the first access point, and ii) requesting said authentication means to authenticate said communication apparatus when said determination means determines that said communication apparatus has not been authenticated by said authentication means.
- To further improve this device, the present invention provides a server device as set out in claim 1.
- The present invention also provides a control method for the server device as set out in claim 4 and a computer readable storage medium as set out in claim 5. Advantageous embodiments thereof are disclosed in corresponding dependent claims.
- Other features of the present invention will become apparent upon reading of detailed description and drawings.
- In the accompanying drawings:
- FIG. 1 is a configuration view of a system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
- FIG. 2 is a block diagram of an access point according to the embodiment of the invention;
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram of a client terminal according to the embodiment of the invention;
- FIG. 4 is a sequential view showing a system operation according to the embodiment of the invention; and
- FIG. 5 is a sequential view of the system operation according to the embodiment of the invention.
- Next, description will be made of an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 1 is a configuration view of a system according to the embodiment of the invention.
- A
reference numeral 101 denotes a network, to which an access point A103, and an access point B104 are connected. The two access points are shown in FIG. 1, but the number of installed points is not limited to two. Each of the access points A103 and B104 can perform wireless communication with aclient terminal 105 present incommunicable ranges - The
reference numeral 105 is the client terminal, which is connected to thenetwork 101 through wireless communication with the access point A103 or B104. Though not shown in FIG. 1, a plurality ofclient terminals 105 may be present. - A
reference numeral 102 denotes an authentication server, which authenticates theclient terminal 105 connected to thenetwork 101, and creates an encipher key used in a wired equivalency privacy (WEP) encipher system. - FIG. 2 is a block diagram of the access point A103.
- A case of the access point B104 is similar.
- A
reference numeral 201 denotes a wireless unit, which transfers wireless data. Thewireless unit 201 is constituted of atransmission unit 210, areception unit 211, and anantenna 212. - A
reference numeral 202 denotes a signal process unit, which detects a signal received by thereception unit 211 to convert it into a digital signal, and modulates the signal in order to transmit a digital signal sent from adata process unit 203 by wireless. In addition, thesignal process unit 202 has a function of adding a header or the like in order to use data sent from thedata process unit 203 for wireless transmission, and removing a header or the like from received data to send it to thedata process unit 203. - The
reference numeral 203 is the data process unit, which is constituted of a transmissiondata process unit 205 for enciphering data from anetwork interface 208 by a WEP encipher system, and a receptiondata process unit 206 for decoding enciphered data. - A
reference numeral 204 denotes a control unit, which executes determination of presence of anew client terminal 105, control of the entire access point A103, and the like. - A
reference numeral 207 denotes a storage unit, which stores an encipher key for WEP enciphering, and information regarding an ID or the like of theclient terminal 105. - The
reference numeral 208 is the network interface, which is an interface between the access point A103 and thenetwork 101. - FIG. 3 is a block diagram of the
client terminal 105. - The
client terminal 105 of the embodiment is constituted of a wireless communication card. - Functions similar to those of the access point A103 shown in FIG. 2 are denoted by similar numerals.
- A
reference numeral 301 denotes a data communication interface, which is connected to an information processor such as a personal computer to perform data communication. - A
reference numeral 302 denotes a storage unit, which stores an encipher key for WEP enciphering, and information regarding an ID or the like of theclient terminal 105 necessary for wireless communication with the access point A103 or the access point B104. According to the embodiment, as an ID of theclient terminal 105, a media access control (MAC) address is used. - Next, description will be made of an operation of the entire system of the embodiment with reference to the drawings.
- First, a process of first connection of the
client terminal 105 to thenetwork 101 through the access point A103 is explained by referring to a sequential view of FIG. 4. - The
client terminal 105 executes open authentication in the wireless LAN to be connected to the access point A103 (5401). - The access point A103 obtains an ID of the client terminal 105 (S402).
- The access point A103 informs the
authentication server 102 of the ID of the client terminal 105 (S403). - The
authentication server 102 determines whether authentication for the connection of theclient terminal 105 to thenetwork 101 has been finished or not, based on the ID informed from the access point A103 (S404). Theclient terminal 105 makes the connection for the first time, and the authentication has not been finished. Thus, it is determined that the authentication has not been finished. - The
authentication server 102 requests theclient terminal 105 to input a user name and a password (S405). - The
client terminal 105 inputs the user name and the password (S406). - In order to enhance secrecy of the user name and the password inputted in step S406, the
client terminal 105 executes irreversible numerical value processing called one-way hash, and informs theauthentication server 102 of its one-way hash data (S407). - The
authentication server 102 collates the one-way hash data informed in step S407 with a data group regarding a user for permitting connection to thenetwork 101, which is saved in a database in theauthentication server 102. If a result of the collation shows coincident data, the connection to thenetwork 101 is permitted to theclient terminal 105, and the ID of theclient terminal 105 is stored (step S408). - The
client terminal 105 and theauthentication server 102 create an encipher key called a WEP session key (S409). The WEP session key is an encipher key, which is used in the WEP encipher system, and valid only for enciphering traffic of theclient terminal 105. - The
authentication server 102 stores the created WEP session key in association with the ID of theclient terminal 105, and informs it to the access point A103 (S410). - The access point A103 enciphers a broadcast key with the WEP session key (S411), and sends the enciphered broadcast key to the client terminal 105 (S412). The broadcast key is an encipher key, which is used when data broadcast from the access point A130 to a plurality of
client terminals 105 is enciphered. - The
client terminal 105 decodes the enciphered broadcast key by using the WEP session key created in step S409 to obtain a broadcast key (S413). - The access point A103 and the
client terminal 105 start WEP encipher sequences (S414, S415). - Then, in communication with one client terminal 105 (point-to-point communication, the access point A103 transfers data enciphered with the WEP session key to perform secure wireless communication (S416). In broadcast communication with a plurality of client terminals 105 (point-to-multipoint communication), the access point A103 transfers data enciphered with the broadcast key to perform secure wireless communication (S416).
- Fig. 5 shows a sequential view of an operation when the
client terminal 105, for which authentication of its connection to thenetwork 101 through the access point A103 has been finished, is moved from thecommunicable range 106 of the access point A103 to thecommunicable range 107 of the access point B104 to be connected to thenetwork 101 through the access point B104. - The client terminal. 105 is moved out of the
communicable range 106 of the access point A103 to be incommunicable with the access point A103 (5501). Then, theclient terminal 105 is moved into thecommunicable range 107 of the access point B104 to be communicable with the access point B104. - The
client terminal 105 executes open authentication to be connected to the access point B104 (S502). - The access point B104 obtains an ID of the client terminal 105 (S503).
- The access point B104 informs the
authentication server 102 of the ID of the client terminal 105 (S504). - The
authentication server 102 determines whether authentication for the connection of theclient terminal 105 to thenetwork 101 has been finished or not, based on the ID informed in step S504, and the stored ID of theclient terminal 105, for which the authentication has been finished (S505). Here, for theclient terminal 105, the authentication of its connection to thenetwork 101 through the access point A103 was finished in step S408 (FIG. 4), and the ID of the client terminal has been stored. Thus, it is determined that the authentication has been finished. - The
authentication server 102 instructs the access point A103 to delete the WEP session key stored in thestorage unit 207 to be used for wireless communication with the client terminal 105 (S506). - The
authentication server 102 informs the access point B104 of the WEP session key stored in association with the ID of theclient terminal 105 in step S410 (FIG. 4) (S507). - The access point B104 enciphers a broadcast key with the WEP session key informed in step S507 (S508), and sends the enciphered broadcast key to the client terminal 105 (S509).
- The
client terminal 105 decodes the enciphered broadcast key by the WEP session key created in step S409 (FIG. 4) to obtain a broadcast key (S510). - The access point B104 and the
client terminal 105 start WEP encipher sequences (S511, S512). - Then, in communication with one client terminal. 105 (point-to-point communication), the access point B104 transfers data enciphered with the same WEP session key as that used for the communication between the
client terminal 105 and the access point A103 to perform secure wireless communication (S513). In broadcast communication with a plurality of client terminals 105 (point-to-multipoint communication), the access point B104 transfers data enciphered with the broadcast key to perform secure wireless communication (S513). - In the embodiment, in step S507, the WEP session key stored in the
authentication server 102 is informed to the access point B104. However, the WEP session key stored in the access point A103 may be informed through theauthentication server 102 to the access point B104: - In the foregoing explanation, the
client terminal 105 was the wireless communication card. However, a function similar to the wireless communication card may be incorporated in a personal computer or personal digital assistants (PDA). - Needless to say, the present invention can be implimented by supplying a computer-readable storage medium, in which software program codes for realizing the functions of the client terminal, the access points, and the authentication server are stored, to a system or a device, and causing the system or a computer (alternatively CPU or MPU) of the device to read and execute the program codes stored in the storage medium.
- In such a case, the program codes read from the storage medium realize the functions of the embodiment themselves, and the storage medium, in which the program codes are stored, constitutes the present invention.
- As the storage medium for supplying the program codes, a ROM, a floppy disk, a hard disk, an optical disk, a magneto-optical disk, a CD-ROM, a CD-R, a magnetic tape, a nonvolatile memory card or the like can be used.
- Needless to say, not only the case of realizing the functions of the embodiment by executing the program codes read by the computer, but also a case where based on instructions of the program codes, a part or all of the actual process is executed by an OS or the like working on the computer to realize the functions of the embodiment are included in the present invention.
- Furthermore, needless to say, a case where the program codes read from the storage medium are written in a CPU or the like provided in a function extension board inserted into the computer or a function extension unit connected to the computer and, then, based on instructions of the program codes, the CPU or the like provided in the function extension board or the function extension unit executes a part or all of the actual process to realize the functions of the embodiment is included in the present invention.
Claims (5)
- A server device (102) comprising:authentication means for authenticating (S404, S408) a communication apparatus (105) which is connected to a network (101) through a first access point (103);informing means for informing (S410) said first access point, to which said communication apparatus is connected, of an encipher key, in accordance with the result of the authentication by said authentication means;determination means for determining (S404 and S505) whether or not said communication apparatus (105) has been authenticated on the basis of identification information of said communication apparatus informed from an access point (104); andcontrol means for i) requesting said informing means to inform (S507) a second access point (124), to which the identification information is notified, of the encipher key informed (S410) to said first access point (103) when said determination means determines that said communication apparatus (106) has been authenticated by said authentication means via the first access point, and ii) requesting said authentication means to authenticate said communication apparatus (105) when said determination means determines that said communication apparatus (106) has not been authenticated by said authentication means.characterised by further comprising instructions means for instructing (S506) the first access point (103) to delete the encipher key when the communication apparatus is connected to the network (101) through the second access point (104).
- The server device according to claim 1, further comprising:creation means for creating (S409) the encipher key used for communication between the communication apparatus (105) and the first access point (103) in accordance with the authentication (S408) by said authentication means; and whereinthe server device (102) is adapted to store the encipher key created by the creation means, for later use in informing (S410) the second access point (104) by said informing means.
- The server device according to claim 1 further comprising:creation means for creating (S409) the encipher key used for communication between the communication apparatus and the first access point (103) in accordance with the authentication (S408) by said authentication means; and whereinthe server device (102) is adapted to obtain from said first access point (103) the encipher key informed (S410) to said first access point (103) by said informing means.
- A control method for a server device (102) comprising:an authentication step (s408) of authenticating a communication apparatus (105) which is connected to a network (101) through a first access point (103);an informing step (S410) of informing said first access point (103), to which said communication apparatus (105) is connected, of an encipher key, in accordance with the result of the authentication in said authentication step;a determination step (S404 and S505) of determining whether or not said communication apparatus (105) has been authenticated on the basis of identification information of said communication apparatus (105) informed from an access point (104); andin dependence upon the determination made in said determination step (S404 and S505):characterised by comprising the step of:i) an informing step (S507) of informing a second access point (124), to which the identification information is notified, of the encipher key informed (S410) to said first access point (103) when it is determined that said communication apparatus (106) has been authenticated via the first access point, andii) an authentication step of authenticating said communication apparatus (105) when it is determined that said communication apparatus (106) has not been authenticated.instructing (S506) the first access point (103) to delete the encipher key when the communication apparatus is connected to the network (101) through the second access point (104).
- A computer readable storage medium having computer-executable instructions that when executed on a computer perform the method steps defined in claim 4.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001385869A JP3870081B2 (en) | 2001-12-19 | 2001-12-19 | COMMUNICATION SYSTEM AND SERVER DEVICE, CONTROL METHOD, COMPUTER PROGRAM FOR IMPLEMENTING THE SAME, AND STORAGE MEDIUM CONTAINING THE COMPUTER PROGRAM |
| JP2001385869 | 2001-12-19 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1322091A1 EP1322091A1 (en) | 2003-06-25 |
| EP1322091B1 true EP1322091B1 (en) | 2007-12-19 |
Family
ID=19187882
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP02258074A Expired - Lifetime EP1322091B1 (en) | 2001-12-19 | 2002-11-22 | Communication system, server device, client device and method for controlling the same |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7424605B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP1322091B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP3870081B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN1213563C (en) |
| DE (1) | DE60224161T2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (48)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8942375B2 (en) | 2002-09-17 | 2015-01-27 | Broadcom Corporation | Method and system for providing multiple encryption in a multi-band multi-protocol hybrid wired/wireless network |
| EP1547299B1 (en) * | 2002-09-17 | 2012-11-14 | Broadcom Corporation | Method and system for providing multiple encryption in a multi-band multi-protocol hybrid wired/wireless network |
| US20040088550A1 (en) * | 2002-11-01 | 2004-05-06 | Rolf Maste | Network access management |
| US7792527B2 (en) * | 2002-11-08 | 2010-09-07 | Ntt Docomo, Inc. | Wireless network handoff key |
| US20040236939A1 (en) * | 2003-02-20 | 2004-11-25 | Docomo Communications Laboratories Usa, Inc. | Wireless network handoff key |
| CN1784851B (en) * | 2003-03-14 | 2013-02-20 | 汤姆森特许公司 | Access method and access point for control terminal device to WLAN |
| CN100527894C (en) * | 2003-03-27 | 2009-08-12 | 汤姆森许可公司 | Secure roaming between wireless access points |
| CN1830190A (en) * | 2003-07-29 | 2006-09-06 | 汤姆森特许公司 | Controlling access to a network using redirection |
| US7447177B2 (en) | 2003-08-26 | 2008-11-04 | Intel Corporation | Method and apparatus of secure roaming |
| EP1517475A1 (en) * | 2003-09-16 | 2005-03-23 | Axalto S.A. | Smart card based encryption in Wi-Fi communication |
| US7930412B2 (en) * | 2003-09-30 | 2011-04-19 | Bce Inc. | System and method for secure access |
| JP2005110112A (en) * | 2003-10-01 | 2005-04-21 | Nec Corp | Method for authenticating radio communication device in communication system, radio communication device, base station and authentication device |
| JP4311174B2 (en) | 2003-11-21 | 2009-08-12 | 日本電気株式会社 | Authentication method, mobile radio communication system, mobile terminal, authentication side device, authentication server, authentication proxy switch, and program |
| US7548744B2 (en) * | 2003-12-19 | 2009-06-16 | General Motors Corporation | WIFI authentication method |
| EP1724691A1 (en) * | 2004-03-08 | 2006-11-22 | Global Friendship Inc. | Electronic terminal device protection system |
| JP2005267529A (en) * | 2004-03-22 | 2005-09-29 | Fujitsu Ltd | Login authentication method, login authentication system, authentication program, communication program, and storage medium |
| JP4689225B2 (en) * | 2004-10-15 | 2011-05-25 | パナソニック株式会社 | Wireless network system, wireless terminal accommodating device, and communication device |
| JP4375197B2 (en) * | 2004-10-25 | 2009-12-02 | 日本電気株式会社 | Wireless LAN system, wireless terminal, wireless base station, wireless terminal communication setting method and program thereof |
| US20070152076A1 (en) * | 2004-12-13 | 2007-07-05 | Chiang Kuo C | Monitoring system with a wireless transmitting/receiving module |
| US7990998B2 (en) * | 2004-12-22 | 2011-08-02 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Connection setup using flexible protocol configuration |
| FI20050393A0 (en) * | 2005-04-15 | 2005-04-15 | Nokia Corp | Replacement of key material |
| KR100619998B1 (en) | 2005-04-30 | 2006-09-06 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method and system for in mobile communication station |
| CN101180848A (en) * | 2005-05-16 | 2008-05-14 | 汤姆森特许公司 | Secure switch in wireless LAN |
| JP4713955B2 (en) * | 2005-06-13 | 2011-06-29 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Authentication system, wireless communication terminal and wireless base station |
| DE202005021930U1 (en) | 2005-08-01 | 2011-08-08 | Corning Cable Systems Llc | Fiber optic decoupling cables and pre-connected assemblies with toning parts |
| US7392037B2 (en) * | 2005-08-19 | 2008-06-24 | Intel Corporation | Wireless communication device and methods for protecting broadcasted management control messages in wireless networks |
| DE102006008745A1 (en) | 2005-11-04 | 2007-05-10 | Siemens Ag | Method and server for providing a mobility key |
| US20070165582A1 (en) * | 2006-01-18 | 2007-07-19 | Puneet Batta | System and method for authenticating a wireless computing device |
| JP4914075B2 (en) * | 2006-01-31 | 2012-04-11 | 株式会社アイ・オー・データ機器 | Encryption key setting method, network system, wireless LAN repeater, wireless LAN adapter, and encryption key setting program |
| DE102006042554B4 (en) * | 2006-09-11 | 2009-04-16 | Siemens Ag | Method and system for continuously transmitting encrypted data of a broadcast service to a mobile terminal |
| JP4841519B2 (en) | 2006-10-30 | 2011-12-21 | 富士通株式会社 | COMMUNICATION METHOD, COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, KEY MANAGEMENT DEVICE, RELAY DEVICE, AND COMPUTER PROGRAM |
| US9531835B2 (en) * | 2007-02-13 | 2016-12-27 | Devicescape Software, Inc. | System and method for enabling wireless social networking |
| JP2008236483A (en) * | 2007-03-22 | 2008-10-02 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Communication method, and terminal device and base station apparatus utilizing same |
| US7907735B2 (en) | 2007-06-15 | 2011-03-15 | Koolspan, Inc. | System and method of creating and sending broadcast and multicast data |
| JP2009130603A (en) * | 2007-11-22 | 2009-06-11 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Communication method and base station device using the same, terminal device and controller |
| KR101655264B1 (en) * | 2009-03-10 | 2016-09-07 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method and system for authenticating in communication system |
| US9197420B2 (en) | 2010-01-06 | 2015-11-24 | International Business Machines Corporation | Using information in a digital certificate to authenticate a network of a wireless access point |
| US9768956B2 (en) * | 2010-07-28 | 2017-09-19 | General Motors Llc | Methods and systems for facilitating communications between vehicles and service providers |
| JP5982389B2 (en) * | 2010-11-17 | 2016-08-31 | ラッカス ワイヤレス, インコーポレイテッド | Cross-access login controller |
| CN102223633B (en) * | 2011-07-06 | 2013-12-04 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method, device and system for authenticating wireless local area network (WLAN) |
| KR101232861B1 (en) | 2012-05-29 | 2013-02-14 | ㈜ 엘케이컴즈 | Network relay system and providing method thereof |
| JP5820355B2 (en) * | 2012-09-28 | 2015-11-24 | 株式会社クボタ | Data communication system for work equipment |
| US10028179B2 (en) * | 2013-05-31 | 2018-07-17 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Reducing signaling during AP to AP handoff in dense networks |
| US9882774B2 (en) | 2015-02-02 | 2018-01-30 | Eero Inc. | Systems and methods for intuitive home networking |
| JP6737955B2 (en) * | 2016-09-27 | 2020-08-12 | エーナイン・ドット・コム インコーポレイテッドA9.com, Inc. | How to share network settings |
| CN106790255A (en) * | 2017-01-24 | 2017-05-31 | 北京元心科技有限公司 | End to end security communication means and system |
| JP2019050446A (en) * | 2017-09-07 | 2019-03-28 | 株式会社アウトスタンディングテクノロジー | Access control method and device thereof |
| CN109194663A (en) * | 2018-09-13 | 2019-01-11 | 郑州云海信息技术有限公司 | A kind of method and device of file storage and downloading based on cloud computing |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1340337A2 (en) * | 2000-09-08 | 2003-09-03 | Reefedge, Inc. | Location-independent packet routing and secure access in a short-range wireless networking environment |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3082686B2 (en) | 1996-11-07 | 2000-08-28 | 日本電気株式会社 | MAC bridge control method and device |
| US6108789A (en) * | 1998-05-05 | 2000-08-22 | Liberate Technologies | Mechanism for users with internet service provider smart cards to roam among geographically disparate authorized network computer client devices without mediation of a central authority |
| US6772331B1 (en) * | 1999-05-21 | 2004-08-03 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method and apparatus for exclusively pairing wireless devices |
| SE519471C2 (en) * | 1999-09-20 | 2003-03-04 | Ericsson Telefon Ab L M | Method for establishing a secure connection between access points and a mobile terminal in a packet switched network |
| GB9922847D0 (en) * | 1999-09-27 | 1999-11-24 | Simoco Int Ltd | Radio communications |
| JP3570310B2 (en) | 1999-10-05 | 2004-09-29 | 日本電気株式会社 | Authentication method and authentication device in wireless LAN system |
| JP3570311B2 (en) | 1999-10-07 | 2004-09-29 | 日本電気株式会社 | Wireless LAN encryption key update system and update method thereof |
| US7486952B1 (en) | 2000-02-09 | 2009-02-03 | Alcatel-Lucent Usa Inc. | Facilitated security for handoff in wireless communications |
| JP3450808B2 (en) * | 2000-08-25 | 2003-09-29 | 株式会社東芝 | Electronic device and connection control method |
| JP2002125270A (en) | 2000-10-18 | 2002-04-26 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | Method for connecting mobile terminal |
| US20020174335A1 (en) * | 2001-03-30 | 2002-11-21 | Junbiao Zhang | IP-based AAA scheme for wireless LAN virtual operators |
| WO2002096151A1 (en) * | 2001-05-22 | 2002-11-28 | Flarion Technologies, Inc. | Authentication system for mobile entities |
| US20030084287A1 (en) * | 2001-10-25 | 2003-05-01 | Wang Huayan A. | System and method for upper layer roaming authentication |
-
2001
- 2001-12-19 JP JP2001385869A patent/JP3870081B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2002
- 2002-11-22 DE DE60224161T patent/DE60224161T2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-11-22 EP EP02258074A patent/EP1322091B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-12-03 CN CNB021548935A patent/CN1213563C/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2002-12-13 US US10/318,861 patent/US7424605B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1340337A2 (en) * | 2000-09-08 | 2003-09-03 | Reefedge, Inc. | Location-independent packet routing and secure access in a short-range wireless networking environment |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE60224161T2 (en) | 2008-12-04 |
| JP2003188885A (en) | 2003-07-04 |
| CN1213563C (en) | 2005-08-03 |
| CN1427554A (en) | 2003-07-02 |
| JP3870081B2 (en) | 2007-01-17 |
| EP1322091A1 (en) | 2003-06-25 |
| DE60224161D1 (en) | 2008-01-31 |
| US20030115460A1 (en) | 2003-06-19 |
| US7424605B2 (en) | 2008-09-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1322091B1 (en) | Communication system, server device, client device and method for controlling the same | |
| KR100778186B1 (en) | Wireless communication system allowing group identification information to be publicly available and to be hidden, wireless access point device, and communication method and program for wireless access point device | |
| CN101534505B (en) | Communication device and communication method | |
| KR100886691B1 (en) | Communication apparatus and method thereof | |
| US20130001301A1 (en) | Controlling Connectivity of a Wireless Smart Card Reader | |
| CN109922474B (en) | Method for triggering network authentication and related equipment | |
| CN101779416B (en) | Communication apparatus, control method thereof, and computer program | |
| JP4345596B2 (en) | Connection authentication in wireless communication network systems | |
| JP2009212732A (en) | Communication device and communication method | |
| JP2006067174A (en) | Control program, communication relay device control method, and communication relay device and system | |
| EP3068091B1 (en) | Network configuration method, and related device and system | |
| JP2005065018A (en) | Wireless lan connection system, wireless lan connection method and wireless terminal | |
| JP2006332863A (en) | Information mobile terminal equipment, and wireless communications system | |
| JP4455076B2 (en) | Wireless communication apparatus authentication method, wireless communication apparatus, computer program, and computer-readable recording medium | |
| US8924710B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for providing session key for WUSB security and method and apparatus for obtaining the session key | |
| EP1713205A1 (en) | Controlling connectivity of a wireless smart card reader | |
| JP2009505271A (en) | Method for performing multiple PSK-based authentications in a single process and system for performing this method | |
| CN115868189A (en) | Method, vehicle, terminal and system for establishing vehicle safety communication | |
| JP2006180110A (en) | Data transmission system, data transmission method, data transmission server, data receiving terminal and data transmitting program | |
| CN115412909A (en) | Communication method and device | |
| CN105722080B (en) | Bluetooth pairing method, master intelligent terminal and slave intelligent terminal | |
| JP5775589B2 (en) | Mobile communication terminal, subscriber authentication module, communication system, and communication method | |
| KR101787727B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for connecting with wireless lan | |
| JP2005277890A (en) | Authentication method | |
| CN117896847A (en) | Method, equipment, communication system and storage medium for establishing communication connection |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK RO SI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20031126 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): DE FI FR GB SE |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20040511 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20040511 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE FI FR GB SE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 60224161 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20080131 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080319 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20071219 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20080922 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20151125 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20151130 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20151127 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 60224161 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20161122 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20170731 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20161130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170601 Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20161122 |