EP0376239A2 - Drill string - Google Patents
Drill string Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0376239A2 EP0376239A2 EP89123928A EP89123928A EP0376239A2 EP 0376239 A2 EP0376239 A2 EP 0376239A2 EP 89123928 A EP89123928 A EP 89123928A EP 89123928 A EP89123928 A EP 89123928A EP 0376239 A2 EP0376239 A2 EP 0376239A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- strips
- rod
- drill pipe
- parts
- pipe according
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 abstract 1
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000005553 drilling Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005096 rolling process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000006096 absorbing agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000035939 shock Effects 0.000 description 2
- 241001136792 Alle Species 0.000 description 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003754 machining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008439 repair process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011343 solid material Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E21—EARTH OR ROCK DRILLING; MINING
- E21B—EARTH OR ROCK DRILLING; OBTAINING OIL, GAS, WATER, SOLUBLE OR MELTABLE MATERIALS OR A SLURRY OF MINERALS FROM WELLS
- E21B17/00—Drilling rods or pipes; Flexible drill strings; Kellies; Drill collars; Sucker rods; Cables; Casings; Tubings
- E21B17/02—Couplings; joints
- E21B17/04—Couplings; joints between rod or the like and bit or between rod and rod or the like
- E21B17/07—Telescoping joints for varying drill string lengths; Shock absorbers
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E21—EARTH OR ROCK DRILLING; MINING
- E21B—EARTH OR ROCK DRILLING; OBTAINING OIL, GAS, WATER, SOLUBLE OR MELTABLE MATERIALS OR A SLURRY OF MINERALS FROM WELLS
- E21B17/00—Drilling rods or pipes; Flexible drill strings; Kellies; Drill collars; Sucker rods; Cables; Casings; Tubings
Definitions
- the invention relates to a drill pipe according to the preamble of claim 1.
- drill rods such as those used particularly in earth drilling equipment, be it a single so-called Kelly rod or be it a telescopic drill rod consisting of several parts
- Kelly rod or be it a telescopic drill rod consisting of several parts
- the known designs are rails with a rectangular cross section, which have been subjected to machining.
- Drill pipe parts of the aforementioned type are often exposed to high and also unfavorable loads. These are stresses that come from the drive side and particularly affect the torque transmission, as well as effects that result from the tool and from the drilling process itself. in addition to the rotary motion usually also have to be considerable Pressure forces must be transferred to the tool via the linkage. In all of this, the strips represent particularly important parts that are often of crucial importance for the durability of the boom and its susceptibility to repairs and its service life.
- the object of the invention is to overcome difficulties and shortcomings which, inter alia, with regard to the points mentioned above occur in practical drilling operations, to counter them effectively and to create a one-piece or multi-part drill pipe which is distinguished by advantageous properties, in particular with regard to its stability and resilience during use, and also with regard to its structure and training . Further problems connected with all of this, with which the invention is concerned, result from the respective explanation of the indicated solution.
- the invention provides that at least three bars for torque transmission are provided on at least one linkage part, which have a curved cross-sectional shape adapted to the outer contour of the base body of the linkage part.
- the forces exerted on the linkage part by the drive torque are introduced in a favorable manner into the linkage part and absorbed by it. This contributes to the smooth running of the boom, the tool and the parts otherwise connected to it. Adverse tilting forces, which could easily cause a drill pipe to bulge or even burst in the case of conventional designs, are avoided. Because the base body is enclosed by strips in three or more areas, alternating bending stresses are particularly well absorbed.
- the arrangement of the strips is expedient so that they are regularly distributed over the circumference and also have the same extent in the circumferential direction. However, a different distribution or arrangement is not excluded. It is particularly advantageous to design and arrange the strips such that they enclose approximately 50% of the circumference of the base body at the points in question where they are not interrupted in the longitudinal direction or are narrowed to form pressure-receiving surfaces.
- the strips in their shape adapted to the outer contour of the base body are made by non-cutting deformation, in particular by rolling.
- the sections for welding on the strips are also expediently produced by non-cutting deformation. It is then no longer necessary to mechanically process the strips before welding them onto the base body.
- such strips produced by rolling or a similar process can also be regarded as particularly favorable in terms of their properties for the use in question here.
- a rod section with three or four strips can be used. However, there is also a large number of strips closed if this appears appropriate according to the circumstances or circumstances. In particular, it can be the case that a rod part has, in addition to an area with three or four strips, another area with a larger number of strips. This is possible for the upper part of an outer tube in a telescopic rod.
- the invention also includes designs of a multi-part linkage in which at least one linkage part has a cylindrical basic shape with three or more strips and at least one other linkage part, namely an inner rod, an angular, e.g. has a square, outer contour or cross-sectional shape.
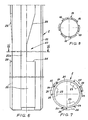
- FIG. 1 can be a three-part telescopic linkage.
- the illustration in FIG. 1 reveals the following elements: an outer rod part 1, which is essentially designed as a round tube, a driver 5, or the like, on a rotary head, not shown. can be connected and can exert both a torque and a compressive force on the linkage, a guide and shock absorber unit 6 arranged in the region of the upper end of the outer linkage part 1 and a fork piece 7 with connection for a cable 8, one with the total number 4 designated shock absorber at the lower end of an innermost Part of the rod-forming inner rod 3 with connector 9 for a tool.
- an outer rod part 1 which is essentially designed as a round tube, a driver 5, or the like, on a rotary head, not shown. can be connected and can exert both a torque and a compressive force on the linkage, a guide and shock absorber unit 6 arranged in the region of the upper end of the outer linkage part 1 and a fork piece 7 with connection for a
- FIG. 2 shows a part of the telescopic rod in a state in which the inner rod 3 is still in a rod part 2 that is directly adjacent to it and coaxial with it, and both rod parts 3, 4 from the outer rod part, namely the outer tube 1, are pushed out. From Fig. 2 it can also be seen that the fork piece 7 is attached to the connection for the rope 8 at the upper end of the inner rod 3.
- the linkage part 1 shown in FIGS. 3 and 4 can be the outer tube of the linkage according to FIGS. 1 and 2.
- the base body 11 of the same is a seamless cylindrical steel tube which has on its outside three strips 12 which are evenly distributed over the circumference. These also consist of steel and are fastened to the base body 11 by welding.
- the strips 12 have a curved cross-sectional shape, as can be clearly seen in FIG. 4.
- Their inner surface, ie the surface facing the tube 11 has the same curvature as the cylindrical outer surface of the tube 11, so that the strips rest against the tube over a relatively large area and thus form a stable unit after welding.
- the number 13 denotes drivers which are located at the lower end of the rod part 1 inside it (as indicated in FIG. 2) tet) and serve to attack the profile of the next rod part 2. The number of these drivers is expediently equal to the strips or the spaces left between them on this next part of the linkage.
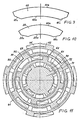
- the object shown in FIGS. 6 and 7 on a somewhat larger scale can in particular be the central rod part 2 of a telescopic drill rod according to FIGS. 1 and 2.
- the base body 21 is a seamless steel tube, on the outer sides of which three strips 22 running along the surface lines are fastened by welding.
- the welding points are designated by the number 24 (corresponding welding points are also found in the outer tube according to FIGS. 3 and 4, but are not shown there).
- FIGS. 6 and 7 also illustrate a location with pressure receiving surfaces 25 on the strips 22.
- the latter here have a narrower area 22a, as a result of which a shoulder or a recess or pocket 27 forming the pressure receiving surfaces 25 is created.
- the strips 22 can be provided with bevels 26, which serves for easier engagement of a driver located on the associated next outer linkage part or a correspondingly profiled drive member on the inside.
- FIG. 7 shows drivers 23 which functionally correspond to drivers 13 in FIG. 4.
- the pressure receiving surfaces explained are also available for the other parts of the boom.
- FIG. 5 How the three linkage parts 1, 2 and 3 of a telescopic linkage with the described features are built into one another is illustrated in FIG. 5 as a section at the point VV in FIG. 1, the driver 5 being the clear one
- the base body 31 of the inner rod part 3 is not a tube, but a rod made of solid material.
- On the outside three strips 32 are attached, to which the above applies accordingly.
- FIG. 8 shows an embodiment of a rod part 14 in which six strips 16, which are regularly distributed over the circumference, are attached to the outside of a tubular base body 15.
- These strips 16 can, like the linkage parts already explained, extend over most of the length of the linkage part 14 and have recesses, pockets or the like. be provided to form pressure receiving surfaces, as was explained in connection with FIGS. 6 and 7.
- it can also be advantageous to provide such a number of strips only in one area of the rod part. This is particularly suitable for the upper area of an outer rod, e.g. the outer rod 1 in the area of the guide unit 6.
- FIG. 11 shows a section corresponding to FIG. 5 in the case of a telescopic drill string consisting of four parts 41, 51, 61 and 71, on each of which four strips 42, 52, 62 and 72 of the type described with pressure transmission surfaces 45, 55, 65 and 75 are available.
- the respective strips are also connected to the associated base body by welding.
- the welds are not shown in Fig. 11 because this is a standard representation of the final state.
- the strips are parts produced by rolling, in particular the parts intended for welding are also formed without cutting.
- FIGS. 9 and 10 show two examples of such rolled strips 10 and 20 each in a front view.
- the strips have a curved profile.
- the curvature of the inner contour 10a or 20a is in each case the same as the contour of the linkage base body with which the strip is to be connected, that is to say circular in the case of a cylindrical base body.
- the outer contour 10b or 20b expediently runs parallel to the inner contour, that is to say also concentrically with the longitudinal axis of the rod part. Another course can also be selected for the outer contour. So a straight or angular contour is not excluded.
- Numbers 10c and 20c denote the chamfered areas on the strips on which the welds are made when they are connected to the respective base body.
- the side surfaces of the strips are at least partially directed radially along their longitudinal course, with reference to the center of the associated rod part. Then there is at least approximately a cross-sectional shape which corresponds to a sector of an annulus.
- the invention relates both to such non-cutting or shaped strips for drill pipe parts, as well as the rod parts provided with the strips, and to a multi-part rod assembly with one or more parts provided with such strips.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Geology (AREA)
- Mining & Mineral Resources (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- General Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Geochemistry & Mineralogy (AREA)
- Earth Drilling (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Die Erfindung bezieht sich auf ein Bohrgestänge nach dem Oberbegriff des Anspruchs 1.The invention relates to a drill pipe according to the preamble of
Bei Bohrgestängen, wie sie besonders bei Erdbohrgeräten verwendet werden, sei es eine einzelne sog Kelly-Stange oder sei es ein aus mehreren Teilen bestehendes Teleskop-Bohrgestänge, ist es bekannt, einen Gestängeteil außenseitig an zwei diametral gegenüberliegenden Stellen mit in Längsrichtung verlaufenden Leisten zu versehen, die zur Übertragung des Drehmoments von einem Antriebsglied auf den Gestängeteil bzw. von einem Gestängeteil auf einen anderen dienen. Bei den bekannten Ausführungen handelt es sich um Schienen mit rechteckigem Querschnitt, die einer spanabhebenden Bearbeitung unterzogen wurden.In the case of drill rods, such as those used particularly in earth drilling equipment, be it a single so-called Kelly rod or be it a telescopic drill rod consisting of several parts, it is known to provide a rod part on the outside at two diametrically opposite points with strips running in the longitudinal direction , which are used to transmit the torque from a drive member to the linkage part or from a linkage part to another. The known designs are rails with a rectangular cross section, which have been subjected to machining.
Bohrgestängeteile der vorgenannten Art sind beim Einsatz vielfach hohen und auch ungünstigen Belastungen ausgesetzt. Es handelt sich sowohl um Beanspruchungen, die von der Antriebsseite her kommen und besonders die Drehmomentübertragung betreffen, als auch um Einwirkungen, die sich vom Werkzeug her und aus dem Bohrvorgang selbst ergeben. außer der Drehbewegung müssen meist auch erhebliche Andruckkräfte über das Gestänge auf das Werkzeug übertragen werden müssen. Die Leisten stellen bei alledem besonders wichtige Teile dar, die für die Beanspruchbarkeit des Gestänges und dessen Reparaturanfälligkeit bzw. dessen Lebensdauer oft entscheidende Bedeutung haben.Drill pipe parts of the aforementioned type are often exposed to high and also unfavorable loads. These are stresses that come from the drive side and particularly affect the torque transmission, as well as effects that result from the tool and from the drilling process itself. in addition to the rotary motion usually also have to be considerable Pressure forces must be transferred to the tool via the linkage. In all of this, the strips represent particularly important parts that are often of crucial importance for the durability of the boom and its susceptibility to repairs and its service life.
Aufgabe der Erfindung ist es, Schwierigkeiten und Unzulänglichkeiten, die u.a. im Hinblick auf die vorstehend angesprochenen Punkte im praktischen Bohrbetrieb auftreten, wirksam zu begegnen und ein ein- oder mehrteiliges Bohrgestänge zu schaffen, das sich durch vorteilhafte Eigenschaften auszeichnet, so insbesondere hinsichtlich seiner Stabilität und Belastbarkeit beim Einsatz, weiterhin auch bezüglich seines Aufbaues und seiner Ausbildung. Weitere mit alledem zusammenhängende Probleme, mit denen sich die Erfindung befaßt, ergeben sich aus der jeweiligen Erläuterung der aufgezeigten Lösung.The object of the invention is to overcome difficulties and shortcomings which, inter alia, with regard to the points mentioned above occur in practical drilling operations, to counter them effectively and to create a one-piece or multi-part drill pipe which is distinguished by advantageous properties, in particular with regard to its stability and resilience during use, and also with regard to its structure and training . Further problems connected with all of this, with which the invention is concerned, result from the respective explanation of the indicated solution.
Die Erfindung sieht vor, daß zumindest an einem Gestängeteil wenigstens drei Leisten zur Drehmomentübertragung vorgesehen sind, die eine der äußeren Kontur des Grundkörpers des Gestängeteiles angepaßte, gekrümmte Querschnittsform aufweisen. Bei einer solchen Ausbildung ergibt sich eine vorteilhafte Kraftverteilung. Die durch das Antriebsmoment auf den Gestängeteil ausgeübten Kräfte werden in günstiger Weise in den Gestängeteil eingeleitet und von ihm aufgenommen. Dies trägt zu einem ruhigen Lauf des Gestänges, des Werkzeuges und der sonst mit ihm verbundenen Teile bei. Nachteilige Kippkräfte, die bei üblichen Ausführungen leicht zu einem Einbeulen eines Gestängerohres oder sogar zum Aufplatzen desselben führen konnten, werden vermieden. Weil der Grundkörper an drei oder mehr Bereichen von Leisten umschlossen ist, werden Biegewechselspannungen besonders gut aufgenommen. Für die Kraftübertragung steht insgesamt eine vergrößerte Fläche zur Verfügung, so daß die spezifische Flächenbe lastung bei gleichen Kräften geringer wird bzw. nun höhere Kräfte übertragen werden können. Sind an den Leisten auch Druckaufnahmeflächen zur Übertragung von Andruckkräften vorhanden, wie es im Rahmen der Erfindung insbesondere der Fall ist, so gilt das Gesagte dafür sinngemäß und entsprechend. Bei alledem läßt sich durch die der Gestängekontur angepaßte Gestalt der Leisten auch eine kompakte Bauform erzielen.The invention provides that at least three bars for torque transmission are provided on at least one linkage part, which have a curved cross-sectional shape adapted to the outer contour of the base body of the linkage part. With such a design, there is an advantageous force distribution. The forces exerted on the linkage part by the drive torque are introduced in a favorable manner into the linkage part and absorbed by it. This contributes to the smooth running of the boom, the tool and the parts otherwise connected to it. Adverse tilting forces, which could easily cause a drill pipe to bulge or even burst in the case of conventional designs, are avoided. Because the base body is enclosed by strips in three or more areas, alternating bending stresses are particularly well absorbed. An enlarged area is available for the power transmission, so that the specific area is load with the same forces becomes lower or higher forces can now be transmitted. If there are also pressure receiving surfaces on the strips for transmitting pressure forces, as is particularly the case within the scope of the invention, what has been said applies analogously and accordingly. In all of this, the shape of the strips, which is adapted to the rod contour, also enables a compact design to be achieved.
Die Anordnung der Leisten ist zweckmäßig so, daß sie regelmäßig über den Umfang verteilt sind und auch die gleiche Erstreckung in Umfangsrichtung haben. Es ist aber auch eine andere Verteilung bzw. Anordnung nicht ausgeschlossen. Mit besonderem Vorteil wird die Ausbildung und Anordnung der Leisten so getroffen, daß sie an den betreffenden Stellen, an denen sie in Längsrichtung nicht unterbrochen oder zur Ausbildung von Druckaufnahmeflächen verschmälert sind, etwa 50% des Umfanges des Grundkörpers umschließen.The arrangement of the strips is expedient so that they are regularly distributed over the circumference and also have the same extent in the circumferential direction. However, a different distribution or arrangement is not excluded. It is particularly advantageous to design and arrange the strips such that they enclose approximately 50% of the circumference of the base body at the points in question where they are not interrupted in the longitudinal direction or are narrowed to form pressure-receiving surfaces.
Gemäß einem besonderen Merkmal der Erfindung sind die Leisten in ihrer der Außenkontur des Grundkörpers angepaßten Form durch spanlose Verformung, insbesondere durch Walzen, hergestellte Teile. Zweckmäßig sind dabei auch die Partien für die Schweißung an den Leisten durch spanlose Verformung hergestellt. Es ist dann vor dem Anschweißen der Leisten an den Grundkörper keine mechanische Bearbeitung wie bisher mehr erforderlich. Darüber hinaus können solche durch Walzen oder einen ähnlichen Vorgang hergestellte Leisten auch hinsichtlich ihrer Eigenschaften für den hier in Rede stehenden Einsatz als besonders günstig angesehen werden.According to a special feature of the invention, the strips in their shape adapted to the outer contour of the base body are made by non-cutting deformation, in particular by rolling. The sections for welding on the strips are also expediently produced by non-cutting deformation. It is then no longer necessary to mechanically process the strips before welding them onto the base body. In addition, such strips produced by rolling or a similar process can also be regarded as particularly favorable in terms of their properties for the use in question here.
In den meisten Fällen kommt eine Ausführung eines Gestängeteiles mit drei oder mit vier Leisten in Betracht. Es ist aber auch eine größere Zahl von Leisten nicht ausge schlossen, wenn dies nach den Umständen oder Gegebenheiten zweckmäßig erscheint. Insbesondere kann es so sein, daß ein Gestängeteil außer einem Bereich mit drei oder mit vier Leisten noch einen anderen Bereich mit einer größeren Anzahl von Leisten aufweist. Dies kommt u.a. für den oberen Teil eines Außenrohres bei einem Teleskop-Gestänge infrage.In most cases, a rod section with three or four strips can be used. However, there is also a large number of strips closed if this appears appropriate according to the circumstances or circumstances. In particular, it can be the case that a rod part has, in addition to an area with three or four strips, another area with a larger number of strips. This is possible for the upper part of an outer tube in a telescopic rod.
Die Erfindung schließt auch Ausführungen eines mehrteiligen Gestänges ein, bei dem wenigstens ein Gestängeteil eine zylindrische Grundform mit drei oder mehr Leisten aufweist und wenigstens ein anderer Gestängeteil, namentlich eine Innenstange, eine eckige, z.B. quadratische, Außenkontur oder Querschnittsform hat.The invention also includes designs of a multi-part linkage in which at least one linkage part has a cylindrical basic shape with three or more strips and at least one other linkage part, namely an inner rod, an angular, e.g. has a square, outer contour or cross-sectional shape.
Weitere Einzelheiten, Merkmale und Vorteile der Erfindung ergeben sich aus der nachstehenden Erläuterung von Ausführungsbeispielen, aus der zugehörigen Zeichnung und aus den Ansprüchen. Es zeigen:
- Fig. 1 ein mehrteiliges Teleskop-Bohrgestänge in eingeschobenem Zustand in einer vereinfachten Ansicht,
- Fig. 2 einen Zustand des Gestänges nach Fig. 1, bei dem mit Ausnahme der Innenstange alle Teile ausgeschoben sind, teilweise im Schnitt,
- Fig. 3 eine Teilansicht eines Gestängeteiles,
- Fig. 4 einen Schnitt nach der Linie IV-IV in Fig. 3,
- Fig. 5 einen Schnitt durch das Gestänge nach Fig. 1 an der Stelle V-V,
- Fig. 6 eine Teilansicht eines Gestängeteiles mit Druckübertragungsflächen,
- Fig. 7 einen Schnitt nach der Linie VII-VII in Fig. 6,
- Fig. 8 einen Schnitt durch einen Gestängeteil mit sechs Leisten,
- Fig. 9 eine Leiste in Stirnansicht,
- Fig. 10 eine andere Leiste in Stirnansicht und
- Fig. 11 einen Schnitt durch ein vierteiliges Teleskop-Bohrgestänge.
- 1 is a multi-part telescopic drill pipe in the inserted state in a simplified view,
- 2 shows a state of the linkage according to FIG. 1, in which all parts except the inner rod are pushed out, partly in section,
- 3 is a partial view of a rod part,
- 4 shows a section along the line IV-IV in FIG. 3,
- 5 shows a section through the linkage according to FIG. 1 at the point VV,
- 6 is a partial view of a rod part with pressure transmission surfaces,
- 7 shows a section along the line VII-VII in FIG. 6,
- 8 shows a section through a rod part with six strips,
- 9 is a bar in front view,
- Fig. 10 shows another bar in front view
- 11 shows a section through a four-part telescopic drill rod.
Wenn in dieser Beschreibung die Angaben "oben" und "unten" verwendet werden, so gilt dies im Hinblick auf die Zeichnung. Zugleich entspricht dies auch den meisten Einsatzfällen des Gestänges selbst.If the information "above" and "below" is used in this description, this applies to the drawing. At the same time, this corresponds to most applications of the boom itself.
Bei dem Gestänge nach Fig. 1 kann es sich um ein dreiteiliges Teleskop-Gestänge handeln. Die Darstellung der Fig. 1 läßt folgende Elemente erkennen: einen im wesentlichen als Rundrohr ausgebildeten äußeren Gestängeteil 1, einen Mitnehmer 5, der an einen nicht gezeigten Kraftdrehkopf od.dgl. anschließbar ist und sowohl ein Drehmoment als auch eine Druckkraft auf das Gestänge ausüben kann, eine im Bereich des oberen Endes des äußeren Gestängeteiles 1 angeordnete Führungs-und Stoßdämpfer-Einheit 6 und ein Gabelstück 7 mit Anschluß für ein Seil 8, einen insgesamt mit der Zahl 4 bezeichneten Stoßdämpfer am unteren Endbereich einer den innersten Teil des Gestänges bildenden Innenstange 3 mit Anschlußstück 9 für ein Werkzeug.1 can be a three-part telescopic linkage. The illustration in FIG. 1 reveals the following elements: an
Die zur Übertragung von Drehmoment und Andruckkräften vom Mitnehmer 6 auf die Gestängeteile und von einem auf den anderen Gestängeteil dienenden Elemente sind aus Fig. 1 nicht ersichtlich. Sie werden nachstehend an Hand der Figuren 3 bis 11 erläutert.The elements used to transmit torque and pressure forces from the driver 6 to the linkage parts and from one element to the other linkage part are not shown in FIG. 1. They are explained below using FIGS. 3 to 11.
Fig. 2 zeigt einen Teil des Teleskop-Gestänges in einem Zustand, bei dem die Innenstange 3 sich noch in einem ihr unmittelbar benachbarten und zu ihr koaxialen nächsten Gestängeteil 2 befindet und beide Gestängeteile 3, 4 aus dem äußeren Gestängeteil, nämlich dem Außenrohr 1, ausgeschoben sind. Aus Fig. 2 ist auch ersichtlich, daß das Gabelstück 7 mit dem Anschluß für das Seil 8 am oberen Ende der Innenstange 3 angebracht ist.2 shows a part of the telescopic rod in a state in which the
Bei dem in den Figuren 3 und 4 gezeigte Gestängeteil 1 kann es sich um das Außenrohr des Gestänges nach Fig 1 und 2 handeln. Der Grundkörper 11 desselben ist ein nahtloses zylindrisches Stahlrohr, das auf seiner Außenseite drei gleichmäßig über den Umfang verteilte Leisten 12 aufweist. Diese bestehen ebenfalls aus Stahl und sind durch Schweißen an dem Grundkörper 11 befestigt. Die Leisten 12 haben eine gekrümmte Querschnittsform, wie Fig. 4 deutlich erkennen läßt. Ihre innere, d.h. dem Rohr 11 zugewandte Fläche hat jeweils die gleiche Krümmung wie die zylindrische Mantelfläche des Rohres 11, so daß die Leisten auf einem verhältnismäßig großen Bereich an dem Rohr anliegen und somit nach dem Verschweißen damit eine stabile Einheit bilden. Mit der Zahl 13 sind Mitnehmer bezeichnet, die sich am unteren Ende des Gestängeteiles 1 in dessen Innerem befinden (wie in Fig. 2 angedeu tet) und zum Angriff an dem Profil des nächsten Gestängeteiles 2 dienen. Die Zahl dieser Mitnehmer ist zweckmäßig gleich der Leisten bzw. der zwischen ihnen belassenen Zwischenräume an diesem nächsten Gestängeteil.The
Bei dem in den Figuren 6 und 7 in etwas größerem Maßstab gezeigten Gegenstand kann es sich insbesondere um den mittleren Gestängeteil 2 eines Teleskop-Bohrgestänges nach Fig. 1 und 2 handeln. Auch hier ist der Grundkörper 21 ein nahtloses Stahlrohr, auf dessen Außenseiten drei entlang der Mantellinien verlaufende Leisten 22 durch Schweißen befestigt sind. Die Schweißstellen sind mit der Zahl 24 bezeichnet (entsprechende Schweißstellen finden sich auch bei dem Außenrohr nach Fig. 3 und 4, sind dort nur nicht wiedergegeben).The object shown in FIGS. 6 and 7 on a somewhat larger scale can in particular be the
Die Figuren 6 und 7 veranschaulichen zugleich eine Stelle mit Druckaufnahmeflächen 25 an den Leisten 22. Die letzteren haben hier einen schmaleren Bereich 22a, wodurch ein die Druckaufnahmeflächen 25 bildender Absatz bzw. eine Ausnehmung oder Tasche 27 entsteht. Von oben her können die Leisten 22 mit Abschrägungen 26 versehen sein, was dem leichteren Ineingriffbringen eines an dem zugeordneten nächstäußeren Gestängeteil befindlichen Mitnehmers bzw. eines entsprechend innenseitig profilierten Antriebsgliedes dient. Die Fig. 7 zeigt Mitnehmer 23, die funktionsmäßig den Mitnehmern 13 in Fig. 4 entsprechen. Die erläuterten Druckaufnahmeflächen sind auch bei den anderen Gestängeteilen vorhanden.FIGS. 6 and 7 also illustrate a location with
Wie die drei Gestängeteile 1, 2 und 3 eines Teleskop-Gestänges mit den erläuterten Merkmalen ineinander gebaut sind, veranschaulicht Fig. 5 als Schnitt an der Stelle V-V in Fig. 1, wobei der Mitnehmer 5 der Deutlich keit halber nur in seinem Umriß und mit seinem Innenprofil strichpunktiert angedeutet ist. Dabei ist auch erkennbar, daß der Grundkörper 31 des inneren Gestängeteil 3 kein Rohr, sondern eine Stange aus Vollmaterial ist. Auf deren Außenseite sind drei Leisten 32 befestigt, wozu das vorstehend Gesagte entsprechend gilt.How the three
Fig. 8 zeigt eine Ausführung eines Gestängeteiles 14, bei dem auf der Außenseite eines rohrförmigen Grundkörpers 15 sechs regelmäßig über den Umfang verteilte Leisten 16 angebracht sind. Diese Leisten 16 können sich wie bei den schon erläuterten Gestängeteilen über den größten Teil der Länge des Gestängeteiles 14 erstrecken und mit Ausnehmungen, Taschen od.dgl. zur Bildung von Druckaufnahmeflächen versehen sein, wie dies im Zusammenhang mit Fig. 6 und 7 erläutert wurde. Es kann aber auch vorteilhaft sein, eine solche Anzahl von Leisten nur in einem Bereich des Gestängeteiles vorzusehen. Insbesondere kommt dies für den oberen Bereich einer Außenstange in Betracht, so z.B. der Außenstange 1 im Bereich der Führungseinheit 6.FIG. 8 shows an embodiment of a
Die Figur 11 zeigt einen der Figur 5 entsprechenden Schnitt bei einem aus vier Teilen 41, 51, 61 und 71 bestehenden Teleskop-Bohrgestänge, an denen jeweils vier Leisten 42, 52, 62 und 72 der erläuterten Art mit Druckübertragungsflächen 45, 55, 65 und 75 vorhanden sind. Die jeweiligen Leisten sind auch hier mit dem zugehörigen Grundkörper durch Schweißen verbunden. Die Schweißstellen sind in Fig. 11 nicht wiedergegeben, weil es sich hier um eine Normdarstellung des Endzustandes handelt.FIG. 11 shows a section corresponding to FIG. 5 in the case of a telescopic drill string consisting of four
Gemäß einem besonderen Merkmal der Erfindung sind die Leisten durch Walzen hergestellte Teile, wobei insbeson dere auch die für die Schweißung bestimmten Partien gleich spanlos mit geformt sind. In den Figuren 9 und 10 sind zwei Beispiele für solche gewalzten Leisten 10 und 20 jeweils in Stirnansicht gezeigt. Die Leisten haben ein gekrümmtes Profil. Dabei ist die Krümmung der Innenkontur 10a bzw. 20a jeweils gleich dem Konturverlauf des Gestänge-Grundkörpers, mit dem die Leiste verbunden werden soll, bei einem zylindrischen Grundkörper also kreisförmig. Die Außenkontur 10b bzw. 20b verläuft zweckmäßig parallel zur Innenkontur, also auch zur Längsachse des Gestängeteiles konzentrisch. Für die Außenkontur kann aber auch ein anderer Verlauf gewählt werden. So ist auch eine gerade oder eckige Kontur nicht ausgeschlossen. Mit den Zahlen 10c und 20c sind die abgeschrägten Partien an den Leisten bezeichnet, an denen bei der Verbindung mit dem jeweiligen Grundkörper die Schweißungen erfolgen. Die Seitenflächen der Leisten sind wenigstens teilweise auf ihrem Längsverlauf radial gerichtet, mit Bezug auf die Mitte des zugehörigen Gestängeteiles. Es ist dann zumindest annähernd eine Querschnittsform vorhanden, die einem Sektor eines Kreisringes entspricht.According to a special feature of the invention, the strips are parts produced by rolling, in particular the parts intended for welding are also formed without cutting. FIGS. 9 and 10 show two examples of such rolled
Gegenstand der Erfindung sind sowohl solche spanlos geformten bzw. gewalten Leisten für Bohrgestängeteile als auch die mit den Leisten versehenen Gestängeteile als auch ein mehrteiliges Gestänge mit einem oder mehreren, mit derartigen Leisten versehenen Teilen.The invention relates both to such non-cutting or shaped strips for drill pipe parts, as well as the rod parts provided with the strips, and to a multi-part rod assembly with one or more parts provided with such strips.
Alle in der vorstehenden Beschreibung erwähnten bzw. in der Zeichnung dargestellten Merkmale sollen, sofern der bekannte Stand der Technik es zuläßt, für sich allein oder auch in Kombinationen als unter die Erfindung fallend angesehen werden.All of the features mentioned in the above description or shown in the drawing, if the known prior art permits, should be regarded as falling within the scope of the invention on their own or in combinations.
Claims (11)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE8816167U | 1988-12-30 | ||
| DE8816167U DE8816167U1 (en) | 1988-12-30 | 1988-12-30 | Drill rods |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0376239A2 true EP0376239A2 (en) | 1990-07-04 |
| EP0376239A3 EP0376239A3 (en) | 1991-04-24 |
Family
ID=6831263
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19890123928 Withdrawn EP0376239A3 (en) | 1988-12-30 | 1989-12-27 | Drill string |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0376239A3 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE8816167U1 (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE4040155A1 (en) * | 1990-07-11 | 1992-01-16 | Dietmar Brussmann | Sinking of deep boreholes by rotary flushing - comprises lowering drill string contg. rotary drill end bit, into the hole then passing flushing fluid through the string |
| GB2242920B (en) * | 1990-04-09 | 1994-07-06 | Trevi | Telescopic bar of a drilling rig |
| DE20301946U1 (en) * | 2003-02-07 | 2004-06-09 | Bauer Maschinen Gmbh | Telescopic drill pipe |
| WO2005095754A1 (en) * | 2004-03-04 | 2005-10-13 | Atlas Copco Secoroc Ab | Telescoping drilling sub |
| AU2004202093B2 (en) * | 2003-01-23 | 2009-04-23 | Atlas Copco Drilling Solutions Inc | Sub Drilling sub |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5263899A (en) * | 1990-06-12 | 1993-11-23 | Hitachi Construction Machinery Co., Ltd. | Cylindrical telescopic kelly-bar apparatus |
| DE4024107C1 (en) * | 1990-07-30 | 1992-04-16 | Eastman Christensen Co., Salt Lake City, Utah, Us |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR61897E (en) * | 1951-10-19 | 1955-05-18 | Process of forging a cylindrical tube to give it any desired profile | |
| DE1287534B (en) * | 1968-03-22 | 1969-01-23 | Delmag Maschinenfabrik | Boring rod for earth drilling equipment |
| DE1904570B1 (en) * | 1969-01-30 | 1970-08-27 | Inst De Proiectari Si Cercetar | Drill rod damper |
| US3999618A (en) * | 1975-01-22 | 1976-12-28 | Smith International, Inc. | Hammer stabilizer |
| DE8714201U1 (en) * | 1987-10-24 | 1988-03-10 | Ing. Günter Klemm, Spezialunternehmen für Bohrtechnik, 5962 Drolshagen | Kelly bar for an earth drilling machine |
| DE8714200U1 (en) * | 1987-10-24 | 1988-03-10 | Ing. Günter Klemm, Spezialunternehmen für Bohrtechnik, 5962 Drolshagen | Kelly bar for an earth drilling machine |
| EP0335059A1 (en) * | 1988-03-25 | 1989-10-04 | I.M.T. -S.r.l. | Set of telescopic boring rods with automatic coupling racks designed to transmit axial forces in both directions and with blocking elements of contiguous rods |
-
1988
- 1988-12-30 DE DE8816167U patent/DE8816167U1/en not_active Expired
-
1989
- 1989-12-27 EP EP19890123928 patent/EP0376239A3/en not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR61897E (en) * | 1951-10-19 | 1955-05-18 | Process of forging a cylindrical tube to give it any desired profile | |
| DE1287534B (en) * | 1968-03-22 | 1969-01-23 | Delmag Maschinenfabrik | Boring rod for earth drilling equipment |
| DE1904570B1 (en) * | 1969-01-30 | 1970-08-27 | Inst De Proiectari Si Cercetar | Drill rod damper |
| US3999618A (en) * | 1975-01-22 | 1976-12-28 | Smith International, Inc. | Hammer stabilizer |
| DE8714201U1 (en) * | 1987-10-24 | 1988-03-10 | Ing. Günter Klemm, Spezialunternehmen für Bohrtechnik, 5962 Drolshagen | Kelly bar for an earth drilling machine |
| DE8714200U1 (en) * | 1987-10-24 | 1988-03-10 | Ing. Günter Klemm, Spezialunternehmen für Bohrtechnik, 5962 Drolshagen | Kelly bar for an earth drilling machine |
| EP0335059A1 (en) * | 1988-03-25 | 1989-10-04 | I.M.T. -S.r.l. | Set of telescopic boring rods with automatic coupling racks designed to transmit axial forces in both directions and with blocking elements of contiguous rods |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB2242920B (en) * | 1990-04-09 | 1994-07-06 | Trevi | Telescopic bar of a drilling rig |
| DE4040155A1 (en) * | 1990-07-11 | 1992-01-16 | Dietmar Brussmann | Sinking of deep boreholes by rotary flushing - comprises lowering drill string contg. rotary drill end bit, into the hole then passing flushing fluid through the string |
| AU2004202093B2 (en) * | 2003-01-23 | 2009-04-23 | Atlas Copco Drilling Solutions Inc | Sub Drilling sub |
| DE20301946U1 (en) * | 2003-02-07 | 2004-06-09 | Bauer Maschinen Gmbh | Telescopic drill pipe |
| EP1445418A1 (en) | 2003-02-07 | 2004-08-11 | BAUER Maschinen GmbH | Telescoping drill string |
| US7163069B2 (en) | 2003-02-07 | 2007-01-16 | Bauer Maschinen Gmbh | Telescopable boring rod mechanism |
| WO2005095754A1 (en) * | 2004-03-04 | 2005-10-13 | Atlas Copco Secoroc Ab | Telescoping drilling sub |
| US7413036B2 (en) | 2004-03-04 | 2008-08-19 | Atlas Copco Drilling Solutions Inc. | Sub drilling sub |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE8816167U1 (en) | 1989-02-23 |
| EP0376239A3 (en) | 1991-04-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| AT392669B (en) | THREADED ARRANGEMENT FOR CONNECTING TWO ELEMENTS IN A PISTON PISTON | |
| DE4113898A1 (en) | CENTERING DEVICE FOR DRILLING AND LINING PIPES | |
| DE3824894A1 (en) | DEVICE ON HAND MACHINE TOOLS FOR TORQUE TRANSMISSION | |
| DE2804778B2 (en) | Telescopic drive shaft | |
| DE102008013227B4 (en) | Method for establishing a connection of a transmission component | |
| AT391969B (en) | LENGTH-CHANGING SIDE STAY | |
| EP0376239A2 (en) | Drill string | |
| DE6906176U (en) | BEARING FOR RELATIVELY MOVING PARTS. | |
| DE68904231T2 (en) | DRILL STRING ELEMENT. | |
| EP1956252B1 (en) | Longitudinal traverse unit for drive trains | |
| WO1996017153A1 (en) | Coupling for anchor bars | |
| DE2856738C2 (en) | Wall contact tool for earth drilling and replaceable wear insert for a wall contact tool | |
| DE2612829C2 (en) | Split steering column | |
| DE8017543U1 (en) | Collapsible roller of a roller shutter | |
| DE8714200U1 (en) | Kelly bar for an earth drilling machine | |
| DE3524865C2 (en) | ||
| DE10146186C1 (en) | Shear element for absorbing tensile forces of pipe connection comprises strand of several sheet metal discs whose thickness is less than their diameter and which are threaded on flexible traction strip | |
| DE2801420A1 (en) | PIPE CONNECTION | |
| DE2721018C2 (en) | Endless caterpillar | |
| DE3239342A1 (en) | Drill column | |
| DE3238978A1 (en) | QUICKLY AROUND THE AXLE OF A ROTATING THORN TO FORM A HOLE SURROUNDED BY A COLLAR IN A METAL PLATE OR IN THE WALL OF A METAL TUBE | |
| DE19915304A1 (en) | Drilling tool for stone, shaped rod of which has at least two ribs which are asymmetrical relative to a vertical central plane | |
| EP0374788B1 (en) | Telescopic drill string | |
| DE8714201U1 (en) | Kelly bar for an earth drilling machine | |
| DE8902528U1 (en) | Drill rods |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN WITHDRAWN |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL |
|
| 18W | Application withdrawn |
Withdrawal date: 19910322 |
|
| R18W | Application withdrawn (corrected) |
Effective date: 19910322 |