EP0355239B1 - Wire matrix print head of the flap armature type - Google Patents
Wire matrix print head of the flap armature type Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0355239B1 EP0355239B1 EP88730170A EP88730170A EP0355239B1 EP 0355239 B1 EP0355239 B1 EP 0355239B1 EP 88730170 A EP88730170 A EP 88730170A EP 88730170 A EP88730170 A EP 88730170A EP 0355239 B1 EP0355239 B1 EP 0355239B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- unit
- print head
- housing
- wire
- matrix print
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 13
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 16
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000013016 damping Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000013013 elastic material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000284 resting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41J—TYPEWRITERS; SELECTIVE PRINTING MECHANISMS, i.e. MECHANISMS PRINTING OTHERWISE THAN FROM A FORME; CORRECTION OF TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS
- B41J2/00—Typewriters or selective printing mechanisms characterised by the printing or marking process for which they are designed
- B41J2/22—Typewriters or selective printing mechanisms characterised by the printing or marking process for which they are designed characterised by selective application of impact or pressure on a printing material or impression-transfer material
- B41J2/23—Typewriters or selective printing mechanisms characterised by the printing or marking process for which they are designed characterised by selective application of impact or pressure on a printing material or impression-transfer material using print wires
- B41J2/235—Print head assemblies
- B41J2/24—Print head assemblies serial printer type
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41J—TYPEWRITERS; SELECTIVE PRINTING MECHANISMS, i.e. MECHANISMS PRINTING OTHERWISE THAN FROM A FORME; CORRECTION OF TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS
- B41J2/00—Typewriters or selective printing mechanisms characterised by the printing or marking process for which they are designed
- B41J2/22—Typewriters or selective printing mechanisms characterised by the printing or marking process for which they are designed characterised by selective application of impact or pressure on a printing material or impression-transfer material
- B41J2/23—Typewriters or selective printing mechanisms characterised by the printing or marking process for which they are designed characterised by selective application of impact or pressure on a printing material or impression-transfer material using print wires
- B41J2/27—Actuators for print wires
- B41J2/275—Actuators for print wires of clapper type
Definitions
- the invention relates to a matrix needle printhead of the hinged armature type, with each pressure needle associated with the electromagnetic coil armature system, the armature being assigned to a needle guide housing and the electromagnetic coils or magnet yokes to a coil carrier housing which can be connected to the needle guide housing.
- hinged anchor system is technically and therefore economically dependent on the manufacture of the individual parts, on their assembly and on their functional accuracy and reliability.
- conventional hinged anchor systems e.g. DE 34 12 856 C2
- the anchors are manufactured as individual pieces and are assembled individually.
- Each anchor requires its own bearing point, which allows it to perform an accurate swivel movement that is as free of play as possible.
- bearing surfaces are formed in the needle guide housing and the end faces of the magnetic yokes are located opposite one another as further bearing surfaces at a precise distance.
- the bearing point is formed laterally by shoulders or overlapping projections to prevent lateral displacement during the swiveling movement (US Pat. No. 4,640,633).
- the invention has for its object to improve the system of anchors and their storage in a matrix needle printhead of the hinged anchor type.
- the object is achieved in a matrix needle printhead of the type of hinged armature initially described according to the invention in that all anchors are held in operating position with respect to one another and connected to one another by means of a sheet metal molded part and form a unit that this unit is centered in the needle guide housing via a plurality of cams distributed over the circumference and in that Cams are provided which also center this unit in the coil carrier housing.
- a first advantage is that the invention eliminates the production of individual anchors and all anchors occupy a precise position that is unchangeable from the other anchors. The unit formed from the anchors and the sheet metal part can now be set more easily than the individual anchors.
- the unit mentioned can be fixed and centered by means of the cams both in the needle guide housing and in the bobbin housing. This creates a permanently accurate storage. In principle, three cams distributed over the circumference are sufficient for centering the unit comprising the armature and the sheet metal part.
- the accuracy of the centering is also increased by the fact that the cams are supported directly on the common flat surface of the magnetic yokes with a support surface.
- a particularly advantageous assignment of the cams occurs when the unit rests with a flat sheet metal part on the flat surface of the magnetic yokes. It was found through experiments that the support of the sheet metal part results in a low-loss system, particularly in this installed state.
- the anchor on the side of the magnetic yoke performs its own tilting movement. In addition, the tilting movements of adjacent anchors remain without influence.
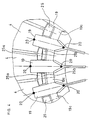
- the matrix needle print head is provided with an electromagnetic coil-armature system 2 assigned to each pressure needle 1, each printing needle 1 being driven by an electromagnetic coil 3, magnetic yokes 3a and 3b with an armature 4, in order to print onto a recording medium 5 via an ink ribbon 6, both on one Abutment 7 lie on it to generate pressure points and characters.
- the printing needles 1 are guided in a printing needle guide 8, which is supported at the outlet of a needle guide housing 9 (FIG. 1).
- the printing needles 1 are in the (drawn) rest position, in which neither the ink ribbon 6 nor the recording medium 5 are touched, with a needle head 1 a under the force of a spring 10 against the associated armature 4.
- all anchors 4 are supported against a damping ring 11 made of elastic material.
- the damping ring 11 is attached to a one-piece magnetic yoke body 13 forming a hub 12 for the magnetic yokes 3a, 3b.
- the magnetic yoke body 13 is part of a coil carrier housing 14, through which power connections 15 are laid to the electromagnetic coils 3 and which is closed by a cover 16 provided with cooling fins.
- the needle guide housing 9 and the bobbin case 14 are held together by a screw 17.
- the entire matrix needle printhead is fastened in the finished state by means of dowel pins 18 on a carriage which can be moved back and forth parallel to the abutment 7.
- FIG. 2 clearly shows the thickness ratio of the armature 4 to the sheet-metal molded part 19.
- the metal sheet-shaped part 19 practically has a thickness of 0.05 mm.
- the needle guide housing 9 forms a shell 21 facing the bobbin housing 14, and the shell 21 forms a flange 22 with a circumferential annular receptacle 23 for an O-ring 24 made of a relatively elastic material.
- the receptacle 23 is provided radially on the outside with cams 25 to be described in more detail.
- step sections 25a and 25b of the cams 25 may be provided, as shown in FIGS. 3 and 4.
- the cams 25 centering the unit 4, 19 in the needle guide housing 9 can also center the unit 4, 19 (as drawn) in the bobbin housing 14 at the same time.
- the cams 25 are supported from the inside with a section 25a laterally past the sheet metal molded part 19 on a common flat surface 27 of all the magnet yokes 3a and 3b.
- the sheet metal part 19 is designed as a completely flat sheet metal part 19 a.
- the centering is visible in FIG. 3 on the armature 4 drawn in the middle by the cams 25 resting against play.
- the anchors 4 shown on the left or right are arranged with play to the cams 25.
- the sheet metal part 19 can also be designed as a leaf spring. It then acts like a film.
- the armature 4 performs a pure tilting movement on the side of the magnet yokes 3a, 3b. This results in a minimal radial movement in the range of hundredths of a millimeter. This movement is absorbed by the rubber O-ring 24.
- a wedge-shaped air gap is created, which disappears when energized, so that the armature 4 lies completely flat, parallel and flat on the magnet yokes 3a and 3b without overshooting. Overshoot is prevented by a restoring force across the cross sections of connecting webs 19c (FIGS. 3 and 4). Nevertheless, the matrix needle print head can be operated at a high frequency.
Landscapes
- Impact Printers (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft einen Matrixnadeldruckkopf der Klappankerbauart, mit jeder Drucknadel zugeordnetem Elektromagnetspule-Anker-System, wobei die Anker einem Nadelführungsgehäuse und die Elektromagnetspulen bzw. Magnet joche einem mit dem Nadelführungsgehäuse verbindbaren Spulenträgergehäuse zugeordnet sind.The invention relates to a matrix needle printhead of the hinged armature type, with each pressure needle associated with the electromagnetic coil armature system, the armature being assigned to a needle guide housing and the electromagnetic coils or magnet yokes to a coil carrier housing which can be connected to the needle guide housing.
Ein derartiges Klappankersystem ist fertigungstechnisch und damit wirtschaftlich von der Herstellung der Einzelteile, von deren Montage und von deren Funktionsgenauigkeit und Zuverlässigkeit abhängig. Bei üblichen Klappankersystemen (z.B. DE 34 12 856 C2) sind die Anker als Einzelstücke hergestellt und werden einzeln montiert. Jeder Anker erfordert eine eigene Lagerstelle, die ihm eine genaue, möglichst spielfreie Schwenkbewegung gestattet. Als Lagerstelle werden hier Auflageflächen im Nadelführungsgehäuse und auf genauen Abstand gegenüberliegend als weitere Auflageflächen die Stirnseiten der Magnetjoche gebildet. Die Lagerstelle ist seitlich durch Absätze oder übergreifende Vorsprünge gebildet, um ein seitliches Verlagern während der Schwenkbewegung zu verhindern (US-PS 4,640,633).Such a hinged anchor system is technically and therefore economically dependent on the manufacture of the individual parts, on their assembly and on their functional accuracy and reliability. In conventional hinged anchor systems (e.g. DE 34 12 856 C2), the anchors are manufactured as individual pieces and are assembled individually. Each anchor requires its own bearing point, which allows it to perform an accurate swivel movement that is as free of play as possible. Here, bearing surfaces are formed in the needle guide housing and the end faces of the magnetic yokes are located opposite one another as further bearing surfaces at a precise distance. The bearing point is formed laterally by shoulders or overlapping projections to prevent lateral displacement during the swiveling movement (US Pat. No. 4,640,633).
Ein solches System wird mit steigender Anzahl des jeder Drucknadel zugeordneten Elektromagnetspule-Anker-Systems problematisch. Hierbei ist von sieben, neun, achtzehn und vierundzwanzig Systemen auszugehen, so daß bei wachsender Anzahl von Drucknadeln auch ein Platz-bzw. Raumproblem entsteht, falls der äußere Durchmesser des Druckkopfes nicht größer und größer werden soll.Such a system becomes problematic as the number of the electromagnetic coil armature system assigned to each pressure needle increases. In this case, seven, nine, eighteen and twenty-four systems can be assumed, so that with increasing number of printing needles, there is also a space or. Space problems arise if the outer diameter of the print head should not get bigger and bigger.
Die einzeln hergestellten Anker können aber nicht vollkommen gleich hergestellt werden. Ebenso sind die Lagerstellen nicht gleich. Es wäre umständlich, zeitraubend und daher zu teuer, die Toleranzen der Lagerstellen mit denjenigen der Anker zu vergleichen und passende Paarungen auszusuchen.However, the individually manufactured anchors cannot be manufactured in the same way. The bearing points are also not the same. It would be cumbersome, time consuming and therefore too expensive to tolerate Compare bearing points with those of the anchors and select suitable pairings.
Der Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, bei einem Matrixnadeldruckkopf der Klappankerbauart das System der Anker und ihrer Lagerung zu verbessern.The invention has for its object to improve the system of anchors and their storage in a matrix needle printhead of the hinged anchor type.
Die gestellte Aufgabe wird bei einem Matrixnadeldruckkopf der eingangs bezeichneten Klappankerbauart erfindungsgemäß dadurch gelöst, daß sämtliche Anker mittels eines Blechformteils zueinander in Betriebslage gehalten und untereinander verbunden sind und eine Einheit bilden, daß diese Einheit über mehrere über den Umfang verteilt angeordnete Nocken im Nadelführungsgehäuse zentriert und daß Nocken vorgesehen sind, die diese Einheit auch im Spulenträgergehäuse zentrieren. Ein erster Vorteil besteht darin, daß aufgrund der Erfindung die Herstellung einzelner Anker entfällt und alle Anker eine genaue Position einnehmen, die zu den anderen Ankern unveränderlich ist. Die aus den Ankern und dem Blechformteil gebildete Einheit läßt sich nunmehr leichter als die einzelnen Anker festlegen. Als weiterer Vorteil kann die genannte Einheit mittels der Nocken sowohl im Nadelführungsgehäuse als auch im Spulenträgergehäuse fixiert und zentriert werden. Damit ist eine bleibend genaue Lagerung geschaffen. Im Prinzip genugen sogar drei über den Umfang verteilte Nocken für eine Zentrierung der Einheit aus Anker und Blechformteil.The object is achieved in a matrix needle printhead of the type of hinged armature initially described according to the invention in that all anchors are held in operating position with respect to one another and connected to one another by means of a sheet metal molded part and form a unit that this unit is centered in the needle guide housing via a plurality of cams distributed over the circumference and in that Cams are provided which also center this unit in the coil carrier housing. A first advantage is that the invention eliminates the production of individual anchors and all anchors occupy a precise position that is unchangeable from the other anchors. The unit formed from the anchors and the sheet metal part can now be set more easily than the individual anchors. As a further advantage, the unit mentioned can be fixed and centered by means of the cams both in the needle guide housing and in the bobbin housing. This creates a permanently accurate storage. In principle, three cams distributed over the circumference are sufficient for centering the unit comprising the armature and the sheet metal part.
Nach der weiteren Erfindung ist vorgesehen, daß die die Einheit im Nadelführungsgehäuse zentrierenden Nocken gleichzeitig die Einheit im Spulenträgergehause zentrieren. Dieser vorschlag erfordert daher nur eine einzige Gattung von Nocken.According to the further invention it is provided that the cams centering the unit in the needle guide housing simultaneously center the unit in the bobbin case. This proposal therefore only requires a single type of cam.
Die Genauigkeit der Zentrierung wird außerdem dadurch noch erhöht, daß die Nocken sich unmittelbar auf der gemeinsamen Planfläche der Magnetjoche mit einer Stützfläche abstützen.The accuracy of the centering is also increased by the fact that the cams are supported directly on the common flat surface of the magnetic yokes with a support surface.
Eine besonders vorteilhafte Zuordnung der Nocken entsteht dann, wenn die Einheit mit einem ebenen Blechformteil auf der Planfläche der Magnetjoche aufliegt. Es wurde durch Versuche gefunden, daß die Auflage des Blechformteils insbesondere in diesem Einbauzustand ein verlustarmes System ergibt. Hierbei führt der Anker auf der Seite des Magnetjochs eine reine eigene kippbewegung aus. Außerdem bleiben die kippbewegungen benachbarter Anker ohne Einfluß.A particularly advantageous assignment of the cams occurs when the unit rests with a flat sheet metal part on the flat surface of the magnetic yokes. It was found through experiments that the support of the sheet metal part results in a low-loss system, particularly in this installed state. The anchor on the side of the magnetic yoke performs its own tilting movement. In addition, the tilting movements of adjacent anchors remain without influence.
In der Zeichnung ist ein Ausführungsbeispiel der Erfindung schematisch dargestellt und wird nachfolgend näher erläutert. Es zeigen:
- Fig. 1 die Hälfte eines axialen Querchnitts durch den Matrixdruckkopf,
- Fig. 2 eine Einzelheit A in dem in Fig. 1 bezeichneten Bereich des Querschnitts A - A in vergrößerter Darstellung,
- Fig. 3 eine Seitenansicht der Einzelheit A und
- Fig. 4 einen noch weiter vergrößerten Ausschnitt der Seitenansicht gemäß Fig. 3.
- 1 shows half of an axial cross section through the matrix print head,
- FIG. 2 shows a detail A in the area of the cross section AA in FIG. 1 in an enlarged illustration, FIG.
- Fig. 3 is a side view of the detail A and
- 4 shows a further enlarged detail of the side view according to FIG. 3.
Der Matrixnadeldruckkopf ist mit einem jeder Drucknadel 1 zugeordneten Elektromagnetspule-Anker-System 2 versehen, wobei jede Druknadel 1 durch eine Elektromagnetspule 3, Magnetjoche 3a und 3b mit Anker 4 angetrieben wird, um auf einen Aufzeichnungsträger 5 über ein Farbband 6, die beide auf einem Schreibwiderlager 7 aufliegen, Druckpunkte und damit Schriftzeichen zu erzeugen. Es können Drucknadeln 1 in einer oder mehreren Spalten mit sieben, neun, achtzehn, vierundzwanzig oder einer größeren Nadelanzahl vorgesehen sein. Die Drucknadeln 1 werden in einer Drucknadelführung 8 geführt, wobei diese am Ausgang eines Nadelführungsgehäuses 9 gelagert ist (Fig. 1). Die Drucknadeln 1 liegen in der (gezeichneten) Ruhestellung, in der weder das Farbband 6 noch der Aufzeichnungsträger 5 berührt werden, mit einem Nadelkopf 1a unter der kraft einer Feder 10 stehend gegen den zugehörigen Anker 4 an. Gleichzeitig stützen sich alle Anker 4 gegen einen Dämpfungsring 11 aus elastischem Werkstoff. Der Dämpfungsring 11 ist an einem zu den Magnetjochen 3a, 3b eine Nabe 12 bildenden einstückigen Magnetjochkörper 13 befestigt. Der Magnetjochkörper 13 ist Teil eines Spulenträgergehäuses 14, durch das Stromanschlüsse 15 zu den Elektromagnetspulen 3 verlegt sind und das durch einen mit Kühlrippen versehenen Deckel 16 verschlossen wird. Das Nadelführungsgehäuse 9 und das Spulenträgergehäuse 14 werden durch eine Schraube 17 zusammengehalten.The matrix needle print head is provided with an electromagnetic coil-
Der gesamte Matrixnadeldruckkopf wird im fertigen Zustand mittels Paßstiften 18 auf einem parallel zum Schreibwiderlager 7 hin- und herbewegbaren Schlitten befestigt.The entire matrix needle printhead is fastened in the finished state by means of
Sämtliche Anker (Fig. 2 und 3) sind mittels eines einstückigen Blechformteils 19 (schon von der Herstellung her) zusammengehalten. Das Blechformteil 19 ist durch Schweißpunkte 20 auf den Ankern 4 befestigt. Fig. 2 zeigt deutlich das Dickenverhältnis des Ankers 4 zu dem Bleckformteil 19. Das Blechformteil 19 besitzt praktisch eine Dicke von 0,05 mm. Das Nadelführungsgehäuse 9 bildet dem Spulenträgergehäuse 14 zugewendet eine Schale 21, und die Schale 21 bildet einen Flansch 22 mit einer umlaufenden ringförmigen Aufnahme 23 für einen O-Ring 24 aus relativ elastischem Werkstoff. Die Aufnahme 23 ist radial außen mit noch näher zu beschreibenden Nocken 25 versehen. Es können für die Zentrierung der Einheit 4, 19, jeweils getrennte Stufen-Abschnitte 25a und 25b der Nocken 25 vorgesehen sein, wie in den Fig. 3 und 4 gezeichnet ist. Die die Einheit 4, 19 im Nadelführungsgehäuse 9 zentrierenden Nocken 25 können die Einheit 4, 19 jedoch auch (wie gezeichnet) gleichzeitig im Spulenträgergehäuse 14 zentrieren. Hierzu stützen sich die Nocken 25 von innen mit einem Abschnitt 25a seitlich am Blechformteil 19 vorbei auf eine gemeinsame Planfläche 27 aller Magnetjoche 3a bzw. 3b ab. In diesem Fall ist es vorteilhaft, wenn der Blechformteil 19 als vollkommen ebener Blechformteil 19a ausgebildet ist. Die Zentrierung ist in Fig. 3 an dem in der Mitte gezeichneten Anker 4 durch spielfreies Anliegen der Nocken 25 sichtbar. Demgegenüber sind die jeweils links oder rechts gezeichneten Anker 4 mit Spiel zu den Nocken 25 angeordnet.All anchors (Fig. 2 and 3) are held together by a one-piece sheet metal part 19 (already from the manufacture). The
Der Blechformteil 19 (bzw. 19a) kann auch als Blattfeder gestaltet sein. Er wirkt dann wie eine Folie. Beim Bestromen der Elektromagnetspule 3 führt der Anker 4 auf der Seite der Magnetjoche 3a, 3b eine reine Kippbewegung aus. Hierbei kommt es radial zu einer minimalen Gleitbewegung im Bereich von Hundertstel mm. Diese Bewegung wird von dem aus Gummi bestehenden O-Ring 24 aufgenommen. Zwischen dem Anker 4 und den Magnetjochen 3a, 3b entsteht ein keilförmiger Luftspalt, der im Bestromungsfall verschwindet, so daß der Anker 4 vollkommen eben, parallel und flach auf den Magnetjochen 3a und 3b aufliegt, ohne überzuschwingen. Ein Überschwingen wird durch eine Rückstellkraft über die Querschnitte von Verbindungsstegen 19c (Fig. 3 und 4) verhindert. Trotzdem kann der Matrixnadeldruckkopf mit einer hohen Frequenz betrieben werden.The sheet metal part 19 (or 19a) can also be designed as a leaf spring. It then acts like a film. When energizing the
Claims (4)
characterised in that
all the armatures (4) are held relative to one another in the operating position and connected together by means of a shaped piece of sheet metal (19) and form a unit (4, 19), that this unit (4, 19) is centred in the wire guidance housing (9) by means of a plurality of lifters (25) distributed across the circumference and that lifters are provided which also centre said unit (4, 19) in the coil support housing (14).
characterised in that
the lifters (25) centring the unit (4, 19) in the wire guidance housing (9) at the same time centre the unit (4, 19) in the coil support housing (14).
characterised in that
the lifters (25) are supported directly on the common end face (27) of the magnet yokes (3a, 3b) by means of a supporting surface (25a).
characterised in that
the unit (4, 19) lies with a flat shaped piece of sheet metal (19a) against the end face (27) of the magnet yokes (3a, 3b).
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE8888730170T DE3869130D1 (en) | 1988-08-01 | 1988-08-01 | FOLDING NEEDLE PRINT HEAD PRINT HEAD. |
| EP88730170A EP0355239B1 (en) | 1988-08-01 | 1988-08-01 | Wire matrix print head of the flap armature type |
| AT88730170T ATE73395T1 (en) | 1988-08-01 | 1988-08-01 | MATRIX PIN PRINT HEAD OF FLAP ANCHOR DESIGN. |
| JP1173889A JPH0260757A (en) | 1988-08-01 | 1989-07-05 | Flap armature type matrix-needle printing head |
| US07/387,607 US5039239A (en) | 1988-08-01 | 1989-07-28 | Matrix pin-print head of the hinged-clapper-armature construction |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP88730170A EP0355239B1 (en) | 1988-08-01 | 1988-08-01 | Wire matrix print head of the flap armature type |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0355239A1 EP0355239A1 (en) | 1990-02-28 |
| EP0355239B1 true EP0355239B1 (en) | 1992-03-11 |
Family
ID=8200558
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP88730170A Expired - Lifetime EP0355239B1 (en) | 1988-08-01 | 1988-08-01 | Wire matrix print head of the flap armature type |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US5039239A (en) |
| EP (1) | EP0355239B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPH0260757A (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE73395T1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE3869130D1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102004028904A1 (en) * | 2004-06-15 | 2006-01-12 | Tallygenicom Computerdrucker Gmbh | Print head for use particularly with a needle matrix printer has ring formed yoke with non ferro-magnetic carrier |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5835474B2 (en) * | 1977-05-26 | 1983-08-02 | エプソン株式会社 | Structure of wire dot printer head |
| US4225250A (en) * | 1978-10-10 | 1980-09-30 | Tally Corporation | Segmented-ring magnet print head |
| IT1128976B (en) * | 1980-08-21 | 1986-06-04 | Olivetti & Co Spa | BALLISTIC WIRE PRINT HEAD |
| JPS59101373A (en) * | 1982-12-01 | 1984-06-11 | Tokyo Electric Co Ltd | Dot printer head |
| JPS6067170A (en) * | 1983-09-26 | 1985-04-17 | Tokyo Electric Co Ltd | Dot printer head |
| IT1162961B (en) * | 1983-10-14 | 1987-04-01 | Olivetti & Co Spa | WIRE OR NEEDLE PRINTER DEVICE PARTICULARLY FOR PERIPHERAL UNITS OF ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS FOR DATA PROCESSING |
| IT1169133B (en) * | 1983-11-23 | 1987-05-27 | Honeywell Inf Systems | ARMATURE GROUP FOR MOSAIC PRINTER HEAD AND RELATED PRODUCTION METHOD |
| US4548521A (en) * | 1983-12-09 | 1985-10-22 | Ncr Corporation | Dot matrix print head |
| JPS60189457A (en) * | 1984-03-08 | 1985-09-26 | Tokyo Electric Co Ltd | Dot printer head |
| US4600321A (en) * | 1985-02-06 | 1986-07-15 | Okun Kwan | Matrix print head |
| US4723854A (en) * | 1985-05-01 | 1988-02-09 | Brother Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Dot-matrix print head and apparatus for supporting pivotable armatures |
-
1988
- 1988-08-01 AT AT88730170T patent/ATE73395T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1988-08-01 DE DE8888730170T patent/DE3869130D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1988-08-01 EP EP88730170A patent/EP0355239B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1989
- 1989-07-05 JP JP1173889A patent/JPH0260757A/en active Pending
- 1989-07-28 US US07/387,607 patent/US5039239A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102004028904A1 (en) * | 2004-06-15 | 2006-01-12 | Tallygenicom Computerdrucker Gmbh | Print head for use particularly with a needle matrix printer has ring formed yoke with non ferro-magnetic carrier |
| DE102004028904B4 (en) * | 2004-06-15 | 2006-08-17 | Tallygenicom Computerdrucker Gmbh | Print head for use particularly with a needle matrix printer has ring formed yoke with non ferro-magnetic carrier |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0355239A1 (en) | 1990-02-28 |
| US5039239A (en) | 1991-08-13 |
| DE3869130D1 (en) | 1992-04-16 |
| ATE73395T1 (en) | 1992-03-15 |
| JPH0260757A (en) | 1990-03-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE3133083A1 (en) | "BALLISTIC WIRE MATRIX PRINT HEAD" | |
| DE2330883A1 (en) | MOSAIC PRINT HEAD | |
| DE3031855A1 (en) | PRINT HEAD. | |
| EP0357860B1 (en) | Wire matrix print head of the flap armature type | |
| DE2342420A1 (en) | MOSAIC PUSH BUTTON | |
| DE68913933T2 (en) | Dot impact printer. | |
| EP0355239B1 (en) | Wire matrix print head of the flap armature type | |
| DE2629267A1 (en) | DRIVE DEVICE FOR A WIRE MATRIX PRINTER | |
| DE3122221C2 (en) | Servo valve | |
| DE4428385A1 (en) | Valve body | |
| DE1802626A1 (en) | Servo control valve | |
| EP0188671B1 (en) | Armature construction group manufacturing process for matrix print heads | |
| DE68919083T2 (en) | POINT MATRICE PRINT HEAD ASSEMBLY. | |
| DE1424430A1 (en) | Magnetic recording device with a rotating disk | |
| DE68920322T2 (en) | MAGNETIC HEAD POSITIONING DEVICE. | |
| DE1206962B (en) | Storage facility | |
| DE2820278C3 (en) | Spring holder for the diaphragm spring in a clutch disc damper | |
| US4648730A (en) | Armature group for mosaic printing head and related manufacturing method | |
| EP0371183B1 (en) | Wire matrix print head of the clapper type | |
| DE69013260T2 (en) | DOT GRID PRINT HEAD. | |
| EP0513576A1 (en) | Apparatus for cutting foil webs | |
| DE3141816C2 (en) | ||
| EP0188669B1 (en) | Matrix printing head | |
| DE68927390T2 (en) | Dot matrix printer with stop print head | |
| DE3040399C2 (en) | Drive module for a multi-module print head of a dot matrix printer |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19890719 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19910723 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 73395 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19920315 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3869130 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19920416 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19920715 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19920717 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19920721 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19920831 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19930801 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Effective date: 19930831 Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19930831 Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19930831 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: MANNESMANN A.G. Effective date: 19930831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19940301 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20030728 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20030813 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040801 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20040801 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050429 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20050801 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20050906 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070301 |