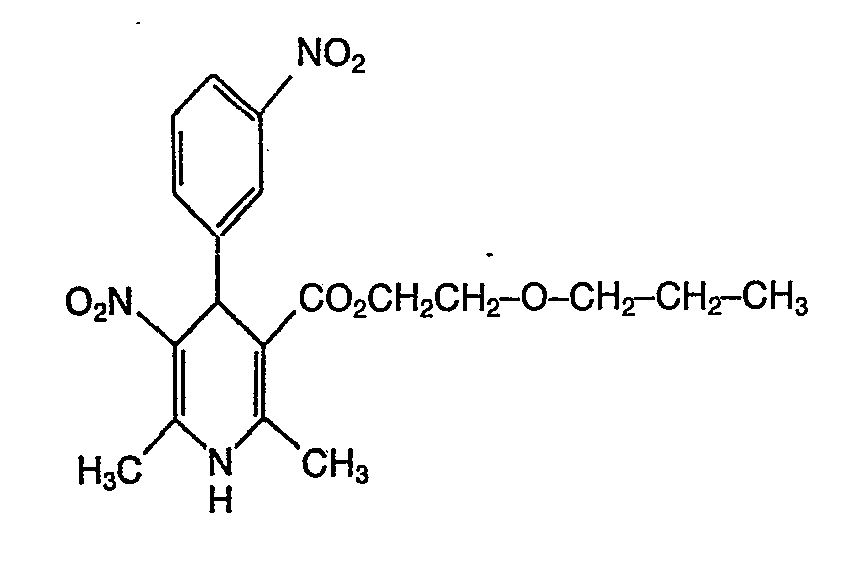
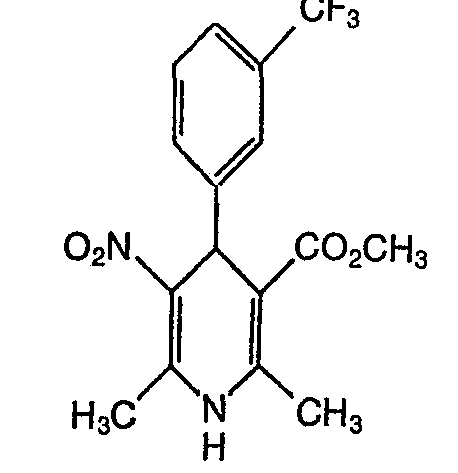
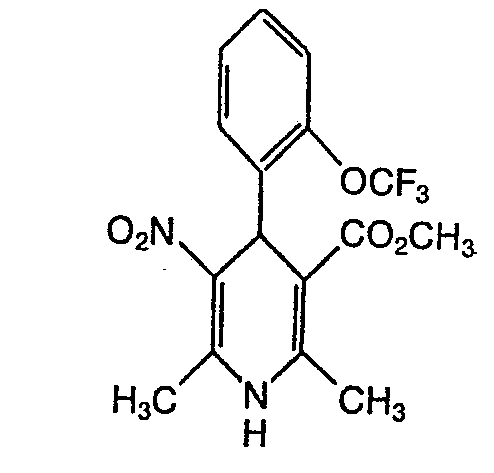
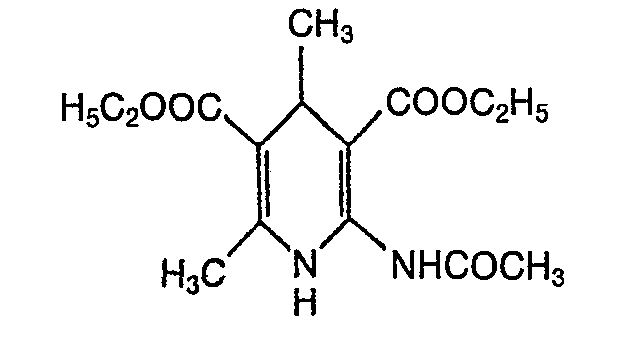
EP0071819B1 - Dihydropyridines with a positive inotropic activity, their use in pharmaceutical preparations, and processes for their preparation - Google Patents
Dihydropyridines with a positive inotropic activity, their use in pharmaceutical preparations, and processes for their preparation Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0071819B1 EP0071819B1 EP82106537A EP82106537A EP0071819B1 EP 0071819 B1 EP0071819 B1 EP 0071819B1 EP 82106537 A EP82106537 A EP 82106537A EP 82106537 A EP82106537 A EP 82106537A EP 0071819 B1 EP0071819 B1 EP 0071819B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- atoms
- alkyl
- phenyl
- halogen
- substituents
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 title claims description 15
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 12
- 125000004925 dihydropyridyl group Chemical group N1(CC=CC=C1)* 0.000 title claims description 10
- 230000009090 positive inotropic effect Effects 0.000 title claims description 10
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 title claims description 4
- 239000000825 pharmaceutical preparation Substances 0.000 title 1
- -1 aliphatic hydrocarbon radical Chemical class 0.000 claims description 182
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 claims description 124
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 117
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 113
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical group 0.000 claims description 113
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 96
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 90
- 125000003545 alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 65
- 125000003710 aryl alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 59
- 150000003254 radicals Chemical class 0.000 claims description 57
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 claims description 52
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 52
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 51
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims description 51
- 125000001072 heteroaryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 45
- 125000001624 naphthyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 44
- 125000005842 heteroatom Chemical group 0.000 claims description 38
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 claims description 34
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 claims description 31
- 125000002252 acyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 29
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 27
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 24
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 20
- 125000004414 alkyl thio group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 19
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 19
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 claims description 19
- 125000002023 trifluoromethyl group Chemical group FC(F)(F)* 0.000 claims description 19
- 125000001797 benzyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 18
- 125000002947 alkylene group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 16
- 125000004122 cyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 16
- 125000003342 alkenyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 15
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 claims description 15
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 15
- 125000000876 trifluoromethoxy group Chemical group FC(F)(F)O* 0.000 claims description 15
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 13
- 125000004196 benzothienyl group Chemical group S1C(=CC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 13
- 125000004076 pyridyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 13
- 125000004433 nitrogen atom Chemical group N* 0.000 claims description 11
- YNGDWRXWKFWCJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-Dihydropyridine Chemical class C1C=CNC=C1 YNGDWRXWKFWCJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- 125000001544 thienyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 9
- 125000006193 alkinyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- 150000005840 aryl radicals Chemical class 0.000 claims description 8
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 8
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000003785 benzimidazolyl group Chemical group N1=C(NC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000001164 benzothiazolyl group Chemical group S1C(=NC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000004541 benzoxazolyl group Chemical group O1C(=NC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000002883 imidazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000000842 isoxazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000002971 oxazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000003373 pyrazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000003226 pyrazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000001725 pyrenyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000000714 pyrimidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000000335 thiazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000001425 triazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000004215 Carbon black (E152) Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- JCXJVPUVTGWSNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nitrogen dioxide Chemical compound O=[N]=O JCXJVPUVTGWSNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfur Chemical compound [S] NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000000499 benzofuranyl group Chemical group O1C(=CC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000004093 cyano group Chemical group *C#N 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000002541 furyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000001188 haloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000003453 indazolyl group Chemical group N1N=C(C2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000001041 indolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000012442 inert solvent Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000002098 pyridazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000004305 thiazinyl group Chemical group S1NC(=CC=C1)* 0.000 claims description 6
- WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Bromine atom Chemical compound [Br] WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 241000700199 Cavia porcellus Species 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000001931 aliphatic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000004603 benzisoxazolyl group Chemical group O1N=C(C2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910052794 bromium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000000259 cinnolinyl group Chemical group N1=NC(=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000008602 contraction Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 150000002081 enamines Chemical class 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000003406 indolizinyl group Chemical group C=1(C=CN2C=CC=CC12)* 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000005956 isoquinolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000004593 naphthyridinyl group Chemical group N1=C(C=CC2=CC=CN=C12)* 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000004592 phthalazinyl group Chemical group C1(=NN=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000002294 quinazolinyl group Chemical group N1=C(N=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000005493 quinolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000001567 quinoxalinyl group Chemical group N1=C(C=NC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 claims description 5
- PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine Chemical compound FF PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromine Substances BrBr GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000001728 carbonyl compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000001153 fluoro group Chemical group F* 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000000524 functional group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 4
- 210000002216 heart Anatomy 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000002576 ketones Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000000094 2-phenylethyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000004104 aryloxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000004941 influx Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000002596 lactones Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 210000005246 left atrium Anatomy 0.000 claims description 3
- CPRRHERYRRXBRZ-SRVKXCTJSA-N methyl n-[(2s)-1-[[(2s)-1-hydroxy-3-[(3s)-2-oxopyrrolidin-3-yl]propan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]carbamate Chemical compound COC(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)N[C@H](CO)C[C@@H]1CCNC1=O CPRRHERYRRXBRZ-SRVKXCTJSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 210000004400 mucous membrane Anatomy 0.000 claims description 3
- SYSQUGFVNFXIIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1,3-benzoxazol-2-yl)phenyl]-4-nitrobenzenesulfonamide Chemical class C1=CC([N+](=O)[O-])=CC=C1S(=O)(=O)NC1=CC=C(C=2OC3=CC=CC=C3N=2)C=C1 SYSQUGFVNFXIIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000006722 reduction reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000004001 thioalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000010933 acylation Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000005917 acylation reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000009833 condensation Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000005494 condensation Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000032050 esterification Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000005886 esterification reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000546 pharmaceutical excipient Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000003141 primary amines Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000005809 transesterification reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical class [H]* 0.000 claims 27
- 229910052740 iodine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 3
- 125000000449 nitro group Chemical group [O-][N+](*)=O 0.000 claims 3
- 239000005864 Sulphur Substances 0.000 claims 2
- KGFYHTZWPPHNLQ-AWEZNQCLSA-N rivaroxaban Chemical compound S1C(Cl)=CC=C1C(=O)NC[C@@H]1OC(=O)N(C=2C=CC(=CC=2)N2C(COCC2)=O)C1 KGFYHTZWPPHNLQ-AWEZNQCLSA-N 0.000 claims 2
- 230000003416 augmentation Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 230000003177 cardiotonic effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 230000007062 hydrolysis Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000006460 hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 125000000956 methoxy group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])O* 0.000 claims 1
- 125000002816 methylsulfanyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])S[*] 0.000 claims 1
- 230000008961 swelling Effects 0.000 claims 1
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 147
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 56
- 235000019441 ethanol Nutrition 0.000 description 48
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 42
- 238000000354 decomposition reaction Methods 0.000 description 34
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 33
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 31
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 23
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 21
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 21
- QCDJOJKIHZQJGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-nitropropan-2-one Chemical compound CC(=O)C[N+]([O-])=O QCDJOJKIHZQJGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 20
- XRMDCWJNPDVAFI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-oxopiperidin-1-ium-4-ol Chemical compound CC1(C)CC(O)CC(C)(C)[N+]1=O XRMDCWJNPDVAFI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 20
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chloroform Chemical compound ClC(Cl)Cl HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 20
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 20
- 229910001868 water Inorganic materials 0.000 description 19
- 150000002431 hydrogen Chemical class 0.000 description 17
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium hydroxide Inorganic materials [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 17
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 17
- WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetonitrile Chemical compound CC#N WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- ZDVRPKUWYQVVDX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(trifluoromethyl)benzaldehyde Chemical compound FC(F)(F)C1=CC=CC=C1C=O ZDVRPKUWYQVVDX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 14
- 235000019198 oils Nutrition 0.000 description 14
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 description 13
- 0 CCC*N(*)*N Chemical compound CCC*N(*)*N 0.000 description 12
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 11
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 11
- HSPVTPHRQMNTQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-nitroprop-1-en-2-amine Chemical compound CC(N)=C[N+]([O-])=O HSPVTPHRQMNTQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 238000001819 mass spectrum Methods 0.000 description 9
- 150000004702 methyl esters Chemical class 0.000 description 9
- 238000010992 reflux Methods 0.000 description 9
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- YNBADRVTZLEFNH-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl nicotinate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=CC=CN=C1 YNBADRVTZLEFNH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyridine Chemical group C1=CC=NC=C1 JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 238000009835 boiling Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 7
- MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dioxygen Chemical compound O=O MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M Potassium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[K+] KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 6
- 125000004494 ethyl ester group Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 6
- 235000011121 sodium hydroxide Nutrition 0.000 description 6
- DELJOESCKJGFML-DUXPYHPUSA-N (e)-3-aminobut-2-enenitrile Chemical compound C\C(N)=C/C#N DELJOESCKJGFML-DUXPYHPUSA-N 0.000 description 5
- ZETIVVHRRQLWFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-nitrobenzaldehyde Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC=CC(C=O)=C1 ZETIVVHRRQLWFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000008020 evaporation Effects 0.000 description 5
- XKORCTIIRYKLLG-ARJAWSKDSA-N methyl (z)-3-aminobut-2-enoate Chemical compound COC(=O)\C=C(\C)N XKORCTIIRYKLLG-ARJAWSKDSA-N 0.000 description 5
- XBLVHTDFJBKJLG-UHFFFAOYSA-N nicotinic acid ethyl ester Natural products CCOC(=O)C1=CC=CN=C1 XBLVHTDFJBKJLG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 5
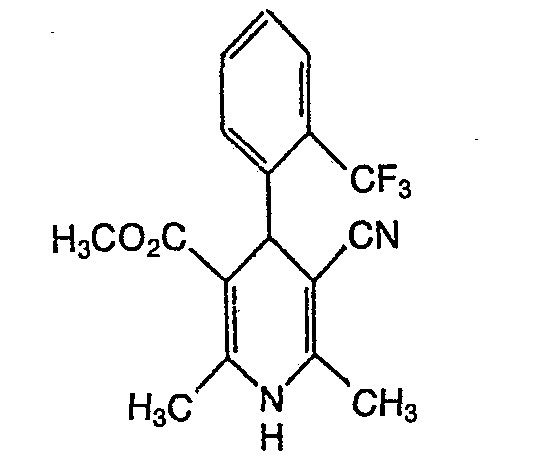
- QTKFDQYPMABWIR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F QTKFDQYPMABWIR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon dioxide Chemical compound O=C=O CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- XTHFKEDIFFGKHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethoxyethane Chemical compound COCCOC XTHFKEDIFFGKHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- WRQNANDWMGAFTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methylacetoacetic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)CC(C)=O WRQNANDWMGAFTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229960000583 acetic acid Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 description 4
- 125000000304 alkynyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000008346 aqueous phase Substances 0.000 description 4
- IJKVHSBPTUYDLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N dihydroxy(oxo)silane Chemical compound O[Si](O)=O IJKVHSBPTUYDLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000003480 eluent Substances 0.000 description 4
- YPMPTULBFPFSEQ-PLNGDYQASA-N ethyl (z)-3-aminobut-2-enoate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)\C=C(\C)N YPMPTULBFPFSEQ-PLNGDYQASA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000012362 glacial acetic acid Substances 0.000 description 4
- HQKMJHAJHXVSDF-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium stearate Chemical compound [Mg+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O HQKMJHAJHXVSDF-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 4
- NQMRYBIKMRVZLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N methylamine hydrochloride Chemical compound [Cl-].[NH3+]C NQMRYBIKMRVZLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- BTFQKIATRPGRBS-UHFFFAOYSA-N o-tolualdehyde Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1C=O BTFQKIATRPGRBS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000000741 silica gel Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910002027 silica gel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- UKVYVZLTGQVOPX-IHWYPQMZSA-N (z)-3-aminobut-2-enoic acid Chemical compound C\C(N)=C\C(O)=O UKVYVZLTGQVOPX-IHWYPQMZSA-N 0.000 description 3
- MYMKVVIJJCGDIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-benzylthiobenzaldehyde Chemical compound S=CC1=CC=CC=C1CC1=CC=CC=C1 MYMKVVIJJCGDIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 125000004182 2-chlorophenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(Cl)=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 3
- GUXKBDHITFXEJG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-methoxycarbonylpyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=CN=CC(C(O)=O)=C1 GUXKBDHITFXEJG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- WFDIJRYMOXRFFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic anhydride Chemical compound CC(=O)OC(C)=O WFDIJRYMOXRFFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- PAYRUJLWNCNPSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Aniline Chemical compound NC1=CC=CC=C1 PAYRUJLWNCNPSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
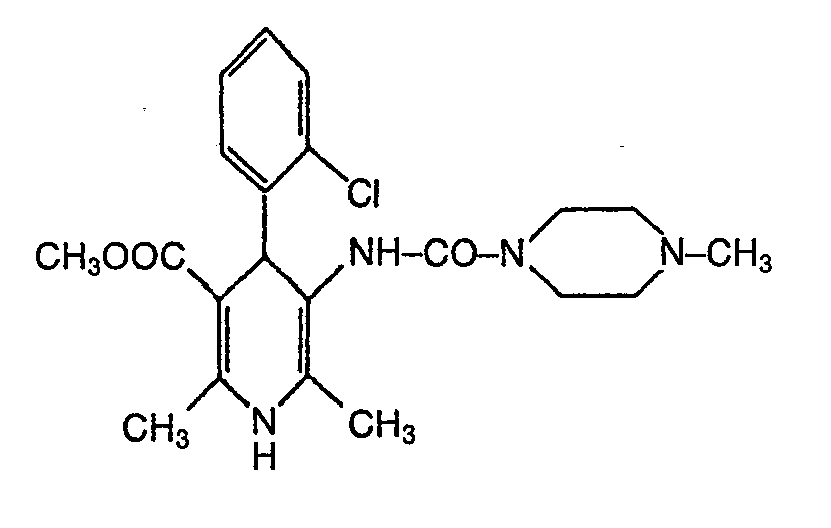
- KFGRULVALDSCIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC1=C(C(C2=C(N1)COC2=O)C1=CC(=CC=C1)Cl)C(=O)O Chemical compound CC1=C(C(C2=C(N1)COC2=O)C1=CC(=CC=C1)Cl)C(=O)O KFGRULVALDSCIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- QOSSAOTZNIDXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dicylcohexylcarbodiimide Chemical compound C1CCCCC1N=C=NC1CCCCC1 QOSSAOTZNIDXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propylene glycol Chemical compound CC(O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium bicarbonate Chemical compound [Na+].OC([O-])=O UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 230000037396 body weight Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 3
- MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethylene glycol Chemical compound OCCOCCO MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 description 3
- 210000002837 heart atrium Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000012071 phase Substances 0.000 description 3
- UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridine Natural products COC1=CC=CN=C1 UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000454 talc Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000012222 talc Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 229910052623 talc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- VCGRFBXVSFAGGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N (1,1-dioxo-1,4-thiazinan-4-yl)-[6-[[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl]methoxy]pyridin-3-yl]methanone Chemical compound CC=1ON=C(C=2C=CC(F)=CC=2)C=1COC(N=C1)=CC=C1C(=O)N1CCS(=O)(=O)CC1 VCGRFBXVSFAGGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CYJZDIBYDLTAOK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-nitro-2h-pyridine Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)N1CC=CC=C1 CYJZDIBYDLTAOK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000005160 1H NMR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 2
- XCFFJQBPMLJYGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F XCFFJQBPMLJYGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QTKRICXKOUIGOK-WAYWQWQTSA-N 2-cyanoethyl (z)-3-aminobut-2-enoate Chemical compound C\C(N)=C\C(=O)OCCC#N QTKRICXKOUIGOK-WAYWQWQTSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001431 2-methylbenzaldehyde Substances 0.000 description 2
- CMWKITSNTDAEDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-nitrobenzaldehyde Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC=CC=C1C=O CMWKITSNTDAEDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SRWILAKSARHZPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-chlorobenzaldehyde Chemical compound ClC1=CC=CC(C=O)=C1 SRWILAKSARHZPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WMPDAIZRQDCGFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-methoxybenzaldehyde Chemical compound COC1=CC=CC(C=O)=C1 WMPDAIZRQDCGFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IYEPVECYWAJPAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-(2-methylpropoxycarbonyl)pyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound C(C(C)C)OC(=O)C=1C=NC=C(C=1)C(=O)O IYEPVECYWAJPAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
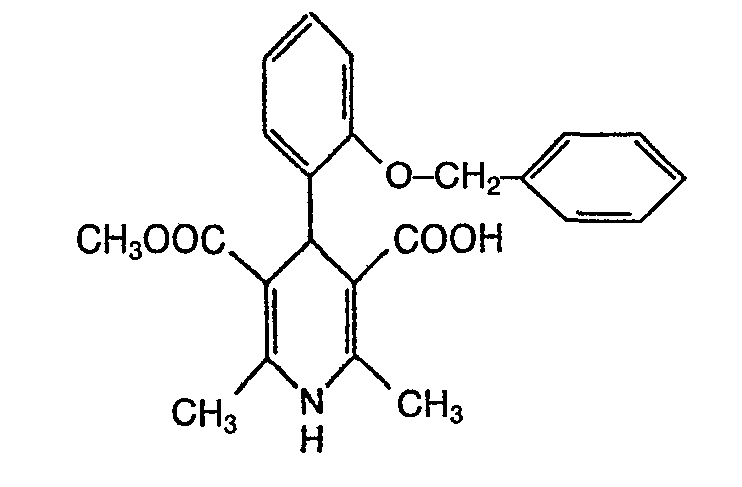
- PJHQSCMKXNRCCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 PJHQSCMKXNRCCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 101100116570 Caenorhabditis elegans cup-2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 2
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L Calcium carbonate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=O VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 101100116572 Drosophila melanogaster Der-1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 2
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerine Chemical compound OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241000282414 Homo sapiens Species 0.000 description 2
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 2
- NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Piperidine Chemical compound C1CCNCC1 NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920003171 Poly (ethylene oxide) Polymers 0.000 description 2
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium chloride Chemical compound [Na+].[Cl-] FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- DBMJMQXJHONAFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium laurylsulphate Chemical compound [Na+].CCCCCCCCCCCCOS([O-])(=O)=O DBMJMQXJHONAFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- WQDUMFSSJAZKTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sodium methoxide Chemical compound [Na+].[O-]C WQDUMFSSJAZKTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920002472 Starch Polymers 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-MICDWDOJSA-N Trichloro(2H)methane Chemical compound [2H]C(Cl)(Cl)Cl HEDRZPFGACZZDS-MICDWDOJSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000002777 acetyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)=O 0.000 description 2
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910002092 carbon dioxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000001569 carbon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000496 cardiotonic agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007795 chemical reaction product Substances 0.000 description 2
- MVPPADPHJFYWMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N chlorobenzene Chemical compound ClC1=CC=CC=C1 MVPPADPHJFYWMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004587 chromatography analysis Methods 0.000 description 2
- MKRTXPORKIRPDG-UHFFFAOYSA-N diphenylphosphoryl azide Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1P(=O)(N=[N+]=[N-])C1=CC=CC=C1 MKRTXPORKIRPDG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003995 emulsifying agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- FOSSIVPTEKYBIE-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-4-[2-[(3-methylphenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC(C)=C1 FOSSIVPTEKYBIE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HPKGXTIXTOJDAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F HPKGXTIXTOJDAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000013312 flour Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000010575 fractional recrystallization Methods 0.000 description 2
- 108700039708 galantide Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000005457 ice water Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000000297 inotrophic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000019359 magnesium stearate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- AWZXSHCRIUFEFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 AWZXSHCRIUFEFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MTAQMFSTFXQMKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C([N+]([O-])=O)C1C1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1Cl MTAQMFSTFXQMKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
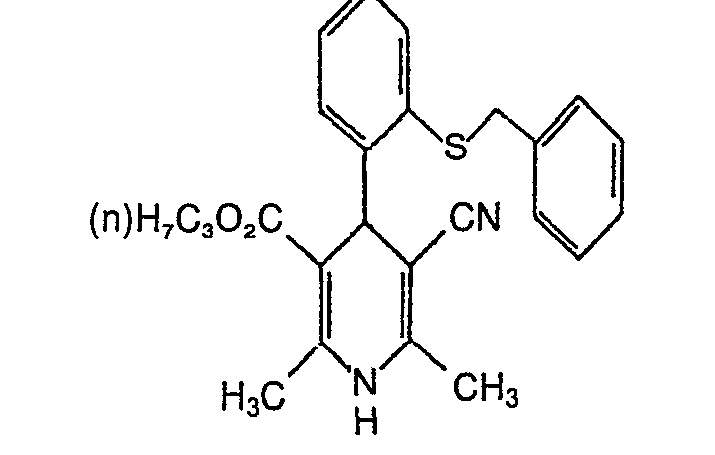
- NHWMGEJDCQMKFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-5-cyano-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C#N)C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 NHWMGEJDCQMKFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 210000004165 myocardium Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 231100000252 nontoxic Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 230000003000 nontoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 125000003261 o-tolyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(*)=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003208 petroleum Substances 0.000 description 2
- YCKAGGHNUHZKCL-XQRVVYSFSA-N propan-2-yl (z)-3-aminobut-2-enoate Chemical compound CC(C)OC(=O)\C=C(\C)N YCKAGGHNUHZKCL-XQRVVYSFSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DIWWDNJUKATEGY-WAYWQWQTSA-N propyl (z)-3-aminobut-2-enoate Chemical compound CCCOC(=O)\C=C(\C)N DIWWDNJUKATEGY-WAYWQWQTSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- QJZUKDFHGGYHMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridine-3-carbaldehyde Chemical compound O=CC1=CC=CN=C1 QJZUKDFHGGYHMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 235000019333 sodium laurylsulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000008107 starch Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000019698 starch Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 238000005728 strengthening Methods 0.000 description 2
- 235000000346 sugar Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000011593 sulfur Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 239000003826 tablet Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000011282 treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- DOMQFIFVDIAOOT-ROUUACIJSA-N (2S,3R)-N-[4-(2,6-dimethoxyphenyl)-5-(5-methylpyridin-3-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl]-3-(5-methylpyrimidin-2-yl)butane-2-sulfonamide Chemical compound COC1=C(C(=CC=C1)OC)N1C(=NN=C1C=1C=NC=C(C=1)C)NS(=O)(=O)[C@@H](C)[C@H](C)C1=NC=C(C=N1)C DOMQFIFVDIAOOT-ROUUACIJSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MAYZWDRUFKUGGP-VIFPVBQESA-N (3s)-1-[5-tert-butyl-3-[(1-methyltetrazol-5-yl)methyl]triazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidin-7-yl]pyrrolidin-3-ol Chemical compound CN1N=NN=C1CN1C2=NC(C(C)(C)C)=NC(N3C[C@@H](O)CC3)=C2N=N1 MAYZWDRUFKUGGP-VIFPVBQESA-N 0.000 description 1
- VALPITSIKKDGSR-WAYWQWQTSA-N (Z)-3-amino-2-propan-2-ylbut-2-enoic acid Chemical compound CC(C)C(=C(/C)N)\C(O)=O VALPITSIKKDGSR-WAYWQWQTSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UKGJZDSUJSPAJL-YPUOHESYSA-N (e)-n-[(1r)-1-[3,5-difluoro-4-(methanesulfonamido)phenyl]ethyl]-3-[2-propyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl]prop-2-enamide Chemical compound CCCC1=NC(C(F)(F)F)=CC=C1\C=C\C(=O)N[C@H](C)C1=CC(F)=C(NS(C)(=O)=O)C(F)=C1 UKGJZDSUJSPAJL-YPUOHESYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZGYIXVSQHOKQRZ-COIATFDQSA-N (e)-n-[4-[3-chloro-4-(pyridin-2-ylmethoxy)anilino]-3-cyano-7-[(3s)-oxolan-3-yl]oxyquinolin-6-yl]-4-(dimethylamino)but-2-enamide Chemical compound N#CC1=CN=C2C=C(O[C@@H]3COCC3)C(NC(=O)/C=C/CN(C)C)=CC2=C1NC(C=C1Cl)=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC=N1 ZGYIXVSQHOKQRZ-COIATFDQSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MOWXJLUYGFNTAL-DEOSSOPVSA-N (s)-[2-chloro-4-fluoro-5-(7-morpholin-4-ylquinazolin-4-yl)phenyl]-(6-methoxypyridazin-3-yl)methanol Chemical compound N1=NC(OC)=CC=C1[C@@H](O)C1=CC(C=2C3=CC=C(C=C3N=CN=2)N2CCOCC2)=C(F)C=C1Cl MOWXJLUYGFNTAL-DEOSSOPVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- APWRZPQBPCAXFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-(1-oxo-2H-isoquinolin-5-yl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-4-yl]pyrazole-4-carboxamide Chemical compound O=C1NC=CC2=C(C=CC=C12)N1N=CC(=C1C(F)(F)F)C(=O)NC1=CC(=NC=C1)C(F)(F)F APWRZPQBPCAXFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ABDDQTDRAHXHOC-QMMMGPOBSA-N 1-[(7s)-5,7-dihydro-4h-thieno[2,3-c]pyran-7-yl]-n-methylmethanamine Chemical compound CNC[C@@H]1OCCC2=C1SC=C2 ABDDQTDRAHXHOC-QMMMGPOBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YEHHYWREOGFYSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2,2-trichloroethyl 3-oxobutanoate Chemical compound CC(=O)CC(=O)OCC(Cl)(Cl)Cl YEHHYWREOGFYSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QJXCFMJTJYCLFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorobenzaldehyde Chemical compound FC1=C(F)C(F)=C(C=O)C(F)=C1F QJXCFMJTJYCLFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LLMLNAVBOAMOEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3-dichlorobenzaldehyde Chemical compound ClC1=CC=CC(C=O)=C1Cl LLMLNAVBOAMOEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KJSCKNKCNSCEQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-dimethyl-3,5-dinitro-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C([N+]([O-])=O)C1C1=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1 KJSCKNKCNSCEQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MZGOEQOUSKNKAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-phenylmethoxyphenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC=C1 MZGOEQOUSKNKAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PNUUTTVJMVKZCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1 PNUUTTVJMVKZCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GBTKFJAHMVOTRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(3-methylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC(C)=C1 GBTKFJAHMVOTRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OOYMUFXKTVHGQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-5-propan-2-yloxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CC(C)OC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 OOYMUFXKTVHGQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PBQJPYDHOYOLQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 PBQJPYDHOYOLQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UQNCXRKGVABEMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1 UQNCXRKGVABEMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LIXHMBPIESTVBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[(3-chlorophenyl)methylsulfanyl]benzaldehyde Chemical compound ClC1=CC=CC(CSC=2C(=CC=CC=2)C=O)=C1 LIXHMBPIESTVBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KLZXAPCLPREJOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[(4-methylphenyl)methoxy]benzaldehyde Chemical compound C1=CC(C)=CC=C1COC1=CC=CC=C1C=O KLZXAPCLPREJOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QCLPHFMNWBWDOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[(4-methylphenyl)methylsulfanyl]benzaldehyde Chemical compound C1=CC(C)=CC=C1CSC1=CC=CC=C1C=O QCLPHFMNWBWDOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VFVHWCKUHAEDMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzaldehyde Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC=C(Cl)C(C=O)=C1 VFVHWCKUHAEDMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OACPOWYLLGHGCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-chloro-6-fluorobenzaldehyde Chemical compound FC1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1C=O OACPOWYLLGHGCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DRKIKNCEAQKIEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-cyanoethyl 2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound C(#N)CCOC(=O)C=1C(C(=C(NC=1C)C)[N+](=O)[O-])C1=CC=C(C=C1)[N+](=O)[O-] DRKIKNCEAQKIEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QVTPWONEVZJCCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-formylbenzonitrile Chemical compound O=CC1=CC=CC=C1C#N QVTPWONEVZJCCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QSULBIGNQKIWSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methoxyethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 QSULBIGNQKIWSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DLRDTWDIGJOPJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methoxyethyl 4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1,2-dimethyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)N(C)C(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1 DLRDTWDIGJOPJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004204 2-methoxyphenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(*)=C(OC([H])([H])[H])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- AHGDKNPPRYOXSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1H-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CC1=C(C(C2=C(N1)COC2=O)C1=C(C=CC=C1)C(F)(F)F)C(=O)O AHGDKNPPRYOXSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YZOPPUOFZXLLIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylpropyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CC(C)COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 YZOPPUOFZXLLIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HJGLYMFTFJQCNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylpropyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CC(C)COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 HJGLYMFTFJQCNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PJKVFARRVXDXAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-naphthaldehyde Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC(C=O)=CC=C21 PJKVFARRVXDXAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BBBJXPCSKOPGLI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-propoxyethyl 3-oxobutanoate Chemical compound CCCOCCOC(=O)CC(C)=O BBBJXPCSKOPGLI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HCDMJFOHIXMBOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(2,6-difluoro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-ethyl-8-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-4,7-dihydropyrrolo[4,5]pyrido[1,2-d]pyrimidin-2-one Chemical compound C=1C2=C3N(CC)C(=O)N(C=4C(=C(OC)C=C(OC)C=4F)F)CC3=CN=C2NC=1CN1CCOCC1 HCDMJFOHIXMBOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BYHQTRFJOGIQAO-GOSISDBHSA-N 3-(4-bromophenyl)-8-[(2R)-2-hydroxypropyl]-1-[(3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-1,3,8-triazaspiro[4.5]decan-2-one Chemical compound C[C@H](CN1CCC2(CC1)CN(C(=O)N2CC3=CC(=CC=C3)OC)C4=CC=C(C=C4)Br)O BYHQTRFJOGIQAO-GOSISDBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NMTUHPSKJJYGML-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(trifluoromethyl)benzaldehyde Chemical compound FC(F)(F)C1=CC=CC(C=O)=C1 NMTUHPSKJJYGML-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YGYGASJNJTYNOL-CQSZACIVSA-N 3-[(4r)-2,2-dimethyl-1,1-dioxothian-4-yl]-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-1h-indole-7-carboxamide Chemical compound C1CS(=O)(=O)C(C)(C)C[C@@H]1C1=CNC2=C(C(N)=O)C=C(C=3C=CC(F)=CC=3)C=C12 YGYGASJNJTYNOL-CQSZACIVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WNEODWDFDXWOLU-QHCPKHFHSA-N 3-[3-(hydroxymethyl)-4-[1-methyl-5-[[5-[(2s)-2-methyl-4-(oxetan-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl]pyridin-2-yl]amino]-6-oxopyridin-3-yl]pyridin-2-yl]-7,7-dimethyl-1,2,6,8-tetrahydrocyclopenta[3,4]pyrrolo[3,5-b]pyrazin-4-one Chemical compound C([C@@H](N(CC1)C=2C=NC(NC=3C(N(C)C=C(C=3)C=3C(=C(N4C(C5=CC=6CC(C)(C)CC=6N5CC4)=O)N=CC=3)CO)=O)=CC=2)C)N1C1COC1 WNEODWDFDXWOLU-QHCPKHFHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SRVXSISGYBMIHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-[3-[3-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)phenyl]-5-chlorophenyl]-3-(5-methyl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)propanoic acid Chemical compound S1C(C)=CN=C1C(CC(O)=O)C1=CC(Cl)=CC(C=2C=C(CC(N)=O)C=CC=2)=C1 SRVXSISGYBMIHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UZDCYOVORLPDBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-acetyl-2-methyl-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2,3,4,4a-tetrahydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridin-5-one Chemical compound CC(=O)C1C(C)NC2=COC(=O)C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F UZDCYOVORLPDBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MXTKYWCJUDWVCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-acetyl-4-(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-2-methyl-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridin-5-one Chemical compound CC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 MXTKYWCJUDWVCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZNFBZGYARFIIDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-benzylthiobenzaldehyde Chemical compound S=CC1=CC=CC(CC=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 ZNFBZGYARFIIDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SBIAKSUUZYFTKS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-chloro-2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(Cl)C1C1=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1 SBIAKSUUZYFTKS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QZMGMXBYJZVAJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-ethoxybenzaldehyde Chemical compound CCOC1=CC=CC(C=O)=C1 QZMGMXBYJZVAJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004207 3-methoxyphenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(*)=C([H])C(OC([H])([H])[H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- JAICGBJIBWDEIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-phenylmethoxybenzaldehyde Chemical compound O=CC1=CC=CC(OCC=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 JAICGBJIBWDEIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NHRMWWGBQZBLMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1Cl NHRMWWGBQZBLMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NZQFPALQJPLGFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(3-nitrophenyl)pyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CN=CC=C1C1=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1 NZQFPALQJPLGFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VJPPLCNBDLZIFG-ZDUSSCGKSA-N 4-[(3S)-3-(but-2-ynoylamino)piperidin-1-yl]-5-fluoro-2,3-dimethyl-1H-indole-7-carboxamide Chemical compound C(C#CC)(=O)N[C@@H]1CN(CCC1)C1=C2C(=C(NC2=C(C=C1F)C(=O)N)C)C VJPPLCNBDLZIFG-ZDUSSCGKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QOCICIGYGQHHAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=C(Cl)C=CC=C1Cl QOCICIGYGQHHAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BGIFMBHVVLMDPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[2-[(2-chlorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC=C1Cl BGIFMBHVVLMDPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UXYDYXKKVUBPIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[2-[(3,4-dichlorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C1 UXYDYXKKVUBPIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PRRIUOPFBRBFIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[2-[(3,5-dimethylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC(C)=CC(C)=C1 PRRIUOPFBRBFIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FJRVQHNDHBQCJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[2-[(3-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC(F)=C1 FJRVQHNDHBQCJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PLUFIRLCLJQRFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[2-[(3-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC(F)=C1 PLUFIRLCLJQRFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LOXYWEFSQSOKBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[2-[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]phenyl]-5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1CC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 LOXYWEFSQSOKBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AHSLHICTYLRUKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[2-[(4-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=C(F)C=C1 AHSLHICTYLRUKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YFCIFWOJYYFDQP-PTWZRHHISA-N 4-[3-amino-6-[(1S,3S,4S)-3-fluoro-4-hydroxycyclohexyl]pyrazin-2-yl]-N-[(1S)-1-(3-bromo-5-fluorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)ethyl]-2-fluorobenzamide Chemical compound CNC[C@@H](NC(=O)c1ccc(cc1F)-c1nc(cnc1N)[C@H]1CC[C@H](O)[C@@H](F)C1)c1cc(F)cc(Br)c1 YFCIFWOJYYFDQP-PTWZRHHISA-N 0.000 description 1
- XYWIPYBIIRTJMM-IBGZPJMESA-N 4-[[(2S)-2-[4-[5-chloro-2-[4-(trifluoromethyl)triazol-1-yl]phenyl]-5-methoxy-2-oxopyridin-1-yl]butanoyl]amino]-2-fluorobenzamide Chemical compound CC[C@H](N1C=C(OC)C(=CC1=O)C1=C(C=CC(Cl)=C1)N1C=C(N=N1)C(F)(F)F)C(=O)NC1=CC(F)=C(C=C1)C(N)=O XYWIPYBIIRTJMM-IBGZPJMESA-N 0.000 description 1
- KVCQTKNUUQOELD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-amino-n-[1-(3-chloro-2-fluoroanilino)-6-methylisoquinolin-5-yl]thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine-7-carboxamide Chemical compound N=1C=CC2=C(NC(=O)C=3C4=NC=NC(N)=C4SC=3)C(C)=CC=C2C=1NC1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1F KVCQTKNUUQOELD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GVSNQMFKEPBIOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methyl-2h-triazole Chemical compound CC=1C=NNN=1 GVSNQMFKEPBIOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SYYZNMGZAARZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-(2-cyanopropoxycarbonyl)-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical class N#CC(C)COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 SYYZNMGZAARZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ABAGNOHSGSJIOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-(3-nitrophenyl)-3-oxopent-4-enoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1 ABAGNOHSGSJIOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VLRITNQJNQFBBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-(carboxymethyl)-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(CC(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1 VLRITNQJNQFBBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RYMXPRVNHVFNQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-O-(2-cyanoethyl) 3-O-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-phenylmethoxyphenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(=O)OCCC#N)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC=C1 RYMXPRVNHVFNQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VUGDHQDLDXAMGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-O-propan-2-yl 3-O-(2,2,2-trichloroethyl) 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate Chemical compound CC(C)OC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(=O)OCC(Cl)(Cl)Cl)C1C1=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1 VUGDHQDLDXAMGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IRPVABHDSJVBNZ-RTHVDDQRSA-N 5-[1-(cyclopropylmethyl)-5-[(1R,5S)-3-(oxetan-3-yl)-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexan-6-yl]pyrazol-3-yl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(C(F)(F)F)C(N)=NC=C1C1=NN(CC2CC2)C(C2[C@@H]3CN(C[C@@H]32)C2COC2)=C1 IRPVABHDSJVBNZ-RTHVDDQRSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UZPDOCXNPCXSOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-butoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(3-methylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC(C)=C1 UZPDOCXNPCXSOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OMTMNUUJXJPAIQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-butoxycarbonyl-4-[2-[(3-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC(F)=C1 OMTMNUUJXJPAIQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OMIQACJSAOKEPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-butoxycarbonyl-4-[2-[(3-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC(OC)=C1 OMIQACJSAOKEPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HYRGQPIPORFSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-butoxycarbonylpyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound C(CCC)OC(=O)C=1C=NC=C(C=1)C(=O)O HYRGQPIPORFSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SWGPIDCNYAYXMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzaldehyde Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1C=O SWGPIDCNYAYXMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GXFVSFMEIRGQBQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-ethoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(3-nitrophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound C(C)OC(=O)C1=C(NC(=C(C1C1=C(C=CC=C1)OCC1=CC(=CC=C1)[N+](=O)[O-])C(=O)O)C)C GXFVSFMEIRGQBQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PJKMWNCFPYFQFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-ethoxycarbonyl-4-[2-[(4-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound C(C)OC(=O)C1=C(NC(=C(C1C1=C(C=CC=C1)OCC1=CC=C(C=C1)F)C(=O)O)C)C PJKMWNCFPYFQFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GHKOMFAUZDGVHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-ethoxycarbonylpyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CN=CC(C(O)=O)=C1 GHKOMFAUZDGVHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SXCPPJJWQNBZFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-phenylmethoxyphenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC=C1 SXCPPJJWQNBZFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OVEJYRNJSFFGCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-phenylmethoxyphenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC(OCC=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 OVEJYRNJSFFGCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MWRHYFJLMSDYPW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-propoxyphenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCOC1=CC=CC(C2C(=C(C)NC(C)=C2C(O)=O)C(=O)OC)=C1 MWRHYFJLMSDYPW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FGBXUNAICUZJRG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(2-phenylethoxy)phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCCC1=CC=CC=C1 FGBXUNAICUZJRG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WTLRXMKQDDVBKS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methoxy]naphthalen-1-yl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C(C1=CC=CC=C1C=C1)=C1OCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 WTLRXMKQDDVBKS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OERLHRHVHYHQLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 OERLHRHVHYHQLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NSTXKCUULNXXRY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 NSTXKCUULNXXRY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IPVZLRTVXAFNME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-naphthalen-1-yl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C12 IPVZLRTVXAFNME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- TYBDNOYAFUVVHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-methoxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1 TYBDNOYAFUVVHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PMUANHCVCWFKLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-methoxycarbonyl-4-[2-[(3-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(O)=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC(OC)=C1 PMUANHCVCWFKLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XHSAZLWYCVYFDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-o-(2-cyanoethyl) 3-o-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(=O)OCCC#N)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 XHSAZLWYCVYFDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KCBWAFJCKVKYHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-(4-cyclopropyl-6-methoxypyrimidin-5-yl)-1-[[4-[1-propan-2-yl-4-(trifluoromethyl)imidazol-2-yl]phenyl]methyl]pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine Chemical compound C1(CC1)C1=NC=NC(=C1C1=NC=C2C(=N1)N(N=C2)CC1=CC=C(C=C1)C=1N(C=C(N=1)C(F)(F)F)C(C)C)OC KCBWAFJCKVKYHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FHSORAJCHFSWCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-(carboxymethyl)pyridine-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC1=CC=C(C(O)=O)C=N1 FHSORAJCHFSWCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KVQHMKXEQYYEEA-HJWRWDBZSA-N 6-hydroxyhexyl (Z)-3-aminobut-2-enoate Chemical compound C\C(N)=C\C(=O)OCCCCCCO KVQHMKXEQYYEEA-HJWRWDBZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UAYJALFSXPGBEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-hydroxyhexyl 2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(=O)OCCCCCCO)C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F UAYJALFSXPGBEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JHKLCZNDTUKHHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-nitronicotinic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)N=C1 JHKLCZNDTUKHHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CYJRNFFLTBEQSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(3-methyl-1-benzothiophen-5-yl)-N-(4-methylsulfonylpyridin-3-yl)quinoxalin-6-amine Chemical compound CS(=O)(=O)C1=C(C=NC=C1)NC=1C=C2N=CC=NC2=C(C=1)C=1C=CC2=C(C(=CS2)C)C=1 CYJRNFFLTBEQSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZRPZPNYZFSJUPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N ARS-1620 Chemical compound Oc1cccc(F)c1-c1c(Cl)cc2c(ncnc2c1F)N1CCN(CC1)C(=O)C=C ZRPZPNYZFSJUPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 240000002470 Amphicarpaea bracteata Species 0.000 description 1
- OKWSRPNIJGIJCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(C)(CC)OC(=O)C1=C(NC(=C(C1C1=C(C=CC=C1)OCC1=CC=C(C=C1)C)C(=O)O)C)C Chemical compound C(C)(CC)OC(=O)C1=C(NC(=C(C1C1=C(C=CC=C1)OCC1=CC=C(C=C1)C)C(=O)O)C)C OKWSRPNIJGIJCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JTSFDVPEPQCXLZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(NC(C)=C(C1C2CCCCC2)Cl)=C1[N+]([O-])=O Chemical compound CC(NC(C)=C(C1C2CCCCC2)Cl)=C1[N+]([O-])=O JTSFDVPEPQCXLZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QSPXAKBCCLRMJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(NC(C)=C(C1c(c(F)c(c(I)c2F)F)c2F)[N+]([O-])=O)=C1C(OC)=O Chemical compound CC(NC(C)=C(C1c(c(F)c(c(I)c2F)F)c2F)[N+]([O-])=O)=C1C(OC)=O QSPXAKBCCLRMJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZAEKQDSVOZXOJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(NC(C)=C(C1c2cc([N+]([O-])=O)ccc2Cl)[N+]([O-])=O)=C1C(OC)=O Chemical compound CC(NC(C)=C(C1c2cc([N+]([O-])=O)ccc2Cl)[N+]([O-])=O)=C1C(OC)=O ZAEKQDSVOZXOJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DZBJULFSUUJJSB-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC1=C(C(C2=C(N1)COC2=O)C3=CC=CC=C3SCC4CCC5=CC=CC=C5C4)C(=O)O Chemical compound CC1=C(C(C2=C(N1)COC2=O)C3=CC=CC=C3SCC4CCC5=CC=CC=C5C4)C(=O)O DZBJULFSUUJJSB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MPRKAXHTTUKDIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC1=CC(C(=C(N1)C)C(=O)O)C2=CC=CC=C2OCC3=CC(=CC=C3)[N+](=O)[O-] Chemical compound CC1=CC(C(=C(N1)C)C(=O)O)C2=CC=CC=C2OCC3=CC(=CC=C3)[N+](=O)[O-] MPRKAXHTTUKDIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LEUQGZJJBSQCRZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC1=CC(C(=C(N1)C)C(=O)O)C2=CC=CC=C2OCC3=CC=C(C=C3)Cl Chemical compound CC1=CC(C(=C(N1)C)C(=O)O)C2=CC=CC=C2OCC3=CC=C(C=C3)Cl LEUQGZJJBSQCRZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DRNMAJMIDLAFCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC1=CC(C(=C(N1)C)C(=O)O)C2=CC=CC=C2OCC3=CC=C(C=C3)F Chemical compound CC1=CC(C(=C(N1)C)C(=O)O)C2=CC=CC=C2OCC3=CC=C(C=C3)F DRNMAJMIDLAFCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RJMWOPWDPLXEQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC1=CC(C(=C(N1)C)C(=O)O)C2=CC=CC=C2OCC3=CC=CC=C3Cl Chemical compound CC1=CC(C(=C(N1)C)C(=O)O)C2=CC=CC=C2OCC3=CC=CC=C3Cl RJMWOPWDPLXEQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NAIVAFLLXXQTCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCC1=C(C(C=C(N1)C)C2=CC=CC=C2C(F)(F)F)[N+](=O)[O-] Chemical compound CCC1=C(C(C=C(N1)C)C2=CC=CC=C2C(F)(F)F)[N+](=O)[O-] NAIVAFLLXXQTCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UBLCGLDTRPHHKU-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCC1=C(C(C=C(N1)C)C2=CC=CC=C2SCC3=CC=CC=C3)[N+](=O)[O-] Chemical compound CCC1=C(C(C=C(N1)C)C2=CC=CC=C2SCC3=CC=CC=C3)[N+](=O)[O-] UBLCGLDTRPHHKU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940127291 Calcium channel antagonist Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000019739 Dicalciumphosphate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004097 EU approved flavor enhancer Substances 0.000 description 1
- GISRWBROCYNDME-PELMWDNLSA-N F[C@H]1[C@H]([C@H](NC1=O)COC1=NC=CC2=CC(=C(C=C12)OC)C(=O)N)C Chemical compound F[C@H]1[C@H]([C@H](NC1=O)COC1=NC=CC2=CC(=C(C=C12)OC)C(=O)N)C GISRWBROCYNDME-PELMWDNLSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010010803 Gelatin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N Glucose Natural products OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AYCPARAPKDAOEN-LJQANCHMSA-N N-[(1S)-2-(dimethylamino)-1-phenylethyl]-6,6-dimethyl-3-[(2-methyl-4-thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidinyl)amino]-1,4-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrazole-5-carboxamide Chemical compound C1([C@H](NC(=O)N2C(C=3NN=C(NC=4C=5SC=CC=5N=C(C)N=4)C=3C2)(C)C)CN(C)C)=CC=CC=C1 AYCPARAPKDAOEN-LJQANCHMSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FEYNFHSRETUBEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-[3-(1,1-difluoroethyl)phenyl]-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-5-oxo-4H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide Chemical compound COc1ccc(cc1)N1N=C(C)C(C(=O)Nc2cccc(c2)C(C)(F)F)C1=O FEYNFHSRETUBEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UEEJHVSXFDXPFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-dimethylaminoethanol Chemical compound CN(C)CCO UEEJHVSXFDXPFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PVNIIMVLHYAWGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Niacin Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CN=C1 PVNIIMVLHYAWGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IDRGFNPZDVBSSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N OCCN1CCN(CC1)c1ccc(Nc2ncc3cccc(-c4cccc(NC(=O)C=C)c4)c3n2)c(F)c1F Chemical compound OCCN1CCN(CC1)c1ccc(Nc2ncc3cccc(-c4cccc(NC(=O)C=C)c4)c3n2)c(F)c1F IDRGFNPZDVBSSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002202 Polyethylene glycol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000021355 Stearic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfurous acid Chemical compound OS(O)=O LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LXRZVMYMQHNYJB-UNXOBOICSA-N [(1R,2S,4R)-4-[[5-[4-[(1R)-7-chloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-1-yl]-5-methylthiophene-2-carbonyl]pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]-2-hydroxycyclopentyl]methyl sulfamate Chemical compound CC1=C(C=C(S1)C(=O)C1=C(N[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](COS(N)(=O)=O)C2)N=CN=C1)[C@@H]1NCCC2=C1C=C(Cl)C=C2 LXRZVMYMQHNYJB-UNXOBOICSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QEKWHKXDESQSTL-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetyl 4-nitrobenzoate Chemical compound CC(=O)OC(=O)C1=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1 QEKWHKXDESQSTL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005903 acid hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000443 aerosol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000008055 alkyl aryl sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940045714 alkyl sulfonate alkylating agent Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000008052 alkyl sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000002220 antihypertensive agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940030600 antihypertensive agent Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000007900 aqueous suspension Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002969 artificial stone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010945 base-catalyzed hydrolysis reactiony Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000003236 benzoyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C(*)=O 0.000 description 1
- CRMUWFFONHBYAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound C1OC(=O)C2=C1NC(C)=C(C(=O)OCC=1C=CC=CC=1)C2C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F CRMUWFFONHBYAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000001124 body fluid Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000010839 body fluid Substances 0.000 description 1
- CODNYICXDISAEA-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromine monochloride Chemical compound BrCl CODNYICXDISAEA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IUGYUAKMTHUQCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N butan-2-yl pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCC(C)OC(=O)C1=CC=CN=C1 IUGYUAKMTHUQCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HYLWCGAFGSEZLK-SREVYHEPSA-N butyl (z)-3-aminobut-2-enoate Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)\C=C(\C)N HYLWCGAFGSEZLK-SREVYHEPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CESOEDHPFPNAQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(3-methylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound C(CCC)OC(=O)C1=C(NC(=CC1C1=C(C=CC=C1)OCC1=CC(=CC=C1)C)C)C CESOEDHPFPNAQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FNIPGVDUWWIVCX-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl 2-methyl-4-(2-methylphenyl)-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C FNIPGVDUWWIVCX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HIVSMOQFNYKPDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl 2-methyl-4-[2-[(3-nitrophenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1 HIVSMOQFNYKPDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YCRQHLYVPHBGSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl 2-methyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 YCRQHLYVPHBGSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IRHGRPVVXFKHII-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F IRHGRPVVXFKHII-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- TZMMLSYNDZOPPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 TZMMLSYNDZOPPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CZPFBRDRESZYLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl 4-(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 CZPFBRDRESZYLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XXMHEFYJWYXPPH-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl 4-(3-chlorophenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1 XXMHEFYJWYXPPH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UEQGUGAIESCIQY-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl 4-[2-(cyclohexylmethylsulfanyl)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1CCCCC1 UEQGUGAIESCIQY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VTSCBRKRPBEIRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl 4-[2-[(3,5-dimethylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound C(CCC)OC(=O)C1=C(NC(=CC1C1=C(C=CC=C1)OCC1=CC(=CC(=C1)C)C)C)C VTSCBRKRPBEIRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SZBSWQAKDQVKLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl 4-[2-[(3-chlorophenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1 SZBSWQAKDQVKLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZQCZUUWZMNPNLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl 4-[2-[(3-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CC=1NC(=CC(C1C(=O)OCCCC)C1=C(C=CC=C1)OCC1=CC(=CC=C1)F)C ZQCZUUWZMNPNLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910000019 calcium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001506 calcium phosphate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002775 capsule Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001732 carboxylic acid derivatives Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000012876 carrier material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000006555 catalytic reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- DGLFSNZWRYADFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N chembl2334586 Chemical compound C1CCC2=CN=C(N)N=C2C2=C1NC1=CC=C(C#CC(C)(O)C)C=C12 DGLFSNZWRYADFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940114081 cinnamate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000029078 coronary artery disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000012043 crude product Substances 0.000 description 1
- SCFWSXWPGYNVRS-SREVYHEPSA-N cyclopentyl (z)-3-aminobut-2-enoate Chemical compound C\C(N)=C\C(=O)OC1CCCC1 SCFWSXWPGYNVRS-SREVYHEPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OKFUBZIKQWXOFY-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclopentyl 2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(=O)OC2CCCC2)C1C1=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1 OKFUBZIKQWXOFY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960002887 deanol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- NZZIMKJIVMHWJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N dibenzoylmethane Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1C(=O)CC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 NZZIMKJIVMHWJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NEFBYIFKOOEVPA-UHFFFAOYSA-K dicalcium phosphate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[Ca+2].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O NEFBYIFKOOEVPA-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 229940038472 dicalcium phosphate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229910000390 dicalcium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- NRNFKRFWZQQDMD-UHFFFAOYSA-M dichloromethylidene(dimethyl)azanium;chloride Chemical compound [Cl-].C[N+](C)=C(Cl)Cl NRNFKRFWZQQDMD-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 150000005690 diesters Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- GDOJFVPTASLSGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethyl 2-acetamido-4,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(NC(C)=O)=C(C(=O)OCC)C1C GDOJFVPTASLSGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RUGNEWAQRDWMGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethyl 2-amino-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1h-pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(N)(C)C(C(=O)OCC)C1C1=CC=CC=C1[N+]([O-])=O RUGNEWAQRDWMGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DIAMASUXNLWQPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethyl 2-amino-4,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(N)=C(C(=O)OCC)C1C DIAMASUXNLWQPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- MPFLRYZEEAQMLQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N dinicotinic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CN=CC(C(O)=O)=C1 MPFLRYZEEAQMLQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000008298 dragée Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- VVXRHKMBVIOUNE-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 1,2,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)N(C)C(C(OC2=O)C)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F VVXRHKMBVIOUNE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PBJXFCQVMPQLKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 1,2-dimethyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)N(C)C(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F PBJXFCQVMPQLKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NGBFXWKSEDDJHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 1-(4-ethylsulfanylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound O=C1OCC2=C1CC(C(=O)OCC)=C(C)N2C1=CC=C(SCC)C=C1 NGBFXWKSEDDJHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UECBLLGPCHBUQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 1-[2-(2-benzoyloxyethylsulfanyl)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound O=C1OCC2=C1CC(C(=O)OCC)=C(C)N2C1=CC=CC=C1SCCOC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 UECBLLGPCHBUQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CFDPMTCUVPCOMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 1-ethyl-2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)N(CC)C(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F CFDPMTCUVPCOMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LZVIYKNFQSMMKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 1-ethyl-2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-4,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)N(CC)C(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 LZVIYKNFQSMMKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DJWCWZHNCDVFBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F DJWCWZHNCDVFBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NTIIWQMESZETRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(3-nitrophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1 NTIIWQMESZETRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JUYVACFFPSBNAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-(3-nitrophenyl)pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound C(C)OC(C1=C(N=CC=C1)C1=CC(=CC=C1)[N+](=O)[O-])=O JUYVACFFPSBNAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CGEOWJVEIAILOR-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-(4-formylphenoxy)acetate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)COC1=CC=C(C=O)C=C1 CGEOWJVEIAILOR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ULWJCOYBYLYBRN-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-(methoxymethyl)-5-oxo-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(COC)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F ULWJCOYBYLYBRN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WJGJSXUAQKNHIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-[(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)methylidene]-3-oxobutanoate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C(C(C)=O)=CC1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 WJGJSXUAQKNHIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VVSTTYFNXFWERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-amino-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(N)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1Cl VVSTTYFNXFWERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KLSFNFOSRDJUOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-ethyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(CC)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F KLSFNFOSRDJUOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LBVLRWDGZSKCMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-4-(2-methylsulfanylphenyl)-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SC LBVLRWDGZSKCMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OTEDEKAAUIWEJL-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-4-[2-(naphthalen-1-ylmethylsulfanyl)phenyl]-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(CSC3=CC=CC=C3C3C4=C(COC4=O)NC(C)=C3C(=O)OCC)=CC=CC2=C1 OTEDEKAAUIWEJL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DHZNHKGKVQPGOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-4-[2-[(2-methylphenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1C DHZNHKGKVQPGOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RSDOUJYKFZHKFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-4-[2-[(3-methylphenyl)methylsulfinyl]phenyl]-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1S(=O)CC1=CC=CC(C)=C1 RSDOUJYKFZHKFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DNEKVRNAWULUMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-4-[2-[(3-nitrophenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1 DNEKVRNAWULUMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FYWJDESUOKGWGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 FYWJDESUOKGWGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XXRQMPVCGJBALF-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 XXRQMPVCGJBALF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DQAKJKISFYEGKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-4-[2-[(4-nitrophenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1 DQAKJKISFYEGKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FTKRFUTZDHCJAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-4-naphthalen-2-yl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC(C3C4=C(COC4=O)NC(C)=C3C(=O)OCC)=CC=C21 FTKRFUTZDHCJAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AYXCWDNJWVVEOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-1-propyl-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)N(CCC)C(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F AYXCWDNJWVVEOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OMEUHLULNSEDGW-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-phenylmethoxyphenyl)-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC=C1 OMEUHLULNSEDGW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SCMZUWYNUVACKD-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-phenylphenyl)-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 SCMZUWYNUVACKD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NCPXEGJUGIXUHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-phenylsulfanylphenyl)-4,7-dihydro-1H-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SC1=CC=CC=C1 NCPXEGJUGIXUHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IUDBKIHXJKDPKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-propan-2-ylsulfanylphenyl)-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SC(C)C IUDBKIHXJKDPKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JOHCFJOEVYTMET-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-(3-phenylmethoxyphenyl)-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C(C=1)=CC=CC=1OCC1=CC=CC=C1 JOHCFJOEVYTMET-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KYKLLNCJFSXBGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(1-phenylethylsulfanyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SC(C)C1=CC=CC=C1 KYKLLNCJFSXBGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VVRBUNCZBXQMDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(2-phenylethylsulfanyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCCC1=CC=CC=C1 VVRBUNCZBXQMDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HAYSMRGFDIGUGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1OC(F)(F)F HAYSMRGFDIGUGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GUBUCBGDZNEYGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methoxy]phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 GUBUCBGDZNEYGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PEKLTXJNCMBPDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methyl]phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1CC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 PEKLTXJNCMBPDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QUVVTSKSOJPAPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 QUVVTSKSOJPAPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- USJRMPJZYRZXSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-pyridin-3-yl-4,7-dihydro-1H-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CN=C1 USJRMPJZYRZXSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HSDKTLKBDJXJQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 3-amino-3-iminopropanoate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)CC(N)=N HSDKTLKBDJXJQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OUYRRXPTFNEXQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1Cl OUYRRXPTFNEXQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XXDORNSAVZNIPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1H-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC(C)=C1C XXDORNSAVZNIPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NLNYZRLGKYOMEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(2-benzylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1CC1=CC=CC=C1 NLNYZRLGKYOMEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AZXKDWPSDPBXHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-1,2-dimethyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)N(C)C(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 AZXKDWPSDPBXHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GXSCSKXGMHCEHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-1-ethyl-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)N(CC)C(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 GXSCSKXGMHCEHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YFPAHKFLZMXSJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,6,7-tetrahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(CNC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 YFPAHKFLZMXSJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NIIQOHPADJXCLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1-propyl-4,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)N(CCC)C(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 NIIQOHPADJXCLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JMPHEYFVUJIQJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 JMPHEYFVUJIQJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WDHHNDHJMREXCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-5-oxo-2-propyl-4,7-dihydro-1H-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound C(C)OC(=O)C=1C(C2=C(NC1CCC)COC2=O)C2=C(C=CC=C2)SCC2=CC=CC=C2 WDHHNDHJMREXCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XUWOBGLCMOSGDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(2-benzylsulfinylsulfanylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SS(=O)CC1=CC=CC=C1 XUWOBGLCMOSGDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GMLMIPIOQHIEBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(2-benzylsulfonylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1S(=O)(=O)CC1=CC=CC=C1 GMLMIPIOQHIEBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FHDPLUXZMUNMJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(2-butylsulfanylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1H-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCCCSC1=CC=CC=C1C1C(C(=O)OCC)=C(C)NC2=C1C(=O)OC2 FHDPLUXZMUNMJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GQYCLPHKDVCVNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(2-chlorophenyl)-2,5,6-trimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C)C1C1=CC=CC=C1Cl GQYCLPHKDVCVNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IJAPUJHRMVGKLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(2-ethylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1CC IJAPUJHRMVGKLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JDMKRGMAQTWTQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(2-methoxycarbonylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(=O)OC JDMKRGMAQTWTQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PBHDYDOJIAFCHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(3-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C(C=1)=CC=CC=1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 PBHDYDOJIAFCHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FWERNRZOMMLSSN-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1,2-dimethyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)N(C)C(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1 FWERNRZOMMLSSN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GAZXUHNSJHXJHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-[2-(2-hydroxyethylsulfanyl)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCCO GAZXUHNSJHXJHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SIMCGHJOVNOJQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-[2-(cyclohexylmethylsulfanyl)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1CCCCC1 SIMCGHJOVNOJQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DFOSMFJPXQYGSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-[2-[(2,5-dichlorophenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC(Cl)=CC=C1Cl DFOSMFJPXQYGSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UFXGXQKLPWMYJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-[2-[(3,4-dichlorophenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C1 UFXGXQKLPWMYJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KXXZZDWZAXZADM-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-[2-[(4-chlorophenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 KXXZZDWZAXZADM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GNNUDXYWDNQKRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-[2-[(4-ethoxycarbonylphenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1H-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=C(C(=O)OCC)C=C1 GNNUDXYWDNQKRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MIEGSZRHDYNYKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-[2-[(4-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=C(F)C=C1 MIEGSZRHDYNYKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GIJVHFFZSWEMPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-[2-[(4-methoxycarbonylphenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=C(C(=O)OC)C=C1 GIJVHFFZSWEMPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OHAFNTFOOCWFSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-[2-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=C(OC)C=C1 OHAFNTFOOCWFSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KAPCQAZCIQVLKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-[2-[(4-tert-butylphenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1H-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=C(C(C)(C)C)C=C1 KAPCQAZCIQVLKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZVQAZCOAFHVLAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-[2-[chloro(phenyl)methyl]sulfanylphenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SC(Cl)C1=CC=CC=C1 ZVQAZCOAFHVLAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CYNVCBUVDFHONF-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 4-acetyloxy-3-oxobutanoate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)CC(=O)COC(C)=O CYNVCBUVDFHONF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LLRQFVMRVPYSCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 5-(2-methylphenyl)-3-oxopent-4-enoate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)CC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CC=C1C LLRQFVMRVPYSCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GASYWQNGISZARS-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 5-(3-nitrophenyl)-3-oxopent-4-enoate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)CC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1 GASYWQNGISZARS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PEYUVZSVGJQDQE-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 6-benzyl-2-methyl-5-nitro-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C=1C(C=2C(=CC=CC=2)C(F)(F)F)C(C(=O)OCC)=C(C)NC=1CC1=CC=CC=C1 PEYUVZSVGJQDQE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 239000000706 filtrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019264 food flavour enhancer Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000008273 gelatin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000159 gelatin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000019322 gelatine Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000011852 gelatine desserts Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 244000243234 giant cane Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000008103 glucose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011187 glycerol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000002334 glycols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000008187 granular material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000010247 heart contraction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- ZKKKOZDQASIYRY-HJWRWDBZSA-N hexyl (z)-3-aminobut-2-enoate Chemical compound CCCCCCOC(=O)\C=C(\C)N ZKKKOZDQASIYRY-HJWRWDBZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HYQNPAVNFIQGAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCCCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F HYQNPAVNFIQGAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QNZLAXONNWOLJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexyl 3-oxobutanoate Chemical compound CCCCCCOC(=O)CC(C)=O QNZLAXONNWOLJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005984 hydrogenation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001965 increasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052500 inorganic mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000001990 intravenous administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010930 lactamization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007273 lactonization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920005610 lignin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000012280 lithium aluminium hydride Substances 0.000 description 1
- VCDOXKMVZZSCQK-ARJAWSKDSA-N methyl (z)-2-aminobut-2-enoate Chemical compound COC(=O)C(\N)=C\C VCDOXKMVZZSCQK-ARJAWSKDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FNYLHZRITYYPGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 1,2,6-trimethyl-5-nitro-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4h-pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)N(C)C(C)=C([N+]([O-])=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F FNYLHZRITYYPGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UZLPFBQPCXHDNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,5,6-trimethyl-4-(2-methylphenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C)C1C1=CC=CC=C1C UZLPFBQPCXHDNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RAGZFOXVRGALGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,5,6-trimethyl-4-(4-methylphenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C)C1C1=CC=C(C)C=C1 RAGZFOXVRGALGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GUQCKSBFHZOQCM-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,5,6-trimethyl-4-[2-(2-phenylethoxy)phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCCC1=CC=CC=C1 GUQCKSBFHZOQCM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CWVGOEHWBXJEGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,5,6-trimethyl-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C)C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F CWVGOEHWBXJEGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZJAZZMCGDHPSRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,5,6-trimethyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 ZJAZZMCGDHPSRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KVTVKSVKLHBIMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,5,6-trimethyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C)C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 KVTVKSVKLHBIMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NOKNHZXOKUQEKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,5,6-trimethyl-4-[2-phenyl-3-(sulfanylmethoxy)phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C)C1C1=CC=CC(OCS)=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 NOKNHZXOKUQEKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JQDLVTSVQMYVOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,5,6-trimethyl-4-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C)C1C1=CC=CC=C1 JQDLVTSVQMYVOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FGBLOUYPRPUTCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,5,6-trimethyl-4-thiophen-3-yl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C)C1C1=CSC=C1 FGBLOUYPRPUTCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JDMJQKHQUZKYIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-methylphenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1C JDMJQKHQUZKYIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SBLSBCBPKRCJRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-phenylmethoxyphenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC(OCC=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 SBLSBCBPKRCJRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- TWPMKPROVHFGIR-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(phenylsulfanylmethoxy)phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OCSC1=CC=CC=C1 TWPMKPROVHFGIR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FPCTUIDNOFBUDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methoxy]naphthalen-1-yl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C(C1=CC=CC=C1C=C1)=C1OCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 FPCTUIDNOFBUDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XONYFFGKQYDFGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-5-nitro-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C([N+]([O-])=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 XONYFFGKQYDFGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BNLWWQLJOAYIHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 BNLWWQLJOAYIHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YGMPYQPUNDAVJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[3-(2-phenylpropyl)-2-sulfanylphenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC(CC(C)C=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1S YGMPYQPUNDAVJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MOIMHLXKSHMHKD-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-naphthalen-1-yl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C12 MOIMHLXKSHMHKD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ORKVPQFJJCKQNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-naphthalen-2-yl-5-nitro-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C([N+]([O-])=O)C1C1=CC=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1 ORKVPQFJJCKQNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BRDFFKVAYVWNJI-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-(3-phenylmethoxyphenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C([N+]([O-])=O)C1C1=CC=CC(OCC=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 BRDFFKVAYVWNJI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZFLWDHHVRRZMEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C([N+]([O-])=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F ZFLWDHHVRRZMEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CNRGLYUEBMNXEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-pyridin-4-yl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C([N+]([O-])=O)C1C1=CC=NC=C1 CNRGLYUEBMNXEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SCDPTAUNWGIQQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-[(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)methylidene]-3-oxobutanoate Chemical compound COC(=O)C(C(C)=O)=CC1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 SCDPTAUNWGIQQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UERYYSOZWMFGLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-[[2-[(3-chlorophenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]methylidene]-3-oxobutanoate Chemical compound COC(=O)C(C(C)=O)=CC1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1 UERYYSOZWMFGLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LZWILHAHBXYXDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-isocyanatopyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=CC=CN=C1N=C=O LZWILHAHBXYXDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PASIWFHNGLTALE-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-methyl-4-[2-[(3-methylphenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC(C)=C1 PASIWFHNGLTALE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WJDDBHBCXOLXMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-phenylmethoxyphenyl)-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC=C1 WJDDBHBCXOLXMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YQNJWPJROXUEHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F YQNJWPJROXUEHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DQPNTQJHVITFNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 3-oxo-5-[2-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]pent-4-enoate Chemical compound COC(=O)CC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CC=C1OC(F)(F)F DQPNTQJHVITFNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ASBCARMGBJFMBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 ASBCARMGBJFMBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VEBCSKHOTBMCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C([N+]([O-])=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 VEBCSKHOTBMCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XBKCPOIYJKYLRR-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 XBKCPOIYJKYLRR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DYNQUEOZYWXAQY-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,2,6-trimethyl-4h-pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)N(C)C(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1Cl DYNQUEOZYWXAQY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AEFMPSANUZDPFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-(2-chlorophenyl)-2,5,6-trimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C)C1C1=CC=CC=C1Cl AEFMPSANUZDPFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OFLLZFPDODWWQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-(2-chlorophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1Cl OFLLZFPDODWWQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XRHXQQDNCDPHBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-(2-chlorophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C([N+]([O-])=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1Cl XRHXQQDNCDPHBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NXNNLESUYGQFGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-(2-cyanophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C([N+]([O-])=O)C1C1=CC=CC=C1C#N NXNNLESUYGQFGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KSKGGFPPHSUSEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-(3-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C([N+]([O-])=O)C1C1=CC=CC(SCC=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 KSKGGFPPHSUSEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WKHYLDCHYNSSQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-(3-chlorophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1 WKHYLDCHYNSSQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SGRNWRVKIDIJKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-(3-ethoxyphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCOC1=CC=CC(C2C(=C(C)NC(C)=C2C(=O)OC)[N+]([O-])=O)=C1 SGRNWRVKIDIJKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VDUMYUHNWWKEFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,5,6-trimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C)C1C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 VDUMYUHNWWKEFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IAHOBYVQLCFMOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-[2-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyl]-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OC1=CC=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C1 IAHOBYVQLCFMOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PXZATWIMKZTSCB-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-[2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-2,5,6-trimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=C(Cl)C=CC=C1Cl PXZATWIMKZTSCB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZVTHKDHXQKMYSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-[2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=C(Cl)C=CC=C1Cl ZVTHKDHXQKMYSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZLVQFPKNZKVGCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-[2-[(3,5-dimethylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC(C)=CC(C)=C1 ZLVQFPKNZKVGCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YZWOXONXHJQDTC-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-[2-[(3-chlorophenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1 YZWOXONXHJQDTC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JCPKFQPRCJPUMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-[2-[(3-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC(OC)=C1 JCPKFQPRCJPUMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SDWCNGLZGZSLIR-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-[2-[(4-chlorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-2,5,6-trimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 SDWCNGLZGZSLIR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CCODRPVOOFCSAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 4-[2-[(4-tert-butylphenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1H-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=C(C(C)(C)C)C=C1 CCODRPVOOFCSAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NSXZXQZEWLWMTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 5-(2-methoxyphenyl)-3-oxopent-4-enoate Chemical compound COC(=O)CC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CC=C1OC NSXZXQZEWLWMTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SESKPBGGNDWLJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 5-(butylcarbamoylamino)-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCCCNC(=O)NC1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(=O)OC)C1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 SESKPBGGNDWLJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CVBAJBNGTCPVLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 5-chloro-2,6-dimethyl-4-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(Cl)C1C1=CC=CC=C1 CVBAJBNGTCPVLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DCHWNCNAHDAWDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 5-cyano-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C#N)C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F DCHWNCNAHDAWDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZFWPYCMMVGBCOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 6-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound N1=CC(C(=O)OC)=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F ZFWPYCMMVGBCOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000609 methyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000001923 methylcellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010981 methylcellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000013336 milk Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008267 milk Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004080 milk Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 235000010755 mineral Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011707 mineral Substances 0.000 description 1
- FMASTMURQSHELY-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-(4-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-3-methyl-n-[(2-methyl-1h-indol-4-yl)methyl]pyridine-4-carboxamide Chemical compound C1=CC=C2NC(C)=CC2=C1CN(C=1C(=CC(F)=CC=1)C)C(=O)C1=CC=NC=C1C FMASTMURQSHELY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NNKPHNTWNILINE-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-cyclopropyl-3-fluoro-4-methyl-5-[3-[[1-[2-[2-(methylamino)ethoxy]phenyl]cyclopropyl]amino]-2-oxopyrazin-1-yl]benzamide Chemical compound CNCCOC1=CC=CC=C1C1(NC=2C(N(C=3C(=C(F)C=C(C=3)C(=O)NC3CC3)C)C=CN=2)=O)CC1 NNKPHNTWNILINE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000015097 nutrients Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCC(C)CCCCCCCCC(O)=O OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZNSPSZULYVCIAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N octyl 2-methyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methylsulfanyl]phenyl]-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 ZNSPSZULYVCIAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GMRFSPAUHGCJBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N octyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F GMRFSPAUHGCJBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DZJYLFGIVHKLEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N octyl 4-(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 DZJYLFGIVHKLEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000020477 pH reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- WYMSBXTXOHUIGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N paraoxon Chemical compound CCOP(=O)(OCC)OC1=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1 WYMSBXTXOHUIGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000036961 partial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000144 pharmacologic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000006187 pill Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001223 polyethylene glycol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000001267 polyvinylpyrrolidone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013855 polyvinylpyrrolidone Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920000036 polyvinylpyrrolidone Polymers 0.000 description 1
- LZMJNVRJMFMYQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N poseltinib Chemical compound C1CN(C)CCN1C(C=C1)=CC=C1NC1=NC(OC=2C=C(NC(=O)C=C)C=CC=2)=C(OC=C2)C2=N1 LZMJNVRJMFMYQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920001592 potato starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000002244 precipitate Substances 0.000 description 1
- AXLMPTNTPOWPLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N prop-2-enyl 3-oxobutanoate Chemical compound CC(=O)CC(=O)OCC=C AXLMPTNTPOWPLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HMAYVUXLYBVUTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-2-yl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CC(C)OC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1 HMAYVUXLYBVUTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FOYVWCVMPPNMDM-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-2-yl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(4-methylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CC(C)OC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=CC1C1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 FOYVWCVMPPNMDM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DHLMIWQTRTWIJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-2-yl 2-[(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)methylidene]-3-oxobutanoate Chemical compound CC(C)OC(=O)C(C(C)=O)=CC1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 DHLMIWQTRTWIJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FZXFSARULLKNBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-2-yl 2-methyl-4-(2-methylphenyl)-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CC(C)OC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1C FZXFSARULLKNBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BNYXZCXAUDKTAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-2-yl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,7-dihydro-1H-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound C(C)(C)OC(=O)C=1C(C2=C(NC=1C)COC2=O)C1=CC(=CC=C1)C(F)(F)F BNYXZCXAUDKTAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IWZBNPRNRWTLBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-2-yl 4-(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,7-dihydro-1h-furo[3,4-b]pyridine-3-carboxylate Chemical compound CC(C)OC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(COC2=O)=C2C1C1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 IWZBNPRNRWTLBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DLLIQYOCTBBMGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N propyl 2-[(2-benzylsulfanylphenyl)methylidene]-3-oxobutanoate Chemical compound CCCOC(=O)C(C(C)=O)=CC1=CC=CC=C1SCC1=CC=CC=C1 DLLIQYOCTBBMGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001953 recrystallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007363 ring formation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012266 salt solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- DCKVNWZUADLDEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N sec-butyl acetate Chemical compound CCC(C)OC(C)=O DCKVNWZUADLDEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000002914 sec-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- XIIOFHFUYBLOLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N selpercatinib Chemical compound OC(COC=1C=C(C=2N(C=1)N=CC=2C#N)C=1C=NC(=CC=1)N1CC2N(C(C1)C2)CC=1C=NC(=CC=1)OC)(C)C XIIOFHFUYBLOLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000008159 sesame oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011803 sesame oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000004760 silicates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- XGVXKJKTISMIOW-ZDUSSCGKSA-N simurosertib Chemical compound N1N=CC(C=2SC=3C(=O)NC(=NC=3C=2)[C@H]2N3CCC(CC3)C2)=C1C XGVXKJKTISMIOW-ZDUSSCGKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 210000002460 smooth muscle Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000017557 sodium bicarbonate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910000030 sodium bicarbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011780 sodium chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000001509 sodium citrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- NLJMYIDDQXHKNR-UHFFFAOYSA-K sodium citrate Chemical compound O.O.[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[O-]C(=O)CC(O)(CC([O-])=O)C([O-])=O NLJMYIDDQXHKNR-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 239000012265 solid product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000008117 stearic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004575 stone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008030 superplasticizer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000006188 syrup Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000020357 syrup Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000010998 test method Methods 0.000 description 1
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Natural products C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-VOTSOKGWSA-M trans-cinnamate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)\C=C\C1=CC=CC=C1 WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-VOTSOKGWSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 238000001665 trituration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000019553 vascular disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000000304 vasodilatating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000015112 vegetable and seed oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008158 vegetable oil Substances 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D401/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings directly linked by a ring-member-to-ring-member bond
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P29/00—Non-central analgesic, antipyretic or antiinflammatory agents, e.g. antirheumatic agents; Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs [NSAID]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/08—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P7/00—Drugs for disorders of the blood or the extracellular fluid
- A61P7/10—Antioedematous agents; Diuretics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/02—Non-specific cardiovascular stimulants, e.g. drugs for syncope, antihypotensives
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/04—Inotropic agents, i.e. stimulants of cardiac contraction; Drugs for heart failure
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D211/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings
- C07D211/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D211/80—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having two double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D211/84—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having two double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms, with at the most one bond to halogen directly attached to ring carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D211/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings
- C07D211/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D211/80—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having two double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D211/84—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having two double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms, with at the most one bond to halogen directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D211/90—Carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D409/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D409/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings
- C07D409/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings directly linked by a ring-member-to-ring-member bond
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D471/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with one nitrogen atom, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D463/00
- C07D471/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with one nitrogen atom, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D463/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D471/04—Ortho-condensed systems
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D491/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed ring system both one or more rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms and one or more rings having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D459/00, C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D489/00
- C07D491/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed ring system both one or more rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms and one or more rings having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D459/00, C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D489/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D491/04—Ortho-condensed systems
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D491/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed ring system both one or more rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms and one or more rings having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D459/00, C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D489/00
- C07D491/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed ring system both one or more rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms and one or more rings having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D459/00, C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D489/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D491/10—Spiro-condensed systems
Description
Die vorliegende Erfindung betrifft die Verwendung von neuen und bekannten Dihydropyridinen in Arzneimitteln mit positiv inotroper Wirkung, neue Verbindungen aus dieser Stoffklasse, diese enthaltende Arzneimittel und ihre Herstellung.The present invention relates to the use of new and known dihydropyridines in medicaments with a positive inotropic effect, new compounds from this class of substances, medicaments containing them and their preparation.
Es ist bereits bekannt geworden, dass 1,4-Dihydropyridine gefässerweiternde Eigenschaften besitzen und als Coronarmittel und Antihypertensiva verwendet werden können (vgl. britisches Patent 1173062; britisches Patent 1358951; DE-OS 2 629 892 und DE-OS 2 752 820). Weiterhin ist bekannt, dass 1,4-Dihydropyridine als Calciumantagonisten eine Hemmung der Kontraktionskraft von glatten und kardialen Muskeln bewirken und zur Behandlung von Coronar- und Gefässerkrankungen eingesetzt werden können (vgl. A. Fleckenstein, Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 17, 149-166 (1977)). Bei Kenntnis dieser Eigenschaften der Dihydropyridine war es nicht vorhersehbar, dass die erfindungsgemässen Verbindungen aus dieser Stoffklasse keine kontraktionshemmende, sondern eine kontraktionskraftverstärkende, am Herzmuskel positiv inotrope Wirkung besitzen.It has already become known that 1,4-dihydropyridines have vasodilatory properties and can be used as coronary agents and antihypertensives (cf. British Patent 1173062; British Patent 1358951; DE-OS 2 629 892 and DE-OS 2 752 820). Furthermore, it is known that 1,4-dihydropyridines act as calcium antagonists to inhibit the contractility of smooth and cardiac muscles and can be used to treat coronary and vascular diseases (cf. A. Fleckenstein, Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 17, 149-166 (1977)). Knowing these properties of the dihydropyridines, it was not foreseeable that the compounds according to the invention from this class of substances would not have a contraction-inhibiting, but rather a contraction-strengthening, positive inotropic effect on the heart muscle.
Die Erfindung betrifft die Verwendung von 1,4-Dihydropyridinen der allgemeinen Formel (l)
- n für 0, 1 oder 2 steht,
- R1
- a) für Wasserstoff, einen geradkettigen, verzweigten, cyclischen, gesättigten oder ungesättigten aliphatischen Kohlenwasserstoffrest steht, der gegebenenfalls 1 bis 3 gleiche oder verschiedene Hetero-Kettenglieder aus der Gruppe 0, CO, SOm (m = 0, 1 oder 2), =N-, NRI oder SiRIIRIII enthält und wobei dieser Kohlenwasserstoffrest gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch Halogen, N02, CN, N3, Hydroxy, Aryl oder Heteroaryl oder
- b) für einen Aryl- oder Heteroarylrest steht, wobei diese Reste gegebenenfalls 1 bis 5 gleiche oder verschiedene Substituenten aus der Gruppe Aryl, Alkyl, Alkenyl, Alkinyl, Alkenoxy, Alkinoxy, Aralkyl, Acyl, Alkylen, Dioxyalkylen, Halogen, CF3, OCF3, SCF3, NO2, NO, CN, N3, CORIV, COORV, ORVI, NR' oder NRVIIIRVIII tragen, wobei die Alkyl-, Alkoxy- und Arylreste der obengenannten Substituenten ihrerseits wieder durch Halogen, CORV oder NRVIIRVIII substituiert sein können oder
- c) für den Rest NRVIIRI steht, und wobei die unter a), b) und c) genannten Reste RI, RII, RIII, RIV, RV, RVI, RVII und RVIII die unten angegebene Bedeutung haben,
- R2
- a) für einen der unter R1 angegebenen Substituenten steht, aber nicht mit diesem identisch sein muss oder
- b) für die Reste NHR' oder
wobei RI, RIX und RX die unten angegebene Bedeutung besitzen,
oder die Substituenten R1 und R2 gemeinsam einen 5- bis 8-gliedrigen, gesättigten oder ungesättigten Ring bilden, der gegebenenfalls 1, 2 oder 3 gleiche oder verschiedene Ringglieder aus der Gruppe 0, S, NR' oder CO enthält und der gegebenenfalls 1 bis 3 gleiche oder verschiedene Substituenten aus der Gruppe Halogen, Hydroxy, Alkyl, Alkoxy, Aryl oder Aralkyl enthält, - R3 für einen der unter R2 angegebenen Substituenten steht, und mit diesem gleich oder von diesem verschieden ist, wobei nur einer der beiden Substituenten R2 oder R3 jeweils für Alkoxy, Alkylthio oder NHR' steht,
- R4
- a) für Wasserstoff, NO2, NO, CN, SOm-RXI (m = 0, 1 oder 2), Halogen,
- b) für einen verzweigten oder unverzweigten, cyclischen, gesättigten oder ungesättigten aliphatischen Kohlenwasserstoffrest steht, der gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch Halogen, OH, CN, Alkoxy, Alkylthio, Aryloxy, COORV oder
- c) für einen aromatischen Kohlenwasserstoffrest oder für einen 5- bis 7-gliedrigen gesättigten oder ungesättigten Heteroring mit 1 bis 4 gleichen oder verschiedenen Heterogliedern aus der Gruppe O, S,-N=, NRI, wobei dieser Heteroring entweder über ein Kohlenstoffatom oder ein Stickstoffatom mit dem Dihydropyridinring verknüpft ist, und wobei der aromatische Kohlenwasserstoffrest und die Heteroringe gegebenenfalls 1 bis 3 gleiche oder verschiedene Substituenten aus der Gruppe Halogen, OH, CN, CF3, OCF3, SCF3, N02, Alkyl, Alkoxy, Aryl und
- d) für den Rest
- e) für den Rest
wobei n', R1', R2', R3', R5', R6' und R7' die für n, R1, R2, R3, R5, R6 und R7 angegebene Bedeutung haben und mit diesen gleich oder von diesen verschieden sind, und R4* und R4** gleich oder verschieden sind und jeweils für einen um ein Wasserstoff verminderten Rest der für R4 unter a) bis d) angegebenen Substituenten stehen, oder - a) für Wasserstoff, NO2, NO, CN, SOm-RXI (m = 0, 1 oder 2), Halogen,
- R2 und R4 gemeinsam einen verzweigten, unverzweigten, gesättigten oder ungesättigten 5- bis 8-gliedrigen Ring bilden, der gegebenenfalls 1, 2 oder 3 gleiche oder verschiedene Ringglieder aus der Gruppe O, CO, CS, C=NRI, =N-, NRI, SOm (m = 0, 1 oder 2) oder SiRIIRIII enthält, und der gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch Halogen, Hydroxy, Alkoxy, Aryl, Aralkyl,
wobei dieser gemeinsame Ring von R2 und R4 auch direkt mit dem gemeinsamen Ring von R1 und R2 anneliert sein kann,
wobei die Reste RI, RII, RIII, RVII , RVIII die unten angegebene Bedeutung haben, - R5 die fürR4 angegebene Bedeutung besitzt und mit R4 gleich oder von diesem verschieden ist, oder
- R5 und R3 gemeinsam einen Ring bilden, der mit dem durch R2 und R4 gebildeten Ring gleich oder von diesem verschieden ist,
- R6 für Wasserstoff, Alkyl oder Halogenalkyl steht, und
- R7
- a) für einen gesättigten, ungesättigten, cyciischen, geradkettigen oder verzweigten aliphatischen Kohlenwasserstoffrest steht, der gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch Halogen, Aryl oder Heteroaryl, oder
- b) für einen Aryl- oder Heteroarylrest steht, der gegebenenfalls 1 bis 5 gleiche oder verschiedene Substituenten aus der Gruppe No2, CN, N3, NO, CF3, Halogen, CORIV, COORV, ORVI
gemeinsam mit dem Stickstoffatom einen 5- bis 7-gliedrigen Ring bilden, der 1 oder 2 gleiche oder verschiedene Heteroringglieder aus der Gruppe O, S oder NRI enthalten kann oder
wobei einer der Reste RVIII oder RVIII für eine aliphatische Acylgruppe mit bis zu 6 Kohlenstoffato- men steht, RIX, RX RXI, RXII und RXIII jeweils gleich oder verschieden sind und für Alkyl, Aryl oder Aralkyl stehen,
wobei die unter R1 bis R8 und unter RI bis RXIII genannten Alkyl-, Aryl-, Aralkyl-, Heteroaryl- und Acylreste sowie der mit RVII und RVIII gebildete Heteroring ihrerseits gegebenenfalls substituiert sind durch OH, CF3, OCF3, CN, NO2, Halogen, niederes Thioalkyl, niederes Alkyl, niederes Alkoxy, Aryl oder Aralkyl,
und wobei als Heteroaryl folgende Substituenten genannt seien:- Thienyl, Furyl, Pyryl, Pyridyl, Chinolyl, isochinolyl, Pyrimidyl, Pyridazinyl, Chinazolyl, Chinoxalyl, Benzothienyl, Pyrazolyl, Imidazolyl, Oxazolyl, Isoxazolyl, Thiazolyl, Triazolyl, Oxydiazolyl, Pyrazinyl, Oxazinyl, Thiazinyl, Indolizinyl, Indolyl, Benzofuranyl, Indazolyl, Benzothienyl, Benzimidazolyl, Benzoxazolyl, Benzthiazolyl, Benztriazolyl, Benzoxadiazolyl, Cinnolinyl, Phthalazinyl, Naphthyridinyl oder Benzotriazinyl, in Form von Isomeren, lsomerengemischen, Racematen und optischen Antipoden sowie ihrer pharmazeutisch unbedenklichen Salze, zur Herstellung von Arzneimitteln mit positiv inotroper Wirkung, die sich insbesondere als Cardiotonika eignen. Dieser kontraktionskraftverstärkende Effekt beruht auch darauf, dass die erfindungsgemässen Verbindungen den Ca++- Einstrom in die Zelle erhöhen und somit auch zur Behandlung von hypotonen Kreislaufzuständen, zur Senkung von Blutzucker, zur Abschwellung von Schleimhäuten und zur Beeinflussung des Salz- und Flüssigkeitshaushaltes geeignet sind.
- n represents 0, 1 or 2,
- R 1
- a) represents hydrogen, a straight-chain, branched, cyclic, saturated or unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbon radical which optionally contains 1 to 3 identical or different hetero chain links from the group 0, CO, SO m (m = 0, 1 or 2), = Contains N-, NR I or SiR II R III and where this hydrocarbon radical is optionally substituted by halogen, N0 2 , CN, N 3 , hydroxy, aryl or heteroaryl or
- b) represents an aryl or heteroaryl radical, these radicals optionally 1 to 5 identical or different substituents from the group aryl, alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, alkenoxy, alkynoxy, aralkyl, acyl, alkylene, dioxyalkylene, halogen, CF 3 , OCF 3 , SCF 3 , NO 2 , NO, CN, N 3 , COR IV , COOR V , OR VI , NR 'or NR VIII R VIII , the alkyl, alkoxy and aryl radicals of the abovementioned substituents in turn being replaced by halogen, COR V or NR VII R VIII can be substituted or
- c) stands for the radical NR VII R I , and wherein the radicals R I , R II , R III , R IV , R V , R VI , R VII and R VIII mentioned under a), b) and c) the below have the meaning given,
- R 2
- a) stands for one of the substituents specified under R 1 , but need not be identical with it or
- b) for the residues NHR 'or
where R I , R IX and R X have the meaning given below,
or the substituents R 1 and R 2 together form a 5- to 8-membered, saturated or unsaturated ring which optionally contains 1, 2 or 3 identical or different ring members from the group 0, S, NR 'or CO and which optionally 1 contains up to 3 identical or different substituents from the group halogen, hydroxy, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl or aralkyl, - R 3 represents one of the substituents indicated under R 2 , and is identical to or different from this, only one of the two substituents R 2 or R 3 each representing alkoxy, alkylthio or NHR ',
- R 4
- a) for hydrogen, NO 2 , NO, CN, SO m -R XI (m = 0, 1 or 2), halogen,
- b) represents a branched or unbranched, cyclic, saturated or unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbon radical which is optionally substituted by halogen, OH, CN, alkoxy, alkylthio, aryloxy, COOR V or
- c) for an aromatic hydrocarbon radical or for a 5- to 7-membered saturated or unsaturated hetero ring with 1 to 4 identical or different hetero members from the group O, S, -N =, NR I , this hetero ring either having a carbon atom or a Nitrogen atom is linked to the dihydropyridine ring, and wherein the aromatic hydrocarbon radical and the hetero rings optionally 1 to 3 identical or different substituents from the group halogen, OH, CN, CF 3 , OCF 3 , SCF 3 , NO 2 , alkyl, alkoxy, aryl and
- d) for the rest
- e) for the rest
where n ' , R 1' , R 2 ' , R 3' , R 5 ' , R 6' and R 7 'have the meaning given for n, R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 5 , R 6 and R 7 have and are the same or different from them, and R 4 * and R 4 ** are the same or different and each stand for a hydrogen-reduced radical of the substituents given for R 4 under a) to d), or - a) for hydrogen, NO 2 , NO, CN, SO m -R XI (m = 0, 1 or 2), halogen,
- R 2 and R 4 together form a branched, unbranched, saturated or unsaturated 5- to 8-membered ring which optionally 1, 2 or 3 identical or different ring members from the group O, CO, CS, C = NR I , = N -, NR I , SO m (m = 0, 1 or 2) or SiR II R III , and which is optionally substituted by halogen, hydroxy, alkoxy, aryl, aralkyl,
this common ring of R 2 and R 4 can also be fused directly to the common ring of R 1 and R 2 ,
where the radicals R I , R II , R III , R VII , R VIII have the meaning given below, - R 5 for R 4 has the meaning given and is different with R 4 equal to or from this, or
- R 5 and R 3 together form a ring which is the same as or different from the ring formed by R 2 and R 4 ,
- R 6 represents hydrogen, alkyl or haloalkyl, and
- R 7
- a) represents a saturated, unsaturated, cyclic, straight-chain or branched aliphatic hydrocarbon radical which is optionally substituted by halogen, aryl or heteroaryl, or
- b) represents an aryl or heteroaryl radical which may optionally have 1 to 5 identical or different substituents from the group No 2 , CN, N 3 , NO, CF3, halogen, COR IV , COOR V , OR VI
together with the nitrogen atom form a 5- to 7-membered ring which may contain 1 or 2 identical or different hetero ring members from the group O, S or NR I or
wherein one of the radicals R VIII or R VIII represents an aliphatic acyl group having up to 6 Kohlenstoffato- men, R IX, R X R XI, R XII and R XIII are in each case identical or different and represent alkyl, aryl or aralkyl,
wherein the alkyl, aryl, aralkyl, heteroaryl and acyl radicals mentioned under R 1 to R 8 and under R I to R XIII and the hetero ring formed with R VII and R VIII are in turn optionally substituted by OH, CF 3 , OCF 3 , CN, NO 2 , halogen, lower thioalkyl, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, aryl or aralkyl,
and the following substituents may be mentioned as heteroaryl:- Thienyl, furyl, pyryl, pyridyl, quinolyl, isoquinolyl, pyrimidyl, pyridazinyl, quinazolyl, quinoxalyl, benzothienyl, pyrazolyl, imidazolyl, Oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, triazolyl, oxydiazolyl, pyrazinyl, oxazinyl, thiazinyl, indolizinyl, indolyl, benzofuranyl, indazolyl, benzothienyl, benzimidazolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzothiazolyl, benztriazolyl, benzoxadiazolethyl, cinnamolethiazolethyl, cinnamolyziazolyl, benzoladiazolyl, methyltriazolyl, methyltriazolyl, methyltriazolyl, methyltriazole , Racemates and optical antipodes and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, for the production of medicaments with a positive inotropic effect, which are particularly suitable as cardiotonics. Increase influx into the cell and are therefore suitable for the treatment of hypotonic circulatory conditions, for lowering blood sugar, for the detumescence of mucous membranes and for influencing the salt and fluid balance - This contraction force enhancing effect and the fact that the compounds of the invention the Ca ++ is based.
Die Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (I) sind solche, die ab einer Konzentration von 10-5 g/ml am linken Vorhof des ilosierten Meerschweinchenherzens eine Kontraktionsverstärkung um mindestens 25% bewirken.The compounds of general formula (I), the contraction gain at least 25%, such effect at the left atrium of the guinea pig heart ilosierten from a concentration of 10- 5 g / ml.
Die linken Vorhöfe von Meerschweinchenherzen werden isoliert und in ein thermostatisiertes Organbad gehängt, welches eine isotonische Mineralsalzlösung, die dem lonenmilieu und dem pH-Wert von Körperflüssigkeiten angepasst ist und geeignete Nährstoffe enthält. Dieses Organbad wird mit einem Gasgemisch bestehend aus Sauerstoff und Kohlendioxyd begast, wobei der Kohlendioxydgehalt so bemessen ist, dass der pH-Wert des Organbades konstant bleibt. Die linken Vorhöfe werden in das Organbad eingespannt, die Spannung wird mittels eines Kraftaufnehmers registriert, wobei ein bestimmter Grundtonus eingestellt wird. Anschliessend werden die linken Vorhöfe kontinuierlich in bestimmten Abständen elektrisch gereizt und die dabei erfolgenden Kontraktionen registriert. Nach Zugabe des Wirkstoffs werden die Kontraktionen weiterhin registriert. Eine Kontraktionsverstärkung um mindestens 25% gilt als signifikante positiv-inotrope Wirkung.The left auricles of guinea pig hearts are isolated and hung in a thermostatted organ bath containing an isotonic mineral salt solution that is adapted to the ionic environment and the pH of body fluids and contains suitable nutrients. This organ bath is gassed with a gas mixture consisting of oxygen and carbon dioxide, the carbon dioxide content being such that the pH of the organ bath remains constant. The left atria are clamped into the organ bath, the tension is registered by means of a force transducer, whereby a certain basic tone is set. The left atria are then continuously electrically stimulated at certain intervals and the contractions that occur are registered. After adding the active ingredient, the contractions are still registered. A contraction gain of at least 25% is considered a significant positive inotropic effect.
Die erfindungsgemässen Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (I) können nach üblichen Methoden auf verschiedene Weise hergestellt werden. Ihre Synthese erfolgt z. B.
- A) durch direkten Aufbau der die Hydropyridinstruktur nach bekannten Dihydropyridinsynthesen oder
- B) durch Umwandlung von funktionellen Gruppen am Dihydropyridingerüst nach bekannten Reaktionsschemen.
- A) by direct construction of the hydropyridine structure according to known dihydropyridine synthesis or
- B) by converting functional groups on the dihydropyridine skeleton according to known reaction schemes.
Der Aufbau der 1,4-Dihydropyridin-Grundstruktur kann erfolgen, indem man
- a) Carbonylverbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (II)
- mit Ketonen der Formel (Ill) und (IV)
- und primären Aminen der Formel (V)
- gegebenenfalls in Gegenwart von inerten Lösungsmitteln umsetzt, oder
- mit Ketonen der Formel (Ill) und (IV)
- b) Carbonylverbindungen der Formel (II)
- mit Enaminen der Formel (VI)
- Ketonen der Formel (IV)
- gegebenenfalls in Gegenwart von inerten Lösungsmitteln umsetzt oder
- mit Enaminen der Formel (VI)
- c) Enamine der Formel (VI)
- mit Ylidenverbindungen der Formel (VII)
- gegebenenfalls in Gegenwart von inerten Lösungsmitteln umsetzt.
- mit Ylidenverbindungen der Formel (VII)
- a) carbonyl compounds of the general formula (II)
- with ketones of the formula (III) and (IV)
- and primary amines of the formula (V)
- if appropriate in the presence of inert solvents, or
- with ketones of the formula (III) and (IV)
- b) carbonyl compounds of the formula (II)
- with enamines of the formula (VI)
- Ketones of formula (IV)
- if appropriate in the presence of inert solvents or
- with enamines of the formula (VI)
- c) enamines of the formula (VI)
- with ylidene compounds of the formula (VII)
- if appropriate in the presence of inert solvents.
- with ylidene compounds of the formula (VII)
Durch Umwandlung einer oder mehrerer funktioneller Gruppen bekannter Dihydropyridine oder auch neuer Dihydropyridine die gemäss Verfahren A) a) bis c) erhalten wurden, können ebenfalls erfindungsgemäss Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (I) nach üblichen Methoden hergestellt werden (vgl. Houben-Weyl, Methoden der Organischen Chemie, Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 1966; Organicum, VEB Deutscher Verlag der Wissenschaften, Berlin 1969; W. Foerst, Neuere Methoden der präparativen organischen Chemie, Bd. 1-5, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim 1961; C. Ferri, Reaktionen der organischen Chemie, Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 1978; Fieser+Fieser, Reagents for Organic Synthesis, Vol. 1-8, J. Wiley & Sons, Inc., London 1967.By converting one or more functional groups of known dihydropyridines or also new dihydropyridines which according to the method ren A) a) to c), compounds of the general formula (I) can also be prepared according to the invention by customary methods (cf. Houben-Weyl, Methods of Organic Chemistry, Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 1966; Organicum, VEB Deutscher Verlag der Wissenschaften, Berlin 1969; W. Foerst, Newer Methods in Preparative Organic Chemistry, Vol. 1-5, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim 1961; C. Ferri, Reactions in Organic Chemistry, Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 1978; Fieser + Fieser, Reagents for Organic Synthesis, Vol. 1-8, J. Wiley & Sons, Inc., London 1967.
Als bevorzugte Umwandlungsreaktionen seien genannt: sauer oder basisch katalysierte Hydrolyse, Veresterung oder Umesterung, Lactamisierung, Kondensation, Acylierung, Reduktion oder Cyclisierung mit jeweils geeigneten Reaktionspartnern oder intramolekularer Art. Als besonders vorteilhaft sei die Lactonisierung erwähnt. Hierzu werden Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (I), in denen die Substituenten R2 und R4 oder/und R3 und R5 freie und/oder durch Schutzgruppen blokkierte Hydroxyl- und Carbonsäurefunktionen enthalten, unter geeigneten basisch oder sauer katalysierten Reaktionsbedingungen, gegebenenfalls unter vorhergehender ganz- oder teilweiser Abspaltung der Schutzgruppen, zu erfindungsgemässen Lactonen der allgemeinen Formel (I) cyclisiert.The following are preferred conversion reactions: acid or base-catalyzed hydrolysis, esterification or transesterification, lactamization, condensation, acylation, reduction or cyclization with in each case suitable reaction partners or intramolecular type. Lactonization should be mentioned as particularly advantageous. For this purpose, compounds of the general formula (I) in which the substituents R 2 and R 4 or / and R 3 and R 5 contain free and / or hydroxyl and carboxylic acid functions blocked by protective groups, under suitable base or acid-catalyzed reaction conditions, optionally under previous complete or partial removal of the protective groups, cyclized to lactones according to the invention of the general formula (I).
In der deutschen Offenlegungsschrift Nr. 2629892 werden einige der möglichen Herstellungsmethoden ausführlicher beschrieben.In German Offenlegungsschrift No. 2629892, some of the possible production methods are described in more detail.
Bevorzugt seien Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (I) genannt, in welcher n für 0, 1 oder 2 steht,
- R'
- a) für Wasserstoff, einen geradkettigen, verzweigten, cyclischen gesättigten oder ungesättigten aliphatischen Kohlenwasserstoffrest mit bis zu 10 C-Atomen steht der gegebenenfalls 1 oder 2 gleiche oder verschiedene Heterokettenglieder aus der Gruppe 0, CO, S, S02, =N- oder NR' enthält und wobei dieser Kohlenwasserstoffrest gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch Halogen, N02, CN, N3, Hydroxy, mit 1 bis 4 C-Atomen, Phenyl, Naphthyl oder Heteroaryl oder
- b) für einen Phenyl-, Naphthyl- oder Heteroarylrest steht, wobei diese Reste gegebenenfalls 1 bis 3 gleiche oder verschiedene Substituenten aus der Gruppe Phenyl, Alkyl, Alkenyl, Alkinyl, Alkenoxy, Alkinoxy mit jeweils bis zu 4 C-Atomen, Aralkyl mit 7 bis 14 C-Atomen, Acyl mit bis zu 6 C-Atomen, Alkylen, Dioxyalkylen mit bis zu 4 Kohlenstoffatomen in der Alkylenkette, Halogen, CF3, OCF3, SCF3, NO2, CN, N3, CORIV, COORV, ORVI, NRI oder NRVIIRVIII tragen, wobei die Alkyl-, Alkoxy-und Arylreste der oben genannten Substituenten ihrerseits wieder durch Halogen, COORV oder NRVIIRVIII substituiert sein können oder
- c) für den Rest NRVIIRI steht,
und wobei die unter a), b) und c) genannten Reste RI, RII, RIII, RIV, RV, RVI, RVII und RVIII die unten angegebene Bedeutung haben, - R2 ein
- a) für einen der unter R1 angegebenen Substituenten steht aber nicht mit diesen identisch sein muss oder
- b) für die Reste NHR' oder
wobei RI, RIX und RX die unten angegebene Bedeutung besitzen,
oder die Substituenten - R1 und R2 gemeinsam einen 5- bis 7-gliedrigen gesättigten oder ungesättigten Ring bilden, der gegebenenfalls ein oder zwei gleiche oder verschiedene Ringglieder aus der Gruppe 0, S, NRI oder CO enthält und der gegebenenfalls ein bis drei gleiche oder verschiedene Substituenten aus der Gruppe Halogen, Hydroxy, Alkyl, Alkoxy mit jeweils 1 bis 4 C-Atomen, Phenyl, Naphthyl oder Aralkyl mit 7 bis 14 C-Atomen enthält,
- R3 für einen der unter R2 angegebenen Substituenten steht und mit diesem gleich oder von diesem verschieden ist, wobei nur einer der beiden Substituenten R2 oder R3 jeweils für Alkoxy, Alkylthio, oder NHR' steht,
- R4
- a) für Wasserstoff, NO2, NO, CN, SOm-RIX (m = 0 oder 2), Halogen,
- b) für einen verzweigten oder unverzweigten, cyclischen, gesättigten oder ungesättigten aliphatischen Kohlenwasserstoffrest mit bis zu 10 C-Atomen steht, der gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch Halogen, OH, CN, Alkoxy, Alkylthio mit jeweils 1 bis 4 Kohlenstoffatomen, Phenyloxy, Naphthoxy, COORV oder
- c) für einen aromatischen Kohlenwasserstoffrest mit 6 bis 10 C-Atomen oder für einen 5- bis 7-gliedrigen gesättigten oder ungesättigten Heteroring mit 1 bis 3 gleichen oder verschiedenen Heterogliedern aus der Gruppe 0, S, -N=, NRI, wobei dieser Heteroring entweder über ein Kohlenstoffatom oder ein Stickstoffatom mit dem Dihydropyridinring verknüpft ist, und wobei der aromatische Kohlenwasserstottrest und die Heteroringe gegebenenfalls 1 bis 3 gleiche oder verschiedene Substituenten aus der Gruppe Halogen, OH, CN, CF3, OCF3, SCF3, NO2, Alkyl, Alkoxy mit jeweils 1 bis 4 C-Atomen, Phenyl, Naphthyl und tragen,
- c) für den Rest
- e) für den Rest
wobei n', R1', R2', R3', R5', R6' und R7' die für n, Rl, R2, R3, R5, R6 und R7 angegebene Bedeutung haben und mit diesen gleich oder von diesen verschieden sind, und - a) für Wasserstoff, NO2, NO, CN, SOm-RIX (m = 0 oder 2), Halogen,
- R4' und R4** gleich oder verschieden sind und jeweils für einen um ein Wasserstoff verminderten Rest der für R4 unter a) bis d) angegebenen Substituenten stehen, oder
- R2 und R4 gemeinsam einen verzweigten, unverzweigten, gesättigten oder ungesättigten 5- bis 7-gliedrigen Ring bilden, der gegebenenfalls 1, 2 oder 3 gleiche oder verschiedene Ringglieder aus der Gruppe 0, CO, CS, C=NRI, =N-, NRI oder SOm (m = 0 oder 2) enthält und der gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch Halogen, Hydroxy, Alkoxy mit 1 bis 4 C-Atomen, Phenyl, Naphthyl, Aralkyl mit 7 bis 14 C-Atomen,
- R5 die für R4 angegebene Bedeutung besitzt und mit R4 gleich oder von diesem verschieden ist,
- R6 für Wasserstoff, Alkyl oder Halogenalkyl mit jeweils 1 bis 4 C-Atomen steht und
- R7
- a) für einen gesättigten, ungesättigten cyclischen, geradkettigen oder verzweigten aliphatischen Kohlenwasserstoffrest mit bis zu 10 C-Atomen steht, der gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch Halogen, Phenyl, Naphthyl oder Heteroaryl oder
- b) einen Phenyl-, Naphthyl- oder Heteroarylrest steht, der gegebenenfalls 1 bis 3 gleiche oder verschiedene Substituenten aus der Gruppe N02, Halogen, CN, N3, NO, CF3, CORIV, COORV, ORVI,
- RVII, RV und RVI jeweils gleich oder verschieden sind und für Wasserstoff, Alkyl mit 1 bis 6 C-Atomen, Phenyl, Naphthyl, Aralkyl mit 7 bis 12 C-Atomen oder Heteroaryl stehen,
- RVII und RVIII jeweils gleich oder verschieden sind und für Wasserstoff, Phenyl, Naphthyl oder Aralkyl mit 7 bis 12 C-Atomen stehen oder für Alkyl mit 1 bis 6 C-Atomen, welches gegebenenfalls durch 0, S oder NR1 unterbrochen ist, stehen oder gemeinsam mit dem Stickstoffatom einen 5- bis 7-gliedrigen Ring bilden, der 1 oder 2 gleiche oder verschiedene Heteroringglieder aus der Gruppe 0, S oder NR' enthalten kann oder
- wobei einer der Reste RVII und RVIII eine aliphatische Acylgruppe mit bis zu 6 Kohlenstoffatomen steht,
- RIX, RX, RXII und RXIII jeweils gleich oder verschieden sind und für Alkyl mit 1 bis 6 C-Atomen, Phenyl, Naphthyl oder Aralkyl mit 7 bis 12 C-Atomen stehen,
- wobei die unter R1 bis R8 und unter RI bis RVIII genannten Alkyl-, Aryl-, Aralkyl-, Heteroaryl- und Acylreste sowie der mit R6 und R7 gebildete Heteroring ihrerseits gegebenenfalls substituiert sind durch OH, CF3, OCF3, CN, NO2, Halogen, Alkyl mit 1 bis 4 C-Atomen, Alkoxy mit 1 bis 4 C-Atomen, Phenyl- oder Benzyl
und wobei als Heteroaryl folgende Substituenten genannt seien:- Thienyl, Furyl, Pyryl, Pyridyl, Chinolyl, Isochinolyl, Pyrimidyl, Pyridazinyl, Chinazolyl, Chinoxalyl, Benzothienyl, Pyrazolyl, Imidazolyl, Oxazolyl, Isoxazolyl, Thiazolyl, Triazolyl, Oxydiazolyl, Pyrazinyl, Oxazinyl, Thiazinyl, Indolizinyl, Indolyl, Benzofuranyl, Indazolyl, Benzothienyl, Benzimidazolyl, Benzoxazolyl, Benzisoxazolyl, Benzthiazolyl, Benztriazolyl, Benzoxadiazolyl, Cinnolinyl, Phthalazinyl, Naphthyridinyl oder Benzotriazinyl, in Form von Isomeren, Isomerengemischen, Racematen und optischen Antipoden sowie ihrer pharmazeutisch unbedenklichen Salze.
- R '
- a) for hydrogen, a straight-chain, branched, cyclic saturated or unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbon radical with up to 10 carbon atoms, the optionally 1 or 2 identical or different hetero chain links from the group 0, CO, S, S0 2 , = N or NR 'contains and wherein this hydrocarbon radical is optionally substituted by halogen, N0 2 , CN, N 3 , hydroxy, having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, phenyl, naphthyl or heteroaryl or
- b) represents a phenyl, naphthyl or heteroaryl radical, these radicals optionally 1 to 3 identical or different substituents from the group phenyl, alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, alkenoxy, alkynoxy each having up to 4 carbon atoms, aralkyl having 7 up to 14 carbon atoms, acyl with up to 6 carbon atoms, alkylene, dioxyalkylene with up to 4 carbon atoms in the alkylene chain, halogen, CF3, OCF 3 , SCF 3 , NO 2 , CN, N 3 , COR IV , COOR V , OR VI , NR I or NR VII R VIII , where the alkyl, alkoxy and aryl radicals of the above-mentioned substituents can in turn be substituted by halogen, COOR V or NR VII R VIII or
- c) represents the rest of NR VII R I ,
and where the radicals R I , R II , R III , R IV , R V , R VI , R VII and R VIII mentioned under a), b) and c) have the meaning given below, - R 2 a
- a) stands for one of the substituents specified under R 1 but need not be identical with them or
- b) for the residues NHR 'or
where R I , R IX and R X have the meaning given below,
or the substituents - R 1 and R 2 together form a 5- to 7-membered saturated or unsaturated ring which optionally contains one or two identical or different ring members from the group 0, S, NR I or CO and which optionally contains one to three identical or different substituents contains from the group halogen, hydroxy, alkyl, alkoxy, each with 1 to 4 carbon atoms, phenyl, naphthyl or aralkyl with 7 to 14 carbon atoms,
- R 3 represents one of the substituents specified under R 2 and is identical to or different from this, only one of the two substituents R 2 or R 3 each representing alkoxy, alkylthio or NHR ',
- R4
- a) for hydrogen, NO 2 , NO, CN, SOm-R IX (m = 0 or 2), halogen,
- b) represents a branched or unbranched, cyclic, saturated or unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbon radical having up to 10 carbon atoms, which is optionally substituted by halogen, OH, CN, alkoxy, alkylthio each having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, phenyloxy, naphthoxy, COOR V or
- c) for an aromatic hydrocarbon radical with 6 to 10 carbon atoms or for a 5- to 7-membered saturated or unsaturated hetero ring with 1 to 3 identical or different hetero members from the group 0, S, -N =, NR I , where this Heteroring is linked to the dihydropyridine ring either via a carbon atom or a nitrogen atom, and wherein the aroma Tische Hydrostottrest and the hetero rings optionally 1 to 3 identical or different substituents from the group halogen, OH, CN, CF 3 , OCF 3 , SCF 3 , NO 2 , alkyl, alkoxy, each with 1 to 4 carbon atoms, phenyl, naphthyl and wear,
- c) for the rest
- e) for the rest
where n ', R 1' , R 2 ' , R 3' , R 5 ' , R 6' and R 7 'have the meaning given for n, R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 5 , R 6 and R 7 have and are the same as or different from them, and - a) for hydrogen, NO 2 , NO, CN, SOm-R IX (m = 0 or 2), halogen,
- R 4 ' and R 4 ** are the same or different and each represent a hydrogen-reduced radical of the substituents given for R 4 under a) to d), or
- R 2 and R 4 together form a branched, unbranched, saturated or unsaturated 5- to 7-membered ring which may contain 1, 2 or 3 identical or different ring members from the group 0, CO, CS, C = NR I , = N -, NR I or SO m (m = 0 or 2) and which is optionally substituted by halogen, hydroxy, alkoxy with 1 to 4 carbon atoms, phenyl, naphthyl, aralkyl with 7 to 14 carbon atoms,
- R 5 has the meaning given for R 4 and is identical to or different from R 4 ,
- R 6 represents hydrogen, alkyl or haloalkyl each having 1 to 4 carbon atoms and
- R 7
- a) represents a saturated, unsaturated cyclic, straight-chain or branched aliphatic hydrocarbon radical having up to 10 carbon atoms, which is optionally substituted by halogen, phenyl, naphthyl or heteroaryl or
- b) a phenyl, naphthyl or heteroaryl radical which may optionally have 1 to 3 identical or different substituents from the group NO 2 , halogen, CN, N 3 , NO, CF 3 , COR IV , COOR V , OR VI ,
- R VII , R V and R VI are each the same or different and represent hydrogen, alkyl having 1 to 6 C atoms, phenyl, naphthyl, aralkyl having 7 to 12 C atoms or heteroaryl,
- R VII and R VIII are in each case identical or different and represent hydrogen, phenyl, naphthyl or aralkyl with 7 to 12 C atoms or for alkyl with 1 to 6 C atoms, which is optionally interrupted by 0, S or NR 1 , stand or together with the nitrogen atom form a 5- to 7-membered ring which may contain 1 or 2 identical or different hetero ring members from the group 0, S or NR 'or
- where one of the radicals R VII and R VIII is an aliphatic acyl group having up to 6 carbon atoms,
- R IX , R X , R XII and R XIII are each the same or different and represent alkyl with 1 to 6 C atoms, phenyl, naphthyl or aralkyl with 7 to 12 C atoms,
- wherein the alkyl, aryl, aralkyl, heteroaryl and acyl radicals mentioned under R 1 to R 8 and under R I to R VIII and the hetero ring formed with R 6 and R 7 are in turn optionally substituted by OH, CF 3 , OCF 3 , CN, NO 2 , halogen, alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, alkoxy having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, phenyl or benzyl
and the following substituents may be mentioned as heteroaryl:- Thienyl, furyl, pyryl, pyridyl, quinolyl, isoquinolyl, pyrimidyl, pyridazinyl, quinazolyl, quinoxalyl, benzothienyl, pyrazolyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, triazolyl, oxydiazolyl, pyrazinyl, oxazinyl, indiazyl, thiazolyl Benzothienyl, benzimidazolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzisoxazolyl, benzthiazolyl, benztriazolyl, benzoxadiazolyl, cinnolinyl, phthalazinyl, naphthyridinyl or benzotriazinyl, in the form of isomers, isomer mixtures, racemates and optical antipodes and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts.
Von besonderem Interesse sind Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (I), in welcher
- n für 0 oder 1 steht,
- R1
- a) für Wasserstoff, einen geradkettigen, verzweigten cyclischen gesättigten oder ungesättigten aliphatischen Kohlenwasserstoffrest mit bis zu 10 C-Atomen steht, der gegebenenfalls durch ein oder zwei gleiche oder verschiedene Heterokettenglieder aus der Gruppe 0, CO, S, = N- oder NR' enthält und wobei dieser Kohlenwasserstoffrest gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch F, CI, Br, N02, CN, OH, Phenyl oder Pyridyl oder
- b) für einen Phenyl-, Naphthyl- oder Pyridylrest steht, wobei diese Reste gegebenenfalls 1 oder 2 gleiche oder verschiedene Substituenten aus der Gruppe Phenyl, Alkyl, Alkenyl, Alkoxy, Alkenoxy mit jeweils bis zu 4 C-Atomen, Benzyl, Acetyl, Alkylen, Dioxyalkylen mit 2 bis 4 C-Atomen, Fluor, Chlor, Brom, CF3, OCF3, SCF3, NO2, CN, COORV, ORVI, NRI oder NRVIIRVIII tragen, wobei die Alkyl-, Alkoxy- und Arylreste der o.g. Substituenten ihrerseits wieder Halogen substituiert sein können oder
- c) für den Rest NRVIIRVIII steht,
und wobei die unter a), b) und c) genannten Reste RI bis RVIII die unten angegebene Bedeutung haben, - R2 a) für einen der unter R1 angegebenen Substituenten steht aber nicht mit diesen identisch sein muss oder
- b) für die Reste NHRI oder
steht,
wobei RI, RIX und RX die unten angegebene Bedeutung besitzen
oder die Substituenten - R1 und R2 gemeinsam einen 5- bis 7-gliedrigen gesättigten oder ungesättigten Ring bilden, der gegebenenfalls 1 oder 2 gleiche oder verschiedene Ringglieder aus der Gruppe 0, S, NRI oder CO enthält und der gegebenenfalls 1 oder 2 gleiche oder verschiedene Substituenten aus der Gruppe Halogen, Hydroxy, Alkyl, Alkoxy mit je 1 bis 4 C-Atomen, Phenyl oder Benzyl enthält,
- R3 für einen der unter R2 angegebenen Substituenten steht und mit diesem gleich oder von diesem verschieden ist, wobei nur einer der beiden Substituenten R2 oder R3 jeweils für Alkoxy, Alkylthio oder NHR' steht,
- R4 a) für Wasserstoff, NO2, CN, SRXI, SO2RXI,
- b) für einen verzweigten oder unverzweigten Alkyl- oder Cycloalkylrest mit bis zu 8 C-Atomen steht, der gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch Halogen, Hydroxy, Cyano, Alkoxy mit 1 bis 4 C-Atomen, Phenyloxy, COORV oder
- c) für einen aromatischen Kohlenwasserstoffrest mit 6 bis 10 C-Atomen oder für einen 5- bis 7-gliedrigen gesättigten oder ungesättigten Heteroring mit 1 bis 3 gleichen oder verschiedenen Heterogliedern aus der Gruppe 0, S, =N-, NRI, wobei dieser Heteroring entweder über ein Kohlenstoffatom oder ein Stickstoffatom mit dem Dihydropyridinring verknüpft ist und wobei der aromatische Kohlenwasserstoffrest und die Heteroringe gegebenenfalls 1 oder 2 gleiche oder verschiedene Substituenten aus der Gruppe Halogen, Hydroxy, Cyano, CF3, NO2, Phenyl, Alkyl und Alkoxy mit je 1 bis 4 C-Atomen tragen,
oder - d) für den Rest
oder
- b) für einen verzweigten oder unverzweigten Alkyl- oder Cycloalkylrest mit bis zu 8 C-Atomen steht, der gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch Halogen, Hydroxy, Cyano, Alkoxy mit 1 bis 4 C-Atomen, Phenyloxy, COORV oder
- R4* und R4** gleich oder verschieden sind und jeweils für einen um ein Wasserstoff verminderten Rest der für R4 unter a) bis d) angegebenen Substituenten stehen, oder
- R2 und R4 gemeinsam einen verzweigten unverzweigten, gesättigten oder ungesättigten 5- bis 7-gliedrigen Ring bilden, der gegebenenfalls 1 oder 2 gleiche oder verschiedene Ringglieder aus der Gruppe 0, CO, CS, C=NRI, =N- oder NR' enthält und der gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch Halogen oder Hydroxy,
- wobei R1 die unten angegebene Bedeutung hat,
- R5 die für R4 angegebene Bedeutung besitzt und mit R4 gleich oder von diesen verschieden ist oder
- R5 und R3 gemeinsam einen Ring bilden, wie er für R2 und R4 definiert ist und mit diesem gleich oder von diesem verschieden ist,
- R6 für Wasserstoff oder Alkyl mit 1 bis 4 C-Atomen steht, welches gegebenenfalls durch Fluor, Chlor oder Brom substituiert ist und
- R 7
- a) für einen gesättigten, ungesättigten cyclischen, geradkettigen oder verzweigten aliphatischen Kohlenwasserstoffrest mit bis zu 8 C-Atomen steht, der gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch Halogen, oder
- b) für einen Phenyl- oder Heteroarylrest steht, der gegebenenfalls 1 bis 3 gleiche oder verschiedene Substituenten aus der Gruppe N02, CN, N3, CF3, Halogen, CORIV, CORV, ORVI, SRXI,
wobei in den vorgenannten Definitionen der Substituenten R1 bis R8 - R' für Wasserstoff, Alkyl mit 1 bis 6 C-Atomen, Phenyl, Naphthyl, Benzyl, Phenethyl, Heteroaryl oder Acyl mit bis zu 4 C-Atomen steht,
- RII und RIII gleich oder verschieden sind und jeweils für Alkyl mit 1 bis 6 C-Atomen, Phenyl, Naphthyl, Benzyl oder Heteroaryl stehen,
- RIV, RV und RVI jeweils gleich oder verschieden sind und für Wasserstoff, Alkyl mit 1 bis 6 C-Atomen, Phenyl, Naphthyl, Benzyl oder Heteroaryl stehen,
- RVII und RVIII die jeweils gleich oder verschieden sind und für Wasserstoff, Phenyl oder Benzyl stehen oder für Alkyl mit 1 bis 6 Kohlenstoffatomen stehen, welches gegebenenfalls durch 0 oder NR1 unterbrochen ist, oder
gemeinsam mit dem Stickstoffatom einen 5- bis 7-gliedrigen Ring bilden, der 1 oder 2 gleiche verschiedene Heteroringglieder aus der Gruppe 0, S oder NR' enthalten kann,
oder
wobei einer der Reste RVII oder RVIII für eine aliphatische Acylgruppe mit bis zu 6 Kohlenstoffatomen steht und - RIX, RX, RXI, RXII und RXIII jeweils gleich oder verschieden sind und für Alkyl mit 1 bis 6 C-Atomen, Phenyl oder Benzyl stehen,
wobei als Heteroaryl folgende Substituenten genannt seien:- Thienyl, Furyl, Pyryl, Pyridyl, Chinolyl, Isochinolyl, Pyrimidyl, Pyridazinyl, Chinazolyl, Chinoxalyl, Benzothienyl, Pyrazolyl, Imidazolyl, Oxazolyl, Isoxazolyl, Thiazolyl, Triazolyl, Oxydiazolyl, Pyrazinyl, Oxazinyl, Thiazinyl, Indolyl, Benzofuranyl, Indazolyl, Benzothienyl, Benzimidazolyl, Benzoxazolyl, Benzisoxazolyl, Benzthiazolyl, Benztriazolyl, oder Benzoxadiazolyl.
- b) für die Reste NHRI oder
- R1
- n represents 0 or 1,
- R 1
- a) represents hydrogen, a straight-chain, branched cyclic saturated or unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbon radical having up to 10 carbon atoms, which optionally contains one or two identical or different hetero chain links from the group 0, CO, S, = N or NR ' and wherein this hydrocarbon radical is optionally substituted by F, CI, Br, N0 2 , CN, OH, phenyl or pyridyl or
- b) represents a phenyl, naphthyl or pyridyl radical, these radicals optionally 1 or 2 identical or different substituents from the group phenyl, alkyl, alkenyl, alkoxy, alkenoxy each having up to 4 carbon atoms, benzyl, acetyl, alkylene , Dioxyalkylene with 2 to 4 carbon atoms, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, CF 3 , OCF 3 , SCF 3 , NO 2 , CN, COOR V , OR VI , NR I or NR VII R VIII , the alkyl, Alkoxy and aryl radicals of the abovementioned substituents can in turn be halogen substituted or
- c) represents the radical NR VII R VIII ,
and wherein the radicals R I to R VIII mentioned under a), b) and c) have the meaning given below, - R 2 a) stands for one of the substituents specified under R 1 but need not be identical to them or
- b) for the residues NHR I or
stands,
where R I , R IX and R X have the meaning given below
or the substituents - R 1 and R 2 together form a 5- to 7-membered saturated or unsaturated ring which optionally contains 1 or 2 identical or different ring members from the group 0, S, NR I or CO and which optionally 1 or 2 identical or different substituents contains from the group halogen, hydroxy, alkyl, alkoxy, each with 1 to 4 carbon atoms, phenyl or benzyl,
- R 3 represents one of the substituents indicated under R 2 and is identical to or different from this, only one of the two substituents R 2 or R 3 each representing alkoxy, alkylthio or NHR ',
- R 4 a) for hydrogen, NO 2 , CN, SR XI , SO 2 R XI ,
- b) represents a branched or unbranched alkyl or cycloalkyl radical having up to 8 carbon atoms, which is optionally substituted by halogen, hydroxy, cyano, alkoxy having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, phenyloxy, COOR V or
- c) for an aromatic hydrocarbon radical with 6 to 10 carbon atoms or for a 5- to 7-membered saturated or unsaturated hetero ring with 1 to 3 identical or different hetero members from the group 0, S, = N-, NR I , where this Heteroring is linked to the dihydropyridine ring either via a carbon atom or a nitrogen atom and the aromatic hydrocarbon radical and the hetero rings optionally have 1 or 2 identical or different substituents from the group consisting of halogen, hydroxy, cyano, CF 3 , NO 2 , phenyl, alkyl and alkoxy each carry 1 to 4 carbon atoms,
or - d) for the rest
or
- b) represents a branched or unbranched alkyl or cycloalkyl radical having up to 8 carbon atoms, which is optionally substituted by halogen, hydroxy, cyano, alkoxy having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, phenyloxy, COOR V or
- R 4 * and R 4 ** are the same or different and each represent a hydrogen-reduced radical of the substituents given for R 4 under a) to d), or
- R 2 and R 4 together form a branched unbranched, saturated or unsaturated 5- to 7-membered ring, which optionally 1 or 2 identical or different ring members from the group 0, CO, CS, C = NR I , = N or NR contains and which is optionally substituted by halogen or hydroxy,
- where R 1 has the meaning given below,
- R 5 has the meaning given for R 4 and is identical to or different from R 4 or
- R 5 and R 3 together form a ring as it is defined for R 2 and R 4 and is identical to or different from it,
- R 6 represents hydrogen or alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, which is optionally substituted by fluorine, chlorine or bromine and
- R 7
- a) represents a saturated, unsaturated cyclic, straight-chain or branched aliphatic hydrocarbon radical having up to 8 C atoms, which is optionally substituted by halogen, or
- b) represents a phenyl or heteroaryl radical which may optionally have 1 to 3 identical or different substituents from the group NO 2 , CN, N 3 , CF 3 , halogen, COR IV , COR V , OR VI , SR XI ,
where in the aforementioned definitions of the substituents R 1 to R 8 - R 'represents hydrogen, alkyl having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, phenyl, naphthyl, benzyl, phenethyl, heteroaryl or acyl having up to 4 carbon atoms,
- R II and R III are the same or different and each represents alkyl having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, phenyl, naphthyl, benzyl or heteroaryl,
- R IV , R V and R VI are each the same or different and represent hydrogen, alkyl having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, phenyl, naphthyl, benzyl or heteroaryl,
- R VII and R VIII are each the same or different and represent hydrogen, phenyl or benzyl or represent alkyl having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, which is optionally interrupted by 0 or NR 1 , or
together with the nitrogen atom form a 5- to 7-membered ring which can contain 1 or 2 identical hetero ring members from the group 0, S or NR ',
or
wherein one of the radicals R VII or R VIII stands for an aliphatic acyl group with up to 6 carbon atoms and - R IX , R X , R XI , R XII and R XIII are each the same or different and represent alkyl having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, phenyl or benzyl,
the following substituents may be mentioned as heteroaryl:- Thienyl, furyl, pyryl, pyridyl, quinolyl, isoquinolyl, pyrimidyl, pyridazinyl, quinazolyl, quinoxalyl, benzothienyl, pyrazolyl, imidazolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, triazolyl, oxydiazolyl, pyrazinyl, oxazanyyl, indazolylyl, indazolylyl, indazolylyl, indazolylyl, indazolylyl, indazolylyl, indazolylylazolyl, indazolylylazolyl, indazazolyl, benzazylyl, indazylyl, benzazylyl, indazylyl, indazylyl Benzimidazolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzisoxazolyl, benzthiazolyl, benztriazolyl, or benzoxadiazolyl.
- b) for the residues NHR I or
- R 1
Insbesondere seien Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (I) genannt, in welcher n für 0 steht,
- R1
- a) für Wasserstoff, einen aliphatischen Kohlenwasserstoffrest mit bis zu 6 C-Atomen, der gegebenenfalls ein Heterokettenglied aus der Gruppe 0, CO, = N- oder NR' enthält und der gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch Halogen, Nitro, Hydroxy oder Phenyl oder
- b) für einen Phenyl- oder Pyridylrest steht, die gegebenenfalls substituiert sind durch Halogen, NO2, CFa, OCF3, CN, COORV oder NRVIIRVIII,
- R2 für einen der unter R1 angegebenen Substituenten steht, aber nicht mit diesem identisch sein muss oder für einen der Reste NHR' oder N = CRXRXI steht,
- R3 für einen der unter R2 angegebenen Substituenten steht und mit diesem gleich oder von diesem verschieden ist,
- R 4
- a) für Wasserstoff, NO2, NRVIIRVIII, NH-CO-NRVIIRVIII oder Halogen steht, oder
- b) für einen Alkylrest mit 1 bis 4 C-Atomen steht, der gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch Halogen, OH, CN, Alkoxy mit 1 bis 4 C-Atomen, COORV oder NRVIIRVIII oder
- c) für Phenyl, Pyridyl oder Thienyl steht, die gegebenenfalls substituiert sind durch Halogen, OH, CN, Alkyl oder Alkoxy mit jeweils 1 bis 4 C-Atomen oder durch NRVIIRVIII oder
- d) für den Rest
- wobei X Sauerstoff bedeutet und Y für eine einfache Bindung, Sauerstoff oder NRI steht und R8 die für R1 angegebene Bedeutung hat und mit dem Substituenten R1 gleich oder von diesem verschieden ist oder
- R4* und R4** gleich oder verschieden sind und jeweils für einen um ein Wasserstoff verminderten Rest der für R4 unter a) bis d) angegebenen Substituenten stehen, oder
- R2 und R4 gemeinsam einen 5- bis 7-gliedrigen Ring bilden, der gegebenenfalls 1 oder 2 verschiedene Ringglieder aus der Gruppe O, CO, CS oder C=NR' enthält und der gegebenenfalls substituiert ist durch Halogen,
- R5 die für R4 angegebene Bedeutung besitzt und mit R4 gleich oder von diesem verschieden ist,
- R6 für Wasserstoff oder Alkyl mit 1 bis 4 C-Atomen steht und R7 die oben angegebene Bedeutung besitzt,
wobei in den vorgenannten Definitionen die mit römischen Ziffern gekennzeichneten Substituenten RI bis RVIII die oben angegebene Bedeutung besitzen.Compounds of the general formula (I) in which n is 0
- R 1
- a) for hydrogen, an aliphatic hydrocarbon radical with up to 6 carbon atoms, which optionally contains a hetero chain link from the group 0, CO, = N- or NR 'and which is optionally substituted by halogen, nitro, hydroxy or phenyl or
- b) represents a phenyl or pyridyl radical which are optionally substituted by halogen, NO 2 , CF a , OCF 3 , CN, COOR V or NR VII R VIII ,
- R 2 stands for one of the substituents given under R 1 , but need not be identical to it, or stands for one of the radicals NHR 'or N = CR X R XI ,
- R 3 represents one of the substituents indicated under R 2 and is identical to or different from this,
- R 4
- a) represents hydrogen, NO 2 , NR VII R VIII , NH-CO-NR VII R VIII or halogen, or
- b) represents an alkyl radical with 1 to 4 carbon atoms, which is optionally substituted by halogen, OH, CN, alkoxy with 1 to 4 carbon atoms, COOR V or NR VII R VIII or
- c) represents phenyl, pyridyl or thienyl, which are optionally substituted by halogen, OH, CN, alkyl or alkoxy each having 1 to 4 carbon atoms or by NR VII R VIII or
- d) for the rest
- where X is oxygen and Y is a simple bond, oxygen or NR I and R 8 has the meaning given for R 1 and is the same as or different from the substituent R 1 or
- R 4 * and R 4 ** are the same or different and each represent a hydrogen-reduced radical of the substituents given for R 4 under a) to d), or
- R 2 and R 4 together form a 5- to 7-membered ring which optionally contains 1 or 2 different ring members from the group O, CO, CS or C = NR 'and which is optionally substituted by halogen,
- R 5 has the meaning given for R 4 and is identical to or different from R 4 ,
- R 6 represents hydrogen or alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms and R 7 has the meaning given above,
wherein in the above definitions, the substituents R I to R VIII marked with Roman numerals have the meaning given above.
Besonders hervorgehoben seien Verbindungen, in denen wenigstens einer der Substituenten R4 und R5 für NO2 stehen,
und/oder
in denen R2 und R4 gemeinsam oder R3 und R5 gemeinsam einen Lactonring bilden.Particular emphasis is given to compounds in which at least one of the substituents R 4 and R 5 is NO 2 ,
and or
in which R 2 and R 4 together or R 3 and R 5 together form a lactone ring.
Die Herstellung der erfindungsgemässen 1,4-Dihydropyridinderivate mit positiv inotroper Wirkung erfolgt nach üblichen Methoden, die für die Herstellung von 1,4-Dihydropyridinen bekannt sind (vgl. z. B. britisches Patent 1 305 793; britisches Patent 1 358 951; DE-OS 2 752 820; DE-OS 2 847 237; DE-OS 2 629 892; DE-OS 2 658 804).The 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives according to the invention with a positive inotropic effect are prepared by customary methods which are known for the preparation of 1,4-dihydropyridines (cf., for example, British patent 1 305 793; British patent 1 358 951; DE -OS 2 752 820; DE-OS 2 847 237; DE-OS 2 629 892; DE-OS 2 658 804).
Einige der erfindungsgemäss verwendbaren Verbindungen sind bereits aus dem Stand der Technik bekannt. Die Verbindungen der Herstellungsbeispiele 1 bis 10, 19 bis 23, 26, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 35 bis 38, 41, 42, 43, 45 und 46 bis 254 sind neu. Diese neuen Verbindungen werden z.T. durch allgemeine Substituentendefinitionen des Standes der Technik umfasst ohne jedoch bisher namentlich genannt worden zu sein.Some of the compounds which can be used according to the invention are already known from the prior art. The compounds of Preparation Examples 1 to 10, 19 to 23, 26, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 35 to 38, 41, 42, 43, 45 and 46 to 254 are new. These new connections are partly encompassed by general substituent definitions of the prior art without having been mentioned so far.
Neu sind auch solche Verbindungen aus der allgemeinen Formel 1, in denen mindestens einer der Substituenten R4 und R5 für die Gruppe
Die vorliegende Erfindung betrifft auch die neuen Verbindungen unter der allgemeinen Formel (I), ihre Herstellung und ihre Verwendung in Arzneimitteln mit positiv inotroper Wirkung.The present invention also relates to the new compounds of the general formula (I), their preparation and their use in medicaments with a positive inotropic effect.
Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel (I), in denen R2 von R3 oder R4 von R5 verschieden ist, können aufgrund der Anwesenheit eines asymmetrischen Kohlenstoffatoms in 4-Position des Dihydropyridinringes als racemische Mischungen oder in Form von optischen Isomeren erhalten werden. Einige der erfindungsgemässen Verbindungen die mindestens 2 asymmetrische Kohlenstoffatome enthalten, können in Form einzelner Diastereomeren oder in Form der Mischungen davon erhalten werden. Die diastereomere Mischung kann unter Anwendung konventioneller Verfahren aufgetrennt werden. Beispielsweise durch fraktionierte Umkristallisation oder durch chromatographische Verfahren. Racemische Mischungen lassen sich nach üblichen Methoden, beispielsweise durch Aufspaltung, durch fraktionierte Umkristallisation eines Salzes mit optisch aktiven Säuren in die jeweiligen optischen lsomeren auftrennen.Compounds of the general formula (I) in which R 2 is different from R 3 or R 4 is different from R 5 can be obtained as racemic mixtures or in the form of optical isomers due to the presence of an asymmetric carbon atom in the 4-position of the dihydropyridine ring. Some of the compounds according to the invention which contain at least 2 asymmetric carbon atoms can be obtained in the form of individual diastereomers or in the form of mixtures thereof. The diastereomeric mixture can be separated using conventional methods. For example, by fractional recrystallization or by chromatographic methods. Racemic mixtures can be separated into the respective optical isomers by customary methods, for example by splitting, by fractional recrystallization of a salt with optically active acids.
Durch die Definition der Substituenten der allgemeinen Formel (I) werden auch einige Verbindungen umfasst, die keine positiv inotrope Wirkung besitzen. Durch die oben angegebene Testmethode am isolierten Meerschweinchenvorhof ist es für den Fachmann jedoch unproblematisch, die erfindungsgemässen Verbindungen mit positiv inotroper Wirkung zu erkennen und von den evtl. umfassten Verbindungen mit negativ inotroper Wirkung zu unterscheiden. Die vorliegende Anmeldung ist auf solche Verbindungen gerichtet, die ab einer Konzentration von 10-5 g/ml im oben angegebenen Test am linken isolierten Vorhof des Meerschweinchenherzens eine Kontraktionsverstärkung um mindestens 25% bewirken.The definition of the substituents of the general formula (I) also includes some compounds which have no positive inotropic action. By means of the above-mentioned test method on the isolated guinea pig atrium, it is unproblematic for the person skilled in the art to recognize the compounds according to the invention with a positive inotropic effect and to distinguish them from the possibly included compounds with a negative inotropic effect. The present application is directed to such compounds / ml effect at a concentration of 10- 5 g in the above test on the left atrium of the guinea pig isolated heart contraction gain at least 25%.
Die folgende Tabelle zeigt beispielhaft die positiv inotrope bzw. kontraktionskraftverstärkende Wirkung um mindestens 25% einiger der erfindungsgemässen Verbindungen.
Die erfindungsgemässen Verbindungen zeigen ein nicht vorhersehbares und wertvolles pharmakologisches Wirkungsspektrum. Sie können als Cardiotonika zur Verbesserung der Herzkontraktilität dienen. Darüber hinaus können sie dadurch, dass sie den Ca++-Einstrom in die Zellen erhöhten, als Antihypotonica, zur Senkung von Blutzukker, zur Abschwellung von Schleimhäuten und zur Beeinflussung des Salz- und Flüssigkeitshaushaltes eingesetzt werden.The compounds according to the invention show an unforeseeable and valuable pharmacological spectrum of activity. They can serve as cardiotonics to improve heart contractility. Moreover, they can by the fact that the Ca ++ - increased influx into the cells, are used as Antihypotonica, for lowering blutzukker, for the detumescence of mucous membranes and for influencing the salt and fluid balance.
Die erfindungsgemässen Verbindungen können in bekannter Weise in die üblichen Formulierungen überführt werden.The compounds according to the invention can be converted into the customary formulations in a known manner.
Die neuen Wirkstoffe können in bekannter Weise in die üblichen Formulierungen übergeführt werden, wie Tabletten, Kapseln, Dragees, Pillen, Granulate, Aerosole, Sirupe, Emulsionen, Suspensionen und Lösungen, unter Verwendung inerter, nicht-toxischer, pharmazeutisch geeigneter Trägerstoffe oder Lösungsmittel. Hierbei soll die therapeutisch wirksame Verbindung jeweils in einer Konzentration von etwa 0,5 bis 90 Gew.-% der Gesamtmischung vorhanden sein, d.h. in Mengen, die ausreichend sind, um den angegebenen Dosierungsspielraum zu erreichen.The new active compounds can be converted into the customary formulations in a known manner, such as tablets, capsules, dragees, pills, granules, aerosols, syrups, emulsions, suspensions and solutions, using inert, non-toxic, pharmaceutically suitable excipients or solvents. Here, the therapeutically active compound should in each case be present in a concentration of about 0.5 to 90% by weight of the total mixture, i.e. in amounts sufficient to achieve the dosage range indicated.
Die Formulierungen werden beispielsweise hergestellt durch Verstrecken der Wirkstoffe mit Lösungsmitteln und/oder Trägerstoffen, gegebenenfalls unter Verwendung von Emulgiermitteln und/oder Dispergiermitteln, wobei z. B. im Fall der Benutzung von Wasser als Verdünnungsmittel gegebenenfalls organische Lösungsmittel als Hilfslösungsmittel verwendet werden können.The formulations are prepared, for example, by stretching the active ingredients with solvents and / or carriers, optionally using emulsifiers and / or dispersants, z. B. in the case of the use of water as a diluent, organic solvents can optionally be used as auxiliary solvents.
Als Hilfsstoffe seien beispielsweise aufgeführt:Examples of auxiliary substances are:
Wasser, nicht-toxische organische Lösungsmittel, wie Paraffine (z.B. Erdölfraktionen), pflanzliche Öle (z.B. Erdnuss-/Sesamöl), Alkohole (z.B. Ethylalkohol, Glycerin), Glykole (z. B. Propylenglykol, Polyethylenglykol), feste Trägerstoffe, wie z.B. natürliche Gesteinsmehle (z.B. Kaoline, Tonerden, Talkum, Kreide), synthetische Gesteinsmehle (z.B. hochdisperse Kieselsäure, Silikate), Zucker (z.B. Rohr-, Milch- und Traubenzucker), Emulgiermittel (z. B. Polyoxyethylen-FettsäureEster, Polyoxyethylen-Fettalkohol-Ether, Alkylsulfonate und Arylsulfonate), Dispergiermittel (z.B. Lignin, Sulfitablaugen, Methylcellulose, Stärke und Polyvinylpyrrolidon) und Gleitmittel (z.B. Magnesiumstearat, Talkum, Stearinsäure und Natriumlaurylsulfat).Water, non-toxic organic solvents such as paraffins (e.g. petroleum fractions), vegetable oils (e.g. peanut / sesame oil), alcohols (e.g. ethyl alcohol, glycerin), glycols (e.g. propylene glycol, polyethylene glycol), solid carriers such as e.g. natural stone flours (e.g. kaolins, clays, talc, chalk), synthetic stone flours (e.g. highly disperse silica, silicates), sugar (e.g. cane, milk and glucose), emulsifiers (e.g. polyoxyethylene fatty acid esters, polyoxyethylene fatty alcohol ethers , Alkyl sulfonates and aryl sulfonates), dispersants (e.g. lignin, sulfite lye, methyl cellulose, starch and polyvinylpyrrolidone) and lubricants (e.g. magnesium stearate, talc, stearic acid and sodium lauryl sulfate).
Die Applikation erfolgt in üblicher Weise, vorzugsweise oral oder parenteral, insbesondere perlingual oder intravenös. Im Falle der oralen Anwendung können Tabletten selbstverständlich ausser den genannten Trägerstoffen auch Zusätze, wie Natriumcitrat, Calciumcarbonat und Dicalciumphosphat zusammen mit verschiedenen Zuschlagstoffen, wie Stärke, vorzugsweise Kartoffelstärke, Gelatine und dergleichen enthalten. Weiterhin können Gleitmittel, wie Magnesiumstearat, Natriumlaurylsulfat und Talkum zum Tablettieren mitverwendet werden. Im Falle wässriger Suspensionen und/oder Elixieren, die für orale Anwendungen gedacht sind, können die Wirkstoffe ausser den obengenannten Hilfsstoffen mit verschiedenen Geschmacksaufbesserern oder Farbstoffen versetzt werden.The application is carried out in the usual way, preferably orally or parenterally, in particular perlingually or intravenously. In the case of oral use, tablets can of course also contain additives, such as sodium citrate, calcium carbonate and dicalcium phosphate, together with various additives, such as starch, preferably potato starch, gelatin and the like, in addition to the carrier substances mentioned. Lubricants such as magnesium stearate, sodium lauryl sulfate and talc can also be used for tableting. In the case of aqueous suspensions and / or elixirs which are intended for oral applications, the active ingredients can be mixed with various flavor enhancers or colorants in addition to the abovementioned auxiliaries.
Für den Fall der parenteralen Anwendung können Lösungen der Wirkstoffe unter Verwendung geeigneter flüssiger Trägermaterialien eingesetzt werden.In the case of parenteral use, solutions of the active ingredients can be used using suitable liquid carrier materials.
Im allgemeinen hat es sich als vorteilhaft erwiesen, bei intravenöser Applikation Mengen von etwa 0,001 bis 1 mg/kg, vorzugsweise etwa 0,01 bis 0,5 mg/kg Körpergewicht zur Erzielung wirksamer Ergebnisse zu verabreichen, und bei oraler Applikation beträgt die Dosierung etwa 0,01 bis 20 mg/kg, vorzugsweise 0,1 bis 10 mg/kg Körpergewicht.In general, it has proven to be advantageous to administer amounts of approximately 0.001 to 1 mg / kg, preferably approximately 0.01 to 0.5 mg / kg of body weight in the case of intravenous administration in order to achieve effective results, and the dosage is approximately in the case of oral administration 0.01 to 20 mg / kg, preferably 0.1 to 10 mg / kg body weight.
Trotzdem kann es gegebenenfalls erforderlich sein, von den genannten Mengen abzuweichen, und zwar in Abhängigkeit vom Körpergewicht des Versuchstieres bzw. der Art des Applikationsweges, aber auch aufgrund der Tierart und deren individuellem Verhalten gegenüber dem Medikament bzw. deren Art von dessen Formulierung und dem Zeitpunkt bzw. Intervall, zu welchem die Verabreichung erfolgt. So kann es in einigen Fällen ausreichend sein, mit weniger als der vorgenannten Mindestmenge auszukommen, während in anderen Fällen die genannte obere Grenze überschritten werden muss. Im Falle der Applikation grösserer Mengen kann es empfehlenswert sein, diese in mehrere Einzelgaben über den Tag zu verteilen. Für die Applikation in der Humanmedizin ist der gleiche Dosierungsspielraum vorgesehen. Sinngemäss gelten hierbei auch die obigen Ausführungen.Nevertheless, it may be necessary to deviate from the quantities mentioned, depending on the body weight of the test animal or the type of application route, but also on the basis of the animal type and its individual behavior towards the medication or its type of formulation and the time or interval at which the administration takes place. In some cases it may be sufficient to make do with less than the aforementioned minimum quantity, while in other cases the above upper limit must be exceeded. In the case of application of larger quantities, it may be advisable to distribute them in several single doses throughout the day. The same dosage range is provided for application in human medicine. The above statements also apply mutatis mutandis.
2-Methyl-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-5-oxo-1,4-dihydro-5,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester
- Ausbeute: 45% der Theorie; Fp.: 195 °C.
- Yield: 45% of theory; Mp: 195 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-(3-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-1,4-dihydro-5,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbon- sänreethvlester
- Ausbeute: 30% der Theorie; Fp.: 180 °C.
- Yield: 30% of theory; Mp .: 180 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-(3-chlorphenyl)-5-oxo-1,4-dihydro-5,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäure- ethlester
- Ausbeute: 50% der Theorie; Fp.: 196 °C.
- Yield: 50% of theory; Mp .: 196 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-(3-chlorphenyl)-5-oxo-1,4-dihydro-5,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäure- DroDvlester ri
- Ausbeute: 42% der Theorie; Fp.: 166 °C.
- Yield: 42% of theory; Mp: 166 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridin-5,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbon- säureDroDvlester
2-Methyl-4-(3-trifluormethylphenyl)-5-oxo-1,4-dihydro-5,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäure-isopropylester
- Ausbeute: 18% der Theorie; Fp.: 219-223 °C.
- Yield: 18% of theory; Mp: 219-223 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-5-oxo-1,4-dihydro-5,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäurebutylester
- Ausbeute: 10% der Theorie; Fp.: 194-195 °C.
- Yield: 10% of theory; Mp: 194-195 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-5-oxo-1,4-dihydro-5,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]-pyridin-3-carbonsäure-(2-methoxy)-ethylester
- Ausbeute: 16% der Theorie; Fp.: 196-197 °C.
- Yield: 16% of theory; Mp .: 196-197 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-(2-benzylthiophenyl)-5-oxo-1,4-dihydro-5,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester
- Ausbeute: 31% der Theorie; Fp.: 189-190 °C (aus EtOH).
- Yield: 31% of theory; Mp: 189-190 ° C (from EtOH).
2-Methyt-4-(2-methy)phenyl)-5-oxo-1,4-dihydro-5,7-dihydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester
- Ausbeute: 45%, Fp. 196-198 °C.
- Yield: 45%, mp 196-198 ° C.
33,8 g (90 mmol) 2-Amino-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäurediethylester wurden zusammen mit 14,6 g (90 mmol) Dichlormethylen-dimethyl-ammoniumchlorid in 200 ml Chlorbenzol 2 Stunden bei 80 °C gerührt. Anschliessend wurde mit Eis gekühlt, das ausgefallene Produkt abgesaugt und in einer kalten 10%igen Natriumbicarbonatlösung aufgenommen. Die wässrige Phase wurde mit Methylenchlorid mehrmals extrahiert. Nach Trocknen der Extrakte über Na2S04 und Abdestillation des Lösungsmittels resultierten 16,6 g'(46% der Theorie) des Reaktionsproduktes vom Schmelzpunkt Fp.: 216-218 °C.33.8 g (90 mmol) of 2-amino-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2-nitrophenyl) pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid diethyl ester together with 14.6 g (90 mmol) Dichloromethylene-dimethyl-ammonium chloride in 200 ml of chlorobenzene for 2 hours at 80 ° C. It was then cooled with ice, the precipitated product was filtered off with suction and taken up in a cold 10% sodium bicarbonate solution. The aqueous phase was extracted several times with methylene chloride. After drying the extracts over Na 2 S0 4 and distilling off the solvent, 16.6 g '(46% of theory) of the reaction product of melting point m.p .: 216-218 ° C resulted.
1,4-Dihydro-2-methyl-5-oxo-7,7-pentamethylen-4-(2'-nitrophenyl)-7H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester
1,4-Dihydro-2,7-dimethyl-4-(2'-methylphenyl)-5-oxo-7H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester
- Analog wurden erhalten:
- The following were obtained analogously:
1,4-Dihydro-2,7-dimethyl-4-(3'-trifluormethylphenyl)-5-oxo-7H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester vom Fp.: 210 °C
1,4-Dihydro-2,7-dimethyl-4-(2'-chlorphenyl)-5-oxo-7H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyridin-4-carbonsäuremethylester vom Fp.: 252-254 °C
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäurecyclopentylester
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(3-nitro- phenyi)-pyridin-5-carbonsäure-(ß-n-propoxy- ethyl)-ester
- Ausbeute: 41% der Theorie.
- Yield: 41% of theory.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-dinitro-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-pyridin
- Ausbeute: 38% der Theorie.
- Yield: 38% of theory.
- Ausbeute: 19% der Theorie.
- Yield: 19% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 50 mmol 3-Trifluormethylbenzaldehyd mit 50 mmol Nitroaceton und 50 mmol ß-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(3-trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 175 °C (Isopropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 42% der Theorie.
- Yield: 42% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 50 mmol 2-Nitrobenzaldehyd mit 50 mmol Nitroaceton und 50 mmol ß-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 190 °C (Isopropanol) als sehr lichtempfindliche Verbindung erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 12% der Theorie.
- Yield: 12% of theory.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäure-(ß-cyanoethyl)-ester
Analog Beispiel 18 wurde durch Umsetzung von 50 mmol 2-Methoxybenzylidenacetessigsäuremethylester und 50 mmol 2-Amino-1-nitrol-propen in Ethanol 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-3-nitro-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 206 °C (Ethanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 44% der Theorie.
- Yield: 44% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 18 wurde durch Umsetzung von 3-Nitro-benzylidenacetessigsäure-(ß-trifluorethyl)-ester mit 2-Amino-1-nitro-1-propen in Ethanol 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäure-(ß-trifluorethyl)-ester vom Schmp. 196 °C (Ethanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 28% der Theorie.
- Yield: 28% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von Pyridin-3-aldehyd mit ß-Aminocrotonsäureethylester und Nitroaceton in Ethanol 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(pyridyl-3)-pyridin-5-carbonsäureethylester vom Schmp. 264 °C (Isopropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 34% der Theorie.
- Yield: 34% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 17 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-Benzylthiobenzaldehyd mit 2-Amino-1-nitro-1-propen und Acetessigsäuremethylester in Ethanol 4-(2-Benzylthiophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitropyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 173 °C (Isopropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 21 % der Theorie.
- Yield: 21% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-Trifluormethylbenzaldehyd mit ß-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester und Nitroaceton in Ethanol 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 176 °C (Ethanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 36% der Theorie.
- Yield: 36% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-Chlorbenzaldehyd mit ß-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester und Nitroaceton in Ethanol 4-(2-Chlorphenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 167 °C (Isopropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 42% der Theorie.
- Yield: 42% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 18 wurde durch Umsetzung von 50 mmol 2-Trifluormethoxybenzylidenacetessigsäuremethylester mit 50 mmol 2-Amino-1-nitro-1-propen in Ethanol 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluormethoxyphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 175 °C(lsopropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 39% der Theorie.
- Yield: 39% of theory.
Die Behandlung von 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäure-(ß-cyanoethyl)-ester in 1,2 Äquivalenten Kaliumhydroxid in wässrigem Ethylenglykoldimethylether bei Raumtemperatur ergibt nach Ansäuern mit verd. HCI 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäure vom Schmp. 183 °C (Zersetzung) (Methanol).
- Ausbeute: 89% der Theorie.
- Yield: 89% of theory.
Beim Erhitzen in Ethanol unter Zusatz einer Spur Schwefelsäure decarboxyliert 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäure (Beispiel 30) zu 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin mit quantitativer Ausbeute.
- Schmp. 201 °C.
- Mp 201 ° C.
Analog Beispiel 18 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-Methylbenzyliden-acetessigsäureethylester mit 2-Amino-1-nitro-1-propen in Ethanol 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-tolyl)-3-nitro- pyridin-5-carbonsäureethylester vom Schmp.155 °C (Isopropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 42% der Theorie.
- Yield: 42% of theory.
2-Acetylamino-4,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäurediethylester
2-Amino-6-methyl-1,4-dihydro-4-(2'-chlorphenyl)-pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester
1,4-Dihydro-4-phenyl-2,3,6-trimethylpyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester
Analog Beispiel 35 wurde am 4-(2-Chlorphenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl- pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäuremethylester durch Reduktion mit LiAIH4 in THF 4-(2-Chlorphenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl- pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 164 °C (Acetonitril) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 30% der Theorie.
- Yield: 30% of theory.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-isopropyl-(2,2,2-trichlorethvll-ester
1,4-Dihydro-2,8-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-(c)-hexylisopropyl- ester
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(pyridyl-3)-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäuremonoethylester
3-Cyano-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester
2,6-Di-(4-nitrophanyl)-4-(4-ethoxycarbonyl- methoxy-1-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäurediethylester
- Ausbeute: 11 % der Theorie; Fp.: 136 °C.
- Yield: 11% of theory; Mp: 136 ° C.
2,6-Dimethyl-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure- diallylester
- Ausbeute: 5% der Theorie; Fp.: 90 bis 91 °C.
- Yield: 5% of theory; Mp .: 90 to 91 ° C.
2,6-Diphenyl-3-5-di(phenylcarbonyl)-1-methyl-4-(3-pyridiyl)-1,4-dihydropyridin
- Ausbeute: 15% der Theorie; Fp.: 238 °C.
- Yield: 15% of theory; Mp: 238 ° C.
Bis-[2,6-dimethyl-5-ethoxycarbonyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridin-3-carbonsäure]-1,6-hexandiylester
- Ausbeute: 37% der Theorie; Fp.: 177 bis 179 °C.
- Yield: 37% of theory; Mp .: 177 to 179 ° C.
Bis-[2,6-dimethyl-5-ethoxycarbonyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridin-3-carbonsäure]-1,12-dodecandiylester
- Ausbeute: 10% der Theorie; Fp.: 103 bis 120 °C.
- Yield: 10% of theory; Mp .: 103 to 120 ° C.
Analog Beispiel 17 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-(4-Methylbenzylthio)-benzaldehyd mit 2-Amino-1-nitro-1-propen und Acetessigsäuremethylester in Ethanol 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-methylbenzyl- thio)-phenyl]-3-nitropyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 160 °C {Isopropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 28% der Theorie.
- Yield: 28% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-Trifluormethylbenzaldehyd mit ß-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester und 1-Nitrobutanon-2 in Ethanol 1,4-Dihydro-2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäure-methylester vom Schmp. 199 °C (Iropropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 31% der Theorie.
- Yield: 31% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-Benzylthiobenzaldehyd mit β-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester und 1-Nitrobutanon-2 in Ethanol 4-(2-Benzylthiophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-nitro-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 122 °C (lsopropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 21 % der Theorie.
- Yield: 21% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 3-Benzylthiobenzaldehyd mit β-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester und Nitroaceton in Ethanol 4-(3-Benzylthiophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitropyridin-5-carbonsäuremethyl-ester vom Schmp. 155 °C (Ethanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 35% der Theorie.
- Yield: 35% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 17 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-Trifluormethylbenzaldehyd mit y-Phenylacetessigsäureethylester und 2-Amino-1-nitro-1-propen in Ethanol 2-Benzyl-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäureethylester vom Schmp. 168 °C erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 12% der Theorie.
- Yield: 12% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 17 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-Trifluormethylbenzaldehyd mit 2-Amino-1-nitro-1-propen und 3-Oxo-hexansäuremethylester in Ethanol 1,4-Dihydro-2-methyl-3-nitro-6-propyl-4-(2-trifluormethyl-phenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 168°C (Isopropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 19% der Theorie.
- Yield: 19% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 3-Ethoxybenzaldehyd mit Nitroaceton und β-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester in Ethanol 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-ethoxyphenyl)-3-nitropyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 127 °C erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 42% der Theorie.
- Yield: 42% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-Benzyl-thiobenzaldehyd mit Nitroaceton und β-Aminocrotonsäure-(β-cyanoethyl)ester in Ethanol-4-(2-Benzylthiophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitropyridin-5-carbonsäure-(ß-cyanoethyl)ester vom Schmp. 173 °C (Isopropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 28% der Theorie.
- Yield: 28% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-Cyanobenzaldehyd mit Nitroaceton und β-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester in Ethanol 4-(2-Cyanophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitropyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 182 °C (Isopropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 28% der Theorie.
- Yield: 28% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2,3-Dichlorbenzaldehyd mit Nitroaceton und ß-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester in Ethanol 4-(2,3-Dichlorphenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitropyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 184 °C erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 39% der Theorie.
- Yield: 39% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-Trifluormethylbenzaldehyd mit Nitroaceton und β-Aminocrotonsäure-(6-hydroxyhexyl)ester in Ethanol 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäure-(6-hydroxyhexyl)ester vom Schmp. 174 °C erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 32% der Theorie.
- Yield: 32% of theory.
Durch Umsetzung von 1 Äquivalent 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäure-(6-hydroxyhexyl)-ester mit 1 Äquivalent 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3- . carboxymethylpyridin-5-carbonsäure und 1,1 Äquivalenten Dicyclohexylcarbodiimid im Methylenchlorid wird 5- 6-[2,6-Dimethyl-5-nitro-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,4-dihydro-pyrid-3-yJcarboxy]-hexyloxy- carbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester als amorphe, gelbe Substanz erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 68%
- m/e: 756 ≙ M⊕
- Yield: 68%
- m / e: 756 ≙ M ⊕
Analog dem vorhergehenden Beispiel erhält man durch Umsetzung von 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäure-(6-hydroxyhexylester) mit 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3-carboxymethyl-pyridin-5-carbonsäure und Dicyclohexylcarbodümid in Methylenchlorid wird 5- 6-[2,3-Dimethyl-5-nitro-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-pyrid-3-ylcarboxy]-hexyloxycarbonyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester als amorphe, gelbe Substanz erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 73%
- m/e: 733 ≙ M⊕
- Yield: 73%
- m / e: 733 ≙ M ⊕
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 5-Chlor-2-nitrobenzaldehyd mit Nitroaceton und ß-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester in Ethanol 4-(5-Chlor-2-nitrophenyl)-2,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-pyridin-5-carbonsäure-methylester vom Schmp. 221 °C (Isopropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 43% der Theorie.
- Yield: 43% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-Chlor-5-nitrobenzaldehyd mit Nitroaceton und ß-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester in Ethanol 4-(2-Chlor-5-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-pyridin-5-carbonsäure-methylester vom Schmp. 219 °C erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 39% der Theorie.
- Yield: 39% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-(3-Chlorbenzylthio)-benzaldehyd mit Nitroaceton und β-Aminocrotonsäure-n-hexylester in Ethanol 4-(3-Chlorbenzylthiophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitropyridin-5-carbonsäure-n-hexylester nach Chromatographie erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 21 % der Theorie.
- Yield: 21% of theory.
Durch Umsetzung von je 10 mmol 2-Trifluormethylbenzaldehyd, Nitroaceton, Amidinoessigesterhydrochlorid und Natriummethylat in 60 ml siedendem Ethanol wurde 6-Amino-1,4-dihydro-2-methyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 210 °C (Isopropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 36% der Theorie.
- Yield: 36% of theory.
Durch Umsetzung von je 10 mmol 2-Trifluormethylbenzaldehyd, Acetessigsäuremethylester, Nitroaceton und Methylaminhydrochlorid in 50 ml Eisessig bei 60 °C für 12 Stunden wurde 1,4-Dihydro-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,2,6-trimethylpyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 156 °C (Isopropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 15% der Theorie.
- Yield: 15% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von β-Naphthylaldehyd, β-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester und Nitroaceton in Ethanol 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-β-naphthyl-3-nitro- pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 163 °C (Isopropanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 42% der Theorie.
- Yield: 42% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von Pentafluorbenzaldehyd mit Nitroaceton und β-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester in Ethanol 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-pentafluor- phenylpyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 231 °C erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 38% der Theorie.
- Yield: 38% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-Chlor-6-fluorbenzaldehyd mit Nitroaceton und β-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester 4-(2-Chlor-6-fluorphenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitropyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 190 °C erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 28% der Theorie.
- Yield: 28% of theory.
Durch Umsetzung von je 1 Äquivalent 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäure mit Dimethylaminoethanol und DCC im Methylenchlorid erhält man 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäure-ß-dimethyl- aminoethylester
- vom Schmp. 132 °C.
- Ausbeute: 84% der Theorie.
- from mp. 132 ° C.
- Yield: 84% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 16 erhält man durch Umsetzung von 3-Benzyloxybenzaldehyd mit Nitroaceton und β-Aminocrotonsäuremethylester 4-(3-Benzyloxyphenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitropyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 181 °C (Isopropanol).
- Ausbeute: 34% der Theorie.
- Yield: 34% of theory.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-methylbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäure-methylester
25g g (110,6 mmol) 2-(4-Methylbenzyloxy)-benz- aldehyd werden mit 11,9 ml (110,6 mmol) Acetessigsäuremethylester in 66 ml Isopropanol verrührt und mit einer frisch zubereiteten Lösung von 0,64 ml Piperidin und 0,38 ml Eisessig in 5,5 ml Isopropanol versetzt. Es wird 1 Stunde bei 60 °C und 4 Stunden bei 40 °C gerührt, abgekühlt und eingeengt. Der Eindampfrückstand wird in Ether gelöst und nacheinander mit ca. 100 ml 1N Salzsäure, zweimal mit Wasser, mit gesättigter Natriumhydrogencarbonatlösung und wieder zweimal mit Wasser gewaschen. Die Etherphase wird getrocknet, filtriert und eingeengt. Man erhält 35,3 g (98,51% der Theorie) eines dunkelgelben Öles, welches roh weiter umgesetzt wird.25g g (110.6 mmol) of 2- (4-methylbenzyloxy) benzaldehyde are stirred with 11.9 ml (110.6 mmol) of methyl acetoacetate in 66 ml of isopropanol and with a freshly prepared solution of 0.64 ml of piperidine and 0.38 ml glacial acetic acid in 5.5 ml isopropanol. The mixture is stirred at 60 ° C. for 1 hour and at 40 ° C. for 4 hours, cooled and concentrated. The evaporation residue is dissolved in ether and washed successively with about 100 ml of 1N hydrochloric acid, twice with water, with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution and again twice with water. The ether phase is dried, filtered and concentrated. 35.3 g (98.51% of theory) of a dark yellow oil are obtained, which is further reacted raw.
werden in 30 ml Diethylenglykol suspendiert und unter Rühren auf 170 bis 180 °C erwärmt, wobei unter Gasentwicklung eine klare Lösung entsteht. Es wird ca. 5 Minuten bei 180 °C gerührt und abgekühlt. Die viskose Lösung wird unter starkem Schütteln in einem Ether/Wasser-Gemisch gelöst, es wird getrennt, die wässrige Phase mit Ether extrahiert und die vereinten Etherphasen mit 1N Natronlauge und zweimal mit Wasser gewaschen. Es wird getrocknet, filtriert und eingeengt. Der erhaltene sirupöse Rückstand wird mit Isopropanol oder Acetonitril im Eisbad kristallisiert und abgesaugt. Es werden 1,6 g 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-methylbenzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 107 °C bis 109 °C erhalten.
-
Analog wurden hergestellt:
-
The following were produced analogously:
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester vom Schmp. 125 bis 128 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester of mp. 125 to 128 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-pyridin-3-carbonsäureisopropylester, isoliert als Öl. Rf-Wert: 0,525; DC-Alurolle, Schichtdicke: 0,2 mm, Kieselgel: 60 F 254, Merck; Fliessmittel: Petrolether/Essigester im Volumenverhältnis 2: 1.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (3-nitrophenyl) pyridine-3-carboxylic acid isopropyl ester, isolated as an oil. R f value: 0.525; DC aluminum roll, layer thickness: 0.2 mm, silica gel: 60 F 254, Merck; Eluent: petroleum ether / ethyl acetate in a volume ratio of 2: 1.
1,4-Dihydro-1,2,6-trimethyl-4-(2-chlorphenyl)-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 142 bis 144 °C.1,4-Dihydro-1,2,6-trimethyl-4- (2-chlorophenyl) pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester, mp. 142 to 144 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-chlorphenyl)-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 129 bis 133 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (3-chlorophenyl) pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester of mp. 129 to 133 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-methylphenyl)-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 127 bis 130 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2-methylphenyl) pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester of mp. 127 to 130 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-chlorphenyl)-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester r
- vom Schmp. 143-146 °C.
- from mp. 143-146 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 110 bis 112 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (3-nitrophenyl) pyridine-3-carboxylic acid, methyl ester, mp. 110 to 112 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-phenylthio- methyloxy-phenyl)-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester als Öl.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-benzyloxy- phenyl)-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 81 bis 83 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2-benzyloxyphenyl) pyridine-3-carboxylic acid, methyl ester, melting point 81 to 83 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-chlorbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 90 bis 94 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (4-chlorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid, methyl ester, mp. 90 to 94 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(2-chlorbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 75 bis 77 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (2-chlorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid, methyl ester, mp. 75 to 77 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(2,6-dichlor- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester
vom Schmp. 125 bis 128 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (2,6-dichlorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester
from mp. 125 to 128 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3,4-dichlor- phenyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester,
isoliert als Schaum. RrWert: 0,65, DC-Fertigplatten Kieselgel 60 F 254, Fliessmittel: Chloroform/ Essigester im Volumenverhältnis 5:1.1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3,4-dichlorophenyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester,
isolated as foam. R r value: 0.65, ready-made DC silica gel 60 F 254 plates, eluent: chloroform / ethyl acetate in a volume ratio of 5: 1.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-methyl- benzyloxy)-naphthyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester,
isoliert als Schaum.1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (4-methylbenzyloxy) naphthyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester,
isolated as foam.
Die wichtigsten Peaks findet man bei m/e = 413 (Molpeak); m/e = 308; m/e = 248; m/e = 166.The most important peaks are found at m / e = 413 (Molpeak); m / e = 308; m / e = 248; m / e = 166.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-methylbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäureisopropyl- ester
vom Schmp. ab 99 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (4-methylbenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid isopropyl ester
from mp. from 99 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-(3-trifluormethyl- benzylthio)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester,
isoliert als Öl. RrWert: 0,84, DC-Alurolle, Schichtdicke: 0,2 mm, Kieselgel 60 F 254, Fliessmittel: Chloroform/Essigester im Volumenverhältnis 5: 1.1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2- (3-trifluoromethyl-benzylthio) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester,
isolated as an oil. R r value: 0.84, DC aluminum roller, layer thickness: 0.2 mm, silica gel 60 F 254, eluent: chloroform / ethyl acetate in a volume ratio of 5: 1.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-methylbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäureisobutylester vom Schmp. ab 57 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (4-methylbenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid isobutyl ester, melting point from 57 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-naphthyl-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester, isoliert als Schaum.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-naphthyl-pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester, isolated as a foam.
Die wichtigsten Massenpeaks sind m/e = 293 (Molpeak); m/e = 166 (M - naphthyl).The most important mass peaks are m / e = 293 (mol peak); m / e = 166 (M - naphthyl).
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-trifluormethyl- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester
vom Schmp. 134 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-trifluoromethyl-benzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester
from mp. 134 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-(4-methylbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäure-sec.- butylester
vom Schmp. ab 78 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2- (4-methylbenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid sec-butyl ester
from 78 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-benzyloxy- phenyl)-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester, isoliert als Öl. RrWert: 0,69, DC-Alurolle, Schichtdicke 0,2 mm, Kieselgel 60 G 254, Merck; Fliessmittel: Chloroform/Essigester im Volumenverhältnis 7: 1.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (3-benzyloxyphenyl) pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester, isolated as an oil. R r value: 0.69, DC aluminum roller, layer thickness 0.2 mm, silica gel 60 G 254, Merck; Superplasticizer: chloroform / ethyl acetate in a volume ratio of 7: 1.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-trifluormethyl- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäure- isobutylester, isoliert als Öl.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-trifluoromethyl-benzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid isobutyl ester, isolated as an oil.
Die wichtigsten Massenpeaks sind:
- m/e = 459 (Molpeak);
- m/e = 402
- m/e = 208 (M-C14H10F3O).
- m / e = 459 (mol peak);
- m / e = 402
- m / e = 208 (MC 14 H 10 F 3 O).
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-nitrobenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 117 bis 118 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-nitrobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid, methyl ester, mp. 117 to 118 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-nitrobenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester vom Schmp. ab 107 bis 109 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-nitrobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester of melting point from 107 to 109 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-fluorbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 68 bis 70 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (4-fluorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid, methyl ester, mp. 68 to 70 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-trifluormethyl- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäure-sec.- butylester,
isoliert als Öl.1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-trifluoromethyl-benzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid, sec-butyl ester,
isolated as an oil.
Die wichtigsten Massenpeaks sind: m/e = 459 (Molpeak); m/e = 402 (M-57).The main mass peaks are: m / e = 459 (Molpeak); m / e = 402 (M-57).
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-fluorbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester vom Schmp. 122 bis 125 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (4-fluorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester of mp. 122 to 125 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3,5-dimethyl- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester
vom Schmp. 127 bis 129 °C (kristallisiert mit 1 Mol Acetonitril).1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3,5-dimethylbenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester
of mp 127 to 129 ° C (crystallized with 1 mole of acetonitrile).
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4,(3-nitrophenyl)-pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester vom Schmp. 107 bis 108 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4, (3-nitrophenyl) pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester, mp. 107 to 108 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3,5-dimethyl- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäure-n-butylester,
isoliert als Öl.1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3,5-dimethylbenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid n-butyl ester,
isolated as an oil.
Die wichtigsten Peaks liegen bei:
- m/e = 417 (M-2); m/e = 300 (M-119) und
- m/e = 208.
- m / e = 417 (M-2); m / e = 300 (M-119) and
- m / e = 208.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-methylbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäure-n-butylester vom Schmp. 104 bis 10 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-methylbenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid n-butyl ester, mp. 104 to 10 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-methylbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 58 bis 62 °C, kristallisiert mit 1 Mol Acetonitril.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-methylbenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid, methyl ester, mp. 58 to 62 ° C., crystallized with 1 mol of acetonitrile.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-fluorbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 109 bis 10 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-fluorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid, methyl ester, mp. 109 to 10 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-fluorbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäure-n-butylester vom Schmp. 105 bis 106 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-fluorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid n-butyl ester, mp. 105 to 106 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-phenylpropyl- mercaptophenyl)-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester,
isoliert als Öl.1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2-phenylpropyl-mercaptophenyl) pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester,
isolated as an oil.
RrWert: 0,46, DC-Alurolle, Schichtdicke: 0,2 mm, Kieselgel 60 F 254 Merck, Fliessmittel: Chloroform.R r value: 0.46, DC aluminum roller, layer thickness: 0.2 mm, silica gel 60 F 254 Merck, eluent: chloroform.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-methoxy- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester
vom Schmp. ab 53 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-methoxybenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester
from 53 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-benzylthio- phenyl)-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2-benzylthiophenyl) pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester.
Die wichtigsten Peaks findet man bei
- m/e = 365 (Molpeak), m/e = 350 (M-15),
- m/e = 306 (M-59), m/e = 274, m/e = 166.
- m / e = 365 (Molpeak), m / e = 350 (M-15),
- m / e = 306 (M-59), m / e = 274, m / e = 166.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethy)-4-[2-(3-methoxy- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3-carbonsäure-n-butylester
- vom Schmp. 144 bis 146 °C.
- from mp. 144 to 146 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-chlorphenyl)-5-phenyl-ureidopyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester
- werden mit 6,4 Mol (30 mmoi) Diphenylphosphorylazid und 4,2 ml (30 mmol) Triethylamin 1 Stunde zum Rückfluss erhitzt. Es wird abgekühlt, mit 2,8 ml (30 mmol) Anilin versetzt und 1 Stunde gekocht. Es wird eingeengt, der feste Eindampfrückstand wird in warmem Essigester gelöst, es wird mit 1N Salzsäure, Wasser, 2N Natronlauge und zweimal mit Wasser gewaschen, getrocknet und eingeengt. Der feste Eindampfrückstand wird mit 100 ml heissem Essigester versetzt, es wird unter Rühren abgekühlt, abgesaugt und mit Essigester gewaschen. Man erhält 4,6 g 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-chlorphenyl)-5-phenyl-ureido-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester vom Schmp. 203 bis 205 °C.
- Analog wurden hergestellt:
- are heated with 6.4 mol (30 mmoi) of diphenylphosphoryl azide and 4.2 ml (30 mmol) of triethylamine to reflux for 1 hour. It is cooled, 2.8 ml (30 mmol) of aniline are added and the mixture is boiled for 1 hour. It is concentrated, the solid evaporation residue is dissolved in warm ethyl acetate, it is washed with 1N hydrochloric acid, water, 2N sodium hydroxide solution and twice with water, dried and concentrated. The solid evaporation residue is mixed with 100 ml of hot ethyl acetate, it is cooled with stirring, suction filtered and washed with ethyl acetate. 4.6 g of 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2-chlorophenyl) -5-phenyl-ureido-pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester of melting point 203 to 205 ° C. are obtained.
- The following were produced analogously:
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-methylbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-5-n-butylureido-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester
vom Schmp. 194 bis 196 °C.
from mp. 194 to 196 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-chlorphenyl)-5-N-morpholinyl)-carbonylamino-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester
vom Schmp. 245 bis 249 °C.
from mp. 245 to 249 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2;6-dimethyl-4-(2-chlorphenyl)-5-(4-N-methylpiperazinyl-carbonylamino)-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester
vom Schmp. 231 °C.
from mp. 231 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-benzyloxy- phenyl)-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-monomethylester
werden in einer Lösung von 2,88 g (72 mmol) Natriumhydroxid in 72 ml Wasser suspendiert und mit 45 ml Dimethoxyethan versetzt. Es wird über Nacht gerührt, mit 100 ml Wasser versetzt und dreimal mit Ether extrahiert. Die wässrige Phase wird am Rotationsverdampfer kurz andestilliert und anschliessend unter Rühren tropfenweise mit konzentrierter Salzsäure angesäuert. Das ausgefallene Produkt wird abgesaugt, mit Wasser gewaschen und getrocknet. Man erhält 6,2 g eines beigegefärbten Produktes vom Schmp. 160 °C unter Zersetzung.
Analog Beispiel 112 wurden hergestellt:1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2-benzyloxyphenyl) pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
are suspended in a solution of 2.88 g (72 mmol) of sodium hydroxide in 72 ml of water and mixed with 45 ml of dimethoxyethane. The mixture is stirred overnight, mixed with 100 ml of water and extracted three times with ether. The aqueous phase is briefly distilled on a rotary evaporator and then acidified dropwise with concentrated hydrochloric acid while stirring. The precipitated product is filtered off, washed with water and dried. 6.2 g of a colored product of mp 160 ° C. are obtained with decomposition.
The following were prepared as in Example 112:
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-(4-methylbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5- dicarbonsäure-monomethylester
vom Schmp. 169 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2- (4-methylbenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
of mp 169 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-chlorbenzyl)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-monomethylester
vom Schmp. 156 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (4-chlorobenzyl) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
of mp. 156 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(2-chlorbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-monomethylester
vom Schmp. 153 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (2-chlorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
of melting point 153 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-phenylmercapto- methoxyphenyl)-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-monomethylester
vom Schmp. 95 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2-phenylmercapto-methoxyphenyl) pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
95 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-phenethyloxy- phenyl)-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-monomethylester
vom Schmp. 100 bis 103 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2-phenethyloxyphenyl) pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
from mp. 100 to 103 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(2,6-dichlor- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure- monomethylester
vom Schmp. 198 bis 201 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (2,6-dichlorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
from mp 198 to 201 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3,4-dichlor- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure- monomethylester
vom Schmp. 138 bis 140 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3,4-dichlorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
from mp. 138 to 140 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-propoxyphenyl)-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-monomethylester
vom Schmp. 175 bis 177°C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (3-propoxyphenyl) pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
from mp. 175 to 177 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-benzyloxyphe- nyl)-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-monomethylester vom Schmp. 148 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (3-benzyloxyphenyl) pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester, mp. 148 ° C. with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-methylbenzyl- oxy)-naphthyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-monomethylester
vom Schmp. 171 bis 179 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (4-methylbenzyloxy) naphthyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
from mp. 171 to 179 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-naphthyl-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-monomethylester
vom Schmp. 175 bis 179 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-naphthyl-pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
from mp. 175 to 179 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-methylbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-mono- isopropylester
vom Schmp. 101 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (4-methylbenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monoisopropyl ester
from mp. 101 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-trifluormethyl- benzylthio)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure- monomethylester
vom Schmp. 90 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-trifluoromethyl-benzylthio) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
of mp 90 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-methylbenzyl- oxy)-phenyi]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-monoisobutylester
vom Schmp. 85 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (4-methylbenzyloxy) phenyi] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monoisobutyl ester
of melting point 85 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-methylbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-mono- sec.-butylester
vom Schmp. 133 bis 140 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (4-methylbenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid mono-sec-butyl ester
from mp. 133 to 140 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-trifluormethyl- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure- monomethylester
vom Schmp. 182 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-trifluoromethyl-benzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
of mp. 182 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-(3-trifluormethyl- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure- monoisobutylester
vom Schmp. 150 bis 153 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2- (3-trifluoromethyl-benzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monoisobutyl ester
from mp. 150 to 153 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-(3-trifluormethyl- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure- mono-sec.-butylester
vom Schmp. 144 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2- (3-trifluoromethyl-benzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid mono-sec.-butyl ester
of mp. 144 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-(3-nitrobenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-monomethylester
vom Schmp. 167 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2- (3-nitrobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
of mp. 167 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-nitrobenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-mono- ethylester
vom Schmp. 172 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-nitrobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monoethyl ester
of mp 172 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-fluorbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-mono- ethylester
vom Schmp. 154 bis 156 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (4-fluorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monoethyl ester
from mp. 154 to 156 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(4-fluorbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-monomethylester
vom Schmp. 181 bis 186 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (4-fluorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
from mp. 181 to 186 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-phenylpropyl- mercaptophenyl)-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure- monomethylester
vom Schmp. ab 94 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- (2-phenylpropyl-mercaptophenyl) pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
from mp. 94 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3,5-dimethyl- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure- monomethylester
vom Schmp. ab 98 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3,5-dimethylbenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
from mp. 98 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3,5-dimethyl- benzyioxy)-phenyi]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure- mono-n-butylester
vom Schmp. ab 85 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3,5-dimethyl-benzyioxy) phenyi] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid mono-n-butyl ester
from mp. from 85 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[3-methylbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-monomethylester vom Schmp. 140 bis 145 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [3-methylbenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester of melting point 140 to 145 ° C. with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-methylbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-mono-n-butylester
vom Schmp. 132 bis 139 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-methylbenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid mono-n-butyl ester
from mp. 132 to 139 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-fluorbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-monomethylester
vom Schmp. 146 bis 149 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-fluorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
from mp. 146 to 149 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-fluorbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure-mono-n-butylester
vom Schmp. 141 bis 144 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-fluorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid mono-n-butyl ester
from mp. 141 to 144 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-methoxy- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure- monomethylester
vom Schmp. 155 bis 160 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-methoxybenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid monomethyl ester
from mp 155 to 160 ° C with decomposition.
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-(3-methoxy- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-3,5-dicarbonsäure- mono-n-butylester
vom Schmp. 145 bis 149 °C unter Zersetzung.1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4- [2- (3-methoxybenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid mono-n-butyl ester
from mp. 145 to 149 ° C with decomposition.
1-Ethyl-2-methyl-4-[2-(3-trifluormethylbenzyl- thio)-phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]-pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 117 bis 119 °C.1-Ethyl-2-methyl-4- [2- (3-trifluoromethylbenzylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester .
Mp .: 117 to 119 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(3-trifluormethylbenzylthio)-phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]-pyridin-3-carbonsäure-2-methoxyethylester. Fp.: 124 bis 125 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (3-trifluoromethylbenzylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid 2-methoxyethyl ester. Mp .: 124 to 125 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(3-trifluormethylbenzylthio)-phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]-pyridin-3-carbonsäurebutylester.
Fp.: 112 bis 120°C.2-Methyl-4 - [ 2- (3-trifluoromethylbenzylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid butyl ester.
Mp .: 112 to 120 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(3-trifluormethylbenzyloxy)-phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]-pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 180 bis 183 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (3-trifluoromethylbenzyloxy) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 180 to 183 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(3-nitrobenzylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 164 bis 166 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (3-nitrobenzylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 164 to 166 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(3-nitrobenzylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäure-n-butylester.
Fp.: 137 bis 139 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (3-nitrobenzylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid n-butyl ester.
Mp .: 137 to 139 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(3-methylbenzylsulfinyl)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.:243-245 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (3-methylbenzylsulfinyl) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp: 243-245 ° C.
4-[2-(Benzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1 H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 243 bis 246 °C.Ethyl 4- [2- (benzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-pyrrolo [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylate.
Mp: 243 to 246 ° C.
4-[2-(Benzylsulfonyl)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 150 bis 152 °C.4- [2- (Benzylsulfonyl) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 150 to 152 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(3-trifluormethylbenzylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]-3-carbonsäuremethylester.
Fp.: 178 bis 181 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (3-trifluoromethylbenzylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] -3-carboxylic acid methyl ester.
Mp .: 178 to 181 ° C.
4-[2-(4-tert.-Butylbenzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahyd rofuro[3,4-b] pyrid i n-3-carbonsäurebutylester.
Fp.: 103 °C.4- [2- (4-tert-Butylbenzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyride in 3-carboxylic acid butyl ester.
Mp .: 103 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(3-trifluormethylbenzyl)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 189 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (3-trifluoromethylbenzyl) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp: 189 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(3-methylbenzylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 150 bis 155 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (3-methylbenzylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 150 to 155 ° C.
4-[2-(3-Chlorbenzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäurebutylester.
Fp.: 167 bis 170 °C.4- [2- (3-Chlorobenzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid butyl ester.
Mp .: 167 to 170 ° C.
4-[2-(4-Ethoxycarbonylbenzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]-pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 157 bis 160 °C.4- [2- (4-Ethoxycarbonylbenzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 157 to 160 ° C.
4-[2-(Benzylthio)phenyl]-2-propyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 167 bis 169 °C.Ethyl 4- [2- (benzylthio) phenyl] -2-propyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylate.
Mp .: 167 to 169 ° C.
4-[2-(Chlorbenzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 87 bis 89 °C.Ethyl 4- [2- (chlorobenzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylate.
Mp .: 87 to 89 ° C.
4-[2-Benzylthio)phenyl]-2-ethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester.
Fp.: 174 bis 176 °C.4- [2-Benzylthio) phenyl] -2-ethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester.
Mp .: 174 to 176 ° C.
4-[2-(4-tert.-Butylbenzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]-pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 127 bis 130 °C.4- [2- (4-tert-Butylbenzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 127 to 130 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(3-methylbenzylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 114 bis 116°C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (3-methylbenzylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 114 to 116 ° C.
4-[2-(4-tert.-Butylbenzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]-pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester.
Fp.: 112 bis 113°C.4- [2- (4-tert-Butylbenzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester.
Mp .: 112 to 113 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(3-methylbenzylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester.
Fp.: 166 bis 168 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (3-methylbenzylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester.
Mp .: 166 to 168 ° C.
4-[2-(3-Chlorbenzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester.
Fp.: 209 bis 211 °C.4- [2- (3-Chlorobenzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester.
Mp: 209-211 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(4-methylbenzylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbon- säureoctylester.
- 1H-NMR (CDCl3): δ = 0,9 (t, J = 7 Hz, 3H), 1,0-1,5 (m, 12H), 2,3 und 2,35 (2s, je 3H), 3,75-4,1 (m, 2H), 4,1 und 4,15 (2d, J = 14 Hz, je 1H), 4,45 (s, 2H), 5,5 (s, 1H) 7,0-7,4 (m, 8H), 8,1 (s, NH) ppm.
- 1 H-NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ = 0.9 (t, J = 7 Hz, 3H), 1.0-1.5 (m, 12H), 2.3 and 2.35 (2s, each 3H ), 3.75-4.1 (m, 2H), 4.1 and 4.15 (2d, J = 14 Hz, each 1H), 4.45 (s, 2H), 5.5 (s, 1H ) 7.0-7.4 (m, 8H), 8.1 (s, NH) ppm.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(4-methylbenzylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäurebutylester.
Fp.: 87 bis 89 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (4-methylbenzylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid butyl ester.
Mp .: 87 to 89 ° C.
4-[2-(Benzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1-propyl-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 132 °C.Ethyl 4- [2- (benzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1-propyl-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylate.
Mp: 132 ° C.
1-Allyl-4-[2-(benzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 115 bis 177 °C.1-Allyl-4- [2- (benzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 115 to 177 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(4-methylbenzylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäure-(2-methoxy)-ethylester.
Fp.: 137 bis 139 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (4-methylbenzylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid (2-methoxy) ethyl ester .
Mp .: 137 to 139 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(4-methylbenzyloxy)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 208 bis 209 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (4-methylbenzyloxy) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 208 to 209 ° C.
4-[2-(benzylthio)phenyl]-1-ethyl-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 80 bis 82 °C.Ethyl 4- [2- (benzylthio) phenyl] -1-ethyl-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylate.
Mp .: 80 to 82 ° C.
4-[2-(Benzylthio)phenyl]-1,2-dimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 188-190 °C.4- [2- (Benzylthio) phenyl] -1,2-dimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp: 188-190 ° C.
4-[3-(Benzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 183 bis 185 °C.4- [3- (Benzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 183 to 185 ° C.
4-[2-(4-Methoxycarbonylbenzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]-pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 102 bis 110 °C.4- [2- (4-Methoxycarbonylbenzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 102 to 110 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(1-phenylethylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 93 bis 110 °C (2 : 3-Diastereomerengemisch).2-Methyl-4- [2- (1-phenylethylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 93 to 110 ° C (2: 3 mixture of diastereomers).
2-Methyl-4-[2-(2-methylbenzylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 217 bis 219 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (2-methylbenzylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 217 to 219 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-4-[3-phenylpropylsulfinyl)-phenyl]-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro(3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 185 bis 186 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo-4- [3-phenylpropylsulfinyl) phenyl] -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro (3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester.
Mp .: 185 to 186 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(4-nitrobenzylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 168 bis 170 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (4-nitrobenzylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 168 to 170 ° C.
4-[2-(Methoxycarbonyl)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 240 bis 249 °C.Ethyl 4- [2- (methoxycarbonyl) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylate.
Mp .: 240 to 249 ° C.
4-[2-(Butylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 163 bis 167 °C.Ethyl 4- [2- (butylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylate.
Mp: 163 to 167 ° C.
4-[2-(2,5-Dichlorbenzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]-pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 244 bis 250 °C.Ethyl 4- [2- (2,5-dichlorobenzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylate.
Mp .: 244 to 250 ° C.
4-[2-(4-Methoxybenzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 83 bis 85 °C.Ethyl 4- [2- (4-methoxybenzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylate.
Mp .: 83 to 85 ° C.
4-[2-(4-Chlorbenzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 97 bis 99 °C.Ethyl 4- [2- (4-chlorobenzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylate.
Mp .: 97 to 99 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(1-methylethylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 193 bis 194 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (1-methylethylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp: 193 to 194 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(3-phenylpropylthio)-phenyl]-1,4,5,7-tetrahydro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 179 bis 180 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo-4- [2- (3-phenylpropylthio) phenyl] -1,4,5,7-tetrahydro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 179 to 180 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-(tetralin-2-yl-methylthio)-phenyl]-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro-[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 102 bis 104 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo-4- [2- (tetralin-2-yl-methylthio) phenyl] -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester.
Mp .: 102 to 104 ° C.
4-(2,3-Dimethylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 225 bis 227 °C.4- (2,3-Dimethylphenyl) -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 225 to 227 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-[2-(2-[phenylcarbonyloxy]-ethylthio)-phenyl]-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro-[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 190 bis 196 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo [2- (2- [phenylcarbonyloxy] ethylthio) phenyl] -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 190 to 196 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(1-naphthylmethylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 93 bis 100 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (1-naphthylmethylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 93 to 100 ° C.
4-[2-(Benzylsulfinylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b] pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 250 °C.4- [2- (Benzylsulfinylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 250 ° C.
4-[2-(3,4-Dichlorbenzylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]-pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 90 bis 95 °C.Ethyl 4- [2- (3,4-dichlorobenzylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylate.
Mp .: 90 to 95 ° C.
4-[3-Benzyloxyphenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 103 bis 104 °C.4- [3-Benzyloxyphenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 103 to 104 ° C.
4-[2-(2-Hydroxyethylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 130 bis 134 °C.4- [2- (2-Hydroxyethylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 130 to 134 ° C.
4-(2-Benzylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 239 bis 240 °C.4- (2-Benzylphenyl) -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp: 239 to 240 ° C.
4-(2-Ethylthio)phenyl-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 235 bis 236 °C.4- (2-Ethylthio) phenyl-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 235 to 236 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(methylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 233 bis 234 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (methylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp: 233 to 234 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(2-phenylethylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 184 bis 185 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (2-phenylethylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 184 to 185 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-[2-(4-methylbenzylthio)phenyl]-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 132 bis 134 °C.2-Methyl-4- [2- (4-methylbenzylthio) phenyl] -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp: 132 to 134 ° C.
4-(2-Benzyloxyphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester.
Fp.: 245 bis 246 °C.4- (2-Benzyloxyphenyl) -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester.
Mp .: 245 to 246 ° C.
4-(2-Ethylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetra- hydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester. Fp.: 197 bis 200 °C.4- (2-Ethylphenyl) -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetra-hydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester. Mp .: 197 to 200 ° C.
4-(2-Benzylthiophenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäure- octylester.
Fp.: 212 °C.4- (2-Benzylthiophenyl) -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid octyl ester.
Mp: 212 ° C.
4-(2-Benzylthiophenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäurebutylester (amorphe Substanz).4- (2-Benzylthiophenyl) -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid butyl ester (amorphous substance).
4-(2-Benzyloxyphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 177 °C.4- (2-Benzyloxyphenyl) -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp: 177 ° C.
4-(2-Benzylthiophenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester.
Fp.: 215 °C.4- (2-Benzylthiophenyl) -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester.
Mp: 215 ° C.
2-Mefhyl-5-oxo-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 228 bis 230 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 228 to 230 ° C.
4-(2-Benzylthiophenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureiso- propylester.
Fp.: 158 bis 161 °C.Isopropyl 4- (2-benzylthiophenyl) -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylate.
Mp 158-161 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-phenylphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 217 bis 220 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo-4- (2-phenylphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 217 to 220 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-(2-methylphenyl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäure- isopropylester.
Fp.: 208 °C.2-Methyl-4- (2-methylphenyl) -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid isopropyl ester.
Mp: 208 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-(2-methylphenyl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäurebutylester.
Fp.: 167 bis 176 °C.2-Methyl-4- (2-methylphenyl) -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid butyl ester.
Mp .: 167 to 176 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-(2-methylphenyl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäure- allylester.
Fp.: 170 bis 175 °C.2-Methyl-4- (2-methylphenyl) -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid allyl ester.
Mp .: 170 to 175 ° C.
3-Acetyl-4-(2-benzylthiophenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin.
Fp.: 212 °C.3-acetyl-4- (2-benzylthiophenyl) -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine.
Mp: 212 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester.
Fp.: 229 bis 233 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester.
Mp: 229 to 233 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-methylphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahyd rofu ro[3,4-b] pyrid i n-3-carbonsäu remethylester.
Fp.: 196 bis 201 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo-4- (2-methylphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuran [3,4-b] pyride in 3-carboxylic acid, remethyl ester.
Mp .: 196 to 201 ° C.
4-(3-Chlorphenyl)-1,2-dimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäure-2-methoxyethylester.
Fp.: 128 bis 133 °C.4- (3-Chlorophenyl) -1,2-dimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid 2-methoxyethyl ester.
Mp .: 128 to 133 ° C.
3-Acetyl-2-methyl-5-oxo-4-[2-trifluormethylphenyl]-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin.
Fp.: 212 bis 213 °C.3-acetyl-2-methyl-5-oxo-4- [2-trifluoromethylphenyl] tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine.
Mp .: 212 to 213 ° C.
2-Methoxymethyl-5-oxo-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro-[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 218 bis 219 °C.2-Methoxymethyl-5-oxo-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 218 to 219 ° C.
4-(3-Chlorphenyl)-1,2-dimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 188 bis 190 °C.4- (3-Chlorophenyl) -1,2-dimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 188 to 190 ° C.
4-(3-Chlorphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetra- hydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3- carbonsäurebutylester. Fp.: 142 bis 144 °C.4- (3-chlorophenyl) -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetra-hydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid butyl ester. Mp .: 142 to 144 ° C.
4-(3-Chlorphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetra- hydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureallylester. Fp.: 164-167 °C.4- (3-Chlorophenyl) -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetra-hydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid allyl ester. Mp: 164-167 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäure-82-pyridyl)-methylester.
Fp.: 209 bis 210 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid-82-pyridyl) methyl ester.
Mp .: 209 to 210 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-1-propyl-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro-[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 106 bis 107 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo-1-propyl-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 106 to 107 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbon- säurebenzylester.
Fp.: 218 bis 219 °C.2-methyl-5-oxo-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid benzyl ester.
Mp .: 218 to 219 ° C.
4-(3-Chlorphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetra- hydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäurehexy)ester. Fp.: 130 bis 133 °C.4- (3-chlorophenyl) -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetra-hydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid hexy) ester. Mp .: 130 to 133 ° C.
1-Ethyl-2-methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro-[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 157 bis 160 °C.1-Ethyl-2-methyl-5-oxo-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 157 to 160 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbon- säureoctylester.
Fp.: 119 bis 120 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid octyl ester.
Mp .: 119 to 120 ° C.
4-(2,3-Dichlorphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 249 bis 251 °C.Ethyl 4- (2,3-dichlorophenyl) -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylate.
Mp: 249 to 251 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-4-(3-pyridyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydro- furo[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 192 bis 194 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo-4- (3-pyridyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp: 192 to 194 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-trifluormethoxyphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 174 bis 176 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo-4- (2-trifluoromethoxyphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 174 to 176 ° C.
2-Methyl-4-(2-naphthyl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetra- hydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester. Fp.: >270°C.2-Methyl-4- (2-naphthyl) -5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester. Mp .:> 270 ° C.
5-Oxo-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,2,7-trimethyl-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]-pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 171 bis 172 °C.5-Oxo-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) -1,2,7-trimethyl-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 171 to 172 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-4-(3-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 180 bis 182 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo-4- (3-trifluoromethylphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 180 to 182 ° C.
2-Ethyl-5-oxo-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 237 bis 239 °C.2-Ethyl-5-oxo-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 237 to 239 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbon- säureallylester.
Fp.: 190 bis 192 °C.2-methyl-5-oxo-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carbon acid allyl ester.
Mp .: 190 to 192 ° C.
1,2-Dimethyl-5-oxo-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 196 bis 197 °C.1,2-Dimethyl-5-oxo-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 196 to 197 ° C.
4-[(2-Fluor-3-chlor)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäuremethylester.
Fp.: 220 bis 223 °C.4 - [(2-Fluoro-3-chloro) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester.
Mp .: 220 to 223 ° C.
4-[2-(Cyclohexylmethylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäurebutylester.
Fp.: 123 bis 128 °C.4- [2- (Cyclohexylmethylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid butyl ester.
Mp .: 123 to 128 ° C.
4-[2-(Cyclohexylmethylthio)phenyl]-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 77 bis 82 °C.4- [2- (Cyclohexylmethylthio) phenyl] -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp .: 77 to 82 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbon- säurehexylester.
Fp.: 164 bis 165 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid hexyl ester.
Mp .: 164 to 165 ° C.
2-Methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-phenylthiophenyl)-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridin-3-carbonsäureethylester.
Fp.: 191 bis 192 °C.2-Methyl-5-oxo-4- (2-phenylthiophenyl) -1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
Mp: 191 to 192 ° C.
4-(2-Chlorphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetra- hydrofuro[3,4-b)pyridin-3-carbonsäureallylester.
Fp.: 206 °C.4- (2-Chlorophenyl) -2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetrahydrofuro [3,4-b) pyridine-3-carboxylic acid allyl ester.
Mp .: 206 ° C.
Analog zu dem Verfahren gemäss Beispiel Nr. 35 werden die folgenden Verbindungen durch Hydrierung mit Lithium-Aluminium-Hydrid aus den entsprechenden Diestern erhalten. 1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4-(2-chlorphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäureethylester
vom Schmp. 112 °C.Analogously to the process according to Example No. 35, the following compounds are obtained from the corresponding diesters by hydrogenation with lithium aluminum hydride. 1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4- (2-chlorophenyl) pyridine-5-carboxylic acid ethyl ester
from mp. 112 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4-(4-chlorphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester
vom Schmp. 94 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4- (4-chlorophenyl) pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester
from mp. 94 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4-(2-methylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester
vom Schmp. 147 bis 153 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4- (2-methylphenyl) pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester
from mp. 147 to 153 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4-[2-(4-methyl- benzylthio)-phenyl]-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester
- vom Schmp.
- 109 bis 111 °C.
- from Schmp.
- 109 to 111 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester
vom Schmp. 145 bis 149 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester
from mp. 145 to 149 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4-(4-methylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethy!ester
vom Schmp. 146 bis 150 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4- (4-methylphenyl) pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester
from mp. 146 to 150 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4-(3-thienyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester
vom Schmp. 150 bis 158 °C.1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4- (3-thienyl) pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester
from mp. 150 to 158 ° C.
1,4-Dihydro-2;3,6-trimethyl-4-(2-benzyloxy- phenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester, isoliert als farbloses Harz.
Massenspektrum: Die wichtigsten Peaks findet man bei:
- m/e = 363, 348, 304, 272, 180.
Mass spectrum: The most important peaks can be found at:
- m / e = 363, 348, 304, 272, 180.
1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4-[2-(4-chlorbenzyl- oxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester, isoliert als farbloses Harz.
Massenspektrum: m/e = 396 (180).1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4- [2- (4-chlorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester, isolated as a colorless resin.
Mass spectrum: m / e = 396 (180).
1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4-[2-(2,6-dichlor- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester,
isoliert als Öl.1,4-dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4- [2- (2,6-dichlorobenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester,
isolated as an oil.
1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4-[2-(4-methyl- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester,
isoliert als Öl.1,4-dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4- [2- (4-methylbenzyloxy) phenyl] pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester,
isolated as an oil.
1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4-(2-phenethyloxy- phenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester, isoliert als gelbes Öl.1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4- (2-phenethyloxyphenyl) pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester, isolated as a yellow oil.
1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4-(2-phenyl- mercaptomethoxyphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester,
- isoliert als gelbes Öl.
- Massenspektrum: m/e = 395 (180).
- isolated as a yellow oil.
- Mass spectrum: m / e = 395 (180).
1,4-Dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4-[3-(4-methyl- benzyloxy)-phenyl]-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester,
isoliert als gelbes Öl.1,4-dihydro-2,3,6-trimethyl-4- [3- (4-methyl-benzyloxy) -phenyl] - pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester,
isolated as a yellow oil.
Analog Beispiel 18 erhält man aus 0,1 Mol 2-Amino-1-nitro-1-propen und 0,1 Mol 2-Chlor-1-phenyl-buten-1-on-3 durch Erhitzen in siedendem Ethanol das 3-Chlor-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-phenyl- pyridin
- vom Schmelzpunkt 192 °C (Isopropanol).
- Ausbeute: 28% der Theorie.
- melting point 192 ° C (isopropanol).
- Yield: 28% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 18 werden 0,1 Mol 2-Amino-1-nitro-1-propen und 0,1 Mol 2-Chlor-1-(3-nitrophenyl)-buten-1-on-3 in siedendem Ethanol erhitzt. Man erhält 3-Chlor-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-pyridin
- vom Schmp. 198 °C (Zers.).
- Ausbeute:
- of melting point 198 ° C (dec.).
- Yield:
Analog Beispiel 18 werden 0,1 Mol Aminocrotonsäuremethylester und 2-Chlor-1-phenyl-buten-1-on-3 in siedendem Ethanol erhitzt. Man erhält 3-Chlor-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-phenyl- pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester
- vom Schmp. 147 °C.
- Ausbeute: 23% der Theorie.
- from mp. 147 ° C.
- Yield: 23% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 18 wurde duch Umsetzung von 2-Nitro-1-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-buten-1-on-3 und Amidinoessigsäureethylester in Ethanol 2-Amino-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-5-nitro-4-(2-trifluormethylphenyl)-pyridin-5-carbon-säureester vom Schmp. 210 °C (Isopropanol) erhalten. Ausbeute: 32% der Theorie.Analogously to Example 18, 2-amino-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-5-nitro-4- (2-trifluoromethylphenyl) pyridine-5-carbon acid ester of mp. 210 ° C (isopropanol) obtained. Yield: 32% of theory.
4-(2-Benzylthiophenyl)-3-cyano-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester
- Schmelzpunkt: 183-185 °C.
- Ausbeute: 15,7 g (58%).
- Melting point: 183-185 ° C.
- Yield: 15.7 g (58%).
Analog Beispiel 261 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-(2-(3-Chlorbenzylthio)-benzyliden)-acetessigsäuremethylester und β-Aminocrotonsäurenitril in Methanol der 4-(2-(3-Chlorbenzylthio)-phenyl)-3-cyano-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethy)pyridin-5-carbonsäuremethylester
- vom Fp.: 155 °C (Methanol) erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 51% der Theorie.
- obtained from mp: 155 ° C (methanol).
- Yield: 51% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 261 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-(2-Benzylthiobenzyliden)-acetessigsäureethylester und β-Aminocrotonsäurenitril in Ethanol der 4-(2-Benzylthiophenyl)-3-cyano-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-pyridin-5-carbonsäureethylester
- vom Fp.: 127 °C erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 49% der Theorie.
- obtained from mp: 127 ° C.
- Yield: 49% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 261 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-(2-Benzylthiobenzyliden)-acetessigsäure-n-propylester und β-Aminocrotonsäurenitril in Ethanol der 4-(2-Benzylthiophenyl)-3-cyano-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-pyridin-5-carbonsäure-n-propylester
- vom Fp.: 101 °C erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 45% der Theorie.
- obtained from mp: 101 ° C.
- Yield: 45% of theory.
Analog Beispiel 261 wurde durch Umsetzung von 2-(2-Benzylthiobenzyliden)-acetessigsäure- isopropylester und ß-Aminocrotonsäurenitril in Ethanol der 4-(2-Benzylthiophenyl)-3-cyano-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethylpyridin-5-carbonsäureisopropylester
- vom Fp.: 152 °C erhalten.
- Ausbeute: 61 % der Theorie.
- obtained from mp: 152 ° C.
- Yield: 61% of theory.
Claims (19)
R3 represents one of the substituents mentioned under R2 and is identical thereto or differs therefrom, only one of the two substituents
R2 or R3 in each case representing alkoxy, alkylthio or NHR!,
in the form of isomers, isomer mixtures, racemates and optical antipodes, and of their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, which, from a concentration of 10-5 g/ml upwards, cause an at least 25% augmentation of the contraction of the isolated left atrium of the guinea pig heart, for the preparation of medicaments which increase the influx of Ca++ into the cell.
in the form of isomers, isomer mixtures, racemates and optical antipodes and of their pharmaceutically acceptable salts.
and acyl with 1 to 4 C atoms,
and in the abovementioned definitions of the substituents R1 to R8
or
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT82106537T ATE26706T1 (en) | 1981-07-30 | 1982-07-20 | DIHYDROPYRIDINES WITH POSITIVE INOTROPIC ACTION, NEW COMPOUNDS, THEIR USE IN PHARMACEUTICALS AND PROCESSES FOR THEIR PRODUCTION. |
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE3130041 | 1981-07-30 | ||
| DE19813130041 DE3130041A1 (en) | 1981-07-30 | 1981-07-30 | Dihydropyridines having a positive inotropic effect, novel compounds, their use in medicaments, and processes for their preparation |
| DE19823206671 DE3206671A1 (en) | 1982-02-25 | 1982-02-25 | Dihydropyridines having positively inotropic action, novel compounds, their use in medicaments and processes for their preparation |
| DE3206671 | 1982-02-25 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0071819A1 EP0071819A1 (en) | 1983-02-16 |
| EP0071819B1 true EP0071819B1 (en) | 1987-04-22 |
| EP0071819B2 EP0071819B2 (en) | 1992-06-10 |
Family
ID=25794943
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP82106537A Expired - Lifetime EP0071819B2 (en) | 1981-07-30 | 1982-07-20 | Dihydropyridines with a positive inotropic activity, their use in pharmaceutical preparations, and processes for their preparation |
Country Status (21)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4532248A (en) |
| EP (1) | EP0071819B2 (en) |
| JP (2) | JPH066535B2 (en) |
| KR (2) | KR890001566B1 (en) |
| AU (1) | AU566502B2 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA1212672A (en) |
| CH (1) | CH656530A5 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE3276112D1 (en) |
| DK (1) | DK339782A (en) |
| ES (1) | ES8305716A1 (en) |
| FI (1) | FI822643L (en) |
| FR (1) | FR2511247B1 (en) |
| GB (1) | GB2105989B (en) |
| HK (1) | HK19389A (en) |
| IE (1) | IE54259B1 (en) |
| IL (1) | IL66405A (en) |
| IT (1) | IT1190929B (en) |
| NL (1) | NL8202958A (en) |
| NZ (1) | NZ201395A (en) |
| PH (1) | PH23086A (en) |
| SG (1) | SG52988G (en) |
Cited By (40)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2514761A1 (en) * | 1981-10-19 | 1983-04-22 | Maruko Pharmaceutical Co | NEW 1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINES, USEFUL AS HYPOTENSEURS |
| EP0104550A2 (en) * | 1982-09-23 | 1984-04-04 | Bayer Ag | Condensed 1,4-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their application as pharmaceutical products |
| EP0106276A2 (en) * | 1982-10-15 | 1984-04-25 | Kyowa Hakko Kogyo Co., Ltd. | 1,4-Dihydropyridine derivatives |
| EP0106275A3 (en) * | 1982-10-15 | 1984-05-23 | Kyowa Hakko Kogyo Co., Ltd. | 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives |
| EP0111453A1 (en) * | 1982-12-10 | 1984-06-20 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Amide derivatives |
| EP0111455A2 (en) * | 1982-12-10 | 1984-06-20 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Unsaturated lactones |
| EP0123095A2 (en) * | 1983-03-25 | 1984-10-31 | Bayer Ag | Chromone- and thiochromone-substited 1,4-dihydropyridine lactones, processes for their preparation and their use as pharmaceutical preparations |
| FR2545826A1 (en) * | 1982-03-22 | 1984-11-16 | Bristol Myers Co | CYCLIC DIHYDROPYRIDYLIMIDATES, AND THEIR PHARMACOLOGICAL APPLICATION |
| EP0125803A2 (en) * | 1983-04-27 | 1984-11-21 | FISONS plc | Pharmaceutically active dihydropyridines |
| EP0132375A2 (en) * | 1983-07-23 | 1985-01-30 | Pfizer Limited | Dihydropyridine anti-ischaemic and antihypertensive agents |
| FR2554109A1 (en) * | 1983-11-01 | 1985-05-03 | Sandoz Sa | NOVEL 1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE DERIVATIVES, THEIR PREPARATION AND USE IN THERAPEUTICS AS MEDICAMENTS |
| EP0141221A1 (en) * | 1983-09-26 | 1985-05-15 | Nissan Chemical Industries Ltd. | 1,4-Dihydropyridine-5-phosphonic acid ester |
| EP0141222A1 (en) * | 1983-09-26 | 1985-05-15 | Nissan Chemical Industries Ltd. | Dihydropyridine-5-phosphonic acid cyclic ester |
| EP0151006A2 (en) * | 1984-01-25 | 1985-08-07 | Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Dihydropyridine compounds, their production, pharmaceutical compositions containing them, and methods of producing these compositions |
| EP0153016A2 (en) * | 1984-02-14 | 1985-08-28 | RECORDATI S.A. CHEMICAL and PHARMACEUTICAL COMPANY | Asymmetrical diesters of 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid |
| EP0164010A2 (en) * | 1984-06-04 | 1985-12-11 | Bayer Ag | 3-Nitro-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their pharmaceutical use |
| EP0165032A2 (en) * | 1984-06-15 | 1985-12-18 | Pfizer Limited | Dihydropyridine anti-ischaemic and antihypertensive agents |
| EP0167371A2 (en) * | 1984-06-28 | 1986-01-08 | Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. | Dihydropyridine compounds, their production, and pharmaceutical compositions containing them |
| EP0183091A2 (en) * | 1984-11-27 | 1986-06-04 | CASSELLA Aktiengesellschaft | 1,4-Dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their use |
| EP0186028A2 (en) * | 1984-12-22 | 1986-07-02 | Bayer Ag | Optically active nitrodihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their use in medicines |
| EP0189057A2 (en) * | 1985-01-22 | 1986-07-30 | Bayer Ag | 5-Aryl-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation as well as use in medicaments |
| EP0214437A2 (en) * | 1985-08-09 | 1987-03-18 | Bayer Ag | Preparation of 1,4-Dihydropyridine derivatives using novel Intermediates |
| EP0237695A2 (en) * | 1986-01-17 | 1987-09-23 | MERCK PATENT GmbH | 1,4-Dihydropyridines |
| EP0241281A2 (en) * | 1986-04-09 | 1987-10-14 | Ortho Pharmaceutical Corporation | Substituted thiacycloalkeno [3,2-b] pyridines, methods of preparation, compositions and method of use |
| EP0244713A2 (en) * | 1986-05-07 | 1987-11-11 | Bayer Ag | 3-Amino-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their use as medicaments |
| EP0299727A1 (en) * | 1987-07-17 | 1989-01-18 | Pfizer Limited | Therapeutic agents |
| EP0308608A1 (en) * | 1987-07-28 | 1989-03-29 | Bayer Ag | Substituted nitro-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their use |
| US4904665A (en) * | 1987-02-26 | 1990-02-27 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | Benzylaminoaryl-dihydropyridinelactones and their use in medicaments |
| EP0432751A2 (en) * | 1989-12-14 | 1991-06-19 | Marion Merrell Dow Inc. | Isomers of 1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-5-nitropyridine-3-carboxylate |
| EP0515940A1 (en) * | 1991-05-30 | 1992-12-02 | Bayer Ag | New 2-amino-5-cyano-1,4-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and use in pharmaceutical compositions |
| WO1994022829A2 (en) * | 1993-04-05 | 1994-10-13 | Synaptic Pharmaceutical Corporation | Dihydropyridines and new uses thereof |
| EP0622363A2 (en) * | 1993-04-27 | 1994-11-02 | Bayer Ag | 2-amino-5-cyano-4-quinolyldihydropyridine esters, process for their preparation and their use in medicine for the treatment of heart-circulatory illnesses |
| EP0622364A2 (en) * | 1993-04-27 | 1994-11-02 | Bayer Ag | 2,6-Disubstituted-4-quinolyl-dihydropyridines |
| EP0622369A2 (en) * | 1993-04-27 | 1994-11-02 | Bayer Ag | 2-Amino-4-quinoline-dihydropyridine, process for preparation and use thereof |
| US5508406A (en) * | 1993-04-27 | 1996-04-16 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | Quinolyl-dihydropyridine esters, processes for their preparation, and their use in medicaments |
| US5550245A (en) * | 1993-04-27 | 1996-08-27 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | 3-quinolyl-substituted dihydropyridines, processes for their preparation and their use in medicaments |
| US5606066A (en) * | 1992-07-10 | 1997-02-25 | Goldmann; Siegfried | Light activable "caged" 1-(2-nitrobenzyl)-substituted 1,4-dihydropyridines |
| US5767131A (en) * | 1993-04-05 | 1998-06-16 | Synaptic Pharmaceutical Corporation | Dihydropyridines and new uses thereof |
| AU709190B2 (en) * | 1996-01-29 | 1999-08-26 | United States Of America, Represented By The Secretary, Department Of Health And Human Services, The | Dihydropyridine-, pyridine-, benzopyran- one- and triazoloquinazoline derivative, their preparation and their use as adenosine receptor antagonists |
| US6211198B1 (en) | 1993-04-05 | 2001-04-03 | Synaptic Pharmaceutical Corporation | Dihydropyridines and new uses thereof |
Families Citing this family (101)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3269219D1 (en) * | 1981-11-17 | 1986-03-27 | Fisons Plc | Dihydropyridines, methods for their production and their formulation and use as pharmaceuticals |
| DE3207982A1 (en) * | 1982-03-05 | 1983-09-08 | Bayer Ag, 5090 Leverkusen | NEW 1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION AND USE THEREOF IN MEDICINAL PRODUCTS |
| DE3209274A1 (en) * | 1982-03-13 | 1983-09-15 | Bayer Ag, 5090 Leverkusen | PYRIDINE CARBONIC ACID ESTER, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF AND THEIR USE AS A MEDICINAL PRODUCT |
| EP0100189B1 (en) * | 1982-07-22 | 1986-05-28 | Pfizer Limited | Dihydropyridine anti-ischaemic and antihypertensive agents |
| US4656181A (en) * | 1982-11-24 | 1987-04-07 | Cermol S.A. | Esters of 1,4-dihydropyridines, processes for the preparation of the new esters, and medicaments containing the same |
| GR79111B (en) * | 1982-12-20 | 1984-10-02 | Lepetit Spa | |
| DE3319956A1 (en) * | 1983-06-01 | 1984-12-06 | Bayer Ag, 5090 Leverkusen | 1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF AND THEIR USE IN MEDICINAL PRODUCTS |
| JPS60120861A (en) * | 1983-12-02 | 1985-06-28 | Otsuka Pharmaceut Co Ltd | Dihydropyridine derivative |
| DE3343658A1 (en) * | 1983-12-02 | 1985-06-13 | Bayer Ag, 5090 Leverkusen | HYDROXY-TETRAHYDROPYRIDINLACTONE, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF AND THEIR USE IN MEDICINAL PRODUCTS |
| US5137889A (en) * | 1983-12-02 | 1992-08-11 | Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Dihydropyridine derivatives and process for preparing the same |
| DE3410645A1 (en) * | 1984-03-23 | 1985-09-26 | Bayer Ag, 5090 Leverkusen | L-ALKYL-SUBSTITUTED 1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE LACTONE, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF AND THEIR USE IN MEDICINAL PRODUCTS |
| IE57810B1 (en) * | 1984-03-27 | 1993-04-21 | Delagrange Lab | 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives,their preparation and their use |
| US4567268A (en) * | 1984-04-03 | 1986-01-28 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Process for preparation of certain tetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]pyridines |
| DE3414801A1 (en) * | 1984-04-19 | 1985-10-24 | Bayer Ag, 5090 Leverkusen | 4- (NITROPHENYL) TETRAHYDROPYRIDINE, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF AND THEIR USE AS A MEDICINAL PRODUCT |
| US4672068A (en) * | 1984-05-04 | 1987-06-09 | Fujirebio Kabushiki Kaisha | Antihypertensive 1,4-dihydropyridines having a conjugated ester |
| GB8412208D0 (en) * | 1984-05-12 | 1984-06-20 | Pfizer Ltd | Quinolone inotropic agents |
| US4731370A (en) * | 1984-06-25 | 1988-03-15 | Toyama Chemical Co., Ltd. | Pyridyl ester containing 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives and salts thereof and pharmaceutical composition containing the same |
| GB2162513B (en) * | 1984-06-25 | 1988-01-20 | Toyama Chemical Co Ltd | Dihydropyridine derivatives |
| FI852359L (en) * | 1984-06-27 | 1985-12-28 | Hoffmann La Roche | DIHYDROPYRIDINDERIVAT. |
| GB8421039D0 (en) * | 1984-08-17 | 1984-09-19 | Wyeth John & Brother Ltd | Heterocyclic compounds |
| NZ212895A (en) * | 1984-08-22 | 1988-07-28 | Glaxo Spa | 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives and pharmaceutical compositions |
| DE3431152A1 (en) * | 1984-08-24 | 1986-03-06 | Cassella Ag, 6000 Frankfurt | METHOD FOR PRODUCING OPTICALLY ACTIVE, SUBSTITUTED 1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE AND THEIR USE AS A MEDICINAL PRODUCT |
| DE3587851D1 (en) * | 1984-09-28 | 1994-07-21 | Byk Gulden Lomberg Chem Fab | New diaryl compounds. |
| JPS6191185A (en) * | 1984-10-11 | 1986-05-09 | Sumitomo Seiyaku Kk | Novel oxadiazolyl-1,4-dihydropyridine derivative |
| US4994476A (en) * | 1984-10-31 | 1991-02-19 | Bristol-Myers Company | Dihydropyridin-3,5-dicarboxylates incorporating aryloxypropanolamine moieties |
| US4616002A (en) * | 1984-11-09 | 1986-10-07 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Dihydro pyridine compounds, compositions and use |
| US4678796A (en) * | 1984-11-30 | 1987-07-07 | Warner-Lambert Company | 2-alkylidene derivatives of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine-2,5-pyridine carboxylic acid dialkyl esters useful for treatment of cardiovascular disorders |
| HUT39179A (en) * | 1984-12-10 | 1986-08-28 | Sandoz Ag | Process for production of derivatives of 1,4-dihydro-piridin |
| JPH0676405B2 (en) * | 1986-06-13 | 1994-09-28 | 日清製粉株式会社 | 1,4-Dihydropyridine derivative and pharmaceutical composition containing the same |
| US4833150A (en) * | 1985-03-14 | 1989-05-23 | Nelson Research & Development Co. | 1,4-dihydropyridines |
| US4652573A (en) * | 1985-03-14 | 1987-03-24 | Nelson Research & Development Co. | Calcium antagonist N-hetero ester 1,4-dihydropyridines |
| JPH0742276B2 (en) * | 1985-03-15 | 1995-05-10 | サントリー株式会社 | Novel N-substituted 3,4-dihydropyrimidine derivative and vasodilator |
| DE3517473A1 (en) * | 1985-05-15 | 1986-11-20 | Bayer Ag, 5090 Leverkusen | PYRIMIDINYL-DIHYDROPYRIDINE, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION AND THEIR USE IN MEDICINAL PRODUCTS |
| US4728652A (en) * | 1985-05-20 | 1988-03-01 | E. R. Squibb & Sons, Inc. | 2-substituted thio or oxy-4-aryl or heterocyclo-5-carboxy-1,4-dihydropyrimidines, composition containing them, and method of using them to reduce blood pressure |
| CA1267416A (en) * | 1985-06-17 | 1990-04-03 | Ila Sircar | 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives useful for the treatment of cardiovascular disorders |
| DE3521761A1 (en) * | 1985-06-19 | 1987-01-02 | Bayer Ag | NEW 1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION AND THEIR USE IN MEDICINAL PRODUCTS |
| ZA863578B (en) * | 1985-06-21 | 1987-02-25 | Hoffmann La Roche | Dihydropyridine derivatives |
| JPS6210087A (en) * | 1985-07-03 | 1987-01-19 | Shionogi & Co Ltd | 4,7-dihydrothieno(2,3-b)pyridine derivative, production thereof and remedy for circulatory disease |
| IT1215298B (en) * | 1985-08-06 | 1990-01-31 | Boehringer Biochemia Srl | 2- (ETEROALCHIL) -1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE AND A PROCESS FOR THEIR PRODUCTION. |
| IT1201454B (en) * | 1985-08-19 | 1989-02-02 | Boehringer Biochemia Srl | 1,4-dihydropyridine-2-SUBSTITUTED |
| EP0226271B1 (en) * | 1985-08-21 | 1990-11-22 | GLAXO S.p.A. | 1,4-dihydropyridine compounds and their preparation and pharmaceutical formulation |
| IT1190405B (en) * | 1985-10-22 | 1988-02-16 | Recordati Chem Pharm | FLAVONE DERIVATIVES |
| GB8527698D0 (en) * | 1985-11-09 | 1985-12-11 | Pfizer Ltd | Dihydropyridine antiischaemic & antihypertensive agents |
| US4788203A (en) * | 1985-11-26 | 1988-11-29 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Cyclized N-substituted-tetrahydropyridine compounds, useful in the treatment of cardiovascular disorders |
| DE3544693A1 (en) * | 1985-12-18 | 1987-06-19 | Bayer Ag | 4-THIENYL-DIHYDROPYRIDINE, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION AND THEIR USE IN MEDICINAL PRODUCTS |
| DE3600596A1 (en) * | 1986-01-11 | 1987-07-16 | Bayer Ag | 4-AMINOARYLDIHYDROPYRIDINLACTONE, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION AND THEIR USE IN MEDICINAL PRODUCTS |
| DE3600594A1 (en) * | 1986-01-11 | 1987-07-16 | Bayer Ag | METHIONINE SUBSTITUTED 1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION AND THEIR USE |
| US5162338A (en) * | 1986-01-11 | 1992-11-10 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | Circulation active 4-aminoaryldihydropryidine lactones |
| IT1204461B (en) * | 1986-02-20 | 1989-03-01 | Glaxo Spa | HETEROCYCLIC DERIVATIVES |
| IT1204462B (en) * | 1986-02-20 | 1989-03-01 | Glaxo Spa | HETEROCYCLIC DERIVATIVES |
| IT1204460B (en) * | 1986-02-20 | 1989-03-01 | Glaxo Spa | HETEROCYCLIC DERIVATIVES |
| IT1204459B (en) * | 1986-02-20 | 1989-03-01 | Glaxo Spa | HETEROCYCLIC DERIVATIVES |
| US4689414A (en) * | 1986-02-24 | 1987-08-25 | E. R. Squibb & Sons, Inc. | 2-(substituted imino)-6-aryl-3,6-dihydro-4-substituted-1,5(2H)-pyrimidinecarboxylic acids and analogs |
| US4849436A (en) * | 1986-03-11 | 1989-07-18 | Nelson Research & Development Co. | 1,4-dihydropyridines |
| US4684656A (en) * | 1986-03-14 | 1987-08-04 | E. R. Squibb & Sons, Inc. | 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-substituted-4-aryl-3-(substituted sulfonyl)-2-thioxo(or oxo)-5-pyrimidinecarboxylic acids and esters and method of using them to lower blood pressure |
| US4855301A (en) * | 1986-10-09 | 1989-08-08 | E. R. Squibb & Sons, Inc. | 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-6-substituted-4-aryl(or heterocyclo)-3-((substituted amino)carbonyl)-2-thioxo (or oxo)-5-pyrimidinecarboxylic acids and esters |
| US4684655A (en) * | 1986-03-14 | 1987-08-04 | E. R. Squibb & Sons, Inc. | 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-substituted-4-aryl-3-substituted-2-thioxo(or oxo)-5-pyrimidinecarboxylic acids and esters and use thereof to lower blood pressure |
| US4845225A (en) * | 1986-04-09 | 1989-07-04 | Ortho Pharmaceutical Corporation | Substituted thiacycloalkeno [3,2-b] pyridines |
| US4705785A (en) * | 1986-04-09 | 1987-11-10 | Ortho Pharmaceutical Corporation | Substituted thiacycloalkeno (3,2-b) pyridines and pharmaceutical compositions and method of use |
| IT1197012B (en) * | 1986-07-29 | 1988-11-25 | Boehringer Biochemia Srl | 2- (ACYLTI) METHYL DIHYDROPYRIDINE, A PROCESS FOR THEIR PREPARATION AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS CONTAINING THEM |
| US4868181A (en) * | 1986-08-04 | 1989-09-19 | E. I. Du Pont De Nemours And Company | 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives with calcium agonist and alpha1 -antagonist activity |
| DE3634066A1 (en) * | 1986-10-07 | 1988-04-21 | Boehringer Mannheim Gmbh | NEW 5-ALKYLBENZIMIDAZOLES, PROCESS FOR THEIR PRODUCTION AND MEDICINAL PRODUCTS |
| JPS63112560A (en) * | 1986-10-29 | 1988-05-17 | Green Cross Corp:The | Dihydropyridine derivative |
| IT1213555B (en) * | 1986-12-11 | 1989-12-20 | Boehringer Biochemia Srl | 2 METHYLOMETHYL HYDROPYRIDINE, A PROCESS FOR THEIR PREPARATION AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS CONTAINING THEM. |
| IT1213440B (en) * | 1986-12-24 | 1989-12-20 | Boehringer Biochemia Srl | 2-DITHIOALKYL-DIHYDROPYRIDINE, A METHOD FOR THEIR PREPARATION AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS WHICH CONTAIN. |
| JPH0688973B2 (en) * | 1987-03-12 | 1994-11-09 | 京都薬品工業株式会社 | 1,4-dihydropyridine derivative |
| IT1203900B (en) * | 1987-04-15 | 1989-02-23 | Lagor Spa | POLES 1,4-DIHYDRO-2,6-DIMETHYLPYRIDIN 3,5-DICARBOXYESTERS USEFUL AS THERMAL STABILIZERS FOR SYNTHETIC POLYMERS |
| GB8709447D0 (en) * | 1987-04-21 | 1987-05-28 | Pfizer Ltd | Dihydropyridines |
| IT1205114B (en) * | 1987-05-29 | 1989-03-15 | Boehringer Biochemia Srl | 2-SELENOMETHYL-1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE, PROCEDURE FOR THEIR PREPARATION AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS CONTAINING THEM |
| DE3732380A1 (en) * | 1987-09-25 | 1989-04-06 | Bayer Ag | DIHYDROPYRIDINETHER, METHOD FOR THEIR PRODUCTION AND THEIR USE |
| US5177211A (en) * | 1988-01-21 | 1993-01-05 | Alter, S.A. | 4-alkyl-1,4-dihydropyridines with PAF-antagonist activity |
| US4879384A (en) * | 1988-06-15 | 1989-11-07 | Ortho Pharmaceutical Corporation | Preparation of thiocycloalkno [3,2-b] pyridines |
| US5075440A (en) * | 1990-05-03 | 1991-12-24 | Ortho Pharmaceutical Corporation | Novel pyrido[2,3-f](1,4)thiazepines and pyrido[3,2-b](1,5)benzothiazepines |
| US5260444A (en) * | 1990-05-07 | 1993-11-09 | Wakunaga Seiyaku Kabushiki Kaisha | Dihydropyridine derivative |
| JPH0413679A (en) * | 1990-05-07 | 1992-01-17 | Wakunaga Pharmaceut Co Ltd | Novel dihydropyridine derivative |
| US5166148A (en) * | 1990-07-09 | 1992-11-24 | The Du Pont Merck Pharmaceutical Company | 2-amino-1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives with calcium agonist and alpha1 -antagonist activity |
| US5100892A (en) * | 1990-11-13 | 1992-03-31 | Glaxo Inc. | Dihydropyridine vasodilator agents |
| US5258519A (en) * | 1990-11-13 | 1993-11-02 | Glaxo Inc. | Dihydropyridine vasodilators agents |
| AU2603197A (en) | 1996-04-10 | 1997-10-29 | United States Of America, Represented By The Secretary, Department Of Health And Human Services, The | Use of an a1 adenosine receptor agonist to treat cerebral ischaemia |
| US6265417B1 (en) * | 1997-12-18 | 2001-07-24 | Abbott Laboratories | Potassium channel openers |
| US6593335B1 (en) * | 1997-12-18 | 2003-07-15 | Abbott Laboratories | Potassium channel openers |
| AU4549399A (en) * | 1998-06-08 | 1999-12-30 | Theravance, Inc. | Novel calcium channel drugs and uses |
| US6897305B2 (en) | 1998-06-08 | 2005-05-24 | Theravance, Inc. | Calcium channel drugs and uses |
| US7101909B2 (en) * | 1998-10-12 | 2006-09-05 | Theravance, Inc. | Calcium channel drugs and uses |
| CZ20014518A3 (en) | 1999-06-14 | 2003-02-12 | Ortho-Mcneil Pharmaceutical, Inc. | Dithiepino[6,5-b]pyridines, compositions containing these compounds and process of their preparation |
| DE60022056T2 (en) | 1999-07-12 | 2006-06-08 | Ortho-Mcneil Pharmaceutical, Inc. | Oxathiophene [6,5-B] dihydropyridine and related compounds and processes |
| AU7102700A (en) | 1999-09-22 | 2001-04-24 | Ortho-Mcneil Pharmaceutical, Inc. | Benzo-fused dithiepino[6,5-b]pyridines, and related compositions and methods |
| AU783470B2 (en) | 2000-01-12 | 2005-10-27 | Ortho-Mcneil Pharmaceutical, Inc. | Benzosulfones with calcium antagonist activity |
| WO2001055152A1 (en) * | 2000-01-27 | 2001-08-02 | Ortho-Mcneil Pharmaceutical, Inc.. | BENZOXATHIEPINO[3,4-b]PYRIDINE DERIVATIVES, PROCESS FOR THEIR PREPARATION AND THEIR USE AS MEDICAMENTS |
| US6538004B2 (en) | 2000-03-03 | 2003-03-25 | Abbott Laboratories | Tricyclic dihydropyrazolone and tricyclic dihydroisoxazolone potassium channel openers |
| CA2403808A1 (en) | 2000-03-23 | 2001-09-27 | Ortho-Mcneil Pharmaceutical, Inc. | Thiepino [3,2-b] dihydropyridines and related compositions and methods |
| EP1296990A2 (en) | 2000-05-30 | 2003-04-02 | Ortho-McNeil Pharmaceutical, Inc. | Dihydropyridine compounds for the inhibition of calcium-influx |
| KR100428398B1 (en) * | 2002-01-23 | 2004-04-28 | 김관진 | Slide fastener of stop pin manufactory machine |
| MXPA05000200A (en) * | 2002-07-02 | 2005-06-06 | Schering Corp | New neuropeptide y y5 receptor antagonists. |
| EP1663227A2 (en) * | 2003-09-10 | 2006-06-07 | Synta Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Dihydropyridine compounds for treating or preventing metabolic disorders |
| WO2009006580A1 (en) * | 2007-07-05 | 2009-01-08 | Cv Therapeutics, Inc. | Optionally condensed dihydropyridine, dihydropyrimidine and dihydropyrane derivatives acting as late sodium channel blockers |
| US20090012103A1 (en) * | 2007-07-05 | 2009-01-08 | Matthew Abelman | Substituted heterocyclic compounds |
| WO2014083383A1 (en) * | 2012-11-28 | 2014-06-05 | Stichting Dienst Landbouwkundig Onderzoek | Substituted dihydropyrtoines for somatic embryogenesis iν plants |
| WO2021253180A1 (en) * | 2020-06-15 | 2021-12-23 | Novartis Ag | Methyl (r) -2- (fluoromethyl) -5-oxo-4-phenyl-4, 5, 6, 7-tetrahydro-1h-cyclopenta [b] pyridine-3-carboxylate and methyl (r) -2- (fluoromethyl) -5-oxo-4-phenyl-1, 4, 5, 7-tetrahydrofuro [3, 4-b] pyridine-3-carboxylate as cav1.2 activators |
| AU2021291799A1 (en) | 2020-06-16 | 2023-01-19 | Novartis Ag | Methyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,7-tetradhydrofuro(3,4- b)pyridine-3-carboxylate compounds as Cav1.2 activators |
| WO2023111799A1 (en) * | 2021-12-13 | 2023-06-22 | Novartis Ag | PYRIDINE-3-CARBOXYLATE COMPOUNDS AS CaV1.2 ACTIVATORS |
Family Cites Families (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1923990C3 (en) * | 1969-05-10 | 1978-11-23 | Bayer Ag | Process for the preparation of N-substituted M-dihydropyridine-S.S-dicarboxylic acid esters |
| US3932645A (en) * | 1971-04-10 | 1976-01-13 | Farbenfabriken Bayer Ag | Pharmaceutical compositions containing unsymmetrical esters of 1,4-dihydropyridine 3,5-dicarboxylic acid |
| DE2117571C3 (en) * | 1971-04-10 | 1979-10-11 | Bayer Ag, 5090 Leverkusen | Asymmetrical 1,4-dihydropyridine-33-dicarboxylic acid esters, process for their preparation and their use as pharmaceuticals |
| DE2218644C3 (en) * | 1972-04-18 | 1982-08-19 | Bayer Ag, 5090 Leverkusen | Basic esters of 1,4-dihydropyridines, processes for their preparation and their use as pharmaceuticals |
| JPS4935277A (en) * | 1972-08-07 | 1974-04-01 | ||
| DE2242786A1 (en) * | 1972-08-31 | 1974-03-14 | Bayer Ag | PROCESS FOR THE MANUFACTURING OF NEW 2-AMINO-1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINES WITH A CARBONYL FUNCTION AND THEIR USE AS A MEDICINAL PRODUCT |
| GB1552911A (en) * | 1975-07-02 | 1979-09-19 | Fujisawa Pharmaceutical Co | 1,4 dihydropyridine derivatives and the preparation thereof |
| DD122524A1 (en) * | 1975-10-17 | 1976-10-12 | ||
| DE2658804A1 (en) * | 1976-12-24 | 1978-07-06 | Bayer Ag | Compsn. with circulatory and cardiac activity - contains a 3-cyano-1,2-di:hydro-pyridine deriv. |
| DE2659665A1 (en) * | 1976-12-30 | 1978-07-13 | Nattermann A & Cie | NEW 1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE DERIVATIVES |
| DE2752820A1 (en) * | 1977-11-26 | 1979-05-31 | Bayer Ag | NEW NITRO-SUBSTITUTED 1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE, THE METHOD FOR THEIR MANUFACTURING AND THEIR USE AS A MEDICINAL PRODUCT |
| NO780094L (en) * | 1978-01-11 | 1979-05-21 | Finn Hallingstad | Procedure for the production of feed for feeding fish in salt water |
| CA1110234A (en) * | 1978-01-18 | 1981-10-06 | Hoffmann-La Roche Limited | 4-pyridone-3-carboxylic acids and process for the preparation thereof |
| JPS5527054A (en) * | 1978-08-15 | 1980-02-26 | Gen Foods Corp | Adsorption method |
| DE2847237A1 (en) * | 1978-10-31 | 1980-05-14 | Bayer Ag | Cardiovascular 1,4-di:hydro-pyridine-3-carboxylic acids prodn. - by alkaline hydrolysis of ester(s) with electron withdrawing substit. |
| US4285955A (en) * | 1978-10-31 | 1981-08-25 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | 1,4-Dihydropyridinecarboxylic acids |
| DE2935451A1 (en) * | 1979-09-01 | 1981-03-19 | Bayer Ag, 5090 Leverkusen | OPTICALLY ACTIVE 1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF AND THEIR USE AS A MEDICINAL PRODUCT |
-
1982
- 1982-02-27 NZ NZ201395A patent/NZ201395A/en unknown
- 1982-07-13 AU AU85945/82A patent/AU566502B2/en not_active Ceased
- 1982-07-14 US US06/398,034 patent/US4532248A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1982-07-20 EP EP82106537A patent/EP0071819B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1982-07-20 DE DE8282106537T patent/DE3276112D1/en not_active Expired
- 1982-07-22 NL NL8202958A patent/NL8202958A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1982-07-27 IL IL66405A patent/IL66405A/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1982-07-27 CH CH4566/82A patent/CH656530A5/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1982-07-28 IT IT22620/82A patent/IT1190929B/en active
- 1982-07-28 FI FI822643A patent/FI822643L/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1982-07-29 FR FR8213257A patent/FR2511247B1/en not_active Expired
- 1982-07-29 IE IE1827/82A patent/IE54259B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1982-07-29 PH PH27645A patent/PH23086A/en unknown
- 1982-07-29 DK DK339782A patent/DK339782A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1982-07-29 ES ES514525A patent/ES8305716A1/en not_active Expired
- 1982-07-29 CA CA000408355A patent/CA1212672A/en not_active Expired
- 1982-07-29 GB GB08221931A patent/GB2105989B/en not_active Expired
- 1982-07-30 KR KR8203412A patent/KR890001566B1/en active
- 1982-07-30 JP JP57132344A patent/JPH066535B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1982-07-30 KR KR1019890001597D patent/KR890001567B1/en active
-
1988
- 1988-04-22 SG SG52988A patent/SG52988G/en unknown
-
1989
- 1989-03-09 HK HK193/89A patent/HK19389A/en not_active IP Right Cessation
-
1992
- 1992-12-16 JP JP4354673A patent/JPH05271078A/en active Pending
Cited By (71)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2514761A1 (en) * | 1981-10-19 | 1983-04-22 | Maruko Pharmaceutical Co | NEW 1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINES, USEFUL AS HYPOTENSEURS |
| FR2545826A1 (en) * | 1982-03-22 | 1984-11-16 | Bristol Myers Co | CYCLIC DIHYDROPYRIDYLIMIDATES, AND THEIR PHARMACOLOGICAL APPLICATION |
| EP0104550A2 (en) * | 1982-09-23 | 1984-04-04 | Bayer Ag | Condensed 1,4-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their application as pharmaceutical products |
| EP0104550A3 (en) * | 1982-09-23 | 1986-11-26 | Bayer Ag | Condensed 1,4-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their application as pharmaceutical products |
| EP0106276A2 (en) * | 1982-10-15 | 1984-04-25 | Kyowa Hakko Kogyo Co., Ltd. | 1,4-Dihydropyridine derivatives |
| EP0106276A3 (en) * | 1982-10-15 | 1984-05-23 | Kyowa Hakko Kogyo Co., Ltd. | 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives |
| EP0106275A3 (en) * | 1982-10-15 | 1984-05-23 | Kyowa Hakko Kogyo Co., Ltd. | 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives |
| EP0111453A1 (en) * | 1982-12-10 | 1984-06-20 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Amide derivatives |
| EP0111455A2 (en) * | 1982-12-10 | 1984-06-20 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Unsaturated lactones |
| EP0111455A3 (en) * | 1982-12-10 | 1984-07-25 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Unsaturated lactones |
| EP0123095A2 (en) * | 1983-03-25 | 1984-10-31 | Bayer Ag | Chromone- and thiochromone-substited 1,4-dihydropyridine lactones, processes for their preparation and their use as pharmaceutical preparations |
| EP0123095A3 (en) * | 1983-03-25 | 1986-12-03 | Bayer Ag | Chromone- and thiochromone-substited 1,4-dihydropyridine lactones, processes for their preparation and their use as pharmaceutical preparations |
| EP0125803A2 (en) * | 1983-04-27 | 1984-11-21 | FISONS plc | Pharmaceutically active dihydropyridines |
| EP0125803A3 (en) * | 1983-04-27 | 1987-01-21 | FISONS plc | Pharmaceutically active dihydropyridines |
| EP0132375A3 (en) * | 1983-07-23 | 1987-07-01 | Pfizer Limited | Dihydropyridine anti-ischaemic and antihypertensive agents |
| EP0132375A2 (en) * | 1983-07-23 | 1985-01-30 | Pfizer Limited | Dihydropyridine anti-ischaemic and antihypertensive agents |
| EP0141221A1 (en) * | 1983-09-26 | 1985-05-15 | Nissan Chemical Industries Ltd. | 1,4-Dihydropyridine-5-phosphonic acid ester |
| EP0141222A1 (en) * | 1983-09-26 | 1985-05-15 | Nissan Chemical Industries Ltd. | Dihydropyridine-5-phosphonic acid cyclic ester |
| US4576934A (en) * | 1983-09-26 | 1986-03-18 | Nissan Chemical Industries Ltd. | Antihypertensive dihydropyridine-5-phosphonic acid cyclic esters |
| WO1985001940A1 (en) * | 1983-11-01 | 1985-05-09 | Sandoz Ag | Derivatives of 1,4-dihydropyridine, preparation thereof and pharmaceutical compositions containing them |
| FR2554109A1 (en) * | 1983-11-01 | 1985-05-03 | Sandoz Sa | NOVEL 1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE DERIVATIVES, THEIR PREPARATION AND USE IN THERAPEUTICS AS MEDICAMENTS |
| EP0151006A2 (en) * | 1984-01-25 | 1985-08-07 | Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Dihydropyridine compounds, their production, pharmaceutical compositions containing them, and methods of producing these compositions |
| EP0151006A3 (en) * | 1984-01-25 | 1987-07-01 | Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. | Dihydropyridine compounds, their production, pharmaceutical compositions containing them, and methods of producing these compositions |
| EP0153016A2 (en) * | 1984-02-14 | 1985-08-28 | RECORDATI S.A. CHEMICAL and PHARMACEUTICAL COMPANY | Asymmetrical diesters of 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid |
| EP0153016A3 (en) * | 1984-02-14 | 1985-10-02 | Recordati S.A. Chemical And Pharmaceutical Company | Asymmetrical diesters of 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid |
| EP0164010A2 (en) * | 1984-06-04 | 1985-12-11 | Bayer Ag | 3-Nitro-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their pharmaceutical use |
| EP0164010A3 (en) * | 1984-06-04 | 1987-08-05 | Bayer Ag | 3-nitro-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their pharmaceutical use |
| EP0165032A2 (en) * | 1984-06-15 | 1985-12-18 | Pfizer Limited | Dihydropyridine anti-ischaemic and antihypertensive agents |
| EP0165032A3 (en) * | 1984-06-15 | 1987-06-16 | Pfizer Limited | Dihydropyridine anti-ischaemic and antihypertensive agents |
| EP0167371A2 (en) * | 1984-06-28 | 1986-01-08 | Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. | Dihydropyridine compounds, their production, and pharmaceutical compositions containing them |
| EP0167371A3 (en) * | 1984-06-28 | 1987-06-16 | Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. | Dihydropyridine compounds, their production, and pharmaceutical compositions containing them |
| EP0183091A3 (en) * | 1984-11-27 | 1987-08-19 | CASSELLA Aktiengesellschaft | 1,4-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their use |
| EP0183091A2 (en) * | 1984-11-27 | 1986-06-04 | CASSELLA Aktiengesellschaft | 1,4-Dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their use |
| US4764516A (en) * | 1984-12-22 | 1988-08-16 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | Mixtures of optically active nitrodihydropyridines active on the circulatory system |
| EP0186028A3 (en) * | 1984-12-22 | 1988-05-25 | Bayer Ag | Optically active nitrodihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their use in medicines |
| EP0186028A2 (en) * | 1984-12-22 | 1986-07-02 | Bayer Ag | Optically active nitrodihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their use in medicines |
| EP0189057A3 (en) * | 1985-01-22 | 1986-10-08 | Bayer Ag | 5-aryl-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation as well as use in medicaments |
| EP0189057A2 (en) * | 1985-01-22 | 1986-07-30 | Bayer Ag | 5-Aryl-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation as well as use in medicaments |
| EP0214437A2 (en) * | 1985-08-09 | 1987-03-18 | Bayer Ag | Preparation of 1,4-Dihydropyridine derivatives using novel Intermediates |
| EP0214437A3 (en) * | 1985-08-09 | 1987-10-14 | Bayer Ag | 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives, their preparation and their use in medicaments |
| US4769375A (en) * | 1985-08-09 | 1988-09-06 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | Circulation-active 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives and use thereas |
| EP0237695A2 (en) * | 1986-01-17 | 1987-09-23 | MERCK PATENT GmbH | 1,4-Dihydropyridines |
| EP0237695A3 (en) * | 1986-01-17 | 1988-12-28 | MERCK PATENT GmbH | 1,4-dihydropyridines |
| EP0241281A2 (en) * | 1986-04-09 | 1987-10-14 | Ortho Pharmaceutical Corporation | Substituted thiacycloalkeno [3,2-b] pyridines, methods of preparation, compositions and method of use |
| EP0241281A3 (en) * | 1986-04-09 | 1989-01-25 | Ortho Pharmaceutical Corporation | Substituted thiacycloalkeno û3,2-b¨ pyridines, methods of preparation, compositions and method of use |
| EP0244713A2 (en) * | 1986-05-07 | 1987-11-11 | Bayer Ag | 3-Amino-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their use as medicaments |
| EP0244713A3 (en) * | 1986-05-07 | 1988-09-07 | Bayer Ag | 3-amino-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their use as medicaments |
| US4904665A (en) * | 1987-02-26 | 1990-02-27 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | Benzylaminoaryl-dihydropyridinelactones and their use in medicaments |
| EP0299727A1 (en) * | 1987-07-17 | 1989-01-18 | Pfizer Limited | Therapeutic agents |
| US4898865A (en) * | 1987-07-28 | 1990-02-06 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | [4-(6-Oxo-1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-3-pyridazinyl) anilino hexyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6 Di methyl 5 nitro 4 aryl pyridine 3-carboxylates |
| EP0308608A1 (en) * | 1987-07-28 | 1989-03-29 | Bayer Ag | Substituted nitro-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their use |
| EP0432751A2 (en) * | 1989-12-14 | 1991-06-19 | Marion Merrell Dow Inc. | Isomers of 1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-5-nitropyridine-3-carboxylate |
| EP0432751A3 (en) * | 1989-12-14 | 1992-02-12 | Marion Merrell Dow Inc. | Isomers of 1-azabicyclo(2.2.2)oct-3-yl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-5-nitropyridine-3-carboxylate |
| US5380851A (en) * | 1991-05-30 | 1995-01-10 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | 2-amino-5-cyano-1,4-dihydropyridines, processes for their preparation |
| US5225558A (en) * | 1991-05-30 | 1993-07-06 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | 2-amino-5-cyano-1,4-dihydropyridines, and their use in medicaments |
| EP0515940A1 (en) * | 1991-05-30 | 1992-12-02 | Bayer Ag | New 2-amino-5-cyano-1,4-dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and use in pharmaceutical compositions |
| US5606066A (en) * | 1992-07-10 | 1997-02-25 | Goldmann; Siegfried | Light activable "caged" 1-(2-nitrobenzyl)-substituted 1,4-dihydropyridines |
| WO1994022829A2 (en) * | 1993-04-05 | 1994-10-13 | Synaptic Pharmaceutical Corporation | Dihydropyridines and new uses thereof |
| US6608086B2 (en) | 1993-04-05 | 2003-08-19 | Synaptic Pharmaceutical Corporation | Dihydropyridines and new uses thereof |
| US6310076B1 (en) | 1993-04-05 | 2001-10-30 | Synaptic Pharmaceutical Corporation | Dihydropyridines and new uses thereof |
| US6211198B1 (en) | 1993-04-05 | 2001-04-03 | Synaptic Pharmaceutical Corporation | Dihydropyridines and new uses thereof |
| US5767131A (en) * | 1993-04-05 | 1998-06-16 | Synaptic Pharmaceutical Corporation | Dihydropyridines and new uses thereof |
| EP0622369A2 (en) * | 1993-04-27 | 1994-11-02 | Bayer Ag | 2-Amino-4-quinoline-dihydropyridine, process for preparation and use thereof |
| US5550245A (en) * | 1993-04-27 | 1996-08-27 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | 3-quinolyl-substituted dihydropyridines, processes for their preparation and their use in medicaments |
| US5514803A (en) * | 1993-04-27 | 1996-05-07 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | 2,6-disubstituted 4-quinolyl-dihydropyridines |
| US5629320A (en) * | 1993-04-27 | 1997-05-13 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | 3-quinolyl-substituted dihydropyridines, and their use in medicaments |
| US5508406A (en) * | 1993-04-27 | 1996-04-16 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | Quinolyl-dihydropyridine esters, processes for their preparation, and their use in medicaments |
| US5504209A (en) * | 1993-04-27 | 1996-04-02 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | 2-amino-5-cyano-4-quinolydihydropyridine esters, processes for their preparation and their use in medicaments |
| EP0622364A2 (en) * | 1993-04-27 | 1994-11-02 | Bayer Ag | 2,6-Disubstituted-4-quinolyl-dihydropyridines |
| EP0622363A2 (en) * | 1993-04-27 | 1994-11-02 | Bayer Ag | 2-amino-5-cyano-4-quinolyldihydropyridine esters, process for their preparation and their use in medicine for the treatment of heart-circulatory illnesses |
| AU709190B2 (en) * | 1996-01-29 | 1999-08-26 | United States Of America, Represented By The Secretary, Department Of Health And Human Services, The | Dihydropyridine-, pyridine-, benzopyran- one- and triazoloquinazoline derivative, their preparation and their use as adenosine receptor antagonists |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE3276112D1 (en) | 1987-05-27 |
| AU566502B2 (en) | 1987-10-22 |
| FR2511247A1 (en) | 1983-02-18 |
| IE54259B1 (en) | 1989-08-02 |
| KR890001566B1 (en) | 1989-05-08 |
| FR2511247B1 (en) | 1986-03-07 |
| US4532248A (en) | 1985-07-30 |
| IT8222620A1 (en) | 1984-01-28 |
| CH656530A5 (en) | 1986-07-15 |
| JPS5826872A (en) | 1983-02-17 |
| HK19389A (en) | 1989-03-17 |
| NL8202958A (en) | 1983-02-16 |
| DK339782A (en) | 1983-01-31 |
| NZ201395A (en) | 1987-02-20 |
| JPH066535B2 (en) | 1994-01-26 |
| IL66405A (en) | 1987-12-31 |
| JPH05271078A (en) | 1993-10-19 |
| IL66405A0 (en) | 1982-11-30 |
| FI822643L (en) | 1983-02-01 |
| CA1212672A (en) | 1986-10-14 |
| EP0071819B2 (en) | 1992-06-10 |
| ES514525A0 (en) | 1983-04-16 |
| GB2105989B (en) | 1986-01-08 |
| AU8594582A (en) | 1983-02-03 |
| IT1190929B (en) | 1988-02-24 |
| IE821827L (en) | 1983-01-30 |
| KR840000494A (en) | 1984-02-22 |
| IT8222620A0 (en) | 1982-07-28 |
| FI822643A0 (en) | 1982-07-28 |
| GB2105989A (en) | 1983-04-07 |
| SG52988G (en) | 1993-02-19 |
| ES8305716A1 (en) | 1983-04-16 |
| PH23086A (en) | 1989-04-10 |
| EP0071819A1 (en) | 1983-02-16 |
| KR890001567B1 (en) | 1989-05-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0071819B1 (en) | Dihydropyridines with a positive inotropic activity, their use in pharmaceutical preparations, and processes for their preparation | |
| EP0088276B1 (en) | Compounds, process for their preparation and their use as pharmaceutical preparations | |
| EP0002208B1 (en) | Nitro 1,4-dihydropyridines, medicaments containing them and their manufacture | |
| EP0176956B1 (en) | Diaryl derivatives | |
| EP0088274A1 (en) | 1,4-Dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their application as pharmaceutical preparations | |
| DE2935451A1 (en) | OPTICALLY ACTIVE 1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF AND THEIR USE AS A MEDICINAL PRODUCT | |
| EP0296316A1 (en) | 1,4-Dihydropyridine enantiomers | |
| DE2756226A1 (en) | 1,4-DIHYDROPYRIDINE COMPOUNDS, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF AND PHARMACEUTICAL AGENTS CONTAINING THE SAME | |
| US4497821A (en) | Medicaments having antihypoxic and ischaemia-protective activity | |
| DE3130041A1 (en) | Dihydropyridines having a positive inotropic effect, novel compounds, their use in medicaments, and processes for their preparation | |
| EP0052300A1 (en) | C-3-linked 1,4-dihydropyridines, their use in pharmaceutical preparations and processes for their preparation | |
| EP0088940B1 (en) | Pyridine-carboxylic-acid esters, process for their preparation and their use as pharmaceutical compositions | |
| EP0039863A1 (en) | 1,4-Dihydropyridines with different substituents in positions 2 and 6, processes for their preparation and their use in medicines | |
| EP0123112A2 (en) | Chromone- and thiochromone-substituted 1,4-dihydropyridines, processes for their preparation and their use in pharmaceutical preparations | |
| EP0110259A1 (en) | 1,4-Dihydropyridines, processes for their preparation and their use in medicines | |
| EP0234196A1 (en) | Substituted 1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid piperazides, process for their preparation and their use in medicaments | |
| EP0157324A2 (en) | Tetrahydrothienopyridines, process for their preparation and their pharmaceutical application | |
| EP0627427A1 (en) | 3-Quinolyl substituted dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their use in drugs | |
| EP0362632A2 (en) | Basic 4-aryl-DHP amides, process for their preparation and their pharmaceutical use | |
| EP0244595A2 (en) | Dihydropyridine derivatives, process for their preparation and their use as pharmaceutical compounds | |
| EP0225574B1 (en) | Novel 1,4-dihydropyridines containing fluorine, process for their preparation and their use as medicaments | |
| EP0242829A1 (en) | Dihydropyridines, process for their preparation and their use as medicaments | |
| DE3206671A1 (en) | Dihydropyridines having positively inotropic action, novel compounds, their use in medicaments and processes for their preparation | |
| WO1988007531A1 (en) | New optically active compounds | |
| EP0314038A1 (en) | Pyrrolidines |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19820720 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed |
Owner name: SOCIETA' ITALIANA BREVETTI S.P.A. |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 26706 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19870515 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3276112 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19870527 |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: GOEDECKE AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT,BERLIN Effective date: 19880119 |
|
| NLR1 | Nl: opposition has been filed with the epo |
Opponent name: GOEDECKE AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT |
|
| PUAH | Patent maintained in amended form |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009272 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT MAINTAINED AS AMENDED |
|
| 27A | Patent maintained in amended form |
Effective date: 19920610 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: AEN |
|
| NLR2 | Nl: decision of opposition | ||
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed |
Owner name: SOCIETA' ITALIANA BREVETTI S.P.A. |
|
| NLR3 | Nl: receipt of modified translations in the netherlands language after an opposition procedure | ||
| ET3 | Fr: translation filed ** decision concerning opposition | ||
| ITTA | It: last paid annual fee | ||
| EPTA | Lu: last paid annual fee | ||
| EAL | Se: european patent in force in sweden |
Ref document number: 82106537.2 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19960626 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Payment date: 19960701 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19960723 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19960725 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19960731 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19970720 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19970720 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19970721 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19970731 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: BAYER A.G. Effective date: 19970731 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19980201 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 19980201 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 82106537.2 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19980612 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19980624 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19980713 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19980720 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19990720 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19990731 Ref country code: FR Free format text: THE PATENT HAS BEEN ANNULLED BY A DECISION OF A NATIONAL AUTHORITY Effective date: 19990731 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19990731 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19990720 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20000503 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| APAH | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNO |