EP0000896B1 - Propenyl amines, processes for their production and pharmaceutical compositions containing them - Google Patents
Propenyl amines, processes for their production and pharmaceutical compositions containing them Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0000896B1 EP0000896B1 EP78100611A EP78100611A EP0000896B1 EP 0000896 B1 EP0000896 B1 EP 0000896B1 EP 78100611 A EP78100611 A EP 78100611A EP 78100611 A EP78100611 A EP 78100611A EP 0000896 B1 EP0000896 B1 EP 0000896B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- formula
- radical
- alkyl
- hydrogen
- compound
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
- 0 *[C@](C=C*)N(*)C(*)(*)* Chemical compound *[C@](C=C*)N(*)C(*)(*)* 0.000 description 2
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D203/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing three-membered rings with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D203/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing three-membered rings with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings
- C07D203/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing three-membered rings with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D203/08—Heterocyclic compounds containing three-membered rings with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with only hydrogen atoms, hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals, directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P31/00—Antiinfectives, i.e. antibiotics, antiseptics, chemotherapeutics
- A61P31/04—Antibacterial agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P31/00—Antiinfectives, i.e. antibiotics, antiseptics, chemotherapeutics
- A61P31/10—Antimycotics
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D207/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D207/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D207/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D207/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with radicals, containing only hydrogen and carbon atoms, attached to ring carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D207/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D207/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D207/30—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having two double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D207/32—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having two double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with only hydrogen atoms, hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D207/33—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having two double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with only hydrogen atoms, hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms with substituted hydrocarbon radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D207/335—Radicals substituted by nitrogen atoms not forming part of a nitro radical
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D209/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings, condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D209/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings, condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom condensed with one carbocyclic ring
- C07D209/04—Indoles; Hydrogenated indoles
- C07D209/10—Indoles; Hydrogenated indoles with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to carbon atoms of the hetero ring
- C07D209/14—Radicals substituted by nitrogen atoms, not forming part of a nitro radical
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D211/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings
- C07D211/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D211/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D211/08—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D211/10—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms with radicals containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D211/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals directly attached to ring carbon atoms with radicals containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms attached to ring carbon atoms with hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to the ring nitrogen atom
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D213/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D213/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D213/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D213/24—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D213/36—Radicals substituted by singly-bound nitrogen atoms
- C07D213/38—Radicals substituted by singly-bound nitrogen atoms having only hydrogen or hydrocarbon radicals attached to the substituent nitrogen atom
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D215/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing quinoline or hydrogenated quinoline ring systems
- C07D215/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing quinoline or hydrogenated quinoline ring systems having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen atoms or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D215/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing quinoline or hydrogenated quinoline ring systems having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen atoms or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to ring carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D223/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing seven-membered rings having one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D223/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing seven-membered rings having one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings
- C07D223/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing seven-membered rings having one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings with only hydrogen atoms, halogen atoms, hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D233/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazole or hydrogenated 1,3-diazole rings, not condensed with other rings
- C07D233/54—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazole or hydrogenated 1,3-diazole rings, not condensed with other rings having two double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D233/64—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazole or hydrogenated 1,3-diazole rings, not condensed with other rings having two double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to ring carbon atoms, e.g. histidine
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D307/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D307/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings
- C07D307/34—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings having two or three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D307/38—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings having two or three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D307/52—Radicals substituted by nitrogen atoms not forming part of a nitro radical
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D333/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D333/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings
- C07D333/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings not substituted on the ring sulphur atom
- C07D333/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings not substituted on the ring sulphur atom with only hydrogen atoms, hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals, directly attached to the ring carbon atoms
- C07D333/14—Radicals substituted by singly bound hetero atoms other than halogen
- C07D333/20—Radicals substituted by singly bound hetero atoms other than halogen by nitrogen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D333/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D333/50—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom condensed with carbocyclic rings or ring systems
- C07D333/52—Benzo[b]thiophenes; Hydrogenated benzo[b]thiophenes
- C07D333/54—Benzo[b]thiophenes; Hydrogenated benzo[b]thiophenes with only hydrogen atoms, hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals, directly attached to carbon atoms of the hetero ring
- C07D333/58—Radicals substituted by nitrogen atoms
Definitions
- This invention relates to propenyl-amines, processes for their production and pharmaceutical compositions containing them.
- the present invention provides a compound of formula I, wherein
- lower alkyl or “lower alkoxy” radical mean containing 1 to 4 carbon atoms, especially 2 or 1 carbon atoms.
- Any alkyl (C 1 ⁇ 12 ) moiety is preferably alkyl (C 2 ⁇ 8 ); phenylalkyl or phenylalkoxy has preferably 7 carbon atoms.
- Any alkenyl or alkynyl radical has preferably 3 to 6 carbon atoms, especially 3 or 4 carbon atoms.
- the multiple bond is in other than the ⁇ , ⁇ position and is conveniently in the remote terminal position.
- An example of an alkenyl group is allyl.
- An example of an alkynyl group is propinyl.
- Cycloalkylalkyl has preferably an alkyl moiety of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, especially 2 or 1 carbon atoms, and a cycloalkyl moiety preferably of 3 to 6 carbon atoms.
- R 4 is cycloalkylalkyl this is especially cyclopentyl alkyl or cyclohexylalkyl.
- R 10 is cycloalkylalkyl this is especially cyclopropylalkyl or cyclobutylalkyl.
- R 7 and R 8 are identical and are both hydrogen.
- R 9 is hydrogen or halogen.
- IIb and IIc the bond to the carbon atom to which R 2 and R 3 are attached is conveniently attached meta to X and para to the ring nitrogen, respectively.
- X is conveniently sulphur, imino or lower alkylamino.
- R 1 is preferably a radical of formula IIb, IIc or IId or especially IIa.
- R 2 is preferably hydrogen.
- R 3 is preferably hydrogen and R 4 is conveniently alkyl.
- R 5 is conveniently hydrogen.
- R 6 when it is a heterocycle, conveniently contains one oxygen or sulphur atom or one or two nitrogen atoms.
- the bond linking R 6 to the vinylene moiety is attached to a ring carbon atom adjacent to a ring heteroatom.
- the ring is unsubstituted or substituted by lower alkyl.
- R 10 is conveniently phenylalkoxy.
- IIIa is conveniently optionally substituted 2 or 4-pyridyl.
- IIIc, IIId, IIIe it is to be appreciated that the bond linking R 6 to the vinylene moiety and R 11 to R 13 may be attached to any of the ring carbon atoms present.
- IIIc is preferably a cycloalk-1-en-1-yl radical.
- R 11 to R 13 are hydrogen.
- q is conveniently 0 or 1. Any double bond in IIIf is conveniently trans.
- R 14 is conveniently alkoxy (C 1 ⁇ 8 ) carbonyl, phenyl or alkyl or phenalkyl.
- R 17 is conveniently halogen and R 18 is conveniently hydrogen.
- R 6 is conveniently IIIc.
- u is conveniently 3, 4 or 5, more conveniently 4.
- m, n, p, q, s, t and v are conveniently chosen to produce a five or six-membered ring.
- the double bond between R 6 and the nitrogen atom preferably has the trans configuration.
- Halogen is conveniently fluorine, or preferably bromine or chlorine.
- R 1 is IIb or IIe and R 6 is IIIa it is to be appreciated that the two radicals R 9 may be the same or different.
- the present invention also provides a process for the production of a compound of formula I, selected from
- Process a) may be effected in conventional manner for the production of tertiary amines by condensation from analogous starting materials.
- the process may be effected in an inert solvent such as a lower alkanol, e.g. ethanol, optionally in aqueous admixture, an aromatic hydrocarbon solvent, e.g. benzene or toluene, a cyclic ether, e.g. dioxane or a carboxylic acid dialkylamide solvent, e.g. dimethylformamide.
- the reaction temperature is conveniently from room temperature to the boiling temperature of the reaction mixture, preferably room temperature.
- the reaction is conveniently effected in the presence of an acid binding agent, such as an alkali metal carbonate, e.g.
- the leaving group A is conveniently iodine or preferably chlorine or bromine, or an organic sulphonyloxy group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, e.g. alkylsulphonyloxy, preferably having 1 to 4 carbon atoms such as mesyloxy, or alkylphenylsulphonyloxy preferably having 7 to 10 carbon atoms such as tosyloxy.
- Process b) may be effected in conventional manner for catalytic hydrogenation in order to produce a compound of formula I wherein the double bond adjacent to R 6 has the cis configuration.
- the process may be effected in conventional manner for a complex metal hydride reduction in order to produce a compound of formula I wherein the double bond has the trans configuration.
- the catalytic hydrogenation may be effected in a solvent, e.g. methanol, ethanol, methylene chloride, pyridine or ethyl acetate.
- the catalyst is preferably palladium on a carrier material such as BaS0 4 or CaC0 3 .
- the catalyst may be pretreated, e.g. with a lead salt, so as to be partially poisoned (e.g. a Lindlar catalyst).
- the hydrogenation may be effected at room temperature and at normal pressure.
- the metal hydride reduction may be effected in conventional manner for a lithium aluminium -hydride or a diisobutylaluminium hydride reduction.
- the reduction is conveniently effected in an inert solvent such as toluene or benzene.
- the reaction is conveniently effected at room temperature.
- Process c) may be effected in conventional manner for a photochemical isomerisation of a cis alkene.
- the reaction may be effected in a solvent such as benzene, petroleum ether, ethanol, or preferably cyclohexane.
- the solution is conveniently irradiated with light from a mercury high or low pressure lamp.
- the reaction is conveniently effected at room temperature.
- an appropriate sensitizer such as eosine or a catalyst such as diphenyldisulphide may be present.
- Process d) may be effected in manner conventional for the "alkylation" of secondary amines (the term “alkylation” being used here to denote introduction of any of the hydrocarbyl groups R 4 ), for example by direct “alkylation” with an “alkylating” agent, for example a halide or sulphate, or by reductive alkylation, in particular by reaction with an appropriate aldehyde and subsequent or simultaneous reduction.
- Reductive "alkylation” is suitably effected in an inert organic solvent, such as a lower alkanol, e.g. methanol, and at an elevated temperature, in particular at the boiling temperature of the reaction medium.
- the subsequent reduction may be effected with, for example, a complex metal hydride reducing agent, e.g. NaBH 4 or LiAIH 4 .
- a complex metal hydride reducing agent e.g. NaBH 4 or LiAIH 4 .
- the reduction may also be effected simultaneously to the alkylation, for example by use of formic acid which may serve both as reducing agent and as a reaction medium.
- side reactions may occur, e.g. reduction of halogen to hydrogen, reduction of a nitro group to an amino group, reduction of an alkenyl moiety to an alkyl moiety and/or reduction of a keto moiety to a carbinol moiety in processes b) or process d) when reductive alkylation is used, or simultaneous cis/trans isomerisation of any double bond present in R 4 or R 6 when process c) is used.
- the reaction conditions should be chosen to avoid such side reactions, and the desired final product isolated using conventional purification techniques, e.g. thin layer chromatography.
- Free base forms of the compounds of formula I may be converted into salt forms and vice versa.
- Suitable acids for acid addition salt formation include hydrochloric acid, fumaric acid and naphthalene-1,5-disulphonic acid.
- non-cyclic amines of formula IV may be made by condensing a compound of formula VIII, or the corresponding iodide or chloride, with a compound of formula R 4 NH 2 .
- cyclic amines of formula IV may be made as follows:- wherein
- Alk lower alkyl
- the compounds of formula VI are new and may be made by reacting an appropriate amine of formula IV with compounds of formulae R 5 ⁇ CHO and under Mannich reaction conditions.
- the title compound may also be made in analogous manner to Examples 3, 4 and 5.
- the title compound may also be made in analogous manner to Examples 1 and 5.
- the title compound may also be prepared by following Examples 1, 4 and 5.
- the title compound may also be prepared by following Examples 1, 3 and 5.
- the title compound may also be prepared in analogous manner to Examples 1, 3 and 4.
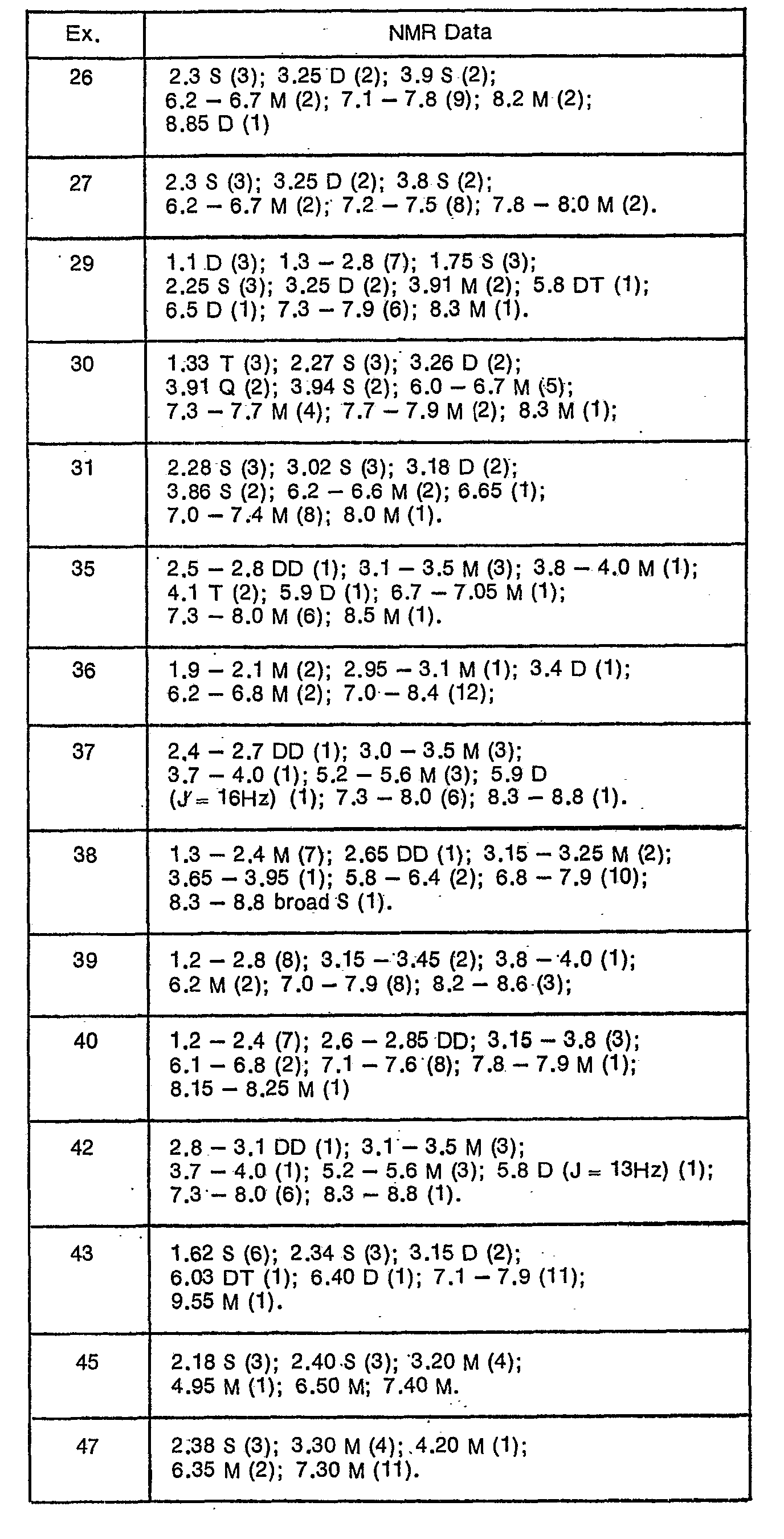
- NMR data on the above-mentioned compounds of formula I, obtained as oils, are given in the following table.
- the compounds of formula I exhibit chemotherapeutic activity.
- they exhibit antimycotic activity, as indicated in vitro with tests against various families and types of mycetes, including Trichophton quinkeanum, Aspergillus fumigatus, Microsporum canis Sporotrychium schenkii and Candida albicans, at concentrations of, for example 0.1 to 100 ⁇ g/ml, and in vivo in the experimental skin mycosis model in guinea pigs. In the latter model, guinea pigs are infected by cutaneous application of Trichophyton quinkeanum.
- test substance is administered daily for 7 days beginning 24 hours after the infection by local application by rubbing the test substance (taken up in polyethylene glycol) on the skin surface, or perorally, the test substance being administered as a suspension.
- the activity is shown on local application at concentrations of from example 0.1 to 2%, in particular 0.1 to 0.6%.
- the oral activity is shown at dosages of, for example, 50 to 100 mg/kg.
- the compounds are therefore indicated for use as anti-mycotic agents.
- daily dose is from 500 to 2000 mg. If desired, this may be administered in divided doses 2 to 4 times a day in unit dosage form containing from about 125 mg to about 1000 mg or in sustained release form.
- the compounds may be used in free base form or in the form of chemotherapeutically acceptable acid addition salts. Such salt forms exhibit the same order of activity as the free base forms.
- the compounds may be admixed with conventional chemotherapeutically acceptable diluents and carriers, and, optionally, other excipients and administered in such forms as tablets or capsules.
- the compounds may alternatively be administered topically in such conventional forms as ointments or creams.
- concentration of the active substance in such topical application forms will of course vary depending on the compound employed, the treatment desired and the nature of the form etc. In general, however, satisfactory results are obtained at concentrations of from 0.05 to 3, in particular 0.1 to 1 wt 96.
- a compound with particularly interesting activity is the compound of Example 4.
- One group of compounds has a formula Ig, wherein
- Another group of compounds comprises those of formula Ih, wherein
- a further group of formula I compounds comprises compounds of formula li, wherein
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Communicable Diseases (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
- Heterocyclic Compounds Containing Sulfur Atoms (AREA)
- Quinoline Compounds (AREA)
- Furan Compounds (AREA)
- Indole Compounds (AREA)
- Pyridine Compounds (AREA)
- Pyrrole Compounds (AREA)
- Acyclic And Carbocyclic Compounds In Medicinal Compositions (AREA)
Description
- This invention relates to propenyl-amines, processes for their production and pharmaceutical compositions containing them.
-
- a) (i) R1 is a radical of formula IIa,
- R7 and R8, independently, are hydrogen, halogen of atomic number from 9 to 53, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, nitro, lower alkyl or lower alkoxy, or a radical of formula IIb, IIc, IId, IIe,
- R9 is hydrogen, halogen of atomic number from 9 to 53, hydroxy, lower alkyl or lower alkoxy,
- X is oxygen, sulphur, imino, lower alkylimino or a radical of formula ―(CH2)r― wherein r is 1, 2 or 3,
- s is 3, 4 or 5, and
- t is 2, 3 or 4, and
- R is hydrogen or lower alkyl, or
- (ii) R1 and R2 together with the carbon atom to which they are bound form a radical of formula IIf or IIg,
- (ii) R1 and R2 together with the carbon atom to which they are bound form a radical of formula IIf or IIg,
- p is 1, 2 or 3,
- R3 and R5, independently, are hydrogen or lower alkyl,
- R4 is alkyl (C1_6), alkenyl (C3―12), alkynyl (C3―12) or cycloalkyl (C3―8)-alkyl (C1―6); and
- R6 is (i) an aromatic, five-membered heterocycle containing one oxygen, sulphur or nitrogen hetero-ring atom and optionally an additional one or two nitrogen hetero-ring atoms and being optionally substituted on a carbon ring atom by halogen of atomic number from 9 to 53, hydroxy, lower alkyl or lower alkoxy, and any nitrogen ring atom present being optionally substituted when possible, by lower alkyl, (ii) a radical of formula Ilia,
- R9 is as defined above, (iii) a radical of formula IIIb,
- R10 is alkyl (C1―12), alkenyl (C3―12), alkynyl (C3―2) cycloalkyl (C3―8) alkyl (C1―6), phenyl-alkyl (C7―12), phenyl, phenylalkoxy (C7―16), or aminoalkyl (C1―12);
- (iv) a radical of formula IIIc, IIId or IIIe,
- (iv) a radical of formula IIIc, IIId or IIIe,
- R11, R12 and R13, independently, are hydrogen or C1―C4 alkyl,
- m is a whole number from 0 to 4,
- n is a whole number from 0 to 3, and
- v is a whole number from 0 to 5,
- (v) a radical of formula IIIf,
- (v) a radical of formula IIIf,
- R14 is C1―C4 alkyl, alkoxy (C1―12)-carbonyl, alkenyl (C3―12), alkynyl (C3―12), phenylalkyl (C7―12) or phenyl,
- R15 and R16, independently, are hydrogen or C1―C4 alkyl, and
- q is a whole number from 0 to 5, or
- (vi) a radical of formula IIIg
- (vi) a radical of formula IIIg
- R17 and R18, independently, are hydrogen, halogen of atomic number from 9 to 53, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, nitro, lower alkyl or lower alkoxy, with the proviso that one of R17 and R18is other than hydrogen, and with the general proviso that R1 is not a radical of formula Ila when R6 is a radical of formula IIIg or phenyl, R2 is hydrogen and R3 is hydrogen or lower alkyl,
- R7 and R8, independently, are hydrogen, halogen of atomic number from 9 to 53, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, nitro, lower alkyl or lower alkoxy, or a radical of formula IIb, IIc, IId, IIe,
- b) R1 is a radical of formula IIa to IIe, as defined above,
- R2, R5 and R6 are as defined above, and
- R3 and R4 together are ―(CH2)u―wherein u is a whole number from 1 to 8.
- As used herein, the terms "lower alkyl" or "lower alkoxy" radical mean containing 1 to 4 carbon atoms, especially 2 or 1 carbon atoms. Any alkyl (C1―12) moiety is preferably alkyl (C2―8); phenylalkyl or phenylalkoxy has preferably 7 carbon atoms. Any alkenyl or alkynyl radical has preferably 3 to 6 carbon atoms, especially 3 or 4 carbon atoms. Preferably the multiple bond is in other than the α, β position and is conveniently in the remote terminal position. An example of an alkenyl group is allyl. An example of an alkynyl group is propinyl. Cycloalkylalkyl has preferably an alkyl moiety of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, especially 2 or 1 carbon atoms, and a cycloalkyl moiety preferably of 3 to 6 carbon atoms. When R4 is cycloalkylalkyl this is especially cyclopentyl alkyl or cyclohexylalkyl. When R10 is cycloalkylalkyl this is especially cyclopropylalkyl or cyclobutylalkyl.
- Conveniently R7 and R8 are identical and are both hydrogen. Conveniently R9 is hydrogen or halogen. In IIb and IIc the bond to the carbon atom to which R2 and R3 are attached is conveniently attached meta to X and para to the ring nitrogen, respectively. X is conveniently sulphur, imino or lower alkylamino. R1 is preferably a radical of formula IIb, IIc or IId or especially IIa. R2 is preferably hydrogen. R3 is preferably hydrogen and R4 is conveniently alkyl. R5 is conveniently hydrogen. R6, when it is a heterocycle, conveniently contains one oxygen or sulphur atom or one or two nitrogen atoms. Preferably the bond linking R6 to the vinylene moiety is attached to a ring carbon atom adjacent to a ring heteroatom. Conveniently the ring is unsubstituted or substituted by lower alkyl. R10 is conveniently phenylalkoxy. IIIa is conveniently optionally substituted 2 or 4-pyridyl. In IIIc, IIId, IIIe it is to be appreciated that the bond linking R6 to the vinylene moiety and R11 to R13 may be attached to any of the ring carbon atoms present. IIIc is preferably a cycloalk-1-en-1-yl radical. Preferably R11 to R13 are hydrogen. q is conveniently 0 or 1. Any double bond in IIIf is conveniently trans. R14 is conveniently alkoxy (C1―8) carbonyl, phenyl or alkyl or phenalkyl. R17 is conveniently halogen and R18 is conveniently hydrogen. R6 is conveniently IIIc. u is conveniently 3, 4 or 5, more conveniently 4.
- The values m, n, p, q, s, t and v are conveniently chosen to produce a five or six-membered ring.
- The double bond between R6 and the nitrogen atom preferably has the trans configuration.
- Halogen is conveniently fluorine, or preferably bromine or chlorine.
- When R1 is IIb or IIe and R6 is IIIa it is to be appreciated that the two radicals R9 may be the same or different.
- The present invention also provides a process for the production of a compound of formula I, selected from
- a) reacting a compound of formula IV,
- R1 to R4 are as defined above, with a compound of formula V,
- A is a leaving group, and
- R5 and R6 are as defined above, or
- R1 to R4 are as defined above, with a compound of formula V,
- b) when R4 and R6 are other than alkynyl reducing a compound of formula VI,
- R1 to R3 and R5 are as defined above, and
- R1 to R3 and R5 are as defined above, and
- c) when the trans form is required isomerising photochemically a compound of formula lc,
- R1 to R6 are as defined above, or
- d) when R3 and R4 together do not form a ―(CH2)u― group introducing the group R4 into a compound ot formula VII,
- R1, R2, R3, R5 and R6 are as defined above.
- Process a) may be effected in conventional manner for the production of tertiary amines by condensation from analogous starting materials. The process may be effected in an inert solvent such as a lower alkanol, e.g. ethanol, optionally in aqueous admixture, an aromatic hydrocarbon solvent, e.g. benzene or toluene, a cyclic ether, e.g. dioxane or a carboxylic acid dialkylamide solvent, e.g. dimethylformamide. The reaction temperature is conveniently from room temperature to the boiling temperature of the reaction mixture, preferably room temperature. The reaction is conveniently effected in the presence of an acid binding agent, such as an alkali metal carbonate, e.g. sodium carbonate. The leaving group A is conveniently iodine or preferably chlorine or bromine, or an organic sulphonyloxy group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, e.g. alkylsulphonyloxy, preferably having 1 to 4 carbon atoms such as mesyloxy, or alkylphenylsulphonyloxy preferably having 7 to 10 carbon atoms such as tosyloxy.
- Process b) may be effected in conventional manner for catalytic hydrogenation in order to produce a compound of formula I wherein the double bond adjacent to R6 has the cis configuration. Alternatively, the process may be effected in conventional manner for a complex metal hydride reduction in order to produce a compound of formula I wherein the double bond has the trans configuration.
- The catalytic hydrogenation may be effected in a solvent, e.g. methanol, ethanol, methylene chloride, pyridine or ethyl acetate. The catalyst is preferably palladium on a carrier material such as BaS04 or CaC03. The catalyst may be pretreated, e.g. with a lead salt, so as to be partially poisoned (e.g. a Lindlar catalyst). The hydrogenation may be effected at room temperature and at normal pressure.
- The metal hydride reduction may be effected in conventional manner for a lithium aluminium -hydride or a diisobutylaluminium hydride reduction. The reduction is conveniently effected in an inert solvent such as toluene or benzene. The reaction is conveniently effected at room temperature.
- Process c) may be effected in conventional manner for a photochemical isomerisation of a cis alkene. The reaction may be effected in a solvent such as benzene, petroleum ether, ethanol, or preferably cyclohexane. The solution is conveniently irradiated with light from a mercury high or low pressure lamp. The reaction is conveniently effected at room temperature. If desired, an appropriate sensitizer such as eosine or a catalyst such as diphenyldisulphide may be present.
- Process d) may be effected in manner conventional for the "alkylation" of secondary amines (the term "alkylation" being used here to denote introduction of any of the hydrocarbyl groups R4), for example by direct "alkylation" with an "alkylating" agent, for example a halide or sulphate, or by reductive alkylation, in particular by reaction with an appropriate aldehyde and subsequent or simultaneous reduction. Reductive "alkylation" is suitably effected in an inert organic solvent, such as a lower alkanol, e.g. methanol, and at an elevated temperature, in particular at the boiling temperature of the reaction medium. The subsequent reduction may be effected with, for example, a complex metal hydride reducing agent, e.g. NaBH4 or LiAIH4. The reduction may also be effected simultaneously to the alkylation, for example by use of formic acid which may serve both as reducing agent and as a reaction medium.
- It is to be appreciated that in any of the above processes, side reactions may occur, e.g. reduction of halogen to hydrogen, reduction of a nitro group to an amino group, reduction of an alkenyl moiety to an alkyl moiety and/or reduction of a keto moiety to a carbinol moiety in processes b) or process d) when reductive alkylation is used, or simultaneous cis/trans isomerisation of any double bond present in R4 or R6 when process c) is used. The reaction conditions should be chosen to avoid such side reactions, and the desired final product isolated using conventional purification techniques, e.g. thin layer chromatography.
- Free base forms of the compounds of formula I may be converted into salt forms and vice versa. Suitable acids for acid addition salt formation include hydrochloric acid, fumaric acid and naphthalene-1,5-disulphonic acid.
-
-
- Alk = lower alkyl.
-
-
- In the following Examples all temperatures are uncorrected and in degrees Centigrade.
- In the tables hereinafter, the following indications are used:-
- 1) All double bonds have the trans configuration; all alkyl groups are unbranched unless stated otherwise.
- 2) If no melting point is given, the free base form of the compound is obtained and this is an oil. Melting points are for the free base form unless specified otherwise.
- 3) Monohydrochloride salt form.
- 4) Dihydrochloride salt form.
- 1.9 g of bromocrotonic acid ethyl ester are added dropwise to a mixture of 1.7 g of N-methyl-N-(1-naphthylmethyl)amine, 1.4 g of K2CO3 and 10 ml dimethylformamide. After the mixture is stirred for 18 hours at room temperature, it is filtered and evaporated under a vacuum. The residue is chromatographed on silica-gel using benzene/ethyl acetate (1:1) as solvent to yield the title compound in free base form, as an oil, after evaporating the appropriate fractions.
- The title compound may also be made in analogous manner to Examples 3, 4 and 5.
- 5 g of N-(3-cyclohex-l-en-1-yl-propynyl)-N-methyl-N-(l-naphthylmethyl)amine are hydrogenated in absolute pyridine using 750 mg Pd/BaS04 as catalyst at room temperature and normal pressure, until the calculated amount of hydrogen is taken up. The reaction mixture is filtered and the pyridine removed in a vacuum. The residue is chromatographed on silica-gel using benzene/ethyl- acetate (9:1) to yield the title compound in free base form as an oil after evaporating the appropriate fractions, m.p. (hydrochloride) 184-188°.
- The title compound may also be made in analogous manner to Examples 1 and 5.
- 28 ml of a 1.2 molar solution of diisobutylaluminium hydride in toluene are added to 5 g of N-(3-cyclohexylpropynyl)-N-methyl-N-(1-naphthylmethyl)amine in absolute benzene. After the mixture is stirred for 3 hours at 40°, water is carefully added. The organic phase is separated off, dried and evaporated to yield the title compound in free base form, as an oil.
- The title compound may also be prepared by following Examples 1, 4 and 5.
- 1.2 g of N-(3-cyclohex-1-en-1-yl-2-cis-propenyl)-N-methyl-N-(1-naphthylmethyl)amine are irradiated for 3 hours with a Hg high pressure lamp (A >300 nm) in 1 litre cyclohexane in the presence of 50 mg diphenyldisulphide at room temperature under an inert gas atmosphere. After the solvent is evaporated, the title compound is obtained in free base form and converted into the hydrochloride, m.p. 184-188
- The title compound may also be prepared by following Examples 1, 3 and 5.
-
- a) 15.2 g of 3-(5'-methyl-2'-thienyl)prop-2-enal and 15.7 g of 1-aminomethylnaphthalene in 350 ml benzene are boiled under reflux until the calculated amount of water has boiled off. 3.6 g of the resulting Schiff base in 100 ml methanol are boiled under reflux with 5 g NaBH4 for 30 minutes to yield N-[3-(5'-methyl-2'-thienyl)-2-trans-propenyl]-N-(1-naphthylmethyl)amine, which is used directly in the next stage. [To isolate this intermediate the reaction mixture is evaporated in a vacuum; the residue is partitioned between aqueous sodium carbonate solution and diethyl ether and the organic phase is evaporated].
- b) The crude reaction mixture obtained in step a) is treated with 20 ml 37% aqueous formaldehyde solution. The mixture is boiled under reflux for 60 minutes, subjected to ice-cooling, treated with 9 g NaBH4 and stirred for another 60 minutes at room temperature. The mixture is evaporated in a vacuum to a residue which is partitioned between aqueous NaHCO3 and diethyl ether. The organic phase is dried and evaporated to yield the title compound in free base form as an oil, m.p. (hydrochloride) 140-156°.
- The title compound may also be prepared in analogous manner to Examples 1, 3 and 4.
-
- R1 and R6 are as follows:
-
- R1, R6 and u are as follows:
- In analogous manner to that described in Examples 1 and 2, the following cis compound of formula I may be produced:
- aa) N-(3-cyclohex-1-en-1-yl-2-cis-propenyl)-2-(1'-naphthyl)piperidine; free base-oil.
- In analogous manner to that described in Examples 1, 3, 4 and 5, the following compounds of formula I may be produced:
- 43) N-cinnamyl-N-methyl-N-[2-(1'-naphthyl)-2-propyl]amine; free base-oil;
- 44) N-(1-acenaphthenyl)-N-methyl-N-(3-phenyl-2-transpropenyl)amine, m.p. (hydrochloride) 210-216°;
- 45) N-(1 -acenaphthenyl)-N-methyl-N-[3-(5'-methyl-2'-thienyl)-2-trans-propenyl]amine, free base-oil;
- 46) N-(6,7,8,8a-tetrahydro-1-acenaphthenyl)-N-methyl-N-(3-phenyl-2-trans-propenyl)amine, m.p. (hydrochloride) 185-192°;
- 47) N-methyl-N-(2,3-dihydro-1-phenalenyl)-N-(3-phenyl-2-trans-propenyl), free base-oil.
- NMR data on the above-mentioned compounds of formula I, obtained as oils, are given in the following table. The data comprises peak position in ppm relative to TMS as standard in CDCI3; type of peak (D = doublet; DD = double doublet; DT = double triplet; M = multiplet; Q = quartet; S = singlet; T = triplet) and in parentheses the corresponding number of hydrogen atoms.
- The compounds of formula I exhibit chemotherapeutic activity. In particular, they exhibit antimycotic activity, as indicated in vitro with tests against various families and types of mycetes, including Trichophton quinkeanum, Aspergillus fumigatus, Microsporum canis Sporotrychium schenkii and Candida albicans, at concentrations of, for example 0.1 to 100 µg/ml, and in vivo in the experimental skin mycosis model in guinea pigs. In the latter model, guinea pigs are infected by cutaneous application of Trichophyton quinkeanum. The test substance is administered daily for 7 days beginning 24 hours after the infection by local application by rubbing the test substance (taken up in polyethylene glycol) on the skin surface, or perorally, the test substance being administered as a suspension. The activity is shown on local application at concentrations of from example 0.1 to 2%, in particular 0.1 to 0.6%. The oral activity is shown at dosages of, for example, 50 to 100 mg/kg.
- The compounds are therefore indicated for use as anti-mycotic agents. As indicated daily dose is from 500 to 2000 mg. If desired, this may be administered in divided doses 2 to 4 times a day in unit dosage form containing from about 125 mg to about 1000 mg or in sustained release form.
- The compounds may be used in free base form or in the form of chemotherapeutically acceptable acid addition salts. Such salt forms exhibit the same order of activity as the free base forms.
- The compounds may be admixed with conventional chemotherapeutically acceptable diluents and carriers, and, optionally, other excipients and administered in such forms as tablets or capsules. The compounds may alternatively be administered topically in such conventional forms as ointments or creams. The concentration of the active substance in such topical application forms will of course vary depending on the compound employed, the treatment desired and the nature of the form etc. In general, however, satisfactory results are obtained at concentrations of from 0.05 to 3, in particular 0.1 to 1 wt 96.
- A compound with particularly interesting activity is the compound of Example 4.
-
- Rll is 1-naphthyl, optionally mono-substituted by lower alkyl or alkoxy,
- u is a whole number from 1 to 8,
- R"6is of formula
- R,9 is hydrogen, hydroxy, lower alkoxy or lower alkyl, or of formula
- R20 is alkyl (C1_12) or phenylalkyl-(C7_12) or of formula
- m, n and v are as defined above.
-
-
- R9 is as defined above,
- R2 and R5 are independently hydrogen or lower alkyl,
- u is a whole number from 1 to 8,
-
- (a) R10 is other than phenyl or phenylalkoxy, and
- (b) when
- (i) a radical of formula IIIa, IIIb or IIIf,
- (ii) a radical of formula IIIc, IIId or IIIe, wherein R11, R12 and R13 are each hydrogen, or (iii) a radical of formula IIIg wherein one of R17 and R18 is hydrogen and the other is hydroxy, lower alkyl or lower alkoxy, or
- (iv) an optionally substituted thiophen or furan radical.
-
-
-
- (i) R10 is other than phenyl or phenylalkoxy and
- (ii) when R1 is a radical of formula IIa,
Claims (9)
Applications Claiming Priority (8)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH1020277 | 1977-08-19 | ||
| CH1020377A CH632251A5 (en) | 1977-08-19 | 1977-08-19 | Process for preparing novel 2-naphthyl-substituted, cyclic, N-allylamine derivatives |
| CH10203/77 | 1977-08-19 | ||
| CH10202/77 | 1977-08-19 | ||
| CH1290977 | 1977-10-24 | ||
| CH12910/77 | 1977-10-24 | ||
| CH12909/77 | 1977-10-24 | ||
| CH1291077 | 1977-10-24 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0000896A2 EP0000896A2 (en) | 1979-03-07 |
| EP0000896A3 EP0000896A3 (en) | 1979-05-30 |
| EP0000896B1 true EP0000896B1 (en) | 1982-10-13 |
Family
ID=27429271
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP78100611A Expired EP0000896B1 (en) | 1977-08-19 | 1978-08-07 | Propenyl amines, processes for their production and pharmaceutical compositions containing them |
Country Status (14)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4680291A (en) |
| EP (1) | EP0000896B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPS5441855A (en) |
| CA (1) | CA1111852A (en) |
| DE (1) | DE2862103D1 (en) |
| DK (1) | DK152114C (en) |
| ES (1) | ES472641A1 (en) |
| FI (1) | FI65774C (en) |
| IE (1) | IE47314B1 (en) |
| IL (1) | IL55382A (en) |
| IT (1) | IT1098253B (en) |
| MY (1) | MY8500040A (en) |
| NZ (1) | NZ188170A (en) |
| PT (1) | PT68448A (en) |
Families Citing this family (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3020113A1 (en) * | 1979-06-08 | 1980-12-18 | Sandoz Ag | 2- (1-NAPHTHYL) PIPERIDINE DERIVATIVE, THE PRODUCTION THEREOF AND THE USE AS AN ANTIMYCOTIC |
| DE19375084I2 (en) * | 1979-08-22 | 2000-11-16 | Novartis Ag | Propenylamine Process for their preparation pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use as medicines |
| NL8003141A (en) * | 1980-05-30 | 1982-01-04 | Akzo Nv | BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE TRICYCLIC AMINES. |
| IT1150211B (en) * | 1981-03-02 | 1986-12-10 | Abbott Lab | 1,2,3,4-TETRAIDRONAFTALENI REPLACED WITH AMINO ALKYLS PHARMACEUTICAL ACTION |
| CH653028A5 (en) * | 1982-02-03 | 1985-12-13 | Sandoz Ag | BENZTHIOPHENALLYLAMINE COMPOUNDS AND METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF. |
| JPS6145A (en) * | 1984-06-09 | 1986-01-06 | Kaken Pharmaceut Co Ltd | Naphthylmethylamine derivative and antifungal containing the same |
| US5334628A (en) * | 1984-06-09 | 1994-08-02 | Kaken Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Amine derivatives, processes for preparing the same and fungicides containing the same |
| JPH0676285B2 (en) * | 1985-11-01 | 1994-09-28 | 三井東圧化学株式会社 | Benzylamine derivative, its production method and its use |
| EP0254677A1 (en) * | 1986-07-08 | 1988-01-27 | Sandoz Ag | Antimycotic 6-phenyl-2-hexen-4-ynamines |
| US5084476A (en) * | 1986-07-15 | 1992-01-28 | Hoffmann-La Roche Inc. | Tetrahydronaphthalene and indane derivatives |
| US5234946A (en) * | 1987-11-27 | 1993-08-10 | Banyu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Substituted alkylamine derivatives |
| JPH03105465U (en) * | 1990-02-16 | 1991-10-31 | ||
| GB9513750D0 (en) * | 1995-07-06 | 1995-09-06 | Sandoz Ltd | Use of allylamines |
| WO1998005645A1 (en) * | 1996-08-01 | 1998-02-12 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | 4-substituted quinoline derivatives having fungicidal activity |
| US6117884A (en) * | 1997-07-31 | 2000-09-12 | Daeuble; John | 4-substituted quinoline derivatives having fungicidal activity |
| JP4509327B2 (en) * | 2000-08-03 | 2010-07-21 | ダイセル化学工業株式会社 | Process for producing N, N-disubstituted-4-aminocrotonic acid ester |
| WO2007014130A2 (en) * | 2005-07-21 | 2007-02-01 | Nomir Medical Technologies, Inc. | Near infrared microbial elimination laser system (nimels) |
| GB0320312D0 (en) * | 2003-08-29 | 2003-10-01 | Novartis Ag | Purification process |
| US20050197512A1 (en) * | 2003-08-29 | 2005-09-08 | Ulrich Beutler | Purification process |
| JP2008504359A (en) * | 2004-07-02 | 2008-02-14 | ワーナー−ランバート カンパニー リミテッド ライアビリティー カンパニー | Compositions and methods for treating pathological infections |
| US20090082469A1 (en) * | 2007-09-26 | 2009-03-26 | Protia, Llc | Deuterium-enriched terbinafine |
| WO2017132912A1 (en) * | 2016-02-03 | 2017-08-10 | 华东理工大学 | Alkylamine with benzoalicyclic substituent and application thereof |
| CN108084125B (en) | 2016-11-23 | 2020-08-18 | 华东理工大学 | Benzoheterocyclylalkylamines and their use |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE609151C (en) * | 1930-02-01 | 1935-02-08 | I G Farbenindustrie Akt Ges | Process for the preparation of amino alcohols with a secondary or tertiary amino group |
| US2601275A (en) * | 1949-10-29 | 1952-06-24 | Givaudan Corp | Aromatic chlorethylamines and their salts |
| DK106378C (en) * | 1962-10-19 | 1967-01-30 | Koninklijke Pharma Fab Nv | Process for the preparation of N-substituted 1-phenyl-2-aminoalkanes or acid addition salts thereof. |
| GB1041987A (en) * | 1964-09-03 | 1966-09-07 | Beecham Group Ltd | Acetylenic compounds |
| GB1134715A (en) * | 1966-02-24 | 1968-11-27 | Geistlich Soehne Ag | Bisphenylalkenylamine derivatives |
| US3784642A (en) * | 1967-11-03 | 1974-01-08 | E Jenny | 1-amine-cyclobutene |
| BE786748A (en) * | 1971-07-26 | 1973-01-26 | Basf Ag | 1-AMINOMETHYL-INDANES-N-SUBSTITUTES |
| BE791133A (en) * | 1971-11-10 | 1973-05-09 | Calgon Corp | NEW CATIONIC MONOMERS AND THEIR MANUFACTURING PROCESSES |
| BE791538A (en) * | 1971-11-19 | 1973-05-17 | Basf Ag | 1-AMINOMETHYL-ACENAPHTENES, THEIR PREPARATION AND THEIR THERAPEUTIC USES |
| BE794598A (en) * | 1972-01-28 | 1973-05-16 | Richardson Merrell Inc | NEW OLEFINIC DERIVATIVES OF PIPERIDINES SUBSTITUTED IN 4 AND THEIR PREPARATION PROCESS |
| JPS4930346A (en) * | 1972-07-18 | 1974-03-18 | ||
| US4139560A (en) * | 1974-02-22 | 1979-02-13 | Ciba Geigy Corporation | Nonylamines |
| HU169507B (en) * | 1974-09-25 | 1976-12-28 | ||
| DE2716943C2 (en) * | 1976-04-28 | 1986-08-14 | Sandoz-Patent-GmbH, 7850 Lörrach | N- (3-Phenyl-2-propenyl) -N- (1-naphthylmethyl) amines, their use and preparation |
-
1978
- 1978-08-07 DE DE7878100611T patent/DE2862103D1/en not_active Expired
- 1978-08-07 EP EP78100611A patent/EP0000896B1/en not_active Expired
- 1978-08-10 DK DK354678A patent/DK152114C/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1978-08-10 FI FI782446A patent/FI65774C/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1978-08-17 IL IL55382A patent/IL55382A/en active IP Right Grant
- 1978-08-17 IE IE1670/78A patent/IE47314B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1978-08-17 ES ES472641A patent/ES472641A1/en not_active Expired
- 1978-08-17 CA CA309,579A patent/CA1111852A/en not_active Expired
- 1978-08-17 NZ NZ188170A patent/NZ188170A/en unknown
- 1978-08-18 IT IT26835/78A patent/IT1098253B/en active
- 1978-08-18 PT PT68448A patent/PT68448A/en unknown
- 1978-08-18 US US06/934,772 patent/US4680291A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1978-08-19 JP JP10137578A patent/JPS5441855A/en active Granted
-
1985
- 1985-12-30 MY MY40/85A patent/MY8500040A/en unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPS5441855A (en) | 1979-04-03 |
| ES472641A1 (en) | 1979-10-16 |
| NZ188170A (en) | 1981-05-01 |
| DK354678A (en) | 1979-02-20 |
| IL55382A0 (en) | 1978-10-31 |
| IT7826835A0 (en) | 1978-08-18 |
| IT1098253B (en) | 1985-09-07 |
| FI65774B (en) | 1984-03-30 |
| US4680291A (en) | 1987-07-14 |
| FI65774C (en) | 1984-07-10 |
| EP0000896A3 (en) | 1979-05-30 |
| CA1111852A (en) | 1981-11-03 |
| IE781670L (en) | 1979-02-19 |
| IE47314B1 (en) | 1984-02-22 |
| IL55382A (en) | 1981-12-31 |
| JPS6317050B2 (en) | 1988-04-12 |
| DK152114B (en) | 1988-02-01 |
| PT68448A (en) | 1978-09-01 |
| MY8500040A (en) | 1985-12-31 |
| DK152114C (en) | 1988-06-20 |
| EP0000896A2 (en) | 1979-03-07 |
| DE2862103D1 (en) | 1982-11-18 |
| FI782446A (en) | 1979-02-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0000896B1 (en) | Propenyl amines, processes for their production and pharmaceutical compositions containing them | |
| EP0024587B1 (en) | Propenylamines, processes for their production, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use as pharmaceuticals | |
| CA2004575A1 (en) | 2-amino-4 or 5-methoxycyclohexyl amides useful as analgesics | |
| EP0288188A1 (en) | 1-Phenyl-3-naphthalenyloxy-propanamines | |
| IE46278B1 (en) | Piperazine derivatives | |
| IE45727B1 (en) | Aralkenylaminomethyl-naphthalene derivatives | |
| CH644582A5 (en) | POLYPRENYLCARBOXYLIC ACID AMIDES. | |
| US5132459A (en) | Propenylamines, processes for their production, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use as pharmaceuticals | |
| CA1049530A (en) | Diphenylpropylamines | |
| EP0230020B1 (en) | 1,2,3,4,4a,9b-hexahydro-4a-aminoalkyldibenzofurans, a process for their preparation and their use as medicaments | |
| US3963780A (en) | N,N'-disubstituted-p-phenylenediamines | |
| US3819708A (en) | N,n'-disubstituted-p-phenylenediamines | |
| US3228984A (en) | 1, 4-bis-cyclic and aryl-amino-[2.2.2] bicyclooctane derivatives | |
| EP0049049A1 (en) | 5-Amino-tetrazole derivatives, processes for their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them | |
| US5317026A (en) | Acetamide derivative and application thereof | |
| GB1604675A (en) | Aminoalkylbenzenes | |
| US3888829A (en) | N,n'-bis(3-hydroxy-2-(3,4-dihydroxy-phenyl)-1-propyl)-aliphatic-diamines | |
| EP0246077B1 (en) | Heteropolycyclic aromatic compounds | |
| US3674807A (en) | 1-p-(omega-aminoalkyl)phenyl-cyclohexanes,cyclohexenes and cyclohexanols | |
| EP0000825B1 (en) | Geminally disubstituted indene derivatives, processes for their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them | |
| EP0318234A2 (en) | Improvements in or relating to selective serotonin uptake inhibitors | |
| US2992231A (en) | Pyrrolidyl derivatives of 3-arylindenes and 3-arylindanes | |
| US3957871A (en) | Chemical compounds and the process for preparing same | |
| Kaiser et al. | Synthesis and anorectic activity of some 1-benzylcyclopropylamines | |
| KR950013104B1 (en) | Amine derivatives processes for production acid their use |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB LU NL SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB LU NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed | ||
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB LU NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 2862103 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19821118 |
|
| EPTA | Lu: last paid annual fee | ||
| EAL | Se: european patent in force in sweden |
Ref document number: 78100611.9 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PFA Free format text: SANDOZ AG TRANSFER- NOVARTIS AG |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19970602 Year of fee payment: 20 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19970602 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19970604 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19970605 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19970609 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: 732E |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19970630 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19970707 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Payment date: 19970813 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: TP |
|
| BE20 | Be: patent expired |
Free format text: 980807 *SANDOZ A.G. |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF EXPIRATION OF PROTECTION Effective date: 19980806 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF EXPIRATION OF PROTECTION Effective date: 19980806 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF EXPIRATION OF PROTECTION Effective date: 19980807 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF EXPIRATION OF PROTECTION Effective date: 19980807 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19980808 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: PE20 Effective date: 19980806 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| NLV7 | Nl: ceased due to reaching the maximum lifetime of a patent |
Effective date: 19980807 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 78100611.9 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |