DE102011077458A1 - Welding components of motor vehicle, comprises providing first component having first connecting portion, second component having second material, providing metallic coating on first connecting portion, welding first and second components - Google Patents
Welding components of motor vehicle, comprises providing first component having first connecting portion, second component having second material, providing metallic coating on first connecting portion, welding first and second components Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- DE102011077458A1 DE102011077458A1 DE102011077458A DE102011077458A DE102011077458A1 DE 102011077458 A1 DE102011077458 A1 DE 102011077458A1 DE 102011077458 A DE102011077458 A DE 102011077458A DE 102011077458 A DE102011077458 A DE 102011077458A DE 102011077458 A1 DE102011077458 A1 DE 102011077458A1
- Authority
- DE
- Germany
- Prior art keywords
- connecting portion
- component
- metallic coating
- welding
- coating
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 125
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 114
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 103
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 69
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 50
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 claims description 26
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 claims description 25
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 claims description 13
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 241001016380 Reseda luteola Species 0.000 description 35
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 11
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 11
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 8
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910010293 ceramic material Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920000049 Carbon (fiber) Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000004026 adhesive bonding Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004917 carbon fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003365 glass fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229920001169 thermoplastic Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920001187 thermosetting polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004416 thermosoftening plastic Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012780 transparent material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- BUHVIAUBTBOHAG-FOYDDCNASA-N (2r,3r,4s,5r)-2-[6-[[2-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-(2-methylphenyl)ethyl]amino]purin-9-yl]-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol Chemical compound COC1=CC(OC)=CC(C(CNC=2C=3N=CN(C=3N=CN=2)[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)O)C=2C(=CC=CC=2)C)=C1 BUHVIAUBTBOHAG-FOYDDCNASA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000357293 Leptobrama muelleri Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000002250 absorbent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011358 absorbing material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000000712 assembly Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000429 assembly Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005137 deposition process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008030 elimination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003379 elimination reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- -1 for example Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000155 melt Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N methane Chemical compound C VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002787 reinforcement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012783 reinforcing fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K26/00—Working by laser beam, e.g. welding, cutting or boring
- B23K26/20—Bonding
- B23K26/32—Bonding taking account of the properties of the material involved
- B23K26/323—Bonding taking account of the properties of the material involved involving parts made of dissimilar metallic material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K26/00—Working by laser beam, e.g. welding, cutting or boring
- B23K26/20—Bonding
- B23K26/32—Bonding taking account of the properties of the material involved
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B15/00—Layered products comprising a layer of metal
- B32B15/04—Layered products comprising a layer of metal comprising metal as the main or only constituent of a layer, which is next to another layer of the same or of a different material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60N—SEATS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR VEHICLES; VEHICLE PASSENGER ACCOMMODATION NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60N2/00—Seats specially adapted for vehicles; Arrangement or mounting of seats in vehicles
- B60N2/68—Seat frames
- B60N2/682—Joining means
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C04—CEMENTS; CONCRETE; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES
- C04B—LIME, MAGNESIA; SLAG; CEMENTS; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF, e.g. MORTARS, CONCRETE OR LIKE BUILDING MATERIALS; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES; TREATMENT OF NATURAL STONE
- C04B37/00—Joining burned ceramic articles with other burned ceramic articles or other articles by heating
- C04B37/02—Joining burned ceramic articles with other burned ceramic articles or other articles by heating with metallic articles
- C04B37/023—Joining burned ceramic articles with other burned ceramic articles or other articles by heating with metallic articles characterised by the interlayer used
- C04B37/026—Joining burned ceramic articles with other burned ceramic articles or other articles by heating with metallic articles characterised by the interlayer used consisting of metals or metal salts
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C25—ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PROCESSES; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C25D—PROCESSES FOR THE ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PRODUCTION OF COATINGS; ELECTROFORMING; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C25D7/00—Electroplating characterised by the article coated
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K2101/00—Articles made by soldering, welding or cutting
- B23K2101/34—Coated articles, e.g. plated or painted; Surface treated articles
- B23K2101/35—Surface treated articles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K2103/00—Materials to be soldered, welded or cut
- B23K2103/08—Non-ferrous metals or alloys
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K2103/00—Materials to be soldered, welded or cut
- B23K2103/50—Inorganic material, e.g. metals, not provided for in B23K2103/02 – B23K2103/26
- B23K2103/52—Ceramics
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C65/00—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor
- B29C65/02—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor by heating, with or without pressure
- B29C65/14—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor by heating, with or without pressure using wave energy, i.e. electromagnetic radiation, or particle radiation
- B29C65/16—Laser beams
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C65/00—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor
- B29C65/02—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor by heating, with or without pressure
- B29C65/14—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor by heating, with or without pressure using wave energy, i.e. electromagnetic radiation, or particle radiation
- B29C65/16—Laser beams
- B29C65/1629—Laser beams characterised by the way of heating the interface
- B29C65/1635—Laser beams characterised by the way of heating the interface at least passing through one of the parts to be joined, i.e. laser transmission welding
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C65/00—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor
- B29C65/78—Means for handling the parts to be joined, e.g. for making containers or hollow articles, e.g. means for handling sheets, plates, web-like materials, tubular articles, hollow articles or elements to be joined therewith; Means for discharging the joined articles from the joining apparatus
- B29C65/7802—Positioning the parts to be joined, e.g. aligning, indexing or centring
- B29C65/7805—Positioning the parts to be joined, e.g. aligning, indexing or centring the parts to be joined comprising positioning features
- B29C65/7808—Positioning the parts to be joined, e.g. aligning, indexing or centring the parts to be joined comprising positioning features in the form of holes or slots
- B29C65/7811—Positioning the parts to be joined, e.g. aligning, indexing or centring the parts to be joined comprising positioning features in the form of holes or slots for centring purposes
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/01—General aspects dealing with the joint area or with the area to be joined
- B29C66/02—Preparation of the material, in the area to be joined, prior to joining or welding
- B29C66/026—Chemical pre-treatments
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/01—General aspects dealing with the joint area or with the area to be joined
- B29C66/02—Preparation of the material, in the area to be joined, prior to joining or welding
- B29C66/028—Non-mechanical surface pre-treatments, i.e. by flame treatment, electric discharge treatment, plasma treatment, wave energy or particle radiation
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/01—General aspects dealing with the joint area or with the area to be joined
- B29C66/05—Particular design of joint configurations
- B29C66/10—Particular design of joint configurations particular design of the joint cross-sections
- B29C66/11—Joint cross-sections comprising a single joint-segment, i.e. one of the parts to be joined comprising a single joint-segment in the joint cross-section
- B29C66/112—Single lapped joints
- B29C66/1122—Single lap to lap joints, i.e. overlap joints
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/01—General aspects dealing with the joint area or with the area to be joined
- B29C66/05—Particular design of joint configurations
- B29C66/20—Particular design of joint configurations particular design of the joint lines, e.g. of the weld lines
- B29C66/24—Particular design of joint configurations particular design of the joint lines, e.g. of the weld lines said joint lines being closed or non-straight
- B29C66/244—Particular design of joint configurations particular design of the joint lines, e.g. of the weld lines said joint lines being closed or non-straight said joint lines being non-straight, e.g. forming non-closed contours
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/50—General aspects of joining tubular articles; General aspects of joining long products, i.e. bars or profiled elements; General aspects of joining single elements to tubular articles, hollow articles or bars; General aspects of joining several hollow-preforms to form hollow or tubular articles
- B29C66/51—Joining tubular articles, profiled elements or bars; Joining single elements to tubular articles, hollow articles or bars; Joining several hollow-preforms to form hollow or tubular articles
- B29C66/53—Joining single elements to tubular articles, hollow articles or bars
- B29C66/532—Joining single elements to the wall of tubular articles, hollow articles or bars
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/50—General aspects of joining tubular articles; General aspects of joining long products, i.e. bars or profiled elements; General aspects of joining single elements to tubular articles, hollow articles or bars; General aspects of joining several hollow-preforms to form hollow or tubular articles
- B29C66/61—Joining from or joining on the inside
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/70—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material
- B29C66/72—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material characterised by the structure of the material of the parts to be joined
- B29C66/721—Fibre-reinforced materials
- B29C66/7212—Fibre-reinforced materials characterised by the composition of the fibres
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/70—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts characterised by the composition, physical properties or the structure of the material of the parts to be joined; Joining with non-plastics material
- B29C66/74—Joining plastics material to non-plastics material
- B29C66/742—Joining plastics material to non-plastics material to metals or their alloys
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C66/00—General aspects of processes or apparatus for joining preformed parts
- B29C66/80—General aspects of machine operations or constructions and parts thereof
- B29C66/81—General aspects of the pressing elements, i.e. the elements applying pressure on the parts to be joined in the area to be joined, e.g. the welding jaws or clamps
- B29C66/812—General aspects of the pressing elements, i.e. the elements applying pressure on the parts to be joined in the area to be joined, e.g. the welding jaws or clamps characterised by the composition, by the structure, by the intensive physical properties or by the optical properties of the material constituting the pressing elements, e.g. constituting the welding jaws or clamps
- B29C66/8126—General aspects of the pressing elements, i.e. the elements applying pressure on the parts to be joined in the area to be joined, e.g. the welding jaws or clamps characterised by the composition, by the structure, by the intensive physical properties or by the optical properties of the material constituting the pressing elements, e.g. constituting the welding jaws or clamps characterised by the intensive physical properties or by the optical properties of the material constituting the pressing elements, e.g. constituting the welding jaws or clamps
- B29C66/81266—Optical properties, e.g. transparency, reflectivity
- B29C66/81267—Transparent to electromagnetic radiation, e.g. to visible light
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29L—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS B29C, RELATING TO PARTICULAR ARTICLES
- B29L2031/00—Other particular articles
- B29L2031/30—Vehicles, e.g. ships or aircraft, or body parts thereof
- B29L2031/3055—Cars
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29L—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS B29C, RELATING TO PARTICULAR ARTICLES
- B29L2031/00—Other particular articles
- B29L2031/771—Seats
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B2605/00—Vehicles
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C04—CEMENTS; CONCRETE; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES
- C04B—LIME, MAGNESIA; SLAG; CEMENTS; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF, e.g. MORTARS, CONCRETE OR LIKE BUILDING MATERIALS; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES; TREATMENT OF NATURAL STONE
- C04B2237/00—Aspects relating to ceramic laminates or to joining of ceramic articles with other articles by heating
- C04B2237/02—Aspects relating to interlayers, e.g. used to join ceramic articles with other articles by heating
- C04B2237/12—Metallic interlayers
- C04B2237/124—Metallic interlayers based on copper
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C04—CEMENTS; CONCRETE; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES
- C04B—LIME, MAGNESIA; SLAG; CEMENTS; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF, e.g. MORTARS, CONCRETE OR LIKE BUILDING MATERIALS; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES; TREATMENT OF NATURAL STONE
- C04B2237/00—Aspects relating to ceramic laminates or to joining of ceramic articles with other articles by heating
- C04B2237/30—Composition of layers of ceramic laminates or of ceramic or metallic articles to be joined by heating, e.g. Si substrates
- C04B2237/32—Ceramic
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C04—CEMENTS; CONCRETE; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES
- C04B—LIME, MAGNESIA; SLAG; CEMENTS; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF, e.g. MORTARS, CONCRETE OR LIKE BUILDING MATERIALS; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES; TREATMENT OF NATURAL STONE
- C04B2237/00—Aspects relating to ceramic laminates or to joining of ceramic articles with other articles by heating
- C04B2237/30—Composition of layers of ceramic laminates or of ceramic or metallic articles to be joined by heating, e.g. Si substrates
- C04B2237/40—Metallic
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C04—CEMENTS; CONCRETE; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES
- C04B—LIME, MAGNESIA; SLAG; CEMENTS; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF, e.g. MORTARS, CONCRETE OR LIKE BUILDING MATERIALS; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES; TREATMENT OF NATURAL STONE
- C04B2237/00—Aspects relating to ceramic laminates or to joining of ceramic articles with other articles by heating
- C04B2237/50—Processing aspects relating to ceramic laminates or to the joining of ceramic articles with other articles by heating
- C04B2237/59—Aspects relating to the structure of the interlayer
- C04B2237/592—Aspects relating to the structure of the interlayer whereby the interlayer is not continuous, e.g. not the whole surface of the smallest substrate is covered by the interlayer
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C04—CEMENTS; CONCRETE; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES
- C04B—LIME, MAGNESIA; SLAG; CEMENTS; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF, e.g. MORTARS, CONCRETE OR LIKE BUILDING MATERIALS; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES; TREATMENT OF NATURAL STONE
- C04B2237/00—Aspects relating to ceramic laminates or to joining of ceramic articles with other articles by heating
- C04B2237/50—Processing aspects relating to ceramic laminates or to the joining of ceramic articles with other articles by heating
- C04B2237/70—Forming laminates or joined articles comprising layers of a specific, unusual thickness
- C04B2237/706—Forming laminates or joined articles comprising layers of a specific, unusual thickness of one or more of the metallic layers or articles
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C04—CEMENTS; CONCRETE; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES
- C04B—LIME, MAGNESIA; SLAG; CEMENTS; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF, e.g. MORTARS, CONCRETE OR LIKE BUILDING MATERIALS; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES; TREATMENT OF NATURAL STONE
- C04B2237/00—Aspects relating to ceramic laminates or to joining of ceramic articles with other articles by heating
- C04B2237/50—Processing aspects relating to ceramic laminates or to the joining of ceramic articles with other articles by heating
- C04B2237/72—Forming laminates or joined articles comprising at least two interlayers directly next to each other
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C25—ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PROCESSES; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C25D—PROCESSES FOR THE ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PRODUCTION OF COATINGS; ELECTROFORMING; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C25D3/00—Electroplating: Baths therefor
- C25D3/02—Electroplating: Baths therefor from solutions
- C25D3/38—Electroplating: Baths therefor from solutions of copper
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Plasma & Fusion (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Electrochemistry (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Aviation & Aerospace Engineering (AREA)
- Transportation (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Laser Beam Processing (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Die vorliegende Erfindung bezieht sich auf ein Verfahren zum Verschweißen von Bauteilen eines Kraftfahrzeuges, auf eine Schweißbaugruppe sowie auf einen Fahrzeugsitz für ein Kraftfahrzeug mit einer derartigen Baugruppe.The present invention relates to a method for welding components of a motor vehicle, to a welding assembly and to a vehicle seat for a motor vehicle with such an assembly.
Bei der Konstruktion von Kraftfahrzeugen erlangen zur Reduktion des Gesamtgewichtes des Kraftfahrzeuges Leichtbaukonstruktionen zunehmend an Bedeutung. Dies betrifft neben dem Antriebsstrang, dem Fahrwerk und der Karosserie auch die Innenraumausstattung, wie beispielsweise die Fahrzeugsitze. Ein derartiger Fahrzeugsitz für ein Kraftfahrzeug ist beispielsweise in der
Vor diesem Hintergrund liegt der vorliegenden Erfindung die Aufgabe zugrunde, ein verbessertes Verfahren zur Verfügung zu stellen, welches es ermöglicht, Bauteile, die keine gemeinsame Schweißeignung aufweisen, miteinander zu verschweißen.Against this background, the object of the present invention is to provide an improved method which makes it possible to weld components which do not have common weldability to one another.
Diese Aufgabe wird erfindungsgemäß durch ein Verfahren mit den Merkmalen des Patentanspruchs 1 und/oder durch eine Schweißbaugruppe mit den Merkmalen des Patentanspruchs 10 gelöst.This object is achieved by a method having the features of
Demgemäß ist ein Verfahren zum Verschweißen von Bauteilen eines Kraftfahrzeugs mit folgenden Verfahrensschritten vorgesehen: Bereitstellen eines ersten Bauteils, welches einen aus einem ersten Basismaterial gebildeten ersten Verbindungsabschnitt aufweist; Bereitstellen eines zweiten Bauteils, welches einen aus einem zweiten Material gebildeten zweiten Verbindungsabschnitt aufweist; Vorsehen einer metallischen Beschichtung auf mindestens dem ersten Verbindungsabschnitt, wobei die metallische Beschichtung mit einem Beschichtungsmaterial gebildet wird, welches mit dem zweiten Material des zweiten Verbindungsabschnitts verschweißbar ist; und Verschweißen des ersten und zweiten Bauteils miteinander, wobei der beschichtete erste Verbindungsabschnitt mit dem zweiten Verbindungsabschnitt verschweißt wird.Accordingly, a method for welding components of a motor vehicle is provided with the following method steps: providing a first component which has a first connecting portion formed from a first base material; Providing a second component having a second connecting portion formed of a second material; Providing a metallic coating on at least the first connecting portion, wherein the metallic coating is formed with a coating material which is weldable to the second material of the second connecting portion; and welding the first and second components together, wherein the coated first connection portion is welded to the second connection portion.
Ferner ist eine Schweißbaugruppe für ein Kraftfahrzeug vorgesehen, mit: einem ersten Bauteil, welches einen aus einem ersten Basismaterial gebildeten ersten Verbindungsabschnitt aufweist; einem zweiten Bauteil, welches einen aus einem zweiten Material gebildeten zweiten Verbindungsabschnitt aufweist; und einer mindestens auf dem ersten Verbindungsabschnitt vorgesehenen metallischen Beschichtung, wobei die metallische Beschichtung mit einem Beschichtungsmaterial gebildet ist, welches mit dem zweiten Material des zweiten Verbindungsabschnittes verschweißt ist.Further, there is provided a welding assembly for a motor vehicle, comprising: a first member having a first connecting portion formed of a first base material; a second member having a second connecting portion formed of a second material; and a metallic coating provided at least on the first connecting portion, wherein the metallic coating is formed with a coating material which is welded to the second material of the second connecting portion.
Die der vorliegenden Erfindung zugrunde liegende Idee besteht darin, zum Verschweißen zweier Bauteile zwischen den beiden Bauteilen eine metallische Beschichtung vorzusehen, welche mit einem der beiden Bauteile verbunden ist und welche derart ausgebildet ist, dass diese mit dem Material des unbeschichteten Bauteils verschweißbar ist. Hierdurch ist es vorteilhaft möglich, zwei mit einem gewählten Schweißverfahren bzw. mit bestimmten Schweißparametern konventionell unverschweißbare Bauteile miteinander zu verschweißen. Das vorliegende Verfahren ermöglicht beispielsweise vorteilhaft den Ersatz eines metallischen Fügepartners durch einen mit einem Kunststoffwerkstoff gebildeten Fügepartner, wobei die Vorteile des Schweißverfahrens insbesondere gegenüber einer formschlüssigen Verbindungstechnik, wie beispielsweise Automatisierbarkeit, Schnelligkeit, Wegfall zusätzlicher Befestigungselemente bei der Ausbildung der Verbindung erhalten bleiben. Dies ermöglicht die Herstellung hochintegrierter Schweißbaugruppen in einem automatisierbaren Verfahren bei deutlich reduziertem Gewichtsaufwand.The idea underlying the present invention is to provide for the welding of two components between the two components, a metallic coating which is connected to one of the two components and which is designed such that it can be welded to the material of the uncoated component. As a result, it is advantageously possible to weld two components that are conventionally nonweldable using a selected welding method or with specific welding parameters. The present method allows, for example, advantageously the replacement of a metallic joining partner by a joining partner formed with a plastic material, the advantages of the welding process in particular over a positive connection technology, such as automation, speed, elimination of additional fasteners remain in the formation of the compound. This allows the production of highly integrated welding assemblies in one automatable process with significantly reduced weight.
Vorteilhafte Ausgestaltungen und Weiterbildungen der vorliegenden Erfindung ergeben sich aus den weiteren Unteransprüchen und aus der Beschreibung in Zusammenschau mit den Figuren der Zeichnung. Advantageous embodiments and further developments of the present invention will become apparent from the other dependent claims and from the description in conjunction with the figures of the drawing.
In einer bevorzugten Ausgestaltung des Verfahrens wird das miteinander Verschweißen des ersten und zweiten Bauteils mittels eines Laserstrahlschweißverfahrens durchgeführt. Hierdurch ist es vorteilhaft möglich, mit hoher Schweißgeschwindigkeit, schmaler Schweißnahtform und geringem thermischen Wärmeeintrag die Bauteile zu fügen. Dies ermöglicht hohe Taktzeiten bei der Anwendung des Verfahrens, wodurch dessen Anwendungsbereich erweitert wird.In a preferred embodiment of the method, the welding together of the first and second component is carried out by means of a laser beam welding method. As a result, it is advantageously possible to join the components with high welding speed, narrow welding seam shape and low thermal heat input. This allows high cycle times in the application of the method, which extends its scope.
In einer typischen Ausgestaltung des Verfahrens wird die metallische Beschichtung auf mindestens dem ersten Verbindungsabschnitt lediglich im Bereich einer beim miteinander Verschweißen des ersten und zweiten Bauteils gebildeten Schweißnaht vorgesehen. Hierdurch wird eine Materialersparnis bei dem Aufbringen der metallischen Beschichtung erzielt, welche die Kosten bei der Anwendung des Verfahrens reduziert und vorteilhaft eine Gewichtsersparnis ermöglicht.In a typical embodiment of the method, the metallic coating is provided on at least the first connecting section only in the region of a weld seam formed when the first and second component are welded together. As a result, a material savings in the application of the metallic coating is achieved, which reduces the cost in the application of the method and advantageously allows weight savings.
In einer weiteren Ausgestaltung des Verfahrens wird das Vorsehen der metallischen Beschichtung galvanisch, insbesondere mittels Aufbringen einer Kupferschicht, durchgeführt, wodurch die metallische Beschichtung kostengünstig, mit konstanter Schichtdicke und schnell auf dem ersten Verbindungsabschnitt aufgebracht wird. Hierdurch wird die Taktzeit bei der Anwendung des Verfahrens reduziert. In a further embodiment of the method, the provision of the metallic coating is carried out galvanically, in particular by applying a copper layer, whereby the metallic coating is applied inexpensively, with a constant layer thickness and quickly on the first connecting section. This reduces the cycle time in the application of the method.
In einer Ausgestaltung des Verfahrens wird bei dem Bereitstellen des ersten Bauteils der erste Verbindungsabschnitt einstückig mit dem ersten Bauteil ausgebildet und/oder bei dem Bereitstellen des zweiten Bauteils wird der zweite Verbindungsabschnitt einstückig mit dem zweiten Bauteil ausgebildet. Hierdurch wird vorteilhaft eine Reduktion der Komponenten erreicht, wodurch die Herstellung der Bauteile vereinfacht und kostenreduziert wird. In an embodiment of the method, when the first component is provided, the first connecting portion is formed integrally with the first component and / or when the second component is provided, the second connecting portion is formed integrally with the second component. As a result, a reduction of the components is advantageously achieved, whereby the manufacture of the components is simplified and cost-reduced.
In einer bevorzugten Ausgestaltung des Verfahrens wird bei dem Bereitstellen des zweiten Bauteils das zweite Material des zweiten Verbindungsabschnitts als zweites Basismaterial des zweiten Verbindungsabschnitts ausgebildet. Hierdurch wird die Herstellung des zweiten Bauteils vereinfacht, wodurch die Herstellungskosten verringert werden.In a preferred embodiment of the method, when providing the second component, the second material of the second connecting portion is formed as a second base material of the second connecting portion. As a result, the production of the second component is simplified, whereby the manufacturing costs are reduced.
In einer bevorzugten Ausgestaltung des Verfahrens wird bei dem Bereitstellen des zweiten Bauteils das zweite Basismaterial des zweiten Verbindungsabschnitts als Metallwerkstoff ausgebildet. Hierdurch wird eine ausreichende Stabilität des zweiten Bauteils erzielt und das zweite Bauteil ist beispielsweise als Blechzuschnitt kostengünstig und schnell herstellbar.In a preferred embodiment of the method, when providing the second component, the second base material of the second connecting portion is formed as a metal material. As a result, a sufficient stability of the second component is achieved and the second component is inexpensive and quick to produce, for example, as a sheet metal blank.
In einer weiteren bevorzugten Ausgestaltung des Verfahrens wird bei dem Bereitstellen des ersten Bauteils das erste Basismaterial des ersten Verbindungsabschnitts als Kunststoffwerkstoff ausgebildet. Hierdurch ist das erste Bauteil kostengünstig und mit geringem Gewicht, beispielsweise als Kunststoffspritzgussteil, herstellbar.In a further preferred embodiment of the method, the first base material of the first connecting portion is formed as a plastic material in the provision of the first component. As a result, the first component is inexpensive and lightweight, for example, as a plastic injection molded part, produced.
In einer ebenso bevorzugten Ausgestaltung des Verfahrens wird bei dem Bereitstellen des zweiten Bauteils das zweite Material des zweiten Verbindungsabschnitts als metallische, insbesondere galvanisch aufgebrachte, Beschichtung eines zweiten Basismaterials des zweiten Verbindungsabschnitts ausgebildet, wobei die metallische Beschichtung des zweiten Verbindungsabschnitts mit einem Beschichtungsmaterial gebildet wird, welches mit der metallischen Beschichtung des ersten Verbindungsabschnitts verschweißbar ist. Hierdurch ist es vorteilhafter Weise möglich, zwei Bauteile mit geringer oder nicht vorhandener Schweißeignung mittels beidseitiger Beschichtung miteinander zu verschweißen. Dies erweitert den Einsatzbereich des Verfahrens.In an equally preferred embodiment of the method, in providing the second component, the second material of the second connecting portion is formed as a metallic, in particular galvanically applied, coating of a second base material of the second connecting portion, wherein the metallic coating of the second connecting portion is formed with a coating material which can be welded to the metallic coating of the first connecting portion. This makes it advantageously possible to weld two components with low or no existing weldability by coating on both sides with each other. This extends the field of application of the method.
In einer bevorzugten Ausgestaltung der Baugruppe ist der erste Verbindungsabschnitt einstückig mit dem ersten Bauteil ausgebildet und/oder der zweite Verbindungsabschnitt ist einstückig mit dem zweiten Bauteil ausgebildet. Hierdurch wird vorteilhaft eine Reduktion der Komponenten der Baugruppe erreicht, wodurch deren Zuverlässigkeit erhöht wird. Ferner werden die Kosten zur Herstellung der Baugruppe reduziert.In a preferred embodiment of the assembly, the first connection portion is integrally formed with the first component and / or the second connection portion is formed integrally with the second component. As a result, a reduction of the components of the assembly is advantageously achieved, whereby their reliability is increased. Furthermore, the cost of manufacturing the assembly is reduced.
In einer weiteren bevorzugten Ausgestaltung der Baugruppe ist das zweite Material des zweiten Verbindungsabschnitts als zweites Basismaterial des zweiten Verbindungsabschnitts ausgebildet, wobei das zweite Basismaterial insbesondere als Metallwerkstoff ausgebildet ist. Hierdurch ist das zweite Bauteil bei hervorragender Festigkeit vorteilhaft kostengünstig herstellbar.In a further preferred embodiment of the assembly, the second material of the second connecting portion is formed as a second base material of the second connecting portion, wherein the second base material is formed in particular as a metal material. As a result, the second component with excellent strength can be advantageously produced inexpensively.
In einer weiteren bevorzugten Ausgestaltung der Baugruppe ist das erste Basismaterial des ersten Verbindungsabschnitts des ersten Bauteils als Kunststoffwerkstoff ausgebildet. Hierdurch ist das erste Bauteil bei geringem Gewicht besonders kostengünstig und einfach herstellbar.In a further preferred embodiment of the assembly, the first base material of the first connecting portion of the first component is formed as a plastic material. As a result, the first component with low weight is particularly inexpensive and easy to produce.
Die oben beschriebenen Ausgestaltungen und Weiterbildungen der vorliegenden Erfindung sind – sofern nichts Anderes ausgeführt ist – frei miteinander kombinierbar. The embodiments and further developments of the present invention described above are - unless otherwise stated - freely combinable with each other.
Die vorliegende Erfindung wird nachfolgend anhand der in den schematischen Figuren der Zeichnung angegebenen Ausführungsbeispiele näher erläutert. Es zeigen dabei:The present invention will be explained in more detail with reference to the exemplary embodiments indicated in the schematic figures of the drawing. It shows:
In den Figuren der Zeichnung bezeichnen – sofern nichts anderes ausgeführt ist – gleiche Bezugszeichen gleiche Bauteile, Elemente und Merkmale.In the figures of the drawing - unless otherwise stated - like reference numerals designate like components, elements and features.
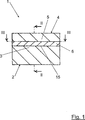
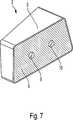
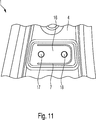
Die
Die Schweißbaugruppe
Die Schweißbaugruppe
Zumindest auf dem ersten Verbindungsabschnitt
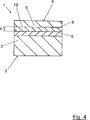
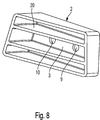
Die
Die Schweißbaugruppe
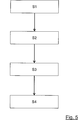
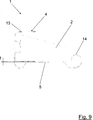
Eine bevorzugte Ausführungsform eines Verfahren zum Verschweißen von Bauteilen
In einem ersten Verfahrensschritt S1 wird das erste Bauteil
In einem weiteren Verfahrensschritt S2 wird das zweite Bauteil
In einem Verfahrensschritt S3 wird die erste metallische Beschichtung
In einem Verfahrensschritt S4 werden die Bauteile
In einer Weiterbildung des Verfahrens gemäß der
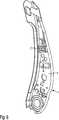
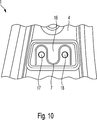
Die
Der Knickschutzblock
Nach dem Beschichten des ersten Verbindungsabschnittes
Nach dem Positionieren des Knickschutzblockes
Im Normalbetrieb der Sitzlehne wirkt lediglich die Schwerkraft bzw. die Fahrbeschleunigung auf den Knickschutzblock
Obwohl die vorliegende Erfindung anhand bevorzugter Ausführungsbeispiele vollständig beschrieben wurde, ist sie darauf nicht beschränkt, sondern auf vielfältige Art und Weise modifizierbar. Insbesondere können Merkmale der einzelnen oben aufgeführten Ausführungsbeispiele beliebig miteinander kombiniert werden.Although the present invention has been fully described in terms of preferred embodiments, it is not limited thereto but is modifiable in a variety of ways. In particular, features of the individual embodiments listed above can be combined as desired.
Die aufgeführten Materialien, Zahlenangaben und Dimensionen sind beispielhaft zu verstehen und dienen lediglich der Erläuterung der Ausführungsformen und Weiterbildungen der vorliegenden Erfindung.The listed materials, numbers and dimensions are to be understood as exemplary and are merely illustrative of the embodiments and further developments of the present invention.
BezugszeichenlisteLIST OF REFERENCE NUMBERS
- 11
- Baugruppemodule
- 22
- erstes Bauteilfirst component
- 33
- erster Verbindungsabschnittfirst connection section
- 44
- zweites Bauteilsecond component
- 55
- zweiter Verbindungsabschnittsecond connection section
- 66
- metallische Beschichtungmetallic coating
- 77
- SchweißnahtWeld
- 88th
- metallische Beschichtungmetallic coating
- 99
- Schweißwurzelweld root
- 1010
- Positionierbohrungpositioning bore
- 1111
- Positionierbohrungpositioning bore
- 1313
- LehnenseitenteilrandBackrest side part edge
- 1414
- LehnenseitenteilrandBackrest side part edge
- 1515
- Oberflächesurface
- 1616
- Oberflächesurface
- 1717
- Positionierbohrungpositioning bore
- 1818
- Positionierbohrungpositioning bore
- 1919
- Oberflächesurface
- 2020
- Verrippungribbing
- dd
- Dickethickness
- ee
- Dickethickness
- tt
- WandstärkeWall thickness
ZITATE ENTHALTEN IN DER BESCHREIBUNG QUOTES INCLUDE IN THE DESCRIPTION
Diese Liste der vom Anmelder aufgeführten Dokumente wurde automatisiert erzeugt und ist ausschließlich zur besseren Information des Lesers aufgenommen. Die Liste ist nicht Bestandteil der deutschen Patent- bzw. Gebrauchsmusteranmeldung. Das DPMA übernimmt keinerlei Haftung für etwaige Fehler oder Auslassungen.This list of the documents listed by the applicant has been generated automatically and is included solely for the better information of the reader. The list is not part of the German patent or utility model application. The DPMA assumes no liability for any errors or omissions.
Zitierte PatentliteraturCited patent literature
- EP 1977927 A2 [0002, 0002] EP 1977927 A2 [0002, 0002]
Claims (15)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102011077458A DE102011077458A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2011-06-14 | Welding components of motor vehicle, comprises providing first component having first connecting portion, second component having second material, providing metallic coating on first connecting portion, welding first and second components |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102011077458A DE102011077458A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2011-06-14 | Welding components of motor vehicle, comprises providing first component having first connecting portion, second component having second material, providing metallic coating on first connecting portion, welding first and second components |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| DE102011077458A1 true DE102011077458A1 (en) | 2012-12-20 |
Family
ID=47228214
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102011077458A Withdrawn DE102011077458A1 (en) | 2011-06-14 | 2011-06-14 | Welding components of motor vehicle, comprises providing first component having first connecting portion, second component having second material, providing metallic coating on first connecting portion, welding first and second components |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| DE (1) | DE102011077458A1 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2014066584A1 (en) * | 2012-10-24 | 2014-05-01 | Magna International Inc. | Laser metal deposition cladding of weld seams in automotive parts |
| US20180243860A1 (en) * | 2017-02-24 | 2018-08-30 | Spirit Aerosystems, Inc. | Structure and method of making same involving welding otherwise non-weldable materials |
| WO2022144058A1 (en) * | 2021-01-04 | 2022-07-07 | Edscha Engineering Gmbh | Spindle assembly for a spindle device |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5343014A (en) * | 1990-07-12 | 1994-08-30 | Nippondenso Co., Ltd. | Method of welding metals of different kind by laser |
| DE10255497A1 (en) * | 2002-11-27 | 2004-06-24 | BLZ Bayerisches Laserzentrum Gemeinnützige Forschungsgesellschaft mbH | Regulation method for a laser spot-welding process, whereby scattering and reflection properties of the laser beam are measured prior to or at the beginning of a weld process in order to determine and regulate beam energy |
| DE102004009651A1 (en) * | 2004-02-27 | 2005-09-22 | BLZ Bayerisches Laserzentrum Gemeinnützige Forschungsgesellschaft mbH | Process for the welding of dissimilar metallic joining partners, in particular aluminum-copper joints |
| EP1806200A1 (en) * | 2004-10-26 | 2007-07-11 | HONDA MOTOR CO., Ltd. | Method for bonding iron-based member with aluminum-based member |
| EP1977927A2 (en) | 2007-04-05 | 2008-10-08 | Brose Fahrzeugteile GmbH & Co. Kommanditgesellschaft Coburg | Vehicle seat |
| EP2070685A1 (en) * | 2006-10-05 | 2009-06-17 | Okayama Prefectural Government | Intermediate member for laser bonding and method of bonding using the same |
| JP2009226420A (en) * | 2008-03-20 | 2009-10-08 | Denso Corp | Laser welding method |
-
2011
- 2011-06-14 DE DE102011077458A patent/DE102011077458A1/en not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5343014A (en) * | 1990-07-12 | 1994-08-30 | Nippondenso Co., Ltd. | Method of welding metals of different kind by laser |
| DE10255497A1 (en) * | 2002-11-27 | 2004-06-24 | BLZ Bayerisches Laserzentrum Gemeinnützige Forschungsgesellschaft mbH | Regulation method for a laser spot-welding process, whereby scattering and reflection properties of the laser beam are measured prior to or at the beginning of a weld process in order to determine and regulate beam energy |
| DE102004009651A1 (en) * | 2004-02-27 | 2005-09-22 | BLZ Bayerisches Laserzentrum Gemeinnützige Forschungsgesellschaft mbH | Process for the welding of dissimilar metallic joining partners, in particular aluminum-copper joints |
| EP1806200A1 (en) * | 2004-10-26 | 2007-07-11 | HONDA MOTOR CO., Ltd. | Method for bonding iron-based member with aluminum-based member |
| EP2070685A1 (en) * | 2006-10-05 | 2009-06-17 | Okayama Prefectural Government | Intermediate member for laser bonding and method of bonding using the same |
| EP1977927A2 (en) | 2007-04-05 | 2008-10-08 | Brose Fahrzeugteile GmbH & Co. Kommanditgesellschaft Coburg | Vehicle seat |
| JP2009226420A (en) * | 2008-03-20 | 2009-10-08 | Denso Corp | Laser welding method |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2014066584A1 (en) * | 2012-10-24 | 2014-05-01 | Magna International Inc. | Laser metal deposition cladding of weld seams in automotive parts |
| US10279431B2 (en) | 2012-10-24 | 2019-05-07 | Magna International Inc. | Laser metal deposition cladding of weld seams in automotive parts |
| US20180243860A1 (en) * | 2017-02-24 | 2018-08-30 | Spirit Aerosystems, Inc. | Structure and method of making same involving welding otherwise non-weldable materials |
| US10661381B2 (en) * | 2017-02-24 | 2020-05-26 | Spirit Aerosystems, Inc. | Structure and method of making same involving welding otherwise non-weldable materials |
| WO2022144058A1 (en) * | 2021-01-04 | 2022-07-07 | Edscha Engineering Gmbh | Spindle assembly for a spindle device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE102009047671A1 (en) | A method for bonding a fiber composite component to a structural component of an aircraft and spacecraft and a corresponding arrangement | |
| DE102010014510A1 (en) | Door for a motor vehicle and process for its manufacture | |
| DE102011120180A1 (en) | body component | |
| DE102008005286A1 (en) | Method for connecting components of a motor vehicle | |
| DE102004003190A1 (en) | Assembly of a motor vehicle body in shell construction | |
| DE102010031774A1 (en) | Roof i.e. sun roof, module arrangement for passenger car, has adhesive bead provided between roof panel element and body of vehicle, and retaining elements connected with panel element by rivet joints and with body by screw connections | |
| DE102006036931A1 (en) | Bonding connection between metal and carbon fiber composite parts for reinforcing outer sheet metal of a vehicle body, comprises fixing elements pre-installed at the composite part and welded with the metal part | |
| DE102011116300B4 (en) | Fiber composite component with metallic connection piece and composite component produced therewith | |
| DE102011077458A1 (en) | Welding components of motor vehicle, comprises providing first component having first connecting portion, second component having second material, providing metallic coating on first connecting portion, welding first and second components | |
| DE102021108564A1 (en) | component of a motor vehicle | |
| DE102011051639A1 (en) | Method for assembling composite sheet metal components of joined structure, involves firmly connecting the outer layer of composite sheet metal component with metal layer of component by applying electromagnetic pulse shape process | |
| WO2008028647A1 (en) | Vehicle component with a hybrid structure | |
| DE102013113552A1 (en) | Carrier part for a car body in shell construction | |
| DE102012015162A1 (en) | Roof assembly for vehicle roof of passenger car, has roof frame element of vehicle roof that is attached with roof planking portion under placement of support element, where roof planking portion is cohesively connected with support element | |
| DE102017005123A1 (en) | Assembly of at least two workpieces and method for joining at least two workpieces to an assembly | |
| WO2019115041A1 (en) | Fiber-reinforced vehicle body | |
| DE102013007423B4 (en) | Arrangement for connecting two components with different thermal expansion coefficients and associated motor vehicle body | |
| DE102017219980A1 (en) | Method for producing a fiber-reinforced vehicle body | |
| EP1838569B1 (en) | Metal-reinforced hybrid structure | |
| DE102020110241A1 (en) | Body pillar, in particular A pillar, for a motor vehicle | |
| DE102014013211A1 (en) | Method for producing a seam connection between an inner part and an outer part | |
| DE102006021457B4 (en) | Metal reinforced plastic carrier for a vehicle | |
| DE102012005507A1 (en) | Shell construction group for motor car, has body parts provided with flange regions, and connectors partially arranged in flange regions, where body parts are firmly interconnected with adhesive bond, and connectors have base bodies | |
| DE102013223302A1 (en) | Method of repairing composite-reinforced metallic structures in hybrid construction | |
| EP4326602B1 (en) | Fastening arrangement with a vehicle roof-frame structure and a roof module |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| R163 | Identified publications notified | ||
| R079 | Amendment of ipc main class |
Free format text: PREVIOUS MAIN CLASS: B23K0026420000 Ipc: B23K0026320000 |
|
| R079 | Amendment of ipc main class |
Free format text: PREVIOUS MAIN CLASS: B23K0026420000 Ipc: B23K0026320000 Effective date: 20131209 |
|
| R005 | Application deemed withdrawn due to failure to request examination |