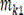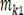CN210942239U - Radius unequal longitudinal three-rotor helicopter - Google Patents
Radius unequal longitudinal three-rotor helicopter Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN210942239U CN210942239U CN201921893493.0U CN201921893493U CN210942239U CN 210942239 U CN210942239 U CN 210942239U CN 201921893493 U CN201921893493 U CN 201921893493U CN 210942239 U CN210942239 U CN 210942239U
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- rotor
- rotors
- helicopter
- wing
- blades
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 claims description 16
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 6
- 125000004122 cyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 40
- 238000005096 rolling process Methods 0.000 description 11
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Toys (AREA)
Abstract
A longitudinal three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses is characterized in that a longitudinal beam is arranged at the top of a helicopter body, a small tower of an airfoil is arranged in front of the helicopter body, a middle of the helicopter body and a back of the helicopter body respectively, the small tower at the back of the helicopter body is higher than the small tower at the front of the helicopter body, a rotor is arranged on each small tower, the rotating surfaces of the three rotors are horizontal and have equal intervals, blades of each rotor are connected with a rotor shaft through a shell pattern, the shell pattern of the rotor is provided with a blade flapping device consisting of a flapping hinge, a shimmying hinge and a variable pitch hinge, a total pitch and periodic variable pitch controller is arranged for controlling the magnitude and the direction of the lifting force of the rotors, a transmission device is arranged for enabling the angular speeds of the three rotors to be the same, the turning directions of the front rotor and the back rotor are the same and are opposite to the turning direction of the middle rotor, each rotor is composed of blades with the same wing profile, the same, the rotor wing synchronizer can keep the phase difference of the three rotor wings constant all the time, and an undercarriage is arranged below the aircraft body and is applied to rescue, transportation and the like.
Description
Technical Field
The utility model relates to a do not rely on airport to adopt many rotors vertical lift, hover, the unequal indulge tandem type three rotor helicopter of radius of flying all around.
Background
The prior known successful methods of helicopters capable of realizing vertical lifting, hovering, front-back left-right flying comprise a single-rotor helicopter and a tandem double-rotor helicopter, wherein the single-rotor helicopter is used for controlling a pitching single-rotor wing and a rolling single-rotor wing, the course of the single-rotor helicopter is specially controlled by a propeller, and the helicopter has the advantages of simple structure and flexible control, but the counter torque of the rotor wing of the single-rotor helicopter needs to be balanced by a tail propeller vertical to a rotating surface, the propeller does not generate a lifting force in the vertical direction and consumes a little power, the tandem double-rotor helicopter has the advantages that because a pair of forward and reverse rotating rotors with the same speed and size are adopted, the counter torques of the rotor wings are mutually offset, a little power is saved, but two rotor wings are required to participate in the control of the pitching single-rotor wing, the rolling single-rotor wing and the course, the pitching single-rotor wing, the rolling single, the course stability is poor.
Disclosure of Invention
In order to save the power of balanced reaction torque, improve the manipulation characteristic of helicopter, the better manipulation characteristic of existing single rotor helicopter has the advantage that the reaction torque of tandem double rotor helicopter's rotor offsets each other again, the utility model provides a radius varies tandem three rotor helicopters, realizes this target.
The utility model provides a technical scheme that its technical problem adopted is: a vertical three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii is characterized in that an undercarriage is arranged below a helicopter body and close to the center of gravity, a longitudinal beam is arranged at the top of the helicopter body, a first small wing-shaped tower is arranged on a cantilever at the front end of the longitudinal beam, a first rotor wing is arranged on the first small tower, the center of the longitudinal beam is arranged above the center of gravity, a second small wing-shaped tower is arranged at the top of the helicopter body above the center of gravity, a second rotor wing is arranged on the second small tower, a third small wing-shaped tower is arranged on a cantilever at the rear end of the longitudinal beam, a third rotor wing is arranged on the third small tower, the three towers are arranged at equal intervals, the third tower is higher than the second small tower, the second small tower is higher than the first small tower, the influence of washing air flow in front of the rotor wings on the rotor wings behind is reduced, the small towers of the wing-shaped towers have the function of vertical tail wings, the intervals of the three rotor wings on the three small towers are equal, and the interval size is smaller than the diameter of the middle rotor wing, the second rotor rotating surface on the second small tower is partially overlapped with the third rotor rotating surface on the third small tower on the horizontal projection, the occupied space of the three rotors is reduced, the rotating surface of each rotor is horizontally arranged, the blade of each rotor is connected with the rotor shaft through a propeller shell, the propeller shell is provided with a blade flapping device consisting of a flapping hinge, a shimmying hinge and a variable pitch hinge, a total pitch controller is arranged to operate the magnitude of the lifting force of the rotors, a periodic variable pitch controller is arranged to operate the dump angle of the rotating surface of the rotor tip, so that the lifting force direction of the rotors is changed, an engine is arranged, the three rotors are driven to rotate simultaneously through a transmission device, the angular speeds of the three rotors are the same, the steering directions of the first rotor and the third rotor are the same, the steering of the first rotor and the second rotor are opposite, each rotor is composed of the same wing type, the same aspect ratio and the same number of blades, the paddle radius of front and back rotor is the same, and the paddle radius of front and back rotor equals middle rotor paddle radius 0.87 times, and the sum of the counter torque that first rotor and third rotor were adopted is equal opposite direction with the counter torque quantity of second rotor, and the counter torque of three rotors offsets each other, and rotor synchronizer makes the phase difference of three rotors remain invariable all the time, prevents rotor paddle collision each other.
The interval that sets up three towelettes equals, and the third towelette is higher than the second towelette, and the second towelette is higher than first towelette, can reduce the rotor in front and wash the influence of air current to the rotor behind down.
The interval of three rotors on the three pylons is equal, and this interval size is less than the diameter of the second rotor, makes first rotor rotating surface on the first pylon and the second rotor rotating surface on the second pylon have the part to overlap on the horizontal projection, and the second rotor rotating surface on the second pylon and the third rotor rotating surface on the third pylon have the part to overlap on the horizontal projection, has saved the occupation space of three rotors.
The paddle shell of each rotor is connected with a rotor shaft through a paddle shell, the paddle shell is provided with a paddle waving device consisting of a waving hinge, a shimmy hinge and a variable pitch hinge, a total pitch controller is arranged for controlling the lift force of the rotor, and a periodic variable pitch controller is arranged for controlling the dumping angle of a rotating surface of a rotor tip, so that the lift force direction of the rotor is changed.
The engine is arranged, the three rotors are driven by the transmission device at the same time, the angular speeds of the three rotors are the same, the first rotor and the third rotor are enabled to rotate in the same direction, and the first rotor and the second rotor are enabled to rotate in opposite directions.
Each rotor wing is composed of blades with the same number, the first rotor wing and the third rotor wing are provided with blades with the same number and the same size, the second rotor wing is provided with blades with the same number, the same airfoil shape and the same aspect ratio as those of the first rotor wing, but the radius of the second rotor wing is larger than that of the first rotor wing, and the radius of the first rotor wing is 0.87 times that of the second rotor wing.
Setting: it adopts two paddles to establish first rotor, and two paddles are adopted to third rotor, and two paddles are adopted to second rotor, and the paddle radius of second rotor isThe first rotor has a blade radius of 0.87%The third rotor also had a blade radius of 0.87 ×When adopting this kind of paddle setting, set up rotor synchronizer and make, the adjacent paddle phase difference of first rotor and second rotor 90, the adjacent paddle phase difference 90 of second rotor and third rotor prevents rotor blade collision each other to reduce the height that the small tower needs.
Or setting: if a first rotor adopts three blades, a third rotor adopts three blades, a second rotor adopts three blades, and the radius of the blades of the second rotor isThe first rotor has a blade radius of 0.87%The third rotor also had a blade radius of 0.87 ×When the blade setting is adopted, the rotor synchronizing device is arranged to ensure that the phase difference between the adjacent blades of the first rotor and the second rotor is 60 degrees, and the phase difference between the adjacent blades of the second rotor and the third rotor is 60 degrees, so that the rotor blades are prevented from colliding with each other, and the height required by the small tower is reduced.
Or further provided with: if a first rotor adopts four blades, a third rotor adopts four blades, a second rotor adopts four blades, and the radius of the blades of the second rotor isThe first rotor has a blade radius of 0.87%The third rotor also had a blade radius of 0.87 ×When adopting this kind of paddle setting, set up rotor synchronizer and make, the adjacent paddle phase difference 45 of first rotor and second rotor, the adjacent paddle phase difference 45 of second rotor and third rotor prevents rotor blade collision each other to reduce the height that the small tower needs.
An undercarriage is arranged under the fuselage near the center of gravity.
The working principle of the vertical three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses is as follows: for convenience of explanation, a rotor with 3 blades is taken as an example, and a first rotor and a third rotor rotate anticlockwise, a second rotor rotates clockwise, the first rotor adopts three blades, the third rotor adopts three blades, and the second rotor adopts three blades.
The rotor synchronizer enables the phase difference between adjacent blades of the first rotor and the second rotor to be always kept at 60 degrees, enables the phase difference between adjacent blades of the second rotor and the third rotor to be always kept at 60 degrees, and therefore even if the distances between the three rotors are equal and smaller than the diameters of the rotors, the blades of the rotors cannot collide with each other.
Let the radius of the first rotor be R1The second rotor has a blade radius R2The third rotor has a blade radius of R3,The width of the first rotor blade is b1The second rotor has a blade width of b2The third rotor has a blade width of b3The angular velocities of the three rotors are the same。
The aspect ratios of the three rotors are the same, so:
setting the solidity of the first rotor wing asThe second rotor has a solidity ofThe third rotor has solidity of。
Wherein K is the blade number of the rotor, and K = 3. The solidity of the three rotors is the same:
the torque formula for the rotor is:
in the formulaThe torque of the rotor is transmitted to the rotor,the torque coefficient of the rotor is such that,the density of the air is higher than that of the air,the radius of the rotor wing is such that,the angular velocity of the rotor.
Since the counter-torque of the rotors is proportional to the torque of the rotors, the torque of the rotors is the same, the counter-torque is also the same, since the first and third rotors are the same, R1=R3,=Therefore, the temperature of the molten steel is controlled,=the reaction torque of the first rotor and the third rotor is the same.
Order to=+I.e. by=2*The sum of the reactive torques of the first and third rotors is equal to the reactive torque of the second rotor, the first and third rotors turn in the same direction and in opposite directions to the direction of the second rotor, and since the angular velocities of the three rotors are the same, the sum of the reactive torques of the first and third rotors is equal in number to the reactive torque of the second rotor and in opposite directions, the reactive torques of the three rotors cancel each other out.
Because the solidity of three rotors is the same, and the wing section is the same, and aspect ratio is the same, and the paddle quantity is the same, so the torque coefficient of rotor is close the same:
equation (11) is simplified as:
since the angular velocities of the three rotors are the same, the blade radius at the second rotor isThe first rotor has a blade radius of 0.87%The third rotor also had a blade radius of 0.87 ×The sum of the reaction torques of the first and third rotors is equal in number to the reaction torque of the second rotor, but in opposite directions, so that the reaction torques of the three rotors cancel each other out.
The accelerator of an engine for driving the rotors is increased, meanwhile, the total distance of the three rotors is increased, the lift force of the three rotors is increased, and when the total lift force is larger than the weight of the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii, the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii vertically ascends.
And reducing the throttle of an engine for driving the rotor, and hovering the unequal-radius tandem three-rotor helicopter when the total lift force is equal to the weight of the unequal-radius tandem three-rotor helicopter.
And continuously reducing the throttle of an engine driving the rotor wing, and when the total lift force is less than the weight of the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii, the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii vertically descends.
When the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii is in the air, the cyclic variable pitch controller of the first rotor is operated to tilt rightwards, the tip rotating surface of the first rotor tilts rightwards, the lift force of the first rotor tilts rightwards, meanwhile, the cyclic variable pitch controller of the third rotor is operated to tilt leftwards, the tip rotating surface of the third rotor tilts leftwards, the lift force of the third rotor tilts leftwards, the first rotor and the third rotor jointly generate a right-steering torque, and the torque drives the helicopter body to steer rightwards; the cyclic pitch controller of manipulating the first rotor wing inclines to the left, the tip rotating surface of the first rotor wing inclines to the left, the lift force of the first rotor wing inclines to the left, meanwhile, the cyclic pitch controller of manipulating the third rotor wing inclines to the right, the tip rotating surface of the third rotor wing inclines to the right, the lift force of the third rotor wing inclines to the right, the first rotor wing and the third rotor wing jointly generate a left steering moment, and the moment drives the fuselage to steer to the left, so that course manipulation is realized.
When the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii is in the air, the cyclic pitch controller for operating the second rotor wing inclines forwards, the rotating surface of the tip of the second rotor wing inclines forwards, the lifting force of the second rotor wing inclines forwards, and the helicopter body inclines forwards; the pitch controller for operating the second rotor wing tilts backwards, the tip rotating surface of the second rotor wing tilts backwards, the lifting force of the second rotor wing tilts backwards, and the machine body tilts backwards to realize pitching operation.
When the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii is in the air, the cyclic pitch controller of the second rotor wing is operated to incline leftward, the rotating plane of the tip of the second rotor wing inclines leftward, and the lift force of the second rotor wing inclines leftward, so that the helicopter body rolls leftward; the cyclic pitch controller for operating the second rotor wing inclines rightwards, the tip rotating surface of the second rotor wing inclines rightwards, and the lift force of the second rotor wing inclines rightwards, so that the aircraft body rolls rightwards, and the roll operation is realized.
When the longitudinal three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses is in the air, the helicopter body is controlled to bow forwards, meanwhile, an accelerator of an engine for driving the three rotors is increased, and the longitudinal three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies forwards; the helicopter body is controlled to tilt backwards, the accelerator of an engine driving the three rotors is increased simultaneously, and the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies backwards; the helicopter body is controlled to roll leftwards, the accelerator of an engine driving the three rotors is increased simultaneously, and the tandem type three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies leftwards; the helicopter body is controlled to roll rightwards, the accelerator of an engine driving the three rotors is increased simultaneously, and the tandem type three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies rightwards.
Pitching and rolling are controlled by the second rotor wing, the course is controlled by the first rotor wing and the third rotor wing, the second rotor wing does not participate in the course control, the course control is independent, the control characteristic of the longitudinal three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses is improved, and the control characteristic is similar to that of a single-rotor helicopter (the single-rotor helicopter, the rotor wings control pitching and rolling, and the tail propeller controls the course).
The blade radius at the second rotor isThe first rotor has a blade radius of 0.87%The third rotor also had a blade radius of 0.87 ×Wherein the coefficient 0.87 is≈,≈The approximate result of (a) is that within plus or minus 5 percent of 0.87, i.e., 0.82-0.92, the reactive torques of the three rotors are substantially cancelled, the uncancelled reactive torques interfere with the heading, and the interference is overcome by the heading steering of the first and third rotors.
The utility model has the advantages that the three rotors are adopted, the load capacity is much larger than that of a single-rotor helicopter, the reaction torques of the three rotors are mutually offset, and the power consumption for overcoming the reaction torque is reduced; the three rotors are adopted, course control is executed by the special rotors, the three rotors are similar to the single-rotor helicopter in control, the rotating surfaces are partially overlapped on the horizontal projection, the occupied space of the tandem three-rotor helicopter is saved, the three rotors adopt the same solidity, the hovering efficiency is improved, and the tandem layout is suitable for flying in narrow places.
Drawings
The present invention will be further explained with reference to the drawings and examples.
Fig. 1 is a three-view diagram of a structure of the utility model of a vertical three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses and two paddles for each rotor.
Fig. 2 is a three-view diagram of the structure of the utility model of the vertical three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses and three blades adopted by each rotor.
Fig. 3 is a three-view diagram of a structure of the present invention, in which each rotor of the vertical three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii adopts four blades.
In the figure 1, a first rotor with two blades, 2, a second rotor with two blades, 3, a third rotor with two blades, 4, a collective and cyclic pitch controller of the first rotor, 5, a collective and cyclic pitch controller of the second rotor, 6, a collective and cyclic pitch controller of the third rotor, 7, a first tower, 8, a second tower, 9, a third tower, 10, a stringer, 11, a fuselage, 12, an undercarriage, 301, a first rotor with three blades, 302, a second rotor with three blades, 303, a third rotor with three blades,
401. a first rotor with four blades is used 402. a second rotor with four blades is used 403. a third rotor with four blades, p.
Detailed Description
In the embodiment shown in fig. 1, a longitudinal beam, hereinafter referred to as a longitudinal beam (10), is arranged at the top of a fuselage (11), a first small tower (7) is arranged on a cantilever at the front end of the longitudinal beam (10), the first small tower (7) of the wing profile plays the role of a vertical tail wing, a first rotor wing (1) consisting of two blades is arranged on the first small tower (7), the center of the longitudinal beam (10) is positioned above the gravity center (P), the top of the machine body (11) above the gravity center (P) is provided with a second small tower (8), the second small tower (8) of the wing profile plays the role of a vertical tail wing, a second rotor wing (2) consisting of two blades is arranged on the second small tower (8), a third small tower (9) is arranged on a cantilever at the rear end of the longitudinal beam (10), the third small tower (9) of the wing profile plays the role of a vertical tail wing, and a third rotor (3) consisting of two blades is arranged on the third small tower (9).
The interval that sets up three towelettes equals, and third towelette (9) are than second towelette height (8), and second towelette (8) are than first towelette height (7), can reduce the influence of rotor downwash air current in front to the rotor behind.
The interval of three rotors on three pylons is equal, and this interval size is less than the diameter of second rotor (2), makes first rotor (1) rotating surface on first pylon (7) and second rotor (2) rotating surface on second pylon (8) have the part to overlap on the horizontal projection, and second rotor (2) rotating surface on second pylon (8) and third rotor (3) rotating surface on third pylon (9) have the part to overlap on the horizontal projection, has saved the occupation space of three rotors.
The paddle shell of each rotor is connected with a rotor shaft through a paddle shell, the paddle shell is provided with a paddle waving device consisting of a waving hinge, a shimmy hinge and a variable pitch hinge, a total pitch controller is arranged for controlling the lift force of the rotor, and a periodic variable pitch controller is arranged for controlling the dumping angle of a rotating surface of a rotor tip, so that the lift force direction of the rotor is changed.
The total pitch and cyclic pitch controller (4) drives the blade pitch of the first rotor (1), the total pitch and cyclic pitch controller (5) drives the blade pitch of the second rotor (2), and the total pitch and cyclic pitch controller (6) drives the blade pitch of the third rotor (3).
The engine is arranged, the three rotors are driven simultaneously through the transmission device, the angular speeds of the three rotors are the same, the steering directions of the first rotor (1) and the third rotor (3) are the same, and the steering directions of the first rotor (1) and the second rotor (2) are opposite.
Setting: the second rotor (2) has a blade radius R2The first rotor (1) has a blade radius of 0.87R2The third rotor (3) also has a blade radius of 0.87R2The rotor wing synchronizer is arranged to ensure that the phase difference between adjacent blades of the first rotor wing (1) and the second rotor wing (2) is 90 degrees, the phase difference between adjacent blades of the second rotor wing (2) and the third rotor wing (3) is 90 degrees, so that the rotor wings are prevented from colliding with each other, and the height required by a small tower is reduced.
An undercarriage (12) is arranged under the fuselage (10) near the center of gravity (P).
The working principle of the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses is as follows: and a first rotor (1) and a third rotor (3) are arranged to rotate anticlockwise, and a second rotor (2) rotates clockwise.
Let the radius of the first rotor (1) be R1The second rotor (2) has a blade radius R2The third rotor (3) has a blade radius R3,The width of the first rotor (1) is b1The width of the second rotor (2) is b2The width of the third rotor (3) is b3The angular velocities of the three rotors are the same。
The aspect ratios of the three rotors are the same, so:
setting the solidity of a first rotor (1) asThe second rotor (2) has a solidity ofThe third rotor (3) has the solidity of。
Wherein K is the blade number of the rotor, and K = 2. The solidity of the three rotors is the same:
the torque formula for the rotor is:
in the formulaTorque of rotorThe torque coefficient of the rotor is such that,the density of the air is higher than that of the air,the radius of the rotor wing is such that,the angular velocity of the rotor.
Since the counter-torque of the rotors is proportional to the torque of the rotors, the torque of the rotors is the same, the counter-torque is also the same, since the first rotor (1) and the third rotor (3) are the same, R is1=R3,=Therefore, the temperature of the molten steel is controlled,=the reaction torque of the first rotor (1) and the third rotor (3) is the same.
Order to=+I.e. by=2*The sum of the reactive torques of the first rotor (1) and the third rotor (3) is equal to the reactive torque of the second rotor (2), the first rotor (1) and the third rotor (3) rotate anticlockwise, the second rotor (2) rotates clockwise, and since the angular speeds of the three rotors are the same, the sum of the reactive torques of the first rotor (1) and the third rotor (3) is equal to the reactive torque of the second rotor (2) in number and the directions are opposite, the reactive torques of the three rotors are mutually offset.
because the solidity of three rotors is the same, and the wing section is the same, and aspect ratio is the same, and the paddle quantity is the same, so the torque coefficient of rotor is close the same:
equation (27) reduces to:
the blade radius of the second rotor (2) is equal toThe first rotor (1) has a blade radius of 0.87%The third rotor (3) also has a blade radius of 0.87%The sum of the reaction torques of the first rotor (1) and the third rotor (3) is equal to the reaction torque of the second rotor (2) in number, but opposite in direction, so that the reaction torques of the three rotors cancel each other.
The accelerator of an engine for driving the rotors is increased, meanwhile, the total distance of the three rotors is increased, the lift force of the three rotors is increased, and when the total lift force is larger than the weight of the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii, the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii vertically ascends.
And reducing the throttle of an engine for driving the rotor, and hovering the unequal-radius tandem three-rotor helicopter when the total lift force is equal to the weight of the unequal-radius tandem three-rotor helicopter.
And continuously reducing the throttle of an engine driving the rotor wing, and when the total lift force is less than the weight of the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii, the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii vertically descends.
When the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii is in the air, a cyclic variable-pitch controller (4) of a first rotor (1) is operated to tilt rightwards, a tip rotating surface of the first rotor (1) tilts rightwards, the lift force of the first rotor (1) tilts rightwards, meanwhile, a cyclic variable-pitch controller (6) of a third rotor (3) tilts leftwards, a tip rotating surface of the third rotor (3) tilts leftwards, the lift force of the third rotor (3) tilts leftwards, the first rotor (1) and the third rotor (3) jointly generate a rightward steering moment, and the moment drives a helicopter body (11) to steer rightwards; the pitch controller (4) of the first rotor (1) is controlled to incline to the left, the tip rotating surface of the first rotor (1) inclines to the left, the lift force of the first rotor (1) inclines to the left, meanwhile, the pitch controller (6) of the third rotor (3) is controlled to incline to the right, the tip rotating surface of the third rotor (3) inclines to the right, the lift force of the third rotor (3) inclines to the right, the first rotor (1) and the third rotor (3) jointly generate a left steering moment, and the moment drives the airframe (11) to steer to the left to realize course control.
When the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii is in the air, the cyclic pitch controller (5) for operating the second rotor (2) inclines forwards, the rotating plane of the tip of the second rotor (2) inclines forwards, the lifting force of the second rotor (2) inclines forwards, and the helicopter body (11) inclines forwards; the pitch controller (5) for operating the second rotor (2) tilts backwards, the tip rotating surface of the second rotor (2) tilts backwards, the lifting force of the second rotor (2) tilts backwards, and the machine body (11) tilts backwards to realize pitching operation.
When the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii is in the air, the cyclic pitch controller (5) of the second rotor (2) is operated to tilt to the left, the tip rotating surface of the second rotor (2) tilts to the left, and the lift force of the second rotor (2) tilts to the left, so that the helicopter body (11) rolls to the left; the cyclic pitch controller for operating the second rotor (2) inclines rightwards, the tip rotating surface of the second rotor (2) inclines rightwards, and the lift force of the second rotor (2) inclines rightwards, so that the fuselage (11) rolls rightwards, and the roll operation is realized.
When the longitudinal three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses is in the air, the helicopter body (11) is controlled to bow forwards, meanwhile, an accelerator of an engine driving the three rotors is increased, and the longitudinal three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies forwards; the helicopter body (11) is controlled to tilt backwards, the accelerator of an engine driving the three rotors is increased simultaneously, and the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies backwards; the helicopter body (11) is controlled to roll leftwards, the accelerator of an engine driving the three rotors is increased simultaneously, and the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies leftwards; the fuselage (11) is controlled to roll rightwards, the accelerator of an engine driving the three rotors is increased simultaneously, and the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies rightwards.
Pitching and rolling are controlled by the second rotor (2), the course is controlled by the first rotor (1) and the third rotor (3), the second rotor (2) does not participate in the course control, the course control is independent, the control characteristic of the three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii and vertical columns is improved, and the three-rotor helicopter is similar to the single-rotor helicopter in control (the single-rotor helicopter, the rotors control pitching and rolling, and the tail propeller controls the course).
In the embodiment shown in fig. 2, a longitudinal beam (10) is arranged at the top of a fuselage (11), a first small tower (7) is arranged on a cantilever at the front end of the longitudinal beam (10), the first small tower (7) of the wing profile plays a role of a vertical tail wing, a first rotor (301) consisting of three blades is arranged on the first small tower (7), the center of the longitudinal beam (10) is positioned above a gravity center (P), a second small tower (8) is arranged at the top of the fuselage (11) above the gravity center (P), the second small tower (8) of the wing profile plays a role of a vertical tail wing, a second rotor (302) consisting of two or three blades is arranged on the second small tower (8), a third small tower (9) is arranged on a cantilever at the rear end of the longitudinal beam (10), the third small tower (9) of the wing profile plays a role of a vertical tail wing, and a third rotor (303) consisting of three blades is arranged on the third small tower (9).
The interval that sets up three towelettes equals, and third towelette (9) are than second towelette height (8), and second towelette (8) are than first towelette height (7), can reduce the influence of rotor downwash air current in front to the rotor behind.
The interval of three rotors on three pylons is equal, and this interval size is less than the diameter of second rotor (2), makes first rotor (1) rotating surface on first pylon (7) and second rotor (2) rotating surface on second pylon (8) have the part to overlap on the horizontal projection, and second rotor (2) rotating surface on second pylon (8) and third rotor (3) rotating surface on third pylon (9) have the part to overlap on the horizontal projection, has saved the occupation space of three rotors.
The paddle shell of each rotor is connected with a rotor shaft through a paddle shell, the paddle shell is provided with a paddle waving device consisting of a waving hinge, a shimmy hinge and a variable pitch hinge, a total pitch controller is arranged for controlling the lift force of the rotor, and a periodic variable pitch controller is arranged for controlling the dumping angle of a rotating surface of a rotor tip, so that the lift force direction of the rotor is changed.
The collective and cyclic pitch controller (4) drives the pitch of the blades of the first rotor (301), the collective and cyclic pitch controller (5) drives the pitch of the blades of the second rotor (302), and the collective and cyclic pitch controller (6) drives the pitch of the blades of the third rotor (303).
The engine is arranged, the three rotors are driven simultaneously through the transmission device, the angular speeds of the three rotors are the same, the steering directions of the first rotor (3011) and the third rotor (303) are the same, and the steering directions of the first rotor (301) and the second rotor (302) are opposite.
Setting: the second rotor (302) has a blade radius R2The first rotor (301) has a blade radius of 0.87R2The third rotor (303) also has a blade radius of 0.87R2The rotor synchronization means are arranged so that the adjacent blades of the first rotor (301) and the second rotor (302) are 60 ° out of phase and the adjacent blades of the second rotor (302) and the third rotor (303) are 60 ° out of phase preventing the rotor blades from colliding with each other and reducing the height required by the pylons.
An undercarriage (12) is arranged under the fuselage (10) near the center of gravity (P).
The working principle of the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses is as follows: the first rotor wing (301) and the third rotor wing (303) rotate anticlockwise, and the second rotor wing (302) rotates clockwise.
Let the blade radius of the first rotor (301) be R1The second rotor (302) has a blade radius R2The third rotor (303) has a blade radius of R3,The width of the first rotor (301) is b1The second rotor (302) has a blade width of b2The width of the third rotor (303) is b3The angular velocities of the three rotors are the same。
The aspect ratios of the three rotors are the same, so:
setting the solidity of a first rotor (301) asThe solidity of the second rotor (302) isThe third rotor (303) has a solidity of。
Wherein K is the blade number of the rotor, and K = 3. The solidity of the three rotors is the same:
the torque formula for the rotor is:
in the formulaThe torque of the rotor is transmitted to the rotor,the torque coefficient of the rotor is such that,the density of the air is higher than that of the air,the radius of the rotor wing is such that,the angular velocity of the rotor.
Since the counter-torque of the rotors is proportional to the torque of the rotors, the torque of the rotors is the same, the counter-torque is also the same, since the first rotor (301) and the third rotor (303) are the same, R is the same1=R3,=Therefore, the temperature of the molten steel is controlled,=the reaction torque of the first rotor (301) and the third rotor (303) is the same.
Order to=+I.e. by=2*The sum of the reactive torques of the first rotor (301) and the third rotor (303) is equal to the reactive torque of the second rotor (302), the first rotor (301) and the third rotor (303) rotate anticlockwise, the second rotor (302) rotates clockwise, and the reactive torques of the three rotors are mutually cancelled because the angular speeds of the three rotors are the same, and the sum of the reactive torques of the first rotor (301) and the third rotor (303) is equal to the reactive torque of the second rotor (302) in number and opposite in direction.
because the solidity of three rotors is the same, and the wing section is the same, and aspect ratio is the same, and the paddle quantity is the same, so the torque coefficient of rotor is close the same:
equation (44) reduces to:
the blade radius at the second rotor (302) is equal toThe first rotor (301) has a blade radius of 0.87%The third rotor (303) also has a blade radius of 0.87 ×The sum of the reaction torques of the first rotor (301) and the third rotor (303) is equal in number to the reaction torque of the second rotor (302), but in opposite directions, so that the reaction torques of the three rotors cancel each other.
The accelerator of an engine for driving the rotors is increased, meanwhile, the total distance of the three rotors is increased, the lift force of the three rotors is increased, and when the total lift force is larger than the weight of the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii, the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii vertically ascends.
And reducing the throttle of an engine for driving the rotor, and hovering the unequal-radius tandem three-rotor helicopter when the total lift force is equal to the weight of the unequal-radius tandem three-rotor helicopter.
And continuously reducing the throttle of an engine driving the rotor wing, and when the total lift force is less than the weight of the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii, the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii vertically descends.
When the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii is in the air, the cyclic pitch controller (4) of the first rotor (301) is operated to tilt rightwards, the tip rotating surface of the first rotor (1) tilts rightwards, the lift force of the first rotor (301) tilts rightwards, meanwhile, the cyclic pitch controller (6) of the third rotor (303) is operated to tilt leftwards, the tip rotating surface of the third rotor (303) tilts leftwards, the lift force of the third rotor (303) tilts leftwards, the first rotor (301) and the third rotor (303) jointly generate a right-turning moment, and the moment drives the fuselage (11) to turn rightwards; the cyclic pitch controller (4) of the first rotor wing (301) is operated to tilt to the left, the tip rotating surface of the first rotor wing (301) tilts to the left, the lift force of the first rotor wing (301) tilts to the left, meanwhile, the cyclic pitch controller (6) of the third rotor wing (303) tilts to the right, the tip rotating surface of the third rotor wing (303) tilts to the right, the lift force of the third rotor wing (303) tilts to the right, the first rotor wing (301) and the third rotor wing (303) jointly generate a left steering moment, and the moment drives the fuselage (11) to steer to the left to realize course steering.
When the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii is in the air, the cyclic controller (5) for operating the second rotor (302) tilts forwards, the rotating plane of the tip of the second rotor (302) tilts forwards, the lifting force of the second rotor (302) tilts forwards, and the fuselage (11) tilts forwards; the cyclic controller (5) for operating the second rotor wing (302) inclines backwards, the rotating surface of the tip of the second rotor wing (302) inclines backwards, the lifting force of the second rotor wing (302) inclines backwards, and the fuselage (11) tilts backwards, so that the pitching operation is realized.
When the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii is in the air, the cyclic pitch controller (5) of the second rotor (302) is operated to tilt to the left, the tip rotating surface of the second rotor (302) tilts to the left, and the lift force of the second rotor (302) tilts to the left, so that the helicopter body (11) rolls to the left; the cyclic controller of the second rotor (302) is operated to tilt to the right, the tip rotating surface of the second rotor (302) is tilted to the right, and the lift force of the second rotor (302) is tilted to the right, so that the fuselage (11) rolls to the right, thereby realizing the roll operation.
When the longitudinal three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses is in the air, the helicopter body (11) is controlled to bow forwards, meanwhile, an accelerator of an engine driving the three rotors is increased, and the longitudinal three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies forwards; the helicopter body (11) is controlled to tilt backwards, the accelerator of an engine driving the three rotors is increased simultaneously, and the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies backwards; the helicopter body (11) is controlled to roll leftwards, the accelerator of an engine driving the three rotors is increased simultaneously, and the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies leftwards; the fuselage (11) is controlled to roll rightwards, the accelerator of an engine driving the three rotors is increased simultaneously, and the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies rightwards.
Pitching and rolling are controlled by a second rotor (302), the course direction is controlled by the first rotor (301) and a third rotor (303), the second rotor (302) does not participate in the course direction control, the course direction control is independent, and the control characteristic of the three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii and longitudes is improved, and is similar to the control characteristic of a single-rotor helicopter (the single-rotor helicopter, the rotors control pitching and rolling, and the tail propeller controls the course direction).
In the embodiment shown in fig. 3, a longitudinal beam (10) is arranged at the top of a fuselage (11), a first small tower (7) is arranged on a cantilever at the front end of the longitudinal beam (10), the first small tower (7) of the wing profile plays a role of a vertical tail wing, a first rotor (401) consisting of four blades is arranged on the first small tower (7), the center of the longitudinal beam (10) is positioned above a gravity center (P), a second small tower (8) is arranged at the top of the fuselage (11) above the gravity center (P), the second small tower (8) of the wing profile plays a role of a vertical tail wing, a second rotor (402) consisting of four blades is arranged on the second small tower (8), a third small tower (9) is arranged on a cantilever at the rear end of the longitudinal beam (10), the third small tower (9) of the wing profile plays a role of a vertical tail wing, and a third rotor (403) consisting of four blades is arranged on the third small tower (9).
The interval that sets up three towelettes equals, and third towelette (9) are than second towelette height (8), and second towelette (8) are than first towelette height (7), can reduce the influence of rotor downwash air current in front to the rotor behind.
The distances among the three rotors on the three small towers are equal, and the distance is smaller than the diameter of the second rotor (402), so that the rotating surface of the first rotor (401) on the first small tower (7) is partially overlapped with the rotating surface of the second rotor (402) on the second small tower (8) in horizontal projection, and the rotating surface of the second rotor (402) on the second small tower (8) is partially overlapped with the rotating surface of the third rotor (403) on the third small tower (9) in horizontal projection, thereby saving the occupied space of the three rotors.
The paddle shell of each rotor is connected with a rotor shaft through a paddle shell, the paddle shell is provided with a paddle waving device consisting of a waving hinge, a shimmy hinge and a variable pitch hinge, a total pitch controller is arranged for controlling the lift force of the rotor, and a periodic variable pitch controller is arranged for controlling the dumping angle of a rotating surface of a rotor tip, so that the lift force direction of the rotor is changed.
A collective and cyclic pitch controller (4) drives the pitch of the blades of a first rotor (401), a collective and cyclic pitch controller (5) drives the pitch of the blades of a second rotor (402), and a collective and cyclic pitch controller (6) drives the pitch of the blades of a third rotor (403).
An engine is arranged, three rotors are driven simultaneously through a transmission device, the angular speeds of the three rotors are the same, the steering directions of the first rotor (401) and the third rotor (403) are the same, and the steering directions of the first rotor (401) and the second rotor (402) are opposite.
Setting: the second rotor (402) has a blade radius R2The first rotor (401) has a blade radius of 0.87R2The third rotor (403) also has a blade radius of 0.87R2The rotor synchronization means are arranged such that adjacent blades of the first rotor (401) and the second rotor (402) are out of phase by 45 DEG and adjacent blades of the second rotor (402) and the third rotor (403) are out of phase by 45 DEG to prevent the rotor blades from colliding with each other and to reduce the height required by the pylons.
An undercarriage (12) is arranged under the fuselage (10) near the center of gravity (P).
The working principle of the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses is as follows: the first rotor (401) and the third rotor (403) are set to rotate anticlockwise, and the second rotor (402) rotates clockwise.
Let the blade radius of the first rotor (401) be R1The second rotor (402) has a blade radius R2The third rotor (403) has a blade radius R3,The width of the first rotor (401) is b1The second rotor (402) has a blade width of b2The width of the third rotor (403) is b3The angular velocities of the three rotors are the same。
The aspect ratios of the three rotors are the same, so:
setting the solidity of a first rotor (401) asThe second rotor (402) has a solidity ofThe third rotor (403) has a solidity of。
Wherein K is the blade number of the rotor, and K = 4. The solidity of the three rotors is the same:
the torque formula for the rotor is:
in the formulaThe torque of the rotor is transmitted to the rotor,the torque coefficient of the rotor is such that,the density of the air is higher than that of the air,the radius of the rotor wing is such that,the angular velocity of the rotor.
Since the counter-torque of the rotors is proportional to the torque of the rotors, the torque of the rotors is the same, the counter-torque is also the same, and since the first rotor (401) and the third rotor (403) are the same, R is the same1=R3,=Therefore, the temperature of the molten steel is controlled,=the reaction torque of the first rotor (401) and the third rotor (403) is the same.
Order to=+I.e. by=2*The sum of the reactive torques of the first rotor (401) and the third rotor (403) is equal to the reactive torque of the second rotor (402), the first rotor (1) and the third rotor (3) rotate anticlockwise, the second rotor (2) rotates clockwise, and the reactive torques of the three rotors are mutually offset due to the fact that the angular speeds of the three rotors are the same, the sum of the reactive torques of the first rotor (1) and the third rotor (3) is equal to the reactive torque of the second rotor (2) in number and the directions are opposite.
because the solidity of three rotors is the same, and the wing section is the same, and aspect ratio is the same, and the paddle quantity is the same, so the torque coefficient of rotor is close the same:
equation (61) is simplified as:
since the angular velocities of the three rotors are the same, the blade radius at the second rotor (402) isThe first rotor (401) has a blade radius of 0.87%The third rotor (403) also has a blade radius of 0.87 ×The sum of the reaction torques of the first rotor (401) and the third rotor (403) is equal in number to the reaction torque of the second rotor (402), but in opposite directions, so that the reaction torques of the three rotors cancel each other.
The accelerator of an engine for driving the rotors is increased, meanwhile, the total distance of the three rotors is increased, the lift force of the three rotors is increased, and when the total lift force is larger than the weight of the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii, the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii vertically ascends.
And reducing the throttle of an engine for driving the rotor, and hovering the unequal-radius tandem three-rotor helicopter when the total lift force is equal to the weight of the unequal-radius tandem three-rotor helicopter.
And continuously reducing the throttle of an engine driving the rotor wing, and when the total lift force is less than the weight of the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii, the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii vertically descends.
When the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii is in the air, a cyclic pitch controller (4) of a first rotor (401) is operated to tilt rightwards, a tip rotating surface of the first rotor (401) tilts rightwards, the lift force of the first rotor (401) tilts rightwards, meanwhile, a cyclic pitch controller (6) of a third rotor (403) is operated to tilt leftwards, a tip rotating surface of the third rotor (403) tilts leftwards, the lift force of the third rotor (403) tilts leftwards, the first rotor (401) and the third rotor (403) jointly generate a right-turning moment, and the moment drives a fuselage (11) to turn rightwards; the cyclic pitch controller (4) of the first rotor wing (401) is operated to tilt to the left, the tip rotating surface of the first rotor wing (401) is tilted to the left, the lift force of the first rotor wing (401) is tilted to the left, meanwhile, the cyclic pitch controller (6) of the third rotor wing (403) is operated to tilt to the right, the tip rotating surface of the third rotor wing (403) is tilted to the right, the lift force of the third rotor wing (403) is tilted to the right, the first rotor wing (401) and the third rotor wing (403) jointly generate a left steering moment, and the moment drives the fuselage (11) to steer to the left to realize course steering.
When the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii is in the air, the cyclic controller (5) for operating the second rotor (402) tilts forwards, the tip rotating surface of the second rotor (402) tilts forwards, the lift force of the second rotor (402) tilts forwards, and the fuselage (11) tilts forwards; the cyclic controller (5) for operating the second rotor (402) tilts backwards, the tip rotating surface of the second rotor (402) tilts backwards, the lifting force of the second rotor (402) tilts backwards, and the fuselage (11) tilts backwards, so that the pitching operation is realized.
When the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii is in the air, the cyclic pitch controller (5) of the second rotor (402) is operated to tilt to the left, the tip rotating surface of the second rotor (402) tilts to the left, and the lift force of the second rotor (402) tilts to the left, so that the helicopter body (11) rolls to the left; the cyclic pitch controller for operating the second rotor (402) tilts to the right, the tip rotation plane of the second rotor (402) tilts to the right, and the lift force of the second rotor (402) tilts to the right, causing the fuselage (11) to roll to the right, thereby effecting roll operation.
When the longitudinal three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses is in the air, the helicopter body (11) is controlled to bow forwards, meanwhile, an accelerator of an engine driving the three rotors is increased, and the longitudinal three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies forwards; the helicopter body (11) is controlled to tilt backwards, the accelerator of an engine driving the three rotors is increased simultaneously, and the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies backwards; the helicopter body (11) is controlled to roll leftwards, the accelerator of an engine driving the three rotors is increased simultaneously, and the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies leftwards; the fuselage (11) is controlled to roll rightwards, the accelerator of an engine driving the three rotors is increased simultaneously, and the tandem three-rotor helicopter with unequal radiuses flies rightwards.
Pitching and rolling are controlled by a second rotor (402), the course direction is controlled by the first rotor (401) and a third rotor (403), the second rotor (402) does not participate in the course direction control, the course direction control is independent, and the control characteristic of the three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii and longitudes is improved, and is similar to the control of a single-rotor helicopter (the single-rotor helicopter, the rotors control the pitching and rolling, and the tail propeller controls the course direction).
Claims (5)
1. A vertical three-rotor helicopter with unequal radii is characterized in that an undercarriage is arranged below a helicopter body and close to the center of gravity, a longitudinal beam is arranged at the top of the helicopter body, a first small wing-shaped tower is arranged on a cantilever at the front end of the longitudinal beam, a first rotor wing is arranged on the first small tower, the center of the longitudinal beam is arranged above the center of gravity, a second small wing-shaped tower is arranged at the top of the helicopter body above the center of gravity, a second rotor wing is arranged on the second small tower, a third small wing-shaped tower is arranged on a cantilever at the rear end of the longitudinal beam, a third rotor wing is arranged on the third small tower, the three towers are arranged at equal intervals, the third tower is higher than the second small tower, the second small tower is higher than the first small tower, the influence of washing air flow in front of the rotor wings on the rotor wings behind is reduced, the small towers of the wing-shaped towers have the function of vertical tail wings, the intervals of the three rotor wings on the three small towers are equal, and the interval size is smaller than the diameter of the middle rotor wing, the second rotor rotating surface on the second small tower is partially overlapped with the third rotor rotating surface on the third small tower on the horizontal projection, the occupied space of the three rotors is reduced, the rotating surface of each rotor is horizontally arranged, the blade of each rotor is connected with the rotor shaft through the shell of the propeller, the shell of the propeller is provided with a blade waving device consisting of a waving hinge, a shimmy hinge and a variable pitch hinge, a total pitch controller is arranged to control the lift force of the rotors, a periodical variable pitch controller is arranged to control the dump angle of the tip rotating surface of the rotors, so that the lift force direction of the rotors is changed, an engine is arranged, and the three rotors are driven to rotate through a transmission device simultaneously, and the three-rotor-propeller-driven helicopter is characterized in that: make the angular velocity of three rotor the same, make turning to of first rotor and third rotor the same, make turning to of first rotor and second rotor opposite, every rotor adopts the same wing section, the same aspect ratio, the paddle of the same quantity is constituteed, the paddle radius of front and back rotor is the same, the paddle radius of front and back rotor equals 0.87 times of middle rotor paddle radius, the sum of the counter torque that first rotor and third rotor were adopted is equal opposite with the counter torque quantity of second rotor, the counter torque of three rotor offsets each other, rotor synchronizer makes the phase difference of three rotors remain invariable all the time, prevent rotor paddle collision each other.
2. The unequal-radius tandem triple-rotor helicopter according to claim 1, wherein the blade radii of the front and rear rotors are the same, and the blade radii of the front and rear rotors are equal to 0.82 to 0.92 times the blade radius of the intermediate rotor.
3. A rotorcraft helicopter according to claim 1, wherein two blades are used for each of the three rotors, and rotor synchronisation means is provided to maintain the phase difference between adjacent blades of the first rotor and the second rotor at 90 ° and the phase difference between adjacent blades of the second rotor and the third rotor at 90 ° to prevent the rotor blades from colliding with each other.
4. A rotorcraft helicopter according to claim 1, wherein three rotors each have three blades, and rotor synchronisation means is provided to maintain the first rotor at 60 ° out of phase with the adjacent blades of the second rotor, and the second rotor at 60 ° out of phase with the adjacent blades of the third rotor to prevent rotor blades from colliding with one another.
5. A rotorcraft helicopter according to claim 1, wherein the three rotors comprise four blades and the rotor synchronisation means is arranged such that the adjacent blades of the first rotor are always at 45 ° out of phase with the adjacent blades of the second rotor and the adjacent blades of the second rotor are always at 45 ° out of phase with the adjacent blades of the third rotor to prevent the rotor blades from colliding with each other.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201921893493.0U CN210942239U (en) | 2019-11-05 | 2019-11-05 | Radius unequal longitudinal three-rotor helicopter |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201921893493.0U CN210942239U (en) | 2019-11-05 | 2019-11-05 | Radius unequal longitudinal three-rotor helicopter |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN210942239U true CN210942239U (en) | 2020-07-07 |
Family
ID=71376307
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201921893493.0U Expired - Fee Related CN210942239U (en) | 2019-11-05 | 2019-11-05 | Radius unequal longitudinal three-rotor helicopter |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN210942239U (en) |
-
2019
- 2019-11-05 CN CN201921893493.0U patent/CN210942239U/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN105539833B (en) | Fixed-wing Multi-axis aircraft | |
| CN106915457B (en) | A kind of variable co-axial helicopter steerable system of the rotor inclinator depth of parallelism up and down | |
| CN108528692A (en) | A kind of folded wing double-rotor aerobat and its control method | |
| CN106828885A (en) | A kind of use jet form control driftage and the tiltrotor of pitching | |
| CN107042885A (en) | A kind of tiltrotor of the duct structure control driftage of use fan and pitching | |
| WO2022113086A1 (en) | Rotorcraft | |
| CN104943859A (en) | Unmanned helicopter | |
| CN210942239U (en) | Radius unequal longitudinal three-rotor helicopter | |
| CN110979649A (en) | Braking differential type rotor propeller fixed wing helicopter | |
| CN109625259A (en) | Cross-arranging type propeller aircraft helicopter | |
| CN110626494A (en) | Tandem three-rotor helicopter | |
| CN111776206A (en) | Three-rotor helicopter with unequal chord lengths | |
| CN205469816U (en) | Stationary vane multiaxis aircraft | |
| CN207482180U (en) | Aircraft | |
| CN110606199A (en) | Radius unequal longitudinal three-rotor helicopter | |
| CN211391681U (en) | Synchronous reverse rotation vertical six-rotor helicopter | |
| CN211055367U (en) | Synchronous reverse rotation longitudinal four-rotor helicopter | |
| CN211055368U (en) | Tandem five-rotor helicopter | |
| CN212172527U (en) | Transverse three-rotor helicopter | |
| CN212448070U (en) | Three-rotor helicopter with unequal chord lengths | |
| CN206278258U (en) | A kind of control system of the rollover of aircraft, driftage and yaw stability | |
| CN210083540U (en) | Tandem multi-rotor heavy-load helicopter | |
| CN110254704A (en) | Division of labor formula propeller aircraft helicopter | |
| CN107757876A (en) | Aircraft | |
| CN110789710A (en) | Negative camber airfoil fuselage brake induced differential multi-rotor helicopter |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |
Granted publication date: 20200707 |