CN201848017U - Zinc ion leading-in electrode catheter in prostatic urethra - Google Patents
Zinc ion leading-in electrode catheter in prostatic urethra Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN201848017U CN201848017U CN2010205976582U CN201020597658U CN201848017U CN 201848017 U CN201848017 U CN 201848017U CN 2010205976582 U CN2010205976582 U CN 2010205976582U CN 201020597658 U CN201020597658 U CN 201020597658U CN 201848017 U CN201848017 U CN 201848017U
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- electrode
- urethra
- zinc ion
- prostate
- bladder
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- PTFCDOFLOPIGGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc dication Chemical compound [Zn+2] PTFCDOFLOPIGGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 title claims abstract description 30
- 210000003708 urethra Anatomy 0.000 title claims abstract description 18
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 30
- 239000000523 sample Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 23
- 210000003128 head Anatomy 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 210000005077 saccule Anatomy 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 239000003792 electrolyte Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 abstract description 11
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 abstract description 6
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 abstract description 6
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 abstract description 3
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 abstract description 2
- 208000027418 Wounds and injury Diseases 0.000 abstract 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 208000014674 injury Diseases 0.000 abstract 1
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 abstract 1
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 32
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 32
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 32
- 210000002307 prostate Anatomy 0.000 description 19
- 201000007094 prostatitis Diseases 0.000 description 16
- 210000001519 tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 13
- 210000004908 prostatic fluid Anatomy 0.000 description 12
- 208000013507 chronic prostatitis Diseases 0.000 description 10
- 238000011282 treatment Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000000844 anti-bacterial effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000008676 import Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 5
- IIZPXYDJLKNOIY-JXPKJXOSSA-N 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@H](COP([O-])(=O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)OC(=O)CCC\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/CCCCC IIZPXYDJLKNOIY-JXPKJXOSSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000004599 antimicrobial Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229940067606 lecithin Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 235000010445 lecithin Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 239000000787 lecithin Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000005518 electrochemistry Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 description 2
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 230000000857 drug effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000002651 drug therapy Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000036039 immunity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000002632 lipids Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 101100433744 Arabidopsis thaliana ABCG28 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100268590 Arabidopsis thaliana ABCG5 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100263946 Arabidopsis thaliana WBC30 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100268592 Oryza sativa subsp. japonica RCN1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 229930182555 Penicillin Natural products 0.000 description 1
- JGSARLDLIJGVTE-MBNYWOFBSA-N Penicillin G Chemical compound N([C@H]1[C@H]2SC([C@@H](N2C1=O)C(O)=O)(C)C)C(=O)CC1=CC=CC=C1 JGSARLDLIJGVTE-MBNYWOFBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Carbonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium chloride Chemical compound [Na+].[Cl-] FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 206010048259 Zinc deficiency Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004700 cellular uptake Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000037976 chronic inflammation Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000006020 chronic inflammation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008260 defense mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007812 deficiency Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000029142 excretion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000499 gel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004907 gland Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000000762 glandular Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035876 healing Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001900 immune effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001771 impaired effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000015181 infectious disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 210000004969 inflammatory cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000003902 lesion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000004779 membrane envelope Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 244000000010 microbial pathogen Species 0.000 description 1
- 230000000242 pagocytic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940049954 penicillin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 210000002381 plasma Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000000664 rectum Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000008458 response to injury Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011780 sodium chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001954 sterilising effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004659 sterilization and disinfection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 208000024891 symptom Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000009885 systemic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011287 therapeutic dose Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000007 visual effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000003752 zinc compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
The utility model relates to a zinc ion leading-in electrode catheter in a prostatic urethra, which is a medical appliance used for directly leading zinc ions into prostatic tissues through the prostatic urethra. The zinc ion leading-in electrode catheter comprises a probe pipe body, wherein a guide head is arranged at the front end of the probe pipe body; a saccule injection channel, a bladder injection channel, a bladder drainage channel and a urethra injection channel are axially arranged in the probe pipe body; a saccule is arranged behind the guide head, and a bladder drainage hole is arranged between the saccule and the guide head; a therapeutic electrode is arranged in an electrode trough of the probe pipe body, and the leading-out end of the therapeutic electrode is connected with an anode plug through the urethra injection channel; and the leading-out end of a cavity-in electrode is connected with a cathode plug through the bladder injection channel. The zinc ion leading-in electrode catheter has good therapeutic effect, short period and high recovery ratio, cannot cause adverse effect of electrochemical injury to any tissue of a human body, and has no interference with any vital organ of the human body.
Description
Technical field
This utility model relates to the prostatitic medical apparatus and instruments of a kind of treatment, relates in particular to zinc ion iontophoresis electrode conduit in a kind of prostate-urethra, is by prostate-urethra, directly imports the medical apparatus and instruments of zinc ion in prostata tissue.
Background technology
Prostatitis is meant the active chronic inflammation due to prostate specific and the non-special infection, thus whole body that causes or local symptom.Prostate has unique anatomical position and physiological structure, and topmost characteristics are exactly that the glandular tube coated outside has one deck lipid film.In the Drug therapy process, this layer peplos can optionally stop to come the antimicrobial drug in the autoblood, causes prostatic fluid Chinese medicine concentration well below blood middle concentration, and the curative effect that medicine is produced focus can't reach the purpose of healing just as " taking totally ineffective measures ".On the contrary, pathogenic microorganism drives in the wrong direction easily on the contrary and enters body of gland and hide wherein, so the obstruct of prostate lipid film also is one of major reason of chronic prostatitis protracted course of disease.
Prostatic specific position and structures shape simple Drug therapy, poor effect, its skin has lipid envelope, be the barrier of medicine, it is local that general medicine is difficult to reach, and do not have drug effect and curative effect, and could arrive lesions position through barrier layer by layer, yet drug effect remains little, so effect is very slow and poor efficiency, and these methods of clinical practice can only play the curative effect of improvement.
In addition, research data shows that zinc can be strengthened the immunity of body, and prevent disease is played an important role.The Stamey sixties in 20th century [ 3 ] at first finds to have in the prostatic fluid a kind of low molecular antibacterial substance, it is called powerful antimicrobial factors, confirmed afterwards that this powerful antimicrobial factors was a kind of zinc compound, its main component is a zinc, and influence the phagocytic function of inflammatory cell, its antibacterial action is similar to penicillin, has the effect that antibacterial ability is organized in direct sterilization and activation raising, is the important factor of local immunity defense mechanism.
Zinc plays an important role in the developing of chronic prostatitis.Participate in prostatic antibacterial defence mechanism, zinc content reduces the immunoreactivity that can influence body, and also directly influencing prostate suppresses Bactericidal ability.The zinc ion deficiency makes prostatic powerful antimicrobial factors generate shortage in the prostate, causes the prostate immunologic hypofunction, and is infected easily.
A large amount of documents confirms that the prostatic fluid zinc content of patients with chronic prostatitis obviously reduces, Anderson [ 4 ] report patients with chronic prostatitis zinc (120 ± 24.8) μ g/ml, and relatively there were significant differences with normal person's zinc (352 ± 49) μ g/ml.Black [ 5 ] is though discover that patients with chronic prostatitis prostate zinc content is low, but its blood plasma zinc content is normal, illustrate that prostatic fluid zinc content reduces that in the body no thanks to zinc deficiency causes, but because the function of prostata tissue cellular uptake and excretion zinc is impaired causes.And find that when chronic prostatitis zinc content obviously reduces and is difficult to and improves.
All studies have shown that at present, the patient of chronic prostatitis, zinc ion quantity is less than the 1/2-1/5 of zinc ion quantity in the normal human prostate in the zinc ion content wretched insufficiency in the prostate, patients with chronic prostatitis prostate.
Summary of the invention
This utility model is at above-mentioned problems of the prior art, through a large amount of test and diligent specially grinding, zinc ion iontophoresis electrode conduit in a kind of prostate-urethra that can be directly replenishes zinc ion in prostata tissue is provided, treatment prostatitis weak curative effect in the prior art, the cycle is long, cure rate is low problem have been solved, and this utility model can not cause electrochemistry damage ill effect to any tissue of human body, to any vital organ of human body all influence disturb.
The technical solution of the utility model is, it comprises the probe body, and the front end of probe body is a guide head; Be provided with sacculus reservoir channel, bladder reservoir channel, bladder drainage passage and urethra reservoir channel vertically in the probe body; Sacculus is located at after the guide head, is provided with the bladder drainage hole between sacculus and the guide head; Therapeutic electrode is arranged in the slot electrode of probe body, and the exit of therapeutic electrode links to each other with anode plug by the urethra reservoir channel; The exit of intracavity electrode links to each other with female jack by the bladder reservoir channel.
The structure of described slot electrode is on the tube wall of probe body groove to be set.
The material of described therapeutic electrode and intracavity electrode is zinc.
Described therapeutic electrode and intracavity electrode are located at the two ends of sacculus respectively.
Isolate by electrolyte between described therapeutic electrode and the prostate-urethra tissue.
Described electrolyte isolation distance is 0.6mm.
The tail end of described probe body is provided with respectively saccule valve, bladder liquid-filling valve, bladder drainage mouth, urethra liquid-filling valve and the anodic-cathodic plug that communicates with separately passage.
This utility model compared with prior art, its advantageous effect is as follows:
1, this utility model passes through said structure, realized in prostata tissue, directly replenishing the purpose of zinc ion, and can be by the adjusting of treatment electric weight, the import volume of control zinc ion, it is the medical apparatus and instruments that can directly carry out clinical use, quite Zhi Qian zinc ion iontophoresis electrode is simple in structure, and manufacture process is easy, can improve 4-5 volume of production doubly in the unit interval.
2, this utility model is owing to be arranged on the zinc therapeutic electrode in the groove of probe body tube wall, the zinc therapeutic electrode all directly is connected conduction with tissue by liquid, and zinc therapeutic electrode of the prior art is the hole by tube wall, by liquid and tissue conduction, so zinc therapeutic electrode of the present utility model has increased 7-9 doubly to in-house release area than preceding catheter electrode by electrolyte.
3, owing to the zinc therapeutic electrode is located in the slot electrode of probe body in the prostate-urethra fully, zinc therapeutic electrode and prostate-urethra tissue have the electrolyte of 0.6mm distance to isolate, so the zinc therapeutic electrode does not contact with any tissue, do not organize and can produce the electrochemistry injury response.
4, because electrochemical soda acid variation does not take place in the zinc therapeutic electrode in the prostate-urethra in saline, so the electrochemistry damage of prostate-urethra inner tissue can not take place.
5, through experimental results show that, this utility model is given 30 coulomb electric charges, and the zinc therapeutic electrode can discharge 11 milligrams zinc ion, imports in-house zinc ion amount about 1 milligram, can reach definite zinc ion therapeutic dose fully, and the zinc concentration of systemic blood is not influenced.
Description of drawings
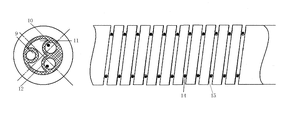
Fig. 1 is a structural representation of the present utility model.
Fig. 2 is a radially sectional structure sketch map of the present utility model.
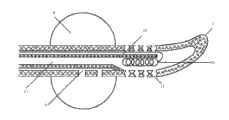
Fig. 3 is an axial sectional structure sketch map of the present utility model.
Among the figure, 1, saccule valve, 2, the bladder liquid-filling valve, 3, anodic-cathodic plug, 4, the bladder drainage mouth, 5, the urethra liquid-filling valve, 6, probe body, 7, guide head, 8, sacculus, 9, sacculus reservoir channel, 10, the bladder reservoir channel, 11, the bladder drainage passage, 12, urethra reservoir channel, 13, the bladder drainage hole, 14, therapeutic electrode, 15, slot electrode, 16, the intracavity electrode.
The specific embodiment
Content of the present utility model is described in detail in conjunction with the accompanying drawings by embodiment, but not limit by embodiment.
Embodiment
As Figure 1-3, probe body 6 usefulness medical silica-gels are made, and electrode is made by zinc; The front end of probe body 6 is a guide head 7; Be provided with sacculus reservoir channel 9, bladder reservoir channel 10, bladder drainage passage 11 and urethra reservoir channel 12 vertically in the probe body 6; The tail end of probe body 6 is provided with respectively saccule valve 1, bladder liquid-filling valve 2, bladder drainage mouth 4, urethra liquid-filling valve 5 and the anodic-cathodic plug 3 that communicates with separately passage; Sacculus 8 is located at after the guide head 7, is provided with bladder drainage hole 13 between sacculus 8 and the guide head 7; Groove is set as slot electrode 15 on the tube wall of probe body 6, therapeutic electrode 14 is arranged in the slot electrode 15, and the exit of therapeutic electrode 14 links to each other with anode plug by urethra reservoir channel 12; The exit of intracavity electrode 16 links to each other with female jack by bladder reservoir channel 10; Described therapeutic electrode 14 and intracavity electrode 16 are located at the two ends of sacculus 8 respectively; Isolate by electrolyte between therapeutic electrode 14 and the prostate-urethra tissue; The isolation distance of electrolyte is 0.6mm.
Operation principle of the present utility model is as follows;
Direct current treatment electric current produces closed circuit in endo-urethral zinc therapeutic electrode by the electrolyte in the electrode groove and prostata tissue, intravesical liquid, intracavity electrode; Endo-urethral zinc therapeutic electrode discharges zinc ion because of losing electronics in prostate, in-house ion current is by prostate, intravesical liquid and intracavity electrode conduction.Because the intracavity electrode is logical galvanic negative current, so there is not loss.Zinc therapeutic electrode in the slot electrode, it is lossy discharging zinc ion in the work, so control treatment electric weight is 30---within 50 coulombs, the zinc therapeutic electrode is controlled in the metering of loss less than electrode 1/3; The situation that can never rupture.
Clinical experiment report of the present utility model is as follows:
1, patient king XX, the man, 49 years old, suffered from chronic prostatitis 7 years, all invalid through several different methods treatments such as microwave, injection of prostate in medicine, the urethra, prostatitis scoring 23 minutes, prostatic fluid routine: lecithin 28%; WBC30/H; Prostatic fluid zinc content 79 μ g/ml.B ultrasonic shows: prostate echo inequality, prostatauxe 3.5X4.2X4.5; Give zinc ion and import treatment, 5mA electric current, 30C electric weight/time; Treated once totally 5 times in 3 days.
Check prostatitis scoring 0 minute, prostatic fluid routine: lecithin 80%; WBC5/H; Prostatic fluid zinc content 330 μ g/ml.B ultrasonic shows: prostate echo is equal, prostate 2.5X3.2X4.2cm.
2, grandson patient X, the man, 42 years old, suffered from chronic prostatitis 3 years, all invalid through several different methods treatments such as microwaves in medicine, rectum, the urethra, prostatitis scoring 28 minutes, prostatic fluid routine: lecithin 38%; WBC29/H; Prostatic fluid zinc content 128 μ g/ml.B ultrasonic shows: prostate echo inequality, prostatauxe 3.3X4.0X4.2; Give zinc ion and import treatment, 5mA electric current, 30C electric weight/time; Treated once totally 5 times in 3 days.
Check prostatitis scoring 0 minute, prostatic fluid routine: the full visual field of lecithin; WBC3-5/H; Prostatic fluid zinc content 354 μ g/ml.B ultrasonic shows: prostate echo is equal, prostate 2.2X3.3X4.0cm.
By above-mentioned test report as can be known, this utility model good effect, the cycle is short, cure rate is high.
Claims (6)
1. zinc ion iontophoresis electrode conduit in the prostate-urethra comprises probe body (6), and the front end of probe body (6) is guide head (7); It is characterized in that popping one's head in and be provided with sacculus reservoir channel (9), bladder reservoir channel (10), bladder drainage passage (11) and urethra reservoir channel (12) vertically in the body (6); Sacculus (8) is located at guide head (7) afterwards, is provided with bladder drainage hole (13) between sacculus (8) and the guide head (7); Therapeutic electrode (14) is arranged in the slot electrode (15) of probe body (6), and the exit of therapeutic electrode (14) links to each other with anode plug by urethra reservoir channel (12); The exit of intracavity electrode (16) links to each other with female jack by bladder reservoir channel (10).
2. zinc ion iontophoresis electrode conduit in the prostate-urethra according to claim 1 is characterized in that the structure of described slot electrode (15) is, on the tube wall of probe body (6) groove is set.
3. zinc ion iontophoresis electrode conduit in the prostate-urethra according to claim 1 is characterized in that described therapeutic electrode (14) and intracavity electrode (16) be located at the two ends of sacculus (8) respectively.
4. zinc ion iontophoresis electrode conduit in the prostate-urethra according to claim 1 is characterized in that isolating by electrolyte between described therapeutic electrode (14) and the prostate-urethra tissue.
5. zinc ion iontophoresis electrode conduit in the prostate-urethra according to claim 4 is characterized in that described electrolyte isolation distance is 0.6mm.
6. zinc ion iontophoresis electrode conduit in the prostate-urethra according to claim 1, the tail end that it is characterized in that described probe body (6) are provided with respectively saccule valve (1), bladder liquid-filling valve (2), bladder drainage mouth (4), urethra liquid-filling valve (5) and the anodic-cathodic plug (3) that communicates with separately passage.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2010205976582U CN201848017U (en) | 2010-11-09 | 2010-11-09 | Zinc ion leading-in electrode catheter in prostatic urethra |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2010205976582U CN201848017U (en) | 2010-11-09 | 2010-11-09 | Zinc ion leading-in electrode catheter in prostatic urethra |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN201848017U true CN201848017U (en) | 2011-06-01 |
Family
ID=44090436
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2010205976582U Expired - Lifetime CN201848017U (en) | 2010-11-09 | 2010-11-09 | Zinc ion leading-in electrode catheter in prostatic urethra |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN201848017U (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101966366A (en) * | 2010-11-09 | 2011-02-09 | 姜其钧 | Zinc ion guide electrode conduit in prostate urethra |
-
2010
- 2010-11-09 CN CN2010205976582U patent/CN201848017U/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101966366A (en) * | 2010-11-09 | 2011-02-09 | 姜其钧 | Zinc ion guide electrode conduit in prostate urethra |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN104114226B (en) | Electroporation device including oblong applicator, ring electrode and base for syringe | |
| GÜRPINAR et al. | Electromotive administration of intravesical lidocaine in patients with interstitial cystitis | |
| CN101966366B (en) | Zinc ion guide electrode conduit in prostate urethra | |
| CN201848017U (en) | Zinc ion leading-in electrode catheter in prostatic urethra | |
| CN101485592B (en) | Prostate gland tissue treatment probe by electric liquefaction | |
| Lugnani et al. | Iontophoresis of drugs in the bladder wall: equipment and preliminary studies | |
| CN104740757A (en) | Ultrasonic and iontophoresis combined transdermal drug delivery device | |
| TW200833345A (en) | Use of vitamin D compounds and mimics thereof to enhance delivery of therapeutics and oxygen to tumors and other tissues | |
| CN102294078A (en) | Therapeutic electrode catheter for guiding ions and medicines into urethra | |
| CN113616666A (en) | Use of sub-mucosal injection of gemcitabine into the bladder for the treatment of bladder cancer | |
| CN204335849U (en) | For the siRNA cutaneous penetration brassiere of mastocarcinoma gene treatment | |
| CN208641511U (en) | A kind of Modulatory character three-cavity structure bile duct brachytherapy drainage tube | |
| CN109431788A (en) | A kind of galvanic corrosion acupuncture needle | |
| RU2466755C2 (en) | Method for conducting intraorganic medicine electrophoresis of bladder | |
| CN221332454U (en) | Injectable pulse catheter electrode device | |
| CN1035101C (en) | Electrolytic probe for curing prostatic diseases | |
| RU2568369C1 (en) | Method of treating prostate adenoma combined with chronic nonbacterial prostatitis | |
| RU101928U1 (en) | Intravesical Electrode for Intraorganic Drug Electrophoresis in Diseases of the Urinary Bladder | |
| CN219286338U (en) | CAP radiation tube of improvement electrode | |
| CN222955809U (en) | An implantable cardiac pacemaker electrode lead | |
| RU2303446C2 (en) | Method for treatment of patients with locally spread squamous cell larynx cancer | |
| CN1183980C (en) | Special element instrument for treating diabetes | |
| RU2306145C1 (en) | Preparation for treating chronic prostatitis | |
| CN2645692Y (en) | Silver probe for prostate gland treatment | |
| CN105381543A (en) | Multifunctional endocrine therapeutic apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| AV01 | Patent right actively abandoned |
Granted publication date: 20110601 Effective date of abandoning: 20130821 |
|
| RGAV | Abandon patent right to avoid regrant |