CN1669337A - Method for producing stereoscopic images from monoscopic images - Google Patents
Method for producing stereoscopic images from monoscopic images Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN1669337A CN1669337A CNA03816485XA CN03816485A CN1669337A CN 1669337 A CN1669337 A CN 1669337A CN A03816485X A CNA03816485X A CN A03816485XA CN 03816485 A CN03816485 A CN 03816485A CN 1669337 A CN1669337 A CN 1669337A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- image
- sequence
- series
- scene
- images
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title abstract 2
- 238000010561 standard procedure Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 51
- 230000009466 transformation Effects 0.000 claims description 27
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 claims description 25
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 claims description 21
- 230000033001 locomotion Effects 0.000 claims description 16
- PXFBZOLANLWPMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 16-Epiaffinine Natural products C1C(C2=CC=CC=C2N2)=C2C(=O)CC2C(=CC)CN(C)C1C2CO PXFBZOLANLWPMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 14
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000013519 translation Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000001131 transforming effect Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 4
- 210000004556 brain Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001788 irregular Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000007 visual effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012952 Resampling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000205 computational method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000001525 retina Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035807 sensation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000087 stabilizing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009012 visual motion Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
- H04N13/20—Image signal generators
- H04N13/261—Image signal generators with monoscopic-to-stereoscopic image conversion
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
- H04N13/10—Processing, recording or transmission of stereoscopic or multi-view image signals
- H04N13/106—Processing image signals
- H04N13/111—Transformation of image signals corresponding to virtual viewpoints, e.g. spatial image interpolation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
- H04N13/20—Image signal generators
- H04N13/204—Image signal generators using stereoscopic image cameras
- H04N13/207—Image signal generators using stereoscopic image cameras using a single 2D image sensor
- H04N13/221—Image signal generators using stereoscopic image cameras using a single 2D image sensor using the relative movement between cameras and objects
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
- H04N13/10—Processing, recording or transmission of stereoscopic or multi-view image signals
- H04N13/189—Recording image signals; Reproducing recorded image signals
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
- H04N13/20—Image signal generators
- H04N13/204—Image signal generators using stereoscopic image cameras
- H04N13/207—Image signal generators using stereoscopic image cameras using a single 2D image sensor
- H04N13/218—Image signal generators using stereoscopic image cameras using a single 2D image sensor using spatial multiplexing
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
- H04N13/20—Image signal generators
- H04N13/204—Image signal generators using stereoscopic image cameras
- H04N13/239—Image signal generators using stereoscopic image cameras using two 2D image sensors having a relative position equal to or related to the interocular distance
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
- H04N13/20—Image signal generators
- H04N13/296—Synchronisation thereof; Control thereof
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
- H04N13/30—Image reproducers
- H04N13/332—Displays for viewing with the aid of special glasses or head-mounted displays [HMD]
- H04N13/334—Displays for viewing with the aid of special glasses or head-mounted displays [HMD] using spectral multiplexing
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
- H04N13/30—Image reproducers
- H04N13/332—Displays for viewing with the aid of special glasses or head-mounted displays [HMD]
- H04N13/337—Displays for viewing with the aid of special glasses or head-mounted displays [HMD] using polarisation multiplexing
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
- H04N13/30—Image reproducers
- H04N13/332—Displays for viewing with the aid of special glasses or head-mounted displays [HMD]
- H04N13/339—Displays for viewing with the aid of special glasses or head-mounted displays [HMD] using spatial multiplexing
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
- H04N13/30—Image reproducers
- H04N13/332—Displays for viewing with the aid of special glasses or head-mounted displays [HMD]
- H04N13/341—Displays for viewing with the aid of special glasses or head-mounted displays [HMD] using temporal multiplexing
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
- H04N13/30—Image reproducers
- H04N13/363—Image reproducers using image projection screens
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
- H04N13/30—Image reproducers
- H04N13/398—Synchronisation thereof; Control thereof
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
- H04N2013/0074—Stereoscopic image analysis
- H04N2013/0088—Synthesising a monoscopic image signal from stereoscopic images, e.g. synthesising a panoramic or high resolution monoscopic image
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Testing, Inspecting, Measuring Of Stereoscopic Televisions And Televisions (AREA)
- Processing Or Creating Images (AREA)
- Stereoscopic And Panoramic Photography (AREA)
- Image Processing (AREA)
Abstract
The invention provides a method for producing a series of stereoscopic pairs of images that can be displayed one after the other as a stereoscopic movie. The sequence of stereoscopic pairs is derived from a sequence of consecutive images of a scene that is obtained by standard techniques using standard equipment. A first image of a pair of images comprising the right and left images of each frame of the stereoscopic series of images is selected from the original sequence of images. Its stereo partner is either selected from the original sequence and/or is generated by transforming images selected from the original sequence of images.
Description
Technical field
The present invention relates to the field of the stereoscopic series of image.More specifically, the present invention relates to a kind of process that is used for producing from a series of continuous two dimensional image of a scene stereoscopic series of image, described image is to utilize the unsettled camera of a standard to obtain.
Background technology
Solid or 3-D photography are based on people's visual theory.Two independently detector (eyes) detect same object from slightly different angle, and they are projected on two planes (retina).Described composograph is sent on the processor (brain), and described processor (brain) is that the degree of depth offers described scene in conjunction with them and with the consciousness of third dimension degree.
Since Wheatstone since for the first time actual proof stereo-picture in 1838, many generations and show that the distinct methods of stereo-picture is developed.Great majority in these methods are based on the method for hardware, for example use two camera or single cameras with two camera lenses with fixed relationship to come a scene photography, and produce the image that the two required width of cloth are shifted a little.
Similarly, many methods of stereo-picture of watching are developed, and comprise and use colour filter or polarizing filter separates two width of cloth images, utilize shutter device that continuous image transmitted is carried out instantaneous selection or the image in view finder is carried out physical separation and they are projected every eyes respectively.Last a kind of method is the method for being used by Wheatstone at first on the one hand, is used in nearest virtual reality technology on the other hand.
Above-mentioned generation and watch the method for stereo-picture to be well known in the art, and do not need here to describe in further detail.
The stereoscopic series of image is the stereo-picture that a series of quilts are watched continuously basically.They produce by the image camera series with two camera lenses that are shifted a little usually, and the frame of described shot record image is right.Every frame is to show described scene with the slightly different angle of its other side.Seem continuously and the film that flows naturally in order to obtain an action of being seen therein, during photographing, need stability to greatest extent.As a result, up to the present, the stereoscopic series of the image of prior art has only by using specialized designs and stable camera to produce.
Produce the right method of seamless solid of inlaying by people [Parallel-Perspective StereoMosaics such as people such as for example Peleg [WO 00/39995] and Zhu from mobile camera, IEEC International Conferenee on Computer Vision, Vancouver, Canada, July 2001, Vol.1 pp.345-352] develop.In order to produce 3-D effect, according to these methods, on stereomontage figure, carry out coupling, rather than on single frame of video, carry out coupling.These methods have adopted telefilm basically, and it is become static mosaic map mosaic.Described synthetic view is static, and does not give spectators to be included in the sensation of the camera motion in the original film.
Up to the present, also there is not to propose to produce the method for the stereoscopic series of image from the telefilm that produces by hand-held camera.And going back the existing method of neither one may be with the original series of audio track and image record together, and duplicates it with described synthetic stereo-picture.
Therefore, the consecutive image that the purpose of this invention is to provide a kind of any series from a scene produces the method for three-dimensional film, wherein exists for the essential parallax condition of people's vision.
Another purpose of the present invention provides and a kind ofly produces the method for three-dimensional film from a series of consecutive images of a scene, and special camera, tripod or stabilizing equipment are not used in the acquisition of described image.
Further aim of the present invention and advantage will be apparent from the following description.
Summary of the invention
The present invention relates to provide a kind of and be used to take the consecutive image sequence of a scene and produce the right method of a series of solids from these images, described solid shows successively to can be used as a three-dimensional film.Described image sequence obtains by the standard technique of using standard device.Described image sequence can comprise the frame of taking with video camera or digital camera or be scanned to produce the analog image of digitized image.Described analog image can be the image of taking with camera or film camera.Described image is to the right of each frame of the stereoscopic series that comprises image and the image on the left side, and described image is to being to select from the original series of image, and/or the image selected from the image original series by conversion produces.
According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the three-dimensional method to sequence of described generation comprises following step:
A) read the original series of the consecutive image of a scene with a kind of equipment that if necessary can the described image of digitlization;
B) described digitized image is stored in the memory cell;
C) subclass of selection image of interest;
D) set of calculating affine transformation between the image in described subclass;
E) piece image in the sequence of subsets of the image of a scene of selection, described image will be right members of first solid of described sequence;
F) describedly begin to the cascaded affine transformation of every width of cloth consecutive image of described selection image by determining from adjacent image, and use described parallax criterion up to finding a suitable stereo partner, promptly a width of cloth can be transformed to another right member of described solid image, is the suitable stereo partner of the picture search of described selection;
G) calculate a plane transformation by the affine transformation of utilizing right member of described solid and cascade between described right member;
H) described plane transformation is applied to described suitable stereo partner;
I) with described solid to being stored in the described memory cell; And
J) for each width of cloth in the residual image of next width of cloth and described selection subclass, repeating step e) to h).
Described parallax criterion is in the picture centre of described selection image and is counted as the pixel count that horizontal translation moves between the three-dimensional right image of possibility.In the original series of image, the search of the suitable stereo partner of the image of selecting in the adjacent image of described selection image both sides, carrying out described series, and be confined to predetermined maximum number at the either side epigraph of described selection image.
The three-dimensional film that is produced by method of the present invention can have an audio track, and it is identical with the audio track that sequence with described consecutive image writes down together basically.
With reference to the accompanying drawings, by the illustrative and the nonrestrictive description of following its preferred embodiment, will be further understood that all above-mentioned and other feature and advantage of the present invention.
Description of drawings
Fig. 1 shows the part of the scene that he is write down when the cameraman walks with uniform rate;
How the scene that Fig. 2 schematically shows Fig. 1 will present on film;
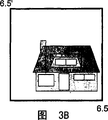
Fig. 3 A schematically shows information about the cabin that comprises to 3F in each frame of Fig. 2;
Fig. 4 A schematically shows for more real situation, the sight line of camera and the intersection of captured scene;
Fig. 4 B schematically shows six successive frames of the telefilm of explanation camera motion effect;
Fig. 5 is a series of images that extract from the successive frame of the telefilm taken with the hand-held commercial video camera;
Fig. 6 shows the result who method of the present invention is applied to one of image shown in Fig. 5; And
Fig. 7 shows and is used for the three-dimensional right of the every width of cloth image of Fig. 5.
Embodiment
Definition: interchangeable when term " sequence of stereoscopic images " and " three-dimensional film " use in this application, refer to the film of its expression by the scene of described camera record.
The objective of the invention is to take the continuous sequence of the digitized image of a scene, and produce a series of three-dimensional right that three-dimensional film shows successively that can be used as from these images.The sequence of resulting stereo-picture shows on the display device such as television set or computer screen, and its three-dimensional feature is observed under the help of conventional anaglyph spectacles.The original series of image obtains by the standard technique of using standard device, and for example comprises the frame of taking with video camera or digital camera or be scanned to produce the analog image of digitized image.Described analog image can be the image of taking with camera or film camera.
Method of the present invention is supermatic, and its various steps utilize a processor unit to carry out, and described processor unit uses for the algorithm known of being familiar with the those of skill in the art aspect the computer vision.
In order to describe method of the present invention, we at first consider a Utopian example.In this case, described method is applied to an image sequence that comes from telefilm, and described telefilm is that the people by a walking utilizes a commercial hand-held camera to take.
Fig. 1 shows a scene of being made up of two rooms and one tree, and he has write down described scene when walking with uniform rate along the street the cameraman.How the scene that Fig. 2 schematically shows Fig. 1 will present on film.As an example, show the profile of a whole frame (frame 7) with thick line.Successive frame is the image that wherein will produce the stereoscopic series of image.
Fig. 2 shows a Utopian state, and described therein camera moves with constant speed, and promptly described motion is the linear translation motion with constant speed.In this case, the right side of the every frame that by digital n mark of a plurality of frames of described film shown in usefulness and align by the corresponding left side that n ' marks.In this idealized state, an object, for example described cabin is visible fully in two successive frames (7 and 8).The single feature of same object, for example Men right side appears in 4 frames (6-9) and the part of this object appears in 6 frames (5-10).
Fig. 2 does not consider such fact: captured scene is three-dimensional, and is made up of three-dimensional body.In conjunction with such fact-be that real lens has the visual field, except that other factors, distance between the focal length of the width of scene on the captured film and object and camera lens is proportional, and the three-dimensional of object means that each successive frame that comprises given object comprises the information (unless not changing between a frame one frame in distance between camera lens and the object and direction certainly) about the varying number of this object.Fig. 3 A schematically shows different information about the cabin that comprises to 3F in each frame of a plurality of frames of Fig. 2, at least a portion in room described in described a plurality of frames is visible.It does not have the dimension of the degree of depth to Fig. 3 A seemingly to the scene shown in the 3F.As mentioned above, the actual object in above-mentioned scene is three-dimensional, and therefore example frame as shown in Figure 3A also will be included in the actual TV film about the information on the left of this room.
Actual telefilm also will be different from above-mentioned perfect condition, because the inhomogeneous and nonlinear motion of camera generally can take place.
In Fig. 4 A, schematically show ideal situation (solid line) and the more sight line of the camera of reality (dotted line) and the intersection of captured scene for Fig. 2.Under reality, the sight line of camera is because of many former thereby mobile brokenly, and some are cameraman results of action voluntarily, and some are not then under its control.One of most important factor be need in the record scene the most remarkable and/most interested feature.This needs for example to cause, and camera lens lifts down, suddenly to write down big room and to lift once more with record tree at a distance when taking cabin.Same cameraman can suspend with the record more details facing to cabin, and then hastily through excessive room, but through after the described tree its camera is being turned to take the present viewable side in described big room.In addition, because factor such as uneven ground, fatigue, strong wind etc., described camera may can not keep its stable and being not intended to and irregular moving of causing by the cameraman.As an extreme example, cameraman even may trip.Also must remember: all objects in a scene may not be static entirely, attempt to follow the tracks of a mobile object also will cause passing described scene frame inhomogeneous continuously.
Fig. 4 B schematically shows six successive frames of the telefilm of explanation camera motion effect.Frame 2 almost drops on the frame 1, shows that camera has kept stable, and slowly moves with respect to described scene.Between frame 2 and frame 3, camera is lifted suddenly and rapid horizontal, and it is slowly reduced in frame 4 and frame 5, and is rotated in frame 6.
To describe method of the present invention with generic term now, and will be described below the described computational details.The method according to this invention is finished the stereoscopic series that produces image from a series of images of a scene by utilizing processor unit to carry out the series of computation step.
In the first step, if necessary, with the original series of image place can the described image of digitlization equipment, and described image is stored in the memory of processor to be used for further processing.The common available equipment that comprises personal computer provides suitable hardware, utilizes described suitable hardware to come the processing of carries out image.Selection comprises the subclass of the image of scene of interest, and utilizes the algorithm come from computer vision field to calculate and store the affine transformation of description from the piece image of described series to the approximate motion of its adjacent image.
Select piece image this subclass from described memory, and check residual image in this subclass, begin and proceed to down piece image from the direct neighbor of selected frame, up to finding that a width of cloth satisfies the image of preassigned, described preassigned guarantees that the image of checking is suitable as the stereo partner of a selected image.Described search is carried out on both direction, and is limited on the one hand the quantity of the image of checking on each direction, limiting described calculating needs, and does not finally obtain result's (this result will not produce the 3-D view of a reality) when calculating is correct.
In case find a suitable the other side, just itself and described selection image and the cascaded affine transformation between them made together to be used for calculating a plane transformation.This plane transformation is applied to described suitable stereo partner now, with obtain one by described selection image and the converted suitable images that in search, finds form three-dimensional right.
It is right to have generated first solid now, and repeats this process now for another image, all finds suitable the other side up to all images for described subclass.
The computational details of this method can be carried out will produce basically the alternative method of equivalent results, and this will be clearly for those of skill in the art.For example, use described method of the present invention, last solid is to forming by the image of originally selecting with by the changing image of using the other side that parallax criterion finds.Similarly, if the affine transformation A between image i and j
IjExpression, the conversion between two width of cloth images can directly be calculated between them in each stage of calculating so, perhaps by cascade A
Ij, A
Jk, A
KlWait and calculate, up to obtaining the cascaded transformation of wanting.On this in method, when calculating beginning, calculate the described affine transformation between each the phase adjacency pair of image in described subclass, and be stored in the memory for future use.
As long as satisfy some primary condition, method of the present invention in addition can from a following image sequence, produce three-dimensional right, described image sequence is taken with hand held camera as mentioned above, and comprises with respect to all of described scene for even departing from of motion of camera.
The most important thing is in these conditions: original two dimensional image must be carried out record in a kind of permission mode of the parallax between at least some images in described series.For example, if camera is embedded on the horizontal plane about the vertical axis of the optical centre by camera lens, between any image, can not there be parallax so, and can not uses method of the present invention.But, if, for described motion a translational component will be arranged also so, and have parallax even described vertical axis is offset the very little quantity in the center of described camera lens.
The degree of the parallax that exists between two width of cloth images is the standard of suitable selection that is used for determine forming three-dimensional right the other side of described selection first image.Usually, this method is used the parallax that will produce the right minimum number of satisfactory stereo.If the quantity of parallax is excessive, the result is tedious for eyes so, and needs a large amount of evaluation works and time.Having been found that in most of the cases, is local found outside between 4 to 18 frames for the other side of any one given image, and described quantity depends on the movement velocity of camera with respect to described scene.Should method of the present invention the time, the operator provides a parallax criterion.Described parallax criterion is the quantity of pixel, and it has expressed picture centre to its horizontal translation motion of position in its other side's image, and this quantity determined by the affine transformation of calculating between two width of cloth images.Determined affine transformation in each step that the suitable stereo partner of given image is searched for, if the mobile parallax criterion that is less than of picture centre, so described search proceeds to gradually the image away from described selection image, is equal to or greater than described parallax parameter up to described moving.If in the hunting zone that allows, do not find suitable stereo partner, can use various computational methods to overcome this problem so.Have been found that only use for its described conversion provide with parallax criterion near uniform images, provided the result of the satisfaction under all situations actually, Here it is with in a preferred embodiment of the invention method.
Second condition is: the motion of captured object can not be too fast with respect to the speed of document image in the original series of image.If this is the case, in order to obtain acceptable result, between consecutive image, too many parallax will be arranged so.
Another condition relates to the motion of object in captured scene.In this case, the conversion of image will be optimum for the object that moves or for background (if being used for background), and described then object will be by fuzzy, and vice versa.Described object of which movement slow more is just few more with observed this effect in final three-dimensional film.
Last condition of using for the best of the inventive method relates to the image processing in the beginning and ending place of described subclass.There is not the enough or not contiguous right usable image of suitable stereo that finds therein in this case.In fact, this problem, the situation as described parallax criterion has overcome satisfactorily.
Fig. 5 is a series of images that extract from 6 successive frames of the telefilm taken with the hand-held commercial home video camera.The representative of these images utilizes a typical segment of the stereoscopic series film of the image that method of the present invention makes.The generic logic of the algorithm that adopts in the preferred embodiment of the present invention will be discussed now, and with shown in Figure 6 for the right transformation results of single solid.
Described starting point is a given scenario Z who comprises n width of cloth image, Z={i
1, i
2... i
n.Now to the every width of cloth image applications image registration techniques algorithm in the described scene [for the example of an appropriate algorithm, referring to Brown, Lisa G., A Survey of Image RegistrationTechnology, ACM Computing Surveys, Dec.1992, Vol.24, No.4, pp.325-376], the set that has produced affine transformation between the image.
In order to limit search degree, digital s and f have been selected, so that s>l and f<n for the suitable stereo partner of every width of cloth image in the original scene.For local scene Z
s={ i
s, i
S+1... i
fIn image, described solid is right determines it is the affine transformation of before having determined by cascade, is equal to or greater than described parallax criterion up to the translational element of described cascaded transformation.
As the example how this final step is carried out, we are with member's image i of local scene Zs
kBe example.Determined from i
kTo image i
K-1Affine transformation.If the translational element of described conversion is equal to or greater than described parallax criterion, i so
kAnd i
K-1It is right to form a solid.If not so, and the symbol of described translational element (element) also with the opposite in sign of described parallax criterion, calculate from i so
kTo i
K+1Affine transformation.If the translational element of described conversion is equal to or greater than described parallax criterion, i so
kAnd i
K+1Be that a solid is right, otherwise then proceed in the same way to calculate, be fit to and image i until obtaining
kForm three-dimensional right image i
K-j(wherein j can be positive or negative).
Select three-dimensional right a kind of algorithm of image applications to calculate the plane transformation T between two width of cloth images for described
p[for the example of an appropriate algorithm referring to Burt, P.J.et.al., Object Tracking With Moving Camera, in Proceedings IEEE Workshopon Visual Motion 1989, pp.2-12].
Now, for every width of cloth image i
k, wherein s-1<k<f+1 has obtained i
kThe changing image i of stereo partner
K ', 0<k '<n wherein.Also obtained the plane transformation T between them
p(k).Utilize this conversion, image k ' is by resampling, and wherein k and k ' are that a solid is right.The result of sampling is described relevant local scene Z
S '={ i
S ', i
(s+1) '... i
F '.Described local scene and relevant local scene alternately will cause three-dimensional illusion to the synchronized projection of right eye and left eye.
Fig. 6 shows the result who method of the present invention is applied to one of image shown in Figure 5.By using target tracking algorism, determined that for the suitable stereo partner of the image in frame 1050 be that stereo partner in frame 1054.Frame 1054w is the image after 1054 conversion, so as 1050 and 1054w be present to two eyes respectively three-dimensional right.Fig. 7 shows three-dimensional right for every width of cloth image of Fig. 5.
The beholder observes image sequence under the help of suitable equipment, to transmit three-dimensional right image respectively to suitable eyes.An example of this evaluation equipment is a pair of shuttered liquid crystal display (LCD) glasses, for example this glasses of being made by Stereographics Corporatio.This glasses are synchronoused working with computer or projecting apparatus, alternately to cover eyes, show the frame of using for the another eyes simultaneously.If the speed of projection is 30 frame per seconds for example,, when the image of on the left side image is seen by left eye respectively so, keep the image of seeing by right eye promptly for every eyes per second 15 frames.Brains merges described two width of cloth images then, to cause the impression of 3-D view from described two dimensional image centering.
Because every width of cloth original continuous image has become the right a member of continuous stereo in the three-dimensional film that is produced by method of the present invention, and the order of described image is maintained in the synthetic film, so the arbitrary audio track that writes down with the original series of image can not duplicate in three-dimensional film basically with changing.
Be noted that the sequence of this method " search " image on both direction, with of the irregular movement of explanation camera with respect to described scene.In addition, how the experienced personnel in this area will know by for example skipping the quantity that repeating frame reduces computing time, non-existent information in the previous frame openly basically in repeating frame.Also can adopt the editing technique of standard, the described three-dimensional film in discontinuous place " smoothly " for example in original video, occur.
Although embodiments of the invention are described by example, but will be understood that, not deviating from spirit of the present invention or surpassing under the prerequisite of scope of claim, can for example carry out the present invention with many variations, modification and change by the conversion of using different order and/or type.
Claims (12)
1. one kind is used for from the three-dimensional right method of the consecutive image sequence generation a series of images of a scene, the solid of described image shows successively to can be used as a three-dimensional film, the sequence of wherein said image obtains by the standard technique of using standard device, and one of them image is to the right of each frame of the described stereoscopic series that comprises image and the image on the left side, the first right width of cloth image of described image is to select from the original series of image, and its stereo partner be from described original series, select and/or the image from the described original series of image, selected by conversion produce.
2. according to the process of claim 1 wherein that described image sequence is to select from the frame of taking with video camera or digital camera.
3. according to the process of claim 1 wherein that described image sequence is to be scanned to produce the analog image of digitized image.
4. according to the method for claim 3, wherein said analog image can be the image of taking with camera or film camera.
5. according to the method for claim 1, comprise following step:
A) a kind ofly can read described single image by using, the equipment of the described image of digitlization is handled the original series of the consecutive image of a scene if necessary, and described image is stored in the memory cell;
B) subclass of selection image of interest;
C) set of calculating affine transformation between the image in described subclass;
D) piece image in the sequence of subsets of the image of a scene of selection, described image will be right members of first solid of described sequence;
E) describedly begin to the cascaded affine transformation of every width of cloth consecutive image of described selection image by determining from adjacent image, and use described parallax criterion up to finding a suitable stereo partner, promptly a width of cloth can be transformed to another right member of described solid image, is the suitable stereo partner of the picture search of described selection;
F) calculate a plane transformation by the affine transformation of utilizing right member of described solid and cascade between described right member;
G) described plane transformation is applied to described selection image;
H) with described solid to being stored in the described memory cell; And
I) for each width of cloth in the residual image of next width of cloth and described selection subclass, repeating step c) to h).
6. according to the method for claim 4, wherein said parallax criterion is expressed as the pixel count of horizontal translation motion.
7. according to the method for claim 4, wherein in the described adjacent image of described selection image both sides, carry out described search.
8. according to the method for claim 4, wherein said search is confined to the image of the maximum quantity on the either side of described selection image.
9. a series of images that produces from the consecutive image sequence of a scene is three-dimensional right, the sequence of wherein said image is to obtain by the standard technique of using standard device, and one of them image is to the right of each frame of the described stereoscopic series that comprises image and the image on the left side, the first right width of cloth image of described image is to select from the original series of image, and its stereo partner be from described original series, select and/or the image from the described original series of image, selected by conversion produce.
10. a series of images that produces from the consecutive image sequence of a scene is three-dimensional right, and the sequence of wherein said image obtains by the described method of use claim 1 to 8.
11. the three-dimensional film that the solid of the image of accessory rights requirement 9 or 10 produces series.
12. according to three-dimensional film claim 11 and that have an audio track in addition, wherein said audio track is identical with the audio track that sequence with the described consecutive image that wherein produces described three-dimensional film writes down together basically.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL150131A IL150131A (en) | 2002-06-10 | 2002-06-10 | Method for converting a sequence of monoscopic images to a sequence of stereoscopic images |
| IL150131 | 2002-06-10 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1669337A true CN1669337A (en) | 2005-09-14 |
Family
ID=28053356
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNA03816485XA Pending CN1669337A (en) | 2002-06-10 | 2003-05-26 | Method for producing stereoscopic images from monoscopic images |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7180536B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP1522195A1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP4351996B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN1669337A (en) |
| AU (1) | AU2003233160A1 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2488925C (en) |
| IL (1) | IL150131A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2003105491A1 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102158725A (en) * | 2011-05-06 | 2011-08-17 | 深圳超多维光电子有限公司 | Stereoscopic image generation method and system |
| CN108476313A (en) * | 2015-12-30 | 2018-08-31 | 创新科技有限公司 | Method for creating sequence of stereoscopic images |
| CN111006586A (en) * | 2019-12-12 | 2020-04-14 | 天目爱视(北京)科技有限公司 | Intelligent control method for 3D information acquisition |
Families Citing this family (31)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8253729B1 (en) * | 1983-05-09 | 2012-08-28 | Geshwind David M | Trimming depth buffer during 2D to 3D conversion |
| GB2405764A (en) * | 2003-09-04 | 2005-03-09 | Sharp Kk | Guided capture or selection of stereoscopic image pairs. |
| FR2873213A1 (en) * | 2004-07-13 | 2006-01-20 | Canon Res Ct France S A S Soc | Stereoscopic signal obtaining method for domestic application, involves forming pairs of images from sequence of monoscopic images based on preset time slot that is function of image acquisition speed, to construct stereoscopic signal |
| FR2873214B1 (en) * | 2004-07-13 | 2008-10-10 | Canon Res Ct France S A S Soc | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OBTAINING STEREOSCOPIC SIGNAL |
| IL166305A0 (en) | 2005-01-14 | 2006-01-15 | Rafael Armament Dev Authority | Automatic conversion from monoscopic video to stereoscopic video |
| FR2888346B1 (en) * | 2005-07-06 | 2008-08-08 | Canon Res Ct France Soc Par Ac | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OBTAINING A SEQUENCE OF STEREOSCOPIC IMAGES FROM A SEQUENCE OF MONOSCOPIC IMAGES |
| CA2627999C (en) * | 2007-04-03 | 2011-11-15 | Her Majesty The Queen In Right Of Canada, As Represented By The Minister Of Industry Through The Communications Research Centre Canada | Generation of a depth map from a monoscopic color image for rendering stereoscopic still and video images |
| US8213711B2 (en) * | 2007-04-03 | 2012-07-03 | Her Majesty The Queen In Right Of Canada As Represented By The Minister Of Industry, Through The Communications Research Centre Canada | Method and graphical user interface for modifying depth maps |
| JP4819834B2 (en) * | 2008-03-03 | 2011-11-24 | 株式会社エヌ・ティ・ティ・ドコモ | 3D image processing apparatus and 3D image processing method |
| WO2010032058A1 (en) | 2008-09-19 | 2010-03-25 | Mbda Uk Limited | Method and apparatus for displaying stereographic images of a region |
| US8330802B2 (en) * | 2008-12-09 | 2012-12-11 | Microsoft Corp. | Stereo movie editing |
| US9172940B2 (en) | 2009-02-05 | 2015-10-27 | Bitanimate, Inc. | Two-dimensional video to three-dimensional video conversion based on movement between video frames |
| US8502864B1 (en) * | 2009-07-28 | 2013-08-06 | Robert Watkins | Systems, devices, and/or methods for viewing images |
| US9380292B2 (en) | 2009-07-31 | 2016-06-28 | 3Dmedia Corporation | Methods, systems, and computer-readable storage media for generating three-dimensional (3D) images of a scene |
| WO2011014419A1 (en) | 2009-07-31 | 2011-02-03 | 3Dmedia Corporation | Methods, systems, and computer-readable storage media for creating three-dimensional (3d) images of a scene |
| US20110025830A1 (en) | 2009-07-31 | 2011-02-03 | 3Dmedia Corporation | Methods, systems, and computer-readable storage media for generating stereoscopic content via depth map creation |
| US8624959B1 (en) * | 2009-09-11 | 2014-01-07 | The Boeing Company | Stereo video movies |
| JP2011082919A (en) * | 2009-10-09 | 2011-04-21 | Sony Corp | Image processing device and method, and program |
| JP2011082918A (en) * | 2009-10-09 | 2011-04-21 | Sony Corp | Image processing device and method, and program |
| JP5402719B2 (en) * | 2010-02-26 | 2014-01-29 | 富士通株式会社 | Stereoscopic image capturing apparatus, stereoscopic image capturing method, and stereoscopic image capturing program |
| US20130037708A1 (en) | 2010-04-26 | 2013-02-14 | Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd. | Polyacrylic acid (salt), polyacrylic acid (salt)-based water-absorbing resin, and process for producing same |
| US20130043384A1 (en) | 2010-04-26 | 2013-02-21 | Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd. | Polyacrylic acid (salt), polyacrylic acid (salt)-based water-absorbing resin, and process for producing same |
| US9344701B2 (en) | 2010-07-23 | 2016-05-17 | 3Dmedia Corporation | Methods, systems, and computer-readable storage media for identifying a rough depth map in a scene and for determining a stereo-base distance for three-dimensional (3D) content creation |
| CN103098458B (en) | 2010-09-10 | 2015-11-25 | 富士胶片株式会社 | Stereoscopic imaging apparatus and stereoscopic imaging method |
| WO2012032826A1 (en) * | 2010-09-10 | 2012-03-15 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Three-dimensional imaging device and three-dimensional imaging method |
| US8908011B2 (en) | 2010-09-17 | 2014-12-09 | Panasonic Corporation | Three-dimensional video creating device and three-dimensional video creating method |
| US9185388B2 (en) | 2010-11-03 | 2015-11-10 | 3Dmedia Corporation | Methods, systems, and computer program products for creating three-dimensional video sequences |
| US8274552B2 (en) | 2010-12-27 | 2012-09-25 | 3Dmedia Corporation | Primary and auxiliary image capture devices for image processing and related methods |
| US10200671B2 (en) | 2010-12-27 | 2019-02-05 | 3Dmedia Corporation | Primary and auxiliary image capture devices for image processing and related methods |
| US20130002811A1 (en) * | 2011-06-28 | 2013-01-03 | Bu Lin-Kai | Three-dimensional imaging method using single-lens image-capture apparatus and three-dimensional image enhancement method based on two-dimensional images |
| DE112014005645A5 (en) | 2013-12-13 | 2016-09-08 | Fts Computertechnik Gmbh | Method and device for observing the environment of a vehicle |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4925294A (en) | 1986-12-17 | 1990-05-15 | Geshwind David M | Method to convert two dimensional motion pictures for three-dimensional systems |
| US5581638A (en) * | 1993-07-26 | 1996-12-03 | E-Systems, Inc. | Method for autonomous image registration |
| US6384859B1 (en) | 1995-03-29 | 2002-05-07 | Sanyo Electric Co., Ltd. | Methods for creating an image for a three-dimensional display, for calculating depth information and for image processing using the depth information |
| US6031564A (en) * | 1997-07-07 | 2000-02-29 | Reveo, Inc. | Method and apparatus for monoscopic to stereoscopic image conversion |
| AUPO894497A0 (en) * | 1997-09-02 | 1997-09-25 | Xenotech Research Pty Ltd | Image processing method and apparatus |
| JP4056154B2 (en) | 1997-12-30 | 2008-03-05 | 三星電子株式会社 | 2D continuous video 3D video conversion apparatus and method, and 3D video post-processing method |
| EP1048167B1 (en) | 1998-09-17 | 2009-01-07 | Yissum Research Development Company Of The Hebrew University Of Jerusalem | System and method for generating and displaying panoramic images and movies |
| CA2361341A1 (en) * | 2001-11-07 | 2003-05-07 | Idelix Software Inc. | Use of detail-in-context presentation on stereoscopically paired images |
-
2002
- 2002-06-10 IL IL150131A patent/IL150131A/en active IP Right Grant
-
2003
- 2003-05-26 JP JP2004512422A patent/JP4351996B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2003-05-26 WO PCT/IL2003/000436 patent/WO2003105491A1/en active Application Filing
- 2003-05-26 CA CA2488925A patent/CA2488925C/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2003-05-26 AU AU2003233160A patent/AU2003233160A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2003-05-26 US US10/517,557 patent/US7180536B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2003-05-26 CN CNA03816485XA patent/CN1669337A/en active Pending
- 2003-05-26 EP EP03727915A patent/EP1522195A1/en not_active Withdrawn
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102158725A (en) * | 2011-05-06 | 2011-08-17 | 深圳超多维光电子有限公司 | Stereoscopic image generation method and system |
| CN102158725B (en) * | 2011-05-06 | 2013-04-10 | 深圳超多维光电子有限公司 | Stereoscopic image generation method and system |
| CN108476313A (en) * | 2015-12-30 | 2018-08-31 | 创新科技有限公司 | Method for creating sequence of stereoscopic images |
| CN108476313B (en) * | 2015-12-30 | 2020-11-27 | 创新科技有限公司 | Method for creating a sequence of stereoscopic images |
| CN111006586A (en) * | 2019-12-12 | 2020-04-14 | 天目爱视(北京)科技有限公司 | Intelligent control method for 3D information acquisition |
| CN111006586B (en) * | 2019-12-12 | 2020-07-24 | 天目爱视(北京)科技有限公司 | Intelligent control method for 3D information acquisition |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| IL150131A (en) | 2007-03-08 |
| CA2488925C (en) | 2010-01-26 |
| US20060092272A1 (en) | 2006-05-04 |
| IL150131A0 (en) | 2002-12-01 |
| AU2003233160A1 (en) | 2003-12-22 |
| EP1522195A1 (en) | 2005-04-13 |
| JP4351996B2 (en) | 2009-10-28 |
| JP2005529559A (en) | 2005-09-29 |
| WO2003105491A1 (en) | 2003-12-18 |
| CA2488925A1 (en) | 2003-12-18 |
| US7180536B2 (en) | 2007-02-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN1669337A (en) | Method for producing stereoscopic images from monoscopic images | |
| EP1836859B1 (en) | Automatic conversion from monoscopic video to stereoscopic video | |
| JP5238429B2 (en) | Stereoscopic image capturing apparatus and stereoscopic image capturing system | |
| US8548269B2 (en) | Seamless left/right views for 360-degree stereoscopic video | |
| CN102428707B (en) | Stereovision-Image Position Matching Apparatus and Stereovision-Image Position Matching Method | |
| EP2659680B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for providing mono-vision in multi-view system | |
| CN1956555A (en) | Apparatus and method for processing 3d picture | |
| CN1700776A (en) | Method for displaying three-dimensional image, method for capturing three-dimensional image, and three-dimensional display apparatus | |
| JPH06194758A (en) | Method and apparatus for formation of depth image | |
| CN202267785U (en) | Naked eye three-dimensional display structure for automatically tracking human eye position | |
| US20120154518A1 (en) | System for capturing panoramic stereoscopic video | |
| WO2005067318A9 (en) | Multi-dimensional imaging apparatus, systems, and methods | |
| US20120154548A1 (en) | Left/right image generation for 360-degree stereoscopic video | |
| Rotem et al. | Automatic video to stereoscopic video conversion | |
| US20120154519A1 (en) | Chassis assembly for 360-degree stereoscopic video capture | |
| CN103828362B (en) | Imaging device and videograph and playback system | |
| CN109379577B (en) | Video generation method, device and equipment of virtual viewpoint | |
| US20240251069A1 (en) | Display device and display method therefor | |
| JP4089912B2 (en) | Digital camera system | |
| CN114268785A (en) | A kind of reciprocating scanning portable device stereo photography method | |
| Peleg et al. | Stereo mosaicing from a single moving video camera | |
| IL166305A (en) | Method for converting a sequence of monoscopic images to a sequence of stereoscopic images | |
| JPH10229566A (en) | Digital camera system | |
| Kawano et al. | Poster: Portable integral photography input/output system using tablet PC and fly's eye lenses | |
| Wang et al. | Adaptive parallax control for multi-view stereo panoramas |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C02 | Deemed withdrawal of patent application after publication (patent law 2001) | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication |