CN1259918C - Use of bile acid or bile salt fatty acid conjugates - Google Patents
Use of bile acid or bile salt fatty acid conjugates Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN1259918C CN1259918C CNB028081870A CN02808187A CN1259918C CN 1259918 C CN1259918 C CN 1259918C CN B028081870 A CNB028081870 A CN B028081870A CN 02808187 A CN02808187 A CN 02808187A CN 1259918 C CN1259918 C CN 1259918C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- acid
- food
- group
- fatty acid
- bile
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07J—STEROIDS
- C07J9/00—Normal steroids containing carbon, hydrogen, halogen or oxygen substituted in position 17 beta by a chain of more than two carbon atoms, e.g. cholane, cholestane, coprostane
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/56—Compounds containing cyclopenta[a]hydrophenanthrene ring systems; Derivatives thereof, e.g. steroids
- A61K31/575—Compounds containing cyclopenta[a]hydrophenanthrene ring systems; Derivatives thereof, e.g. steroids substituted in position 17 beta by a chain of three or more carbon atoms, e.g. cholane, cholestane, ergosterol, sitosterol
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/54—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic compound
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/54—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic compound
- A61K47/542—Carboxylic acids, e.g. a fatty acid or an amino acid
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/54—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic compound
- A61K47/543—Lipids, e.g. triglycerides; Polyamines, e.g. spermine or spermidine
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/54—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic compound
- A61K47/554—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic compound the modifying agent being a steroid plant sterol, glycyrrhetic acid, enoxolone or bile acid
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P1/00—Drugs for disorders of the alimentary tract or the digestive system
- A61P1/16—Drugs for disorders of the alimentary tract or the digestive system for liver or gallbladder disorders, e.g. hepatoprotective agents, cholagogues, litholytics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/06—Antihyperlipidemics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/08—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis
- A61P3/10—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis for hyperglycaemia, e.g. antidiabetics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P43/00—Drugs for specific purposes, not provided for in groups A61P1/00-A61P41/00
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P7/00—Drugs for disorders of the blood or the extracellular fluid
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/10—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system for treating ischaemic or atherosclerotic diseases, e.g. antianginal drugs, coronary vasodilators, drugs for myocardial infarction, retinopathy, cerebrovascula insufficiency, renal arteriosclerosis
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07J—STEROIDS
- C07J41/00—Normal steroids containing one or more nitrogen atoms not belonging to a hetero ring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07J—STEROIDS
- C07J41/00—Normal steroids containing one or more nitrogen atoms not belonging to a hetero ring
- C07J41/0005—Normal steroids containing one or more nitrogen atoms not belonging to a hetero ring the nitrogen atom being directly linked to the cyclopenta(a)hydro phenanthrene skeleton
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07J—STEROIDS
- C07J41/00—Normal steroids containing one or more nitrogen atoms not belonging to a hetero ring
- C07J41/0033—Normal steroids containing one or more nitrogen atoms not belonging to a hetero ring not covered by C07J41/0005
- C07J41/0055—Normal steroids containing one or more nitrogen atoms not belonging to a hetero ring not covered by C07J41/0005 the 17-beta position being substituted by an uninterrupted chain of at least three carbon atoms which may or may not be branched, e.g. cholane or cholestane derivatives, optionally cyclised, e.g. 17-beta-phenyl or 17-beta-furyl derivatives
Abstract
The present invention relates to the use of a bile acid or bile salt fatty acid conjugate of general formula II W - X - G in which G is a bile acid or bile salt radical, which, if desired, is conjugated in position 24 with a suitable amino acid, W stands for one or two fatty acid radicals having 14-22 carbon atoms and X stands for a suitable bonding member or for a direct C=C bond between said bile acid or bile salt radical and the fatty acid(s) or of a pharmaceutical composition comprising same for the reduction of Cholesterol in blood, for the treatment of Fatty Liver, Hyperglycemia and Diabetes.
Description
The present invention relates to some new purposes of cholic acid or cholate fatty acid conjugate.
At application number is 123, there are some known cholic acid or cholate fatty acid to grip thing [BAFAC I] altogether in Israel's patent of 998, its general formula is W-X-G (I), wherein G is a kind of cholic acid or cholate group, if necessary, it on 24 with a kind of suitable aminoacid conjugation, W represents one or both fatty acid groups with 18-22 carbon atom, X represents the NH key between described cholic acid or cholate group and the fatty acid.
Know that from its description general formula is the cholesterol calculus that the chemical compound of I and the pharmaceutical composition that contains this chemical compound are used for dissolving bile, stop the appearance of described cholelithiasis or repeat, and reduce or stop purposes in the arteriosclerosis.The method for the treatment of these diseases also is known.
Now surprised discovery BAFACs has other purposes with the pharmaceutical composition that contains it, wherein W represents one or both fatty acid groups that contains 14-22 carbon atom, and X represents a kind of suitable linking group or the two key (chemical compounds of general formula I I of a kind of direct C=C between described cholic acid or cholate group and the fatty acid; After this be called BAFACs II), they can be used as:
A. reduce the concentration of cholesterol in the blood;
B. treat fatty liver; With
C. treat hyperglycemia and diabetes.
Described BAFACs also can be used for these treatment of diseases with the pharmaceutical composition that contains it.
Become key firmly can not allow enteral and/or bacterial enzyme in absorption process separate substantially.Therefore ester bond is inappropriate, because it separates easily.Become the preferred NH key of key, but also can be other suitable linking group, for example sulfur, phosphorus, oxygen-ether etc.
Becoming key can be α or beta comfiguration, and can connect at the diverse location of cholic acid molecule, and 3,6,7,12 and 24 is preferred.
Related disease, its treatment new purposes historical and that be used for the treatment of are described in the back.
A. the reduction of cholesterol concentration in the blood
Hypercholesterolemia is deleterious to health.It is a risk factor in some principal disease episode process, for example ischemic heart desease, myocardial infarction, external perihaemal canal disease, possible apoplexy.The reduction of cholesterol concentration is useful to some of them treatment of diseases or prevention in the blood.Therapy to hypercholesterolemia is reduce the liver endogenous cholesterol synthetic at present.The Si Dating (statins) that is used for this purpose can suppress the HMG CoA-reductase.Yet the major part of health inner cholesterol derives from the cholesterol in the food.Well-known dietary restrictions is invalid.The Lon exchanger resin has been used for being fixed in the enteric cavity in conjunction with cholic acid (catastate of cholesterol) and with them, drains with Excreta.They have some effects to blood cholesterol levels, but their prior side effects limit their application.
Shown that BAFACs can reduce the hypercholesterolemia that is caused by food in some animals, even edible continuously hypercholesterolemia of these animals and food rich in fat.
B. treat fatty liver
Fatty liver is one of current the most general hepatopathy.It is because the too much accumulation of fat causes in the liver.It shows as the little and/or bulla fat drop of the varying number that is present in the liver organization on the histology.Fatty liver may be caused by medicine, chemicals, disease, antibacterial etc.But the food of main cause excess intake causes (mainly being health) problem of obesity.
Because overweight phenomenon day by day increases in the affluent society, the fashion trend of fatty liver is also increasing.Fatty liver can be further development of fat hepatitis and liver cirrhosis, and is accompanied by the increase of M ﹠ M.
The best Therapeutic Method of fatty liver that is caused by diet is to adhere to fat-reducing.Yet this is difficult to reach as you know.
Have been found that BAFACs II can reduce and prevent fatty liver.This point has obtained proof in the process of the continuous excess intake food of some animals.
C. treat hyperglycemia and diabetes
Diabetes are a kind of carbohydrate (glucose) metabolic disturbance diseases.It roughly is divided into 1 class, and insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) (IDDM) is characterized by shortage insulin and 2 classes, and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) wherein mainly is an insulin resistant.NIDDM often is accompanied by obesity and/or fatty liver.The hyperglycemia that other is also arranged.Treatment of diabetes comprises diet, insulin injection and/or oral hypoglycemia medicine.The target of treatment is to make blood sugar content normalization.Diabetes, glycosuria condition of disease especially out of control causes severe complications.
Have been found that BAFACs can reduce the blood sugar level of the animal that suffers from IDDM and NIDDM and make its normalization.
The present invention will be described by following embodiment and accompanying drawing, but be not limited to them.
" conventional food " composed as follows in described embodiment:
In the accompanying drawings,
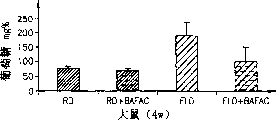
Accompanying drawing 1A, 1B and 1C represent rodent empty stomach blood sugar concentration in the therapeutic scheme that uses or do not use BAFAC (150mg/Kg/ days), for example:
Accompanying drawing 1A: rat (4 week)
Accompanying drawing 1B: hamster (3 week)
Accompanying drawing 1C: mice (16 days) and
Accompanying drawing 2 expression C57J/L kind mouse on the feed food rich in fat+/-BAFAC lipoid/protein rate in the liver after (150mg/Kg/ days) 5 week.
Embodiment 1
1. male hamster
Use the Golden Syrian hamster (Anilab, Rehovot, Israel) of heavy 90-110gm of 4-6 week to experimentize.To take food 10 week of a kind of lithogenic food (No.1) to them. this food is by conventional food and be added with 1% cholesterol, 1.2% palmitic acid, 2% Semen Maydis oil composition (according to people such as Ayyad, Lipids, 1992; 27:993-998 revises).Half of these animals by the gastric gavage in addition feed be suspended in 3 β-Semen arachidis hypogaeae amide groups-7 α in the saline, 12 α-dihydro-(dihidroxy)-5 β-cholane-24-acid, its dosage is 150mg/Kg/ days.Similarly the take food saline of equivalent of control animal.With these Animal Anesthesia, take out cardiac blood and analyze after 10 week.Take out liver and other organ.Cholesterol level in the serum is measured by autoanalyzer.
2. mice
Use the C57J/L kind male mice (Jackson laboratory, the Maine State, the U.S.) of heavy 20-25gm of 4-6 week to experimentize.To their feed conventional food and additional with (%w/w) butter fat 15, cholesterol 1, cholic acid 0.5, (according to people such as Khanuja, Proc.Natnl.Acad.Sci.USA 1995 for Semen Maydis oil 2; 92:7729-33 revises) a 4-8 week.Lithogenic food #2) they half is suspended in 3 β-Semen arachidis hypogaeae amide groups-7 α in the saline by gastric gavage feed, and 12 α-dihydro (dihidroxy)-5 β-cholane-24-acid, its dosage are 150mg/Kg/ days.The saline of second half equivalent of similarly taking food.With these Animal Anesthesia, take out cardiac blood and analyze after 4-8 week.Take out liver and other organ.Cholesterol level in the serum is measured by autoanalyzer.
In C57J/L kind male mice (Jackson laboratory, the Maine State, the U.S.) feed 8 week of a kind of lithogenic food (No.2) of heavy 20-25gm of another group 4-6 week, the conventional food of then taking food is 8 week again.On the feed in the conventional food process in 8 week, these animals are suspended in 3 β-Semen arachidis hypogaeae amide-7 α in the saline by the feed of gastric gavage, and 12 α-dihydro (dihidroxy)-5 β-cholane-24-acid, its dosage are 150mg/Kg/ days.Through after 16 total week,, take out cardiac blood and analyze these Animal Anesthesia.Take out liver and other organ.Cholesterol level in the serum is analyzed as stated above.
The 3rd treated animal is taken food 16 week of conventional food fully, then carries out similar analysis.Below table 1 provided the size of animal and the result of each group
Table 1: the serum cholesterol of experimental animal (mg%) (average+StD)
| Animal | Food | Persistent period (W) | n | Simple food | n | Food+BAFAC II |
| Mice C57J/L kind | Lithogenic 2 | 4 | 5 | 270(21.7) | 5 | 143(19.8) |
| ″ | ″ | 6 | 6 | 274(4.1) | 7 | 125(10.8) |
| ″ | ″ | 8 | 5 | 264(5.8) | 5 | 139(0.7) |
| Hamster Golden Syrian | Lithogenic 1 | 10 | 5 | 257(32.7) | 5 | 202(59.6) |
| Mice C57J/L kind | Lithogenic 2 is conventional food then | 8 }16 8 | 6 | 101(10.1) | 7 | 65(6.8) |
| Simple regular diet | 16 | 4 | 81(5.5) |
Data in the table 1 show that BAFACs II has reduced the cholesterol levels in many groups mice and the hamster blood significantly.
Embodiment 2
The histology method
The existence of fatty liver is section to be marked with the pathologist who does not know to treat by double-blind method to estimate.
The scoring system is as follows:
Fat-free liver
The liver surface of slight fatty liver<5% is attacked
The liver surface of moderate fatty liver 5-<25% is attacked
Significantly the liver surface of fatty liver 25-50% is attacked
The liver surface of serious fatty liver>50% is attacked
1. hamster
Male Golden Syrian hamster (Anilab, rehovot, Israel) with the heavy 90-110gm of 4-6 experimentizes.To they feed lithogenic food (No.1).The extra feed of they half 150mg/kg/ days be suspended in 3 β-Semen arachidis hypogaeae amide groups-7 α in the saline, 12 α-dihydro (dihidroxy)-5 β-cholane-24-acid.Chemical compound be to be suspended in the saline by the gastric gavage to give.The saline and control animals is similarly only taken food.After 10 week with these Animal Anesthesia and slaughter.Take out liver and other organ and place formalin to carry out tissue detection.
2. mice
With the C57 kind male mice of the heavy 20-25gm in 4-6 week (Jackson laboratory, the Maine State. the U.S.) experimentize.To their feed " western " food circulation 2000:102:1822-27 such as () George, wherein contain the cholesterol of 1.5gm/kg and 42% fat, 43% carbohydrate and 15% protein (percentage ratio of heat).They half is by gastric gavage brinish 3 β of 150mg/kg/ days be suspended in-Semen arachidis hypogaeae amide groups-7 α that additionally takes food, 12 α-dihydro (dihidroxy)-5 β-cholane-24-acid.And second half saline of similarly only taking food.After 4 week with these Animal Anesthesia and slaughter.Take out liver and other organ and place formalin, in order to tissue detection.
Below table 2 provided quantity and the tissue detection result of animal in each group.
Table 2: the fatty liver value of laboratory animal
| Animal | Food | Persistent period (week) | n | Contrast (value) | n | + BAFAC (scoring) | ||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Average | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Average | |||||
| Hamster, Golden Syrian | Lithogenic 1 | 10 | 7 | 7 | 4a | 7 | 6 | 1 | 0.28 | |||||||
| C57J/L kind mice | Western | 4 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 1.5b | 14 | 12. | 1 | 1 | 0.35 | ||||
A-vesicle fat
B-mixes (vesicle and bulla) fat
The data of table 2 show that BAFACs can reduce and/or prevent fatty liver.
Embodiment 3
BAFACs tests with 3 kinds of animals the influence of fasting glucose: hamster, rat and mice.These animals keep conventional feed or higher fatty acid feed (as specifying).Half animal is the BAFAC in the 0.5ml saline of being scattered in of 150mg/Kg by the gastric gavage dosage of taking food every day in each group, and second half is similarly by only the take food saline of equivalent of gavage.In whole experiment all animal all 22 ℃ keep down 12hr the daytime/circulation at night.Arbitrarily drink water
1. hamster
4 weeks (90-100gm) male Golden Syrian hamster a kind of fatty liver food of taking food, this food is by cholesterol (1%), soft ester acid (1.2%), and butter (6%), Adeps Sus domestica (10%), and Semen Maydis oil (2%) joins and forms in the conventional food.Blood sugar level is to slaughter mensuration under the state on an empty stomach animal after 3 week of experiment.5 control animals and 5 laboratory animals are arranged.
2. rat
4 weeks (100-200gm) male Wistar rat feed conventional food or be rich in Adeps Sus domestica (10%), cholesterol (2.5%) and cholic acid (0.5%) food rich in fat (w/w).After 4 week of experiment these animals are slaughtered on an empty stomach and obtain blood and organ specimen.150mg/Kg/ days BAFAC of half animal feed in each group; The saline of remaining feed equivalent.7 mouse feed conventional food are arranged in contrast and test group, 6 mouse feed food rich in fat are arranged in each group.
The hamster of feed food rich in fat and rat have all developed into the NIDDM model of fatty liver (by the chemical measurement conclusive evidence of liver fat), high fasting glucose and representative type.
3. mice
4 weeks (approximately 20gm) male ICR mouse feed conventional food.Streptozotocin (this can cause the infringement of pancreas islet cells and Simulation with I DDM) at the first day lumbar injection 200mg/Kg that tests.Test after 16 days and animal to be slaughtered and to obtain fasting blood glucose level.Be provided with 3 groups of experiments, every group of 7 animals.Matched group-the conventional food of only taking food.The animal of injection streptozotocin (Stz) is divided into BAFAC two classes of only taking food saline and taking food 150mg/Kg/ days by gavage by gavage.The BAFAC that is used for all the hyperglycemia researchs conjugate that to be a kind of arachidic acid be connected with amido link with cholic acid (at 3) (C-20 BAFAC, Aramchol).
The result of study of experiment 3 is represented in accompanying drawing 1A, 1B and 1C.(RD-conventional food, FLD-fatty liver food, Stz-streptozotocin).
In all laboratory animals, replenish feed BAFAC as can be seen and can both reduce fasting blood glucose level significantly.The blood sugar level of suffering from the animal of fatty liver reduced-and (hamster and rat) represent NIDDM and represent IDDM with the mice of injection streptozotocin.BAFACs is to the not influence (not having hyperglycemia or fatty liver) of blood sugar level of the rat of normal feed.
Embodiment 4
The C57J/L kind mice (Jackson laboratory, the Maine State, the U.S.) that nearly weighs 20gm greatly with 4 week experimentizes.Take food a kind of higher fatty acid 5 week of lithogenic food to them, this food is by cholesterol 1%, and cholic acid 0.5%, Adeps Sus domestica 10%, butter 6%, soft ester acid 1.2% and Semen Maydis oil 2% (w/w) are added to be formed in the conventional food.Except that above-mentioned food, these animals every days is suspended in the BAFACs (150mg/Kg) in the saline or the saline of the equivalent of only taking food by gastric gavage or feed.The BAFACs conjugate that to be cholic acid (on 3) connect by amido link with soft ester acid (C-16) or arachidic acid (C-20) or mountain Yu acid (C-22).Control animal (n=5) feed saline, laboratory animal feed C-16 conjugate (n=5), C-20 conjugate (n=5), or C-22 conjugate (n=3).After 5 week, after empty stomach one went up the whole night, he ordered Animal Anesthesia with gram, takes out liver, and he orders kill animals with excessive gram.Liver specimens homogenate in the buffer saline of 5ml with 0.5gm.By Folch method chloroform: 2: 1 vol/vol of methanol) from homogenate, extract the liver lipoid.Half Floch solution extraction with homogenate with 5ml.After the solvent evaporation lipoid is weighed, repeatedly evaporating solvent is up to the lipoid constant weight.Protein according to the Bradford method with quantitative (the Bradford M.M.Annal.Biochem.1976 of the homogenate sample of another equal portions; 72:248).
Calculate lipoid and proteinic ratio (mg/mg).The result of each group with average provide (+St.Dev.).Class value is: control animal: 7.9+/-2.32, C-16 BAFAC 2.25+/-1.20, C-20 BAFAC 1.44+/-1.18 and C-22 BAFAC 3.00+/-1.08.The result represents with accompanying drawing 2.
Data show according to the described effect of claim and have obtained checking by some conjugates, some of them almost with embodiment 1,2, the same with the C-20 conjugate that uses in 3 is effective.
Claims (4)
1. one kind has general formula I I
W-X-G
Wherein G is cholic acid or cholate group, it on 24 with or not with the aminoacid conjugation, on behalf of one or both, W have the fatty acid group of 14-22 carbon atom, X represents a kind of suitable linking group or the two keys of the direct C=C between cholic acid or cholate group and the fatty acid, and wherein said suitable linking group provides base in the absorption process of conjugate
This does not understand conjugated firm connection, and its condition is that described linking group is not an ester group, cholic acid or cholate fatty acid conjugate or contain the purposes that this Pharmaceutical composition of gripping thing altogether is used to prepare the medicine for the treatment of fatty liver.
2. purposes according to claim 1, wherein the linking group in the chemical compound of general formula I I is NH.
3. according to each described purposes of claim 1 to 2, wherein the fatty acid in the chemical compound of general formula I I is selected from: mountain Yu acid, arachidic acid and hard ester acid.
4. according to each described purposes of claim 1 to 2, the chemical compound of wherein said general formula I I is 3 β-Semen arachidis hypogaeae amide groups-7 α, 12 alpha-dihydroxy-s-5 β-cholane-24-acid.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL142650 | 2001-04-17 | ||
| IL142650A IL142650A (en) | 1998-04-08 | 2001-04-17 | Use of bile acid or bile salt fatty acids conjugates for the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions for reducing cholesterol, treating fatty liver and treating hyperglycemia and diabetes |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1529603A CN1529603A (en) | 2004-09-15 |
| CN1259918C true CN1259918C (en) | 2006-06-21 |
Family
ID=11075322
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB028081870A Expired - Lifetime CN1259918C (en) | 2001-04-17 | 2002-04-15 | Use of bile acid or bile salt fatty acid conjugates |
Country Status (24)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US7501403B2 (en) |
| EP (2) | EP1379254B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP4324706B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR100883080B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN1259918C (en) |
| AT (2) | ATE365044T1 (en) |
| AU (2) | AU2002307771B2 (en) |
| BR (1) | BR0208924A (en) |
| CA (2) | CA2703688C (en) |
| CY (1) | CY1106853T1 (en) |
| CZ (2) | CZ309042B6 (en) |
| DE (2) | DE60220775T2 (en) |
| DK (2) | DK1379254T3 (en) |
| EA (1) | EA007565B1 (en) |
| ES (2) | ES2289137T3 (en) |
| HU (1) | HU230548B1 (en) |
| IL (1) | IL142650A (en) |
| MX (1) | MXPA03009553A (en) |
| NO (2) | NO333910B1 (en) |
| NZ (1) | NZ528868A (en) |
| PL (2) | PL211438B1 (en) |
| PT (2) | PT1790346E (en) |
| UA (1) | UA78699C2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2002083147A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL142650A (en) | 1998-04-08 | 2007-06-03 | Galmed Int Ltd | Use of bile acid or bile salt fatty acids conjugates for the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions for reducing cholesterol, treating fatty liver and treating hyperglycemia and diabetes |
| US8975246B2 (en) | 2001-04-17 | 2015-03-10 | Galmed Research And Development Ltd. | Bile acid or bile salt fatty acid conjugates |
| US20100311708A1 (en) * | 2007-07-25 | 2010-12-09 | Tarek Moustafa | Use of nor-bile acids in the treatment of arteriosclerosis |
| US9314444B2 (en) | 2009-01-12 | 2016-04-19 | Biokier, Inc. | Composition and method for treatment of NASH |
| US9006288B2 (en) | 2009-01-12 | 2015-04-14 | Biokier, Inc. | Composition and method for treatment of diabetes |
| SI2376077T1 (en) | 2009-01-12 | 2017-09-29 | Biokier Inc. | Composition and method for treatment of diabetes |
| EP2391370B1 (en) | 2009-02-02 | 2015-06-03 | Galmed Research and Development Ltd. | Methods and compositions for treating alzheimer's disease |
| US20120202890A1 (en) | 2011-02-08 | 2012-08-09 | Nian Wu | Polymer-carbohydrate-lipid conjugates |
| WO2013166176A1 (en) * | 2012-05-01 | 2013-11-07 | Catabasis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Fatty acid conjugates of statin and fxr agonists; compositions and method of uses |
| CN103571617A (en) * | 2012-07-26 | 2014-02-12 | 丰益(上海)生物技术研发中心有限公司 | Improved animal fat processing technology |
| KR101702251B1 (en) * | 2012-11-29 | 2017-02-02 | 에스티팜 주식회사 | Bile acid oligomer conjugate for novel vesicular transport and use thereof |
| IL227890A0 (en) * | 2013-08-08 | 2014-01-30 | Galderm Therapeutics Ltd | Anti-aging compositions comprising bile acid and fatty acid conjugates |
| WO2016199137A1 (en) * | 2015-06-10 | 2016-12-15 | Galmed Research And Development Ltd. | Low dose compositions of aramchol salts |
| US11571431B2 (en) | 2013-12-04 | 2023-02-07 | Galmed Research And Development Ltd | Aramchol salts |
| DK3077047T3 (en) * | 2013-12-04 | 2019-07-15 | Galmed Res & Development Ltd | ARAMCHOLSALTE |
| CA2950128A1 (en) * | 2014-06-01 | 2015-12-10 | Galmed Research And Development Ltd. | Fatty acid bile acid conjugates for treatment of lipodystrophy |
| IL243707A0 (en) | 2016-01-20 | 2016-05-01 | Galmed Res And Dev Ltd | Treatment for modulating gut microbiota |
| US11197870B2 (en) | 2016-11-10 | 2021-12-14 | Galmed Research And Development Ltd | Treatment for hepatic fibrosis |
| CN116687850A (en) | 2022-02-24 | 2023-09-05 | 甘莱制药有限公司 | Pharmaceutical composition containing cyclic phosphonate compound, preparation method and application thereof |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3859437A (en) * | 1972-06-02 | 1975-01-07 | Intellectual Property Dev Corp | Reducing cholesterol levels |
| US3856953A (en) * | 1973-05-15 | 1974-12-24 | Intellectual Property Dev Corp | Method of treating fatty liver |
| IT1167478B (en) * | 1981-07-24 | 1987-05-13 | Carlo Scolastico | URSODESOXICOLIC ACID DERIVATIVES |
| IT1167479B (en) * | 1981-07-24 | 1987-05-13 | Carlo Scolastico | DERIVATIVES OF CHENODEXOXYLIC ACID |
| JPS6164701A (en) * | 1984-09-06 | 1986-04-03 | Meito Sangyo Kk | Cationized dextran derivative/polyuronic acid polyelectrolyte complex and its use |
| DE3930696A1 (en) * | 1989-09-14 | 1991-03-28 | Hoechst Ag | GALLENSAEUREDERIVATE, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF, USE AS MEDICAMENT |
| US5278320A (en) * | 1992-09-11 | 1994-01-11 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Cholesterol lowering compounds produced by directed biosynthesis |
| DE4432708A1 (en) * | 1994-09-14 | 1996-03-21 | Hoechst Ag | Modified bile acids, process for their preparation and their use |
| AU1289899A (en) * | 1997-10-31 | 1999-05-24 | Arch Development Corporation | Methods and compositions for regulation of 5-alpha reductase activity |
| US20030153541A1 (en) * | 1997-10-31 | 2003-08-14 | Robert Dudley | Novel anticholesterol compositions and method for using same |
| IL123998A (en) * | 1998-04-08 | 2004-09-27 | Galmed Int Ltd | Bile salt conjugates and pharmaceutical compositions containing them |
| IL142650A (en) * | 1998-04-08 | 2007-06-03 | Galmed Int Ltd | Use of bile acid or bile salt fatty acids conjugates for the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions for reducing cholesterol, treating fatty liver and treating hyperglycemia and diabetes |
| US6620821B2 (en) * | 2000-06-15 | 2003-09-16 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and method |
| JP2006306800A (en) * | 2005-04-28 | 2006-11-09 | Kirin Brewery Co Ltd | Farnesoid x receptor activator |
-
2001
- 2001-04-17 IL IL142650A patent/IL142650A/en active IP Right Grant
-
2002
- 2002-04-15 DE DE60220775T patent/DE60220775T2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-04-15 PL PL387458A patent/PL211438B1/en unknown
- 2002-04-15 EA EA200301017A patent/EA007565B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2002-04-15 CA CA2703688A patent/CA2703688C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-04-15 KR KR1020037013339A patent/KR100883080B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2002-04-15 AT AT02761957T patent/ATE365044T1/en active
- 2002-04-15 DE DE60232559T patent/DE60232559D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-04-15 ES ES02761957T patent/ES2289137T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-04-15 WO PCT/IL2002/000303 patent/WO2002083147A1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2002-04-15 MX MXPA03009553A patent/MXPA03009553A/en active IP Right Grant
- 2002-04-15 AT AT07002485T patent/ATE432705T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2002-04-15 PT PT07002485T patent/PT1790346E/en unknown
- 2002-04-15 UA UA2003109404A patent/UA78699C2/en unknown
- 2002-04-15 HU HU0400801A patent/HU230548B1/en unknown
- 2002-04-15 CN CNB028081870A patent/CN1259918C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-04-15 US US10/474,032 patent/US7501403B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-04-15 JP JP2002580951A patent/JP4324706B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-04-15 CZ CZ2008296A patent/CZ309042B6/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2002-04-15 NZ NZ528868A patent/NZ528868A/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2002-04-15 PL PL366585A patent/PL205057B1/en unknown
- 2002-04-15 EP EP02761957A patent/EP1379254B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-04-15 PT PT02761957T patent/PT1379254E/en unknown
- 2002-04-15 DK DK02761957T patent/DK1379254T3/en active
- 2002-04-15 BR BR0208924-6A patent/BR0208924A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2002-04-15 AU AU2002307771A patent/AU2002307771B2/en not_active Expired
- 2002-04-15 DK DK07002485T patent/DK1790346T3/en active
- 2002-04-15 ES ES07002485T patent/ES2328966T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-04-15 CA CA2444266A patent/CA2444266C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-04-15 EP EP07002485A patent/EP1790346B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-04-15 CZ CZ20032710A patent/CZ300489B6/en not_active IP Right Cessation
-
2003
- 2003-10-15 NO NO20034609A patent/NO333910B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
-
2007
- 2007-01-19 AU AU2007200191A patent/AU2007200191B2/en not_active Expired
- 2007-09-07 CY CY20071101160T patent/CY1106853T1/en unknown
-
2009
- 2009-01-28 US US12/361,291 patent/US8110564B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2013
- 2013-09-10 NO NO20131219A patent/NO335087B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Also Published As
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN1259918C (en) | Use of bile acid or bile salt fatty acid conjugates | |
| CN1759834B (en) | Application of berberine or associated with Simvastatin in preparing product for preventing or curing disease or symptom related to blood fat | |
| US8975246B2 (en) | Bile acid or bile salt fatty acid conjugates | |
| AU2002307771A1 (en) | Use of bile acid or bile salt fatty acid conjugates | |
| Haywood et al. | Metal (molybdenum, copper) accumulation and retention in brain, pituitary and other organs of ammonium tetrathiomolybdate-treated sheep | |
| MORITA et al. | Vitamin D toxicosis in cats: natural outbreak and experimental study | |
| Juste et al. | Inducing cholesterol precipitation from pig bile with β-cyclodextrin and cholesterol dietary supplementation | |
| WO1992001475A1 (en) | Compositions based on active principles of hydrophobic medicaments solubilizable in an aqueous solvent | |
| JP3029902B2 (en) | Serum lipid increasing agent | |
| JP3179090B2 (en) | Calcium absorption promoter | |
| Giudice et al. | Clinical findings associated with Borrelia burgdorferi infection in the dog | |
| CN1323659C (en) | New usage of agmatine | |
| CA2479632C (en) | Method for increasing the bone mineral density of a mammal using n-acylated glucosamines | |
| TW202339780A (en) | Method of treating metabolic syndrome using sarcodia ceylanica extract extracted by low temperature water having the effect of assisted improvement for treating metabolic syndrome | |
| Matsuzaki et al. | The role of branched-chain amino acids and aromatic amino acids of various tissues and the degenerations of skeletal muscle fiber in liver cirrhosis model rat | |
| CN1141195A (en) | Zinc chelate prostate extract, the mfg. method and application thereof | |
| Davie et al. | P12. Elevation of serum osteocalcin associated with mobilisation of bone aluminium by desferrioxamine | |
| Hamdy et al. | P13. The indirect assessment of parathyroid bone disease in renal failure: use of thallium-technetium parathyroid scanning | |
| Singh | Pathological Alteration in Thymus of White Leg Horn Chicks during experimental Ascaridiasis | |
| CN1634109A (en) | Prescription with fat metabolism regulating function and its preparing method | |
| Ahmed | The Organizing Committee· | |
| GRAVIS | ACTA CHIRURGIAE PLASTIC AE 3 4, 2, 1992 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| ASS | Succession or assignment of patent right |
Owner name: GALE MEADE RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT CO., LTD. Free format text: FORMER OWNER: G.S.T.X. LTD. Effective date: 20150416 |
|
| C41 | Transfer of patent application or patent right or utility model | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right |
Effective date of registration: 20150416 Address after: Israel Tel Aviv Patentee after: GALMED RES and DEV LTD Address before: Cara Malta Patentee before: G.S.T.X. Ltd. |
|
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term | ||
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term |
Granted publication date: 20060621 |