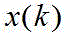CN114237042A - Smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control method and system - Google Patents
Smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control method and system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114237042A CN114237042A CN202111414896.4A CN202111414896A CN114237042A CN 114237042 A CN114237042 A CN 114237042A CN 202111414896 A CN202111414896 A CN 202111414896A CN 114237042 A CN114237042 A CN 114237042A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- current moment
- moment
- pressure
- neural network
- current
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 42
- 238000003062 neural network model Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 23
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 claims description 118
- 238000013528 artificial neural network Methods 0.000 claims description 87
- 210000002569 neuron Anatomy 0.000 claims description 28
- 230000003044 adaptive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 230000036278 prepulse Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 abstract description 15
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 18
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 16
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 16
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 13
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 8
- 230000001629 suppression Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 210000000707 wrist Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000003745 diagnosis Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000010355 oscillation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010009 beating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000006978 adaptation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003205 muscle Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000001537 neural effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008447 perception Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035485 pulse pressure Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000029058 respiratory gaseous exchange Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G05—CONTROLLING; REGULATING
- G05B—CONTROL OR REGULATING SYSTEMS IN GENERAL; FUNCTIONAL ELEMENTS OF SUCH SYSTEMS; MONITORING OR TESTING ARRANGEMENTS FOR SUCH SYSTEMS OR ELEMENTS
- G05B13/00—Adaptive control systems, i.e. systems automatically adjusting themselves to have a performance which is optimum according to some preassigned criterion
- G05B13/02—Adaptive control systems, i.e. systems automatically adjusting themselves to have a performance which is optimum according to some preassigned criterion electric
- G05B13/04—Adaptive control systems, i.e. systems automatically adjusting themselves to have a performance which is optimum according to some preassigned criterion electric involving the use of models or simulators
- G05B13/042—Adaptive control systems, i.e. systems automatically adjusting themselves to have a performance which is optimum according to some preassigned criterion electric involving the use of models or simulators in which a parameter or coefficient is automatically adjusted to optimise the performance
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/02—Detecting, measuring or recording pulse, heart rate, blood pressure or blood flow; Combined pulse/heart-rate/blood pressure determination; Evaluating a cardiovascular condition not otherwise provided for, e.g. using combinations of techniques provided for in this group with electrocardiography or electroauscultation; Heart catheters for measuring blood pressure
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/48—Other medical applications
- A61B5/4854—Diagnosis based on concepts of traditional oriental medicine
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B2562/00—Details of sensors; Constructional details of sensor housings or probes; Accessories for sensors
- A61B2562/02—Details of sensors specially adapted for in-vivo measurements
- A61B2562/0252—Load cells
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Alternative & Traditional Medicine (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Feedback Control In General (AREA)
Abstract
The application belongs to the technical field of manipulator control, and discloses a method and a system for controlling pulse feeling pre-pressure by a smart finger, wherein pressure data output by a pressure sensor of the fingertip of the smart finger is obtained; calculating the difference between the pressure data at the current moment and the expected pre-pressure at the current moment as the tracking error at the current moment; calculating the interference force estimation value at the current moment by using a self-adaptive RBF neural network model according to the pressure data; generating motor control input data at the current moment according to the expected prepressing force at the next moment, the interference force estimation value at the current moment and the tracking error at the current moment, and sending the motor control input data at the current moment to a motor of the smart finger to compensate the external interference; the interference in the pulse wave acquisition process can be effectively eliminated, and the control precision of the pre-pressure is improved, so that the real validity of the acquired pulse wave data is guaranteed.
Description
Technical Field
The application relates to the technical field of manipulator control, in particular to a smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control method and system.
Background
In the traditional Chinese medicine pulse diagnosis process, doctors sense the pulse beating condition of wrists of patients through fingers, so that the disease condition is diagnosed according to the pulse beating condition. However, the traditional Chinese medicine pulse diagnosis has the practical problems of low standardization degree and subjective pulse condition judgment due to different accumulated experiences and slight perception differences of traditional Chinese medical doctors.
Therefore, some automatic traditional Chinese medicine pulse diagnosis devices are available on the market at present, and the wrist pulse mouth pulse waves are collected mainly through a manipulator. For example, the smart finger shown in fig. 3 is a mechanical finger in such a manipulator, and comprises a base body 1 ', a finger 2' with one end hinged to the base body 1 ', a pressure sensor 3' arranged at the other end of the finger 2 ', and a motor 5' for pushing the finger 2 'to swing through a screw transmission mechanism 4'. When the smart finger works, the control system controls the motor 5 'to rotate so that the fingertip of the finger 2' is pressed at the wrist pulse of a patient to acquire pulse waves.
In practical application, the accuracy of the pre-pressure between the fingertip of the smart finger and the wrist of the patient affects the accuracy of the acquired pulse wave, and the existing PID controller is generally adopted to control the smart finger, and although the existing PID controller can adjust the pre-pressure, the existing PID controller is difficult to effectively remove the interference caused by the muscle shake or breathing of the patient in the acquisition process, so that the control accuracy of the pre-pressure is low, and the real effectiveness of the acquired pulse wave data is difficult to ensure.
Disclosure of Invention
The application aims to provide a smart finger pulse feeling prepressure control method and system, which can effectively eliminate interference in a pulse wave acquisition process and improve control precision of prepressure, thereby being beneficial to ensuring the real validity of acquired pulse wave data.
In a first aspect, the present application provides a method for controlling pre-pulse pressure for a smart finger, which is used for controlling a motor of the smart finger, and comprises the following steps:
A1. acquiring pressure data output by a pressure sensor of a smart finger tip; the pressure data comprises pressure data at the current moment and pressure data before the current moment;
A2. calculating the difference between the pressure data at the current moment and the expected pre-pressure at the current moment as the tracking error at the current moment;
A3. calculating the interference force estimation value at the current moment by using a self-adaptive RBF neural network model according to the pressure data;
A4. and generating motor control input data of the current moment according to the expected pre-pressure of the next moment, the interference force estimation value of the current moment and the tracking error of the current moment, and sending the motor control input data of the current moment to the motor of the smart finger to compensate the external interference.
The smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control method uses a self-adaptive RBF neural network model to calculate the estimated value of the interference force at the current moment according to the pressure data output by a pressure sensor of a smart finger tip at the current moment and output before the current moment, and the expected pre-pressure at the next moment, the interference force estimation value at the current moment and the tracking error at the current moment are used for generating the motor control input data at the current moment so as to control the motor of the smart finger, compared with the general PID control mode, the control mode based on the self-adaptive RBF neural network can lead the output pressure to reach the set pressure target more quickly, the pulse wave data acquisition method has the advantages of overshoot suppression and error setting, can quickly set and eliminate disturbance in the pulse wave acquisition process, and improves the control precision of pre-pressure, thereby being beneficial to ensuring the real effectiveness of the acquired pulse wave data.
Preferably, step a4 includes:
calculating the motor control input data at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,inputting data for the motor control at the present moment,for the desired pre-pressure at the next moment,for the tracking error at the present time instant,for the estimated value of the disturbance force at the present moment,is a control parameter andis less than 1 in absolute value, and,is a state matrix of the current time, an
WhereinIs the pressure data at the present moment in time,the pressure data is the ith last pressure data before the current time, n is the total number of the obtained pressure data, and k is the data serial number of the current time.
The motor control input data generated by the method can effectively realize the compensation of external interference, thereby ensuring the control precision of the pre-pressure.
Preferably, the adaptive RBF neural network model calculates the interference force estimation value at the current time according to the following formula:
wherein,for the estimated value of the disturbance force at the present moment,outputting a weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,a neuron output quantity matrix of the hidden layer of the RBF neural network at the current moment,is the state matrix at the current moment.
Preferably, after the step A2 and before the step A3, the method further comprises the steps of:
and adjusting the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the previous moment according to the tracking error at the previous moment and the tracking error at the current moment to obtain the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the current moment.
Before the calculation of the interference force estimated value is carried out each time, the RBF neural network output weight matrix is adjusted according to the tracking error at the previous moment and the tracking error at the current moment, so that the accumulation of calculation errors can be avoided, the calculation result of the interference force estimated value is more accurate, and the control precision of the pre-pressure is further improved.
Preferably, the step of adjusting the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the previous time according to the tracking error at the previous time and the tracking error at the current time to obtain the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the current time includes:
calculating an error function for the current time according to the following formula:
wherein,as a function of the error at the current time,for the tracking error at the present time instant,for the tracking error at the last moment in time,is an error parameter andis greater than zero and is greater than zero,is the auxiliary control signal at the present moment,in order to be a function of the discretization,in the form of a discrete time delay factor,is a control parameter andis less than 1;
calculating an increment matrix of the RBF neural network output weight matrix at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,outputting an increment matrix of the weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,、are control constants and are all positive numbers,for an approximation error that is non-zero,is a neuron output quantity matrix of the hidden layer of the RBF neural network at the previous moment,is the state matrix of the last moment;
calculating the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,outputting a weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,for RBF neural network output at the last momentAnd (6) outputting a weight matrix.
In a second aspect, the application provides a smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system, which is used for controlling a motor of a smart finger and comprises an interference estimation module, a controller and a comparison module;
the interference estimation module is used for acquiring pressure data output by the pressure sensor of the dexterous finger tip at the current moment and output before the current moment, calculating an estimated value of the interference force at the current moment by using a self-adaptive RBF neural network model according to the pressure data, and sending the estimated value of the interference force at the current moment to the controller;
the comparison module is used for acquiring pressure data output by the pressure sensor of the fingertip of the smart finger at the current moment, calculating the difference between the pressure data at the current moment and expected pre-pressure at the current moment as a tracking error at the current moment, and sending the tracking error at the current moment to the controller;
the controller is used for generating motor control input data of the current moment according to expected pre-pressure of the next moment, the interference force estimation value of the current moment and the tracking error of the current moment, and sending the motor control input data of the current moment to the motor of the smart finger so as to compensate external interference.
The smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system calculates the interference force estimation value at the current moment by using a self-adaptive RBF neural network model according to the pressure data output by the pressure sensor of the smart finger tip at the current moment and the pressure data output before the current moment, and the expected pre-pressure at the next moment, the interference force estimation value at the current moment and the tracking error at the current moment are used for generating the motor control input data at the current moment so as to control the motor of the smart finger, compared with a general PID controller, the control mode based on the self-adaptive RBF neural network can enable the output pressure to reach the set pressure target more quickly, the pulse wave data acquisition method has the advantages of overshoot suppression and error setting, can quickly set and eliminate disturbance in the pulse wave acquisition process, and improves the control precision of pre-pressure, thereby being beneficial to ensuring the real effectiveness of the acquired pulse wave data.
Preferably, the controller is configured to, when generating the motor control input data at the current time based on the desired pre-pressure at the next time, the interference force estimation value at the current time, and the tracking error at the current time, perform:
calculating the motor control input data at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,inputting data for the motor control at the present moment,for the desired pre-pressure at the next moment,for the tracking error at the present time instant,for the estimated value of the disturbance force at the present moment,is a control parameter andis less than 1 in absolute value, and,is a state matrix of the current time, an
WhereinIs at presentThe pressure data at the time of day is,the pressure data is the ith last pressure data before the current time, n is the total number of the obtained pressure data, and k is the data serial number of the current time.
The motor control input data generated by the method can effectively realize the compensation of external interference, thereby ensuring the control precision of the pre-pressure.
Preferably, the interference estimation module comprises an RBF network approximation unit; the RBF network approximation unit is used for calculating the interference force estimation value at the current moment by using a self-adaptive RBF neural network model according to the pressure data;
the self-adaptive RBF neural network model calculates the interference force estimation value at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,for the estimated value of the disturbance force at the present moment,outputting a weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,a neuron output quantity matrix of the hidden layer of the RBF neural network at the current moment,is the state matrix at the current moment.
Preferably, the interference estimation module further comprises an adaptive rate adjustment unit; and the self-adaptive rate adjusting unit is used for adjusting the RBF neural network output weight matrix at the previous moment according to the tracking error at the previous moment and the tracking error at the current moment to obtain the RBF neural network output weight matrix at the current moment.
Before the calculation of the interference force estimated value is carried out each time, the RBF neural network output weight matrix is adjusted according to the tracking error at the previous moment and the tracking error at the current moment, so that the accumulation of calculation errors can be avoided, the calculation result of the interference force estimated value is more accurate, and the control precision of the pre-pressure is further improved.
Preferably, the adaptive rate adjusting unit, when adjusting the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the previous time according to the tracking error at the previous time and the tracking error at the current time to obtain the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the current time, performs:
calculating an error function for the current time according to the following formula:
wherein,as a function of the error at the current time,for the tracking error at the present time instant,for the tracking error at the last moment in time,is an error parameter andis greater than zero and is greater than zero,is the auxiliary control signal at the present moment,in order to be a function of the discretization,in the form of a discrete time delay factor,is a control parameter andis less than 1;
calculating an increment matrix of the RBF neural network output weight matrix at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,outputting an increment matrix of the weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,、are control constants and are all positive numbers,for an approximation error that is non-zero,is a neuron output quantity matrix of the hidden layer of the RBF neural network at the previous moment,is the state matrix of the last moment;
calculating the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,outputting a weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,and outputting the weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the previous moment.
Has the advantages that:
according to the method and the system for controlling the pulse feeling pre-pressure of the smart finger, pressure data output by a pressure sensor of the fingertip of the smart finger is obtained; the pressure data comprises pressure data at the current moment and pressure data before the current moment; calculating the difference between the pressure data at the current moment and the expected pre-pressure at the current moment as the tracking error at the current moment; calculating the interference force estimation value at the current moment by using a self-adaptive RBF neural network model according to the pressure data; generating motor control input data of the current moment according to the expected pre-pressure of the next moment, the interference force estimation value of the current moment and the tracking error of the current moment, and sending the motor control input data of the current moment to the motor of the smart finger to compensate the external interference; compared with a general PID control mode, the control mode based on the self-adaptive RBF neural network can enable the output pressure to reach the set pressure target more quickly, has more advantages in overshoot suppression and error setting, can quickly set and eliminate disturbance in the pulse wave acquisition process, improves the control precision of pre-pressure, and is beneficial to ensuring the real effectiveness of the acquired pulse wave data.
Additional features and advantages of the application will be set forth in the description which follows, and in part will be obvious from the description, or may be learned by the practice of the application.
Drawings
Fig. 1 is a flowchart of a method for controlling a pressure for palpating a pulse by a smart finger according to an embodiment of the present application.
Fig. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of a smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system according to an embodiment of the present application.
Fig. 3 is a schematic view of a conventional dexterous finger.
Fig. 4 is a graph showing pressure data changes of the pressure control system for palpating the pulse with the dexterous finger in the first experiment.
Fig. 5 is a graph of pressure data change of the PID control system in experiment one.
Fig. 6 is a graph comparing the tracking errors of the two systems in experiment one.
Fig. 7 is a graph showing pressure data changes of the smart finger pulse feeling pressure control system in the second experiment.
Fig. 8 is a graph showing changes in pressure data of the PID control system in experiment two.
Fig. 9 is a graph comparing the tracking errors of the two systems in experiment two.
Fig. 10 is a graph comparing the first pressure data change for the two systems in experiment three.
Fig. 11 is a graph comparing the second pressure data change for the two systems in experiment three.
Fig. 12 is a graph comparing the third pressure data change for the two systems in experiment three.
Description of reference numerals: 1. an interference estimation module; 101. an RBF network approximation unit; 102. an adaptive rate adjustment unit; 2. a controller; 3. a comparison module; 90. dexterous fingers; 91. a motor; 92. a pressure sensor.
Detailed Description
The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application will be clearly and completely described below with reference to the drawings in the embodiments of the present application, and it is obvious that the described embodiments are only a part of the embodiments of the present application, and not all of the embodiments. The components of the embodiments of the present application, generally described and illustrated in the figures herein, can be arranged and designed in a wide variety of different configurations. Thus, the following detailed description of the embodiments of the present application, presented in the accompanying drawings, is not intended to limit the scope of the claimed application, but is merely representative of selected embodiments of the application. All other embodiments, which can be derived by a person skilled in the art from the embodiments of the present application without making any creative effort, shall fall within the protection scope of the present application.
It should be noted that: like reference numbers and letters refer to like items in the following figures, and thus, once an item is defined in one figure, it need not be further defined and explained in subsequent figures. Meanwhile, in the description of the present application, the terms "first", "second", and the like are used only for distinguishing the description, and are not to be construed as indicating or implying relative importance.
Referring to fig. 1, fig. 1 is a method for controlling a pulse feeling pressure of a smart finger according to some embodiments of the present application, for controlling a motor of the smart finger, including the steps of:
A1. acquiring pressure data output by a pressure sensor of a smart finger tip; the pressure data comprises pressure data at the current moment and pressure data before the current moment;
A2. calculating the difference between the pressure data at the current moment and the expected pre-pressure at the current moment as the tracking error at the current moment;
A3. calculating the interference force estimation value at the current moment by using a self-adaptive RBF neural network model according to the pressure data;
A4. and generating motor control input data at the current moment according to the expected prepressing force at the next moment, the interference force estimation value at the current moment and the tracking error at the current moment, and sending the motor control input data at the current moment to the motor of the smart finger to compensate the external interference.
The smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control method uses a self-adaptive RBF neural network model to calculate the estimated value of the interference force at the current moment according to the pressure data output by a pressure sensor of a smart finger tip at the current moment and output before the current moment, and the expected pre-pressure at the next moment, the interference force estimation value at the current moment and the tracking error at the current moment are used for generating the motor control input data at the current moment so as to control the motor of the smart finger, compared with the general PID control mode, the control mode based on the self-adaptive RBF neural network can lead the output pressure to reach the set pressure target more quickly, the pulse wave data acquisition method has the advantages of overshoot suppression and error setting, can quickly set and eliminate disturbance in the pulse wave acquisition process, and improves the control precision of pre-pressure, thereby being beneficial to ensuring the real effectiveness of the acquired pulse wave data.
In practical application, the motor 5 'of the smart finger has a motor driver, and the step a4 sends the motor control input data of the current time to the motor 5' of the smart finger, which is actually sent to the motor driver of the motor 5 ', and the motor driver, after receiving the motor control input data, drives the motor 5' to rotate by a corresponding angle.
In some embodiments, the method for controlling the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure is applied to the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system shown in fig. 2, and the specific structure of the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system is described with reference to the following description.
In practical application, after the smart finger starts to work, the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system periodically generates motor control input data at a preset frequency and sends the motor control input data to a motor of the smart finger, and meanwhile, periodically receives and records pressure data measured by a pressure sensor of the fingertip of the smart finger at the same frequency. Therefore, in step a1, the pressure data at the current time and the pressure data before the current time may be read from a memory (e.g., a cache or other memory).
Wherein, step a2 can be expressed by the following formula:
wherein,for the tracking error at the present time instant,is the pressure data at the present moment in time,k is the expected pre-pressure at the current time, and k is the data sequence number at the current time. For the pulse wave acquisition process, since it is necessary to keep the pre-pressure constant, the desired pre-pressure at any time is the same fixed value, which can be set in advance, for example, assuming that the fixed value is M, M can be used to replace M in the above formula。
In some preferred embodiments, step a4 includes:
calculating the motor control input data at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,inputting data for the motor control at the present moment,for the desired pre-pressure at the next moment,for the tracking error at the present time instant,for the estimated value of the disturbance force at the present moment,is a control parameter andis less than 1: (The value of (c) can be set according to actual conditions),is a state matrix of the current time, an
WhereinIs the pressure data at the present moment in time,the pressure data is the ith last pressure data before the current time, and n is the total number of the acquired pressure data.
The motor control input data generated by the method can effectively realize the compensation of external interference, thereby ensuring the control precision of the pre-pressure.
Preferably, the adaptive RBF neural network model used in step a3 calculates the interference force estimate at the current time according to the following formula:
wherein,for the estimated value of the disturbance force at the present moment,outputting a weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,as the RBF neural net of the current timeThe matrix of neuron output quantities of the envelope stratum,is the state matrix at the current moment. Wherein, for the condition that m (m can be set according to actual needs) neurons exist in the hidden layer of the RBF neural network,the output quantity of each neuron comprises m output quantities of neurons, and the output quantity of each neuron is calculated according to the following Gaussian function:
wherein,is the output of the jth neuron,is a matrix of the states at the current time,is the central vector matrix (constant) of the jth neuron,is the width vector matrix (constant) of the gaussian basis function of the jth neuron.
In some preferred embodiments, after step a2 and before step A3, further comprising the steps of:
and adjusting the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the previous moment according to the tracking error at the previous moment and the tracking error at the current moment to obtain the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the current moment.
Before the calculation of the interference force estimated value is carried out each time, the RBF neural network output weight matrix is adjusted according to the tracking error at the previous moment and the tracking error at the current moment, so that the accumulation of calculation errors can be avoided, the calculation result of the interference force estimated value is more accurate, and the control precision of the pre-pressure is further improved. In practical application, if the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network is not adjusted, because the interference force estimated value obtained by each calculation inevitably has an error, the pressure data output by the pressure sensor contains the influence of the error, and the pressure data obtained in advance is needed when the interference force estimated value at the current moment is calculated, so that the calculation error of the interference force estimated value is gradually accumulated.
In this embodiment, the step of adjusting the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the previous time according to the tracking error at the previous time and the tracking error at the current time to obtain the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the current time includes:
B1. calculating an error function for the current time according to the following formula:
wherein,as a function of the error at the current time,for the tracking error at the present time instant,for the tracking error at the last moment in time,is an error parameter andgreater than zero (which can be set according to actual needs),is the auxiliary control signal at the present moment,in order to be a function of the discretization,in the form of a discrete time delay factor,is a control parameter andis less than 1;
wherein,can be set according to actual needs to ensureApproaching 0 over time, e.g., in some embodiments,can be calculated according to the following formula:
wherein,is the first signal value at the present moment,is the second signal value at the present moment in time,、to control the constants and all positive numbers (which can be set according to actual needs),as a function of the error at the last time instant,is a neuron output quantity matrix of the hidden layer of the RBF neural network at the previous moment,is the state matrix of the last moment;
B2. calculating an increment matrix of the RBF neural network output weight matrix at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,outputting an increment matrix of the weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,、are control constants and are all positive numbers,a non-zero approximation error (which can be set according to actual needs),is a neuron output quantity matrix of the hidden layer of the RBF neural network at the previous moment,is the state matrix of the last moment;
B3. calculating the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,outputting a weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,and outputting the weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the previous moment.
According to the method for controlling the pulse feeling pressure of the smart finger, the pressure data output by the pressure sensor of the fingertip of the smart finger is obtained; the pressure data comprises pressure data at the current moment and pressure data before the current moment; calculating the difference between the pressure data at the current moment and the expected pre-pressure at the current moment as the tracking error at the current moment; calculating the interference force estimation value at the current moment by using a self-adaptive RBF neural network model according to the pressure data; generating motor control input data at the current moment according to the expected prepressing force at the next moment, the interference force estimation value at the current moment and the tracking error at the current moment, and sending the motor control input data at the current moment to a motor of the smart finger to compensate the external interference; compared with a general PID control mode, the control mode based on the self-adaptive RBF neural network can enable the output pressure to reach the set pressure target more quickly, has more advantages in overshoot suppression and error setting, can quickly set and eliminate disturbance in the pulse wave acquisition process, improves the control precision of pre-pressure, and is beneficial to ensuring the real effectiveness of the acquired pulse wave data.
Referring to fig. 2, the present application provides a smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system for controlling a motor 91 of a smart finger 90, comprising an interference estimation module 1, a controller 2 and a comparison module 3;
the interference estimation module 1 is used for acquiring pressure data output by a pressure sensor 92 of a fingertip of the smart finger 90 at the current moment and output before the current moment, calculating an estimated value of interference force at the current moment by using a self-adaptive RBF neural network model according to the pressure data, and sending the estimated value of the interference force at the current moment to the controller 2;
the comparison module 3 is used for acquiring pressure data output by the pressure sensor 92 of the fingertip of the smart finger 90 at the current moment, calculating a difference between the pressure data at the current moment and an expected pre-pressure at the current moment to serve as a tracking error at the current moment, and sending the tracking error at the current moment to the controller 2;
the controller 2 is configured to generate motor control input data at the current time according to the expected pre-pressure at the next time, the interference force estimation value at the current time, and the tracking error at the current time, and send the motor control input data at the current time to the motor 91 of the smart finger 90 to compensate for external interference.
The smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system calculates the estimated value of the interference force at the current moment by using a self-adaptive RBF neural network model according to the pressure data output by the pressure sensor 92 of the fingertip of the smart finger 90 at the current moment and the pressure data output before the current moment, and generates motor control input data of the present time using the desired pre-pressure of the next time, the interference force estimation value of the present time, and the tracking error of the present time to control the motor 91 of the smart finger 90, compared with a general PID controller, the control mode based on the self-adaptive RBF neural network can enable the output pressure to reach the set pressure target more quickly, the pulse wave data acquisition method has the advantages of overshoot suppression and error setting, can quickly set and eliminate disturbance in the pulse wave acquisition process, and improves the control precision of pre-pressure, thereby being beneficial to ensuring the real effectiveness of the acquired pulse wave data.
The structure of the dexterous finger 90 is the same as that of the dexterous finger shown in fig. 3, in practical application, the motor 91 of the dexterous finger 90 has a motor driver, the controller 2 sends the motor control input data of the current moment to the motor 91 of the dexterous finger 90, which actually means to the motor driver of the motor 91, and the motor driver drives the motor 91 to rotate by a corresponding angle after receiving the motor control input data.
In practical applications, the system for controlling pulse pressure of a smart finger further comprises a memory (e.g. a buffer memory or other memory), after the smart finger 90 starts to work, the controller 2 periodically generates and transmits motor control input data to the motor 91 of the smart finger 90 at a predetermined frequency, and the memory periodically receives and records pressure data measured by the pressure sensor 92 of the fingertip of the smart finger 90 at the same frequency. Thus, the disturbance estimation module 1 may read the pressure data at the present time and the pressure data before the present time from the memory. The comparison module 3 may read the pressure data at the present moment from the memory.
The comparison module 3 may calculate the tracking error at the current time according to the following formula:
wherein,for the tracking error at the present time instant,is the pressure data at the present moment in time,k is the expected pre-pressure at the current time, and k is the data sequence number at the current time. For the pulse wave acquisition process, since it is necessary to keep the pre-pressure constant, the desired pre-pressure at any time is the same fixed value, which can be set in advance, for example, assuming that the fixed value isM, then M can be substituted for one in the above formula。
In some preferred embodiments, the controller 2 is configured to perform, when generating the motor control input data at the current time based on the desired pre-pressure at the next time, the disturbance force estimate at the current time, and the tracking error at the current time:
calculating the motor control input data at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,inputting data for the motor control at the present moment,for the desired pre-pressure at the next moment,for the tracking error at the present time instant,for the estimated value of the disturbance force at the present moment,is a control parameter andis less than 1: (The value of (c) can be set according to actual conditions),is as followsA state matrix of previous time instants, an
WhereinIs the pressure data at the present moment in time,the pressure data is the ith last pressure data before the current time, and n is the total number of the acquired pressure data.
The motor control input data generated by the method can effectively realize the compensation of external interference, thereby ensuring the control precision of the pre-pressure.
Preferably, the interference estimation module 1 comprises an RBF network approximation unit 101; the RBF network approximation unit 101 is used for calculating the interference force estimation value at the current moment by using a self-adaptive RBF neural network model according to the pressure data;
specifically, the adaptive RBF neural network model calculates the interference force estimation value at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,for the estimated value of the disturbance force at the present moment,outputting a weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,a neuron output quantity matrix of the hidden layer of the RBF neural network at the current moment,is at presentA state matrix of time instants. Wherein, for the condition that m (m can be set according to actual needs) neurons exist in the hidden layer of the RBF neural network,the output quantity of each neuron comprises m output quantities of neurons, and the output quantity of each neuron is calculated according to the following Gaussian function:
wherein,is the output of the jth neuron,is a matrix of the states at the current time,is the central vector matrix (constant) of the jth neuron,is the width vector matrix (constant) of the gaussian basis function of the jth neuron.
In some preferred embodiments, the interference estimation module 1 further comprises an adaptation rate adjustment unit 102; the adaptive rate adjusting unit 102 is configured to adjust the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the previous time according to the tracking error at the previous time and the tracking error at the current time, so as to obtain the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the current time.
Before the calculation of the interference force estimated value is carried out each time, the RBF neural network output weight matrix is adjusted according to the tracking error at the previous moment and the tracking error at the current moment, so that the accumulation of calculation errors can be avoided, the calculation result of the interference force estimated value is more accurate, and the control precision of the pre-pressure is further improved. In practical applications, if the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network is not adjusted, since the interference force estimation value obtained by each calculation inevitably has an error, the pressure data output by the pressure sensor 92 contains the influence of the error, and the pressure data obtained in advance is needed to be used when the interference force estimation value at the current moment is calculated, which may cause the calculation error of the interference force estimation value to be gradually accumulated.
Preferably, the adaptive rate adjusting unit 102 performs, when adjusting the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the previous time according to the tracking error at the previous time and the tracking error at the current time to obtain the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the current time:
calculating an error function for the current time according to the following formula:
wherein,as a function of the error at the current time,for the tracking error at the present time instant,for the tracking error at the last moment in time,is an error parameter andgreater than zero (as required)To be set up),is the auxiliary control signal at the present moment,in order to be a function of the discretization,in the form of a discrete time delay factor,is a control parameter andis less than 1;
wherein,can be set according to actual needs to ensureApproaching 0 over time, e.g., in some embodiments,can be calculated according to the following formula:
wherein,is the value of the first signal and is,is the value of the second signal and is,、to control the constants and all positive numbers (which can be set according to actual needs),as a function of the error at the last time instant,is a neuron output quantity matrix of the hidden layer of the RBF neural network at the previous moment,is the state matrix of the last moment;
calculating an increment matrix of the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network according to the following formula:
wherein,outputting an increment matrix of the weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,、are control constants and are all positive numbers,a non-zero approximation error (which can be set according to actual needs),is a neuron output quantity matrix of the hidden layer of the RBF neural network at the previous moment,is the state matrix of the last moment;
calculating the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,outputting a weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,and outputting the weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the previous moment.
The control effect of the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system is compared with that of the traditional PID control system through experiments.
Experiment one
The same expected pre-pressure changing in sine wave is input as an input signal to the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system and the conventional PID control system, respectively, the pressure data output by the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system (i.e. the pressure data output by the pressure sensor of the fingertip) is shown in fig. 4 (where the dotted line is the expected pre-pressure change curve and the solid line is the output pressure data change curve), the pressure data output by the conventional PID control system is shown in fig. 5 (where the dotted line is the expected pre-pressure change curve and the solid line is the output pressure data change curve), the comparison between the tracking error of the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system and the tracking error of the conventional PID control system is shown in fig. 6, and it can be seen that the rise time of the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system and the conventional PID control system is 0.18s and 0.30s respectively, the adjusting time is 0.25s and 0.5s respectively, the overshoot amount is 0.5gf and 2.7gf respectively, and although the magnitude of the data difference between the two is small, the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system has better dynamic performance and faster adjusting speed; as can be seen from fig. 6, compared with the conventional PID control system, the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system of the present application has smaller tracking error and smaller tracking error fluctuation range, which indicates that the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system of the present application has better adaptability and follow-up performance.
Experiment two
The same expected pre-pressure changing in square wave is used as an input signal to be input into the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system and the traditional PID control system, the pressure data output by the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system is shown in FIG. 7 (wherein, the dotted line is an expected pre-pressure change curve, the solid line is an output pressure data change curve), the pressure data output by the traditional PID control system is shown in FIG. 8 (wherein, the dotted line is an expected pre-pressure change curve, the solid line is an output pressure data change curve), a comparison graph of the tracking error of the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system and the tracking error of the traditional PID control system is shown in FIG. 9, and as can be seen from the graph, the two types of control systems can reach the set pressure more quickly, obvious overshoot and steady-state errors do not occur, and the control effect can meet the design requirement; however, the traditional PID control system generates stronger oscillation in the adjusting process, the adjusting time of the traditional PID control system is 4 times that of the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system, and meanwhile, the maximum offset of 26.36gf and the overshoot of-52.72% occur in the adjusting process, so that the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system has the advantages of better control effect, stronger anti-interference capability and better adaptability and follow-up performance.
Experiment three
The same expected pre-pressure with step change is respectively input into the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system and the traditional PID control system, wherein three times of experiments are respectively carried out by utilizing step values of 50gf, 100gf and 150gf, the comparison graphs of the pressure data output by the two systems are respectively shown in fig. 10, 11 and 12, as can be seen from the graphs, in the 50gf step response experiment, the dynamic performance difference of the two systems is smaller, but in the 100gf and 150gf step response experiments, the traditional PID control system generates certain oscillation in the initial stage, so under the condition that the rising time is almost the same, the adjusting time of the traditional PID control system is respectively 1.79 times and 2 times of the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system, the overshoot generated by the oscillation of the system is respectively 0.3 percent and 10.13 percent larger than that of the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system, therefore, under the condition of the same adjustment speed, the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system can enable the overshoot of the system to be lower; as can be seen from fig. 10-12, compared with the conventional PID control system, the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system of the present application has smaller tracking error and tracking error fluctuation range, so that the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system of the present application has stronger setting capability for the error, and can relatively stably maintain the system pressure near the set value, thereby effectively improving the pulse wave data acquisition quality.
According to the smart finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system, pressure data output by the pressure sensor of the finger tip of the smart finger is acquired; the pressure data comprises pressure data at the current moment and pressure data before the current moment; calculating the interference force estimation value at the current moment by using a self-adaptive RBF neural network model according to the pressure data; calculating the difference between the pressure data at the current moment and the expected pre-pressure at the current moment as the tracking error at the current moment; generating motor control input data at the current moment according to the expected prepressing force at the next moment, the interference force estimation value at the current moment and the tracking error at the current moment, and sending the motor control input data at the current moment to a motor of the smart finger to compensate the external interference; compared with a general PID control mode, the control mode based on the self-adaptive RBF neural network can enable the output pressure to reach the set pressure target more quickly, has more advantages in overshoot suppression and error setting, can quickly set and eliminate disturbance in the pulse wave acquisition process, improves the control precision of pre-pressure, and is beneficial to ensuring the real effectiveness of the acquired pulse wave data.
In this document, relational terms such as first and second, and the like may be used solely to distinguish one entity or action from another entity or action without necessarily requiring or implying any actual such relationship or order between such entities or actions.
The above description is only an example of the present application and is not intended to limit the scope of the present application, and various modifications and changes may be made by those skilled in the art. Any modification, equivalent replacement, improvement and the like made within the spirit and principle of the present application shall be included in the protection scope of the present application.
Claims (10)
1. A dexterous finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control method is used for controlling a motor of a dexterous finger and is characterized by comprising the following steps:
A1. acquiring pressure data output by a pressure sensor of a smart finger tip; the pressure data comprises pressure data at the current moment and pressure data before the current moment;
A2. calculating the difference between the pressure data at the current moment and the expected pre-pressure at the current moment as the tracking error at the current moment;
A3. calculating the interference force estimation value at the current moment by using a self-adaptive RBF neural network model according to the pressure data;
A4. and generating motor control input data of the current moment according to the expected pre-pressure of the next moment, the interference force estimation value of the current moment and the tracking error of the current moment, and sending the motor control input data of the current moment to the motor of the smart finger to compensate the external interference.
2. The method for controlling the pre-pulse pressure of a dexterous finger as claimed in claim 1, wherein step a4 comprises:
calculating the motor control input data at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,inputting data for the motor control at the current moment,for the desired pre-pressure at the next moment,for the tracking error at the current time instant,for the estimate of the disturbance force at the current moment,is a control parameter andis less than 1 in absolute value, and,is a state matrix of the current time, an
3. The dexterous finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control method according to claim 1,
the self-adaptive RBF neural network model calculates the interference force estimation value at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,for the estimate of the disturbance force at the current moment,outputting a weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,a neuron output quantity matrix of the hidden layer of the RBF neural network at the current moment,and k is the state matrix at the current moment and the data sequence number at the current moment.
4. The dexterous finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control method according to claim 3, wherein after step A2 and before step A3, further comprising the steps of:
and adjusting the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the previous moment according to the tracking error at the previous moment and the tracking error at the current moment to obtain the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the current moment.
5. The method for controlling pre-pulse pressure according to claim 4, wherein the step of adjusting the RBF neural network output weight matrix at the previous time according to the tracking error at the previous time and the tracking error at the current time to obtain the RBF neural network output weight matrix at the current time comprises:
calculating an error function for the current time according to the following formula:
wherein,as a function of the error at the current time,for the tracking error at the current time instant,for the tracking error at the last moment in time,is an error parameter andis greater than zero and is greater than zero,is the auxiliary control signal at the present moment,in order to be a function of the discretization,in the form of a discrete time delay factor,is a control parameter andis less than 1;
calculating an increment matrix of the RBF neural network output weight matrix at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,outputting an increment matrix of a weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,、are control constants and are all positive numbers,for an approximation error that is non-zero,is a neuron output quantity matrix of the hidden layer of the RBF neural network at the previous moment,is the state matrix of the last moment;
calculating the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the current moment according to the following formula:
6. A dexterous finger pulse feeling pre-pressure control system is used for controlling a motor of a dexterous finger and is characterized by comprising an interference estimation module, a controller and a comparison module;
the interference estimation module is used for acquiring pressure data output by the pressure sensor of the dexterous finger tip at the current moment and output before the current moment, calculating an estimated value of the interference force at the current moment by using a self-adaptive RBF neural network model according to the pressure data, and sending the estimated value of the interference force at the current moment to the controller;
the comparison module is used for acquiring pressure data output by the pressure sensor of the fingertip of the smart finger at the current moment, calculating the difference between the pressure data at the current moment and expected pre-pressure at the current moment as a tracking error at the current moment, and sending the tracking error at the current moment to the controller;
the controller is used for generating motor control input data of the current moment according to expected pre-pressure of the next moment, the interference force estimation value of the current moment and the tracking error of the current moment, and sending the motor control input data of the current moment to the motor of the smart finger so as to compensate external interference.
7. The smart finger pulse pre-pressure control system according to claim 6, wherein the controller is configured to perform, when generating the motor control input data at the current time based on the desired pre-pressure at the next time, the interference force estimation value at the current time, and the tracking error at the current time:
calculating the motor control input data at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,inputting data for the motor control at the current moment,for the desired pre-pressure at the next moment,for the tracking error at the current time instant,for the estimate of the disturbance force at the current moment,is a control parameter andis less than 1 in absolute value, and,is a state matrix of the current time, an
8. The smart finger pulse pre-pressure control system of claim 6, wherein the interference estimation module comprises an RBF network approximation unit; the RBF network approximation unit is used for calculating the interference force estimation value at the current moment by using a self-adaptive RBF neural network model according to the pressure data;
the self-adaptive RBF neural network model calculates the interference force estimation value at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,for the estimate of the disturbance force at the current moment,outputting a weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,a neuron output quantity matrix of the hidden layer of the RBF neural network at the current moment,and k is the state matrix at the current moment and the data sequence number at the current moment.
9. The smart finger pulse pre-pressure control system of claim 8, wherein the interference estimation module further comprises an adaptive rate adjustment unit; and the self-adaptive rate adjusting unit is used for adjusting the RBF neural network output weight matrix at the previous moment according to the tracking error at the previous moment and the tracking error at the current moment to obtain the RBF neural network output weight matrix at the current moment.
10. The system for controlling pre-pulse pressure according to claim 9, wherein the adaptive rate adjusting unit performs, when the RBF neural network output weight matrix at the previous time is obtained by adjusting the RBF neural network output weight matrix at the previous time according to the tracking error at the previous time and the tracking error at the current time:
calculating an error function for the current time according to the following formula:
wherein,as a function of the error at the current time,for the tracking error at the current time instant,for the tracking error at the last moment in time,is an error parameter andis greater than zero and is greater than zero,is the auxiliary control signal at the present moment,in order to be a function of the discretization,in the form of a discrete time delay factor,is a control parameter andis less than 1;
calculating an increment matrix of the RBF neural network output weight matrix at the current moment according to the following formula:
wherein,outputting an increment matrix of a weight matrix for the RBF neural network at the current moment,、are control constants and are all positive numbers,for an approximation error that is non-zero,is RBF god of the last momentA matrix of neuron output quantities via the hidden layer of the network,is the state matrix of the last moment;
calculating the output weight matrix of the RBF neural network at the current moment according to the following formula:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111414896.4A CN114237042B (en) | 2021-11-25 | 2021-11-25 | Pulse feeling pre-pressure control method and system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111414896.4A CN114237042B (en) | 2021-11-25 | 2021-11-25 | Pulse feeling pre-pressure control method and system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114237042A true CN114237042A (en) | 2022-03-25 |
| CN114237042B CN114237042B (en) | 2022-06-03 |
Family
ID=80751248
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111414896.4A Active CN114237042B (en) | 2021-11-25 | 2021-11-25 | Pulse feeling pre-pressure control method and system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114237042B (en) |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS63309241A (en) * | 1987-06-11 | 1988-12-16 | Omron Tateisi Electronics Co | Digital electronic hemomanometer |
| CN108803335A (en) * | 2018-06-25 | 2018-11-13 | 南京邮电大学 | A kind of out of order removing method of DC servo motor control |
| CN110675933A (en) * | 2019-09-06 | 2020-01-10 | 南京邮电大学 | Finger mirror image rehabilitation training system |
| CN110871450A (en) * | 2019-11-28 | 2020-03-10 | 季华实验室 | Dexterous finger mechanism, manipulator and control method |
-
2021
- 2021-11-25 CN CN202111414896.4A patent/CN114237042B/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS63309241A (en) * | 1987-06-11 | 1988-12-16 | Omron Tateisi Electronics Co | Digital electronic hemomanometer |
| CN108803335A (en) * | 2018-06-25 | 2018-11-13 | 南京邮电大学 | A kind of out of order removing method of DC servo motor control |
| CN110675933A (en) * | 2019-09-06 | 2020-01-10 | 南京邮电大学 | Finger mirror image rehabilitation training system |
| CN110871450A (en) * | 2019-11-28 | 2020-03-10 | 季华实验室 | Dexterous finger mechanism, manipulator and control method |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| 孟庆涛等: ""灵巧手指"的位置/力模糊控制算法研究", 《桂林电子工业学院学报》 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114237042B (en) | 2022-06-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN106456064B (en) | Offline glucose control based on previous epochs | |
| Marko et al. | Sensitivity to prediction error in reach adaptation | |
| Chee et al. | Optimal H/sup/spl infin//insulin injection control for blood glucose regulation in diabetic patients | |
| Makin et al. | Superior arm-movement decoding from cortex with a new, unsupervised-learning algorithm | |
| US8792976B2 (en) | Brain machine interface | |
| JP2017523852A (en) | Mobile horizon state initializer for control applications | |
| JP2006500982A5 (en) | ||
| CN105982735B (en) | The method for improving the master-slave mode remote tele-operation surgery systems transparency and stability | |
| WO2013043903A1 (en) | Apparatus and methods for synaptic update in a pulse-coded network | |
| Li | Decoding methods for neural prostheses: where have we reached? | |
| CN114237042B (en) | Pulse feeling pre-pressure control method and system | |
| CN109620187B (en) | Central arterial pressure calculation method and device | |
| Hu et al. | A generalized predictive control for remote cardiovascular surgical systems | |
| CN111933268A (en) | Time-lag error prediction control method for vascular intervention surgical robot system | |
| Crevecoeur et al. | Filtering compensation for delays and prediction errors during sensorimotor control | |
| CN108763614B (en) | Parameter identification method for elastic-sliding distribution parameter model of piezoelectric ceramic actuator | |
| Su et al. | Oxygen uptake estimation in humans during exercise using a Hammerstein model | |
| CN111341451B (en) | Model-free adaptive predictive control method with interference compensation for glycemic control | |
| CN110352460A (en) | Artificial pancreas | |
| Dodek et al. | Maximizing performance of linear model predictive control of glycemia for T1DM subjects | |
| CN114147710B (en) | Robot control method and device, robot and storage medium | |
| KR102427048B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for predicting motion intention of a user wearing a shoulder-worn exoskeletion device | |
| Salesch et al. | Model based optimization of a novel ventricular assist device: Iterative parameter estimation and optimal control of physiological variables of a novel dual pump setup for left ventricular assist devices | |
| CN111897205B (en) | Piezoelectric driver feedforward control compensation method based on PID inverse | |
| KR102387841B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for driving wearable robot with tendon-sheath mechanism |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |