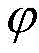Mobile robot dynamic collision avoidance planning method based on GRU network model
Technical Field
The invention relates to the field of mobile robot navigation, in particular to a dynamic collision avoidance planning method for a mobile robot based on a GRU network model.
Background
When the mobile robot works in an unknown environment, the dynamic collision avoidance planning of a local path is carried out by sensing surrounding environment information through the laser range finder, the safety of the path is guaranteed when the planning is carried out, and meanwhile the real-time performance is also met. At present, a plurality of documents about autonomous collision avoidance of mobile robots exist, most collision avoidance methods utilize traditional algorithms or group intelligent methods, and the algorithms need to establish an environment model and iterate the algorithms, so that the calculation time of the algorithms is prolonged, and the real-time performance is influenced. In the modern day with highly developed science and technology, deep learning gradually enters the lives of people, and the rise of unmanned automobiles is the specific application of deep learning networks in the aspects of collision avoidance and path planning. Compared with the traditional algorithm, the deep learning algorithm does not need to construct a model, and after a large amount of training, the strong nonlinear fitting capacity of the deep learning network can express various input and output. For a trained network, the iteration of the algorithm is not needed, and the corresponding output result can be obtained only through forward propagation, so that the real-time performance is good.
For the problem of dynamic collision avoidance of the mobile robot, the result of the planning is not only related to the environmental information at the current moment, but also comprehensively considers the environmental information and the planning result at the previous moments, the input information is related to the time sequence, and in order to process the input data related to the time sequence, a proper network needs to be selected.
Aiming at the problem of robot collision avoidance in an unknown environment, the invention designs a collision avoidance algorithm based on a deep learning network, and under the action of the algorithm, the robot can have a high intelligent dynamic planning level by using simple sensing equipment, so that the reaction speed of the mobile robot is superior to that of the traditional collision avoidance algorithm on the premise of ensuring safety.
Disclosure of Invention
The invention aims to design a collision avoidance algorithm based on a deep learning network aiming at the robot collision avoidance problem in an unknown environment, the robot can have a high intelligent dynamic programming level by using simple sensing equipment under the action of the algorithm, and the reaction speed of the mobile robot is superior to that of the traditional collision avoidance algorithm on the premise of ensuring safety.
A dynamic collision avoidance planning method for a mobile robot based on a GRU network model is characterized by comprising an input layer, a hidden layer and an output layer; the input original data is changed into 61-dimensional data after normalization and combination processing, and the 61-dimensional data sequentially enters an input layer, a hidden layer and an output layer.
The input layer receives input data with 61 dimensions, wherein the first 60-dimensional data is distance information detected by a laser range finder, and the last one-dimensional data is an angle of a connection line between the mobile robot and a target point in a global coordinate system
The data is stored in the form of row vectors, and the input layer and the hidden layer are in a full connection mode.
The hidden layer is two layers in total, the hidden layer 1 is composed of 40 GRU module units, the hidden layer 2 comprises 30 neurons, and the connection mode between the hidden layers is full connection.
The output layer comprises 2 neurons which respectively correspond to the direction theta and the speed v of the mobile robot in the global coordinate system at the next planned moment; the hidden layer data output then enters the output layer in a fully connected manner through the activation function.
A dynamic collision avoidance planning method for a mobile robot based on a GRU network model is characterized by comprising the following implementation methods:
the method comprises the following steps: establishing a coordinate system model, wherein the origin of the coordinate system is selected at the center of the laser range finder, the X axis points to the right front of the laser range finder, and the Y axis points to the left of the laser range finder; the horizontal opening angle of the laser range finder is 180 degrees, the maximum detection radius is set to be 8m, 181 beams are totally formed, and the beam angle is 1 degree;
step two: collecting and preprocessing sample data, performing dynamic collision avoidance and path planning by a mobile robot under the control of a teacher system in a simulation training field, collecting the sample data at the same time, wherein each group of sample data has 184 dimensions, then performing normalization processing, merging the collected data from 1 to 181 dimensions, keeping the 182 th dimension unchanged, and inputting the processed data with 61 dimensions;
step three: inputting the 61-dimensional data into an input layer;
step four: the GRU module unit in the hidden layer receives input data from the input layer in time sequence, firstly xt-9Producing an output h after forward propagationt-9,ht-9And xt-8Together asThe next unit inputs, and so on, the data is transmitted in this way, the output of the module at the last moment is the output of the unit structure, and the calculation formula of the GRU output value is:
zt=σ(xtWz+ht-1Uz)
rt=σ(xtWr+ht-1Ur)
wherein: z is a radical of
t、r
tRespectively representing the output of an update gate and a reset gate at the time t; x is the number of
tAnd h
tInput and output vectors at time t; w
z、W
rAnd W is the module input and update gate, reset gate and
an inter-weight matrix; u shape
z、U
rAnd U is the output of the module at the time t-1, the refresh gate, the reset gate and
an inter-weight matrix;
step five: transmitting the calculation result of the hidden layer to an output layer to be used as the direction theta and the speed v of the mobile robot in the global coordinate system at the next moment;
step six: training a GRU network model; initializing the weight of the GRU network model by using standard positive-space distribution;
step seven: training times k is 0, i is 0;
step eight: randomly extracting data [ x ] of 10 continuous time instants from a training sett-9,…,xt]Input network for obtaining corresponding output y through forward propagation processt;
Step nine: computing network output ytAnd a corresponding label ltAn error of (2);
step ten: updating the weight by using a gradient descent algorithm;
step eleven: if i is more than or equal to 500, making i equal to 0, randomly selecting 50 sequences in the test set, testing by using the current network, calculating the mean square error, and stopping training if the mean square error in the test set is not reduced for 10 times continuously;
step twelve: k +1, i + 1;
step thirteen: if k is larger than the maximum training times, jumping to the step fourteen, otherwise, jumping to the step eight;
fourteen steps: finishing the training; and obtaining the trained GRU network model.
The invention has the beneficial effects that:
after the network training is finished, the mobile robot uses the training result of the GRU network model to perform dynamic collision avoidance planning in an unknown environment and compares the dynamic collision avoidance planning with the ant colony algorithm, the two algorithms can enable the mobile robot to avoid all obstacles, the route is smooth, and the algorithm can guarantee the safety of the robot. However, the reaction time of the mobile robot is short under the GRU network model, the real-time performance is higher, and the high efficiency of the algorithm is proved.
Drawings
FIG. 1 is a diagram of a coordinate system of a mobile robot according to the present invention;
FIG. 2 shows the angle θ of the present invention
A schematic diagram;
FIG. 3 is a diagram of a GRU-based dynamic path planning model according to the present invention;
FIG. 4 is a time-series expanded view of a single GRU modular unit of the present invention;
fig. 5 is a diagram of the effect of GRU network and ant colony algorithm planning in the present invention.
Detailed Description
The invention is further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
And (3) constructing a coordinate system model, as shown in fig. 1, wherein a global coordinate system adopts a northeast coordinate system, the lower left corner of a map is an origin, the east-righting direction is an X-axis, the north-righting direction is a Y-axis, the origin of a local coordinate system is selected at the center of the laser range finder, the X-axis points to the front of the laser range finder, and the Y-axis points to the left of the laser range finder. The horizontal opening angle of the laser range finder is 180 degrees, the maximum detection radius is 8m, 181 wave beams are totally formed, and the wave beam angle is 1 degree.
Collecting and processing sample data, wherein before training, sample data collection and processing are firstly carried out, a mobile robot carries out dynamic collision avoidance and path planning under the control of a teacher system in a simulation training field, and simultaneously sample data are collected, wherein each group of sample data has 184 dimensions, the data of the first 181 dimensions are obtained by collecting surrounding environment information by a laser range finder, the sensor returns 181 points representing distances, the data of the second 182 dimensions are angle information of a connecting line of the mobile robot and a target point in a global coordinate system, as shown in figure 2,
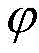
namely, 182 th dimension data. The last two-dimensional data are the robot's heading angle θ and velocity v. Where the first 182-dimensional data are input values to the network and the last two-dimensional data are training labels. In order to make the training result more accurate, the data must be correspondingly processed before entering the input layer, firstly, normalization processing is carried out, then, the data of 1 to 181 dimensions are merged, finally, the data of 182 th dimension is kept unchanged, and the input data has 61 dimensions after processing.
The mobile robot dynamically plans the structural design of the GRU network model, and the structural design of the GRU network model designed by the invention is shown in figure 3. According to the forward propagation direction, input original data are changed into 61-dimension data after normalization and combination processing, and the input data sequentially enter an input layer, a hidden layer and an output layer.
An input layer: the input data of the layer is 61-dimensional, wherein the first 60-dimensional data is distance information detected by a laser range finder, and the last one-dimensional data is an angle of a connection line of the mobile robot and a target point in a global coordinate system
The data is stored in the form of row vectors, and the input layer and the hidden layer are in a full connection mode.
Hiding the layer: the hidden layer is two layers in total, hidden layer 1 comprises 40 GRU modular unit, and hidden layer 2 contains 30 neurons, and the connection mode between the hidden layer is full connection.
An output layer: the number of neurons in the output layer is 2, and the neurons respectively correspond to the direction theta and the speed v of the mobile robot in the global coordinate system at the next planned moment. The hidden layer data output then enters the output layer in a fully connected manner through the activation function.
The most important structure in the above-mentioned GRU network model is the GRU module unit, each unit includes two gate control units, namely an update gate and a reset gate, and the inputs of the two gates are the current time input xtAnd the output h of the previous momentt-1The long-term information can be retained by the cooperation of the two doors. The calculation method of the unit output is shown as the following formula:
zt=σ(xtWz+ht-1Uz)
rt=σ(xtWr+ht-1Ur)
wherein: z is a radical of
t、r
tRespectively representing the output of an update gate and a reset gate at the time t; x is the number of
tAnd h
tInput and output vectors at time t; w
z、W
rAnd W is the module input and update gate, reset gate and
an inter-weight matrix; u shape
z、U
rAnd U is the output and update gate of the module at the time t-1,Reset gate and
the weight matrix of (2).
The GRU module units are expanded according to time sequence as shown in FIG. 4, the GRU module units receive input data according to time sequence, firstly, xt-9Producing an output h after forward propagationt-9,ht-9And xt-8The data are transmitted in this way, and the output of the module at the last moment is the output of the unit structure.
GRU network model training process:
the method comprises the following steps: initializing the weight of the GRU network model by using standard positive-space distribution;
step two: training times k is 0, i is 0;
step three: randomly extracting data [ x ] of 10 continuous time instants from a training sett-9,…,xt]Input network for obtaining corresponding output y through forward propagation processt;
Step four: computing network output ytAnd a corresponding label ltAn error of (2);
step five: updating the weight by using a gradient descent algorithm;
step six: if i is more than or equal to 500, making i equal to 0, randomly selecting 50 sequences in the test set, testing by using the current network, calculating the mean square error, and stopping training if the mean square error in the test set is not reduced for 10 times continuously;
step seven: k +1, i + 1;
step eight: if k is larger than the maximum training times, jumping to the step nine, otherwise, jumping to the step three;
step nine: and finishing the training.
The invention has the following effects:
after the network training is finished, the mobile robot uses the training result of the GRU network model to perform dynamic collision avoidance planning in an unknown environment and compares the dynamic collision avoidance planning with the ant colony algorithm, the result is shown in fig. 5, and as can be seen from the figure, the two algorithms can enable the mobile robot to avoid all obstacles, and the route is smooth, which indicates that the algorithm can ensure the safety of the robot. The average reaction time required by the robot for collision avoidance under the two algorithms is 236ms and 391ms respectively, so that the reaction time of the mobile robot under the GRU network model is obviously short, the real-time performance is higher, and the high efficiency of the algorithm is proved.