CN107739373B - Preparation method of ketoconazole - Google Patents
Preparation method of ketoconazole Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN107739373B CN107739373B CN201710973139.8A CN201710973139A CN107739373B CN 107739373 B CN107739373 B CN 107739373B CN 201710973139 A CN201710973139 A CN 201710973139A CN 107739373 B CN107739373 B CN 107739373B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- formula
- compound shown
- ketoconazole
- reaction
- preparing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- XMAYWYJOQHXEEK-OZXSUGGESA-N (2R,4S)-ketoconazole Chemical compound C1CN(C(=O)C)CCN1C(C=C1)=CC=C1OC[C@@H]1O[C@@](CN2C=NC=C2)(C=2C(=CC(Cl)=CC=2)Cl)OC1 XMAYWYJOQHXEEK-OZXSUGGESA-N 0.000 title claims abstract description 47
- 229960004125 ketoconazole Drugs 0.000 title claims abstract description 47
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 title abstract description 23
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 65
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 37
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 18
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 25
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 20
- RAXXELZNTBOGNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N imidazole Natural products C1=CNC=N1 RAXXELZNTBOGNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 18
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Trifluoroacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(F)(F)F DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000012024 dehydrating agents Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000002378 acidificating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- PYOKUURKVVELLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N trimethyl orthoformate Chemical compound COC(OC)OC PYOKUURKVVELLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- ZPQOPVIELGIULI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-dichlorobenzene Chemical compound ClC1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1 ZPQOPVIELGIULI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanesulfonic acid Chemical compound CS(O)(=O)=O AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N O-Xylene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1C CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N toluene-4-sulfonic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C=C1 JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000008096 xylene Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- FUKOTTQGWQVMQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2-bromoacetyl) 2-bromoacetate Chemical compound BrCC(=O)OC(=O)CBr FUKOTTQGWQVMQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- LSTRKXWIZZZYAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-bromoacetyl bromide Chemical compound BrCC(Br)=O LSTRKXWIZZZYAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- LMBFAGIMSUYTBN-MPZNNTNKSA-N teixobactin Chemical compound C([C@H](C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H](CO)C(=O)N[C@H](CCC(N)=O)C(=O)N[C@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H](CO)C(=O)N[C@H]1C(N[C@@H](C)C(=O)N[C@@H](C[C@@H]2NC(=N)NC2)C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)O[C@H]1C)[C@@H](C)CC)=O)NC)C1=CC=CC=C1 LMBFAGIMSUYTBN-MPZNNTNKSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052794 bromium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- JMMWKPVZQRWMSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N isopropanol acetate Natural products CC(C)OC(C)=O JMMWKPVZQRWMSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940011051 isopropyl acetate Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- GWYFCOCPABKNJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N isovaleric acid Chemical compound CC(C)CC(O)=O GWYFCOCPABKNJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940098779 methanesulfonic acid Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000003944 tolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- YNJBWRMUSHSURL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trichloroacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(Cl)(Cl)Cl YNJBWRMUSHSURL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- GKASDNZWUGIAMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N triethyl orthoformate Chemical compound CCOC(OCC)OCC GKASDNZWUGIAMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 abstract description 11
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 abstract description 11
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 abstract description 6
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 abstract description 6
- WNXJIVFYUVYPPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-dioxolane Chemical compound C1COCO1 WNXJIVFYUVYPPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 abstract description 5
- GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromine Chemical compound BrBr GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 abstract description 5
- 125000003236 benzoyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C(*)=O 0.000 abstract description 4
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 abstract description 4
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 abstract description 3
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 abstract description 2
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 36
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 15
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 11
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 10
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 8
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 7
- WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetonitrile Chemical compound CC#N WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylsulphoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerine Chemical compound OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 5
- 210000000170 cell membrane Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 239000012043 crude product Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 4
- XMCRWEBERCXJCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ethanone Chemical compound CC(=O)C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1Cl XMCRWEBERCXJCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 241000233866 Fungi Species 0.000 description 3
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- -1 p-toluenesulfonyloxy Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 238000010992 reflux Methods 0.000 description 3
- YYROPELSRYBVMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-toluenesulfonyl chloride Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(Cl)(=O)=O)C=C1 YYROPELSRYBVMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241000222120 Candida <Saccharomycetales> Species 0.000 description 2
- BRLQWZUYTZBJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Epichlorohydrin Chemical group ClCC1CO1 BRLQWZUYTZBJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L Magnesium sulfate Chemical compound [Mg+2].[O-][S+2]([O-])([O-])[O-] CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 239000007832 Na2SO4 Substances 0.000 description 2
- VSCWAEJMTAWNJL-UHFFFAOYSA-K aluminium trichloride Chemical compound Cl[Al](Cl)Cl VSCWAEJMTAWNJL-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 2
- 230000000844 anti-bacterial effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000008346 aqueous phase Substances 0.000 description 2
- BRTFVKHPEHKBQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromocyclopentane Chemical compound BrC1CCCC1 BRTFVKHPEHKBQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000005034 decoration Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008686 ergosterol biosynthesis Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 230000002538 fungal effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004128 high performance liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000005457 ice water Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000010413 mother solution Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001953 recrystallisation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910000030 sodium bicarbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium bicarbonate Substances [Na+].OC([O-])=O UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 229910052938 sodium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000002194 synthesizing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- JRMUNVKIHCOMHV-UHFFFAOYSA-M tetrabutylammonium bromide Chemical compound [Br-].CCCC[N+](CCCC)(CCCC)CCCC JRMUNVKIHCOMHV-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- DYLIWHYUXAJDOJ-OWOJBTEDSA-N (e)-4-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)but-2-en-1-ol Chemical compound NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2C\C=C\CO DYLIWHYUXAJDOJ-OWOJBTEDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LRWZZZWJMFNZIK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-chloro-3-methyloxirane Chemical compound CC1OC1Cl LRWZZZWJMFNZIK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241001480043 Arthrodermataceae Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000228212 Aspergillus Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000894006 Bacteria Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000222122 Candida albicans Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000223205 Coccidioides immitis Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001527609 Cryptococcus Species 0.000 description 1
- 102000002004 Cytochrome P-450 Enzyme System Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010015742 Cytochrome P-450 Enzyme System Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010049479 Gastrointestinal fungal infection Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000228402 Histoplasma Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000235395 Mucor Species 0.000 description 1
- 208000031888 Mycoses Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000010195 Onychomycosis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 240000004808 Saccharomyces cerevisiae Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000223230 Trichosporon Species 0.000 description 1
- 201000007096 Vulvovaginal Candidiasis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- VJZJGRMLFMJRGG-BXUZGUMPSA-N [(2s,4r)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methanol Chemical compound O1[C@H](CO)CO[C@]1(C=1C(=CC(Cl)=CC=1)Cl)CN1C=NC=C1 VJZJGRMLFMJRGG-BXUZGUMPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000007171 acid catalysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000843 anti-fungal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940121375 antifungal agent Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000003429 antifungal agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010533 azeotropic distillation Methods 0.000 description 1
- PASDCCFISLVPSO-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoyl chloride Chemical compound ClC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 PASDCCFISLVPSO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940095731 candida albicans Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000007697 cis-trans-isomerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 201000003486 coccidioidomycosis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000006297 dehydration reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010511 deprotection reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037304 dermatophytes Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000000950 dibromo group Chemical group Br* 0.000 description 1
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- GKIPXFAANLTWBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N epibromohydrin Chemical group BrCC1CO1 GKIPXFAANLTWBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000007062 hydrolysis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006460 hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000015181 infectious disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000002452 interceptive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000004193 piperazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000006239 protecting group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009885 systemic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D405/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings linked by a carbon chain containing only aliphatic carbon atoms
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Plural Heterocyclic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine synthesis, and particularly relates to a preparation method of ketoconazole. The preparation method of ketoconazole provided by the invention comprises the following steps: s101: and (2) mixing the compound shown in the formula I and the compound shown in the formula II in an acid medium for reaction to obtain the ketoconazole. The compound shown in the formula I and the compound shown in the formula II have large steric hindrance, so that the cis-trans selectivity of 1, 3-dioxolane formed by the mixed reaction of the compound shown in the formula I and the compound shown in the formula II is remarkably improved, the step of removing benzoyl is omitted, the production period of ketoconazole is shortened, the cost is reduced, the use of dangerous substances such as liquid bromine is reduced, and the technical defects of multiple steps, low yield and low purity in the prior art in the ketoconazole synthesis process are overcome.
Description
Technical Field
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine synthesis, and particularly relates to a preparation method of ketoconazole.
Background
Ketoconazole (Ketoconazole) is an imidazole antifungal drug, has a structural formula shown as the following formula III, and has a chemical name of 1- (4- (4- ((2- ((1H-imidazole-1-yl) methyl) -2- (2, 4-dichlorophenyl) -1, 3-dioxolan-4-yl) methoxyl) piperazine-1-yl) ethanone.
In 1978, ketoconazole was researched and developed by the pharmaceutical company of Yankee, Belgium, and has an action mechanism of inhibiting the biosynthesis of ergosterol on fungal cell membranes, influencing the permeability of the cell membranes and inhibiting the growth of the cell membranes. Has antibacterial and bactericidal effects on dermatophytes, yeast (Candida, Pityrosporum, Torulopsis, Cryptococcus), biphase fungi and fungi; except for entomomycetales, the product has weak effect on aspergillus, trichosporon, some darkling sporophyceae and mucor. The product has effect in inhibiting ergosterol biosynthesis on fungal cell membrane by interfering with activity of cytochrome P-450 of fungi highly selectively. Can be used for treating superficial and deep mycoses, such as skin and nail tinea, vaginal candidiasis, gastrointestinal fungal infections, etc., and systemic infections caused by Candida albicans, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasma bacteria, etc.
Heeres et al (j.med.chem.1979.22(8).1003) reported for the first time a synthetic route for ketoconazole as shown in figure 1.2, 4-dichloroacetophenone and glycerol are subjected to acid catalysis to obtain a 1, 3-dioxolane intermediate, the bromocyclopentane intermediate obtained by the reaction without separation and liquid bromine is continuously separated from benzoyl chloride to obtain cis-bromobenzoate, the cis-bromobenzoate is then subjected to reaction with imidazole and hydrolysis to remove a benzoyl protecting group, the cis-bromobenzoate is then subjected to reaction with p-toluenesulfonyl chloride to obtain active ester, and the active ester is reacted with a piperazine side chain to obtain ketoconazole. The synthetic route is long, and has 7 steps in total, wherein the first step of reaction has low steric hindrance to cause poor cis-trans isomerization selectivity, a benzoyl protecting group has to be introduced for removing the trans isomer, then the protecting group needs to be removed, and finally the whole route has two steps, and more trans isomers are removed, so that the yield is relatively low, and the production cost is high.
No other new synthesis route is found in the literature reports afterwards, and the literature (research on synthesis process of antifungal ketoconazole intermediate, li haibo, university of sichuan, thesis of master scholars) reports a method for obtaining bromocyclopentane intermediate by reacting 2, 4-dichloroacetophenone with liquid bromine first and then with glycerol, but because the 2, 4-dichloroacetophenone and the liquid bromine have poor selectivity, a dibromo product is easily formed, the purification difficulty is high, and the synthesis route has no advantages compared with Herres. Other literature reports have focused on how to optimize the route to Herres.
In summary, a preparation method for synthesizing ketoconazole, which is more environment-friendly, simpler, high in yield and high in purity, has not yet been researched.
Disclosure of Invention
In view of the above, the invention provides a preparation method of ketoconazole, which can effectively solve the technical defects of multiple steps, low yield and low purity of the current ketoconazole synthesis process.
The invention provides a preparation method of ketoconazole, which comprises the following steps:
s101: mixing a compound shown as a formula I and a compound shown as a formula II in an acid medium for reaction to obtain ketoconazole,
preferably, the acidic medium is one or more of methanesulfonic acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, sulfuric acid, acetic acid, trifluoroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid.
Preferably, the acidic medium is trifluoroacetic acid.
Preferably, the molar ratio of the acidic medium to the compound of formula I is greater than 1: 3.
preferably, the reaction system of the compound shown in the formula I and the compound shown in the formula II in the S101 further comprises a dehydrating agent; the compound shown in the formula I, the compound shown in the formula II and a dehydrating agent are mixed in an acid medium to carry out chemical reaction or form an azeotrope to remove water generated by the mixed reaction of the compound shown in the formula I and the compound shown in the formula II so as to promote the S101 reaction.
More preferably, the compound represented by the formula I, the compound represented by the formula II and the dehydrating agent are mixed in an acidic medium to carry out a chemical reaction, specifically, the dehydrating agent is added to carry out azeotropic removal of water produced in the mixed reaction of the compound represented by the formula I and the compound represented by the formula II so as to promote the reaction.
Preferably, the dehydrating agent is one or more of toluene, xylene, triethyl orthoformate and trimethyl orthoformate.
Preferably, the dehydrating agent is toluene.
Wherein the azeotropic dehydration reaction is specifically carried out at 25-60 ℃ for 16 hours.
Preferably, the synthesis steps of the compound shown in the formula I are as follows:
s201: reacting a compound shown as a formula IV with a compound shown as a formula V in water and an organic solvent to obtain a compound shown as a formula I,
Wherein the OMs are specifically p-toluenesulfonyloxy; the OTs are specifically methylsulfonyloxy;
more preferably, the compound shown in the formula V is epichlorohydrin or epibromohydrin.
Preferably, the organic solvent is one or more of toluene, xylene, ethyl acetate, isopropyl acetate, acetone, methanol and ethanol.
Preferably, the synthesis of the compound of formula ii is as follows:
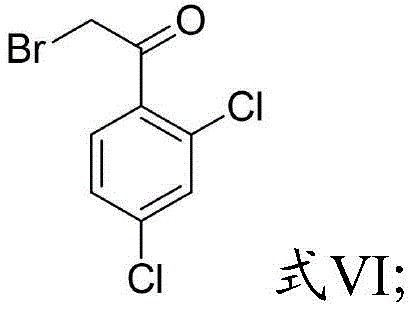
s301: m-dichlorobenzene and 2-bromoacetic anhydride or 2-bromoacetyl bromide are mixed and reacted to obtain a reaction solution containing a formula VI,
s302: and mixing the reaction solution containing the formula VI with imidazole for reaction to obtain the compound shown in the formula II.
The invention aims to overcome the technical defects of multiple steps and low yield and purity in the prior art for synthesizing ketoconazole, and therefore, the preparation method of ketoconazole disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: mixing a compound shown in a formula I and a compound shown in a formula II in an acid medium for reaction to obtain ketoconazole, wherein,
the compound shown in the formula I and the compound shown in the formula II have large steric hindrance, so that the cis-trans selectivity of 1, 3-dioxolane formed by the mixed reaction of the compound shown in the formula I and the compound shown in the formula II is remarkably improved, the step of removing benzoyl is omitted, finally, the production period and the cost are greatly reduced, and the use of dangerous substances such as liquid bromine is reduced. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is a ketoconazole synthesis route with high industrial feasibility, environmental friendliness, controllable quality and low cost.
Drawings
In order to more clearly illustrate the embodiments of the present invention or the technical solutions in the prior art, the drawings used in the description of the embodiments or the prior art will be briefly described below.
FIG. 1 shows a synthesis scheme of ketoconazole reported in the literature;
FIG. 2 shows the chemical structure of ketoconazole;
FIG. 3 shows a synthetic scheme of the present invention providing a process for the preparation of ketoconazole;
FIG. 4 shows a synthetic route to the disclosed formula I of the present invention;
FIG. 5 shows a synthetic route to the disclosed formula II of the present invention;
fig. 6 shows an HPLC chart of analytical detection of ketoconazole prepared in example 1 according to the methods for substances in each theory of ketoconazole in the chinese pharmacopoeia 2015 edition.
Detailed Description
The invention provides a preparation method of ketoconazole, which is used for solving the technical defects of multiple steps, low yield and low purity of the ketoconazole synthesized in the prior art.
The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below, and it is obvious that the described embodiments are only a part of the embodiments of the present invention, and not all embodiments. All other embodiments, which can be derived by a person skilled in the art from the embodiments given herein without making any creative effort, shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
The raw materials of the following examples are all commercially available or self-made.
Example 1
Referring to fig. 3 to 5, the present invention provides a preparation method of ketoconazole, and the specific preparation steps of example 1 are as follows:
s401: the preparation method of the compound shown in the formula II comprises the following steps: preparing a 500mL three-necked bottle, adding dry dichloromethane (280mL) and aluminum trichloride (26.68g, 0.20mol), slowly dropping 2-bromoacetic anhydride (28.59g, 0.11mol) at 25 ℃, stirring for 30 minutes, dropping m-dichlorobenzene (14.70g, 0.1mol), heating up, refluxing and stirring for 16 hours to obtain a reaction solution, slowly dropping the reaction solution into ice water, controlling the temperature to be not more than 10 ℃, completely dropping to 25 ℃, stirring for 30 minutes, separating, discarding the upper layer, washing the lower layer twice with 30mL of water, drying with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, concentrating to obtain a light yellow solid compound shown in the formula VI, wherein the yield is 24.1g, the yield is 90%, and directly using the product in the next step, or recrystallizing with ethanol to obtain a white solid compound containing the compound shown in the formula VI; preparing a 250mL three-necked bottle, adding a compound shown in a formula VI (21.7g and 0.09mol) and dichloromethane (150mL), adding imidazole (6.12g and 0.09mol) at a temperature not exceeding 10 ℃, reacting at 5-10 ℃ for 5 hours after the addition is finished, then adding dichloromethane (50mL), adjusting the pH to 12 by using a 10% NaOH aqueous solution, layering, discarding the upper layer, washing the lower layer twice by using water (30mL), drying, and concentrating dichloromethane to obtain a light yellow solid compound shown in a formula II, wherein the yield is 19.97g, and the yield is 87%, and the light yellow solid compound is directly used in the next step.
S402: a process for the preparation of a compound of formula I: preparing a 250mL three-neck flask, adding water (60mL), NaOH (4.40g, 0.11mol) and toluene (100mL), adding tetrabutylammonium bromide (0.5g) and a compound (22.03g, 0.10mol) shown in formula IV and epichlorohydrin (13.88g, 0.15eq.) at 25 ℃ for reacting for 16 hours, separating out a product, then cooling to 5 ℃, filtering, washing with water and toluene, adding a wet product into water (100mL), and then adding a mass fraction of the wet product to be 30% sulfuric acid to pH 2, stirring at 25 deg.C for 24 hr, and adding saturated NaHCO3Adjusting the pH to greater than 8, extracting the aqueous phase three times with dichloromethane (60mL), combining the three dichloromethane layers, and adding anhydrous Na2SO4Drying and then concentrating to dryness gave the compound of formula I in 20.07g yield of 75% for the next reaction or recrystallization from acetonitrile/diethyl ether.
S403: preparation of ketoconazole: preparing a 250mL three-necked bottle, sequentially adding DMSO (60mL), toluene (20mL), a compound shown in formula I (14.72g, 0.05mol) and a compound shown in formula II (12.76g, 0.05mol), slowly dropwise adding trifluoroacetic acid (20.52g, 0.18mol), heating, refluxing for 16 hours by using a water separator, cooling to 25 ℃, adjusting the pH to 9 by using a 30% NaOH aqueous solution, slowly dripping water (150mL) into the reaction system to separate out ketoconazole, cooling to 5 ℃, stirring for 1 hour, filtering, washing with water until the pH of a mother solution is neutral to obtain a crude product, recrystallizing and drying the crude product in ethyl acetate to obtain a product meeting the standards of Chinese pharmacopoeia, wherein the yield is 21.26g and 80%.
Example 2
Referring to fig. 3 to 5, the present invention provides a preparation method of ketoconazole, and the specific preparation steps of example 1 are as follows:
s501: the preparation method of the compound shown in the formula II comprises the following steps: adding dry dichloromethane (280mL) and aluminum trichloride (26.68g, 0.20mol) into a 500mL three-necked bottle, slowly dropping 2-bromoacetyl bromide (22.20g, 0.11mol) at 25 ℃, stirring for 30 minutes, then dropping m-dichlorobenzene (14.70g, 0.1mol), heating up, refluxing and stirring for 16 hours to obtain a reaction solution, slowly dropping the reaction solution into ice water at a temperature not exceeding 10 ℃, heating to 25 ℃ after dropping, stirring for 30 minutes, separating liquid, discarding the upper layer, washing the lower layer twice with 30mL of water, drying with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, concentrating to obtain a light yellow solid compound shown in the formula VI, and directly using 21.96g, 82%) in the next step, or recrystallizing with ethanol to obtain a white solid compound shown in the formula VI; a250 mL mechanically stirred three-necked flask was prepared, the compound of formula VI (21.7g, 0.09mol), triethylamine (10.93g, 0.108mol), dichloromethane (150mL) and imidazole (6.13g, 0.09mol) were added while controlling the temperature not to exceed 10 ℃, after the addition, the reaction was carried out at 5-10 ℃ for 5 hours, dichloromethane (50mL) was added, the upper layer was discarded after separation, the lower layer was washed twice with water (30mL), and after drying, dichloromethane was concentrated to give the compound of formula II as a pale yellow solid with a yield of 21.12g and a yield of 92% and was used directly in the next step.
S502: a process for the preparation of a compound of formula I: preparing a 250mL three-neck flask, adding water (60mL), NaOH (4.40g, 0.11mol) and acetone (100mL), adding tetrabutylammonium bromide (0.5g) and a compound (22.03g, 0.10mol) shown in formula IV at 25 ℃, adding epoxy chloropropane (13.88g, 0.15eq.) for reacting for 16 hours, separating out a product, then cooling to 5 ℃, filtering, washing with water and acetone, adding a wet product into water (100mL), then adjusting the pH to 2 by using sulfuric acid with the mass fraction of 30%, stirring and reacting for 24 hours at 25 ℃, and using saturated NaHCO3Adjusting the pH to greater than 8, extracting the aqueous phase three times with dichloromethane (60mL), combining the three dichloromethane layers, and adding anhydrous Na2SO4Drying and then concentrating to dryness gave the compound of formula I in 17.93g yield 67% for the next reaction or recrystallization from acetonitrile/diethyl ether.
S503: the preparation method of ketoconazole comprises the following steps: preparing a 250mL three-necked bottle, sequentially adding DMSO (60mL), trimethyl orthoformate (3.54g, 0.03mol), a compound shown as a formula I (14.72g, 0.05mol) and a compound shown as a formula II (12.76g, 0.05mol), slowly dropwise adding acetic acid (10.81g, 0.18mol), heating to 60 ℃, reacting for 16 hours, cooling to 25 ℃, adjusting the pH to 9 by using a 30% NaOH aqueous solution, slowly dripping water (150mL) into the reaction system to separate out ketoconazole, cooling to 5 ℃, stirring for 1 hour, filtering, washing with water until the pH of a mother solution is neutral to obtain a crude product, recrystallizing the crude product in ethyl acetate to obtain a product meeting the standards of Chinese pharmacopoeia, wherein the yield is 19.83g, and the yield is 75%.
Example 3
The purity of the obtained ketoconazole is detected, and the result is shown in fig. 6, and fig. 6 is an HPLC diagram of the ketoconazole prepared in example 1 of the present invention, which is analyzed and detected according to the methods of the relevant substances in each theory of ketoconazole in chinese pharmacopoeia 2015 edition, and the result shows that the purity is 99.076%, and it can be known from fig. 6 that 1, 3-dioxolane has very high cis-trans selectivity, and the very high cis-trans selectivity can be obtained without additionally adding the reaction of upper protection and deprotection, so that the cis-trans selectivity of 1, 3-dioxolane can be significantly improved by using the preparation method of the present invention.
The foregoing is only a preferred embodiment of the present invention, and it should be noted that, for those skilled in the art, various modifications and decorations can be made without departing from the principle of the present invention, and these modifications and decorations should also be regarded as the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (9)
1. A method for preparing ketoconazole, which is characterized by comprising the following steps:
s101: mixing a compound shown as a formula I and a compound shown as a formula II in an acidic medium for reaction to obtain ketoconazole, wherein the molar using amount ratio of the acidic medium to the compound shown as the formula I is more than 1: 3;
2. the method for preparing ketoconazole according to claim 1, wherein the acidic medium is one or more of methanesulfonic acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, sulfuric acid, acetic acid, trifluoroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid.
3. The method for preparing ketoconazole according to claim 2, wherein the acidic medium is trifluoroacetic acid.
4. The method for preparing ketoconazole according to claim 1, wherein the reaction system of S101 further comprises a dehydrating agent; the compound shown in the formula I, the compound shown in the formula II and a dehydrating agent are mixed in an acid medium to carry out chemical reaction or form an azeotrope to remove water generated by the mixed reaction of the compound shown in the formula I and the compound shown in the formula II so as to promote the S101 reaction.
5. The method for preparing ketoconazole according to claim 4, wherein the dehydrating agent is one or more of toluene, xylene, triethyl orthoformate and trimethyl orthoformate.
6. The method for preparing ketoconazole according to claim 5, wherein the dehydrating agent is toluene.
7. The method for preparing ketoconazole according to claim 1, wherein the compound of formula I is synthesized by the following steps:
s201: reacting a compound shown as a formula IV with a compound shown as a formula V in water and an organic solvent to obtain a compound shown as a formula I,
wherein X of formula V is Cl, Br, I, OMs or OTs.
8. The method of claim 7, wherein the organic solvent is one or more of toluene, xylene, ethyl acetate, isopropyl acetate, acetone, methanol, and ethanol.
9. The method for preparing ketoconazole according to claim 1, wherein the compound of formula ii is synthesized by the following steps:
s301: m-dichlorobenzene and 2-bromoacetic anhydride or 2-bromoacetyl bromide are mixed and reacted to obtain a reaction solution containing a formula VI,
s302: and mixing the reaction solution containing the formula VI with imidazole for reaction to obtain the compound shown in the formula II.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710973139.8A CN107739373B (en) | 2017-10-18 | 2017-10-18 | Preparation method of ketoconazole |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710973139.8A CN107739373B (en) | 2017-10-18 | 2017-10-18 | Preparation method of ketoconazole |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN107739373A CN107739373A (en) | 2018-02-27 |
| CN107739373B true CN107739373B (en) | 2021-01-15 |
Family
ID=61237338
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710973139.8A Active CN107739373B (en) | 2017-10-18 | 2017-10-18 | Preparation method of ketoconazole |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN107739373B (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN117736148A (en) * | 2023-08-16 | 2024-03-22 | 盐城凯利药业有限公司 | Production process of ketoconazole |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101302213A (en) * | 2008-06-30 | 2008-11-12 | 寿光富康制药有限公司 | Preparation of methanesulfonic acid active ester |
| CN103724271A (en) * | 2014-01-15 | 2014-04-16 | 上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院卢湾分院 | Substituted imidazole-1-ethylene compound and application thereof |
-
2017
- 2017-10-18 CN CN201710973139.8A patent/CN107739373B/en active Active
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101302213A (en) * | 2008-06-30 | 2008-11-12 | 寿光富康制药有限公司 | Preparation of methanesulfonic acid active ester |
| CN103724271A (en) * | 2014-01-15 | 2014-04-16 | 上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院卢湾分院 | Substituted imidazole-1-ethylene compound and application thereof |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| Kazuhiro Yamada,等.Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel azole derivatives as selective potent inhibitors of brassinosteroid biosynthesis.《Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry》.2013,第21卷(第9期),第2451-2461页. * |
| Stereoselective Syntheses of Both Enantiomers of Ketoconazole from (R)- and (S)-Epichlorohydrin;Pelayo Camps,等;《Tetrahedron: Asymmetry》;19951231;第6卷(第6期);第1283-1294页 * |
| Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel azole derivatives as selective potent inhibitors of brassinosteroid biosynthesis;Kazuhiro Yamada,等;《Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry》;20131231;第21卷(第9期);第2451-2461页 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN107739373A (en) | 2018-02-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US4119641A (en) | 2-Aryl-4-aryloxymethyl-1,3-dioxolanes | |
| KR900005696B1 (en) | Process for preparing substituted 1- hydroxyethyltriazolyl derivatives | |
| CN103588730B (en) | One prepares the synthetic method of triazole fungicide type (III) compound | |
| EP2847173B1 (en) | Method for preparation of medetomidine | |
| CN108623456B (en) | Preparation method of butylphthalide and pharmaceutical intermediate thereof | |
| CN107739373B (en) | Preparation method of ketoconazole | |
| EP3929191A1 (en) | Method for preparing voriconazole and intermediate thereof | |
| Wahbi et al. | Aromatic ethers of 1-aryl 2-(1H-azolyl) ethanol: Study of antifungal activity | |
| CN104774195A (en) | Optically pure itraconazole key intermediate, synthetic method thereof, and method for synthesizing optically pure itraconazole from the intermediate | |
| JPH03163077A (en) | Fungicidal 4- (4- (4- (4- ((2-(2, 4-difluorophenyl)- 2-(1h-azolylmethyl)-1, 3-dioxolane- 4-yl) methoxy) phenyl) -1-piperazinyl) phenyl) triazolones and imidazolones | |
| CN106117186B (en) | A kind of preparation method of voriconazole and its intermediate | |
| JP6851149B2 (en) | Method for producing piperidine compound | |
| JPS6135196B2 (en) | ||
| CN106008449A (en) | Cheap synthetic method of watermelon ketone | |
| CN102432566B (en) | 2-(4-phenoxyphenyl)oxirane and preparation method and application thereof | |
| BR102013027313A2 (en) | Process for the selective preparation of (1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl) alkanols, hydrazinyl alkanol compound obtained by such process and its use | |
| CN114315609A (en) | Process for preparing cis-2-aminocyclohexanol | |
| US4209447A (en) | Imidazole derivatives and intermediates in their preparation | |
| Landais et al. | Studies on the Mercury‐Desilylation of Chiral Cyclopropylmethylsilanes‐A Stereocontrolled Access to Carba‐Sugars | |
| US20110288315A1 (en) | Process for production of optically active compound | |
| CN102786488A (en) | Preparation method of intermediate for synthesis of micafungin and derivative thereof | |
| EP2456758B1 (en) | A process for preparing trisubstituted phenyl derivatives comprising a (1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)alkyl group | |
| JP2000505466A (en) | Azole compounds with antifungal activity for human and veterinary use | |
| JP4201268B2 (en) | Method for producing imidazole derivatives and salts thereof | |
| PT86890B (en) | Process for the preparation of 1- (1-ARYL-2-HYDROXY-ETHYL) - IMIDAZOES AND THEIR SALTS AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS CONTAINING THEM |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |