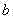CN103313298A - Node redundancy detection method for heterogeneous sensor network - Google Patents
Node redundancy detection method for heterogeneous sensor network Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN103313298A CN103313298A CN2013101038586A CN201310103858A CN103313298A CN 103313298 A CN103313298 A CN 103313298A CN 2013101038586 A CN2013101038586 A CN 2013101038586A CN 201310103858 A CN201310103858 A CN 201310103858A CN 103313298 A CN103313298 A CN 103313298A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- node
- redundancy
- neighbor
- network
- redundant
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D30/00—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks
- Y02D30/70—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks in wireless communication networks
Landscapes
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
- Small-Scale Networks (AREA)
Abstract
The invention relates to a node redundancy detection method for a heterogeneous sensor network, wherein judgment is performed with different redundancy rules by adopting an algorithm that nodes are classified according to positions of neighbor nodes. Aiming at a scheduling method for covering nodes in a traditional isomorphic network, the method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: classifying the neighbor nodes into three types according to node positions in a sensor network with two sensing distances; and judging with different redundancy rules so as to judge whether the nodes can sleep. Meanwhile, the traditional redundancy judgment flow is also changed so as to achieve the purpose of preventing blind points from being covered. The problem of redundancy caused by high-density deployment of nodes is solved, and the life cycle of the network is prolonged.
Description
Technical field
The present invention relates to a kind of method of novel judgement heterogeneous wireless sensor network interior nodes redundancy, belong to the field of node scheduling in the sensor network, particularly a kind of for guaranteeing
KIn the situation of coverage rate, realize heterogeneous wireless sensor network node scheduling method with the classification situation of neighbor node.
Background technology
Wireless sensor network is that over the past two years, wireless sensor network had obtained the expert and paid close attention to widely and study along with micro-electro-mechanical systems the unify development of wireless communication technology and a kind of new network of occurring.In general, wireless sensor network by be deployed in a large number the cheapness in the monitored area, miniature sensor node forms, form the network system of multi-hop ad hoc by communication, object information in synergistically perception, the acquisition and processing network monitor zone, and an information that monitors sends to the observer.
Because the restriction of the various factorss such as cost and volume, the battery capacity of single-sensor node is often limited.In addition since sensor node quantity many, have a very wide distribution, and the circumstance complication of deployment region, some zone or even personnel can not arrive, thereby the node battery is replaced and the supplemental node energy all is infeasible.So how in the situation that the life span of individual node energy constraint, the whole network system of the shorter prolongation of life span is a significant challenge in the Design of Wireless Sensor Network.
In order in the situation of the performance that does not affect network, to prolong the life cycle of whole network, normally used method is just to strengthen the quantity of node when disposing, and then by node is dispatched, utilize the redundancy determination rule to close redundant node, energy saving reaches the also purpose of prolong network lifetime of improving service quality.
Main target when the design node dispatching algorithm has:
(1) energy efficiency: just must make the least possible node in running order the life cycle that will prolong network under the prerequisite of the service quality that does not affect network.
(2) spreadability: how to guarantee in the network coverage that each target area is at least in the sensing range of a sensor node;
(3) connectedness: Node Scheduling Algorithms in Line should guarantee that the covering of monitored area and this regional active node are communicated with, thereby guarantees the timely transmission of data message.
These solution of problems can make whole sensor network come monitoring objective with the energy cost of minimum, thereby reach the purpose that prolongs network lifetime.
Wireless sensor network can be divided into homogeneous network and heterogeneous network according to node sensing radius is whether identical.
At present, all concentrate on the network to isomorphism for the research great majority of wireless sensor network, be that all node resources all are the same in the network, the node type of research is relatively single, and in the configuration of the sensor network of reality and using, because the shape of monitored area etc., often heterogeneous network can be obtained better effect.So this paper article the determination methods of node redundancy in a kind of heterogeneous sensor network.
Summary of the invention
Technical problem:The objective of the invention is to propose a kind of node redundancy detection side for heterogeneous sensor network
Method is judged redundant node in the heterogeneous network, thus the life cycle of effectively improving network.
Technical scheme:For the dispatching method of overlay node in traditional homogeneous network, the present invention proposes the method that the node redundancy in the heterogeneous wireless sensor network is judged in.The method is in the sensor network that two kinds of distance of reaction are arranged, and neighbor node is divided three classes by node location, judge by different redundant rules, thereby whether decision node can dormancy.Simultaneously, also traditional redundancy determination flow process is made change, reached the purpose that prevents from covering the blind spot appearance.
Node redundancy detection method for heterogeneous sensor network of the present invention according to the position relationship of effective neighbor node and node, is divided into three kinds with remaining effective neighbor node,
Class1: node
Be node
Effective neighbor node, and
,
, this moment we
As first kind neighbor node, be designated as
Wherein
S (a) and S (b)Be respectively node
aAnd node
bThe sensing range area,
RaWith
RbBe respectively node
aAnd node
bThe perception radius,
D (a, b)Refer to node
aAnd node
bBetween geometric distance; Satisfy the network coverage neighbor node number of appointment
Satisfy condition
, wherein
The network coverage for appointment;
Type 2: node satisfies
, namely
And
This moment we
As the Equations of The Second Kind neighbor node, be designated as
, according to how much calculating, in this case, central angle is
The dash area area that two circles intersect is
In this case, the number of calculating the neighbor node of the coverage rate satisfy as can be known appointment is
Type 3: node satisfies
, this moment handle
As the 3rd class neighbor node, be designated as
The intersection area is
Need to satisfy and specify the neighbor node number of coverage rate to be
Redundant node is judged:
A) first kind neighbor node number
Number be at least
, the Equations of The Second Kind neighbor node
With the 3rd class neighbor node
Number be at least
Perhaps
Judge the concrete steps in redundant stage:
Step1: for the complete node of initialization, by from small to large ordering, the node that energy is low carries out first the redundancy assessment according to the node primary power;
Step2: whether redundant with the redundant node judging rules decision node that proposes in the literary composition;
Step3: if node redundancy is then waited for
Prepare after time to enter resting state, node is not redundant, then still is operating state;
Step4: prepare to enter the node of resting state, inform message RAM if receive redundancy, just carry out the redundancy assessment, assessment does not satisfy condition, and enters operating state, and assessment satisfies condition, and then broadcasts redundancy and informs message RAM, and enter resting state.
Beneficial effect:The present invention relates to a kind of method of novel judgement heterogeneous wireless sensor network interior nodes redundancy and realize heterogeneous wireless sensor network node scheduling method with the classification situation of neighbor node, be mainly used in solving the problem of energy consumption in the heterogeneous network.In the research of most of sensor network, we only pay close attention to the situation of homogeneous network.This patent after considering real world applications, in the heterogeneous network that research emphasis is placed on, the node scheduling situation of primary study heterogeneous network.In general homogeneous network, we with the method for random schedule artificial close the life cycle that some nodes prolong network, in this patent method of selecting redundant node is improved, used the classify method of comparison of neighbor node is selected redundant node.
Therefore, beneficial effect of the present invention comprises the scope that has increased node scheduling research, has reduced blindness and the time complexity of selecting redundant node, has realized improving the purpose of network lifecycle.
Description of drawings
Fig. 1 is sponsor's sector schematic diagram.
Fig. 6 is the central angle of Equations of The Second Kind neighbor node
The calculating schematic diagram.
Fig. 7 is
As
The schematic diagram of the 3rd class neighbor node.
Fig. 8 is the flow chart of embodiment.
Embodiment
The present invention is based on the redundance judging method of heterogeneous network, taked the neighbor node Judgments Strategies In The Categorical to learn whether node can enter resting state.
One, transducer covering problem:
1. identical induction range:
Definition 1:Neighbours.Node
Neighbours collection may be defined as
, wherein
Be the set of node of deployment region,
The expression node
To node
Between distance.
Be node
Sensing range, for node
, it for the mathematic condition of redundant node is
, the sensing range node of the neighbor node that they are all
The superset of sensing range, its expression formula is
Definition 2:Shared sector.Such as Fig. 1, node
With node
Be neighbours, both induction regions intersect at
With
2 points, the sector of formation is by the limit
The limit
And arc
Form, this sector region can be defined as node
To node
The sector, note is done
, the central angle of this sector is
Be sensing range is identical
Wireless sensor network in, by
Can derive
As shown in Figure 2, only need to judge whether the set of central angle can realize
The condition of all standing of namely satisfying.Calculate as can be known according to how much
By
As can be known
Different induction ranges:
Although the node in the zone of wireless sensor network is high-density deployment, do not refer to that all neighbor nodes all are that effectively in the present invention, we only consider the situation of effective neighbor node.In the sensor network of isomery, effectively neighbor node refers to for node
, the arbitrary node in the zone
As long as satisfy
, then arbitrarily
All belong to node
Effective neighbor node.
As shown in Figure 3, work as node
Be node
Effective neighbor node, and satisfy condition
,
The time, i.e. node
Induction zone comprise node fully
Induction zone, in this case, do not need through redundancy assessment node
Can directly close.
According to the position relationship of effective neighbor node and node, we are divided into three kinds with remaining effective neighbor node.
Class1: node
Be node
Effective neighbor node, and satisfy condition
With
, as shown in Figure 4, this moment we
As first kind neighbor node, be designated as
Type 2: node satisfies
, namely satisfy condition
With
As shown in Figure 5, this moment we
As the Equations of The Second Kind neighbor node, be designated as
As shown in Figure 6, can be calculated central angle according to how much is
Type 3: node satisfies
, as shown in Figure 7, this moment we
As the 3rd class neighbor node, be designated as
Two. the coverage rate in the heterogeneous network:
Definition 3:Areal coverage: for any point in the given target area, its coverage rate refers to that this point is at least by the time of the perception of sensor node zone covering and the ratio of its network operation time.Mathematic expectaion with the coverage rate in whole zone in this patent is defined as the network coverage, that is:
, wherein
Cover the probability of a given area for each sensor node,
Number for node in the zone.
The network coverage is satisfied
, wherein,
Be given coverage rate lower limit.The number of probes that namely satisfies the coverage rate in the specified scope satisfies:
For first kind neighbor node
,
Be node
Sensing range in the number of the neighbor node that satisfies condition.Condition handle according to the network coverage
Substitution can get,
Satisfy condition
For the Equations of The Second Kind neighbor node
, by known central angle
Can obtaining then, the crossing dash area area of two circles is
In this case, the number of calculating the neighbor node of the coverage rate satisfy as can be known appointment is
For the 3rd class neighbor node
, the area of dash area calculated and equally with type 2 to be this moment
In like manner, need the satisfied neighbor node number of coverage rate of specifying to be
Three. the redundancy determination rule:
3.
;
For convenience of description, our supposition has following application example.In the appointed area
In, 100 nodes of random placement, the induction radius of the node of a part is
, the induction radius of remainder is
The transmission radius of two kinds of nodes all is
Starting stage:
After node deployment is wireless sensor network, organize themselves into net after, just carry out the setting of starting stage, in the starting stage, by communicating by letter between node and the node, each node is learnt the positional information of oneself and the information of each neighbor node.
At first, individual node sends the position and informs message PAM in its communication radius, wherein comprise the positional information of node self among the PAM, ID number and the current energy that has.In order to prevent losing of channel confliction and information, each node is time of random wait before sending PAM message
Simultaneously, in order to solve connective problem, according to different radiuses
With
, communication radius is made as 2
With 2
After the PAM of all nodes message sends, can receive location message and the energy message of its neighbor node.
After collecting the information of neighbor node, node just is in state undetermined.In traditional node scheduling, be all to use redundant rule to judge traversal once all nodes, then obtain redundant node, among the present invention according to precedence function f (E
i, ID
i) decide which node to be introduced into the redundancy determination stage.E wherein
iBe the current energy of node a, ID
iBe ID number of node a, precedence function f and ENERGY E
iBe the inverse proportion function, the node that namely energy is lower more is introduced into the redundancy determination stage.Deterministic process as shown in Figure 8.
Concrete steps:
Step1: for the complete node of initialization, according to precedence function
, the node that energy is low carries out first the redundancy assessment.
Step2: whether redundant with redundant Rules of Assessment decision node.
Step3: if node redundancy is then waited for
Prepare to enter resting state after time.Node is not redundant, then still is operating state.
Step4: prepare to enter the node of resting state, inform message RAM if receive redundancy, just carry out the redundancy assessment, assessment does not satisfy condition, and enters operating state, and assessment satisfies condition, and then broadcasts redundancy and informs message RAM, and enter resting state.
Claims (1)
1. a node redundancy detection method that is used for heterogeneous sensor network is characterized in that according to the position relationship of effective neighbor node and node remaining effective neighbor node being divided into three types,
Class1: node
Be node
Effective neighbor node, and
,
, this moment we
As first kind neighbor node, be designated as
Wherein
S (a) and S (b)Be respectively node
aAnd node
bThe sensing range area,
RaWith
RbBe respectively node
aAnd node
bThe perception radius,
D (a, b)Refer to node
aAnd node
bBetween geometric distance; Satisfy the network coverage neighbor node number of appointment
Satisfy condition
, wherein
The network coverage for appointment;
Type 2: node satisfies
, namely
And
This moment we
As the Equations of The Second Kind neighbor node, be designated as
, according to how much calculating, in this case, central angle is
The dash area area that two circles intersect is
In this case, the number of calculating the neighbor node of the coverage rate satisfy as can be known appointment is
Type 3: node satisfies
, this moment handle
As the 3rd class neighbor node, be designated as
The intersection area is
Need to satisfy and specify the neighbor node number of coverage rate to be
Redundant node is judged:
A) first kind neighbor node number
Number be at least
, the Equations of The Second Kind neighbor node
With the 3rd class neighbor node
Number be at least
Perhaps
Judge the concrete steps in redundant stage:
Step1: for the complete node of initialization, by from small to large ordering, the node that energy is low carries out first the redundancy assessment according to the node primary power;
Step2: whether redundant with the redundant node judging rules decision node that proposes in the literary composition;
Step3: if node redundancy is then waited for
Prepare after time to enter resting state, node is not redundant, then still is operating state;
Step4: prepare to enter the node of resting state, inform message RAM if receive redundancy, just carry out the redundancy assessment, assessment does not satisfy condition, and enters operating state, and assessment satisfies condition, and then broadcasts redundancy and informs message RAM, and enter resting state.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2013101038586A CN103313298A (en) | 2013-03-28 | 2013-03-28 | Node redundancy detection method for heterogeneous sensor network |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2013101038586A CN103313298A (en) | 2013-03-28 | 2013-03-28 | Node redundancy detection method for heterogeneous sensor network |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN103313298A true CN103313298A (en) | 2013-09-18 |
Family
ID=49137971
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2013101038586A Pending CN103313298A (en) | 2013-03-28 | 2013-03-28 | Node redundancy detection method for heterogeneous sensor network |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN103313298A (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104284453A (en) * | 2014-10-30 | 2015-01-14 | 扬州大学 | Networking method for wireless sensor network with few redundant links |
| CN107911828A (en) * | 2017-11-15 | 2018-04-13 | 中国人民解放军国防科技大学 | Deployment method using unmanned aerial mobile platform as base station cluster |
| CN110267323A (en) * | 2019-05-21 | 2019-09-20 | 杭州电子科技大学 | A kind of connection target K covering method based on adjustable the perception radius model |
| CN111757443A (en) * | 2020-06-29 | 2020-10-09 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | Node dormancy method, system, terminal device and computer readable storage medium |
| CN111836282A (en) * | 2020-06-28 | 2020-10-27 | 中南大学 | Three-dimensional WSN node scheduling method and storage medium |
| CN113965297A (en) * | 2021-08-30 | 2022-01-21 | 国网山东省电力公司信息通信公司 | Power communication network redundant node state scheduling method and system |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101917777A (en) * | 2010-08-03 | 2010-12-15 | 北京航空航天大学 | Wireless sensor network node sleep qualification judging method based on cooperation between neighboring nodes |
| CN103002590A (en) * | 2012-11-23 | 2013-03-27 | 南京邮电大学 | Scheduling method of directed nodes in wireless sensor network |
-
2013
- 2013-03-28 CN CN2013101038586A patent/CN103313298A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101917777A (en) * | 2010-08-03 | 2010-12-15 | 北京航空航天大学 | Wireless sensor network node sleep qualification judging method based on cooperation between neighboring nodes |
| CN103002590A (en) * | 2012-11-23 | 2013-03-27 | 南京邮电大学 | Scheduling method of directed nodes in wireless sensor network |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| TIAN D,GEORGANAS N: "Location and calculation-free node-scheduling schemes in large wireless sensor networks", 《AD HOC NETWORKS》 * |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104284453A (en) * | 2014-10-30 | 2015-01-14 | 扬州大学 | Networking method for wireless sensor network with few redundant links |
| CN104284453B (en) * | 2014-10-30 | 2018-10-23 | 扬州大学 | A kind of networking method of wireless sensor network of less redundant link |
| CN107911828A (en) * | 2017-11-15 | 2018-04-13 | 中国人民解放军国防科技大学 | Deployment method using unmanned aerial mobile platform as base station cluster |
| CN107911828B (en) * | 2017-11-15 | 2021-02-05 | 中国人民解放军国防科技大学 | Deployment method using unmanned aerial mobile platform as base station cluster |
| CN110267323A (en) * | 2019-05-21 | 2019-09-20 | 杭州电子科技大学 | A kind of connection target K covering method based on adjustable the perception radius model |
| CN111836282A (en) * | 2020-06-28 | 2020-10-27 | 中南大学 | Three-dimensional WSN node scheduling method and storage medium |
| CN111757443A (en) * | 2020-06-29 | 2020-10-09 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | Node dormancy method, system, terminal device and computer readable storage medium |
| CN113965297A (en) * | 2021-08-30 | 2022-01-21 | 国网山东省电力公司信息通信公司 | Power communication network redundant node state scheduling method and system |
| CN113965297B (en) * | 2021-08-30 | 2023-10-03 | 国网山东省电力公司信息通信公司 | Power communication network redundant node state scheduling method and system |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN103313298A (en) | Node redundancy detection method for heterogeneous sensor network | |
| Pasolini et al. | Smart city pilot projects using LoRa and IEEE802. 15.4 technologies | |
| Abdollahzadeh et al. | Deployment strategies in the wireless sensor network: A comprehensive review | |
| Bagci et al. | An energy aware fuzzy approach to unequal clustering in wireless sensor networks | |
| Lin et al. | TADP: Enabling temporal and distantial priority scheduling for on-demand charging architecture in wireless rechargeable sensor networks | |
| Chang et al. | Obstacle-resistant deployment algorithms for wireless sensor networks | |
| Liu et al. | Distributed clustering algorithms for data-gathering in wireless mobile sensor networks | |
| Lee et al. | Modeling and optimization of energy efficient routing in wireless sensor networks | |
| CN102281608B (en) | Wireless sensor network clustering routing method based on fuzzy control | |
| CN106507423A (en) | A kind of wireless sensor network routing method based on the reachable domain of dynamic | |
| Marks | A survey of multi-objective deployment in wireless sensor networks | |
| CN104135752B (en) | A kind of wireless sensor network cluster head node system of selection and cluster-dividing method | |
| Chen et al. | Artificial intelligence-empowered path selection: A survey of ant colony optimization for static and mobile sensor networks | |
| Chen et al. | Speed control of mobile chargers serving wireless rechargeable networks | |
| CN102938892A (en) | Method for designing cross-layer protocol for cognitive wireless sensor network | |
| CN110087273A (en) | The method of Wireless sensor network clustering routing, wireless sensor network protocols platform | |
| CN103002590A (en) | Scheduling method of directed nodes in wireless sensor network | |
| Patil et al. | Some issues in clustering algorithms for wireless sensor networks | |
| Bhakare et al. | An energy-efficient grid based clustering topology for a wireless sensor network | |
| CN101917777B (en) | Wireless sensor network node sleep qualification judging method based on cooperation between neighboring nodes | |
| Cho et al. | Towards persistent surveillance and reconnaissance using a connected swarm of multiple UAVs | |
| Xu et al. | GSMS: a barrier coverage algorithm for joint surveillance quality and network lifetime in WSNs | |
| Mohiddin et al. | Energy‐Efficient Enhancement for the Prediction‐Based Scheduling Algorithm for the Improvement of Network Lifetime in WSNs | |
| Curiac et al. | Urban traffic control system architecture based on wireless sensor-actuator networks | |
| Singh et al. | Analysis of lifetime of wireless sensor network with base station moving on different paths |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C02 | Deemed withdrawal of patent application after publication (patent law 2001) | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication |
Application publication date: 20130918 |