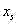CN102079125B - Model-free control method for focal distance of injection molded plastic lens - Google Patents
Model-free control method for focal distance of injection molded plastic lens Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102079125B CN102079125B CN 201010599452 CN201010599452A CN102079125B CN 102079125 B CN102079125 B CN 102079125B CN 201010599452 CN201010599452 CN 201010599452 CN 201010599452 A CN201010599452 A CN 201010599452A CN 102079125 B CN102079125 B CN 102079125B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- control
- point
- focal length
- working point
- model
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 144
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 21
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 21
- 239000002991 molded plastic Substances 0.000 title abstract description 6
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 56
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 21
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 15
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 claims description 48
- 238000001746 injection moulding Methods 0.000 claims description 39
- 238000002789 length control Methods 0.000 claims description 18
- 238000012795 verification Methods 0.000 claims description 17
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000005457 optimization Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000012805 post-processing Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000010606 normalization Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000007781 pre-processing Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 3
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 abstract description 3
- 238000004134 energy conservation Methods 0.000 abstract description 3
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 abstract description 3
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000009776 industrial production Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000003908 quality control method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000011218 segmentation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 241000193935 Araneus diadematus Species 0.000 description 1
- 102100029469 WD repeat and HMG-box DNA-binding protein 1 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 101710097421 WD repeat and HMG-box DNA-binding protein 1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010049040 Weight fluctuation Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012512 characterization method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003050 experimental design method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013213 extrapolation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004088 simulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Injection Moulding Of Plastics Or The Like (AREA)
Abstract
The invention discloses a model-free control method for the focal distance of an injection molded plastic lens. According to the invention, aiming at the problems such as frequent change of operation parameters, difficulty of process modeling, limited model precision and the like existing in the focal distance control process of the injection molded plastic lens, the model-free control method for the focal distance of the injection molded plastic lens is designed according to the characteristics of the injection molded plastic lens that the cost in the production process is low and the batch can be repeated, thus the control on the focal distance of the plastic lens is realized. By utilizing the control method, the control overhead can be reduced, and the control time is shortened, thereby improving the focal distance control efficiency, and being beneficial to the energy conservation and emission reduction in the production process of injection molded lenses.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to the field of focal length control of injection molding plastic lenses, in particular to a model-free focal length control method of injection molding plastic lenses.
Background
The focal length of the lens is linearly related to the diopter of the lens, and the focal length is an important quality index of the plastic optical lens, and the size and the stability of the lens reflect the quality characteristics of the lens. Focal length control is of great importance for quality control of lenses, especially for plastic optical lenses produced by injection molding. Because injection molding is a complex, multistage and nonlinear intermittent production process, and many process parameters influencing the focal length of an injection molding lens cause difficulty in establishing a process model, uncertain factors such as noise and the like often exist in the actual injection molding process, which cause difficulty in efficiently realizing the focal length control of the lens.
From the perspective of product quality control, in the field of focus control of injection molded lenses at present, common methods include: firstly, a trial and error method, which obtains a better control working point by repeatedly adjusting process parameters according to experience by an operator, is simple and easy to implement, but is very time-consuming, inefficient and heavily dependent on the personal experience of the operator; secondly, a test design method, which is to determine a test scheme through test design, carry out a test, collect focal length information of each test point, analyze or fit data, predict an optimal working point through an approximate fitting model to realize lens focal length control; the method has the advantages that the number of tests can be reduced through a well-designed test, and the process characteristics can be discovered as much as possible; the method has the defects that the experimental design method still needs more experience assistance and is difficult to implement on line, and only approximate local optimal working points can be found, so the control precision of the method is not high; third, a model-based focus control method; the method needs a prior model as a basis, and can be divided into two categories, namely a mechanism model and an identification regression model based on test data according to different models depending on the prior model. The method has the advantages of simple implementation, off-line implementation and the like on the basis of the existing model; however, due to the complexity of the injection molding process, the focal length characterization of the plastic lens is difficult to realize, and a mechanism model between the focal length and each process parameter cannot be accurately established. The regression model based on the data generally needs to be obtained through a large number of experiments, the workload is often large, and the extrapolation performance of the model is not ideal; the model is therefore a big bottleneck of the method. Meanwhile, the injection molding process has the characteristic of frequent change of working points, and materials, molds and some process conditions are often required to be changed in the industrial production process. In case of a change of these elements, the original model accuracy cannot be applied at all to a new production process. Therefore, the focus control method based on the model usually needs to consume a lot of time, effort and tests to establish the process model, and the control accuracy of the focus control method is necessarily limited by the corresponding model accuracy, which causes that the efficiency of the focus control method is low in the actual implementation process, and the control accuracy cannot be effectively guaranteed.
In summary, the currently used focus control method often requires sufficient experience of operators and needs a lot of tests and time investment, and is high in control cost, low in implementation efficiency, and not beneficial to energy conservation, emission reduction and environmental protection.
Considering that the injection molding process has the characteristics of low unit production cost, rapidness and easiness in repetition, even if the focal lengths of products produced in the first few or even dozens of batches cannot meet the requirements, as long as the focal lengths can continuously approach the control indexes and reach the requirements after a certain batch, the consumed capital cost and time cost are negligible compared with those of the traditional control method. Therefore, a focal length model-free control method based on a parallel perturbation method is provided according to the low cost and batch repeatability of the production process of the injection molding plastic lens.
The parallel Perturbation method (SPSA) is a nonlinear Stochastic Approximation method proposed by j.c. spider in 1992. (J.C.Spall. multivariable storage optimization Using a simulation optimization, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol.37, pp. 332-341.) this method is a Gradient-based optimization method, but its Gradient information is approximated by a function value; the method has the advantages that only function value information is needed in the searching process; meanwhile, the parallel perturbation strategy is adopted, so that the information quantity required by gradient estimation can be greatly reduced, and the method is particularly suitable for the multi-dimensional parameter optimization problem, and is convenient to implement and high in efficiency. However, in the actual industrial production process, the method is sensitive to process noise, and under the condition that uncertain factors such as noise exist, the accuracy of gradient estimation is poor, and the working efficiency of the method is low. Therefore, in the invention, the existence of uncertainty in the focal length control process is considered, the improvement is carried out on the basis of the parallel perturbation method, and the model-free control method for the focal length of the injection molding plastic lens is provided. The method has better robustness and noise resistance.
The invention realizes the model-free control of the lens focal length by utilizing the characteristics of low cost and repeatable batch in the production process of the injection molding plastic lens, reduces the control overhead and shortens the control time; the method has important significance for improving the focal length control efficiency of the injection molding lens and realizing energy conservation and emission reduction in the industrial production process.
Disclosure of Invention
The invention aims to provide a model-free and efficient focal length control method aiming at the defects and shortcomings of the existing injection molding plastic lens focal length control method.
The invention adopts the following technical scheme for realizing the aim of the invention: a model-free control method for focal length of an injection molding plastic lens comprises the following steps:
(1) the method is initialized: set of focus modeless control method parametersWherein:is a focal length control index set value,for the focus target deviation tolerance to be met,for the focus fluctuation variance tolerance,in order to repeat the number of tests,in order to repeat the number of measurements,in order to verify the number of tests,for the maximum number of test points to be counted,are parallel perturbation method coefficients. Is provided withIs provided withThe process parameters can be respectively defined as:(ii) a Order toCharacterizing the second one formed by the combination of these process parametersAnd controlling the working point. Setting the initial control operating point by the operator,The number of the process parameters is shown; will be provided withNormalization is carried out, and the vector of the normalized control working point is(ii) a Setting control operating point count。
(2) And (3) controlling the working point iteration based on a parallel perturbation method: the continuous control working point sequence of the production is set as(ii) a WhereinThe focus estimation has already been carried out,for a new control operating point vector to be estimated, byThe parallel perturbation method is used for generating,the specific production method is as follows.
a. Order to,“"means the symbol is divided by the integer,is the remainder; if it is not=0, turn (f); if it is not=1, go (b); if it is not=2, go (e).
b. Updating the gain of the parallel perturbation method according to a formula,The gain is updated.
c. Generation of new ones by Monte CarloDimension random vector-perturbation vectorWherein each dimension of the vector is randomly generated by a Bernoulli distribution, wherein the probabilities of generating +1, -1 are all 0.5.
d. Generating a positive perturbation point: generating a forward shot point according to the perturbation vector:(ii) a Order to=And (4) turning to the step (3).
f. Order to(ii) a If s =0, let=Turning to the step (3); otherwise, estimating atApproximate gradient at point:(ii) a Wherein,is an estimate of the focal length of the last control operating point.
g. Search for the next iteration point along the approximate gradient direction:(ii) a Order to=And (4) turning to the step (3).
(3) Model-free estimation preprocessing: control operating point to be estimatedIs a normalized process parameter combination vector; in the pretreatment stage, theThe corresponding physical process parameters can be obtained by carrying out reverse normalization(ii) a After conversion, it is necessary to ensureStill meeting the physical constraints of the process parameters. Is provided withIs a feasible process parameter ifThen, then(ii) a Otherwise, getWhereinIs Euclidean norm, i.e. the process parameterDistance in feasible domainNearest point to replaceAs an alternative to controlling the operating point.
(4) Controlling a working point on-line test: according to the control operating pointModifying the corresponding technological parameter value on the operation panel of the injection molding machine to ensure that the technological parameter valueIs set to. Producing plastic lens by injection molding machine, measuring lens focal length by lensometer, and repeating measurementAnd recording the corresponding focal length measurement(ii) a WhereinThe numbers are numbered for the times of the on-line tests,the number of measurements is numbered.
(5) Model-free estimation post-processing: in the model-free post-processing stage of the control working point, the number of repeated tests is initially set according to the model-free control methodCalling (4) to control the working point to perform online test until the test timesTo achieveAt this time, the working point can be calculated at the control working pointFocal length estimate of (b):。
(6) and (3) verifying a control working point: if the operating point is controlledEstimate of the focal length ofSatisfies the following conditions:,if the absolute value operation is represented, the focal length index is considered to be initially reached, otherwise, the step (7) is carried out; due to uncertain factors such as noise, additional measures are requiredThe additional verification test is added, and the step (4) is calledNext, the verification value was obtained by the following formula: (ii) a If the verification value satisfiesThen the optimum process parameters control the operating pointTurning to (8); otherwise, the step (7) is carried out.
(7) Controlling the working point to count: controlling operating point countingIf, ifTurning to the step (2); otherwise, returning to the step (1) to readjust the optimization goals and parameters.
(8) And (3) implementation of an optimal control working point:namely the optimal control working point found by the method. According toSetting relevant technological parameters for controlling focal length on the control panel of the injection molding machine respectively to ensure that the technological parametersIs set to(ii) a And performing online implementation on the optimal working point, wherein the focal length of the produced injection molding lens meets the control target.
The invention has the beneficial effects that:
(1) the invention realizes the control of the focal length of the injection molding lens without depending on a model, avoids the great cost and time investment of model establishment and improves the efficiency of focal length control;
(2) the method does not depend on a model, greatly reduces the dependence on the knowledge and information of the known process, does not need human intervention in the optimization control process, can automatically run, is convenient to implement on line, and greatly reduces the implementation cost and difficulty;
(3) the method adopts a parallel perturbation method to realize the gradient approximation of the multivariable problem by using a small amount of tests, thereby improving the efficiency of the model-free control method;
(4) because the injection molding process often has certain randomness, the accurate optimal control working point is difficult to obtain based on the modeling method; the method can effectively overcome noise and model deviation by implementing on line and introducing anti-randomness measures, and finds a real and reliable optimal focal length control working point.
Drawings
FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of the operation of the present invention;
FIG. 2 is a schematic workflow of the present invention;
FIG. 3 is a schematic flow chart of a parallel perturbation method for generating a sequence of control working points in the present invention;
FIG. 4 shows the control effect of the present invention on the plastic focus control of an injection molding machine.
Detailed Description
The present invention is described in detail below with reference to the attached drawings. FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of the present invention, in which a parallel perturbation method is used to iteratively generate a control working point sequence, each control working point is subjected to parameter setting by an injection molding machine control panel and is implemented on an injection molding machine on line, model-free estimation is performed by model-free estimation preprocessing, on-line experiments, model-free post-processing and the like and fed back to the parallel perturbation method, the parallel perturbation method updates the control working point sequence according to a feedback result to generate a new control working point to be estimated, the process is continuously repeated until a control target requirement is met and a model-free control method verification link is performed, and at this time, the output of the control method is an optimal control working point, thereby realizing the focus control of the plastic lens.
Fig. 2 is a schematic view of the working process of the present invention. A model-free control method for focal length of an injection molding plastic lens comprises the following steps:
(1) the method is initialized: set of focus modeless control method parametersWherein:is a focal length control index set value,for the focus target deviation tolerance to be met,for the focus fluctuation variance tolerance,in order to repeat the number of tests,in order to repeat the number of measurements,in order to verify the number of tests,for the maximum number of test points to be counted,are parallel perturbation method coefficients. Is provided withThe process parameters can be respectively defined as:(ii) a Order toCharacterizing the second one formed by the combination of these process parametersAnd controlling the working point. Setting the initial control operating point by the operator,The number of the process parameters is shown; will be provided withNormalization is carried out, and the vector of the normalized control working point is(ii) a Setting control operating point count。
(2) And (3) controlling the working point iteration based on a parallel perturbation method: the continuous control working point sequence of the production is set as(ii) a WhereinThe focus estimation has already been carried out,is newThe control working point vector to be estimated is generated by a parallel perturbation method,the specific production method is as follows.
a. Order to,“"means the symbol is divided by the integer,is the remainder; if it is not=0, turn (f); if it is not=1, go (b); if it is not=2, go (e).
b. Updating the gain of the parallel perturbation method according to a formula,The gain is updated.
c. Generation of new ones by Monte CarloDimension random vector-perturbation vectorWherein each dimension of the vector is randomly generated by a Bernoulli distributionThe probabilities of generating +1 and-1 are all 0.5.
d. Generating a positive perturbation point: generating a forward shot point according to the perturbation vector:(ii) a Order to=And (4) turning to the step (3).
f. Order to(ii) a If s =0, let=Turning to the step (3); otherwise, estimating atApproximate gradient at point:(ii) a Wherein,is an estimate of the focal length of the last control operating point.
g. Search for the next iteration point along the approximate gradient direction:(ii) a Order to=And (4) turning to the step (3).
(3) Model-free estimation preprocessing: control operating point to be estimatedIs a normalized process parameter combination vector; in the pretreatment stage, theThe corresponding physical process parameters can be obtained by carrying out reverse normalization(ii) a After conversion, it is necessary to ensureStill meeting the physical constraints of the process parameters. Is provided withIs a feasible process parameter ifThen, then(ii) a Otherwise, getWhereinAs Euclidean norm, i.e. distance in the feasible domain using process parametersNearest point to replaceAs an alternative to controlling the operating point.
(4) Controlling a working point on-line test: according to the control operating pointModifying the corresponding process parameter value on the operation panel of the injection molding machine to enable the first stepThe set value of each process parameter is. Producing plastic lens by injection molding machine, measuring lens focal length by lensometer, and repeating measurementAnd recording the corresponding focal length measurement(ii) a WhereinThe numbers are numbered for the times of the on-line tests,the number of measurements is numbered.
(5) Model-free estimation post-processing: in the model-free post-processing stage of the control working point, the number of repeated tests is initially set according to the model-free control methodCalling (4) to control the working point to perform online test until the test timesTo achieveAt this time, the working point can be calculated at the control working pointFocal length estimate of (b):。
(6) and (3) verifying a control working point: if the operating point is controlledEstimate of the focal length ofSatisfies the following conditions:,if the absolute value operation is represented, the focal length index is considered to be initially reached, otherwise, the step (7) is carried out; due to uncertain factors such as noise, additional measures are requiredThe additional verification test is added, and the step (4) is calledNext, the verification value was obtained by the following formula: (ii) a If the verification value satisfiesThen the optimum process parameters control the operating pointTurning to (8); otherwise, the step (7) is carried out.
(7) Controlling the working point to count: controlling operating point countingIf, ifTurning to the step (2); otherwise, returning to the step (1) to readjust the optimization goals and parameters.
(8) And (3) implementation of an optimal control working point:namely the optimal control working point found by the method. According toSetting relevant technological parameters for controlling focal length on the control panel of the injection molding machine respectively to ensure that the technological parametersIs set to(ii) a And performing online implementation on the optimal working point, wherein the focal length of the produced injection molding lens meets the control target.
FIG. 3 is a schematic flow chart of the parallel perturbation method for generating control working points in the invention.
Examples
The following describes an implementation process of a model-free control method for the focal length of an injection lens by taking the focal length control of a plastic magnifier lens as an example.
Firstly, initializing the method through the step (1); focal length control target of the lens=90 mm, and the focal length target deviation tolerance is set according to the focal length noise fluctuation condition of the lens and the focal length tolerance of the lensmm, weight fluctuation variance tolerancemm, number of repeated testsNumber of repeated measurementsNumber of verification testsMaximum number of testsCoefficient of parallel perturbation algorithm(ii) a Selecting the technological parameters to be optimized as follows: the injection pressure, the dwell pressure and the dwell time, wherein the injection section is divided into a first section and a second section for respective control, the segmentation point of which is also a key process parameter. Thus, in the lens focus control problem, a total of 5 process parameters are required to be adjusted, and the process parameters are selectedInitial values of numbers are:105 bar (bar) for the first injection section, 105 bar for the second injection section, 45% of the injection stroke for the first and second injection sections, 80 bar for the holding pressure, and 8 second for the holding time; to pairNormalization is performed so that each dimension variable is [0,100 ]]Interval, normalized vector。
Turning to the step (2), iteratively generating a control working point sequence by a parallel perturbation method, wherein the generated sequence is determined by a parallel perturbation method sequence generation flow related by the invention; assume that the current control operating point is generated as。
In step (3), forModel-free estimation preprocessing is carried out to generate corresponding control working points which can be implemented on line。
Executing the step (4) to control the working pointPerforming an on-line test according toChanging parameter setting of injection molding machine by control panel of injection molding machine, starting injection molding process, producing a plastic lens, and measuring focal length of the lens by a lensometerAnd recorded, measured three times in total, corresponding to the measured values:,,。
step (5) performing model-free post-processing on the control working point due to repeated test timesTherefore, it is required to call (4) for final productionA plastic lens and record its focal length (,,;,,) (ii) a The estimated value at that point is。
Step (6) for controlling the working pointAnd (4) carrying out verification: if it is notFocal length estimate of a pointSatisfies the following conditions:mm,representing absolute value operation, the focus control index is considered to be initially reached, at which time additional operations are requiredSecondary additional verification test; otherwise, turning to (7); and (5) calling the step (4) twice during verification test, and obtaining a verification value through the following formula:(ii) a If the verification value satisfiesmm, optimal process parameter control set valueTurning to (8); otherwise, turning to the step (7).
In step (7), the test operating points are countedIf, ifIf yes, continuing to generate a control working point by using a parallel perturbation method in the step (2); otherwise, the optimization targets and parameters need to be adjusted again in the step (1), and a new control process needs to be executed again.
Namely the optimal control working point found by the method. According toThe technological parameters related to the focus control are set on the control panel of the injection molding machine, wherein the pressure of the first injection section is 109 bar (bar), the pressure of the second injection section is 120 bar, the segmentation points of the first injection section and the second injection section are 41 percent of the injection stroke, the pressure maintaining pressure is 77 bar, and the pressure maintaining time is 5.9 second. The focal length of the injection-molded product produced under the parameter setting can meet the control target.
Fig. 4 (a) is a control effect diagram of the embodiment, and an optimal control operating point is finally found through 7 iterations; to further illustrate the performance of the control method, FIG. 4 (b) provides a graph showing the results from a different initial setting parameter(s) (b)) And starting another control track, and under the control track, carrying out 6 iterations on model-free control to reach an optimal control working point. The result proves that the method can overcome the process noise to search the set focal length control target under a small number of test times and a small number of iteration batches, and ensure the stability of the optimal control test point.
As described above, the present invention utilizes the low cost and batch repeatable nature of the injection molded plastic lens manufacturing process to design a model-less control method for lens focal length. The control method can reduce the lens control overhead and shorten the control time; the practical application result shows that the invention has ideal application effect.
Claims (2)
1. A model-free control method for focal length of an injection molding lens is characterized by mainly comprising the following steps:
(1) the method is initialized: set of focus modeless control method parametersWherein: f. oftgIs a focal length control index set value, mu is a focal length target deviation tolerance, sigma is a focal length fluctuation variance tolerance, tau is a repeated test frequency,for repeated measurement times, χ is the number of verification tests, Max is the maximum test point count, and { a, A, c, α, γ } is the coefficient of the parallel perturbation method; n process parameters are set, which can be respectively defined as x(1),…,x(n)(ii) a Order toCharacterizing a pth control operating point formed by the combination of process parameters; setting the initial control operating point by the operatorn is the number of process parameters; x is to be1Normalization is carried out, and the vector of the normalized control working point isSetting the control working point count s to be 0;
(2) and (3) controlling the working point iteration based on a parallel perturbation method: the continuous control working point sequence of the production is set asWhereinThe focus estimation has already been carried out,for a new control working point vector to be estimated, a parallel perturbation method is used for generating:
(3) model-free estimation preprocessing: control operating point to be estimatedIs a normalized process parameter combination vector; in the pretreatment stage, theThe corresponding physical process parameter x can be obtained by carrying out reverse normalizations(ii) a After conversion, x needs to be ensuredsStill meet the physical constraint of the technological parameter; let xi be a feasible range of process parameters, if xsE.g. xi, xs=xs(ii) a Otherwise, get xs≡arg min{||x-xs| | x ∈ xi }, where | | | x-xsI | is the Euclidean norm, i.e. the distance x in the feasible domain using the process parameterssNearest point to replace xsAs an alternative control operating point;
(4) controlling a working point on-line test: according to the control operating pointModifying the corresponding process parameter value on the operation panel of the injection molding machine to ensure that the set value of the process parameter k isProducing plastic lens by injection molding machine, measuring lens focal length by lensometer, and repeating measurementAnd recording the corresponding focal length measurementWherein i is an online test frequency number, and j is a measurement frequency number;
(5) model-free estimation post-processing: in the model-free post-processing stage of the control working point, the repeated test times tau are initially set according to the model-free control method, the (4) is called to carry out the on-line test of the control working point until the test times i reach tau, and at the moment, the control working point x can be calculatedsFocal length estimate of (b):
(6) and (3) verifying a control working point: if the operating point x is controlledsAt an estimated value f of the focal lengthsSatisfies the following conditions: d (x)s)=abs(fs-ftg) Mu is less than or equal to mu, abs (·) represents absolute value operation, then the focal length index is considered to be initially reached, otherwise, step (7) is carried out; for the reason of uncertain factors, additional X times of additional verification tests are needed, the step (4) is called, and the verification value is obtained through the following formula If the verification value satisfiesThe optimal process parameter controls the operating point xopt=xsTurning to (8); otherwise, connecting to step (7);
(7) controlling the working point to count: controlling the working point count s to be s +1, and if s is less than Max, turning to the step (2); otherwise, returning to the step (1) to readjust the optimization targets and parameters;
(8) and (3) implementation of an optimal control working point:namely the optimal control working point found by the method; according to xoptRespectively setting the relevant process parameters of focal length control on the control panel of the injection molding machine to ensure that the set value of the process parameter k isAnd performing online implementation on the optimal working point, wherein the focal length of the produced injection molding lens meets the control target.
2. The method for mold-less control of focal length of injection molded lens according to claim 1, wherein in the step (2), the step (2) is performedThe specific production method is as follows:
(a) let flag = s |3, "|" denote an integer division symbol, and flag is the remainder; if flag =0, turn (f); if flag =1, turn (b); if flag =2, turn (e);
(b) updating the gain of the parallel perturbation method according to the formula ak=a/(A+k)α,ck=c/kγUpdating the gain;
(c) generation of a new n-dimensional random vector-perturbation vector delta by Monte CarlokWherein each dimension of the vector is randomly generated by a Bernoulli distribution, wherein the probabilities of generating +1, -1 are all 0.5;
(d) generating a positive perturbation point: generating a forward shot point x from the perturbation vectork-phus=xk+ckΔk(ii) a Order to Turning to the step (3);
(f) order toIf s =0, letTurning to the step (3); otherwise, estimate at x from perturbation pointskApproximate gradient at point gk=(fs-1-fs)/2ckΔk(ii) a Wherein f iss-1Is the last controlFocal length estimation of a working point is made;
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 201010599452 CN102079125B (en) | 2010-12-22 | 2010-12-22 | Model-free control method for focal distance of injection molded plastic lens |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 201010599452 CN102079125B (en) | 2010-12-22 | 2010-12-22 | Model-free control method for focal distance of injection molded plastic lens |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102079125A CN102079125A (en) | 2011-06-01 |
| CN102079125B true CN102079125B (en) | 2013-04-17 |
Family
ID=44085416
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 201010599452 Expired - Fee Related CN102079125B (en) | 2010-12-22 | 2010-12-22 | Model-free control method for focal distance of injection molded plastic lens |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN102079125B (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108447737B (en) * | 2018-05-18 | 2019-06-14 | 厦门理工学院 | A kind of relay base quality optimization system based on simplex search |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5914884A (en) * | 1997-01-02 | 1999-06-22 | General Electric Company | Method for evaluating moldability characteristics of a plastic resin in an injection molding process |
| CN1715036A (en) * | 2004-06-29 | 2006-01-04 | 钰德科技股份有限公司 | Jet forming method and its device without suture |
| CN101094763A (en) * | 2004-12-30 | 2007-12-26 | 博士伦公司 | Core locking assembly and method for orientation of asymmetric tooling |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG91321A1 (en) * | 2000-03-27 | 2002-09-17 | Sumitomo Heavy Industries | Method for controlling an injection molding machine capable of reducing variations in weight of molded products |
| JP2006015538A (en) * | 2004-06-30 | 2006-01-19 | Canon Inc | Injection molding method and production system control method using it |
-
2010
- 2010-12-22 CN CN 201010599452 patent/CN102079125B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5914884A (en) * | 1997-01-02 | 1999-06-22 | General Electric Company | Method for evaluating moldability characteristics of a plastic resin in an injection molding process |
| CN1715036A (en) * | 2004-06-29 | 2006-01-04 | 钰德科技股份有限公司 | Jet forming method and its device without suture |
| CN101094763A (en) * | 2004-12-30 | 2007-12-26 | 博士伦公司 | Core locking assembly and method for orientation of asymmetric tooling |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| JP特开2006-15538A 2006.01.19 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN102079125A (en) | 2011-06-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Chetverikov | Testing regression monotonicity in econometric models | |
| CN108287471B (en) | Parameter self-tuning method of MIMO offset format model-free controller based on system error | |
| CN113544599A (en) | Method for executing a process and optimizing a control signal used in the process | |
| CN102101352B (en) | Model-free weight controlling method for injection molding product | |
| US11860590B2 (en) | Model-free optimization method of process parameters of injection molding | |
| CN107609298A (en) | A kind of Jiles Atherton model parameter identification methods and device | |
| CN111784057A (en) | Short-term power load prediction combination method based on snapshot feedback mechanism | |
| CN110765704A (en) | Novel automatic deep neural network modeling method applied to microwave device | |
| CN114841106A (en) | Integrated circuit optimization method and system based on rule-guided genetic algorithm | |
| CN102079125B (en) | Model-free control method for focal distance of injection molded plastic lens | |
| CN104772878A (en) | Product weight control method based on iteration modeling and optimization for injection molding process | |
| CN113408622A (en) | Non-invasive load identification method and system considering characteristic quantity information expression difference | |
| Wei et al. | A bayesian approach to robust inverse reinforcement learning | |
| CN108447737B (en) | A kind of relay base quality optimization system based on simplex search | |
| CN111259340A (en) | Saturated load prediction method based on logistic regression | |
| CN107222328B (en) | Method and device for predicting saturation inflection point | |
| CN115932594A (en) | Multi-innovation least square online parameter identification method for power battery | |
| CN104298213A (en) | Index time varying gain type iterative learning control algorithm based on reference batch | |
| CN115167150A (en) | Batch process two-dimensional off-orbit strategy staggered Q learning optimal tracking control method with unknown system dynamics | |
| CN112861315A (en) | One-dimensional descent search method for non-convex single-target optimal power flow global solution of power system | |
| CN107947181B (en) | Decoupling full-linear optimal power flow model based on similar hot start environment | |
| Lu et al. | Quality control of batch process using natural gradient based model-free optimization | |
| Kek et al. | First-Order Linear Ordinary Differential Equation for Regression Modelling | |
| CN117094130B (en) | Fractional order piezoelectric ceramic identification method based on maximum likelihood least square algorithm | |
| CN114311574B (en) | Injection speed optimization control method, system and device of injection molding machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |
Granted publication date: 20130417 Termination date: 20191222 |
|
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |