JP4599657B2 - Data providing system, content providing apparatus, and content processing apparatus - Google Patents
Data providing system, content providing apparatus, and content processing apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4599657B2 JP4599657B2 JP2000126305A JP2000126305A JP4599657B2 JP 4599657 B2 JP4599657 B2 JP 4599657B2 JP 2000126305 A JP2000126305 A JP 2000126305A JP 2000126305 A JP2000126305 A JP 2000126305A JP 4599657 B2 JP4599657 B2 JP 4599657B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- data
- content
- key data
- key
- unit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Information Transfer Between Computers (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、コンテンツデータを提供するデータ提供システム、コンテンツ提供装置、およびコンテンツ処理装置に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
暗号化されたコンテンツデータを所定の契約を交わしたユーザのデータ処理装置に配給し、当該データ処理装置において、コンテンツデータを復号して再生および記録するデータ提供システムがある。
このようなデータ提供システムの一つに、音楽データを配信する従来のEMD(Electronic Music Distribution: 電子音楽配信)システムがある。
【0003】
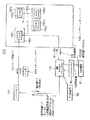
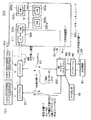
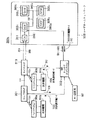
図100は、従来のEMDシステム700の構成図である。
図100に示すEMDシステム700では、コンテンツプロバイダ701a,701bが、サービスプロバイダ710に対し、コンテンツデータ704a,704b,704cと、著作権情報705a,705b,705cとを、それぞれ相互認証後に得たセッション鍵データで暗号化してオンラインで供給したり、あるいはオフラインで供給する。ここで、著作権情報705a,705b,705cには、例えば、SCMS(Serial Copy Management System) 情報、コンテンツデータに埋め込むことを要請する電子透かし情報およびサービスプロバイダ710の伝送プロトコルに埋め込むことを要請する著作権に関する情報などがある。
【0004】
サービスプロバイダ710は、受信したコンテンツデータ704a,704b,704cと、著作権情報705a,705b,705cとをセッション鍵データを用いて復号する。
そして、サービスプロバイダ710は、復号したあるいはオフラインで受け取ったコンテンツデータ704a,704b,704cに、著作権情報705a,705b,705cを埋め込んで、コンテンツデータ707a,707b,707cを生成する。このとき、サービスプロバイダ710は、例えば、著作権情報705a,705b,705cのうち電子透かし情報をコンテンツデータ704a,704b,704cに所定の周波数領域を変更して埋め込み、当該コンテンツデータをユーザに送信する際に用いるネットワークプロトコルにSCMS情報を埋め込む。
さらに、サービスプロバイダ710は、コンテンツデータ707a,707b,707cを、鍵データベース706から読み出したコンテンツ鍵データKca,Kcb,Kccを用いてそれぞれ暗号化する。その後、サービスプロバイダ710は、暗号化されたコンテンツデータ707a,707b,707cを格納したセキュアコンテナ722を、相互認証後に得たセッション鍵データによって暗号化してユーザの端末装置709に存在するCA(Conditional Access)モジュール711に送信する。
【0005】
CAモジュール711は、セキュアコンテナ722をセッション鍵データを用いて復号する。また、CAモジュール711は、電子決済やCAなどの課金機能を用いて、サービスプロバイダ710の鍵データベース706からコンテンツ鍵データKca,Kcb,Kccを受信し、これをセッション鍵データを用いて復号する。これにより、端末装置709において、コンテンツデータ707a,707b,707cを、それぞれコンテンツ鍵データKca,Kcb,Kccを用いて復号することが可能になる。
このとき、CAモジュール711は、コンテンツ単位で課金処理を行い、その結果に応じた課金情報721を生成し、これをセッション鍵データで暗号化した後に、サービスプロバイダ710の権利処理モジュール720に送信する。
この場合に、CAモジュール711は、サービスプロバイダ710が自らの提供するサ一ビスに関して管理したい項目であるユーザの契約(更新)情報および月々基本料金などのネットワーク家賃の徴収と、コンテンツ単位の課金処理と、ネットワークの物理層のセキュリティー確保とを行う。
【0006】
サービスプロバイダ710は、CAモジュール711から課金情報721を受信すると、サービスプロバイダ710とコンテンツプロバイダ701a,701b,701cとの間で利益配分を行う。
このとき、サービスプロバイダ710から、コンテンツプロバイダ701a,701b,701cへの利益配分は、例えば、JASRAC(Japanese Society for Rights of Authors, Composers and Publishers:日本音楽著作権協会)を介して行われる。また、JASRACによって、コンテンツプロバイダの利益が、当該コンテンツデータの著作権者、アーティスト、作詞・作曲家および所属プロダクションなどに分配される。
【0007】
また、端末装置709では、コンテンツ鍵データKca,Kcb,Kccを用いて復号したコンテンツデータ707a,707b,707cを、RAM型の記録媒体723などに記録する際に、著作権情報705a,705b,705cのSCMSビットを書き換えて、コピー制御を行う。すなわち、ユーザ側では、コンテンツデータ707a,707b,707cに埋め込まれたSCMSビットに基づいて、コピー制御が行われ、著作権の保護が図られている。
【0008】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
ところで、SCMSは、CD(Compact Disc)からDAT(Digital Audio Tape)への録音を防止するために規定されたものであり、DATとDATとの間での複製が可能である。また、コンテンツデータに電子透かし情報を埋め込んだ場合も、問題が生じたときに、対象となっているコンテンツデータを提供したコンテンツプロバイダを特定するに止まり、違法なコピーを技術的に阻止するものではない。
従って、上述した図100に示すEMDシステム700では、コンテンツプロバイダの権利(利益)が十分に保護されないという問題がある。
【0009】
また、上述したEMDシステム700では、コンテンツプロバイダの著作権情報をサービスプロバイダがコンテンツデータに埋め込むため、コンテンツプロバイダは当該埋め込みが要求通りに行われているかを監査する必要がある。また、コンテンツプロバイダは、サービスプロバイダが契約通りに、コンテンツデータの配信を行っているかを監査する必要がある。そのため、監査のための負担が大きいという問題がある。
【0010】
また、上述したEMDシステム700では、ユーザの端末装置709からの課金情報721を、サービスプロバイダ710の権利処理モジュール720で処理するため、ユーザによるコンテンツデータの利用に応じてコンテンツプロバイダが受けるべき利益を、コンテンツプロバイダが適切に受けられるかどうかが懸念される。
【0011】
本発明は上述した従来技術の問題点に鑑みてなされ、コンテンプロバイダの権利者(関係者)の利益を適切に保護できるデータ提供システム、コンテンツ提供装置、およびコンテンツ処理装置を提供することを目的とする。
また、本発明は、コンテンプロバイダの権利者の利益を保護するための監査の負担を軽減できるデータ提供システム、コンテンツ提供装置、およびコンテンツ処理装置を提供することを目的とする。
【0012】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上述した従来技術の問題点を解決し、上述した目的を達成するために、本発明の第1の観点のデータ提供システムは、ネットワークに接続されたコンテンツ提供装置、コンテンツ処理装置、および購入処理装置を有し、前記コンテンツ提供装置から前記コンテンツ処理装置へコンテンツデータを送信し、前記購入処理装置において購入された購入期間に応じて前記コンテンツ処理装置に前記コンテンツデータを利用させるために、前記購入処理装置は、前記ネットワークを通じて、前記コンテンツデータについての所定の利用期間毎に有効な複数の配信用鍵データを前記コンテンツ提供装置へ送信し、前記複数の配信用鍵データのうちの、前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを前記コンテンツ処理装置へ送信し、前記コンテンツ提供装置は、前記コンテンツデータを記憶する記憶部と、前記記憶部に記憶された前記コンテンツデータをコンテンツ鍵データで暗号化するコンテンツ暗号化部と、前記ネットワークに接続され、前記購入処理装置から前記複数の配信用鍵データを受信するコンテンツ提供装置用の通信部と、受信した各前記配信用鍵データを用いて前記コンテンツ鍵データを暗号化し、複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを生成するコンテンツ鍵暗号化部と、暗号化された前記コンテンツデータ、および前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを有するセキュアコンテナデータを生成するセキュアコンテナデータ生成部とを有し、前記コンテンツ提供装置用の通信部は、前記セキュアコンテナデータをコンテンツ処理装置へ送信することにより、前記コンテンツデータおよび前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データをコンテンツ処理装置へ送信し、前記コンテンツ処理装置は、前記ネットワークに接続され、前記購入処理装置から前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを受信し、前記コンテンツ提供装置用の通信部から前記セキュアコンテナデータを受信するコンテンツ処理装置用の通信部と、受信した前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて、受信した前記セキュアコンテナデータに含まれる前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データのうちの、当該配信用鍵データにより暗号化されたコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを復号するコンテンツ鍵復号部と、前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて復号されたコンテンツ鍵データを用いて、前記セキュアコンテナデータの前記コンテンツデータを復号するコンテンツ復号部とを有する。
【0013】
本発明の第2の観点のコンテンツ提供装置は、コンテンツデータを記憶する記憶部と、前記記憶部に記憶された前記コンテンツデータをコンテンツ鍵データで暗号化するコンテンツ暗号化部と、ネットワークに接続され、前記ネットワークから前記コンテンツデータについての所定の利用期間毎に有効な複数の配信用鍵データを受信する通信部と、受信した各前記配信用鍵データを用いて前記コンテンツ鍵データを暗号化し、複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを生成するコンテンツ鍵暗号化部と、暗号化された前記コンテンツデータ、および前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを有するセキュアコンテナデータを生成するセキュアコンテナデータ生成部とを有し、前記通信部は、前記ネットワークへ前記セキュアコンテナデータを送信することにより、前記コンテンツデータおよび前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データをコンテンツ処理装置へ送信する。
【0016】
本発明の第3の観点のデータ提供システムは、ネットワークに接続された請求項2記載のコンテンツ提供装置および購入処理装置を有するデータ提供システムであって、前記購入処理装置は、前記ネットワークを通じて前記コンテンツ提供装置へ、前記コンテンツデータについての所定の利用期間毎に有効な前記複数の配信用鍵データを送信する。
【0017】
本発明の第4の観点のコンテンツ処理装置は、ネットワークに接続され、前記ネットワークから、コンテンツ鍵データで暗号化されたコンテンツデータおよび前記コンテンツデータについての所定の利用期間毎に有効な複数の配信用鍵データにより暗号化された複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを有するセキュアコンテナデータと、前記複数の配信用鍵データのうちの、購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データとを受信する通信部と、受信した前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて、受信した前記セキュアコンテナデータに含まれる前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データのうちの、当該配信用鍵データにより暗号化されたコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを復号するコンテンツ鍵復号部と、前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて復号されたコンテンツ鍵データを用いて、前記セキュアコンテナデータの前記コンテンツデータを復号するコンテンツ復号部とを有する。
【0018】
本発明の第5の観点のコンテンツ処理装置は、コンテンツ鍵データで暗号化されたコンテンツデータおよび前記コンテンツデータについての所定の利用期間毎に有効な複数の配信用鍵データにより暗号化された複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを有するセキュアコンテナデータを記憶可能な記憶部と、前記複数の配信用鍵データのうちの、購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを受信する通信部と、受信した前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて、記憶されている前記セキュアコンテナデータに含まれる前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データのうちの、当該配信用鍵データにより暗号化されたコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを復号するコンテンツ鍵復号部と、前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて復号されたコンテンツ鍵データを用いて、前記セキュアコンテナデータの前記コンテンツデータを復号するコンテンツ復号部とを有する。
【0020】
本発明の第6の観点のコンテンツ処理装置は、コンテンツ鍵データで暗号化されたコンテンツデータおよび前記コンテンツデータについての所定の利用期間毎に有効な複数の配信用鍵データにより暗号化された複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを有するセキュアコンテナデータが記録された記録媒体を読取可能な読取部と、前記複数の配信用鍵データのうちの、購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを受信する通信部と、受信した前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて、読み取られる前記セキュアコンテナデータに含まれる前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データのうちの、当該配信用鍵データにより暗号化されたコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを復号するコンテンツ鍵復号部と、前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて復号されたコンテンツ鍵データを用いて、前記セキュアコンテナデータの前記コンテンツデータを復号するコンテンツ復号部とを有する。
【0027】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の実施形態に係わるEMD(Electronic Music Distribution: 電子音楽配信)システムについて説明する。
本実施形態において、ユーザに配信されるコンテンツ(Content) データとは、音楽データ、映像データおよびプログラムなど情報そのものが価値を有するデジタルデータをいい、以下、音楽データを例に説明する。
【0028】
第1実施形態
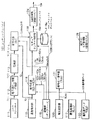
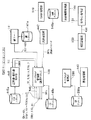
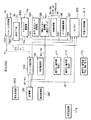
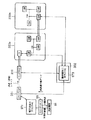
図1は、本実施形態のEMDシステム100の構成図である。図1に示すように、EMDシステム100は、コンテンツプロバイダ101、EMDサービスセンタ(クリアリング・ハウス、以下、ESCとも記す)102およびユーザホームネットワーク103を有する。ここで、コンテンツプロバイダ101とSAM1051〜1054が、それぞれ請求項1などに係わるデータ提供装置とデータ処理装置に対応している。また、EMDサービスセンタ102は管理装置である。先ず、EMDシステム100の概要について説明する。EMDシステム100では、コンテンツプロバイダ101は、自らが提供しようとするコンテンツのコンテンツデータCの使用許諾条件などの権利内容を示す権利書(UCP:Usage Control Policy)データ106を、高い信頼性のある権威機関であるEMDサービスセンタ102に送信する。権利書データ106は、EMDサービスセンタ102によって権威化(認証)される。
【0029】
また、コンテンツプロバイダ101は、コンテンツ鍵データKcでコンテンツデータCを暗号化してコンテンツファイルCFを生成すると共に、コンテンツ鍵データKcをEMDサービスセンタ102から配給された対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD56 で暗号化する。そして、コンテンツプロバイダ101は、暗号化されたコンテンツ鍵データKcおよびコンテンツファイルCFと自らの署名データとを格納(カプセル化)したセキュアコンテナ(本発明のモジュール)104を、インターネットなどのネットワーク、デジタル放送あるいは記録媒体などを用いて、ユーザホームネットワーク103に配給する。
このように、本実施形態では、デジタルのコンテンツデータCをカプセル化して提供することで、従来の記録媒体と密着したデジタルコンテンツを、記録媒体から切り離して、デジタルコンテンツ単体に存在価値を持たせることができる。
ここで、セキュアコンテナは、どのような流通経路(配送チャンネル)を介して提供されても、コンテンツデータC(商品)を販売するときの最も基本となる商品カプセルである。具体的には、セキュアンテナは、課金を行うための暗号情報や、コンテンツデータCの中身の正当性、コンテンツデータを作成した者の正当性およびコンテンツデータの流通業者の正当性を検証するための署名データや、コンテンツデータに埋め込む電子透かし情報に関する情報などの著作権に係わる情報を含む商品カプセルである。
【0030】
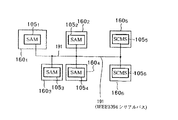
ユーザホームネットワーク103は、例えば、ネットワーク機器1601 およびAV機器1602 〜1604 を有する。
ネットワーク機器1601 は、SAM(Secure Application Module) 1051 を内蔵している。
AV機器1602 〜1604 は、それぞれSAM1052 〜1054 を内蔵している。SAM1051 〜1054 相互間は、例えば、IEEE(Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) 1394シリアルインタフェースバスなどのバス191を介して接続されている。
【0031】
SAM1051 〜1054 は、ネットワーク機器1601 がコンテンツプロバイダ101からネットワークなどを介してオンラインで受信したセキュアコンテナ104、および/または、コンテンツプロバイダ101からAV機器1602 〜1604 に記録媒体を介してオフラインで供給されたセキュアコンテナ104を対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を用いて復号した後に、署名データの検証を行う。
SAM1051 〜1054 に供給されたセキュアコンテナ104は、ネットワーク機器1601 およびAV機器1602 〜1604 において、ユーザの操作に応じて購入・利用形態が決定された後に、再生や記録媒体への記録などの対象となる。
SAM1051 〜1054 は、上述したセキュアコンテナ104の購入・利用の履歴を利用履歴(Usage Log) データ108として記録する。
利用履歴データ108は、例えば、EMDサービスセンタ102からの要求に応じて、ユーザホームネットワーク103からEMDサービスセンタ102に送信される。
【0032】
EMDサービスセンタ102は、利用履歴データ108に基づいて、課金内容を決定(計算)し、その結果に基づいて、ペイメントゲートウェイ90を介して銀行などの決済機関91に決済を行なう。これにより、ユーザホームネットワーク103のユーザが決済機関91に支払った金銭が、EMDサービスセンタ102による決済処理によって、コンテンツプロバイダ101に支払われる。
また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、一定期間毎に、決済レポートデータ107をコンテンツプロバイダ101に送信する。
【0033】
本実施形態では、EMDサービスセンタ102は、認証機能、鍵データ管理機能および権利処理(利益分配)機能を有している。
すなわち、EMDサービスセンタ102は、中立の立場にある最高の権威機関であるルート認証局92に対しての(ルート認証局92の下層に位置する)セカンド認証局(Second Certificate Authority)としての役割を果たし、コンテンツプロバイダ101およびSAM1051 〜1054 において署名データの検証処理に用いられる公開鍵データの公開鍵証明書データに、EMDサービスセンタ102の秘密鍵データによる署名を付けることで、当該公開鍵データの正当性を認証する。また、前述したように、EMDサービスセンタ102は、コンテンツプロバイダ101の権利書データ106を登録して権威化することも、EMDサービスセンタ102の認証機能の一つである。
また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、例えば、配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 などの鍵データの管理を行なう鍵データ管理機能を有する。
また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、権威化した権利書データ106に記述された標準小売価格SRP(Suggested Retailer' Price) とSAM1051 〜SAM1054 から入力した利用履歴データ108とに基づいて、ユーザによるコンテンツの購入・利用に対して決済を行い、ユーザが支払った金銭をコンテンツプロバイダ101に分配する権利処理(利益分配)機能を有する。
【0034】
以下、コンテンツプロバイダ101の各構成要素について詳細に説明する。
〔コンテンツプロバイダ101〕
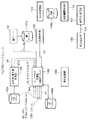
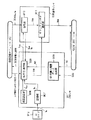
図2は、コンテンツプロバイダ101の機能ブロック図であり、ユーザホームネットワーク103のSAM1051 〜1054 との間で送受信されるデータに関連するデータの流れが示されている。
また、図3には、コンテンツプロバイダ101とEMDサービスセンタ102との間で送受信されるデータに関連するデータの流れが示されている。
なお、図3以降の図面では、署名データ処理部、および、セッション鍵データKSES を用いた暗号化・復号部に入出力するデータの流れは省略している。
【0035】
図2および図3に示すように、コンテンツプロバイダ101は、コンテンツマスタソースサーバ111、電子透かし情報付加部112、圧縮部113、暗号化部114、乱数発生部115、暗号化部116、署名処理部117、セキュアコンテナ作成部118、セキュアコンテナデータベース118a、記憶部119、相互認証部120、暗号化・復号部121、権利書データ作成部122、SAM管理部124およびEMDサービスセンタ管理部125を有する。
コンテンツプロバイダ101は、EMDサービスセンタ102との間で通信を行う前に、例えば、自らが生成した公開鍵データ、自らの身分証明書および銀行口座番号(決済を行う口座番号)をオフラインでEMDサービスセンタ102に登録し、自らの識別子(識別番号)CP_IDを得る。また、コンテンツプロバイダ101は、EMDサービスセンタ102から、EMDサービスセンタ102の公開鍵データと、ルート認証局92の公開鍵データとを受ける。
以下、図2および図3に示すコンテンツプロバイダ101の各機能ブロックについて説明する。
【0036】
コンテンツマスタソースサーバ111は、ユーザホームネットワーク103に提供するコンテンツのマスタソースであるコンテンツデータを記憶し、提供しようとするコンテンツデータS111を電子透かし情報付加部112に出力する。
【0037】
電子透かし情報付加部112は、コンテンツデータS111に対して、ソース電子透かし情報(Source Watermark)Ws、コピー管理用電子透かし情報(Copy Control Watermark)Wcおよびユーザ電子透かし情報(User Watermark)Wuなどを埋め込んでコンテンツデータS112を生成し、コンテンツデータS112を圧縮部113に出力する。
【0038】
ソース電子透かし情報Wsは、コンテンツデータの著作権者名、ISRCコード、オーサリング日付、オーサリング機器ID(Identification Data) 、コンテンツの配給先などの著作権に関する情報である。コピー管理用電子透かし情報Wcは、アナログインタフェース経由でのコピー防止用のためのコピー禁止ビットを含む情報である。ユーザ電子透かし情報Wuには、例えば、セキュアコンテナ104の配給元および配給先を特定するためのコンテンツプロバイダ101の識別子CP_IDおよびユーザホームネットワーク103のSAM1051 〜1054 の識別子SAM_ID1 〜SAM_ID4 が含まれる。
また、電子透かし情報付加部112は、必要であれば、検索エンジンでコンテンツデータの検索を行うためのリンク用のIDを電子透かし情報としてコンテンツデータS111に埋め込む。
本実施形態では、好ましくは、各々の電子透かし情報の情報内容と埋め込み位置とを、電子透かし情報管理データとして定義し、EMDサービスセンタ102において電子透かし情報管理データを管理する。電子透かし情報管理データは、例えば、ユーザホームネットワーク103内のネットワーク機器1601 およびAV機器1602 〜1604 が、電子透かし情報の正当性を検証する際に用いられる。
例えば、ユーザホームネットワーク103では、電子透かし情報管理データに基づいて、電子透かし情報の埋め込み位置および埋め込まれた電子透かし情報の内容の双方が一致した場合に電子透かし情報が正当であると判断することで、偽りの電子透かし情報の埋め込みを高い確率で検出できる。
【0039】
圧縮部113は、コンテンツデータS112を、例えば、ATRAC3(Adaptive Transform Acoustic Coding 3)(商標)などの音声圧縮方式で圧縮し、圧縮したコンテンツデータS113を暗号化部114に出力する。
【0040】
暗号化部114は、コンテンツ鍵データKcを共通鍵として用い、DES(Data Encryption Standard)やTriple DESなどの共通鍵暗号化方式で、コンテンツデータS113を暗号化してコンテンツデータCを生成し、これをセキュアコンテナ作成部118に出力する。
また、暗号化部114は、コンテンツ鍵データKcを共通鍵として用い、A/V伸長用ソフトウェアSoftおよびメタデータMetaを暗号化した後に、セキュアコンテナ作成部117に出力する。
【0041】
DESは、56ビットの共通鍵を用い、平文の64ビットを1ブロックとして処理する暗号化方式である。DESの処理は、平文を撹拌し、暗号文に変換する部分(データ撹拌部)と、データ撹拌部で使用する鍵(拡大鍵)データを共通鍵データから生成する部分(鍵処理部)とからなる。DESの全てのアルゴリズムは公開されているので、ここでは、データ撹拌部の基本的な処理を簡単に説明する。
【0042】
先ず、平文の64ビットは、上位32ビットのH0 と下位32ビットのL0 とに分割される。鍵処理部から供給された48ビットの拡大鍵データK1 および下位32ビットのL0 を入力とし、下位32ビットのL0 を撹拌したF関数の出力が算出される。F関数は、数値を所定の規則で置き換える「換字」およびビット位置を所定の規則で入れ替える「転置」の2種類の基本変換から構成されている。次に、上位32ビットのH0 と、F関数の出力との排他的論理和が算出され、その結果はL1 とされる。また、L0 は、H1 とされる。
そして、上位32ビットのH0 および下位32ビットのL0 を基に、以上の処理を16回繰り返し、得られた上位32ビットのH16および下位32ビットのL16が暗号文として出力される。復号は、暗号化に使用した共通鍵データを用いて、上記の手順を逆さにたどることで実現される。
【0043】
乱数発生部115は、所定ビット数の乱数を発生し、当該乱数をコンテンツ鍵データKcとして暗号化部114および暗号化部116に出力する。
なお、コンテンツ鍵データKcは、コンテンツデータが提供する楽曲に関する情報から生成してもよい。コンテンツ鍵データKcは、例えば、所定時間毎に更新される。
【0044】
暗号化部116は、後述するようにしてEMDサービスセンタ102から受信されて記憶部119に記憶された配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 のうち対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 を入力し、当該配信用鍵データを共通鍵として用いたDESなどの共通暗号化方式によって図4(B)に示すコンテンツ鍵データKc、権利書データ106、SAMプログラム・ダウンロード・コンテナSDC1 〜SDC3 および署名・証明書モジュールMod1 を暗号化した後に、セキュアコンテナ作成部117に出力する。
署名・証明書モジュールMod1 には、図4(B)に示すように、署名データSIG2,CP〜SIG4,CP、コンテンツプロバイダ101の公開鍵データKCP,Pの公開鍵証明書CERCPおよび当該公開鍵証明書CERCPに対してのEMDサービスセンタ102の署名データSIG1,ESC が格納されている。
また、SAMプログラム・ダウンロード・コンテナSDC1 〜SDC3 は、SAM1051 〜1054 内でプログラムのダウンロードを行なう際に用いられるダウンロード・ドライバと、権利書データ(UCP)U106のシンタックス(文法)を示すUCP−L(Label) .R(Reader)と、SAM1051 〜1054 に内蔵された記憶部(フラッシュ−ROM)の書き換えおよび消去をブロック単位でロック状態/非ロック状態にするためのロック鍵データとを格納している。
【0045】
なお、記憶部119は、例えば、公開鍵証明書データを記憶するデータベース、配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 を記憶するデータベースおよびキーファイルKFを記憶するデータベースなどの種々のデータベースを備えている。
【0046】
署名処理部117は、署名を行なう対象となるデータのハッシュ値をとり、コンテンツプロバイダ101の秘密鍵データKCP,Sを用いて、その署名データSIGを作成する。
【0047】
なお、ハッシュ値は、ハッシュ関数を用いて生成される。ハッシュ関数は、対象となるデータを入力とし、当該入力したデータを所定のビット長のデータに圧縮し、ハッシュ値として出力する関数である。ハッシュ関数は、ハッシュ値(出力)から入力を予測することが難しく、ハッシュ関数に入力されたデータの1ビットが変化したとき、ハッシュ値の多くのビットが変化し、また、同一のハッシュ値を持つ入力データを探し出すことが困難であるという特徴を有している。
【0048】
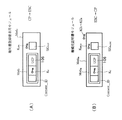
セキュアコンテナ作成部118は、図4(A)に示すように、ヘッダデータと、暗号化部114から入力したそれぞれコンテンツ鍵データKcで暗号化されたコンテンツデータC、A/V伸長用ソフトウェアSoftおよびメタデータMetaとを格納したコンテンツファイルCFを生成する。
ここで、A/V伸長用ソフトウェアSoftは、ユーザホームネットワーク103のネットワーク機器1601 およびAV機器1602 〜1604 において、コンテンツファイルCFを伸長する際に用いられるソフトウェアであり、例えば、ATRAC3方式の伸長用ソフトウェアである。
【0049】
また、セキュアコンテナ作成部118は、図4(B)に示すように、暗号化部116から入力した対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 で暗号化されたコンテンツ鍵データKc、権利書データ(UCP)106およびSAMプログラム・ダウンロード・コンテナSDC1 〜SDC3 および署名・証明書モジュールMod1 を格納したキーファイルKFを生成する。
そして、セキュアコンテナ作成部118は、図4(A),(B)に示すコンテンツファイルCFおよびキーファイルKFと、図4(C)に示すコンテンツプロバイダ101の公開鍵データKCPおよび署名データSIG1,ESC とを格納したセキュアコンテナ104を生成し、これをセキュアコンテナデータバース118aに格納した後に、ユーザからの要求に応じてSAM管理部124に出力する。
このように、本実施形態では、コンテンツプロバイダ101の公開鍵データKCP,Pの公開鍵証明書CERCPをセキュアコンテナ104に格納してユーザホームネットワーク103に送信するイン・バンド(In-band) 方式を採用している。従って、ユーザホームネットワーク103は、公開鍵証明書CERCPを得るための通信をEMDサービスセンタ102との間で行う必要がない。
なお、本発明では、公開鍵証明書CERCPをセキュアコンテナ104に格納しないで、ユーザホームネットワーク103がEMDサービスセンタ102から公開鍵証明書CERCPを得るアウト・オブ・バンド(Out-Of-band) 方式を採用してもよい。
【0050】
相互認証部120は、コンテンツプロバイダ101がEMDサービスセンタ102およびユーザホームネットワーク103との間でオンラインでデータを送受信する際に、それぞれEMDサービスセンタ102およびユーザホームネットワーク103との間で相互認証を行ってセッション鍵データ(共有鍵)KSES を生成する。セッション鍵データKSES は、相互認証を行う度に新たに生成される。
【0051】
暗号化・復号部121は、コンテンツプロバイダ101がEMDサービスセンタ102およびユーザホームネットワーク103にオンラインで送信するデータを、セッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化する。
また、暗号化・復号部121は、コンテンツプロバイダ101がEMDサービスセンタ102およびユーザホームネットワーク103からオンラインで受信したデータを、セッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号する。
【0052】
権利書データ作成部122は、権利書データ106を作成し、これを暗号化部116に出力する。
権利書データ106は、コンテンツデータCの運用ルールを定義した記述子(ディスクリプター)であり、例えば、コンテンツプロバイダ101の運用者が希望する標準小売価格SRP(Suggested Retailer' Price) やコンテンツデータCの複製ルールなどが記述されている。
【0053】
SAM管理部124は、セキュアコンテナ104を、オフラインおよび/またはオンラインでユーザホームネットワーク103に供給する。
SAM管理部124は、CD−ROMやDVD(Digital Versatile Disc)などのROM型の記録媒体(メディア)を用いてセキュアコンテナ104をオフラインでユーザホームネットワーク103に配給する場合には、配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 などを用いてセキュアコンテナ104を暗号化して記録媒体に記録する。そして、この記録媒体は、販売などにより、ユーザホームネットワーク103にオフラインで供給される。
【0054】
本実施形態では、セキュアコンテナ(商品カプセル)104は、図5に示すように、OSIレイヤ層におけるアプリケーション層で定義される。また、プレゼンテーション層やトランスポート層に相当するカプセルは、セキュアコンテナを配送するための配送プロトコルとして、セキュアコンテナ104とは別に定義される。従って、セキュアコンテナ104を配送プロトコルに依存しないで定義できる。すなわち、セキュアコンテナ104を、例えばオンラインおよびオフラインの何れの形態でユーザホームネットワーク103に供給する場合でも、共通のルールに従って定義および生成できる。
例えば、セキュアコンテナ104をネットワークを使って供給する場合には、セキュアコンテナ104をコンテンツプロバイダ101の領域で定義し、プレゼンテーション層およびトランスポート層をセキュアコンテナ104をユーザホームネットワーク103まで搬送するための搬送ツールと考える。
また、オフラインの場合に、ROM型の記録媒体を、セキュアコンテナ104をユーザホームネットワーク103に搬送する搬送キャリアとして考える。
【0055】
図6は、ROM型の記録媒体130を説明するための図である。
図6に示すように、ROM型の記録媒体130は、ROM領域131、RAM領域132およびメディアSAM133を有する。
ROM領域131には、図4(A)に示したコンテンツファイルCFが記憶されている。
また、RAM領域132には、図4(B)、(C)に示したキーファイルKFおよび公開鍵証明書データCERCPと機器の種類に応じて固有の値を持つ記録用鍵データKSTR とを引数としてMAC(Message Authentication Code) 関数を用いて生成したと署名データと、当該キーファイルKFおよび公開鍵証明書データCERCPとを記録媒体に固有の値を持つメディア鍵データKMED を用いて暗号化したデータとが記憶される。
また、RAM領域132には、例えば、不正行為などで無効となったコンテンツプロバイダ101およびSAM1051 〜1055 を特定する公開鍵証明書破棄データ(リボケーションリスト)が記憶される。
また、また、RAM領域132には、後述するようにユーザホームネットワーク103のSAM1051 〜1054 においてコンテンツデータCの購入・利用形態が決定されたときに生成される利用制御状態(UCS)データ166などが記憶される。これにより、利用制御状態データ166がRAM領域132に記憶されることで、購入・利用形態が決定したROM型の記録媒体130となる。
メディアSAM133には、例えば、ROM型の記録媒体130の識別子であるメディアIDと、メディア鍵データKMED とが記憶されている。
メディアSAM133は、例えば、相互認証機能を有している。
【0056】
また、SAM管理部124は、セキュアコンテナ104を、ネットワークやデジタル放送などを用いてオンラインでユーザホームネットワーク103に配信する場合には、暗号化・復号部121においてセッション鍵データKSES を用いてセキュアコンテナ104を暗号化した後に、ネットワークを介してユーザホームネットワーク103に配信する。
本実施形態では、SAM管理部、EMDサービスセンタ管理部、並びに後述するコンテンツプロバイダ管理部およびサービスプロバイダ管理部として、例えば、内部の処理内容の監視(モニタリング)および改竄ができないあるいは困難な耐タンパ性の構造を持つ通信ゲートウェイが用いられる。
【0057】
ここで、コンテンツプロバイダ101からユーザホームネットワーク103へのコンテンツデータCの配給は、上述したように記録媒体130を用いて行う場合とネットワークを使ってオンラインで行う場合との何れでも権利書データ106が格納された共通の形式のセキュアコンテナ104を用いる。従って、ユーザホームネットワーク103のSAM1051 〜1054 では、オフラインおよびオンラインの何れの場合でも、共通の権利書データ106に基づいた権利処理を行なうことができる。
【0058】
また、上述したように、本実施形態では、セキュアコンテナ104内に、コンテンツ鍵データKcで暗号化されたコンテンツデータCと、当該暗号化を解くためのコンテンツ鍵データKcとを同封するイン・バンド(In-Band) 方式を採用している。イン・バンド方式では、ユーザホームネットワーク103の機器で、コンテンツデータCを再生しようとするときに、コンテンツ鍵データKcを別途配信する必要がなく、ネットワーク通信の負荷を軽減できるという利点がある。また、コンテンツ鍵データKcは配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 で暗号化されているが、配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 は、EMDサービスセンタ102で管理されており、ユーザホームネットワーク103のSAM1051 〜1055 に事前に(SAM1051 〜1054 がEMDサービスセンタ102に初回にアクセスする際に)配信されているので、ユーザホームネットワーク103では、EMDサービスセンタ102との間をオンラインで接続することなく、オフラインで、コンテンツデータCの利用が可能になる。
なお、本発明は、コンテンツデータCとコンテンツ鍵データKcとを別々に、ユーザホームネットワーク103に供給するアウト・オブ・バンド(Out-Of-Band) 方式を採用できる柔軟性を有している。
【0059】
EMDサービスセンタ管理部125は、EMDサービスセンタ102から6カ月分の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 およびそれぞれに対応した署名データSIGKD1,ESC 〜SIGKD6,ESC と、コンテンツプロバイダ101の公開鍵データKCP,Pを含む公開鍵証明書CERCPおよびその署名データSIG1,ESC と、決済レポートデータ107とを受信すると、これらを暗号化・復号部121においてセッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号した後に、記憶部119に記憶する。
決済レポートデータ107は、例えば、EMDサービスセンタ102が図1に示す決済機関91に対して行なったコンテンツプロバイダ101に関する決済の内容が記述されている。
【0060】
また、EMDサービスセンタ管理部125は、提供するコンテンツデータCのグローバルユニーク(Global Unique) な識別子Content_ID、公開鍵データKCP,Pおよびそれらの署名データSIG9,CPを、EMDサービスセンタ102に送信し、EMDサービスセンタ102から、公開鍵データKCP,Pの公開鍵証明書データCERCPを入力する。
また、EMDサービスセンタ管理部125は、権利書データ106をEMDサービスセンタ102に登録する際に、図7(A)に示すように、提供するコンテンツデータCのグルーバルユニークな識別子Content_ID、コンテンツ鍵データKcおよび権利書データ106を格納したモジュールMod3 と、その署名データSIG5,CPとを格納した権利書登録要求用モジュールMod2 を作成し、これを暗号化・復号部121においてセッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化した後に、ネットワークを介してEMDサービスセンタ102に送信する。
EMDサービスセンタ管理部125としては、前述したように、例えば、内部の処理内容の監視(モニタリング)および改竄ができないあるいは困難な耐タンパ性の構造を持つ通信ゲートウェイが用いられる。
【0061】
以下、図2および図3を参照しながら、コンテンツプロバイダ101における処理の流れを説明する。
なお、以下に示す処理を行う前提として、コンテンツプロバイダ101の関係者は、例えば、自らの身分証明書および決済処理を行う銀行口座などを用いて、オフラインで、EMDサービスセンタ102に登録処理を行い、グローバルユニークな識別子CP_IDを得ている。識別子CP_IDは、記憶部119に記憶される。
【0062】
以下、コンテンツプロバイダ101が、EMDサービスセンタ102に、自らの秘密鍵データKCP,Sに対応する公開鍵データKCP,Sの正当性を証明する公開鍵証明書データCERCPを要求する場合の処理を図3および図8を参照しながら説明する。
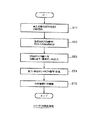
図8は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップSA1:コンテンツプロバイダ101は、例えば真性乱数発生器から構成される乱数発生部115を用いて乱数を発生して秘密鍵データKCP,Sを生成する。
ステップSA2:コンテンツプロバイダ101は、秘密鍵データKCP,Sに対応する公開鍵データKCP,Pを作成して記憶部119に記憶する。
ステップSA3:コンテンツプロバイダ101のEMDサービスセンタ管理部125は、コンテンツプロバイダ101の識別子CP_IDおよび公開鍵データKCP,Pを記憶部119から読み出す。
そして、EMDサービスセンタ管理部125は、識別子CP_IDおよび公開鍵データKCP,Pを含む公開鍵証明書データ発行要求をEMDサービスセンタ102に送信する。
ステップSA4:EMDサービスセンタ管理部125は、当該発行要求に応じて、公開鍵証明書データCERCPおよびその署名データSIG1,ESC をEMDサービスセンタ102から入力して記憶部119に書き込む。
【0063】
以下、コンテンツプロバイダ101が、EMDサービスセンタ102から配信用鍵データを受信する処理を図3を参照しながら説明する。
なお、以下に示す処理を行う前提として、コンテンツプロバイダ101は、EMDサービスセンタ102から既に公開鍵証明書データCERCPを得ている必要がある。
EMDサービスセンタ管理部125が、EMDサービスセンタ102から6カ月分の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 およびその署名データSIGKD1,ESC 〜SIGKD6,ESC を入力し、これを記憶部119内の所定のデータベースに記憶する。
そして、署名処理部117において、記憶部119に記憶された署名データSIGKD1,ESC 〜SIGKD6,ESC の正当性が確認された後に、記憶部119に記憶されている配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 が有効なものとして扱われる。
【0064】
以下、コンテンツプロバイダ101がユーザホームネットワーク103のSAM1051 にセキュアコンテナ104を送信する場合の処理を図2および図9を参照しながら説明する。
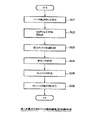
図9は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
なお、以下の例では、コンテンツプロバイダ101からSAM1051 にセキュアコンテナ104を送信する場合を例示するが、セキュアコンテナ104をSAM1052 〜1054 に送信する場合も、SAM1051 を介してSAM1052 〜1054 に送信される点を除いて同じである。
【0065】
ステップSB1:コンテンツデータS111がコンテンツマスタソースサーバ111から読み出されて電子透かし情報付加部112に出力される。
電子透かし情報付加部112は、コンテンツデータS111に電子透かし情報を埋め込んでコンテンツデータS112を生成し、これを圧縮部113に出力する。
ステップSB2:圧縮部113は、コンテンツデータS112を、例えばATRAC3方式で圧縮してコンテンツデータS113を作成し、これを暗号化部114に出力する。
【0066】
ステップSB3:乱数発生部115は、乱数を発生してコンテンツ鍵データKcを生成し、これを暗号化部114に出力する。
【0067】
ステップSB4:暗号化部114は、コンテンツデータS113と、記憶部119から読み出されたメタデータMetaおよびA/V伸長用ソフトウェアSoftとを、コンテンツ鍵データKcを用いて暗号化してセキュアコンテナ作成部118に出力する。この場合に、メタデータMetaは暗号化しなくてもよい。
そして、セキュアコンテナ作成部118は、図4(A)に示すコンテンツファイルCFを作成する。また、署名処理部117において、コンテンツファイルCFのハッシュ値がとられ、秘密鍵データKCP,Sを用いて署名データSIG6,CPが生成される。
【0068】
ステップSB5:署名処理部117は、コンテンツデータC、コンテンツ鍵データKcおよび権利書データ106のそれぞれに対してハッシュ値をとり、秘密鍵データKCP,Sを用いて、それぞれのデータの作成者(提供者)の正当性を示す署名データSIG2,CP,SIG3,CP,SIG4,CPを作成する。
また、暗号化部116は、図4(B)に示すコンテンツ鍵データKc、権利書データ106、SAMプログラム・ダウンロード・コンテナSD1 〜SD3 および署名・証明書モジュールMod1 を、対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 で暗号化してセキュアコンテナ作成部118に出力する。
そして、セキュアコンテナ作成部118は、図4(B)に示すキーファイルKFを作成する。
また、署名処理部117は、キーファイルKFのハッシュ値をとり、秘密鍵データKCP,Sを用いて、署名データSIG7,CPを作成する。
【0069】
ステップSB6:セキュアコンテナ作成部118は、図4(A)に示すコンテンツファイルCFおよびその署名データSIG6,CPと、図4(B)に示すキーファイルKFおよびその署名データSIG7,CPと、図4(C)に示す公開鍵証明書データCERCPおよびその署名データSIG1,ESC とを格納したセキュアコンテナ104を作成し、これを、セキュアコンテナデータベース118aに記憶する。
ステップSB7:セキュアコンテナ作成部118は、例えばユーザからの要求(リクエスト)に応じてユーザホームネットワーク103に提供しようとするセキュアコンテナ104をセキュアコンテナデータベース118aから読み出して、相互認証部120とSAM1051 との間の相互認証によって得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化・復号部121において暗号化した後に、SAM管理部124を介してユーザホームネットワーク103のSAM1051 に送信する。
【0070】
以下、コンテンツプロバイダ101が、EMDサービスセンタ102に権利書データ106およびコンテンツ鍵データKcを登録して権威化することを要求する場合の処理を図3を参照して説明する。
権利書データ106およびコンテンツ鍵データKcの権威化要求処理は、個々のコンテンツデータC毎に行われる。
【0071】
この場合には、署名処理部117において、記憶部119から読み出したコンテンツデータCのグローバルユニークな識別子Content_ID、コンテンツ鍵データKcおよび権利書データ作成部122から入力した権利書データ106からなるモジュールMod3 のハッシュ値が求められ、秘密鍵データKCP,Sを用いて署名データSIG5,CPが生成される。
そして、図7(A)に示す権利登録要求用モジュールMod2 を、相互認証部120とEMDサービスセンタ102との間の相互認証によって得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化・復号部121において暗号化した後に、EMDサービスセンタ管理部125からEMDサービスセンタ102に送信する。
【0072】
本実施形態では、EMDサービスセンタ102において権利書データ106およびコンテンツ鍵データKcを権威化した後に、コンテンツプロバイダ101がEMDサービスセンタ102から権威化されたことを証明する権威化証明書モジュールを受信しない場合、すなわちコンテンツプロバイダ101において配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 を用いて暗号化を行ってキーファイルKFを作成する場合を例示する。
但し、本発明は、例えば、EMDサービスセンタ102において権利書データ106およびコンテンツ鍵データKcを権威化した後に、EMDサービスセンタ102からコンテンツプロバイダ101に、配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 を用いて暗号化した図7(B)に示す権威化証明書モジュールMod2aを送信してもよい。
権威化証明書モジュールMod2aは、コンテンツデータCのグローバルユニークな識別子Content_ID、コンテンツ鍵データKcおよび権利書データ作成部122から入力した権利書データ106を格納したモジュールMod3aと、秘密鍵データKESC,S を用いたモジュールMod3aの署名データSIG5a,ESCとを格納している。
この場合には、コンテンツプロバイダ101は、例えば、セキュアコンテナ104内に、権威化証明書モジュールMod2aを格納してSAM1051 〜1054 に配給する。
なお、EMDサービスセンタ102は、それぞれ異なる月に対応する配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 を用いて暗号化した6カ月分の権威化証明書モジュールMod2aを生成し、これらをまとめてコンテンツプロバイダ101に送信してもよい。
【0073】
〔EMDサービスセンタ102〕
EMDサービスセンタ102は、認証(CA:Certificate Authority) 機能、鍵管理(Key Management)機能および権利処理(Rights Clearing) (利益分配)機能を有する。
図10は、EMDサービスセンタ102の機能の構成図である。
図10に示すように、EMDサービスセンタ102は、鍵サーバ141、鍵データベース141a、決算処理部142、署名処理部143、決算機関管理部144、証明書・権利書管理部145、CERデータベース145a、コンテンツプロバイダ管理部148、CPデータベース148a、SAM管理部149、SAMデータベース149a、相互認証部150および暗号化・復号部151を有する。
なお、図10には、EMDサービスセンタ102内の機能ブロック相互間のデータの流れのうち、コンテンツプロバイダ101との間で送受信されるデータに関連するデータの流れが示されている。
また、図11には、EMDサービスセンタ102内の機能ブロック相互間のデータの流れのうち、SAM1051 〜1054 および図1に示す決済機関91との間で送受信されるデータに関連するデータの流れが示されている。
【0074】
鍵サーバ141は、鍵データベース141aに記憶された各々有効期間が1カ月の配信用鍵データを要求に応じて読み出してコンテンツプロバイダ管理部148およびSAM管理部149に出力する。
また、鍵データベース141a配信用鍵データKDの他に、記録用鍵データKSTR 、メディア鍵データKMED およびMAC鍵データKMAC などの鍵データを記憶する一連の鍵データースからなる。
【0075】
決算処理部142は、SAM1051 〜1054 から入力した利用履歴データ108と、証明書・権利書管理部145から入力した標準小売価格データSRPおよび販売価格とに基づいて決済処理を行い、決済レポートデータ107および決済請求権データ152を作成し、決済レポートデータ107をコンテンツプロバイダ管理部148に出力し、決済請求権データ152を決算機関管理部144に出力する。
なお、決算処理部142は、販売価格に基づいて、違法なダンピング価格による取り引きが行われたか否かを監視する。
ここで、利用履歴データ108は、ユーザホームネットワーク103におけるセキュアコンテナ104の購入、利用(再生、記録および転送など)の履歴を示し、決算処理部142においてセキュアコンテナ104に関連したラインセンス料の支払い額を決定する際に用いられる。
【0076】
利用履歴データ108には、例えば、セキュアコンテナ104に格納されたコンテンツデータCの識別子Content_ID、セキュアコンテナ104を配給したコンテンツプロバイダ101の識別子CP_ID、セキュアコンテナ104内のコンテンツデータCの圧縮方法、セキュアコンテナ104を記録した記録媒体の識別子Media_ID、セキュアコンテナ104を配給を受けたSAM1051 〜1054 の識別子SAM_ID、当該SAM1051 〜1054 のユーザのUSER_IDなどが記述されている。従って、EMDサービスセンタ102は、コンテンツプロバイダ101の所有者以外にも、例えば、圧縮方法や記録媒体などのライセンス所有者に、ユーザホームネットワーク103のユーザが支払った金銭を分配する必要がある場合には、予め決められた分配率表に基づいて各相手に支払う金額を決定し、当該決定に応じた決済レポートデータ107および決済請求権データ152を作成する。当該分配率表は、例えば、セキュアコンテナ104に格納されたコンテンツデータ毎に作成される。
また、決済請求権データ152は、当該データに基づいて、決済機関91に金銭の支払いを請求できる権威化されたデータであり、例えば、ユーザが支払った金銭を複数の権利者に配給する場合には、個々の権利者毎に作成される。
なお、決済機関91は、決済が終了すると、当該決済機関の利用明細書をEMDサービスセンタ102に送る。EMDサービスセンタ102は、当該利用明細書の内容を、対応する権利者に通知する。
【0077】
決算機関管理部144は、決算処理部142が生成した決済請求権利データ152を図1に示すペイメントゲートウェイ90を介して決済機関91に送信する。
なお、後述するように、決算機関管理部144は、決済請求権データ152を、コンテンツプロバイダ101などの権利者に送信し、権利者自らが、受信した決済請求権データ152を用いて決済機関91に決済を行ってもよい。
また、決算機関管理部144は、署名処理部143において決済請求権データ152のハッシュ値をとり、秘密鍵データKESC,S を用いて生成した署名データSIG99を決済請求権データ152と共に決済機関91に送信する。
【0078】
証明書・権利書管理部145は、CERデータベース145aに登録されて権威化された公開鍵証明書データCERCPおよび公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1〜CERSAM4などを読み出すと共に、コンテンツプロバイダ101の権利書データ106およびコンテンツ鍵データKcなどをCERデータベース145aに登録して権威化する。
なお、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1〜CERSAM4を格納するデータベースと、権利書データ106およびコンテンツ鍵データKcとを個別に設けてもよい。
このとき、証明書・権利書管理部145は、例えば、権利書データ106およびコンテンツ鍵データKcなどのハッシュ値をとり、秘密鍵データKESC,S を用いた署名データを付した権威化されたそれぞれの証明書データを作成する。
【0079】
コンテンツプロバイダ管理部148は、コンテンツプロバイダ101との間で通信する機能を有し、登録されたコンテンツプロバイダ101の識別子CP_IDなどを管理するCPデータベース148aにアクセスできる。
【0080】
SAM管理部149は、ユーザホームネットワーク103内のSAM1051 〜1054 との間で通信する機能を有し、登録されたSAMの識別子SAM_IDやSAM登録リストなどを記録したSAMデータベース149aにアクセスできる。
【0081】
以下、EMDサービスセンタ102内での処理の流れを説明する。
先ず、EMDサービスセンタ102からコンテンツプロバイダ101およびユーザホームネットワーク103内のSAM1051 〜1054 への配信用鍵データを送信する際の処理の流れを、図10および図11を参照しながら説明する。
図10に示すように、鍵サーバ141は、所定期間毎に、例えば、6カ月分の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 を鍵データベース141aから読み出してコンテンツプロバイダ管理部148に出力する。
また、署名処理部143は、配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 の各々のハッシュ値をとり、EMDサービスセンタ102の秘密鍵データKESC,S を用いて、それぞれに対応する署名データSIGKD1,ESC 〜SIGKD6,ESC を作成し、これをコンテンツプロバイダ管理部148に出力する。
コンテンツプロバイダ管理部148は、この6カ月分の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 およびそれらの署名データSIGKD1,ESC 〜SIGKD6,ESC を、相互認証部150と図3に示す相互認証部120と間の相互認証で得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化した後に、コンテンツプロバイダ101に送信する。
【0082】
また、図11に示すように、鍵サーバ141は、所定期間毎に、例えば、3カ月分の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を鍵データベース141aから読み出してSAM管理部149に出力する。
また、署名処理部143は、配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 の各々のハッシュ値をとり、EMDサービスセンタ102の秘密鍵データKESC,S を用いて、それぞれに対応する署名データSIGKD1,ESC 〜SIGKD3,ESC を作成し、これをSAM管理部149に出力する。
SAM管理部149は、この3カ月分の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 およびそれらの署名データSIGKD1,ESC 〜SIGKD3,ESC を、相互認証部150とSAM1051 〜1054 と間の相互認証で得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化した後に、SAM1051 〜1054 に送信する。
【0083】
以下、EMDサービスセンタ102がコンテンツプロバイダ101から、公開鍵証明書データCERCPの発行要求を受けた場合の処理を、図10および図12を参照しながら説明する。
図12は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップSC1:コンテンツプロバイダ管理部148は、コンテンツプロバイダ101の識別子CP_ID、公開鍵データKCP,Pおよび署名データSIG9,CPを含む公開鍵証明書データ発行要求をコンテンツプロバイダ101から受信すると、これらを、相互認証部150と図3に示す相互認証部120と間の相互認証で得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号する。
ステップSC2:当該復号した署名データSIG9,CPの正当性を署名処理部143において確認した後に、識別子CP_IDおよび公開鍵データKCP,Pに基づいて、当該公開鍵証明書データ発行要求を出したコンテンツプロバイダ101がCPデータベース148aに登録されているか否かを確認する。
【0084】
ステップSC3:証明書・権利書管理部145は、当該コンテンツプロバイダ101の公開鍵証明書データCERCPをCERデータベース145aから読み出してコンテンツプロバイダ管理部148に出力する。
【0085】
ステップSC4:署名処理部143は、公開鍵証明書データCERCPのハッシュ値をとり、EMDサービスセンタ102の秘密鍵データKESC,S を用いて、署名データSIG1,ESC を作成し、これをコンテンツプロバイダ管理部148に出力する。
ステップSC5:コンテンツプロバイダ管理部148は、公開鍵証明書データCERCPおよびその署名データSIG1,ESC を、相互認証部150と図3に示す相互認証部120と間の相互認証で得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化した後に、コンテンツプロバイダ101に送信する。
【0086】
以下、EMDサービスセンタ102がSAM1051 から、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1の発行要求を受けた場合の処理を、図11および図13を参照しながら説明する。
図13は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップSD1:SAM管理部149は、SAM1051 の識別子SAM1 _ID、公開鍵データKSAM1,Pおよび署名データSIG8,SAM1を含む公開鍵証明書データ発行要求をSAM1051 から受信すると、これらを、相互認証部150とSAM1051 と間の相互認証で得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号する。
【0087】
ステップSD2:当該復号した署名データSIG8,SAM1の正当性を署名処理部143において確認した後に、識別子SAM1 _IDおよび公開鍵データKSAM1,Pに基づいて、当該公開鍵証明書データの発行要求を出したSAM1051 がSAMデータベース149aに登録されているか否かを確認する。
ステップSD3:証明書・権利書管理部145は、当該SAM1051 の公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1をCERデータベース145aから読み出してSAM管理部149に出力する。
【0088】
ステップSD4:署名処理部143は、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1のハッシュ値をとり、EMDサービスセンタ102の秘密鍵データKESC,S を用いて、署名データSIG50,ESCを作成し、これをSAM管理部149に出力する。
ステップSD5:SAM管理部149は、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1およびその署名データSIG50,ESCを、相互認証部150とSAM1051 と間の相互認証で得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化した後に、SAM1051 に送信する。
なお、SAM1052 〜1054 が、公開鍵証明書データを要求した場合の処理は、対象がSAM1052 〜1054 に代わるのみで、基本的に上述したSAM1051 の場合と同じである。
なお、本発明では、EMDサービスセンタ102は、例えば、SAM1051 の出荷時に、SAM1051 の秘密鍵データKSAM1,Sおよび公開鍵データKSAM1,PをSAM1051 の記憶部に記憶する場合には、当該出荷時に、公開鍵データKSAM1,Pの公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1を作成してもよい。
このとき、当該出荷時に、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1を、SAM1051 の記憶部に記憶してもよい。
【0089】
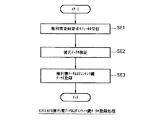
以下、EMDサービスセンタ102が、コンテンツプロバイダ101から権利書データ106およびコンテンツ鍵データKcの登録要求を受けた場合の処理を、図10および図14を参照しながら説明する。
図14は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップSE1:コンテンツプロバイダ管理部148は、コンテンツプロバイダ101から図7(A)に示す権利書登録要求モジュールMod2 を受信すると、相互認証部150と図3に示す相互認証部120と間の相互認証で得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて権利書登録要求モジュールMod2 を復号する。
【0090】
ステップSE2:署名処理部143において、鍵データベース141aから読み出した公開鍵データKcpを用いて、署名データSIG5,CPの正当性を検証する。
ステップSE3:証明書・権利書管理部145は、権利書登録要求モジュールMod2 に格納された権利書データ106およびコンテンツ鍵データKcを、CERデータベース145aに登録する。
【0091】
以下、EMDサービスセンタ102において決済処理を行なう場合の処理を図11および図15を参照しながら説明する。
図15は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップSF1:SAM管理部149は、ユーザホームネットワーク103の例えばSAM1051 から利用履歴データ108およびその署名データSIG200,SAM1を入力すると、利用履歴データ108および署名データSIG200,SAM1を、相互認証部150とSAM1051 との間の相互認証によって得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号し、SAM1051 の公開鍵データKSAM1による署名データSIG200,SAM1の検証を行なった後に、決算処理部142に出力する。
【0092】
ステップSF2:決算処理部142は、SAM管理部149から入力した利用履歴データ108と、証明書・権利書管理部145を介してCERデータベース145aから読み出した権利書データ106に含まれる標準小売価格データSRPおよび販売価格とに基づいて決済処理を行い、決済請求権データ152および決済レポートデータ107を生成する。なお、決済請求権データ152および決済レポートデータ107の生成は、SAMから利用履歴データ108を入力する度に行ってもよいし、所定の期間毎に行ってもよい。
ステップSF3:決算処理部142は、決済請求権データ152を決算機関管理部144に出力する。
決算機関管理部144は、決済請求権データ152およびその署名データSIG99を、相互認証およびセッション鍵データKSES による復号を行なった後に、図1に示すペイメントゲートウェイ90を介して決済機関91に送信する。
これにより、決済請求権データ152に示される金額の金銭が、コンテンツプロバイダ101に支払われる。
なお、EMDサービスセンタ102は、決済請求権データ152をコンテンツプロバイダ101に送信し、コンテンツプロバイダ101が決済請求権データ152を用いて決済記載91に金銭を請求してもよい。
【0093】
ステップSF4:決算処理部142は、決済レポートデータ107をコンテンツプロバイダ管理部148に出力する。
決済レポートデータ107は、上述したように、例えば、EMDサービスセンタ102が図1に示す決済機関91に対して行なったコンテンツプロバイダ101に関する決済の内容が記述されている。
コンテンツプロバイダ管理部148は、決済レポートデータ107を、相互認証部150と図3に示す相互認証部120と間の相互認証で得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化した後に、コンテンツプロバイダ101に送信する。
【0094】
また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、前述したように、権利書データ106を登録(権威化)した後に、EMDサービスセンタ102からコンテンツプロバイダ101に、図7(B)に示す権威化証明書モジュールMod2aを配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 で暗号化して送信してもよい。
【0095】
また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、その他に、SAM1051 〜1054 の出荷時の処理と、SAM登録リストの登録処理とを行なうが、これらの処理については後述する。
【0096】
〔ユーザホームネットワーク103〕
ユーザホームネットワーク103は、図1に示すように、ネットワーク機器1601 およびA/V機器1602 〜1604 を有している。
ネットワーク機器1601 は、SAM1051 を内蔵している。また、AV機器1602 〜1604 は、それぞれSAM1052 〜1054 を内蔵している。
SAM1051 〜1054 の相互間は、例えば、IEEE1394シリアルインタフェースバスなどのバス191を介して接続されている。
なお、AV機器1602 〜1604 は、ネットワーク通信機能を有していてもよいし、ネットワーク通信機能を有しておらず、バス191を介してネットワーク機器1601 のネットワーク通信機能を利用してもよい。
また、ユーザホームネットワーク103は、ネットワーク機能を有していないAV機器のみを有していてもよい。
【0097】
以下、ネットワーク機器1601 について説明する。
図16ネットワーク機器1601 の構成図である。
図16に示すように、ネットワーク機器1601 は、SAM1051 、通信モジュール162、復号・伸長モジュール163、購入・利用形態決定操作部165、ダウンロードメモリ167、再生モジュール169および外部メモリ201を有する。
【0098】
SAM1051 〜1054 は、コンテンツ単位の課金処理をおこなうモジュールであり、EMDサービスセンタ102との間で通信を行う。
SAM1051 〜1054 は、例えば、EMDサービスセンタ102によって仕様およびバージョンなどが管理され、家庭機器メーカに対し、搭載の希望があればコンテンツ単位の課金を行うブラックボックスの課金モジュールとしてライセンス譲渡される。例えば、家庭機器開発メーカは、SAM1051 〜1054 のIC(Integrated Circuit)の内部の仕様を知ることはできず、EMDサービスセンタ102が当該ICのインタフェースなどを統一化し、それに従ってネットワーク機器1601 およびAV機器1602 〜1604 に搭載される。
【0099】
SAM1051 〜1054 は、その処理内容が外部から完全に遮蔽され、その処理内容を外部から監視および改竄不能であり、また、内部に予め記憶されているデータおよび処理中のデータを外部から監視および改竄不能な耐タンパ(Tamper Registance) 性を持ったハードウェアモジュール(ICモジュールなど)である。
SAM1051 〜1054 の機能をICという形で実現する場合は、IC内部に秘密メモリを持ち、そこに秘密プログラムおよび秘密データが格納される。SAMをICという物理的形態にとらわれず、その機能を機器の何れかの部分に組み込むことができれば、その部分をSAMとして定義してもよい。
【0100】
以下、SAM1051 の機能について詳細に説明する。
なお、SAM1052 〜1054 は、SAM1051 と基本的に同じ機能を有している。
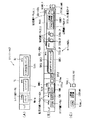
図17は、SAM1051 の機能の構成図である。
なお、図17には、コンテンツプロバイダ101からのセキュアコンテナ104を入力し、セキュアコンテナ104内のキーファイルKFを復号する処理に関連するデータの流れが示されている。
図17に示すように、SAM1051 は、相互認証部170、暗号化・復号部171,172,173、コンテンツプロバイダ管理部180、誤り訂正部181、ダウンロードメモリ管理部182、セキュアコンテナ復号部183、復号・伸長モジュール管理部184、EMDサービスセンタ管理部185、利用監視部186、課金処理部187、署名処理部189、SAM管理部190、メディアSAM管理部197、スタック(作業)メモリ200および外部メモリ管理部811を有する。
なお、AV機器1602 〜1604 はダウンロードメモリ167を有していないため、SAM1052 〜1054 にはダウンロードメモリ管理部182は存在しない。
【0101】
なお、図17に示すSAM1051 の所定の機能は、例えば、図示しないCPUにおいて秘密プログラムを実行することによって実現される。
また、スタックメモリ200には、以下に示す処理を経て、図18に示すように、利用履歴データ108およびSAM登録リストが記憶される。
ここで、外部メモリ201のメモリ空間は、SAM1051 の外部(例えば、ホストCPU810)からは見ることはできず、SAM1051 のみが外部メモリ201の記憶領域に対してのアクセスを管理できる。
外部メモリ201としては、例えば、フラッシュメモリあるいは強誘電体メモリ(FeRAM)などが用いられる。
また、スタックメモリ200としては、例えばSARAMが用いられ、図19に示すように、セキュアコンテナ104、コンテンツ鍵データKc、権利書データ(UCP)106、記憶部192のロック鍵データKLOC 、コンテンツプロバイダ101の公開鍵証明書CERCP、利用制御状態データ(UCS)166、およびSAMプログラム・ダウンロード・コンテナSDC1 〜SDC3 などが記憶される。
【0102】
以下、SAM1051 の機能のうち、コンテンツプロバイダ101からのセキュアコンテナ104を入力したときの各機能ブロックの処理内容を図17を参照しながら説明する。
【0103】
相互認証部170は、SAM1051 がコンテンツプロバイダ101およびEMDサービスセンタ102との間でオンラインでデータを送受信する際に、コンテンツプロバイダ101およびEMDサービスセンタ102との間で相互認証を行ってセッション鍵データ(共有鍵)KSES を生成し、これを暗号化・復号部171に出力する。セッション鍵データKSES は、相互認証を行う度に新たに生成される。
【0104】
暗号化・復号部171は、コンテンツプロバイダ101およびEMDサービスセンタ102との間で送受信するデータを、相互認証部170が生成したセッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化・復号する。
【0105】
誤り訂正部181は、セキュアコンテナ104を誤り訂正してダウンロードメモリ管理部182に出力する。
なお、ユーザホームネットワーク103は、セキュアコンテナ104が改竄されているか否かを検出する機能を有していてもよい。
本実施形態では、誤り訂正部181を、SAM1051 に内蔵した場合を例示したが、誤り訂正部181の機能を、例えばホストCPU810などのSAM1051 の外部に持たせてもよい。
【0106】
ダウンロードメモリ管理部182は、図16に示すようにダウンロードメモリ167が相互認証機能を持つメディアSAM167aを有している場合には、相互認証部170とメディアSAM167aとの間で相互認証を行った後に、誤り訂正後のセキュアコンテナ104を、相互認証によって得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化して図16に示すダウンロードメモリ167に書き込む。ダウンロードメモリ167としては、例えば、メモリスティックなどの不揮発性半導体メモリが用いられる。
なお、図20に示すように、HDD(Hard Disk Drive) などの相互認証機能を備えていないメモリをダウンロードメモリ211として用いる場合には、ダウンロードメモリ211内はセキュアではないので、コンテンツファイルCFをダウンロードメモリ211にダウンロードし、機密性の高いキーファイルKFを例えば、図17に示すスタックメモリ200にダウンロードする。
【0107】
セキュアコンテナ復号部183は、ダウンロードメモリ管理部182から入力したセキュアコンテナ104に格納されたキーファイルKFを、記憶部192から読み出した対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を用いて復号し、署名処理部189において署名データSIG2,CP〜SIG4,CPの正当性、すなわちコンテンツデータC、コンテンツ鍵データKcおよび権利書データ106の作成者の正当性を確認した後に、スタックメモリ200に書き込む。
【0108】
EMDサービスセンタ管理部185は、図1に示すEMDサービスセンタ102との間の通信を管理する。
【0109】
署名処理部189は、記憶部192から読み出したEMDサービスセンタ102の公開鍵データKESC,P およびコンテンツプロバイダ101の公開鍵データKCP,Pを用いて、セキュアコンテナ104内の署名データの検証を行なう。
【0110】
記憶部192は、SAM1051 の外部から読み出しおよび書き換えできない秘密データとして、図21に示すように、配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 、SAM_ID、ユーザID、パスワード、情報参照用ID、SAM登録リスト、記録用鍵データKSTR 、ルートCAの公開鍵データKR-CA,P、EMDサービスセンタ102の公開鍵データKESC,P 、メディア鍵データKMED 、EMDサービスセンタ102の公開鍵データKESC,P 、SAM1051 の秘密鍵データKSAM1,S、SAM1051 の公開鍵データKSAM1,Pを格納した公開鍵証明書CERSAM1、EMDサービスセンタ102の秘密鍵データKESC,S を用いた公開鍵証明書CERESC の署名データSIG22、復号・伸長モジュール163との間の相互認証用の元鍵データ、メディアSAMとの間の相互認証用の元鍵データを記憶している。
また、記憶部192には、図17に示す少なくとも一部の機能を実現するための秘密プログラムが記憶されている。
記憶部192としては、例えば、フラッシュ−EEPROM(Electrically Erasable Programmable RAM)が用いられる。
【0111】
以下、SAM1051 の処理の流れのうち、コンテンツプロバイダ101からのセキュアコンテナ104を入力したときの処理の流れを説明する。
先ず、EMDサービスセンタ102から受信した配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を記憶部192に格納する際のSAM1051 内での処理の流れを図17を参照しながら説明する。
この場合には、先ず、相互認証部170と図10に示す相互認証部150との間で相互認証が行われる。
次に、当該相互認証によって得られたセッション鍵データKSES で暗号化された3カ月分の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 およびその署名データSIGKD1,ESC 〜SIGKD3,ESC が、EMDサービスセンタ102からEMDサービスセンタ管理部185を介してスタックメモリ811に書き込まれる。
次に、暗号化・復号部171において、セッション鍵データKSES を用いて、配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 およびその署名データSIGKD1,ESC 〜SIGKD3,ESC が復号される。
次に、署名処理部189において、スタックメモリ811に記憶された署名データSIGKD1,ESC 〜SIGKD3,ESC の正当性が確認された後に、配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 が記憶部192に書き込まれる。
【0112】
以下、セキュアコンテナ104をコンテンツプロバイダ101から入力し、セキュアコンテナ104内のキーファイルKFを復号する際のSAM1051 内での処理の流れを図17および図22を参照しながら説明する。
図22は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップSG1:図17に示すSAM1051 の相互認証部170と図2に示す相互認証部120との間で相互認証が行なわれる。
暗号化・復号部171は、当該相互認証によって得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて、コンテンツプロバイダ管理部180を介してコンテンツプロバイダ101から受信したセキュアコンテナ104を復号する。
【0113】
ステップSG2:署名処理部189は、図4(C)に示す署名データSIG1,ESC の検証を行なった後に、図4(C)に示す公開鍵証明書データCERCP内に格納されたコンテンツプロバイダ101の公開鍵データKCP,Pを用いて、署名データSIG6,CP,SIG7,CPの正当性を確認する。
コンテンツプロバイダ管理部180は、署名データSIG6,CP,SIG7,CPの正当性が確認されると、セキュアコンテナ104を誤り訂正部181に出力する。
誤り訂正部181は、セキュアコンテナ104を誤り訂正した後に、ダウンロードメモリ管理部182に出力する。
【0114】
ステップSG3:ダウンロードメモリ管理部182は、相互認証部170と図16に示すメディアSAM167aとの間で相互認証を行なった後に、セキュアコンテナ104をダウンロードメモリ167に書き込む。
【0115】
ステップSG4:ダウンロードメモリ管理部182は、相互認証部170と図16に示すメディアSAM167aとの間で相互認証を行なった後に、セキュアコンテナ104に格納された図4(B)に示すキーファイルKFをダウンロードメモリ167から読み出してセキュアコンテナ復号部183に出力する。
そして、セキュアコンテナ復号部183は、記憶部192から入力した対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を用いて、キーファイルKFを復号し、図4(B)に示す署名・証明書モジュールMod1 に格納された署名データSIG1,ESC 、SIG2,CP〜SIG4,CPを署名処理部189に出力する。
【0116】
ステップSG5:署名処理部189は、図4(B)に示す署名データSIG1,ESC の検証を行なった後に、図4(B)に示す公開鍵証明書データCERCP内に格納された公開鍵データKESC,P を用いて署名データSIG2,CP〜SIG4,CPの検証を行なう。これにより、コンテンツデータC、コンテンツ鍵データKcおよび権利書データ106の作成者の正当性が検証される。
【0117】
ステップSG6:セキュアコンテナ復号部183は、署名データSIG2,CP〜SIG4,CPの正当性が確認されると、キーファイルKFをスタックメモリ200に書き込む。
【0118】
以下、ダウンロードメモリ167にダウンロードされたコンテンツデータCを利用・購入する処理に関連する各機能ブロックの処理内容を図23を参照しながら説明する。
【0119】
利用監視部186は、スタックメモリ200から権利書データ106および利用制御状態データ166を読み出し、当該読み出した権利書データ106および利用制御状態データ166によって許諾された範囲内でコンテンツの購入・利用が行われるように監視する。
ここで、権利書データ106は、図17を用いて説明したように、復号後にスタックメモリ200に記憶された図4(B)に示すキーファイルKF内に格納されている。
また、利用制御状態データ166は、後述するように、ユーザによって購入形態が決定されたときに、スタックメモリ200に記憶される。
【0120】
課金処理部187は、図16に示す購入・利用形態決定操作部165からの操作信号S165に応じた利用履歴データ108を作成する。
ここで、利用履歴データ108は、前述したように、ユーザによるセキュアコンテナ104の購入および利用の形態の履歴を記述しており、EMDサービスセンタ102において、セキュアコンテナ104の購入に応じた決済処理およびラインセンス料の支払いを決定する際に用いられる。
【0121】
また、課金処理部187は、必要に応じて、スタックメモリ200から読み出した販売価格あるいは標準小売価格データSRPをユーザに通知する。
ここで、販売価格および標準小売価格データSRPは、復号後にスタックメモリ200に記憶された図4(B)に示すキーファイルKFの権利書データ106内に格納されている。
課金処理部187による課金処理は、利用監視部186の監視の下、権利書データ106が示す使用許諾条件などの権利内容および利用制御状態データ166に基づいて行われる。すなわち、ユーザは、当該権利内容などに従った範囲内でコンテンツの購入および利用を行う。
【0122】
また、課金処理部187は、操作信号S165に基づいて、ユーザによるコンテンツの購入形態を記述した利用制御状態(UCS: Usage Control Status)データ166を生成し、これをスタックメモリ200に書き込む。
コンテンツの購入形態としては、例えば、購入者による再生や当該購入者の利用のための複製に制限を加えない買い切りや、再生する度に課金を行なう再生課金などがある。
ここで、利用制御状態データ166は、ユーザがコンテンツの購入形態を決定したときに生成され、以後、当該決定された購入形態で許諾された範囲内でユーザが当該コンテンツの利用を行なうように制御するために用いられる。利用制御状態データ166には、コンテンツのID、購入形態、当該購入形態に応じた価格、当該コンテンツの購入が行なわれたSAMのSAM_ID,購入を行なったユーザのUSER_IDなどが記述されている。
【0123】
なお、決定された購入形態が再生課金である場合には、例えば、SAM1051 からコンテンツプロバイダ101に利用制御状態データ166をコンテンツデータCの購入と同時にリアルタイムに送信し、コンテンツプロバイダ101がEMDサービスセンタ102に、利用履歴データ108を所定の期間内にSAM1051 に取りにいくことを指示する。
また、決定された購入形態が買い切りである場合には、例えば、利用制御状態データ166が、コンテンツプロバイダ101およびEMDサービスセンタ102の双方にリアルタイムに送信される。このように、本実施形態では、何れの場合にも、利用制御状態データ166をコンテンツプロバイダ101にリアルタイムに送信する。
【0124】
EMDサービスセンタ管理部185は、外部メモリ管理部811を介して外部メモリ201から読み出した利用履歴データ108をEMDサービスセンタ102に送信する。
このとき、EMDサービスセンタ管理部185は、署名処理部189において、秘密鍵データKSAM1,sを用いて利用履歴データ108の署名データSIG200,SAM1を作成し、署名データSIG200,SAM1を利用履歴データ108と共にEMDサービスセンタ102に送信する。
EMDサービスセンタ102への利用履歴データ108の送信は、例えば、EMDサービスセンタ102からの要求に応じてあるいは定期的に行ってもよいし、利用履歴データ108に含まれる履歴情報の情報量が所定以上になったときに行ってもよい。当該情報量は、例えば、外部メモリ201の記憶容量に応じて決定される。
【0125】
ダウンロードメモリ管理部182は、例えば、図16に示す購入形態決定操作部165からの操作信号S165に応じてコンテンツの再生動作が行われる場合に、ダウンロードメモリ167から読み出したコンテンツデータC、スタックメモリ200から読み出したコンテンツ鍵データKcおよび課金処理部187から入力したユーザ電子透かし情報用データ196を復号・伸長モジュール管理部184に出力する。
また、復号・伸長モジュール管理部184は、図16に示す購入形態決定操作部165からの操作信号S165に応じてコンテンツの試聴動作が行われる場合に、ダウンロードメモリ167から読み出したコンテンツファイルCF、並びにスタックメモリ200から読み出したコンテンツ鍵データKcおよび半開示パラメータデータ199を復号・伸長モジュール管理部184に出力する。
【0126】
ここで、半開示パラメータデータ199は、権利書データ106内に記述されており、試聴モード時のコンテンツの取り扱いを示している。復号・伸長モジュール163では、半開示パラメータデータ199に基づいて、暗号化されたコンテンツデータCを、半開示状態で再生することが可能になる。半開示の手法としては、例えば、復号・伸長モジュール163がデータ(信号)を所定のブロックを単位として処理することを利用して、半開示パラメータデータ199によって、コンテンツ鍵データKcを用いて復号を行うブロックと復号を行わないブロックとを指定したり、試聴時の再生機能を限定したり、試聴可能な期間を限定するものなどがある。
【0127】
以下、SAM1051 内での処理の流れについて説明する。
先ず、コンテンツプロバイダ101からダウンロードメモリ167にダウンロードされたセキュアコンテナ104の購入形態を決定するまでの処理の流れを図23および図24を参照しながら説明する。
図24は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップSH1:課金処理部187において、ユーザによる図16に示す購入・利用形態決定操作部165の操作によって、試聴モードを示す操作信号S165が発生したか否かが判断され、発生したと判断された場合にはステップSH2の処理が行われ、そうでない場合にはステップSH3の処理が行われる。
【0128】
ステップSH2:課金処理部187によって、例えば、ダウンロードメモリ167に記憶されているコンテンツファイルCFが、復号・伸長モジュール管理部184を介して、図16に示す復号・伸長モジュール163に出力される。
このとき、コンテンツファイルCFに対して、相互認証部170とメディアSAM167aとの間の相互認証およびセッション鍵データKSES による暗号化・復号と、相互認証部170と相互認証部220との間の相互認証およびセッション鍵データKSES による暗号化・復号とが行なわれる。
コンテンツファイルCFは、図16に示す復号部221において復号された後に、復号部222に出力される。
【0129】
また、スタックメモリ200から読み出されたコンテンツ鍵データKcおよび半開示パラメータデータ199が、図16に示す復号・伸長モジュール163に出力される。このとき、相互認証部170と相互認証部220との間の相互認証後に、コンテンツ鍵データKcおよび半開示パラメータデータ199に対してセッション鍵データKSES による暗号化および復号が行なわれる。
次に、復号された半開示パラメータデータ199が半開示処理部225に出力され、半開示処理部225からの制御によって、復号部222によるコンテンツ鍵データKcを用いたコンテンツデータCの復号が半開示で行われる。
次に、半開示で復号されたコンテンツデータCが、伸長部223において伸長された後に、電子透かし情報処理部224に出力される。
次に、電子透かし情報処理部224においてユーザ電子透かし情報用データ196がコンテンツデータCに埋め込まれた後、コンテンツデータCが再生モジュール169において再生され、コンテンツデータCに応じた音響が出力される。
【0130】
ステップSH3:ユーザが購入・利用形態決定操作部165を操作して購入形態を決定すると、当該決定した購入形態を示す操作信号S165が課金処理部187に出力される。
ステップSH4:課金処理部187において、決定された購入形態に応じた利用履歴データ108および利用制御状態データ166が生成され、利用履歴データ108が外部メモリ管理部811を介して外部メモリ201に書き込まれると共に、利用制御状態データ166がスタックメモリ200に書き込まれる。
以後は、利用監視部186において、利用制御状態データ166によって許諾された範囲で、コンテンツの購入および利用が行なわれるように制御(監視)される。
【0131】
ステップSH5:スタックメモリ200に格納されているキーファイルKFに、利用制御状態データ166が加えられ、購入形態が決定した後述する図29(B)に示す新たなキーファイルKF1 が生成される。キーファイルKF1 は、スタックメモリ200に記憶される。
図29(B)に示すように、キーファイルKF1 に格納された利用制御状態データ166はストレージ鍵データKSTR を用いてDESのCBCモードを利用して暗号化されている。また、当該ストレージ鍵データKSTR をMAC鍵データとして用いて生成したMAC値であるMAC300 が付されている。また、利用制御状態データ166およびMAC300 からなるモジュールは、メディア鍵データKMED を用いてDESのCBCモードを利用して暗号化されている。また、当該モジュールには、当該メディア鍵データKMED をMAC鍵データとして用いて生成したMAC値であるMAC301 が付されている。
【0132】
以下、ダウンロードメモリ167に記憶されている購入形態が既に決定されたコンテンツデータCを再生する場合の処理の流れを、図23および図25を参照しながら説明する。
図25は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップSI1:課金処理部187が、ユーザによる操作に応じて、再生を行うコンテンツを指定した操作信号S165を入力する。
ステップSI2:課金処理部187は、利用監視部186の監視下で、操作信号S165に基づいて、ダウンロードメモリ167に記憶されているコンテンツファイルCFが読み出される。
【0133】
ステップSI3:当該読み出されたコンテンツファイルCFが図16に示す復号・伸長モジュール163に出力される。このとき、図23に示す相互認証部170と、図16に示す復号・伸長モジュール163の相互認証部220との間で相互認証が行われる。
また、スタックメモリ200から読み出されたコンテンツ鍵データKcが復号・伸長モジュール163に出力される。
【0134】
ステップSI4:復号・伸長モジュール163の復号部222において、コンテンツ鍵データKcを用いたコンテンツファイルCFの復号と、伸長部223による伸長処理とが行なわれ、再生モジュール169において、コンテンツデータCが再生される。
ステップSI5:課金処理部187によって、操作信号S165に応じて、外部メモリ201に記憶されている利用履歴データ108が更新される。
利用履歴データ108は、外部メモリ201から読み出された後、相互認証を経て、EMDサービスセンタ管理部185を介して、署名データSIG200,SAM1と共にEMDサービスセンタ102に送信される。
【0135】
以下、図26に示すように、例えば、ネットワーク機器1601 のダウンロードメモリ167にダウンロードされた既に購入形態が決定されたコンテンツファイルCFおよびキーファイルKFを、バス191を介して、AV機器1602 のSAM1052 に転送する場合のSAM1051 内での処理の流れを図27および図28を参照しながら説明する。
図28は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップSJ1:ユーザは、購入・利用形態決定操作部165を操作して、ダウンロードメモリ167に記憶された所定のコンテンツをAV機器1602 に転送することを指示し、当該操作に応じた操作信号S165が、課金処理部187に出力される。
これにより、課金処理部187は、操作信号S165に基づいて、外部メモリ201に記憶されている利用履歴データ108を更新する。
【0136】
ステップSJ2:ダウンロードメモリ管理部182は、ダウンロードメモリ167から読み出した図29(A)に示すコンテンツファイルCFをSAM管理部190に出力する。
ステップSJ3:スタックメモリ200から読み出した図29(B)に示すキーファイルKF1 を、署名処理部189およびSAM管理部190に出力する。
ステップSJ4:署名処理部189は、スタックメモリ200から読み出したキーファイルKF1 の署名データSIG42,SAM1 を作成し、これをSAM管理部190に出力する。
また、SAM管理部190は、記憶部192から、図29(C)に示す公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1およびその署名データSIG22,ESCを読み出す。
【0137】
ステップSJ5:相互認証部170は、SAM1052 との間で相互認証を行って得たセッション鍵データKSES を暗号化・復号部171に出力する。
SAM管理部190は、図29(A),(B),(C)に示すデータからなる新たなセキュアコンテナを作成する。
ステップSJ6:暗号化・復号部171において、セッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化した後に、図26に示すAV機器1602 のSAM1052 に出力する。
このとき、SAM1051 とSAM1052 との間の相互認証と並行して、IEEE1394シリアルバスであるバス191の相互認証が行われる。
【0138】
以下、図26に示すように、SAM1051 から入力したコンテンツファイルCFなどを、RAM型などの記録媒体(メディア)に書き込む際のSAM1052 内での処理の流れを、図30および図31を参照しながら説明する。
図31は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
【0139】
ステップSK1:SAM1052 のSAM管理部190は、図26に示すように、図29(A)に示すコンテンツファイルCFと、図29(B)に示すキーファイルKF1 およびその署名データSIG42,SAM1 と、図29(C)に示す公開鍵署名データCERSAM1およびその署名データSIG22,ESCとを、ネットワーク機器1601 のSAM1051 から入力する。
そして、暗号化・復号部171において、SAM管理部190が入力したコンテンツファイルCFと、キーファイルKF1 およびその署名データSIG42,SAM1 と、公開鍵署名データCERSAM1およびその署名データSIG22,ESCとが、相互認証部170とSAM1051 の相互認証部170との間の相互認証によって得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号される。
次に、セッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号されたキーファイルKF1 およびその署名データSIG42,SAM1 と、公開鍵署名データCERSAM1およびその署名データSIG22,ESCとが、スタックメモリ200に書き込まれる。
【0140】
ステップSK2:署名処理部189は、スタックメモリ200から読み出した署名データSIG22,ESCを、記憶部192から読み出した公開鍵データKESC,P を用いて検証して、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1の正当性を確認する。
そして、署名処理部189は、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1の正当性を確認すると、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1に格納された公開鍵データKSAM1,Pを用いて、署名データSIG42,SAM1 の正当を確認する。
次に、署名データSIG42,SAM1 の正当性、すなわちキーファイルKF1 の作成者の正当性が確認されると、図29(B)に示すキーファイルKF1 をスタックメモリ200から読み出して暗号化・復号部173に出力する。
なお、当該例では、キーファイルKF1 の作成者と送信元とが同じ場合を述べたが、キーファイルKF1 の作成者と送信元とが異なる場合には、キーファイルKF1 に対して作成者の署名データと送信者と署名データとが作成され、署名処理部189において、双方の署名データの正当性が検証される。
【0141】
ステップSK3:暗号化・復号部173は、記憶部192から読み出した記録用鍵データKSTR 、メディア鍵データKMED および購入者鍵データKPIN を用いてキーファイルKF1 を順に暗号化してメディアSAM管理部197に出力する。
なお、メディア鍵データKMED は、図27に示す相互認証部170と図26に示すRAM型の記録媒体250のメディアSAM252との間の相互認証によって記憶部192に事前に記憶されている。
【0142】
ここで、記録用鍵データKSTR は、例えばSACD(Super Audio Compact Disc)、DVD(Digital Versatile Disc)機器、CD−R機器およびMD(Mini Disc) 機器などの種類(当該例では、AV機器1602 )に応じて決まるデータであり、機器の種類と記録媒体の種類とを1対1で対応づけるために用いられる。なお、SACDとDVDとでは、ディスク媒体の物理的な構造が同じであるため、DVD機器を用いてSACDの記録媒体の記録・再生を行うことができる場合がある。記録用鍵データKSTR は、このような場合において、不正コピーを防止する役割を果たす。
【0143】
また、メディア鍵データKMED は、記録媒体(当該例では、RAM型の記録媒体250)にユニークなデータである。
メディア鍵データKMED は、記録媒体(当該例では、図26に示すRAM型の記録媒体250)側に格納されており、記録媒体のメディアSAMにおいてメディア鍵データKMED を用いた暗号化および復号を行うことがセキュリティの観点から好ましい。このとき、メディア鍵データKMED は、記録媒体にメディアSAMが搭載されている場合には、当該メディアSAM内に記憶されており、記録媒体にメディアSAMが搭載されていない場合には、例えば、RAM領域内のホストCPU810の管理外の領域に記憶されている。
なお、本実施形態のように、機器側のSAM(当該例では、SAM1052 )とメディアSAM(当該例では、メディアSAM252)との間で相互認証を行い、セキュアな通信経路を介してメディア鍵データKMED を機器側のSAMに転送し、機器側のSAMにおいてメディア鍵データKMED を用いた暗号化および復号を行なってもよい。
本実施形態では、記録用鍵データKSTR およびメディア鍵データKMED が、記録媒体の物理層のレベルのセキュリティを保護するために用いられる。
【0144】
また、購入者鍵データKPIN は、コンテンツファイルCFの購入者を示すデータであり、例えば、コンテンツを買い切りで購入したときに、当該購入したユーザに対してEMDサービスセンタ102によって割り当てられる。購入者鍵データKPIN は、EMDサービスセンタ102において管理される。
【0145】
ステップSK4:メディアSAM管理部197は、SAM管理部190から入力したコンテンツファイルCFおよび暗号化・復号部173から入力したキーファイルKF1 を、図26に示す記録モジュール260に出力する。
そして、記録モジュール260は、メディアSAM管理部197から入力したコンテンツファイルCFおよびキーファイルKF1 を、図26に示すRAM型の記録媒体250のRAM領域251に書き込む。この場合に、キーファイルKF1 を、メディアSAM252内に書き込むようにしてもよい。
【0146】
以下、コンテンツの購入形態が未決定の図6に示すROM型の記録媒体130をユーザホームネットワーク303がオフラインで配給を受けた場合に、AV機器1602 において購入形態を決定する際の処理の流れを図32、図33、図34、図35を参照しながら説明する。
ステップSL1:AV機器1602 のSAM1052 は、先ず、図33に示す相互認証部170と図6に示すROM型の記録媒体130のメディアSAM133との間で相互認証を行った後に、メディアSAM133からメディア鍵データKMED を入力する。
なお、SAM1052 が、事前にメディア鍵データKMED を保持している場合には、当該入力を行わなくても良い。
【0147】
ステップSL2:ROM型の記録媒体130のRAM領域132に記録されているセキュアコンテナ104に格納された図4(B),(C)に示すキーファイルKFおよびその署名データSIG7,CPと、公開鍵証明書データCERCPおよびその署名データSIG1,ESC とが、メディアSAM管理部197を介して入力され、これらがスタックメモリ200に書き込まれる。
【0148】
ステップSL3:署名処理部189において、署名データSIG1,ESC の正当性を確認した後に、公開鍵証明書データCERCPから公開鍵データKCP,Pを取り出し、この公開鍵データKCP,Pを用いて、署名データSIG7,CPの正当性、すなわちキーファイルKFの作成者の正当性を検証する。
【0149】
ステップSL4:署名処理部189において署名データSIG7,CPの正当性が確認されると、スタックメモリ200からセキュアコンテナ復号部183に、キーファイルKFを読み出す。
そして、セキュアコンテナ復号部183において、対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を用いて、キーファイルKFを復号する。
【0150】
ステップSL5:署名処理部189において、公開鍵データKESC,P を用いて、キーファイルKFに格納された署名データSIG1,ESCMの正当性を確認した後に、キーファイルKF内の公開鍵証明書データCERCPに格納された公開鍵データKCP,Pを用いて、署名データSIG2,CP〜SIG4,CPの正当性、すなわちコンテンツデータC、コンテンツ鍵データKcおよび権利書データ106の作成者の正当性を検証する。
【0151】
ステップSL6:課金処理部187において、ユーザによる図16に示す購入・利用形態決定操作部165の操作によって、試聴モードを示す操作信号S165が発生したか否かが判断され、発生したと判断された場合にはステップSL7の処理が行われ、そうでない場合にはステップSL8の処理が行われる。
【0152】
ステップSL7:図33に示す相互認証部170と図32に示す復号・伸長モジュール163との間で相互認証を行った後に、SAM1052 の復号・伸長モジュール管理部184は、スタックメモリ200に記憶されているコンテンツ鍵データKcおよび権利書データ106に格納された半開示パラメータデータ199、並びにROM型の記録媒体130のROM領域131から読み出したコンテンツデータCを図32に示す復号・伸長モジュール163に出力する。次に、復号・伸長モジュール163において、コンテンツデータCがコンテンツ鍵データKcを用いて半開示モードで復号された後に伸長され、再生モジュール270に出力される。そして、再生モジュール270において、復号・伸長モジュール163からのコンテンツデータCが試聴モードで再生される。
【0153】
ステップSL8:ユーザによる図32に示す購入形態決定操作部165の購入操作によってコンテンツの購入形態が決定され、当該決定された購入形態を示す操作信号S165が課金処理部187に入力される。
【0154】
ステップSL9:課金処理部187は、操作信号S165に応じた利用制御状態データ166を作成し、これをスタックメモリ200に書き込む。
また、課金処理部187は、利用履歴データ108を作成あるいは更新する。
【0155】
ステップSL10:スタックメモリ200から暗号化・復号部173に、例えば、図4(B)に示すキーファイルKFに利御制御状態データ166を格納した図29(B)に示す新たなキーファイルKF1 が出力される。
【0156】
ステップSL11:暗号化・復号部173は、スタックメモリ200から読み出した図29(B)に示すキーファイルKF1 を、記憶部192から読み出した記録用鍵データKSTR 、メディア鍵データKMED および購入者鍵データKPIN を用いて順次に暗号化してメディアSAM管理部197に出力する。
【0157】
ステップSL12:図33に示す相互認証部170と図32に示すメディアSAM133との間で相互認証を行った後に、SAM管理部197は、暗号化・復号部173から入力したキーファイルKF1 を図32に示す記録モジュール271を介してROM型の記録媒体130のRAM領域132あるいはメディアSAM133内に書き込む。
これにより、購入形態が決定されたROM型の記録媒体130が得られる。
このとき、課金処理部187が生成した利用制御状態データ166および利用履歴データ108は、所定のタイミングで、スタックメモリ200および外部メモリ201からそれぞれ読み出しされたEMDサービスセンタ102に送信される。
【0158】
以下、図36に示すように、AV機器1603 において購入形態が未決定のROM型の記録媒体130からセキュアコンテナ104を読み出してAV機器1602 に転送し、AV機器1602 において購入形態を決定してRAM型の記録媒体250に書き込む際の処理の流れを図37および図38を用いて説明する。
図37は、SAM1053 における当該処理のフローチャートである。
図38は、SAM1052 における当該処理のフローチャートである。 なお、ROM型の記録媒体130からRAM型の記録媒体250へのセキュアコンテナ104の転送は、図1に示すネットワーク機器1601 およびAV機器1601 〜1604 のいずれの間で行ってもよい。
【0159】
ステップSM11(図37):AV機器1603 のSAM1053 とROM型の記録媒体130のメディアSAM133との間で相互認証を行い、ROM型の記録媒体130のメディア鍵データKMED1をSAM1053 に転送する。
このとき、同様に、V機器1602 のSAM1052 とRAM型の記録媒体250のメディアSAM252との間で相互認証を行い、RAM型の記録媒体250のメディア鍵データKMED2をSAM1052 に転送する。
【0160】
ステップSM12:SAM1053 は、RAM領域132から読み出した図4(B),(C)キーファイルKF、署名データSIG7,CP、公開鍵証明書データCERCPおよびその署名データSIG1,ESC とを、図40に示す暗号化・復号部172において、対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を用いて順に復号する。
次に、暗号化・復号部172で復号されたコンテンツファイルCFは、暗号化・復号部171に出力され、SAM1053 と1052 との間の相互認証によって得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化された後に、SAM管理部190に出力される。
また、暗号化・復号部172で復号されたキーファイルKFは、暗号化・復号部171および署名処理部189に出力される。
【0161】
ステップSM13:署名処理部189は、SAM1053 の秘密鍵データKSAM3,Sを用いて、キーファイルKFの署名データSIG350,SAM3を作成し、これを暗号化・復号部171に出力する。
【0162】
ステップSM14:暗号化・復号部171は、記憶部192から読み出したSAM1053 の公開鍵証明書データCERSAM3およびその署名データSIG351,ESC と、キーファイルKFおよびその署名データSIG350,SAM3と、ROM型の記録媒体130のROM領域131から読み出した図4(A)に示すコンテンツファイルCFとを、SAM1053 と1052 との間の相互認証によって得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化した後に、SAM管理部190を介して、AV機器1602 のSAM1052 に出力する。
【0163】
ステップSN1(図38):SAM1052 では、図41に示すように、SAM管理部190を介してSAM1053 から入力されたコンテンツファイルCFが、暗号化・復号部171においてセッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号された後に、メディアSAM管理部197を介してRAM型の記録媒体250のRAM領域251に書き込まれる。
また、SAM管理部190を介してSAM1053 から入力されたキーファイルKFおよびその署名データSIG350,SAM3と、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM3およびその署名データSIG351,ESC とが、スタックメモリ200に書き込まれた後に、暗号化・復号部171においてセッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号される。
【0164】
ステップSN2:当該復号された署名データSIG351,ECS が、署名処理部189において署名検証され、その正当性が確認されると、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM3に格納された公開鍵データKSAM3を用いて、署名データSIG350,SAM3の正当性、すなわちキーファイルKFの送信元の正当性が確認される。
そして、署名データSIG350,SAM3の正当性が確認されると、スタックメモリ200からキーファイルKFが読み出されてセキュアコンテナ復号部183に出力される。
【0165】
ステップSN3:セキュアコンテナ復号部183は、対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を用いて、キーファイルKFを復号し、所定の署名検証を経た後に、当該復号したキーファイルKFをスタックメモリ200に書き込む。
その後、スタックメモリ200に記憶されている既に復号されたキーファイルKFに格納された権利書データ106が、利用監視部186に出力される。そして、利用監視部186によって、権利書データ106に基づいて、コンテンツの購入形態および利用形態が管理される。
【0166】
ステップSN4:課金処理部187において、ユーザによる図16に示す購入・利用形態決定操作部165の操作によって、試聴モードを示す操作信号S165が発生したか否かが判断され、発生したと判断された場合にはステップSN5の処理が行われ、そうでない場合にはステップSN6の処理が行われる。
【0167】
ステップSN5:ユーザによって試聴モードが選択されると、既にセッション鍵データKSES で復号されたコンテンツファイルCFのコンテンツデータCと、スタックメモリ200に記憶されたコンテンツ鍵データKc、権利書データ106から得られた半開示パラメータデータ199およびユーザ電子透かし情報用データ196とが、相互認証を経た後に、図36に示す復号・伸長モジュール管理部184を介して再生モジュール270に出力される。そして、再生モジュール270において、試聴モードに対応したコンテンツデータCの再生が行われる。
【0168】
ステップSN6:ユーザによる図36に示す購入・利用形態決定操作部165の操作によってコンテンツの購入・利用形態が決定され、当該決定に応じた操作信号S165が、課金処理部187に出力される。
ステップSN7:課金処理部187において、決定された購入・利用形態に応じて利用制御状態データ166および利用履歴データ108が生成され、これがスタックメモリ200および外部メモリ201にそれぞれ書き込まれる。
【0169】
ステップSN8:スタックメモリ200から読み出された利用制御状態データ166を格納した例えば図29(B)に示すキーファイルKF1 が作成され、これが暗号化・復号部173に出力される。
ステップSN9:暗号化・復号部173において記憶部192から読み出した記録用鍵データKSTR 、メディア鍵データKMED2および購入者鍵データKPIN を用いて順に暗号化され、メディアSAM管理部197に出力される。
ステップSN10:メディアSAM管理部197によって、キーファイルKF1 が、図36に示す記録モジュール271によってRAM型の記録媒体250のRAM領域251あるいはメディアSAM252に書き込まれる。
また、利用制御状態データ166および利用履歴データ108は、所定のタイミングで、EMDサービスセンタ102に送信される。
以下、SAM1051 〜1054 の実現方法について説明する。
SAM1051 〜1054 の機能をハードウェアとして実現する場合は、メモリを内蔵したASIC型のCPUを用いて、そのメモリには、図17に示す各機能を実現するためのセキュリティー機能モジュールやコンテンツの権利処理をおこなうプログラムモジュールおよび鍵データなどの機密度の高いデータが格納される。暗号ライブラリーモジュール(公開鍵暗号、共通鍵暗号、乱数発生器、ハッシュ関数)、コンテンツの使用制御用のプログラムモジュール、課金処理のプログラムモジュールなど、一連の権利処理用のプログラムモジュールは、例えば、ソフトウェアとして実装される。
【0170】
例えば、図17に示す暗号化・復号部171などのモジュールは、例えば、処理速度の問題でハードウエアとしてASIC型のCPU内のIPコアとして実装される。クロック速度やCPUコード体系などの性能によっては、暗号化・復号部171をソフトウェアとして実装してもよい。
また、図17に示す記憶部192や、図17に示す機能を実現するためのプログラムモジュールおよびデータを格納するメモリとしては、例えば、不揮発メモリー(フラッシュ−ROM)が用いられ、作業用メモリとしてはSRAMなどの高速書き込み可能なメモリが用いられる。なお、その他にも、SAM1051 〜1054 に内蔵されるメモリとして、強誘電体メモリー(FeRAM)を用いてもよい。
また、SAM1051 〜1054 には、その他に、コンテンツの利用のための有効期限や契約期間などで日時の検証に使用する時計機能が内蔵されている。
【0171】
上述したように、SAM1051 〜1054 は、プログラムモジュールや、データおよび処理内容を外部から遮蔽した耐タンパ性の構造を持っている。SAM1051 〜1054 を搭載した機器のホストCPUのバス経由で、当該SAMのIC内部のメモリに格納されている秘密性の高いプログラムおよびデータの内容や、SAMのシステムコンフィギュレーション(System Configuration)関連のレジスタ群および暗号ライブラリーや時計のレジスタ群などの値が、読み出されたり、新規に書き込まれたりしないように、すなわち、搭載機器のホストCPUが割り付けているアドレス空間内に存在しないように、当該SAMでは、CPU側のメモリー空間を管理するMMU(Memory Magagement Unit)を用いて、搭載機器側のホストCPUからは見えないアドレス空間を設定する。
また、SAM1051 〜1054 は、X線や熱などの外部からの物理的な攻撃にも耐え得る構造をもち、さらにデバッグ用ツール(ハードウエアICE、ソフトウエアICE)などを用いたリアルタイムデバッグ(リバースエンジニアリング)が行われても、その処理内容が分からないか、あるいは、デバッグ用ツールそのものがIC製造後には使用できないような構造をしている。
SAM1051 〜1054 自身は、ハードウエア的な構造においては、メモリを内蔵した通常のASIC型のCPUであり、機能は当該CPUを動作させるソフトウェアに依存するが、暗号機能と耐タンパ性のハードウェア構造を有している点が、一般的なASIC型のCPUと異なる。
【0172】
SAM1051 〜1054 の機能を全てソフトウエアで実現する場合は、耐タンパ性を持ったモジュール内部で閉じてソフトウエア処理をおこなう場合と、通常のセットに搭載されているホストCPU上のソフトウエア処理で行い、当該処理のときにのみ解読することが不可能となる仕掛けをする場合とがある。前者は、暗号ライブラリモジュールがIPコアではなく、通常のソフトウェアモジュールとしてメモリに格納される場合と同じであり、ハードウェアとして実現する場合と同様に考えられる。一方、後者は、タンパーレジスタントソフトウェアと呼ばれるもので、ICE(デバッガ)で実行状況を解読されても、そのタスクの実行順序がバラバラであったり(この場合には、区切ったタスク単体でプログラムとしての意味があるように、すなわち前後のラインに影響がでないようにタスク切りを行う)、タスクそのものが暗号化されており、一種のセキュア処理を目的としたタスクスケジューラ(MiniOS)と同様に実現できる。当該タスクスケジューラは、ターゲットプログラムに埋め込まれている。
【0173】
次に、図16に示す復号・伸長モジュール163について説明する。
図16に示すように、復号・伸長モジュール163は、相互認証部220、復号部221、復号部222、伸長部223、電子透かし情報処理部224および半開示処理部225を有する。
相互認証部220は、復号・伸長モジュール163がSAM1051 からデータを入力する際に、図26に示す相互認証部170との間で相互認証を行ってセッション鍵データKSES を生成する。
【0174】
復号部221は、SAM1051 から入力したコンテンツ鍵データKc、半開示パラメータデータ199、ユーザ電子透かし情報用データ196およびコンテンツデータCを、セッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号する。そして、復号部221は、復号したコンテンツ鍵データKcおよびコンテンツデータCを復号部222に出力し、復号したユーザ電子透かし情報用データ196を電子透かし情報処理部224に出力し、半開示パラメータデータ199を半開示処理部225に出力する。
【0175】
復号部222は、半開示処理部225からの制御に基づいて、コンテンツ鍵データKcを用いて、コンテンツデータCを半開示状態で復号し、復号したコンテンツデータCを伸長部223に出力する。
【0176】
伸長部223は、復号されたコンテンツデータCを伸長して、電子透かし情報処理部224に出力する。
伸長部223は、例えば、図4(A)に示すコンテンツファイルCFに格納されたA/V伸長用ソフトウェアを用いて伸長処理を行い、例えば、ATRAC3方式で伸長処理を行う。
【0177】
電子透かし情報処理部224は、復号されたユーザ電子透かし情報用データ196に応じたユーザ電子透かし情報を、復号されたコンテンツデータCに埋め込み、新たなコンテンツデータCを生成する。電子透かし情報処理部224は、当該新たなコンテンツデータCを再生モジュール169に出力する。
このように、ユーザ電子透かし情報は、コンテンツデータCを再生するときに、復号・伸長モジュール163において埋め込まれる。
なお、本発明では、コンテンツデータCにユーザ電子透かし情報用データ196を埋め込まないようにしてもよい。
【0178】
半開示処理部225は、半開示パラメータデータ199に基づいて、例えば、コンテンツデータCのうち復号を行わないブロックと、復号を行うブロックとを復号部222に指示する。
また、半開示処理部225は、その他に、半開示パラメータデータ199に基づいて、試聴時の再生機能を限定したり、試聴可能な期間を限定するなどの制御を行う。
【0179】
再生モジュール169は、復号および伸長されたコンテンツデータCに応じた再生を行う。
【0180】
次に、コンテンツプロバイダ101、EMDサービスセンタ102およびユーザホームネットワーク103の間で、秘密鍵データを用いて生成した署名データを付したデータおよび公開鍵証明書データを送受信する際のデータフォーマットについて説明する。
図42(A)は、コンテンツプロバイダ101からSAM1051 にデータDataをイン・バンド方式で送信する場合のデータフォーマットを説明するための図である。
この場合には、コンテンツプロバイダ101からSAM1051 に、コンテンツプロバイダ101とSAM1051 との間の相互認証によって得たセッション鍵データKSES で暗号化したモジュールMod50が送信される。
モジュールMod50には、モジュールMod51およびその秘密鍵データKCP,Sによる署名データSIGCPが格納されている。
モジュールMod51には、コンテンツプロバイダ101の秘密鍵データKCP,Pを格納した公開鍵証明書データCERCPと、公開鍵証明書データCERCPに対しての秘密鍵データKESC,S による署名データSIGESC と、送信するデータDataとが格納されている。
このように、公開鍵証明書データCERCPを格納したモジュールMod50を、コンテンツプロバイダ101からSAM1051 に送信することで、SAM1051 において署名データSIGCPの検証を行なう際に、EMDサービスセンタ102からSAM1051 に公開鍵証明書データCERCPを送信する必要がなくなる。
【0181】
図42(B),(C)は、コンテンツプロバイダ101からSAM1051 にデータDataをアウト・オブ・バンド方式で送信する場合のデータフォーマットを説明するための図である。
この場合には、コンテンツプロバイダ101からSAM1051 に、コンテンツプロバイダ101とSAM1051 との間の相互認証によって得たセッション鍵データKSES で暗号化した図42(B)に示すモジュールMod52が送信される。
モジュールMod52には、送信するデータDataと、その秘密鍵データKCP,Sによる署名データSIGCPとが格納されている。
また、EMDサービスセンタ102からSAM1051 には、EMDサービスセンタ102とSAM1051 との間の相互認証によって得たセッション鍵データKSES で暗号化した図42(C)に示すモジュールMod53が送信される。
モジュールMod53には、コンテンツプロバイダ101の公開鍵証明書データCERCPと、その秘密鍵データKESC,S による署名データSIGESC とが格納されている。
【0182】
図42(D)は、SAM1051 からコンテンツプロバイダ101にデータDataをイン・バンド方式で送信する場合のデータフォーマットを説明するための図である。
この場合には、SAM1051 からコンテンツプロバイダ101に、コンテンツプロバイダ101とSAM1051 との間の相互認証によって得たセッション鍵データKSES で暗号化したモジュールMod54が送信される。
モジュールMod54には、モジュールMod55およびその秘密鍵データKSAM1,Sによる署名データSIGSAM1が格納されている。
モジュールMod55には、SAM1051 の秘密鍵データKSAM1,Pを格納した公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1と、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1に対しての秘密鍵データKESC,S による署名データSIGESC と、送信するデータDataとが格納されている。
このように、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1を格納したモジュールMod55を、SAM1051 からコンテンツプロバイダ101に送信することで、コンテンツプロバイダ101において署名データSIGSAM1の検証を行なう際に、EMDサービスセンタ102からコンテンツプロバイダ101に公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1を送信する必要がなくなる。
【0183】
図42(E),(F)は、SAM1051 からコンテンツプロバイダ101にデータDataをアウト・オブ・バンド方式で送信する場合のデータフォーマットを説明するための図である。
この場合には、SAM1051 からコンテンツプロバイダ101に、コンテンツプロバイダ101とSAM1051 との間の相互認証によって得たセッション鍵データKSES で暗号化した図42(E)に示すモジュールMod56が送信される。
モジュールMod56には、送信するデータDataと、その秘密鍵データKSAM1,Sによる署名データSIGSAM1とが格納されている。
また、EMDサービスセンタ102からコンテンツプロバイダ101には、EMDサービスセンタ102とコンテンツプロバイダ101との間の相互認証によって得たセッション鍵データKSES で暗号化した図42(F)に示すモジュールMod57が送信される。
モジュールMod57には、SAM1051 の公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1と、その秘密鍵データKESC,S による署名データSIGESC とが格納されている。
【0184】
図43(G)は、コンテンツプロバイダ101からEMDサービスセンタ102にデータDataをイン・バンド方式で送信する場合のデータフォーマットを説明するための図である。
この場合には、コンテンツプロバイダ101からEMDサービスセンタ102に、コンテンツプロバイダ101とEMDサービスセンタ102との間の相互認証によって得たセッション鍵データKSES で暗号化したモジュールMod58が送信される。
モジュールMod58には、モジュールMod59およびその秘密鍵データKCP,Sによる署名データSIGCPが格納されている。
モジュールMod59には、コンテンツプロバイダ101の秘密鍵データKCP,Pを格納した公開鍵証明書データCERCPと、公開鍵証明書データCERCPに対しての秘密鍵データKESC,S による署名データSIGESC と、送信するデータDataとが格納されている。
【0185】
図43(H)は、コンテンツプロバイダ101からEMDサービスセンタ102にデータDataをアウト・オブ・バンド方式で送信する場合のデータフォーマットを説明するための図である。
この場合には、コンテンツプロバイダ101からEMDサービスセンタ102に、コンテンツプロバイダ101とEMDサービスセンタ102との間の相互認証によって得たセッション鍵データKSES で暗号化した図43(H)に示すモジュールMod60が送信される。
モジュールMod60には、送信するデータDataと、その秘密鍵データKCP,Sによる署名データSIGCPとが格納されている。
このとき、EMDサービスセンタ102にはコンテンツプロバイダ101の公開鍵証明書データCERCPは既に登録されている。
【0186】
図43(I)は、SAM1051 からEMDサービスセンタ102にデータDataをイン・バンド方式で送信する場合のデータフォーマットを説明するための図である。
この場合には、SAM1051 からEMDサービスセンタ102に、EMDサービスセンタ102とSAM1051 との間の相互認証によって得たセッション鍵データKSES で暗号化したモジュールMod61が送信される。
モジュールMod61には、モジュールMod62およびその秘密鍵データKSAM1,Sによる署名データSIGSAM1が格納されている。
モジュールMod62には、SAM1051 の秘密鍵データKSAM1,Pを格納した公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1と、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1に対しての秘密鍵データKESC,S による署名データSIGESC と、送信するデータDataとが格納されている。
【0187】
図43(J)は、SAM1051 からEMDサービスセンタ102にデータDataをアウト・オブ・バンド方式で送信する場合のデータフォーマットを説明するための図である。
この場合には、SAM1051 からEMDサービスセンタ102に、EMDサービスセンタ102とSAM1051 との間の相互認証によって得たセッション鍵データKSES で暗号化した図43(J)に示すモジュールMod63が送信される。
モジュールMod63には、送信するデータDataと、その秘密鍵データKSAM1,Sによる署名データSIGSAM1とが格納されている。
このとき、EMDサービスセンタ102にはSAM1051 の公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1は既に登録されている。
【0188】
以下、SAM1051 〜1054 の出荷時におけるEMDサービスセンタ102への登録処理について説明する。
なお、SAM1051 〜1054 の登録処理は同じであるため、以下、SAM1051 の登録処理について述べる。
SAM1051 の出荷時には、図11に示すEMDサービスセンタ102の鍵サーバ141によって、SAM管理部149を介して、図17などに示す記憶部192に以下に示す鍵データが初期登録される。
また、SAM1051 には、例えば、出荷時に、記憶部192などに、SAM1051 がEMDサービスセンタ102に初回にアクセスする際に用いられるプログラムなどが記憶される。
すなわち、記憶部192には、例えば、図21において左側に「*」が付されているSAM1051 の識別子SAM_ID、記録用鍵データKSTR 、ルート認証局2の公開鍵データKR-CA、EMDサービスセンタ102の公開鍵データKESC,P 、SAM1051 の秘密鍵データKSAM1,S、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1およびその署名データSIG22,ESC、復号・伸長モジュール163およびメディアSAMとの間の認証用鍵データを生成するための元鍵データが初期登録で記憶される。
なお、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1は、SAM1051 を出荷後に登録する際にEMDサービスセンタ102からSAM1051 に送信してもよい。
【0189】
ここで、ルート認証局2の公開鍵データKR-CAは、インターネットの電子商取引などでは一般的に使用されているRSAを使用し、データ長は例えば1024ビットである。公開鍵データKR-CAは、図1に示すルート認証局2によって発行される。
また、EMDサービスセンタ102の公開鍵データKESC,P は、短いデータ長でRSAと同等あるいはそれ以上の強度を持つ楕円曲線暗号を利用して生成され、データ長は例えば160ビットである。但し、暗号化の強度を考慮すると、公開鍵データKESC,P は192ビット以上であることが望ましい。また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、ルート認証局92に公開鍵データKESC,P を登録する。
また、ルート認証局92は、公開鍵データKESC,P の公開鍵証明書データCERESC を作成する。公開鍵データKESC,P を格納した公開鍵証明書データCERESC は、好ましく、SAM1051 の出荷時に記憶部192に記憶される。この場合に、公開鍵証明書データCERESC は、ルート認証局92の秘密鍵データKROOT,Sで署名されている。
【0190】
EMDサービスセンタ102は、乱数を発生してSAM1051 の秘密鍵データKSAM1,S、を生成し、これとペアとなる公開鍵データKSAM1,Pを生成する。
また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、ルート認証局92の認証をもらって、公開鍵データKSAM1,Pの公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1を発行し、これに自らの秘密鍵データKESC,S を用いて署名データを添付する。すなわち、EMDサービスセンタ102は、セカンドCA(認証局)として機能を果たす。
【0191】
また、SAM1051 には、図11に示すEMDサービスセンタ102のSAM管理部149により、EMDサービスセンタ102の管理下にある一意(ユニーク)な識別子SAM_IDが割り当てられ、これがSAM1051 の記憶部192に格納されると共に、図11に示すSAMデータベース149aにも格納され、EMDサービスセンタ102によって管理される。
【0192】
また、SAM1051 は、出荷後、例えば、ユーザによってEMDサービスセンタ102と接続され、登録手続を行うと共に、EMDサービスセンタ102から記憶部192に配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 が転送される。
すなわち、SAM1051 を利用するユーザは、コンテンツをダウンロードする前にEMDサービスセンタ102に登録手続が必要である。この登録手続は、例えば、SAM1051 を搭載している機器(当該例では、ネットワーク機器1601 )を購入したときに添付された登録用紙などを用いて、ユーザ本人が自己を特定する情報を記載して例えば郵便などのオフラインで行なわれる。
SAM1051 は、上述した登録手続を経た後でないと使用できない。
【0193】
EMDサービスセンタ102は、SAM1051 のユーザによる登録手続に応じて、ユーザに固有の識別子USER_IDを発行し、例えば、図11に示すSAMデータベース149aにおいて、SAM_IDとUSER_IDとの対応関係を管理し、課金時に利用する。
また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、SAM1051 のユーザに対して情報参照用識別子IDと、初回に使用されるパスワードを割り当て、これをユーザに通知する。ユーザは、情報参照用識別子IDとパスワードとを用いて、EMDサービスセンタ102に、例えば現在までのコンテンツデータの利用状況(利用履歴)などを情報の問い合わせを行なうことができる。
また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、ユーザの登録時に、クレジットカード会社などに身分の確認を行なったり、オフラインで本人の確認を行なう。
【0194】
次に、図21に示すように、SAM1051 内の記憶部192にSAM登録リストを格納する手順について説明する。
図1に示すSAM1051 は、例えば、バス191としてIEEE1394シリアルバスを用いた場合に、バス191に接続された機器の電源を立ち上げたり、新しい機器をバス191に接続したときに生成されるトポロジーマップを利用して、自分の系に存在するSAM1052 〜SAM1054 のSAM登録リストを得る。
なお、IEEE1394シリアルバスであるバス191に応じて生成されたトポロジーマップは、例えば、図44に示すように、バス191にSAM1051 〜1054 に加えてAV機器1605 ,1606 のSCMS処理回路1055 ,1056 が接続されている場合に、SAM1051 〜1054 およびSCMS処理回路1055 ,1056 を対象として生成される。
従って、SAM1051 は、当該トポロジーマップから、SAM1051 〜1054 についての情報を抽出してSAM登録リストを生成する。
【0195】
SAM登録リストのデータフォーマットは、例えば、図45に示される。
そして、SAM1051 は、当該SAM登録リストを、EMDサービスセンタ102に登録して署名を得る。
これらの処理は、バス191のセッションを利用してSAM1051 が自動的に行い、EMDサービスセンタ102にSAM登録リストの登録命令を発行する。
EMDサービスセンタ102は、SAM1051 から図45に示すSAM登録リストを受けると、有効期限を確認する。そして、EMDサービスセンタ102は、登録時にSAM1051 より指定された決済機能の有無を参照して対応する部分の設定を行う。また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、リボケーションリストをチェックしてSAM登録リスト内のリボケーションフラグを設定する。リボケーションリストは、例えば、不正使用などを理由にEMDサービスセンタ102によって使用が禁止されている(無効な)SAMのリストである。
また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、決済時にはSAM1051 に対応するSAM登録リストを取り出し、その中に記述されたSAMがリボケーションリストに含まれているかを確認する。また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、SAM登録リストに署名を添付する。
なお、SAMリホケーションリストは、同一系の(同一のバス191に接続されている)SAMのみを対象として生成され、各SAMに対応するリボケーションンフラグによって、当該SAMの有効および無効を示している。
【0196】
以下、図1に示すコンテンツプロバイダ101の全体動作について説明する。
図46は、コンテンツプロバイダ101の全体動作のフローチャートである。
ステップS1:EMDサービスセンタ102は、コンテンツプロバイダ101が所定の登録処理を経た後に、コンテンツプロバイダ101の公開鍵データKCP,Pの公開鍵証明書CERCPをコンテンツプロバイダ101に送信する。
また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、SAM1051 〜1054 が所定の登録処理を経た後に、SAM1051 〜1054 の公開鍵データKSAM1,P〜KSAM4,Pの公開鍵証明書CERCP1 〜CERCP4 をSAM1051 〜1054 に送信する。
また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、相互認証を行った後に、各々有効期限が1カ月の6カ月分の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 をコンテンツプロバイダ101に送信し、3カ月分の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 をユーザホームネットワーク103に送信する。
このように、EMDシステム100では、配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を予めSAM1051 〜1054 に配給しているため、SAM1051 〜1054 とEMDサービスセンタ102との間がオフラインの状態でも、SAM1051 〜1054 においてコンテンツプロバイダ101から配給されたセキュアコンテナ104を復号して購入・利用できる。この場合に、当該購入・利用の履歴は利用履歴データ108に記述され、利用履歴データ108は、SAM1051 〜1054 とEMDサービスセンタ102とが接続されたときに、EMDサービスセンタ102に自動的に送信されるため、EMDサービスセンタ102における決済処理を確実に行うことができる。なお、EMDサービスセンタ102が、所定の期間内に、利用履歴データ108を回収できないSAMについては、リボケーションリストで無効の対象とする。
なお、利用制御状態データ166は、原則として、リアルタイムで、SAM1051 〜1054 からEMDサービスセンタ102に送信される。
【0197】
ステップS2:コンテンツプロバイダ101は、相互認証を行った後に、図7(A)に示す権利登録要求モジュールMod2 を、EMDサービスセンタ102に送信する。
そして、EMDサービスセンタ102は、所定の署名検証を行った後に、権利書データ106およびコンテンツ鍵データKcを登録して権威化する。
【0198】
ステップS3:コンテンツプロバイダ101は、対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 などを用いて暗号化を行って、図4(A),(B)に示すコンテンツファイルCFおよびキーファイルKFを作成し、これらと図4(C)に示す公開鍵証明書データCERcpとを格納したセキュアコンテナ104を、オンラインおよび/またはオフラインで、ユーザホームネットワーク103に配給する。
【0199】
ステップS4:ユーザホームネットワーク103のSAM1051 〜SAM1054 は、セキュアコンテナ104を対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 などを用いて復号し、セキュアコンテナ104の作成者および送信者と正当性を検証するための署名検証などを行い、セキュアコンテナ104が正当なコンテンツプロバイダ101から送信されたか否かを確認する。
【0200】
ステップS5:SAM1051 〜SAM1054 において、ユーザによる図16に示す購入・利用形態決定操作部165の操作に応じた操作信号S165に基づいて、購入・利用形態を決定する。
このとき、図23に示す利用監視部186において、セキュアコンテナ104に格納された権利書データ106に基づいて、ユーザによるコンテンツファイルCFの購入・利用形態が管理される。
【0201】
ステップS6:SAM1051 〜SAM1054 の図23に示す課金処理部187において、操作信号S165に基づいて、ユーザによる購入・利用形態の決定の操作を記述した利用履歴データ108および利用制御状態データ166が生成し、これらをEMDサービスセンタ102に送信する。
【0202】
ステップS7:EMDサービスセンタ102は、図11に示す決算処理部142において、利用履歴データ108に基づいて決済処理を行い、決済請求権データ152および決済レポートデータ107を作成する。EMDサービスセンタ102は、決済請求権データ152およびその署名データSIG99を、図1に示すペイメントゲートウェイ90を介して、決済機関91に送信する。また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、決済レポートデータ107をコンテンツプロバイダ101に送信する。
【0203】
ステップS8:決済機関91において、署名データSIG99の検証を行った後に、決済請求権データ152に基づいて、ユーザが支払った金額が、コンテンツプロバイダ101の所有者に分配される。
【0204】
以上説明したように、EMDシステム100では、図4に示すフォーマットのセキュアコンテナ104をコンテンツプロバイダ101からユーザホームネットワーク103に配給し、セキュアコンテナ104内のキーファイルKFについての処理をSAM1051 〜1054 内で行う。
また、キーファイルKFに格納されたコンテンツ鍵データKcおよび権利書データ106は、配信鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を用いて暗号化されており、配信鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を保持しているSAM1051 〜1054 内でのみ復号される。そして、SAM1051 〜1054 では、耐タンパ性を有するモジュールであり、権利書データ106に記述されたコンテンツデータCの取り扱い内容に基づいて、コンテンツデータCの購入形態および利用形態が決定される。
従って、EMDシステム100によれば、ユーザホームネットワーク103におけるコンテンツデータCの購入および利用を、コンテンツプロバイダ101の関係者が作成した権利書データ106の内容に基づいて確実に行わせることができる。
【0205】
また、EMDシステム100では、コンテンツプロバイダ101からユーザホームネットワーク103へのコンテンツデータCの配給を、オンラインおよびオフラインの何れの場合でもセキュアコンテナ104を用いて行うことで、SAM1051 〜1054 におけるコンテンツデータCの権利処理を双方の場合において共通化できる。
【0206】
また、EMDシステム100では、ユーザホームネットワーク103内のネットワーク機器1601 およびAV機器1602 〜1604 においてコンテンツデータCを購入、利用、記録および転送する際に、常に権利書データ106に基づいて処理を行うことで、共通の権利処理ルールを採用できる。
【0207】
第1実施形態の第1変形例
上述した実施形態では、図4(B)に示すように、コンテンツプロバイダ101において配信用鍵データKDを用いてキーファイルKFを暗号化し、SAM1051 〜1054 において配信用鍵データKDを用いてキーファイルKFを復号する場合を例示したが、図1に示すように、コンテンツプロバイダ101からSAM1051 〜1054 にセキュアコンテナ104を直接供給する場合には、配信用鍵データKDを用いたキーファイルKFの暗号化は必ずしも行なわなくてもよい。 このように、配信用鍵データKDを用いてキーファイルKFを暗号化することは、後述する第2実施形態のように、コンテンツプロバイダからユーザホームネットワークにサービスプロバイダを介してコンテンツデータを供給する場合に、配信用鍵データKDをコンテンツプロバイダおよびユーザホームネットワークにのみ保持させることで、サービスプロバイダによる不正行為を抑制する際に大きな効果を発揮する。
但し、上述した第1実施形態の場合でも、配信用鍵データKDを用いてキーファイルKFを暗号化することは、コンテンツデータの不正利用の抑制力を高める点で効果がある。
【0208】
また、上述した実施形態では、図4(B)に示すキーファイルKF内の権利書データ106内に標準小売価格データSRPを格納する場合を例示したが、セキュアコンテナ104内のキーファイルKFの外に、標準小売価格データSRP(プライスタグデータ)を格納してもよい。この場合には、標準小売価格データSRPに対して秘密鍵データKcpを用いて作成した署名データを添付する。
【0209】
第1実施形態の第2変形例
上述した第1実施形態では、図1に示すように、EMDサービスセンタ102が、自らが生成した決済請求権データ152を用いて、ペイメントゲートウェイ90を介して決済機関91で決済処理を行なう場合を例示したが、例えば、図47に示すように、EMDサービスセンタ102からコンテンツプロバイダ101に決済請求権データ152を送信し、コンテンツプロバイダ101自らが、決済請求権データ152を用いて、ペイメントゲートウェイ90を介して決済機関91に対して決済処理を行なってもよい。
【0210】
第1実施形態の第3変形例
上述した第1実施形態では、単数のコンテンツプロバイダ101からユーザホームネットワーク103のSAM1051 〜1054 に、セキュアコンテナ104を供給する場合を例示したが、2以上のコンテンツプロバイダ101a,101bからSAM1051 〜1054 にそれぞれセキュアコンテナ104a,104bを供給するようにしてもよい。
図48は、コンテンツプロバイダ101a,101bを用いる場合の第1実施形態の第3変形例に係わるEMDシステムの構成図である。
この場合には、EMDサービスセンタ102は、コンテンツプロバイダ101aおよび101bに、それぞれ6カ月分の配信用鍵データKDa1 〜KDa6 およびKDb1 〜KDb6 を配信する。
また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、SAM1051 〜1054 に、3カ月分の配信用鍵データKDa1 〜KDa3 およびKDb1 〜KDb3 を配信する。
【0211】
そして、コンテンツプロバイダ101aは、独自のコンテンツ鍵データKcaを用いて暗号化したコンテンツファイルCFaと、コンテンツ鍵データKcaおよび権利書データ106aなどを対応する期間の配信用鍵データKDa1 〜KDa6 を用いて暗号化したキーファイルKFaとを格納したセキュアコンテナ104aをSAM1051 〜1054 にオンラインおよび/またはオフランで供給する。
このとき、キーファイルの識別子として、EMDサービスセンタ102が配付するグローバルユニークな識別子Content_IDが用いられ、EMDサービスセンタ102によって、コンテンツデータが一元的に管理される。
また、コンテンツプロバイダ101bは、独自のコンテンツ鍵データKcbを用いて暗号化したコンテンツファイルCFbと、コンテンツ鍵データKcbおよび権利書データ106bなどを対応する期間の配信用鍵データKDb1 〜KDb6 を用いて暗号化したキーファイルKFbとを格納したセキュアコンテナ104bをSAM1051 〜1054 にオンラインおよび/またはオフランで供給する。
【0212】
SAM1051 〜1054 は、セキュアコンテナ104aについては、対応する期間の配信用鍵データKDa1 〜KDa3 を用いて復号を行い、所定の署名検証処理などを経てコンテンツの購入形態を決定し、当該決定された購入形態および利用形態などに応じて生成した利用履歴データ108aおよび利用制御状態データ166aをEMDサービスセンタ102に送信する。
また、SAM1051 〜1054 は、セキュアコンテナ104bについては、対応する期間の配信用鍵データKDb1 〜KDb3 を用いて復号を行い、所定の署名検証処理などを経てコンテンツの購入形態を決定し、当該決定された購入形態および利用形態などに応じて生成した利用履歴データ108bおよび利用制御状態データ166bをEMDサービスセンタ102に送信する。
【0213】
EMDサービスセンタ102では、利用履歴データ108aに基づいて、コンテンツプロバイダ101aについての決済請求権データ152aを作成し、これを用いて決済機関91に対して決済処理を行なう。
また、EMDサービスセンタ102では、利用履歴データ108bに基づいて、コンテンツプロバイダ101bについての決済請求権データ152bを作成し、これを用いて決済機関91に対して決済処理を行なう。
【0214】
また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、権利書データ106a,106bを登録して権威化を行なう。このとき、EMDサービスセンタ102は、権利書データ106a,106bに対応するキーファイルKFa,KFbに対して、グローバルユニークな識別子Content_IDを配付する。
また、EMDサービスセンタ102は、コンテンツプロバイダ101a,101bの公開鍵証明書データCERcpa ,CERCPb を発行し、これに自らの署名データSIG1b,ESC,SIG1a,ESCを付してその正当性を認証する。
【0215】
第2実施形態
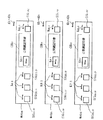
上述した実施形態では、コンテンツプロバイダ101からユーザホームネットワーク103のSAM1051 〜1054 にコンテンツデータを直接配給する場合を例示したが、本実施形態では、コンテンツプロバイダが提供するコンテンツデータを、サービスプロバイダを介してユーザホームネットワークのSAMに配給する場合について説明する。
【0216】
図49は、本実施形態のEMDシステム300の構成図である。図49に示すように、EMDシステム300は、コンテンツプロバイダ301、EMDサービスセンタ302、ユーザホームネットワーク303、サービスプロバイダ310、ペイメントゲートウェイ90および決済機関91を有する。コンテンツプロバイダ301、SAM3051〜3054およびサービスプロバイダ310は、それぞれ請求項3などに係わるデータ提供装置、データ処理装置およびデータ配給装置に対応している。また、EMDサービスセンタ302は、管理装置である。コンテンツプロバイダ301は、サービスプロバイダ310に対してコンテンツデータを供給する点を除いて、前述した第1実施形態のコンテンツプロバイダ101と同じである。また、EMDサービスセンタ302は、コンテンツプロバイダ101およびSAM5051〜5054に加えて、サービスプロバイダ310に対しても認証機能、鍵データ管理機能および権利処理機能を有する点を除いて、前述した第1実施形態のEMDサービスセンタ102と同じである。また、ユーザホームネットワーク303は、ネットワーク機器3601およびAV機器3602〜3604を有している。ネットワーク機器3601はSAM3051およびCAモジュール311を内蔵しており、AV機器3602〜3604はそれぞれSAM3052〜3054を内蔵している。ここで、SAM3051〜3054は、サービスプロバイダ310からセキュアコンテナ304の配給を受ける点と、コンテンツプロバイダ301に加えてサービスプロバイダ310についての署名データの検証処理およびSP用購入履歴データ(データ配給装置用購入履歴データ)309の作成を行なう点とを除いて、前述した第1実施形態のSAM1051〜1054と同じである。
【0217】
先ず、EMDシステム300の概要について説明する。
EMDシステム300では、コンテンツプロバイダ301は、自らが提供しようとするコンテンツのコンテンツデータCの使用許諾条件などの権利内容を示す前述した第1実施形態と同様の権利書(UCP:Usage Control Policy)データ106を、高い信頼性のある権威機関であるEMDサービスセンタ302に送信する。
権利書データ106は、EMDサービスセンタ302に登録されて権威化(認証)される。
【0218】
また、コンテンツプロバイダ301は、コンテンツ鍵データKcでコンテンツデータCを暗号化してコンテンツファイルCFを生成する。また、コンテンツプロバイダ301は、EMDサービスセンタ302から配給された対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 を用いて、コンテンツ鍵データKcおよび権利書データ106を暗号化し、それらを格納したキーファイルKFを作成する。そして、コンテンツプロバイダ301は、コンテンツファイルCF、キーファイルKFおよび自らの署名データとを格納したセキュアコンテナ104を、インターネットなどのネットワーク、デジタル放送、記録媒体あるいは非公式なプロトコルを用いて、あるいはオフラインなどでサービスプロバイダ310に供給する。
【0219】
サービスプロバイダ310は、コンテンツプロバイダ301からセキュアコンテナ104を受け取ると、署名データの検証を行なって、セキュアコンテナ104が正当なコンテンツプロバイダ301によって作成されたものであるか、並びに送り主の正当性を確認する。
次に、サービスプロバイダ310は、例えばオフラインで通知されたコンテンツプロバイダ301が希望するコンテンツに対しての価格(SRP)に、自らのサービスの価格を加算した価格を示すプライスタグデータ(PT)312を作成する。
そして、サービスプロバイダ310は、セキュアコンテナ104から取り出したコンテンツファイルCFおよびキーファイルKFと、プライスタグデータ312と、これらに対しての自らの秘密鍵データKSP,Sによる署名データとを格納したセキュアコンテナ304を作成する。
このとき、キーファイルKFは、配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 によって暗号化されており、サービスプロバイダ310は当該配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 を保持していないため、サービスプロバイダ310はキーファイルKFの中身を見たり、書き換えたりすることはできない。
また、EMDサービスセンタ302は、プライスタグデータ312を登録して権威化する。
【0220】
サービスプロバイダ310は、オンラインおよび/またはオフラインでセキュアコンテナ304をユーザホームネットワーク303に配給する。
このとき、オフラインの場合には、セキュアコンテナ304はSAM3051 〜3054 にそのまま供給される。一方、オンラインの場合には、サービスプロバイダ310とCAモジュール311との間で相互認証を行い、セキュアコンテナ304をサービスプロバイダ310においてセッション鍵データKSES を用いた暗号化して送信し、CAモジュール311において受信したセキュアコンテナ304をセッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号した後に、SAM3051 〜3054 に転送する。
【0221】
次に、SAM3051 〜3054 において、セキュアコンテナ304を、EMDサービスセンタ302から配給された対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を用いて復号した後に、署名データの検証処理を行う。
SAM3051 〜3054 に供給されたセキュアコンテナ304は、ネットワーク機器3601 およびAV機器3602 〜3604 において、ユーザの操作に応じて購入・利用形態が決定された後に、再生や記録媒体への記録などの対象となる。
SAM3051 〜3054 は、上述したセキュアコンテナ304の購入・利用の履歴を利用履歴(Usage Log) データ308として記録する。
利用履歴データ(履歴データまたは管理装置用履歴データ)308は、例えば、EMDサービスセンタ302からの要求に応じて、ユーザホームネットワーク303からEMDサービスセンタ302に送信される。
【0222】
EMDサービスセンタ302は、利用履歴データ308に基づいて、コンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310の各々について、課金内容を決定(計算)し、その結果に基づいて、ペイメントゲートウェイ90を介して銀行などの決済機関91に決済を行なう。これにより、ユーザホームネットワーク103のユーザが支払った金銭が、EMDサービスセンタ102による決済処理によって、コンテンツプロバイダ101およびサービスプロバイダ310に分配される。
【0223】
本実施形態では、第1実施形態と同様に、デジタルのコンテンツデータCをカプセル化して提供することで、従来の記録媒体と密着したデジタルコンテンツを、記録媒体から切り離して、デジタルコンテンツ単体に存在価値を持たせることができる。
ここで、セキュアコンテナは、どのような流通経路(配送チャンネル)を介して提供されても、コンテンツデータC(商品)を販売するときの最も基本となる商品カプセルである。具体的には、セキュアコンテナは、課金を行うための暗号情報や、コンテンツデータCの中身の正当性、コンテンツデータを作成した者の正当性およびコンテンツデータの流通業者の正当性を検証するための署名データや、コンテンツデータに埋め込む電子透かし情報に関する情報などの著作権に係わる情報を含む商品カプセルである。
【0224】
また、本実施形態では、EMDサービスセンタ302は、認証機能、鍵データ管理機能および権利処理(利益分配)機能を有している。
すなわち、EMDサービスセンタ302は、中立の立場にある最高の権威機関であるルート認証局92に対してのセカンド認証局(Second Certificate Authority)としての役割を果たし、コンテンツプロバイダ301、サービスプロバイダ310およびSAM3051 〜3054 において署名データの検証処理に用いられる公開鍵データの公開鍵証明書データに、EMDサービスセンタ302の秘密鍵データによる署名を付けることで、当該公開鍵データの正当性を認証する。また、前述したように、コンテンツプロバイダ301の権利書データ106およびサービスプロバイダ310のプライスタグデータ312を登録して権威化することも、EMDサービスセンタ302の認証機能によるものである。
また、EMDサービスセンタ302は、例えば、配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 などの鍵データの管理を行なう鍵データ管理機能を有する。
また、EMDサービスセンタ302は、コンテンツプロバイダ301が登録した権利書データ106とSAM3051 〜SAM3054 から入力した利用履歴データ308とサービスプロバイダ310が登録したプライスタグデータ312とに基づいて、ユーザホームネットワーク303のユーザによるコンテンツの購入・利用に対して決済を行い、ユーザが支払った金銭をコンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310に分配して支払う権利処理(利益分配)機能を有する。
【0225】
以下、コンテンツプロバイダ301の各構成要素について詳細に説明する。
〔コンテンツプロバイダ301〕
図50は、コンテンツプロバイダ301の機能ブロック図であり、サービスプロバイダ310との間で送受信されるデータに関連するデータの流れが示されている。
図50に示すように、コンテンツプロバイダ301は、コンテンツマスタソースサーバ111、電子透かし情報付加部112、圧縮部113、暗号化部114、乱数発生部115、暗号化部116、署名処理部117、セキュアコンテナ作成部118、セキュアコンテナデータベース118a、記憶部119、相互認証部120、暗号化・復号部121、権利書データ作成部122、EMDサービスセンタ管理部125およびサービスプロバイダ管理部324を有する。
【0226】
図50において、図2と同一符号を付した構成要素は、前述した第1実施形態において図2および図3を参照しながら説明した同一符号の構成要素と同じである。
すなわち、コンテンツプロバイダ301は、図2に示すSAM管理部124の代わりにサービスプロバイダ管理部324を設けた構成をしている。
サービスプロバイダ管理部324は、セキュアコンテナ作成部118から入力したセキュアコンテナ104を、オフラインおよび/またはオンラインで、図49に示すサービスプロバイダ310に提供する。セキュアコンテナ104には、第1実施形態と同様に、図4(A),(B),(C)に示すコンテンツファイルCFおよびその署名データSIG6,CPと、キーファイルKFおよびその署名データSIG7,CPと、公開鍵証明書データCERCPおよびその署名データSIG1,ESC とが格納されている。
【0227】
サービスプロバイダ管理部324は、セキュアコンテナ104をオンラインでサービスプロバイダ310に配信する場合には、暗号化・復号部121においてセッション鍵データKSES を用いてセキュアコンテナ104を暗号化した後に、ネットワークを介してサービスプロバイダ310に配信する。
【0228】
また、図3に示したコンテンツプロバイダ101内でのデータの流れは、サービスプロバイダ310にも同様に適用される。
【0229】
〔サービスプロバイダ310〕
サービスプロバイダ310は、コンテンツプロバイダ301から提供を受けたセキュアコンテナ104内のコンテンツファイルCFおよびキーファイルKFと、自らが生成したプライスタグデータ312とを格納したセキュアコンテナ304を、オンラインおよび/またはオフラインで、ユーザホームネットワーク303のネットワーク機器3601 およびAV機器3602 〜3604 に配給する。
サービスプロバイダ310によるコンテンツ配給のサービス形態には、大きく分けて、独立型サービスと連動型サービスとがある。
独立型サービスは、例えば、コンテンツを個別に配給するダウンロード専用のサービスである。また、連動型サービスは、番組、CM(広告)に連動してコンテンツを配給するサービスであり、例えば、ドラマ番組のストリーム内にドラマの主題歌や挿入歌のコンテンツが格納してある。ユーザは、ドラマ番組を見ているときに、そのストリーム中にある主題歌や挿入歌のコンテンツを購入できる。
【0230】
図51は、サービスプロバイダ310の機能ブロック図である。
なお、図51には、コンテンツプロバイダ301から供給を受けたセキュアコンテナ104に応じたセキュアコンテナ304をユーザホームネットワーク303に供給する際のデータの流れが示されている。
図51に示すように、サービスプロバイダ310は、コンテンツプロバイダ管理部350、記憶部351、相互認証部352、暗号化・復号部353、署名処理部354、セキュアコンテナ作成部355、セキュアコンテナデータベース355a、プライスタグデータ作成部356、ユーザホームネットワーク管理部357、EMDサービスセンタ管理部358およびユーザ嗜好フィルタ生成部920を有する。
【0231】
以下、コンテンツプロバイダ301から供給を受けたセキュアコンテナ104からセキュアコンテナ304を作成し、これをユーザホームネットワーク303に配給する際のサービスプロバイダ310内での処理の流れを図51および図52を参照しながら説明する。
図52は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップSZ1:コンテンツプロバイダ管理部350は、オンラインおよび/またはオフラインで、コンテンツプロバイダ301から図4に示すセキュアコンテナ104の供給を受けてセキュアコンテナ104を記憶部351に書き込む。
このとき、コンテンツプロバイダ管理部350は、オンラインの場合には、図50に示す相互認証部120と図51に示す相互認証部352との間の相互認証によって得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて、セキュアコンテナ104を暗号化・復号部353において復号した後に、記憶部351に書き込む。
【0232】
ステップSZ2:署名処理部354において、記憶部351に記憶されているセキュアコンテナ104の図4(C)に示す署名データSIG1,ESC を、記憶部351から読み出したEMDサービスセンタ302の公開鍵データKESC,P を用いて検証し、その正当性が認められた後に、図4(C)に示す公開鍵証明書データCERCPから公開鍵データKCP,Pを取り出す。
ステップSZ3:署名処理部354は、当該取り出した公開鍵データKCP,Pを用いて、記憶部351に記憶されているセキュアコンテナ104の図4(A),(B)に示す署名データSIG6,CP,SIG7,CPの検証を行う。
【0233】
ステップSZ4:プライスタグデータ作成部356は、例えばコンテンツプロバイダ301からオフラインで通知されたコンテンツプロバイダ301が要求するコンテンツに対しての価格に、自らのサービスの価格を加算した価格を示すプライスタグデータ312を作成し、これをセキュアコンテナ作成部355に出力する。
【0234】
ステップSZ5:署名処理部354は、コンテンツファイルCF、キーファイルKFおよびプライスタグデータ312のハッシュ値をとり、サービスプロバイダ310の秘密鍵データKSP,Pを用いて、署名データSIG62,SP ,SIG63,SP ,SIG64,SP を作成し、これをセキュアコンテナ作成部355に出力する。
【0235】
ステップSZ6:セキュアコンテナ作成部355は、図53(A)〜(D)に示すように、コンテンツファイルCFおよびその署名データSIG62,SP と、キーファイルKFおよびその署名データSIG63,ESCと、プライスタグデータ312およびその署名データSIG64,SP と、公開鍵証明書データCERSPおよびその署名データSIG61,ESCとを格納したセキュアコンテナ304を作成し、セキュアコンテナデータベース355aに格納する。そして、セキュアコンテナ作成部355は、ユーザホームネットワーク303からの要求に応じたセキュアコンテナ304をセキュアコンテナデータベース355aから読み出してユーザホームネットワーク管理部357に出力する。
このとき、セキュアコンテナ304は、複数のコンテンツファイルCFと、それらにそれぞれ対応した複数のキーファイルKFとを格納した複合コンテナであってもよい。例えば、単数のセキュアコンテナ304内に、それぞれ曲、ビデオクリップ、歌詞カード、ライナーノーツおよびジャケットに関する複数のコンテンツファイルCFを単数のセキュアコンテナ304に格納してもよい。これらの複数のコンテンツファイルCFなどは、ディレクトリー構造でセキュアコンテナ304内に格納してもよい。
【0236】
また、セキュアコンテナ304は、デジタル放送で送信される場合には、MHEG(Multimedia and Hypermedia information coding Experts Group)プロトコルが用いられ、インターネットで送信される場合にはXML/SMIL/HTML(Hyper TextMarkup Language) プロトコルが用いられる。
このとき、コンテンツファイルCFおよびキーファイルKFは、コンテンツプロバイダ301によって一元的に管理され、セキュアコンテナ304を送信するプロトコルに依存しない。すなわち、コンテンツファイルCFおよびキーファイルKFは、MHEGおよびHTMLのプロトコルをトンネリングした形でセキュアコンテナ304内に格納される。
【0237】
ステップSZ7:ユーザホームネットワーク管理部357は、セキュアコンテナ304を、オフラインおよび/またはオンラインでユーザホームネットワーク303に供給する。
ユーザホームネットワーク管理部357は、セキュアコンテナ304をオンラインでユーザホームネットワーク303のネットワーク機器3601 に配信する場合には、相互認証後に、暗号化・復号部352においてセッション鍵データKSES を用いてセキュアコンテナ304を暗号化した後に、ネットワークを介してネットワーク機器3601 に配信する。
【0238】
なお、ユーザホームネットワーク管理部357は、セキュアコンテナ304を例えば衛星などを介して放送する場合には、セキュアコンテナ304をスクランブル鍵データKSCR を用いて暗号化する。また、スクランブル鍵データKSCR をワーク鍵データKW を暗号化し、ワーク鍵データKW をマスタ鍵データKM を用いて暗号化する。
そして、ユーザホームネットワーク管理部357は、セキュアコンテナ304と共に、スクランブル鍵データKSCR およびワーク鍵データKW を、衛星を介してユーザホームネットワーク303に送信する。
また、例えば、マスタ鍵データKM を、ICカードなどに記憶してオフラインでユーザホームネットワーク303に配給する。
【0239】
また、ユーザホームネットワーク管理部357は、ユーザホームネットワーク303から、当該サービスプロバイダ310が配給したコンテンツデータCに関してのSP用購入履歴データ309を受信すると、これを記憶部351に書き込む。
サービスプロバイダ310は、将来のサービス内容を決定する際に、SP用購入履歴データ309を参照する。また、ユーザ嗜好フィルタ生成部920は、SP用購入履歴データ309に基づいて、当該SP用購入履歴データ309を送信したSAM3051 〜3054 のユーザの嗜好を分析してユーザ嗜好フィルタデータ900を生成し、これをユーザホームネットワーク管理部357を介してユーザホームネットワーク303のCAモジュール311に送信する。
【0240】
図54には、サービスプロバイダ310内におけるEMDサービスセンタ302との間の通信に関連するデータの流れが示されている。
なお、以下に示す処理を行う前提として、サービスプロバイダ310の関係者は、例えば、自らの身分証明書および決済処理を行う銀行口座などを用いて、オフラインで、EMDサービスセンタ302に登録処理を行い、グローバルユニークな識別子SP_IDを得ている。識別子SP_IDは、記憶部351に記憶される。
【0241】
先ず、サービスプロバイダ310が、EMDサービスセンタ302に、自らの秘密鍵データKSP,Sに対応する公開鍵データKSP,Sの正当性を証明する公開鍵証明書データCERSPを要求する場合の処理を図54を参照しながら説明する。
先ず、サービスプロバイダ310は、真性乱数発生器を用いて乱数を発生して秘密鍵データKSP,Sを生成し、当該秘密鍵データKSP,Sに対応する公開鍵データKSP,Pを作成して記憶部351に記憶する。
EMDサービスセンタ管理部358、サービスプロバイダ310の識別子SP_IDおよび公開鍵データKSP,Pを記憶部351から読み出す。
そして、EMDサービスセンタ管理部358は、識別子SP_IDおよび公開鍵データKSP,Pを、EMDサービスセンタ302に送信する。
そして、EMDサービスセンタ管理部348は、当該登録に応じて、公開鍵証明書データCERSPおよびその署名データSIG61,ESCをEMDサービスセンタ302から入力して記憶部351に書き込む。
【0242】
次に、サービスプロバイダ310が、EMDサービスセンタ302にプライスタグデータ312を登録して権威化する場合の処理を図54を参照して説明する。
【0243】
この場合には、署名処理部354において、プライスタグデータ作成部356が作成したプライスタグデータ312と記憶部351から読み出したグローバルユニークな識別子Content_IDとを格納したモジュールMod103 のハッシュ値が求められ、秘密鍵データKSP,Sを用いて署名データSIG80,SP が生成される。
また、記憶部351から公開鍵証明書データCERSPおよびその署名データSIG61,ESCが読み出される。
そして、図55に示すプライスタグ登録要求用モジュールMod102 を、相互認証部352とEMDサービスセンタ302との間の相互認証によって得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化・復号部353において暗号化した後に、EMDサービスセンタ管理部358からEMDサービスセンタ302に送信する。
なお、モジュールMod103 に、サービスプロバイダ310のグローバルユニークな識別子SP_IDを格納してもよい。
【0244】
また、EMDサービスセンタ管理部358は、EMDサービスセンタ302から受信した決済レポートデータ307sを記憶部351に書き込む。
【0245】
また、EMDサービスセンタ管理部358は、EMDサービスセンタ302から受信したマーケティング情報データ904を記憶部351に記憶する。
マーケティング情報データ904は、サービスプロバイダ310が今後配給するコンテンツデータCを決定する際に参考にされる。
【0246】
〔EMDサービスセンタ302〕
EMDサービスセンタ302は、前述したように、認証局(CA:Certificate Authority) 、鍵管理(Key Management)局および権利処理(Rights Clearing) 局としての役割を果たす。
図56は、EMDサービスセンタ302の機能の構成図である。
図56に示すように、EMDサービスセンタ302は、鍵サーバ141、鍵データベース141a、決済処理部442、署名処理部443、決算機関管理部144、証明書・権利書管理部445、CERデータベース445a、コンテンツプロバイダ管理部148、CPデータベース148a、SAM管理部149、SAMデータベース149a、相互認証部150、暗号化・復号部151、サービスプロバイダ管理部390、SPデータベース390a、ユーザ嗜好フィルタ生成部901およびマーケティング情報データ生成部902を有する。
図56において、図10および図11と同じ符号を付した機能ブロックは、第1実施形態で説明した同一符号の機能ブロックと略同じ機能を有している。
以下、図56において、新たな符号を付した機能ブロックについて説明する。
なお、図56には、EMDサービスセンタ302内の機能ブロック相互間のデータの流れのうち、サービスプロバイダ310との間で送受信されるデータに関連するデータの流れが示されている。
また、図57には、EMDサービスセンタ302内の機能ブロック相互間のデータの流れのうち、コンテンツプロバイダ301との間で送受信されるデータに関連するデータの流れが示されている。
また、図58には、EMDサービスセンタ302内の機能ブロック相互間のデータの流れのうち、図49に示すSAM3051 〜3054 および決済機関91との間で送受信されるデータに関連するデータの流れが示されている。
【0247】
決算処理部442は、図58に示すように、SAM3051 〜3054 から入力した利用履歴データ308と、証明書・権利書管理部445から入力した標準小売価格データSRPおよびプライスタグデータ312に基づいて決済処理を行う。なお、この際に、決済処理部442は、サービスプロバイダ310によるダンピングの有無などを監視する。
決済処理部442は、決済処理により、図58に示すように、コンテンツプロバイダ301についての決済レポートデータ307cおよび決済請求権データ152cを作成し、これらをそれぞれコンテンツプロバイダ管理部148および決算機関管理部144に出力する。
また、決済処理により、図56および図58に示すように、サービスプロバイダ310についての決済レポートデータ307sおよび決済請求権データ152sを作成し、これらをそれぞれサービスプロバイダ管理部390および決算機関管理部144に出力する。
ここで、決済請求権データ152c,152sは、当該データに基づいて、決済機関91に金銭の支払いを請求できる権威化されたデータである。
【0248】
ここで、利用履歴データ308は、第1実施形態で説明した利用履歴データ108と同様に、セキュアコンテナ304に関連したラインセンス料の支払いを決定する際に用いられる。利用履歴データ308には、例えば、図59に示すように、セキュアコンテナ304に格納されたコンテンツデータCの識別子Content_ID、セキュアコンテナ304に格納されたコンテンツデータCを提供したコンテンツプロバイダ301の識別子CP_ID、セキュアコンテナ304を配給したサービスプロバイダ310の識別子SP_ID、コンテンツデータCの信号諸元データ、セキュアコンテナ304内のコンテンツデータCの圧縮方法、セキュアコンテナ304を記録した記録媒体の識別子Media_ID、セキュアコンテナ304を配給を受けたSAM3051 〜3054 の識別子SAM_ID、当該SAM1051 〜1054 のユーザのUSER_IDなどが記述されている。従って、EMDサービスセンタ302は、コンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310の所有者以外にも、例えば、圧縮方法や記録媒体などのライセンス所有者に、ユーザホームネットワーク303のユーザが支払った金銭を分配する必要がある場合には、予め決められた分配率表に基づいて各相手に支払う金額を決定し、当該決定に応じた決済レポートデータおよび決済請求権データを作成する。
【0249】
証明書・権利書管理部445は、CERデータベース445aに登録されて権威化された公開鍵証明書データCERcp、公開鍵証明書データCERSPおよび公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1〜CERSAM2などを読み出すと共に、コンテンツプロバイダ301の権利書データ106およびコンテンツ鍵データKc、並びにサービスプロバイダ310のプライスタグデータ312などをCERデータベース445aに登録して権威化する。
このとき、証明書・権利書管理部445は、権利書データ106、コンテンツ鍵データKcおよびプライスタグデータ312などのハッシュ値をとり、秘密鍵データKESC,S を用いた署名データを付して権威化証明書データを作成する。
【0250】
コンテンツプロバイダ管理部148は、コンテンツプロバイダ101との間で通信する機能を有し、登録されているコンテンツプロバイダ101の識別子CP_IDなどを管理するCPデータベース148aにアクセスできる。
【0251】
ユーザ嗜好フィルタ生成部901は、利用履歴データ308に基づいて、当該利用履歴データ308を送信したSAM3051 〜3054 のユーザの嗜好に応じたコンテンツデータCを選択するためのユーザ嗜好フィルタデータ903を生成し、ユーザ嗜好フィルタデータ903をSAM管理部149を介して、当該利用履歴データ308を送信したSAM3051 〜3054 に送信する。
【0252】
マーケティング情報データ生成部902は、利用履歴データ308に基づいて、例えば、複数のサービスプロバイダ310によってユーザホームネットワーク103に配給されたコンテンツデータCの全体の購入状況などを示すマーケティング情報データ904を生成し、これをサービスプロバイダ管理部390を介して、サービスプロバイダ310に送信する。サービスプロバイダ310は、マーケティング情報データ904を参考にして、今後提供するサービスの内容を決定する。
【0253】
以下、EMDサービスセンタ302内での処理の流れを説明する。
EMDサービスセンタ302からコンテンツプロバイダ301への配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 の送信と、EMDサービスセンタ302からSAM3051 〜3054 への配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 の送信とは、第1実施形態の場合と同様に行なわれる。
【0254】
また、EMDサービスセンタ302がコンテンツプロバイダ301から、公開鍵証明書データの発行要求を受けた場合の処理も、証明書・権利書管理部445がCERデータベース445aに対して登録を行なう点を除いて、前述した第1実施形態の場合と同様に行なわれる。
【0255】
以下、EMDサービスセンタ302がサービスプロバイダ310から、公開鍵証明書データの発行要求を受けた場合の処理を、図56および図60を参照しながら説明する。
図60は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップSO1:サービスプロバイダ管理部390は、予めEMDサービスセンタ302によって与えられたサービスプロバイダ310の識別子SP_ID、公開鍵データKSP,Pおよび署名データSIG70,SP を含む公開鍵証明書データ登録要求をサービスプロバイダ310から受信すると、これらを、相互認証部150と図51に示す相互認証部352と間の相互認証で得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号する。
【0256】
ステップSO2:当該復号した署名データSIG70,SP の正当性を署名処理部443において確認した後に、識別子SP_IDおよび公開鍵データKSP,Pに基づいて、当該公開鍵証明書データの発行要求を出したサービスプロバイダ310がSPデータベース390aに登録されているか否かを確認する。
ステップSO3:証明書・権利書管理部445は、当該サービスプロバイダ310の公開鍵証明書データCERSPをCERデータベース445aから読み出してサービスプロバイダ管理部390に出力する。
【0257】
ステップSO4:署名処理部443は、公開鍵証明書データCERSPのハッシュ値をとり、EMDサービスセンタ302の秘密鍵データKESC,S を用いて、署名データSIG61,ESCを作成し、これをサービスプロバイダ管理部390に出力する。
ステップSO5:サービスプロバイダ管理部390は、公開鍵証明書データCERSPおよびその署名データSIG61,ESCを、相互認証部150と図51に示す相互認証部352と間の相互認証で得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて暗号化した後に、サービスプロバイダ310に送信する。
【0258】
なお、EMDサービスセンタ302がSAM1051 〜1054 から、公開鍵証明書データの発行要求を受けた場合の処理は、第1実施形態と同様である。
また、EMDサービスセンタ302が、コンテンツプロバイダ301から権利書データ106の登録要求を受けた場合の処理も、第1実施形態と同様である。
【0259】
次に、EMDサービスセンタ302が、サービスプロバイダ310からプライスタグデータ312の登録要求を受けた場合の処理を、図56および図61を参照しながら説明する。
図61は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップSP1:サービスプロバイダ管理部390がサービスプロバイダ310から図55に示すプライスタグ登録要求モジュールMod102 を受信すると、相互認証部150と図51に示す相互認証部352との間の相互認証で得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いてプライスタグ登録要求モジュールMod102 を復号する。
【0260】
ステップSP2:当該復号したプライスタグ登録要求モジュールMod102 に格納された署名データSIG80,SP の正当性を署名処理部443において確認する。
【0261】
ステップSP3:証明書・権利書管理部445は、プライスタグ登録要求モジュールMod102 に格納されたプライスタグデータ312を、CERデータベース445aに登録して権威化する。
【0262】
次に、EMDサービスセンタ302において決済を行なう場合の処理を図58および図62を参照しながら説明する。
図62は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップSQ1:SAM管理部149は、ユーザホームネットワーク303の例えばSAM3051 から利用履歴データ308およびその署名データSIG205,SAM1を入力すると、利用履歴データ308および署名データSIG205,SAM1を、相互認証部150とSAM3051 〜3054 との間の相互認証によって得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号し、SAM3051 の公開鍵データKSAM1,pを用いて署名データSIG205,SAM1の検証を行なった後に、決算処理部442に出力する。
【0263】
ステップSQ2:決済処理部442は、SAM3051 から入力した利用履歴データ308と、証明書・権利書管理部445から入力した標準小売価格データSRPおよびプライスタグデータ312とに基づいて決済処理を行う。
決済処理部442は、決済処理により、図58に示すように、コンテンツプロバイダ301についての決済レポートデータ307cおよび決済請求権データ152cと、サービスプロバイダ310についての決済レポートデータ307sおよび決済請求権データ152sとを作成する。
なお、決済処理部442による決済処理は、利用履歴データ308を入力する毎に行ってもよいし、所定の期間毎に行ってもよい。
【0264】
ステップSQ3:図56および図58に示すように、コンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310についての決済請求権データ152c,152sを作成し、これらを決算機関管理部144に出力する。
決算機関管理部144は、決済請求権データ152c,152sと、それらについて秘密鍵データKESC,S を用いて作成した署名データとを、相互認証およびセッション鍵データKSES による復号を行なった後に、図49に示すペイメントゲートウェイ90を介して決済機関91に送信する。
これにより、決済請求権データ152cに示される金額の金銭がコンテンツプロバイダ301に支払われ、決済請求権データ152sに示される金額の金銭がサービスプロバイダ310に支払われる。
なお、EMDサービスセンタ302は、決済請求権データ152c,152sをそれぞれコンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310に送信してもよい。この場合には、コンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310が、当該受信した決済請求権データ152c,152sに基づいて決済機関91に金銭を請求する。
【0265】
ステップSQ4:コンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310についての決済レポートデータS307c,S307sが、それぞれコンテンツプロバイダ管理部148およびサービスプロバイダ管理部390を介して、コンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310に出力される。
【0266】
EMDサービスセンタ302は、その他に、第1実施形態のEMDサービスセンタ102と同様に、SAM3051 〜3054 の出荷時の処理と、SAM登録リストの登録処理とを行なう。
【0267】
〔ユーザホームネットワーク303〕
ユーザホームネットワーク303は、図49に示すように、ネットワーク機器3601 およびA/V機器3602 〜3604 を有している。
ネットワーク機器3601 は、CAモジュール311およびSAM3051 を内蔵している。また、AV機器3602 〜3604 は、それぞれSAM3052 〜3054 を内蔵している。
SAM3051 〜3054 の相互間は、例えば、1394シリアルインタフェースバスなどのバス191を介して接続されている。
なお、AV機器3602 〜3604 は、ネットワーク通信機能を有していてもよいし、ネットワーク通信機能を有しておらず、バス191を介してネットワーク機器3601 のネットワーク通信機能を利用してもよい。
また、ユーザホームネットワーク303は、ネットワーク機能を有していないAV機器のみを有していてもよい。
【0268】
以下、ネットワーク機器3601 について説明する。
図63は、ネットワーク機器3601 の構成図である。
図63に示すように、ネットワーク機器3601 は、通信モジュール162、CAモジュール311、復号モジュール905、SAM3051 、復号・伸長モジュール163、購入・利用形態決定操作部165、ダウンロードメモリ167、再生モジュール169および外部メモリ201を有する。
図63において、図16と同一符号を付した構成要素は、第1実施形態で説明した同一符号の構成要素と同じである。
【0269】
通信モジュール162は、サービスプロバイダ310との間の通信処理を行なう。
具体的には、通信モジュール162は、サービスプロバイダ310から衛星放送などで受信したセキュアコンテナ304を復号モジュール905に出力する。
また、通信モジュール162は、サービスプロバイダ310に電話回線などを介してSP用購入履歴データ309を受信したユーザ嗜好フィルタデータ900をCAモジュール311に出力すると共に、CAモジュール311から入力したSP用購入履歴データ309を電話回線などを介してサービスプロバイダ310に送信する。
【0270】
図64は、CAモジュール311および復号モジュール905の機能ブロック図である。
図64に示すように、CAモジュール311は、相互認証部906、記憶部907、暗号化・復号部908およびSP用購入履歴データ生成部909を有する。
相互認証部906は、CAモジュール311とサービスプロバイダ310との間で電話回線を介してデータを送受信する際に、サービスプロバイダ310との間で相互認証を行ってセッション鍵データKSES を生成し、これを暗号化・復号部908に出力する。
【0271】
記憶部907は、例えば、サービスプロバイダ310とユーザとの間で契約が成立した後に、サービスプロバイダ310からICカード912などを用いてオフラインで供給されたマスタ鍵データKM を記憶する。
【0272】
暗号化・復号部908は、復号モジュール905の復号部910からそれぞれ暗号化されたスクランブル鍵データKSCR およびワーク鍵データKW を入力し、記憶部907から読み出したマスタ鍵データKM を用いてワーク鍵データKW を復号する。そして、暗号化・復号部908は、当該復号したワーク鍵データKW を用いてスクランブル鍵データKSCR を復号し、当該復号したスクランブル鍵データKSCR を復号部910に出力する。
また、暗号化・復号部908は、電話回線などを介して通信モジュール162がサービスプロバイダ310から受信したユーザ嗜好フィルタデータ900を、相互認証部906からのセッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号して復号モジュール905のセキュアコンテナ選択部911に出力する。
また、暗号化・復号部908は、SP用購入履歴データ生成部909から入力したSP用購入履歴データ309を、相互認証部906からのセッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号して通信モジュール162を介してサービスプロバイダ310に送信する。
【0273】
SP用購入履歴データ生成部909は、図63に示す購入・利用形態決定操作部165を用いてユーザによるコンテンツデータCの購入操作に応じた操作信号S165、またはSAM3051 からの利用制御状態データ166に基づいて、サービスプロバイダ310に固有のコンテンツデータCの購入履歴を示すSP用購入履歴データ309を生成し、これを暗号化・復号部908に出力する。
SP用購入履歴データ309は、例えば、サービスプロバイダ310が配信サービスに関してユーザから徴収したい情報、月々の基本料金(ネットワーク家賃)、契約(更新)情報および購入履歴情報などを含む。
【0274】
なお、CAモジュール311は、サービスプロバイダ310が課金機能を有している場合には、サービスプロバイダ310の課金データベース、顧客管理データベースおよびマーケティング情報データベースと通信を行う。この場合に、CAモジュール311は、コンテンツデータの配信サービスについての課金データをサービスプロバイダ310に送信する。
【0275】
復号モジュール905は、復号部910およびセキュアコンテナ選択部911を有する。
復号部910は、通信モジュール162から、それぞれ暗号化されたセキュアコンテナ304、スクランブル鍵データKSCR およびワーク鍵データKW を入力する。
そして、復号部910は、暗号化されたスクランブル鍵データKSCR およびワーク鍵データKW をCAモジュール311の暗号化・復号部908に出力し、暗号化・復号部908から復号されたスクランブル鍵データKSCR を入力する。
そして、復号部910は、暗号化されたセキュアコンテナ304を、スクランブル鍵データKSCR を用いて復号した後に、セキュアコンテナ選択部911に出力する。
【0276】
なお、セキュアコンテナ304が、MPEG2 Transport Stream 方式でサービスプロバイダ310から送信される場合には、例えば、復号部910は、TS Packet 内のECM(Entitlement Control Message) からスクランブル鍵データKSCR を取り出し、EMM(Entitlement Management Message)からワーク鍵データKW を取り出す。
ECMには、その他に、例えば、チャンネル毎の番組属性情報などが含まれている。また、EMMは、その他に、ユーザ(視聴者)毎に異なる個別試聴契約情報などが含まれている。
【0277】
セキュアコンテナ選択部911は、復号部910から入力したセキュアコンテナ304を、CAモジュール311から入力したユーザ嗜好フィルタデータ900を用いてフィルタリング処理して、ユーザの嗜好に応じたセキュアコンテナ304を選択してSAM3051 に出力する。
【0278】
次に、SAM3051 について説明する。
なお、SAM3051 は、サービスプロバイダ310についての署名検証処理を行なうなど、コンテンツプロバイダ301に加えてサービスプロバイダ310に関しての処理を行う点を除いて、図17〜図41を用いて前述した第1実施形態のSAM1051 と基本的に行なう機能および構造を有している。
また、SAM3052 〜3054 は、SAM3051 と基本的に同じ機能を有している。
すなわち、SAM3051 〜3054 は、コンテンツ単位の課金処理をおこなうモジュールであり、EMDサービスセンタ302との間で通信を行う。
【0279】
以下、SAM3051 の機能について詳細に説明する。
図65は、SAM3051 の機能の構成図である。
なお、図65には、サービスプロバイダ310からセキュアコンテナ304を入力し、セキュアコンテナ304内のキーファイルKFを復号する処理に関連するデータの流れが示されている。
図65に示すように、SAM3051 は、相互認証部170、暗号化・復号部171,172,173、誤り訂正部181、ダウンロードメモリ管理部182、セキュアコンテナ復号部183、復号・伸長モジュール管理部184、EMDサービスセンタ管理部185、利用監視部186、署名処理部189、SAM管理部190、記憶部192、メディアSAM管理部197、スタックメモリ200、サービスプロバイダ管理部580、課金処理部587、署名処理部598および外部メモリ管理部811を有する。
なお、図65に示すSAM3051 の所定の機能は、SAM1051 の場合と同様に、CPUにおいて秘密プログラムを実行することによって実現される。
図65において、図17と同じ符号を付した機能ブロックは、第1実施形態で説明した同一符号の機能ブロックと同じである。
【0280】
また、図63に示す外部メモリ201には、第1実施形態で説明した処理および後述する処理を経て、利用履歴データ308およびSAM登録リストが記憶される。
また、スタックメモリ200には、図66に示すように、コンテンツ鍵データKc、権利書データ(UCP)106、記憶部192のロック鍵データKLOC 、コンテンツプロバイダ301の公開鍵証明書データCERCP、サービスプロバイダ310の公開鍵証明書データCERSP、利用制御状態データ(UCS)366、SAMプログラム・ダウンロード・コンテナSDC1 〜SDC3 およびプライスタグデータ312などが記憶される。
【0281】
以下、SAM3051 の機能ブロックのうち、図65において新たに符号を付した機能ブロックについて説明する。
署名処理部589は、記憶部192あるいはスタックメモリ200から読み出したEMDサービスセンタ302の公開鍵データKESC,P 、コンテンツプロバイダ301の公開鍵データKcp,pおよびサービスプロバイダ310の公開鍵データKSP,Pを用いて、セキュアコンテナ304内の署名データの検証を行なう。
【0282】
課金処理部587は、図67に示すように、図63に示す購入・利用形態決定操作部165からの操作信号S165と、スタックメモリ200から読み出されたプライスタグデータ312とに基づいて、ユーザによるコンテンツの購入・利用形態に応じた課金処理を行う。
課金処理部587による課金処理は、利用監視部186の監視の下、権利書データ106が示す使用許諾条件などの権利内容および利用制御状態データ166に基づいて行われる。すなわち、ユーザは、当該権利内容などに従った範囲内でコンテンツの購入および利用を行うことができる。
【0283】
また、課金処理部587は、課金処理において、利用履歴データ308を生成し、これを外部メモリ管理部811を介して外部メモリ201に書き込む。
ここで、利用履歴データ308は、第1実施形態の利用履歴データ108と同様に、EMDサービスセンタ302において、セキュアコンテナ304に関連したラインセンス料の支払いを決定する際に用いられる。
【0284】
また、課金処理部587は、操作信号S165に基づいて、ユーザによるコンテンツの購入・利用形態を記述した利用制御状態(UCS: Usage Control Status)データ166を生成し、これを外部メモリ管理部811を介して外部メモリ201に書き込む。
コンテンツの購入形態としては、例えば、購入者による再生や当該購入者の利用のための複製に制限を加えない買い切りや、再生する度に課金を行なう再生課金などがある。
ここで、利用制御状態データ166は、ユーザがコンテンツの購入形態を決定したときに生成され、以後、当該決定された購入形態で許諾された範囲内でユーザが当該コンテンツの利用を行なうように制御するために用いられる。利用制御状態データ166には、コンテンツのID、購入形態、買い切り価格、当該コンテンツの購入が行なわれたSAMのSAM_ID,購入を行なったユーザのUSER_IDなどが記述されている。
【0285】
なお、決定された購入形態が再生課金である場合には、例えば、SAM3051 からサービスプロバイダ310に利用制御状態データ166をリアルタイムに送信し、サービスプロバイダ310がEMDサービスセンタ302に、利用履歴データ108をSAM1051 に取りにいくことを指示する。
また、決定された購入形態が買い切りである場合には、例えば、利用制御状態データ166が、サービスプロバイダ310およびEMDサービスセンタ302にリアルタイムに送信される。
【0286】
また、SAM3051 では、EMDサービスセンタ管理部185がEMDサービスセンタ302から受信したユーザ嗜好フィルタデータ903が、サービスプロバイダ管理部580に出力される。そして、サービスプロバイダ管理部580において、図63に示す復号モジュール905から入力したセキュアコンテナ304が、ユーザ嗜好フィルタデータ903に基づいてフィルタリングされてユーザの嗜好に応じたセキュアコンテナ304が選択され、当該選択されたセキュアコンテナ304が誤り訂正部181に出力される。これにより、SAM3051 において、当該SAM3051 のユーザが契約している全てのサービスプロバイダ310を対象として、当該ユーザによるコンテンツデータCの購入状況から得られた当該ユーザの嗜好に基づいたコンテンツデータCの選択処理が可能になる。
【0287】
以下、SAM3051 内での処理の流れを説明する。
EMDサービスセンタ302から受信した配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を記憶部192に格納する際のSAM3051 内での処理の流れは、前述したSAM1051 の場合と同様である。
【0288】
以下、セキュアコンテナ304をサービスプロバイダ310から入力し、セキュアコンテナ304内のキーファイルKFを復号する際のSAM3051 内での処理の流れを図65および図68を参照しながら説明する。
図68は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップSR1:相互認証部170と図51に示すサービスプロバイダ310の相互認証部352との間で相互認証が行なわれる。
暗号化・復号部171は、当該相互認証によって得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて、サービスプロバイダ管理部580を介してサービスプロバイダ310から受信した図53に示すセキュアコンテナ304を復号する。
【0289】
ステップSR2:署名処理部589は、図53(D)に示す署名データSIG61,ESCの検証を行なった後に、図53(D)に示す公開鍵証明書データCERSP内に格納されたサービスプロバイダ310の公開鍵データKSP,Pを用いて、署名データSIG62,SP ,SIG63,SP ,SIG64,SP の正当性を確認する。
サービスプロバイダ管理部580は、署名データSIG62,SP ,SIG63,SP ,SIG64,SP の正当性が確認されると、セキュアコンテナ304を誤り訂正部181に出力する。
誤り訂正部181は、セキュアコンテナ304を誤り訂正した後に、ダウンロードメモリ管理部182に出力する。
【0290】
ステップSR3:ダウンロードメモリ管理部182は、相互認証部170と図63に示すメディアSAM167aとの間で相互認証を行なった後に、セキュアコンテナ304をダウンロードメモリ167に書き込む。
【0291】
ステップSR4:ダウンロードメモリ管理部182は、相互認証部170と図63に示すメディアSAM167aとの間で相互認証を行なった後に、セキュアコンテナ304に格納された図53(B)に示すキーファイルKFを読み出してセキュアコンテナ復号部183に出力する。
そして、セキュアコンテナ復号部183は、記憶部192から入力した対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を用いて、キーファイルKFを復号する。
【0292】
ステップSR5:セキュアコンテナ復号部183は、図53(B)に示す署名・証明書モジュールMod1 に格納された署名データSIG1,ESC 、SIG2,cp〜SIG4,cpを署名処理部589に出力する。
署名処理部589は、図53(B)に示す署名データSIG1,ESC の検証を行なった後に、公開鍵証明書データCERcp内に格納された公開鍵データKCP,Pを用いて署名データSIG2,cp〜SIG4,cpの検証を行なう。
【0293】
ステップSR6:セキュアコンテナ復号部183は、署名データSIG2,cp〜SIG4,cpの正当性が確認されると、キーファイルKFをスタックメモリ200に書き込む。
【0294】
以下、サービスプロバイダ310からダウンロードメモリ167にダウンロードされたセキュアコンテナ304の購入形態を決定するまでの処理の流れを図67および図69を参照しながら説明する。
図69は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップSS1:課金処理部587において、ユーザによる図63に示す購入・利用形態決定操作部165の操作によって、試聴モードを示す操作信号S165が入力されたか否かが判断あれ、入力されたと判断された場合にはステップSS2の処理が実行され、そうでない場合にはステップSS3の処理が実行される。
【0295】
ステップSS2:例えば、ダウンロードメモリ167に記憶されているコンテンツファイルCFが、復号・伸長モジュール管理部184を介して、図63に示す復号・伸長モジュール163に出力される。
このとき、コンテンツファイルCFに対して、相互認証部170とメディアSAM167aとの間の相互認証およびセッション鍵データKSES による暗号化・復号と、相互認証部170と相互認証部220との間の相互認証およびセッション鍵データKSES による暗号化・復号とが行なわれる。
コンテンツファイルCFは、図63に示す復号部221において復号された後に、復号部222に出力される。
【0296】
また、スタックメモリ200から読み出されたコンテンツ鍵データKcおよび半開示パラメータデータ199が、図63に示す復号・伸長モジュール163に出力される。このとき、相互認証部170と相互認証部220との間の相互認証後に、コンテンツ鍵データKcおよび半開示パラメータデータ199に対してセッション鍵データKSES による暗号化および復号が行なわれる。
次に、復号された半開示パラメータデータ199が半開示処理部225に出力され、半開示処理部225からの制御によって、復号部222によるコンテンツ鍵データKcを用いたコンテンツデータCの復号が半開示で行われる。
次に、半開示で復号されたコンテンツデータCが、伸長部223において伸長された後に、電子透かし情報処理部224に出力される。
次に、電子透かし情報処理部224においてユーザ電子透かし情報用データ196がコンテンツデータCに埋め込まれた後、コンテンツデータCが再生モジュール169において再生され、コンテンツデータCに応じた音響が出力される。
【0297】
ステップSS3:コンテンツを試聴したユーザが、購入・利用形態決定操作部165を操作して購入形態を決定すると、当該決定した購入形態を示す操作信号S165が課金処理部187に出力される。
【0298】
ステップSS4:課金処理部187において、決定された購入形態に応じた利用履歴データ308および利用制御状態データ166が生成され、利用履歴データ308が外部メモリ管理部811を介して外部メモリ201に書き込まれると共に利用制御状態データ166がスタックメモリ200に書き込まれる。
以後は、利用監視部186において、利用制御状態データ166によって許諾された範囲で、コンテンツの購入および利用が行なわれるように制御(監視)される。
【0299】
ステップSS5:スタックメモリ200に格納されているキーファイルKFに、利用制御状態データ166が加えられ、購入形態が決定した後述する図71に示す新たなキーファイルKF11が生成される。キーファイルKF11は、スタックメモリ200に記憶される。
図71に示すように、キーファイルKF1 に格納された利用制御状態データ166はストレージ鍵データKSTR を用いてDESのCBCモードを利用して暗号化されている。また、当該ストレージ鍵データKSTR をMAC鍵データとして用いて生成したMAC値であるMAC300 が付されている。また、利用制御状態データ166およびMAC300 からなるモジュールは、メディア鍵データMED を用いてDESのCBCモードを利用して暗号化されている。また、当該モジュールには、当該メディア鍵データKMED をMAC鍵データとして用いて生成したMAC値であるMAC301 が付されている。
【0300】
次に、ダウンロードメモリ167に記憶されている購入形態が既に決定されたコンテンツデータCを再生する場合の処理の流れを、図67および図70を参照しながら説明する。
図70は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
ステップST1:例えば、ユーザによる操作に応じて、再生対象となるコンテンツの指定をSAMが受ける。
【0301】
ステップST2:利用監視部186の監視下で、操作信号S165に基づいて、ダウンロードメモリ167に記憶されているコンテンツファイルCFが読み出される。
ステップST3:当該読み出されたコンテンツファイルCFが、図63に示す復号・伸長モジュール163に出力される。
また、スタックメモリ200から読み出されたコンテンツ鍵データKcが復号・伸長モジュール163に出力される。
【0302】
ステップST4:復号・伸長モジュール163の復号部222において、コンテンツ鍵データKcを用いたコンテンツファイルCFの復号と、伸長部223による伸長処理とが行なわれ、再生モジュール169において、コンテンツデータCが再生される。
ステップST5:課金処理部587において、操作信号S165に応じて、利用履歴データ308が更新される。
利用履歴データ308は、秘密鍵データKSAM1,Sを用いて作成したそれぞれ署名データSIG205,SAM1と共に、EMDサービスセンタ管理部185を介して、所定のタイミングで、EMDサービスセンタ302に送信される。
【0303】
以下、図72に示すように、例えば、ネットワーク機器3601 のダウンロードメモリ167にダウンロードされた既に購入形態が決定されたコンテンツファイルCFを、バス191を介して、AV機器3602 のSAM3052 に転送する場合のSAM3051 内での処理の流れを図73および図74を参照しながら説明する。
ステップSU1:ユーザは、購入・利用形態決定操作部165を操作して、ダウンロードメモリ167に記憶された所定のコンテンツをAV機器3602 に転送することを指示し、当該操作に応じた操作信号S165が、課金処理部587に出力される。
これにより、課金処理部587は、操作信号S165に基づいて、スタックメモリ200に記憶されている利用履歴データ308を更新する。
【0304】
ステップSU2:ダウンロードメモリ管理部182は、ダウンロードメモリ167から読み出した図75(A)に示すコンテンツファイルCFをSAM管理部190に出力する。
ステップSU3:スタックメモリ200から読み出した図75(B)に示す既に購入形態が決定されたキーファイルKF11を、署名処理部589およびSAM管理部190に出力する。
ステップSU4:署名処理部589は、キーファイルKF11の署名データSIG80,SAM1 を作成し、これをSAM管理部190に出力する。
【0305】
ステップSU5:SAM管理部190は、記憶部192から、図75(C)に示す公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1およびその署名データSIG22,ESCを読み出す。
また、相互認証部170は、SAM3052 との間で相互認証を行って得たセッション鍵データKSES を暗号化・復号部171に出力する。
SAM管理部190は、図75(A),(B),(C)に示すデータからなるセキュアコンテナを作成する。
【0306】
ステップSU6:暗号化・復号部171において、セッション鍵データKSES を用いて当該セキュアコンテナを暗号化して作成して、図73に示すAV機器3602 のSAM3052 に出力する。
【0307】
以下、図72に示すように、SAM3051 から入力したコンテンツファイルCFなどを、RAM型などの記録媒体(メディア)に書き込む際のSAM3052 内での処理の流れを、図76および図77を参照しながら説明する。
図77は、当該処理のフローチャートである。
【0308】
ステップSV1:SAM3052 のSAM管理部190は、図76に示すように、図75(A)に示すコンテンツファイルCF、図75(B)に示すキーファイルKF11およびその署名データSIG80,SAM1 と、図75(C)に示す公開鍵署名データCERSAM1およびその署名データSIG22,ESCとを、ネットワーク機器3601 のSAM3051 から入力する。
そして、暗号化・復号部171において、SAM管理部190が入力したコンテンツファイルCFと、キーファイルKF11およびその署名データSIG80,SAM1 と、公開鍵署名データCERSAM1およびその署名データSIG22,ESCとが、相互認証部170とSAM3051 の相互認証部170との間の相互認証によって得られたセッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号される。
【0309】
次に、セッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号されたコンテンツファイルCFがメディアSAM管理部197に出力される。
また、セッション鍵データKSES を用いて復号されたキーファイルKF11およびその署名データSIG80,SAM1 と、公開鍵署名データCERSAM1およびその署名データSIG22,ESCとが、スタックメモリ200に書き込まれる。
【0310】
ステップSV2:署名処理部589は、スタックメモリ200から読み出した署名データSIG22,ESCを、記憶部192から読み出した公開鍵データKESC,P を用いて検証して、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1の正当性を確認する。
そして、署名処理部589は、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1の正当性を確認すると、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1に格納された公開鍵データKSAM1,Pを用いて、署名データSIG80,SAM1 の正当性を確認する。
【0311】
ステップSV3:署名データSIG80,SAM1 の正当性を確認されると、図75(B)に示すキーファイルKF11をスタックメモリ200から読み出して暗号化・復号部173に出力する。
そして、暗号化・復号部173は、記憶部192から読み出した記録用鍵データKSTR 、メディア鍵データKMED および購入者鍵データKPIN を用いてキーファイルKF11を順に暗号化してメディアSAM管理部197に出力する。
【0312】
ステップSV4:メディアSAM管理部197は、SAM管理部190から入力したコンテンツファイルCFおよび暗号化・復号部173から入力したキーファイルKF11を、図72に示す記録モジュール260に出力する。
そして、記録モジュール260は、メディアSAM管理部197から入力したコンテンツファイルCFおよびキーファイルKF11を、図72に示すRAM型の記録媒体250のRAM領域251に書き込む。
【0313】
なお、SAM3051 内での処理のうち、コンテンツの購入形態が未決定のROM型の記録媒体の購入形態を決定する際のAV機器3602 内での処理の流れ、AV機器3603 において購入形態が未決定のROM型の記録媒体からセキュアコンテナ304を読み出してこれをAV機器3602 に転送してRAM型の記録媒体に書き込む際の処理の流れは、サービスプロバイダ310の秘密鍵データを用いた署名データの署名データの検証を行なう点と、購入形態を決定したキーファイル内にプライスタグデータ312を格納する点を除いて、第1実施形態のSAM1051 の場合と同じである。
【0314】
次に、図49に示すEMDシステム300の全体動作について説明する。
図78および図79は、EMDシステム300の全体動作のフローチャートである。
ここでは、サービスプロバイダ310からユーザホームネットワーク303にオンラインでセキュアコンテナ304を送信する場合を例示して説明する。
なお、以下に示す処理の前提として、EMDサービスセンタ302へのコンテンツプロバイダ301、サービスプロバイダ310およびSAM3051 〜3054 の登録は既に終了しているものとする。
【0315】
ステップS21:EMDサービスセンタ302は、コンテンツプロバイダ301の公開鍵データKCP,Pの公開鍵証明書CERCPを、自らの署名データSIG1,ESC と共にコンテンツプロバイダ301に送信する。
また、EMDサービスセンタ302は、コンテンツプロバイダ301の公開鍵データKSP,Pの公開鍵証明書CERSPを、自らの署名データSIG61,ESCと共にサービスプロバイダ310に送信する。
また、EMDサービスセンタ302は、各々有効期限が1カ月の6カ月分の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 をコンテンツプロバイダ301に送信し、3カ月分の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 をユーザホームネットワーク303のSAM3051 〜3054 に送信する。
【0316】
ステップS22:コンテンツプロバイダ301は、図7(A)に示す権利登録要求モジュールMod2 を、EMDサービスセンタ302に送信する。
そして、EMDサービスセンタ302は、所定の署名検証を行った後に、権利書データ106およびコンテンツ鍵データKcを登録して権威化(認証)する。
【0317】
ステップS23:コンテンツプロバイダ301は、署名データの作成処理や、SIG対応する期間の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 などを用いた暗号化処理を経て、図4(A),(B),(C)に示すデータを格納したセキュアコンテナ104を、サービスプロバイダ310に供給する。
【0318】
ステップS24:サービスプロバイダ310は、図4(C)に示す署名データSIG1,ESC を検証した後に、公開鍵証明書データCERCPに格納された公開鍵データKCP,Pを用いて、図4(A),(B)に示す署名データSIG6,CPおよびSIG7,CPを検証して、セキュアコンテナ104が正当なコンテンツプロバイダ301から送信されたものであるかを確認する。
【0319】
ステップS25:サービスプロバイダ310は、プライスタグデータ312を作成し、プライスタグデータ312を格納した図53に示すセキュアコンテナ304を作成する。
【0320】
ステップS26:サービスプロバイダ310は、図55に示すプライスタグ登録要求モジュールMod102 を、EMDサービスセンタ302に送信する。
そして、EMDサービスセンタ302は、所定の署名検証を行った後に、プライスタグデータ312を登録して権威化する。
【0321】
ステップS27:サービスプロバイダ310は、例えば、ユーザホームネットワーク303のCAモジュール311からの要求に応じて、ステップS25で作成したセキュアコンテナ304を、オンラインあるいはオフラインで、図63に示すネットワーク機器3601 の復号モジュール905に送信する。
【0322】
ステップS28:CAモジュール311は、SP用購入履歴データ309を作成し、これを所定のタイミングで、サービスプロバイダ310に送信する。
【0323】
ステップS29:SAM3051 〜3054 のいずれかにおいて、図53(D)に示す署名データSIG61,ESCを検証した後に、公開鍵証明書データCERSPに格納された公開鍵データKSP,Pを用いて、図53(A),(B),(C)に示す署名データSIG62,SP 、SIG63,SP ,SIG64,SP を検証して、セキュアコンテナ304が正当なサービスプロバイダ310から送信されたものであるかを確認する。
【0324】
ステップS30:SAM3051 〜3054 のいずれかにおいて、配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を用いて、図53(B)に示すキーファイルKFを復号する。そして、SAM3051 〜3054 のいずれかにおいて、図53(B)に示す署名データSIG1,ESC を検証した後に、公開鍵証明書データCERCPに格納された公開鍵データKCP,Pを用いて、図53(B)に示す署名データSIG2,CP,SIG3,CPおよびSIG4,CPを検証して、コンテンツデータC、コンテンツ鍵データKcおよび権利書データ106が正当なコンテンツプロバイダ301によって作成されたものであるかを確認する。
【0325】
ステップS31:ユーザが図63の購入・利用形態決定操作部165を操作してコンテンツの購入・利用形態を決定する。
【0326】
ステップS32:ステップS31において生成された操作信号S165に基づいて、SAM3051 〜3054 において、セキュアコンテナ304の利用履歴(Usage Log) データ308が生成される。
SAM3051 〜3054 からEMDサービスセンタ302に、利用履歴データ308およびその署名データSIG205,SAM1が送信される。
【0327】
EMDサービスセンタ302は、利用履歴データ308に基づいて、コンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310の各々について、課金内容を決定(計算)し、その結果に基づいて、決済請求権データ152c,152sを作成する。
【0328】
EMDサービスセンタ302は、ペイメントゲートウェイ90を介して決済機関91に、決済請求権データ152c,152sを自らの署名データと共に送信し、これにより、ユーザホームネットワーク303のユーザが決済機関91に支払った金銭が、コンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310の所有者に分配される。
【0329】
以上説明したように、EMDシステム300では、図4に示すフォーマットのセキュアコンテナ104をコンテンツプロバイダ301からサービスプロバイダ310に配給し、セキュアコンテナ104内のコンテンツファイルCFおよびキーファイルKFをそのまま格納したセキュアコンテナ304をサービスプロバイダ310からユーザホームネットワーク303に配給し、キーファイルKFについての処理をSAM3051 〜3054 内で行う。
また、キーファイルKFに格納されたコンテンツ鍵データKcおよび権利書データ106は、配信鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を用いて暗号化されており、配信鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を保持しているSAM3051 〜3054 内でのみ復号される。そして、SAM3051 〜3054 では、耐タンパ性を有するモジュールであり、権利書データ106に記述されたコンテンツデータCの取り扱い内容に基づいて、コンテンツデータCの購入形態および利用形態が決定される。
【0330】
従って、EMDシステム300によれば、ユーザホームネットワーク303におけるコンテンツデータCの購入および利用を、サービスプロバイダ310における処理とは無関係に、コンテンツプロバイダ101の関係者が作成した権利書データ106の内容に基づいて確実に行わせることができる。すなわち、EMDシステム300にれば、権利書データ106をサービスプロバイダ310が管理できないようできる。
そのため、EMDシステム300によれば、異系列の複数のサービスプロバイダ310を介してユーザホームネットワーク303にコンテンツデータCが配給された場合でも、ユーザホームネットワーク303における当該コンテンツデータCについての権利処理を、コンテンツプロバイダ301が作成した共通の権利書データ106に基づいて行わせることができる。
【0331】
また、EMDシステム300では、サービスプロバイダ310からユーザホームネットワーク103へのコンテンツデータCの配給を、オンラインおよびオフラインの何れの場合でもセキュアコンテナ304を用いて行うことで、双方の場合において、SAM3051 〜3054 におけるコンテンツデータCの権利処理を共通化できる。
【0332】
また、EMDシステム300では、ユーザホームネットワーク303内のネットワーク機器3601 およびAV機器3602 〜3604 においてコンテンツデータCを購入、利用、記録および転送する際に、常に権利書データ106に基づいて処理を行うことで、共通の権利処理ルールを採用できる。
【0333】
また、EMDシステム300によれば、EMDサービスセンタ302が、認証機能、鍵データ管理機能および権利処理(利益分配)機能を有することから、コンテンツの利用に伴ってユーザが支払った金額が、コンテンツプロバイダ301およびEMDサービスセンタ302の所有者に、予め決められた比率に従って確実に分配される。
また、EMDシステム300によれば、同じコンテンツプロバイダ301が供給した同じコンテンツファイルCFについての権利書データ106は、サービスプロバイダ310のサービス形態とは無関係に、そのままSAM3051 〜3054 に供給される。従って、SAM3051 〜3054 において、権利書データ106に基づいて、コンテンツプロバイダ301の意向通りに、コンテンツファイルCFの利用を行わせることができる。
すなわち、EMDシステム300によれば、コンテンツを用いたサービスおよびユーザによるコンテンツの利用が行われる際に、従来のように監査組織725に頼ることなく、技術的な手段によって、コンテンツプロバイダ301の所有者の権利および利益を確実に守ることができる。
【0334】
第2実施形態の第1変形例
図80は、第2実施形態の第1変形例に係わる2個のサービスプロバイダを用いたEMDシステム300aの構成図である。
図80において、図49と同一符号を付した構成要素は、第2実施形態で説明した同一符号の構成要素と同じである。
図80に示すように、EMDシステム300aでは、コンテンツプロバイダ301からサービスプロバイダ310aおよび310bに、同じセキュアコンテナ104を供給する。
【0335】
サービスプロバイダ310aは、例えば、コンテンツをドラマ番組の提供サービスを行っており、当該サービスにおいて、当該ドラマ番組に関連するコンテンツデータCと、当該コンテンツデータCについて独自に作成したプライスタグデータ312aとを格納したセキュアコンテナ304aを作成し、これをネットワーク機器3601 に配給する。
また、サービスプロバイダ310bは、例えば、カラオケサービスを提供しており、当該サービスにおいて、当該カラオケサービスに関連するコンテンツデータCと、当該コンテンツデータCについて独自に作成したプライスタグデータ312bとを格納したセキュアコンテナ304bを作成し、これをネットワーク機器3601 に配給する。
ここで、セキュアコンテナ304a,304bのフォーマットは、図53を用いた説明したセキュアコンテナ304と同じである。
【0336】
ネットワーク機器360a1 には、サービスプロバイダ310a,310bの各々に対応したCAモジュール311a,311bが設けられている。
CAモジュール311a,311bは、自らの要求に応じたセキュアコンテナ304a,304bの配給を、それぞれサービスプロバイダ310a,310bから受ける。
【0337】
次に、CAモジュール311a,311bは、配給されたセキュアコンテナ304a,304bに応じたSP用購入履歴データ309a,309bをそれぞれ作成し、これらをそれぞれサービスプロバイダ310a,310bに送信する。
また、CAモジュール311a,311bは、セキュアコンテナ304a,304bをセッション鍵データKSES で復号した後に、SAM3051 〜3054 に出力する。
【0338】
次に、SAM3051 〜3054 において、共通の配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を用いて、セキュアコンテナ304a,304b内のキーファイルKFが復号され、共通の権利書データ106に基づいて、ユーザからの操作に応じたコンテンツの購入・利用に関する処理が行われ、それに応じた利用履歴データ308が作成される。
【0339】
そして、SAM3051 〜3054 からEMDサービスセンタ302に、利用履歴データ308が送信される。
【0340】
EMDサービスセンタ302では、利用履歴データ308に基づいて、コンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310a,310bの各々について、課金内容を決定(計算)し、その結果に基づいて、それぞれに対応する決済請求権データ152c,152sa,152sbを作成する。
【0341】
EMDサービスセンタ302は、ペイメントゲートウェイ90を介して決済機関91に、決済請求権データ152c,152sa,152sbを送信し、これにより、ユーザホームネットワーク303のユーザが決済機関91に支払った金銭が、コンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310a,310bの所有者に分配される。
【0342】
上述したように、EMDシステム300bによれば、同じコンテンツファイルCFをサービスプロバイダに310a,310bに供給する場合に、当該コンテンツファイルCFについての権利書データ106を配信用鍵データKD1 〜KD6 で暗号化してサービスプロバイダに310a,310bに供給し、サービスプロバイダに310a,310bは暗号化された権利書データ106をそのまま格納したセキュアコンテナ304a,304bをユーザホームネットワークに配給する。そのため、ユーザホームネットワーク内のSAM3051 〜3054 では、コンテンツファイルCFをサービスプロバイダに310a,310bの何れから配給を受けた場合でも、共通の権利書データ106に基づいて権利処理を行うことができる。
【0343】
なお、上述した第1変形例では、2個のサービスプロバイダを用いた場合を例示したが、本発明では、サービスプロバイダの数は任意である。
【0344】
第2実施形態の第2変形例
図81は、第2実施形態の第2変形例に係わる複数のコンテンツプロバイダを用いたEMDシステム300bの構成図である。
図81において、図49と同一符号を付した構成要素は、第2実施形態で説明した同一符号の構成要素と同じである。
図81に示すように、EMDシステム300bでは、コンテンツプロバイダ301a,301bからサービスプロバイダ310に、それぞれセキュアコンテナ104a,104bが供給される。
【0345】
サービスプロバイダ310は、例えば、コンテンツプロバイダ301a,301bが供給したコンテンツを用いてサービスを提供しており、セキュアコンテナ104aについてのプライスタグデータ312aと、セキュアコンテナ104bについてのプライスタグデータ312bとをそれぞれ生成し、これらを格納したセキュアコンテナ304cを作成する。
図81に示すように、セキュアコンテナ304cには、コンテンツファイルCFa,CFb、キーファイルKFa,KFb、プライスタグデータ312a,312b、それらの各々についてのサービスプロバイダ310の秘密鍵データKCP,Sによる署名データが格納されている。
【0346】
セキュアコンテナ304cは、ユーザホームネットワーク303のネットワーク機器3601 のCAモジュール311で受信された後に、SAM3051 〜3054 において処理される。
【0347】
SAM3051 〜3054 では、配信用鍵データKDa1 〜KDa3 を用いて、キーファイルKFaが復号され、権利書データ106aに基づいて、コンテンツファイルCFaについてのユーザからの操作に応じた購入・利用に関する処理が行われ、その履歴が利用履歴データ308に記述される。
また、SAM3051 〜3054 において、配信用鍵データKDb1 〜KDb3 を用いて、キーファイルKFbが復号され、権利書データ106bに基づいて、コンテンツファイルCFbについてのユーザからの操作に応じた購入・利用に関する処理が行われ、その履歴が利用履歴データ308に記述される。
【0348】
そして、SAM3051 〜3054 からEMDサービスセンタ302に、利用履歴データ308が送信される。
【0349】
EMDサービスセンタ302では、利用履歴データ308に基づいて、コンテンツプロバイダ301a,301bおよびサービスプロバイダ310の各々について、課金内容を決定(計算)し、その結果に基づいて、それぞれに対応する決済請求権データ152ca,152cb,152sを作成する。
【0350】
EMDサービスセンタ302は、ペイメントゲートウェイ90を介して決済機関91に、決済請求権データ152ca,152cb,152sを送信し、これにより、ユーザホームネットワーク303のユーザが決済機関91に支払った金銭が、コンテンツプロバイダ301a,301bおよびサービスプロバイダ310の所有者に分配される。
【0351】
上述したように、EMDシステム300bによれば、セキュアコンテナ304c内に格納されたコンテンツファイルCFa,CFbの権利書データ106a,106bは、コンテンツプロバイダ301a,301bが作成したものをそのまま用いるため、SAM3051 〜3054 内において、権利書データ106a,106bに基づいて、コンテンツファイルCFa,CFbについての権利処理がコンテンツプロバイダ301a,301bの意向に沿って確実に行われる。
【0352】
なお、図81に示す第2変形例では、2個のコンテンツプロバイダを用いた場合を例示したが、コンテンツプロバイダの数は任意である。
また、コンテンツプロバイダおよびサービスプロバイダの双方が複数であってもよい。
【0353】
第2実施形態の第3変形例
図82は、第2実施形態の第3変形例に係わるEMDシステムの構成図である。
上述した第2実施形態では、EMDサービスセンタ302が決済機関91に対して、コンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310の決済を行う場合を例示したが、本発明では、例えば、図82に示すように、EMDサービスセンタ302において、利用履歴データ308に基づいて、コンテンツプロバイダ301のための決済請求権データ152cと、サービスプロバイダ310のための決済請求権データ152sとを作成し、これらをそれぞれコンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310に送信するようにしてもよい。
この場合には、コンテンツプロバイダ301は、決済請求権データ152cを用いて、ペイメントゲートウェイ90aを介して決済機関91aに決済を行う。
また、サービスプロバイダ310は、決済請求権データ152sを用いて、ペイメントゲートウェイ90bを介して決済機関91bに決済を行う。
【0354】
第2実施形態の第4変形例
図83は、第2実施形態の第4変形例に係わるEMDシステムの構成図である。
上述した第2実施形態では、例えば現行のインターネットのようにサービスプロバイダ310が課金機能を有していない場合を例示したが、現行のデジタル放送などのようにサービスプロバイダ310が課金機能を有している場合には、CAモジュール311において、セキュアコンテナ304に関するサービスプロバイダ310のサービスに対しての利用履歴データ308sを作成してサービスプロバイダ310に送信する。
そして、サービスプロバイダ310は、利用履歴データ308sに基づいて、課金処理を行って決済請求権データ152sを作成し、これを用いてペイメントゲートウェイ90bを介して決済機関91bに決済を行う。
一方、SAM3051 〜3054 は、セキュアコンテナ304に関するコンテンツプロバイダ301の権利処理に対しての利用履歴データ308cを作成し、これをEMDサービスセンタ302に送信する。
EMDサービスセンタ302は、利用履歴データ308cに基づいて、決済請求権データ152cを作成し、これをコンテンツプロバイダ301に送信する。
コンテンツプロバイダ301は、決済請求権データ152cを用いて、ペイメントゲートウェイ90aを介して決済機関91aに決済を行う。
【0355】
第2実施形態の第5変形例
上述した実施形態では、図49に示すように、EMDサービスセンタ302のユーザ嗜好フィルタ生成部901において、SAM3051 などから受信した利用履歴データ308に基づいて、ユーザ嗜好フィルタデータ903を生成する場合を例示したが、例えば、図67に示すSAM3051 などの利用監視部186で生成した利用制御状態データ166をリアルタイムでEMDサービスセンタ302に送信するようにして、SP用購入履歴データ309において、利用制御状態データ166に基づいてユーザ嗜好フィルタデータ903を生成するようにしてもよい。
【0356】
第2実施形態の第6変形例
コンテンツプロバイダ301、サービスプロバイダ310およびSAM3051 〜3054 は、それぞれ自らの公開鍵データKCP,P,KSP,P,KSAM1,P〜KSAM4,Pの他に、自らの秘密鍵データKCP,S,KSP,S,KSAM1,S〜KSAM4,SをEMDサービスセンタ302に登録してもよい。
このようにすることで、EMDサービスセンタ302は、緊急時に、国家あるいは警察機関などからの要請に応じて、秘密鍵データKCP,S,KSP,S,KSAM1,S〜KSAM4,Sを用いて、コンテンツプロバイダ301とサービスプロバイダ310との間の通信、サービスプロバイダ310とSAM3051 〜3054 との間の通信、並びにユーザホームネットワーク303内でのSAM3051 〜3054 相互間での通信のうち対象となる通信を盗聴することが可能になる。
また、SAM3051 〜3054 については、出荷時に、EMDサービスセンタ302によって秘密鍵データKSAM1,S〜KSAM4,Sを生成し、これをSAM3051 〜3054 に格納すると共にEMDサービスセンタ302が保持(登録)するようにしてもよい。
【0357】
第2実施形態の第7変形例
上述した実施形態では、コンテンツプロバイダ301、サービスプロバイダ310およびSAM3051 〜3054 が、相互に通信を行う場合に、EMDサービスセンタ302から事前に公開鍵証明書データCERCP,CERSP,CERSAM1〜CERSAN4を取得し、イン・バンド方式で通信先に送信する場合を例示したが、本発明では、通信先への公開鍵証明書データの送信形態として種々の形態を採用できる。
例えば、コンテンツプロバイダ301、サービスプロバイダ310およびSAM3051 〜3054 が、相互に通信を行う場合に、EMDサービスセンタ302から事前に公開鍵証明書データCERCP,CERSP,CERSAM1〜CERSAN4を取得し、当該通信に先立ってアウト・オブ・バンド方式で通信先に送信してもよい。
また、コンテンツプロバイダ301、サービスプロバイダ310およびSAM3051 〜3054 が、通信時に、EMDサービスセンタ302から公開鍵証明書データCERCP,CERSP,CERSAM1〜CERSAN4を取得してもよい。
【0358】
図84は、公開鍵証明書データの取得(入手)ルートの形態を説明するための図である。
なお、図84において、図49と同じ符号を付した構成要素は、前述した同一符号の構成要素と同じである。また、ユーザホームネットワーク303aは、前述したユーザホームネットワーク303と同じである。ユーザホームネットワーク303bでは、IEEE1394シリアルバスであるバス191を介してSAM30511〜30514を接続している。
【0359】
コンテンツプロバイダ301がサービスプロバイダ310の公開鍵証明書データCERSPを取得する場合には、例えば、通信に先立ってサービスプロバイダ310からコンテンツプロバイダ301に公開鍵証明書データCERSPを送信する場合(図84中(3))と、コンテンツプロバイダ301がEMDサービスセンタ302から公開鍵証明書データCERSPを取り寄せる場合(図84中(1))とがある。
【0360】
また、サービスプロバイダ310がコンテンツプロバイダ301の公開鍵証明書データCERCPを取得する場合には、例えば、通信に先立ってコンテンツプロバイダ301からサービスプロバイダ310に公開鍵証明書データCERCPを送信する場合(図84中(2))と、サービスプロバイダ310がEMDサービスセンタ302から公開鍵証明書データCERCPを取り寄せる場合(図84中(4))とがある。
【0361】
また、サービスプロバイダ310がSAM3051 〜3054 の公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1〜CERSAM4を取得する場合には、例えば、通信に先立ってSAM3051 〜3054 からサービスプロバイダ310に公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1〜CERSAM4を送信する場合(図84中(6))と、サービスプロバイダ310がEMDサービスセンタ302から公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1〜CERSAM4を取り寄せる場合(図84中(4))とがある。
【0362】
また、SAM3051 〜3054 がサービスプロバイダ310の公開鍵証明書データCERSPを取得する場合には、例えば、通信に先立ってサービスプロバイダ310からSAM3051 〜3054 に公開鍵証明書データCERSPを送信する場合(図84中(5))と、SAM3051 〜3054 がEMDサービスセンタ302から公開鍵証明書データCERSPを取り寄せる場合(図84中(7)など)とがある。
【0363】
また、SAM3051 がSAM3052 の公開鍵証明書データCERSAM2を取得する場合には、例えば、通信に先立ってSAM3052 からSAM3051 に公開鍵証明書データCERSAM2を送信する場合(図84中(8))と、SAM3051 がEMDサービスセンタ302から公開鍵証明書データCERSAM2を取り寄せる場合(図84中(7)など)とがある。
【0364】
また、SAM3052 がSAM3051 の公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1を取得する場合には、例えば、通信に先立ってSAM3051 からSAM3052 に公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1を送信する場合(図84中(9))と、SAM3052 が自らEMDサービスセンタ302から公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1を取り寄せる場合と、SAM3051 が搭載されたネットワーク機器を介して公開鍵証明書データCERSAM1を取り寄せる場合(図84中(7),(8))とがある。
【0365】
また、SAM3054 がSAM30513の公開鍵証明書データCERSAM13 を取得する場合には、例えば、通信に先立ってSAM30513からSAM3054 に公開鍵証明書データCERSAM13 を送信する場合(図84中(12))と、SAM3054 が自らEMDサービスセンタ302から公開鍵証明書データCERSAM13 を取り寄せる場合(図84中(10))と、ユーザホームネットワーク303b内のネットワーク機器を介して公開鍵証明書データCERSAM13 を取り寄せる場合とがある。
【0366】
また、SAM30513がSAM3054 の公開鍵証明書データCERSAM4を取得する場合には、例えば、通信に先立ってSAM3054 からSAM30513に公開鍵証明書データCERSAM4を送信する場合(図84中(11))と、SAM30513が自らEMDサービスセンタ302から公開鍵証明書データCERSAM4を取り寄せる場合(図84中(13))と、ユーザホームネットワーク303b内のネットワーク機器を介して公開鍵証明書データCERSAM4を取り寄せる場合とがある。
【0367】
第2実施形態における公開鍵証明書破棄リスト(データ)の取り扱い
第2実施形態では、EMDサービスセンタ302において、不正行為などに用いられたコンテンツプロバイダ301、サービスプロバイダ310およびSAM3051 〜3054 が他の装置と通信できないようにするために、当該不正行為に用いられた装置の公開鍵証明書データを無効にする公開鍵証明書破棄データを作成する。そして、当該公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL(Certificate Revocation List) を、コンテンツプロバイダ301、サービスプロバイダ310およびSAM3051 〜3054 に送信する。
なお、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRLは、EMDサービスセンタ302の他に、例えば、コンテンツプロバイダ301、サービスプロバイダ310およびSAM3051 〜3054 において生成してもよい。
【0368】
先ず、EMDサービスセンタ302が、コンテンツプロバイダ301の公開鍵証明書データCERCPを無効にする場合について説明する。
図85に示すように、EMDサービスセンタ302は、公開鍵証明書データCERCPを無効にすることを示す公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL1 をサービスプロバイダ310に送信する(図85中(1))。サービスプロバイダ310は、コンテンツプロバイダ301から入力した署名データを検証する際に、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL1 を参照して公開鍵証明書データCERCPの有効性を判断し、有効であると判断した場合に公開鍵データKCP,Pを用いた署名検証を行い、無効であると判断した場合に当該署名検証を行わずにコンテンツプロバイダ301からのデータを無効にする。なお、データを無効にするのではなく、通信を拒絶するようにしてもよい。
【0369】
また、EMDサービスセンタ302は、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL1 を、サービスプロバイダ310の流通資源を利用して放送型あるいはオンデマンド型のいずれか一方で、ユーザホームネットワーク303内の例えばSAM3051 に送信する(図85中(1),(2))。SAM3051 は、サービスプロバイダ310から入力したセキュアコンテナ内に格納されたコンテンツプロバイダ301の署名データを検証する際に、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL1 を参照して公開鍵証明書データCERCPの有効性を判断し、有効であると判断した場合に公開鍵データKCP,Pを用いた署名検証を行い、無効であると判断した場合に当該署名検証を行わずに当該セキュアコンテナを無効にする。
なお、EMDサービスセンタ302は、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL1 を、ユーザホームネットワーク303内のネットワーク機器を介してSAM3051 に直接送信してもよい(図85中(3))。
【0370】
次に、EMDサービスセンタ302が、サービスプロバイダ310の公開鍵証明書データCERSPを無効にする場合について説明する。
図86に示すように、EMDサービスセンタ302は、公開鍵証明書データCERSPを無効にすることを示す公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL2 をコンテンツプロバイダ301に送信する(図86中(1))。コンテンツプロバイダ301は、サービスプロバイダ310から入力した署名データを検証する際に、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL2 を参照して公開鍵証明書データCERSPの有効性を判断し、有効であると判断した場合に公開鍵データKSP,Pを用いた署名検証を行い、無効であると判断した場合に当該署名検証を行わずにサービスプロバイダ310からのデータを無効にする。
【0371】
また、EMDサービスセンタ302は、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL2 を、サービスプロバイダ310の流通資源を利用して放送型あるいはオンデマンド型のいずれか一方で、ユーザホームネットワーク303内の例えばSAM3051 に送信する(図86中(2))。SAM3051 は、サービスプロバイダ310から入力したセキュアコンテナ内に格納されたサービスプロバイダ310の署名データを検証する際に、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL2 を参照して公開鍵証明書データCERSPの有効性を判断し、有効であると判断した場合に公開鍵デー
KSP,Pを用いた署名検証を行い、無効であると判断した場合に当該署名検証を行わずに当該セキュアコンテナを無効にする。
この場合に、サービスプロバイダ310内において、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL2 の送受信を行うモジュールは、耐タンパ性を有している必要がある。また、サービスプロバイダ310内において、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL2 は、サービスプロバイダ310の関係者による改竄な困難な領域に格納される必要がある。
なお、EMDサービスセンタ302は、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL2 を、ユーザホームネットワーク303内のネットワーク機器を介してSAM3051 に直接送信してもよい(図86中(3))。
【0372】
次に、EMDサービスセンタ302が、例えばSAM3052 の公開鍵証明書データCERSAM2を無効にする場合について説明する。
図87に示すように、EMDサービスセンタ302は、公開鍵証明書データCERSAM2を無効にすることを示す公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 をコンテンツプロバイダ301に送信する(図87中(1))。コンテンツプロバイダ301は、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 をサービスプロバイダ310に送信する。
サービスプロバイダ310は、自らの流通資源を利用して放送型あるいはオンデマンド型のいずれか一方で、ユーザホームネットワーク303内の例えばSAM3051 に公開鍵証明書破棄データCRLSAM1を送信する(図87中(1))。
SAM3051 は、SAM3052 から入力したデータに付加されたSAM3052 の署名データを検証する際に、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 を参照して公開鍵証明書データCERSAM2の有効性を判断し、有効であると判断した場合に公開鍵データKSAM2,Pを用いた署名検証を行い、無効であると判断した場合に当該署名検証を行わずに当該データを無効にする。
この場合に、サービスプロバイダ310内において、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 の送受信を行うモジュールは、耐タンパ性を有している必要がある。また、サービスプロバイダ310内において、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 は、サービスプロバイダ310の関係者による改竄な困難な領域に格納される必要がある。
【0373】
EMDサービスセンタ302は、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 をサービスプロバイダ310を介してSAM3051 に送信してもよい(図87中(1),(2))。
また、EMDサービスセンタ302は、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 を、ユーザホームネットワーク303内のネットワーク機器を介してSAM3051 に直接送信してもよい(図87中(3))。
【0374】
また、EMDサービスセンタ302は、例えばSAM3052 の公開鍵証明書データCERSAM2を無効にすることを示す公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 を作成し、これを保管する。
また、ユーザホームネットワーク303は、バス191に接続されているSAMのSAM登録リストSRLを作成し、これをEMDサービスセンタ302に送信する(図88中(1))。
EMDサービスセンタ302は、SAM登録リストに示されるSAM3051 〜3054 のうち、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 によって無効にすることが示されているSAM(例えばSAM3052 )を特定し、SAM登録リストSRL内の当該SAMに対応する破棄フラグを無効を示すように設定して新たなSAM登録リストSRLを作成する。
次に、EMDサービスセンタ302は、当該生成したSAM登録リストSRLをSAM3051 に送信する(図88中(1))。
SAM3051 は、他のSAMと通信を行う際に、SAM登録リストSRLの破棄フラグを参照して、署名データの検証の有無および通信を許否するか否かを決定する。
【0375】
また、EMDサービスセンタ302は、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 を作成し、これをコンテンツプロバイダ301に送信する(図88中(2))。
コンテンツプロバイダ301は、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 をサービスプロバイダ310に送信する(図88中(2))。
次に、サービスプロバイダ310は、自らの流通資源を利用して放送型あるいはオンデマンド型のいずれか一方で、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 をSAM3051 に送信する(図88中(2))。
SAM3051 は、自らが作成したSAM登録リストに示されるSAM3051 〜3054 のうち、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 によって無効にすることが示されているSAM(例えばSAM3052 )を特定し、SAM登録リストSRL内の当該SAMに対応する破棄フラグを無効を示すように設定する。
以後、SAM3051 は、他のSAMと通信を行う際に、当該SAM登録リストSRLの破棄フラグを参照して、署名データの検証の有無および通信を許否するか否かを決定する。
【0376】
また、EMDサービスセンタ302は、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 を作成し、これをサービスプロバイダ310に送信する(図88中(3))。
次に、サービスプロバイダ310は、自らの流通資源を利用して放送型あるいはオンデマンド型のいずれか一方で、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 をSAM3051 に送信する(図88中(3))。
SAM3051 は、自らが作成したSAM登録リストに示されるSAM3051 〜3054 のうち、公開鍵証明書破棄データCRL3 によって無効にすることが示されているSAM(例えばSAM3052 )を特定し、SAM登録リストSRL内の当該SAMに対応する破棄フラグを無効を示すように設定する。
以後、SAM3051 は、他のSAMと通信を行う際に、当該SAM登録リストSRLの破棄フラグを参照して、署名データの検証の有無および通信を許否するか否かを決定する。
【0377】
EMDサービスセンタ302の役割等
図89は、図49に示すEMDサービスセンタ(クリアリングハウス))302の機能を権利管理用クリアリングハウス950と、電子決済用クリアリングハウス951とに分割した場合のEMDシステムの構成図である。
当該EMDシステムでは、電子決済用クリアリングハウス951において、ユーザホームネットワーク303a,303bのSAMからの利用履歴データ308に基づいて、決済処理(利益分配処理)を行い、コンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310の決済請求権データをそれぞれ生成し、ペイメントゲートウェイ90を介して決済機関91において決済を行う。
【0378】
また、権利管理用クリアリングハウス950は、電子決済用クリアリングハウス951からの決済通知に応じたコンテンツプロバイダ301およびサービスプロバイダ310の決済レポートを作成し、それらをコンテンツプロバイダ301およびコンテンツプロバイダ301に送信する。
また、コンテンツプロバイダ301の権利書データ106およびコンテンツ鍵データKcの登録(権威化)などを行う。
なお、図90に示すように、権利管理用クリアリングハウス950と電子決済用クリアリングハウス951とを単体の装置内に収納すると、図49に示すEMDサービスセンタ302となる。
【0379】
また、本発明は、例えば、図91に示すように、EMDサービスセンタ302に、権利管理用クリアリングハウス960の機能を設け、権利管理用クリアリングハウス960において、権利書データ106の登録などを行うと共に、SAMからの利用履歴データ308に基づいてサービスプロバイダ310の決済請求権データを作成し、これをサービスプロバイダ310に送信してもよい。この場合には、サービスプロバイダ310は、自らの課金システムを電子決済用クリアリングハウス961として利用し、権利管理用クリアリングハウス960からの決済請求権データに基づいて決済を行う。
【0380】
また、本発明は、例えば、図92に示すように、EMDサービスセンタ302に、権利管理用クリアリングハウス970の機能を設け、権利管理用クリアリングハウス970において、権利書データ106の登録などを行うと共に、SAMからの利用履歴データ308に基づいてコンテンツプロバイダ301の決済請求権データを作成し、これをコンテンツプロバイダ301に送信してもよい。この場合には、コンテンツプロバイダ301は、自らの課金システムを電子決済用クリアリングハウス961として利用し、権利管理用クリアリングハウス970からの決済請求権データに基づいて決済を行う。
【0381】
第2実施形態の第8変形例
上述した第2実施形態では、図49に示すEMDシステム300において、コンテンツプロバイダ301からサービスプロバイダ310に図4に示すフォーマットのセキュアコンテナ104を提供し、サービスプロバイダ310からユーザホームネットワーク303に図53に示すフォーマットのセキュアコンテナ304を配給する場合を例示した。
すなわち、上述した第2実施形態では、図4および図53に示すように、セキュアコンテナ104およびセキュアコンテナ304内に、それぞれ単数のコンテンツファイルCFと、当該コンテンツファイルCFに対応する単数のキーファイルKFを格納した場合を例示した。
本発明では、セキュアコンテナ104およびセキュアコンテナ304内に、それぞれ複数のコンテンツファイルCFと、当該複数のコンテンツファイルCFにそれぞれ対応する複数のキーファイルKFとを格納してもよい。
【0382】
図93は、本変形例において、図49に示すコンテンツプロバイダ301からサービスプロバイダ310に提供されるセキュアコンテナ104aのフォーマットを説明するための図である。
図93に示すように、セキュアコンテナ104aには、コンテンツファイルCF101 ,CF102 ,CF103 、キーファイルKF101 ,KF102 ,KF103 、公開鍵証明書データCERCP、署名データSIG1,ESC および署名データSIG250,CPが格納されている。
ここで、署名データSIG250,CPは、コンテンツプロバイダ301において、コンテンツファイルCF101 ,CF102 ,CF103 、キーファイルKF101 ,KF102 ,KF103 、公開鍵証明書データCERCPおよび署名データSIG1,ESC の全体に対してハッシュ値をとり、コンテンツプロバイダ301の秘密鍵データKcp,sを用いて生成される。
【0383】
コンテンツファイルCF101 には、ヘッダ、リンクデータLD1 、メタデータMeta1 、コンテンツデータC1 およびA/V伸長用ソフトウェアSoft1 が格納されている。
ここで、コンテンツデータC1 およびA/V伸長用ソフトウェアSoft1 は、前述したコンテンツ鍵データKc1 を用いて暗号化されており、メタデータMeta1 は必要に応じてコンテンツ鍵データKc1 を用いて暗号化されている。
また、コンテンツデータC1 は、例えば、ATRAC3方式で圧縮されている。A/V伸長用ソフトウェアSoft1 は、ATRAC3方式の伸長用のソフトウェアである。
また、リンクデータLD1 は、キーファイルKF101 にリンクすることを示している。
【0384】
コンテンツファイルCF102 には、ヘッダ、リンクデータLD1 、メタデータMeta2 、コンテンツデータC2 およびA/V伸長用ソフトウェアSoft2 が格納されている。
ここで、コンテンツデータC2 およびA/V伸長用ソフトウェアSoft2 は、前述したコンテンツ鍵データKc2 を用いて暗号化されており、メタデータMeta2 は必要に応じてコンテンツ鍵データKc2 を用いて暗号化されている。
また、コンテンツデータC2 は、例えば、MPEG2方式で圧縮されている。
A/V伸長用ソフトウェアSoft2 は、MPEG2方式の伸長用のソフトウェアである。
また、リンクデータLD2 は、キーファイルKF102 にリンクすることを示している。
【0385】
コンテンツファイルCF103 には、ヘッダ、リンクデータLD3 、メタデータMeta3 、コンテンツデータC3 およびA/V伸長用ソフトウェアSoft3 が格納されている。
ここで、コンテンツデータC3 およびA/V伸長用ソフトウェアSoft3 は、前述したコンテンツ鍵データKc3 を用いて暗号化されており、メタデータMeta3 は必要に応じてコンテンツ鍵データKc3 を用いて暗号化されている。
また、コンテンツデータC3 は、例えば、JPEG方式で圧縮されている。A/V伸長用ソフトウェアSoft3 は、JPEG方式の伸長用のソフトウェアである。
また、リンクデータLD3 は、キーファイルKF103 にリンクすることを示している。
【0386】
キーファイルKF101 には、ヘッダと、それぞれ配信鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を用いて暗号化されたコンテンツ鍵データKc1 、権利書データ1061 、SAMプログラム・ダウンロード・コンテナSDC1 および署名・証明書モジュールMod200 とが格納されている。
ここで、署名・証明書モジュールMod200 には、図94(A)に示すように、それぞれコンテンツデータC1 ,コンテンツ鍵データKc1 および権利書データ1061 のハッシュ値をとり、コンテンツプロバイダ301の秘密鍵データKCP,Sを用いて作成した署名データSIG211,CP,SIG212,CP,SIG213,CPと、公開鍵データKCP,Pの公開鍵証明書データCERCPと、当該公開鍵証明書データCERCPに対してのEMDサービスセンタ302の署名データSIG1,ESC とが格納されている。
【0387】
キーファイルKF102 には、ヘッダと、それぞれ配信鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を用いて暗号化されたコンテンツ鍵データKc2 、権利書データ1062 、SAMプログラム・ダウンロード・コンテナSDC2 および署名・証明書モジュールMod201 とが格納されている。
ここで、署名・証明書モジュールMod201 には、図94(B)に示すように、それぞれコンテンツデータC2 ,コンテンツ鍵データKc2 および権利書データ1062 のハッシュ値をとり、コンテンツプロバイダ301の秘密鍵データKCP,Sを用いて作成した署名データSIG221,CP,SIG222,CP,SIG223,CPと、公開鍵証明書データCERCPと、当該公開鍵証明書データCERCPに対しての署名データSIG1,ESC とが格納されている。
【0388】
キーファイルKF103 には、ヘッダと、それぞれ配信鍵データKD1 〜KD3 を用いて暗号化されたコンテンツ鍵データKc3 、権利書データ1063 、SAMプログラム・ダウンロード・コンテナSDC3 および署名・証明書モジュールMod202 とが格納されている。
ここで、署名・証明書モジュールMod202 には、図94(C)に示すように、それぞれコンテンツデータC3 ,コンテンツ鍵データKc3 および権利書データ1063 のハッシュ値をとり、コンテンツプロバイダ301の秘密鍵データKCP,Sを用いて作成した署名データSIG231,CP,SIG232,CP,SIG233,CPと、公開鍵証明書データCERCPと、当該公開鍵証明書データCERCPに対しての署名データSIG1,ESC とが格納されている。
【0389】
サービスプロバイダ310は、図93に示すセキュアコンテナ104aの配給を受けると、EMDサービスセンタ302の公開鍵データKESC,P を用いて公開鍵証明書データCERcpの正当性を確認した後に、当該公開鍵証明書データCERCPに格納された公開鍵データKcp,Pを用いて、署名データSIG250,CPの正当性を確認する。
そして、サービスプロバイダ310は、署名データSIG250,CPの正当性を確認すると、図95に示すように、セキュアコンテナ104aから得たコンテンツファイルCF101 ,CF102 ,CF103 およびキーファイルKF101 ,KF102 ,KF103 と、サービスプロバイダ310の公開鍵証明書データCERSPと、署名データSIG61,ESCと、プライスタグデータ3121 ,3122 ,3123 と、署名データSIG260,SPとを格納したセキュアコンテナ304aを作成する。
ここで、プライスタグデータ3121 ,3122 ,3123 は、それぞれコンテンツデータC1 ,C2 ,C3 の販売価格を示している。
また、署名データSIG260,SPは、コンテンツファイルCF101 ,CF102 ,CF103 、キーファイルKF101 ,KF102 ,KF103 、公開鍵証明書データCERSPと、署名データSIG61,ESCおよびプライスタグデータ3121 ,3122 ,3123 の全体に対してハッシュ値をとり、サービスプロバイダ310の秘密鍵データKSp,sを用いて生成される。
【0390】
サービスプロバイダ310は、図95に示すセキュアコンテナ304aをユーザホームネットワーク303に配給する。
ユーザホームネットワーク303では、SAM3051 〜3054 において、セキュアコンテナ304aに格納された署名データSIG61,ESCの正当性を確認した後に、公開鍵証明書データCERspに格納された公開鍵データKSP,KP を用いて、署名データSIG260,SPの正当性を確認する。
その後、SAM3051 〜3054 は、コンテンツデータC101 ,C102 ,C103 についての権利処理を、リンクデータLD1 ,LD2 ,LD3 に示されるリンク状態に応じて、それぞれキーファイルKF101 ,KF102 ,KF103 に基づいて行う。
【0391】
なお、上述した第8変形例では、コンテンツプロバイダ301において、図93に示すように、コンテンツプロバイダ301において、コンテンツファイルCF101 ,CF102 ,CF103 、キーファイルKF101 ,KF102 ,KF103 、公開鍵証明書データCERCPおよび署名データSIG1,ESC の全体に対しての署名データSIG250,CPを作成する場合を例示したが、例えば、コンテンツファイルCF101 ,CF102 ,CF103 およびキーファイルKF101 ,KF102 ,KF103 のそれぞれについて署名データを作成し、これをセキュアコンテナ104a内に格納してもよい。
また、上述した第8変形例では、サービスプロバイダ310において、図95に示すように、コンテンツファイルCF101 ,CF102 ,CF103 、キーファイルKF101 ,KF102 ,KF103 、公開鍵証明書データCERSPと、署名データSIG61,ESCおよびプライスタグデータ3121 ,3122 ,3123 の全体に対しての署名データSIG260,SPを作成する場合を例示したが、これらの各々についての署名データを作成し、これらをセキュアコンテナ304aに格納するようにしてもよい。
【0392】
また、上述した第8変形例では、セキュアコンテナ304において、単数のサービスプロバイダ310から提供を受けた複数のコンテンツファイルCF101 ,CF102 ,CF103 を単数のセキュアコンテナ304aに格納してユーザホームネットワーク303に配給する場合を例示したが、図81に示すように、複数のコンテンツプロバイダ301a,301bから提供を受けた複数のコンテンツファイルCFを、単数のセキュアコンテナに格納してユーザホームネットワーク303に配給してもよい。
【0393】
なお、図93に示すフォーマットは、前述した第1実施形態において、図1に示すコンテンツプロバイダ101からユーザホームネットワーク103にセキュアコンテナ104を送信する場合にも同様に適用できる。
【0394】
また、上述した実施形態では、EMDサービスセンタにおいて、SAMから入力した利用履歴データに基づいて決済処理を行う場合を例示したが、SAMにおいてコンテンツの購入形態が決定される度に利用制御状態データをSAMからEMDサービスセンタに送信し、EMDサービスセンタにおいて、受信した利用制御状態データを用いて決済処理を行ってもよい。
【0395】
以下、コンテンツプロバイダ101において作成されるコンテンツファイルCFおよびキーファイルKFなどの概念をまとめる。
コンテンツプロバイダ101がインターネットを用いてコンテンツを提供する場合には、図96に示すように、ヘッダ、コンテンツID、コンテンツ鍵データKcを用いた暗号化されたコンテンツデータCおよび署名データを含むコンテンツファイルCFが作成される。当該コンテンツデータCの取り扱いを示す権利書データと、コンテンツ鍵データKcとが、所定の信頼機関であるEMDサービスセンタ102,302の配信用鍵データによって暗号化された後に、キーファイルKFに格納される。また、キーファイルKFには、ヘッダ、コンテンツID、必要に応じてメタデータ、署名データが格納される。
そして、コンテンツファイルCFおよびキーファイルKFが、コンテンツプロバイダ101からユーザホームネットワーク103,303に直接提供されたり、コンテンツプロバイダ101からサービスプロバイダ310を介してユーザホームネットワーク103,303に提供される。
【0396】
また、コンテンツプロバイダ101がインターネットを用いてコンテンツを提供する場合に、図97に示すように、キーファイルKF内にコンテンツ鍵データKcを格納しないで、所定の信頼機関であるEMDサービスセンタ102,302の配信用鍵データによって暗号化したコンテンツ鍵データKcをEMDサービスセンタ102,302からユーザホームネットワーク103,303に提供してもよい。
【0397】
また、コンテンツプロバイダ101がデジタル放送を用いてコンテンツを提供する場合に、例えば、図98に示すように、コンテンツ鍵データKcを用いて暗号化したコンテンツデータCと署名データとを、コンテンツプロバイダ101からユーザホームネットワーク103,303に、直接あるいはサービスプロバイダ310を介して提供する。この場合に、図97に示すキーファイルKFに対応する鍵データブロックを、コンテンツプロバイダ101からユーザホームネットワーク103,303に、直接あるいはサービスプロバイダ310を介して提供する。
また、この場合に、例えば、図99に示すように、所定の信頼機関であるEMDサービスセンタ102,302の配信用鍵データによって暗号化したコンテンツ鍵データKcをEMDサービスセンタ102,302からユーザホームネットワーク103,303に提供してもよい。
【0398】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように、本発明によれば、データ提供装置の関係者の利益が適切に保護される。
また、本発明によれば、権利書データなどが不正に改竄されることを適切に回避できる。
また、本発明によれば、データ提供装置の関係者の利益を保護するための監査の負担を軽減できる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】図1は、本発明の第1実施形態のEMDシステムの全体構成図である。
【図2】図2は、図1に示すコンテンツプロバイダの機能ブロック図であり、ユーザホームネットワークのSAMとの間で送受信されるデータに関連するデータの流れを示す図である。
【図3】図3は、図1に示すコンテンツプロバイダの機能ブロック図であり、コンテンツプロバイダとEMDサービスセンタとの間で送受信されるデータに関連するデータの流れを示す図である。
【図4】図4は、図1に示すコンテンツプロバイダからSAMに送信されるセキュアコンテナのフォーマットを説明するための図である。
【図5】図5は、OSIレイヤ層と、本実施形態のセキュアコンテナの定義との対応関係を説明するための図である。
【図6】図6は、ROM型の記録媒体を説明するための図である。
【図7】図7(A)はコンテンツプロバイダからEMDサービスセンタに送信される権利登録要求用モジュールのフォーマットを説明するための図、図7(B)はEMDサービスセンタからコンテンツプロバイダに送信される権利化証明書モジュールを説明するための図である。
【図8】図8は、第1実施形態において、コンテンツプロバイダが、EMDサービスセンタに、自らの秘密鍵データに対応する公開鍵データの正当性を証明する公開鍵証明書データを要求する場合の処理のフローチャートである。
【図9】図9は、第1実施形態において、コンテンツプロバイダがユーザホームネットワークのSAMにセキュアコンテナを送信する場合の処理のフローチャートである。
【図10】図10は、図1に示すEMDサービスセンタの機能ブロック図であり、コンテンツプロバイダとの間で送受信されるデータに関連するデータの流れを示す図である。
【図11】図11は、図1に示すEMDサービスセンタの機能ブロック図であり、SAMおよび図1に示す決済機関との間で送受信されるデータに関連するデータの流れを示す図である。
【図12】図12は、第1実施形態において、EMDサービスセンタがコンテンツプロバイダから公開鍵証明書データの発行要求を受けた場合の処理のフローチャートである。
【図13】図13は、第1実施形態において、EMDサービスセンタがSAMから、公開鍵証明書データの発行要求を受けた場合の処理のフローチャートである。
【図14】図14は、第1実施形態において、EMDサービスセンタがコンテンツプロバイダから権利書データおよびコンテンツ鍵データの登録要求を受けた場合の処理のフローチャートである。
【図15】図15は、第1実施形態において、EMDサービスセンタが決済処理を行なう場合の処理のフローチャートである。
【図16】図16は、図1に示すユーザホームネットワーク内のネットワーク機器の構成図である。
【図17】図17は、図1に示すユーザホームネットワーク内のSAMの機能ブロック図であり、コンテンツプロバイダから受信したセキュアコンテナを復号するまでのデータの流れを示す図である。
【図18】図18は、図16に示す外部メモリに記憶されるデータを説明するための図である。
【図19】図19は、スタックメモリに記憶されるデータを説明するための図である。
【図20】図20は、図1に示すユーザホームネットワーク内のネットワーク機器のその他の構成図である。
【図21】図21は、図17に示す記憶部に記憶されるデータを説明するための図である。
【図22】図22は、第1実施形態において、セキュアコンテナをコンテンツプロバイダから入力し、セキュアコンテナ内のキーファイルKFを復号する際のSAM内での処理のフローチャートである。
【図23】図23は、図1に示すユーザホームネットワーク内のSAMの機能ブロック図であり、コンテンツデータを利用・購入する処理などに関連するデータの流れを示す図である。
【図24】図24は、第1実施形態において、コンテンツプロバイダからダウンロードメモリにダウンロードされたセキュアコンテナの購入形態を決定するまでの処理のフローチャートである。
【図25】図25は、第1実施形態において、ダウンロードメモリに記憶されている購入形態が既に決定されたコンテンツデータを再生する場合の処理のフローチャートである。
【図26】図26は、図16に示すネットワーク機器のダウンロードメモリにダウンロードされた既に購入形態が決定されたコンテンツファイルを、AV機器のSAMに転送する場合の転送元のSAM内での処理の流れを説明するための図である。
【図27】図27は、図26に示す場合における転送元のSAM内でのデータの流れを示す図である。
【図28】図28は、第1実施形態において、ネットワーク機器のダウンロードメモリにダウンロードされた既に購入形態が決定されたコンテンツファイルおよびキーファイルを、他のAV機器のSAMに転送する場合のSAM内での処理のフローチャートである。
【図29】図29は、購入形態が決定したセキュアコンテナのフォーマットを説明するための図である。
【図30】図30は、図26に示す場合において、転送先のSAMにおいて、入力したコンテンツファイルなどを、RAM型あるいはROM型の記録媒体(メディア)に書き込む際のデータの流れを示す図である。
【図31】図31は、第1実施形態において、他のSAMから入力したコンテンツファイルなどを、RAM型などの記録媒体に書き込む際のSAM内での処理のフローチャートである。
【図32】図32、コンテンツの購入形態が未決定の図6に示すROM型の記録媒体をユーザホームネットワークがオフラインで配給を受けた場合に、AV機器において購入形態を決定する際の処理の流れを説明するための図である。
【図33】図33は、図32に示す場合において、SAM内でのデータの流れを示す図である。
【図34】図34は、第1実施形態において、コンテンツの購入形態が未決定の図5に示すROM型の記録媒体をユーザホームネットワークがオフラインで配給を受けた場合に、AV機器において購入形態を決定する際の処理のフローチャートである。
【図35】図35は、図34のフローチャートの続きのフローチャートである。
【図36】図36は、ユーザホームネットワーク内のAV機器において購入形態が未決定のROM型の記録媒体からセキュアコンテナを読み出して、これを他のAV機器に転送してRAM型の記録媒体に書き込む際の処理の流れを説明するための図である。
【図37】図37は、図36に示すように、第1のAV機器において購入形態が未決定のROM型の記録媒体からセキュアコンテナを読み出して第2のAV機器に転送し、第2のAV機器において購入形態を決定してRAM型の記録媒体に書き込む際の第1のAV機器の処理のフローチャートである。
【図38】図38は、図37に示す場合の第2のAV機器の処理のフローチャートである。
【図39】図39は、図38に示すフローチャートの続きのフローチャートである。
【図40】図40は、図36に示す場合における転送元のSAM内でのデータの流れを示す図である。
【図41】図41は、図36に示す場合における転送先のSAM内でのデータの流れを示す図である。
【図42】図42は、図1に示すコンテンツプロバイダ、EMDサービスセンタおよびSAMの相互間で、イン・バント方式およびアウト・バンド方式で、送受信されるデータのフォーマットを説明するための図である。
【図43】図43は、図1に示すコンテンツプロバイダ、EMDサービスセンタおよびSAMの相互間で、イン・バント方式およびアウト・バンド方式で、送受信されるデータのフォーマットを説明するための図である。
【図44】図44は、バスへの機器の接続形態の一例を説明するための図である。
【図45】図45は、SAM登録リストのデータフォーマットを説明するための図である。
【図46】図46は、図1に示すコンテンツプロバイダの全体動作のフローチャートである。
【図47】図47は、本発明の第1実施形態の第2変形例を説明するための図である。
【図48】図48は、本発明の第1実施形態の第3変形例を説明するための図である。
【図49】図49は、本発明の第2実施形態のEMDシステムの全体構成図である。
【図50】図50は、図49に示すコンテンツプロバイダの機能ブロック図であり、サービスプロバイダに送信されるセキュアコンテナに関するデータの流れを示す図である。
【図51】図51は、図49に示すサービスプロバイダの機能ブロック図であり、ユーザホームネットワークとの間で送受信されるデータの流れを示す図である。
【図52】図52は、第2実施形態において、コンテンツプロバイダから供給を受けたセキュアコンテナからセキュアコンテナを作成し、これをユーザホームネットワークに配給する際のサービスプロバイダの処理のフローチャートである。
【図53】図53は、図49に示すサービスプロバイダからユーザホームネットワークに送信されるセキュアコンテナのフォーマットを説明するための図である。
【図54】図54は、図49に示すサービスプロバイダの機能ブロック図であり、EMDサービスセンタとの間で送受信されるデータの流れを示す図である。
【図55】図55は、サービスプロバイダからEMDサービスセンタに送信されるプライスタグ登録要求用モジュールのフォーマットを説明するための図である。
【図56】図56は、図49に示すEMDサービスセンタの機能ブロック図であり、サービスプロバイダとの間で送受信されるデータに関連するデータの流れを示す図である。
【図57】図57は、図49に示すEMDサービスセンタの機能ブロック図であり、コンテンツプロバイダとの間で送受信されるデータに関連するデータの流れを示す図である。
【図58】図58は、図49に示すEMDサービスセンタの機能ブロック図であり、SAMとの間で送受信されるデータに関連するデータの流れを示す図である。
【図59】図59は、利用履歴データの内容を説明するための図である。
【図60】図60は、第2実施形態において、EMDサービスセンタがサービスプロバイダから公開鍵証明書データの発行要求を受けた場合の処理のフローチャートである。
【図61】図61は、第2実施形態において、EMDサービスセンタが、サービスプロバイダからプライスタグデータの登録要求を受けた場合の処理のフローチャートである。
【図62】図62は、第2実施形態において、EMDサービスセンタが決済を行なう場合の処理のフローチャートである。
【図63】図63は、図49に示すネットワーク機器の構成図である。
【図64】図64は、図63に示すCAモジュールの機能ブロック図である。
【図65】図65は、図63に示すSAMの機能ブロック図であり、セキュアコンテナを入力してから復号するまでのデータの流れを示す図である。
【図66】図66は、図65に示す記憶部に記憶されるデータを説明するための図である。
【図67】図67は、図63に示すSAMの機能ブロック図であり、コンテンツの購入・利用形態を決定する場合などのデータの流れを示す図である。
【図68】図68は、第2実施形態において、セキュアコンテナをサービスプロバイダから入力し、セキュアコンテナ内のキーファイルを復号する際のSAMの処理のフローチャートである。
【図69】図69は、第2実施形態において、サービスプロバイダからダウンロードメモリにダウンロードされたセキュアコンテナの購入形態を決定するまでのSAMの処理のフローチャートである。
【図70】図70は、ダウンロードメモリに記憶されている購入形態が既に決定されたコンテンツデータを再生する場合の処理のフローチャートである。
【図71】図71は、購入形態が決定された後のキーファイルのフォーマットを説明するための図である。
【図72】図72は、図63に示すネットワーク機器のダウンロードメモリにダウンロードされた既に購入形態が決定されたコンテンツファイルを、AV機器のSAMに転送する場合の転送先のSAM内での処理の流れを説明するための図である。
【図73】図49は、図72に示す場合の転送元のSAM内でのデータの流れを示す図である。
【図74】図74は、図72に示すように、例えば、ネットワーク機器のダウンロードメモリにダウンロードされた既に購入形態が決定されたコンテンツファイルを、AV機器のSAMに転送する場合の転送元のSAMの処理のフローチャートである。
【図75】図75は、ネットワーク機器のSAMからAV機器のSAMに転送される購入形態が既に決定されたセキュアコンテナのフォーマットを説明するための図である。
【図76】図51は、図72に示す場合の転送先のSAM内でのデータの流れを示す図である。
【図77】図77は、図72に示すように、他のSAMから入力したコンテンツファイルなどを、RAM型などの記録媒体に書き込む際のSAMの処理のフローチャートである。
【図78】図78は、図49に示すEMDシステムの全体動作のフローチャートである。
【図79】図79は、図49に示すEMDシステムの全体動作のフローチャートである。
【図80】図80は、本発明の第2実施形態の第1変形例に係わる2個のサービスプロバイダを用いたEMDシステムの構成図である。
【図81】図81は、本発明の第2実施形態の第2変形例に係わる複数のコンテンツプロバイダを用いたEMDシステムの構成図である。
【図82】図82は、本発明の第2実施形態の第3変形例に係わるEMDシステムの構成図である。
【図83】図83は、本発明の第2実施形態の第4変形例に係わるEMDシステムの構成図である。
【図84】図84は、公開鍵証明書データの取得ルートの形態を説明するための図である。
【図85】図85は、コンテンツプロバイダの公開鍵証明書データを無効にする場合の処理を説明するための図である。
【図86】図86は、サービスプロバイダの公開鍵証明書データを無効にする場合の処理を説明するための図である。
【図87】図87は、SAMの公開鍵証明書データを無効にする場合の処理を説明するための図である。
【図88】図88は、SAMの公開鍵証明書データを無効にする場合のその他の処理を説明するための図である。
【図89】図89は、図49に示すEMDシステムにおいて、EMDサービスセンタの代わりに権利管理用クリアリングハウスおよび電子決済用クリアリングハウスを設けた場合を説明するための図である。
【図90】図90は、図89に示す権利管理用クリアリングハウスおよび電子決済用クリアリングハウスを単体のEMDサービスセンタ内に設けた場合のEMDシステムの構成図である。
【図91】図91は、サービスプロバイダが電子決済用クリアリングハウスに直接的に決済を行う場合のEMDシステムの構成図である。
【図92】図92は、コンテンツプロバイダが電子決済用クリアリングハウスに直接的に決済を行う場合のEMDシステムの構成図である。
【図93】図93は、本発明の第2実施形態の第8変形例において、図49に示すコンテンツプロバイダからサービスプロバイダに提供されるセキュアコンテナのフォーマットを説明するための図である。
【図94】図94は、図93に格納されたモジュールの詳細なフォーマットを説明するための図である。
【図95】図95は、本発明の第2実施形態の第8変形例において、図49に示すサービスプロバイダからSAMに提供されるセキュアコンテナのフォーマットを説明するための図である。
【図96】図96は、インターネットを用いてセキュアコンテナを提供する場合の概念図である。
【図97】図97は、インターネットを用いてセキュアコンテナを提供する場合のその他の概念図である。
【図98】図98は、デジタル放送を用いてセキュアコンテナを提供する場合の概念図である。
【図99】図99は、デジタル放送を用いてセキュアコンテナを提供する場合のその他の概念図である。
【図100】図100は、従来のEMDシステムの構成図である。
【符号の説明】
90…ペイメントゲートウェイ、91…決済機関、92…ルート認証局、100,300…EMDシステム、101,301…コンテンツプロバイダ、102,302…EMDサービスセンタ、103,303…ユーザホームネットワーク、104,304…セキュアコンテナ、1051 〜1054 ,3051 〜3054 …SAM、106…権利書データ、107,307…決済レポートデータ、108,308…利用履歴データ、1601 …ネットワーク機器、1602 〜1604 …AV機器、152,152c,152s…決済請求権データ、191…バス、310…サービスプロバイダ、311…CAモジュール、312…プライスタグデータ、CF…コンテンツファイル、KF…キーファイル、Kc…コンテンツ鍵データ[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention provides a data providing system for providing content data., Content providing apparatus, and content processing apparatusAbout.
[0002]
[Prior art]
There is a data providing system that distributes encrypted content data to a data processing device of a user who has a predetermined contract, and decrypts and reproduces and records the content data in the data processing device.
One such data providing system is a conventional EMD (Electronic Music Distribution) system that distributes music data.
[0003]
FIG. 100 is a configuration diagram of a
In the EMD
[0004]
The
Then, the
Furthermore, the
[0005]
The
At this time, the
In this case, the
[0006]
Upon receiving the
At this time, the profit distribution from the
[0007]
Further, in the terminal device 709, when the
[0008]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
By the way, SCMS is defined to prevent recording from a CD (Compact Disc) to a DAT (Digital Audio Tape) and can be duplicated between the DAT and the DAT. In addition, even when digital watermark information is embedded in content data, when a problem occurs, it is only possible to specify the content provider that provided the target content data, and technically prevent illegal copying. Absent.
Therefore, the
[0009]
In the
[0010]
Further, in the
[0011]
The present invention has been made in view of the above-described problems of the prior art, and is a data providing system capable of appropriately protecting the interests of the content provider's right holder (related party)., Content providing apparatus, and content processing apparatusThe purpose is to provide.
The present invention also provides a data providing system capable of reducing the burden of auditing for protecting the interests of content provider rights holders., Content providing apparatus, and content processing apparatusThe purpose is to provide.
[0012]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to solve the above-described problems of the prior art and achieve the above-described object, a data providing system according to a first aspect of the present invention includes a content providing apparatus, a content processing apparatus, and a purchase processing apparatus connected to a network. Content data is transmitted from the content providing device to the content processing device, and sent to the purchase processing device.PurchasedDepending on the purchase periodPrevious to content processing deviceIn order to use the content data, the purchase processing deviceThrough, A plurality of distribution key data valid for each predetermined usage period of the content data is transmitted to the content providing device, and the distribution key data valid for the purchase period among the plurality of distribution key data The aboveContent processing deviceThe content providing device is connected to the network, a storage unit that stores the content data, a content encryption unit that encrypts the content data stored in the storage unit with content key data, A communication unit for a content providing device that receives the plurality of distribution key data from the purchase processing device, and encrypts the content key data using each of the received distribution key data, and encrypts the plurality of content key data A content key encryption unit that generates encrypted data, and a secure container data generation unit that generates secure container data including encrypted content data and encrypted data of the plurality of content key data, The communication unit for the content providing apparatus performs content processing on the secure container data. The content data and the plurality of content key data are transmitted to a content processing device by transmitting to the device, and the content processing device is connected to the network and is effective for distribution from the purchase processing device during the purchase period. Using the communication unit for the content processing device that receives the key data and receives the secure container data from the communication unit for the content providing device, and the received distribution key data that is valid during the purchase period A content key decrypting unit for decrypting encrypted data of the content key data encrypted by the distribution key data among the encrypted data of the plurality of content key data included in the secure container data; and during the purchase period Using the content key data decrypted using valid delivery key data, And a content decoder which decodes the content data Interview A container data.
[0013]
A content providing apparatus according to a second aspect of the present invention is connected to a network, a storage unit that stores content data, a content encryption unit that encrypts the content data stored in the storage unit with content key data, and a network. A communication unit that receives a plurality of distribution key data effective for each predetermined usage period of the content data from the network, and encrypts the content key data using each of the received distribution key data. Content key encryption unit for generating encrypted data of content key data, and secure container data generation unit for generating secure container data having the encrypted content data and encrypted data of the plurality of content key data And the communication unit transmits the secure container to the network. By transmitting over data, transmitting the content data and the plurality of content key data to the content processing apparatus.
[0016]
A data providing system according to a third aspect of the present invention is a data providing system comprising the content providing apparatus and the purchase processing apparatus according to
[0017]
BookInvention No.4Point of viewThe content processing apparatus is connected to a network, and from the network, the content data encrypted with content key data and a plurality of distribution key data encrypted with a plurality of distribution key data effective for each predetermined use period of the content data A communication unit that receives secure container data having encrypted data of content key data and a distribution key data that is valid during the purchase period among the plurality of distribution key data, and valid during the received purchase period Using the distribution key data, the encrypted data of the content key data encrypted by the distribution key data among the encrypted data of the plurality of content key data included in the received secure container data Decryption using content key decryption unit for decryption and distribution key data effective for the purchase period The using content key data, and a content decoder which decodes the content data of the secure container data.
[0018]
First of the present invention5Point of viewThe content processing apparatus stores content data encrypted with content key data and encrypted data of a plurality of content key data encrypted with a plurality of distribution key data effective for each predetermined usage period of the content data. A storage unit that can store the secure container data, a communication unit that receives distribution key data that is valid during the purchase period among the plurality of distribution key data, and a distribution key that is valid during the received purchase period Using the data, decrypt the encrypted data of the content key data encrypted by the distribution key data among the encrypted data of the plurality of content key data included in the stored secure container data Content key data decrypted using a content key decryption unit and distribution key data valid during the purchase period Used, and a content decoder which decodes the content data of the secure container data.
[0020]
BookInvention No.6Point of viewThe content processing apparatus stores content data encrypted with content key data and encrypted data of a plurality of content key data encrypted with a plurality of distribution key data effective for each predetermined usage period of the content data. A reading unit capable of reading a recording medium on which secure container data is recorded; a communication unit that receives distribution key data that is valid for a purchase period out of the plurality of distribution key data; and the received purchase period The content key data encrypted by the distribution key data out of the encrypted data of the plurality of content key data included in the secure container data to be read using the distribution key data effective for Decrypted using a content key decrypting unit that decrypts the data and the distribution key data that is valid during the purchase period Content key data using, and a content decoder which decodes the content data of the secure container data.
[0027]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, an EMD (Electronic Music Distribution) system according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described.
In the present embodiment, content data distributed to a user refers to digital data whose information itself is valuable, such as music data, video data, and programs, and will be described below using music data as an example.
[0028]
First embodiment
FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of an
[0029]
In addition, the
As described above, in the present embodiment, by providing digital content data C in an encapsulated manner, the digital content that is in close contact with the conventional recording medium is separated from the recording medium, and the digital content alone has a presence value. Can do.
Here, the secure container is the most basic product capsule when selling the content data C (product) regardless of the distribution channel (delivery channel). Specifically, the secure antenna verifies the encryption information for charging, the validity of the content data C, the validity of the person who created the content data, and the validity of the distributor of the content data. This is a product capsule containing copyright information such as signature data and information on digital watermark information embedded in content data.
[0030]
The user home network 103 is, for example, a network device 160.1And
[0031]
SAM1051~ 105FourThe
SAM1051~ 105FourThe
SAM1051~ 105FourRecords the above-described purchase / use history of the
The
[0032]
The
Further, the
[0033]
In the present embodiment, the
That is, the
In addition, the
In addition, the
[0034]
Hereinafter, each component of the
[Content provider 101]
FIG. 2 is a functional block diagram of the
FIG. 3 shows a data flow related to data transmitted and received between the
In FIG. 3 and subsequent drawings, the signature data processing unit and the session key data KSESThe flow of data input / output to / from the encryption / decryption unit using is omitted.
[0035]
2 and 3, the
Before communicating with the
Hereinafter, each functional block of the
[0036]
The content
[0037]
The watermark
[0038]
The source digital watermark information Ws is information related to copyrights such as the copyright holder name of content data, ISRC code, authoring date, authoring device ID (Identification Data), and content distribution destination. The copy management digital watermark information Wc is information including a copy prohibition bit for preventing copy via an analog interface. The user digital watermark information Wu includes, for example, the identifier CP_ID of the
Further, if necessary, the digital watermark
In the present embodiment, preferably, the information content and the embedding position of each digital watermark information are defined as digital watermark information management data, and the
For example, the user home network 103 determines that the digital watermark information is valid based on the digital watermark information management data when both the embedded position of the digital watermark information and the contents of the embedded digital watermark information match. Thus, embedding of false digital watermark information can be detected with high probability.
[0039]
The
[0040]
The
The
[0041]
DES is an encryption method that uses a 56-bit common key and processes 64 bits of plain text as one block. The DES process consists of a part that stirs plaintext and converts it into ciphertext (data stirring part), and a part that generates key (expanded key) data used in the data stirring part from the common key data (key processing part). Become. Since all DES algorithms are open to the public, the basic processing of the data agitation unit will be briefly described here.
[0042]
First, the 64 bits of plaintext are the upper 32 bits of H0And lower 32 bits L0And divided. 48-bit extended key data K supplied from the key processing unit1And lower 32 bits L0, And the lower 32 bits of L0The output of the F function obtained by stirring is calculated. The F function is composed of two types of basic transformations: “substitution” in which numerical values are replaced by a predetermined rule and “transposition” in which bit positions are replaced by a predetermined rule. Next, the upper 32 bits of H0And the output of the F function are calculated, and the result is L1It is said. L0Is H1It is said.
And the upper 32 bits of H0And lower 32 bits L0Based on the above, the above process is repeated 16 times, and the obtained upper 32 bits of H16And lower 32 bits L16Is output as ciphertext. Decryption is realized by following the above procedure in reverse using the common key data used for encryption.
[0043]
The random
Note that the content key data Kc may be generated from information related to the music provided by the content data. The content key data Kc is updated every predetermined time, for example.
[0044]
The
Signature / Certificate Module Mod1Includes signature data SIG as shown in FIG.2, CP~ SIG4, CP, Public key data K of
SAM program download container SDC1~ SDCThreeSAM1051~ 105FourUCP-L (Label), which indicates the syntax of the download driver used when downloading the program in the U.S. and the rights document data (UCP) U106. R (Reader) and SAM1051~ 105FourAnd lock key data for setting a lock state / unlock state in units of blocks for rewriting and erasing of a storage unit (flash-ROM) incorporated in the memory.
[0045]
The
[0046]
The
[0047]
The hash value is generated using a hash function. The hash function is a function that receives target data, compresses the input data into data having a predetermined bit length, and outputs the data as a hash value. In the hash function, it is difficult to predict the input from the hash value (output). When one bit of the data input to the hash function changes, many bits of the hash value change, and the same hash value is changed. It has the feature that it is difficult to find the input data it has.
[0048]
As shown in FIG. 4A, the secure
Here, the A / V decompression software Soft is the
[0049]
Further, as shown in FIG. 4B, the secure
Then, the secure
Thus, in this embodiment, the public key data K of the
In the present invention, the public key certificate CERCPIs stored in the
[0050]
The
[0051]
The encryption /
Also, the encryption /
[0052]
The rights document
The
[0053]
The
When distributing the
[0054]
In the present embodiment, the secure container (product capsule) 104 is defined in the application layer in the OSI layer layer as shown in FIG. Further, capsules corresponding to the presentation layer and the transport layer are defined separately from the
For example, when the
Further, in the case of offline, the ROM type recording medium is considered as a transport carrier that transports the
[0055]
FIG. 6 is a diagram for explaining the ROM
As shown in FIG. 6, the ROM
The
In the
Further, the
Further, the
The media SAM 133 includes, for example, a media ID that is an identifier of the ROM
The media SAM 133 has, for example, a mutual authentication function.
[0056]
When the
In the present embodiment, as the SAM management unit, EMD service center management unit, content provider management unit, and service provider management unit, which will be described later, for example, internal processing contents cannot be monitored (monitored) and tamper resistant. A communication gateway having the following structure is used.
[0057]
Here, the distribution of the content data C from the
[0058]
As described above, in the present embodiment, in-band that encloses the content data C encrypted with the content key data Kc and the content key data Kc for decrypting the encryption in the
Note that the present invention has the flexibility to adopt an out-of-band method in which the content data C and the content key data Kc are separately supplied to the user home network 103.
[0059]
The EMD service
The
[0060]
The EMD service
When the EMD service
As the EMD service
[0061]
Hereinafter, the flow of processing in the
In addition, as a premise for performing the processing shown below, the parties related to the
[0062]
Thereafter, the
FIG. 8 is a flowchart of the process.
Step SA1: The
Step SA2: The
Step SA3: The EMD service
Then, the EMD service
Step SA4: The EMD service
[0063]
Hereinafter, a process in which the
As a premise for performing the following processing, the
The EMD service
Then, in the
[0064]
Hereinafter, the
FIG. 9 is a flowchart of the process.
In the following example, the
[0065]
Step SB1: The content data S111 is read from the content
The digital watermark
Step SB2: The
[0066]
Step SB3: The random
[0067]
Step SB4: The
Then, the secure
[0068]
Step SB5: The
The
Then, the secure
In addition, the
[0069]
Step SB6: The secure
Step SB7: The secure
[0070]
Hereinafter, processing when the
The authority request processing for the
[0071]
In this case, in the
The right registration request module Mod shown in FIG.2Session key data K obtained by mutual authentication between the
[0072]
In the present embodiment, after authorizing the
However, in the present invention, for example, after the
Authoritative certificate module Mod2aIs a module Mod that stores the globally unique identifier Content_ID of the content data C, the content key data Kc, and the
In this case, the
The
[0073]
[EMD service center 102]
The
FIG. 10 is a functional configuration diagram of the
As shown in FIG. 10, the
FIG. 10 shows a data flow related to data transmitted to and received from the
FIG. 11 shows the
[0074]
The
In addition to the
[0075]
The
The
Here, the
[0076]
The
Further, the payment request
When the settlement is completed, the
[0077]
The settlement
As will be described later, the account settlement
In addition, the settlement
[0078]
The certificate / rights
Public key certificate data CERSAM1~ CERSAM4, A
At this time, the certificate /
[0079]
The content
[0080]
The
[0081]
Hereinafter, the flow of processing in the
First, the
As shown in FIG. 10, the
In addition, the
The content
[0082]
Also, as shown in FIG. 11, the
In addition, the
The
[0083]
Hereinafter, the
FIG. 12 is a flowchart of the process.
Step SC1: The content
Step SC2: The decrypted signature data SIG9, CPAfter the
[0084]
Step SC3: The certificate / rights
[0085]
Step SC4: The
Step SC5: The content
[0086]
Hereinafter, the
FIG. 13 is a flowchart of the process.
Step SD1: The
[0087]
Step SD2: The decrypted signature data SIG8, SAM1After the
Step SD3: The certificate /
[0088]
Step SD4: The
Step SD5: The
SAM1052~ 105FourHowever, when the public key certificate data is requested, the target is the
In the present invention, the
At this time, at the time of shipment, the public key certificate data CERSAM1SAM1051You may memorize | store in the memory | storage part.
[0089]
Hereinafter, processing when the
FIG. 14 is a flowchart of the process.
Step SE1: The content
[0090]
Step SE2: Public key data K read from the
Step SE3: The certificate / rights
[0091]
In the following, processing when the
FIG. 15 is a flowchart of the process.
Step SF1: The
[0092]
Step SF2: The
Step SF3: The
The settlement
As a result, the amount of money indicated in the
The
[0093]
Step SF4: The
As described above, the
The content
[0094]
Further, as described above, the
[0095]
In addition, the
[0096]
[User home network 103]
As shown in FIG. 1, the user home network 103 includes a network device 160.1And A /
SAM1051~ 105FourAre connected via a
Further, the user home network 103 may have only AV devices that do not have a network function.
[0097]
Hereinafter, the
FIG. 16
As shown in FIG. 16, the
[0098]
SAM1051~ 105FourIs a module that performs charging processing in units of content, and performs communication with the
SAM1051~ 105FourFor example, specifications and versions are managed by the
[0099]
SAM1051~ 105FourThe processing contents are completely shielded from the outside, the processing contents cannot be monitored and tampered from the outside, and the data stored in advance and the data being processed cannot be monitored and tampered from the outside. This is a hardware module (such as an IC module) having tamper resistance.
SAM1051~ 105FourWhen the above function is realized in the form of an IC, a secret memory is provided in the IC, and a secret program and secret data are stored therein. The SAM may be defined as a SAM as long as the function can be incorporated into any part of the device without being limited to the physical form of IC.
[0100]
Hereinafter, SAM1051The function of will be described in detail.
SAM1052~ 105FourSAM1051And has basically the same function.
FIG. 17 shows the
FIG. 17 shows the flow of data related to the process of inputting the
As shown in FIG.1Includes a
[0101]
Note that the
Further, the
Here, the memory space of the
As the
As the
[0102]
Hereinafter, SAM1051Among these functions, processing contents of each functional block when the
[0103]
The
[0104]
The encryption /
[0105]
The
Note that the user home network 103 may have a function of detecting whether or not the
In this embodiment, the
[0106]
When the
As shown in FIG. 20, when a memory that does not have a mutual authentication function such as an HDD (Hard Disk Drive) is used as the
[0107]
The secure
[0108]
The EMD service
[0109]
The
[0110]
The
The
As the
[0111]
Hereinafter, SAM1051The flow of processing when the
First, the distribution key data KD received from the
In this case, first, mutual authentication is performed between the
Next, the session key data K obtained by the mutual authenticationSESKey data KD for 3 months encrypted with1~ KDThreeAnd its signature data SIGKD1, ESC~ SIGKD3, ESCIs written from the
Next, in the encryption /
Next, in the
[0112]
Hereinafter, the
FIG. 22 is a flowchart of the process.
Step SG1: SAM105 shown in FIG.1Mutual authentication is performed between the
The encryption /
[0113]
Step SG2: The
The content
The
[0114]
Step SG3: The download
[0115]
Step SG4: The download
Then, the secure
[0116]
Step SG5: The
[0117]
Step SG6: The secure
[0118]
Hereinafter, processing contents of each functional block related to processing for using / purchasing the content data C downloaded to the
[0119]
The
Here, the
Further, the usage
[0120]
The
Here, as described above, the
[0121]
Further, the
Here, the sales price and the standard retail price data SRP are stored in the
The billing process by the
[0122]
In addition, the
Examples of the content purchase mode include purchase purchase without restriction on reproduction by the purchaser and duplication for use by the purchaser, and reproduction charge for charging each time reproduction is performed.
Here, the usage
[0123]
In the case where the determined purchase form is regenerative charging, for example, the
Further, when the determined purchase form is a buyout, for example, the usage
[0124]
The EMD service
At this time, the EMD service
The
[0125]
For example, the content data C read from the
The decryption / decompression
[0126]
Here, the
[0127]
Hereinafter, SAM1051The flow of processing within will be described.
First, the flow of processing until the purchase form of the
FIG. 24 is a flowchart of the process.
Step SH1: In the
[0128]
Step SH2: The
At this time, for the content file CF, the mutual authentication between the
The content file CF is decrypted by the
[0129]
Further, the content key data Kc and the
Next, the decrypted
Next, the content data C decrypted by the semi-disclosure is decompressed by the
Next, after the user digital
[0130]
Step SH3: When the user operates the purchase / use form determining
Step SH4: The
Thereafter, the
[0131]
Step SH5: The usage
As shown in FIG. 29B, the key file KF1The usage
[0132]
Hereinafter, the flow of processing when the content data C for which the purchase form stored in the
FIG. 25 is a flowchart of the process.
Step SI1: The
Step SI2: The charging
[0133]
Step SI3: The read content file CF is output to the decryption /
Further, the content key data Kc read from the
[0134]
Step SI4: The
Step SI5: The
After the
[0135]
Hereinafter, for example, as shown in FIG.1The content file CF and the key file KF that have already been downloaded and downloaded to the
FIG. 28 is a flowchart of the process.
Step SJ1: The user operates the purchase / use form
Thereby, the
[0136]
Step SJ2: The download
Step SJ3: The key file KF shown in FIG. 29B read from the
Step SJ4: The
In addition, the
[0137]
Step SJ5: The
The
Step SJ6: In the encryption /
At this time, SAM1051And SAM1052In parallel with the mutual authentication between the two, the mutual authentication of the
[0138]
Hereinafter, as shown in FIG.1SAM 105 when writing a content file CF or the like input from a RAM type recording medium (media)2The flow of the process will be described with reference to FIGS. 30 and 31. FIG.
FIG. 31 is a flowchart of the process.
[0139]
Step SK1: SAM1052As shown in FIG. 26, the
Then, in the encryption /
Next, session key data KSESKey file KF decrypted using1And its signature data SIG42, SAM1And public key signature data CERSAM1And its signature data SIG22, ESCAre written in the
[0140]
Step SK2: The
Then, the
Next, the signature data SIG42, SAM1Legitimacy, ie key file KF1Is confirmed, the key file KF shown in FIG.1Is read from the
In this example, the key file KF1I mentioned the case where the creator and sender are the same, but the key file KF1If the creator and sender of the key are different, the key file KF1The signature data of the creator, the sender, and the signature data are created, and the
[0141]
Step SK3: The encryption /
Media key data KMEDAre stored in advance in the
[0142]
Here, the recording key data KSTRAre, for example, types such as SACD (Super Audio Compact Disc), DVD (Digital Versatile Disc) equipment, CD-R equipment, and MD (Mini Disc) equipment (in this example, AV equipment 160).2), And is used for one-to-one correspondence between device types and recording medium types. In addition, since the physical structure of the disk medium is the same between SACD and DVD, there are cases where recording / reproduction of the SACD recording medium can be performed using a DVD device. Key data for recording KSTRPlays a role in preventing unauthorized copying in such a case.
[0143]
Media key data KMEDIs data unique to the recording medium (in this example, the RAM type recording medium 250).
Media key data KMEDIs stored on the recording medium (in this example, the RAM
Note that, as in this embodiment, the SAM on the device side (in this example, the SAM 1052) And the media SAM (media SAM 252 in this example), and the media key data K is transmitted via a secure communication path.MEDIs transferred to the SAM on the device side, and the media key data K in the SAM on the device sideMEDEncryption and decryption may be performed using.
In this embodiment, recording key data KSTRAnd media key data KMEDIs used to protect the physical layer level security of the recording medium.
[0144]
Purchaser key data KPINIs data indicating the purchaser of the content file CF, and is assigned by the
[0145]
Step SK4: The media
Then, the
[0146]
Hereinafter, when the
Step SL1:
SAM1052Is media key data K in advanceMED, The input may not be performed.
[0147]
Step SL2: The key file KF and its signature data SIG shown in FIGS. 4B and 4C stored in the
[0148]
Step SL3: In the
[0149]
Step SL4: Signature data SIG in the
Then, in the secure
[0150]
Step SL5: In the
[0151]
Step SL6: The
[0152]
Step SL7: After performing mutual authentication between the
[0153]
Step SL8: The purchase mode of the content is determined by the purchase operation of the purchase mode
[0154]
Step SL9: The
In addition, the
[0155]
Step SL10: The new key file KF shown in FIG. 29B in which the interest
[0156]
Step SL11: The encryption /
[0157]
Step SL12: After performing mutual authentication between the
Thereby, the ROM
At this time, the usage
[0158]
Hereinafter, as shown in FIG.ThreeThe
FIG. 37 shows the
FIG. 38 shows the
[0159]
Step SM11 (FIG. 37):
At this time, similarly, the
[0160]
Step SM12: SAM105Three4B and 4C read from the
Next, the content file CF decrypted by the encryption /
The key file KF decrypted by the encryption /
[0161]
Step SM13: The
[0162]
Step SM14: The encryption /
[0163]
Step SN1 (FIG. 38): SAM1052Then, as shown in FIG. 41, the
In addition, the
[0164]
Step SN2: The decrypted signature data SIG351, ECSWhen the
And signature data SIG350, SAM3Is confirmed, the key file KF is read from the
[0165]
Step SN3: The secure
Thereafter, the
[0166]
Step SN4: The
[0167]
Step SN5: When the trial listening mode is selected by the user, the session key data K is alreadySESThe content data C of the content file CF decrypted by the above, the content key data Kc stored in the
[0168]
Step SN6: The purchase / use form of the content is determined by the operation of the purchase / use form determining
Step SN7: The
[0169]
Step SN8: For example, the key file KF shown in FIG. 29B storing the usage
Step SN9: Recording key data K read from the
Step SN10: The media
Further, the usage
Hereinafter, SAM1051~ 105FourThe realization method will be described.
SAM1051~ 105FourWhen the above function is realized as hardware, an ASIC type CPU with a built-in memory is used, and in the memory, a security function module for realizing each function shown in FIG. Stores sensitive data such as modules and key data. A series of rights processing program modules such as a cryptographic library module (public key cryptography, common key cryptography, random number generator, hash function), content usage control program module, billing processing program module, etc. are software, for example. Implemented as
[0170]
For example, modules such as the encryption /
Moreover, as a memory for storing the
In addition, SAM1051~ 105FourIn addition, there is a built-in clock function that is used to verify the date and time in the expiration date and contract period for content use.
[0171]
As mentioned above, SAM1051~ 105FourHas a tamper-resistant structure that shields program modules and data and processing contents from the outside. SAM1051~ 105FourThe contents of highly confidential programs and data stored in the internal memory of the SAM IC, the SAM system configuration related registers and encryption via the host CPU bus of the device equipped with the SAM In the SAM, in order to prevent values such as library and clock registers from being read or newly written, that is, not in the address space allocated by the host CPU of the mounted device, Using an MMU (Memory Magagement Unit) that manages the memory space on the CPU side, an address space that is invisible to the host CPU on the mounted device side is set.
In addition, SAM1051~ 105FourHas a structure that can withstand physical attacks from the outside such as X-rays and heat, and real-time debugging (reverse engineering) is performed using debugging tools (hardware ICE, software ICE). However, the processing contents are not known or the debugging tool itself cannot be used after the IC is manufactured.
SAM1051~ 105FourThe hardware itself is a normal ASIC type CPU with a built-in memory, and the function depends on the software that operates the CPU, but it has a cryptographic function and a tamper resistant hardware structure. This is different from a general ASIC type CPU.
[0172]
SAM1051~ 105FourWhen all the functions are implemented by software, the software processing is performed by closing the module inside a tamper-resistant module and the software processing on the host CPU installed in the normal set. There are cases in which it is impossible to decipher only at the time of processing. The former is the same as the case where the cryptographic library module is stored in the memory as a normal software module instead of the IP core, and is considered the same as the case where it is realized as hardware. On the other hand, the latter is called tamper resistant software, and even if the execution status is deciphered by ICE (debugger), the execution order of the tasks may be different (in this case, the divided task itself as a program) The task itself is encrypted and can be implemented in the same way as a task scheduler (MiniOS) for the purpose of a kind of secure processing. . The task scheduler is embedded in the target program.
[0173]
Next, the decoding /
As illustrated in FIG. 16, the decryption /
In the
[0174]
The
[0175]
Based on the control from the
[0176]
The
The
[0177]
The digital watermark
Thus, the user digital watermark information is embedded in the decoding /
In the present invention, the user digital
[0178]
Based on the
In addition, the
[0179]
The
[0180]
Next, a data format for transmitting / receiving data with signature data generated using private key data and public key certificate data between the
FIG. 42A shows the
In this case, the
Module Mod50The module Mod51And its secret key data KCP, SSignature data by SIGCPIs stored.
Module Mod51Includes the secret key data K of the
Thus, public key certificate data CERCPModule Mod that stores50From the
[0181]
42B and 42C show
In this case, the
Module Mod52Includes data Data to be transmitted and its secret key data KCP, SSignature data by SIGCPAnd are stored.
Also, the
Module Mod53Includes the public key certificate data CER of the
[0182]
FIG. 42D illustrates the
In this case, SAM1051From
Module Mod54The module Mod55And its secret key data KSAM1, SSignature data by SIGSAM1Is stored.
Module Mod55SAM1051Secret key data KSAM1, PPublic key certificate data CERSAM1And public key certificate data CERSAM1Secret key data forESC, SSignature data by SIGEscAnd data Data to be transmitted are stored.
Thus, public key certificate data CERSAM1Module Mod that stores55SAM1051The signature data SIG is transmitted from the
[0183]
42E and 42F show the SAM 105.1FIG. 6 is a diagram for explaining a data format when data Data is transmitted from the
In this case, SAM1051From
Module Mod56Includes data Data to be transmitted and its secret key data KSAM1, SSignature data by SIGSAM1And are stored.
Also, the
Module Mod57SAM1051Public key certificate data CERSAM1And its secret key data KESC, SSignature data by SIGEscAnd are stored.
[0184]
FIG. 43G is a diagram for explaining a data format when data Data is transmitted from the
In this case, the session key data K obtained by mutual authentication between the
Module Mod58The module Mod59And its secret key data KCP, SSignature data by SIGCPIs stored.
Module Mod59Includes the secret key data K of the
[0185]
FIG. 43H is a diagram for explaining a data format when data Data is transmitted from the
In this case, the session key data K obtained by mutual authentication between the
Module Mod60Includes data Data to be transmitted and its secret key data KCP, SSignature data by SIGCPAnd are stored.
At this time, the
[0186]
FIG. 43I shows the configuration of the
In this case, SAM1051From the
Module Mod61The module Mod62And its secret key data KSAM1, SSignature data by SIGSAM1Is stored.
Module Mod62SAM1051Secret key data KSAM1, PPublic key certificate data CERSAM1And public key certificate data CERSAM1Secret key data forESC, SSignature data by SIGEscAnd data Data to be transmitted are stored.
[0187]
FIG. 43J shows the SAM105.15 is a diagram for explaining a data format when data Data is transmitted from the
In this case, SAM1051From the
Module Mod63Includes data Data to be transmitted and its secret key data KSAM1, SSignature data by SIGSAM1And are stored.
At this time, the
[0188]
Hereinafter, SAM1051~ 105FourRegistration processing to the
SAM1051~ 105FourSince the registration process of SAM105 is the same, hereinafter SAM1051The registration process will be described.
In addition, SAM1051For example, the
That is, the
Public key certificate data CERSAM1SAM1051Is registered after shipment from the
[0189]
Here, the public key data K of the
Also, public key data K of the
In addition, the
[0190]
The
In addition, the
[0191]
In addition, SAM1051Is assigned a unique identifier SAM_ID under the management of the
[0192]
In addition, SAM1051After shipping, for example, the user is connected to the
That is, SAM1051A user who uses the EMD service center needs to register with the
SAM1051Can only be used after the registration procedure described above.
[0193]
The
In addition, the
In addition, the
[0194]
Next, as shown in FIG.1A procedure for storing the SAM registration list in the
Note that the topology map generated according to the
Therefore, SAM1051From the topology map, SAM1051~ 105FourThe SAM registration list is generated by extracting information about the.
[0195]
The data format of the SAM registration list is shown in FIG. 45, for example.
And SAM1051Registers the SAM registration list in the
These processes are performed by using the session of the
The
In addition, the
Note that the SAM revocation list is generated only for SAMs of the same system (connected to the same bus 191), and indicates whether the SAM is valid or invalid by the revocation flag corresponding to each SAM. Yes.
[0196]
Hereinafter, the overall operation of the
FIG. 46 is a flowchart of the overall operation of the
Step S1: The
In addition, the
Further, after performing the mutual authentication, the
Thus, in the
Note that the usage
[0197]
Step S2: After the
Then, after performing a predetermined signature verification, the
[0198]
Step S3: The
[0199]
Step S4:
[0200]
Step S5: SAM1051~ SAM105FourThe purchase / use form is determined based on an operation signal S165 according to the operation of the purchase / use form determining
At this time, the
[0201]
Step S6: SAM1051~ SAM105Four23, the
[0202]
Step S7: The
[0203]
Step S8: In the
[0204]
As described above, in the
The content key data Kc and the
Therefore, according to the
[0205]
In the
[0206]
In the
[0207]
First modification of the first embodiment
In the embodiment described above, as shown in FIG. 4B, the
However, even in the case of the first embodiment described above, encrypting the key file KF using the distribution key data KD is effective in increasing the suppression of unauthorized use of content data.
[0208]
Further, in the above-described embodiment, the case where the standard retail price data SRP is stored in the
[0209]
Second modification of the first embodiment
In the first embodiment described above, as shown in FIG. 1, the
[0210]
Third modification of the first embodiment
In the first embodiment described above, the
FIG. 48 is a configuration diagram of an EMD system according to a third modification of the first embodiment when the
In this case, the
In addition, the
[0211]
Then, the content provider 101a distributes the content file CFa encrypted using the original content key data Kca, the distribution key data KDa for the period corresponding to the content key data Kca, the
At this time, a globally unique identifier Content_ID distributed by the
Further, the
[0212]
SAM1051~ 105FourIs the distribution key data KDa for the corresponding period for the secure container 104a.1~ KDaThreeIs used to determine the purchase mode of the content through a predetermined signature verification process, etc., and the usage history data 108a and the usage control state data 166a generated according to the determined purchase mode and usage mode are EMD. Transmit to the
In addition, SAM1051~ 105FourIs the distribution key data KDb for the corresponding period for the secure container 104b.1~ KDbThreeIs used to determine the purchase mode of the content through a predetermined signature verification process, etc., and the usage history data 108b and the usage control state data 166b generated according to the determined purchase mode and usage mode are EMD Transmit to the
[0213]
The
Further, the
[0214]
Further, the
In addition, the
[0215]
Second embodiment
In the embodiment described above, the
[0216]
FIG. 49 is a configuration diagram of the
[0217]
First, an outline of the
In the
The
[0218]
In addition, the
[0219]
When the
Next, the
The
At this time, the key file KF is the distribution key data KD.1~ KD6And the
Further, the
[0220]
The
At this time, in the case of offline, the
[0221]
Next, SAM3051~ 305FourThe distribution key data KD for the corresponding period distributed from the
SAM3051~ 305FourThe
SAM3051~ 305FourRecords the purchase / use history of the
The usage history data (history data or management device history data) 308 is transmitted from the
[0222]
The
[0223]
In the present embodiment, as in the first embodiment, by providing digital content data C in an encapsulated form, the digital content that is in close contact with the conventional recording medium is separated from the recording medium, and the digital content alone is present. Can be given.
Here, the secure container is the most basic product capsule when selling the content data C (product) regardless of the distribution channel (delivery channel). Specifically, the secure container verifies the encryption information for charging, the validity of the content data C, the validity of the person who created the content data, and the validity of the distributor of the content data. This is a product capsule containing copyright information such as signature data and information on digital watermark information embedded in content data.
[0224]
In the present embodiment, the
That is, the
In addition, the
Also, the
[0225]
Hereinafter, each component of the
[Content Provider 301]
FIG. 50 is a functional block diagram of the
As shown in FIG. 50, the
[0226]
50, the same reference numerals as those in FIG. 2 are the same as the same reference numerals as those described with reference to FIGS. 2 and 3 in the first embodiment.
That is, the
The service
[0227]
When distributing the
[0228]
Further, the data flow in the
[0229]
[Service Provider 310]
The
There are roughly two types of content distribution service forms by the service provider 310: an independent service and a linked service.
The stand-alone service is, for example, a download-only service that distributes content individually. The linked service is a service that distributes contents in conjunction with programs and CMs (advertisements). For example, the contents of drama theme songs and insertion songs are stored in a drama program stream. When a user is watching a drama program, the user can purchase contents of a theme song or an insertion song in the stream.
[0230]
FIG. 51 is a functional block diagram of the
FIG. 51 shows a data flow when supplying the
As shown in FIG. 51, the
[0231]
Hereinafter, the process flow in the
FIG. 52 is a flowchart of the process.
Step SZ1: The content
At this time, in the case of online, the content
[0232]
Step SZ2: In the
Step SZ3: The
[0233]
Step SZ4: The price tag
[0234]
Step SZ5: The
[0235]
Step SZ6: The secure
At this time, the
[0236]
The
At this time, the content file CF and the key file KF are centrally managed by the
[0237]
Step SZ7: The user home
The user home
[0238]
Note that the user home
Then, the user home
For example, master key data KMIs stored in an IC card or the like and distributed to the
[0239]
When the user home
The
[0240]
FIG. 54 shows a flow of data related to communication with the
In addition, as a premise for performing the processing shown below, a person concerned with the
[0241]
First, the
First, the
EMD service
The EMD service
Then, the EMD service center management unit 348 responds to the registration with the public key certificate data CER.SPAnd its signature data SIG61, ESCIs input from the
[0242]
Next, processing when the
[0243]
In this case, the module Mod that stores the
Further, the public key certificate data CER is stored from the storage unit 351.SPAnd its signature data SIG61, ESCIs read out.
Then, the price tag registration request module Mod shown in FIG.102Session key data K obtained by mutual authentication between the
Module Mod103In addition, a globally unique identifier SP_ID of the
[0244]
Further, the EMD service
[0245]
Further, the EMD service
The
[0246]
[EMD Service Center 302]
As described above, the
FIG. 56 is a functional configuration diagram of the
As shown in FIG. 56, the
In FIG. 56, functional blocks having the same reference numerals as those in FIGS. 10 and 11 have substantially the same functions as the functional blocks having the same reference numerals described in the first embodiment.
In the following, a functional block with a new reference numeral in FIG. 56 will be described.
FIG. 56 shows a data flow related to data transmitted / received to / from the
FIG. 57 shows a data flow related to data transmitted to and received from the
FIG. 58 shows the
[0247]
As shown in FIG.1~ 305FourThe payment processing is performed based on the
As shown in FIG. 58, the
Further, as shown in FIG. 56 and FIG. 58, the
Here, the settlement claim
[0248]
Here, similarly to the
[0249]
The certificate / rights
At this time, the certificate / rights
[0250]
The content
[0251]
Based on the
[0252]
Based on the
[0253]
Hereinafter, the flow of processing in the
Distribution key data KD from the
[0254]
The processing when the
[0255]
Hereinafter, processing when the
FIG. 60 is a flowchart of the processing.
Step SO1: The service
[0256]
Step SO2: The decrypted signature data SIG70, SPAfter the
Step SO3: The certificate / rights
[0257]
Step SO4: The
Step SO5: The service
[0258]
Note that the
The processing when the
[0259]
Next, processing when the
FIG. 61 is a flowchart of the processing.
Step SP1: The service
[0260]
Step SP2: The decrypted price tag registration request module Mod102Signature data SIG stored in80, SPIs verified in the
[0261]
Step SP3: The certificate / rights
[0262]
Next, processing when making a settlement at the
FIG. 62 is a flowchart of the processing.
Step SQ1: The
[0263]
Step SQ2: The
As shown in FIG. 58, the
The payment processing by the
[0264]
Step SQ3: As shown in FIGS. 56 and 58, payment request
The settlement
As a result, the amount of money indicated in the settlement claim
Note that the
[0265]
Step SQ4: Settlement report data S307c and S307s for the
[0266]
In addition, the
[0267]
[User home network 303]
As shown in FIG. 49, the
SAM3051~ 305FourAre connected via a
Further, the
[0268]
Hereinafter, the
FIG. 63 shows a network device 360.1FIG.
As shown in FIG. 63, the
In FIG. 63, the constituent elements having the same reference numerals as those in FIG. 16 are the same as the constituent elements having the same reference numerals described in the first embodiment.
[0269]
The
Specifically, the
Further, the
[0270]
FIG. 64 is a functional block diagram of the
As shown in FIG. 64, the
When the
[0271]
The
[0272]
The encryption / decryption unit 908 is scrambled key data K encrypted from the decryption unit 910 of the decryption module 905.SCRAnd work key data KWAnd the master key data K read from the
Also, the encryption / decryption unit 908 receives the user
Also, the encryption / decryption unit 908 uses the SP
[0273]
The SP purchase history
The SP
[0274]
Note that the
[0275]
The
The decryption unit 910 receives the encrypted
Then, the decryption unit 910 receives the encrypted scramble key data KSCRAnd work key data KWIs output to the encryption / decryption unit 908 of the
Then, the decryption unit 910 converts the encrypted
[0276]
Note that when the
In addition, the ECM includes, for example, program attribute information for each channel. In addition, the EMM includes individual trial listening contract information that is different for each user (viewer).
[0277]
The secure
[0278]
Next, SAM3051Will be described.
SAM3051The
Also, SAM3052~ 305FourSAM3051And has basically the same function.
That is, SAM3051~ 305FourIs a module that performs charging processing in units of content, and performs communication with the
[0279]
Hereinafter, SAM3051The function of will be described in detail.
FIG. 65 shows the
FIG. 65 shows the data flow related to the process of inputting the
As shown in FIG.1Are a
Note that the
In FIG. 65, functional blocks denoted by the same reference numerals as those in FIG. 17 are the same as the functional blocks having the same reference numerals described in the first embodiment.
[0280]
63, the
In addition, as shown in FIG. 66, the
[0281]
Hereinafter, SAM3051Of these functional blocks, the functional blocks newly denoted with reference to FIG. 65 will be described.
The
[0282]
As shown in FIG. 67, the
The billing process by the
[0283]
Further, the
Here, similarly to the
[0284]
In addition, the
Examples of the content purchase mode include purchase purchase without restriction on reproduction by the purchaser and duplication for use by the purchaser, and reproduction charge for charging each time reproduction is performed.
Here, the usage
[0285]
In the case where the determined purchase form is regenerative charging, for example, SAM3051Usage
Further, when the determined purchase form is a buy-out, for example, the usage
[0286]
Also, SAM3051Then, the user
[0287]
Hereinafter, SAM3051The flow of processing within will be described.
Distribution key data KD received from the
[0288]
Hereinafter, the
FIG. 68 is a flowchart of the processing.
Step SR1: Mutual authentication is performed between the
The encryption /
[0289]
Step SR2: The
The service
The
[0290]
Step SR3: The download
[0291]
Step SR4: The download
Then, the secure
[0292]
Step SR5: The secure
The
[0293]
Step SR6: The secure
[0294]
Hereinafter, the flow of processing until the purchase form of the
FIG. 69 is a flowchart of the processing.
Step SS1: In the
[0295]
Step SS2: For example, the content file CF stored in the
At this time, for the content file CF, the mutual authentication between the
The content file CF is decrypted by the
[0296]
Also, the content key data Kc and the
Next, the decrypted
Next, the content data C decrypted by the semi-disclosure is decompressed by the
Next, after the user digital
[0297]
Step SS3: When the user who auditioned the content operates the purchase / use form determining
[0298]
Step SS4: The
Thereafter, the
[0299]
Step SS5: The usage
As shown in FIG. 71, the key file KF1The usage
[0300]
Next, the flow of processing when the content data C for which the purchase form stored in the
FIG. 70 is a flowchart of the process.
Step ST1: For example, the SAM receives designation of content to be reproduced in accordance with a user operation.
[0301]
Step ST2: Under the monitoring of the
Step ST3: The read content file CF is output to the decryption /
Further, the content key data Kc read from the
[0302]
Step ST4: The
Step ST5: In the
[0303]
Hereinafter, as shown in FIG. 72, for example, a
Step SU1: The user operates the purchase / usage mode
Thereby, the
[0304]
Step SU2: The download
Step SU3: Key file KF that has already been determined to be purchased as shown in FIG. 75B read from the
Step SU4: The
[0305]
Step SU5: The
In addition, the
The
[0306]
Step SU6: In the encryption /
[0307]
Hereinafter, as shown in FIG.1SAM 305 when writing a content file CF or the like input from a RAM type recording medium (media)2The flow of the process will be described with reference to FIGS. 76 and 77.
FIG. 77 is a flowchart of the processing.
[0308]
Step SV1: SAM305276, as shown in FIG. 76, the content file CF shown in FIG. 75A and the key file KF shown in FIG.11And its signature data SIG80, SAM1And public key signature data CER shown in FIG.SAM1And its signature data SIG22, ESCAnd the network device 360.1SAM3051Enter from.
Then, in the encryption /
[0309]
Next, session key data KSESThe content file CF decrypted using is output to the media
Session key data KSESKey file KF decrypted using11And its signature data SIG80, SAM1And public key signature data CERSAM1And its signature data SIG22, ESCAre written in the
[0310]
Step SV2: The
Then, the
[0311]
Step SV3: Signature data SIG80, SAM1Is confirmed, the key file KF shown in FIG.11Is read from the
Then, the encryption /
[0312]
Step SV4: The media
Then, the
[0313]
SAM3051AV device 360 for determining the purchase mode of a ROM type recording medium whose content purchase mode has not yet been determined.2 Process flow,
[0314]
Next, the overall operation of the
78 and 79 are flowcharts of the overall operation of the
Here, a case where the
Note that the
[0315]
Step S21: The
The
Also, the
[0316]
Step S22: The
Then, after performing a predetermined signature verification, the
[0317]
Step S23: The
[0318]
Step S24: The
[0319]
Step S25: The
[0320]
Step S26: The
The
[0321]
Step S27: The
[0322]
Step S28: The
[0323]
Step S29: SAM3051~ 305FourAny of the signature data SIG shown in FIG.61, ESCAfter verifying the public key certificate data CERSPPublic key data K stored inSP, PIs used to sign data SIG shown in FIGS. 53 (A), (B), (C).62, SP, SIG63, SP, SIG64, SPTo confirm whether the
[0324]
Step S30: SAM3051~ 305FourIn any of the above, the distribution key data KD1~ KDThreeIs used to decrypt the key file KF shown in FIG. And SAM3051~ 305FourAny of the signature data SIG shown in FIG.1, ESCAfter verifying the public key certificate data CERCPPublic key data K stored inCP, PThe signature data SIG shown in FIG.2, CP, SIG3, CPAnd SIG4, CPTo confirm whether the content data C, the content key data Kc, and the
[0325]
Step S31: The user operates the purchase / use form determining
[0326]
Step S32: Based on the operation signal S165 generated in step S31, the
SAM3051~ 305FourTo the
[0327]
The
[0328]
The
[0329]
As described above, in the
The content key data Kc and the
[0330]
Therefore, according to the
Therefore, according to the
[0331]
In the
[0332]
In the
[0333]
Further, according to the
Further, according to the
That is, according to the
[0334]
First modification of the second embodiment
FIG. 80 is a configuration diagram of an
In FIG. 80, constituent elements denoted by the same reference numerals as those in FIG. 49 are the same as constituent elements having the same reference numerals described in the second embodiment.
As shown in FIG. 80, in the
[0335]
The
In addition, the
Here, the format of the
[0336]
Network device 360a1Are provided with
The
[0337]
Next, the
Further, the
[0338]
Next, SAM3051~ 305FourCommon key data for distribution KD1~ KDThreeIs used to decrypt the key file KF in the
[0339]
And SAM3051~ 305FourThe
[0340]
Based on the
[0341]
The
[0342]
As described above, according to the
[0343]
In the first modification described above, the case where two service providers are used is illustrated, but in the present invention, the number of service providers is arbitrary.
[0344]
Second modification of the second embodiment
FIG. 81 is a configuration diagram of an
In FIG. 81, the constituent elements having the same reference numerals as those in FIG. 49 are the same as the constituent elements having the same reference numerals described in the second embodiment.
As shown in FIG. 81, in the
[0345]
For example, the
As shown in FIG. 81, the
[0346]
The
[0347]
SAM3051~ 305FourThen, the distribution key data KDa1~ KDaThreeIs used to decrypt the key file KFa, and based on the
Also, SAM3051~ 305FourIn the distribution key data KDb1~ KDbThreeIs used, the key file KFb is decrypted, processing based on purchase / use of the content file CFb according to the operation from the user is performed based on the
[0348]
And SAM3051~ 305FourThe
[0349]
The
[0350]
The
[0351]
As described above, according to the
[0352]
In the second modification shown in FIG. 81, the case where two content providers are used is illustrated, but the number of content providers is arbitrary.
There may be a plurality of content providers and service providers.
[0353]
Third modification of the second embodiment
FIG. 82 is a configuration diagram of an EMD system according to a third modification of the second embodiment.
In the second embodiment described above, the
In this case, the
Further, the
[0354]
Fourth modification of the second embodiment
FIG. 83 is a configuration diagram of an EMD system according to a fourth modification of the second embodiment.
In the second embodiment described above, for example, the case where the
Then, the
On the other hand, SAM3051~ 305FourCreates usage history data 308 c for the right processing of the
The
The
[0355]
Fifth modification of the second embodiment
In the above-described embodiment, as shown in FIG. 49, the user preference
[0356]
Sixth modification of the second embodiment
In this way, the
Also, SAM3051~ 305FourFor the secret key data K by the
[0357]
Seventh modification of the second embodiment
In the above-described embodiment, the
For example,
In addition, the
[0358]
FIG. 84 is a diagram for explaining the form of the acquisition (acquisition) route of public key certificate data.
In FIG. 84, the constituent elements denoted by the same reference numerals as those in FIG. 49 are the same as the constituent elements having the same reference numerals. The
[0359]
The
[0360]
In addition, the
[0361]
In addition, the
[0362]
Also, SAM3051~ 305FourIs the public key certificate data CER of the
[0363]
Also, SAM3051SAM3052Public key certificate data CERSAM2For example, when acquiring
[0364]
Also, SAM3052SAM3051Public key certificate data CERSAM1For example, when acquiring
[0365]
Also, SAM305FourSAM30513Public key certificate data CERSAM13For example, when acquiring
[0366]
Also, SAM30513SAM305FourPublic key certificate data CERSAM4For example, when acquiring
[0367]
Handling of public key certificate revocation list (data) in the second embodiment
In the second embodiment, in the
In addition to the
[0368]
First, the
As shown in FIG. 85, the
[0369]
Also, the
The
[0370]
Next, the
As shown in FIG. 86, the
[0371]
Also, the
KSP, PIf the signature is verified using invalidation and it is determined to be invalid, the secure container is invalidated without performing the signature verification.
In this case, in the
The
[0372]
Next, the
As shown in FIG. 87, the
The
SAM3051SAM3052SAM305 added to data input from2Public key certificate revocation data CRL when verifying signature dataThreeRefers to the public key certificate data CERSAM2The validity of the public key data K is determined when it is determined that it is valid.SAM2, PIf the signature is verified using invalidation, the data is invalidated without performing the signature verification.
In this case, in the
[0373]
The
Also, the
[0374]
The
Further, the
The
Next, the
SAM3051When communicating with other SAMs, with reference to the discard flag of the SAM registration list SRL, the presence / absence of verification of signature data and whether or not communication is permitted are determined.
[0375]
Also, the
The
Next, the
SAM3051Is the SAM305 shown in the SAM registration list created by itself.1~ 305FourAmong them, public key certificate revocation data CRLThreeSAM indicated to be invalidated by (e.g. SAM305)2) Is specified, and a discard flag corresponding to the SAM in the SAM registration list SRL is set to indicate invalidity.
After that, SAM3051When communicating with other SAMs, with reference to the discard flag of the SAM registration list SRL, the presence / absence of verification of signature data and whether or not to permit communication are determined.
[0376]
Also, the
Next, the
SAM3051Is the SAM305 shown in the SAM registration list created by itself.1~ 305FourAmong them, public key certificate revocation data CRLThreeSAM indicated to be invalidated by (e.g. SAM305)2) Is specified, and the discard flag corresponding to the SAM in the SAM registration list SRL is set to indicate invalidity.
After that, SAM3051When communicating with other SAMs, with reference to the discard flag of the SAM registration list SRL, the presence / absence of verification of signature data and whether or not to permit communication are determined.
[0377]
Role of
FIG. 89 is a configuration diagram of the EMD system when the function of the EMD service center (clearing house) 302 shown in FIG. 49 is divided into a rights
In the EMD system, the
[0378]
Further, the rights
Also, registration (authorization) of the
As shown in FIG. 90, when the right
[0379]
Further, according to the present invention, for example, as shown in FIG. 91, the
[0380]
In the present invention, for example, as shown in FIG. 92, the
[0381]
Eighth modification of the second embodiment
In the second embodiment described above, in the
That is, in the second embodiment described above, as shown in FIGS. 4 and 53, a single content file CF and a single key file KF corresponding to the content file CF are respectively stored in the
In the present invention, a plurality of content files CF and a plurality of key files KF respectively corresponding to the plurality of content files CF may be stored in the
[0382]
FIG. 93 is a diagram for explaining the format of the
As shown in FIG. 93, the
Here, the signature data SIG250, CPIn the
[0383]
Content file CF101In the header, link data LD1, Metadata Meta1, Content data C1And A / V decompression software Soft1Is stored.
Here, the content data C1And A / V decompression software Soft1Is the content key data Kc described above1Is encrypted using the metadata Meta1Is content key data Kc as required1It is encrypted using
Content data C1Is compressed by, for example, the ATRAC3 method. A / V decompression software Soft1Is ATRAC3 type decompression software.
Link data LD1Is the key file KF101To link to.
[0384]
Content file CF102In the header, link data LD1, Metadata Meta2, Content data C2And A / V decompression software Soft2Is stored.
Here, the content data C2And A / V decompression software Soft2Is the content key data Kc described above2Is encrypted using the metadata Meta2Is content key data Kc as required2It is encrypted using
Content data C2Is compressed by, for example, the MPEG2 system.
A / V decompression software Soft2Is software for decompression of the MPEG2 system.
Link data LD2Is the key file KF102To link to.
[0385]
Content file CF103In the header, link data LDThree, Metadata MetaThree, Content data CThreeAnd A / V decompression software SoftThreeIs stored.
Here, the content data CThreeAnd A / V decompression software SoftThreeIs the content key data Kc described aboveThreeIs encrypted using the metadata MetaThreeIs content key data Kc as requiredThreeIt is encrypted using
Content data CThreeIs compressed by, for example, the JPEG method. A / V decompression software SoftThreeIs software for decompression in JPEG format.
Link data LDThreeIs the key file KF103To link to.
[0386]
Key file KF101Includes a header and each distribution key data KD.1~ KDThreeContent key data Kc encrypted using1,
Here, the signature / certificate module Mod200As shown in FIG. 94 (A), each of the content data C1, Content key data Kc1And
[0387]
Key file KF102Includes a header and each distribution key data KD.1~ KDThreeContent key data Kc encrypted using2,
Here, the signature / certificate module Mod201As shown in FIG. 94 (B), each of the content data C2, Content key data Kc2And
[0388]
Key file KF103Includes a header and each distribution key data KD.1~ KDThreeContent key data Kc encrypted usingThree,
Here, the signature / certificate module Mod202As shown in FIG. 94 (C), each of the content data CThree, Content key data KcThreeAnd
[0389]
When the
Then, the
Here,
Also, the signature data SIG260, SPIs the content file CF101, CF102, CF103, Key file KF101, KF102, KF103, Public key certificate data CERSPAnd signature data SIG61, ESCAnd
[0390]
The
In the
Then SAM3051~ 305FourIs the content data C101, C102, C103Rights data about the link data LD1, LD2, LDThreeEach key file KF101, KF102, KF103Based on.
[0390]
In the above-described eighth modification, the
Further, in the above-described eighth modification, the
[0392]
Further, in the above-described eighth modification, the
[0393]
The format shown in FIG. 93 can be similarly applied to the case where the
[0394]
In the above-described embodiment, the case where the EMD service center performs a payment process based on the usage history data input from the SAM has been exemplified. The payment processing may be performed using the usage control state data transmitted from the SAM to the EMD service center and received at the EMD service center.
[0395]
Hereinafter, concepts such as the content file CF and the key file KF created in the
When the
Then, the content file CF and the key file KF are directly provided from the
[0396]
When the
[0397]
When the
Also, in this case, for example, as shown in FIG. 99, the content key data Kc encrypted with the distribution key data of the EMD service centers 102 and 302, which are predetermined trust organizations, is sent from the EMD service centers 102 and 302 to the user home You may provide to network 103,303.
[0398]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, the interests of the parties involved in the data providing apparatus are appropriately protected.
Further, according to the present invention, it is possible to appropriately avoid illegally tampering with the rights document data.
Furthermore, according to the present invention, it is possible to reduce the burden of auditing for protecting the interests of the parties related to the data providing apparatus.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is an overall configuration diagram of an EMD system according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a functional block diagram of the content provider shown in FIG. 1 and shows a data flow related to data transmitted to and received from a SAM of a user home network.
FIG. 3 is a functional block diagram of the content provider shown in FIG. 1, and is a diagram showing a flow of data related to data transmitted and received between the content provider and the EMD service center.
FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining a format of a secure container transmitted from the content provider shown in FIG. 1 to the SAM.
FIG. 5 is a diagram for explaining a correspondence relationship between an OSI layer layer and a definition of a secure container according to the present embodiment.
FIG. 6 is a diagram for explaining a ROM type recording medium;
7A is a diagram for explaining a format of a right registration request module transmitted from the content provider to the EMD service center, and FIG. 7B is transmitted from the EMD service center to the content provider. It is a figure for demonstrating the rights-certification certificate module.
FIG. 8 shows a case where the content provider requests the EMD service center for public key certificate data certifying the validity of the public key data corresponding to its own private key data in the first embodiment. It is a flowchart of a process.
FIG. 9 is a flowchart of processing when a content provider transmits a secure container to a SAM of a user home network in the first embodiment.
FIG. 10 is a functional block diagram of the EMD service center shown in FIG. 1, and shows a data flow related to data transmitted / received to / from a content provider.
11 is a functional block diagram of the EMD service center shown in FIG. 1, and shows a data flow related to data transmitted / received between the SAM and the clearing house shown in FIG.
FIG. 12 is a flowchart of processing when the EMD service center receives a public key certificate data issuance request from a content provider in the first embodiment.
FIG. 13 is a flowchart of processing when the EMD service center receives a public key certificate data issuance request from the SAM in the first embodiment;
FIG. 14 is a flowchart of processing when an EMD service center receives a request for registration of rights document data and content key data from a content provider in the first embodiment.
FIG. 15 is a flowchart of processing when an EMD service center performs settlement processing in the first embodiment.
FIG. 16 is a configuration diagram of a network device in the user home network shown in FIG. 1;
FIG. 17 is a functional block diagram of the SAM in the user home network shown in FIG. 1, and shows a data flow until the secure container received from the content provider is decrypted.
FIG. 18 is a diagram for explaining data stored in the external memory shown in FIG. 16;
FIG. 19 is a diagram for explaining data stored in a stack memory;
20 is another configuration diagram of the network device in the user home network shown in FIG. 1. FIG.
FIG. 21 is a diagram for explaining data stored in a storage unit illustrated in FIG. 17;
FIG. 22 is a flowchart of processing in the SAM when the secure container is input from the content provider and the key file KF in the secure container is decrypted in the first embodiment.
FIG. 23 is a functional block diagram of the SAM in the user home network shown in FIG. 1, and shows a data flow related to processing for using / purchasing content data.
FIG. 24 is a flowchart of processing up to determining a purchase form of a secure container downloaded from a content provider to a download memory in the first embodiment.
FIG. 25 is a flowchart of processing in the case of playing back content data for which the purchase form stored in the download memory has already been determined in the first embodiment.
FIG. 26 is a flowchart showing the processing in the transfer source SAM when transferring the content file downloaded to the download memory of the network device shown in FIG. It is a figure for demonstrating a flow.
FIG. 27 is a diagram illustrating a data flow in the transfer source SAM in the case illustrated in FIG. 26;
FIG. 28 is a diagram showing an example of a SAM in a case where a content file and a key file that have already been downloaded and downloaded to a network device download memory are transferred to a SAM of another AV device in the first embodiment; FIG.
FIG. 29 is a diagram for explaining a format of a secure container whose purchase form is determined;
FIG. 30 is a diagram showing a data flow when an input content file or the like is written in a RAM type or ROM type recording medium (media) in the transfer destination SAM in the case shown in FIG. 26; is there.
FIG. 31 is a flowchart of processing in the SAM when a content file or the like input from another SAM is written in a RAM type recording medium in the first embodiment.
FIG. 32 shows a process for determining a purchase form in an AV device when the user home network receives distribution of the ROM type recording medium shown in FIG. It is a figure for demonstrating a flow.
FIG. 33 is a diagram showing a data flow in the SAM in the case shown in FIG. 32;
FIG. 34 is a diagram showing a purchase form in the AV device when the user home network receives distribution of the ROM type recording medium shown in FIG. 5 whose content purchase form has not yet been decided in the first embodiment. It is a flowchart of the process at the time of determining.
FIG. 35 is a flowchart that is a continuation of the flowchart of FIG. 34;
FIG. 36 is a diagram illustrating a process of reading a secure container from a ROM type recording medium whose purchase form has not yet been determined in an AV device in a user home network, transferring the secure container to another AV device, and converting it into a RAM type recording medium. It is a figure for demonstrating the flow of the process at the time of writing.
FIG. 37 is a diagram illustrating a process of reading a secure container from a ROM-type recording medium whose purchase form is undetermined in the first AV device and transferring it to the second AV device as shown in FIG. It is a flowchart of the process of the 1st AV apparatus at the time of determining a purchase form and writing in a RAM type recording medium in AV apparatus.
FIG. 38 is a flowchart of processing of the second AV device in the case shown in FIG. 37;
FIG. 39 is a flowchart subsequent to the flowchart shown in FIG. 38;
40 is a diagram showing a data flow in the transfer source SAM in the case shown in FIG. 36. FIG.
41 is a diagram showing a data flow in the transfer destination SAM in the case shown in FIG. 36; FIG.
42 is a diagram for explaining a format of data transmitted / received between the content provider, the EMD service center, and the SAM shown in FIG. 1 by using an in-band method and an out-band method. .
43 is a diagram for explaining a format of data transmitted / received between the content provider, the EMD service center, and the SAM shown in FIG. 1 using an in-band method and an out-band method. .
FIG. 44 is a diagram for explaining an example of a connection form of devices to a bus.
FIG. 45 is a diagram for explaining a data format of a SAM registration list;
46 is a flowchart of the overall operation of the content provider shown in FIG. 1. FIG.
FIG. 47 is a view for explaining a second modification of the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 48 is a view for explaining a third modification of the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 49 is an overall configuration diagram of an EMD system according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 50 is a functional block diagram of the content provider shown in FIG. 49, and is a diagram showing a flow of data related to the secure container transmitted to the service provider.
51 is a functional block diagram of the service provider shown in FIG. 49, and shows a flow of data transmitted / received to / from the user home network.
FIG. 52 is a flowchart of processing of a service provider when a secure container is created from a secure container supplied from a content provider and distributed to a user home network in the second embodiment.
53 is a diagram for explaining a format of a secure container transmitted from the service provider shown in FIG. 49 to the user home network. FIG.
54 is a functional block diagram of the service provider shown in FIG. 49, and shows a flow of data transmitted / received to / from the EMD service center.
FIG. 55 is a diagram for explaining a format of a price tag registration request module transmitted from a service provider to an EMD service center.
FIG. 56 is a functional block diagram of the EMD service center shown in FIG. 49, and shows a data flow related to data transmitted to and received from the service provider.
FIG. 57 is a functional block diagram of the EMD service center shown in FIG. 49, and shows a data flow related to data transmitted to and received from the content provider.
FIG. 58 is a functional block diagram of the EMD service center shown in FIG. 49, and shows a data flow related to data transmitted to and received from the SAM.
FIG. 59 is a diagram for explaining the contents of usage history data;
FIG. 60 is a flowchart of processing when the EMD service center receives a public key certificate data issuance request from a service provider in the second embodiment.
FIG. 61 is a flowchart of processing when the EMD service center receives a price tag data registration request from a service provider in the second embodiment;
FIG. 62 is a flowchart of processing when an EMD service center performs settlement in the second embodiment.
63 is a block diagram of the network device shown in FIG. 49. FIG.
64 is a functional block diagram of the CA module shown in FIG. 63. FIG.
FIG. 65 is a functional block diagram of the SAM shown in FIG. 63, and shows a data flow from input of a secure container to decryption.
66 is a diagram for explaining data stored in a storage unit illustrated in FIG. 65. FIG.
67 is a functional block diagram of the SAM shown in FIG. 63, and shows a data flow when determining a content purchase / use form.
FIG. 68 is a flowchart of SAM processing when a secure container is input from a service provider and a key file in the secure container is decrypted in the second embodiment.
FIG. 69 is a flowchart of SAM processing up to determining a purchase form of a secure container downloaded to a download memory from a service provider in the second embodiment.
FIG. 70 is a flowchart of processing in the case of reproducing content data for which a purchase form stored in the download memory has already been determined.
FIG. 71 is a diagram for explaining a format of a key file after a purchase form is determined.
72 is a diagram of processing in a transfer destination SAM when transferring a content file downloaded to the download memory of the network device shown in FIG. 63 and already determined as a purchase form to the SAM of the AV device; It is a figure for demonstrating a flow.
FIG. 49 is a diagram showing a data flow in the transfer source SAM in the case shown in FIG. 72;
74 is a transfer source SAM when transferring, for example, a content file already downloaded in a download memory of a network device and determined to be purchased to the SAM of the AV device as shown in FIG. It is a flowchart of the process of.
FIG. 75 is a diagram for explaining a format of a secure container in which a purchase form to be transferred from a network device SAM to an AV device SAM is already determined;
FIG. 51 is a diagram showing a data flow in the transfer destination SAM in the case shown in FIG. 72;
FIG. 77 is a flowchart of SAM processing when a content file or the like input from another SAM is written to a recording medium such as a RAM type as shown in FIG. 72.
78 is a flowchart of the overall operation of the EMD system shown in FIG. 49. FIG.
FIG. 79 is a flowchart of overall operation of the EMD system shown in FIG. 49;
FIG. 80 is a configuration diagram of an EMD system using two service providers according to a first modification of the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 81 is a configuration diagram of an EMD system using a plurality of content providers according to a second modification of the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 82 is a block diagram of an EMD system according to a third modification of the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 83 is a block diagram of an EMD system according to a fourth modification of the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 84 is a diagram for explaining a form of an acquisition route for public key certificate data;
FIG. 85 is a diagram for explaining processing when invalidating public key certificate data of a content provider;
[Fig. 86] Fig. 86 is a diagram for describing processing in the case of invalidating public key certificate data of a service provider.
FIG. 87 is a diagram for explaining processing when invalidating SAM public key certificate data;
FIG. 88 is a diagram for explaining other processing when invalidating the SAM public key certificate data;
FIG. 89 is a diagram for explaining a case where a rights management clearing house and an electronic settlement clearing house are provided in place of the EMD service center in the EMD system shown in FIG. 49;
90 is a configuration diagram of an EMD system when the rights management clearing house and the electronic settlement clearing house shown in FIG. 89 are provided in a single EMD service center.
FIG. 91 is a block diagram of an EMD system when a service provider makes a payment directly to an electronic payment clearinghouse.
FIG. 92 is a configuration diagram of an EMD system when a content provider makes a payment directly to an electronic payment clearinghouse.
FIG. 93 is a diagram for explaining a format of a secure container provided from the content provider shown in FIG. 49 to the service provider in the eighth modification of the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 94 is a diagram for explaining a detailed format of a module stored in FIG. 93;
FIG. 95 is a diagram for explaining a format of a secure container provided to the SAM from the service provider shown in FIG. 49 in the eighth modification example of the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 96 is a conceptual diagram when a secure container is provided using the Internet.
FIG. 97 is another conceptual diagram when a secure container is provided using the Internet.
FIG. 98 is a conceptual diagram when a secure container is provided using digital broadcasting.
FIG. 99 is another conceptual diagram when a secure container is provided using digital broadcasting.
FIG. 100 is a configuration diagram of a conventional EMD system.
[Explanation of symbols]
90 ... Payment gateway, 91 ... Settlement organization, 92 ... Root certificate authority, 100, 300 ... EMD system, 101, 301 ... Content provider, 102, 302 ... EMD service center, 103, 303 ... User home network, 104, 304 ... Secure container, 1051~ 105Four3051~ 305Four... SAM, 106 ... Rights data, 107,307 ... Settlement report data, 108,308 ... Usage history data, 1601... Network equipment, 1602~ 160Four... AV equipment, 152, 152c, 152s ... Payment claim data, 191 ... Bus, 310 ... Service provider, 311 ... CA module, 312 ... Price tag data, CF ... Content file, KF ... Key file, Kc ... Content key data
Claims (6)
前記購入処理装置は、
前記ネットワークを通じて、前記コンテンツデータについての所定の利用期間毎に有効な複数の配信用鍵データを前記コンテンツ提供装置へ送信し、前記複数の配信用鍵データのうちの、前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを前記コンテンツ処理装置へ送信し、
前記コンテンツ提供装置は、
前記コンテンツデータを記憶する記憶部と、
前記記憶部に記憶された前記コンテンツデータをコンテンツ鍵データで暗号化するコンテンツ暗号化部と、
前記ネットワークに接続され、前記購入処理装置から前記複数の配信用鍵データを受信するコンテンツ提供装置用の通信部と、
受信した各前記配信用鍵データを用いて前記コンテンツ鍵データを暗号化し、複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを生成するコンテンツ鍵暗号化部と、
暗号化された前記コンテンツデータ、および前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを有するセキュアコンテナデータを生成するセキュアコンテナデータ生成部と
を有し、
前記コンテンツ提供装置用の通信部は、
前記セキュアコンテナデータをコンテンツ処理装置へ送信することにより、前記コンテンツデータおよび前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データをコンテンツ処理装置へ送信し、
前記コンテンツ処理装置は、
前記ネットワークに接続され、前記購入処理装置から前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを受信し、前記コンテンツ提供装置用の通信部から前記セキュアコンテナデータを受信するコンテンツ処理装置用の通信部と、
受信した前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて、受信した前記セキュアコンテナデータに含まれる前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データのうちの、当該配信用鍵データにより暗号化されたコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを復号するコンテンツ鍵復号部と、
前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて復号されたコンテンツ鍵データを用いて、前記セキュアコンテナデータの前記コンテンツデータを復号するコンテンツ復号部と
を有する
データ提供システム。Connected content providing apparatus to a network, the content processing apparatus, and a purchase processing unit sends said content data from the content providing apparatus to the content processing apparatus, the Oite purchased purchased period to the purchase processing unit to use the previous SL content data to the content processing apparatus according to,
The purchase processing apparatus includes:
Through the network, a plurality of distribution key data effective for each predetermined usage period of the content data is transmitted to the content providing apparatus, and the distribution of the plurality of distribution key data effective during the purchase period Key data to the content processing device ,
The content providing apparatus includes:
A storage unit for storing the content data;
A content encryption unit that encrypts the content data stored in the storage unit with content key data;
A communication unit for a content providing device connected to the network and receiving the plurality of distribution key data from the purchase processing device;
A content key encryption unit that encrypts the content key data using each of the received distribution key data and generates encrypted data of a plurality of content key data;
A secure container data generating unit that generates secure container data having the encrypted content data and encrypted data of the plurality of content key data, and
The communication unit for the content providing device includes:
By transmitting the secure container data to the content processing device, the content data and the plurality of content key data are transmitted to the content processing device,
The content processing apparatus includes:
A communication unit for a content processing device that is connected to the network, receives key data for distribution effective from the purchase processing device during the purchase period, and receives the secure container data from the communication unit for the content providing device;
Content encrypted with the distribution key data out of the encrypted data of the plurality of content key data included in the received secure container data, using the distribution key data valid for the received purchase period A content key decrypting unit for decrypting the encrypted data of the key data;
A data providing system comprising: a content decrypting unit that decrypts the content data of the secure container data using content key data decrypted using distribution key data valid during the purchase period.
前記記憶部に記憶された前記コンテンツデータをコンテンツ鍵データで暗号化するコンテンツ暗号化部と、
ネットワークに接続され、前記ネットワークから前記コンテンツデータについての所定の利用期間毎に有効な複数の配信用鍵データを受信する通信部と、
受信した各前記配信用鍵データを用いて前記コンテンツ鍵データを暗号化し、複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを生成するコンテンツ鍵暗号化部と、
暗号化された前記コンテンツデータ、および前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを有するセキュアコンテナデータを生成するセキュアコンテナデータ生成部と
を有し、
前記通信部は、
前記ネットワークへ前記セキュアコンテナデータを送信することにより、前記コンテンツデータおよび前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データをコンテンツ処理装置へ送信する
コンテンツ提供装置。A storage unit for storing content data;
A content encryption unit that encrypts the content data stored in the storage unit with content key data;
A communication unit connected to a network and receiving a plurality of distribution key data valid for each predetermined usage period of the content data from the network;
A content key encryption unit that encrypts the content key data using each of the received distribution key data and generates encrypted data of a plurality of content key data;
A secure container data generating unit that generates secure container data having the encrypted content data and encrypted data of the plurality of content key data, and
The communication unit is
A content providing device that transmits the content data and the plurality of content key data to a content processing device by transmitting the secure container data to the network.
前記購入処理装置は、
前記ネットワークを通じて前記コンテンツ提供装置へ、前記コンテンツデータについての所定の利用期間毎に有効な前記複数の配信用鍵データを送信する
データ提供システム。A data providing system comprising the content providing device and the purchase processing device according to claim 2 connected to a network,
The purchase processing apparatus includes:
A data providing system for transmitting the plurality of distribution key data effective for each predetermined usage period of the content data to the content providing apparatus through the network.
受信した前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて、受信した前記セキュアコンテナデータに含まれる前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データのうちの、当該配信用鍵データにより暗号化されたコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを復号するコンテンツ鍵復号部と、
前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて復号されたコンテンツ鍵データを用いて、前記セキュアコンテナデータの前記コンテンツデータを復号するコンテンツ復号部と
を有するコンテンツ処理装置。Content data encrypted with content key data and a plurality of content key data encrypted with a plurality of distribution key data valid for each predetermined usage period of the content data are connected to the network. A communication unit that receives secure container data having encrypted data and distribution key data that is valid during a purchase period among the plurality of distribution key data;
Content encrypted with the distribution key data out of the encrypted data of the plurality of content key data included in the received secure container data, using the distribution key data valid for the received purchase period A content key decrypting unit for decrypting the encrypted data of the key data;
A content processing apparatus comprising: a content decrypting unit configured to decrypt the content data of the secure container data using content key data decrypted using distribution key data valid during the purchase period.
前記複数の配信用鍵データのうちの、購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを受信する通信部と、
受信した前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて、記憶されている前記セキュアコンテナデータに含まれる前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データのうちの、当該配信用鍵データにより暗号化されたコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを復号するコンテンツ鍵復号部と、
前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて復号されたコンテンツ鍵データを用いて、前記セキュアコンテナデータの前記コンテンツデータを復号するコンテンツ復号部と
を有するコンテンツ処理装置。Secure container data having content data encrypted with content key data and encrypted data of a plurality of content key data encrypted with a plurality of distribution key data valid for each predetermined usage period of the content data A storage unit capable of storing;
Of the plurality of distribution key data, a communication unit that receives distribution key data effective during a purchase period;
Using the received distribution key data valid during the purchase period, the encrypted data of the plurality of content key data included in the stored secure container data is encrypted with the distribution key data. A content key decrypting unit for decrypting encrypted data of the content key data,
A content processing apparatus comprising: a content decrypting unit configured to decrypt the content data of the secure container data using content key data decrypted using distribution key data valid during the purchase period.
前記複数の配信用鍵データのうちの、購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを受信する通信部と、
受信した前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて、読み取られる前記セキュアコンテナデータに含まれる前記複数のコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データのうちの、当該配信用鍵データにより暗号化されたコンテンツ鍵データの暗号化データを復号するコンテンツ鍵復号部と、
前記購入期間に有効な配信用鍵データを用いて復号されたコンテンツ鍵データを用いて、前記セキュアコンテナデータの前記コンテンツデータを復号するコンテンツ復号部と
を有するコンテンツ処理装置。Secure container data having content data encrypted with content key data and encrypted data of a plurality of content key data encrypted with a plurality of distribution key data valid for each predetermined usage period of the content data A reading unit capable of reading the recorded recording medium;
Of the plurality of distribution key data, a communication unit that receives distribution key data effective during a purchase period;
Content encrypted with the distribution key data out of the encrypted data of the plurality of content key data included in the secure container data read using the distribution key data valid for the received purchase period A content key decrypting unit for decrypting the encrypted data of the key data;
A content processing apparatus comprising: a content decrypting unit configured to decrypt the content data of the secure container data using content key data decrypted using distribution key data valid during the purchase period.
Priority Applications (9)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000126305A JP4599657B2 (en) | 1999-07-07 | 2000-04-21 | Data providing system, content providing apparatus, and content processing apparatus |
| EP00944282A EP1120715A4 (en) | 1999-07-06 | 2000-07-06 | Data providing system, device, and method |
| KR1020017002903A KR100721078B1 (en) | 1999-07-06 | 2000-07-06 | Data processing device, data providing system, and data providing method |
| CNB008015910A CN1304977C (en) | 1999-07-06 | 2000-07-06 | Data providing system, device, and method |
| KR1020067027607A KR100751199B1 (en) | 1999-07-06 | 2000-07-06 | Management device and data processing device |
| US09/786,516 US7073073B1 (en) | 1999-07-06 | 2000-07-06 | Data providing system, device, and method |
| CNA2006101667342A CN1967559A (en) | 1999-07-06 | 2000-07-06 | Data providing system, method therefor and control device therefor |
| PCT/JP2000/004488 WO2001002968A1 (en) | 1999-07-06 | 2000-07-06 | Data providing system, device, and method |
| US11/397,002 US7886159B2 (en) | 1999-07-06 | 2006-04-03 | Data providing system and apparatus and methods of same |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP19356299 | 1999-07-07 | ||
| JP11-193562 | 1999-07-07 | ||
| JP2000126305A JP4599657B2 (en) | 1999-07-07 | 2000-04-21 | Data providing system, content providing apparatus, and content processing apparatus |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2001075924A JP2001075924A (en) | 2001-03-23 |
| JP2001075924A5 JP2001075924A5 (en) | 2007-04-26 |
| JP4599657B2 true JP4599657B2 (en) | 2010-12-15 |
Family
ID=26507947
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000126305A Expired - Fee Related JP4599657B2 (en) | 1999-07-06 | 2000-04-21 | Data providing system, content providing apparatus, and content processing apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4599657B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002358092A (en) * | 2001-06-01 | 2002-12-13 | Sony Corp | Voice synthesizing system |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07131452A (en) * | 1993-11-04 | 1995-05-19 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Digital information protection method and its processor |
| JPH08181965A (en) * | 1994-12-26 | 1996-07-12 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Electronic rental system |
| JPH09507598A (en) * | 1994-10-10 | 1997-07-29 | フィリップス エレクトロニクス ネムローゼ フェンノートシャップ | Database system with local information supported by remote dynamic information |
| JPH10512074A (en) * | 1995-02-13 | 1998-11-17 | インタートラスト テクノロジーズ コーポレイション | System and method for secure transaction management and electronic rights protection |
| JPH11507774A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1999-07-06 | スピラス インコーポレイテッド | Access control system and method for data storage medium |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE504085C2 (en) * | 1995-02-01 | 1996-11-04 | Greg Benson | Methods and systems for managing data objects in accordance with predetermined conditions for users |
| JPH1041933A (en) * | 1996-07-22 | 1998-02-13 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | Decoder |
-
2000
- 2000-04-21 JP JP2000126305A patent/JP4599657B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07131452A (en) * | 1993-11-04 | 1995-05-19 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Digital information protection method and its processor |
| JPH09507598A (en) * | 1994-10-10 | 1997-07-29 | フィリップス エレクトロニクス ネムローゼ フェンノートシャップ | Database system with local information supported by remote dynamic information |
| JPH08181965A (en) * | 1994-12-26 | 1996-07-12 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Electronic rental system |
| JPH10512074A (en) * | 1995-02-13 | 1998-11-17 | インタートラスト テクノロジーズ コーポレイション | System and method for secure transaction management and electronic rights protection |
| JPH11507774A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1999-07-06 | スピラス インコーポレイテッド | Access control system and method for data storage medium |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2001075924A (en) | 2001-03-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR100751199B1 (en) | Management device and data processing device | |
| US8095578B2 (en) | Data processing system and method therefor | |
| KR100798199B1 (en) | Data processing apparatus, data processing system, and data processing method therefor | |
| JP2001175606A5 (en) | ||
| KR100682290B1 (en) | Contents management system, device, method, and program storage medium | |
| US7376624B2 (en) | Secure communication and real-time watermarking using mutating identifiers | |
| US6996544B2 (en) | Multiple party content distribution system and method with rights management features | |
| US7310731B2 (en) | Contents processing system | |
| JP2001175605A (en) | Data processor | |
| WO2002080448A1 (en) | Information processing apparatus | |
| WO2001016776A1 (en) | Information transmission system, transmitter, and transmission method as well as information reception system, receiver and reception method | |
| JP2001094554A (en) | Information transmission system, information transmission device, information reception device, and information transmitting method | |
| JP2001022271A (en) | Data providing system, method therefor and control device therefor | |
| JP2001022844A (en) | System and method for providing data, managing device and data processor | |
| JP4599657B2 (en) | Data providing system, content providing apparatus, and content processing apparatus | |
| JP2001094549A (en) | Data providing system and its method | |
| JP2001094557A (en) | Data providing system and its method, data providing device, and data processor | |
| JP2002312243A (en) | Information processing device and method, recording medium and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070313 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070313 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100302 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100426 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100727 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100805 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20100831 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20100913 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131008 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131008 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |