KR20190016040A - Control and management of traffic signal system through VANET - Google Patents
Control and management of traffic signal system through VANET Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20190016040A KR20190016040A KR1020187037406A KR20187037406A KR20190016040A KR 20190016040 A KR20190016040 A KR 20190016040A KR 1020187037406 A KR1020187037406 A KR 1020187037406A KR 20187037406 A KR20187037406 A KR 20187037406A KR 20190016040 A KR20190016040 A KR 20190016040A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- traffic
- data
- aforementioned
- vanet
- vehicle
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/01—Detecting movement of traffic to be counted or controlled
- G08G1/0104—Measuring and analyzing of parameters relative to traffic conditions
- G08G1/0108—Measuring and analyzing of parameters relative to traffic conditions based on the source of data
- G08G1/0112—Measuring and analyzing of parameters relative to traffic conditions based on the source of data from the vehicle, e.g. floating car data [FCD]
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/01—Detecting movement of traffic to be counted or controlled
- G08G1/0104—Measuring and analyzing of parameters relative to traffic conditions
- G08G1/0125—Traffic data processing
- G08G1/0129—Traffic data processing for creating historical data or processing based on historical data
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/01—Detecting movement of traffic to be counted or controlled
- G08G1/0104—Measuring and analyzing of parameters relative to traffic conditions
- G08G1/0137—Measuring and analyzing of parameters relative to traffic conditions for specific applications
- G08G1/0145—Measuring and analyzing of parameters relative to traffic conditions for specific applications for active traffic flow control
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/07—Controlling traffic signals
- G08G1/08—Controlling traffic signals according to detected number or speed of vehicles
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/07—Controlling traffic signals
- G08G1/081—Plural intersections under common control
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/09—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions
- G08G1/095—Traffic lights
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/09—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions
- G08G1/0962—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions having an indicator mounted inside the vehicle, e.g. giving voice messages
- G08G1/0967—Systems involving transmission of highway information, e.g. weather, speed limits
- G08G1/096708—Systems involving transmission of highway information, e.g. weather, speed limits where the received information might be used to generate an automatic action on the vehicle control
- G08G1/096716—Systems involving transmission of highway information, e.g. weather, speed limits where the received information might be used to generate an automatic action on the vehicle control where the received information does not generate an automatic action on the vehicle control
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/09—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions
- G08G1/0962—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions having an indicator mounted inside the vehicle, e.g. giving voice messages
- G08G1/0967—Systems involving transmission of highway information, e.g. weather, speed limits
- G08G1/096708—Systems involving transmission of highway information, e.g. weather, speed limits where the received information might be used to generate an automatic action on the vehicle control
- G08G1/096725—Systems involving transmission of highway information, e.g. weather, speed limits where the received information might be used to generate an automatic action on the vehicle control where the received information generates an automatic action on the vehicle control
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/09—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions
- G08G1/0962—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions having an indicator mounted inside the vehicle, e.g. giving voice messages
- G08G1/0967—Systems involving transmission of highway information, e.g. weather, speed limits
- G08G1/096733—Systems involving transmission of highway information, e.g. weather, speed limits where a selection of the information might take place
- G08G1/096741—Systems involving transmission of highway information, e.g. weather, speed limits where a selection of the information might take place where the source of the transmitted information selects which information to transmit to each vehicle
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/09—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions
- G08G1/0962—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions having an indicator mounted inside the vehicle, e.g. giving voice messages
- G08G1/0967—Systems involving transmission of highway information, e.g. weather, speed limits
- G08G1/096733—Systems involving transmission of highway information, e.g. weather, speed limits where a selection of the information might take place
- G08G1/09675—Systems involving transmission of highway information, e.g. weather, speed limits where a selection of the information might take place where a selection from the received information takes place in the vehicle
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/09—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions
- G08G1/0962—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions having an indicator mounted inside the vehicle, e.g. giving voice messages
- G08G1/0967—Systems involving transmission of highway information, e.g. weather, speed limits
- G08G1/096766—Systems involving transmission of highway information, e.g. weather, speed limits where the system is characterised by the origin of the information transmission
- G08G1/096775—Systems involving transmission of highway information, e.g. weather, speed limits where the system is characterised by the origin of the information transmission where the origin of the information is a central station
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W84/00—Network topologies
- H04W84/18—Self-organising networks, e.g. ad-hoc networks or sensor networks
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Atmospheric Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
Abstract
도시의 교통신호시스템 (TLS)의 프로그래밍은 복잡한 최적화의 문제입니다. 실제 프로세스의 주된 문제점은 트래픽 흐름의 변화를 반영하기 위해 정기적으로 반복해야 하는 장기적이며 값비싸고 애매한 프로세스라는 것입니다. 본 발명품은 실시간으로 교통 데이터를 수집하고 교통관리시스템으로 전송하기 위한 차량 애드혹 네트워크 (VANET)의 활용을 통해 구성됩니다. VANET은 현재 IEEE 802.11p 표준으로 정의됩니다. TLS를 제어하기 위해 다른 기법들과 관련하여 VANET을 사용할 것을 제안합니다. 이 발명품은 실제 TLS를 보다 효율적으로 프로그래밍하고 실시간으로 네트워크를 관리하며 도시 계획 연구, 교통 계획 또는 특별 이벤트 (스포츠, 문화, 퍼레이드 등) 의 종료를 시뮬레이션 하는데 사용될 수 있습니다. 또한 존재하거나 개발될 효율적인 알고리즘을 통해 실시간으로 TLS를 프로그래밍할 수 있습니다.Programming the city's traffic signal system (TLS) is a matter of complex optimization. The main problem with real-world processes is that they are long-term, expensive and obscure processes that must be repeated regularly to reflect changes in the traffic flow. The present invention is configured through utilization of a vehicle ad hoc network (VANET) for collecting traffic data in real time and transmitting it to a traffic management system. VANET is currently defined by the IEEE 802.11p standard. We suggest using VANET in conjunction with other techniques to control TLS. This invention can be used to more effectively program actual TLS, manage the network in real time, and simulate the termination of urban planning studies, transportation plans or special events (sports, culture, parades, etc.). TLS can also be programmed in real time through efficient algorithms that exist or will be developed.
Description
본 발명은 유체 순환을 유발하기 위한 교통신호를 제어하고 관리하는데 사용되는 시스템의 분야에 속합니다.The present invention is in the field of systems used to control and manage traffic signals to cause fluid circulation.
기존의 현재 시스템 Existing current system
도시의 교통신호시스템 (TLS)의 프로그래밍은 복잡한 최적화의 문제입니다. 도시의 대부분의 TLS는 전자 기계 시스템 또는 마이크로 프로세서로 제어됩니다. 실시간으로 TLS를 제어하기 위해 설계된 시스템은 거의 없으며 우리가 알고 있는 바로는 어떠한 도시도 실시간으로 주요 TLS를 자동으로 제어할 수 없습니다.Programming the city's traffic signal system (TLS) is a matter of complex optimization. Most TLS in cities are controlled by electromechanical systems or microprocessors. Few systems are designed to control TLS in real time, and as we know, no city can automatically control major TLS in real time.
일반적으로 TLS의 프로그래밍 계획은 하루 그리고 한 주간 중 특정 기간에 (예: 15:00 ~ 18:00) 다시 프로그래밍됩니다. 이 계획은 이후 수년에 걸쳐 적용됩니다. 또한, 심지어 피크 기간에도, 차량의 흐름에 변화가 발생합니다. 차량의 도착이 푸아송 법칙과 같은 통계적 방법으로 시뮬레이션이 되기 때문에 이 방법론은 이러한 변화를 고려할 수 없습니다. 이 발명품은 매 0.1 초 혹은 이하의 시간 마다 각 차량의 위치와 속도를 제공하기 때문에 차량 이동의 정확한 분포 정보를 제공합니다. 또한 반감응 또는 완전 감응 시스템은 주기의 지속 시간을 변경할 수 있게 해주지만 포장 도로 아래에 루프 검지기를 설치해야 하며 이러한 시스템은 네트워크 전반에 걸쳐 설치되지 않습니다. 추가로 이러한 시스템을 유지하는데 상당한 비용이 소요됩니다. 이 발명품은 이러한 루프 검지기를 대체하고 거리 교차로에 있는 신호등을 관리하는 관리자에게 보다 정확한 정보를 제공합니다.In general, the programming plan for TLS is reprogrammed for a day and for a period of one week, such as 15:00 to 18:00. This plan will be applied over the next several years. In addition, even during peak periods, changes in vehicle flow occur. This methodology can not account for this change, since the arrival of a vehicle is simulated by statistical methods such as Poisson's Law. This invention provides precise distribution information of vehicle movement because it provides the position and speed of each vehicle every 0.1 second or less. Semi-sensitive or fully-sensitive systems also allow you to change the duration of the cycle, but you must install a loop detector under the pavement and these systems will not be installed across the network. In addition, maintaining these systems can be prohibitively expensive. This invention replaces these loop detectors and provides more accurate information to administrators managing traffic lights at street intersections.
TLS 프로그래밍을 위한 교통기술자협회 (ITE) 가 권장하는 현재 절차는 그림 1과 같습니다. 이는 복잡하고 길고 비용이 많이 드는 프로세스로 정기적으로 수정해야 합니다. 이 방법은 대부분의 도시, 기관 및 공공 행정 기관에서 사용되며 여전히 가장 신뢰할 수 있는 방법입니다. 이 프로세스는 과거의 순환 데이터를 가지고 처리됩니다. 교통 엔지니어와 운송 전문가가 적용할 시스템 프로그래밍은 이러한 데이터를 통해 결정합니다. 모델링은 일반적으로 특수 시뮬레이션 소프트웨어를 사용하여 수행됩니다. 이러한 소프트웨어는 다양한 최적화 시나리오를 모델링하고 성능 측정 (대기 시간, 평균 속도, 대기열의 길이 등) 정보를 제공할 수 있습니다. 이는 순환 전문가가 만족할만한 솔루션을 찾을 때까지 다양한 시나리오를 적용할 것을 필요로 하는 반복적인 과정입니다 The current procedure recommended by the Traffic Technicians Association (ITE) for TLS programming is shown in Figure 1. This is a complex, lengthy, and costly process that needs to be fixed on a regular basis. This method is used by most cities, institutions and public administration agencies and is still the most reliable method. This process is handled with past cyclical data. This data is used to determine system programming to be applied by the transportation engineer and the transportation specialist. Modeling is usually done using special simulation software. These software can model various optimization scenarios and provide information on performance measurements (latency, average speed, queue length, etc.). This is an iterative process that requires cycling experts to apply various scenarios until they find a satisfactory solution
. 최상으로 보이는 솔루션은 그대로 유지되고 현장에서 구현하기 전에 다시 유효성을 검사합니다 (그림 1, 구현 및 미세 조정 참조). 프로그래밍은 하나 또는 다수의 교차로에서 수행됩니다. TLS 계획이 수립되면 수년 동안 변경되지 않습니다.. The best-looking solution remains intact and validated again before implementation in the field (see Figure 1, Implementation and Fine-tuning). Programming is done at one or many intersections. Once a TLS plan is established, it will not change for many years.
ITE 프로세스의 핵심 요소는 현장, 출발지-목적지 조사 혹은 그 외 수단으로 수집한 데이터의 신뢰성에 기반하고 있습니다. The key elements of the ITE process are based on the reliability of data collected by field, source-destination surveys or other means.
모든 현대 기술이 사용 가능하더라도 일부 연구는 수동으로 수행하는 것이 최선입니다. 자동화 장비를 사용하려면 실용적이지 않을 수 있는 설치와 노력이 필요합니다. 특정 유형의 정보는 직접 수동적인 관찰 없이는 얻기가 어렵습니다. 예를 들어 교차로에서의 회전은 직접 수동적인 관찰 없이는 추적하기가 어렵습니다. 차량의 크기는 차량 클래스 (트럭, 버스, 승용차)를 판단하는데 활용할 수 있지만 개인 승용차와 택시의 차이 등은 식별할 수 없습니다. 수동 관찰은 데이터의 기록을 지원하는 다양한 휴대용 장치 (핸즈 카운터, 레이더 미터 등)나 데이터를 기록할 수 있는 종이 양식을 사용하여 완전한 수동 방식을 활용하여 진행할 수 있습니다. 반자동화 방법은 주로 공압 도로 튜브와 이러한 튜브에 연결할 수 있는 광범위하게 다양한 기록 장치의 사용에 우선적으로 의존합니다. 이러한 장치는 일반적으로 이동이 가능하므로 다른 위치로 이동할 수 있습니다. 기타 휴대용 장치도 사용할 수 있습니다. 완전 자동화된 연구는 일반적으로 고정식 또는 이동식 컴퓨터 스테이션과의 연결과 함께 영구적으로 설치된 다양한 검출기 또는 센서를 적극 활용합니다. 또한 동일한 영구 검출기 및 센서가 감응 및/또는 적응 신호를 작동하는 데 사용됩니다. 센서 기술의 성장은 이처럼 이러한 장치를 대규모 네트워크에 설치하는 방향으로 나아가고 있습니다.Although all modern technology is available, it is best to do some research manually. Automation equipment requires installation and effort that may not be practical. Certain types of information are difficult to obtain without direct manual observation. For example, rotation at an intersection is difficult to track without direct manual observation. The size of the vehicle can be used to determine the class of the vehicle (truck, bus, passenger car), but can not identify the difference between a private car and taxi. Manual observations can be carried out using fully manual methods using a variety of portable devices (hands-free counters, radar meters, etc.) that support the recording of data or paper forms that can record data. Semi-automated methods primarily rely on the use of pneumatic road tubes and a wide variety of recorders that can be connected to these tubes. These devices are generally portable and can be moved to other locations. Other portable devices are also available. Fully automated research generally utilizes a variety of permanently installed detectors or sensors with connection to stationary or mobile computer stations. The same permanent detectors and sensors are also used to operate the sensitive and / or adaptive signals. The growth of sensor technology is moving toward the deployment of these devices in large networks.
(참조: 트래픽 엔지니어링 매뉴얼, 제4판, Roger P. Roess, Elena S. Prassas, William R. McShane, ch. 8, 2011).(See: Traffic Engineering Manual, Fourth Edition, Roger P. Roess, Elena S. Prassas, and William R. McShane, ch. 8, 2011).
이 발명품은 완전히 다른 패러다임을 기반으로 합니다. 더 이상 차량의 위치 또는 교통의 흐름을 확인하는 것은 센서 또는 다른 장치가 아니라 매 순간마다 위치, 속도 및 기타 정보를 시스템에 전송하는 차량입니다. 따라서 트래픽 데이터를 얻기 위해 더 이상 수동으로 셈을 하거나 센서를 설치할 필요가 없습니다. 수동으로 셈을 하거나 대규모 센서를 설치하지 않고도 트래픽 데이터를 보다 정확하게 수집할 수 있습니다. This invention is based on a completely different paradigm. It is no longer a sensor or other device to check the position of a vehicle or the flow of traffic, but rather the vehicle that transfers position, speed and other information to the system every moment. So you no longer have to manually compute or install sensors to get traffic data. You can collect traffic data more accurately without having to manually compute or install a large sensor.
데이터 수집의 목표는 특정 위치로 통과하는 차량의 수를 세는 것입니다. 각 교차로를 통과하고 양방향으로 통과하는 차량의 수를 수동으로 산정하기 위해 현장에 기술자를 보내는 것도 간혹 필요합니다. The goal of data collection is to count the number of vehicles passing through to a specific location. It is sometimes necessary to send an engineer to the site to manually estimate the number of vehicles passing through each intersection and in both directions.
이러한 데이터는 수단을 확립하고 가능한 현실을 유사하게 반영하는데 사용됩니다. 이러한 데이터는 시뮬레이션 또는 계산에 사용될 순환의 흐름을 대략적으로 나타냅니다.These data are used to establish the means and reflect similarly as possible reality. This data roughly represents the flow of the circulation to be used in the simulation or calculation.
본 발명품에서 신호등은 VANET으로 수집된 데이터를 사용하여 프로그래밍할 수 있습니다. 따라서 이러한 데이터를 수동으로 수집하거나 센서를 설치하기 위해 현장에 가지 않아도 됩니다. 또한, TLS는 VANET에서 수집한 데이터의 기능에 따라 정기적으로 또는 필요에 따라 업데이트될 수 있습니다.In the present invention, the traffic lights can be programmed using data collected by the VANET. Therefore, you do not have to go to the site to collect these data manually or install a sensor. In addition, TLS can be updated on a regular basis or as needed, depending on the functionality of the data collected by VANET.
본 발명품The present invention
본 발명품은 이 문서에서 그림을 통해 제안하는 데이터 수집 과정과 데이터의 독창적인 사용과 구체적으로 관련성이 있습니다; 이 발명품으로 인해 도로에 머물면서 데이터를 수집 할 사람이 더이상 필요하지 않습니다. 데이터는 VANET을 사용하여 수집되며 데이터베이스에서 활용됩니다.This invention is specifically relevant to the data collection process proposed and the creative use of the data in this document; This invention no longer requires people to stay on the road and collect data. The data is collected using VANET and utilized in the database.
본 발명품은 무엇보다도 현재의 TLS를 프로그래밍하기 위해 VANET으로 트래픽 데이터를 수집하고자 구성되었습니다. 현재의 TLS의 프로그래밍은 현장에서 측정된 과거의 교통의 흐름 데이터(예: 수동 계산)에 기반하고 있습니다. 본 발명품은 VANET을 사용하여 이러한 교통 데이터를 수집하여 현재의 (검출 루프와 함께 정적인 또는 적응적인) TLS를 프로그래밍하는데 사용하기 위해 구성되었습니다. 본 발명품은 도시, 정부 기관 또는 공공 행정 기관에서 사용하는 방법보다 경제적으로 보다 정확한 데이터를 수집할 수 있습니다.The present invention is designed to collect traffic data with VANET to program current TLS. The programming of current TLS is based on historical traffic flow data measured in the field (eg manual calculation). The present invention has been configured for use with VANET to collect such traffic data and to program the current TLS (static or adaptive with detection loop). The present invention is more economical and more accurate than the methods used by cities, government agencies, or public administration agencies.
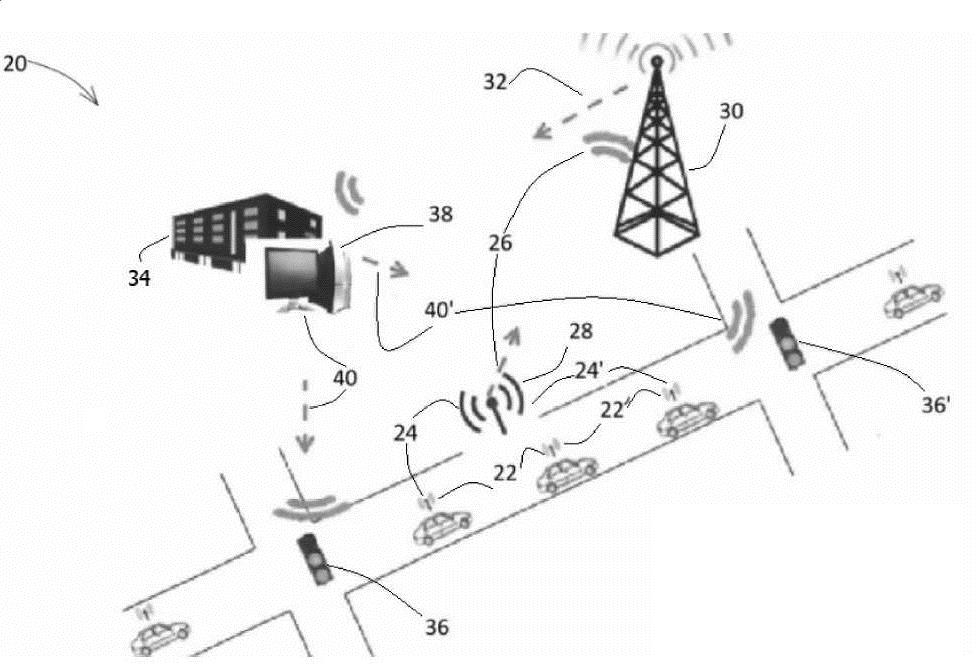
VANET이 2000년초에 발명된 주된 이유는 도로 상의 안전을 개선시키기 위해서였습니다. 이는 (예를 들어) 차량의 운전자에게 정보를 제공함으로서 가능합니다. 본 발명품은 트래픽 데이터를 수집하고 교통관리시스템으로 전송하기 위한 차량 애드혹 네트워크 (VANET)의 활용으로 구성됩니다. 이는 VANET에서 처음 계획한 것과 동일한 용도는 아닙니다. VANET은 현재 IEEE 802.11p 표준으로 정의됩니다. VANET에서 모든 차량은 임시 네트워크의 노드 역할을 합니다. 각 차량은 약 300미터 이내의 범위에서 다른 차량으로부터 상태 관련 정보를 매 분할 초 (0.1초 혹은 이하) 마다 수신할 수 있습니다. VANET에서 이용 가능한 정보는 각 차량의 속도, 가속도, 위치, 제동 시스템 등에 관한 정보입니다. 이 정보는 도로를 따라 설치된 통신 스테이션 ― 노변 장치 (RSU) 로 전송되어 기지국으로 전달됩니다 (그림 2 참조). 이를 차량과 차량 간 (V2V), 차량과 인프라 간 (V2I) 그리고 인프라와 인프라 간 (I2I)의 통신 모드라고 합니다. VANET은 전용 주파수 스펙트럼 75 MHz 대역폭과 정부 당국에서 할당된 5.9 GHz에서 작동합니다. 또한 VANET은 다양한 기상 조건 (비, 안개, 눈)에서도 작동할 수 있습니다.The main reason VANET was invented in early 2000 was to improve road safety. This is possible, for example, by providing information to the driver of the vehicle. The invention consists of utilizing a vehicle ad hoc network (VANET) to collect traffic data and transmit it to a traffic management system. This is not the same as originally planned for VANET. VANET is currently defined by the IEEE 802.11p standard. In VANET, every vehicle acts as a node in the ad hoc network. Each vehicle can receive status-related information from other vehicles in every second (0.1 second or less) within a range of about 300 meters. The information available on the VANET is information on the speed, acceleration, position, braking system, etc. of each vehicle. This information is sent to the communication station-RSU (RSU) installed along the road and forwarded to the base station (see Figure 2). This is called the communication mode between vehicle and vehicle (V2V), between vehicle and infrastructure (V2I), and between infrastructure and infrastructure (I2I). VANET operates at a dedicated frequency spectrum of 75 MHz bandwidth and 5.9 GHz allocated by the government authority. VANET can also operate in a variety of weather conditions (rain, fog, snow).
IEEE 802.11p 표준은 IEEE 802.11 표준을 수정한 것입니다. 유럽, 아시아 또는 그 외 대륙에서는 세계의 일부 국가 또는 지역에서는 다를 수 있는 국제 표준화 기관의 규정에 따라 표준을 조정하거나 명칭을 변경할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 유럽에서는 802.11p가 차량 및 인프라를 위한 GeonetWorking 프로토콜을 지원하는 표준 ITS-G5의 기반으로 사용되었습니다. 국제 표준화 기관의 의도는 VANET과 관련된 표준을(명칭에 상관없이) 가능한 한 호환이 되도록 만드는 것입니다.The IEEE 802.11p standard is a modification of the IEEE 802.11 standard. In Europe, Asia, or other continents, standards may be adjusted or changed in accordance with the rules of an international standardization body that may be different in some countries or regions of the world. For example, in Europe, 802.11p was used as the basis for the standard ITS-G5, which supports the GeonetWorking protocol for vehicles and infrastructure. The intent of the international standardization body is to make the VANET-related standards (regardless of their name) as compatible as possible.
이 기술을 활용하여 데이터를 수집하고 제어 센터에 설치된 시스템에 전달할 것을 제안합니다 (그림 3 및 기타). 그 후 이 데이터를 사용하여 이전에 설명되었고 그림 1에 보이는 ITE 프로세스에서 순환 전문가가 실제로 활용하는 것처럼 TLS의 프로그래밍을 위한 다양한 시나리오를 테스트하는데 사용할 수 있습니다. 또한 도시 연구와 같은 다른 용도로도 이러한 데이터를 사용할 수도 있습니다. We suggest using this technology to collect the data and pass it on to the systems installed in the Control Center (Figure 3 and others). This data can then be used to test various scenarios for programming TLS as previously described and actually utilized by cycling experts in the ITE process shown in Figure 1. You can also use this data for other purposes, such as urban research.
데이터 수집 방법과 시스템 아키텍처는 독일 베를린에 있는 독일항공우주센터 DLR에서 열린 2016 SUMO 컨퍼런스에서 발표된 기사에 설명되어 있습니다 (VANET를 통한 신호등 관리 시스템의 개선, Francois Vaudrin, eng., Laval University and Laurence Capus, Ph.D., Laval University, Conference SUMO 2016 - 트래픽, 이동성, 물류, 절차, 베를린). Data collection methods and system architecture are described in an article published at the 2016 SUMO conference at the German Aerospace Center DLR in Berlin, Germany (Francois Vaudrin, eng., Laval University and Laurence Capus , Ph.D., Laval University, Conference SUMO 2016 - Traffic, Mobility, Logistics, Procedures, Berlin).
어떠한 발명품, PCT, 특허 또는 출원 중인 특허도 본 발명품과 같이 신호등 시스템의 프로그래밍을 위해 시행 중인 표준 및 방법론을 기반으로 정확하고 기능적인 결과물을 제공하지 못합니다.No invention, PCT, patents or pending patents provide accurate and functional results based on the standards and methodologies in force for the programming of traffic light systems, such as the present invention.
어떠한 발명품, PCT, 특허 또는 출원 중인 특허도 VANET의 데이터를 사용하여 실제 적응 시스템과 동일한 작업을 수행하는 본 발명품과 같이 정확하고 기능적인 결과물을 제공하지 못합니다.No invention, PCT, patents or pending patents provide accurate and functional results, such as the present invention, using the data of VANET to perform the same tasks as the actual adaptation system.
어떠한 발명품, PCT, 특허 또는 출원 중인 특허도 실시간으로 TLS를 관리 및 제어하기 위해 VANET의 데이터를 사용하는 본 발명품과 같이 정확하고 기능적인 결과물을 제공하지 못합니다.No invention, PCT, patent or pending patent can provide accurate and functional results, such as inventions using VANET data to manage and control TLS in real time.
어떠한 발명품, PCT, 특허 또는 출원 중인 특허도 교통 경찰관들과 순환 및 TLS를 통제하는데 도움을 주기 위해 VANET의 데이터를 사용하는 본 발명품과 같이 정확하고 기능적인 결과물을 제공하지 못합니다.No invention, PCT, patents or pending patents provide accurate and functional results, such as inventions using data from VANET to help control circulation and TLS with traffic policemen.
어떠한 발명품, PCT, 특허 또는 출원 중인 특허도 다양한 도시 연구를 위해 VANET의 데이터를 사용하는 본 발명품과 같이 정확하고 기능적인 결과물을 제공하지 못합니다.No invention, PCT, patent, or pending patent can provide accurate and functional results, such as the invention using VANET data for various urban studies.
본 발명품의 장점Advantages of the present invention
본 발명품은 기존의 방법보다 정확하고 완전합니다. 본 발명품은 시뮬레이션을 위한 더 많은 데이터를 수집하고 ITE 프로세스를 준수하게 해줄 것입니다. The present invention is more accurate and complete than the existing methods. The present invention will collect more data for the simulation and make it compliant with the ITE process.
또한 현장에서 수동으로 셈을 하거나 센서와 카메라 및 루프 감지기와 같은 기타 고가의 장비를 설치하여 순환 데이터를 수집할 필요가 있습니다. 이러한 값비싼 프로세스는 더 이상 이 발명품으로 인해 필요하지 않습니다. 본 발명품의 방법을 통한 데이터의 수집은 더욱 간단하고 비용이 저렴하며 유지 보수가 거의 필요하지 않습니다. You may also need to manually calculate in the field or install other expensive equipment such as sensors and cameras and loop detectors to collect circular data. These expensive processes are no longer required by this invention. The collection of data through the inventive method is simpler, less costly, and requires little maintenance.
이 발명품의 장점은 매 분할 초마다 다수의 매개 변수를 구할 수 있다는 것입니다 (각 차량의 속도, 위치, 각 차량 사이의 거리 등). 공공 행정기관은 프로그래밍 계획을 원하는만큼 자주 수정할 수 있습니다. 변화가 관측되는 경우 시스템이 실시간으로 데이터를 제공하기 때문에 현장으로 돌아가서 새로 측정할 필요없이 신속하게 시뮬레이션을 수행할 수 있습니다.The advantage of this invention is that a large number of parameters can be obtained (every vehicle speed, position, distance between each vehicle, etc.) every second. Public administrations can modify their programming plan as often as they like. When changes are observed, the system provides real-time data, so you can go back to the scene and quickly simulate without having to take a new measurement.
본 발명품은 특정 알고리즘에 대한 권리를 주장하지 않지만 실제 TLS (루프 탐지 기능을 갖춘 정적 또는 적응적 TLS)를 프로그래밍하거나 실시간으로 TLS를 제어하는 새로운 알고리즘을 개발하기 위한 정확한 정보와 데이터를 제공하는 (특히 인공 지능 분야에서) 혁신적인 방법임을 주장합니다.The present invention does not claim a right for a particular algorithm, but it does not claim the right to a particular algorithm, but provides accurate information and data for programming a real TLS (static or adaptive TLS with loop detection capability) or developing a new algorithm for controlling TLS in real time In the field of artificial intelligence).
이러한 매개 변수는 현재 사용할 수 없으며 순환, 운송 및 컴퓨터 전문가들이 보다 정확한 모델을 만들고 새롭고 효율적인 알고리즘을 개발할 수 있도록 해줄 것입니다. These parameters are currently not available and will allow circulation, transportation, and computer professionals to create more accurate models and develop new and efficient algorithms.
본 발명품은 시뮬레이션 소프트웨어에 의해 검증된 효과적인 알고리즘을 구현하는 데 필요한 요소들을 제공합니다. 본 발명품은 실제로 복잡한 TLS 네트워크의 관리를 가능하게 해줍니다.The present invention provides the elements necessary to implement effective algorithms validated by simulation software. The present invention enables the management of complex TLS networks in practice.
제어 센터로 데이터를 전송하고 제어 센터는 적절한 알고리즘으로 이를 처리하고 전용 인터넷 네트워크를 사용하여 각 교차로에 설치된 무선 장치에 지침을 전송합니다. Data is sent to the Control Center, which then processes it with the appropriate algorithms and sends instructions to the wireless devices installed at each intersection using a dedicated Internet network.
본 발명품은 공공 행정 기관이 자체 작업 방법을 사용하면서 인프라를 크게 변경하지 않으며 구현할 수 있도록 충분히 상세히 설명되어 있습니다. The invention has been described in sufficient detail to enable the public administration to implement its own work method without significantly changing the infrastructure.
이 방법은 또한 도시 계획 연구, 교통 계획 또는 특별 이벤트 (스포츠, 문화, 축제, 퍼레이드 등)의 종료를 시뮬레이션하기 위해 다른 상황에서도 사용할 수 있습니다. 쉬운 식별을 위해 동일한 번호는 동일한 부분을 나타내는 그림을 참조하며 다음의 설명을 통해 본 발명품을 더욱 쉽게 이해 할 수 있습니다.This method can also be used in other situations to simulate the termination of urban planning studies, transportation plans or special events (sports, culture, festivals, parades, etc.). For ease of identification, the same number refers to the figure that represents the same part, and the invention is more readily understood with the following description.
그림.1은 선행 기술에서 비롯된 신호 타이밍 환경의 계획서입니다.
그림.2는 차량 애드혹 네트워크 (VANET) 시스템의 보기입니다.
그림.3은 현재 발명품의 보기입니다.
그림.4는 교통 경찰관이 순환을 제어하는데 도움을 주는 현재 발명품의 보기입니다.
그림. 5는 데이터를 저장하고 현재의 TLS를 프로그램 하는데 사용되는 본 발명품의 보기입니다. Figure 1 is a proposal for a signal timing environment from prior art.
Figure 2 is an example of a vehicle ad hoc network (VANET) system.
Figure 3 is a view of the present invention.
Figure 4 is a view of the current invention that helps a traffic police officer to control the circulation.
Drawing. 5 is an example of the invention used to store data and program the current TLS.
다음의 설명과 함께 제공되는 그림에서 숫자는 다양한 그림에서의 동일한 부분을 나타냅니다.In the figures provided with the following explanations, the numbers represent the same parts in the various figures.
그림. 1은 2009년 “교통 엔지니어 연구소” 가 발행한 교통 신호 타이밍 매뉴얼의 신호 시간 프로세스 계획 18을 보여줍니다. 이 그림은 현재의 신호등 시스템 프로세스를 개발하기 위해 실현 될 보여줍니다, 프로그램 및 현재의 (검출 루프 기능이 있는 정적 또는 적응) 교통신호시스템을 개발, 프로그램 그리고 구현하기 위해 실현해야 하는 프로세스를 보여줍니다. . 이 프로세스는 교통 제어 및 TLS을 위한 규범, 표준, 규정, 운송 법률, 특정 지역의 고려 사항, 운영 및 유지 관리 규정 그리고 국제적으로 인정되는 방법을 준수합니다. Drawing. 1 shows the signaling
그림 .2는 VANET (차량의 애드혹 네트워크) 의 작동 방식을 보여 줍니다. 세 가지 종류의 상호 통신 방식이 있습니다: Figure 2 shows how the VANET (ad hoc network of vehicles) works. There are three types of intercommunication:
-
차량 간 통신 22,22' 각 차량은 약 300미터 이내의 범위에서 다른 차량으로부터 상태 관련 정보를 매 분할 초 (0.1초 혹은 이하) 마다 수신할 수 있습니다. - Inter -
- 이 정보는 도로를 따라 설치된 통신국 (노변 장치 - RSU)으로 전송되며 24,24" 이는 차량과 노변 간의 통신입니다. - This information is transmitted to a communication station (RSU) installed along the road. 24,24 " This is the communication between the vehicle and the roadside.
-
그리고 기지국으로의 도로 RSU의 전달 정보를 30따라 설치된 통신국 26 (노변 간 통신). - and the
이러한 데이터는 속도, 가속도, 제동 시스템 등의 정보입니다. 이 정보는 일반적인 방법 (예: 수동 계산, 탐지 루프 또는 출발지-목적지 조사)으로 수집한 데이터보다 훨씬 정확합니다. 또한 운전자들을 향한 교통 경찰관의 통신 간 신호인 25가 있으며 이는 RSU를 향한 교통 경찰관의 통신인 25'와 기지국 30을 향한 교통 경찰관 통신인 25''입니다.These data are information such as speed, acceleration, and braking system. This information is much more accurate than the data collected in the usual way (eg manual calculation, detection loop or source-destination survey). There is also a communication between a
그림 3은 신호등을 지시하는데 사용되는 본 발명품의 방법20을 보여줍니다; 각 차량은 데이터 22,22 '를 도로의 다른 차량에 전송하거나 24, 24'를 RSU 28로 전송하고, 교통 신호등 36,36'를 각각 프로그램 하는데 사용되는 신호 40,40' 를 생성하는 알고리즘 38을 운영하는 컴퓨터 제어 센터 34로 전송됩니다. 첫 번째 단계는 VANET의 단계입니다: 각 차량이 제공 및 교환하는 데이터는 22,22' 는 도로 측 장비 안테나 28로 전송되고 24,24', 도로 측 장비 안테나는 신호 26을 기지국 30으로 보냅니다. 기지국은 신호 32를 제어 센터 34에 전송합니다. Figure 3 shows a
그림 4는 스포츠 이벤트, 문화, 퍼레이드, 공사 동요, 시위 등과 같은 이벤트가 진행 시 순환을 관리하는데 사용되는 본 발명품의 방법을 보여줍니다; 컴퓨터 제어 센터 34는 기지국 30에서 수신한 데이터 32를 분석하고 40,40'신호를 각 교통 경찰관 42,42'에게 보내어 이벤트가 진행 시 수동으로 트래픽을 관리합니다. 또한 차량 간 통신 22, 22'를 보고 각 차량은 약 300미터 이내의 범위에서 다른 차량으로부터 상태 관련 정보를 매 분할 초 (0.1초 혹은 이하) 마다 수신할 수 있습니다. 앞서 언급한 정보는 도로를 따라 설치된 도로 노변 장치 28에 전송되고24 도로 RSU 전달 정보는 26 교통을 수동으로 제어하기 위해 TLS가 작동하지 않는 동안 수동으로 교통을 지시하도록 해주는 신호를 제공하기 위해 컴퓨터 제어 센터로 이러한 정보를 32 전송한 기지국 30 (도로간 통신)에 전달됩니다. Figure 4 shows how the invention can be used to manage cycling events such as sporting events, culture, parades, construction fluctuations, demonstrations, etc.; The
그림. 5 제어 센터 34,에서의 데이터베이스 기호 44를 보여주며 기지국 30이 제공하는 트래픽 데이터 32는 데이터베이스 44에 저장되고, 이러한 데이터는 시뮬레이터에서 시뮬레이션을 수행하거나 현재 정적 및 적응형 시스템에 수행되는 방식으로 TLS를 프로그래밍하는 작업 등에 사용할 수 있습니다. 이러한 데이터는 또한 도시 연구에도 사용될 수 있습니다. 또한 차량 간 통신 22, 22'를 보고 각 차량은 약 300미터 이내의 범위에서 다른 차량으로부터 상태 관련 정보를 매 분할 초 (0.1초 혹은 이하) 마다 수신할 수 있습니다. 앞서 언급한 정보는 통신국, 도로를 따라 설치된 도로 측 장치로 전송되며 24,24' 이는 차량과 노변간의 통신입니다. 그리고 도로 RSU 전달 정보26 은 이러한 정보를 32 컴퓨터 제어 센터와 데이터베이스 44로 전송한 기지국 30(노변간 통신)에 전송됩니다. 이 데이터베이스는 데이터를 저장하고 데이터를 가지고 현재 정적 및 적응 시스템에 수행되는 방식과 같이 시뮬레이션을 수행하는데 사용됩니다. 이러한 데이터는 또한 도시 연구에도 사용될 수 있습니다. Drawing. 5 shows the
본 발명품의 요약SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
본 발명품은 차량 애드혹 네트워크(축약해서 VANET), 시스템 혹은 다음의 단계로 구성된 방법을 통해 제공되는 데이터를 사용하여 신호등을 프로그래밍하는 방법입니다:The present invention is a method of programming a traffic light using data provided through a vehicle ad hoc network (abbreviated as VANET), a system, or a method comprising the following steps:
a. VANET에서 신호등 시스템의 프로그래밍에 개입하는데 사용되는 알고리즘을 운영하는 컴퓨터 제어 센터로 데이터를 전송합니다. 이러한 데이터는 무선 통신탑을 통해 컴퓨터 제어 센터 또는 노변 장치로 전송될 수 있습니다. 전송의 주파수는 VANET의 작동에서와 같이 현행 표준 IEEE.802.11p에 의거하여 승인된 주파수일 수 있습니다. 이러한 표준은 VANET의 책임 당국에 의해 시간이 지남에 따라 수정, 개정, 업데이트 또는 교체될 수 있습니다. a. VANET transmits data to a computer control center that operates the algorithms used to intervene in the programming of the traffic light system. Such data can be transmitted to the computer control center or the sidewalk device via a radio tower. The frequency of the transmission may be an approved frequency in accordance with the current standard IEEE 802.11p, as in the operation of the VANET. These standards may be modified, revised, updated or replaced over time by the responsible authority of VANET.
b. 알고리즘을 사용하여 이러한 데이터를 처리합니다. 각 도로 구간의 평균 점유율에 기반한 알고리즘이 (예를 들어) 사용될 수 있지만 어떠한 정확한 알고리즘도 도시, 정부 기관 또는 공공 행정 기관의 선택에 따라 사용될 수 있습니다. b. We use algorithms to process these data. An algorithm based on the average occupancy of each road segment can be used (for example), but any exact algorithm can be used at the choice of city, government agency or public administration.
c. 컴퓨터 제어 센터와 신호등 시스템 사이에 보안 통신 시스템을 구축합니다. 전용 인터넷 네트워크 또는 무선 통신은 이 단계에서 사용될 수 있는 보안 통신 시스템입니다. 이 보안 통신 시스템은 광섬유일수도 있고 혹은 암호화되거나 인식되는 유효한 보안 방식일수도 있습니다. c. Establish a secure communication system between the computer control center and the traffic light system. A dedicated Internet network or wireless communication is a secure communication system that can be used at this stage. This secure communication system may be fiber optic or it may be a valid security method that is encrypted or recognized.
d. 신호등을 지시하는 도로의 각 교차점에 무선 장치를 설치합니다. 이러한 신호등 시스템은 실제 시스템으로서 정적, 반감응 또는 완전 감응식이 될 수 있습니다. d. Install the wireless device at each intersection on the road that points to the traffic light. These traffic light systems can be static, semi-active or fully-active systems.
e. 보안 통신 시스템을 통해 알고리즘이 제공하는 신호를 무선 장치로 보냅니다. e. A secure communication system sends the signal provided by the algorithm to the wireless device.
본 발명품을 통해 신호 손실의 위험이 최소화됩니다. 본 발명품을 통해서 언제든지 데이터를 구할 수 있습니다. 이러한 데이터는 속도, 가속도, 제동 시스템 등과 관련된 정보입니다. VANET의 이러한 데이터는 0.1초의 최소 주파수로 실시간으로 컴퓨터 제어 센터로 전송할 수 있습니다. 이러한 데이터를 통해 교통 엔지니어 연구소 (그림 1)가 권장하는 프로세스에 따라 현행 TLS를 프로그래밍할 수 있습니다. 이러한 데이터와 이 시스템은 또한 실시간으로 TLS를 제어할 수 있도록 해줍니다.This invention minimizes the risk of signal loss. Data can be obtained at any time through this invention. These data are related to speed, acceleration, braking system, and so on. This data from the VANET can be transmitted to the computer control center in real time with a minimum frequency of 0.1 second. These data enable you to program your current TLS according to the process recommended by the Transportation Engineer Institute (Figure 1). This data and this system also allows you to control TLS in real time.
본 발명품은 스포츠 이벤트, 문화, 퍼레이드, 공사로 인한 혼란 또는 시위 등과 같은 이벤트가 진행 시 신호등을 관리하는데 사용됩니다. 이벤트가 진행될 시 교통을 통제하는 교통 경찰관들에게 포괄적인 필수 정보를 제공하기 위해 의사결정 센터가 마련됩니다. 본 발명품은 또한 도시 연구를 하고 운송 연구를 계획하는데 활용될 수 있습니다. The invention is used to manage traffic lights during events such as sports events, culture, parades, construction confusion or protests. A decision-making center is set up to provide comprehensive essential information to traffic police officers who control traffic when the event takes place. The invention can also be used for urban research and transportation research planning.
VANET에서 제공하는 데이터는 데이터베이스 44에 저장될 수 있으며 통계법 (예: 푸아송 법칙)에 근거한 현재의 가정 사항보다 실제 교통의 흐름과 운전자의 행동을 보다 정확하게 나타내기 위한 시뮬레이터에 사용될 수 있습니다. The data provided by the VANET can be stored in
이러한 데이터는 컴퓨터 제어 센터에서 교통 정보를 처리하고 차량 운전자에게 메시지를 전송하여 차량 주행을 조정하여 차량이 동시적으로 더욱 잘 순환할 수 있도록 함으로써 전체 순환의 유동성을 촉진하는데 사용됩니다.This data is used to facilitate the circulation of the entire cycle by allowing the vehicle to cycle more simultaneously by handling traffic information at the computer control center and by sending a message to the vehicle driver to adjust the vehicle's travel.
이러한 데이터는 상기 언급한 컴퓨터 제어 센터의 교통 정보를 처리하고 속도를 조정하고 교통 흐름을 촉진하기 위해 자율 주행차에 신호를 전송하는데 사용됩니다.These data are used to transmit the signals to autonomous vehicles to process the traffic information of the computer control center mentioned above, to adjust the speed and to facilitate traffic flow.
이러한 데이터는 상기 언급한 컴퓨터 제어 센터의 교통 정보를 처리하고 속도를 조정하고 교통 흐름을 촉진하기 위해 운전자에 신호를 전송하는데 사용됩니다.These data are used to signal traffic to the above-mentioned computer control center, to signal the driver to adjust the speed and facilitate traffic flow.
이러한 데이터는 상기 언급한 컴퓨터 제어 센터의 교통 정보를 처리하고 전체 교통의 유동성을 촉진하기 위해 신호등의 프로그래밍을 수정하기 위해 TLS에 신호를 전송하는데 사용됩니다.These data are used to signal the TLS to modify the programming of the traffic lights to process the above-mentioned computer control center traffic information and to facilitate the flow of the entire traffic.
본 발명품은 제어 센터의 교통 정보를 처리하고, 운전자에게 메시지를 전송하고, 자율 주행차에 신호를 전송하고, 신호등의 프로그래밍을 수정하고, 출입구에서 시스템을 제어하고, 자동차 도로를 빠져 나가고 교통의 흐름을 촉진하는데 사용됩니다. 본 발명품은 시행 중인 방법에 따라 정적 신호등 시스템을 프로그래밍하기 위해 수동으로나 센서를 통해 혹은 그 외의 수단으로 교통 데이터를 수집할 필요성을 대체해줍니다.The present invention processes the traffic information of the control center, transmits a message to the driver, transmits a signal to the autonomous vehicle, corrects programming of the traffic lights, controls the system at the entrance, . The present invention replaces the need to collect traffic data manually or through sensors or other means to program a static traffic light system in accordance with the method in force.
본 발명에서 표준 IEEE 802.11p는 VANET의 책임 당국에 의해 시간이 지남에 따라 수정, 개정, 업데이트, 개명 또는 교체될 수 있습니다.In the present invention, standard IEEE 802.11p may be modified, revised, updated, renamed or replaced over time by the responsible authority of VANET.
본 발명에서 표준 IEEE 802.11p는 수정될 수 있으며 표준은 일부 국가 또는 지역에서는 다를 수 있는 국제 표준화 기관의 규정에 따라 개정, 업데이트, 개명 또는 교체될 수 있습니다 (VANET와 관련하여 표준 혹은 기준에 부여된 명칭에 상관없이).In the present invention, the standard IEEE 802.11p may be modified and the standard may be revised, updated, renamed or replaced in accordance with the provisions of the International Standardization Organization, which may be different in some countries or regions. Regardless of its name).
부가된 도면에 대한 즉각적인 설명은 직설적 방식으로 설명되었고 본 문서에 기술된 선호하는 구현 사항은 본 발명의 범위 내에서 실현 가능한 그 외의 구현 사항을 어떠한 방식으로도 제한할 의도가 없음을 분명히 이해해야 합니다. 창의적이고 새로운 것으로 요구되는 사안은 다음의 클레임에 한해서만 제한됩니다.It should be appreciated that an immediate description of the attached drawings is presented in a straightforward manner and that the preferred implementations described in this document are not intended to limit in any way other implementations feasible within the scope of the present invention. Issues that are creative and new are limited to the following claims.
18
선행 기술, 신호 타이밍 프로세스
20
본 발명의 방법
22, 22',22'',22'''
차량간 통신
24,24',24'',24'''
차량-도로통신
25
운전자를 향한 경찰관의 통신
25'
길가 안테나를 향한 경찰 통신
25''
기지국을 향한 경찰관의 통신
26,26'
길가-기지국간의 통신
28,28',28'',28'''
도로 측 안테나 또는 도로 측 장치 - RSU
30
기지국
32
신호
34
제어 센터
36,36'
교통 신호
38
알고리즘
40
알고리즘을 통한 신호 생성
42,42'
교통 경찰관
44
데이터베이스 기호18 Prior art, signal timing process
20 The method of the present invention
22, 22 ', 22'',22''' inter-vehicle communication
24, 24 ', 24'',24''' vehicle-road communication
25 Police officer's communication towards the driver
25 'Police Communications for Roadside Antennas
25 '' Police officer's communication to base station
26,26 'Roadside-to-base station communication
28, 28 ', 28'',28''' Roadside Antenna or Roadside Device - RSU
30 base station
32 signal
34 Control Center
36,36 'Traffic signal
38 algorithm
40 Signal Generation with Algorithm
42,42 'Traffic police officer
44 Database symbols
Claims (28)
a. 교통 신호를 프로그램 하는데 사용되는 알고리즘을 운영하는 컴퓨터 제어 센터로 VANET의 데이터를 전송,
b. 앞서 언급한 알고리즘을 사용하여 데이터를 처리,
c. 컴퓨터 제어 센터와 신호등 사이에 보안 통신 시스템을 구축,
d. 신호등을 지시하는 도로의 각 교차점에 무선 장치를 설치,
e. 보안 통신 시스템을 통해 알고리즘이 제공하는 신호를 무선 장치로 전송,
이러한 방법은 실시간으로 순환 트래픽을 관리하고 필요에 따라 시뮬레이션 시나리오를 만들기 위해 언제든지 데이터를 구할 수 있도록 해줍니다. Vehicle Ad Hoc Network As a method of programming traffic lights with VANET data, the following steps are included:
a. The computer control center, which operates the algorithm used to program the traffic signals, transmits the data of the VANET,
b. Using the algorithms mentioned above to process,
c. Building a secure communication system between computer control center and traffic lights,
d. The wireless device is installed at each intersection of the road indicating the traffic light,
e. The signal provided by the algorithm through a secure communication system is transmitted to the wireless device,
These methods allow you to manage your circulation traffic in real time and retrieve your data at any time to create simulation scenarios as needed.
The standard IEEE 802.11p mentioned above may be modified and the standard referred to above may be revised, updated, renamed or replaced in accordance with the provisions of the International Standardization Organization, which may be different in some countries or regions Regardless of the name given to it) if any of claims 1 to 27 of the method
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CA2016/050582 WO2017201600A1 (en) | 2016-05-24 | 2016-05-24 | Control and manage traffic light system with vanet |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20190016040A true KR20190016040A (en) | 2019-02-15 |
Family
ID=60412050
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020187037406A KR20190016040A (en) | 2016-05-24 | 2016-05-24 | Control and management of traffic signal system through VANET |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP3465657A4 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2019526092A (en) |
| KR (1) | KR20190016040A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN110140157A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2017201600A1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20240017604A (en) | 2022-08-01 | 2024-02-08 | 이화여자대학교 산학협력단 | Traffic information system and traffic information management method based on vanet environment |
| KR20240050001A (en) | 2022-10-11 | 2024-04-18 | 영남대학교 산학협력단 | Traffic image information management method, recording medium and information management system for performing the same |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI660331B (en) * | 2018-03-22 | 2019-05-21 | 創新交通科技有限公司 | Method and equipment for generating offset of traffic signal by using travel time |
| CN109658768B (en) * | 2018-12-27 | 2020-12-25 | 交通运输部科学研究院 | Virtual reality's many people are with scene mixed traffic flow simulation experiment platform |
Family Cites Families (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH06266993A (en) * | 1993-03-11 | 1994-09-22 | Hitachi Ltd | Highway traffic controller |
| DE10022812A1 (en) * | 2000-05-10 | 2001-11-22 | Daimler Chrysler Ag | Method for determining the traffic situation on the basis of reporting vehicle data for a traffic network with traffic-regulated network nodes |
| ES2314364T3 (en) * | 2003-01-17 | 2009-03-16 | Continental Automotive Systems Us, Inc. | TRAFFIC SIGNAL PRIORITY SYSTEM BASED ON MOBILE EVENTS. |
| JP4003957B2 (en) * | 2003-03-07 | 2007-11-07 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Data communication method, data communication service providing method, emergency vehicle passage notification method, emergency vehicle passage notification service provision method, wireless spot service implementation method, wireless spot service provision method, emergency vehicle passage notification program, and emergency vehicle passage notification program recording medium |
| JP2006343814A (en) * | 2005-06-07 | 2006-12-21 | Sumitomo Electric Ind Ltd | Traffic control system and on-vehicle device to transmit information to this system |
| CN1936999A (en) * | 2006-10-17 | 2007-03-28 | 大连理工大学 | City area-traffic cooperative control method based wireless sensor network |
| EP1959414B1 (en) * | 2007-02-14 | 2010-11-10 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Method and apparatus for estimating a travel time of a travel route |
| CN101079772A (en) * | 2007-04-05 | 2007-11-28 | 复旦大学 | Intelligent traffic control system based on ZigBee wireless communication |
| CN101493992B (en) * | 2008-12-19 | 2010-12-08 | 浙江工业大学 | Control method for single-point self-organizing traffic signal based on wireless sensor network |
| US9154982B2 (en) * | 2009-04-02 | 2015-10-06 | Trafficcast International, Inc. | Method and system for a traffic management network |
| CN102063796B (en) * | 2010-09-26 | 2013-06-05 | 广西工学院 | Intelligent traffic control system and method based on wireless Mesh ad hoc network |
| CN102157071A (en) * | 2011-03-22 | 2011-08-17 | 芜湖伯特利汽车安全系统有限公司 | Intelligent traffic management system and control method based on inter-vehicle network |
| CN102737503B (en) * | 2012-06-20 | 2014-10-29 | 东南大学 | Communication connectivity analysis method for bus dynamic scheduling under internet of vehicles environment |
| CN102867422B (en) * | 2012-09-13 | 2014-08-13 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Vehicle ad hoc network-based real-time single-point intersection signal lamp control method |
| US9070290B2 (en) * | 2013-03-16 | 2015-06-30 | Donald Warren Taylor | Apparatus and system for monitoring and managing traffic flow |
| WO2015042776A1 (en) * | 2013-09-24 | 2015-04-02 | Harman International Industries, Incorporated | Message broadcasting in vanet |
| US9361802B2 (en) * | 2014-07-16 | 2016-06-07 | Sony Corporation | Vehicle ad hoc network (VANET) |
| CN104240522A (en) * | 2014-09-04 | 2014-12-24 | 中山大学 | Self-adaptive crossroad control technology based on vehicle area network and fuzzy neural network |
| CN204256963U (en) * | 2014-12-10 | 2015-04-08 | 辽宁省交通高等专科学校 | A kind of intersection traffic signal lamp real-time control apparatus based on GPS |
-
2016
- 2016-05-24 EP EP16902617.6A patent/EP3465657A4/en active Pending
- 2016-05-24 JP JP2018561702A patent/JP2019526092A/en active Pending
- 2016-05-24 WO PCT/CA2016/050582 patent/WO2017201600A1/en active Search and Examination
- 2016-05-24 KR KR1020187037406A patent/KR20190016040A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2016-05-24 CN CN201680086139.XA patent/CN110140157A/en active Pending
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20240017604A (en) | 2022-08-01 | 2024-02-08 | 이화여자대학교 산학협력단 | Traffic information system and traffic information management method based on vanet environment |
| KR20240050001A (en) | 2022-10-11 | 2024-04-18 | 영남대학교 산학협력단 | Traffic image information management method, recording medium and information management system for performing the same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3465657A1 (en) | 2019-04-10 |
| WO2017201600A1 (en) | 2017-11-30 |
| CN110140157A (en) | 2019-08-16 |
| EP3465657A4 (en) | 2020-05-27 |
| JP2019526092A (en) | 2019-09-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11669653B2 (en) | Simulated vehicle traffic for autonomous vehicles | |
| US9070290B2 (en) | Apparatus and system for monitoring and managing traffic flow | |
| EP3507942B1 (en) | Wireless network optimization | |
| CN105761500B (en) | Traffic accident treatment method and traffic accident treatment device | |
| Uppoor et al. | Generation and analysis of a large-scale urban vehicular mobility dataset | |
| KR20190016040A (en) | Control and management of traffic signal system through VANET | |
| CN107784835A (en) | Traffic behavior model prediction system and its Forecasting Methodology based on traffic data analyzing | |
| CN104680820A (en) | Traffic flow car networking system and traffic flow control method based on gradient field | |
| CN104134344A (en) | Road traffic network emergency evacuation route generation method based on Internet of vehicles | |
| KR102377637B1 (en) | Hybride Traffic Signal Control System and Method thereof | |
| CN102324182A (en) | Traffic road information detection system based on cellular network and detection method thereof | |
| US20180286223A1 (en) | System and method for providing real-time and predictive speed, traffic signal timing, station dwell time, and departure window information to transit vehicle | |
| CN104392617A (en) | Bus priority control system | |
| Nayak et al. | PHVA: A position based high speed vehicle detection algorithm for detecting high speed vehicles using vehicular cloud | |
| CN204348075U (en) | A kind of bus priority control system | |
| CN102831487A (en) | Flow predicted result verification method based on historical scheduled flight running data analysis | |
| US11482103B2 (en) | Control and manage traffic light system with VANET | |
| Alkhatib | Proposed simple low cost system for road traffic counting | |
| Mitsakis et al. | Large scale deployment of cooperative mobility systems in Europe: COMPASS4D | |
| US11682298B2 (en) | Practical method to collect and measure real-time traffic data with high accuracy through the 5G network and accessing these data by cloud computing | |
| Ma et al. | Evaluation of the integrated application of intelligent transportation system technologies using stochastic incident generation and resolution modeling | |
| Zhang et al. | Design and implementation of a vehicle-to-vehicle based traffic information system | |
| CA3024602C (en) | Control and manage traffic light system with vanet | |
| CN110379174B (en) | Traffic control system based on 5G positioning and video analysis technology | |
| Pinzel et al. | V2V-and V2X-Communication data within a distributed computing platform for adaptive radio channel modelling |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E601 | Decision to refuse application |