JP5317093B2 - Learning content generation device, learning content generation method, program for causing a computer to function as the learning content generation device, and computer-readable recording medium storing the program - Google Patents
Learning content generation device, learning content generation method, program for causing a computer to function as the learning content generation device, and computer-readable recording medium storing the program Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5317093B2 JP5317093B2 JP2008099404A JP2008099404A JP5317093B2 JP 5317093 B2 JP5317093 B2 JP 5317093B2 JP 2008099404 A JP2008099404 A JP 2008099404A JP 2008099404 A JP2008099404 A JP 2008099404A JP 5317093 B2 JP5317093 B2 JP 5317093B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- word
- words
- language
- sentence
- learning content
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Electrically Operated Instructional Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は情報処理に関し、特に、予め準備された文に基づいて学習用の問題文を生成するための技術に関する。 The present invention relates to information processing, and more particularly to a technique for generating a problem sentence for learning based on a sentence prepared in advance.
電子辞書、携帯電話機のような情報処理装置は、辞書機能あるいは電話機能という本来の機能に加えて、新たな機能が追加されている。たとえば、電子辞書は、発音機能を有している。また、携帯電話機は、辞書機能、文書編集機能などを有している。情報処理装置は、このような本来の情報処理機能としての使用態様に加えて、学習支援装置としても機能する。たとえば、予め作成された問題を携帯電話機に保存しておき、携帯電話機の使用者が、出題される問題に解答するというような仕様態様がある。 An information processing apparatus such as an electronic dictionary or a mobile phone has a new function added to the original function such as a dictionary function or a telephone function. For example, the electronic dictionary has a pronunciation function. In addition, the mobile phone has a dictionary function, a document editing function, and the like. The information processing apparatus also functions as a learning support apparatus in addition to such usage as the original information processing function. For example, there is a specification mode in which a problem created in advance is stored in a mobile phone, and a user of the mobile phone answers a question to be asked.
たとえば、特開2003−195733号公報(特許文献1)は、自己の学習目標を達成すると同時に、語学学習も自然に効率的に行う事が可能な教育システム及び教育方法を開示している。 For example, Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2003-195733 (Patent Document 1) discloses an education system and an education method that can achieve language learning as well as achieve a learning goal of the subject.
また、特開2007−072594号公報(特許文献2)は、原文の語句に、正しい訳語を訳振りする翻訳装置及び翻訳方法を開示している。
しかしながら、情報処理装置に問題文のような学習コンテンツを予め格納する構成では、出題される問題は、予め作成された問題に限られ、また、出題のパターンのバリエーションにも限界がある。 However, in the configuration in which learning content such as a question sentence is stored in advance in the information processing apparatus, the question to be asked is limited to a problem created in advance, and there is a limit to variations in the question pattern.
本発明は、上述のような問題点を解決するためになされたものであって、その目的は、問題を容易に生成できる学習コンテンツ生成装置を提供することである。 The present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems, and an object thereof is to provide a learning content generation apparatus that can easily generate a problem.
他の目的は、問題を容易に生成できる学習コンテンツ生成方法を提供することである。
他の目的は、問題を容易に生成できる学習コンテンツ生成装置としてコンピュータを機能させるためのプログラムを提供することである。
Another object is to provide a learning content generation method that can easily generate a problem.
Another object is to provide a program for causing a computer to function as a learning content generation apparatus that can easily generate a problem.
さらに他の目的は、問題を容易に生成できる学習コンテンツ生成装置としてコンピュータを機能させるためのプログラムを格納した記録媒体を提供することである。 Still another object is to provide a recording medium storing a program for causing a computer to function as a learning content generation apparatus that can easily generate a problem.
この発明のある局面に従う学習コンテンツ生成装置は、画面を表示する表示手段と、第1の言語によって複数の単語から構成される例文を格納する記憶手段と、学習コンテンツ生成装置を制御する制御手段とを備える。制御手段は、複数の単語のうちのいずれかの単語に基づいて、例文と異なる問題文を生成し、問題文を、表示手段に表示させる。 A learning content generation device according to an aspect of the present invention includes a display unit that displays a screen, a storage unit that stores an example sentence composed of a plurality of words in a first language, and a control unit that controls the learning content generation device. Is provided. The control means generates a question sentence different from the example sentence based on any one of the plurality of words, and causes the display means to display the question sentence.
好ましくは、制御手段は、複数の単語の配列を変更することにより、例文における単語の配列と異なる問題文を生成する。 Preferably, the control unit generates a question sentence different from the word arrangement in the example sentence by changing the arrangement of the plurality of words.
好ましくは、記憶手段は、第1の言語の単語の辞書を格納している。制御手段は、辞書から、単語をランダムに選択し、複数の単語に、選択された単語を含めた単語群中の単語の配列を変更した問題文を生成する。 Preferably, the storage means stores a dictionary of words in the first language. The control means randomly selects a word from the dictionary, and generates a question sentence in which the arrangement of words in the word group including the selected word is changed to a plurality of words.
好ましくは、辞書は、類義語辞書を含む。
好ましくは、辞書は、第1の言語の単語を当該言語の文法規則に従って変化させることによって得られる変化形を含んでいる。制御手段は、複数の単語のいずれかの変化形を、複数の単語の配列の変更後の配列に含めることにより、問題文を生成する。
Preferably, the dictionary includes a synonym dictionary.
Preferably, the dictionary includes a variation obtained by changing a word of the first language according to a grammatical rule of the language. The control means generates a question sentence by including any variation of the plurality of words in the modified array of the plurality of words.
好ましくは、記憶手段は、第1の言語の単語の辞書を格納している。制御手段は、複数の単語から第1の単語を選択し、辞書から、複数の候補単語を選択し、例文を構成する複数の単語から、第1の単語を除いた残りの単語からなる一連の単語と、第1の単語の削除を示すための表示と、複数の候補単語とに基づいて、問題文を生成する。 Preferably, the storage means stores a dictionary of words in the first language. The control means selects a first word from a plurality of words, selects a plurality of candidate words from a dictionary, and a series of remaining words excluding the first word from a plurality of words constituting an example sentence A question sentence is generated based on the word, the display for indicating the deletion of the first word, and the plurality of candidate words.
好ましくは、辞書は、類義語辞書を含む。制御手段は、複数の候補単語として、第1の単語の複数の類義語を選択する。 Preferably, the dictionary includes a synonym dictionary. The control means selects a plurality of synonyms of the first word as the plurality of candidate words.
好ましくは、辞書は、第1の言語の単語を当該言語の文法規則に従って変化させることによって得られる変化形を含んでいる。制御手段は、複数の候補単語として、複数の単語のいずれかの変化形を選択する。 Preferably, the dictionary includes a variation obtained by changing a word of the first language according to a grammatical rule of the language. The control means selects any variation of the plurality of words as the plurality of candidate words.
好ましくは、記憶手段は、第1の言語の単語の辞書を格納している。制御手段は、複数の単語から第1の単語を選択し、辞書から、第1の単語と異なる第2の単語を選択し、複数の単語から第1の単語を除いた残りの単語と、第2の単語とをランダムに配列することにより、問題文を生成する。 Preferably, the storage means stores a dictionary of words in the first language. The control means selects a first word from the plurality of words, selects a second word different from the first word from the dictionary, and removes the first word from the plurality of words, A question sentence is generated by randomly arranging two words.
好ましくは、辞書は、第1の言語の単語を当該言語の文法規則に従って変化させることによって得られる変化形を含んでいる。制御手段は、辞書から、第1の単語の変化形を第2の単語として選択する。 Preferably, the dictionary includes a variation obtained by changing a word of the first language according to a grammatical rule of the language. The control means selects a variation of the first word as the second word from the dictionary.
好ましくは、辞書は、類義語辞書を含む。制御手段は、第1の単語の類義語を第2の単語として選択する。 Preferably, the dictionary includes a synonym dictionary. The control means selects a synonym of the first word as the second word.
好ましくは、記憶手段は、第1の言語の例文の第2の言語による翻訳文を格納している。制御手段は、第1の言語による問題文と、第2の言語による翻訳文とを、表示手段に表示させる。 Preferably, the storage unit stores a translated sentence of the example sentence in the first language in the second language. The control means causes the display means to display the problem sentence in the first language and the translated sentence in the second language.
この発明の他の局面に従うと、コンピュータによる学習コンテンツの生成方法が提供される。コンピュータは、プロセッサと、メモリと、ディスプレイ装置とを備えている。この方法は、プロセッサが、第1の言語によって複数の単語から構成される例文を、メモリからロードするステップと、プロセッサが、複数の単語のうちのいずれかの単語に基づいて、例文と異なる問題文を生成するステップと、プロセッサが、問題文をディスプレイに表示させるステップとを含む。 When the other situation of this invention is followed, the production | generation method of the learning content by a computer is provided. The computer includes a processor, a memory, and a display device. The method includes a step in which a processor loads an example sentence composed of a plurality of words in a first language from a memory, and the processor is different from the example sentence based on any one of the plurality of words. Generating a sentence; and causing the processor to display the question sentence on a display.
この発明の他の局面に従うと、コンピュータを学習コンテンツ生成装置として機能させるためのプログラムが提供される。コンピュータは、プロセッサと、メモリと、ディスプレイ装置とを備えている。プログラムは、プロセッサに、第1の言語によって複数の単語から構成される例文を、メモリからロードするステップと、複数の単語のうちのいずれかの単語に基づいて、例文と異なる問題文を生成するステップと、問題文をディスプレイに表示させるステップとを実行させる。 If the other situation of this invention is followed, the program for functioning a computer as a learning content production | generation apparatus will be provided. The computer includes a processor, a memory, and a display device. The program loads the processor with an example sentence composed of a plurality of words in the first language from the memory, and generates a question sentence different from the example sentence based on any one of the plurality of words. A step and a step of displaying a question sentence on a display are executed.
この発明のさらに他の局面に従うと、上記のプログラムを格納した、コンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体が提供される。 According to still another aspect of the present invention, a computer-readable recording medium storing the above program is provided.
本発明によると、問題を容易に生成することができる。 According to the present invention, problems can be easily generated.
以下、図面を参照しつつ、本発明の実施の形態について説明する。以下の説明では、同一の部品には同一の符号を付してある。それらの名称および機能も同じである。したがって、それらについての詳細な説明は繰り返さない。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. In the following description, the same parts are denoted by the same reference numerals. Their names and functions are also the same. Therefore, detailed description thereof will not be repeated.
[ハードウェア構成]
図1を参照して、本発明の実施の形態に係る学習コンテンツ生成装置の具体的構成について説明する。図1は、本実施の形態に係る学習コンテンツ生成装置を実現するコンピュータシステム100のハードウェア構成を表わすブロック図である。なお、学習コンテンツ生成装置は、コンピュータシステム100以外に、携帯電話機、辞書、PDA(Personal Digital Assistant)などによっても実現可能である。
[Hardware configuration]
With reference to FIG. 1, a specific configuration of the learning content generation apparatus according to the embodiment of the present invention will be described. FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a hardware configuration of a
コンピュータシステム100は、主たる構成要素として、プログラムを実行するCPU(Central Processing Unit)110と、コンピュータシステム100に対する指示の入力を受けるマウス120およびキーボード130と、CPU110によるプログラムの実行により生成されたデータ、又はマウス120若しくはキーボード130を介して入力されたデータを揮発的に格納するRAM(Random Access Memory)140と、データを不揮発的に格納するハードディスク150と、光ディスク駆動装置160と、モニタ110と、通信I/F(Interface)190とを含む。各構成要素は、相互にデータバスによって接続されている。光ディスク駆動装置160には、CD−ROM(Compact Disc - Read Only Memory)162その他の光ディスクが装着される。
The
コンピュータシステム100における処理は、各ハードウェアおよびCPU110により実行されるソフトウェアによって実現される。このようなソフトウェアは、ハードディスク150に予め記憶されている場合がある。また、ソフトウェアは、CD−ROM162その他の記憶媒体に格納されて、プログラムプロダクトとして流通している場合もある。あるいは、ソフトウェアは、いわゆるインターネットに接続されている情報提供事業者によってダウンロード可能なプログラムプロダクトとして提供される場合もある。このようなソフトウェアは、光ディスク駆動装置160その他の読取装置によりその記憶媒体から読み取られて、あるいは、通信I/F190を介してダウンロードされた後、ハードディスク150に一旦格納される。そのソフトウェアは、CPU110によってハードディスク150から読み出され、RAM140に実行可能なプログラムの形式で格納される。CPU110は、そのプログラムを実行する。
Processing in the
図1に示されるコンピュータシステム100を構成する各構成要素は、一般的なものである。したがって、本発明の本質的な部分は、RAM140、ハードディスク150、CD−ROM162その他の記憶媒体に格納されたソフトウェア、あるいはネットワークを介してダウンロード可能なソフトウェアであるともいえる。なお、コンピュータシステム100の各ハードウェアの動作は周知であるので、詳細な説明は繰り返さない。
Each component constituting the
なお、記録媒体としては、CD−ROM、FD(Flexible Disk)、ハードディスクに限られず、磁気テープ、カセットテープ、光ディスク(MO(Magnetic Optical Disc)/MD(Mini Disc)/DVD(Digital Versatile Disc))、IC(Integrated Circuit)カード(メモリカードを含む)、光カード、マスクROM、EPROM(Electronically Programmable Read-Only Memory)、EEPROM(Electronically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory)、フラッシュROMなどの半導体メモリ等の固定的にプログラムを担持する媒体でもよい。 The recording medium is not limited to a CD-ROM, FD (Flexible Disk), and hard disk, but is a magnetic tape, a cassette tape, an optical disk (MO (Magnetic Optical Disc) / MD (Mini Disc) / DVD (Digital Versatile Disc)). IC (Integrated Circuit) card (including memory card), optical card, mask ROM, EPROM (Electronically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory), EEPROM (Electronically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory), fixing of flash ROM and other semiconductor memories Alternatively, it may be a medium carrying a program.
ここでいうプログラムとは、CPUにより直接実行可能なプログラムだけでなく、ソースプログラム形式のプログラム、圧縮処理されたプログラム、暗号化されたプログラム等を含む。 The program here includes not only a program directly executable by the CPU but also a program in a source program format, a compressed program, an encrypted program, and the like.
[機能構成]
図2を参照して、本発明の実施の形態に係る学習コンテンツ生成装置200の構成について説明する。図2は、学習コンテンツ生成装置200によって実現される機能の構成を表わすブロック図である。学習コンテンツ生成装置200は、入力部210と、出力部220と、制御部230と、記憶部240と、プログラムモジュール部250と、メインメモリ部270とを備える。
[Function configuration]
With reference to FIG. 2, the configuration of learning
入力部210は、学習コンテンツ生成装置200に対する操作の入力を受け付ける。入力部210は、その操作に応じた信号を制御部230に送出する。入力部210は、キーボード、ボタンその他の入力スイッチとして、あるいは、タッチパネルとして実現される。他の局面においては、入力部210は、圧電感知式のセンサーを用いて構成される。
The
出力部220は、制御部230による制御に基づいて、学習コンテンツ生成装置200の外部に情報を出力する。ある局面において、出力部220は、ディスプレイ装置として実現される。また他の局面において、出力部220は、音声を出力するスピーカとして実現され得る。
The
制御部230は、学習コンテンツ生成装置200の動作を制御する。ある局面において、制御部230は、プロセッサ、FPGA(Field Programmable Gate Array)等によって実現される。制御部230は、入力部210から送られた信号に基づいて、記憶部240に格納されているデータ、プログラムモジュール部250に格納されているプログラムモジュール、あるいはメインメモリ部270に保持されるデータに基づいて、学習コンテンツ生成装置200が有する機能を実現するための処理を実行する。たとえば、制御部230は、入力部210に対する操作に基づいて、英文の並べ替え問題を出力する。他の局面において、制御部230は、英文と和文とを出力部220に表示させる。
The
記憶部240は、対訳例文データベース241と、英語辞書データ242と、日本語辞書データ243と、英語シソーラスデータ244と、日本語シソーラスデータ245とを含む。記憶部240は、さらに、並べ替え問題生成テンプレート246と、穴埋め問題生成テンプレート247と、誤り指摘問題生成テンプレート248とを含む。記憶部240は、フラッシュメモリ、ハードディスクその他の不揮発メモリによって実現される。他の局面において、記憶部240は、着脱可能な記録媒体によって実現されてもよい。
The
プログラムモジュール部250は、対訳例文選択部251と、並べ替え問題生成部252と、穴埋め問題生成部253と、誤り指摘問題生成部254と、英語文法処理部255と、日本語文法処理部256と、乱数発生部257と、乱数正規化部258と、変化形探索部259と、類義語探索部260と、辞書引き部261とを含む。これらは、ある局面において、プロセッサによって実現されるプログラムとして実現される。プログラムモジュール部250は、フラッシュメモリ、ハードディスク、ROMその他の不揮発記録媒体上で実現される。プログラムモジュール部250と記憶部240とは、物理的に同一のあるいは別個の記憶装置において実現される。
The
対訳例文選択部251は、制御部230の命令に従って、記憶部240から対訳例文を選択するように構成されている。たとえば、対訳例文選択部251は、ランダムに対訳例文を選択する。あるいは、他の局面において、対訳例文選択部251は、問題の正答率の低い例文を選択する構成であってもよい。
The bilingual example
並べ替え問題生成部252は、制御部230の命令に従って、並べ替え問題生成テンプレート246と、対訳例文データベース241から選択した例文および訳文とを用いて、正規の文章を構成する複数の単語の語順を並べ替えた問題を生成する。
The rearrangement
穴埋め問題生成部253は、制御部230の命令に従って、穴埋め問題生成テンプレート247と、対訳例文データベース241から選択した例文および訳文とを用いて、正規の文章から単語を除いた文章を、穴埋め問題として生成する。
The filling-in-place
誤り指摘問題生成部254は、制御部230の命令に従って、誤り指摘問題生成テンプレート248と、対訳例文データベース241から選択した例文および訳文とを用いて、正規の文章を構成するいずれかの単語の形式を変更した文章を、誤り指摘問題として生成する。
The error indication
英語文法処理部255は、英語辞書データ242を参照して、単語の変化形(過去形、過去分詞形、現在分詞形、複数形、比較級、最上級など)から原形の単語を特定する。
The English
日本語文法処理部256は、日本語辞書データ243を参照して、日本語の単語の原形から変化形(動詞、形容詞、形容動詞の活用形など)を構成する。他の局面において、日本語文法処理部256は、変化形から原形を特定する。
The Japanese
乱数発生部257は、0〜1の間の連続した区間の内部にある数値を、この区間内で等確率で発生させる。
The
乱数正規化部258は、乱数発生部257によって発生された乱数を、目的に合うような数値(たとえば、整数)に変換する。本実施の形態においては、たとえば、使用する範囲の対訳例文データベースに含まれている、対訳例文データベース241を構成するデータレコードの数が500組であるとする。そして、それぞれの組に1〜500が連番で付与されているとする。この場合、乱数正規化部258からの出力は、乱数発生部257によって発生された乱数(0〜1)の間の連続した数値を、1〜500の間のいずれかの整数(等確率で発生するもの)に変換したものとなる。
The random
なお、他の局面において、乱数発生部257と乱数正規化部258とが、一体として、たとえば乱数発生部として機能してもよい。上記の例では、他の局面に従う乱数発生部は、たとえば、いきなり1〜500の間のいずれかの整数を等確率で発生することになる。
In another aspect, random
変化形探索部259は、英語辞書データ242を参照して、制御部230によって指定された単語の情報(原形、変化形など)を獲得する。たとえば、動詞の場合、原形を含めた変化形は、「原形」、「三人称単数現在形」、「過去形」、「過去分詞形」、「ing形」を検索する。
The
類義語探索部260は、英語シソーラスデータ244を参照して、制御部230によって指定された単語の類義語を検索する。他の局面において、類義語探索部260は、日本語シソーラスデータ245を参照して、制御部230によって指定された単語の類義語を検索する。
The
辞書引き部261は、変化形探索部259または類義語探索部260からの出力に基づいて、探索のために指定された英語辞書データ242または日本語辞書データ243を参照する。
The
図2を再び参照して、メインメモリ部270は、文数カウンタ271と、単語数カウンタ272と、対訳例文バッファ273と、原文単語バッファ274と、テンポラリ単語バッファ275と、語順入れ替え結果バッファ276と、穴埋め選択肢バッファ277と、誤り問題バッファ278と、問題文バッファ279と、入れ替え済み単語数カウンタ280とを含む。ある局面において、メインメモリ部270は、RAMその他の揮発メモリとして実現される。
Referring again to FIG. 2, the
[データ構造]
図3から図7を参照して、本実施の形態に係る学習コンテンツ生成装置200のデータ構造について説明する。図3は、対訳例文データベース241におけるデータの格納の一態様を概念的に表わす図である。
対訳例文データベース241は、複数の例文を含む。各例文は、1組の対訳例文(英・日などの2種類の言語による)を含む。なお、例文の言語は、日本語と英語に限られず、中国語、韓国語、フランス語、ドイツ語その他の言語であってもよい。
[data structure]
With reference to FIGS. 3 to 7, the data structure of learning
The bilingual
より詳しくは、対訳例文データベース241は、英語例文データ310と、日本語例文データ320と、アライメントデータ330と、テンポラリフラグ350とを含む。
More specifically, the bilingual
英語例文データ310は、複数の英語の例文を含む。各例文は、ID(Identification)と、当該例文を構成する単語と、当該単語の品詞と、当該単語の変化形とを含む。
The English
対訳例文データベース241は、複数の日本語例文データ320を含む。各日本語例文データは、IDと、当該例文を構成する単語と、当該単語の品詞と、当該単語の変化形とを含む。
The bilingual
アライメントデータ330は、当該英語例文と当該日本語例文との対応関係を規定している。アライメントデータ330は、英語例文を構成する単語と、日本語例文を構成する単語とのそれぞれに基づいて、英語と日本語との対応関係が規定され得るグループごとに、IDが割り付けられ、各IDに、当該グループを構成する単語の番号がそれぞれ英語単語番号と日本語単語番号として関連付けられている。
The
テンポラリフラグ350は、当該例文テンプレートが使用済であるか否かを表わすデータを保持する。テンポラリフラグ350は、制御部230の制御に基づいて書き換えられ、またリセットの命令に基づいて初期化され得る。
The
図4は、英語辞書データ242の構成を概念的に表わす図である。英語単語辞書データ242は、IDと、見出しと、品詞と、変化形と、意味を示すデータとを含む。当該意味を示すデータは、意味カテゴリと、意味コードと、訳語とを含む。当該英語単語が複数の意味を有する場合には、当該意味を示すデータは、それぞれの意味に応じて複数の項目が規定される。
FIG. 4 is a diagram conceptually showing the configuration of
図4に示される例では、変化形(動詞の場合「三人称単数現在形」、「過去形」、「過去分詞形」、「ing形」)のフルスペルが辞書データに記述されている。他の局面において、単語が規則に応じて変化する構成である場合には、何らかの変化形コード(当該規則を示すコード)のみを記述して、変化の規則により変化形を得る方式にしてもよい。このような構成によると、メモリの使用量を抑制することができる。 In the example shown in FIG. 4, the full spelling of the change form (in the case of a verb “third-person singular present form”, “past form”, “past participle form”, “ing form”) is described in the dictionary data. In another aspect, when a word is configured to change according to a rule, only a certain change code (a code indicating the rule) may be described and a change form may be obtained based on the change rule. . According to such a configuration, the amount of memory used can be suppressed.
また、本実施の形態においては、動詞の変化形の例が示されているが、その他の品詞の場合は、当該品詞に関連する変化形が含まれる。たとえば、単語が名詞であれば、変化形は「原形」「複数形」が含まれる。当該単語が形容詞または副詞であれば、変化形として、「比較級」「最上級」が用いられる。 Further, in the present embodiment, an example of a variation of a verb is shown, but in the case of other parts of speech, a variation associated with the part of speech is included. For example, if the word is a noun, the variations include “original form” and “plural form”. If the word is an adjective or adverb, as a variation, "comparatives""superlative" is used.
図5は、日本語辞書データ243の構成を概念的に表わす図である。日本語辞書データ243は、IDと、見出しと、品詞と、変化形と、意味を示すデータとを含む。当該意味を示すデータは、意味カテゴリと、意味コードと、訳語とを含む。当該日本語の単語が複数の意味を有する場合には、当該意味を示すデータのその意味に応じてそれぞれ規定される。
FIG. 5 is a diagram conceptually showing the configuration of
IDは、日本語の単語をそれぞれ識別する。見出しとしては、たとえば、当該単語の先頭の文字が用いられる。 The ID identifies each Japanese word. As the headline, for example, the first character of the word is used.
図4および図5に示される各辞書データは、たとえば学習コンテンツ生成装置200の製造事業者によって予め入力される。
Each dictionary data shown in FIGS. 4 and 5 is input in advance by, for example, the manufacturer of learning
図6は、英語シソーラスデータ244におけるシソーラスデータの概念を示す図である。図6に示される例では、単語thing(物)のシソーラスが展開されている。具体的には、単語thingには、別の連語「physical thing」が規定されている。この単語physical thingには、さらに別の単語foodsが規定されている。単語foodsには、別の単語として、seasoningと単語vegetableその他の単語はそれぞれ関連付けられている。単語seasoningには、さらに別の単語として、単語salt、単語sugar、単語spiceなどが関連付けられている。さらに、単語spiceには、他の単語として単語pepperと単語chiliその他の単語が関連付けられている。
FIG. 6 is a diagram showing the concept of thesaurus data in the
図7は、英語シソーラスデータ244におけるデータの一態様を概念的に表わす図である。英語シソーラスデータ244は、各単語ごとに、IDと、意味カテゴリと、代表語と、トップノードからの距離と、上位ノードと、下位ノードとを含む。IDは、当該単語を特定する。意味カテゴリは、当該単語が含まれる英語シソーラスの分類を規定する。代表語は、当該英語シソーラスデータの代表(たとえば単語seasoning)を表わす。トップノードからの距離は、当該単語seasoningとその単語の元に規定されている単語thingとの距離を表わす。図6に示される例では、単語seasoningは、単語thingから、単語physical thingと単語foodsとを経ている。その間、3つのノードが含まれている。そこで、トップノードからの距離は「3」として規定される。
FIG. 7 is a diagram conceptually showing an aspect of data in
下位ノードは、当該単語seasoningの下位に規定される単語のノードを示す。図6に示される例では、単語seasoningには、他の単語として単語salt、sugar、spiceなどが関連付けられているため下位ノードとして各単語のIDがそれぞれ関連付けられる。 The lower node indicates a node of a word defined below the word seasoning. In the example illustrated in FIG. 6, the word seasoning is associated with the word salt, sugar, spice, and the like as other words, so the ID of each word is associated as a lower node.
[制御構造]
(語順並べ替え問題生成)
図8から図11を参照して、本実施の形態に係る学習コンテンツ生成装置200の制御構造の一態様について説明する。図8から図11は、学習コンテンツ生成装置200が語順並べ替え問題を生成するために実行する処理の一部を表わすフローチャートである。
[Control structure]
(Word order rearrangement problem generation)
With reference to FIGS. 8 to 11, one aspect of the control structure of learning
ステップS810にて、制御部230は、文数カウンタ271に「0」をセットして初期化する。
In step S810,
ステップS820にて、制御部230は、対訳例文データベース241のすべての例文の組について、「使用済み」のフラグ(テンポラリフラグ350)をクリアする。
In step S820,
ステップS830にて、制御部230は、対訳例文データベース241から、乱数発生部257の出力結果に基づいて、1組の例文、テンプレートの組を選択する。制御部230は、その選択した組の番号をたとえば変数kとして設定する。
In step S830,
ステップS840にて、制御部230は、組kの例文の組に「使用」のフラグが設定されているか否かを判定する。制御部230は、当該フラグが設定されていると判定すると(ステップS840にてYES)、制御をステップS830に戻す。そうでない場合には(ステップS840にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS900に切り換える。この場合、制御部230は、他の例文を選択し直す。
In step S840,
ステップS900にて、制御部230は、組kの例文から、語順の入れ替えを行ない、余計な単語を加え、その単語を語順入れ替え結果バッファ276に格納する。ステップS900の処理の詳細は、図9において詳述する。
In step S <b> 900,
ステップS850にて、制御部230は、その語順入れ替え結果から、並べ替え問題生成テンプレート246を用いて問題文を生成する。
In step S850,
ステップS860にて、制御部230は、組kの例文の組のテンポラリフラグ350に、「使用済み」のフラグを設定する。
In step S860,
ステップS870にて、制御部230は、文数カウンタ271の数値を1進める(インクリメントする)。
In step S870,
ステップS880にて、制御部230は、文数カウンタ271の数値がn(nは規定の問題文の数)に到達したか否かを判定する。制御部230は、文数カウンタ271の数値がnに到達したと判定すると(ステップS880にてYES)、制御をステップS890に切り換える。そうでない場合には(ステップS880にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS830に戻す。
In step S880,
ステップS890にて、制御部230は、生成した問題文を出力部220に出力させる。たとえば、問題文はモニタ180に表示される。他の局面において、制御部230は、問題文を音声として出力してもよい。
In step S890,
図9および図10を参照して、ステップS900の詳細について説明する。図9および図10は、制御部230による語順の入れ替え、余計な単語の追加などの処理を表わすフローチャートである。
Details of step S900 will be described with reference to FIGS. 9 and 10. FIG. 9 and FIG. 10 are flowcharts showing processing by the
図9を参照して、ステップS902にて、制御部230は、対象文の単語数をカウントし、その個数nwを単語数カウンタ272にセットする。
Referring to FIG. 9, in step S902,
ステップS904にて、制御部230は、入れ替え済み単語数カウンタ280に0をセットする(初期化する)。制御部230は、入れ替え済み単語数カウンタ280に格納されている数値を変数nw1とする。
In step S904,
ステップS906にて、制御部230は、単語nw+1個の領域を持つ語順入れ替え結果バッファ276をメインメモリ部270に確保する。
In step S906,
ステップS908にて、制御部230は、単語nw+1個の領域を持つ原文単語バッファ274を、メインメモリ部270に確保し、当該領域を初期化する。
In step S908,
ステップS910にて、制御部230は、対象文を単語ごとに切り分けて、各単語を原文単語バッファ274の単語番号1からnwの領域にそれぞれ格納する。
In step S910,
ステップS912にて、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274から、乱数発生部257および乱数正規化部258の各出力に基づいて、1個の単語を選択する。制御部230は、その単語の番号として変数jを使用する(1≦j≦nw)。
In step S912,
ステップS914にて、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274の単語jの領域に、「チェック済」フラグが設定されているか否かを判定する。制御部230は、当該フラグが設定されていると判定すると(ステップS914にてYES)、制御をステップS912に戻す。そうでない場合には(ステップS914にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS916に切り換える。
In
ステップS916にて、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274の単語jの領域に、「チェック済」フラグを立てる。
In step S 916,
ステップS918にて、制御部230は、単語jがそれ自身とは形の異なる原形もしくは変化形を持っているか否かを判定する。制御部230は、当該単語jが原形もしくは変化形を持っていると判定すると(ステップS918にてYES)、制御をステップS920に切り換える。そうでない場合には(ステップS918にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS912に戻す。
In step S918,
ステップS920にて、制御部230は、単語jについて、それ自身とは形の異なる原型もしくは変化形を、英語辞書データ242から取得し、テンポラリ単語バッファ275に、その取得した原形もしくは変化形を格納する。
In
ステップS922にて、制御部230は、テンポラリ単語バッファ275に格納されている単語を、原文単語バッファ274の領域nw+1に格納する。
In step S922,
図10を参照して、ステップS924にて、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274の単語番号nw+1の領域についての「使用済」フラグを初期化する。
Referring to FIG. 10, in step S924,
ステップS926にて、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274から、乱数発生部257および乱数正規化部285の出力結果に基づいて、1個の単語を選択する。制御部230は、その単語の番号を変数iを用いて特定する(1≦i≦nw+1)。
In step S926,
ステップS928にて、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274の単語iの領域に、「使用済」フラグが設定されているか否かを判定する。制御部230は、「使用済」フラグが設定されているか否かを判定する。制御部230は、その領域に「使用済」フラグが設定されていると判定すると(ステップS928にてYES)、制御をステップ926に戻す。そうでない場合には、(ステップS928にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS930に切り換える。
In step S928,
ステップS930にて、制御部230は、変数iが1であり、かつ、単語iの頭文字が大文字であり、かつ、単語iが単語辞書に掲載されておらず、かつ、単語iの頭文字を小文字で変換した単語が単語辞書に掲載されているか否かを判定する。制御部230は、そのような単語が英語辞書データ242に含まれていると判定すると(ステップS930にてYES)、制御をステップS932に切り換える。そうでない場合には、(ステップS930にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS934に切り換える。
In step S930,
ステップS932にて、制御部230は、単語iの頭文字を小文字に変換した単語を、語順入れ替え結果バッファ276のnw+1番目にセットする。
In step S932,
ステップS934にて、制御部230は、単語iを、語順入れ替え結果バッファ276のnw1番目にセットする。
In step S934,
ステップS936にて、制御230は、原文単語バッファ274の単語iの領域に、「使用済」フラグを設定する。
In step S936,
ステップS938にて、制御部230は、入れ替え済み単語数カウンタ280の装置(nw1)を1進める。
In step S938,
ステップS940にて、制御部230は、入れ替え済み単語数カウンタ280の値が値nw+1に到達したか否かを判定する。制御部230は、入れ替え済み単語数カウンタ280の値がnw+1に到達したと判定すると(ステップS940にてYES)、制御をメイン処理(図8)に戻す。そうでない場合には(ステップS940にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS926に戻す。
In step S940,
以上のようにして、本発明の実施の形態に係る学習コンテンツ生成装置200は、予め格納された複数組の例文および訳文からランダムに一組の例文および訳文を選択する。学習コンテンツ生成装置200は、例文を構成する単語をランダムに並べ替えて、語順並べ替え問題を生成する。より詳しくは、制御部230は、複数の単語に、選択された単語を含めた単語群中の単語の配列を変更した問題文を生成する。これにより、学習コンテンツ生成装置200の使用者は、語順並べ替え問題を簡易に楽しめることができる。
As described above, learning
なお、本実施の形態においては、学習コンテンツ生成装置200は、使用された対訳例文データベース241から、日本語文(訳文)を使用して、ヒントとしてこれをそのまま添えて出力している。これは、以下の理由による。すなわち、英語に、変化形を変えた余分な1単語を加えた場合、その余分な1単語を除く(そして並べ替える)、というやり方(学習コンテンツ生成装置200が意図した正解)以外にも、別の1単語を除いて並べ替えることで、英語文として正しい文ができる可能性がある。そこで、使用者による正解を、本実施の形態に係る学習コンテンツ生成装置200が意図した正解のみに絞るために、原文に対応する訳文を添えて、これに対応するような英語文を組み立てさせるような問題を出力する。
In the present embodiment, the learning
このような構成にしたのは、本実施の形態に係る学習コンテンツ生成装置200が、ある英単語群の並びが英語文として正しく成り立っているかどうかを自動的に判定する構成を備えていないためである。したがって、仮に、他の局面に従う学習コンテンツ生成装置が、ある英単語群の並びが英語文として正しく成り立っているかどうかを自動的に判定するような構成を備えている場合には、上記のステップS918、ステップS920における変化形を求める処理で、当該構成を取り入れてもよい。
The reason for this configuration is that the learning
より具体的には、当該構成は、たとえば、1)変化形を余分な1単語として加えた上で、2)他の1単語を除去し、3)元の対訳例文データの英語文以外で英語文として成り立つ場合があるか否かを判定し、4)もしそれがあれば、その変化形は採用しないようにする、というものである。このような構成を取り入れることにより、他の局面に従う学習コンテンツ生成装置は、元の対訳例文データベースの英語文以外に正解は存在しないような問題を生成することができる。これにより、日本語文を添えなくても問題として成立させることができる。 More specifically, the configuration includes, for example, 1) adding a variation as one extra word, 2) removing another one word, and 3) English other than the English sentence of the original bilingual example sentence data It is determined whether or not there is a case where it can hold as a sentence. 4) If there is, the change form is not adopted. By adopting such a configuration, the learning content generation device according to another aspect can generate a problem in which there is no correct answer other than the English sentence in the original bilingual example sentence database. Thereby, it can be established as a problem without adding a Japanese sentence.
あるいは、さらに他の局面において、本実施の形態に係る学習コンテンツ生成装置200は、並べ替え問題を生成した後、その問題に正解が複数通り存在しないか否かを人間が判定し、その判定の結果を学習コンテンツ生成装置200に入力するように構成してもよい。この場合でも、日本語文を添えなくても 問題として成立させることができる。
Alternatively, in yet another aspect, learning
<第1の変形例>
図11を参照して、学習コンテンツ生成装置200による語順並べ替え問題の生成の他の態様について説明する。図11は、学習コンテンツ生成装置200がシソーラスデータを用いて語順並べ替え問題を生成する場合に実行する処理の手順を表わすフローチャートである。
<First Modification>
With reference to FIG. 11, another aspect of generating the word order rearrangement problem by the learning
ステップS1118にて、制御部230は、英語シソーラスデータ244において、単語jの意味情報の位置から意味距離2以内に単語が存在し、かつ、その単語が原文単語バッファ274に格納されている単語のいずれとも一致しないか否かを判定する。制御部230は、そのような状況を満たすと判定すると(ステップS1118にてYES)、制御をステップS1120に切り換える。そうでない場合には(ステップS1118にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS912に戻す。
In step S 1118,
ステップS1120にて、制御部230は、英語シソーラスデータ244において、単語jの意味情報の位置から意味距離2以内に存在する単語の1つを、テンポラリ単語バッファ275に格納する。ここで、単語jの意味情報の位置から意味距離2以内に存在する単語とは、原文単語バッファ274に格納されている単語のいずれとも一致しないものである。
In step S 1120,
なお、意味距離の値は「2」に限られない。それよりも大きくても、あるいは、小さくてもよい。また、類義語の定義として、「意味距離」の概念を用いたが、その他の概念が用いられてもよい。 The value of the semantic distance is not limited to “2”. It may be larger or smaller. Further, although the concept of “semantic distance” is used as the definition of the synonym, other concepts may be used.
<第2の変形例>
さらに他の局面において、並べ替え問題に含まれる単語として、元の単語の変化形が用いられてもよい。この局面に従う辞書データの1つである英語辞書データ242は、通常の電子辞書のように、英語の文法規則に従って変化させることによって得られる変化形を含む。制御部230は、複数の単語のいずれかの変化形を、複数の単語の配列の変更後の配列に含めることにより、問題文を生成してもよい。このような構成により、並べ替え問題のバリエーションを増やすことができる。
<Second Modification>
In yet another aspect, a variation of the original word may be used as the word included in the sorting problem. The
(穴埋め問題の生成)
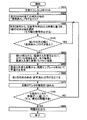
図12から図14を参照して、学習コンテンツ生成装置200が穴埋め問題を生成する場合の制御構造について説明する。図12から図14は、制御部230が実行する一連の動作の一部を表わすフローチャートである。なお、前述の処理と同一の処理には同一のステップ番号を付してある。したがって、それらの説明は繰り返さない。
(Generate hole filling problem)
With reference to FIG. 12 to FIG. 14, a control structure when the learning
図12を参照して、ステップS840にて、制御部230は、組kの例文、テンプレートの組に「使用済」フラグが設定されているか否かを判定する。制御部230は、「使用済」フラグが設定されていると判定すると(ステップS840にてYES)、制御をステップS830に戻す。そうでない場合には(ステップS840にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS1300に切り換える。
Referring to FIG. 12, in step S840,
ステップS1300にて、制御部230は、組kの例文から、空欄箇所を設定し、選択肢を加え、その結果を原文単語バッファ274および穴埋め選択肢バッファ277にそれぞれ格納する。ステップS1300の処理は、図13において詳述する。
In step S1300,
ステップS1250にて、制御部230は、穴埋め選択肢バッファ277の格納の結果から、問題テンプレート(穴埋め問題生成テンプレート247)を用いて、問題文を生成する。
In step S 1250,
図13を参照して、ステップS1306にて、制御部230は、選択肢3個の領域を持つ穴埋め選択肢バッファ277をメインメモリ部270に確保する。
Referring to FIG. 13, in step S <b> 1306,
ステップS1308にて、制御部230は、単語nw個の領域を持つ原文単語バッファ274を、メインメモリ部270に確保し、当該メモリ領域を初期化する。
In step S1308,
ステップS1312にて、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274から、乱数発生部257、乱数正規化部258の各出力結果に基づいて、1個の単語を選択する。制御部230は、その選択した単語の番号を変数iを用いて表わす(1≦i≦nw)。
In step S1312,
ステップS1314にて、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274の単語iの領域に「使用済」フラグがあるか否かを判定する。制御部230は、当該領域に「使用済」フラグがあると判定すると(ステップS1314にてYES)、制御をステップS1312に戻す。そうでない場合には(ステップS1314にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS1318に切り換える。
In step S1314,
ステップS1318にて、制御部230は、単語iがそれ自身とは形の異なる原形または変化形を複数個持っているか否かを判定する。制御部230は、当該単語がそのような条件を満たしていると判定すると(ステップS1318にてYES)、制御をステップS1320に切り換える。そうでない場合には(ステップS1318にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS914に切り換える。
In step S1318,
ステップS1320にて、制御部230は、穴埋め問題バッファ277の3個の選択肢の領域のうち1つの領域を、乱数発生部257、乱数正規化部258の各出力結果に基づいて選択して、その選択した選択肢領域に単語iを格納する。
In step S1320,
ステップS1322にて、制御部230は、単語iについて、それ自身とは形の異なる原形または変化形を2個取得し、穴埋め問題バッファ277の3個の選択肢領域のうちの残りの2つにその取得した単語を格納する。
In step S1322,
ステップS1324にて、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274の単語iを削除する。制御部230は、制御をメイン処理(図12)に戻す。
In step S1324,
以上のようにして、本実施の形態に係る学習コンテンツ生成装置200によると、テンプレートを用いて、穴埋め問題を生成することができる。したがって、学習コンテンツ生成装置200の使用者は、容易に穴埋め問題を生成することができる。
As described above, according to learning
<第3の変形例>
図14を参照して、穴埋め問題生成の他の態様について説明する。図14は、制御部230が実行する他の処理の一部を表わすフローチャートである。なお、前述の処理と同一の処理には、同一のステップ番号を付してある。したがって、そのような処理の説明は繰り返さない。
<Third Modification>
With reference to FIG. 14, another aspect of the hole filling problem generation will be described. FIG. 14 is a flowchart showing a part of another process executed by
ステップS1410にて、制御部230は、英語シソーラスデータ244に基づいて、単語iの意味情報の位置から意味距離2以内に複数の単語が存在しており、かつ、各単語が原文単語バッファ274に格納されている単語のいずれとも一致しないか否かを判定する。制御部230は、そのような条件が成立していると判定すると(ステップS1410にてYES)、制御をステップS1320に切り換える。そうでない場合には(ステップS1410にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS914に切り換える。
In step S1410, based on
ステップS1412にて、制御部230は、英語シソーラスデータ244について、単語iの意味情報の位置から意味距離2以内に存在しており、かつ、原文単語バッファ274の中の単語のいずれとも一致しない単語を2個取得し、穴埋め問題バッファ277の3個の選択肢領域のうちの残りの2つの領域にそれぞれ格納する。
In step S1412, the
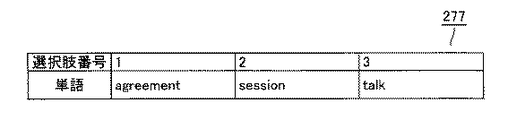
図15は、単語agreementについてのシソーラスの構成を概念的に表わす図である。図15を参照して、単語agreementは、連語「interaction among people」に関連付けられている。この連語は、他の単語として、単語sessionと単語talkなどにもそれぞれ関連付けられている。 FIG. 15 is a diagram conceptually showing the structure of the thesaurus for the word agreement. Referring to FIG. 15, the word agreement is associated with the collocation “interaction among people”. This collocation is also associated with other words, such as the word session and the word talk.
図16および図17を参照して、学習コンテンツ生成装置200による誤り指摘問題の生成について説明する。図16および図17は、それぞれ、制御部230が実行する動作の一部を表わすフローチャートである。なお、前述の処理と同一の処理には同一のステップ番号を付してある。したがって、そのような処理の説明は繰り返さない。
With reference to FIG. 16 and FIG. 17, generation of an error indication problem by the learning
ステップS1600にて、制御部230は、組kの例文から1単語を誤らせた語句を生成し、その生成の結果を、誤り問題バッファ278に格納する。処理の詳細は、図17を参照して説明する。
In step S1600,
ステップS1510にて、制御部230は、誤り問題バッファ278の格納の結果に基づいて、誤り指摘問題生成テンプレート248を用いて問題文を生成する。
In step S 1510,
図17を参照して、ステップS1604にて、制御部230は、単語数nw個の領域を持つ誤り問題バッファ278を、メインメモリ部270に確保する。
Referring to FIG. 17, in step S <b> 1604,
ステップS1318にて、制御部230は、単語iがそれ自身とは形の異なる原形または変化形を持っているか否かを判定する。制御部230は、そのような条件が成立していると判定すると(ステップS1318にてYES)、制御をステップS1620に切り換える。そうでない場合には(ステップS1318にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS1630に切り換える。
In step S1318,
ステップS1620にて、制御部230は、単語iについて、英語辞書データ242から単語i自身とは形の異なる原形または変化形を取得し、テンポラリ単語バッファ275にその取得した原型または変化形を格納する。
In step S1620,
ステップS1622にて、制御部230は、変数iの値が1であるか否かを判定する。制御部230は、変数iが1であると判定すると(ステップS1622にてYES)、制御をステップS1624に切り換える。そうでない場合には(ステップS1622にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS1626に切り換える。
In step S1622,
ステップS1624にて、制御部230は、テンポラリ単語バッファ275の単語の先頭文字を大文字に変換する。
In step S1624,
ステップS1626にて、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274の単語のうち、単語i以外の単語を誤り問題バッファ278にコピーする。
In step S <b> 1626,
ステップS1628にて、制御部230は、テンポラリ単語バッファ275の単語を誤り問題バッファ278の単語iの領域に格納する。
In step S 1628,
ステップS1630にて、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274の単語jの領域に、「使用済」フラグを設定する。
In step S 1630,
制御部230は、ステップS1628の処理を終了すると、制御をメイン処理(図16)に戻す。
When the process of step S1628 ends,
ここで、図18を参照して、本実施の形態に係る学習コンテンツ生成装置200が備える他の辞書の構造について説明する。図18は、単語yearの辞書構造を概念的に表わす図である。なお、他の単語についても同様に規定される。
Here, with reference to FIG. 18, the structure of another dictionary provided in learning
当該単語yearの辞書は、IDと、見出しと、品詞と、変化形と、意味を示すデータとを含む。意味を示すデータは、意味カテゴリと、意味コードと、訳語とを含む。当該単語は複数の意味を有する場合には、当該意味を示すデータの各意味に応じて複数存在し得る。 The dictionary of the word year includes an ID, a headline, a part of speech, a variation, and data indicating meaning. The data indicating meaning includes a semantic category, a semantic code, and a translated word. When the word has a plurality of meanings, a plurality of words may exist according to the meanings of the data indicating the meanings.
IDは、単語yearを識別する。見出しは、当該単語yearそれ自身を示す。品詞は、当該単語の品詞を示す。変化形は、当該単語について存在し得る変化形を示す。単語が名詞である場合には、変化形として複数形(years)が規定される。 The ID identifies the word year. The headline indicates the word year itself. The part of speech indicates the part of speech of the word. A variation indicates a variation that may exist for the word. When the word is a noun, a plural form (years) is defined as a variation.
意味について、単語yearの場合、本実施の形態において2つの意味が規定されている。1つの意味は、「TIME」の意味カテゴリを有するものであって、訳語として「年」が割り当てられている。また他の意味として、意味カテゴリ「TIME-UNIT」について訳語「年間」が規定されている。 Regarding the meaning, in the case of the word year, two meanings are defined in the present embodiment. One meaning has a meaning category of “TIME”, and “year” is assigned as a translation. As another meaning, the translated word “year” is defined for the semantic category “TIME-UNIT”.
図19を参照して、学習コンテンツ生成装置200による誤り指摘問題生成の他の態様について説明する。図19は、制御部230が実行する動作の一部を表わすフローチャートである。なお、前述の処理と同一の処理には同一のステップ番号を付してある。したがって、それらのステップについての説明は繰り返さない。
With reference to FIG. 19, another aspect of the error indication problem generation by the learning
ステップS1314にて、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274の単語iの領域に、「使用済」フラグが設定されているか否かを判定する。制御部230は、当該領域に「使用済」フラグが設定されていると判定すると(ステップS1314にてYES)、制御をステップS1312に戻す。そうでない場合には(ステップS1314にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS1720に切り換える。
In step S1314,
ステップS1720にて、制御部230は、英語シソーラスデータ244において、単語iの「原形の」意味情報の位置から意味距離2以内に単語が存在し、かつ、その単語が原文単語バッファ274のうちの単語のいずれとも一致しないか否かを判定する。制御部230は、そのような条件が成立していると判定すると(ステップS1720にてYES)、制御をステップS1730に切り換える。そうでない場合には(ステップS1720にてNO)、制御部230は、制御をステップS1630に切り換える。
In step S1720,
ステップS1730にて、制御部230は、英語シソーラスデータ244において、単語iの「原形の」意味情報の位置から意味距離2以内に存在し、かつ、原文単語バッファ中の単語のいずれとも一致しない単語を取得し、単語iと同じ変化形に変化させて、その変化させた単語をテンポラリ単語バッファ275に格納する。
In step S1730,
図20を参照して、英語シソーラスデータ244の他の態様について説明する。図20は、単語extendのシソーラスの構造を表わす図である。単語extendは、関連する語句として連語「change in size」に関連付けられている。この連語にはさらに他の単語expand、単語shrinkなどが関連付けられている。
With reference to FIG. 20, another aspect of the
[動作]
図21から図41を参照して、以上のような構造およびフローチャートに基づく本実施の形態に係る学習コンテンツ生成装置200の動作について説明する。
[Operation]
With reference to FIGS. 21 to 41, the operation of learning
入力部210に対する操作に基づいて、問題生成の命令が受け付けられると、文数カウンタ271と単語数カウンタ272と入れ替え済み単語数カウンタ280とがそれぞれ初期化される(図21から図23)。メインメモリ部270において、語順入れ替え結果バッファ276が確保される(図24)。対訳例文データベース241からランダムに選択された英語原文が、原文単語バッファ領域274に格納される(図25)。
When a problem generation command is received based on an operation on the
ここで、図26を参照して、単語extendについての辞書の構造について説明する。単語extendは、辞書構造として、IDと、見出しと、品詞と、変化形と、意味を示すデータとを含む。単語extendについてID(00632308)が割り当てられている。見出しは、当該単語自身が使用される。品詞は、「動詞」として規定されている。変化形は、3単元と、過去形と、過去分詞形と、ing(現在分子形)とを含む。 Here, with reference to FIG. 26, the structure of the dictionary for the word extend will be described. The word extend includes, as a dictionary structure, an ID, a headline, a part of speech, a variation, and data indicating meaning. An ID (00632308) is assigned to the word extend. For the headline, the word itself is used. Part of speech is defined as a “verb”. Variations include three units, past tense, past participle form, and ing (current molecular form).
意味を示すデータとして、2つの意味(訳語:「継続・する」と「延長・する」)とが使用されている。 As meaning data, two meanings (translation: “continue / continue” and “extend / extend”) are used.
図26を参照して、単語番号「6」の単語extendedについて、当該単語を含む辞書ID(=00632308)が参照され、図27に示されるように、その辞書からing形として単語extendingが選択され、テンポラリ単語バッファ275に格納される。
Referring to FIG. 26, for the word extended with the word number “6”, the dictionary ID (= 00632308) including the word is referred to, and as shown in FIG. 27, the word extending is selected as the ing form from the dictionary. , Stored in
テンポラリ単語バッファ275に格納された単語(extending)は、後述する単語の入れ替え問題の生成に用いられる。
The word (extending) stored in the
図28を参照して、原文単語バッファ領域274において、単語の入れ替えの候補を選択するために使用された単語extended(単語番号6)には、その選択されたことを示すフラグがセットされる(フラグ=1)。
Referring to FIG. 28, in the original
そして、図29に示されるように、テンポラリ単語バッファ275に格納された単語extendingが原文単語バッファ領域274の空き領域(単語番号11)に格納される。
Then, as shown in FIG. 29, the word extending stored in the
原文単語バッファ274においてこのように格納されたデータを用いて、語順入れ替え問題が生成される。
Using the data stored in this way in the
まず、図30を参照して、語順入れ替え結果バッファ276において、最初の単語が語順1の領域に格納される。図30に示される例では、単語automaticallyが語順1の領域に格納されている。その入れ替えが行なわれると、入れ替え済み単語数カウンタ280の値が1インクリメントされる(nw1=1)(図31)。
First, referring to FIG. 30, the first word is stored in the
そのような入れ替え処理が原文単語バッファ274に格納されている単語および/または記号の数だけ行なわれると(図29に示される例では11回)、図32に示されるように、語順が入れ替えられた問題文が語順入れ替え結果バッファ276において完成する。
When such replacement processing is performed by the number of words and / or symbols stored in the original word buffer 274 (11 times in the example shown in FIG. 29), the word order is changed as shown in FIG. The completed question sentence is completed in the word order change result
[テンプレート]
図33を参照して、並べ替え問題テンプレート246について説明する。図33は、並べ替え問題テンプレート246の構成を概念的に表わす図である。並べ替え問題テンプレート246は、並べ替え問題の出題であることを示す問題文(定型)と、正規の文章を構成する単語をランダムに並べることを規定するテンプレートと、当該正規の文章の訳文の表示を規定するテンプレートとを含む。なお、他の局面において、訳文を表示しない構成が並べ替え問題テンプレート246に使用されてもよい。
[template]
The
[表示態様]
図34を参照して、本実施の形態に係る学習コンテンツ生成装置200の画面の表示態様について説明する。図34は、モニタ180における問題文の表示態様を表わす図である。
[Display mode]
With reference to FIG. 34, the display mode of the screen of learning
学習コンテンツ生成装置200の使用者が、たとえば問題文の生成の開始を指示すると(たとえばエンターキーを押下すると)、学習コンテンツ生成装置200は、前述のフローチャートに基づく処理を実行し、英文を構成する単語の語順を入れ替えた問題を生成する。図34に示されるように、学習コンテンツ生成装置200は、その生成した問題文をモニタ180に表示させる。
For example, when the user of the learning
図35から図41を参照して、並べ替え問題の他の態様について説明する。図35を参照して、原文単語バッファ274に格納されている原文において、単語automatically(単語番号5)が、類義語の探索の対象になった場合について説明する。この場合、類義語探索部260は、図36に示されるようなシソーラス構造を用いて、単語automaticallyから意味距離2以内の単語を求める。たとえば、図36に示される例において、単語automaticallyのシソーラスは、連語「way of operation」と、単語manually,smoothlyなどがそれぞれ規定されている。ここで、単語と単語との間あるいは単語と連語との間のリンク1つを意味距離1と定義すると、単語automaticallyから意味距離1において連語「way of operation」が存在しており、単語automaticallyから意味距離2において、単語manuallyと単語smoothlyがそれぞれ存在している。そこで、類義語探索部260は、意味距離2が定義されている場合には、図36に示されるようなシソーラスから単語manuallyまたは単語smoothlyなどをランダムに選択し、その選択した単語をテンポラリ単語バッファ275に格納する(図37)。
With reference to FIGS. 35 to 41, another aspect of the rearrangement problem will be described. Referring to FIG. 35, a case will be described in which the word automatically (word number 5) is a target for searching for synonyms in the original text stored in original
なお、本実施の形態においては、類義語の定義を「シソーラス構造上における意味距離2以内」としているが、類義語の定義はこれに限られない。制御部230は、テンポラリ単語バッファ275に格納した類義語manuallyを原文単語バッファ274の空き領域(単語番号11)に格納する(図38)。また、入れ替えの対象として選択された単語automaticallyには、当該単語が選択されたことを示すフラグ「1」をセットする。
In this embodiment, the definition of the synonym is “within the
その後、制御部230は、最初の領域(語順1)にランダムに単語を選択し(たとえば単語agreement)、その単語を語順入れ替え結果バッファ276に格納する(図39)。同様にして、原文単語バッファ274に格納されている単語並べ替え処理を繰り返すと、語順が入れ替えられた問題が完成する(図40)。
Thereafter,
そこで、制御部230は、語順入れ替え結果バッファ276に格納されているデータを用いて出力部220にその問題文を出力する。学習コンテンツ生成装置200が図1に示されるコンピュータシステムで実現される場合には、モニタ180は、問題文と、語順が入れ替えられた単語の列とヒントとして日本語の訳文とをそれぞれ表示する(図41)。
Therefore, the
[穴埋め問題の生成]
図42から図51を参照して、穴埋め問題を生成する場合の学習コンテンツ生成装置200の動作について説明する。以下の説明では、選択肢が3つある場合について説明するが、選択肢の数はこれに限られない。選択肢は、2つでもよく、あるいは、4つ以上でもよい。
[Generate hole filling problem]
With reference to FIG. 42 to FIG. 51, the operation of the learning
制御部230は、メインメモリ部270のメモリ領域を初期化した後、原文単語バッファ274において、穴埋め問題の生成への対象となる原文を格納する(図42)。制御部230は、穴埋め選択肢バッファ277において、少なくとも選択肢の数だけメモリ領域を確保する。この例では、制御部230は、3つのメモリ領域を確保する。制御部230は、乱数発生部257と乱数正規化部258とに基づいて、穴埋め問題の対象となる単語を選択する。図42に示される原文では、単語番号6(単語extended)が選択される。制御部230は、その選択した単語を穴埋め選択肢バッファ277のいずれかの領域に格納する(図43)。制御部230は、英語辞書データ242を参照して当該選択した単語extendedの原形または変化形をさらに選択する。もし、選択の候補が選択肢の数よりも多い場合には、制御部230は、乱数発生部257および乱数正規化部258に基づいて選択的に原形または変化形を決定してもよい。制御部230は、選択した原形または変化形を穴埋め選択肢バッファ277の他の領域に格納する(図44)。
After initializing the memory area of the
図45を参照して、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274において、穴埋め問題の対象として選択した単語extendedを削除し、単語番号6の領域に当該単語が問題文の候補として選択されたことを示すフラグ「1」を設定する。
Referring to FIG. 45,
図46を参照して、制御部230は、穴埋め問題生成テンプレート247を用いて、原文単語バッファ274に格納されているデータと、穴埋め選択肢バッファ277に格納されているデータとを用いて、穴埋め問題を生成する。制御部230が生成した問題文は、穴埋め問題生成テンプレート247に従って、図47に示されるように、モニタ180に表示される。
Referring to FIG. 46,
以上のようにして、本発明の実施の形態に係る学習コンテンツ生成装置200は、穴埋め問題を生成するため、学習コンテンツ生成装置200の使用者は、容易に、穴埋め問題に取り組むことができる。
As described above, the learning
<第4の変形例>
図48から図51を参照して、穴埋め問題として類義語が用いられる場合について説明する。制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274に格納されている原文(図42)から、穴埋めの問題の候補となる単語を選択し、その選択した単語を穴埋め選択肢バッファ277の領域に書き込む(図48)。制御部230は、シソーラスを用いて(図15)、選択した単語agreementの類義語session、talkを選択する。制御部230は、その選択した各類義語を穴埋め選択肢バッファ277にそれぞれ格納する(図49)。
<Fourth Modification>
A case where synonyms are used as the hole filling problem will be described with reference to FIGS. 48 to 51. The
図50を参照して、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274において、単語番号2に格納されていた単語agreementを削除し、その単語が問題の作成のために用いられたことを示すフラグ「1」を設定する。
Referring to FIG. 50,
図51を参照して、制御部230は、穴埋め問題生成テンプレート247を用いて(図46)、穴埋め選択肢バッファ277に格納されている単語と、原文単語バッファ274に原文からランダムに選択した番号の単語を消去して当該番号の単語欄をブランクにした穴空き文(図50)とに基づいて、生成した穴埋め問題をモニタ180に表示させる。
Referring to FIG. 51,
<第5の変形例>
さらに他の局面において、学習コンテンツ生成装置200は、消去された単語の他の形を、穴埋め問題の解答の候補として含んでもよい。具体的な態様の一例として、単数形が消去された場合における複数形、動詞の原形が消去された場合における過去形などが回答の候補として使用されてもよい。このようにしても、問題のバリエーションを増やすことができる。
<Fifth Modification>
In still another aspect, the learning
この局面において、英語辞書データ242は、英単語を英語の文法規則に従って変化させることによって得られる変化形を含んでいる。制御部230は、複数の候補単語として、複数の単語のいずれかの当該変化形を選択する。制御部230は、その変化形も含む単語を、複数の候補単語として出力する。
In this aspect, the
[誤り指摘問題の生成]
図52から図62を参照して、学習コンテンツ生成装置200による誤り指摘問題の生成の一態様について説明する。図52を参照して、制御部230は、対訳例文データベース241からランダムに選択した原文を原文単語バッファ274に格納する。制御部230は、乱数発生部257と乱数正規化部258とを用いて、誤り指摘問題の候補となる単語を選択する。たとえば、制御部230は、単語番号9に格納されている単語yearsを選択する。制御部230は、選択した単語yearsを含む単語辞書(図18)を参照し、単語yearsが複数形である場合におけるその単語の原形yearを特定する。図53を参照して、制御部230は、その特定した単語をテンポラリ単語バッファ275に格納する。
[Generating an error indication problem]
With reference to FIGS. 52 to 62, an aspect of generating an error indication problem by the learning
図54を参照して、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274に格納されている単語のうち、単語番号9(問題文の候補として選択された単語)を除く単語を、誤り問題バッファ278に格納する。
Referring to FIG. 54,
図55を参照して、制御部230は、さらに、誤り問題バッファ278に対して、テンポラリ単語バッファ275に格納されている単語yearを格納する。その結果、複数形が意図的に原形に変更された問題文が、誤り問題として生成される。
Referring to FIG. 55,
図56参照して、制御部230は、誤り指摘問題生成テンプレート248を用いて、誤り問題バッファ278に格納されているデータをそのテンプレートに当てはめて、問題文を生成する。図57を参照して、制御部230は、その生成した問題文をモニタ180に表示させる(図57)。
Referring to FIG. 56,
<第6の変形例>
図58から図62を参照して、誤り指摘問題として類義語が使用される場合について説明する。
<Sixth Modification>
A case where a synonym is used as an error indication problem will be described with reference to FIGS.
図58を参照して、制御部230は、原文単語バッファ274に、対訳例文データベース241からランダムに選択した問題文を格納する。制御部230は、乱数発生部257および乱数正規化部258の各出力に基づいて、誤り指摘問題の対象となる単語を選択する。たとえば、制御部230は、単語番号6(単語extended)を選択する。制御部230は、その選択した単語の原形を辞書データを用いて特定し、その原形からシソーラスを用いて類義語を選択する(図20)。たとえば、類義語の選択基準として意味距離2が規定されている場合には、制御部230は、単語extendの類義語として単語expand、単語shrinkなどの単語を選択し得る。制御部230は、乱数発生部275および乱数正規化部258を用いていずれかの単語を選択する。たとえば、制御部230は、単語shrinkを選択する。
Referring to FIG. 58,
図59を参照して、選択された単語は過去形であるため、制御部230は、選択した単語を辞書データを用いて過去形に変形し、その過去形をテンポラリ単語バッファ275に格納する。
Referring to FIG. 59, since the selected word is a past tense,
図60を参照して、制御部230は、誤り問題バッファ278において、問題の候補として選択した単語番号6の領域をブランクにした状態で原文単語バッファ274に格納されている単語を格納する。この場合、制御部230は、単語extended以外の単語を誤り問題バッファ278に格納する。
Referring to FIG. 60,
図61を参照して、制御部230は、テンポラリ単語バッファ275に格納されている単語shrinkedを、単語番号6の領域に格納する。
Referring to FIG. 61,
図62を参照して、制御部230は、誤り問題バッファ278に格納されている完成文をモニタ180に表示させる。
Referring to FIG. 62,
以上のようにして、本発明の実施の形態に係る学習コンテンツ生成装置200は、予め準備された複数組の例文および訳文をランダムに選択し、その選択した一組の例文および訳文を用いて、例文を構成する単語の入れ替え、変形、除去を行なうことにより、問題を生成する。したがって、予め問題を保持する必要がないため、学習コンテンツ生成装置200は、起動されるごとに、ランダムな出題を行なうことができる。また、学習コンテンツ生成装置200は、問題数の制約を受けることなく、多くのバリエーションの問題を生成することができる。これにより、簡易に問題を生成できる学習コンテンツ生成装置200を提供することができる。
As described above, the learning
今回開示された実施の形態はすべての点で例示であって制限的なものではないと考えられるべきである。本発明の範囲は上記した説明ではなくて特許請求の範囲によって示され、特許請求の範囲と均等の意味および範囲内でのすべての変更が含まれることが意図される。 The embodiment disclosed this time should be considered as illustrative in all points and not restrictive. The scope of the present invention is defined by the terms of the claims, rather than the description above, and is intended to include any modifications within the scope and meaning equivalent to the terms of the claims.
本発明は、情報処理装置、たとえば、パーソナルコンピュータ、PDAのような情報処理端末、電子辞書などに適用可能である。 The present invention can be applied to an information processing apparatus such as a personal computer, an information processing terminal such as a PDA, an electronic dictionary, and the like.
100 コンピュータシステム、162 CD−ROM。 100 Computer system, 162 CD-ROM.
Claims (12)
画面を表示する表示手段と、
第1の言語によって複数の単語から構成される第1の言語の例文と、前記第1の言語の例文を第2の言語に翻訳した翻訳文とを対応付けて格納し、該第1の言語の単語の品詞と当該言語の変化形とを対応付けて辞書データとして格納した記憶手段と、
前記学習コンテンツ生成装置を制御する制御手段とを備え、
前記制御手段は、
前記第1の言語の例文を構成する前記複数の単語からランダムに1の単語を選択し、
前記選択された前記1の単語の変化形を前記辞書データから取得して、前記選択された1の単語の変化形が複数あるか否かを判定し、前記選択された1の単語の変化形が複数個ないと判定される場合は、前記複数の単語から1の単語をランダムに再選択し、前記再選択された1の単語について前記判定を行い、
前記選択された1の単語の変化形が複数あると判定される場合は、前記辞書データから、前記選択された1の単語と同一の品詞の複数の単語を取得し、取得した複数の単語を前記変化形に変化させた複数の候補単語を前記記憶手段から選択し、
前記例文を構成する複数の単語から、前記選択された1の単語を除いた残りの単語からなる一連の単語と、前記選択された1の単語の削除を示すための表示と、前記選択された1の単語と前記複数の候補単語とを選択肢として表示する問題文を生成し、
前記問題文を、前記表示手段に表示させる、学習コンテンツ生成装置。 A learning content generation device,
Display means for displaying a screen;
A first language example sentence composed of a plurality of words in a first language and a translated sentence obtained by translating the example sentence in the first language into a second language are stored in association with each other. Storage means for storing the part of speech of the word and the variation of the language as dictionary data in association with each other;
Control means for controlling the learning content generation device,
The control means includes
Randomly selecting one word from the plurality of words constituting the example sentence of the first language;
The variation of the selected one word is obtained from the dictionary data, and it is determined whether or not there are a plurality of variations of the selected one word, and the variation of the selected one word When it is determined that there are not a plurality of words, one word is re-selected at random from the plurality of words, and the determination is performed on the re-selected one word.
When it is determined that there are a plurality of variations of the selected one word , a plurality of words having the same part of speech as the selected one word are acquired from the dictionary data , and the acquired plurality of words are A plurality of candidate words changed to the changed form are selected from the storage means,
A series of words consisting of the remaining words excluding the selected one word from a plurality of words constituting the example sentence, a display for indicating deletion of the selected one word , and the selected Generating a question sentence that displays one word and the plurality of candidate words as options;
A learning content generation apparatus that causes the display unit to display the question sentence.
画面を表示する表示手段と、
第1の言語によって複数の単語から構成される第1の言語の例文と、前記第1の言語の例文を第2の言語に翻訳した翻訳文とを対応付けて格納し、該第1の言語の単語の品詞と当該言語の変化形とを対応付けて辞書データとして格納した記憶手段と、
前記学習コンテンツ生成装置を制御する制御手段とを備え、
前記制御手段は、
前記第1の言語の例文を構成する前記複数の単語からランダムに1の単語を選択し、
前記選択された前記1の単語の変化形を前記辞書データから取得して、前記選択された前記1の単語の変化形があるか否かを判定し、前記選択された前記1の単語の変化形がないと判定される場合は、前記複数の単語から1の単語をランダムに再選択し、前記再選択された1の単語について前記判定を行い、
前記選択された1の単語の変化形があると判定される場合は、前記辞書データから、前記1の単語と同一の品詞で当該1の単語とは異なる別の単語を取得し、取得した当該別の単語を前記変化形に変化させた候補単語を前記記憶手段から選択し、
前記例文を構成する複数の単語から、前記選択された1の単語を除いた残りの単語からなる一連の単語と、前記選択された1の単語の削除を示すための表示と、前記選択された1の単語と前記複数の候補単語とを選択肢として表示する問題文を生成し、
前記問題文を、前記表示手段に表示させる、学習コンテンツ生成装置。 A learning content generation device,
Display means for displaying a screen;
A first language example sentence composed of a plurality of words in a first language and a translated sentence obtained by translating the example sentence in the first language into a second language are stored in association with each other. Storage means for storing the part of speech of the word and the variation of the language as dictionary data in association with each other;
Control means for controlling the learning content generation device,
The control means includes
Randomly selecting one word from the plurality of words constituting the example sentence of the first language;
The variation of the selected one word is obtained from the dictionary data, and it is determined whether there is a variation of the selected one word, and the variation of the selected one word When it is determined that there is no shape, one word is randomly reselected from the plurality of words, and the determination is performed on the one reselected word,
If it is determined that there is variation of 1 word said selected, said from the dictionary data to get the different different word from the word of the 1 in the same part of speech a word of the one, acquired the A candidate word obtained by changing another word into the variation is selected from the storage means;
A series of words consisting of the remaining words excluding the selected one word from a plurality of words constituting the example sentence, a display for indicating deletion of the selected one word , and the selected Generating a question sentence that displays one word and the plurality of candidate words as options;
A learning content generation apparatus that causes the display unit to display the question sentence.
前記制御手段は、前記1の単語の類義語を前記別の単語として選択する、請求項2に記載の学習コンテンツ生成装置。 The dictionary includes a synonym dictionary;
It said control means selects the one word synonyms as said another word, the learning content generation apparatus of claim 2.
前記プロセッサが、前記第1の言語の例文を構成する前記複数の単語からランダムに1の単語を選択し、前記選択された前記1の単語の変化形を前記辞書データから取得して、前記選択された1の単語の変化形が複数あるか否かを判定し、前記選択された1の単語の変化形が複数個ないと判定される場合は、前記複数の単語から1の単語をランダムに再選択し、前記再選択された1の単語について前記判定を行うステップと、
前記プロセッサが、前記選択された1の単語の変化形が複数あると判定される場合は、前記辞書データから、前記選択された1の単語と同一の品詞の複数の単語を取得し、取得した複数の単語を前記変化形に変化させた複数の候補単語を前記メモリから選択するステップと、
前記プロセッサが、前記例文を構成する複数の単語から、前記選択された1の単語を除いた残りの単語からなる一連の単語と、前記選択された1の単語の削除を示すための表示と、前記選択された1の単語と前記複数の候補単語とを選択肢として表示する問題文を生成するステップと、
前記プロセッサが、前記問題文を前記ディスプレイ装置に表示させるステップとを含む、学習コンテンツの生成方法。 A learning content generating method by a computer, wherein the computer converts a processor, a first language example sentence composed of a plurality of words in a first language, and a first language example sentence into a second language. And a display device, a memory that stores the translated sentence translated into the dictionary data in association with the part of speech of the word in the first language and the variation of the language,
The processor randomly selects one word from the plurality of words constituting the example sentence of the first language, obtains a variation of the selected one word from the dictionary data, and selects the selection It is determined whether or not there is a plurality of variations of the selected one word, and when it is determined that there are not a plurality of variations of the selected one word, one word is randomly selected from the plurality of words Reselecting and making the determination for the reselected one word;
When it is determined that there are a plurality of variations of the selected one word , the processor acquires a plurality of words having the same part of speech as the selected one word from the dictionary data , and acquired Selecting, from the memory, a plurality of candidate words obtained by changing a plurality of words into the variation;
A series of words including a remaining word obtained by removing the selected one word from a plurality of words constituting the example sentence; and a display for indicating deletion of the selected one word ; Generating a question sentence that displays the selected one word and the plurality of candidate words as options;
And a step of causing the processor to display the question sentence on the display device.
前記プロセッサが、前記第1の言語の例文を構成する前記複数の単語からランダムに1の単語を選択し、前記選択された前記1の単語の変化形を前記辞書データから取得して、前記選択された前記1の単語の変化形があるか否かを判定し、前記選択された前記1の単語の変化形がないと判定される場合は、前記複数の単語から1の単語をランダムに再選択し、前記再選択された1の単語について前記判定を行うステップと、
前記プロセッサが、前記選択された1の単語の変化形があると判定される場合は、前記辞書データから、前記1の単語と同一の品詞で当該1の単語とは異なる別の単語を取得し、取得した当該別の単語を前記変化形に変化させた候補単語を前記メモリから選択するステップと、
前記プロセッサが、前記例文を構成する複数の単語から、前記選択された1の単語を除いた残りの単語からなる一連の単語と、前記選択された1の単語の削除を示すための表示と、前記選択された1の単語と前記複数の候補単語とを選択肢として表示する問題文を生成するステップと、
前記プロセッサが、前記問題文を、前記ディスプレイ装置に表示させるステップとを含む、学習コンテンツの生成方法。 A learning content generating method by a computer, wherein the computer converts a processor, a first language example sentence composed of a plurality of words in a first language, and a first language example sentence into a second language. And a display device, a memory that stores the translated sentence translated into the dictionary data in association with the part of speech of the word in the first language and the variation of the language,
The processor randomly selects one word from the plurality of words constituting the example sentence of the first language, obtains a variation of the selected one word from the dictionary data, and selects the selection It is determined whether there is a variation of the selected one word, and if it is determined that there is no variation of the selected one word, one word is re-randomly selected from the plurality of words. Selecting and making the determination for the reselected one word;
Wherein the processor, when the variation of the first word said selected is determined that there is the from the dictionary data to get the different different word from the word of the 1 in the same part of speech a word of the 1 Selecting from the memory a candidate word obtained by changing the acquired another word into the change form;
A series of words including a remaining word obtained by removing the selected one word from a plurality of words constituting the example sentence; and a display for indicating deletion of the selected one word ; Generating a question sentence that displays the selected one word and the plurality of candidate words as options;
And a step of causing the processor to display the question sentence on the display device.
前記選択するステップは、前記1の単語の類義語を前記別の単語として選択することを含む、請求項7に記載の学習コンテンツの生成方法。 The dictionary data includes synonym dictionary data ,
Step includes selecting the first word synonyms as said another word, a method of generating a learning content according to claim 7, wherein said selecting.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008099404A JP5317093B2 (en) | 2008-04-07 | 2008-04-07 | Learning content generation device, learning content generation method, program for causing a computer to function as the learning content generation device, and computer-readable recording medium storing the program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008099404A JP5317093B2 (en) | 2008-04-07 | 2008-04-07 | Learning content generation device, learning content generation method, program for causing a computer to function as the learning content generation device, and computer-readable recording medium storing the program |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009251292A JP2009251292A (en) | 2009-10-29 |
| JP2009251292A5 JP2009251292A5 (en) | 2011-04-28 |
| JP5317093B2 true JP5317093B2 (en) | 2013-10-16 |
Family
ID=41312072
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008099404A Expired - Fee Related JP5317093B2 (en) | 2008-04-07 | 2008-04-07 | Learning content generation device, learning content generation method, program for causing a computer to function as the learning content generation device, and computer-readable recording medium storing the program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5317093B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012165585A1 (en) * | 2011-06-03 | 2012-12-06 | ココネ株式会社 | Learning system |
| CN102693660A (en) * | 2012-05-18 | 2012-09-26 | 苏州慧飞信息科技有限公司 | Poetry teaching software |
| CN106843621A (en) | 2017-02-27 | 2017-06-13 | 武汉华星光电技术有限公司 | Flexible touching display screen and preparation method thereof |
| JP7287412B2 (en) * | 2021-03-24 | 2023-06-06 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Information processing device, information processing method and program |
| JP7312418B1 (en) * | 2023-06-14 | 2023-07-21 | 博 村上 | English grammar learning support system |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3811992B2 (en) * | 1996-06-12 | 2006-08-23 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Electronic learning machine |
| JP2002268536A (en) * | 2001-03-07 | 2002-09-20 | Tsubota Toru | Problem forming system, problem forming method and program for making computer execute problem forming processing |
| JP4018673B2 (en) * | 2004-07-29 | 2007-12-05 | 株式会社国際電気通信基礎技術研究所 | Multiple choice language test question automatic creation program |
| JP4827163B2 (en) * | 2004-10-27 | 2011-11-30 | Kddi株式会社 | Test question distribution system |
-
2008
- 2008-04-07 JP JP2008099404A patent/JP5317093B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2009251292A (en) | 2009-10-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2008268684A (en) | Voice reproducing device, electronic dictionary, voice reproducing method, and voice reproducing program | |
| JP2003015803A (en) | Japanese input mechanism for small keypad | |
| JP5317093B2 (en) | Learning content generation device, learning content generation method, program for causing a computer to function as the learning content generation device, and computer-readable recording medium storing the program | |
| JP2003196280A (en) | Text generating method and text generating device | |
| JP2012073519A (en) | Reading-aloud support apparatus, method, and program | |
| JP2000298667A (en) | Kanji converting device by syntax information | |
| JP4200874B2 (en) | KANSEI information estimation method and character animation creation method, program using these methods, storage medium, sensitivity information estimation device, and character animation creation device | |
| JP4845523B2 (en) | Character processing apparatus, method, program, and recording medium | |
| JP6619932B2 (en) | Morphological analyzer and program | |
| JP2009157888A (en) | Transliteration model generation device, transliteration apparatus, and computer program therefor | |
| KR101543024B1 (en) | Method and Apparatus for Translating Word based on Pronunciation | |
| JP6805927B2 (en) | Index generator, data search program, index generator, data search device, index generation method, and data search method | |
| JP6881077B2 (en) | Discrimination program, discrimination device and discrimination method | |
| KR100918489B1 (en) | Method Of Comparing Similarities of Texts And System Of Comparing Similarities of Texts | |
| KR102573967B1 (en) | Apparatus and method providing augmentative and alternative communication using prediction based on machine learning | |
| JP5293091B2 (en) | Data processing apparatus, computer program thereof, and data processing method | |
| JP7115187B2 (en) | Information processing device, information processing method and program | |
| JP2006065542A (en) | Machine translation method | |
| JP2001109740A (en) | Device and method for preparing chinese document | |
| JP5229448B2 (en) | Reading imparting device and program | |
| JP5664042B2 (en) | SEARCH DEVICE, SEARCH METHOD, SEARCH PROGRAM, AND SEARCH SYSTEM | |
| JP5297234B2 (en) | Method and system for reducing the error for long sounds and prompt sounds using a Japanese alias database and providing a single character search function when using a Japanese input device | |
| Pahisa-Solé | Compansion system for a pictogram-based AAC application in Catalan | |
| KR20200011794A (en) | Data processing system and method for language learning | |
| JPH06289889A (en) | Speech synthesizing device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110309 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110309 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20111215 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20111220 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120217 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130312 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130509 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130611 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130703 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |