JP4894708B2 - Imaging device - Google Patents
Imaging device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4894708B2 JP4894708B2 JP2007258455A JP2007258455A JP4894708B2 JP 4894708 B2 JP4894708 B2 JP 4894708B2 JP 2007258455 A JP2007258455 A JP 2007258455A JP 2007258455 A JP2007258455 A JP 2007258455A JP 4894708 B2 JP4894708 B2 JP 4894708B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- image
- subject
- trimming
- image data
- moving image
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Television Signal Processing For Recording (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
Description
本発明は、動画撮影機能を備えた撮像装置に関する。 The present invention relates to an imaging apparatus having a moving image shooting function.
従来から、動画撮影機能を備えた電子カメラにおいて、動画撮影中に静止画のデータを生成できるものが知られている。一例として、特許文献1には、動画撮影中に静止画撮影指示があった場合には動画のフレームに識別情報を付加し、静止画の読み出し時には識別情報のあるフレームを出力する構成が開示されている。
ところで、従来技術では動画の1フレームを静止画として出力するにすぎない。そのため、静止画として出力されるフレームでは主要被写体が好ましい構図で撮影されているとは限らず、静止画としての出来映えが劣ることが多い点で改善の余地があった。 By the way, in the prior art, only one frame of a moving image is output as a still image. For this reason, in the frame output as a still image, the main subject is not necessarily photographed with a preferable composition, and there is room for improvement in that the performance as a still image is often inferior.
本発明は上記従来技術の課題を解決するためのものである。本発明の目的は、動画撮影時により好ましい構図の静止画像を取得できる手段を提供することである。 The present invention is to solve the above-mentioned problems of the prior art. An object of the present invention is to provide means capable of acquiring a still image having a more preferable composition at the time of moving image shooting.
第1の発明に係る撮像装置は、撮像素子と、メモリと、動画像データ生成部と、記録インターフェースと、入力部と、被写体認識部と、トリミング処理部とを備える。撮像素子は、所定間隔ごとに被写体を撮像して、各々の画像のデータを出力する。メモリは、画像のデータを一時的に保持する。動画像データ生成部は、複数の画像から動画像データを生成する。記録インターフェースは、動画像データを記憶媒体に記録する。入力部は、静止画記録の指示入力を受け付ける。被写体認識部は、画像から認識対象の被写体を検出する。トリミング処理部は、指示入力のときに撮像された画像から認識対象の被写体を含む部分領域をトリミングし、認識対象の被写体が所定の構図で配置されたトリミング画像のデータを生成する。また、トリミング処理部は、画像の端から認識対象の被写体までの余白量に基づいて、画像を縦長にトリミングする第1処理と画像を横長にトリミングする第2処理とを切り替える。 An imaging apparatus according to a first invention includes an imaging device, a memory, a moving image data generation unit, a recording interface, an input unit, a subject recognition unit, and a trimming processing unit. The imaging device images a subject at predetermined intervals and outputs data of each image. The memory temporarily holds image data. The moving image data generation unit generates moving image data from a plurality of images. The recording interface records moving image data on a storage medium. The input unit accepts a still image recording instruction input. The subject recognition unit detects a subject to be recognized from the image. The trimming processing unit trims a partial area including a subject to be recognized from an image captured at the time of inputting an instruction, and generates data of a trimmed image in which the subject to be recognized is arranged with a predetermined composition. The trimming processing unit switches between a first process for trimming an image vertically and a second process for trimming an image horizontally based on the amount of margin from the edge of the image to the subject to be recognized.
第2の発明は、第1の発明において、画像の解像度は、動画像データの1フレームの解像度よりも高く設定される。 In a second aspect based on the first aspect, the resolution of the image is set higher than the resolution of one frame of the moving image data.
第3の発明は、第1または第2の発明において、トリミング処理部は、トリミング画像を黄金比で分割する縦横のラインの交点上に認識対象の被写体が位置するように、トリミングの位置を決定する。 In a third aspect based on the first or second aspect, the trimming processing unit determines a trimming position so that a subject to be recognized is positioned at an intersection of vertical and horizontal lines dividing the trimmed image by the golden ratio. To do.
第4の発明は、第1から第3のいずれかの発明において、トリミング処理部は、画像内での認識対象の被写体の大きさに基づいて、トリミングの範囲を決定する。 In a fourth aspect based on any one of the first to third aspects, the trimming processing unit determines a trimming range based on a size of a subject to be recognized in an image.
本発明によれば、動画撮影中における静止画記録の指示入力に応じて認識対象の被写体を含む部分領域が画像からトリミングされ、認識対象が所定の構図で配置されたトリミング画像を取得できる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to acquire a trimmed image in which a partial area including a subject to be recognized is trimmed from an image in response to a still image recording instruction input during moving image shooting, and the recognition target is arranged in a predetermined composition.
図1は本実施形態の電子カメラの構成を示すブロック図である。本実施形態の電子カメラは、静止画撮影機能と動画撮影機能とを備えている。 FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the electronic camera of this embodiment. The electronic camera of this embodiment has a still image shooting function and a moving image shooting function.
電子カメラは、撮像光学系11と、撮像素子12と、撮像素子駆動回路13と、信号処理回路14と、第1フレームメモリ15と、第2フレームメモリ16と、動画像データ生成部17と、RAM18と、静止画像データ生成部19と、記録I/F20と、モニタ21と、入力部22と、CPU23およびバス24とを有している。ここで、動画像データ生成部17、静止画像データ生成部19、記録I/F20、モニタ21、CPU23はバス24を介してそれぞれ接続されている。また、撮像素子駆動回路13および入力部22は、それぞれCPU23に接続されている。
The electronic camera includes an image pickup
撮像光学系11は、ズームレンズやフォーカシングレンズを含む複数のレンズ群で構成されている。なお、簡単のため、図1では撮像光学系11を1枚のレンズとして図示する。
The imaging
撮像素子12は、撮像光学系11を通過した光束による被写体像を光電変換してアナログの画像信号を生成する。この撮像素子12の出力は信号処理回路14に接続されている。なお、本実施形態の撮像素子12は、3264×2448画素の画像を60fpsのフレームレートで読み出し可能なCMOSセンサで構成されている。
The
撮像素子駆動回路13は、CPU23の指示に基づいて、撮像素子12に対してタイミングパルスを供給する。なお、撮像素子12の電荷蓄積時間や信号読み出しのタイミングは、撮像素子駆動回路13のタイミングパルスで調整されることとなる。
The image
信号処理回路14は、撮像素子12の出力に対してアナログ信号処理を施す前段のアナログフロントエンド回路(AFE)と、デジタル信号処理を施す後段のデジタルフロントエンド回路(DFE)とを内部に有している。信号処理回路14のAFEは、相関二重サンプリングや、画像信号のゲインの調整や、画像信号のA/D変換を行う。また、信号処理回路14のDFEは、ディジタルデータのクランプ補正や、暗電流成分のオフセット補正などを実行する。なお、信号処理回路14の出力は、第1フレームメモリ15および第2フレームメモリ16にそれぞれ接続されている。
The
第1フレームメモリ15および第2フレームメモリ16は、動画撮影時に生成される画像のデータを一時的に保持するバッファメモリである。第1フレームメモリ15は動画像データ生成部17と接続されており、動画像データの生成に使用される。また、第2フレームメモリ16は静止画像データ生成部19と接続されており、後述のトリミング画像のデータの生成に使用される。
The
動画像データ生成部17は、動画像に関する画像処理を行うASICである。この動画像データ生成部17は、第1フレームメモリ15の1フレーム分の画像のデータに対して各種の画像処理(色補間処理、階調変換処理、輪郭強調処理、ホワイトバランス調整など)を実行する。また、動画像データ生成部17は、各フレームの解像度変換処理や、所定の画像フォーマットでの圧縮処理(例えば、Motion−JPEG、Motion−JPEG2000、MPEG−2など)を実行し、動画像データを生成する。なお、動画像データ生成部17は、モニタ21の表示画像のデータも生成する。
The moving image
RAM18は、被写体認識を行うときに用いる特徴情報を記憶した不揮発性の記憶媒体であって、静止画像データ生成部19と接続されている。なお、本実施形態の電子カメラでは、人間、動物、建築物、乗物などを含むあらゆる物を認識対象の被写体として登録することが可能である。
The
ここで、上記の特徴情報は、一例として被写体の画像のデータで構成される。また、特徴情報は、撮像画像の輪郭成分、輝度、色差、コントラスト比などのパラメータを示すデータであってもよい。さらに、認識対象の被写体が人物の顔である場合には、顔の特徴点の位置、各特徴点の相対距離などを特徴情報とすることもできる。 Here, the feature information is composed of image data of a subject as an example. The feature information may be data indicating parameters such as the contour component, brightness, color difference, and contrast ratio of the captured image. Furthermore, when the subject to be recognized is a human face, the position of the facial feature point, the relative distance of each feature point, and the like can be used as the feature information.
静止画像データ生成部19は、静止画像に関する画像処理を行うASICである。この静止画像データ生成部19は、第1フレームメモリ15の1フレーム分の画像のデータに対して、各種の画像処理や圧縮処理を実行する。また、静止画像データ生成部19は、被写体認識部25およびトリミング処理部26として機能する。
The still image
被写体認識部25は、RAM18に予め用意された特徴情報に基づいて、画像内に含まれる主要被写体を認識する。一例として、被写体認識部25は、上記の特徴情報に基づいて、画像の被写体を解析するマッチング処理を実行する。このとき、被写体認識部25は、例えば、画像の輝度成分、色差成分、輪郭成分、コントラスト比などのパターンの共通性に着目してマッチング処理を実行する。次に、被写体認識部25は、上記のマッチング処理の結果に基づいて、画像の被写体と特徴情報との類似度を求める。そして、被写体認識部25は、上記の類似度が閾値以上となる場合にはその特徴情報に対応する被写体が画像内に存在するものと判定する。ここで、被写体認識部25は、各々の顔の特徴情報をRAM18に予め登録することで、電子カメラで人物認証を行うこともできる。また、被写体認識部25は、個人認証をすることなく人物の顔領域を検出する公知の顔検出処理を行うこともできる。
The subject recognition unit 25 recognizes a main subject included in the image based on feature information prepared in advance in the
トリミング処理部26は、被写体認識部25の出力に基づいて、画像のうちから認識対象の被写体を含む部分領域を切り出すトリミング処理を実行する。なお、トリミング処理部26は、画像を縦長にトリミングする第1処理と、画像を横長にトリミングする第2処理とを切り替えることが可能である。
Based on the output of the subject recognition unit 25, the
記録I/F20には、記憶媒体27を接続するための2つのコネクタが形成されている。そして、記録I/F20は、コネクタに接続された記憶媒体27に対してデータの書き込み/読み込みを実行する。特に、本実施形態の記録I/F20は、動画記録用の記憶媒体27と、静止画記録用の記憶媒体27とにそれぞれ同時に書き込み可能となっている。また、上記の記憶媒体27は、ハードディスクや、半導体メモリを内蔵したメモリカードなどで構成される。なお、図1では記憶媒体27の一例としてメモリカードを図示する。
Two connectors for connecting the
モニタ21は、CPU23の指示する画面を表示する。例えば、モニタ21には、動画記録時に撮像した画像がリアルタイムに動画表示されて電子ファインダとして機能する。また、モニタ21には、GUI(Graphical User Interface)形式の入力が可能なメニュー画面を表示することができる。ここで、上記のメニュー画面では、(1)認識対象とする被写体の指定、(2)静止画像の解像度の指定、(3)静止画の構図の指定、などの項目をユーザーがCPU23に対して設定できる。なお、メニュー画面での入力および表示に関する処理は、いずれもCPU23によって実行される。
The
入力部22は、例えば、十字状のカーソルキー、決定釦、キャプチャ釦などで構成される。そして、入力部22は電子カメラの各種入力をユーザーから受け付ける。例えば、入力部22は、上記のメニュー画面での入力操作や、動作モードの切替操作などを受け付ける。特に、上記のキャプチャ釦は、動画撮影中に静止画の撮像タイミングの入力をユーザーから受け付ける。
The
CPU23は、電子カメラの各部を統括的に制御するプロセッサである。一例として、CPU23は、撮影時においてAF演算およびAE演算などを公知の手段で実行する。
The
以下、図2の流れ図を参照しつつ、本実施形態における電子カメラの動画撮影時の動作例を説明する。なお、図2の例では、画像を縦長にトリミングする第1処理が初期設定で選択されていることを前提として説明を行う。 Hereinafter, with reference to the flowchart of FIG. 2, an operation example of the electronic camera at the time of moving image shooting in the present embodiment will be described. In the example of FIG. 2, the description will be made on the assumption that the first process for trimming an image vertically is selected by default.
ステップ101:CPU23は、動画撮影の開始指示入力をユーザーから受け付けると、撮像素子12を駆動させて動画撮影を開始する。
Step 101: When receiving a moving image shooting start instruction input from the user, the
具体的には、撮像素子12は、動画撮影時において3264×2448画素の画像を60fpsのフレームレートで出力する。撮像素子12からの出力は、信号処理回路14をパイプライン式に通過して第1フレームメモリ15および第2フレームメモリ16にそれぞれバッファリングされる。動画像データ生成部17は、第1フレームメモリ15の画像のデータから所定の動画像フォーマットに準拠した動画像データを生成する。このとき、動画像データ生成部17は、画像の上下をカットしてアスペクト比を16:9にするとともに、画像の解像度変換を行って動画像の1フレームの解像度を1920×1080画素に調整する。なお、最終的に動画像データは、記録I/F20を介して動画用の記憶媒体27に記録される。
Specifically, the
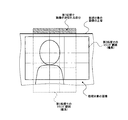
また、動画撮影時には、CPU23の制御によって、撮像素子12で撮影した画像がモニタ21に表示される。図3は、動画撮影時におけるモニタ21の表示画面の一例を示す図である。本実施形態のモニタ21の表示画面では、撮像素子12で撮像された全体画像(アスペクト比4:3)と、動画像データの画像の範囲(アスペクト比16:9)とが示される。これにより、ユーザーは表示画面における動画像の範囲を確認しつつ、全体画像によって静止画の撮影タイミングを判断できる。
At the time of moving image shooting, an image captured by the
ステップ102:CPU23は、キャプチャ釦による静止画撮影の入力があったか否かを判定する。上記入力がある場合(YES側)にはS103に移行する。一方、上記入力がない場合(NO側)にはS112に移行する。
Step 102: The
ステップ103:この場合、CPU23は静止画データの生成を開始する。そして、CPU23は、第2フレームメモリ16に保存されている画像のうちで、キャプチャ釦の押圧のときに撮像されたフレーム(3264×2448画素)を処理対象の画像に指定する。
Step 103: In this case, the
ステップ104:被写体認識部25は、処理対象の画像(S103)に対する被写体認識処理を実行する。なお、本実施形態では、認識対象の被写体として、特定人物の顔を認証する場合を前提として以下の説明を行う。 Step 104: The subject recognition unit 25 executes subject recognition processing for the processing target image (S103). In the present embodiment, the following description is given on the assumption that the face of a specific person is authenticated as the subject to be recognized.
ステップ105:CPU23は、S104において、処理対象の画像(S103)から認識対象の被写体が検出できたか否かを判定する。認識対象の被写体が検出できた場合(YES側)にはS106に移行する。一方、認識対象の被写体が検出できない場合(NO側)にはS111に移行する。
Step 105: In S104, the
ステップ106:トリミング処理部26は、認識対象の被写体のサイズに基づいて、処理対象の画像(S103)のトリミング範囲の大きさを決定する。このとき、トリミング処理部26は、認識対象の被写体とトリミング範囲とのサイズの比が予め指定されている場合には、その比に従ってトリミング範囲の大きさを指定する。
Step 106: The trimming
一例として、人物が認識対象であって、画像を縦長にトリミングする第1処理のときには、トリミング処理部26は以下のようにトリミング範囲の大きさを決定する。一般に、画面内の主要物を約1:1.618のいわゆる黄金比にしたがって配置すると、画面に安定感をもたらす構図となることが経験的に知られている。特に、人物のポートレートの場合には顔の大きさも構図決定の一要素となる。
As an example, when a person is a recognition target and in the first processing for trimming an image vertically long, the trimming
そのため、本実施形態のトリミング処理部26は、トリミング範囲の縦寸法(Y)に対して被写体の顔の高さ(YF)が38.2%となるように上記のYの値を決定する。すなわち、顔の高さ(YF)を1とすると、トリミング範囲の縦寸法(Y)は2.618倍(1/0.382)となる。その後、トリミング処理部26は、所定のアスペクト比(4:3,3:2,16:9など)に従ってトリミング範囲の横寸法(X)を上記のYの値から求める(図4参照)。
Therefore, the trimming
ステップ107:トリミング処理部26は、認識対象の被写体が所定の構図で収まるように、処理対象の画像(S103)のトリミング範囲を決定する。一例として、トリミング処理部26は、トリミング画像を黄金比で分割する縦横のラインの交点上に認識対象の被写体が位置するように、トリミング範囲を決定する。
Step 107: The trimming
図4を参照しつつ、人物が認識対象であって、画像を縦長にトリミングする第1処理の場合を具体的に説明する。トリミング処理部26は、顔の中心点(例えば眉間の位置や、顔領域の重心の位置)が、トリミング画像をそれぞれ約1:1.618の比率で縦横に分割するライン(すなわち、XおよびYをそれぞれ38.2%と61.8%に分割するライン)の交点上に位置するようにトリミング範囲を決定する。なお、図4の例では、トリミング画像の左上を起点として座標(0.382X,0.382Y)の位置に顔の中心がくるように構図を設定した。
With reference to FIG. 4, the case of the first process in which a person is a recognition target and an image is cropped vertically will be specifically described. The trimming
ステップ108:トリミング処理部26は、S107のトリミング範囲の構図において、処理対象の画像の端から認識対象の被写体までの余白量が確保できるか(すなわち、処理対象の画像内にトリミング範囲が収まるか)否かを判定する。上記要件を満たす場合(YES側)にはS110に移行する。一方、上記要件を満たさない場合(NO側)にはS109に移行する。
Step 108: In the composition of the trimming range in S107, the trimming
本実施形態の電子カメラでは、動画撮影を行いつつ必要に応じて静止画撮影を行うため、動画撮影の主要被写体が認証対象と異なる場合には、認証対象の被写体が画像の隅に位置する場合も多い。また、実際の撮影では、レンズの焦点距離と被写体までの距離との制限から、認識対象の被写体の周囲まで写し込まれていない場合も想定される。例えば、非広角のレンズでは、人物などの被写体の周囲を十分に写し込もうとすると被写体までの距離を数m〜十数m確保する必要があるが、実際の撮影では障害物の存在などによって被写体までの距離を十分確保できない場合も多い。 In the electronic camera of the present embodiment, still image shooting is performed as necessary while shooting a movie. Therefore, when the main subject of movie shooting is different from the authentication target, the authentication target subject is located in the corner of the image. There are also many. In actual shooting, there may be a case where the image is not captured to the periphery of the subject to be recognized due to the restriction between the focal length of the lens and the distance to the subject. For example, with a non-wide-angle lens, it is necessary to secure a distance to the subject of several meters to several tens of meters in order to sufficiently capture the surroundings of a subject such as a person. In many cases, a sufficient distance to the subject cannot be secured.
上記のような場合には、トリミング範囲が処理対象の画像からはみ出すこともあり、そのままトリミングを行うと画像の一部が切れて見映えが悪くなる。そのため、S108でのトリミング処理部26は、処理対象の画像内にトリミング範囲が収まるか否かを判定している。
In such a case, the trimming range may protrude from the processing target image, and if trimming is performed as it is, a part of the image is cut and the appearance is deteriorated. Therefore, the trimming
具体的には、トリミング処理部26は、トリミング範囲の構図(認証対象の被写体の位置)と、認識対象の被写体の大きさとから、認識対象の被写体の周囲に確保すべき余白量を求める。次に、トリミング処理部26は、処理対象の画像において、認識対象の被写体から画像の端までの長さ(画素数)を求める。そして、トリミング処理部26は、上記の長さが余白量以上の場合には、処理対象の画像内にトリミング範囲が収まると判定する。
Specifically, the trimming
一例として、図4を参照しつつ、人物が認識対象であって、画像を縦長にトリミングする第1処理の場合を考える。この場合には、人物の顔の上端から画面上端までの余白量は、トリミング範囲の縦寸法(Y)の19.1%に相当する。そのため、トリミング処理部26は、画面上端側の余白量として19.1Yを閾値とし、処理対象の画像において人物の顔上端から画像上端までの長さが閾値以上となるか否かを判定する。勿論、画面の下側および画面の左右についても、トリミング処理部26が同様の判定をそれぞれ実行する。
As an example, consider the case of the first processing in which a person is a recognition target and an image is cropped vertically with reference to FIG. In this case, the margin amount from the upper end of the person's face to the upper end of the screen corresponds to 19.1% of the vertical dimension (Y) of the trimming range. Therefore, the trimming
ステップ109:トリミング処理部26は、画像を横長にトリミングする第2処理に切り替えてトリミング範囲の再設定を実行する。この場合にも、トリミング処理部26は、横長のトリミング画像を黄金比で分割する縦横のラインの交点上に認識対象の被写体が位置するように、トリミング範囲を決定する(図5参照)。
Step 109: The trimming
なお、S109で第2処理に切り替えても認識対象の周囲に十分な余白を確保できない場合には、CPU23はS111に処理を移行するようにしてもよい(図2の流れ図ではこの場合の図示は省略する)。
If sufficient margins cannot be secured around the recognition target even after switching to the second process in S109, the
ステップ110:トリミング処理部26は、S107またはS109で決定されたトリミング範囲で処理対象の画像(S103)をトリミングして静止画像のデータを生成する。このとき、静止画像データ生成部19は、上記のトリミング画像に解像度変換を施して所定の画素数に調整するようにしてもよい。その後、静止画像のデータは、記録I/F20を介して静止画用の記憶媒体27に記録される。なお、S110の処理後はS112に移行する。
Step 110: The trimming
ステップ111:静止画像データ生成部19は、トリミングを行うことなく画像の解像度変換を実行して静止画像のデータを生成する。すなわち、この場合には、処理対象の画像(S103)と同じ構図の低解像度画像が静止画像のデータとなる。その後、静止画像のデータは、記録I/F20を介して静止画用の記憶媒体27に記録される。
Step 111: The still image
ステップ112:CPU23は、動画撮影の終了入力をユーザーから受け付けたか否かを判定する。上記入力がある場合(YES側)には、CPU23は動画撮影を終了する。一方、上記入力がない場合(NO側)にはS102に戻ってCPU23は上記動作を繰り返す。以上で図2の流れ図の説明を終了する。
Step 112: The
以下、本実施形態の電子カメラの作用効果を述べる。本実施形態の電子カメラでは、動画撮影中にキャプチャ釦が押圧されると、認識対象の被写体を含む画像の部分領域をトリミングして、主要被写体が所定の構図で配置された静止画像を取得できる。特に、本実施形態では、黄金比に基づいて被写体の位置および大きさが自動的に決定される。そのため、ユーザーは煩雑な操作を行うことなく、好ましい構図の静止画像を容易に取得できる。 Hereinafter, operational effects of the electronic camera of the present embodiment will be described. In the electronic camera of this embodiment, when a capture button is pressed during moving image shooting, a partial area of an image including a recognition target subject can be trimmed to obtain a still image in which the main subject is arranged in a predetermined composition. . In particular, in the present embodiment, the position and size of the subject are automatically determined based on the golden ratio. Therefore, the user can easily obtain a still image with a preferred composition without performing complicated operations.
また、本実施形態の電子カメラでは、動画像データの1フレームよりも解像度の高い画像からトリミングを行って静止画像を生成する。そのため、動画像と比べて解像度が同等以上のトリミング画像を取得することも可能となる。 In the electronic camera of this embodiment, a still image is generated by performing trimming from an image having a resolution higher than one frame of moving image data. Therefore, it is also possible to acquire a trimmed image having a resolution equal to or higher than that of the moving image.
さらに、本実施形態の電子カメラでは、処理対象の画像内にトリミング範囲が収まらない場合にはトリミングの範囲を切り替えるため、好ましい構図の静止画像を取得できる可能性が大幅に向上する。 Furthermore, in the electronic camera according to the present embodiment, the trimming range is switched when the trimming range does not fit in the image to be processed, so that the possibility that a still image with a preferred composition can be acquired is greatly improved.
(実施形態の補足事項)
(1)上記実施形態では認識対象の被写体を人物とする例を説明したが、認識対象の被写体は人物に限定されることなく、動物、建築物、乗物などのあらゆる物を対象とすることができる。勿論、被写体認識として電子カメラで顔検出のみを行い、顔認証を行わないようにしてもよい。
(Supplementary items of the embodiment)
(1) In the above embodiment, an example in which the subject to be recognized is a person has been described. However, the subject to be recognized is not limited to a person, and may be any object such as an animal, a building, or a vehicle. it can. Of course, only face detection may be performed by the electronic camera as subject recognition, and face authentication may not be performed.
(2)トリミング画像における主要被写体の位置は、上記実施形態の例に限定されることはない。例えば、図4において、トリミング画像の左上を起点として、座標(0.618X,0.382Y)、(0.382X,0.618Y)、(0.618X,0.618Y)の交点のいずれかに認識対象の被写体を配置する構図としてもよい。 (2) The position of the main subject in the trimmed image is not limited to the example in the above embodiment. For example, in FIG. 4, the upper left corner of the trimmed image is the starting point, and any of the intersections of coordinates (0.618X, 0.382Y), (0.382X, 0.618Y), (0.618X, 0.618Y). A composition in which a subject to be recognized may be arranged.
(3)また、上記実施形態において、画像を横長にトリミングする第2処理を初期設定で選択し、画像を横長にトリミングすると処理対象の画像内にトリミング範囲が収まらないときに第1処理に切り替えるようにしてもよい。 (3) In the above embodiment, when the second process for trimming an image in landscape orientation is selected as an initial setting, and the image is trimmed in landscape orientation, the trimming range does not fit in the processing target image, and the first process is switched. You may do it.
なお、本発明は、その精神またはその主要な特徴から逸脱することなく他の様々な形で実施することができる。そのため、上述した実施形態はあらゆる点で単なる例示に過ぎず、限定的に解釈してはならない。本発明は、特許請求の範囲によって示されるものであって、本発明は明細書本文にはなんら拘束されない。さらに、特許請求の範囲の均等範囲に属する変形や変更は、全て本発明の範囲内である。 It should be noted that the present invention can be implemented in various other forms without departing from the spirit or main features thereof. Therefore, the above-described embodiment is merely an example in all respects and should not be interpreted in a limited manner. The present invention is defined by the claims, and the present invention is not limited to the text of the specification. Further, all modifications and changes belonging to the equivalent scope of the claims are within the scope of the present invention.
12…撮像素子、15,16…フレームメモリ、17…動画像データ生成部、18…RAM、19…静止画像データ生成部、20…記録I/F、22…入力部、23…CPU、25…被写体認識部、26…トリミング処理部、27…記憶媒体
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (4)
前記画像のデータを一時的に保持するメモリと、
複数の前記画像から動画像データを生成する動画像データ生成部と、
前記動画像データを記憶媒体に記録する記録インターフェースと、
静止画記録の指示入力を受け付ける入力部と、
前記画像から認識対象の被写体を検出する被写体認識部と、
前記指示入力のときに撮像された前記画像から前記認識対象の被写体を含む部分領域をトリミングし、前記認識対象の被写体が所定の構図で配置されたトリミング画像のデータを生成するとともに、前記画像の端から前記認識対象の被写体までの余白量に基づいて、前記画像を縦長にトリミングする第1処理と前記画像を横長にトリミングする第2処理とを切り替えるトリミング処理部と、
を備えることを特徴とする撮像装置。 An image sensor that images a subject at predetermined intervals and outputs data of each image;
A memory for temporarily storing the image data;
A moving image data generation unit that generates moving image data from a plurality of the images;
A recording interface for recording the moving image data in a storage medium;
An input unit for receiving still image recording instruction input;
A subject recognition unit for detecting a subject to be recognized from the image;
The instruction trimmed partial region including the subject of the recognition target from the captured the image when the input, with the object of the recognition target generates data arranged trimming image in a predetermined composition, of the image A trimming processing unit that switches between a first process for trimming the image vertically and a second process for trimming the image horizontally based on a margin amount from an end to the subject to be recognized ;
An imaging apparatus comprising:
前記画像の解像度は、前記動画像データの1フレームの解像度よりも高く設定されることを特徴とする撮像装置。 The imaging device according to claim 1,
An image pickup apparatus, wherein the resolution of the image is set higher than the resolution of one frame of the moving image data.
前記トリミング処理部は、前記トリミング画像を黄金比で分割する縦横のラインの交点上に前記認識対象の被写体が位置するように、前記トリミングの位置を決定することを特徴とする撮像装置。 In the imaging device according to claim 1 or 2,
The image pickup apparatus, wherein the trimming processing unit determines the trimming position so that the subject to be recognized is positioned on an intersection of vertical and horizontal lines that divide the trimmed image by a golden ratio.
前記トリミング処理部は、前記画像内での前記認識対象の被写体の大きさに基づいて、前記トリミングの範囲を決定することを特徴とする撮像装置。 In the imaging device according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
The imaging apparatus, wherein the trimming processing unit determines the trimming range based on a size of a subject to be recognized in the image .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007258455A JP4894708B2 (en) | 2007-10-02 | 2007-10-02 | Imaging device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007258455A JP4894708B2 (en) | 2007-10-02 | 2007-10-02 | Imaging device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009089220A JP2009089220A (en) | 2009-04-23 |
| JP2009089220A5 JP2009089220A5 (en) | 2010-11-25 |
| JP4894708B2 true JP4894708B2 (en) | 2012-03-14 |
Family
ID=40661979
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007258455A Expired - Fee Related JP4894708B2 (en) | 2007-10-02 | 2007-10-02 | Imaging device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4894708B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5495760B2 (en) * | 2009-12-17 | 2014-05-21 | オリンパスイメージング株式会社 | Imaging device |
| US9113064B2 (en) | 2009-11-05 | 2015-08-18 | Olympus Corporation | Image pickup apparatus and image acquisition method |
| JP2013153375A (en) | 2012-01-26 | 2013-08-08 | Sony Corp | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and recording medium |
| JP6171628B2 (en) * | 2013-06-28 | 2017-08-02 | 株式会社ニコン | Imaging apparatus, control program, and electronic device |
| JP6104077B2 (en) | 2013-07-01 | 2017-03-29 | オリンパス株式会社 | Photographing equipment and photographing method |
| JP2019186791A (en) | 2018-04-12 | 2019-10-24 | シャープ株式会社 | Imaging apparatus, control method of the imaging apparatus, and control program |
| JP7145638B2 (en) | 2018-05-07 | 2022-10-03 | シャープ株式会社 | ELECTRONIC DEVICE, IMAGING METHOD, CONTROL DEVICE, AND CONTROL PROGRAM |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4379728B2 (en) * | 2005-01-31 | 2009-12-09 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and program thereof |
| JP2006287744A (en) * | 2005-04-01 | 2006-10-19 | Canon Inc | Image processing method and device therefor |
| JP4898284B2 (en) * | 2006-05-15 | 2012-03-14 | オリンパスイメージング株式会社 | camera |
-
2007
- 2007-10-02 JP JP2007258455A patent/JP4894708B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2009089220A (en) | 2009-04-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI425826B (en) | Image selection device and method for selecting image | |
| US8823861B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, image display apparatus, imaging method, method of displaying image and method of correcting position of focusing-area frame | |
| US7801360B2 (en) | Target-image search apparatus, digital camera and methods of controlling same | |
| JP6157242B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and image processing method | |
| JP5623915B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP5087856B2 (en) | Electronic camera | |
| US9538085B2 (en) | Method of providing panoramic image and imaging device thereof | |
| JP4894708B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP2005286940A (en) | Digital still camera and its control method | |
| US9185294B2 (en) | Image apparatus, image display apparatus and image display method | |
| US8441554B2 (en) | Image capturing apparatus capable of extracting subject region from captured image | |
| KR101433121B1 (en) | Image processing device for generating composite image having predetermined aspect ratio | |
| US20100188520A1 (en) | Imaging device and storage medium storing program | |
| JP2010141649A (en) | Image capturing apparatus and face detecting method and program | |
| WO2016008359A1 (en) | Object movement track image synthesizing method, device and computer storage medium | |
| JP2007180931A (en) | Image display device and imaging device | |
| JP4127521B2 (en) | Digital camera and control method thereof | |
| JP5510287B2 (en) | Subject detection apparatus, subject detection method, and program | |
| JP2007148691A (en) | Image processor | |
| JP6671323B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP4807582B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, imaging apparatus, and program thereof | |
| JP4632417B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and control method thereof | |
| JP4877186B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program | |
| JP2008172395A (en) | Imaging apparatus and image processing apparatus, method, and program | |
| JP5417920B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, electronic camera, and image processing program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100929 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20101006 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20111122 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20111129 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20111212 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4894708 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150106 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150106 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |