JP4460110B2 - Navigation device - Google Patents
Navigation device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4460110B2 JP4460110B2 JP2000140891A JP2000140891A JP4460110B2 JP 4460110 B2 JP4460110 B2 JP 4460110B2 JP 2000140891 A JP2000140891 A JP 2000140891A JP 2000140891 A JP2000140891 A JP 2000140891A JP 4460110 B2 JP4460110 B2 JP 4460110B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- point
- guide
- guidance
- data
- guide point
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
- Instructional Devices (AREA)
- Navigation (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、車両に搭載され、予め設定される経路に沿って車両が走行するときに、予め経路上に設定される案内地点で、画面表示や音声などで経路案内を行うナビゲーション装置に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来から、自動車などの車両に搭載される車両用ナビゲーション装置では、車両の現在位置である自車位置を地図上に表示する機能とともに、予め設定される経路に沿って経路案内を行う機能が備えられている。経路は、車両用ナビゲーション装置のユーザが作成して指定したり、始点と終点とを指定して、途中の経路として適切なルートを車両用ナビゲーション装置側で探索して設定したりすることができる。経路上には、進路を変える必要がある交差点など、運転支援の必要性が高い案内地点が選択される。
【0003】
案内地点で案内する情報は、実際に車両が案内地点に到達する前に案内地点データとしてデータ化され、案内地点到達時に適切なタイミングで案内情報を運転者に伝えることが可能になっている。案内地点データとして必要な情報として、案内地点自体に関する情報と、隣接する案内地点間の情報とがある。
【0004】
特開平8−278158号公報には、音声による経路案内用の音声フレーズを示すデータを、交差点や分岐点等の経路案内用のデータとして記憶手段に格納しておき、各案内地点毎に記憶手段から読み出して、音声で案内する先行技術が開示されている。
【0005】
案内地点間の情報は、2つの交差点が連続して存在し、進路を連続して変更しなければならないようなときに重要となる。経路上で先に通る案内地点での案内は、後に通る案内地点を考慮して行わなければ、円滑に車両を運転することが困難になる。しかしながら、案内地点データを、経路に沿って順次作成する場合、各案内地点自体についての情報は案内地点が確定した段階で全て確定することができるけれども、案内地点間の情報は、次の案内地点が決まらないと、確定しない。そこで、各案内地点について、案内地点として確定した段階で、案内地点自体の情報を基に案内地点データを生成し、後続の案内地点が確定した段階で、案内地点間の情報を、先の案内地点について生成した案内地点データに追加するようにしている。
【0006】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
前述のように、案内地点で案内地点自体についての情報とともに、案内地点間の情報も案内する場合は、案内地点間の情報は、車両が先に通過する方の案内地点についての案内地点データに追加するようにしている。案内地点データを経路の進行方向順に生成して行く段階で、次の案内地点データが決まらないと、手前の案内地点での案内地点データが確定しない。このため、案内地点データの作成処理が煩雑になってしまう。
【0007】
本発明の目的は、案内地点間の情報に基づく案内のための処理を円滑に行うことができるナビゲーション装置を提供することである。
【0008】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明は、予め設定される経路に従って、経路案内を行うナビゲーション装置において、
前記予め設定される経路に沿って案内地点を設定し、前記経路案内を行う案内地点自体の情報である地点データ部と、該案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報である地点間データ部と、を表す案内地点データを各案内地点毎に生成するデータ生成手段と、
前記データ生成手段によって生成された前記案内地点データを格納するデータ記憶手段と、
各案内地点について案内地点データを読み出して車両の案内を行う際に、前記データ記憶手段に格納されている該案内地点の直後に案内される案内地点についての案内地点データを参照して経路案内を行うデータ案内手段とを備え、
前記地点間データ部は、経路上後方の案内地点の案内地点データに含まれて記憶され、
前記データ生成手段は、案内地点データのうち、地点データ部をまず作成し、その後地点間データ部を作成し、
前記データ記憶手段は、前記経路の始点から終点の方向順に案内地点データを記憶することを特徴とするナビゲーション装置である。
【0009】
本発明に従えば、ナビゲーション装置は、予め設定される経路に従って、経路案内を行い、データ生成手段、データ記憶手段、データ案内手段を含む。データ生成手段は、車両に対して経路案内を行う案内地点を経路に沿って設定し、各案内地点毎に案内すべき内容を表す案内地点データを生成する。データ記憶手段は、経路の始点から終点の方向順に、データ生成手段によって生成された案内地点データを格納する。データ生成手段は、各案内地点で生成する案内地点データに、その案内地点に対し経路で直前に設定される案内地点との間に関する情報を含める。データ案内手段は、経路に従って各案内地点についての案内地点データを読み出して車両の案内を行う際に、その案内地点直後の案内地点についての案内地点データを参照して、案内地点間に関する情報についても案内を行う。案内地点間に関する情報は、経路上後方の案内地点側に、後方側の案内地点自体についての案内地点データとともに、データ生成手段によって生成される。案内地点データ生成の時点では、経路上先行する案内地点は既に決まっており、その案内地点データも確定しているので、後続の案内地点についての案内地点データの生成とともに案内地点間に関する情報も容易に確定させることができ、案内地点データの作成処理を円滑化することができる。
【0010】
また本発明で前記案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報は、該案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との距離であることを特徴とする。
【0011】
本発明に従えば、案内地点前記案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報は、該案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との距離であり、この距離に基づいて先行する案内地点と後続の案内地点とを連続して案内するか否かを判断することができる。
【0012】
また本発明で前記案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報は、該案内地点の情報と該案内地点の直後に案内される情報とを連続的に案内する音声フレーズであることを特徴とする。
【0013】
本発明に従えば、前記案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報は、該案内地点の情報と該案内地点の直後に案内される情報とを連続的に案内を行う音声フレーズであり、音声フレーズを再生して、両方の案内地点についての案内を円滑に行うことができる。
【0014】
また本発明で前記案内地点と該案内直後の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報は、該案内地点の情報と該案内地点の直後に案内される情報とを連続的に案内するための拡大図であることを特徴とする。
【0015】
本発明に従えば、案内地点と該案内直後の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報は、案内地点の情報と該案内地点の直後に案内される情報とを連続的に案内を行うための拡大図であり、拡大図を表示して、連続した経路案内を判りやすく行うことができる。
【0016】
また本発明で前記案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報は、該案内地点の情報と該案内地点の直後に案内される情報に共通する方面名称であることを特徴とする。
【0017】
本発明に従えば、案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報は、該案内地点の情報と該案内地点の直後に案内される情報に共通する方面名称であり、先行する案内地点で複数の方面名称が存在しても、後方の案内地点と共通する方面名称を用いて、経路に沿った案内を判りやすく行うことができる。
また本発明は、予め設定される経路に従って、複数の案内地点で経路案内を行うナビゲーション方法において、
前記予め設定される経路に沿って案内地点を設定し、前記経路案内を行う案内地点自体の情報である地点データ部と、該案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報である地点間データ部と、を表す案内地点データを各案内地点毎に生成し、
前記生成された記案内地点データを格納するデータを記憶し、
各案内地点について案内地点データを読み出して車両の案内を行う際に、該案内地点の直後に案内される案内地点についての案内地点データを参照して経路案内を行い、
前記地点間データ部は、経路上後方の案内地点の案内地点データに含まれて記憶され、
前記案内地点データのうち、地点データ部をまず作成し、その後地点間データ部を作成し、
前記経路の始点から終点の方向順に案内地点データを記憶することを特徴とするナビゲーション方法である。
また本発明は、経路案内を行うナビゲーション装置において、
少なくとも2つの方向に分岐する第1の分岐点よりも手前の第2の分岐点の案内として、前記第1の分岐点で進行すべき方面名称を案内する経路案内手段を有することを特徴とするナビゲーション装置である。
【0018】
【発明の実施の形態】
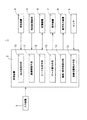
図1は、本発明の実施の一形態である車両用ナビゲーション装置1の概略的なシステム構成を示す。車両用ナビゲーション装置1としての主要な機能は、処理装置2のプログラム動作によって実現される。処理装置2には、入力装置3、受信装置4、地図記録媒体5、記憶装置6、表示装置7、音声出力装置8およびセンサ9などが接続される。入力装置3は、車両の運転者などの車両用ナビゲーション装置1の利用者からの入力操作を受ける。受信装置4は、GPS電波などを受信して、車両の現在位置などの情報を取得する。地図記録媒体5は、CD−ROMやDVD−ROMなどの着脱可能な大容量記録媒体であり、道路地図データや、音声フレーズや、ランドマーク等の各種画像描画用部品などが読み出し可能に記録されている。記憶装置6には、各種情報やデータが記憶される。表示装置7は、液晶表示パネルなどで画像表示を行う。交差点などの案内地点では、地図記録媒体5に記録されている音声出力装置8は、経路案内のための音声情報を出力する。センサ9は、車両の走行状態に関する情報を検出する。音声情報は、地図記録媒体5に、道路地図データとともに記録されている音声フレーズを利用する。
【0019】
処理装置2は、プログラム動作によって、地点登録手段10、経路探索手段11、データ生成手段12、データ案内手段13、描画/表示制御手段14および自車位置検出手段15などとして動作する。地点登録手段10は、出発地である始点と目的地である終点とを入力装置3から入力して指定すれば、経路の始点や終点として記憶装置6に登録する。経路探索手段11は、記憶装置6に登録されている始点と終点との間の適切なルートを経路として探索し、探索結果を記憶装置6に記憶しておくことができる。最終目的地までの間に、経由すべき地点を指定したり、経路探索に条件を付けることもできる。データ生成手段12は、経路に沿って、予め定める条件で案内地点を設定し、各案内地点で経路案内を行うための案内地点データを生成する。経路は、経路探索手段11で探索して設定するばかりではなく、利用者が入力装置3から直接指定することもできる。データ生成手段が生成した案内地点データは、データ記憶手段である記憶装置6に、始点から終点までの方向に沿って、順次的に格納される。
【0020】
データ案内手段13は、車両の現在位置が案内地点に到達すると、記憶装置6に格納されている当該案内地点の案内地点データから案内地点についての情報と、経路上で隣接する前方の案内地点の案内地点データから案内地点間の情報とを読み出し、経路案内を行う。描画/表示制御手段14は、地図データ画面を作成し、自車位置の表示を行ったり、交差点などの案内地点での運転者に対する経路案内を行ったりするための画像も描画する。自車位置検出手段15は、受信装置4がGPS電波を受信して取得する位置情報に基づいて車両の現在位置を検出したり、センサ9からの走行状態の情報に基づいて、推測航法で車両の現在位置を推定したり、車両の現在位置を道路データ上に補正するマップマッチングを行ったりする。
【0021】
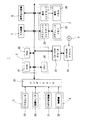
図2は、図1に示す車両用ナビゲーション装置1の概略的な電気的構成を示す。図1の処理装置2は、CPU20、ROM21およびRAM22を含む。CPU20は、ROM21に予め格納されているプログラムに従って動作し、図1に示す処理装置2としての各機能を実現する。RAM22には、プログラム動作に必要なワークエリアなどが設定される。RAM22は、図1の記憶装置6としても動作する。地図記録媒体5としてのCD−ROMから道路地図データ、音声フレーズ、描画用部品データなどを読み出すために、CD−ROMデコーダ23およびCD−ROMドライバ24が設けられる。CD−ROMデコーダ23は、CD−ROMドライバ24が地図記録媒体5から読みとったデータを、利用可能なデータ形式に戻す。
【0022】
図1の表示装置7は、グラフィックコントローラ25、グラフィックメモリ26、表示コントローラ27および表示パネル28を含む。グラフィックメモリ26には、表示パネル28で画像表示する内容がグラフィックコントローラ25によって描画され、表示コントローラ27を経由して表示パネル28に転送される。車両が走行中で、案内地点に接近していないときは、車両の現在位置を中心として道路地図を表示する画像が生成される。案内地点では、車両の進路を案内する画像表示が行われる。
【0023】
図1のセンサ9は、方位センサ29および距離センサ30を含む。方位センサ29は、たとえば振動ジャイロなどであって、車両の進行方向の変化を検出して、相対的な方位を算出するために用いる。地磁気センサなどの絶対方位を検出するセンサを用いることもできる。距離センサ30は、車両の走行距離を検出する。方位センサ29が検出する車両の進行方向の方位と、距離センサ30が検出する車両の走行距離とを組み合わせれば、推測航法である基準位置からの車両の相対的な移動を求めることができる。
【0024】
車両の絶対的な現在位置は、図1の受信装置4に含まれるGPS受信機31からのGPS電波受信情報から知ることができる。また、無線機32を介して、位置情報を知ることもできる。方位センサ29、距離センサ30、GPS受信機31および無線機32からの出力は、インターフェース33を介してCPU20に入力される。
【0025】
図3は、経路に沿って設定される案内地点データのデータ構造を示す。経路の始点側から終点側の順に、案内地点に対応して、案内地点データ40,41,42,…がそれぞれ図1のデータ生成手段12によって生成され、記憶装置6に格納される。案内地点データ40,41,42,…には、その案内地点自体についての情報である地点データ部40a,41a,42a,…と、手前側に隣接する案内地点(直前に案内される案内地点)との間についての情報である地点間データ部40b,41b,42b,…とが含まれる。地点データ部40a,41a,42a,…は、その案内地点についての位置を示す「位置情報」、車両を案内すべき方位を示す「案内方位」、およびその案内地点が交差点であるときの「交差点名称」などを含む。地点間データ部40b,41b,42b,…は、案内地点間の距離を示す「前の案内地点までの距離」、案内地点を連続して音声案内するための「連続案内フレーズ」、分岐点などが案内地点となるときに、分岐方向を案内するための「方面名称」、案内地点を画像で連続するための「連続拡大図データ」などを含む。
【0026】
図4は、図3に示すような案内地点データ40,41,42,…を作成する手順を示す。図1のデータ生成手段12は、ステップa1から手順を開始し、ステップa2では、経路探索手段11によって探索され、記憶装置6に格納されている経路探索結果を始点側から終点に向かって調査する。経路探索結果は、道路を始点、終点、交差点、分岐点などのノードと、ノード間を接続するリンクとの組み合わせで表現されている。ステップa3では、各ノードについて、案内地点か否かが判断される。案内地点は、たとえば、3以上のリンクが接続され、かつ進入角度と脱出角度との差が基準値よりも大きい場合や、高速道路などでの進路変更や道路種別の変更を伴う進路変更を行う場合などに設定される。
【0027】
ステップa3で案内地点であると判断されると、ステップa4では、案内地点データのうち、地点データ部が作成される。ステップa5では、一つ前の案内地点データはあるか否かが判断される。一つ前の案内地点データがあると判断されれば、ステップa6で、案内地点データのうち、地点間データ部が作成される。次にステップa7で、案内地点データ作成終了条件を満たしているか否かが判断される。条件が満たされていれば、ステップa8で手順を終了する。作成終了条件としては、調査の対象が終点に達したことや、現在位置から所定距離に達したことなどを用いることができる。ステップa3、ステップa5またはステップa7で条件が満たされていないと判断されれば、ステップa2に戻る。
【0028】
図5は、本実施形態のように案内地点間の情報を用いることによって、連続した交差点案内が行われる状態を示す。図5(a)は、単独の交差点であるノード50に、4つのリンク51,52,53,54が接続され、経路はリンク51,54間に設定されている状態を示す。表示装置7の表示画面では、単独の交差点についての右折の案内が行われ、音声案内でも、たとえば「右です」などのように案内が行われる。図5(b)では、2つのノード60a,60bが連続した案内地点となり、リンク61,62,63,64,65,66,67のうち、リンク61,64,65が経路に設定されている場合、手前のノード60aを右折し、後のノード60bを左折するように案内する連続拡大図が表示され、音声案内も「右です。その先左です」のように連続して行われる。車両が手前のノード60aを過ぎると、音声案内は、「左です」に変わる。このような連続案内を行うか否かは、地点間データ部の「前の交差点までの距離」に従って判定される。たとえばこの距離が100m以下なら連続案内を行うように設定することができる。
【0029】
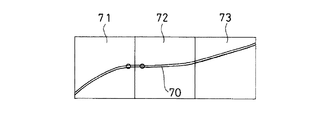
図6は、「前の交差点までの距離」が後の案内地点が決まらないと確定しない場合の例を示す。経路に沿う案内地点の調査は、複数のブロックに分割されている道路地図データにアクセスして行う。経路70が複数のブロック71,72,73に分割されて存在しているとき、一つのブロック71について調査が終了しても、次のブロック72について調査を行うことができない。記憶装置6の記憶容量の関係で、全部のブロック71,72,73を同時に地図記録媒体5から読み出すことができないときには、ブロック単位の読み出しとなる。このような場合、次のブロックを読み出して案内地点を調査するまで、距離などの情報が不明となる。
【0030】
図7は、方面名称について示す。高速道路などでは、ジャンクションや出口に、接続する方向を方面名称で表示している。ジャンクションや出口に対応するノードについての情報にも、実際に表示される方面名称がデータとして含まれている。たとえば、経路80が高速道路の本線を分岐点81まで走行し、分岐点81から分岐点82でA方面に向かう他の高速道路に移行する場合を想定する。分岐点82は、出口Bに向かう道路に設けられているものとする。分岐点81,82は、連続した案内地点としての距離的な条件を満たしていなくても、分岐点81についての案内の際に、分岐点82での進路を考慮して案内した方が判りやすくなる。すなわち、分岐点81については、方面名称として、A方面とB方面とが道路地図データから読み取られている場合、B方面は経路と無関係であるので、案内対象から除外した方が判りやすい。分岐点82に方面名称としてA方面のみが読み取られていれば、分岐点81での案内の際に、共通なA方面で案内することができる。分岐点81の方面名称にA方面が含まれていないときは、方面名称での案内は行わないようにする。B方面で案内すると、運転者を迷わせる結果となる可能性がある。
【0031】
【発明の効果】
以上のように本発明によれば、案内地点間に関する情報を、経路の後方側の案内地点について生成する案内地点データに含めるので、案内地点データ生成の時点では、経路上先行する案内地点は既に決まっており、案内地点データの作成処理を円滑化することができる。いったん生成された案内地点データに、後から案内地点間の情報を付加することがないので、案内地点データの管理も簡易化することができる。
【0032】
また本発明によれば、案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報は、該案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との距離であり、この距離に基づいて先行する案内地点と後続の案内地点とを連続して案内するか否かを判断することができる。
【0033】
また本発明によれば、案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報は、該案内地点の情報と該案内地点の直後に案内される情報とを連続的に案内する音声フレーズであり、音声フレーズを再生して、両方の案内地点についての案内を円滑に行うことができる。
【0034】
また本発明によれば、案内地点と該案内直後の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報は、該案内地点の情報と該案内地点の直後に案内される情報とを連続的に案内するための拡大図であり、拡大図を表示して、連続した経路案内を判りやすく行うことができる。
【0035】
また本発明によれば、案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報は、該案内地点の情報と該案内地点の直後に案内される情報に共通する方面名称を用いて、経路に沿った案内を判りやすく行うことができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の実施の一形態としての車両用ナビゲーション装置1の概略的なシステム構成を示すブロック図である。
【図2】図1の車両用ナビゲーション装置1の概略的な電気的構成を示すブロック図である。
【図3】図1のデータ生成手段12が生成する案内地点データのデータ構造を示す図である。
【図4】図1のデータ生成手段12が案内地点データを作成する手順を示すフローチャートである。
【図5】図1の実施形態で交差点を単独で案内する場合と連続して案内する場合とを示す図である。
【図6】図1の実施形態で案内地点間の距離を求めることができない場合の例を示す図である。
【図7】図1の実施形態で、方面案内を行う場合の例を示す図である。
【符号の説明】
1 車両用ナビゲーション装置
2 処理装置
3 入力装置
5 地図記録媒体
6 記憶装置
7 表示装置
8 音声出力装置
10 地点登録手段
11 経路探索手段
12 データ作成手段
13 データ案内手段
15 自車位置検出手段
20 CPU
21 ROM
22 RAM
29 方位センサ
30 距離センサ
31 GPS受信機
40,41,42,…案内地点データ
40a,41a,42a,…地点データ部
40b,41b,42b,…地点間データ部
50,60a,60b ノード
51,52,53,54,61,62,63,64,65,66,67 リンク
70,80 経路
71,72,73 ブロック
81,82 分岐点[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention is mounted on a vehicle, when the vehicle along a path that is set in advance travels, at the guide point that is set in advance on the path to a row UNA navigation device route guidance or the like screen display and sound .
[0002]
[Prior art]
2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, a vehicle navigation device mounted on a vehicle such as an automobile has a function of displaying a vehicle position that is the current position of the vehicle on a map and a function of performing route guidance along a preset route. It has been. The route can be created and designated by the user of the vehicle navigation device, or the start point and the end point can be designated, and an appropriate route can be searched and set on the vehicle navigation device side as an intermediate route. . On the route, a guide point having a high necessity for driving support, such as an intersection where the course needs to be changed, is selected.
[0003]
Information to be guided at the guide point is converted into data as guide point data before the vehicle actually reaches the guide point, and the guide information can be transmitted to the driver at an appropriate timing when the vehicle reaches the guide point. Information necessary as guide point data includes information on the guide point itself and information between adjacent guide points.
[0004]
In JP-A-8-278158, data indicating a voice phrase for route guidance by voice is stored in a storage means as route guidance data such as an intersection or a branch point, and the storage means is stored for each guidance point. The prior art which reads from the above and guides by voice is disclosed.
[0005]
Information between guide points is important when two intersections exist continuously and the course must be changed continuously. It is difficult to drive the vehicle smoothly unless guidance at a guide point that passes first on the route is performed in consideration of a guide point that passes later. However, when the guide point data is sequentially created along the route, information about each guide point itself can be determined at the stage where the guide point is determined. If it is not decided, it will not be confirmed. Therefore, for each guide point, when it is determined as a guide point, guide point data is generated based on the information of the guide point itself, and when the subsequent guide point is determined, information between the guide points is transferred to the previous guide point. It is added to the guide point data generated for the point.
[0006]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
As described above, when the information between the guide points is also provided along with the information about the guide points themselves, the information between the guide points is included in the guide point data for the guide point of the vehicle passing first. I try to add it. If the next guide point data is not determined at the stage of generating the guide point data in the order in which the route travels, the guide point data at the previous guide point cannot be determined. For this reason, the process of creating guide point data becomes complicated.
[0007]
An object of the present invention is to provide a Luna navigation device can smoothly perform processing for guidance based on information between the guide point.
[0008]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The present invention provides a navigation device that provides route guidance according to a preset route.
A guide point is set along the preset route, and a point data part that is information on the guide point itself that performs the route guidance, and the guide point and the guide point that is guided immediately before the guide point Data generating means for generating, for each guide point, guide point data representing the point-to- point data part ,
Data storage means for storing the guide point data generated by the data generation means;
When the guidance of the vehicle reads the guidance point data for each guidance point, route guidance with reference to guidance point data for guide point which the guided after the data storage means the guide point that is stored immediately and a data guide means for performing,
The point-to-point data part is included and stored in the guide point data of the guide point at the rear of the route,
The data generation means first creates a point data portion of the guide point data, and then creates an inter-point data portion,
Wherein the data storage means is a to Luna navigation device and wherein storing the guidance point data in the direction order of the end point from the start point of the path.
[0009]
According to the present invention, navigation system, according to the route set in advance, it performs route guidance, including data generating means, data storage means, data guide means. The data generation means sets a guide point for performing route guidance for the vehicle along the route, and generates guide point data representing contents to be guided for each guide point. The data storage means stores the guide point data generated by the data generation means in the order from the start point to the end point of the route. The data generation means includes information on the distance between the guide point set immediately before the guide point and the guide point data generated at each guide point. Data guiding means, when the guidance of the vehicle reads the guidance point data for each guide point according to the route, with reference to the guidance point data for guide point immediately after the guide point, for the information about the inter-guiding point Give guidance. Information relating to the distance between the guide points is generated by the data generation means on the guide point side on the rear side of the route together with the guide point data on the guide point on the rear side. At the time of the guide point data generation, the guide point that precedes the route has already been determined, and the guide point data has also been determined, so it is easy to generate the guide point data for the subsequent guide points and the information between the guide points The guide point data creation process can be facilitated.
[0010]
In the present invention, the information between the guide point and the guide point that is guided immediately before the guide point is a distance between the guide point and the guide point that is guided immediately before the guide point. To do.
[0011]
According to the present invention, the information between the guide point and the guide point that is guided immediately before the guide point is the distance between the guide point and the guide point that is guided immediately before the guide point . Based on this distance, it is possible to determine whether to guide the preceding guidance point and the subsequent guidance point continuously.
[0012]
In the present invention, the information between the guide point and the guide point that is guided immediately before the guide point is a voice that continuously guides the information on the guide point and the information that is guided immediately after the guide point. It is a phrase.
[0013]
According to the present invention, the information between the guide point and the guide point that is guided immediately before the guide point continuously guides the information on the guide point and the information that is guided immediately after the guide point. The voice phrase is played, and the voice phrase can be reproduced to smoothly guide both the guide points.
[0014]
The information between the guide point is guided to the following or preceding in the guide point and the guide in the present invention, for continuously guiding the information is guided immediately after the information and the guide point the guide point It is the enlarged view of.
[0015]
According to the present invention, the information between the guidance point and the guidance point that is guided immediately after the guidance continuously guides the information on the guidance point and the information that is guided immediately after the guidance point. For this reason, it is possible to display a magnified view for easy understanding of continuous route guidance.
[0016]
In the present invention, the information between the guide point and the guide point that is guided immediately before the guide point is a common name for the information on the guide point and the information that is guided immediately after the guide point. It is characterized by.
[0017]
According to the present invention, the information between the guidance point and the guidance point that is guided immediately before the guidance point is a common name for the information on the guidance point and the information that is guided immediately after the guidance point. Even if there are a plurality of direction names at the preceding guidance point, it is possible to perform guidance along the route in an easy-to-understand manner by using the direction name common to the rear guidance point.
Further, the present invention provides a navigation method for performing route guidance at a plurality of guidance points according to a preset route.
A guide point is set along the preset route, and a point data part that is information on the guide point itself that performs the route guidance, and the guide point and the guide point that is guided immediately before the guide point Data for each guidance point is generated for each guidance point.
Storing data for storing the generated guide point data;
When the guidance point data is read for each guidance point to guide the vehicle, route guidance is performed with reference to the guidance point data for the guidance point that is guided immediately after the guidance point,
The point-to-point data part is included and stored in the guide point data of the guide point at the rear of the route,
Of the guidance point data, first create a point data part, then create a point-to-point data part,
The navigation method is characterized in that guide point data is stored in the direction from the start point to the end point of the route .
The present invention provides a navigation apparatus for performing route guidance,
It has a route guidance means for guiding the name of the direction to travel at the first branch point as a guide for the second branch point before the first branch point that branches in at least two directions. It is a navigation device.
[0018]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
FIG. 1 shows a schematic system configuration of a
[0019]
The
[0020]
When the current position of the vehicle arrives at the guide point, the data guide means 13 obtains information on the guide point from the guide point data of the guide point stored in the
[0021]
FIG. 2 shows a schematic electrical configuration of the
[0022]
The
[0023]
The
[0024]
The absolute current position of the vehicle can be known from GPS radio wave reception information from the
[0025]
FIG. 3 shows a data structure of guide point data set along the route. .. Are generated by the data generation means 12 of FIG. 1 and stored in the
[0026]
FIG. 4 shows a procedure for creating
[0027]
If it is determined in step a3 that it is a guidance point, in step a4, a point data part is created among the guidance point data. In step a5, it is determined whether there is any previous guidance point data. If it is determined that there is a previous guidance point data, in step a6, among proposals within location data, point-to-point data unit is created. Next, in step a7, it is determined whether or not the guide point data creation end condition is satisfied. If the condition is satisfied, the procedure ends at step a8. As the creation end condition, it is possible to use the fact that the object of the survey has reached the end point, the fact that it has reached a predetermined distance from the current position, or the like. If it is determined in step a3, step a5, or step a7 that the condition is not satisfied, the process returns to step a2.
[0028]
FIG. 5 shows a state where continuous intersection guidance is performed by using information between guide points as in the present embodiment. FIG. 5A shows a state in which four
[0029]
FIG. 6 shows an example in which the “distance to the previous intersection” is not determined unless the subsequent guide point is determined. The survey of the guide points along the route is performed by accessing the road map data divided into a plurality of blocks. When the
[0030]
FIG. 7 shows the direction name. On highways, the direction of connection is indicated by the direction name at junctions and exits. The information about the node corresponding to the junction or exit also includes the direction name actually displayed as data. For example, it is assumed that the
[0031]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, the information about the guidance point is included in the guidance point data generated for the guidance point on the rear side of the route. The guide point data creation process can be facilitated. Since information between guide points is not added to the guide point data once generated, management of the guide point data can be simplified.
[0032]
According to the present invention, the information between the guide point is guided immediately before the guide point and the guide point is the distance between the guide points is guided to the immediately preceding point in the point and guiding the guide, the Based on the distance, it can be determined whether to guide the preceding guidance point and the subsequent guidance point continuously.
[0033]
According to the present invention, the information between the guidance point and the guidance point that is guided immediately before the guidance point continuously guides the information on the guidance point and the information that is guided immediately after the guidance point. is an audio phrase that, to play the voice phrases, a guide for both the guide point of can be carried out smoothly.
[0034]
According to the present invention, the information between the guidance point and the guidance point that is guided immediately after the guidance continuously guides the information on the guidance point and the information that is guided immediately after the guidance point. This is an enlarged view for displaying the enlarged view so that continuous route guidance can be easily understood.
[0035]
Further, according to the present invention, the information between the guide point and the guide point that is guided immediately before the guide point has a direction name common to the information of the guide point and the information that is guided immediately after the guide point. It is possible to make guidance along the route easy to understand.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a schematic system configuration of a
2 is a block diagram showing a schematic electrical configuration of the
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing a data structure of guidance point data generated by the data generation means 12 of FIG. 1;
FIG. 4 is a flowchart showing a procedure for creating guide point data by the data generation means 12 of FIG. 1;
FIGS. 5A and 5B are diagrams showing a case where an intersection is guided independently and a case where guidance is continuously provided in the embodiment of FIG.
6 is a diagram showing an example when the distance between guide points cannot be obtained in the embodiment of FIG.
7 is a diagram showing an example in the case of performing direction guidance in the embodiment of FIG.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF
21 ROM
22 RAM
29
Claims (7)
前記予め設定される経路に沿って案内地点を設定し、前記経路案内を行う案内地点自体の情報である地点データ部と、該案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報である地点間データ部と、を表す案内地点データを各案内地点毎に生成するデータ生成手段と、
前記データ生成手段によって生成された前記案内地点データを格納するデータ記憶手段と、
各案内地点について案内地点データを読み出して車両の案内を行う際に、前記データ記憶手段に格納されている該案内地点の直後に案内される案内地点についての案内地点データを参照して経路案内を行うデータ案内手段とを備え、
前記地点間データ部は、経路上後方の案内地点の案内地点データに含まれて記憶され、
前記データ生成手段は、案内地点データのうち、地点データ部をまず作成し、その後地点間データ部を作成し、
前記データ記憶手段は、前記経路の始点から終点の方向順に案内地点データを記憶することを特徴とするナビゲーション装置。In a navigation device that provides route guidance according to a preset route,
A guide point is set along the preset route, and a point data part that is information on the guide point itself that performs the route guidance, and the guide point and the guide point that is guided immediately before the guide point Data generating means for generating, for each guide point, guide point data representing the point-to- point data part ,
Data storage means for storing the guide point data generated by the data generation means;
When the guidance of the vehicle reads the guidance point data for each guidance point, route guidance with reference to guidance point data for guide point which the guided after the data storage means the guide point that is stored immediately and a data guide means for performing,
The point-to-point data part is included and stored in the guide point data of the guide point at the rear of the route,
The data generation means first creates a point data portion of the guide point data, and then creates an inter-point data portion,
It said data storage means, characteristics and be Luna navigation device storing a guidance point data from the start point of the path in the direction the order of the end point.
前記予め設定される経路に沿って案内地点を設定し、前記経路案内を行う案内地点自体の情報である地点データ部と、該案内地点と該案内地点の直前に案内される案内地点との間の情報である地点間データ部と、を表す案内地点データを各案内地点毎に生成し、
前記生成された案内地点データを記憶し、
各案内地点について案内地点データを読み出して車両の案内を行う際に、該案内地点の直後に案内される案内地点についての案内地点データを参照して経路案内を行い、
前記地点間データ部は、経路上後方の案内地点の案内地点データに含まれて記憶され、
前記案内地点データのうち、地点データ部をまず作成し、その後地点間データ部を作成し、
前記経路の始点から終点の方向順に案内地点データを記憶することを特徴とするナビゲーション方法。In a navigation method for performing route guidance at a plurality of guidance points according to a preset route,
A guide point is set along the preset route, and a point data part that is information on the guide point itself that performs the route guidance, and the guide point and the guide point that is guided immediately before the guide point Data for each guidance point is generated for each guidance point.
Storing the generated guide point data;
When the guidance point data is read for each guidance point to guide the vehicle, route guidance is performed with reference to the guidance point data for the guidance point that is guided immediately after the guidance point,
The point-to-point data part is included and stored in the guide point data of the guide point at the rear of the route,
Of the guidance point data, first create a point data part, then create a point-to-point data part,
Guide point data is stored in the direction from the start point to the end point of the route .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000140891A JP4460110B2 (en) | 2000-05-12 | 2000-05-12 | Navigation device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000140891A JP4460110B2 (en) | 2000-05-12 | 2000-05-12 | Navigation device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2001324341A JP2001324341A (en) | 2001-11-22 |
| JP2001324341A5 JP2001324341A5 (en) | 2007-06-28 |
| JP4460110B2 true JP4460110B2 (en) | 2010-05-12 |
Family
ID=18648097
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000140891A Expired - Fee Related JP4460110B2 (en) | 2000-05-12 | 2000-05-12 | Navigation device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4460110B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5179569B2 (en) * | 2008-04-02 | 2013-04-10 | パイオニア株式会社 | Navigation device, route guidance method, and route guidance program |
| JP5389207B2 (en) * | 2012-03-07 | 2014-01-15 | パイオニア株式会社 | Navigation device, route guidance method, and route guidance program |
-
2000
- 2000-05-12 JP JP2000140891A patent/JP4460110B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2001324341A (en) | 2001-11-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7945383B2 (en) | Route determination method and apparatus for navigation system | |
| JP2001272240A (en) | Navigation device | |
| JP2007240400A (en) | Navigation device and plural route uniting method | |
| US20090119003A1 (en) | Navigation system and route guidance method | |
| JP2003344081A (en) | Method for guiding route using network | |
| JP3517075B2 (en) | Navigation device | |
| JP2000241189A (en) | Vehicle guidance method for navigation apparatus | |
| JP3366782B2 (en) | Route guidance device | |
| JP4460110B2 (en) | Navigation device | |
| JP2000283772A (en) | Running position indication apparatus | |
| JP4099401B2 (en) | Navigation device | |
| JP4133265B2 (en) | Navigation device | |
| JP2000180194A (en) | Destination candidate display method of route searching system | |
| JP3585720B2 (en) | Car navigation system | |
| JPH09292254A (en) | Running position display device | |
| JP2001165688A (en) | Navigation device | |
| JP2001165674A (en) | Navigation device | |
| JPH10239079A (en) | Navigation device | |
| JPH09133541A (en) | Traveling route guide unit | |
| JP2007003365A (en) | Vehicle mounted navigation device and its routing technique | |
| JP3766502B2 (en) | Navigation device | |
| JP2000205880A (en) | Method for drawing crossing location map | |
| JP4439318B2 (en) | Navigation device and road display method | |
| JP3708372B2 (en) | Route display method for in-vehicle navigation system | |
| JP2766402B2 (en) | In-vehicle navigator |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070511 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070511 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20090618 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090623 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090824 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20100209 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20100212 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4460110 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130219 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140219 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150219 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |