JP4129783B2 - Remote access system and remote access method - Google Patents
Remote access system and remote access method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4129783B2 JP4129783B2 JP2002201472A JP2002201472A JP4129783B2 JP 4129783 B2 JP4129783 B2 JP 4129783B2 JP 2002201472 A JP2002201472 A JP 2002201472A JP 2002201472 A JP2002201472 A JP 2002201472A JP 4129783 B2 JP4129783 B2 JP 4129783B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- certificate
- access
- attribute
- attribute certificate
- authority
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/06—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for supporting key management in a packet data network
- H04L63/061—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for supporting key management in a packet data network for key exchange, e.g. in peer-to-peer networks
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/08—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for authentication of entities
- H04L63/0823—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for authentication of entities using certificates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/08—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for authentication of entities
- H04L63/0869—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for authentication of entities for achieving mutual authentication
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L12/00—Data switching networks
- H04L12/28—Data switching networks characterised by path configuration, e.g. LAN [Local Area Networks] or WAN [Wide Area Networks]
- H04L12/2803—Home automation networks
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L12/00—Data switching networks
- H04L12/28—Data switching networks characterised by path configuration, e.g. LAN [Local Area Networks] or WAN [Wide Area Networks]
- H04L12/2803—Home automation networks
- H04L12/2816—Controlling appliance services of a home automation network by calling their functionalities
- H04L12/2818—Controlling appliance services of a home automation network by calling their functionalities from a device located outside both the home and the home network
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、所定のリソースに対して遠隔地からアクセスするリモートアクセスシステム及びリモートアクセス方法に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
近年、ネットワークに接続可能な情報家電等の各種機器が開発されており、これにともない、家庭内ネットワークをはじめとして様々な機器を対象としたネットワークが構築されつつある。また、このような状況に応じて、屋外等の遠隔地から屋内に設けられた各種情報家電又はパーソナルコンピュータ等の各種情報処理端末若しくはサーバ装置等に対して、ユーザが所持する携帯電話機や携帯情報端末機(Personal Digital Assistants;PDA)等の機器を用いてリモートアクセスすることによって享受できるサービスが各種提案されている。
【0003】
このようなサービスにおいては、当該サービスを提供するサーバ装置等のハードウェアやソフトウェア、さらにはデータといった各種リソースに対する不正なユーザのアクセスを排除すべく、認証及びアクセス権の管理を行うことが必須とされている。
【0004】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
ところで、上述したサービスとしては、既に実施されているものもあり、個別に認証の仕組みを構築している。しかしながら、このようなサービスにおいては、個人単位の権限(操作)をも含めた認証方式が未だ確立されていないのが現状である。
【0005】
また、個人単位の権限管理の手法としては、いわゆるID(IDentification)パスワードを用いた認証方式があるが、このIDパスワードを用いた認証方式においては、仕組みが非常に煩雑となり、処理負担が大きいといった問題があった。
【0006】
本発明は、このような実情に鑑みてなされたものであり、いわゆる属性証明書(Attribute Certificate;AC)を用いて権限管理を行うことにより、リモートアクセスを行う際に、リソースにアクセスする機器自体等のエンティティのみならず、アクセスさせたいリソース毎に、権限単位での制御を容易且つ安全に行うことができるリモートアクセスシステム及びリモートアクセス方法を提供することを目的とする。
【0007】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上述した目的を達成する本発明にかかるリモートアクセスシステムは、所定のリソースに対して遠隔地からアクセスするリモートアクセスシステムであって、当該リモートアクセスシステムは、アクセス対象となるアクセス対象機器と、前記アクセス対象機器に対してアクセスするアクセス機器と、前記アクセス機器に対して、前記アクセス対象機器のプロキシとして働く接続機器とからなり、前記アクセス機器は、前記リソースに対するアクセス権限及び前記接続機器が前記アクセス対象機器に対するプロキシとしての役割を果たすためのプロキシ情報が記述されている属性証明書を記憶する記憶手段と、前記記憶手段に記憶される前記属性証明書を、前記接続機器に対して送信して提示する第1の提示手段とを備え、前記接続機器は、前記アクセス機器から受信した前記属性証明書を、前記アクセス対象として指定されている前記アクセス対象機器に対して送信して提示する第2の提示手段を備え、前記アクセス対象機器は、前記接続機器から受信した前記属性証明書に記述されている前記アクセス権限及び前記プロキシ情報の内容を検証する検証手段と、前記検証手段による検証結果に基づいて、前記リソースに対する前記アクセス機器のアクセス許可を決定する決定手段とを備えることを特徴としている。
【0008】
このような本発明にかかるリモートアクセスシステムは、少なくともリソースに対するアクセス権限を証明書に記述し、この証明書を、アクセス機器からアクセス対象機器に対して接続機器を介して送信して提示し、リソースに対するアクセス機器のアクセスを検証する。
【0009】
また、上述した目的を達成する本発明にかかるリモートアクセス方法は、アクセス対象となるアクセス対象機器と、前記アクセス対象機器に対してアクセスするアクセス機器と、前記アクセス機器に対して、前記アクセス対象機器のプロキシとして働く接続機器とからなるリモートアクセスシステムにて、所定のリソースに対して遠隔地からアクセスするリモートアクセス方法であって、前記アクセス機器は、前記リソースに対するアクセス権限及び前記接続機器が前記アクセス対象機器に対するプロキシとしての役割を果たすためのプロキシ情報が記述されている属性証明書を記憶手段に記憶し、前記記憶手段に記憶される前記属性証明書を、前記接続機器に対して提示し、前記接続機器は、前記アクセス機器から受信した前記属性証明書を、前記アクセス対象として指定されている前記アクセス対象機器に対して送信して提示し、前記アクセス対象機器は、前記接続機器から受信した前記属性証明書に記述されている前記アクセス権限及び前記プロキシ情報の内容を検証し、検証結果に基づいて、前記リソースに対する前記アクセス機器のアクセス許可を決定することを特徴としている。
【0010】
このような本発明にかかるリモートアクセス方法は、少なくともリソースに対するアクセス権限を証明書に記述し、この証明書を、アクセス機器からアクセス対象機器に対して接続機器を介して送信して提示し、リソースに対するアクセス機器のアクセスを検証する。
【0011】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明を適用した具体的な実施の形態について図面を参照しながら詳細に説明する。
【0012】
この実施の形態は、所定のリソースに対して遠隔地からアクセスするリモートアクセスシステムである。このリモートアクセスシステムは、ISO(International Organization for Standardization)/IEC(International Electrotechnical Commission) 9594−8、又はITU−T X.509に基づく属性証明書(Attribute Certificate;AC)を用いて権限管理を行うことにより、リモートアクセスを行う際に、リソースにアクセスする機器自体等のエンティティのみならず、アクセスさせたいリソース毎に、権限単位での制御を容易に行うことができるものである。また、このリモートアクセスシステムは、属性証明書を利用する際に、リソースが属するネットワークの入り口となるゲートウェイを経由して、リソースとこのリソースにアクセスしようとする機器との間で属性証明書の授受を行うことにより、属性証明書の送付ルートを確認することを可能とし、セキュリティを向上させることができるものである。
【0013】
まず、リモートアクセスシステムの説明に先だって、当該リモートアクセスシステムにて用いる電子証明書である公開鍵証明書(Public Key Certificate;PKC)及び上述した属性証明書の概略について説明する。
【0014】
まず、公開鍵証明書について説明する。公開鍵証明書は、いわゆる公開鍵暗号方式における独立した所定の第三者機関である証明書発行認証局(Certification Authority;CA又はIssuer Authority;IA)によって発行されるものである。
【0015】
ここで、公開鍵暗号方式について説明する。公開鍵暗号方式は、発信者と受信者との鍵を異なるものとして、一方の鍵を不特定のユーザが使用可能な公開鍵とし、他方の鍵を秘密に保つ秘密鍵とするものである。公開鍵暗号方式は、暗号化及び復号に共通の鍵を用いるいわゆる共通鍵暗号方式と異なり、秘密に保つ必要がある秘密鍵を特定の1人が持てばよいため、共通鍵暗号方式と比較して鍵の管理において有利である。公開鍵暗号方式の代表的なものとしては、いわゆるRSA(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)暗号がある。このRSA暗号は、例えば150桁程度の非常に大きな2つの素数の積の素因数分解処理の困難性を利用するものである。
【0016】
公開鍵暗号方式は、不特定多数のユーザに公開鍵を使用可能とするものであり、配布する公開鍵が正当なものであるか否かを証明するために公開鍵証明書を用いる方法が広く用いられている。例えば、公開鍵暗号方式においては、ある特定のユーザAが対となる公開鍵と秘密鍵とを生成し、生成した公開鍵を証明書発行認証局に対して送付して公開鍵証明書を取得し、この公開鍵証明書を一般に公開する。一方、不特定のユーザは、公開鍵証明書に基づいて所定の手続きを経ることによって公開鍵を取得し、平文たる文書等を暗号化して特定のユーザAに対して送付する。そして、ユーザAは、不特定のユーザから送付された暗号化文書を秘密鍵を用いて復号する等の処理を行う。公開鍵暗号方式は、このような暗号方式である。
【0017】
また、公開鍵暗号方式においては、ユーザAは、秘密鍵を用いて平文たる文書等に署名を付加し、不特定のユーザが公開鍵証明書に基づいて所定の手続きを経ることによって公開鍵を取得し、その署名の検証を行うことが可能となる。例えば、公開鍵暗号方式においては、証明書発行認証局が公開鍵証明書を参照して公開鍵を判別すると、任意の平文たる文書等をユーザAに対して送付し、秘密鍵を用いて暗号化させ、再度送り返させる。証明書発行認証局は、ユーザAから送付された暗号化文書を公開鍵を用いて復号することにより、署名の正当性を検証することができる。
【0018】
このような公開鍵暗号方式における公開鍵証明書は、管理者たるユーザが自己を識別するための情報や公開鍵等を証明書発行認証局に提出することにより、証明書発行認証局側が当該証明書発行認証局を識別するための情報や有効期限等の情報を付加し、さらに証明書発行認証局による署名を付加して作成される。
【0019】
具体的には、公開鍵証明書は、図1及び図2に示すようなフォーマットから構成される。なお、同図においては、公開鍵証明書を構成する各フィールド毎の項目と、これらの各項目に対する説明とを記載している。
【0020】
図1に示すバージョン(version)は、公開鍵証明書のフォーマットのバージョン情報を記述するフィールドであり、例えばフォーマットがバージョン3である場合にはバージョン3を示す"2"が記述される。
【0021】
シリアルナンバ(serial Number)は、証明書発行認証局によって設定される公開鍵証明書のシリアルナンバを記述するフィールドであり、例えばシーケンシャルな番号が記述される。
【0022】
署名アルゴリズム識別子、及びアルゴリズムパラメータ(signature algorithm Identifier algorithm parameters)は、公開鍵証明書の署名アルゴリズムを識別するための情報とそのパラメータとを記述するフィールドである。署名アルゴリズムとしては、例えば楕円曲線暗号又はRSA暗号があり、署名アルゴリズムとして楕円曲線暗号が適用されている場合には、アルゴリズムパラメータとしてパラメータ及び鍵長が記述され、署名アルゴリズムとしてRSA暗号が適用されている場合には、アルゴリズムパラメータとして鍵長が記述される。
【0023】
発行者(issuer)は、公開鍵証明書の発行者、すなわち、証明書発行認証局の名称を識別可能とする形式(Distinguished Name)で記述するフィールドである。
【0024】
有効期限(validity)は、公開鍵証明書の有効期限である開始日時(not Before)及び終了日時(not After)を記述するフィールドである。
【0025】
サブジェクト(subject)は、ユーザである認証対象者の名前を記述するフィールドであり、例えばユーザ機器の識別子やサービス提供主体の識別子等が記述される。
【0026】
サブジェクト公開鍵情報(subject Public Key Info algorithm subject Public key)は、ユーザの公開鍵情報としての鍵アルゴリズムや鍵情報自体を記述するフィールドであり、鍵アルゴリズムとしては、例えば楕円曲線暗号又はRSA暗号がある。
【0027】
これらの各フィールドは、公開鍵証明書のフォーマットがバージョン1以降のバージョンであるものに含まれるフィールドであり、以下に示す各フィールドは、バージョン3であるものに追加されるフィールドである。
【0028】
証明局鍵識別子(authority Key Identifier-key Identifier, authority Cert Issuer, authority Cert Serial Number)は、証明書発行認証局の署名確認用の鍵を識別するための情報であり、8進数表記の鍵識別番号、一般名称(General Name)形式の証明書発行認証局の名称、及び認証番号を記述するフィールドである。
【0029】
サブジェクト鍵識別子(subject key Identifier)は、複数の鍵を公開鍵証明書において証明する場合に各鍵を識別するための識別子を記述するフィールドである。
【0030】
鍵使用目的(key usage)は、鍵の使用目的を指定するフィールドであり、(0)ディジタル署名用(digital Signature)、(1)否認防止用(non Repudiation)、(2)鍵の暗号化用(key Encipherment)、(3)メッセージの暗号化用(data Encipherment)、(4)共通鍵配送用(key Agreement)、(5)認証の署名確認用(key Cert Sign)、(6)失効リストの署名確認用(CRL Sign)、(7)鍵交換時(key Agreement)データの暗号化にのみ利用(encipher Only)、及び(8)鍵交換時データの復号にのみ利用(decipher Only)の各使用目的が設定される。
【0031】
秘密鍵有効期限(private Key Usage Period)は、ユーザが有する秘密鍵の有効期限である開始日時(not Before)及び終了日時(not After)を記述するフィールドであり、デフォルトでは、公開鍵証明書の有効期限と公開鍵の有効期限と秘密鍵の有効期限とは互いに同一とされる。
【0032】
図2に示す認証局ポリシー(Certificate Policy)は、証明書発行認証局の証明書発行ポリシーを記述するフィールドであり、例えばISO/IEC 9834−1に準拠したポリシーID(policy Identifier)や認証基準(policy Qualifiers)が記述される。
【0033】
ポリシー・マッピング(policy Mappings)は、証明書発行認証局を認証する場合にのみ記述されるフィールドであり、証明書発行を行う証明書発行認証局のポリシー(issuer Domain Policy)と被認証ポリシー(subject Domain Policy)とのマッピングを規定する。
【0034】
サポート・アルゴリズム(supported Algorithms)は、ディレクトリ(X.500)のアトリビュートを定義するフィールドである。サポート・アルゴリズムは、コミュニケーションの相手がディレクトリ情報を利用する場合に、事前にそのアトリビュートを知らせるのに用いる。
【0035】
サブジェクト別名(subject Alt Name)は、ユーザの別名を一般名称(General Name)形式で記述するフィールドである。
【0036】
発行者別名(issuer Alt Name)は、証明書発行者の別名を記述するフィールドである。
【0037】
サブジェクト・ディレクトリ・アトリビュート(subject Directory Attributes)は、ユーザの任意の属性を記述するフィールドである。
【0038】
基本制約(basic Constraints)は、証明対象の公開鍵が証明書発行認証局の署名用であるかユーザのものであるかを区別するためのフィールドである。
【0039】
許容サブツリー制約名(name Constraints permitted Subtrees)は、被認証者が証明書発行認証局である場合にのみ使用される公開鍵証明書の有効領域を示すフィールドである。
【0040】
制約ポリシー(policy Constraints)は、認証パスの残りに対する明確な認証ポリシーIDや禁止ポリシーマップを要求する制限を記述するフィールドである。
【0041】
CRL参照ポイント(Certificate Revocation List Distribution Points)は、ユーザが公開鍵証明書を利用する際に、この公開鍵証明書が失効していないかどうかを確認するための失効リストの参照ポイントを記述するフィールドである。
【0042】
署名は、公開鍵証明書発行者、すなわち、証明書発行認証局の署名フィールドである。電子署名は、公開鍵証明書の全体に対していわゆるハッシュ関数を適用してハッシュ値を生成し、このハッシュ値に対して証明書発行認証局の秘密鍵を用いて暗号化して生成したデータである。
【0043】
証明書発行認証局は、このようなフォーマットからなる公開鍵証明書を発行するとともに、有効期限が切れた公開鍵証明書を更新し、不正を行ったユーザの排斥を行うための不正者リストの作成、管理、配布、すなわち、リボケーション(revocation)を行う。また、証明書発行認証局は、必要に応じて、公開鍵及び秘密鍵の生成も行う。
【0044】
一方、この公開鍵証明書を利用するユーザは、自己が有する証明書発行認証局の公開鍵を用いて当該公開鍵証明書の電子署名を検証し、電子署名の検証に成功すると、公開鍵証明書に基づいて公開鍵を取得し、この公開鍵を利用することができる。したがって、公開鍵証明書を利用する全てのユーザは、当該公開鍵証明書を発行した証明書発行認証局の公開鍵を有しているか取得する必要がある。
【0045】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、後述するように、このような公開鍵証明書を各エンティティに保持させる。
【0046】
つぎに、属性証明書について説明する。属性証明書は、証明書発行認証局とは異なるローカルな機関である属性認証局(Attribute Authority;AA)によって発行されるものである。
【0047】
属性証明書は、図3及び図4に示すようなフォーマットから構成される。なお、同図においては、属性証明書を構成する各フィールド毎の項目と、これらの各項目に対する説明とを記載している。
【0048】
図3に示すバージョン(version)は、属性証明書のフォーマットのバージョン情報を記述するフィールドであり、例えばフォーマットがバージョン2(1)である場合にはバージョン2(1)を示す"1"が記述される。
【0049】
ホルダー(holder)は、属性証明書が結び付けられた公開鍵証明書の所有者を特定するためのフィールドである。ホルダーには、ベース認証局識別子(base Certificate ID)として、属性証明書の所有者が有する公開鍵証明書の発行者名(issuer)、属性証明書の所有者が有する公開鍵証明書のシリアルナンバ(serial)、属性証明書の所有者が有する公開鍵証明書の発行者を識別するための固有の識別子(issuer UID)が記述される。また、ホルダーには、公開鍵証明書におけるサブジェクト(subject)又はサブジェクト別名(subject Alt Name)と同一とされる属性証明書の所有者の名称(entity name)が記述される。さらに、ホルダーには、将来、属性証明書が識別情報(identity)や公開鍵証明書にリンクされていない場合を想定して、例えば公開鍵のハッシュが記述されるオブジェクト・ダイジェスト情報(object Digest Info)が記述される。
【0050】
発行者(issuer)は、属性証明書に署名した発行者の情報を指定するフィールドである。
【0051】
署名(signature)は、属性証明書の署名を有効にするために使用するアルゴリズムを識別するための識別子を記述するフィールドである。
【0052】
シリアルナンバ(serial Number)は、属性認証局が各属性証明書に割り振るシリアルナンバを記述するフィールドである。
【0053】
属性証明書有効期限(attr Cert Validity Period)は、属性証明書の有効期限である開始日時(not Before)及び終了日時(not After)を記述するフィールドである。
【0054】
図4に示す属性(attributes)は、属性証明書の所有者の特権に関する情報を記述するフィールドであり、例えば、文章でアクセスが許可された対象物を記述してもよく、システム側で用意しておいたアクセスすることができるコードを記述してもよく、ある平文を暗号化する鍵を記述してもよい。例えば、属性には、属性証明書の検証者が当該属性証明書の所有者を認証する場合に利用するサービスに関する認証情報(Service Authentication Information)、属性証明書の検証者が用いる当該属性証明書の所有者のアクセス許可情報(Access Identity)、課金のために属性証明書の所有者を特定するための情報(Charging Identity)、属性証明書の所有者のグループへの帰属関係を示す情報(Group)、属性証明書の所有者に与えられる役割を示す情報(Role)、属性証明書の所有者に対する秘密情報の使用許可に関する情報(Clearance)が記述される。
【0055】
発行者固有識別子(issuer Unique ID)は、属性証明書の発行者の公開鍵証明書で指定されている場合に利用されるフィールドである。
【0056】
拡張情報(extensions)は、属性証明書の所有者の情報ではなく属性証明書の情報を記述するフィールドであり、サーバ及び/又はサービス管理者が属性証明書の所有者の監査を行い不正行為の検出、すなわち特定をするために用いる情報(Audit Identity)、属性証明書が対象とするサーバ及び/又はサービスを示す情報(AC Targeting)、属性証明書の検証者による当該属性証明書の署名確認の補助情報である属性証明書の発行者の鍵情報(Authority Key)、属性証明書の検証者による当該属性証明書の失効状態確認の補助情報であるOCSPレスポンダのURI(Uniform Resource Identifiers)を示す情報(Authority Information Access)、属性証明書の検証者による当該属性証明書の失効状態確認の補助情報であるCRL(Certificate Revocation List)配布点のURIを示す情報(CRL Distribution)、当該属性証明書に対応する失効情報がないことを示す情報(No Revocation)、提出者が所有者以外である場合に利用され、属性証明書を提出することができるエンティティを示す情報(Proxy Info)が記述される。
【0057】
署名(signature Value)は、属性認証局によってつけられた署名を記述するフィールドである。
【0058】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、後述するように、このようなフォーマットからなる属性証明書を各エンティティに保持させることにより、あるエンティティに対していかなる権限が許可されているのかを検証することができる。
【0059】
リモートアクセスシステムは、以上のような公開鍵証明書及び属性証明書を用いて構築される。
【0060】
以下、これらの公開鍵証明書及び属性証明書を用いたリモートアクセスシステムについて説明する。
【0061】
まず、リモートアクセスシステムの概念について説明する。なお、ここでは、説明の便宜上、家庭内に設けられた各種情報家電又はパーソナルコンピュータ等の各種情報処理端末若しくはサーバ装置等をアクセスの対象とし、これらの機器に対して携帯電話機や携帯情報端末機(Personal Digital Assistants;PDA)等の携帯機器を所持するユーザが屋外からアクセスするものとして説明する。
【0062】
リモートアクセスシステムは、ITU−T(International Telecommunication Union-Telecommunication sector) X.509で定義されているPMI(Privilege management Infrastructure)の機能の1つである属性証明書を用いた権限プロキシ機能により、アクセスさせたいリソース毎に、権限単位での制御を行う。
【0063】
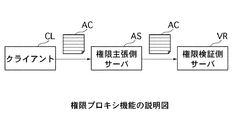
ここで、権限プロキシ機能について図5を用いて説明する。
【0064】
同図に示すように、属性証明書ACを保持するクライアントCLと、このクライアントCLの権限を検証する権限検証側サーバVRとの間に、クライアントCLの権限を主張する権限主張側サーバASが介在するシステムを考える。
【0065】
この場合、クライアントCLは、権限検証側サーバVRに対してアクセスしようとする際には、権限主張側サーバASに対して属性証明書ACを提示し、これに応じて、権限主張側サーバASは、クライアントCLから提示された属性証明書ACを、権限検証側サーバVRに対して提示する。
【0066】
しかしながら、この場合、権限検証側サーバVRは、権限主張側サーバASから提示された属性証明書ACが、権限主張側サーバASの属性証明書ではないことから、アクセスを許可しない旨の検証結果を出すことになる。すなわち、このようなシステムにおいては、属性証明書を直接的に授受する装置間で、権限の主張及び検証が行われることから、クライアントCLが権限検証側サーバVRに対して自己の権限を主張しようとする際には、クライアントCLから権限検証側サーバVRに対して直接的に属性証明書ACを提示する必要がある。
【0067】
そこで、このようなシステムにおいては、先に図4に示した拡張情報(extensions)におけるプロシキ情報(Proxy Info)を利用する。このプロシキ情報は、上述したように、属性証明書の提出者が所有者以外である場合に利用され、属性証明書を提出することができるエンティティを示す情報である。
【0068】
したがって、このようなシステムにおいては、クライアントCLは、権限検証側サーバVRに対してアクセスしようとする際には、属性証明書を提出できるエンティティとして権限検証側サーバVRを含む旨を示すプロシキ情報を記述した属性証明書ACを権限主張側サーバASに対して提示し、これに応じて、権限主張側サーバASは、クライアントCLから提示された属性証明書ACを、権限検証側サーバVRに対して提示する。
【0069】
これにより、権限検証側サーバVRは、権限主張側サーバASから提示された属性証明書ACにおけるプロシキ情報を参照して当該属性証明書ACを検証し、アクセスを許可する旨の検証結果を出すことが可能となる。
【0070】
このように、属性証明書ACを保持するクライアントCLと、このクライアントCLの権限を検証する権限検証側サーバVRとの間に、クライアントCLの権限を主張する権限主張側サーバASが介在するシステムにおいては、プロシキ情報に属性証明書ACの提出先を記述することにより、クライアントCLが権限検証側サーバVRに対してアクセスすることが可能となる。
【0071】
リモートアクセスシステムは、このような権限プロキシ機能を利用する。概念的には、リモートアクセスシステムは、図6に示すように、上述した公開鍵証明書を発行する証明書発行認証局CAと、上述した属性証明書を発行する属性認証局AAと、アクセスの対象となる対象機器101,102と、これらの対象機器101,102が属する家庭内ネットワークと他のネットワークとを相互に接続するためのインターフェースであるホームゲートウェイと20と、対象機器101,102に対してアクセスするためにユーザが所持する携帯機器30とを、エンティティとして備える。
【0072】
証明書発行認証局CAは、公開鍵暗号方式における独立した所定の第三者機関であって、ISO/IEC 9594−8、又はITU−T X.509に基づく電子証明書である公開鍵証明書を発行する。具体的には、証明書発行認証局CAは、公開鍵証明書PKCT1,PKCT2を、それぞれ、対象機器101,102に対して発行するとともに、公開鍵証明書PKCGをホームゲートウェイ20に対して発行するとともに、公開鍵証明書PKCMを携帯機器30に対して発行する。なお、この公開鍵証明書の発行の形態は、様々なものが考えられるが、例えば、対象機器101,102、ホームゲートウェイ20、及び携帯機器30の製造時にデータとして埋め込むことが考えられる。
【0073】
属性認証局AAは、証明書発行認証局CAとは論理的に異なるローカルな機関であって、権限管理を行うために用いる電子証明書である属性証明書を発行する。属性認証局AAは、証明書発行認証局CAからホームゲートウェイ20に対して発行された公開鍵証明書PKCGにより、ホームゲートウェイ20の認証を行う。そして、属性認証局AAは、例えばホームゲートウェイ20がユーザサイドに渡ってから初回接続時等に、携帯機器30に対して属性証明書ACPを発行する許可を与えるための属性証明書ACLを、ホームゲートウェイ20に対して発行する。なお、この属性証明書ACLについては、後に詳述するものとする。
【0074】
対象機器101,102は、それぞれ、図5における権限検証側サーバVRに相当するものである。対象機器101,102は、それぞれ、例えば、ネットワークに接続可能な各種情報家電や、パーソナルコンピュータ等の各種情報処理端末若しくはホームサーバ等のサーバ装置を想定したものであり、家庭内ネットワークを構成する機器である。なお、本発明におけるリソースとは、後に具体的な適用例を述べるように、ログインするこれらの対象機器101,102そのものを示す場合がある他、これらの対象機器101,102が保持するファイル等のデータやその他の各種情報を含む概念であるが、ここでは説明の便宜上、対象機器101,102そのものをリソースとするものとして説明する。対象機器101,102は、それぞれ、証明書発行認証局CAによって発行された公開鍵証明書PKCT1,PKCT2を保持し、これらの公開鍵証明書PKCT1,PKCT2を用いてホームゲートウェイ20との間で相互認証を行う。また、対象機器101,102は、それぞれ、携帯機器30がアクセスする際に送信した属性証明書ACPをホームゲートウェイ20を介して受信し、この属性証明書ACPの検証を行う。
【0075】
ホームゲートウェイ20は、図5における権限主張側サーバASに相当するものである。ホームゲートウェイ20は、例えば、いわゆるホームルータ、ファイアウォール、及び/又はブリッジといった概念を含むものであり、異なるプロトコルのネットワーク同士の接続を可能とするネットワークの入り口に相当する機器であり、対象機器101,102が属する家庭内ネットワークと他のネットワークとを相互に接続するためのインターフェースとして機能する。ホームゲートウェイ20は、証明書発行認証局CAによって発行された公開鍵証明書PKCGを保持し、この公開鍵証明書PKCGを用いて対象機器101,102、携帯機器30、及び属性認証局AAとの間で相互認証を行う。また、ホームゲートウェイ20は、携帯機器30に対して属性証明書ACPを発行する許可を与えるための属性証明書ACLが属性認証局AAによって発行されると、この属性証明書ACLを保持し、この属性証明書ACLに基づいて、携帯機器30に対して属性証明書ACPを発行する。なお、この属性証明書ACPについては、後に詳述するものとする。さらに、ホームゲートウェイ20は、携帯機器30から送信された属性証明書ACPを受信すると、この属性証明書ACPを対象機器101,102のそれぞれに対して送信して提示する。
【0076】
携帯機器30は、図5におけるクライアントCLに相当するものである。携帯機器30は、屋外にいるユーザが所持する携帯電話機や携帯情報端末機等の機器であり、いわゆるインターネット等のセキュアでないネットワークNTを介してホームゲートウェイ20に対して接続可能とされる。携帯機器30は、証明書発行認証局CAによって発行された公開鍵証明書PKCMを保持し、この公開鍵証明書PKCMを用いてホームゲートウェイ20との間で相互認証を行う。また、携帯機器30は、リソースとしての対象機器101,102のそれぞれに対してアクセスすることを認証するための属性証明書ACPがホームゲートウェイ20によって発行されると、この属性証明書ACPをIC(Integrated Circuit)カード等に格納すること等によって保持する。そして、携帯機器30は、対象機器101,102のそれぞれに対してアクセスしようと試みる際に、ICカード等に格納された属性証明書ACPを用いたログイン操作を行うことにより、この属性証明書ACPをホームゲートウェイ20に対して送信して提示する。
【0077】
このようなリモートアクセスシステムにおいては、上述したように、2つの属性証明書ACL,ACPが使用される。
【0078】
まず、属性証明書ACLについて説明する。
【0079】
属性証明書ACLは、上述したように、携帯機器30に対して属性証明書ACPを発行する許可をホームゲートウェイ20に対して与えるために、属性認証局AAからホームゲートウェイ20に対して発行されるものである。例えば、この属性証明書ACLには、図7にタイプとして登録されているオブジェクトID(Object ID;OID)及び値の例の抜粋を示す先に図4に示した属性(attributes)における各フィールドのうち、当該属性証明書ACLの所有者たるホームゲートウェイ20に与えられる役割を示す情報(Role)を用いて、携帯機器30に対して属性証明書ACPを発行する許可を与える旨を示す情報を記述することができる。
【0080】
ここで、"ロール(Role)"の概念について説明する。
【0081】
この"ロール(Role)"の概念を用いた権限管理の手法は、本件出願人が先に出願している特願2002−029636に記載したものである。
【0082】
すなわち、この権限管理の手法においては、概念的には、図8に示すように、例えば権限AU11,AU12,・・・,AU21,AU22,・・・といった所定の権限を定義する枠組みを1つの役割(ロール)R1,R2とし、例えば個人M1,M2,M3といった少なくとも1人以上の個人がこのロールR1,R2に属するものとされる。
【0083】
この権限管理の手法においては、各個人M1,M2,M3がそれぞれ有する属性証明書であって当該個人M1,M2,M3が属しているロールを示す情報が記述されている役割割当証明書(Role Assignment Certificate)RAACが、属性認証局AAによって発行されるとともに、ロール毎に発行される属性証明書であって当該ロールに許可されている権限を示す情報が記述されている役割定義証明書(Role Specification Certificate)RSACが、役割認証局(Role Authority)RAによって発行される。なお、役割認証局RAは、属性認証局AAと同一であってもよいが、ここでは説明の便宜上、論理的に独立な機関であるものとする。
【0084】
この権限管理の手法においては、各ロールの定義については、役割認証局RAによって発行される役割定義証明書RSACを用いる。すなわち、この権限管理の手法においては、ロール毎に、許可される手続きが定義されるが、この情報が、役割認証局RAによって発行される役割定義証明書RSACに記述される。
【0085】
この役割定義証明書RSACは、先に図3及び図4に示した属性証明書のフォーマットにしたがって作成されるものであり、少なくとも、当該役割定義証明書RSACの発行者たる役割認証局RAの名前を示す情報、ロールを識別するためのロール名といったロールの情報、システムによってコード又は操作名が記述されるものであって許可される操作を示す情報等の各種情報が記述される。
【0086】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、携帯機器30に対して属性証明書ACPを発行する許可を与える旨を示す情報を含む各種情報が記述された役割定義証明書RSACが役割認証局RAによって発行され、権限AU11,AU12,・・・,AU21,AU22,・・・が定義されたリソース、すなわち、先に示した図6においては対象機器101,102がこの役割定義証明書RSACを保持する。
【0087】
一方、この権限管理の手法においては、各ロールに対する役割の割り当てについては、属性認証局AAによって発行される役割割当証明書RAACを用いる。すなわち、この権限管理の手法においては、個人M1,M2,M3毎に、各役割が定義されるが、この情報が、属性認証局AAによって発行される役割割当証明書RAACに記述される。
【0088】
この役割割当証明書RAACも、役割定義証明書RSACと同様に、先に図3及び図4に示した属性証明書のフォーマットにしたがって作成されるものであり、少なくとも、当該役割割当証明書RAACの発行者たる属性認証局AAの名前を示す情報、ロールを識別するためのロール名といったロールの情報、対応する役割定義証明書RSACと関連付けを行うための役割定義証明書RSACへの参照ポイントを示す情報としての役割認証局RAの名前を示す情報等の各種情報が記述される。
【0089】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、このような各種情報が記述された役割割当証明書RAACが属性証明書ACLとして属性認証局AAによって発行され、個人M1,M2,M3、すなわち、先に示した図6においてはホームゲートウェイ20が、この役割割当証明書RAACを保持する。
【0090】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、このような"ロール(Role)"の概念を用いることにより、携帯機器30に対して属性証明書ACPを発行する許可を与える旨を示す情報を記述した属性証明書ACLを、属性認証局AAによってホームゲートウェイ20に対して発行することができる。これにより、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、この属性証明書ACLを保持したホームゲートウェイ20によって属性証明書ACPを携帯機器30に対して発行することが可能となる。
【0091】
なお、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、携帯機器30に対して属性証明書ACPを発行する許可を与える旨を示す情報を属性証明書ACLに記述するために、当該属性証明書ACLの所有者たるホームゲートウェイ20に与えられる役割を示す情報(Role)を用いるのではなく、図7に示した属性(attributes)における各フィールドのうち、属性証明書の検証者が当該属性証明書の所有者を認証する場合に利用するサービスに関する認証情報(Service Authentication Information)や、属性証明書の検証者が用いる当該属性証明書の所有者のアクセス許可情報(Access Identity)等を用いて、同情報を記述することも可能である。
【0092】
また、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、権限委譲エクステンションを用い、属性証明書ACPを発行する対象及び権限を制御するようにしてもよい。例えば、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、Basic Attribute Constraintsエクステンションを用いて、ホームゲートウェイ20には携帯機器30に対して属性証明書ACPを発行できる旨を示し、さらに、ホームゲートウェイ20からは権限委譲を許可しない旨を設定することが考えられる。
【0093】
このように、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、携帯機器30に対して属性証明書ACPを発行する許可をホームゲートウェイ20に与える手法として、様々なものが考えられる。
【0094】
つぎに、属性証明書ACPについて説明する。
【0095】
属性証明書ACPは、ある公開鍵証明書を保持している機器又はユーザに対する権限が記述されたものであり、ここでは、公開鍵証明書PKCMを保持している携帯機器30に対する権限として、リソースとしての対象機器101,102のそれぞれに対してアクセスすることを許可する旨の情報が記述されたものである。例えば、この属性証明書ACPには、先に図7に示した属性(attributes)における各フィールドのうち、属性証明書ACPの検証者たる対象機器101,102のそれぞれが当該属性証明書ACPの所有者を認証する場合に利用するサービスに関する認証情報(Service Authentication Information)や、属性証明書ACPの検証者たる対象機器101,102のそれぞれが用いる当該属性証明書ACPの所有者のアクセス許可情報(Access Identity)等を用いて、アクセスする対象、アクセスできる操作(権限)、及びアクセスするための認証情報がある場合には当該認証情報を記述することができる。また、属性証明書ACPには、図9にタイプとして登録されているオブジェクトID(Object ID;OID)及びクリティカル又は値の例の抜粋を示す先に図4に示した拡張情報(extensions)における各フィールドのうち、プロシキ情報(Proxy Info)を用いて、当該属性証明書ACPを経由させるホームゲートウェイ20の情報が記述される。
【0096】
ここで、プロシキ情報は、具体的には、図10に示すように記述されるものである。
【0097】
属性証明書ACPには、このようなプロシキ情報におけるターゲット(Target)として、ホームゲートウェイ20を識別するためのアドレスや識別子が記述されるとともに、ホームゲートウェイ20が保持する公開鍵証明書PKCGを示す情報が記述される。
【0098】
このように、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、携帯機器30に対する権限として、リソースとしての対象機器101,102のそれぞれに対してアクセスすることを許可する旨の情報が記述されるとともに、プロシキ情報として、ホームゲートウェイ20の情報が記述された属性証明書ACPを、ホームゲートウェイ20から携帯機器30に対して発行することができる。これにより、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、対象機器101,102が、それぞれ、この属性証明書ACPをホームゲートウェイ20を介して受信した場合には、プロシキ情報におけるターゲットを検証し、且つ、ホームゲートウェイ20から送信された属性証明書であることを検証することになる。
【0099】
さて、このようなリモートアクセスシステムにおいては、具体的には、図11に示すように、当該リモートアクセスシステムを構築するための準備フェーズP1が行われると、任意の携帯機器をリソースに対してアクセスする機器として登録するための登録フェーズP2が行われる。これにより、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、登録された携帯機器が任意の操作を行うことが可能となり、実際に携帯機器が任意の操作を行う際には、アクセスフェーズP3が行われる。また、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、必要に応じて、任意の携帯機器をリソースに対してアクセスする機器から除外するためのアクセス削除フェーズP4や、任意の携帯機器の権限を変更するためのアクセス変更フェーズP5が行われる。
【0100】
以下、これら5つの各フェーズについて説明する。
【0101】
まず、準備フェーズP1について説明する。
【0102】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、当該リモートアクセスシステムを構築するための準備フェーズP1として、各エンティティが相互認証可能となるように、証明書発行認証局CAにより、各エンティティに対して認証のための公開鍵証明書を発行する。すなわち、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、上述したように、各エンティティの製造時等に、証明書発行認証局CAにより、公開鍵証明書PKCT1,PKCT2を、それぞれ、対象機器101,102に対して発行するとともに、公開鍵証明書PKCGをホームゲートウェイ20に対して発行するとともに、公開鍵証明書PKCMを携帯機器30に対して発行する。
【0103】
リモートアクセスシステムは、このような準備フェーズP1を経ることにより、各エンティティが相互認証可能な状態に構築される。
【0104】
つぎに、登録フェーズP2について説明する。
【0105】
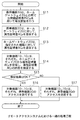
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、任意の携帯機器としての携帯機器30をリソースに対してアクセスする機器として登録するための登録フェーズP2として、図12に示す工程が行われる。
【0106】
まず、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、同図に示すように、ステップS1において、属性認証局AAにより、上述した準備フェーズP1にて証明書発行認証局CAによって発行されてホームゲートウェイ20に保持されている公開鍵証明書PKCGを用いて、ホームゲートウェイ20との間で相互認証を行う。この相互認証は、ホームゲートウェイ20自体に対する認証であり、ホームゲートウェイ20が正当なものであるか否かを認証するためのものである。
【0107】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS2において、属性認証局AAにより、ホームゲートウェイ20がユーザサイドに渡ってから初回接続時等に、携帯機器30に対して属性証明書ACPを発行する許可を与えるための属性証明書ACLを、ホームゲートウェイ20に対して発行する。これにともない、ホームゲートウェイ20は、属性認証局AAから送信された属性証明書ACLを保持する。
【0108】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS3において、ホームゲートウェイ20により、ユーザからの指示にしたがい、接続する機器、すなわち、対象機器101,102のそれぞれの情報を登録するとともに、その対象機器101,102のそれぞれに対してリモートからアクセスしてもよい携帯機器30に対して上述したプロシキ情報を記述した属性証明書ACPを発行する。
【0109】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS4において、携帯機器30により、上述した準備フェーズP1にて証明書発行認証局CAによって発行されて保持している公開鍵証明書PKCMを用いて、ホームゲートウェイ20との間で相互認証を行う。
【0110】
そして、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS5において、携帯機器30により、ホームゲートウェイ20から送信された属性証明書ACPをICカード等に格納して保持し、一連の登録フェーズP2を終了する。
【0111】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、このような一連の工程からなる登録フェーズP2を経ることにより、リソースに対してアクセスする機器として、携帯機器30を登録することができる。このようにしてリソースに対してアクセスする携帯機器30の登録がされたリモートアクセスシステムにおいては、登録された携帯機器30が任意の操作を行うことが可能となる。
【0112】
つぎに、アクセスフェーズP3について説明する。
【0113】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、登録された携帯機器30がリソースに対してアクセスする際には、アクセスフェーズP3として、図13に示す工程が行われる。
【0114】
まず、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、同図に示すように、ステップS11において、携帯機器30により、保持している公開鍵証明書PKCMを用いて、ホームゲートウェイ20との間で相互認証を行う。
【0115】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS12において、携帯機器30により、保持している属性証明書ACPをホームゲートウェイ20に対して送信して提示する。
【0116】
これに応じて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS13において、ホームゲートウェイ20により、携帯機器30から提示された属性証明書ACPの内容に基づいて、当該属性証明書ACPを、アクセスする対象として指定された機器、すなわち、対象機器101,102のいずれか又は双方に対して送信して提示する。
【0117】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS14において、対象機器101,102のいずれか又は双方により、ホームゲートウェイ20から送信された属性証明書ACPを受信し、上述したプロシキ情報や属性といった当該属性証明書ACPの内容を検証する。
【0118】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS15において、属性証明書ACPの検証結果が正当なものであった場合には、ステップS16において、対象機器101,102のいずれか又は双方によって携帯機器30のアクセスを許可し、一連のアクセスフェーズP3を終了する。一方、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS15において、属性証明書ACPの検証結果が不当なものであった場合には、ステップS17において、対象機器101,102のいずれか又は双方によって携帯機器30のアクセスを拒否し、一連のアクセスフェーズP3を終了する。
【0119】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、このような一連の工程からなるアクセスフェーズP3を経ることにより、対象機器101,102のそれぞれによって携帯機器30の権限を判別することができ、アクセスが許可された携帯機器30は、任意の操作を行うことが可能となる。
【0120】
つぎに、アクセス削除フェーズP4について説明する。
【0121】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、任意の携帯機器をリソースに対してアクセスする機器から除外したい場合には、アクセス削除フェーズP4として、図14に示す工程が行われる。
【0122】
まず、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、同図に示すように、ステップS21において、ホームゲートウェイ20により、ユーザからの指示にしたがい、対象機器101,102のそれぞれに対してリモートからアクセスしてもよい携帯機器30に対して発行した属性証明書ACPに対するCRL(ACRL)を作成し、このCRL(ACRL)を保持する。
【0123】
このように、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、属性証明書ACPに対するCRL(ACRL)を作成することにより、携帯機器30からホームゲートウェイ20に対してアクセスがあった場合には、ホームゲートウェイ20によってアクセスを拒否することができ、携帯機器30をリソースに対してアクセスする機器から除外することができる。特に、リモートアクセスシステムは、複数人のユーザの間で携帯機器30の貸借がある場合や携帯機器30を紛失した場合といった携帯機器30の側の都合による場合等には、属性証明書ACPに対するCRL(ACRL)を作成するのみで、携帯機器30をリソースに対してアクセスする機器から除外することができる。
【0124】
ただし、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、このような操作を繰り返し行うことにより、CRL(ACRL)のサイズが大きくなり、取り扱いに不便を生じるおそれがある。
【0125】
そこで、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、正当なユーザが自らの意思で携帯機器30をリソースに対してアクセスする機器から除外したい場合等には、ステップS21の処理に続いて、以下のステップS22乃至ステップS24の処理を行うようにしてもよい。
【0126】
すなわち、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS22において、携帯機器30により、保持している公開鍵証明書PKCMを用いて、ホームゲートウェイ20との間で相互認証を行う。
【0127】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS23において、ホームゲートウェイ20からの指示にしたがい、携帯機器30により、保持している属性証明書ACPを削除する。
【0128】
そして、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS24において、ホームゲートウェイ20により、ステップS21にて作成したCRL(ACRL)を削除し、一連のアクセス削除フェーズP4を終了する。
【0129】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、このような一連の工程からなるアクセス削除フェーズP4を経ることにより、携帯機器30をリソースに対してアクセスする機器から除外することができる。
【0130】
最後に、アクセス変更フェーズP5について説明する。
【0131】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、任意の携帯機器の権限を変更したい場合には、アクセス変更フェーズP5として、図15に示す工程が行われる。
【0132】
まず、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、同図に示すように、ステップS31において、ホームゲートウェイ20により、ユーザからの指示にしたがい、携帯機器30に対してプロシキ情報を記述した新たな属性証明書ACPを発行する。
【0133】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS32において、携帯機器30により、保持している公開鍵証明書PKCMを用いて、ホームゲートウェイ20との間で相互認証を行う。
【0134】
そして、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS33において、携帯機器30により、ホームゲートウェイ20から送信された新たな属性証明書ACPを、元の属性証明書ACPと置換してICカード等に格納して保持し、一連のアクセス変更フェーズP5を終了する。
【0135】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、このような一連の工程からなるアクセス変更フェーズP5を経ることにより、携帯機器30の権限を変更することができる。これにより、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、携帯機器30が新たな任意の操作を行うことが可能となる。
【0136】
以上のように、リモートアクセスシステムは、プロシキ情報が記述された属性証明書ACPを用いて権限管理を行うことができる。
【0137】
さて、以下では、このようなリモートアクセスシステムを具体的に適用した適用例について説明する。なお、本発明におけるリソースとは、上述したように、ログインする機器そのものを示す場合がある他、これらの機器が保持するファイル等のデータやその他の各種情報を含む概念であるが、ここでは、これらリソースの具体例についても言及する。
【0138】
まず、リモートアクセスシステムの適用例としては、ホームサーバやパーソナルコンピュータ等の情報処理端末が保持するデータへのリモートアクセスを行うデータアクセスシステムがあげられる。
【0139】
このデータアクセスシステムにおいては、ホームサーバや情報処理端末が保持するデータがリソースとなり、携帯機器を用いてユーザが行う操作は、データを保持するホームサーバや情報処理端末に対するデータアクセスとなる。
【0140】
このようなデータアクセスシステムにおいては、ホームゲートウェイによって適切なプロシキ情報を記述した属性証明書ACPを携帯機器に対して発行し、携帯機器がデータにアクセスする際に、当該属性証明書ACPをホームゲートウェイを介してホームサーバや情報処理端末に対して提示する。これにより、データアクセスシステムにおいては、携帯機器を用いてホームゲートウェイを介してデータに対してアクセスすることが可能となる。
【0141】
このように、リモートアクセスシステムは、ホームサーバやパーソナルコンピュータ等の情報処理端末が保持するデータに対するデータアクセスシステムに適用することができる。
【0142】
また、リモートアクセスシステムの他の適用例としては、家電カメラを用いた画像撮影による情報取得システムがあげられる。
【0143】
具体的に説明するために、例えば家庭内の冷蔵庫の在庫を情報として取得する情報取得システムを考える。この情報取得システムにおいては、冷蔵庫内部の画像がリソースとなり、携帯機器を用いてユーザが行う操作は、取得した画像を閲覧することによる冷蔵庫の在庫確認となる。
【0144】
このような情報取得システムにおいては、ホームゲートウェイによって適切なプロシキ情報を記述した属性証明書ACPを携帯機器に対して発行し、携帯機器が家電カメラが内部に取り付けられた冷蔵庫にアクセスする際に、当該属性証明書ACPをホームゲートウェイを介して冷蔵庫に対して提示する。これにより、情報取得システムにおいては、ユーザが外出している最中であっても、ユーザが所持する携帯機器を用いてホームゲートウェイを介して家電カメラを操作し、冷蔵庫内部の画像を取得することが可能となる。
【0145】
このように、リモートアクセスシステムは、家電カメラを用いた画像撮影による情報取得システムに適用することができる。
【0146】
さらに、リモートアクセスシステムの他の適用例としては、任意の場所の画像撮影による情報取得システムがあげられる。
【0147】
具体的に説明するために、例えば所定の会員である旨を証明するための会員カードの画像を取得することによって会員であるか否かを認証する情報取得システムを考える。この情報取得システムにおいては、家庭等の任意の場所にある会員カードの画像がリソースとなり、携帯機器を用いてユーザが行う操作は、会員カードの認証者に画像を閲覧させることによって会員である旨を証明するものとなる。
【0148】
このような情報取得システムにおいては、ホームゲートウェイによって適切なプロシキ情報を記述した属性証明書ACPを携帯機器に対して発行し、携帯機器が会員カードを撮影するカメラにアクセスする際に、当該属性証明書ACPをホームゲートウェイを介してカメラに対して提示する。これにより、情報取得システムにおいては、会員カードがユーザの手元にない場合であっても、ユーザが所持する携帯機器を用いてホームゲートウェイを介してカメラを操作し、会員カードの画像を取得することが可能となる。
【0149】
このように、リモートアクセスシステムは、任意の場所の画像撮影による情報取得システムに適用することができる。
【0150】
さらにまた、リモートアクセスシステムの他の適用例としては、屋外からのリモート操作による家電操作を行う家電操作システムがあげられる。
【0151】
具体的に説明するために、例えば家庭内のエアーコンディショナ機器のオン/オフ操作を行う家電操作システムを考える。この家電操作システムにおいては、エアーコンディショナ機器自体がリソースとなり、携帯機器を用いてユーザが行う操作は、このリソースとしてのエアーコンディショナ機器をリモート操作するためのリモートコントローラに対するアクセスとなる。
【0152】
このような家電操作システムにおいては、ホームゲートウェイによって適切なプロシキ情報を記述した属性証明書ACPを携帯機器に対して発行し、携帯機器がリモートコントローラにアクセスする際に、当該属性証明書ACPをホームゲートウェイを介してリモートコントローラに対して提示する。これにより、家電操作システムにおいては、ユーザが外出している最中であっても、ユーザが所持する携帯機器を用いてホームゲートウェイを介してリモートコントローラを操作し、エアーコンディショナ機器のオン/オフ操作を行うことが可能となる。
【0153】
このように、リモートアクセスシステムは、屋外からのリモート操作による家電操作を行う家電操作システムに適用することができる。
【0154】
以上説明したように、本発明の実施の形態として示したリモートアクセスシステムは、プロシキ情報が記述された属性証明書ACPを用いて権限管理を行うことにより、携帯機器30からリソースとしての対象機器101,102のそれぞれに対してリモートアクセスを行う際に、対象機器101,102毎に、権限単位での制御を容易に行うことができる。
【0155】
また、このリモートアクセスシステムは、属性証明書ACPを利用する際に、リソースとしての対象機器101,102のそれぞれが属するネットワークの入り口となるホームゲートウェイ20を経由して、対象機器101,102のそれぞれと携帯機器30との間で属性証明書ACPの授受を行うことにより、属性証明書ACPの送付ルートが一義に決定されることから、属性証明書ACPの送付ルートを確認することができ、セキュリティを向上させることができる。
【0156】
なお、本発明は、上述した実施の形態に限定されるものではない。例えば、上述した実施の形態では、アクセスの対象となる対象機器101,102が属する家庭内ネットワークの入り口となるホームゲートウェイ20が携帯機器30に対して属性証明書ACPを発行するものとして説明したが、本発明は、属性証明書ACPを発行するエンティティに拘泥するものではなく、ホームゲートウェイ20は、少なくとも属性証明書ACPの内容に応じて、当該属性証明書ACPを適切な提示先に提示する機能を有するものであればよい。
【0157】
この具体例として、あるネットワークの入り口としてのホームゲートウェイによって発行された属性証明書ACPを用いて、他のネットワークに属するリソースにアクセスするリモートアクセスシステムについて説明する。
【0158】
このリモートアクセスシステムは、概念的には、図16に示すように、第1の家庭内ネットワークに属する対象機器101,102と、これらの対象機器101,102が属する第1の家庭内ネットワークの入り口となるホームゲートウェイと201と、対象機器101,102に対してアクセスするためにユーザが所持する携帯機器301と、第1の家庭内ネットワークとは異なる第2の家庭内ネットワークに属する対象機器103と、この対象機器103が属する第2の家庭内ネットワークの入り口となるホームゲートウェイと202と、対象機器103に対してアクセスするために他のユーザが所持する携帯機器302と、図示しないが、上述した証明書発行認証局CA及び属性認証局AAとを、エンティティとして備える。
【0159】
すなわち、このリモートアクセスシステムは、第1の家庭内ネットワークから構成される図6に示したようなシステムと、他の家屋等の第2のネットワークから構成される同様のシステムとが、併存しているものである。
【0160】
対象機器101,102は、それぞれ、第1の家庭内ネットワークを構成する機器であり、図示しない証明書発行認証局CAによって発行された公開鍵証明書PKCT1,PKCT2を保持し、これらの公開鍵証明書PKCT1,PKCT2を用いてホームゲートウェイ201との間で相互認証を行う。また、対象機器101,102は、それぞれ、携帯機器301がアクセスする際に送信した属性証明書ACP1をホームゲートウェイ201を介して受信し、この属性証明書ACP1の検証を行う。
【0161】
ホームゲートウェイ201は、対象機器101,102が属する第1の家庭内ネットワークと他のネットワークとを相互に接続するためのインターフェースとして機能する。ホームゲートウェイ201は、図示しない証明書発行認証局CAによって発行された公開鍵証明書PKCG1を保持し、この公開鍵証明書PKCG1を用いて対象機器101,102、携帯機器301、及び図示しない属性認証局AAとの間で相互認証を行う。また、ホームゲートウェイ201は、携帯機器301に対して属性証明書ACP1を発行する許可を与えるための属性証明書ACL1が図示しない属性認証局AAによって発行されると、この属性証明書ACL1を保持し、この属性証明書ACL1に基づいて、携帯機器301に対して属性証明書ACP1を発行する。さらに、ホームゲートウェイ201は、携帯機器301から送信された属性証明書ACP1を受信すると、この属性証明書ACP1を対象機器101,102のそれぞれに対して送信して提示する。
【0162】
さらにまた、ホームゲートウェイ201は、アクセスすることができる他のネットワークにおけるホームゲートウェイを示す情報が記述された後に詳述する属性証明書ACHが図示しない属性認証局AAによって発行されると、この属性証明書ACHを保持し、この属性証明書ACHに基づいて、第2の家庭内ネットワークにおけるホームゲートウェイ202と通信を行うことが可能とされる。ホームゲートウェイ201は、この属性証明書ACHを第2の家庭内ネットワークにおけるホームゲートウェイ202に対して送信して提示することにより、第2の家庭内ネットワークに属する対象機器103に対するアクセス許可を得るための属性証明書ACP1'をホームゲートウェイ202によって発行してもらい、携帯機器301に対してこの属性証明書ACP1'を送信する。そして、ホームゲートウェイ201は、携帯機器301から送信された属性証明書ACP1'を受信すると、この属性証明書ACP1'を属性証明書ACHとともにホームゲートウェイ202に対して送信して提示する。なお、この属性証明書ACP1'については、後に詳述するものとする。
【0163】
携帯機器301は、通常は、第1の家庭内ネットワークに属する対象機器101,102のそれぞれに対してアクセスするための機器であり、インターネット等のセキュアでないネットワークNTを介してホームゲートウェイ201に対して接続可能とされる。携帯機器301は、図示しない証明書発行認証局CAによって発行された公開鍵証明書PKCM1を保持し、この公開鍵証明書PKCM1を用いてホームゲートウェイ201との間で相互認証を行う。携帯機器301は、リソースとしての対象機器101,102のそれぞれに対してアクセスすることを認証するための属性証明書ACP1がホームゲートウェイ201によって発行されると、この属性証明書ACP1をICカード等に格納すること等によって保持する。そして、携帯機器301は、対象機器101,102のそれぞれに対してアクセスしようと試みる際に、ICカード等に格納された属性証明書ACP1を用いたログイン操作を行うことにより、この属性証明書ACP1をホームゲートウェイ201に対して送信して提示する。
【0164】
また、携帯機器301は、第2の家庭内ネットワークに属する対象機器103もアクセスの対象とすることができる。このとき、携帯機器301は、リソースとしての対象機器103に対してアクセスすることを認証するための属性証明書ACP1'がホームゲートウェイ202によって発行され、ホームゲートウェイ201を介してこの属性証明書ACP1'を受信すると、この属性証明書ACP1'をICカード等に格納すること等によって保持する。そして、携帯機器301は、対象機器103に対してアクセスしようと試みる際に、ICカード等に格納された属性証明書ACP1'を用いたログイン操作を行うことにより、この属性証明書ACP1'をホームゲートウェイ201に対して送信して提示する。
【0165】
対象機器103は、第2の家庭内ネットワークを構成する機器であり、図示しない証明書発行認証局CAによって発行された公開鍵証明書PKCT3を保持し、この公開鍵証明書PKCT3を用いてホームゲートウェイ202との間で相互認証を行う。また、対象機器103は、携帯機器302がアクセスする際に送信した属性証明書ACP2をホームゲートウェイ202を介して受信し、この属性証明書ACP2の検証を行う。さらに、対象機器103は、携帯機器301のアクセス対象とされた場合には、当該携帯機器301がアクセスする際に送信した属性証明書ACP1'と、ホームゲートウェイ201が送信した属性証明書ACHとを、ホームゲートウェイ202を介して受信し、これらの属性証明書ACP1',ACHの検証を行う。
【0166】
ホームゲートウェイ202は、対象機器103が属する第2の家庭内ネットワークと他のネットワークとを相互に接続するためのインターフェースとして機能する。ホームゲートウェイ202は、図示しない証明書発行認証局CAによって発行された公開鍵証明書PKCG2を保持し、この公開鍵証明書PKCG2を用いて対象機器103、携帯機器302、及び図示しない属性認証局AAとの間で相互認証を行う。また、ホームゲートウェイ202は、携帯機器302に対して属性証明書ACP2を発行する許可を与えるための属性証明書ACL2が図示しない属性認証局AAによって発行されると、この属性証明書ACL2を保持し、この属性証明書ACL2に基づいて、携帯機器302に対して属性証明書ACP2を発行する。さらに、ホームゲートウェイ202は、携帯機器302から送信された属性証明書ACP2を受信すると、この属性証明書ACP2を対象機器103に対して送信して提示する。
【0167】
さらにまた、ホームゲートウェイ202は、ホームゲートウェイ201から属性証明書ACHを受信すると、この属性証明書ACHに基づいて、属性証明書ACP1'をホームゲートウェイ201に対して発行する。そして、ホームゲートウェイ202は、ホームゲートウェイ201を介して携帯機器301から送信された属性証明書ACP1'と、ホームゲートウェイ201から送信された属性証明書ACHとを受信すると、これらの属性証明書ACP1',ACH対象機器103に対して送信して提示する。
【0168】
携帯機器302は、第2の家庭内ネットワークに属する対象機器103に対してアクセスするための機器であり、インターネット等のセキュアでないネットワークNTを介してホームゲートウェイ202に対して接続可能とされる。携帯機器302は、図示しない証明書発行認証局CAによって発行された公開鍵証明書PKCM2を保持し、この公開鍵証明書PKCM2を用いてホームゲートウェイ202との間で相互認証を行う。また、携帯機器302は、リソースとしての対象機器103に対してアクセスすることを認証するための属性証明書ACP2がホームゲートウェイ202によって発行されると、この属性証明書ACP2をICカード等に格納すること等によって保持する。そして、携帯機器302は、対象機器103に対してアクセスしようと試みる際に、ICカード等に格納された属性証明書ACP2を用いたログイン操作を行うことにより、この属性証明書ACP2をホームゲートウェイ202に対して送信して提示する。
【0169】
このようなリモートアクセスシステムにおいては、上述した2つの属性証明書ACL,ACPの他、2つの属性証明書ACH,ACP1'が使用される。
【0170】
まず、属性証明書ACHについて説明する。
【0171】
属性証明書ACHは、上述したように、アクセスすることができる他のネットワークにおけるエンティティ、具体的にはホームゲートウェイ202を示す情報が記述されたものであり、図示しない属性認証局AAによって署名されてホームゲートウェイ201に対して発行されるものである。例えば、この属性証明書ACHには、上述した属性(attributes)における各フィールドのうち、アクセス許可情報(Access Identity)等を用いて、アクセスすることができる他のネットワークにおけるエンティティとしてのホームゲートウェイ202を示す情報を記述することができる。
【0172】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、アクセスすることができる他のネットワークにおけるエンティティとしてのホームゲートウェイ202を示す情報を記述した属性証明書ACHを、ホームゲートウェイ201からの要求に応じて、ホームゲートウェイ202によって発行することができる。これにより、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、この属性証明書ACHを保持したホームゲートウェイ201を介して携帯機器301が対象機器103に対してアクセスすることが可能となる。
【0173】
つぎに、属性証明書ACP1'について説明する。
【0174】
属性証明書ACP1'は、上述した属性証明書ACPと同様に、ある公開鍵証明書を保持している機器又はユーザに対する権限が記述されたものであり、ここでは、公開鍵証明書PKCM1を保持している携帯機器301に対する権限として、第2の家庭内ネットワークに属するリソースとしての対象機器103に対してアクセスすることを許可する旨の情報が記述されたものである。例えば、この属性証明書ACP1'は、属性(attributes)については上述した属性証明書ACPと同様に、認証情報(Service Authentication Information)やアクセス許可情報(Access Identity)等を用いて、アクセスする対象、アクセスできる操作(権限)、及びアクセスするための認証情報がある場合には当該認証情報が記述される一方で、プロシキ情報(Proxy Info)としては、当該属性証明書ACP1'を経由させる2つのホームゲートウェイ201,202を識別するためのアドレスや識別子等の情報が記述されたものとなる。
【0175】
このように、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、携帯機器301に対する権限として、第2の家庭内ネットワークに属するリソースとしての対象機器103に対してアクセスすることを許可する旨の情報が記述されるとともに、プロシキ情報として、2つのホームゲートウェイ201,202の情報が記述された属性証明書ACP1'を、ホームゲートウェイ202からホームゲートウェイ201を介して携帯機器301に対して発行することができる。これにより、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、対象機器103が、この属性証明書ACP1'をホームゲートウェイ202を介して受信した場合には、プロシキ情報におけるターゲットを検証し、且つ、2つのホームゲートウェイ201,202を介して受信した属性証明書であることを検証することになる。
【0176】
さて、このようなリモートアクセスシステムにおいては、具体的には、先に図11に示したように、準備フェーズP1、登録フェーズP2、アクセスフェーズP3、アクセス削除フェーズP4、及びアクセス変更フェーズP5が行われる。なお、以下では、携帯機器301によって第2の家庭内ネットワークに属する対象機器103に対してアクセスするものとして説明する。
【0177】
まず、準備フェーズP1について説明する。
【0178】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、当該リモートアクセスシステムを構築するための準備フェーズP1として、各エンティティが相互認証可能となるように、証明書発行認証局CAにより、各エンティティに対して認証のための公開鍵証明書を発行する。すなわち、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、上述したように、各エンティティの製造時等に、証明書発行認証局CAにより、公開鍵証明書PKCT1,PKCT2,PKCT3を、それぞれ、対象機器101,102,103に対して発行するとともに、公開鍵証明書PKCG1,PKCG2を、それぞれ、ホームゲートウェイ201,202に対して発行するとともに、公開鍵証明書PKCM1,PKCM2を、それぞれ、携帯機器301,302に対して発行する。
【0179】
リモートアクセスシステムは、このような準備フェーズP1を経ることにより、各エンティティが相互認証可能な状態に構築される。
【0180】
つぎに、登録フェーズP2について説明する。
【0181】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、任意の携帯機器としての携帯機器30をリソースに対してアクセスする機器として登録するための登録フェーズP2として、図17に示す工程が行われる。
【0182】
まず、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、同図に示すように、ステップS41において、属性認証局AAにより、上述した準備フェーズP1にて証明書発行認証局CAによって発行されてホームゲートウェイ201に保持されている公開鍵証明書PKCG1を用いて、ホームゲートウェイ201との間で相互認証を行う。この相互認証は、ホームゲートウェイ201自体に対する認証であり、ホームゲートウェイ201が正当なものであるか否かを認証するためのものである。
【0183】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS42において、属性認証局AAにより、ホームゲートウェイ201がユーザサイドに渡ってから初回接続時等に、携帯機器301に対して属性証明書ACP1を発行する許可を与えるための属性証明書ACL1を、ホームゲートウェイ201に対して発行する。この際、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ホームゲートウェイ201が他のホームゲートウェイ202に対してアクセスする場合には、属性認証局AAにより、ホームゲートウェイ202に対してアクセスできる旨の情報が記述された属性証明書ACHを、ホームゲートウェイ201に対して発行する。これにともない、ホームゲートウェイ201は、属性認証局AAから送信された2つの属性証明書ACL1,ACHを保持する。
【0184】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS43において、ホームゲートウェイ201により、ユーザからの指示にしたがい、接続する機器、すなわち、対象機器101,102のそれぞれの情報を登録するとともに、その対象機器101,102のそれぞれに対してリモートからアクセスしてもよい携帯機器301に対して上述したプロシキ情報を記述した属性証明書ACP1を発行する。
【0185】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、携帯機器301から他のホームゲートウェイ202を介して対象機器103に対してアクセスしたい場合には、ステップS44において、ホームゲートウェイ201により、保持している属性証明書ACHを他のホームゲートウェイ202に対して送信して提示し、上述したプロシキ情報を記述した属性証明書ACP1'を発行してもらう。これにともない、ホームゲートウェイ202は、属性証明書ACP1'を発行し、この属性証明書ACP1'をホームゲートウェイ201に対して送信する。
【0186】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS45において、携帯機器301により、上述した準備フェーズP1にて証明書発行認証局CAによって発行されて保持している公開鍵証明書PKCM1を用いて、ホームゲートウェイ201との間で相互認証を行う。
【0187】
そして、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS46において、携帯機器301により、ホームゲートウェイ201から送信された属性証明書ACP1,ACP1'をICカード等に格納して保持し、一連の登録フェーズP2を終了する。
【0188】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、このような一連の工程からなる登録フェーズP2を経ることにより、リソースに対してアクセスする機器として、携帯機器301を登録することができる。このようにしてリソースに対してアクセスする携帯機器301の登録がされたリモートアクセスシステムにおいては、登録された携帯機器301が任意の操作を行うことが可能となる。
【0189】
つぎに、アクセスフェーズP3について説明する。
【0190】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、登録された携帯機器301がリソースに対してアクセスする際には、アクセスフェーズP3として、図18に示す工程が行われる。
【0191】
まず、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、同図に示すように、ステップS51において、携帯機器301により、保持している公開鍵証明書PKCM1を用いて、ホームゲートウェイ201との間で相互認証を行う。
【0192】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS52において、携帯機器301により、保持している属性証明書ACP1,ACP1'のいずれかをホームゲートウェイ201に対して送信して提示する。具体的には、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、対象機器101,102のいずれか又は双方に対してアクセスする場合には、携帯機器301により、保持している属性証明書ACP1をホームゲートウェイ201に対して送信して提示する一方で、対象機器103に対してアクセスする場合には、携帯機器301により、保持している属性証明書ACP1'をホームゲートウェイ201に対して送信して提示する。
【0193】
ここで、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、携帯機器301により、保持している属性証明書ACP1をホームゲートウェイ201に対して送信して提示した場合には、先に図13中ステップS13乃至ステップS17に示した処理と同様の処理を行うが、ここでは、携帯機器301は、保持している属性証明書ACP1'をホームゲートウェイ201に対して送信して提示するものとして説明する。
【0194】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS53において、ホームゲートウェイ201により、携帯機器301から提示された属性証明書ACP1'におけるプロシキ情報を検証し、アクセス対象の機器が自己の配下にある第1の家庭内ネットワークとは異なる第2の家庭内ネットワークに属する対象機器103である旨を把握すると、2つの属性証明書ACP1',ACHを、第2の家庭内ネットワークを司るホームゲートウェイ202に対して送信して提示する。
【0195】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS54において、ホームゲートウェイ202により、ホームゲートウェイ201から提示された2つの属性証明書ACP1',ACHの内容に基づいて、当該属性証明書ACP1',ACHを、アクセスする対象として指定された機器、すなわち、対象機器103に対して送信して提示する。
【0196】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS55において、対象機器103により、ホームゲートウェイ202から送信された2つの属性証明書ACP1',ACHを受信し、上述したプロシキ情報や属性といった当該属性証明書ACP1',ACHの内容を検証する。
【0197】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS56において、属性証明書ACP1',ACHの検証結果が正当なものであった場合には、ステップS57において、対象機器103によって携帯機器301のアクセスを許可し、一連のアクセスフェーズP3を終了する。一方、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS56において、属性証明書ACP1',ACHの検証結果が不当なものであった場合には、ステップS58において、対象機器103によって携帯機器301のアクセスを拒否し、一連のアクセスフェーズP3を終了する。
【0198】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、このような一連の工程からなるアクセスフェーズP3を経ることにより、対象機器103によって携帯機器301の権限を判別することができ、アクセスが許可された携帯機器301は、任意の操作を行うことが可能となる。
【0199】
つぎに、アクセス削除フェーズP4について説明する。
【0200】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、任意の携帯機器をリソースに対してアクセスする機器から除外したい場合には、アクセス削除フェーズP4として、図19に示す工程が行われる。なお、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、携帯機器301が対象機器101,102をアクセス対象としている場合には、先に図14に示した処理と同様の処理を行えばよく、ここでは、携帯機器301が対象機器103をアクセス対象としており、携帯機器301を対象機器103に対してアクセスする機器から除外したい場合について説明する。
【0201】
まず、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、図19に示すように、ステップS61において、ホームゲートウェイ201により、ユーザからの指示にしたがい、対象機器103に対してリモートからアクセスしてもよい携帯機器301に対して発行した属性証明書ACP1'に対するCRL(ACRL)の作成をホームゲートウェイ202に対して要求する。
【0202】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS62において、ホームゲートウェイ202により、ホームゲートウェイ201からの要求にしたがい、属性証明書ACP1'に対するCRL(ACRL)を作成する。
【0203】
そして、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS63において、ホームゲートウェイ202により、作成した属性証明書ACP1'に対するCRL(ACRL)をホームゲートウェイ201に対して送信して配布する。これにともない、ホームゲートウェイ201は、ホームゲートウェイ202から送信された属性証明書ACP1'に対するCRL(ACRL)を保持する。
【0204】
このように、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、属性証明書ACP1'に対するCRL(ACRL)をホームゲートウェイ202によって作成することにより、携帯機器301からホームゲートウェイ201を介して対象機器103に対してアクセスがあった場合には、ホームゲートウェイ201によってアクセスを拒否することができ、携帯機器301をリソースに対してアクセスする機器から除外することができる。
【0205】
また、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、上述したように、正当なユーザが自らの意思で携帯機器30をリソースに対してアクセスする機器から除外したい場合等には、ステップS63の処理に続いて、先に図14中ステップS22乃至ステップS24に示した処理と同様の処理を行うようにしてもよい。
【0206】
すなわち、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS64において、携帯機器301により、保持している公開鍵証明書PKCM1を用いて、ホームゲートウェイ201との間で相互認証を行う。
【0207】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS65において、ホームゲートウェイ201からの指示にしたがい、携帯機器301により、保持している属性証明書ACP1'を削除する。
【0208】
そして、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS66において、ホームゲートウェイ201により、ステップS63にて保持したCRL(ACRL)を削除し、一連のアクセス削除フェーズP4を終了する。
【0209】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、このような一連の工程からなるアクセス削除フェーズP4を経ることにより、携帯機器301をリソースとしての対象機器103に対してアクセスする機器から除外することができる。
【0210】
なお、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、対象機器103の側の都合により、携帯機器301を当該対象機器103に対してアクセスする機器から除外したい場合には、ステップS61の処理をスキップし、ユーザからの指示にしたがい、ステップS62からの処理を行えばよいことになる。
【0211】
最後に、アクセス変更フェーズP5について説明する。
【0212】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、任意の携帯機器の権限を変更したい場合には、アクセス変更フェーズP5として、図20に示す工程が行われる。なお、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、第1の家庭内ネットワークにおけるリソースに対する携帯機器301の権限を変更したい場合には、先に図15に示した処理と同様の処理を行えばよく、ここでは、第2の家庭内ネットワークにおけるリソースに対する携帯機器301の権限を変更したい場合について説明する。
【0213】
まず、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、図20に示すように、ステップS71において、ホームゲートウェイ201により、ユーザからの指示にしたがい、保持している属性証明書ACHを他のホームゲートウェイ202に対して送信して提示し、プロシキ情報を記述した新たな属性証明書ACP1'を発行してもらう。これにともない、ホームゲートウェイ202は、新たな属性証明書ACP1'を発行し、この属性証明書ACP1'をホームゲートウェイ201に対して送信する。
【0214】
続いて、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS72において、携帯機器301により、保持している公開鍵証明書PKCM1を用いて、ホームゲートウェイ201との間で相互認証を行う。
【0215】
そして、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、ステップS73において、携帯機器301により、ホームゲートウェイ201から送信された新たな属性証明書ACP1'を、元の属性証明書ACP1'と置換してICカード等に格納して保持し、一連のアクセス変更フェーズP5を終了する。
【0216】
リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、このような一連の工程からなるアクセス変更フェーズP5を経ることにより、携帯機器301の権限を変更することができる。これにより、リモートアクセスシステムにおいては、携帯機器301が新たな任意の操作を行うことが可能となる。
【0217】
以上のように、リモートアクセスシステムは、プロシキ情報が記述された属性証明書ACP1'を用いて、通常では携帯機器301からはアクセスすることができない第2の家庭内ネットワークにおけるリソースに対する権限管理を行うことができる。
【0218】
このように、本発明は、携帯機器が通常アクセスできるネットワークの入り口としてのホームゲートウェイが当該携帯機器に対して属性証明書ACPを発行するのではなく、他のネットワークの入り口としてのホームゲートウェイといった任意のエンティティが属性証明書ACPを発行するものであってもよく、ホームゲートウェイは、属性証明書ACPの内容を検証できるものであればよい。
【0219】
また、上述した実施の形態では、家庭内ネットワークにおけるリソースに対してアクセスするものとして説明したが、本発明は、任意のネットワークに対して適用することができる。
【0220】
さらに、上述した実施の形態では、リソースに対してアクセス機器として携帯機器を用いて説明したが、本発明は、このような機器としては、携帯型の機器に限らずいかなる機器をも適用することができる。
【0221】
さらにまた、本発明は、各エンティティの動作をハードウェアで実現するのみならず、ソフトウェアで実現することもできる。本発明は、ソフトウェアで実現する場合には、例えば各エンティティが備えるCPU(Central Processing Unit)によって上述したリモートアクセスを行うためのリモートアクセスプログラムを実行することにより、各機能を実現することができる。このリモートアクセスプログラムは、例えばいわゆるコンパクトディスク(Compact Disc)等の所定の記録媒体やインターネット等の伝送媒体によって提供することができる。
【0222】
このように、本発明は、その趣旨を逸脱しない範囲で適宜変更が可能であることはいうまでもない。
【0223】
【発明の効果】
以上詳細に説明したように、本発明にかかるリモートアクセスシステムは、所定のリソースに対して遠隔地からアクセスするリモートアクセスシステムであって、当該リモートアクセスシステムは、アクセス対象となるアクセス対象機器と、前記アクセス対象機器に対してアクセスするアクセス機器と、前記アクセス機器に対して、前記アクセス対象機器のプロキシとして働く接続機器とからなり、前記アクセス機器は、前記リソースに対するアクセス権限及び前記接続機器が前記アクセス対象機器に対するプロキシとしての役割を果たすためのプロキシ情報が記述されている属性証明書を記憶する記憶手段と、前記記憶手段に記憶される前記属性証明書を、前記接続機器に対して送信して提示する第1の提示手段とを備え、前記接続機器は、前記アクセス機器から受信した前記属性証明書を、前記アクセス対象として指定されている前記アクセス対象機器に対して送信して提示する第2の提示手段を備え、前記アクセス対象機器は、前記接続機器から受信した前記属性証明書に記述されている前記アクセス権限及び前記プロキシ情報の内容を検証する検証手段と、前記検証手段による検証結果に基づいて、前記リソースに対する前記アクセス機器のアクセス許可を決定する決定手段とを備える。
【0224】
したがって、本発明にかかるリモートアクセスシステムは、少なくともリソースに対するアクセス権限を証明書に記述し、この証明書を、アクセス機器からアクセス対象機器に対して接続機器を介して送信して提示し、リソースに対するアクセス機器のアクセスを検証することにより、リソース毎に、権限単位での制御を容易に行うことができ、また、証明書の送付ルートを確認することができ、セキュリティを向上させることができる。
【0225】
また、本発明にかかるリモートアクセス方法は、アクセス対象となるアクセス対象機器と、前記アクセス対象機器に対してアクセスするアクセス機器と、前記アクセス機器に対して、前記アクセス対象機器のプロキシとして働く接続機器とからなるリモートアクセスシステムにて、所定のリソースに対して遠隔地からアクセスするリモートアクセス方法であって、前記アクセス機器は、前記リソースに対するアクセス権限及び前記接続機器が前記アクセス対象機器に対するプロキシとしての役割を果たすためのプロキシ情報が記述されている属性証明書を記憶手段に記憶し、前記記憶手段に記憶される前記属性証明書を、前記接続機器に対して提示し、前記接続機器は、前記アクセス機器から受信した前記属性証明書を、前記アクセス対象として指定されている前記アクセス対象機器に対して送信して提示し、前記アクセス対象機器は、前記接続機器から受信した前記属性証明書に記述されている前記アクセス権限及び前記プロキシ情報の内容を検証し、検証結果に基づいて、前記リソースに対する前記アクセス機器のアクセス許可を決定する。
【0226】
したがって、本発明にかかるリモートアクセス方法は、少なくともリソースに対するアクセス権限を証明書に記述し、この証明書を、アクセス機器からアクセス対象機器に対して接続機器を介して送信して提示し、リソースに対するアクセス機器のアクセスを検証することにより、リソース毎に、権限単位での制御を容易に行うことが可能となり、また、証明書の送付ルートを確認することができ、セキュリティを向上させることが可能となる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 公開鍵証明書のフォーマットを説明する図である。
【図2】 公開鍵証明書のフォーマットを説明する図であって、図1に示す項目に続く残りの項目を説明する図である。
【図3】 属性証明書のフォーマットを説明する図である。
【図4】 属性証明書のフォーマットを説明する図であって、図3に示す項目に続く残りの項目を説明する図である。
【図5】 権限プロキシ機能を説明するための図である。
【図6】 本発明の実施の形態として示すリモートアクセスシステムの概念図である。
【図7】 図4に示す属性証明書の項目のうち、属性における各フィールドの抜粋を示す図である。
【図8】 ロールの概念を用いた権限管理の手法について説明する図である。
【図9】 図4に示す属性証明書の項目のうち、拡張情報における各フィールドの抜粋を示す図である。
【図10】 図4に示す属性証明書の項目のうち、拡張情報におけるプロシキ情報の具体的な記述内容を説明する図である。
【図11】 同リモートアクセスシステムにて行われる各フェーズを説明するためのフローチャートである。
【図12】 同リモートアクセスシステムにおける登録フェーズとしての一連の工程を説明するためのフローチャートである。
【図13】 同リモートアクセスシステムにおけるアクセスフェーズとしての一連の工程を説明するためのフローチャートである。
【図14】 同リモートアクセスシステムにおけるアクセス削除フェーズとしての一連の工程を説明するためのフローチャートである。
【図15】 同リモートアクセスシステムにおけるアクセス変更フェーズとしての一連の工程を説明するためのフローチャートである。
【図16】 本発明の他の実施の形態として示すリモートアクセスシステムの概念図である。
【図17】 同リモートアクセスシステムにおける登録フェーズとしての一連の工程を説明するためのフローチャートである。
【図18】 同リモートアクセスシステムにおけるアクセスフェーズとしての一連の工程を説明するためのフローチャートである。
【図19】 同リモートアクセスシステムにおけるアクセス削除フェーズとしての一連の工程を説明するためのフローチャートであって、携帯機器を他のネットワークに属する対象機器に対してアクセスする機器から除外する場合における一連の工程を説明するためのフローチャートである。
【図20】 同リモートアクセスシステムにおけるアクセス変更フェーズとしての一連の工程を説明するためのフローチャートであって、他のネットワークにおけるリソースに対する携帯機器の権限を変更する場合における一連の工程を説明するためのフローチャートである。
【符号の説明】
101,102,103 対象機器、 20,201,202 ホームゲートウェイ、 30,301,302 携帯機器、 AA 属性認証局、 AC,ACH,ACL,ACL1,ACL2,ACP,ACP1,ACP2,ACP1' 属性証明書、 AS 権限主張側サーバ、 AU11,AU12,・・・,AU21,AU22,・・・ 権限、 CA 証明書発行認証局、 CL クライアント、 M1,M2,M3 個人、 NT ネットワーク、 PKCG,PKCG1,PKCG2,PKCM,PKCM1,PKCM2,PKCT1,PKCT2,PKCT3 公開鍵証明書、 R1,R2 ロール、 RA 役割認証局、 RAAC 役割割当証明書、 RSAC 役割定義証明書、 VR 権限検証側サーバ[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a remote access system and a remote access method for accessing a predetermined resource from a remote location.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In recent years, various devices such as information home appliances that can be connected to a network have been developed, and accordingly, networks targeting various devices including a home network are being constructed. In addition, depending on the situation, mobile phones and mobile information possessed by the user with respect to various information home appliances or various information processing terminals such as personal computers or server devices provided indoors from remote locations such as outdoors Various services that can be enjoyed by remote access using a device such as a terminal (Personal Digital Assistants; PDA) have been proposed.
[0003]
In such a service, it is essential to manage authentication and access rights in order to eliminate unauthorized user access to hardware and software such as server devices that provide the service, and various resources such as data. Has been.
[0004]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
Incidentally, some of the services described above have already been implemented, and an authentication mechanism is individually constructed. However, in such a service, an authentication method including authority (operation) for each individual unit has not been established yet.
[0005]
In addition, as a method of authority management for each individual, there is an authentication method using a so-called ID (IDentification) password. However, in this authentication method using an ID password, the mechanism becomes very complicated and the processing load is heavy. There was a problem.
[0006]
The present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and by performing authority management using a so-called attribute certificate (AC), the device itself that accesses resources when performing remote access. It is an object of the present invention to provide a remote access system and a remote access method capable of easily and safely performing control in units of authority for each resource to be accessed as well as entities such as the above.
[0007]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
A remote access system according to the present invention that achieves the above-described object is a remote access system that accesses a predetermined resource from a remote location, and the remote access system includes an access target device to be accessed and the access An access device that accesses the target device, and a connection device that acts as a proxy for the access target device with respect to the access device, and the access device has an access right to the resource Proxy information for the connected device to serve as a proxy for the access target device Is described attribute Storage means for storing a certificate, and the storage means stored in the storage means attribute Certificate Connected equipment Against Send Present First Presenting means, and the connection device includes: Second presenting means for transmitting and presenting the attribute certificate received from the access device to the access target device designated as the access target The access target device includes: Based on the verification result by the verification unit, the verification unit for verifying the access authority and the content of the proxy information described in the attribute certificate received from the connected device, Determination means for determining access permission of the access device to the resource When It is characterized by having.
[0008]
In such a remote access system according to the present invention, at least the access authority to the resource is described in the certificate, and the certificate is transmitted from the access device to the access target device through the connected device and presented, Verify access device access.
[0009]
In addition, the remote access method according to the present invention that achieves the above-described object includes an access target device to be accessed, an access device that accesses the access target device, and the access target device for the access device. A remote access method for accessing a predetermined resource from a remote location in a remote access system comprising a connected device that acts as a proxy for the access device, wherein the access device has an access right to the resource Proxy information for the connected device to serve as a proxy for the access target device Is described attribute The certificate is stored in the storage means, and the certificate stored in the storage means attribute Certificate Connected equipment And the connected device is The attribute certificate received from the access device is transmitted and presented to the access target device designated as the access target The access target device is The access authority and the proxy information described in the attribute certificate received from the connected device are verified, and the verification result The access permission of the access device to the resource is determined based on the above.
[0010]
In such a remote access method according to the present invention, at least an access right to a resource is described in a certificate, and this certificate is transmitted from an access device to an access target device via a connected device and presented. Verify access device access.
[0011]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, specific embodiments to which the present invention is applied will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
[0012]
This embodiment is a remote access system that accesses a predetermined resource from a remote location. This remote access system is based on ISO (International Organization for Standardization) / IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) 9594-8, or ITU-TX. By performing authority management using an attribute certificate (AC) based on 509, when performing remote access, not only entities such as the device itself that accesses the resource, but also authority for each resource to be accessed Control in units can be easily performed. In addition, when using an attribute certificate, this remote access system sends and receives the attribute certificate between the resource and a device that attempts to access the resource via a gateway that is the entrance of the network to which the resource belongs. By doing this, it is possible to check the route of sending the attribute certificate and improve the security.
[0013]
First, prior to the description of the remote access system, an outline of a public key certificate (PKC), which is an electronic certificate used in the remote access system, and the attribute certificate described above will be described.
[0014]
First, the public key certificate will be described. The public key certificate is issued by a certificate authority (CA) or issuer authority (IA) which is an independent predetermined third party in the so-called public key cryptosystem.
[0015]
Here, the public key cryptosystem will be described. In the public key cryptosystem, the sender and receiver have different keys, one key is a public key that can be used by an unspecified user, and the other key is a secret key that keeps it secret. Unlike the so-called common key cryptosystem, which uses a common key for encryption and decryption, the public key cryptosystem is compared with the common key cryptosystem because a specific one person has a secret key that needs to be kept secret. This is advantageous for key management. A typical public key cryptosystem is a so-called RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) cipher. This RSA cipher utilizes the difficulty of prime factorization processing of a product of two very large prime numbers of about 150 digits, for example.
[0016]
Public key cryptography is a method that allows a public key to be used by an unspecified number of users, and a method using a public key certificate is widely used to prove whether or not a public key to be distributed is valid. It is used. For example, in the public key cryptosystem, a public key and a private key paired by a specific user A are generated, and the generated public key is sent to a certificate issuing certificate authority to obtain a public key certificate The public key certificate is made public. On the other hand, an unspecified user acquires a public key through a predetermined procedure based on a public key certificate, encrypts a plain text document, etc., and sends it to a specific user A. Then, the user A performs processing such as decrypting an encrypted document sent from an unspecified user using a secret key. The public key encryption method is such an encryption method.
[0017]
In public key cryptography, user A adds a signature to a plain text document using a secret key, and an unspecified user passes a predetermined procedure based on a public key certificate to obtain a public key. It is possible to obtain and verify the signature. For example, in the public key cryptosystem, when the certificate issuing certificate authority refers to the public key certificate to determine the public key, an arbitrary plain text document or the like is sent to the user A and encrypted using the private key. And send it back again. The certificate issuing certificate authority can verify the validity of the signature by decrypting the encrypted document sent from the user A using the public key.
[0018]
A public key certificate in such a public key cryptosystem is submitted by the certificate issuing CA to the certificate issuing CA by submitting information, public key, etc. for the user as an administrator to identify himself / herself. It is created by adding information for identifying the certificate issuing certificate authority, information such as the expiration date, and adding a signature by the certificate issuing certificate authority.
[0019]
Specifically, the public key certificate has a format as shown in FIGS. In the figure, items for each field constituting the public key certificate and explanations for these items are described.
[0020]
The version (version) shown in FIG. 1 is a field for describing version information of the format of the public key certificate. For example, when the format is
[0021]
The serial number is a field that describes the serial number of the public key certificate set by the certificate issuing certificate authority, and describes, for example, a sequential number.
[0022]
The signature algorithm identifier and algorithm parameter (signature algorithm Identifier algorithm parameters) are fields describing information for identifying the signature algorithm of the public key certificate and its parameters. As the signature algorithm, for example, there is elliptic curve encryption or RSA encryption. When elliptic curve encryption is applied as the signature algorithm, parameters and key lengths are described as algorithm parameters, and RSA encryption is applied as the signature algorithm. If it is, the key length is described as an algorithm parameter.
[0023]
The issuer (issuer) is a field described in a format (Distinguished Name) that makes it possible to identify the name of the issuer of the public key certificate, that is, the certificate issuing certificate authority.
[0024]
The validity period (validity) is a field that describes a start date and time (not Before) and an end date and time (not After), which are validity periods of the public key certificate.
[0025]
The subject (subject) is a field that describes the name of an authentication subject who is a user. For example, an identifier of a user device or an identifier of a service provider is described.
[0026]
The subject public key information (subject public key information subject public key) is a field that describes a key algorithm as the user's public key information and the key information itself. Examples of the key algorithm include elliptic curve cryptography and RSA cryptography. .
[0027]
Each of these fields is a field included in the public key
[0028]
The certificate authority key identifier (authority key identifier-key identifier, authority Cert Issuer, authority Cert Serial Number) is information for identifying the key for verifying the signature of the certificate issuing certificate authority, and is a key identification number in octal notation. The field describes the name of the certificate issuing certificate authority in the general name format and the authentication number.
[0029]
The subject key identifier is a field describing an identifier for identifying each key when a plurality of keys are proved in a public key certificate.
[0030]
The key usage (key usage) is a field for specifying the purpose of use of the key. (0) Digital signature (1) Digital signature (1) Non-repudiation (2) Key encryption (Key Encipherment), (3) Message encryption (data Encipherment), (4) Common key distribution (key Agreement), (5) Authentication signature verification (key Cert Sign), (6) Revocation list Use for signature verification (CRL Sign), (7) key agreement (key agreement) only for data encryption (encipher only), and (8) key exchange only for decryption (decipher only) The purpose is set.
[0031]
Private key usage period (private key usage period) is a field that describes the start date and time (not Before) and end date and time (not After), which are the expiration dates of the private key that the user has. By default, the public key certificate The expiration date, the expiration date of the public key, and the expiration date of the secret key are the same.
[0032]
The certificate authority policy (Certificate Policy) shown in FIG. 2 is a field that describes the certificate issuing policy of the certificate issuing certificate authority. For example, a policy ID (policy identifier) or authentication standard (compliant with ISO / IEC 9834-1) policy Qualifiers).
[0033]
Policy Mappings is a field that is described only when authenticating a certificate issuing certificate authority. The policy of the certificate issuing certificate authority that issues the certificate (issuer Domain Policy) and the subject policy (subject) Specify mapping with Domain Policy.
[0034]
“Supported Algorithms” is a field for defining attributes of the directory (X.500). The support algorithm is used to notify the attribute in advance when a communication partner uses directory information.
[0035]
The subject alternative name (subject Alt Name) is a field that describes a user alternative name in a general name format.
[0036]
The issuer alias (issuer Alt Name) is a field that describes an alias of the certificate issuer.
[0037]
A subject directory attribute (subject Directory Attributes) is a field describing arbitrary attributes of a user.
[0038]
The basic constraints (basic constraints) is a field for distinguishing whether the public key to be certified is for the signature of the certificate issuing certificate authority or the user.
[0039]
The permitted subtree constraint name (name Constraints permitted Subtrees) is a field indicating the valid area of the public key certificate used only when the person to be authenticated is a certificate issuing certificate authority.
[0040]
The constraint policy (policy Constraints) is a field describing a restriction that requires a clear authentication policy ID or prohibition policy map for the rest of the authentication path.
[0041]
CRL reference point (Certificate Revocation List Distribution Points) is a field that describes a revocation list reference point for confirming whether or not this public key certificate has been revoked when the user uses the public key certificate. It is.
[0042]
The signature is a signature field of a public key certificate issuer, that is, a certificate issuing certificate authority. An electronic signature is data generated by applying a so-called hash function to the entire public key certificate and encrypting this hash value with the private key of the certificate issuing certificate authority. is there.
[0043]
The Certificate Issuing Certification Authority issues a public key certificate in such a format, updates the public key certificate that has expired, and creates a list of fraudsters for rejecting fraudulent users. Create, manage, and distribute, that is, revocation. Further, the certificate issuing certificate authority also generates a public key and a private key as necessary.
[0044]
On the other hand, a user who uses this public key certificate verifies the electronic signature of the public key certificate using the public key of the certificate issuing certificate authority that he / she owns. A public key is obtained based on the certificate, and this public key can be used. Therefore, all users who use the public key certificate need to acquire whether they have the public key of the certificate issuing certificate authority that issued the public key certificate.
[0045]
In the remote access system, each public entity holds such a public key certificate as will be described later.
[0046]
Next, the attribute certificate will be described. The attribute certificate is issued by an attribute authority (AA) which is a local organization different from the certificate issuing certificate authority.
[0047]
The attribute certificate has a format as shown in FIGS. In the figure, items for each field constituting the attribute certificate and explanations for these items are described.
[0048]
The version (version) shown in FIG. 3 is a field that describes version information of the format of the attribute certificate. For example, when the format is version 2 (1), “1” indicating version 2 (1) is described. Is done.
[0049]
The holder is a field for specifying the owner of the public key certificate to which the attribute certificate is linked. The holder includes the issuer name (issuer) of the public key certificate possessed by the owner of the attribute certificate, and the serial number of the public key certificate possessed by the owner of the attribute certificate as the base certificate ID. (Serial) describes a unique identifier (issuer UID) for identifying the issuer of the public key certificate possessed by the owner of the attribute certificate. The holder describes the name of the owner of the attribute certificate that is the same as the subject or subject alternative name (subject Alt Name) in the public key certificate. Furthermore, assuming that the attribute certificate is not linked to identification information (identity) or public key certificate in the future, for example, the object digest information (object Digest Info) in which the hash of the public key is described is included in the holder. ) Is described.
[0050]
The issuer (issuer) is a field for designating information of an issuer who has signed the attribute certificate.
[0051]
The signature is a field describing an identifier for identifying an algorithm used to validate the signature of the attribute certificate.
[0052]
The serial number is a field that describes a serial number that the attribute authority assigns to each attribute certificate.
[0053]
The attribute certificate validity period (attr Cert Validity Period) is a field that describes a start date and time (not Before) and an end date and time (not After) that are the validity period of the attribute certificate.
[0054]
The attributes shown in FIG. 4 are fields that describe information related to the privileges of the owner of the attribute certificate. For example, an object to which access is permitted by text may be described, and prepared by the system side. A code that can be accessed may be described, or a key for encrypting a certain plaintext may be described. For example, the attribute includes authentication information (Service Authentication Information) related to a service used when the attribute certificate verifier authenticates the owner of the attribute certificate, and the attribute certificate used by the attribute certificate verifier. Access permission information of the owner (Access Identity), information for identifying the owner of the attribute certificate for charging (Charging Identity), and information indicating the attribution relationship of the owner of the attribute certificate to the group (Group) In addition, information (Role) indicating the role given to the owner of the attribute certificate and information (Clearance) regarding permission to use the secret information for the owner of the attribute certificate are described.
[0055]
The issuer unique identifier (issuer Unique ID) is a field used when specified by the public key certificate of the issuer of the attribute certificate.
[0056]
Extension information is a field that describes attribute certificate information, not attribute certificate owner information, and the server and / or service administrator audits the attribute certificate owner to verify fraud. Information used for detection, that is, identification (Audit Identity), information indicating the server and / or service targeted by the attribute certificate (AC Targeting), and signature verification of the attribute certificate by the verifier of the attribute certificate Information indicating the key information (Authority Key) of the issuer of the attribute certificate, which is auxiliary information, and URI (Uniform Resource Identifiers) of the OCSP responder, which is auxiliary information for checking the revocation status of the attribute certificate by the verifier of the attribute certificate (Authority Information Access), indicates the URI of the CRL (Certificate Revocation List) distribution point, which is auxiliary information for checking the revocation status of the attribute certificate by the verifier of the attribute certificate Information (CRL Distribution), information indicating that there is no revocation information corresponding to the attribute certificate (No Revocation), entity that can be used when the submitter is other than the owner and can submit the attribute certificate Information (Proxy Info) to be indicated is described.
[0057]
The signature (signature value) is a field describing a signature attached by the attribute certificate authority.
[0058]
In the remote access system, as will be described later, by holding an attribute certificate having such a format in each entity, it is possible to verify what authority is granted to a certain entity.
[0059]
The remote access system is constructed using the public key certificate and attribute certificate as described above.
[0060]
A remote access system using these public key certificates and attribute certificates will be described below.
[0061]
First, the concept of the remote access system will be described. Here, for convenience of explanation, various information home appliances provided in the home, various information processing terminals such as personal computers, or server devices are targeted for access, and mobile phones and portable information terminals are connected to these devices. A description will be given assuming that a user having a portable device such as (Personal Digital Assistants; PDA) accesses from outside.
[0062]
The remote access system is an ITU-T (International Telecommunication Union-Telecommunication sector). By a privilege proxy function using an attribute certificate, which is one of PMI (Privilege management Infrastructure) functions defined in 509, control is performed in units of privileges for each resource to be accessed.
[0063]
Here, the authority proxy function will be described with reference to FIG.
[0064]
As shown in the figure, an authority asserting server AS that asserts the authority of the client CL is interposed between the client CL that holds the attribute certificate AC and the authority verifying server VR that verifies the authority of the client CL. Think of a system to do.
[0065]
In this case, when the client CL tries to access the authority verifying server VR, the client CL presents the attribute certificate AC to the authority claiming server AS, and the authority claiming server AS responds accordingly. The attribute certificate AC presented from the client CL is presented to the authority verification side server VR.
[0066]
However, in this case, since the attribute certificate AC presented by the authority claiming server AS is not the attribute certificate of the authority claiming server AS, the authority verification server VR returns a verification result indicating that access is not permitted. Will be put out. That is, in such a system, since authority is claimed and verified between devices that directly exchange attribute certificates, the client CL will assert its own authority to the authority verifying server VR. In this case, it is necessary to present the attribute certificate AC directly from the client CL to the authority verification server VR.
[0067]
Therefore, in such a system, the proxy information (Proxy Info) in the extension information (extensions) shown in FIG. 4 is used. As described above, this proxy information is used when the attribute certificate submitter is other than the owner, and is information indicating an entity that can submit the attribute certificate.
[0068]
Therefore, in such a system, when the client CL tries to access the authority verification server VR, the proxy information indicating that the authority verification server VR is included as an entity that can submit the attribute certificate is provided. The described attribute certificate AC is presented to the authority claiming server AS. In response, the authority claiming server AS sends the attribute certificate AC presented from the client CL to the authority verification server VR. Present.
[0069]
Thereby, the authority verification server VR verifies the attribute certificate AC with reference to the proxy information in the attribute certificate AC presented from the authority asserting server AS, and outputs a verification result indicating that access is permitted. Is possible.
[0070]
As described above, in the system in which the authority claiming server AS that asserts the authority of the client CL is interposed between the client CL that holds the attribute certificate AC and the authority verifying server VR that verifies the authority of the client CL. By describing the submission destination of the attribute certificate AC in the proxy information, the client CL can access the authority verification side server VR.
[0071]
The remote access system uses such an authority proxy function. Conceptually, as shown in FIG. 6, the remote access system includes a certificate issuing certificate authority CA that issues the public key certificate described above, an attribute certificate authority AA that issues the attribute certificate described above, and an access authority.
[0072]
The certificate issuing certificate authority CA is an independent predetermined third party in the public key cryptosystem, and is ISO / IEC 9594-8 or ITU-T X.264. A public key certificate which is an electronic certificate based on 509 is issued. Specifically, the certificate issuing certificate authority CA creates a public key certificate PKC. T1 , PKC T2 , Each of the
[0073]
The attribute authority AA is a local institution that is logically different from the certificate issuing authority CA, and issues an attribute certificate that is an electronic certificate used for authority management. The attribute certification authority AA is a public key certificate PKC issued to the
[0074]
[0075]
The
[0076]
The
[0077]
In such a remote access system, as described above, two attribute certificates AC L , AC P Is used.
[0078]
First, attribute certificate AC L Will be described.
[0079]
Attribute certificate AC L As described above, the attribute certificate AC is sent to the
[0080]
Here, the concept of “Role” will be described.
[0081]
The method of authority management using the concept of “Role” is described in Japanese Patent Application No. 2002-029636 filed earlier by the present applicant.
[0082]
That is, in this authority management method, conceptually, for example, as shown in FIG. 11 , AU 12 , ..., AU 21 , AU 22 A single role (role) is defined as a framework for defining predetermined authority such as. 1 , R 2 For example, individual M 1 , M 2 , M 3 At least one person such as this role R 1 , R 2 It belongs to.
[0083]
In this authority management method, each individual M 1 , M 2 , M 3 Each of the attribute certificates possessed by 1 , M 2 , M 3 A role assignment certificate RAAC in which information indicating a role to which the user belongs is issued by the attribute authority AA and is an attribute certificate issued for each role. A role specification certificate RSAC in which information indicating the authorized authority is described is issued by a role authority RA. The role certification authority RA may be the same as the attribute certification authority AA, but here it is assumed that it is a logically independent organization for convenience of explanation.
[0084]
In this authority management method, the role definition certificate RSAC issued by the role certification authority RA is used for the definition of each role. That is, in this authority management method, a permitted procedure is defined for each role, but this information is described in the role definition certificate RSAC issued by the role certification authority RA.
[0085]
This role definition certificate RSAC is created according to the format of the attribute certificate shown in FIGS. 3 and 4, and at least the name of the role certification authority RA that is the issuer of the role definition certificate RSAC. Various information such as information indicating role, role information such as a role name for identifying a role, information indicating a code or operation name and information indicating an allowed operation are described by the system.
[0086]
In the remote access system, the attribute certificate AC for the
[0087]
On the other hand, in this authority management method, the role assignment certificate RAAC issued by the attribute certificate authority AA is used for the role assignment to each role. That is, in this authority management technique, the individual M 1 , M 2 , M 3 Each role is defined for each, and this information is described in the role assignment certificate RAAC issued by the attribute authority AA.
[0088]
This role assignment certificate RAAC is created according to the format of the attribute certificate shown in FIGS. 3 and 4 in the same manner as the role definition certificate RSAC. Information indicating the name of the attribute certification authority AA as an issuer, role information such as a role name for identifying the role, and a reference point to the role definition certificate RSAC for associating with the corresponding role definition certificate RSAC Various information such as information indicating the name of the role certification authority RA as information is described.
[0089]
In the remote access system, the role assignment certificate RAAC in which such various information is described is the attribute certificate AC. L Issued by Attribute Certification Authority AA 1 , M 2 , M 3 That is, in FIG. 6 shown above, the
[0090]
In the remote access system, the attribute certificate AC is given to the
[0091]
In the remote access system, the attribute certificate AC for the
[0092]
In the remote access system, the attribute certificate AC is used by using the authority delegation extension. P You may make it control the object and authority which issue. For example, in the remote access system, the attribute certificate AC is sent to the
[0093]
As described above, in the remote access system, the attribute certificate AC is supplied to the
[0094]
Next, attribute certificate AC P Will be described.
[0095]
Attribute certificate AC P Describes the authority for a device or user holding a certain public key certificate. Here, the public key certificate PKC M As an authority for the
[0096]
Here, the proxy information is specifically described as shown in FIG.
[0097]
Attribute certificate AC P Describes the address and identifier for identifying the
[0098]
As described above, in the remote access system, as the authority for the
[0099]
Now, in such a remote access system, specifically, as shown in FIG. 11, when a preparation phase P1 for constructing the remote access system is performed, an arbitrary portable device is accessed for a resource. A registration phase P2 for registering as a device to be performed is performed. Thus, in the remote access system, the registered mobile device can perform any operation, and when the mobile device actually performs any operation, the access phase P3 is performed. In the remote access system, if necessary, an access deletion phase P4 for excluding any portable device from a device accessing the resource, or an access changing phase for changing the authority of any portable device. P5 is performed.
[0100]
Hereinafter, each of these five phases will be described.
[0101]
First, the preparation phase P1 will be described.
[0102]
In the remote access system, as a preparation phase P1 for constructing the remote access system, a public key for authentication is issued to each entity by the certificate issuing certificate authority CA so that the entities can perform mutual authentication. Issue a certificate. That is, in the remote access system, as described above, the public key certificate PKC is issued by the certificate issuing certificate authority CA at the time of manufacturing each entity. T1 , PKC T2 , Each of the
[0103]
The remote access system is constructed in such a state that each entity can mutually authenticate through such a preparation phase P1.
[0104]
Next, the registration phase P2 will be described.
[0105]
In the remote access system, the steps shown in FIG. 12 are performed as a registration phase P2 for registering the
[0106]
First, in the remote access system, as shown in the figure, in step S1, the attribute certificate authority AA issues the certificate in the preparation phase P1 and holds it in the
[0107]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, in step S2, the attribute certificate authority AA sends the attribute certificate AC to the
[0108]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, in step S3, according to an instruction from the user by the
[0109]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, in step S4, the public key certificate PKC issued and held by the certificate issuing certificate authority CA in the above-described preparation phase P1 by the
[0110]
In the remote access system, the attribute certificate AC transmitted from the
[0111]
In the remote access system, the
[0112]
Next, the access phase P3 will be described.
[0113]
In the remote access system, when the registered
[0114]
First, in the remote access system, as shown in the figure, the public key certificate PKC held by the
[0115]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, the attribute certificate AC held by the
[0116]
Accordingly, in the remote access system, the attribute certificate AC presented from the
[0117]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, in step S14, the
[0118]
In the remote access system, in step S15, the attribute certificate AC P If the verification result is valid, in step S16, the
[0119]
In the remote access system, the
[0120]
Next, the access deletion phase P4 will be described.
[0121]
In the remote access system, when it is desired to exclude any portable device from the device that accesses the resource, the process shown in FIG. 14 is performed as the access deletion phase P4.
[0122]
First, in the remote access system, as shown in the figure, in step S21, the
[0123]
Thus, in the remote access system, the attribute certificate AC P By creating a CRL (ACRL) for the
[0124]
However, in the remote access system, by repeatedly performing such an operation, the size of the CRL (ACRL) increases, which may cause inconvenience in handling.
[0125]
Therefore, in the remote access system, when a legitimate user wants to exclude the
[0126]
That is, in the remote access system, the public key certificate PKC held by the
[0127]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, the attribute certificate AC held by the
[0128]
In the remote access system, in step S24, the
[0129]
In the remote access system, the
[0130]
Finally, the access change phase P5 will be described.
[0131]
In the remote access system, when it is desired to change the authority of an arbitrary portable device, the process shown in FIG. 15 is performed as the access change phase P5.
[0132]
First, in the remote access system, as shown in the figure, in step S31, a new attribute certificate AC in which proxy information is described for the
[0133]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, the public key certificate PKC held by the
[0134]
In the remote access system, the new attribute certificate AC transmitted from the
[0135]
In the remote access system, the authority of the
[0136]
As described above, the remote access system uses the attribute certificate AC describing the proxy information. P Permission management can be performed using.
[0137]
Now, an application example in which such a remote access system is specifically applied will be described below. In addition, as described above, the resource in the present invention may be a device that logs in itself, and is a concept including data such as a file held by these devices and other various information. Specific examples of these resources are also mentioned.
[0138]
First, as an application example of a remote access system, there is a data access system that performs remote access to data held by an information processing terminal such as a home server or a personal computer.
[0139]
In this data access system, data held by a home server or information processing terminal is a resource, and an operation performed by a user using a portable device is data access to the home server or information processing terminal holding the data.
[0140]
In such a data access system, an attribute certificate AC describing appropriate proxy information by the home gateway. P Is issued to the mobile device, and when the mobile device accesses the data, the attribute certificate AC P Is presented to the home server or information processing terminal via the home gateway. Thereby, in the data access system, it becomes possible to access the data via the home gateway using the portable device.
[0141]
Thus, the remote access system can be applied to a data access system for data held by an information processing terminal such as a home server or a personal computer.
[0142]
As another application example of the remote access system, there is an information acquisition system by image capturing using a home appliance camera.
[0143]
In order to explain specifically, consider an information acquisition system that acquires, for example, the inventory of a refrigerator in the home as information. In this information acquisition system, the image inside the refrigerator becomes a resource, and the operation performed by the user using the portable device is the inventory check of the refrigerator by browsing the acquired image.
[0144]
In such an information acquisition system, the attribute certificate AC describing appropriate proxy information by the home gateway. P Is issued to the portable device, and when the portable device accesses the refrigerator in which the home appliance camera is mounted, the attribute certificate AC P To the refrigerator via the home gateway. Thereby, in the information acquisition system, even when the user is out, the home appliance camera is operated via the home gateway using the portable device possessed by the user, and the image inside the refrigerator is acquired. Is possible.
[0145]
In this way, the remote access system can be applied to an information acquisition system by image shooting using a home appliance camera.
[0146]
Furthermore, as another application example of the remote access system, there is an information acquisition system by photographing an image at an arbitrary place.
[0147]
To explain specifically, consider an information acquisition system that authenticates whether or not a member is a member by acquiring an image of a member card for proving that the member is a predetermined member. In this information acquisition system, an image of a member card in an arbitrary place such as a home becomes a resource, and an operation performed by a user using a portable device is a member by having the member card certifier view the image. Prove that.
[0148]
In such an information acquisition system, the attribute certificate AC describing appropriate proxy information by the home gateway. P Is issued to the mobile device, and when the mobile device accesses the camera that shoots the membership card, the attribute certificate AC P To the camera via the home gateway. Thereby, in the information acquisition system, even when the member card is not in the user's hand, the user operates the camera via the home gateway using the portable device possessed by the user to acquire the member card image. Is possible.
[0149]
As described above, the remote access system can be applied to an information acquisition system by photographing an image at an arbitrary place.
[0150]
Furthermore, as another application example of the remote access system, there is a home appliance operation system that performs home appliance operation by remote operation from outside.
[0151]
In order to explain specifically, for example, consider a home appliance operation system that performs an on / off operation of an air conditioner device in a home. In this home appliance operation system, the air conditioner device itself becomes a resource, and an operation performed by the user using the portable device is an access to a remote controller for remotely operating the air conditioner device as this resource.
[0152]
In such home appliance operation system, attribute certificate AC describing appropriate proxy information by the home gateway. P Is issued to the mobile device, and when the mobile device accesses the remote controller, the attribute certificate AC P Is presented to the remote controller via the home gateway. As a result, in the home appliance operation system, even when the user is out, the remote controller is operated via the home gateway using the portable device owned by the user, and the air conditioner device is turned on / off. The operation can be performed.
[0153]
Thus, the remote access system can be applied to a home appliance operation system that performs home appliance operations by remote operation from the outdoors.
[0154]
As described above, the remote access system shown as the embodiment of the present invention has the attribute certificate AC in which the proxy information is described. P By performing authority management using, the
[0155]
This remote access system also uses the attribute certificate AC P When using the
[0156]
The present invention is not limited to the embodiment described above. For example, in the above-described embodiment, the
[0157]
As an example of this, an attribute certificate AC issued by a home gateway as an entrance to a network P A remote access system for accessing resources belonging to other networks will be described using FIG.
[0158]
As shown in FIG. 16, this remote access system conceptually has a
[0159]
That is, in this remote access system, the system as shown in FIG. 6 configured by the first home network and the similar system configured by the second network such as other houses coexist. It is what.
[0160]
[0161]
[0162]
Furthermore, the
[0163]
[0164]
In addition, the
[0165]
[0166]
[0167]
Furthermore, the
[0168]
[0169]
In such a remote access system, the above-mentioned two attribute certificates AC L , AC P In addition, two attribute certificates AC H , AC P1 'Is used.
[0170]
First, attribute certificate AC H Will be described.
[0171]
Attribute certificate AC H As described above, entities in other networks that can be accessed, specifically the
[0172]
In a remote access system, the
[0173]
Next, attribute certificate AC P1 Explain '.
[0174]
Attribute certificate AC P1 'Is the attribute certificate AC P In the same way, the authority for a device or user holding a certain public key certificate is described. Here, the public key certificate PKC M1 Mobile device 30 holding 1 As an authority for the
[0175]
Thus, in the remote access system, the
[0176]
In the remote access system, specifically, as shown in FIG. 11, the preparation phase P1, the registration phase P2, the access phase P3, the access deletion phase P4, and the access change phase P5 are performed. Is called. In the following, the
[0177]
First, the preparation phase P1 will be described.
[0178]
In the remote access system, as a preparation phase P1 for constructing the remote access system, a public key for authentication is issued to each entity by the certificate issuing certificate authority CA so that the entities can perform mutual authentication. Issue a certificate. That is, in the remote access system, as described above, the public key certificate PKC is issued by the certificate issuing certificate authority CA at the time of manufacturing each entity. T1 , PKC T2 , PKC T3 , Each of the
[0179]
The remote access system is constructed in such a state that each entity can mutually authenticate through such a preparation phase P1.
[0180]
Next, the registration phase P2 will be described.
[0181]
In the remote access system, the process shown in FIG. 17 is performed as a registration phase P2 for registering the
[0182]
First, in the remote access system, as shown in the figure, in step S41, the attribute gateway is issued by the certificate issuing authority CA in the above-described preparation phase P1 by the attribute authority AA. 1 Public key certificate PKC held in G1 Using the
[0183]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, in step S42, the attribute authentication authority AA performs the
[0184]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, in step S43, the
[0185]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, the
[0186]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, in step S45, the
[0187]
In the remote access system, in step S46, the
[0188]
In the remote access system, the
[0189]
Next, the access phase P3 will be described.
[0190]
In the remote access system, the registered
[0191]
First, in the remote access system, as shown in FIG. 1 Holds the public key certificate PKC M1 Using the
[0192]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, in step S52, the
[0193]
Here, in the remote access system, the
[0194]
In the remote access system, in step S53, the
[0195]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, in step S54, the
[0196]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, in step S55, the
[0197]
In the remote access system, in step S56, the attribute certificate AC P1 ', AC H If the verification result is valid, in step S57, the
[0198]
In the remote access system, the
[0199]
Next, the access deletion phase P4 will be described.
[0200]
In the remote access system, when it is desired to exclude any portable device from the device that accesses the resource, the process shown in FIG. 19 is performed as the access deletion phase P4. In the remote access system, the
[0201]
First, in the remote access system, as shown in FIG. 1 In accordance with an instruction from the user, the
[0202]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, in step S62, the
[0203]
In the remote access system, in step S63, the
[0204]
Thus, in the remote access system, the attribute certificate AC P1 CRL (ACRL) for '
[0205]
Further, in the remote access system, as described above, when a legitimate user wants to exclude the
[0206]
That is, in the remote access system, in step S64, the
[0207]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, in step S65, the
[0208]
In the remote access system, in step S66, the
[0209]
In the remote access system, the
[0210]
In the remote access system, the
[0211]
Finally, the access change phase P5 will be described.
[0212]
In the remote access system, when it is desired to change the authority of any portable device, the process shown in FIG. 20 is performed as the access change phase P5. In the remote access system, the
[0213]
First, in the remote access system, as shown in FIG. 1 According to the instruction from the user, the stored attribute certificate AC H The other home gateway 20 2 A new attribute certificate AC that is sent and presented to and describes proxy information P1 'Is issued. Accordingly, the
[0214]
Subsequently, in the remote access system, in step S72, the
[0215]
In the remote access system, in step S73, the
[0216]
In the remote access system, the
[0217]
As described above, the remote access system uses the attribute certificate AC describing the proxy information. P1 'Is normally used for the
[0218]
Thus, according to the present invention, the home gateway as the entrance of the network that can be normally accessed by the mobile device is assigned the attribute certificate AC to the mobile device. P Any entity such as a home gateway as an entrance to another network P The home gateway may issue an attribute certificate AC. P Anything that can verify the contents of is acceptable.
[0219]
Further, in the above-described embodiment, it has been described that the resource in the home network is accessed. However, the present invention can be applied to any network.
[0220]
Furthermore, in the above-described embodiment, the description has been given using the portable device as the access device for the resource. However, the present invention is not limited to the portable device, and any device can be applied. Can do.
[0221]
Furthermore, according to the present invention, the operation of each entity can be realized not only by hardware but also by software. When the present invention is realized by software, for example, each function can be realized by executing a remote access program for performing the above-described remote access by a CPU (Central Processing Unit) included in each entity. The remote access program can be provided by a predetermined recording medium such as a so-called compact disc or a transmission medium such as the Internet.
[0222]
Thus, it goes without saying that the present invention can be modified as appropriate without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
[0223]
【The invention's effect】
As described above in detail, the remote access system according to the present invention is a remote access system that accesses a predetermined resource from a remote location, and the remote access system includes an access target device to be accessed, The access device includes an access device that accesses the access target device, and a connection device that acts as a proxy for the access target device with respect to the access device, and the access device has an access right to the resource. Proxy information for the connected device to serve as a proxy for the access target device Is described attribute Storage means for storing a certificate, and the storage means stored in the storage means attribute Certificate Connected equipment Against Send Present First Presenting means, and the connection device includes: Second presenting means for transmitting and presenting the attribute certificate received from the access device to the access target device designated as the access target The access target device includes: Based on the verification result by the verification unit, the verification unit for verifying the access authority and the content of the proxy information described in the attribute certificate received from the connected device, Determination means for determining access permission of the access device to the resource When Is provided.
[0224]
Therefore, the remote access system according to the present invention describes at least the access authority to the resource in the certificate, and transmits and presents this certificate from the access device to the access target device via the connected device, By verifying access of the access device, it is possible to easily perform control in units of authority for each resource, and it is possible to check a certificate transmission route and improve security.
[0225]
The remote access method according to the present invention includes an access target device to be accessed, an access device that accesses the access target device, and a connection device that acts as a proxy for the access target device with respect to the access device. A remote access method for accessing a predetermined resource from a remote location in a remote access system comprising: the access device has an access right to the resource Proxy information for the connected device to serve as a proxy for the access target device Is described attribute The certificate is stored in the storage means, and the certificate stored in the storage means attribute Certificate Connected equipment And the connected device is The attribute certificate received from the access device is transmitted and presented to the access target device designated as the access target The access target device is The access authority and the proxy information described in the attribute certificate received from the connected device are verified, and the verification result To determine access permission of the access device for the resource.
[0226]
Therefore, in the remote access method according to the present invention, at least the access authority to the resource is described in the certificate, and the certificate is transmitted from the access device to the access target device via the connected device and presented, and the resource By verifying the access of the access device, it becomes possible to easily control in units of authority for each resource, and it is possible to check the route for sending the certificate and improve security. Become.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram for explaining a format of a public key certificate.
FIG. 2 is a diagram for explaining the format of a public key certificate, and for explaining the remaining items following the items shown in FIG.
FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating a format of an attribute certificate.
FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining the format of an attribute certificate and explaining the remaining items following the items shown in FIG. 3;
FIG. 5 is a diagram for explaining an authority proxy function;
FIG. 6 is a conceptual diagram of a remote access system shown as an embodiment of the present invention.
7 is a diagram showing an excerpt of each field in the attribute among the items of the attribute certificate shown in FIG.
FIG. 8 is a diagram for explaining an authority management method using the concept of roles.
9 is a diagram showing an excerpt of each field in the extended information among the items of the attribute certificate shown in FIG.
10 is a diagram for explaining specific description contents of proxy information in extended information among the items of the attribute certificate shown in FIG. 4; FIG.
FIG. 11 is a flowchart for explaining each phase performed in the remote access system;
FIG. 12 is a flowchart for explaining a series of steps as a registration phase in the remote access system.
FIG. 13 is a flowchart for explaining a series of steps as an access phase in the remote access system.
FIG. 14 is a flowchart for explaining a series of steps as an access deletion phase in the remote access system.
FIG. 15 is a flowchart for explaining a series of steps as an access change phase in the remote access system.
FIG. 16 is a conceptual diagram of a remote access system shown as another embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 17 is a flowchart for explaining a series of steps as a registration phase in the remote access system.
FIG. 18 is a flowchart for explaining a series of steps as an access phase in the remote access system.
FIG. 19 is a flowchart for explaining a series of steps as an access deletion phase in the remote access system, and a series of steps when a portable device is excluded from devices that access a target device belonging to another network; It is a flowchart for demonstrating a process.
FIG. 20 is a flowchart for explaining a series of steps as an access change phase in the remote access system, for explaining a series of steps when changing authority of a mobile device for a resource in another network; It is a flowchart.
[Explanation of symbols]
10 1 , 10 2 , 10 3 Target device, 20, 20 1 , 20 2
Claims (6)
当該リモートアクセスシステムは、
アクセス対象となるアクセス対象機器と、
前記アクセス対象機器に対してアクセスするアクセス機器と、
前記アクセス機器に対して、前記アクセス対象機器のプロキシとして働く接続機器とからなり、
前記アクセス機器は、
前記リソースに対するアクセス権限及び前記接続機器が前記アクセス対象機器に対するプロキシとしての役割を果たすためのプロキシ情報が記述されている属性証明書を記憶する記憶手段と、
前記記憶手段に記憶される前記属性証明書を、前記接続機器に対して送信して提示する第1の提示手段と
を備え、
前記接続機器は、
前記アクセス機器から受信した前記属性証明書を、前記アクセス対象として指定されている前記アクセス対象機器に対して送信して提示する第2の提示手段を備え、
前記アクセス対象機器は、
前記接続機器から受信した前記属性証明書に記述されている前記アクセス権限及び前記プロキシ情報の内容を検証する検証手段と、
前記検証手段による検証結果に基づいて、前記リソースに対する前記アクセス機器のアクセス許可を決定する決定手段と
を備えることを特徴とするリモートアクセスシステム。A remote access system for accessing a predetermined resource from a remote location,
The remote access system
Access target device to be accessed,
An access device for accessing the access target device;
It consists of a connected device that acts as a proxy for the access target device with respect to the access device,
The access device is:
Storage means for storing an access certificate for the resource and an attribute certificate in which proxy information for the connected device to serve as a proxy for the access target device is described;
First attribute means for transmitting and presenting the attribute certificate stored in the storage means to the connected device ;
The connection device is
Second attribute means for transmitting and presenting the attribute certificate received from the access device to the access target device designated as the access target ;
The access target device is:
Verification means for verifying the access authority and the content of the proxy information described in the attribute certificate received from the connected device;
Remote access system, characterized in that on the basis of the verification result by the verification means, and a determining means for determining permission of said access device to said resource.
を特徴とする請求項1記載のリモートアクセスシステム。The remote access system according to claim 1, wherein the connection device connects a network including the access target device to another network.
前記接続機器は、前記認証局によって発行された前記発行許可証明書を前記アクセス機器に対して発行すること
を特徴とする請求項1記載のリモートアクセスシステム。A certificate authority that issues an issuance permission certificate that is a certificate for granting permission to issue the attribute certificate to the access device;
The remote access system according to claim 1, wherein the connection device issues the issue permission certificate issued by the certificate authority to the access device.
を特徴とする請求項3記載のリモートアクセスシステム。The attribute certificate, the role information that indicates a role given to the connected device, remote access of claim 3, wherein the including information that gives permission to issue the attribute certificate to the access device system.
を特徴とする請求項1記載のリモートアクセスシステム。The remote access system according to claim 1, further comprising a certificate authority that issues a public key certificate based on a public key cryptosystem to each entity constituting the remote access system.
前記アクセス対象機器に対してアクセスするアクセス機器と、
前記アクセス機器に対して、前記アクセス対象機器のプロキシとして働く接続機器とからなるリモートアクセスシステムにて、
所定のリソースに対して遠隔地からアクセスするリモートアクセス方法であって、
前記アクセス機器は、
前記リソースに対するアクセス権限及び前記接続機器が前記アクセス対象機器に対するプロキシとしての役割を果たすためのプロキシ情報が記述されている属性証明書を記憶手段に記憶し、
前記記憶手段に記憶される前記属性証明書を、前記接続機器に対して提示し、
前記接続機器は、
前記アクセス機器から受信した前記属性証明書を、前記アクセス対象として指定され ている前記アクセス対象機器に対して送信して提示し、
前記アクセス対象機器は、
前記接続機器から受信した前記属性証明書に記述されている前記アクセス権限及び前記プロキシ情報の内容を検証し、
検証結果に基づいて、前記リソースに対する前記アクセス機器のアクセス許可を決定すること
を特徴とするリモートアクセス方法。Access target device to be accessed,
An access device for accessing the access target device;
With respect to the access device, in a remote access system comprising a connection device that acts as a proxy for the access target device,
A remote access method for accessing a predetermined resource from a remote location,
The access device is:
Storing in the storage means an attribute certificate in which proxy information for the access authority to the resource and the connected device to serve as a proxy for the access target device is described;
Presenting the attribute certificate stored in the storage means to the connected device ;
The connection device is
The attribute certificate received from the access device is transmitted to the access target device designated as the access target and presented ,
The access target device is:
Verifying the access authority and the content of the proxy information described in the attribute certificate received from the connected device;
A remote access method, wherein access permission of the access device for the resource is determined based on a verification result .
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002201472A JP4129783B2 (en) | 2002-07-10 | 2002-07-10 | Remote access system and remote access method |
| EP03015192A EP1381201A2 (en) | 2002-07-10 | 2003-07-04 | System, method and program for remote access to a resource using certificates |
| US10/617,069 US20040078573A1 (en) | 2002-07-10 | 2003-07-10 | Remote access system, remote access method, and remote access program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002201472A JP4129783B2 (en) | 2002-07-10 | 2002-07-10 | Remote access system and remote access method |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004046430A JP2004046430A (en) | 2004-02-12 |
| JP2004046430A5 JP2004046430A5 (en) | 2005-05-19 |
| JP4129783B2 true JP4129783B2 (en) | 2008-08-06 |
Family
ID=29728465
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002201472A Expired - Fee Related JP4129783B2 (en) | 2002-07-10 | 2002-07-10 | Remote access system and remote access method |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20040078573A1 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP1381201A2 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP4129783B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (63)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN100452699C (en) * | 2001-09-27 | 2009-01-14 | 松下电器产业株式会社 | Encryption device, a decrypting device, a secret key generation device, a copyright protection system and a cipher communication device |
| MXPA06000880A (en) * | 2003-07-24 | 2006-04-19 | Koninkl Philips Electronics Nv | Hybrid device and person based authorized domain architecture. |
| US20050144144A1 (en) * | 2003-12-30 | 2005-06-30 | Nokia, Inc. | System and method for authenticating a terminal based upon at least one characteristic of the terminal located at a position within an organization |
| DE102004004048A1 (en) * | 2004-01-27 | 2005-08-18 | Siemens Ag | Communication system, method for registering a communication relationship and network connection computer |
| KR20050096040A (en) * | 2004-03-29 | 2005-10-05 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method for playbacking content using portable storage by digital rights management, and portable storage for the same |
| US7539858B2 (en) * | 2004-04-05 | 2009-05-26 | Nippon Telegraph And Telephone Corporation | Packet encryption substituting device, method thereof, and program recording medium |
| JP2005309780A (en) * | 2004-04-21 | 2005-11-04 | Ntt Docomo Inc | Ic card and authority transfer control method |
| US8141142B2 (en) | 2005-02-14 | 2012-03-20 | International Business Machines Corporation | Secure authentication of service users of a remote service interface to a storage media |
| JP2007011692A (en) * | 2005-06-30 | 2007-01-18 | I System Kk | Authentication system |
| GB0517303D0 (en) * | 2005-08-23 | 2005-10-05 | Netronome Systems Inc | System and method for processing secure transmissions |
| WO2007031654A1 (en) * | 2005-09-15 | 2007-03-22 | France Telecom | Operating method, gateway, system and system for entry management |
| KR100791291B1 (en) | 2006-02-10 | 2008-01-04 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method and apparatus using DRM contents with roaming in device |
| WO2007108114A1 (en) * | 2006-03-22 | 2007-09-27 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Domain participation method, attribute certificate selection method, communication terminal, ic card, ce device, attribute certificate issuing station, and content server |
| US8132245B2 (en) * | 2006-05-10 | 2012-03-06 | Appia Communications, Inc. | Local area network certification system and method |
| KR100791298B1 (en) * | 2006-05-19 | 2008-01-04 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Apparatus and method for controlling device of home network |
| US9602880B2 (en) | 2006-12-29 | 2017-03-21 | Kip Prod P1 Lp | Display inserts, overlays, and graphical user interfaces for multimedia systems |
| US11316688B2 (en) | 2006-12-29 | 2022-04-26 | Kip Prod P1 Lp | Multi-services application gateway and system employing the same |
| WO2008085204A2 (en) * | 2006-12-29 | 2008-07-17 | Prodea Systems, Inc. | Demarcation between application service provider and user in multi-services gateway device at user premises |
| US20170344703A1 (en) | 2006-12-29 | 2017-11-30 | Kip Prod P1 Lp | Multi-services application gateway and system employing the same |
| US9569587B2 (en) | 2006-12-29 | 2017-02-14 | Kip Prod Pi Lp | Multi-services application gateway and system employing the same |
| US11783925B2 (en) | 2006-12-29 | 2023-10-10 | Kip Prod P1 Lp | Multi-services application gateway and system employing the same |
| US8619668B2 (en) * | 2007-06-07 | 2013-12-31 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Mobility management mode selection in multiple access wireless networks |
| JP2009258683A (en) * | 2008-03-20 | 2009-11-05 | Semiconductor Energy Lab Co Ltd | Numbering method, numbering device, and laser direct drawing apparatus |
| FR2930390B1 (en) * | 2008-04-21 | 2010-04-16 | Etsem Ltd | METHOD FOR SECURE DIFFUSION OF DIGITAL DATA TO AN AUTHORIZED THIRD PARTY |
| US8146159B2 (en) * | 2009-01-20 | 2012-03-27 | Check Point Software Technologies, Ltd. | Methods for inspecting security certificates by network security devices to detect and prevent the use of invalid certificates |
| JP5250456B2 (en) * | 2009-03-10 | 2013-07-31 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Communication equipment system and card type equipment |
| US20110161663A1 (en) * | 2009-12-29 | 2011-06-30 | General Instrument Corporation | Intelligent caching for ocsp service optimization |
| US8732475B2 (en) * | 2011-08-17 | 2014-05-20 | Comcast Cable Communication, Llc | Authentication and binding of multiple devices |
| US8909918B2 (en) | 2011-10-05 | 2014-12-09 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | Techniques to classify virtual private network traffic based on identity |
| EP2634990A1 (en) * | 2012-03-02 | 2013-09-04 | Thomson Licensing | Home gateway with secure access |
| JP5373151B2 (en) * | 2012-05-21 | 2013-12-18 | シャープ株式会社 | Information processing apparatus, information processing apparatus control method, controlled apparatus, controlled apparatus control method, server, server control method, pairing system, control program, and recording medium |
| US9215075B1 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2015-12-15 | Poltorak Technologies Llc | System and method for secure relayed communications from an implantable medical device |
| US9887982B2 (en) * | 2013-10-09 | 2018-02-06 | Digicert, Inc. | Accelerating OCSP responses via content delivery network collaboration |
| US10454783B2 (en) | 2014-02-05 | 2019-10-22 | Apple Inc. | Accessory management system using environment model |
| US10177933B2 (en) | 2014-02-05 | 2019-01-08 | Apple Inc. | Controller networks for an accessory management system |
| EP3086253B1 (en) * | 2013-12-16 | 2017-12-13 | Panasonic Intellectual Property Management Co., Ltd. | Authentication system, and authentication method |
| CN108259159B (en) | 2014-02-05 | 2021-02-05 | 苹果公司 | Method and system for pairing between a controller and an accessory |
| JP6270542B2 (en) * | 2014-02-28 | 2018-01-31 | 大阪瓦斯株式会社 | Authentication system |
| CN112134708A (en) * | 2014-04-15 | 2020-12-25 | 创新先进技术有限公司 | Authorization method, authorization request method and device |
| WO2015184382A2 (en) * | 2014-05-30 | 2015-12-03 | Apple Inc. | Controller networks for an accessory management system |
| US9449187B2 (en) * | 2014-08-11 | 2016-09-20 | Document Dynamics, Llc | Environment-aware security tokens |
| US10114939B1 (en) * | 2014-09-22 | 2018-10-30 | Symantec Corporation | Systems and methods for secure communications between devices |
| US10171532B2 (en) * | 2014-09-30 | 2019-01-01 | Citrix Systems, Inc. | Methods and systems for detection and classification of multimedia content in secured transactions |
| US9906497B2 (en) | 2014-10-06 | 2018-02-27 | Cryptzone North America, Inc. | Multi-tunneling virtual network adapter |
| US9148408B1 (en) | 2014-10-06 | 2015-09-29 | Cryptzone North America, Inc. | Systems and methods for protecting network devices |
| US10206170B2 (en) | 2015-02-05 | 2019-02-12 | Apple Inc. | Dynamic connection path detection and selection for wireless controllers and accessories |
| JP6765061B2 (en) * | 2015-08-28 | 2020-10-07 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Authentication system and authentication method |
| US9866519B2 (en) | 2015-10-16 | 2018-01-09 | Cryptzone North America, Inc. | Name resolving in segmented networks |
| US9736120B2 (en) | 2015-10-16 | 2017-08-15 | Cryptzone North America, Inc. | Client network access provision by a network traffic manager |
| US10412048B2 (en) | 2016-02-08 | 2019-09-10 | Cryptzone North America, Inc. | Protecting network devices by a firewall |
| WO2017160557A1 (en) * | 2016-03-18 | 2017-09-21 | Pcms Holdings, Inc. | System and method for network-level smart home security |
| US10951601B2 (en) | 2016-03-31 | 2021-03-16 | Sony Corporation | Information processing apparatus and information processing method |
| US9560015B1 (en) | 2016-04-12 | 2017-01-31 | Cryptzone North America, Inc. | Systems and methods for protecting network devices by a firewall |
| JP6767903B2 (en) * | 2017-03-21 | 2020-10-14 | Kddi株式会社 | Devices, information terminals, authentication management servers and device authentication systems |
| US10496508B2 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2019-12-03 | Apple Inc. | Accessory communication control |
| US11805009B2 (en) | 2018-06-03 | 2023-10-31 | Apple Inc. | Configuring accessory network connections |
| US10595073B2 (en) | 2018-06-03 | 2020-03-17 | Apple Inc. | Techniques for authorizing controller devices |
| CN109495257B (en) * | 2018-12-18 | 2021-08-06 | 国家电网有限公司 | Data acquisition unit encryption method based on improved SM2 cryptographic algorithm |
| US11283623B1 (en) * | 2019-06-03 | 2022-03-22 | Wells Fargo Bank, N.A. | Systems and methods of using group functions certificate extension |
| JP7215342B2 (en) * | 2019-06-06 | 2023-01-31 | 富士通株式会社 | COMMUNICATION PROGRAM, COMMUNICATION METHOD, AND COMMUNICATION DEVICE |
| JP2022020143A (en) * | 2020-07-20 | 2022-02-01 | 富士通株式会社 | Communication program, communication device and communication method |
| US20220329576A1 (en) * | 2021-04-09 | 2022-10-13 | Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development Lp | Securing communication between a cloud platform and an application hosted on an on-premise private network |
| KR102463051B1 (en) | 2021-11-23 | 2022-11-03 | 펜타시큐리티시스템 주식회사 | Driving negotiation method and apparatus |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5416842A (en) * | 1994-06-10 | 1995-05-16 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Method and apparatus for key-management scheme for use with internet protocols at site firewalls |
| US5588060A (en) * | 1994-06-10 | 1996-12-24 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Method and apparatus for a key-management scheme for internet protocols |
| US5892900A (en) * | 1996-08-30 | 1999-04-06 | Intertrust Technologies Corp. | Systems and methods for secure transaction management and electronic rights protection |
| US5867494A (en) * | 1996-11-18 | 1999-02-02 | Mci Communication Corporation | System, method and article of manufacture with integrated video conferencing billing in a communication system architecture |
| US6317838B1 (en) * | 1998-04-29 | 2001-11-13 | Bull S.A. | Method and architecture to provide a secured remote access to private resources |
| US6463474B1 (en) * | 1999-07-02 | 2002-10-08 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | Local authentication of a client at a network device |
| US6434568B1 (en) * | 1999-08-31 | 2002-08-13 | Accenture Llp | Information services patterns in a netcentric environment |
| US6332163B1 (en) * | 1999-09-01 | 2001-12-18 | Accenture, Llp | Method for providing communication services over a computer network system |
-
2002
- 2002-07-10 JP JP2002201472A patent/JP4129783B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2003
- 2003-07-04 EP EP03015192A patent/EP1381201A2/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2003-07-10 US US10/617,069 patent/US20040078573A1/en not_active Abandoned
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1381201A2 (en) | 2004-01-14 |
| JP2004046430A (en) | 2004-02-12 |
| US20040078573A1 (en) | 2004-04-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4129783B2 (en) | Remote access system and remote access method | |
| JP2004046430A5 (en) | ||
| US7844816B2 (en) | Relying party trust anchor based public key technology framework | |
| US10567370B2 (en) | Certificate authority | |
| JP4674044B2 (en) | System and method for providing a key management protocol that allows a client to verify authorization | |
| KR100925329B1 (en) | Method and apparatus of mutual authentication and key distribution for downloadable conditional access system in digital cable broadcasting network | |
| AU2004254771B2 (en) | User authentication system | |
| CN1681238B (en) | Key allocating method and key allocation system for encrypted communication | |
| JP5604176B2 (en) | Authentication cooperation apparatus and program thereof, device authentication apparatus and program thereof, and authentication cooperation system | |
| US20060126848A1 (en) | Key authentication/service system and method using one-time authentication code | |
| US20070214356A1 (en) | Method and system for authentication between electronic devices with minimal user intervention | |
| JP2004015530A (en) | Access right management system, relay server and method therefor, as well as computer program | |
| KR101452708B1 (en) | CE device management server, method for issuing DRM key using CE device management server, and computer readable medium | |
| MXPA04007546A (en) | Method and system for providing third party authentification of authorization. | |
| JP6667371B2 (en) | Communication system, communication device, communication method, and program | |
| JP2001186122A (en) | Authentication system and authentication method | |
| WO2008002081A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for authenticating device in multi domain home network environment | |
| JP4332071B2 (en) | Client terminal, gateway device, and network system including these | |
| CN107347073B (en) | A kind of resource information processing method | |
| KR20090054774A (en) | Method of integrated security management in distribution network | |
| JP2003233594A (en) | Access right management system, access right management method, access right management program and recording medium recording access right management program | |
| Vossaert et al. | User-centric identity management using trusted modules | |
| Dumas et al. | LocalPKI: An interoperable and IoT friendly PKI | |
| KR100905315B1 (en) | Authentication service method using public certification in mobile environment | |
| Lee et al. | Home network device authentication: Device authentication framework and device certificate profile |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040428 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20040428 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040622 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20050527 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20050810 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20070413 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20070705 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070829 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20080428 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20080511 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110530 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |