JP2006073618A - Optical element and manufacturing method thereof - Google Patents
Optical element and manufacturing method thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2006073618A JP2006073618A JP2004252499A JP2004252499A JP2006073618A JP 2006073618 A JP2006073618 A JP 2006073618A JP 2004252499 A JP2004252499 A JP 2004252499A JP 2004252499 A JP2004252499 A JP 2004252499A JP 2006073618 A JP2006073618 A JP 2006073618A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- electrode
- semiconductor layer
- led element
- external electrode
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Led Device Packages (AREA)
- Led Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は光学素子に関し、特に、高度な加工技術を要することなく、既存の設備および既知の製造方法を使用しながら素子全体に占める発光面積を大にでき、実装性に優れ、電気的接続の信頼性が大で、良好な放熱性を有する光学素子およびその製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to an optical element, and in particular, without requiring advanced processing technology, the light emitting area occupying the entire element can be increased while using existing equipment and a known manufacturing method, and is excellent in mountability and electrical connection. The present invention relates to an optical element having high reliability and good heat dissipation and a method for manufacturing the same.
従来の光学素子として、サファイア等の光透過性の下地基板上にIII族窒化物系化合物半導体等の半導体結晶を成長させたLED素子(Light Emitting Diode:以下、LED素子という。)が知られている。LED素子は、n型およびp型の窒化物系化合物半導体層(以下、半導体層という)に通電することによって発光層内で発光し、発光に基づく光を外部放射する。 As a conventional optical element, an LED element (Light Emitting Diode: hereinafter referred to as an LED element) in which a semiconductor crystal such as a group III nitride compound semiconductor is grown on a light-transmitting base substrate such as sapphire is known. Yes. The LED element emits light in the light emitting layer by energizing n-type and p-type nitride compound semiconductor layers (hereinafter referred to as semiconductor layers), and emits light based on the light emission to the outside.
LED素子のn型およびp型の半導体層に通電するにあたって、LED素子最上層のp型半導体層に通電する第1の電極を設け、更に、p型半導体層からエッチングを施すことにより露出させたn型半導体層に第2の電極を設けて、ワイヤボンディングによって外部回路との電気的接続を行うことが知られている。このようなLED素子では、光取り出し面に第1の電極が設けられるためにLED素子から出射される光の取り出しが妨げられるという不都合がある。 When energizing the n-type and p-type semiconductor layers of the LED element, a first electrode for energizing the p-type semiconductor layer, which is the uppermost layer of the LED element, is provided and further exposed by etching from the p-type semiconductor layer. It is known that a second electrode is provided on an n-type semiconductor layer and is electrically connected to an external circuit by wire bonding. In such an LED element, since the first electrode is provided on the light extraction surface, extraction of light emitted from the LED element is hindered.
一方、外部回路との電気的接続をワイヤによらずにAu等のパンプを介してフリップチップ接合し、発光層での発光に基づく光をサファイア基板側から取り出すようにしたLED素子が提案されている。このようなLED素子では、短絡を生じることなく、かつバンプ接合に必要な面積の第1および第2の電極を設ける必要があり、そのことによって素子全体に占める発光面積を大にすることが難しいという不都合がある。 On the other hand, an LED element has been proposed in which electrical connection with an external circuit is flip-chip bonded via a pump such as Au without using a wire, and light based on light emission in the light emitting layer is extracted from the sapphire substrate side. Yes. In such an LED element, it is necessary to provide the first and second electrodes having an area necessary for bump bonding without causing a short circuit, and thus it is difficult to increase the light emitting area in the entire element. There is an inconvenience.
かかる問題を解消するものとして、LED素子のn型半導体層およびp型半導体層に電圧印加を行うための電極を側面部に設けたLED素子が提案されている(例えば、特許文献1参照。)。 In order to solve such a problem, an LED element in which an electrode for applying a voltage to the n-type semiconductor layer and the p-type semiconductor layer of the LED element is provided on the side surface has been proposed (for example, see Patent Document 1). .
特許文献1に記載されるLED素子は、特許文献1の図1に示されているように、積層部の両側面部およびサファイア基板の両側面部に、たとえば酸化シリコン(SiO2)製の絶縁層を形成されている。一方の絶縁層は、積層部の最表面に位置するp型GaN層の端面部と接触する箇所にエッチングが施されている。また他方の絶縁膜は、n型GaN層の端面部と接触する箇所にエッチングが施されており、エッチングの部位を介してp型GaN層およびn型GaN層に導通する導電性膜からなる電極が絶縁層の外表面に設けられている。
As shown in FIG. 1 of
特許文献1に記載されるLED素子によれば、半導体発光素子の積層部の表面部に電極は形成されていないため、発光層から発せられる光は効率よく上方向へ出射することとなる。また、発光層がエッチングによってその面積が減じられているようなこともなく、発光層の発光面積としては、サファイア基板と同一の大きな面積に形成しておくことができる。したがって、積層部の最表面の部位から上向きに出射される光量を大きくでき、発光強度を高めることができるとしている。
しかし、特許文献1に記載されるLED素子によると、サファイア基板に積層部を形成し、これをダイシングしてチップに分割した後に絶縁層に対してエッチングを行い、エッチング部位を介してp型GaN層およびn型GaN層に導通する電極を設けているため、個々のチップに対する微細かつ高度な加工技術を要し、一括多量生産が難しいという問題がある。また、電気的接続性の向上が図られても、発光に伴って生じる熱に対して充分な放熱性が得られなければ発光効率は向上せず、高輝度化、大出力化を実現することができない。
However, according to the LED element described in
従って、本発明の目的は、高度な加工技術を要することなく、既存の設備および既知の製造方法を使用しながら素子全体に占める発光面積を大にでき、実装性に優れ、電気的接続の信頼性が大で、良好な放熱性を有する光学素子およびその製造方法を提供することにある。 Therefore, the object of the present invention is to increase the light emitting area in the entire device using existing equipment and a known manufacturing method without requiring advanced processing technology, and is excellent in mountability and reliability of electrical connection. It is an object of the present invention to provide an optical element having a high performance and a good heat dissipation property and a method for manufacturing the same.
本発明は、上記の目的を達成するため、発光層を含む半導体層と、素子全幅より小なる幅を有する前記半導体層の周縁に設けられ、前記発光層に給電するn側およびp側の電極とを有することを特徴とする光学素子を提供する。 In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a semiconductor layer including a light emitting layer and n-side and p-side electrodes provided on the periphery of the semiconductor layer having a width smaller than the entire width of the element and supplying power to the light emitting layer. The optical element characterized by having these.
また、本発明は、上記の目的を達成するため、ウエハー状の下地基板に半導体材料を積層して発光層を含む半導体層を形成する半導体層形成工程と、前記半導体層の表面から所定の幅および深さを有するように前記半導体層を除去して露出部を形成する半導体層除去工程と、前記露出部に前記半導体層のn層およびp層へ給電する電極を形成する電極形成工程と、前記電極が素子周縁に露出するように前記下地基板および前記半導体層を切断して素子化する素子化工程とを含むことを特徴とする光学素子の製造方法を提供する。 In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a semiconductor layer forming step of forming a semiconductor layer including a light emitting layer by laminating a semiconductor material on a wafer-like base substrate, and a predetermined width from the surface of the semiconductor layer. And a semiconductor layer removing step of removing the semiconductor layer so as to have a depth to form an exposed portion, and an electrode forming step of forming electrodes for supplying power to the n layer and the p layer of the semiconductor layer in the exposed portion, There is provided an optical element manufacturing method including an element forming step of cutting the base substrate and the semiconductor layer into an element so that the electrode is exposed at the periphery of the element.
本発明によれば、素子全体に占める発光面積を大にでき、高度かつ高価な設備を要することなく実装性に優れ、電気的接続の信頼性が大で、サイズが大であっても良好な放熱性を付与することができる。 According to the present invention, the light emitting area occupying the entire element can be increased, and it is excellent in mountability without requiring sophisticated and expensive equipment, the reliability of electrical connection is large, and even if the size is large, it is good. Heat dissipation can be imparted.
(第1の実施の形態)
(LED素子1の構成)
図1は、第1の実施の形態に係るLED素子を示し、(a)は素子対角線方向に切断した縦断面図、(b)はLED素子の光取り出し面側から見た平面図である。
(First embodiment)
(Configuration of LED element 1)
1A and 1B show an LED element according to a first embodiment, in which FIG. 1A is a longitudinal sectional view cut in a diagonal direction of the element, and FIG. 1B is a plan view seen from the light extraction surface side of the LED element.
このLED素子1は、図1(a)に示すように、サファイア基板10上にIII族窒化物系化合物半導体を結晶成長させたものであり、サファイア基板10上にAlNバッファ層11と、III族窒化物系化合物半導体層によって構成されるn−GaN層12と、発光層13と、p−GaN層14と、p−GaN層14に電流を拡散させるpコンタクト電極15とを順次積層し、GaN系半導体層100の側面に光透過性を有する絶縁層16と、p−GaN層14からn−GaN層12にかけてエッチングで除去することにより露出したn−GaN層12に設けられるn外部電極17と、サファイア基板10上のAlNバッファ層11からpコンタクト電極15にかけてのGaN系半導体層100の側面に設けられるp外部電極18と、n外部電極17からp外部電極18にかけての素子表面を覆う光透過性を有する絶縁層19とを有する。
As shown in FIG. 1A, the
以下の説明においては、サファイア基板10上のAlNバッファ層11から絶縁層19にかけての部分をGaN系半導体層100としている。このLED素子1の発光層13から放射される光の発光波長は460nmである。
In the following description, the portion from the
III族窒化物系化合物半導体層の形成方法は、特に限定されないが、周知の有機金属気相成長法(MOCVD法)、分子線結晶成長法(MBE法)、ハライド系気相成長法(HVPE法)、スパッタ法、イオンプレーティング法、電子シャワー法等によって形成することができる。なお、LED素子の構成としては、ホモ構造、ヘテロ構造若しくはダブルへテロ構造のものを用いることができる。さらに、量子井戸構造(単一量子井戸構造若しくは多重量子井戸構造)を採用することもできる。 The formation method of the group III nitride compound semiconductor layer is not particularly limited, but the well-known metal organic chemical vapor deposition method (MOCVD method), molecular beam crystal growth method (MBE method), halide vapor phase epitaxy method (HVPE method). ), A sputtering method, an ion plating method, an electron shower method, or the like. In addition, as a structure of a LED element, the thing of a homo structure, a hetero structure, or a double hetero structure can be used. Furthermore, a quantum well structure (single quantum well structure or multiple quantum well structure) can also be adopted.
pコンタクト電極15は、p−GaN層14に電流を拡散させるとともに、外部との良好な電気的接続性を付与するためのものであり、本実施の形態では光反射性を有するRhによって形成されている。なお、pコンタクト電極15は、p−GaN層14とオーミック接触可能な材料であれば光透過性を有するITO(Indium Tin Oxide)、ZnO、Au/Co、Ni/Ti等の透光性材料で形成されても良い。
The p-
絶縁層16は、SiO2からなり、GaN系半導体層の側面を覆うように設けられてn外部電極17およびp外部電極18がGaN系半導体層100と短絡することを防止する。なお、SiO2に代えてSiN等の他の絶縁性材料を用いることもできる。
The
n外部電極17はV/Alからなり、p外部電極18はTiによって形成されている。これらの外部電極は、素子側面での電気的接合およびpコンタクト電極15側での面実装を可能とするために素子側面からpコンタクト電極15形成面にかけての素子周縁に露出するように形成されている。ここでいう素子周縁とは、例えば、図1に示すLED素子1の側面、および絶縁層19の設けられるGaN系半導体層100表面の縁である。その形成長は、n外部電極17が隣接する2辺の側面全体、p外部電極18はn外部電極17が形成される2辺に対向する2辺の一部に設けられており、p外部電極18の形成領域はn外部電極17より小となるように設けられる。なお、表面に半田メッキを施しても良い。
The n
(LED素子1の製造工程)
図2(a)から(d)は、第1の実施の形態に係るLED素子の製造工程(LED素子の側面に絶縁層16を設ける工程まで)を示す図である。なお、以下の説明では、ウエハー状のサファイア基板10に対して半導体層を形成し、これを切り離して素子化する製造工程について説明を容易にするために、LED素子1となる部分を中心に示している。
(Manufacturing process of LED element 1)
FIGS. 2A to 2D are diagrams showing the LED element manufacturing process (up to the process of providing the
(GaN系半導体層形成工程)
まず、図2(a)に示すように、結晶成長の下地基板となるウエハー状のサファイア基板10上にMOCVD法によってAlNバッファ層11、GaN系半導体層100、およびpコンタクト電極15を形成する。
(GaN-based semiconductor layer formation process)
First, as shown in FIG. 2A, an
(第1のエッチング工程)
次に、図2(b)に示すように、GaN系半導体層100に対してドライエッチングを行い、n外部電極およびp外部電極を設ける領域についてGaN系半導体層100の表面からn−GaN層12にかけて半導体層をその積層方向に除去することにより、GaN系半導体層100の側面に露出部12Aを設ける。なお、pコンタクト電極15は、露出部12Aに形成後にフォトレジストを施してpコンタクト電極15を形成し、その後フォトレジストを除去することによって形成するようにしても良い。
(First etching process)
Next, as shown in FIG. 2B, dry etching is performed on the GaN-based
(絶縁層16の形成工程)
次に、図2(c)に示すように、エッチング後のGaN系半導体層100に対し、SiO2系材料からなる絶縁層16を蒸着法によって設ける。
(Formation process of insulating layer 16)
Next, as shown in FIG. 2C, an insulating
(第2のエッチング工程)
次に、図2(d)に示すように、絶縁層16を形成されたGaN系半導体層100にフォトレジストを施してエッチングを行い、その後フォトレジストを除去することによって、GaN系半導体層100の側面以外の部分に設けられている絶縁層16を除去することにより、露出部12Aの一部およびpコンタクト電極15を露出させる。
(Second etching process)
Next, as shown in FIG. 2D, a photoresist is applied to the GaN-based
図3(a)から(c)は、第1の実施の形態に係るLED素子の製造工程(電極形成工程から完成まで)を示す図である。 FIGS. 3A to 3C are views showing the LED element manufacturing process (from the electrode forming process to completion) according to the first embodiment.
(pコンタクト電極15の形成工程)
電極形成工程は、まず、図3(a)に示すように、n外部電極側の露出部12Aに蒸着によってV/Alからなるn外部電極17を形成する。次に、p外部電極側の露出部12Aに蒸着によってTiからなるp外部電極18を形成する。なお、n外部電極17を構成する材料は、n−GaN層12とオーミック接触可能な材料であれば良く、上記したV/Al以外の他の材料、例えば、Tiで形成することもできる。また、p外部電極18を構成する材料は、pコンタクト電極15と電気接続可能な特性を有するものであれば良く、上記したTi以外の他の材料、例えば、Alで形成することもできる。
(Process for forming p-contact electrode 15)
In the electrode formation step, first, as shown in FIG. 3A, an n
また、n外部電極17およびp外部電極18ともにTiによって形成することも可能である。この場合には同一工程でn外部電極17およびp外部電極18を一括的に設けることができ、製造工程の簡略化を図れる。
Further, both the n
(電極形成工程)
次に、図3(b)に示すように、電極部分を含むGaN系半導体層100の上面、n外部電極17、およびp外部電極18の形成領域にかけて、SiO2系材料からなる絶縁層16を蒸着法によって設ける。
(Electrode formation process)
Next, as shown in FIG. 3B, an insulating
(絶縁層19の形成工程)
次に、絶縁層16を形成されたGaN系半導体層100にフォトレジストを施してエッチングを行い、その後フォトレジストを除去することによってn外部電極17およびp外部電極18の短絡防止と保護層としての絶縁層19を設ける。素子周縁のn外部電極17およびp外部電極18については絶縁層19は除かれている。
(Formation process of the insulating layer 19)
Next, a photoresist is applied to the GaN-based
(素子化工程)
次に、n外部電極17およびp外部電極18を有するGaN系半導体層100およびサファイア基板10を図示しないダイサーで素子サイズに切断することにより、図3(c)に示すようにLED素子1が形成される。なお、素子化における切断はダイサーによるもの以外に、例えば、スクライブ等による加工も可能である。
(Element fabrication process)
Next, the GaN-based
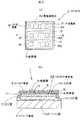
図4は、第1の実施の形態に係るLED素子の実装状態を示し、(a)は基板へのフリップチップ実装例、(b)は凹部を設けた基板へのフリップチップ実装状態を示す図である。LED素子1は、図4(a)に示すようにエポキシ系の絶縁性接着剤41によって配線パターン22を表面に有するセラミックスの基板23の表面に接着固定される。n外部電極17およびp外部電極18は、半田20Aによって配線パターン22とリフロー接合されている。なお、絶縁性接着剤41は、熱伝導性の良好なものであれば他のものであっても良く、接着性を有しないペーストや、シート状の形態でLED素子2と基板23との密着性が得られるものであれば良い。また、耐熱性が高く、接着性が良好であればより望ましい。
4A and 4B show a mounting state of the LED element according to the first embodiment, in which FIG. 4A shows an example of flip chip mounting on a substrate, and FIG. 4B shows a flip chip mounting state on a substrate provided with a recess. It is. As shown in FIG. 4A, the
基板23は、配線パターン22との絶縁性が確保できれば、上記したセラミックス、ガラスエポキシ、ポリイミドと導電箔の積層体からなるフレキシブル基板等の絶縁性基板に代えて、Cu、Al等の熱伝導性に優れる金属材料に絶縁処理を施した導電性基板を用いることもできる。
If the
また、n外部電極17とp外部電極18との短絡が生じないのであれば、絶縁性接着剤41に代えて導電性を有する材料で基板23に対しLED素子1を支持固定するようにしても良い。このような材料として、例えば、Au、Cu、又はAlのフィラを含有したシリコーン樹脂からなる導電性ペーストを用いることができる。
If the short circuit between the n
また、n外部電極17およびp外部電極18による配線パターン22への電気的接続についても、半田20Aによるものに限定されず、例えば、導電性を有する接着剤(例えば、AgペーストやAu、Cu、Al等の導電性フィラーを含有させたエポキシ樹脂)等であっても良い。
Further, the electrical connection to the
また、図4(b)示すように、素子位置決め用の凹部23Aを有する基板23を用意し、凹部23AにLED素子1のpコンタクト電極15形成側が挿入されるように固定することも可能である。凹部23Aの内部には絶縁性接着剤41が塗布されてLED素子1のpコンタクト電極15形成側を接着固定している。また、n外部電極17およびp外部電極18は、図4(a)と同様に半田20Aによって配線パターン22とリフロー接合されている。
Also, as shown in FIG. 4B, it is possible to prepare a
(LED素子1の動作)
以下に、図4(a)に示す第1の実施の形態のLED素子1の動作について説明する。
(Operation of LED element 1)
Below, operation | movement of the
配線パターン22を図示しない電源部に接続して通電することにより、LED素子1のn外部電極17とp外部電極18を介して発光層13に通電される。発光層13は、通電に基づいて発光して青色光を生じる。青色光のうちサファイア基板10側に放射される光は、サファイア基板10を透過して外部に放射される。また、LED素子1の発光に基づいて生じた熱は、絶縁性接着剤41を介して基板23へ熱伝導する。
When the
(第1の実施の形態の効果)
第1の実施の形態によると、以下の効果が得られる。
(1)ウエハー状のサファイア基板10に対する半導体発光素子の製造プロセスに基づいてn外部電極17およびp外部電極18を発光層13の周囲に設けたLED素子1を形成するので、既存の設備を使用し、かつ既知の製造方法を使用して容易にLED素子1を一括多量製造することができる。
(Effects of the first embodiment)
According to the first embodiment, the following effects can be obtained.
(1) Since the
(2)光取り出し面にではなくGaN系半導体層100の側面を除去してn外部電極17とp外部電極18とをLED素子1の周縁に設けたので、発光層13で生じた光がn外部電極17、p外部電極18によって殆ど遮られることがなくなる。また、外部電極の配置に基づいて同一素子サイズで発光層13の発光面積を大にでき、発光強度が向上するとともに光取り出し性の良好な高輝度のLED素子1を得ることができる。
(2) Since the n
(3)フリップチップ型実装およびフェイスアップ型実装のいずれの形態でも配線パターン22等への電気的接続が可能であり、用途に応じた実装形態を選択できるほか、いずれの実装形態にも該当しない、例えば、LED素子1の一側面を電気的、機械的に接合するといった実装も可能となり、多様な実装形態を提供できる。
(3) Either flip-chip type mounting or face-up type mounting can be electrically connected to the
(4)非発光部となるワイヤボンディングスペースや、n電極バンプスペースを無くするか、あるいは極めて小にすることができるので、小サイズのLED素子1であっても十分な発光エリア面積/発光素子面積の比を得ることができる。そのため、さらに小サイズのLED素子として、素子幅に近い電極間隔を有するLED素子1を具現化することができる。例えば、0.1mm角で実用性のある発光エリアを有したLED素子1の製造が可能である。仮に、LED素子1の下面でAuスタッドバンプ実装を行うn側およびp側の両電極が設けられる場合、それぞれについて直径0.1mm程度のサイズの電極が必要となり、0.1×0.2mm2未満のLED素子1を作成することは困難である。
(4) Since the wire bonding space and the n-electrode bump space serving as a non-light emitting portion can be eliminated or made extremely small, a sufficient light emitting area / light emitting element even with a small
(5)LED素子1のn外部電極17とp外部電極18とを素子側面の2辺に連続するように設けているので、半田20Aのリフロー接合による接合面積を大にでき、安定した実装性および良好な放熱性が得られる。また、バンプ接合のように高い位置決め精度を要することなしに確実な実装を可能とする。なお、n外部電極17およびp外部電極18については、図1(b)に示したように必ずしも2辺に連続したものでなくても良く、不連続であっても良い。
(5) Since the n
(6)LED素子1のフリップチップ接合時にGaN系半導体層100側が基板23に面接触するとともに、半田20Aによってn外部電極17、p外部電極18が電気的に接合されるので、接合強度が大になる。また、サファイア基板を介さずにGaN系半導体層100から基板23へ熱伝導させることができ、放熱性に優れる。また、LED素子1の接合界面に封止樹脂が介在しないので、熱膨張による接合剥がれを生じることがなく、信頼性に優れる。
(6) Since the GaN-based
なお、第1の実施の形態では、III族窒化物系化合物半導体を用いた青色系LED素子について説明したが、LED素子1は青色系に限定されず、他の発光色を生じるものであっても良い。また、半導体材料についてもIII族窒化物系化合物半導体以外の他の半導体材料であっても良い。
In the first embodiment, a blue LED element using a group III nitride compound semiconductor has been described. However, the
また、III族窒化物系化合物半導体を成長させる下地基板としてのサファイア基板10に代えて、例えば、GaN基板を用いることもできる。
Further, for example, a GaN substrate can be used instead of the
また、図4(a)で説明したように、LED素子1のpコンタクト電極15側を実装面としてフリップチップ型の実装形態で使用する場合、pコンタクト電極15をITOで形成したLED素子1を使用し、これをガラス等の光透過性を有する材料で形成した基板23に対してpコンタクト電極15側が実装面となるように面実装することで、基板23側に光を取り出すことが可能になる。
Further, as described with reference to FIG. 4A, when the
(第2の実施の形態)
(LED素子1の構成)
図5は、第2の実施の形態に係るLED素子を示し、(a)は平面図、(b)は(a)のA−A部における断面図、(c)は半田接続時の状態を示すサファイア基板側から見た平面図である。このLED素子1は、長尺状に5つの発光領域を有するように形成されて複数のn外部電極17とp外部電極18とを有し、p外部電極18は(b)に示すように電極接続部18Aを介してRhからなるpコンタクト電極15と接続されている。この長尺型のLED素子1においても、n外部電極17とp外部電極18とが側面に取り出されて充分な接合性を得ることのできる接合幅を有するように構成されており、n外部電極17とp外部電極18は、LED素子1の相対する長辺部に配置されている。また、LED素子1の相対する短辺部にはn外部電極17が露出している。
(Second Embodiment)
(Configuration of LED element 1)
5A and 5B show an LED element according to the second embodiment, where FIG. 5A is a plan view, FIG. 5B is a cross-sectional view taken along the line AA in FIG. 5A, and FIG. It is the top view seen from the sapphire substrate side to show. This
n外部電極17およびp外部電極18は、(c)に示すように半田20Aによって基板(図示せず)に設けられる配線パターンにフリップチップ接合される。
The n
(第2の実施の形態の効果)
第2の実施の形態によると、第1の実施の形態の好ましい効果に加えてLED素子1を長尺構造としても配線を容易に行えることから、光量が必要となる用途に最適なLED素子1を提供することができる。また、LED素子1の側面に所定の接合幅を有して設けられたn外部電極17とp外部電極18により、均一かつ良好な電気的接合性が得られる。
(Effect of the second embodiment)
According to the second embodiment, in addition to the preferable effect of the first embodiment, the
また、図5(a)に示すように、複数の発光領域が設けられる素子構造においても、第1の実施の形態の効果で述べたようにGaN系半導体層100側から実装面(図示せず)に速やかに熱伝導されることから、高出力化に際して放熱性に余裕のある構成を実現することができる。
Further, as shown in FIG. 5A, also in the element structure provided with a plurality of light emitting regions, the mounting surface (not shown) from the GaN-based
なお、第2の実施の形態では、発光領域が5つ設けられた長尺状のLED素子1を説明したが、発光領域の数、大きさ、形状については用途等に応じて任意に設定することができる。
In addition, in 2nd Embodiment, although the
また、上記したLED素子1は、図5(c)に示すフリップチップ接合による用途に限定されず、pコンタクト電極15をITO、ZnO、Au/Co、Ni/Ti等の透光性材料で形成し、サファイア基板10側を実装面に搭載するフェイスアップ型のLED素子1として用いることもできる。
Further, the
(第3の実施の形態)
(LED素子1の構成)
図6は、第3の実施の形態に係るLED素子を示し、(a)は平面図、(b)は(a)のB−B部における断面図である。このLED素子1は、ラージサイズ(1mm角)のLED素子1であり、素子側面から発光領域内にくし型に伸延されたn外部電極17を有するとともにpコンタクト電極15とp外部電極18とを接続する電極接続部18Aを複数設けた構成を有する。この第3の実施の形態のLED素子1においても、n外部電極17およびp外部電極18を素子側面に対向して露出させるとともに一側面全幅にわたって形成している。
(Third embodiment)
(Configuration of LED element 1)
6A and 6B show an LED element according to the third embodiment, wherein FIG. 6A is a plan view and FIG. 6B is a cross-sectional view taken along the line BB in FIG. This
pコンタクト電極15は、GaN系半導体層100側から光を取り出すLED素子1として用いる場合には、ITO等の透光性材料を用いることができる。また、サファイア基板10側から光を取り出すLED素子1として用いる場合には、上記した透光性材料に加えてRh等の光反射性を有する導電性材料を用いることもできる。
The p-
(第3の実施の形態の効果)
第3の実施の形態によると、光取り出し面にn外部電極17およびp外部電極18を設けずに側面に配置したことにより、ラージサイズのLED素子1において素子内部から光取り出しが可能な面積を大にでき、そのことによって光取り出し性の良好なLED素子1が得られる。また、素子側面に対向してn外部電極17およびp外部電極18を形成したので、外部との接合面積を大にでき、接合強度、放熱性、電流の均一分散性を向上させることができる。また、Auバンプを用いた実装と比べて実装時に位置決め等の面倒な調整を必要とせずに確実に実装することができる。
(Effect of the third embodiment)
According to the third embodiment, since the n
また、ラージサイズのLED素子1では、標準サイズのLED素子1と比べて発熱量が大になるが、n外部電極17およびp外部電極18を側面に配置したことにより、実装基板等に全面を密着させることが可能であり、そのことによって充分な放熱性を確保することができる。
In addition, the large-
なお、第3の実施の形態では、LED素子1の側面に対向するようにn外部電極17およびp外部電極18を配置し、その全幅にわたって露出させた構成としているが、n外部電極17およびp外部電極18が短絡することなくLED素子1の側面に露出する構成であれば、これら電極を任意の場所およびサイズで形成することが可能である。
In the third embodiment, the n
また、第3の実施の形態では、電極接続部18Aが9つ設けられたLED素子1を説明したが、電極接続部18Aの数、大きさ、形状については用途等に応じて任意に設定することができる。
Further, in the third embodiment, the
(第4の実施の形態)
(LED素子1の構成)
図7は、第4の実施の形態に係るLED素子を示す平面図である。このLED素子1は、ラージサイズのLED素子1の側面に沿うようにn外部電極17およびp外部電極18を設けた構成を有する。このような構成としても、第3の実施の形態で説明したように、接合強度、放熱性、電流の均一分散性を向上させることができる。
(Fourth embodiment)
(Configuration of LED element 1)
FIG. 7 is a plan view showing an LED element according to the fourth embodiment. The
(第5の実施の形態)
(LED素子1の構成)
図8は、第5の実施の形態に係るLED素子を示す平面図である。このLED素子1は、ラージサイズのLED素子1の側面にn外部電極17およびp外部電極18を配置し、更に側面からLED素子1の中央に向かう方向にn電極17Bおよびp電極18Bを伸延してくし状に形成した構成を有する。このような構成としても、第3の実施の形態で説明したように、接合強度、放熱性の向上を図ることができる。また、n外部電極17およびp外部電極18からくし状に伸延したn電極17Bおよびp電極18Bを設けることで、発光領域に対する電流の均一分散性をより向上させることができる。
(Fifth embodiment)
(Configuration of LED element 1)
FIG. 8 is a plan view showing an LED element according to the fifth embodiment. In this
(第6の実施の形態)
(LED素子1の配線構造)
図9は、第6の実施の形態としてLED素子を銅リードに接続した実装状態を示す図である。銅リード21は、銅合金を所定のリード形状に予めプレス等による加工により形成されたものであり、LED素子1の側面において半田メッキ20による半田接合に基づいてn外部電極17とp外部電極18に接続されている。LED素子1は、Rhからなるpコンタクト電極15を有しており、そのことによってサファイア基板10側から外部に光を取り出す構成を有する。なお、n−GaN層12は、カソード側およびアノード側に給電する銅リード21,21と側面において面接触しているが、この接触面ではオーミック接触していないことから短絡は生じない。
(Sixth embodiment)
(Wiring structure of LED element 1)
FIG. 9 is a diagram showing a mounted state in which LED elements are connected to copper leads as the sixth embodiment. The
図9においては、一対の銅リード21が電気的接続と機械的支持を兼ねる構成となっており、LED素子1を銅リード21で支持することによって宙吊りにした状態を示している。なお、LED素子1および銅リード21の保護および光取り出し向上の点から、LED素子1および銅リード21をエポキシ樹脂等の封止材料で一体的に封止する構成とすることが好ましい。また、銅リード21とLED素子1とを電気的に接合するものとして、上記した半田メッキ20以外の導電性接合材を用いることもできる。このような導電性接合材として、例えば、Agペーストや導電性フィラーを含有したエポキシ接着剤等を用いることができる。
In FIG. 9, the pair of copper leads 21 is configured to serve both as an electrical connection and a mechanical support, and the
(LED素子1の動作)
以下に、図9に示すLED素子1の動作について説明する。
(Operation of LED element 1)
Below, operation | movement of the
銅リード21を図示しない電源部に接続して通電することにより、LED素子1のn外部電極17とp外部電極18を介して発光層13に通電される。発光層13は、通電に基づいて発光して青色光を生じる。青色光のうちサファイア基板10側に放射される光は、サファイア基板10から外部に放射される。また、青色光のうちpコンタクト電極15側に放射される光は、pコンタクト電極15で反射されてサファイア基板10から外部に放射される。
When the
(第6の実施の形態の効果)
第6の実施の形態によると、以下の効果が得られる。
(1)光取り出し面にn外部電極17とp外部電極18とを設けずにLED素子1の側面に設けているので、図9に示すようにフェイスアップ型、フリップチップ型のいずれの実装形態にも該当しない実装が可能になる。このことにより、薄型でコンパクトな実装が可能となり、封止材料による封止性の向上、パッケージの小型化を図ることができる。また、銅リード21はLED素子1より薄ければ、側面からの光取り出しをより向上させることができるので、より望ましい。
(Effect of 6th Embodiment)
According to the sixth embodiment, the following effects can be obtained.
(1) Since the n
(2)素子側面に熱伝導性の良好な銅リード21が配置されるので、LED素子1の発光に基づいて生じた光の外部放射を阻害することなく、発熱に基づく熱がGaN系半導体層100および半田メッキ20を介して速やかに放熱される。
(2) Since the
なお、第6の実施の形態では、Rhからなるpコンタクト電極15を有したLED素子1としたが、ITO等の透光性材料からなるpコンタクト電極15を設けることによって、サファイア基板10側およびGaN系半導体層100側の両方から光取り出しを行うことが可能となる。
In the sixth embodiment, the
(LED素子1の他の接続構成)
図10は、第7の実施の形態に係るLED素子の他の実装状態を示し、(a)は第1の実装状態を示す縦断面図、(b)は第2の実装状態を示す縦断面図である。
(Other connection configuration of LED element 1)
FIG. 10 shows another mounting state of the LED element according to the seventh embodiment, (a) is a longitudinal sectional view showing the first mounting state, and (b) is a longitudinal section showing the second mounting state. FIG.
図10(a)に示す第1の実装状態では、LED素子1はITO等の透光性材料からなるpコンタクト電極15を有し、サファイア基板10側がAl2O3からなる絶縁性の基板23に図示しない接着剤によって接着固定されており、n外部電極17とp外部電極18は半田20Aによって基板23の表面に設けられる配線パターン22に電気的に接続されている。
In the first mounting state shown in FIG. 10A, the
半田20Aは、例えば、Agペースト等の導電性接着剤を代わりに用いることも可能である。また、他の導電性接着剤として、導電性フィラー含有のエポキシ接着剤等であっても良い。
As the
また、導電性接着剤が光透過性を有するものであっても良い。例えば、透明なエポキシ樹脂に導電性フィラーを含有させた導電性接着剤を用いると、LED素子1の側面から光を取り出すことが可能になる。
Further, the conductive adhesive may be light transmissive. For example, when a conductive adhesive in which a conductive filler is contained in a transparent epoxy resin is used, light can be extracted from the side surface of the
基板23は、光透過性を有するものであっても良い。この場合には、GaN系半導体層100側からの光取り出しに加えてサファイア基板10側から基板23への光取り出しが可能になる。
The
また、基板23は、Cu、Al等の導電性を有する材料で形成されていても良い。この場合、基板23を介して短絡を生じることのないように表面に絶縁層を設ける必要はあるが、放熱性を確保するうえで金属等の導電性材料を選択することは有効である。
The
図10(b)に示す第2の実装状態では、LED素子1を基板23に形成された凹部23Aに収容している構成において第1の実装状態と相違している。この凹部23Aは傾斜面23Bを有しており、収容されたLED素子1の周囲に空間が形成されるようになっている。LED素子1は凹部23Aに収容されることによって基板23表面からの突出量が抑えられており、かつ、傾斜面23BとLED素子1との間に空間に充填された半田20Aによって一対の配線パターン22と電気的に接続される。
The second mounting state shown in FIG. 10B is different from the first mounting state in the configuration in which the
なお、図10(b)に示す基板23は、光反射性を有する金属材料で形成しても良い。この場合、表面に絶縁層を設ける必要はあるが、傾斜面23Bを反射面としてLED素子1側面方向に放射された光を反射に基づいて取り出すことが可能になる。また、半田20Aは、光透過性を有する導電性接着剤であっても良く、この場合には電気接合部分における光取り出しが可能になる。
Note that the
(第7の実施の形態の効果)
(1)第1の実装状態において、LED素子1の側面に設けられたn外部電極17とp外部電極18に対して半田20Aによる電気的接合がなされるので、GaN系半導体層100からの光取り出し面積を大にできる。また、素子側面における電気的接合は、半田20A以外にも導電性接着剤等による接合を選択することも可能であり、用途に応じた適切な接合方法を選択できる。また、基板23を光透過性材料で形成した場合において、基板23側からの光取り出しを実現できる。
(Effect of 7th Embodiment)
(1) In the first mounting state, the n
(2)第2の実装状態において、凹部23Aを有した基板23にLED素子1を埋設することにより、第1の実装状態の好ましい効果に加えてLED素子1の位置決めが容易に行えるとともに、基板23の表面からの素子突出量を抑えてコンパクトなパッケージを実現できる。また、凹部23Aに傾斜面23Bが設けられているので、素子側面に放射された光を傾斜面23Bで反射させて外部放射させることができる。
(2) In the second mounting state, by embedding the
(第8の実施の形態)
(LED素子1の構成)
図11は、第8の実施の形態に係るLED素子の実装状態を示す縦断面図である。このLED素子1は、図4(a)で説明したLED素子1のサファイア基板10をリフトオフした構成において図4(a)のLED素子1と相違している。
(Eighth embodiment)
(Configuration of LED element 1)
FIG. 11 is a longitudinal sectional view showing a mounted state of the LED element according to the eighth embodiment. This
LED素子1は、サファイア基板10側からレーザ光を照射することによってサファイア基板10およびAlNバッファ層11をリフトオフしたものである。なお、リフトオフに伴ってn−GaN層12の表面にAlNバッファ層11が残存することがあり、この場合には酸洗浄によってAlNバッファ層11を除去することが好ましい。
The
このLED素子1は、配線パターン22に接続された図示しない電源部からn外部電極17およびp外部電極を介して発光層13に電圧を印加することにより発光層13において発光する。発光に基づく光のうち、n-GaN層12側に放射された光はn-GaN層12から外部放射される。また、pコンタクト電極15側に放射された光はRhで形成されたpコンタクト電極15で反射されてn-GaN層12から外部放射される。
The
なお、pコンタクト電極15をITO等の透光性材料で形成し、かつ、基板23を光透過性を有する材料で形成することによって、実装側であるGaN系半導体層100側から光取り出しおよび放熱を行える構成としても良い。
The p-
(第8の実施の形態の効果)
第8の実施の形態によると、フリップチップ接合されたLED素子1のn−GaN層12から光取り出しが可能になることによって、GaN系半導体層100から外部放射されない層内閉込光を低減でき、外部放射効率に優れる発光装置を形成することが可能になる。
(Effect of 8th Embodiment)
According to the eighth embodiment, light can be extracted from the n-
また、LED素子1の側面にn外部電極17およびp外部電極18が配置されるので、LED素子1を薄く形成でき、実装対象の小型化や形状に伴う制約を回避することが可能になる。また、絶縁層19を介した基板23への放熱性にも優れる。
In addition, since the n
なお、LED素子1の保護の点から、n−GaN層12の表面を透光性材料で覆うか、配線パターン22、基板23とともにエポキシ樹脂等の封止部材で封止することが好ましい。
From the viewpoint of protecting the
また、n−GaN層12の表面に凹凸等の形状加工を施すことにより、層内閉込光を低減し、外部放射効率を向上させる構成としても良い。
Moreover, it is good also as a structure which reduces the confinement light in a layer and improves external radiation efficiency by giving shape processing, such as an unevenness | corrugation, to the surface of the n-
(第9の実施の形態)
(LED素子1の構成)
図12は、第9の実施の形態に係るLED素子の実装状態を示す縦断面図である。このLED素子1は、図12で説明したLED素子1のn−GaN層12側に配線パターン22を有した高屈折率材料であるガラス部材30を光透過性接着剤42によって接着固定することにより構成されている。LED素子1のpコンタクト電極15はRhによって形成されている。
(Ninth embodiment)
(Configuration of LED element 1)
FIG. 12 is a longitudinal sectional view showing a mounted state of the LED element according to the ninth embodiment. This
光透過性接着剤42は、LED素子1から放射される光の透過性を妨げることのないエポキシ系の接着剤が用いられる。
As the light-transmitting adhesive 42, an epoxy-based adhesive that does not interfere with the transmission of light emitted from the
n外部電極17およびp外部電極18は、光透過性を有するとともに導電性を有する接着剤24によって配線パターン22に電気的に接続されている。この接着剤24は、前述したように導電性フィラーを含有させたエポキシ樹脂等を用いることができる。
The n
このLED素子1は、配線パターン22に接続された図示しない電源部からn外部電極17およびp外部電極を介して発光層13に電圧を印加することにより発光層13において発光する。発光に基づく光のうち、n-GaN層12側に放射された光はn-GaN層12から光透過性接着剤42を介してガラス部材30に入射し、ガラス部材30から外部放射される。また、pコンタクト電極15側に放射された光はRhで形成されたpコンタクト電極15で反射されてn-GaN層12からガラス部材30に入射し、ガラス部材30から外部放射される。
The
また、ガラス部材30との界面で全反射され、GaN系半導体層100を横伝搬する光の一部は、LED素子1の側面から接着剤20Bに入射することにより外部放射される。
Further, a part of the light that is totally reflected at the interface with the glass member 30 and propagates laterally through the GaN-based
(第9の実施の形態の効果)
第9の実施の形態によると、光透過性接着剤42を介してガラス部材30にLED素子1を接着することにより、バックライト等の透過照明の用途に適切な光源を提供することができる。
(Effect of 9th Embodiment)
According to the ninth embodiment, by adhering the
なお、第9の実施の形態では、pコンタクト電極15を光反射性を有するRhで形成したが、ITO等の透光性材料で形成してGaN系半導体層100側からも光が取り出せる構成としても良い。
In the ninth embodiment, the p-
(LED素子1の構成)
図13は、第10の実施の形態に係るラージサイズ(1mm角)のLED素子を示し、(a)は縦断面図、(b)は(a)の絶縁層形成面側から見た平面図である。
(Configuration of LED element 1)
FIG. 13 shows a large-size (1 mm square) LED element according to the tenth embodiment, wherein (a) is a longitudinal sectional view, and (b) is a plan view as viewed from the insulating layer forming surface side of (a). It is.
このLED素子1は、(b)に示すように素子中央部にGaN系半導体層100からn-GaN層12にかけて形成された穴部1Aを有し、この穴部1Aの内部にエッチングによって露出させたn−GaN層12を覆うように設けられるn外部電極17と、GaN系半導体層100の外側部を覆うように設けられてpコンタクト電極15に電気的に接続されるp外部電極18とを備えている。LED素子1のpコンタクト電極15はRhによって形成されている。
This
このLED素子1はn外部電極17およびp外部電極18に対応する半田メッキ20のパターンに対応した配線パターンを有する基板等へのフリップチップ接合が可能である。
The
(第10の実施の形態の効果)
第10の実施の形態によると、素子中央部にn外部電極17を設け、素子外周にp外部電極18を設けるようにしたので、ラージサイズのLED素子1であっても発光層13を全面にわたって均一に発光させることができる。
(Effect of 10th Embodiment)
According to the tenth embodiment, the n
また、第10の実施の形態のLED素子1をフリップチップ接合することによって、実装基板等への優れた放熱性を確保しながら良好な発光特性が得られる。
Further, by flip chip bonding the
また、第10の実施の形態においても、フェイスアップ型LED素子1として用いる場合にはpコンタクト電極15をITO等の透光性材料で形成することが可能であり、そのことによってフェイスアップ接合時における光取り出し性の低下を最小限に留めながら優れたワイヤ接合性が得られる。。
Also in the tenth embodiment, when used as the face-up
なお、上記した各実施の形態では、光学素子としてLED素子を説明したが、LED素子に限定されず、太陽電池、受光素子等の他の光学素子およびその製造方法についても適用が可能である。 In each of the above-described embodiments, the LED element is described as the optical element. However, the present invention is not limited to the LED element, and can be applied to other optical elements such as a solar cell and a light receiving element, and a manufacturing method thereof.
1…LED素子、1A…穴部、10…サファイア基板、11…AlNバッファ層、12…n−GaN層、12A…露出部、13…発光層、14…p−GaN層、15…pコンタクト電極、16…絶縁層、17…n外部電極、18…p外部電極、18A…電極接続部、19…絶縁層、20…半田メッキ、21…銅リド、22…配線パターン、23…基板、24…ワイヤ、25…絶縁性接着剤、26…金属薄膜、30…ガラス部材、40…Rh電極、100…GaN系半導体層
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (13)
前記半導体層の表面から所定の幅および深さを有するように前記半導体層を除去して露出部を形成する半導体層除去工程と、
前記露出部に前記半導体層のn層およびp層へ給電する電極を形成する電極形成工程と、
前記電極が素子周縁に露出するように前記下地基板および前記半導体層を切断して素子化する素子化工程とを含むことを特徴とする光学素子の製造方法。 A semiconductor layer forming step of forming a semiconductor layer including a light emitting layer by laminating a semiconductor material on a wafer-like base substrate;
Removing the semiconductor layer so as to have a predetermined width and depth from the surface of the semiconductor layer to form an exposed portion; and
Forming an electrode for supplying power to the n layer and the p layer of the semiconductor layer in the exposed portion;
A method of manufacturing an optical element, comprising: an element forming step of cutting the base substrate and the semiconductor layer into an element so that the electrode is exposed at the periphery of the element.
前記n層および前記p層間の絶縁を確保するように前記絶縁層を除去して前記n層および前記p層に対応する電極形成領域を形成する絶縁層除去工程と、
前記電極形成領域に前記n層および前記p層にそれぞれ接続される外部電極を形成する外部電極形成工程とを含むことを特徴とする請求項8記載の光学素子の製造方法。 The electrode forming step includes an insulating layer forming step of forming an insulating layer that covers surfaces of the semiconductor layer and the exposed portion;
An insulating layer removing step of removing the insulating layer so as to ensure insulation between the n layer and the p layer to form an electrode formation region corresponding to the n layer and the p layer;
The method for manufacturing an optical element according to claim 8, further comprising an external electrode forming step of forming external electrodes connected to the n layer and the p layer, respectively, in the electrode forming region.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004252499A JP2006073618A (en) | 2004-08-31 | 2004-08-31 | Optical element and manufacturing method thereof |
| US11/157,174 US20060001035A1 (en) | 2004-06-22 | 2005-06-21 | Light emitting element and method of making same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004252499A JP2006073618A (en) | 2004-08-31 | 2004-08-31 | Optical element and manufacturing method thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006073618A true JP2006073618A (en) | 2006-03-16 |
| JP2006073618A5 JP2006073618A5 (en) | 2007-03-15 |
Family
ID=36153951
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004252499A Withdrawn JP2006073618A (en) | 2004-06-22 | 2004-08-31 | Optical element and manufacturing method thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2006073618A (en) |
Cited By (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008130799A (en) * | 2006-11-21 | 2008-06-05 | Sharp Corp | Semiconductor light-emitting element and method for manufacturing semiconductor light-emitting element |
| WO2009057241A1 (en) * | 2007-11-01 | 2009-05-07 | Panasonic Corporation | Semiconductor light emitting element and semiconductor light emitting device using the same |
| JP2010199395A (en) * | 2009-02-26 | 2010-09-09 | Nichia Corp | Semiconductor light-emitting element |
| JP2012169392A (en) * | 2011-02-14 | 2012-09-06 | Nichia Chem Ind Ltd | Light-emitting device |
| JP2014067876A (en) * | 2012-09-26 | 2014-04-17 | Nichia Chem Ind Ltd | Light-emitting device and method for manufacturing the same |
| JP2014158028A (en) * | 2013-02-18 | 2014-08-28 | Lextar Electronics Corp | Sub-mount of light emitting diode and light emitting device manufacturing method using the same |
| JP2014195064A (en) * | 2013-02-28 | 2014-10-09 | Nichia Chem Ind Ltd | Light-emitting device and process of manufacturing the same |
| JP2015061072A (en) * | 2013-09-17 | 2015-03-30 | 隆達電子股▲ふん▼有限公司 | Light emitting diode |
| KR101826032B1 (en) * | 2011-03-24 | 2018-02-06 | 엘지디스플레이 주식회사 | Light emitting diode chip and method for fabricating the same |
| CN109479354A (en) * | 2016-07-18 | 2019-03-15 | 株式会社流明斯 | Micro- LED array display device |
| WO2019181309A1 (en) * | 2018-03-19 | 2019-09-26 | ソニー株式会社 | Semiconductor light-emitting element and semiconductor light-emitting element production method |
| US10454010B1 (en) | 2006-12-11 | 2019-10-22 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Transparent light emitting diodes |
| US11955583B2 (en) | 2020-12-01 | 2024-04-09 | Lumileds Llc | Flip chip micro light emitting diodes |
-
2004
- 2004-08-31 JP JP2004252499A patent/JP2006073618A/en not_active Withdrawn
Cited By (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008130799A (en) * | 2006-11-21 | 2008-06-05 | Sharp Corp | Semiconductor light-emitting element and method for manufacturing semiconductor light-emitting element |
| US10454010B1 (en) | 2006-12-11 | 2019-10-22 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Transparent light emitting diodes |
| US10658557B1 (en) | 2006-12-11 | 2020-05-19 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Transparent light emitting device with light emitting diodes |
| US10644213B1 (en) | 2006-12-11 | 2020-05-05 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Filament LED light bulb |
| US10593854B1 (en) | 2006-12-11 | 2020-03-17 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Transparent light emitting device with light emitting diodes |
| WO2009057241A1 (en) * | 2007-11-01 | 2009-05-07 | Panasonic Corporation | Semiconductor light emitting element and semiconductor light emitting device using the same |
| WO2009057311A1 (en) * | 2007-11-01 | 2009-05-07 | Panasonic Corporation | Semiconductor light emitting element and semiconductor light emitting device using the same |
| JPWO2009057311A1 (en) * | 2007-11-01 | 2011-03-10 | パナソニック株式会社 | Semiconductor light emitting element and semiconductor light emitting device using the same |
| US8309975B2 (en) | 2007-11-01 | 2012-11-13 | Panasonic Corporation | Semiconductor light emitting element and semiconductor light emitting device using the same |
| JP2010199395A (en) * | 2009-02-26 | 2010-09-09 | Nichia Corp | Semiconductor light-emitting element |
| JP2012169392A (en) * | 2011-02-14 | 2012-09-06 | Nichia Chem Ind Ltd | Light-emitting device |
| KR101826032B1 (en) * | 2011-03-24 | 2018-02-06 | 엘지디스플레이 주식회사 | Light emitting diode chip and method for fabricating the same |
| JP2014067876A (en) * | 2012-09-26 | 2014-04-17 | Nichia Chem Ind Ltd | Light-emitting device and method for manufacturing the same |
| JP2014158028A (en) * | 2013-02-18 | 2014-08-28 | Lextar Electronics Corp | Sub-mount of light emitting diode and light emitting device manufacturing method using the same |
| JP2014195064A (en) * | 2013-02-28 | 2014-10-09 | Nichia Chem Ind Ltd | Light-emitting device and process of manufacturing the same |
| JP2015061072A (en) * | 2013-09-17 | 2015-03-30 | 隆達電子股▲ふん▼有限公司 | Light emitting diode |
| CN109479354A (en) * | 2016-07-18 | 2019-03-15 | 株式会社流明斯 | Micro- LED array display device |
| CN109479354B (en) * | 2016-07-18 | 2021-05-14 | 株式会社流明斯 | Micro LED array display device |
| WO2019181309A1 (en) * | 2018-03-19 | 2019-09-26 | ソニー株式会社 | Semiconductor light-emitting element and semiconductor light-emitting element production method |
| JPWO2019181309A1 (en) * | 2018-03-19 | 2021-03-11 | ソニー株式会社 | Semiconductor light emitting element and manufacturing method of semiconductor light emitting element |
| JP7331833B2 (en) | 2018-03-19 | 2023-08-23 | ソニーグループ株式会社 | Semiconductor light emitting device and method for manufacturing semiconductor light emitting device |
| US11929591B2 (en) | 2018-03-19 | 2024-03-12 | Sony Corporation | Semiconductor light-emitting device and method of manufacturing semiconductor light-emitting device |
| US11955583B2 (en) | 2020-12-01 | 2024-04-09 | Lumileds Llc | Flip chip micro light emitting diodes |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8026527B2 (en) | LED structure | |
| KR102543183B1 (en) | Semiconductor light emitting device | |
| KR101978968B1 (en) | Semiconductor light emitting device and light emitting apparatus | |
| US7429750B2 (en) | Solid-state element and solid-state element device | |
| US20060001035A1 (en) | Light emitting element and method of making same | |
| JP5462433B2 (en) | Semiconductor light emitting device having integrated electronic components | |
| JP5973693B2 (en) | Light emitting device and light emitting device package | |
| EP3534413B1 (en) | Semiconductor device package | |
| KR101276053B1 (en) | Semiconductor light emitting device and light emitting apparatus | |
| JP4459871B2 (en) | Light emitting diode having an adhesive layer with a heat path | |
| JP6558654B2 (en) | Optoelectronic semiconductor chip, optoelectronic semiconductor component, and production method of optoelectronic semiconductor chip | |
| JP2006100787A (en) | Light emitting device and light emitting element | |
| JP2014195064A (en) | Light-emitting device and process of manufacturing the same | |
| US9406635B2 (en) | Semiconductor light emitting device and semiconductor light emitting device package using the same | |
| KR102461968B1 (en) | Light emitting device | |
| US7126163B2 (en) | Light-emitting diode and its manufacturing method | |
| JP2006073618A (en) | Optical element and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2007067184A (en) | Led package | |
| KR20180000032A (en) | Semiconductor light emitting device package | |
| CN113169253A (en) | Micro light-emitting diode and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR101360881B1 (en) | Light emitting diode with conductive connect line | |
| US11888091B2 (en) | Semiconductor light emitting device and light emitting device package | |
| KR100600374B1 (en) | Package for vertical type light emitting diode array and fabricating method thereof | |
| JP2009135538A (en) | Method of manufacturing solid-state element device | |
| JP2004289182A (en) | Semiconductor light emitting device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070130 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070222 |
|
| A761 | Written withdrawal of application |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A761 Effective date: 20081027 |