CN216318989U - Ultraviolet light disinfection chamber structure without disinfection dead angle - Google Patents
Ultraviolet light disinfection chamber structure without disinfection dead angle Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN216318989U CN216318989U CN202123135079.3U CN202123135079U CN216318989U CN 216318989 U CN216318989 U CN 216318989U CN 202123135079 U CN202123135079 U CN 202123135079U CN 216318989 U CN216318989 U CN 216318989U
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- quartz
- disinfection
- slide
- slides
- ultraviolet light
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Abstract
The utility model discloses an ultraviolet light disinfection cavity structure without disinfection dead angles, which comprises three quartz slides with the same size and thickness, wherein the three quartz slides are all rectangular quartz slides formed in a whole block, the adjacent quartz slides are adhered at the outer edges of the long edges, and the section of a disinfection cavity formed by the three mutually adhered quartz slides is an equilateral triangle; and an ultraviolet lamp strip arranged along the length direction of the quartz slide is arranged on the back side of each quartz slide and serves as an ultraviolet light source, and the ultraviolet lamp strip, the shortest connecting line corresponding to the two long sides of the quartz slide and the quartz slide form an equilateral triangle together. The utility model can effectively reduce the size of a radiation dead angle in the ultraviolet disinfection cavity, and the device to be disinfected is enabled to stagger the radiation dead angle through the spacing between the structures so as to ensure the effect of no disinfection dead angle.
Description
Technical Field
The utility model relates to the technical field of medical instrument disinfection, in particular to an ultraviolet disinfection cavity structure without disinfection dead angles.
Background
With the progress of society and the growing concern of people on health, the requirements for disinfection and sterilization treatment in the field of medical appliances are higher and higher, generally speaking, the medical appliances refer to instruments, equipment, apparatuses, in-vitro diagnostic reagents and calibrators, materials and other similar or related articles which are directly or indirectly used for human bodies, and the medical appliances can be used as media to cause secondary infection of pathogenic bacteria, so that before being used, pathogenic microorganisms on the medical appliances need to be killed to achieve the harmless requirements, so that the transmission path of infectious diseases is cut off, and the purpose of preventing and controlling the secondary infection is achieved.
The existing medical apparatus disinfection methods mainly comprise a damp-heat disinfection method, a dry-heat disinfection method, an ultraviolet radiation disinfection method, a gas disinfection method and a filter disinfection method; among them, the moist heat sterilization method is a method of sterilizing microorganisms by denaturing proteins and nucleic acids in microbial cells by means of high-pressure saturated steam, superheated water spray, or the like. The method has strong sterilization capability and low sterilization cost, and is the most effective sterilization method with the most extensive application in thermal sterilization; the dry heat sterilization method utilizes dry hot air to kill microorganisms, and the wet heat sterilization method and the dry heat sterilization method have the defects that the dry heat sterilization method is not suitable for medical appliances with poor heat stability and moisture absorption; the gas sterilization method utilizes a disinfectant in a gasification state for sterilization, but the sterilization gas usually has combustible explosiveness, teratogenicity and residual toxicity, so that certain use risk exists; the filtration sterilization method is a method for removing microorganisms in gas or liquid by utilizing the principle that bacteria cannot pass through a compact porous filter material, is commonly used for sterilization of gas, heat-unstable medicine solution or raw materials, and is not suitable for sterilization of medical instruments.
For the above reasons, the existing medical instruments are often sterilized and sterilized by ultraviolet radiation sterilization, which uses ultraviolet light with specific wavelength to irradiate the surface of the medical instrument, and uses the characteristic of protein absorbing ultraviolet light to generate energy transmission and accumulation, and finally destroys DNA and RNA of microorganisms, so that they lose replication and reproductive capacity, thereby achieving the purpose of sterilization without using any chemical medicine. However, the ultraviolet sterilization equipment in the prior art has the defect of radiation dead angles, which is mainly caused by the light source characteristics of the ultraviolet light source, a quartz glass slide is required to be arranged for guiding the irradiation surface of the light source, and because the arc quartz glass slide has high process cost and a light-gathering effect, the quartz glass slides generally adopt a plane glass slide, when a cavity is manufactured, the glass slides are connected with each other by using an external bracket or a sintering mode, and the intersection of the two glass slides and the sintering surface are opaque, so that the part can not conduct light, and finally, the radiation dead angles occur in the area corresponding to the position, so that the microbial residues are caused, and the medical apparatus sterilized by ultraviolet light can not achieve real high-level sterilization.
SUMMERY OF THE UTILITY MODEL
The technical problem to be solved by the utility model is to provide an ultraviolet disinfection cavity structure without disinfection dead angles, and the arrangement mode of quartz slides is redesigned, so that medical instruments can perfectly avoid radiation dead angles in the disinfection process, and the disinfection effect of the medical instruments is ensured.
The technical problem solved by the utility model is realized by adopting the following technical scheme:
an ultraviolet light disinfection cavity structure without disinfection dead angles comprises three quartz slides with the same size and thickness, wherein the quartz slides are all rectangular quartz slides formed in a whole block, the three quartz slides are fixed in position and jointly form a cylindrical cavity to serve as a disinfection cavity, and the cross section of the disinfection cavity is in an equilateral triangle shape;
the back side of each quartz slide is provided with an ultraviolet light source arranged along the length direction of the quartz slide so that the ultraviolet light source irradiates the whole quartz slide from the outer side.
As a further limitation, the quartz slide is fixed in position by a fixing bracket.
As a further limitation, the quartz slides are connected and fixed in a sintering mode.
As a further limitation, the irradiation intensity of the ultraviolet light source on the surface of the quartz slide is not less thanμm/cm2Wherein X is the optical loss coefficient of the corresponding quartz slide.
Has the advantages that: the ultraviolet light disinfection cavity structure without disinfection dead angles is designed according to a light path structure, and guides ultraviolet light through quartz slides, so that irradiation dead angles generated at the intersection parts of the slides are reduced to the maximum extent and avoided, and medical instruments in the disinfection cavity between the three quartz slides are disinfected without dead angles.
Drawings
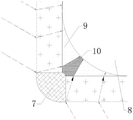
Fig. 1 is a schematic view of the structure of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a diagram of the optical path structure of the position of the radiation dead angle at the edge of the slide glass.
FIG. 3 is a diagram of the structure of the optical path at the radiation dead angle position of the edge of the two slides when the included angle between the two slides is a right angle.
FIG. 4 is a diagram of the structure of the optical path at the radiation dead angle position of the edge of the two slides when the included angle between the two slides is obtuse.
Wherein: 1. a first ultraviolet lamp strip; 2. a first quartz slide; 3. a second quartz slide; 4. a second ultraviolet lamp strip; 5. a third quartz slide; 6. a third ultraviolet lamp strip; 7. a quartz slide sintering section; 8. an appliance to be disinfected; 9. an illumination area; 10. the dead angle area is illuminated.
Detailed Description
In order to make the technical means, the creation characteristics, the achievement purposes and the effects of the utility model easy to understand, the utility model is further explained below by combining the specific drawings.
It should be noted that if directional indications (such as according to the upper, lower, left, right, front and rear … …) are involved in the embodiment of the present invention, the directional indications are only used to explain the relative positional relationship, movement, etc. of the components in a specific posture (according to the figure), and if the specific posture is changed, the directional indications are changed accordingly.
In the following examples, it will be understood by those skilled in the art that, unless otherwise defined, all terms (including technical and scientific terms) used herein have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this application belongs.
Referring to fig. 1, in this embodiment, the ultraviolet disinfection chamber structure includes three quartz slides with the same size and thickness, that is, a first quartz slide 2, a second quartz slide 3, and a third quartz slide 5, where the first quartz slide 2, the second quartz slide 3, and the third quartz slide 5 are all rectangular quartz slides formed in one piece, the first quartz slide 2, the second quartz slide 3, and the third quartz slide 5 are vertically placed in the length direction, and are sintered and connected to form a cylindrical cavity with an isosceles triangle cross section as shown in fig. 1, and an inner side surface of the cylindrical cavity is a disinfection chamber for placing a medical instrument therein for disinfection.
The embodiment of the utility model is an ultraviolet light disinfection chamber, and an ultraviolet light band is arranged on the outer side of each quartz slide and is used as an ultraviolet light source, namely, the ultraviolet light band is correspondingly arranged on a first ultraviolet light band 1 on the outer side of a first quartz slide 2, a second ultraviolet light band 4 on the outer side of a second quartz slide 3 and a third ultraviolet light band 6 on the outer side of a third quartz slide 5. The first ultraviolet lamp strip 1, the second ultraviolet lamp strip 4 and the third ultraviolet lamp strip 6 are arranged at the same positions at the outer sides of the corresponding first quartz slide 2, the second quartz slide 3 and the third quartz slide 5, taking the first ultraviolet lamp strip 1 as an example, the connecting line of the two side edges of the first ultraviolet lamp strip 1 and the first quartz slide 2 and the section line of the first quartz slide 2 jointly form an equilateral triangle as shown by the dotted line in fig. 1. Meanwhile, the dotted line also represents the irradiation surface of the corresponding ultraviolet lamp on the quartz slide; since the first slide glass 2 and the third slide glass 5 are joined by the slide glass sintering portion 7, a sintering seam is inevitably formed between the first slide glass 2 and the third slide glass 5.
In the state shown in fig. 1, the ultraviolet light irradiation situation at the edge position of the sterilization chamber corresponding to the lower left corner position is described, the optical path structure is shown in fig. 2, the dotted line with the arrow indicates the optical path, the ultraviolet light emitted from the first ultraviolet light strip 1 and the third ultraviolet light strip 6 at the outer sides of the first quartz slide 2 and the third quartz slide 5 is irradiated at the edge position corresponding to the first quartz slide 2 and the third quartz slide 5 according to the pattern, because the quartz slide has the thickness, a certain refraction is generated in the quartz slide, and after the refraction and emission, the ultraviolet light is irradiated into the sterilization chamber according to the area shown by the optical path, so as to obtain the illumination area 9 and the illumination dead angle area 10 shown in fig. 2, therefore, in the sterilization chamber, if the apparatus has a certain outer diameter, even if both sides abut against the inner walls at both sides of the first quartz slide 2 and the third quartz slide 5 according to the pattern shown in fig. 1, the illumination dead angle region 10 is also staggered by the angle between the first quartz slide 2 and the third quartz slide 5.
If the first quartz slide 2 and the third quartz slide 5 are unfolded to form a right angle according to the pattern shown in fig. 3, the light path diagram at the right angle position is shown in fig. 3, under the condition of the light path diagram, the illumination dead angle area 10 extends to one side in the disinfection cavity more obviously, under the condition of the to-be-disinfected tool 8 with the same size, the dead angle area 10 can be seen to cover a fan-shaped area on the surface of the to-be-disinfected tool 8, and the fan-shaped area cannot be disinfected through ultraviolet light irradiation due to the existence of the dead angle area 10.
If the included angle between the first quartz slide 2 and the third quartz slide 5 is further unfolded to be in an obtuse angle state, then the light path diagram at the position is obtained as shown in fig. 4, under the condition of the light path diagram, the extension amount of the illumination dead-angle area 10 to one side in the disinfection cavity is geometrically increased, under the condition of the instruments 8 to be disinfected with the same size, the coverage area of the dead-angle area 10 to the surface of the instruments 8 to be disinfected is larger and more obvious, so that the area of the areas which cannot be disinfected by ultraviolet light is larger.
In the embodiment of fig. 2, 3 and 4, the illumination state between the first quartz slide 2 and the third quartz slide 5 only represents the condition of the same quartz slide sintering part 7, namely under the condition of the same quartz slide sintering part 7 of the same slide, the technical proposal of the utility model can obtain the dead angle area 10 with the smallest size and close to the corner in the disinfection chamber, and the dead angle area 10 can be staggered when the apparatus to be disinfected 8 with the corner size is put in, namely the apparatus to be disinfected 8 is larger than the sintering size in the slide in the condition.
In addition, the size of the dead angle region 10 between the first quartz slide 2 and the third quartz slide 5 is also related to the sintering process, that is, the sintering process of the quartz slide sintering part 7 can be optimized by the process so that the gap between the first quartz slide 2 and the third quartz slide 5 is reduced, under the condition of the slide sintering process common in the prior art, the bonding gap between the first quartz slide 2 and the third quartz slide 5 is usually 1.2-3 mm, and the tool to be sterilized 8 with the outer diameter (including the equipment fillet) larger than 8mm can be staggered from the dead angle region 10; under the optimal glass slide bonding process condition, the bonding gap between the first quartz glass slide 2 and the third quartz glass slide 5 can be reduced to 0.5-0.8 mm, the to-be-sterilized instrument 8 with the outer diameter (including the equipment fillet) larger than 1.5mm can be staggered from the dead angle area 10, and the medical to-be-sterilized instrument 8 with the outer diameter smaller than 1.5mm in the market only has a needle point and a blade surface of a cutter, so the technical scheme has wide application range.
In another embodiment, the first quartz slide 2, the second quartz slide 3, and the third quartz slide 5 may also be fixed in position by using a fixing bracket, so as to minimize the gap between the first quartz slide 2 and the third quartz slide 5, the gap between the first quartz slide 2 and the second quartz slide 3, and the gap between the second quartz slide 3 and the third quartz slide 5, which always exists and can only be reduced by the process.
In order to illustrate the effect of the present invention, the bonding gap between the first quartz glass slide 2 and the third quartz glass slide 5 is enlarged under the condition shown in fig. 2 to obtain a dead angle region 10 and an illumination region 9 which are large enough to perform measurement.
Firstly, ultraviolet lamp irradiation intensity tests are carried out on a first ultraviolet lamp strip 1, a second ultraviolet lamp strip 4 and a third ultraviolet lamp strip 6 through measurement, during the tests, the tests are carried out according to the ultraviolet sterilizer sanitary requirement GB28235-2020, the environment temperature is controlled to be 22 ℃, the relative humidity is 45%, the equipment is powered on, an ultraviolet illuminometer probe is placed at the center of a disinfection cabin, ultraviolet irradiation values are respectively measured and recorded, the first ultraviolet lamp strip 1, the second ultraviolet lamp strip 4 and the third ultraviolet lamp strip 6 are respectively detected repeatedly for 3 times, ultraviolet light with the wavelength of 275nm is detected, and the irradiation intensity test results corresponding to the ultraviolet lamp strips are obtained as follows:
corresponding first ultraviolet lamp strip 1, second ultraviolet lamp strip 4, third ultraviolet lamp strip 6 are installed into equipment, and the sterilization effect is measured respectively under the condition of appendix G of ultraviolet sterilizer sanitary requirement GB 28235-2020: the test strains were: bacillus subtilis var niger (ATCC 9372) spore (provided by Proc. military medical sciences); the test carrier is: polytetrafluoroethylene tubes (6 mm in outer diameter, 4mm in inner diameter and 3cm in length) are sterilized for later use; bacterial suspension is prepared, and the concentration of the suspension is 108And (3) taking 20 mu l of the solution transfer gun to dye the outer wall of the test carrier, uniformly coating the solution transfer gun, and drying the solution transfer gun in an incubator at 37 ℃ to prepare the bacteria-infected carrier.
Placing the carriers infected with the bacteria in the dead angle area 10 and the illumination area 9 respectively, starting the ultraviolet lamp band for disinfection for 60s, taking out the carriers for counting, taking the dead angle area 10 as a positive control group, calculating a killing logarithm value, repeating the test for three times, wherein the carriers infected with the bacteria in the illumination area 9 all grow aseptically, and the positive control group obtains the following results:
| test number | Action time (S) | Positive control colony count (CFU/sample) | Log value of colony number recovered from positive control group | Killing |
| 1 | 60 | 2800000 | 6.45 | ≥3.00 |
| 2 | 60 | 2500000 | 6.4 | ≥3.00 |
| 3 | 60 | 2600000 | 6.41 | ≥3.00 |
Therefore, the killing logarithm values of the bacillus subtilis var niger spores on the outer wall of the polytetrafluoroethylene tube carrier in the illumination area 9 are all more than or equal to 3.00, and the requirements of ultraviolet sterilizer sanitary requirements GB28235-2020 are met; whereas the dead-angle area 10 has no bactericidal effect.
The foregoing shows and describes the general principles, essential features, and advantages of the utility model. It will be understood by those skilled in the art that the present invention is not limited to the embodiments described above, which are described in the specification and illustrated only to illustrate the principle of the present invention, but that various changes and modifications may be made therein without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention, which fall within the scope of the utility model as claimed. The scope of the utility model is defined by the appended claims and equivalents thereof.
Claims (4)
1. The ultraviolet light disinfection cavity structure without disinfection dead angles is characterized by comprising three quartz slides with the same size and thickness, wherein the quartz slides are all rectangular quartz slides formed in one piece, the three quartz slides are fixed in position and jointly form a cylindrical cavity to serve as a disinfection cavity, and the cross section of the disinfection cavity is in an equilateral triangle shape;
the back side of each quartz slide is provided with an ultraviolet light source arranged along the length direction of the quartz slide so that the ultraviolet light source irradiates the whole quartz slide from the outer side.
2. The UV disinfection chamber structure without disinfection dead corners of claim 1, wherein the quartz slide is fixed in position by a fixing bracket.
3. The ultraviolet disinfection chamber structure without disinfection dead corners of claim 1, wherein the quartz slides are connected and fixed in a sintering manner between every two quartz slides.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202123135079.3U CN216318989U (en) | 2021-12-14 | 2021-12-14 | Ultraviolet light disinfection chamber structure without disinfection dead angle |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202123135079.3U CN216318989U (en) | 2021-12-14 | 2021-12-14 | Ultraviolet light disinfection chamber structure without disinfection dead angle |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN216318989U true CN216318989U (en) | 2022-04-19 |
Family
ID=81164751
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202123135079.3U Active CN216318989U (en) | 2021-12-14 | 2021-12-14 | Ultraviolet light disinfection chamber structure without disinfection dead angle |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN216318989U (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114159595A (en) * | 2021-12-14 | 2022-03-11 | 湖南海尔斯医疗科技有限公司 | Ultraviolet light disinfection chamber structure without disinfection dead angle |
-
2021
- 2021-12-14 CN CN202123135079.3U patent/CN216318989U/en active Active
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114159595A (en) * | 2021-12-14 | 2022-03-11 | 湖南海尔斯医疗科技有限公司 | Ultraviolet light disinfection chamber structure without disinfection dead angle |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8481985B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for producing a high level of disinfection in air and surfaces | |
| US20220133920A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for sterilizing and disinfecting air and surfaces and protecting a zone from external microbial contamination | |
| US9700642B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for sterilizing and disinfecting air and surfaces and protecting a zone from external microbial contamination | |
| US6576188B1 (en) | Surface and air sterilization using ultraviolet light and ultrasonic waves | |
| Ohkawa et al. | Pulse-modulated, high-frequency plasma sterilization at atmospheric-pressure | |
| CN104368020B (en) | Ultraviolet laser sterilization system | |
| EP1261699A1 (en) | Protecting molecules in biologically derived compositions while treating with broad-spectrum pulsed light | |
| CN216318989U (en) | Ultraviolet light disinfection chamber structure without disinfection dead angle | |
| Hooks et al. | Use of the carbon dioxide laser in sterilization of endodontic reamers | |
| WO2020155852A1 (en) | Ultrasonic probe sterilizer | |
| CN114159595A (en) | Ultraviolet light disinfection chamber structure without disinfection dead angle | |
| AU779193B2 (en) | Methods of inactivating pathogens using broad-spectrum pulsed light | |
| CN205095065U (en) | Ultraviolet sterilizer | |
| WO2019061035A1 (en) | Ultraviolet system for disinfection and ultraviolet disinfection method | |
| CN104511034B (en) | Ultrasonic-B probe sterilizer | |
| CN104840980A (en) | Medical instrument disinfection box | |
| CN204411342U (en) | Ultrasonic-B probe disinfector | |
| WO2021155727A1 (en) | Clothes disinfection device | |
| CN201524282U (en) | Ultraviolet sterilization apparatus | |
| CN1456358A (en) | Device and method for fast inactivating causative agent in gas with microwave | |
| CN106421864A (en) | Improved method and improved equipment for generating high disinfection effect in air and surface | |
| CN2621678Y (en) | Appts. for fast inactivating air pathogen by microwave | |
| Walker et al. | The efficacy of ultraviolet radiation for sterilizing tools used for surgically implanting transmitters into fish | |
| CN215780170U (en) | Microwave device for killing bacteria and viruses | |
| CN211236431U (en) | Microscopic imaging system for epidemiological analysis |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |