WO2019146513A1 - 流体漏れ検出機器及び往復動型流体圧機器 - Google Patents
流体漏れ検出機器及び往復動型流体圧機器 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2019146513A1 WO2019146513A1 PCT/JP2019/001402 JP2019001402W WO2019146513A1 WO 2019146513 A1 WO2019146513 A1 WO 2019146513A1 JP 2019001402 W JP2019001402 W JP 2019001402W WO 2019146513 A1 WO2019146513 A1 WO 2019146513A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- cylinder head
- piston rod
- fluid
- annular member
- press
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B15/00—Fluid-actuated devices for displacing a member from one position to another; Gearing associated therewith
- F15B15/08—Characterised by the construction of the motor unit
- F15B15/14—Characterised by the construction of the motor unit of the straight-cylinder type
- F15B15/1423—Component parts; Constructional details
- F15B15/1428—Cylinders
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B15/00—Fluid-actuated devices for displacing a member from one position to another; Gearing associated therewith
- F15B15/08—Characterised by the construction of the motor unit
- F15B15/14—Characterised by the construction of the motor unit of the straight-cylinder type
- F15B15/1423—Component parts; Constructional details
- F15B15/1433—End caps
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B15/00—Fluid-actuated devices for displacing a member from one position to another; Gearing associated therewith
- F15B15/08—Characterised by the construction of the motor unit
- F15B15/14—Characterised by the construction of the motor unit of the straight-cylinder type
- F15B15/1423—Component parts; Constructional details
- F15B15/1457—Piston rods
- F15B15/1461—Piston rod sealings
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B15/00—Fluid-actuated devices for displacing a member from one position to another; Gearing associated therewith
- F15B15/20—Other details, e.g. assembly with regulating devices
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B19/00—Testing; Calibrating; Fault detection or monitoring; Simulation or modelling of fluid-pressure systems or apparatus not otherwise provided for
- F15B19/005—Fault detection or monitoring
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B20/00—Safety arrangements for fluid actuator systems; Applications of safety devices in fluid actuator systems; Emergency measures for fluid actuator systems
- F15B20/005—Leakage; Spillage; Hose burst
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16J—PISTONS; CYLINDERS; SEALINGS
- F16J15/00—Sealings
- F16J15/002—Sealings comprising at least two sealings in succession
- F16J15/004—Sealings comprising at least two sealings in succession forming of recuperation chamber for the leaking fluid
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16J—PISTONS; CYLINDERS; SEALINGS
- F16J15/00—Sealings
- F16J15/16—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces
- F16J15/32—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with elastic sealings, e.g. O-rings
- F16J15/3204—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with elastic sealings, e.g. O-rings with at least one lip
- F16J15/3232—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with elastic sealings, e.g. O-rings with at least one lip having two or more lips
- F16J15/3236—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with elastic sealings, e.g. O-rings with at least one lip having two or more lips with at least one lip for each surface, e.g. U-cup packings
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16J—PISTONS; CYLINDERS; SEALINGS
- F16J15/00—Sealings
- F16J15/16—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces
- F16J15/32—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with elastic sealings, e.g. O-rings
- F16J15/3296—Arrangements for monitoring the condition or operation of elastic sealings; Arrangements for control of elastic sealings, e.g. of their geometry or stiffness
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16J—PISTONS; CYLINDERS; SEALINGS
- F16J15/00—Sealings
- F16J15/56—Other sealings for reciprocating rods
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B2211/00—Circuits for servomotor systems
- F15B2211/50—Pressure control
- F15B2211/505—Pressure control characterised by the type of pressure control means
- F15B2211/50509—Pressure control characterised by the type of pressure control means the pressure control means controlling a pressure upstream of the pressure control means
- F15B2211/50518—Pressure control characterised by the type of pressure control means the pressure control means controlling a pressure upstream of the pressure control means using pressure relief valves
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B2211/00—Circuits for servomotor systems
- F15B2211/60—Circuit components or control therefor
- F15B2211/63—Electronic controllers
- F15B2211/6303—Electronic controllers using input signals
- F15B2211/6306—Electronic controllers using input signals representing a pressure
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B2211/00—Circuits for servomotor systems
- F15B2211/80—Other types of control related to particular problems or conditions
- F15B2211/86—Control during or prevention of abnormal conditions
- F15B2211/863—Control during or prevention of abnormal conditions the abnormal condition being a hydraulic or pneumatic failure
- F15B2211/864—Failure of an output member, e.g. actuator or motor failure
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B2211/00—Circuits for servomotor systems
- F15B2211/80—Other types of control related to particular problems or conditions
- F15B2211/865—Prevention of failures
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B2211/00—Circuits for servomotor systems
- F15B2211/80—Other types of control related to particular problems or conditions
- F15B2211/87—Detection of failures
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a fluid leak detection device and a reciprocating fluid pressure device.
- a reciprocating fluid pressure device such as a fluid pressure cylinder or a shock absorber
- the working fluid may leak from between the cylinder head and the piston rod due to deterioration of the seal member provided on the inner periphery of the cylinder head. If the amount of leakage of the working fluid is increased, the reciprocating fluid pressure device may not be able to achieve its intended performance. For these reasons, it has been proposed that a fluid leak detection device be attached to a cylinder head to detect a leak of working fluid (JPS 62-240275A).
- the fluid leak detection device disclosed in JPS62-240275A is attached to the cylinder head using a bolt. Therefore, in order to attach the fluid leak detection device to the cylinder head of the reciprocating fluid pressure device, it is necessary to form a hole for fixing the bolt in the cylinder head, and the fluid leak detection device can be easily attached. Can not.
- the present invention aims to facilitate the installation of a fluid leak detection device on a cylinder head.
- the fluid leak detector is attached to the cylinder head and formed into an annular member through which the piston rod passes, and an annular member, from between the outer periphery of the piston rod and the inner periphery of the cylinder head
- the annular member has a press-in portion press-fit into an annular groove formed in the cylinder head.
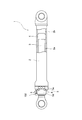
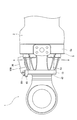
- FIG. 1 is a partial sectional view of a hydraulic cylinder according to an embodiment of the present invention.
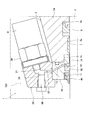
- FIG. 2 is an enlarged cross-sectional view of the hydraulic cylinder shown in FIG. 1 showing a fluid leak detector.
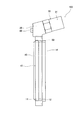
- FIG. 3 is a front view of a fluid leak detection device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 4 is an enlarged cross-sectional view of a hydraulic cylinder used with no fluid leak detection device attached, corresponding to FIG.
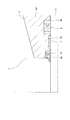
- FIG. 5 is an enlarged view showing the periphery of the cylinder head.
- FIG. 6 is an enlarged view showing the periphery of the cylinder head, and shows a state rotated 90 degrees around the axis from the state shown in FIG.
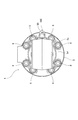
- FIG. 7 is an axial view of the hydraulic cylinder shown in FIG.
- the hydraulic cylinder 1 includes a cylindrical cylinder tube 2, a piston rod 3 inserted into the cylinder tube 2, and a piston 4 provided at one end of the piston rod 3.
- the piston 4 is slidable along the inner peripheral surface of the cylinder tube 2, and the inside of the cylinder tube 2 is divided by the piston 4 into a rod side chamber 2 a and an opposite rod side chamber 2 b.
- the piston rod 3 extends from the open end of the cylinder tube 2.
- hydraulic fluid is selectively introduced from the hydraulic pressure source (not shown) to the rod side chamber 2 a or the opposite rod side chamber 2 b, the piston rod 3 moves relative to the cylinder tube 2.
- the hydraulic cylinder 1 is operated to expand and contract.
- a cylinder head 5 At the open end of the cylinder tube 2 is provided a cylinder head 5 through which the piston rod 3 is inserted.
- the cylinder head 5 is fastened to the open end of the cylinder tube 2 using a plurality of bolts 6 as fastening members.
- annular grooves 5 a and 5 b are formed on the inner periphery of the cylinder head 5.
- a bush 7 as a bearing for slidably supporting the piston rod 3 is disposed.
- a U-packing 8 as a sealing member is disposed in the annular groove 5b.
- the U-packing 8 is compressed between the outer periphery of the piston rod 3 and the inner periphery of the cylinder head 5 to seal between them. Thereby, the hydraulic oil in the rod side chamber 2a (see FIG. 1) can be prevented from leaking to the outside.
- the bush 7 and the U-packing 8 are provided on the inner periphery of the cylinder head 5 in this order in the direction in which the hydraulic cylinder 1 contracts, but may be provided in the reverse order.
- the U-packing 8 is worn by the expansion / contraction operation of the hydraulic cylinder 1, that is, the reciprocation of the piston rod 3, and the sealability gradually decreases.
- the sealing performance decreases, the amount of hydraulic fluid leaking from the rod side chamber 2a between the outer periphery of the piston rod 3 and the inner periphery of the cylinder head 5 increases.
- the hydraulic cylinder 1 may not be able to exhibit the desired performance.
- the hydraulic cylinder 1 is provided with a fluid leak detection device 100 in order to grasp the deterioration in performance caused by the hydraulic fluid leak.
- the fluid leak detection device 100 includes an annular member 10 attached to the tip of the cylinder head 5 through which the piston rod 3 is inserted, a sensor holder 20 provided on the outer periphery of the annular member 10, and a sensor And a pressure sensor 30 as a detector held by the holder 20.
- the sensor holder 20 is fastened to the annular member 10 using a bolt not shown.
- the pressure sensor 30 is screwed and fixed to a hole 21 formed in the sensor holder 20.
- Annular grooves 11 and 12 are formed on the inner periphery of the annular member 10.
- a dust seal 40 which prevents dust from entering the cylinder tube 2 from the outside, is press-fit into the annular groove 11, and a U-packing 50 as a seal member is disposed in the annular groove 12.
- the dust seal 40 and the U-packing 50 are provided in this order in the direction in which the hydraulic cylinder 1 contracts.
- the U-packing 50 is compressed between the outer periphery of the piston rod 3 and the inner periphery of the annular member 10 to seal between them.
- the hydraulic oil introduced from the rod side chamber 2a (see FIG. 1) to the annular groove 12 through the gap between the outer periphery of the piston rod 3 and the inner periphery of the cylinder head 5 is prevented from leaking into the annular groove 11. it can.
- the annular member 10 is formed with a passage 13 passing between the bottom of the annular groove 12 and the outer periphery of the annular member 10.
- the U-packing 50 is disposed in the annular groove 12 so as not to close the opening of the passage 13, and the hydraulic oil guided to the annular groove 12 flows into the passage 13.
- the sensor holder 20 is formed with a passage 22 communicating the passage 13 of the annular member 10 and the hole 21 of the sensor holder 20. Therefore, the hydraulic oil that has flowed into the passage 13 is guided to the hole 21 of the sensor holder 20 through the passage 22.
- the pressure sensor 30 is attached to the sensor holder 20 so as to detect the pressure of the hydraulic fluid introduced to the hole 21 of the sensor holder 20.
- the pressure in the bore 21 increases with the increase of the amount of hydraulic fluid introduced into the bore 21.
- the amount of hydraulic fluid introduced into the hole 21 increases with the increase of the amount of hydraulic fluid leaking from the rod side chamber 2a (see FIG. 1) between the outer periphery of the piston rod 3 and the inner periphery of the cylinder head 5. Therefore, by measuring the pressure in the hole 21 using the pressure sensor 30, it is possible to grasp the leakage amount of the hydraulic oil.
- the pressure sensor 30 transmits a signal corresponding to the detected pressure by a transmitter 31 to a processing unit (not shown) in a wired or wireless manner.
- the processing unit determines the deterioration state of the U-packing 8 based on the detected pressure. If the detected pressure is equal to or less than a preset threshold value, the processing unit determines that the U-packing 8 replacement time has not been reached. When the detected pressure exceeds a preset threshold value, the processing unit determines that the U-packing 8 replacement time has been reached, and the U-packing 8 replacement time has been reached by a not-shown warning lamp or the like. Notify the operator.
- deterioration of the U-packing 8 can be known based on the pressure detected by the pressure sensor 30 of the fluid leak detection device 100. Therefore, the replacement time of the U-packing 8 can be easily managed.
- the annular member 10 has a press-fit portion 14 which is press-fit into an annular groove 5 c formed in the cylinder head 5.
- the outer diameter of the press-fit portion 14 is slightly larger than the inner diameter of the annular groove 5 c in a state before being press-fitted into the annular groove 5 c. Therefore, the press-fit portion 14 is tightened by the annular groove 5 c in a state of being press-fitted into the annular groove 5 c. Thereby, the press-fit portion 14 is fixed in the annular groove 5 c, and the annular member 10 is attached to the cylinder head 5.
- the annular member 10 can be attached to the cylinder head 5 by press-fitting the press-fit portion 14 into the annular groove 5c. Therefore, the fluid leak detection device 100 can be attached to the cylinder head 5 without forming a hole for fixing a fastening member such as a bolt in the cylinder head 5.
- the annular member 10 is attached to the cylinder head 5 by press-fitting the press-fit portion 14 into the annular groove 5 c, the position of the pressure sensor 30 in the circumferential direction can be easily adjusted when attaching the annular member 10 to the cylinder head 5 can do.
- the cylinder head 5 has a holding portion 5 d for holding the bush 7 and the U-packing 8, and a flange portion 5 e projecting radially from the holding portion 5 d.
- a plurality of holes (not shown) penetrating in the axial direction are formed in the flange portion 5e.
- the bolt 6 is inserted through the hole of the flange 5 e to press the flange 5 e against the open end of the cylinder tube 2.
- the bolts 6 are arranged side by side in the circumferential direction, and axially project from the flange portion 5 e of the cylinder head 5.
- the fluid leak detection device 100 is attached to the tip of the cylinder head 5 such that the pressure sensor 30 is disposed between the bolts 6 adjacent in the circumferential direction. Therefore, interference between the pressure sensor 30 and the bolt 6 can be prevented. Therefore, the pressure sensor 30 can be disposed in the vicinity of the flange portion 5e of the cylinder head 5, and the hydraulic cylinder 1 can be miniaturized.
- the pressure sensor 30 may be disposed between the bolts 6, and the fluid leak detection device 100 may be mounted on the cylinder head 5 by a method other than press fitting. It may be attached.
- the outer diameter of the press-in portion 14 is substantially equal to the outer diameter of the dust seal 40. Therefore, as shown in FIG. 4, the dust seal 40 removed from the annular groove 11 of the annular member 10 can be press-fit into the annular groove 5 c of the cylinder head 5 instead of the press-fit portion 14 of the annular member 10. Therefore, the hydraulic cylinder 1 can be used with the fluid leak detection device 100 removed from the cylinder head 5 and the dust seal 40 attached to the cylinder head 5.
- the fluid leak detection device 100 can be easily attached and used, and the fluid leak detection device 100 can be easily detached and used.
- the fluid leak detection device 100 when the hydraulic cylinder 1 is used in a state where the fluid leak detection device 100 is not attached, the fluid leak detection device 100 is used when it is necessary to manage the amount of hydraulic fluid leak due to a change in the use environment. To easily manage the amount of hydraulic fluid leakage. The same applies to the reverse.
- the sensor holder 20 is also provided with a relief valve 60 connected to the passage 13 of the annular member 10 in parallel with the pressure sensor 30.
- the sensor holder 20 is formed with a branch passage 23 branched from the passage 22, and the branch passage 23 is provided with a relief valve 60.
- the relief valve 60 opens when the pressure of the hydraulic oil in the branch passage 23 reaches a predetermined pressure, and discharges the hydraulic oil from the passage 22 through the branch passage 23 to the outside.
- the pressure in the passage 22 is limited by the relief valve 60 to a predetermined pressure.
- this predetermined pressure is also referred to as "opening pressure".
- the valve opening pressure of the relief valve 60 is set smaller than the pressure of the hydraulic fluid when the press-fit portion 14 of the annular member 10 is extracted from the annular groove 5c by the hydraulic fluid. Therefore, it is possible to prevent the force that the press-fit portion 14 is extracted from the annular groove 5c from acting on the annular member 10. As a result, the fluid leak detection device 100 can be more reliably attached to the cylinder head 5 even when the sealing performance of the U-packing 8 is reduced and the amount of leakage is increased.
- the bush 7 is provided coaxially with the inner periphery of the cylinder head 5 instead of the inner periphery of the annular member 10. Therefore, the piston rod 3 can be supported coaxially with the cylinder head 5.
- the annular member 10 can be provided coaxially with the piston rod 3 by press-fitting the press-fit portion 14 into the annular groove 5 c and attaching the annular member 10 coaxially to the cylinder head 5.
- the press-fit portion 14 of the annular member 10 is press-fit into the annular groove 5 c of the cylinder head 5, whereby the annular member 10 is attached to the cylinder head 5. Therefore, the fluid leak detection device 100 can be easily attached to the cylinder head 5 as compared with the case where the annular member 10 is attached to the cylinder head 5 using a fastening member such as a bolt.
- the hydraulic oil leaking from between the outer periphery of the piston rod 3 and the inner periphery of the cylinder head 5 is guided to the passage 13 by the U-packing 50. Therefore, the hydraulic oil can be reliably guided by the pressure sensor 30, and the leakage of the hydraulic oil can be detected more reliably.
- the relief valve 60 can prevent the force that the press-in portion 14 is extracted from the annular groove 5c from acting on the annular member 10. Therefore, the fluid leak detection device 100 can be attached to the cylinder head 5 more reliably.
- the present embodiment is a fluid leak detection for detecting a leak of hydraulic oil from between a piston rod 3 extending from a cylinder tube 2 and a cylinder head 5 provided in the cylinder tube 2 and through which the piston rod 3 is inserted.
- the device 100 is related.
- the fluid leak detection device 100 is attached to the cylinder head 5 and formed into an annular member 10 through which the piston rod 3 is inserted, and the annular member 10, and hydraulic oil from between the outer periphery of the piston rod 3 and the inner periphery of the cylinder head 5
- the annular member 10 has a press-fitting portion 14 press-fit into an annular groove 5 c formed in the cylinder head 5.
- the pressure sensor 30 detects a hydraulic fluid introduced through the passage 13.
- the annular member 10 can be attached to the cylinder head 5 by press-fitting the press-fit portion 14 of the annular member 10 into the annular groove 5 c of the cylinder head 5. Therefore, the fluid leak detection device 100 can be easily attached to the cylinder head 5.
- the fluid leak detection device 100 is provided on the inner periphery of the annular member 10 and closes the space between the inner periphery of the annular member 10 and the outer periphery of the piston rod 3 to U packing 50 which leads hydraulic fluid to passage 13 from between.
- the fluid leak detection device 100 further includes a relief valve 60 connected to the passage 13 in parallel with the pressure sensor 30 and opening when the pressure in the passage 13 reaches a predetermined pressure, and the predetermined pressure is press-fit by hydraulic oil The pressure of the hydraulic oil when the portion 14 is withdrawn from the annular groove 5c is smaller.
- the relief valve 60 can prevent the force that the press-in portion 14 is extracted from the annular groove 5 c from acting on the annular member 10. Therefore, the fluid leak detection device 100 can be attached to the cylinder head 5 more reliably.
- the hydraulic cylinder 1 is provided on the cylinder tube 2, the piston rod 3 extending from the cylinder tube 2, the cylinder tube 2, the cylinder head 5 through which the piston rod 3 is inserted, and the cylinder head 5.
- a passage 13 formed in the annular member 10 and through which the hydraulic oil is introduced from between the outer periphery of the piston rod 3 and the inner periphery of the cylinder head 5, and the hydraulic oil introduced through the passage 13 A pressure sensor 30 is provided, and the annular member 10 has a press-fit portion 14 press-fitted into an annular groove 5 c formed in the cylinder head 5.
- the annular member 10 can be attached to the cylinder head 5 by press-fitting the press-fit portion 14 of the annular member 10 into the annular groove 5 c of the cylinder head 5. Therefore, the fluid leak detection device 100 can be easily attached to the cylinder head 5.
- the hydraulic cylinder 1 further includes a bush 7 provided on the inner periphery of the cylinder head 5 and slidably supporting the piston rod 3.
- the piston rod 3 can be supported coaxially with the cylinder head 5.
- the hydraulic cylinder 1 further includes a plurality of bolts 6 protruding from the cylinder head 5, and the pressure sensor 30 is disposed between the bolts 6.
- the pressure sensor 30 can be disposed in the vicinity of the cylinder head 5, and the hydraulic cylinder 1 can be miniaturized.
- the reciprocating fluid pressure device is the hydraulic cylinder 1
- the fluid leak detection device 100 may be used for a shock absorber or the like as a reciprocating fluid pressure device.
- a working fluid not only hydraulic fluid but water and other liquids may be used, for example.
- the sealing member was U packing 8 and 50 .
- the present invention is not limited to this, and any type of seal member may be disposed in a compressed state between the piston rod 3 and the cylinder head 5 or the annular member 10 so as to prevent leakage of hydraulic oil.
- it may be an O-ring.
- the detector may be a sensor that detects the hydraulic oil leak by detecting the pressure force of the U-packing 50.
- the passage 13 opens at the bottom of the annular groove 12.
- the passage 13 may be formed to open to the inner peripheral surface of the press-fit portion 14 through the press-fit portion 14.
- the annular groove 12 and the press-fit portion 14 can be brought close to each other, and the fluid leak detection device 100 can be miniaturized.
Abstract
流体漏れ検出機器(100)は、シリンダヘッド(5)に取り付けられ、ピストンロッド(3)が挿通する環状部材(10)と、環状部材(10)に形成され、ピストンロッド(3)の外周とシリンダヘッド(5)の内周との間から作動油が導かれる通路(13)と、通路(13)を通じて導かれる作動油を検出する圧力センサ(30)と、を備え、環状部材(10)は、シリンダヘッド(5)に形成される環状溝(5c)に圧入される圧入部(14)を有する。
Description
本発明は、流体漏れ検出機器及び往復動型流体圧機器に関する。
流体圧シリンダや緩衝器等の往復動型流体圧機器では、シリンダヘッドの内周に設けられるシール部材の劣化により、シリンダヘッドとピストンロッドとの間から作動流体が漏れることがある。作動流体の漏れ量が増加すると、往復動型流体圧機器が所期の性能を発揮できなくなるおそれがある。このような理由から、流体漏れ検出機器をシリンダヘッドに取り付け、作動流体の漏れを検出することが提案されている(JPS62-240275A)。
JPS62-240275Aに開示される流体漏れ検出機器は、ボルトを用いてシリンダヘッドに取り付けられている。そのため、この流体漏れ検出機器を往復動型流体圧機器のシリンダヘッドに取り付けるためには、ボルトを固定するための穴をシリンダヘッドに形成する必要があり、流体漏れ検出機器を容易に取り付けることができない。
本発明は、シリンダヘッドへの流体漏れ検出機器の取り付けを容易にすることを目的とする。
本発明のある態様によれば、流体漏れ検出器は、シリンダヘッドに取り付けられ、ピストンロッドが挿通する環状部材と、環状部材に形成され、ピストンロッドの外周とシリンダヘッドの内周との間から作動流体が導かれる通路と、通路を通じて導かれる作動流体を検出する検出器と、を備え、環状部材は、シリンダヘッドに形成される環状溝に圧入される圧入部を有する。
以下、図面を参照して、本発明の実施形態に係る流体漏れ検出機器100及び流体漏れ検出機器100を備える往復動型流体圧機器としての油圧シリンダ1について説明する。
図1に示すように、油圧シリンダ1は、筒状のシリンダチューブ2と、シリンダチューブ2に挿入されるピストンロッド3と、ピストンロッド3の一端に設けられるピストン4と、を備える。ピストン4は、シリンダチューブ2の内周面に沿って摺動自在であり、シリンダチューブ2の内部は、ピストン4によってロッド側室2aと反ロッド側室2bとに区画される。
ピストンロッド3は、シリンダチューブ2の開口端から延出している。図示しない油圧源からロッド側室2a又は反ロッド側室2bに選択的に作動油が導かれると、ピストンロッド3は、シリンダチューブ2に対して移動する。これにより、油圧シリンダ1は伸縮作動する。
シリンダチューブ2の開口端には、ピストンロッド3が挿通するシリンダヘッド5が設けられる。シリンダヘッド5は、締結部材としての複数のボルト6を用いてシリンダチューブ2の開口端に締結される。
図2に示すように、シリンダヘッド5の内周には環状溝5a,5bが形成されている。環状溝5aには、ピストンロッド3を摺動自在に支持する軸受としてのブッシュ7が配置される。
環状溝5bには、シール部材としてのUパッキン8が配置される。Uパッキン8は、ピストンロッド3の外周とシリンダヘッド5の内周との間で圧縮されており、これらの間を封止する。これにより、ロッド側室2a(図1参照)内の作動油が外部に漏れることを防止することができる。
なお、ブッシュ7及びUパッキン8は、油圧シリンダ1が収縮する方向にこの順でシリンダヘッド5の内周に設けられているが、逆の順で設けられていてもよい。
Uパッキン8は、油圧シリンダ1の伸縮動作、即ちピストンロッド3の往復動により摩耗し、シール性が徐々に低下する。シール性の低下に伴って、ロッド側室2aからピストンロッド3の外周とシリンダヘッド5の内周との間を通じて漏れる作動油の量が増加する。作動油の漏れ量が増加すると、油圧シリンダ1は、所期の性能を発揮できなくなるおそれがある。油圧シリンダ1は、作動油の漏れに伴う性能の低下を把握するために、流体漏れ検出機器100を備える。
以下、図2及び図3を参照して、流体漏れ検出機器100について詳述する。
図2及び図3に示すように、流体漏れ検出機器100は、シリンダヘッド5の先端に取り付けられピストンロッド3が挿通する環状部材10と、環状部材10の外周に設けられるセンサホルダ20と、センサホルダ20に保持される検出器としての圧力センサ30と、を備える。センサホルダ20は、図示しないボルトを用いて環状部材10に締結される。圧力センサ30は、センサホルダ20に形成される穴21に螺合により固定されている。
環状部材10の内周には、環状溝11,12が形成される。環状溝11には、外部からシリンダチューブ2内へのダストの侵入を防止するダストシール40が圧入され、環状溝12には、シール部材としてのUパッキン50が配置される。ダストシール40及びUパッキン50は、油圧シリンダ1が収縮する方向にこの順で設けられる。
Uパッキン50は、ピストンロッド3の外周と環状部材10の内周との間で圧縮されており、これらの間を封止する。これにより、ロッド側室2a(図1参照)からピストンロッド3の外周とシリンダヘッド5の内周との間を通じて環状溝12に導かれた作動油が環状溝11に漏れ出るのを防止することができる。
環状部材10には、環状溝12の底面と環状部材10の外周との間を貫通する通路13が形成される。Uパッキン50は、通路13の開口を塞がないように環状溝12に配置されており、環状溝12に導かれた作動油は、通路13に流入する。
センサホルダ20には、環状部材10の通路13とセンサホルダ20の穴21とを連通する通路22が形成されている。そのため、通路13に流入した作動油は、通路22を通じてセンサホルダ20の穴21に導かれる。
圧力センサ30は、センサホルダ20の穴21に導かれる作動油の圧力を検出するようにセンサホルダ20に取り付けられる。穴21内の圧力は、穴21に導かれる作動油の量の増加とともに増加する。また、穴21に導かれる作動油の量は、ロッド側室2a(図1参照)からピストンロッド3の外周とシリンダヘッド5の内周との間を通じて漏れる作動油の量の増加とともに増加する。したがって、圧力センサ30を用いて穴21内の圧力を測定することにより、作動油の漏れ量を把握することが可能になる。
また、作動油の漏れ量は、Uパッキン8の劣化により増加するので、作動油の漏れ量を把握することにより、Uパッキン8の劣化を把握することが可能になる。具体的には、圧力センサ30は、検出した圧力に応じた信号をトランスミッタ31により図示しない処理部に有線又は無線で送信する。処理部は、検出された圧力に基づいて、Uパッキン8の劣化状態を判定する。検出された圧力が予め設定された閾値以下である場合には、処理部は、Uパッキン8の交換時期に達していないと判断する。検出された圧力が予め設定された閾値を越えた場合には、処理部は、Uパッキン8の交換時期に達したと判断し、図示しない警告ランプ等により、Uパッキン8の交換時期に達したことをオペレータに通知する。
このように、油圧シリンダ1では、流体漏れ検出機器100の圧力センサ30により検出された圧力に基づいてUパッキン8の劣化を知ることができる。したがって、Uパッキン8の交換時期を容易に管理することができる。
次に、流体漏れ検出機器100を油圧シリンダ1のシリンダヘッド5に取り付けるための構造について説明する。
環状部材10は、シリンダヘッド5に形成される環状溝5cに圧入される圧入部14を有する。具体的には、圧入部14の外径は、環状溝5cに圧入される前の状態において、環状溝5cの内径と比較してやや大きい。そのため、圧入部14は、環状溝5cに圧入された状態では、環状溝5cにより締められる。これにより、圧入部14が環状溝5c内に固定され、環状部材10がシリンダヘッド5に取り付けられる。
このように、流体漏れ検出機器100では、圧入部14を環状溝5cに圧入することにより、環状部材10をシリンダヘッド5に取り付けることができる。したがって、ボルト等の締結部材を固定するための穴をシリンダヘッド5に形成することなく流体漏れ検出機器100をシリンダヘッド5に取り付けることができる。
また、環状部材10は、環状溝5cへの圧入部14の圧入によってシリンダヘッド5に取り付けられるため、環状部材10をシリンダヘッド5に取り付ける際に、周方向における圧力センサ30の位置を容易に調整することができる。
図2、図5及び図6に示すように、シリンダヘッド5は、ブッシュ7及びUパッキン8を保持する保持部5dと、保持部5dから径方向に突出するフランジ部5eと、を有する。フランジ部5eには軸方向に貫通する複数の孔(図示省略)が形成される。ボルト6は、フランジ部5eの孔を挿通し、フランジ部5eをシリンダチューブ2の開口端に押し付ける。
ボルト6は、周方向に並べて配置され、シリンダヘッド5のフランジ部5eから軸方向に突出している。流体漏れ検出機器100は、圧力センサ30が周方向に隣り合うボルト6どうしの間に配置されるようにシリンダヘッド5の先端に取り付けられる。そのため、圧力センサ30とボルト6との干渉を防ぐことができる。したがって、圧力センサ30をシリンダヘッド5のフランジ部5eの近傍に配置することができ、油圧シリンダ1を小型化することができる。
なお、油圧シリンダ1を小型化するとの目的を達成するためには、ボルト6どうしの間に圧力センサ30が配置されていればよく、流体漏れ検出機器100は圧入以外の方法によってシリンダヘッド5に取り付けられていてもよい。
また、圧入部14の外径は、ダストシール40の外径と略等しい。そのため、図4に示すように、環状部材10の環状溝11から取り外したダストシール40を、環状部材10の圧入部14に代えてシリンダヘッド5の環状溝5cに圧入することができる。したがって、流体漏れ検出機器100をシリンダヘッド5から取り外しダストシール40をシリンダヘッド5に取り付けた状態で油圧シリンダ1を使用することができる。
このように、油圧シリンダ1では、流体漏れ検出機器100を取り付けて使用可能な状態と、流体漏れ検出機器100を取り外して使用可能な状態と、に容易に変えることができる。
例えば、油圧シリンダ1が流体漏れ検出機器100が取り付けられていない状態で使用されている場合に、使用環境の変化によって作動油の漏れ量を管理する必要が生じた際に、流体漏れ検出機器100を取り付けて作動油の漏れ量を容易に管理することができる。その逆についても同様である。
また、センサホルダ20には、圧力センサ30と並列に環状部材10の通路13に接続されるリリーフ弁60が設けられる。具体的には、センサホルダ20には、通路22から分岐する分岐通路23が形成され、分岐通路23にリリーフ弁60が設けられる。リリーフ弁60は、分岐通路23における作動油の圧力が所定の圧力に達すると開弁し、通路22から分岐通路23を通じて作動油を外部に排出する。このように、通路22内の圧力は、リリーフ弁60によって所定の圧力に制限される。以下において、この所定の圧力を「開弁圧」とも称する。
リリーフ弁60の開弁圧は、環状部材10の圧入部14が作動油により環状溝5cから抜き出されるときの作動油の圧力よりも小さく設定される。したがって、圧入部14が環状溝5cから抜き出されるような力が環状部材10に作用するのを防止することができる。これにより、Uパッキン8のシール性が低下して漏れ量が増加したときにも流体漏れ検出機器100をより確実にシリンダヘッド5に取り付けておくことができる。
また、ブッシュ7は、環状部材10の内周ではなく、シリンダヘッド5の内周に同軸に設けられる。したがって、ピストンロッド3をシリンダヘッド5と同軸に支持することができる。環状溝5cに圧入部14を圧入して環状部材10をシリンダヘッド5に同軸に取り付けることにより、環状部材10をピストンロッド3と同軸に設けることができる。
以上の実施形態によれば、以下に示す効果を奏する。
流体漏れ検出機器100では、環状部材10の圧入部14が、シリンダヘッド5の環状溝5cに圧入され、これにより、環状部材10がシリンダヘッド5に取り付けられる。したがって、ボルト等の締結部材を用いて環状部材10をシリンダヘッド5に取り付ける場合と比較して、流体漏れ検出機器100をシリンダヘッド5に容易に取り付けることができる。
また、流体漏れ検出機器100では、ピストンロッド3の外周とシリンダヘッド5の内周との間から漏れる作動油は、Uパッキン50により通路13に導かれる。したがって、作動油を圧力センサ30により確実に導くことができ、作動油の漏れをより確実に検出することができる。
また、流体漏れ検出機器100では、リリーフ弁60により、圧入部14が環状溝5cから抜き出されるような力が環状部材10に作用するのを防止することができる。したがって、流体漏れ検出機器100をより確実にシリンダヘッド5に取り付けておくことができる。
以下、本発明の実施形態の構成、作用、及び効果をまとめて説明する。
本実施形態は、シリンダチューブ2から延出するピストンロッド3と、シリンダチューブ2に設けられピストンロッド3が挿通するシリンダヘッド5と、の間からの作動油の漏れを検出するための流体漏れ検出機器100に係る。流体漏れ検出機器100は、シリンダヘッド5に取り付けられ、ピストンロッド3が挿通する環状部材10と、環状部材10に形成され、ピストンロッド3の外周とシリンダヘッド5の内周との間から作動油が導かれる通路13と、通路13を通じて導かれる作動油を検出する圧力センサ30と、を備え、環状部材10は、シリンダヘッド5に形成される環状溝5cに圧入される圧入部14を有する。
この構成では、環状部材10の圧入部14をシリンダヘッド5の環状溝5cに圧入することによって、環状部材10をシリンダヘッド5に取り付けることができる。したがって、流体漏れ検出機器100をシリンダヘッド5に容易に取り付けることができる。
また、流体漏れ検出機器100は、環状部材10の内周に設けられ、環状部材10の内周とピストンロッド3の外周との間を塞いでピストンロッド3の外周とシリンダヘッド5の内周との間から通路13へ作動油を導くUパッキン50を更に備える。
この構成では、ピストンロッド3の外周とシリンダヘッド5の内周との間から漏れる作動油は、Uパッキン50により通路13に導かれる。したがって、作動油の漏れをより確実に検出することができる。
流体漏れ検出機器100は、圧力センサ30と並列に通路13に接続され、通路13内の圧力が所定の圧力に達すると開弁するリリーフ弁60を更に備え、所定の圧力は、作動油により圧入部14が環状溝5cから抜き出されるときの作動油の圧力よりも小さい。
この構成では、リリーフ弁60により、圧入部14が環状溝5cから抜き出されるような力が環状部材10に作用するのを防止することができる。したがって、流体漏れ検出機器100をより確実にシリンダヘッド5に取り付けておくことができる。
油圧シリンダ1は、シリンダチューブ2と、シリンダチューブ2から延出するピストンロッド3と、シリンダチューブ2に設けられ、ピストンロッド3が挿通するシリンダヘッド5と、シリンダヘッド5に取り付けられ、ピストンロッド3が挿通する環状部材10と、環状部材10に形成され、ピストンロッド3の外周とシリンダヘッド5の内周との間から作動油が導かれる通路13と、通路13を通じて導かれる作動油を検出する圧力センサ30と、を備え、環状部材10は、シリンダヘッド5に形成される環状溝5cに圧入された圧入部14を有する。
この構成では、環状部材10の圧入部14をシリンダヘッド5の環状溝5cに圧入することによって、環状部材10をシリンダヘッド5に取り付けることができる。したがって、流体漏れ検出機器100をシリンダヘッド5に容易に取り付けることができる。
また、油圧シリンダ1は、シリンダヘッド5の内周に設けられ、ピストンロッド3を摺動自在に支持するブッシュ7を更に備える。
この構成では、ピストンロッド3をシリンダヘッド5と同軸に支持することができる。
また、油圧シリンダ1は、シリンダヘッド5から突出する複数のボルト6を更に備え、圧力センサ30は、ボルト6どうしの間に配置される。
この構成では、ボルト6と圧力センサ30との干渉を防止することができる。したがって、圧力センサ30をシリンダヘッド5の近傍に配置することができ、油圧シリンダ1を小型化することができる。
以上、本発明の実施形態について説明したが、上記実施形態は本発明の適用例の一部を示したに過ぎず、本発明の技術的範囲を上記実施形態の具体的構成に限定する趣旨ではない。
上記実施形態では、往復動型流体圧機器が油圧シリンダ1である場合について説明した。これに限らず、流体漏れ検出機器100は、往復動型流体圧機器として緩衝器等に用いられてもよい。また、作動流体としては、作動油に限らず、例えば、水やその他の液体が用いられてもよい。
また、上記実施形態では、シール部材がUパッキン8,50である場合について説明した。これに限らず、シール部材は、ピストンロッド3とシリンダヘッド5又は環状部材10との間に圧縮された状態で配置され、作動油の漏れを防止することができるものであればどのような形式であってもよく、例えばOリングであってもよい。
また、上記実施形態では、検出器が圧力センサ30である場合について説明した。検出器は、Uパッキン50の緊迫力を検出することにより作動油の漏れを検出するセンサであってもよい。
また、上記実施形態では、通路13は、環状溝12の底面に開口する。通路13は、圧入部14を通って圧入部14の内周面に開口するように形成されていてもよい。通路13が環状溝12の底面に開口する構成では、環状溝12と圧入部14とを近づけることができ、流体漏れ検出機器100を小型化することができる。
本願は2018年1月29日に日本国特許庁に出願された特願2018-012565に基づく優先権を主張し、この出願の全ての内容は参照により本明細書に組み込まれる。
Claims (6)
- シリンダチューブから延出するピストンロッドと、前記シリンダチューブに設けられ前記ピストンロッドが挿通するシリンダヘッドと、の間からの作動流体の漏れを検出するための流体漏れ検出機器であって、
前記シリンダヘッドに取り付けられ、前記ピストンロッドが挿通する環状部材と、
前記環状部材に形成され、前記ピストンロッドの外周と前記シリンダヘッドの内周との間から作動流体が導かれる通路と、
前記通路を通じて導かれる作動流体を検出する検出器と、を備え、
前記環状部材は、前記シリンダヘッドに形成される環状溝に圧入される圧入部を有する
流体漏れ検出機器。 - 請求項1に記載の流体漏れ検出機器であって、
前記環状部材の内周に設けられ、前記環状部材の内周と前記ピストンロッドの外周との間を塞いで前記ピストンロッドの外周と前記シリンダヘッドの内周との間から前記通路へ作動流体を導くシール部材を更に備える
流体漏れ検出機器。 - 請求項1に記載の流体漏れ検出機器であって、
前記検出器と並列に前記通路に接続され、前記通路内の圧力が所定の圧力に達すると開弁するリリーフ弁を更に備え、
前記所定の圧力は、作動流体により前記圧入部が前記環状溝から抜き出されるときの作動流体の圧力よりも小さい
流体漏れ検出機器。 - 往復動型流体圧機器であって、
シリンダチューブと、
前記シリンダチューブから延出するピストンロッドと、
前記シリンダチューブに設けられ、前記ピストンロッドが挿通するシリンダヘッドと、
前記シリンダヘッドに取り付けられ、前記ピストンロッドが挿通する環状部材と、
前記環状部材に形成され、前記ピストンロッドの外周と前記シリンダヘッドの内周との間から作動流体が導かれる通路と、
前記通路を通じて導かれる作動流体を検出する検出器と、を備え、
前記環状部材は、前記シリンダヘッドに形成される環状溝に圧入された圧入部を有する
往復動型流体圧機器。 - 請求項4に記載の往復動型流体圧機器であって、
前記シリンダヘッドの内周に設けられ、前記ピストンロッドを摺動自在に支持する軸受を更に備える
往復動型流体圧機器。 - 請求項4に記載の往復動型流体圧機器であって、
前記シリンダヘッドから突出し、前記シリンダヘッドを前記シリンダチューブに締結する複数の締結部材を更に備え、
前記検出器は、前記締結部材どうしの間に配置される
往復動型流体圧機器。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201980007328.7A CN111566358B (zh) | 2018-01-29 | 2019-01-18 | 流体泄漏检测设备和往复运动型流体压力设备 |
| DE112019000578.2T DE112019000578B4 (de) | 2018-01-29 | 2019-01-18 | Fluidleckage-erfassungsvorrichtung und hin- und herbewegende fluiddruckvorrichtung |
| US16/961,607 US11225985B2 (en) | 2018-01-29 | 2019-01-18 | Fluid leakage detection device and reciprocating fluid pressure device |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018-012565 | 2018-01-29 | ||
| JP2018012565A JP6677751B2 (ja) | 2018-01-29 | 2018-01-29 | 流体漏れ検出機器、及び往復動型流体圧機器 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2019146513A1 true WO2019146513A1 (ja) | 2019-08-01 |
Family
ID=67395438
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2019/001402 WO2019146513A1 (ja) | 2018-01-29 | 2019-01-18 | 流体漏れ検出機器及び往復動型流体圧機器 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11225985B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6677751B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN111566358B (ja) |
| DE (1) | DE112019000578B4 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2019146513A1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP4153870A4 (en) * | 2020-07-02 | 2023-12-13 | Ozel, Ali | CYLINDER PISTON END CAP AND LOCKING MECHANISM THAT CAN BE INTEGRATED INTO HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS UNDER FULL SAFE LOAD |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS56158561U (ja) * | 1980-04-28 | 1981-11-26 | ||
| JP2005221069A (ja) * | 2003-06-20 | 2005-08-18 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | シリンダーリーク検出構造及び同検出方法 |
| JP2009174555A (ja) * | 2008-01-21 | 2009-08-06 | Komatsu Ltd | ダストシールシステム |
| WO2017077786A1 (ja) * | 2015-11-04 | 2017-05-11 | Kyb株式会社 | 液漏れ検知装置 |
| JP2017207078A (ja) * | 2016-05-16 | 2017-11-24 | Kyb株式会社 | 液漏れ検知装置 |
| JP2018054021A (ja) * | 2016-09-29 | 2018-04-05 | 日本バルカー工業株式会社 | 液体漏れ検知ユニット |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS62240275A (ja) | 1986-04-09 | 1987-10-21 | 株式会社日立製作所 | 油圧エレベ−タ |
| JPH06207608A (ja) | 1993-01-12 | 1994-07-26 | Toshiba Mach Co Ltd | 油圧装置の油漏れ検知方法 |
| CN203655776U (zh) * | 2013-12-26 | 2014-06-18 | 海卓泰克液压技术(苏州)有限公司 | 变浆油缸 |
| CN104006029A (zh) | 2014-05-12 | 2014-08-27 | 天津优瑞纳斯液压机械有限公司 | 具有漏油检测结构的液压缸 |
| CN105864148B (zh) * | 2016-05-10 | 2017-09-22 | 燕山大学 | 一种液压缸用密封圈泄漏量的定量测量装置及测量方法 |
| CN206111726U (zh) * | 2016-11-01 | 2017-04-19 | 常州海宏液压设备有限公司 | 活塞杆外泄漏自动检测冻干机油缸 |
-
2018
- 2018-01-29 JP JP2018012565A patent/JP6677751B2/ja active Active
-
2019
- 2019-01-18 WO PCT/JP2019/001402 patent/WO2019146513A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2019-01-18 DE DE112019000578.2T patent/DE112019000578B4/de active Active
- 2019-01-18 US US16/961,607 patent/US11225985B2/en active Active
- 2019-01-18 CN CN201980007328.7A patent/CN111566358B/zh active Active
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS56158561U (ja) * | 1980-04-28 | 1981-11-26 | ||
| JP2005221069A (ja) * | 2003-06-20 | 2005-08-18 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | シリンダーリーク検出構造及び同検出方法 |
| JP2009174555A (ja) * | 2008-01-21 | 2009-08-06 | Komatsu Ltd | ダストシールシステム |
| WO2017077786A1 (ja) * | 2015-11-04 | 2017-05-11 | Kyb株式会社 | 液漏れ検知装置 |
| JP2017207078A (ja) * | 2016-05-16 | 2017-11-24 | Kyb株式会社 | 液漏れ検知装置 |
| JP2018054021A (ja) * | 2016-09-29 | 2018-04-05 | 日本バルカー工業株式会社 | 液体漏れ検知ユニット |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP4153870A4 (en) * | 2020-07-02 | 2023-12-13 | Ozel, Ali | CYLINDER PISTON END CAP AND LOCKING MECHANISM THAT CAN BE INTEGRATED INTO HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS UNDER FULL SAFE LOAD |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US11225985B2 (en) | 2022-01-18 |
| US20210079936A1 (en) | 2021-03-18 |
| JP6677751B2 (ja) | 2020-04-08 |
| DE112019000578B4 (de) | 2024-04-11 |
| CN111566358A (zh) | 2020-08-21 |
| DE112019000578T5 (de) | 2020-11-19 |
| JP2019132293A (ja) | 2019-08-08 |
| CN111566358B (zh) | 2023-02-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2812555B2 (ja) | ピストン密閉緩衝装置 | |
| KR101052195B1 (ko) | 유체압기기의 시일구조 | |
| US20200256451A1 (en) | Sealing array for a transmission, in particular for the output shaft of a transmission, and transmission having the sealing array | |
| CN108603559B (zh) | 活塞缸总成 | |
| RU2692885C1 (ru) | Гидро(пневмо)цилиндр | |
| WO2011111488A1 (ja) | 流体圧シリンダ | |
| KR20150032727A (ko) | 나사 풀림 방지 구조 | |
| KR850000614A (ko) | 로울샤프트에로울 링을 고정시키기 위한 장치 | |
| EP3214337B1 (en) | Shock absorber | |
| WO2019146513A1 (ja) | 流体漏れ検出機器及び往復動型流体圧機器 | |
| RU2692867C1 (ru) | Гидро(пневмо)цилиндр | |
| US9447878B2 (en) | Piston seal assembly | |
| RU2679993C2 (ru) | Гидро(пневмо)цилиндр | |
| US6796216B2 (en) | Guide for the piston rod of a piston-cylinder assembly | |
| US20060032369A1 (en) | Piston-piston rod retaining assembly for a hydraulic piston and cylinder unit | |
| WO2015012003A1 (ja) | 流体圧シリンダ | |
| JP7369011B2 (ja) | シリンダ装置 | |
| WO2019146459A1 (ja) | 流体漏れ検出機器及び往復動型流体圧機器 | |
| CN109667928B (zh) | 用于致动变速器的选择器杆的设定装置 | |
| KR102569737B1 (ko) | 고압 디젤 연료 펌프 | |
| US20210388904A1 (en) | Mechanical seal and rotary union having a mechanical seal | |
| US20120006016A1 (en) | Hydropneumatic piston reservoir | |
| WO2016185982A1 (ja) | 液圧シリンダ | |
| JP2019132293A5 (ja) | ||
| US20240077125A1 (en) | Vibration damper |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 19744031 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| DPE1 | Request for preliminary examination filed after expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed from 20040101) | ||
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 19744031 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |