WO2015079417A1 - Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives - Google Patents
Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015079417A1 WO2015079417A1 PCT/IB2014/066422 IB2014066422W WO2015079417A1 WO 2015079417 A1 WO2015079417 A1 WO 2015079417A1 IB 2014066422 W IB2014066422 W IB 2014066422W WO 2015079417 A1 WO2015079417 A1 WO 2015079417A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- alkyl
- optionally substituted
- halogen
- fluoro
- cyclopropyl
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 CC(*)(*)Oc(c(N)ncn1)c1Cl Chemical compound CC(*)(*)Oc(c(N)ncn1)c1Cl 0.000 description 7
- LAVPRNBTAJISIC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Clc1ncnc(Cl)c1OCc1ccccc1 Chemical compound Clc1ncnc(Cl)c1OCc1ccccc1 LAVPRNBTAJISIC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PLOZXUFHBRJLFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nc1ncnc(Cl)c1O Chemical compound Nc1ncnc(Cl)c1O PLOZXUFHBRJLFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D239/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings
- C07D239/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D239/24—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D239/28—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D239/46—Two or more oxygen, sulphur or nitrogen atoms
- C07D239/47—One nitrogen atom and one oxygen or sulfur atom, e.g. cytosine
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/495—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with two or more nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine or tetrazines
- A61K31/505—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/495—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with two or more nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine or tetrazines
- A61K31/505—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim
- A61K31/506—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/495—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with two or more nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine or tetrazines
- A61K31/505—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim
- A61K31/513—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim having oxo groups directly attached to the heterocyclic ring, e.g. cytosine
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P29/00—Non-central analgesic, antipyretic or antiinflammatory agents, e.g. antirheumatic agents; Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs [NSAID]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
- A61P35/02—Antineoplastic agents specific for leukemia
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D401/10—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings linked by a carbon chain containing aromatic rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D401/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D403/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00
- C07D403/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings
- C07D403/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D405/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P20/00—Technologies relating to chemical industry
- Y02P20/50—Improvements relating to the production of bulk chemicals
- Y02P20/55—Design of synthesis routes, e.g. reducing the use of auxiliary or protecting groups
Definitions
- the present invention describes new amino pyrimidine derivatives that are good drug candidates.
- the compounds of the present invention may generally exhibit a selective inhibition of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk).
- Btk The essential role of Btk in autoimmune disease is underlined by the observations that Btk-deficient mice are protected in standard preclinical models for rheumatoid arthritis (Jansson & Holmdahl 1993), systemic lupus erythematosus (Steinberg et al. 1982), as well as allergic disease and anaphylaxis (Hata et al. 1998). In addition, many cancers and lymphomas express Btk and appear to be dependent on Btk function (Davis et al. 2010). The role of BTK in diseases including autoimmunity, inflammation and cancer has been recently reviewed (Tan et al. 2013; Rickert 2013).
- Inhibition of Btk activity by the compounds of the present invention may therefore be useful in the treatment of a wide range of disorders, particularly Btk-related diseases or disorders.
- This may include, but is not limited to autoimmune disorders and inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus or vasculitic conditions. It may include, but is not limited to allergic diseases, airway diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or conditions caused by delayed or immediate type hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis. It may include, but is not limited to acute or chronic transplant rejection or graft versus host disease.
- autoimmune disorders and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus or vasculitic conditions. It may include, but is not limited to allergic diseases, airway diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or conditions caused by delayed or immediate type hypersensitivity and ana
- the present invention provides a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof;
- R1 is hydrogen, C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxy
- R2 is hydrogen or halogen
- R3 is hydrogen or halogen
- R4 is hydrogen
- R5 is hydrogen or halogen
- R6 and R7 stand independently from each other for H, C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxyl, C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl optionally substituted by halogen or hydroxy, or halogen;
- R8, R9, R, R', R10 and R1 1 independently from each other stand for H, or C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkoxy; or any two of R8, R9, R, R', R10 and R1 1 together with the carbon atom to which they are bound may form a 3 - 6 membered saturated carbocyclic ring;
- R12 is hydrogen or C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by halogen or C C 6 alkoxy
- R12 and any one of R8, R9, R, R', R10 or R1 1 together with the atoms to which they are bound may form a 4, 5, 6 or 7 membered azacyclic ring, which ring may optionally be substituted by halogen, cyano, hydroxyl, CrC f , alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy;
- n 0 or 1 ;
- R13 is C 2 -C 6 alkenyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl, C C 6 alkoxy or N,N-di-C C 6 alkyl amino; C 2 -C 6 alkynyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy; or C 2 -C 6 alkylenyl oxide optionally substituted by CrC f , alkyl.
- Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof wherein,
- R1 is hydrogen, or C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxy
- R2 is halogen
- R3 is hydrogen
- R4 is hydrogen
- R5 is halogen
- R6 and R7 stand independently from each other for H, C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxyl, C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl optionally substituted by halogen or hydroxy, or halogen;
- R8, R9, R10 and R1 1 independently from each other stand for H, or C C 6 alkyl; or any two of R8, R9, R10 and R1 1 together with the carbon atom to which they are bound may form a 3 - 6 membered saturated carbocyclic ring;
- R and R' are hydrogen
- R12 is hydrogen or CrCei alkyl optionally substituted by halogen
- R12 and any one of R8, R9, R, R', R10 or R1 1 together with the atoms to which they are bound may form a 4, 5, 6 or 7 membered azacyclic ring, which ring may optionally be substituted by halogen, cyano, hydroxyl, CrC f , alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy;
- n 0 or 1 ;
- R13 is C 2 -C 6 alkenyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy; C 2 -C 6 alkynyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy; or C 2 -C 6 alkylenyl oxide optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl.
- Embodiment 3 of the present invention provides a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof wherein,
- R1 is hydrogen, or C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxy
- R2 is halogen
- R3 is hydrogen
- R4 is hydrogen
- R5 is halogen
- R6 and R7 stand independently from each other for H, C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxyl, C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl optionally substituted by halogen or hydroxy, or halogen;
- R8, R9, R10 and R1 1 independently from each other stand for H, or C C 6 alkyl; or any two of R8, R9, R10 and R1 1 together with the carbon atom to which they are bound may form a 3 - 6 membered saturated carbocyclic ring;
- R and R' are hydrogen
- R12 is hydrogen or CrCei alkyl optionally substituted by halogen
- R12 and any one of R8, R9, R, R', R10 or R1 1 together with the atoms to which they are bound may form a 4, 5, 6 or 7 membered azacyclic ring, which ring may optionally be substituted by halogen, cyano, hydroxyl, CrC f , alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy;
- n 0 or 1 ;
- R13 is C 2 -C 6 alkenyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy; C 2 -C 6 alkynyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy; or C 2 -C 6 alkylenyl oxide optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl.
- Embodiment 4 of the present invention provides a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof wherein,
- R1 is hydrogen, C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxy
- R2 is hydrogen or halogen
- R3 is hydrogen or halogen
- R6 and R7 stand independently from each other for H, C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxyl, C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl optionally substituted by halogen or hydroxy, or halogen;
- R8, R9, R10 and R1 1 independently from each other stand for H, or C C 6 alkyl; or any two of R8, R9, R10 and R1 1 together with the carbon atom to which they are bound may form a 3 - 6 membered saturated carbocyclic ring;
- R and R' are hydrogen
- R12 is hydrogen or CrCei alkyl optionally substituted by halogen
- R12 and any one of R8, R9, R, R', R10 or R1 1 together with the atoms to which they are bound may form a 4, 5, 6 or 7 membered azacyclic ring, which ring may optionally be substituted by halogen, cyano, hydroxyl, CrC f , alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy;
- n 0 or 1 ;
- R13 is C 2 -C 6 alkenyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy; C 2 -C 6 alkynyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy; or C 2 -C 6 alkylenyl oxide optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl.
- Embodiment 5 of the present invention provides a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof wherein,
- R1 is hydrogen, C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxy
- R2 is hydrogen or halogen
- R3 is hydrogen or halogen
- R6 and R7 stand independently from each other for H, C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxyl, C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl optionally substituted by halogen or hydroxy, or halogen;
- R8, R9, R10 and R1 1 independently from each other stand for H, or C C 6 alkyl; or any two of R8, R9, R10 and R1 1 together with the carbon atom to which they are bound may form a 3 - 6 membered saturated carbocyclic ring;
- R and R' are hydrogen
- R12 is hydrogen or CrCei alkyl optionally substituted by halogen
- R12 and any one of R8, R9, R, R', R10 or R1 1 together with the atoms to which they are bound may form a 4, 5, 6 or 7 membered azacyclic ring, which ring may optionally be substituted by halogen, cyano, hydroxyl, C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy;
- n 0 or 1 ;
- R13 is C 2 -C 6 alkenyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy; C 2 -C 6 alkynyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy; or C 2 -C 6 alkylenyl oxide optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl.
- Embodiment 6 of the present invention provides a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof wherein,
- R1 is hydrogen, or C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxy
- R2 is halogen
- R3 is hydrogen
- R4 is hydrogen
- R5 is halogen
- R6 and R7 stand independently from each other for H, C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxyl, C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl optionally substituted by halogen or hydroxy, or halogen;
- R8, R9, R10 and R1 1 independently from each other stand for H, or C C 6 alkyl;
- R and R' are hydrogen;
- R12 is hydrogen or CrCei alkyl optionally substituted by halogen;
- n 0 or 1 ;
- R13 is C 2 -C 6 alkenyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy; C 2 -C 6 alkynyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy; or C 2 -C 6 alkylenyl oxide optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl.
- Embodiment 7 of the present invention provides a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof wherein,
- R1 is hydrogen, or C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxy
- R2 is halogen
- R3 is hydrogen
- R4 is hydrogen
- R5 is halogen
- R6 and R7 stand independently from each other for H, C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxyl, C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl optionally substituted by halogen or hydroxy, or halogen;
- R8 and R9 independently from each other stand for H, or C C 6 alkyl;
- R and R' are hydrogen
- R12 and any one of R10 or R1 1 together with the atoms to which they are bound may form a 4, 5, 6 or 7 membered azacyclic ring, which ring may optionally be substituted by halogen, cyano, hydroxyl, C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy;
- n 0 or 1 ;
- R13 is C 2 -C 6 alkenyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy; C 2 -C 6 alkynyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy; or C 2 -C 6 alkylenyl oxide optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl.
- Embodiment 8 of the present invention provides a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof wherein,
- R1 is hydrogen, or C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxy
- R2 is halogen
- R3 is hydrogen
- R4 is hydrogen
- R5 is halogen
- R6 and R7 stand independently from each other for H, C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxyl, C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl optionally substituted by halogen or hydroxy, or halogen
- R8, R9, R10 and R1 1 independently from each other stand for H, or C C 6 alkyl
- R and R' are hydrogen
- R12 is hydrogen or C ⁇ alkyl optionally substituted by halogen
- n 0 or 1 ;
- R13 is C 2 -C 6 alkenyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy.
- Embodiment 9 of the present invention provides a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof wherein,
- R1 is hydrogen, or C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxy
- R2 is fluoro
- R3 is hydrogen
- R4 is hydrogen
- R5 is halogen
- R6 and R7 stand independently from each other for H, C C 6 alkyl optionally substituted by hydroxyl, C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl optionally substituted by halogen or hydroxy, or halogen;
- R8 and R9 independently from each other stand for H, or C C 6 alkyl
- R12 and any one of R10 or R1 1 together with the atoms to which they are bound may form a 4, 5, 6 or 7 membered azacyclic ring, which ring may optionally be substituted by halogen, cyano, hydroxyl, C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy;
- n 0;
- R13 is C 2 -C 6 alkenyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy; or C 2 -C 6 alkynyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy.
- Embodiment 10 of the present invention provides a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof wherein,
- R1 is C C 6 alkyl
- R2 is fluoro
- R3 is hydrogen
- R4 is hydrogen
- R5 is fluoro
- R6 and R7 stand independently from each other for H, C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl, or halogen;
- R8, R9, R10 and R1 1 stand for H;
- R12 is methyl;
- n 0;
- R13 is C 2 -C 6 alkenyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl.
- R1 is methyl or hydroxymethyl
- R2 is hydrogen or fluoro
- R3 is hydrogen
- R1 is methyl or hydroxymethyl and R2 and R3 are independently hydrogen or fluoro;
- R4 is hydrogen
- R5 is fluoro
- R6 is H and R7 is C 3 -C 6 -cycloalkyl and in particular cyclopropyl;
- R7 is H and R6 is C 3 -C 6 -cycloalkyl and in particular cyclopropyl;
- R8, R9, RI O and R1 1 stand for H;
- R12 and any one of R8, R9, R, R',R10 or R1 1 together with the atoms to which they are bound may form a 4, 5, 6 or 7 membered azacyclic ring, which ring may optionally be substituted by halogen, hydroxyl, C C 6 alkyl or C C 6 alkoxy;
- R8, R9, R10 and R1 1 independently from each other stand for H, or C C 6 alkyl; or any two of R8, R9, R, R', R10 and R1 1 together with the carbon atom to which they are bound may form a 3 - 6 membered saturated carbocyclic ring;
- R12 is hydrogen and R13 stands for C 2 -C 6 alkenyl optionally substituted by C C 6 alkyl;
- R12 is methyl
- the present invention provides a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof for use as a medicament. ln another embodiment the present invention provides a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof for use in the treatment of a disease or disorder mediated by Btk.
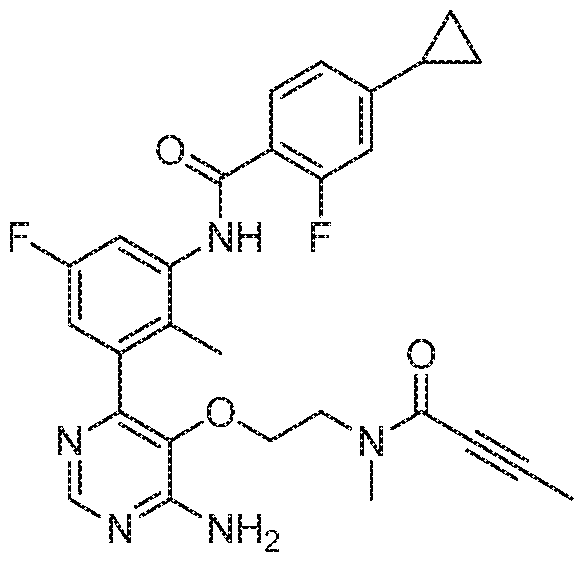
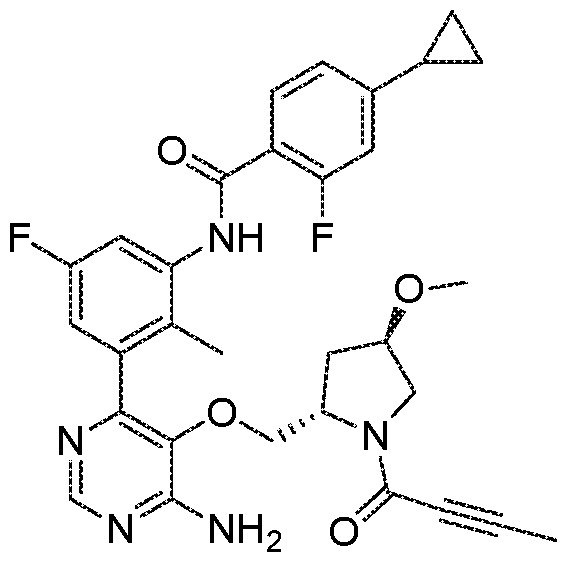
- the present invention provides a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, which is selected from:
- C1-C6 alkyl refers to a fully saturated branched or unbranched hydrocarbon moiety having up to 6 carbon atoms. Unless otherwise provided, it refers to hydrocarbon moieties having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, 1 to 4 carbon atoms or 1 to 2 carbon atoms.
- Representative examples of alkyl include, but are not limited to, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, / ' so-propyl, n-butyl, sec-butyl, / ' so-butyl, fe/f-butyl, n- pentyl, isopentyl, neopentyl, n-hexyl and the like.
- C2-C6 alkenyl refers to an unsaturated branched or unbranched hydrocarbon moiety having 2 to 6 carbon atoms. Unless otherwise provided, C2-C6 alkenyl refers to moieties having 2 to 6 carbon atoms, 2 to 5 carbon atoms, or 2 to 4 carbon atoms.
- alkenyl include, but are not limited to, ethenyl, n-propenyl, / ' so-propenyl, n-butenyl, sec-butenyl, / ' so-butenyl, tert- butenyl, n-pentenyl, isopentenyl, neopentenyl, n-hexenyl, and the like.
- C 2 -C 6 alkynyl refers to an unsaturated branched or unbranched hydrocarbon moiety having 2 to 6 carbon atoms, containing at least one triple bond, and which is attached to the rest of the molecule by a single bond.
- C 2 - 4 alkynyl is to be construed accordingly. Examples of C 2 - 6 alkynyl include, but are not limited to, ethynyl, prop-1 -ynyl, but-1 -ynyl, pent-1 -ynyl and penta-1 ,4-diynyl and the like.
- C C 6 alkoxy refers to alkyl-O-, wherein alkyl is defined herein above.
- Representative examples of alkoxy include, but are not limited to, methoxy, ethoxy, propoxy, 2-propoxy, butoxy, fe/f-butoxy, pentyloxy, hexyloxy, cyclopropyloxy-, cyclohexyloxy- and the like.
- alkoxy groups have about 1 to 6 carbon atoms, 1 to 4 carbon atoms or 1 to 2 carbon atoms.
- Ci Ci.ealkylamino refers to a moiety of the formula -N(R a )-R a where each R a is a C 1-6 alkyl , which may be the same or different, as defined above.
- C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyi refers to saturated monocyclic hydrocarbon groups of 3-6 carbon atoms. Cycloalkyi may also be referred to as a carbocyclic ring and vice versa additionally referring to the number of carbon atoms present. Unless otherwise provided, cycloalkyi refers to cyclic hydrocarbon groups having between 3 and 6 ring carbon atoms or between 3 and 4 ring carbon atoms. Exemplary monocyclic hydrocarbon groups include, but are not limited to, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, and cyclohexyl.
- C 2 -C 6 alkylenyl oxide refers to a branched or unbranched hydrocarbon moiety comprising an epoxy group and having from 2 to 6 carbon atoms.
- Representative examples include ethylenyl oxide, propylenyl oxide, butylenyl 1 ,2-oxide, butylenyl 2,3-oxide, butylenyl 3,4-oxide, pentylenyl oxide, hexylenyl oxide, and the like.
- azacyclic ring refers to a saturated or unsaturated monocyclic hydrocarbon group of 3 - 7 carbon atoms as defined for “cycloalkyi", wherein one carbon atom is replaced by a nitrogen atom. It may be also referred to "azacycloalkyl” or “aza hydrocarbon”. Unless otherwise provided, azacycloalkyl refers to cyclic aza- hydrocarbon groups having between 2 and 6 ring carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom, between 2 and 4 ring carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom, or between 2 and 3 ring carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom. Exemplary azacyclic groups include, but are not limited to, aziridinyl, azetidinly, pyrrolidinyl, piperidinyl, azepanyl, dihydroazepinyl and the like.
- halogen refers to fluoro, chloro, bromo, and iodo.
- salt refers to an acid addition or base addition salt of a compound of the invention.
- Salts include in particular “pharmaceutically acceptable salts”.
- pharmaceutically acceptable salts refers to salts that retain the biological effectiveness and properties of the compounds of this invention and, which typically are not biologically or otherwise undesirable.
- the compounds of the present invention are capable of forming acid and/or base salts by virtue of the presence of amino and/or carboxyl groups or groups similar thereto.
- Pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salts can be formed with inorganic acids and organic acids, e.g., acetate, aspartate, benzoate, besylate, bromide/hydrobromide, bicarbonate/carbonate, bisulfate/sulfate, camphorsulfonate, chloride/hydrochloride, chlortheophyllonate, citrate, ethandisulfonate, fumarate, gluceptate, gluconate, glucuronate, hippurate, hydroiodide/iodide, isethionate, lactate, lactobionate, laurylsulfate, malate, maleate, malonate, mandelate, mesylate, methylsulphate, naphthoate, napsylate, nicotinate, nitrate, octadecanoate, oleate, oxalate, palmitate, pamoate, phosphate/hydrogen phosphate/dihydrogen
- Inorganic acids from which salts can be derived include, for example, hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, phosphoric acid, and the like.
- Organic acids from which salts can be derived include, for example, acetic acid, propionic acid, glycolic acid, oxalic acid, maleic acid, malonic acid, succinic acid, fumaric acid, tartaric acid, citric acid, benzoic acid, mandelic acid, methanesulfonic acid, ethanesulfonic acid, toluenesulfonic acid, sulfosalicylic acid, and the like.
- Pharmaceutically acceptable base addition salts can be formed with inorganic and organic bases.
- Inorganic bases from which salts can be derived include, for example, ammonium salts and metals from columns I to XII of the periodic table.
- the salts are derived from sodium, potassium, ammonium, calcium, magnesium, iron, silver, zinc, and copper; particularly suitable salts include ammonium, potassium, sodium, calcium and magnesium salts.
- Organic bases from which salts can be derived include, for example, primary, secondary, and tertiary amines, substituted amines including naturally occurring substituted amines, cyclic amines, basic ion exchange resins, and the like.
- Certain organic amines include isopropylamine, benzathine, cholinate, diethanolamine, diethylamine, lysine, meglumine, piperazine and tromethamine.
- the pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the present invention can be synthesized from a basic or acidic moiety, by conventional chemical methods.
- such salts can be prepared by reacting free acid forms of these compounds with a stoichiometric amount of the appropriate base (such as Na, Ca, Mg, or K hydroxide, carbonate, bicarbonate or the like), or by reacting free base forms of these compounds with a stoichiometric amount of the appropriate acid.
- a stoichiometric amount of the appropriate base such as Na, Ca, Mg, or K hydroxide, carbonate, bicarbonate or the like
- Such reactions are typically carried out in water or in an organic solvent, or in a mixture of the two.
- use of non-aqueous media like ether, ethyl acetate, ethanol, isopropanol, or acetonitrile is desirable, where practicable.
- any formula given herein is also intended to represent unlabeled forms as well as isotopically labeled forms of the compounds.
- Isotopically labeled compounds have structures depicted by the formulas given herein except that one or more atoms are replaced by an atom having a selected atomic mass or mass number.
- isotopes that can be incorporated into compounds of the invention include isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous, fluorine, and chlorine, such as 2 H, 3 H, 11 C, 13 C, 14 C, 15 N, 18 F 31 P, 32 P, 35 S, 36 CI, 125 l respectively.
- the invention includes various isotopically labeled compounds as defined herein, for example those into which radioactive isotopes, such as 3 H and 14 C, or those into which non-radioactive isotopes, such as 2 H and 13 C are present.
- isotopically labeled compounds are useful in metabolic studies (with 14 C), reaction kinetic studies (with, for example 2 H or 3 H), detection or imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET) or single- photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) including drug or substrate tissue distribution assays, or in radioactive treatment of patients.
- PET positron emission tomography
- SPECT single- photon emission computed tomography
- an 18 F or labeled compound may be particularly desirable for PET or SPECT studies.
- Isotopically-labeled compounds of formula (I) can generally be prepared by conventional techniques known to those skilled in the art or by processes analogous to those described in the accompanying Examples and Preparations using an appropriate isotopically-labeled reagents in place of the non-labeled reagent previously employed.
- isotopic enrichment factor means the ratio between the isotopic abundance and the natural abundance of a specified isotope.
- a substituent in a compound of this invention is denoted deuterium, such compound has an isotopic enrichment factor for each designated deuterium atom of at least 3500 (52.5% deuterium incorporation at each designated deuterium atom), at least 4000 (60% deuterium incorporation), at least 4500 (67.5% deuterium incorporation), at least 5000 (75% deuterium incorporation), at least 5500 (82.5% deuterium incorporation), at least 6000 (90% deuterium incorporation), at least 6333.3 (95% deuterium incorporation), at least 6466.7 (97% deuterium incorporation), at least 6600 (99% deuterium incorporation), or at least 6633.3 (99.5% deuterium incorporation).
- solvates in accordance with the invention include those wherein the solvent of crystallization may be isotopically substituted, e.g. D 2 0, de- acetone, d 6 -DMSO.
- Compounds of the invention i.e. compounds of formula (I) that contain groups capable of acting as donors and/or acceptors for hydrogen bonds may be capable of forming co- crystals with suitable co-crystal formers.
- These co-crystals may be prepared from compounds of formula (I) by known co-crystal forming procedures. Such procedures include grinding, heating, co-subliming, co-melting, or contacting in solution compounds of formula (I) with the co-crystal former under crystallization conditions and isolating co- crystals thereby formed.
- Suitable co-crystal formers include those described in WO 2004/078163.
- the invention further provides co-crystals comprising a compound of formula (I).
- the term "pharmaceutically acceptable carrier” includes any and all solvents, dispersion media, coatings, surfactants, antioxidants, preservatives (e.g., antibacterial agents, antifungal agents), isotonic agents, absorption delaying agents, salts, preservatives, drug stabilizers, binders, excipients, disintegration agents, lubricants, sweetening agents, flavoring agents, dyes, and the like and combinations thereof, as would be known to those skilled in the art (see, for example, Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences, 18th Ed. Mack Printing Company, 1990, pp. 1289- 1329). Except insofar as any conventional carrier is incompatible with the active ingredient, its use in the therapeutic or pharmaceutical compositions is contemplated.
- a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the present invention refers to an amount of the compound of the present invention that will elicit the biological or medical response of a subject, for example, reduction or inhibition of an enzyme or a protein activity, or ameliorate symptoms, alleviate conditions, slow or delay disease progression, or prevent a disease, etc.
- a therapeutically effective amount refers to the amount of the compound of the present invention that, when administered to a subject, is effective to (1) at least partially alleviating, inhibiting, preventing and/or ameliorating a condition, or a disorder or a disease (i) mediated by Btk, or (ii) associated with Btk activity, or (iii) characterized by activity (normal or abnormal) of Btk; or (2) reducing or inhibiting the activity of Btk; or (3) reducing or inhibiting the expression of Btk.
- a therapeutically effective amount refers to the amount of the compound of the present invention that, when administered to a cell, or a tissue, or a non-cellular biological material, or a medium, is effective to at least partially reducing or inhibiting the activity of Btk; or reducing or inhibiting the expression of Btk partially or completely.
- the term "subject” refers to an animal. Typically the animal is a mammal. A subject also refers to for example, primates (e.g., humans, male or female), cows, sheep, goats, horses, dogs, cats, rabbits, rats, mice, fish, birds and the like. In certain embodiments, the subject is a primate. In yet other embodiments, the subject is a human.
- the term “inhibit”, “inhibition” or “inhibiting” refers to the reduction or suppression of a given condition, symptom, or disorder, or disease, or a significant decrease in the baseline activity of a biological activity or process.
- the term “treat”, “treating” or “treatment” of any disease or disorder refers in one embodiment, to ameliorating the disease or disorder (i.e., slowing or arresting or reducing the development of the disease or at least one of the clinical symptoms thereof).
- “treat”, “treating” or “treatment” refers to alleviating or ameliorating at least one physical parameter including those which may not be discernible by the patient.
- “treat”, “treating” or “treatment” refers in one embodiment, to ameliorating the disease or disorder (i.e., slowing or arresting or reducing the development of the disease or at least one of the clinical symptoms thereof).
- “treat”, “treating” or “treatment” refers to alleviating or ameliorating at least one physical parameter including those which may not be discernible by the patient.
- treatment refers to modulating the disease or disorder, either physically, (e.g., stabilization of a discernible symptom), physiologically, (e.g., stabilization of a physical parameter), or both.
- “treat”, “treating” or “treatment” refers to preventing or delaying the onset or development or progression of the disease or disorder.
- a subject is "in need of” a treatment if such subject would benefit biologically, medically or in quality of life from such treatment.
- any asymmetric atom e.g. , carbon or the like
- any asymmetric atom can be present in racemic or enantiomerically enriched, for example the (R)-, (S)- or (R,S)- configuration.
- each asymmetric atom has at least 50 % enantiomeric excess, at least 60 % enantiomeric excess, at least 70 %
- a compound of the present invention can be in the form of one of the possible isomers, rotamers, atropisomers, tautomers or mixtures thereof, for example, as substantially pure geometric (c/ ' s or trans) isomers, diastereomers, optical isomers (antipodes), racemates or mixtures thereof.
- Any resulting mixtures of isomers can be separated on the basis of the physicochemical differences of the constituents, into the pure or substantially pure geometric or optical isomers, diastereomers, racemates, for example, by chromatography and/or fractional crystallization.
- any resulting racemates of final products or intermediates can be resolved into the optical antipodes by known methods, e.g. , by separation of the diastereomeric salts thereof, obtained with an optically active acid or base, and liberating the optically active acidic or basic compound.
- a basic moiety may thus be employed to resolve the compounds of the present invention into their optical antipodes, e.g. , by fractional crystallization of a salt formed with an optically active acid, e.g.
- Racemic products can also be resolved by chiral chromatography, e.g. , high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) using a chiral adsorbent.
- HPLC high pressure liquid chromatography
- the compounds of the present invention can also be obtained in the form of their hydrates, or include other solvents used for their crystallization.
- the compounds of the present invention may inherently or by design form solvates with pharmaceutically acceptable solvents (including water); therefore, it is intended that the invention embrace both solvated and unsolvated forms.
- solvate refers to a molecular complex of a compound of the present invention
- solvent molecules are those commonly used in the pharmaceutical art, which are known to be innocuous to the recipient, e.g., water, ethanol, and the like.
- solvent molecules are those commonly used in the pharmaceutical art, which are known to be innocuous to the recipient, e.g., water, ethanol, and the like.
- hydrate refers to the complex where the solvent molecule is water.
- the compounds of the present invention including salts, hydrates and solvates thereof, may inherently or by design form polymorphs.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of the present invention and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
- the pharmaceutical composition can be formulated for particular routes of administration such as oral administration, parenteral administration, and rectal administration, etc.
- the pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention can be made up in a solid form (including without limitation capsules, tablets, pills, granules, powders or suppositories), or in a liquid form (including without limitation solutions, suspensions or emulsions).
- compositions can be subjected to conventional pharmaceutical operations such as sterilization and/or can contain conventional inert diluents, lubricating agents, or buffering agents, as well as adjuvants, such as preservatives, stabilizers, wetting agents, emulsifiers and buffers, etc.
- the pharmaceutical compositions are tablets or gelatin capsules comprising the active ingredient together with a) diluents, e.g. , lactose, dextrose, sucrose, mannitol, sorbitol, cellulose and/or glycine; b) lubricants, e.g. , silica, talcum, stearic acid, its magnesium or calcium salt and/or polyethyleneglycol; for tablets also c) binders, e.g. , magnesium aluminum silicate, starch paste, gelatin, tragacanth, methylcellulose, sodium carboxymethylcellulose and/or polyvinylpyrrolidone; if desired d) disintegrants, e.g. , starches, agar, alginic acid or its sodium salt, or effervescent mixtures; and/or e) absorbents, colorants, flavors and sweeteners.
- diluents e.g. , lactose, dex
- Tablets may be either film coated or enteric coated according to methods known in the art.
- compositions for oral administration include an effective amount of a compound of the invention in the form of tablets, lozenges, aqueous or oily suspensions, dispersible powders or granules, emulsion, hard or soft capsules, or syrups or elixirs.
- Compositions intended for oral use are prepared according to any method known in the art for the manufacture of pharmaceutical compositions and such compositions can contain one or more agents selected from the group consisting of sweetening agents, flavoring agents, coloring agents and preserving agents in order to provide pharmaceutically elegant and palatable preparations. Tablets may contain the active ingredient in admixture with nontoxic pharmaceutically acceptable excipients which are suitable for the manufacture of tablets.
- excipients are, for example, inert diluents, such as calcium carbonate, sodium carbonate, lactose, calcium phosphate or sodium phosphate; granulating and disintegrating agents, for example, corn starch, or alginic acid; binding agents, for example, starch, gelatin or acacia; and lubricating agents, for example magnesium stearate, stearic acid or talc.
- the tablets are uncoated or coated by known techniques to delay disintegration and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract and thereby provide a sustained action over a longer period.
- a time delay material such as glyceryl monostearate or glyceryl distearate can be employed.
- Formulations for oral use can be presented as hard gelatin capsules wherein the active ingredient is mixed with an inert solid diluent, for example, calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate or kaolin, or as soft gelatin capsules wherein the active ingredient is mixed with water or an oil medium, for example, peanut oil, liquid paraffin or olive oil.
- an inert solid diluent for example, calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate or kaolin
- water or an oil medium for example, peanut oil, liquid paraffin or olive oil.
- compositions are aqueous isotonic solutions or suspensions, and suppositories are advantageously prepared from fatty emulsions or suspensions.
- Said compositions may be sterilized and/or contain adjuvants, such as preserving, stabilizing, wetting or emulsifying agents, solution promoters, salts for regulating the osmotic pressure and/or buffers. In addition, they may also contain other therapeutically valuable substances.
- Said compositions are prepared according to conventional mixing, granulating or coating methods, respectively, and contain about 0.1-75%, or contain about 1 -50%, of the active ingredient.
- compositions for transdermal application include an effective amount of a compound of the invention with a suitable carrier.
- Carriers suitable for transdermal delivery include absorbable pharmacologically acceptable solvents to assist passage through the skin of the host.
- transdermal devices are in the form of a bandage comprising a backing member, a reservoir containing the compound optionally with carriers, optionally a rate controlling barrier to deliver the compound of the skin of the host at a controlled and predetermined rate over a prolonged period of time, and means to secure the device to the skin.
- compositions for topical application include aqueous solutions, suspensions, ointments, creams, gels or sprayable formulations, e.g. , for delivery by aerosol or the like.
- topical delivery systems will in particular be appropriate for dermal application, e.g., for the treatment of skin cancer, e.g., for prophylactic use in sun creams, lotions, sprays and the like. They are thus particularly suited for use in topical, including cosmetic, formulations well-known in the art.
- Such may contain solubilizers, stabilizers, tonicity enhancing agents, buffers and
- a topical application may also pertain to an inhalation or to an intranasal application. They may be conveniently delivered in the form of a dry powder (either alone, as a mixture, for example a dry blend with lactose, or a mixed component particle, for example with phospholipids) from a dry powder inhaler or an aerosol spray presentation from a pressurised container, pump, spray, atomizer or nebuliser, with or without the use of a suitable propellant.
- a dry powder either alone, as a mixture, for example a dry blend with lactose, or a mixed component particle, for example with phospholipids
- the present invention further provides anhydrous pharmaceutical compositions and dosage forms comprising the compounds of the present invention as active ingredients, since water may facilitate the degradation of certain compounds.
- Anhydrous pharmaceutical compositions and dosage forms of the invention can be prepared using anhydrous or low moisture containing ingredients and low moisture or low humidity conditions.
- An anhydrous pharmaceutical composition may be prepared and stored such that its anhydrous nature is maintained. Accordingly, anhydrous compositions are packaged using materials known to prevent exposure to water such that they can be included in suitable formulary kits. Examples of suitable packaging include, but are not limited to, hermetically sealed foils, plastics, unit dose containers (e. g. , vials), blister packs, and strip packs.
- compositions and dosage forms that comprise one or more agents that reduce the rate by which the compound of the present invention as an active ingredient will decompose.
- agents which are referred to herein as “stabilizers,” include, but are not limited to, antioxidants such as ascorbic acid, pH buffers, or salt buffers, etc.
- the compounds of formula I in free form or in salt form exhibit valuable pharmacological properties, e.g. Btk modulating properties, e.g. as indicated by in vitro and in vivo tests as provided in the next sections and are therefore indicated for therapy.
- Btk modulating properties e.g. as indicated by in vitro and in vivo tests as provided in the next sections and are therefore indicated for therapy.
- Compounds of the invention may be useful in the treatment of an indication selected from: Autoimmune disorders, inflammatory diseases, allergic diseases, airway diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), transplant rejection; diseases in which antibody production, antigen presentation, cytokine production or lymphoid organogenesis are abnormal or are undesirable;
- COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- rheumatoid arthritis including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SOJIA), gout, pemphigus vulgaris, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, systemic lupus
- SOJIA systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- gout pemphigus vulgaris
- idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura systemic lupus
- erythematosus erythematosus
- multiple sclerosis myasthenia gravis
- Sjogren's syndrome autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- vasculitides cryoglobulinemia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, chronic autoimmune urticaria, allergy (atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, allergic rhinitis), atherosclerosis, type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis, morbus Crohn, pancreatitis, glomerolunephritis, Goodpasture's syndrome, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Grave's disease, antibody-mediated transplant rejection (AMR), graft versus host disease, B cell-mediated hyperacute, acute and chronic transplant rejection; thromboembolic disorders, myocardial infarct, angina pectoris, stroke, ischemic disorders, pulmonary embolism; cancers of haematopoietic origin including but not limited to multiple myeloma; leukemia; acute myelogenous leukemia; chronic myelogenous leukemia; lymphocytic leukemia; myeloid leukemia
- compounds of the invention may be useful in the treatment of autoimmune disorders, inflammatory diseases, allergic diseases, airway diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), transplant rejection, cancers e.g. of hematopoietic origin or solid tumors.
- autoimmune disorders inflammatory diseases, allergic diseases, airway diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), transplant rejection, cancers e.g. of hematopoietic origin or solid tumors.
- COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- compounds of the invention may be useful in the treatment of cancers of haematopoietic origin including but not limited to multiple myeloma; leukemia; acute myelogenous leukemia; chronic myelogenous leukemia; lymphocytic leukemia; myeloid leukemia; non-Hodgkin lymphoma; lymphomas; polycythemia vera; essential thrombocythemia; myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia; anf / or Waldenstroem disease.
- compounds of the invention may be useful in the treatment of chronic autoimmune urticaria, allergy (atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, allergic rhinitis), atherosclerosis, type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis, morbus Crohn, pancreatitis, glomerolunephritis, Goodpasture's syndrome, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and/or Grave's disease.
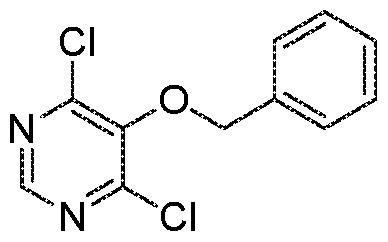
- Agents of the invention may be prepared by a reaction sequence involving an alkylation of 4-amino-6-chloro- pyrimidin-5-ol 1 with an alkyl halide 2 using an appropriate base, Suzuki coupling with a boronic ester using an appropriate palladium catalyst, such as bis(triphenylphosphine)- palladium(ll) dichloride, deprotection using an appropriate acid, such as TFA or HCI, followed by amide formation of the ammonium salt or the free amine with an acid using an appropriate coupling reagent, such as T3P, and an appropriate base, such as DIPEA, or with an acid chloride using an appropriate base, such as DIPEA, as shown in
- compounds of the invention may be prepared by an alternative reaction sequence (shown below) comprising the steps of reacting the amino hydroxypyrimidine 1 with the hydroxyl amino-alkyl-derivative 2' in a Mitsunobu reaction to furnish intermediate 3, which intermediate 3 is then reacted via a Suzuki-coupling to yield intermediate 5, which is then deprotected to yield intermediate 6, which is then amidated with an acid or acid chloride to yield the final product 7 as already described in scheme 1.
- DIAD Diisopropyl azodicarboxylate
- DIPEA /V-Diisopropylethylamine
- T3P Propylphosphonic anhydride
- Eluent A Water + 0.05% formic acid + 3.75 mM ammonium acetate.
- Eluent B Acetonitrile + 0.04% formic acid.
- Agents of the invention may be prepared by a reaction sequence involving an alkylation of 4-amino-6-chloropyrimidin-5-ol (1 ) with an alkyl halide (2) using an appropriate base, Suzuki coupling with a boronic ester (4) usind an appropriate palladium catalyst, such as bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(ll) dichloride, deprotection using an appropriate acid, such as TFA or HCI to form intermediate 6, which is reacted with an appropriate acid or acid chloride using an appropriate coupling reagent, such as T3P, and an appropriate base, such as DIPEA, or in the case of an acid chloride using a base, such as DIPEA, to yield compound 7, i.e. a compound of the invention, as shown in Scheme 1 :
- cyclopropylboronic acid (9.68 g, 1 12.69 mmol) and potassium phosphate (35.70 g, 168.00 mmol) in toluene (250 mL) was degassed with argon for 5 min. Then, tricyclohexylphosphine (2.36 g, 8.41 mmol) and water (1 .82 mL, 101 .00 mmol) were added and the mixture was again degassed with argon for 5 min. Palladium(ll) acetate (0.94 g, 4.21 mmol) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred at 100 °C overnight. The mixture was partitioned between EtOAc and water. The suspension was filtered through a pad of Celite.
- agents of the invention may be prepared by a reaction sequence involving Mitsunobu reaction of 4-amino-6-chloropyrimidin-5-ol with an alcohol of formula 2' using an appropriate azodicarboxylate, such as DIAD, and Smopex-301 or triphenylphosphine; thereupon the reaction sequences of scheme 1 are being carried out, i.e.
- Example 6 147 mg, 0.290 mmol in THF (1 .0 mL) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred at RT for 5 hr. The mixture was diluted with water and extracted with EtOAc. The organic layer was washed with water and brine, dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified by preparative HPLC (Xterra 150, water/acetonitrile gradient) to afford Example 11 as a white solid after lyophilization.
- Triphenylphosphine (169 mg, 0.64 mmol) was added to the filtrate.
- the filtrate was concentrated and the residue was purified by flash chromatography (silica;cyclohexane/EtOAc gradient, 5-40%).
- the residue was triturated with a mixture of diethyl ether and pentane (1 :1 ) and filtered.
- the filter cake was washed with pentane and dried in vacuum to afford INT 13 as a white solid.
- MS (ESI): [M+H] + 406.3, rt 1 .40 min.
- INT 18 was prepared according to Scheme 2 following a procedure analogous to INT 10 replacing A/-Boc-/V-methyl-2-hydroxyethylamine with (S)-2-(Boc-amino)-1 -propanol in step 1 , and replacing TFA with HCI in step 3 to afford INT 18 as the hydrochloride salt.
- Example 18 To a solution of Example 18 (152 mg, 0.29 mmol) in THF (10 mL) was added DIPEA (0.200 mL, 1 .15 mmol) followed by di-fe/f-butyl dicarbonate (233 mg, 1 .07 mmol) and 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine (4 mg, 0.033 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at RT overnight. More di-fe/f-butyl dicarbonate (100 mg, 0.46 mmol) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred at RT for 1 .5 hr. The mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by flash chromatography (silica;
- INT 23 was prepared following a procedure analogous to INT 2 replacing 1 -bromo-5- fluoro-2-methyl-3-nitro-benzene with acetic acid 2-bromo-6-(6-cyclopropyl-1 -oxo-3,4- dihydro-1 H-isoquinolin-2-yl)-benzyl ester (WO2010/000633).
- INT 26 was prepared according to Scheme 2 following a procedure analogous to step 3 of Example 6 replacing INT 9 with INT 25.
- INT 27 was prepared according to Scheme 2 following a procedure analogous to INT 26 replacing INT 24 with INT 8 in step 3, and purifying the TFA salt over a SPE cartridge (PL-HC03 MP resin) to afford INT 27 as the free amine in step 4.
- the filtrate was directly loaded onto a silica cartridge and purified by flash chromatography (silica; heptane/acetone gradient, 0-80%) to afford a white solid.
- the residue was triturated in acetonitrile, filtered off, and rinsed with acetonitrile.
- the solid was dried in vacuum to afford Example 25 as a white solid.
- INT 28 was prepared following a procedure analogous to WO2002/102790.
- INT 30 was prepared according to Scheme 2 following a procedure analogous to of Example 6 replacing A/-Boc-/V-methyl-2-hydroxyethylamine with INT 29.
- INT 35 was prepared according to Scheme 2 following a procedure analogous to step 2 of Example 26 replacing INT 28 with (S)-/V-Boc-azetidine-2-carboxylic acid.
- INT 36 was prepared according to Scheme 2 following a procedure analogous to step 1 of Example 6 replacing A/-Boc-/V-methyl-hydroxyethylamine with INT 35.
- agents of the invention may be prepared by a reaction sequence involving deprotection e.g. with a Lewis acid of 4,6-dichloro-5-methoxypyrimidine 8 to yield 4,6- dichloro-5-hydroxyoxy-pyrimidine 9, followed by a Mitsunobu reaction of the pyrimidinol with an alcohol compound 2' using an appropriate azodicarboxylate, such as DIAD, and Smopex-301 or triphenylphosphine to yield intermediate 10, followed by a nucleophilic aromatic substitution e.g. with ammonia in water to yield the aminopyrimidine intermediate 3. Thereupon intermediate 3 is converted into a final compound of the invention, i.e.
- INT 43 was prepared according to Scheme 3 following a procedure analogous to step 2 of Example 6 replacing INT 8 with INT 42.
- INT 44 was prepared according to Scheme 3 following a procedure analogous to step 3 of Example 6 replacing INT 9 with INT 43 and purifying the crude by flash
- agents of the invention may be prepared by a reaction sequence involving alkylation of 4,6-dichloro-5-hydroxy-pyrimidine 9 with benzyl bromide using an appropriate base, such as potassium carbonate, followed by nucleophilic aromatic substitution with ammonium hydroxide to yield the aminopyrimidine 12, Suzuki coupling with a boronic ester 4 using an appropriate catalyst, such as bis(triphenylphosphine)- palladium(ll) dichloride to yield the benzylated intermediate 13. Cleavage of the benzyl group, e.g. by hydrogenation, followed by a Mitsunobu reaction of the pyrimidinol with an alcohol of formula 2' using an appropriate azodicarboxylate, such as DIAD, and
- INT 52 (2.95 g, 6.35 mmol) in THF (30 mL) was added TBAF (1 .0 M in THF, 7.5 mL, 7.50 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at RT for 2.5 hr. The mixture was concentrated and the residue was taken up in EtOAc. The organic phase was washed with water and brine, dried over sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography (silica; cyclohexane/EtOAc gradient, 0- 100%) to afford INT 53 as a colorless residue.
- the inhibitory activity of the present compounds against Btk was assessed in a biochemical enzyme assay.
- Assay plates in 384 well format were prepared with 8-point serial dilutions for the test compounds on a Thermo CatX workstation equipped with a Innovadyne Nanodrop Express.
- the assay plates were prepared by addition of 50 nl per well of compound solution in 90 % DMSO.
- kinase reactions were started by stepwise addition of 4.5 ⁇ per well of peptide/ATP-solution (4 ⁇ FITC-Ahx- TSELKKVVALYDYMPMNAND-NH2, 164 ⁇ ATP) in kinase buffer (50mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 1 mM DTT, 0.02% Tween20, 0.02% BSA, 0.6% DMSO, 10 mM beta- glycerophosphate, and 10 ⁇ sodium orthovanadate, 18 mM MgCI2, 1 mM MnCI2) and 4.5 ⁇ per well of enzyme solution (6.4nM full-lenght human recombinant BTK) in kinase buffer.
- peptide/ATP-solution 4 ⁇ FITC-Ahx- TSELKKVVALYDYMPMNAND-NH2, 164 ⁇ ATP
- kinase buffer 50mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 1 mM DTT, 0.02% Tween
- Kinase reactions were incubated at 30°C for 60 minutes and subsequently terminated by addition of 16 ⁇ per well of stop solution (100 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 5 % DMSO, 0.1 % Caliper coating reagent, 10 mM EDTA, and 0.015 % Brij35).
- Stop solution 100 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 5 % DMSO, 0.1 % Caliper coating reagent, 10 mM EDTA, and 0.015 % Brij35.
- Kinase reactions were analyzed on a Caliper LC3000 workstation by separating phosphorylated and unphosphorylated peptides and kinase activities were calculated from the amounts of newly formed phospho-peptide.
- Inhibition data were calculated by comparison to control reactions without enzyme (100 % inhibition) and without inhibitors (0 % inhibition). The concentration of inhibitor required for 50 % inhibition (IC50) was calculated from the inhibition in response to inhibitor concentrations.
- the inhibitory activity of the present compounds in blood was assessed in the following in vitro B cell activation assay.
- Whole blood was collected from the abdominal aorta of anaesthetized adult male Lewis rats and was anticoagulated with 100 U/ml sodium heparin. Blood was then diluted to 50 % with high glucose DMEM
- compounds of the invention may generally be useful in the treatment of an indication selected from:
- Autoimmune disorders inflammatory diseases, allergic diseases, airway diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), transplant rejection; diseases in which antibody production, antigen presentation, cytokine production or lymphoid organogenesis are abnormal or are undesirable; including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SOJIA), gout, pemphigus vulgaris, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, Sjogren's syndrome, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)-associated vasculitides, cryoglobulinemia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, chronic autoimmune urticaria, allergy (atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, allergic rhinitis), atherosclerosis, type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, ulcer
- glomerolunephritis Goodpasture's syndrome, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Grave's disease, antibody-mediated transplant rejection (AMR), graft versus host disease, B cell-mediated hyperacute, acute and chronic transplant rejection; thromboembolic disorders, myocardial infarct, angina pectoris, stroke, ischemic disorders, pulmonary embolism; cancers of haematopoietic origin including but not limited to multiple myeloma; a leukaemia; acute myelogenous leukemia; chronic myelogenous leukemia; lymphocytic leukemia; myeloid leukemia; non-Hodgkin lymphoma; lymphomas; polycythemia vera; essential thrombocythemia; myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia; and Waldenstroem disease.
- AMR antibody-mediated transplant rejection
- graft versus host disease B cell-mediated hyperacute, acute and chronic transplant rejection
- the therapy is selected from a disease which may be treated by an antagonist of Bruton's tyrosine kinase.
- the invention provides a method of treating a disease which is treated by the modulation of Btk- comprising administration of a therapeutically acceptable amount of a compound of formula (I) or a salt thereof.
- the disease is selected from the afore-mentioned lists
- the compound of the present invention may be administered either simultaneously with, or before or after, one or more other therapeutic agent.
- the compound of the present invention may be administered separately, by the same or different route of
- the compounds of formula (I) may be administered as the sole active ingredient or in conjunction with, e.g. as an adjuvant to, other drugs e.g. immunosuppressive or immunomodulating agents or other anti-inflammatory agents, e.g. for the treatment or prevention of alio- or xenograft acute or chronic rejection or inflammatory or autoimmune disorders, or a chemotherapeutic agent, e.g a malignant cell anti-proliferative agent.
- the compounds of formula (I) may be used in combination with a calcineurin inhibitor, e.g. cyclosporin A or FK 506; a rmTOR inhibitor, e.g.
- rapamycin 40-O-(2- hydroxyethyl)-rapamycin, CCI779, ABT578, AP23573, AP23464, AP23675, AP23841 , TAFA-93, biolimus-7 or biolimus-9; an ascomycin having immunosuppressive properties, e.g. ABT-281 , ASM981 , etc.; corticosteroids; cyclophosphamide; azathioprene;
- methotrexate methotrexate; leflunomide; mizoribine; mycophenolic acid or salt; mycophenolate mofetil; 15-deoxyspergualine or an immunosuppressive homologue, analogue or derivative thereof; a PKC inhibitor, e.g. as disclosed in WO 02/38561 or WO 03/82859, e.g. the compound of Example 56 or 70; a JAK3 kinase inhibitor, e.g. N-benzyl-3,4-dihydroxy- benzylidene-cyanoacetamide a-cyano-(3,4-dihydroxy)-]N-benzylcinnamamide
- mono-citrate also called CP-690,550
- sphingosine-1 -phosphate receptor modulators such as FTY720 (fingolimod), or compounds disclosed in WO 2005/000833
- immunosuppressive monoclonal antibodies e.g., monoclonal antibodies to leukocyte receptors, e.g., MHC, CD2, CD3, CD4, CD7, CD8, CD25, CD28, CD40, CD45, CD52, CD58, CD80, CD86 or their ligands
- other immunomodulatory compounds e.g.
- a recombinant binding molecule having at least a portion of the extracellular domain of CTLA4 or a mutant thereof, e.g. an at least extracellular portion of CTLA4 or a mutant thereof joined to a non-CTLA4 protein sequence, e.g. CTLA4lg (for ex. designated ATCC 68629) or a mutant thereof, e.g. LEA29Y; adhesion molecule inhibitors, e.g. LFA- 1 antagonists, ICAM-1 or -3 antagonists, VCAM-4 antagonists or VLA-4 antagonists; or a chemotherapeutic agent, e.g.
- a compound of formula (I) may be selected from a PI3K inhibitor (e.g. pan, or alpha, beta, gamma, delta selectives), TNF inhibitors, IL1 beta inhibitors, IL17 inhibitors, and inhibitors of IL6 or IL receptor.
- a PI3K inhibitor e.g. pan, or alpha, beta, gamma, delta selectives
- TNF inhibitors IL1 beta inhibitors
- IL17 inhibitors IL6 or IL receptor
- co-administration or “combined administration” or the like as utilized herein are meant to encompass administration of the selected therapeutic agents to a single patient, and are intended to include treatment regimens in which the agents are not necessarily administered by the same route of administration or at the same time.
- pharmaceutical combination means a product that results from the mixing or combining of more than one active ingredient and includes both fixed and non-fixed combinations of the active ingredients.
- fixed combination means that the active ingredients, e.g. a compound of formula (I) and a co-agent, are both administered to a patient simultaneously in the form of a single entity or dosage.
- non-fixed combination means that the active ingredients, e.g. a compound of formula (I) and a co-agent, are both administered to a patient as separate entities either simultaneously, concurrently or sequentially with no specific time limits, wherein such administration provides therapeutically effective levels of the 2 compounds in the body of the patient.
- cocktail therapy e.g. the administration of 3 or more active ingredients.
- the invention provides a product comprising a compound of formula (I) and at least one other therapeutic agent as a combined preparation for simultaneous, separate or sequential use in therapy.
- the therapy is the treatment of a disease or condition mediated by Btk kinases.
- Products provided as a combined preparation include a composition comprising the compound of formula (I) and the other therapeutic agent(s) together in the same pharmaceutical composition, or the compound of formula (I) and the other therapeutic agent(s) in separate form, e.g. in the form of a kit.
- the invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of formula (I) and another therapeutic agent(s).
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of formula (I) and another therapeutic agent(s).
- composition may comprise a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, as described above.
- the invention provides a kit comprising two or more separate pharmaceutical compositions, at least one of which contains a compound of formula (I).
- the kit comprises means for separately retaining said compositions, such as a container, divided bottle, or divided foil packet.
- a container, divided bottle, or divided foil packet An example of such a kit is a blister pack, as typically used for the packaging of tablets, capsules and the like.
- the kit of the invention may be used for administering different dosage forms, for example, oral and parenteral, for administering the separate compositions at different dosage intervals, or for titrating the separate compositions against one another.
- the kit of the invention typically comprises directions for
- the combination therapies of the invention the compound of the invention and the other therapeutic agent may be manufactured and/or formulated by the same or different manufacturers.
- the compound of the invention and the other therapeutic may be brought together into a combination therapy: (i) prior to release of the combination product to physicians (e.g. in the case of a kit comprising the compound of the invention and the other therapeutic agent); (ii) by the physician themselves (or under the guidance of the physician) shortly before administration; (iii) in the patient themselves, e.g. during sequential administration of the compound of the invention and the other therapeutic agent.
- the invention provides the use of a compound of formula (I) for treating a disease or condition mediated by Btk kinases, wherein the medicament is prepared for administration with another therapeutic agent.
- the invention also provides the use of another therapeutic agent for treating a disease or condition mediated by Btk , wherein the medicament is administered with a compound of formula (I).
- the invention also provides a compound of formula (I) for use in a method of treating a disease or condition mediated by Btk, wherein the compound of formula (I) is prepared for administration with another therapeutic agent.
- the invention also provides another therapeutic agent for use in a method of treating a disease or condition mediated by Btk , wherein the other therapeutic agent is prepared for administration with a compound of formula (I).
- the invention also provides a compound of formula (I) for use in a method of treating a disease or condition mediated by Btk , wherein the compound of formula (I) is administered with another therapeutic agent.
- the invention also provides another therapeutic agent for use in a method of treating a disease or condition mediated by Btk, wherein the other therapeutic agent is administered with a compound of formula (I).
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Rheumatology (AREA)
- Pain & Pain Management (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Plural Heterocyclic Compounds (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
- Compositions Of Macromolecular Compounds (AREA)
- Nitrogen And Oxygen Or Sulfur-Condensed Heterocyclic Ring Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (38)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| MYPI2016701223A MY179059A (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| EP20158961.1A EP3689865B1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| NZ718835A NZ718835A (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| CA2926908A CA2926908C (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| UAA201603623A UA117256C2 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| MYPI2020002915A MY191381A (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| RS20171206A RS56657B1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| MX2016006908A MX367911B (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives. |
| LTEP14821285.5T LT3074386T (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| KR1020227009823A KR102421388B1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| EP14821285.5A EP3074386B1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| CU2016000078A CU24384B1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | DERIVATIVES OF N- (3- (6-AMINOPIRIDIN-4-IL) PHENYL) BENZAMIDA AS BTK INHIBITORS |
| PL17191467T PL3299368T3 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| EP17191467.4A EP3299368B1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| ES14821285.5T ES2655527T3 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| JP2016535053A JP6342495B2 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel aminopyrimidine derivatives |
| MA39055A MA39055B1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | New aminopyrimidine derivatives |
| CN201910288376.XA CN110172056B (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Aminopyrimidine derivatives |
| NO14821285A NO3074386T3 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | |
| PL14821285T PL3074386T3 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| TN2016000128A TN2016000128A1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives. |
| DK14821285.5T DK3074386T3 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel aminopyrimidine derivatives |
| BR112016010397-1A BR112016010397B1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | AMINO PYRIMIDINE DERIVATIVES, THEIR USES AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION |
| AP2016009158A AP2016009158A0 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| EA201691125A EA031218B1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| AU2014356069A AU2014356069B2 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| SI201430536T SI3074386T1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| CN201480058515.5A CN105683181B (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | New aminopyridine derivative |
| EP23161775.4A EP4219478A1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Method of preparing amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| KR1020167013830A KR102380539B1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| ZA2016/02275A ZA201602275B (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2016-04-05 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| IL244943A IL244943B (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2016-04-06 | N-[3-(5-oxy-6-amino-pyrimidin-4-yl)phenyl]benzamide derivatives and pharmaceutical compositions comprising them |
| PH12016500791A PH12016500791B1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2016-04-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| CR20160244A CR20160244A (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2016-05-27 | Novel Amino Pyrimidine Derivatives |
| HK16111636.9A HK1223368A1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2016-10-06 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| CY20171101345T CY1119705T1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2017-12-22 | New aminopyrimidine derivatives |
| HRP20171999TT HRP20171999T1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2017-12-27 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| CY20201100478T CY1122924T1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2020-05-25 | NEW AMINOPYRIMIDINE DERIVATIVES |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP13195081 | 2013-11-29 | ||
| EP13195081.8 | 2013-11-29 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015079417A1 true WO2015079417A1 (en) | 2015-06-04 |
Family
ID=49674216
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/IB2014/066422 WO2015079417A1 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2014-11-28 | Novel amino pyrimidine derivatives |
Country Status (43)
Cited By (64)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2016014530A1 (en) | 2014-07-21 | 2016-01-28 | Novartis Ag | Combinations of low, immune enhancing. doses of mtor inhibitors and cars |
| WO2016014553A1 (en) | 2014-07-21 | 2016-01-28 | Novartis Ag | Sortase synthesized chimeric antigen receptors |
| WO2016014565A2 (en) | 2014-07-21 | 2016-01-28 | Novartis Ag | Treatment of cancer using humanized anti-bcma chimeric antigen receptor |
| WO2016025880A1 (en) | 2014-08-14 | 2016-02-18 | Novartis Ag | Treatment of cancer using gfr alpha-4 chimeric antigen receptor |
| WO2016044605A1 (en) | 2014-09-17 | 2016-03-24 | Beatty, Gregory | Targeting cytotoxic cells with chimeric receptors for adoptive immunotherapy |
| WO2016057841A1 (en) | 2014-10-08 | 2016-04-14 | Novartis Ag | Compositions and methods of use for augmented immune response and cancer therapy |
| WO2016057705A1 (en) | 2014-10-08 | 2016-04-14 | Novartis Ag | Biomarkers predictive of therapeutic responsiveness to chimeric antigen receptor therapy and uses thereof |
| WO2016061142A1 (en) | 2014-10-14 | 2016-04-21 | Novartis Ag | Antibody molecules to pd-l1 and uses thereof |
| WO2016090034A2 (en) | 2014-12-03 | 2016-06-09 | Novartis Ag | Methods for b cell preconditioning in car therapy |
| WO2016164580A1 (en) * | 2015-04-07 | 2016-10-13 | Novartis Ag | Combination of chimeric antigen receptor therapy and amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| WO2016164731A2 (en) | 2015-04-08 | 2016-10-13 | Novartis Ag | Cd20 therapies, cd22 therapies, and combination therapies with a cd19 chimeric antigen receptor (car) - expressing cell |
| WO2017019894A1 (en) | 2015-07-29 | 2017-02-02 | Novartis Ag | Combination therapies comprising antibody molecules to lag-3 |
| WO2017019897A1 (en) | 2015-07-29 | 2017-02-02 | Novartis Ag | Combination therapies comprising antibody molecules to tim-3 |
| WO2017106656A1 (en) | 2015-12-17 | 2017-06-22 | Novartis Ag | Antibody molecules to pd-1 and uses thereof |
| WO2017112741A1 (en) | 2015-12-22 | 2017-06-29 | Novartis Ag | Mesothelin chimeric antigen receptor (car) and antibody against pd-l1 inhibitor for combined use in anticancer therapy |
| WO2017149515A1 (en) | 2016-03-04 | 2017-09-08 | Novartis Ag | Cells expressing multiple chimeric antigen receptor (car) molecules and uses therefore |
| WO2018102787A1 (en) | 2016-12-03 | 2018-06-07 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for determining car-t cells dosing |
| WO2018201056A1 (en) | 2017-04-28 | 2018-11-01 | Novartis Ag | Cells expressing a bcma-targeting chimeric antigen receptor, and combination therapy with a gamma secretase inhibitor |
| WO2018201051A1 (en) | 2017-04-28 | 2018-11-01 | Novartis Ag | Bcma-targeting agent, and combination therapy with a gamma secretase inhibitor |
| WO2018223101A1 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2018-12-06 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Articles of manufacture and methods for treatment using adoptive cell therapy |
| WO2019006427A1 (en) | 2017-06-29 | 2019-01-03 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Mouse model for assessing toxicities associated with immunotherapies |
| US10221245B2 (en) | 2013-03-16 | 2019-03-05 | Novartis Ag | Treatment of cancer using humanized anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor |
| WO2019090003A1 (en) | 2017-11-01 | 2019-05-09 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Chimeric antigen receptors specific for b-cell maturation antigen (bcma) |
| WO2019089858A2 (en) | 2017-11-01 | 2019-05-09 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods of assessing or monitoring a response to a cell therapy |
| WO2019089969A2 (en) | 2017-11-01 | 2019-05-09 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Antibodies and chimeric antigen receptors specific for b-cell maturation antigen |
| WO2019109053A1 (en) | 2017-12-01 | 2019-06-06 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for dosing and for modulation of genetically engineered cells |
| WO2019118937A1 (en) | 2017-12-15 | 2019-06-20 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Anti-cct5 binding molecules and methods of use thereof |
| US10357514B2 (en) | 2014-04-07 | 2019-07-23 | The Trustees Of The University Of Pennsylvania | Treatment of cancer using anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor |
| US10457647B2 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2019-10-29 | Novartis Ag | Amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| WO2019213282A1 (en) | 2018-05-01 | 2019-11-07 | Novartis Ag | Biomarkers for evaluating car-t cells to predict clinical outcome |
| WO2019227003A1 (en) | 2018-05-25 | 2019-11-28 | Novartis Ag | Combination therapy with chimeric antigen receptor (car) therapies |
| WO2019241426A1 (en) | 2018-06-13 | 2019-12-19 | Novartis Ag | Bcma chimeric antigen receptors and uses thereof |
| US10525083B2 (en) | 2016-10-07 | 2020-01-07 | Novartis Ag | Nucleic acid molecules encoding chimeric antigen receptors comprising a CD20 binding domain |
| WO2020021447A1 (en) | 2018-07-25 | 2020-01-30 | Novartis Ag | Nlrp3 inflammasome inhibitors |
| WO2020092854A2 (en) | 2018-11-01 | 2020-05-07 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Chimeric antigen receptors specific for g protein-coupled receptor class c group 5 member d (gprc5d) |
| WO2020092848A2 (en) | 2018-11-01 | 2020-05-07 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for treatment using chimeric antigen receptors specific for b-cell maturation antigen |
| WO2020102770A1 (en) | 2018-11-16 | 2020-05-22 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods of dosing engineered t cells for the treatment of b cell malignancies |
| EP3660042A1 (en) | 2014-07-31 | 2020-06-03 | Novartis AG | Subset-optimized chimeric antigen receptor-containing t-cells |
| WO2020113194A2 (en) | 2018-11-30 | 2020-06-04 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for treatment using adoptive cell therapy |
| WO2020160050A1 (en) | 2019-01-29 | 2020-08-06 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Antibodies and chimeric antigen receptors specific for receptor tyrosine kinase like orphan receptor 1 (ror1) |
| EP3712171A1 (en) | 2014-08-19 | 2020-09-23 | Novartis AG | Treatment of cancer using a cd123 chimeric antigen receptor |
| EP3722316A1 (en) | 2014-07-21 | 2020-10-14 | Novartis AG | Treatment of cancer using a cd33 chimeric antigen receptor |
| WO2020234780A1 (en) | 2019-05-23 | 2020-11-26 | Novartis Ag | Methods of treating asthma using a bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| WO2020234715A1 (en) | 2019-05-17 | 2020-11-26 | Novartis Ag | Nlrp3 inflammasome inhibitors |
| WO2020234782A1 (en) | 2019-05-23 | 2020-11-26 | Novartis Ag | Methods of treating chronic spontaneous urticaria using a bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| WO2020234779A1 (en) | 2019-05-23 | 2020-11-26 | Novartis Ag | Crystalline forms of a btk inhibitor |
| WO2020234781A1 (en) | 2019-05-23 | 2020-11-26 | Novartis Ag | Methods of treating sjögren's syndrome using a bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| WO2021133894A1 (en) * | 2019-12-23 | 2021-07-01 | Biogen Ma Inc. | Btk inhibitors |
| WO2021207689A2 (en) | 2020-04-10 | 2021-10-14 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods and uses related to cell therapy engineered with a chimeric antigen receptor targeting b-cell maturation antigen |
| WO2022034529A1 (en) | 2020-08-14 | 2022-02-17 | Novartis Ag | Heteroaryl substituted spiropiperidinyl derivatives and pharmaceutical uses thereof |
| US11365252B2 (en) | 2016-07-20 | 2022-06-21 | University Of Utah Research Foundation | CD229 CAR T cells and methods of use thereof |
| WO2022162513A1 (en) | 2021-01-26 | 2022-08-04 | Novartis Ag | Pharmaceutical composition |
| WO2022212893A1 (en) | 2021-04-02 | 2022-10-06 | Biogen Ma Inc. | Combination treatment methods of multiple sclerosis |
| WO2023031840A1 (en) | 2021-09-03 | 2023-03-09 | Novartis Ag | Lou064 for treating multiple sclerosis |
| WO2023111802A1 (en) | 2021-12-14 | 2023-06-22 | Novartis Ag | Methods of treatment using lou064 |
| WO2023161887A1 (en) | 2022-02-28 | 2023-08-31 | Novartis Ag | Remibrutinib for use in the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa |
| CN117024354A (en) * | 2023-10-08 | 2023-11-10 | 天津凯莱英制药有限公司 | Preparation method of Rui Mi Buti Ni |
| WO2023250400A1 (en) | 2022-06-22 | 2023-12-28 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Treatment methods for second line therapy of cd19-targeted car t cells |
| WO2024031091A2 (en) | 2022-08-05 | 2024-02-08 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Chimeric antigen receptors specific for gprc5d and bcma |
| WO2024028782A1 (en) | 2022-08-03 | 2024-02-08 | Novartis Ag | Nlrp3 inflammasome inhibitors |
| WO2024069507A1 (en) | 2022-09-30 | 2024-04-04 | Novartis Ag | Synthesis methods and intermediates for the production of remibrutinib |
| EP4378957A2 (en) | 2015-07-29 | 2024-06-05 | Novartis AG | Combination therapies comprising antibody molecules to pd-1 |
| WO2024129778A2 (en) | 2022-12-13 | 2024-06-20 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Chimeric antigen receptors specific for baff-r and cd19 and methods and uses thereof |
| RU2828460C2 (en) * | 2019-05-23 | 2024-10-14 | Новартис Аг | Crystalline forms of btk inhibitor |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR113796A1 (en) * | 2017-11-06 | 2020-06-10 | Lilly Co Eli | BRUTON TYROSINE KINASE (BTK) INHIBITING COMPOUNDS |
| CN108069911A (en) * | 2017-12-14 | 2018-05-25 | 中国药科大学 | 6- amino -2- phenyl pyrimidine classes compound, preparation method and medical usage |
| WO2022033569A1 (en) * | 2020-08-14 | 2022-02-17 | 苏州晶云药物科技股份有限公司 | Crystal forms of benzamide compounds and preparation method therefor |
Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2002038561A1 (en) | 2000-11-07 | 2002-05-16 | Novartis Ag | Indolylmaleimide derivatives as protein kinase c inhibitors |
| WO2002102790A1 (en) | 2001-06-15 | 2002-12-27 | Vicuron Pharmaceuticals Inc. | N-formyl hydroxylamine compounds as inhibitors of pdf |
| WO2003082859A1 (en) | 2002-04-03 | 2003-10-09 | Novartis Ag | Indolylmaleimide derivatives |
| WO2004052359A1 (en) | 2002-12-09 | 2004-06-24 | The Board Of Regents Of The University Of Texas System | Methods for selectively inhibiting janus tyrosine kinase 3 (jak3) |
| WO2004078163A2 (en) | 2003-02-28 | 2004-09-16 | Transform Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pharmaceutical co-crystal compositions of drugs such as carbamazepine, celecoxib, olanzapine, itraconazole, topiramate, modafinil, 5-fluorouracil, hydrochlorothiazide, acetaminophen, aspirin, flurbiprofen, phenytoin and ibuprofen |
| WO2005000833A1 (en) | 2003-05-19 | 2005-01-06 | Irm, Llc | Immunosuppressant compounds and compositions |
| WO2005066156A1 (en) | 2004-01-12 | 2005-07-21 | Cytopia Research Pty Ltd | Selective kinase inhibitors |
| WO2010000633A1 (en) | 2008-07-02 | 2010-01-07 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Novel phenylpyrazinones as kinase inhibitors |
| WO2010100070A1 (en) * | 2009-03-02 | 2010-09-10 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Inhibitors of bruton's tyrosine kinase |
| WO2013083666A1 (en) * | 2011-12-09 | 2013-06-13 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Inhibitors of bruton's tyrosine kinase |
Family Cites Families (32)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6303652B1 (en) | 1998-08-21 | 2001-10-16 | Hughes Institute | BTK inhibitors and methods for their identification and use |
| GB0005345D0 (en) | 2000-03-06 | 2000-04-26 | Mathilda & Terence Kennedy Ins | Methods of treating sepsis septic shock and inflammation |
| CA2426508A1 (en) | 2000-10-23 | 2002-05-16 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | Modulators of bruton's tyrosine kinase and bruton's tyrosine kinase intermediates and methods for their identification and use in the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis and related disease states |
| EP2322201A3 (en) | 2002-10-29 | 2011-07-27 | Genentech, Inc. | Compositions and methods for the treatment of immune related diseases |
| EP1473039A1 (en) | 2003-05-02 | 2004-11-03 | Centre National De La Recherche Scientifique (Cnrs) | Use of inhibitors and antisense oligonucleotides of BTK for the treatment of proliferative mastocytosis |
| KR101357524B1 (en) | 2005-03-10 | 2014-02-03 | 질레드 코네티컷 인코포레이티드 | Certain Substituted Amides, Method of Making, And Method of Use Thereof |
| JP2010502751A (en) | 2006-09-11 | 2010-01-28 | シージーアイ ファーマシューティカルズ,インコーポレイティド | Kinase inhibitors and methods of using and identifying kinase inhibitors |
| AR063946A1 (en) * | 2006-09-11 | 2009-03-04 | Cgi Pharmaceuticals Inc | CERTAIN REPLACED PIRIMIDINS, THE USE OF THE SAME FOR THE TREATMENT OF DISEASES MEDIATED BY THE INHIBITION OF THE ACTIVITY OF BTK AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS THAT UNDERSTAND THEM. |
| EP2532235A1 (en) | 2006-09-22 | 2012-12-12 | Pharmacyclics, Inc. | Inhibitors of bruton's tyrosine kinase |
| CA2680589A1 (en) | 2007-03-14 | 2008-09-18 | Universita' Degli Studi Di Milano - Bicocca | Modulator compounds of the drug resistance in epithelial tumour cells |
| ES2554615T3 (en) | 2008-05-06 | 2015-12-22 | Gilead Connecticut, Inc. | Substituted amides, method of preparation and use as Btk inhibitors |
| MX2011000661A (en) | 2008-07-16 | 2011-05-25 | Pharmacyclics Inc | Inhibitors of bruton's tyrosine kinase for the treatment of solid tumors. |
| US20100261776A1 (en) | 2008-11-07 | 2010-10-14 | The Research Foundation Of State University Of New York | Bruton's tyrosine kinase as anti-cancer drug target |
| CA2748414A1 (en) | 2009-04-24 | 2010-10-28 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Inhibitors of bruton's tyrosine kinase |
| AU2011219764A1 (en) * | 2010-02-26 | 2012-08-16 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Thienopyrimidines containing a substituted alkyl group for pharmaceutical compositions |
| UY33241A (en) * | 2010-02-26 | 2011-09-30 | Boehringer Ingelheim Int | ? Tienopyrimidines containing heterocycloalkyl for pharmaceutical compositions ?. |
| US20120071497A1 (en) | 2010-06-03 | 2012-03-22 | Pharmacyclics, Inc. | Methods of treating abc-dlbcl using inhibitors of bruton's tyrosine kinase |
| EP2694486B1 (en) | 2011-04-01 | 2018-01-10 | University of Utah Research Foundation | Substituted n-(3-(pyrimidin-4-yl)phenyl)acrylamide analogs as tyrosine receptor kinase btk inhibitors |
| MX355728B (en) | 2011-05-17 | 2018-04-27 | Univ California | Kinase inhibitors. |
| BR112013030442B1 (en) | 2011-06-10 | 2021-11-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | PYRIMIDINE AND PYRIDINE COMPOUNDS WITH BTK INHIBITORY ACTIVITY, THEIR USES, COMPOSITION, AND KIT |
| AU2012275275A1 (en) | 2011-06-28 | 2014-01-23 | Pharmacyclics Llc | Methods and compositions for inhibition of bone resorption |
| KR20140058543A (en) | 2011-07-08 | 2014-05-14 | 노파르티스 아게 | Novel pyrrolo pyrimidine derivatives |
| EP3778896A1 (en) | 2011-08-09 | 2021-02-17 | Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center | Methods and compositions for inhibiting the growth and/or proliferation of myc-driven tumor cells |
| US20140303191A1 (en) | 2011-10-19 | 2014-10-09 | Pharmacyclics, Inc. | Use of inhibitors of bruton's tyrosine kinase (btk) |
| AR088570A1 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2014-06-18 | Celgene Avilomics Res Inc | METHODS TO TREAT AN ILLNESS OR DISORDER RELATED TO BRUTON TYROSINE KINASE |
| US20150011751A1 (en) | 2012-03-09 | 2015-01-08 | Carna Biosciences, Inc. | Novel triazine derivative |
| WO2013157021A1 (en) | 2012-04-20 | 2013-10-24 | Advinus Therapeutics Limited | Bicyclic compounds, compositions and medicinal applications thereof |
| AU2013250726B2 (en) | 2012-04-20 | 2017-01-05 | Advinus Therapeutics Limited | Substituted hetero-bicyclic compounds, compositions and medicinal applications thereof |
| WO2013173518A1 (en) | 2012-05-16 | 2013-11-21 | Pharmacyclics, Inc. | Inhibitors of bruton's tyrosine kinase |
| MX2015001802A (en) | 2012-08-10 | 2015-05-07 | Boehringer Ingelheim Int | Heteroaromatic compounds as bruton's tyrosine kinase (btk) inhibitors. |
| CA2887435A1 (en) | 2012-10-04 | 2014-04-10 | University Of Utah Research Foundation | Substituted n-(3-(pyrimidin-4-yl)phenyl)acrylamide analogs as tyrosine receptor kinase btk inhibitors |
| US9512084B2 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2016-12-06 | Novartis Ag | Amino pyrimidine derivatives |
-
2014
- 2014-11-13 US US14/540,140 patent/US9512084B2/en active Active
- 2014-11-27 JO JOP/2014/0341A patent/JO3314B1/en active
- 2014-11-27 UY UY0001035858A patent/UY35858A/en active IP Right Grant
- 2014-11-27 AR ARP140104439A patent/AR098549A1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2014-11-28 EP EP14821285.5A patent/EP3074386B1/en active Active
- 2014-11-28 AP AP2016009158A patent/AP2016009158A0/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 SI SI201432031T patent/SI3689865T1/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 ES ES20158961T patent/ES2947770T3/en active Active
- 2014-11-28 PE PE2016000683A patent/PE20160869A1/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 MA MA39055A patent/MA39055B1/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 EP EP23161775.4A patent/EP4219478A1/en active Pending
- 2014-11-28 RS RS20171206A patent/RS56657B1/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 MY MYPI2016701223A patent/MY179059A/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 TW TW103141506A patent/TWI652261B/en active
- 2014-11-28 CN CN201910288376.XA patent/CN110172056B/en active Active
- 2014-11-28 ES ES14821285.5T patent/ES2655527T3/en active Active
- 2014-11-28 SI SI201430536T patent/SI3074386T1/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 KR KR1020227009823A patent/KR102421388B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2014-11-28 FI FIEP20158961.1T patent/FI3689865T3/en active
- 2014-11-28 HU HUE14821285A patent/HUE037588T2/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 LT LTEP17191467.4T patent/LT3299368T/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 SI SI201431570T patent/SI3299368T1/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 CA CA2926908A patent/CA2926908C/en active Active
- 2014-11-28 UA UAA201603623A patent/UA117256C2/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 NZ NZ718835A patent/NZ718835A/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 LT LTEP20158961.1T patent/LT3689865T/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 PL PL20158961.1T patent/PL3689865T3/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 NO NO14821285A patent/NO3074386T3/no unknown
- 2014-11-28 CU CU2016000078A patent/CU24384B1/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 HU HUE17191467A patent/HUE049794T2/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 MY MYPI2020002915A patent/MY191381A/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 DK DK14821285.5T patent/DK3074386T3/en active
- 2014-11-28 PT PT171914674T patent/PT3299368T/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 LT LTEP14821285.5T patent/LT3074386T/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 ES ES17191467T patent/ES2791525T3/en active Active
- 2014-11-28 HU HUE20158961A patent/HUE062248T2/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 RS RS20230437A patent/RS64275B1/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 PT PT201589611T patent/PT3689865T/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 PT PT148212855T patent/PT3074386T/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 AU AU2014356069A patent/AU2014356069B2/en active Active
- 2014-11-28 WO PCT/IB2014/066422 patent/WO2015079417A1/en active Application Filing
- 2014-11-28 MX MX2016006908A patent/MX367911B/en active IP Right Grant
- 2014-11-28 DK DK17191467.4T patent/DK3299368T3/en active
- 2014-11-28 EP EP20158961.1A patent/EP3689865B1/en active Active
- 2014-11-28 DK DK20158961.1T patent/DK3689865T3/en active
- 2014-11-28 CN CN201480058515.5A patent/CN105683181B/en active Active
- 2014-11-28 HR HRP20230585TT patent/HRP20230585T1/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 JP JP2016535053A patent/JP6342495B2/en active Active
- 2014-11-28 TN TN2016000128A patent/TN2016000128A1/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 RS RS20200550A patent/RS60251B1/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 PL PL17191467T patent/PL3299368T3/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 PL PL14821285T patent/PL3074386T3/en unknown
- 2014-11-28 EA EA201691125A patent/EA031218B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2014-11-28 BR BR112016010397-1A patent/BR112016010397B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2014-11-28 KR KR1020167013830A patent/KR102380539B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2014-11-28 EP EP17191467.4A patent/EP3299368B1/en active Active
-
2016
- 2016-04-05 ZA ZA2016/02275A patent/ZA201602275B/en unknown
- 2016-04-06 IL IL244943A patent/IL244943B/en active IP Right Grant
- 2016-04-21 US US15/135,296 patent/US20160235746A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2016-04-28 PH PH12016500791A patent/PH12016500791B1/en unknown
- 2016-05-03 CL CL2016001055A patent/CL2016001055A1/en unknown
- 2016-05-27 CR CR20160244A patent/CR20160244A/en unknown
- 2016-05-27 SV SV2016005206A patent/SV2016005206A/en unknown
- 2016-06-20 EC ECIEPI201654826A patent/ECSP16054826A/en unknown
- 2016-10-06 HK HK16111636.9A patent/HK1223368A1/en unknown
-
2017
- 2017-12-22 CY CY20171101345T patent/CY1119705T1/en unknown
- 2017-12-27 HR HRP20171999TT patent/HRP20171999T1/en unknown
-
2018
- 2018-05-08 US US15/974,190 patent/US10457647B2/en active Active
- 2018-05-16 JP JP2018094772A patent/JP6667573B2/en active Active
- 2018-09-10 HK HK18111597.4A patent/HK1252317A1/en unknown
-
2019
- 2019-09-16 US US16/571,405 patent/US11180460B2/en active Active
-
2020
- 2020-05-12 HR HRP20200775TT patent/HRP20200775T1/en unknown
- 2020-05-25 CY CY20201100478T patent/CY1122924T1/en unknown
-
2021
- 2021-10-22 US US17/508,054 patent/US11673868B2/en active Active
-
2023
- 2023-05-01 US US18/309,948 patent/US20230312483A1/en active Pending
- 2023-06-27 CY CY20231100301T patent/CY1126056T1/en unknown
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2002038561A1 (en) | 2000-11-07 | 2002-05-16 | Novartis Ag | Indolylmaleimide derivatives as protein kinase c inhibitors |
| WO2002102790A1 (en) | 2001-06-15 | 2002-12-27 | Vicuron Pharmaceuticals Inc. | N-formyl hydroxylamine compounds as inhibitors of pdf |
| WO2003082859A1 (en) | 2002-04-03 | 2003-10-09 | Novartis Ag | Indolylmaleimide derivatives |
| WO2004052359A1 (en) | 2002-12-09 | 2004-06-24 | The Board Of Regents Of The University Of Texas System | Methods for selectively inhibiting janus tyrosine kinase 3 (jak3) |
| WO2004078163A2 (en) | 2003-02-28 | 2004-09-16 | Transform Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pharmaceutical co-crystal compositions of drugs such as carbamazepine, celecoxib, olanzapine, itraconazole, topiramate, modafinil, 5-fluorouracil, hydrochlorothiazide, acetaminophen, aspirin, flurbiprofen, phenytoin and ibuprofen |
| WO2005000833A1 (en) | 2003-05-19 | 2005-01-06 | Irm, Llc | Immunosuppressant compounds and compositions |
| WO2005066156A1 (en) | 2004-01-12 | 2005-07-21 | Cytopia Research Pty Ltd | Selective kinase inhibitors |
| WO2010000633A1 (en) | 2008-07-02 | 2010-01-07 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Novel phenylpyrazinones as kinase inhibitors |
| WO2010100070A1 (en) * | 2009-03-02 | 2010-09-10 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Inhibitors of bruton's tyrosine kinase |
| WO2013083666A1 (en) * | 2011-12-09 | 2013-06-13 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Inhibitors of bruton's tyrosine kinase |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| "Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences", 1985, MACK PUBLISHING COMPANY |
| "Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences", 1990, MACK PRINTING COMPANY, pages: 1289 - 1329 |
| STAHL; WERMUTH: "Handbook of Pharmaceutical Salts: Properties, Selection, and Use", 2002, WILEY-VCH |
Cited By (89)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10927184B2 (en) | 2013-03-16 | 2021-02-23 | Novartis Ag | Treatment of cancer using humanized anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor |
| US10221245B2 (en) | 2013-03-16 | 2019-03-05 | Novartis Ag | Treatment of cancer using humanized anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor |
| US10457647B2 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2019-10-29 | Novartis Ag | Amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| US11180460B2 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2021-11-23 | Novartis Ag | Amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| US11673868B2 (en) | 2013-11-29 | 2023-06-13 | Novartis Ag | Amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| US10357514B2 (en) | 2014-04-07 | 2019-07-23 | The Trustees Of The University Of Pennsylvania | Treatment of cancer using anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor |
| WO2016014553A1 (en) | 2014-07-21 | 2016-01-28 | Novartis Ag | Sortase synthesized chimeric antigen receptors |
| WO2016014530A1 (en) | 2014-07-21 | 2016-01-28 | Novartis Ag | Combinations of low, immune enhancing. doses of mtor inhibitors and cars |
| WO2016014565A2 (en) | 2014-07-21 | 2016-01-28 | Novartis Ag | Treatment of cancer using humanized anti-bcma chimeric antigen receptor |
| EP3722316A1 (en) | 2014-07-21 | 2020-10-14 | Novartis AG | Treatment of cancer using a cd33 chimeric antigen receptor |
| EP4205749A1 (en) | 2014-07-31 | 2023-07-05 | Novartis AG | Subset-optimized chimeric antigen receptor-containing cells |
| EP3660042A1 (en) | 2014-07-31 | 2020-06-03 | Novartis AG | Subset-optimized chimeric antigen receptor-containing t-cells |
| WO2016025880A1 (en) | 2014-08-14 | 2016-02-18 | Novartis Ag | Treatment of cancer using gfr alpha-4 chimeric antigen receptor |
| EP3712171A1 (en) | 2014-08-19 | 2020-09-23 | Novartis AG | Treatment of cancer using a cd123 chimeric antigen receptor |
| WO2016044605A1 (en) | 2014-09-17 | 2016-03-24 | Beatty, Gregory | Targeting cytotoxic cells with chimeric receptors for adoptive immunotherapy |
| EP3967709A1 (en) | 2014-09-17 | 2022-03-16 | Novartis AG | Targeting cytotoxic cells with chimeric receptors for adoptive immunotherapy |
| WO2016057705A1 (en) | 2014-10-08 | 2016-04-14 | Novartis Ag | Biomarkers predictive of therapeutic responsiveness to chimeric antigen receptor therapy and uses thereof |
| WO2016057841A1 (en) | 2014-10-08 | 2016-04-14 | Novartis Ag | Compositions and methods of use for augmented immune response and cancer therapy |
| WO2016061142A1 (en) | 2014-10-14 | 2016-04-21 | Novartis Ag | Antibody molecules to pd-l1 and uses thereof |
| EP4245376A2 (en) | 2014-10-14 | 2023-09-20 | Novartis AG | Antibody molecules to pd-l1 and uses thereof |
| WO2016090034A2 (en) | 2014-12-03 | 2016-06-09 | Novartis Ag | Methods for b cell preconditioning in car therapy |
| WO2016164580A1 (en) * | 2015-04-07 | 2016-10-13 | Novartis Ag | Combination of chimeric antigen receptor therapy and amino pyrimidine derivatives |
| US11149076B2 (en) | 2015-04-08 | 2021-10-19 | Novartis Ag | CD20 therapies, CD22 therapies, and combination therapies with a CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-expressing cell |
| EP4056588A1 (en) | 2015-04-08 | 2022-09-14 | Novartis AG | Cd20 therapies, cd22 therapies, and combination therapies with a cd19 chimeric antigen receptor (car)- expressing cell |
| WO2016164731A2 (en) | 2015-04-08 | 2016-10-13 | Novartis Ag | Cd20 therapies, cd22 therapies, and combination therapies with a cd19 chimeric antigen receptor (car) - expressing cell |
| US10253086B2 (en) | 2015-04-08 | 2019-04-09 | Novartis Ag | CD20 therapies, CD22 therapies, and combination therapies with a CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-expressing cell |
| WO2017019897A1 (en) | 2015-07-29 | 2017-02-02 | Novartis Ag | Combination therapies comprising antibody molecules to tim-3 |
| EP3964528A1 (en) | 2015-07-29 | 2022-03-09 | Novartis AG | Combination therapies comprising antibody molecules to lag-3 |
| EP3878465A1 (en) | 2015-07-29 | 2021-09-15 | Novartis AG | Combination therapies comprising antibody molecules to tim-3 |
| WO2017019894A1 (en) | 2015-07-29 | 2017-02-02 | Novartis Ag | Combination therapies comprising antibody molecules to lag-3 |
| EP4378957A2 (en) | 2015-07-29 | 2024-06-05 | Novartis AG | Combination therapies comprising antibody molecules to pd-1 |
| WO2017106656A1 (en) | 2015-12-17 | 2017-06-22 | Novartis Ag | Antibody molecules to pd-1 and uses thereof |
| EP4424322A2 (en) | 2015-12-17 | 2024-09-04 | Novartis AG | Antibody molecules to pd-1 and uses thereof |
| WO2017112741A1 (en) | 2015-12-22 | 2017-06-29 | Novartis Ag | Mesothelin chimeric antigen receptor (car) and antibody against pd-l1 inhibitor for combined use in anticancer therapy |
| WO2017149515A1 (en) | 2016-03-04 | 2017-09-08 | Novartis Ag | Cells expressing multiple chimeric antigen receptor (car) molecules and uses therefore |
| US11365252B2 (en) | 2016-07-20 | 2022-06-21 | University Of Utah Research Foundation | CD229 CAR T cells and methods of use thereof |
| US11026976B2 (en) | 2016-10-07 | 2021-06-08 | Novartis Ag | Nucleic acid molecules encoding chimeric antigen receptors comprising a CD20 binding domain |
| USRE49847E1 (en) | 2016-10-07 | 2024-02-27 | Novartis Ag | Nucleic acid molecules encoding chimeric antigen receptors comprising a CD20 binding domain |
| US10525083B2 (en) | 2016-10-07 | 2020-01-07 | Novartis Ag | Nucleic acid molecules encoding chimeric antigen receptors comprising a CD20 binding domain |
| US11872249B2 (en) | 2016-10-07 | 2024-01-16 | Novartis Ag | Method of treating cancer by administering immune effector cells expressing a chimeric antigen receptor comprising a CD20 binding domain |
| WO2018102787A1 (en) | 2016-12-03 | 2018-06-07 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for determining car-t cells dosing |
| EP4279136A2 (en) | 2016-12-03 | 2023-11-22 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for determining car-t cells dosing |
| WO2018201056A1 (en) | 2017-04-28 | 2018-11-01 | Novartis Ag | Cells expressing a bcma-targeting chimeric antigen receptor, and combination therapy with a gamma secretase inhibitor |
| WO2018201051A1 (en) | 2017-04-28 | 2018-11-01 | Novartis Ag | Bcma-targeting agent, and combination therapy with a gamma secretase inhibitor |
| US11413310B2 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2022-08-16 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Articles of manufacture and methods for treatment using adoptive cell therapy |
| US11944647B2 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2024-04-02 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Articles of manufacture and methods for treatment using adoptive cell therapy |
| WO2018223101A1 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2018-12-06 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Articles of manufacture and methods for treatment using adoptive cell therapy |
| WO2019006427A1 (en) | 2017-06-29 | 2019-01-03 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Mouse model for assessing toxicities associated with immunotherapies |
| US11623961B2 (en) | 2017-11-01 | 2023-04-11 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Antibodies and chimeric antigen receptors specific for B-cell maturation antigen |
| WO2019089969A2 (en) | 2017-11-01 | 2019-05-09 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Antibodies and chimeric antigen receptors specific for b-cell maturation antigen |
| WO2019090003A1 (en) | 2017-11-01 | 2019-05-09 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Chimeric antigen receptors specific for b-cell maturation antigen (bcma) |
| US12031975B2 (en) | 2017-11-01 | 2024-07-09 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods of assessing or monitoring a response to a cell therapy |
| WO2019089858A2 (en) | 2017-11-01 | 2019-05-09 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods of assessing or monitoring a response to a cell therapy |
| WO2019109053A1 (en) | 2017-12-01 | 2019-06-06 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for dosing and for modulation of genetically engineered cells |
| US12006356B2 (en) | 2017-12-15 | 2024-06-11 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Anti-CCT5 binding molecules and chimeric antigen receptors comprising the same |
| WO2019118937A1 (en) | 2017-12-15 | 2019-06-20 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Anti-cct5 binding molecules and methods of use thereof |
| WO2019213282A1 (en) | 2018-05-01 | 2019-11-07 | Novartis Ag | Biomarkers for evaluating car-t cells to predict clinical outcome |
| WO2019227003A1 (en) | 2018-05-25 | 2019-11-28 | Novartis Ag | Combination therapy with chimeric antigen receptor (car) therapies |
| WO2019241426A1 (en) | 2018-06-13 | 2019-12-19 | Novartis Ag | Bcma chimeric antigen receptors and uses thereof |
| WO2020021447A1 (en) | 2018-07-25 | 2020-01-30 | Novartis Ag | Nlrp3 inflammasome inhibitors |
| WO2020092854A2 (en) | 2018-11-01 | 2020-05-07 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Chimeric antigen receptors specific for g protein-coupled receptor class c group 5 member d (gprc5d) |
| WO2020092848A2 (en) | 2018-11-01 | 2020-05-07 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for treatment using chimeric antigen receptors specific for b-cell maturation antigen |
| WO2020102770A1 (en) | 2018-11-16 | 2020-05-22 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods of dosing engineered t cells for the treatment of b cell malignancies |
| WO2020113194A2 (en) | 2018-11-30 | 2020-06-04 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for treatment using adoptive cell therapy |
| EP4427810A2 (en) | 2018-11-30 | 2024-09-11 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods for treatment using adoptive cell therapy |
| WO2020160050A1 (en) | 2019-01-29 | 2020-08-06 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Antibodies and chimeric antigen receptors specific for receptor tyrosine kinase like orphan receptor 1 (ror1) |
| WO2020234715A1 (en) | 2019-05-17 | 2020-11-26 | Novartis Ag | Nlrp3 inflammasome inhibitors |
| CN113811301A (en) * | 2019-05-23 | 2021-12-17 | 诺华股份有限公司 | Methods of treating sjogren's syndrome using bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| RU2828460C2 (en) * | 2019-05-23 | 2024-10-14 | Новартис Аг | Crystalline forms of btk inhibitor |
| EP4442321A2 (en) | 2019-05-23 | 2024-10-09 | Novartis AG | Methods of treating sjögren's syndrome using a bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| WO2020234781A1 (en) | 2019-05-23 | 2020-11-26 | Novartis Ag | Methods of treating sjögren's syndrome using a bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| WO2020234779A1 (en) | 2019-05-23 | 2020-11-26 | Novartis Ag | Crystalline forms of a btk inhibitor |
| WO2020234780A1 (en) | 2019-05-23 | 2020-11-26 | Novartis Ag | Methods of treating asthma using a bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| WO2020234782A1 (en) | 2019-05-23 | 2020-11-26 | Novartis Ag | Methods of treating chronic spontaneous urticaria using a bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| WO2021133894A1 (en) * | 2019-12-23 | 2021-07-01 | Biogen Ma Inc. | Btk inhibitors |
| WO2021207689A2 (en) | 2020-04-10 | 2021-10-14 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods and uses related to cell therapy engineered with a chimeric antigen receptor targeting b-cell maturation antigen |
| WO2022034529A1 (en) | 2020-08-14 | 2022-02-17 | Novartis Ag | Heteroaryl substituted spiropiperidinyl derivatives and pharmaceutical uses thereof |
| WO2022162513A1 (en) | 2021-01-26 | 2022-08-04 | Novartis Ag | Pharmaceutical composition |
| WO2022212893A1 (en) | 2021-04-02 | 2022-10-06 | Biogen Ma Inc. | Combination treatment methods of multiple sclerosis |
| WO2023031840A1 (en) | 2021-09-03 | 2023-03-09 | Novartis Ag | Lou064 for treating multiple sclerosis |
| WO2023111802A1 (en) | 2021-12-14 | 2023-06-22 | Novartis Ag | Methods of treatment using lou064 |
| WO2023161887A1 (en) | 2022-02-28 | 2023-08-31 | Novartis Ag | Remibrutinib for use in the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa |
| WO2023250400A1 (en) | 2022-06-22 | 2023-12-28 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Treatment methods for second line therapy of cd19-targeted car t cells |
| WO2024028782A1 (en) | 2022-08-03 | 2024-02-08 | Novartis Ag | Nlrp3 inflammasome inhibitors |
| WO2024031091A2 (en) | 2022-08-05 | 2024-02-08 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Chimeric antigen receptors specific for gprc5d and bcma |
| WO2024069507A1 (en) | 2022-09-30 | 2024-04-04 | Novartis Ag | Synthesis methods and intermediates for the production of remibrutinib |
| WO2024129778A2 (en) | 2022-12-13 | 2024-06-20 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Chimeric antigen receptors specific for baff-r and cd19 and methods and uses thereof |
| CN117024354B (en) * | 2023-10-08 | 2023-12-08 | 天津凯莱英制药有限公司 | Preparation method of Rui Mi Buti Ni |
| CN117024354A (en) * | 2023-10-08 | 2023-11-10 | 天津凯莱英制药有限公司 | Preparation method of Rui Mi Buti Ni |
Also Published As
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11673868B2 (en) | Amino pyrimidine derivatives | |
| US9233111B2 (en) | Pyrrolo pyrimidine derivatives | |
| US20240208947A1 (en) | Jak1 selective inhibitors |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14821285 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| DPE1 | Request for preliminary examination filed after expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed from 20040101) | ||
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 244943 Country of ref document: IL |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2926908 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: IDP00201602662 Country of ref document: ID |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 12016500791 Country of ref document: PH |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2014356069 Country of ref document: AU Date of ref document: 20141128 Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 139550140003002102 Country of ref document: IR |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2014821285 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2014821285 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 39055 Country of ref document: MA |
|
| REG | Reference to national code |
Ref country code: BR Ref legal event code: B01A Ref document number: 112016010397 Country of ref document: BR |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20167013830 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 000683-2016 Country of ref document: PE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 16138728 Country of ref document: CO Ref document number: MX/A/2016/006908 Country of ref document: MX |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2016535053 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: CR2016-000244 Country of ref document: CR |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 201691125 Country of ref document: EA |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: A201603623 Country of ref document: UA |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 112016010397 Country of ref document: BR Kind code of ref document: A2 Effective date: 20160509 |