WO2014153122A1 - Poly-perfluoroalkyl substituted polyethyleneimine foam stabilizers and film formers - Google Patents
Poly-perfluoroalkyl substituted polyethyleneimine foam stabilizers and film formers Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2014153122A1 WO2014153122A1 PCT/US2014/029174 US2014029174W WO2014153122A1 WO 2014153122 A1 WO2014153122 A1 WO 2014153122A1 US 2014029174 W US2014029174 W US 2014029174W WO 2014153122 A1 WO2014153122 A1 WO 2014153122A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- foam
- polyamine
- composition
- fire
- group
- Prior art date
Links
- 125000005010 perfluoroalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 title claims abstract description 18
- 239000004872 foam stabilizing agent Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 10
- 229920002873 Polyethylenimine Polymers 0.000 title abstract description 15
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 86
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 56
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 56
- -1 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 40
- 229920000768 polyamine Polymers 0.000 claims description 35
- YCKRFDGAMUMZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine atom Chemical compound [F] YCKRFDGAMUMZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 29
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 29
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 claims description 29
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 claims description 25
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 claims description 18
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000002209 hydrophobic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- 229920001282 polysaccharide Polymers 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000005017 polysaccharide Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 125000003277 amino group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000003792 electrolyte Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000002562 thickening agent Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000000845 anti-microbial effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000003115 biocidal effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000003139 biocide Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000005187 foaming Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims 2
- 150000004676 glycans Chemical class 0.000 claims 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 abstract description 20
- 239000002798 polar solvent Substances 0.000 abstract description 9
- 239000002244 precipitate Substances 0.000 abstract description 5
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 abstract description 2
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 abstract 1
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 abstract 1
- 235000008504 concentrate Nutrition 0.000 description 53
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 49
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 14
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 13
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 12
- 229920002313 fluoropolymer Polymers 0.000 description 12
- 239000004811 fluoropolymer Substances 0.000 description 11
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 description 10
- 229920000591 gum Polymers 0.000 description 10
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 10
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethylene glycol Natural products OCCO LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 150000004804 polysaccharides Chemical class 0.000 description 7
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 6
- 239000004215 Carbon black (E152) Substances 0.000 description 5
- MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N anhydrous diethylene glycol Natural products OCCOCCO MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 5
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N monopropylene glycol Natural products CC(O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- SVTBMSDMJJWYQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylpentane-2,4-diol Chemical compound CC(O)CC(C)(C)O SVTBMSDMJJWYQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerine Chemical compound OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229920002472 Starch Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 239000012298 atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 4
- XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrogen iodide Chemical compound I XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 4
- 235000019698 starch Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- DDLBHIIDBLGOTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropane-1-sulfonic acid Chemical compound ClCC(O)CS(O)(=O)=O DDLBHIIDBLGOTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910019142 PO4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 238000005804 alkylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000012267 brine Substances 0.000 description 3
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N citric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000004821 distillation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 150000002148 esters Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 229920006158 high molecular weight polymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 230000001965 increasing effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 235000021317 phosphate Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000013535 sea water Substances 0.000 description 3
- HPALAKNZSZLMCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;chloride;hydrate Chemical compound O.[Na+].[Cl-] HPALAKNZSZLMCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920001285 xanthan gum Polymers 0.000 description 3
- NLXLAEXVIDQMFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia chloride Chemical compound [NH4+].[Cl-] NLXLAEXVIDQMFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920002307 Dextran Polymers 0.000 description 2
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 229920000161 Locust bean gum Polymers 0.000 description 2
- CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L Magnesium sulfate Chemical compound [Mg+2].[O-][S+2]([O-])([O-])[O-] CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 229920003171 Poly (ethylene oxide) Polymers 0.000 description 2
- ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Potassium Chemical compound [K] ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sulfate Chemical compound [O-]S([O-])(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Urea Chemical compound NC(N)=O XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005273 aeration Methods 0.000 description 2
- 235000010443 alginic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000000783 alginic acid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000615 alginic acid Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229960001126 alginic acid Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 150000004781 alginic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 150000001340 alkali metals Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000002168 alkylating agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229940100198 alkylating agent Drugs 0.000 description 2
- LLEMOWNGBBNAJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N biphenyl-2-ol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 LLEMOWNGBBNAJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229920002678 cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 2
- UHZZMRAGKVHANO-UHFFFAOYSA-M chlormequat chloride Chemical compound [Cl-].C[N+](C)(C)CCCl UHZZMRAGKVHANO-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000002118 epoxides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 150000002170 ethers Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 230000008014 freezing Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007710 freezing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000013505 freshwater Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229940083124 ganglion-blocking antiadrenergic secondary and tertiary amines Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 235000011187 glycerol Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229940051250 hexylene glycol Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 239000003112 inhibitor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 235000010420 locust bean gum Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000000711 locust bean gum Substances 0.000 description 2
- YIXJRHPUWRPCBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N magnesium nitrate Chemical compound [Mg+2].[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O YIXJRHPUWRPCBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005580 one pot reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000007530 organic bases Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000010452 phosphate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000003755 preservative agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000003141 primary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000007142 ring opening reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 159000000000 sodium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000008107 starch Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000003467 sulfuric acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229920003169 water-soluble polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000000080 wetting agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- OMDQUFIYNPYJFM-XKDAHURESA-N (2r,3r,4s,5r,6s)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-[[(2r,3s,4r,5s,6r)-4,5,6-trihydroxy-3-[(2s,3s,4s,5s,6r)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-2-yl]methoxy]oxane-3,4,5-triol Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@H]1OC[C@@H]1[C@@H](O[C@H]2[C@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)O1 OMDQUFIYNPYJFM-XKDAHURESA-N 0.000 description 1
- VILCJCGEZXAXTO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2,2-tetramine Chemical compound NCCNCCNCCN VILCJCGEZXAXTO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OVSKIKFHRZPJSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,4-D Chemical compound OC(=O)COC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1Cl OVSKIKFHRZPJSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- URDCARMUOSMFFI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl-(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]acetic acid Chemical compound OCCN(CC(O)=O)CCN(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O URDCARMUOSMFFI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XYUINKARGUCCQJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-imino-n-propylpropan-1-amine Chemical compound CCCNCCC=N XYUINKARGUCCQJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QYYMDNHUJFIDDQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-chloro-2-methyl-1,2-thiazol-3-one;2-methyl-1,2-thiazol-3-one Chemical compound CN1SC=CC1=O.CN1SC(Cl)=CC1=O QYYMDNHUJFIDDQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GJCOSYZMQJWQCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9H-xanthene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2CC3=CC=CC=C3OC2=C1 GJCOSYZMQJWQCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 244000215068 Acacia senegal Species 0.000 description 1
- 229920001817 Agar Polymers 0.000 description 1
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O Ammonium Chemical compound [NH4+] QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 1
- 108010053481 Antifreeze Proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000416162 Astragalus gummifer Species 0.000 description 1
- CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-M Bromide Chemical compound [Br-] CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229920002134 Carboxymethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N Dextrotartaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MDNWOSOZYLHTCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichlorophen Chemical compound OC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1CC1=CC(Cl)=CC=C1O MDNWOSOZYLHTCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RPNUMPOLZDHAAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethylenetriamine Chemical compound NCCNCCN RPNUMPOLZDHAAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KCXVZYZYPLLWCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N EDTA Chemical compound OC(=O)CN(CC(O)=O)CCN(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O KCXVZYZYPLLWCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZLSWBLPERHFHIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fenoprop Chemical compound OC(=O)C(C)OC1=CC(Cl)=C(Cl)C=C1Cl ZLSWBLPERHFHIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine Chemical compound FF PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000926 Galactomannan Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001503 Glucan Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000084 Gum arabic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000569 Gum karaya Polymers 0.000 description 1
- HTTJABKRGRZYRN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Heparin Chemical compound OC1C(NC(=O)C)C(O)OC(COS(O)(=O)=O)C1OC1C(OS(O)(=O)=O)C(O)C(OC2C(C(OS(O)(=O)=O)C(OC3C(C(O)C(O)C(O3)C(O)=O)OS(O)(=O)=O)C(CO)O2)NS(O)(=O)=O)C(C(O)=O)O1 HTTJABKRGRZYRN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004354 Hydroxyethyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000663 Hydroxyethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002153 Hydroxypropyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lithium Chemical compound [Li] WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000057 Mannan Polymers 0.000 description 1
- AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanesulfonic acid Chemical group CS(O)(=O)=O AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000881 Modified starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002230 Pectic acid Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004372 Polyvinyl alcohol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002125 Sokalan® Polymers 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tartaric acid Natural products [H+].[H+].[O-]C(=O)C(O)C(O)C([O-])=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920001615 Tragacanth Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002310 Welan gum Polymers 0.000 description 1
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000010489 acacia gum Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000205 acacia gum Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002378 acidificating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000008272 agar Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940023476 agar Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000010419 agar Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 125000001931 aliphatic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229910052784 alkaline earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000001342 alkaline earth metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003973 alkyl amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000005599 alkyl carboxylate group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910000147 aluminium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- IMUDHTPIFIBORV-UHFFFAOYSA-N aminoethylpiperazine Chemical compound NCCN1CCNCC1 IMUDHTPIFIBORV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000019270 ammonium chloride Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000003863 ammonium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001450 anions Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000002528 anti-freeze Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004599 antimicrobial Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008346 aqueous phase Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001580 bacterial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 1
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-M bisulphate group Chemical group S([O-])(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000001110 calcium chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004202 carbamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003178 carboxy group Chemical group [H]OC(*)=O 0.000 description 1
- 235000010948 carboxy methyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000001768 carboxy methyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008112 carboxymethyl-cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010418 carrageenan Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920001525 carrageenan Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000000679 carrageenan Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940113118 carrageenan Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000001913 cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003086 cellulose ether Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000013522 chelant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001805 chlorine compounds Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000004587 chromatography analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007979 citrate buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000354 decomposition reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000008367 deionised water Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001934 delay Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229960002086 dextran Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229960000633 dextran sulfate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- GYZLOYUZLJXAJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N diglycidyl ether Chemical compound C1OC1COCC1CO1 GYZLOYUZLJXAJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 description 1
- KSDGSKVLUHKDAL-UHFFFAOYSA-L disodium;3-[2-carboxylatoethyl(dodecyl)amino]propanoate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].CCCCCCCCCCCCN(CCC([O-])=O)CCC([O-])=O KSDGSKVLUHKDAL-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 239000012153 distilled water Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000921 elemental analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- NBVXSUQYWXRMNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N fluoromethane Chemical compound FC NBVXSUQYWXRMNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004088 foaming agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002334 glycols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229930182470 glycoside Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 150000004820 halides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000005843 halogen group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000008233 hard water Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000669 heparin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229960002897 heparin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- WGCNASOHLSPBMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydroxyacetaldehyde Natural products OCC=O WGCNASOHLSPBMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000019447 hydroxyethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000010977 hydroxypropyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000001863 hydroxypropyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000013067 intermediate product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005342 ion exchange Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000010494 karaya gum Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000002576 ketones Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000014666 liquid concentrate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008258 liquid foam Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052744 lithium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052943 magnesium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000019341 magnesium sulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910021645 metal ion Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000019426 modified starch Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000178 monomer Substances 0.000 description 1
- LSHROXHEILXKHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N n'-[2-[2-[2-(2-aminoethylamino)ethylamino]ethylamino]ethyl]ethane-1,2-diamine Chemical compound NCCNCCNCCNCCNCCN LSHROXHEILXKHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229930014626 natural product Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 150000002823 nitrates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- MGFYIUFZLHCRTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N nitrilotriacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CN(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O MGFYIUFZLHCRTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002736 nonionic surfactant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010534 nucleophilic substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000010292 orthophenyl phenol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004306 orthophenyl phenol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013808 oxidized starch Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- LCLHHZYHLXDRQG-ZNKJPWOQSA-N pectic acid Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)O[C@H](C(O)=O)[C@@H]1OC1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](OC2[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O2)C(O)=O)O)[C@@H](C(O)=O)O1 LCLHHZYHLXDRQG-ZNKJPWOQSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920001277 pectin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000010987 pectin Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000001814 pectin Substances 0.000 description 1
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K phosphate Chemical compound [O-]P([O-])([O-])=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N phosphoric acid Substances OP(O)(O)=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000003013 phosphoric acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000000704 physical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920002401 polyacrylamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000010318 polygalacturonic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006254 polymer film Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000006116 polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920002451 polyvinyl alcohol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000915 polyvinyl chloride Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000001253 polyvinylpolypyrrolidone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013809 polyvinylpolypyrrolidone Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920000523 polyvinylpolypyrrolidone Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011591 potassium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000001103 potassium chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000002924 primary amino group Chemical group [H]N([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005096 rolling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001542 size-exclusion chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011780 sodium chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008234 soft water Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007928 solubilization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005063 solubilization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052712 strontium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- CIOAGBVUUVVLOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N strontium atom Chemical compound [Sr] CIOAGBVUUVVLOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003871 sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000001629 suppression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000008399 tap water Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011975 tartaric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000002906 tartaric acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- FAGUFWYHJQFNRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetraethylenepentamine Chemical compound NCCNCCNCCNCCN FAGUFWYHJQFNRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Natural products C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000009974 thixotropic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-M toluene-4-sulfonate Chemical group CC1=CC=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C=C1 JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 125000005208 trialkylammonium group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002827 triflate group Chemical group FC(S(=O)(=O)O*)(F)F 0.000 description 1
- 235000010493 xanthan gum Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000230 xanthan gum Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940082509 xanthan gum Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 1
- UHVMMEOXYDMDKI-JKYCWFKZSA-L zinc;1-(5-cyanopyridin-2-yl)-3-[(1s,2s)-2-(6-fluoro-2-hydroxy-3-propanoylphenyl)cyclopropyl]urea;diacetate Chemical compound [Zn+2].CC([O-])=O.CC([O-])=O.CCC(=O)C1=CC=C(F)C([C@H]2[C@H](C2)NC(=O)NC=2N=CC(=CC=2)C#N)=C1O UHVMMEOXYDMDKI-JKYCWFKZSA-L 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A62—LIFE-SAVING; FIRE-FIGHTING
- A62D—CHEMICAL MEANS FOR EXTINGUISHING FIRES OR FOR COMBATING OR PROTECTING AGAINST HARMFUL CHEMICAL AGENTS; CHEMICAL MATERIALS FOR USE IN BREATHING APPARATUS
- A62D1/00—Fire-extinguishing compositions; Use of chemical substances in extinguishing fires
- A62D1/0071—Foams
- A62D1/0085—Foams containing perfluoroalkyl-terminated surfactant
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A62—LIFE-SAVING; FIRE-FIGHTING
- A62D—CHEMICAL MEANS FOR EXTINGUISHING FIRES OR FOR COMBATING OR PROTECTING AGAINST HARMFUL CHEMICAL AGENTS; CHEMICAL MATERIALS FOR USE IN BREATHING APPARATUS
- A62D1/00—Fire-extinguishing compositions; Use of chemical substances in extinguishing fires
- A62D1/0071—Foams
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C303/00—Preparation of esters or amides of sulfuric acids; Preparation of sulfonic acids or of their esters, halides, anhydrides or amides
- C07C303/26—Preparation of esters or amides of sulfuric acids; Preparation of sulfonic acids or of their esters, halides, anhydrides or amides of esters of sulfonic acids
- C07C303/30—Preparation of esters or amides of sulfuric acids; Preparation of sulfonic acids or of their esters, halides, anhydrides or amides of esters of sulfonic acids by reactions not involving the formation of esterified sulfo groups
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C309/00—Sulfonic acids; Halides, esters, or anhydrides thereof
- C07C309/63—Esters of sulfonic acids
- C07C309/64—Esters of sulfonic acids having sulfur atoms of esterified sulfo groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms
- C07C309/69—Esters of sulfonic acids having sulfur atoms of esterified sulfo groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of a carbon skeleton substituted by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F7/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 4 or 14 of the Periodic Table
- C07F7/02—Silicon compounds
- C07F7/08—Compounds having one or more C—Si linkages
- C07F7/0834—Compounds having one or more O-Si linkage
- C07F7/0838—Compounds with one or more Si-O-Si sequences
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F7/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 4 or 14 of the Periodic Table
- C07F7/02—Silicon compounds
- C07F7/08—Compounds having one or more C—Si linkages
- C07F7/0834—Compounds having one or more O-Si linkage
- C07F7/0838—Compounds with one or more Si-O-Si sequences
- C07F7/0872—Preparation and treatment thereof
- C07F7/0889—Reactions not involving the Si atom of the Si-O-Si sequence
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G73/00—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a linkage containing nitrogen with or without oxygen or carbon in the main chain of the macromolecule, not provided for in groups C08G12/00 - C08G71/00
- C08G73/02—Polyamines
- C08G73/0206—Polyalkylene(poly)amines
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K5/00—Use of organic ingredients
- C08K5/04—Oxygen-containing compounds
- C08K5/10—Esters; Ether-esters
- C08K5/12—Esters; Ether-esters of cyclic polycarboxylic acids
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K5/00—Use of organic ingredients
- C08K5/16—Nitrogen-containing compounds
- C08K5/17—Amines; Quaternary ammonium compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K5/00—Use of organic ingredients
- C08K5/16—Nitrogen-containing compounds
- C08K5/34—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen in the ring
- C08K5/3467—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen in the ring having more than two nitrogen atoms in the ring
- C08K5/3472—Five-membered rings
- C08K5/3475—Five-membered rings condensed with carbocyclic rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K5/00—Use of organic ingredients
- C08K5/36—Sulfur-, selenium-, or tellurium-containing compounds
- C08K5/41—Compounds containing sulfur bound to oxygen
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L79/00—Compositions of macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming in the main chain of the macromolecule a linkage containing nitrogen with or without oxygen or carbon only, not provided for in groups C08L61/00 - C08L77/00
- C08L79/02—Polyamines
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K3/00—Materials not provided for elsewhere
- C09K3/18—Materials not provided for elsewhere for application to surfaces to minimize adherence of ice, mist or water thereto; Thawing or antifreeze materials for application to surfaces
Definitions
- Perfluoroalkyl surfactants are commonly used in the preparation of aqueous fire- fighting foams (AFFFs). These surfactants are effective when used in preparing foams used to extinguish fires caused by non-polar fuels such as hydrocarbons, and act by covering the surface of the burning fuel with a vapor- suppressing film. However, such foams are ineffective in fighting fires caused by polar solvents, such as alcohols, ketones, or
- AR-AFFFs alcohol-resistant firefighting foams
- AR-AFFF formulations contain water-soluble polymers that prevent the foam from collapsing on polar fuels and that also significantly lengthen the foam drain time by increasing the viscosity of the aqueous phase.
- the polymers most commonly used are polysaccharides such as xanthan and rhamsan gums. The dissolved gum precipitates from the foam solution when it contacts the polar fuel and forms a soft mat, or membrane, between the foam blanket and fuel to block further intermixing.
- Foam stabilizers are provided containing a highly branched substituted polyamine where the amino groups of the polyamine are substituted with (a) -(CH 2 ) m (CF 2 ) n F, where m is 1-12 and n is 4-16; and (b) a hydrophilic moiety selected from the group consisting of -(CH 2 ) p CHOH(CH 2 ) q S0 3 " , (CH 2 ) p CHOH(CH 2 ) q NH 4 + and (CH 2 ) p COO ⁇ ; where p and q independently are 1-6 and p+q is 2-8.
- the substituted polyamine has an average molecular weight Mw of between about 5 kDa and 25 kDa prior to substitution; and the stabilizer has a fluorine content of about 15 to about 25%.
- the amino groups of the polyamine may be further substituted with a siloxane moiety such as (R 3 SiO) 2 Si(R)(CH 2 )30CH 2 CHOHCH 2 - or
- n may be 4-6, for example, or may be 6.
- m may be 1 or 2, and in certain embodiments may be 1 or 2.
- p and q may be 1 or 2.
- the weight average molecular weight M w of the unsubstituted polyamine is about 10 kDa.
- a siloxane moiety may optionally be added to the polymer by reacting the highly branche
- aqueous film-forming firefighting composition concentrates containing (a) an effective amount of a foam stabilizing agent as described above.
- the concentrate may further contain (b) an effective amount of a monomeric perfluoroalkyl surfactant, and/or (c) an effective amount of at least one non-fluorinated surfactant.
- the composition optionally may further contain an effective amount of one or more components selected from the group consisting of: a foam aid, a freeze protection composition, a composition containing ion sequestering, buffer, and anti-corrosion components, a biocide and antimicrobial composition, an electrolyte composition, and a polysaccharide gum thickener.
- Fire-fighting foams also are provided, containing a foam stabilizer or composition as described above, together with methods of making such foams by foaming a composition as described above with an aqueous liquid, such as liquids containing fresh water, brackish water and salt water. Methods of fighting fires by contacting a fire with these foams are provided.
- Novel water-soluble polymers are provided that are useful as foam stabilizers and film forming agents in firefighting foams.
- the novel polymers have low solubility in polar solvents and improve the stability of firefighting foams when the foams are used to fight fires fueled by such polar solvents.
- the polymers precipitate from the foam and form a liquid or solid film at the polar solvent/foam interface. This precipitate significantly delays the collapse and destruction of the foam, thereby enhancing the fire extinguishing and burnback resistance properties of the foam.
- AR-AFFF firefighting concentrates and compositions containing the novel polymers are also provided.
- the presence of the novel polymers in these compositions permits the use of lowered amounts of polysaccharide film-forming gums, and even allows use of compositions that lack gums altogether. Lowering or removing the gum concentration in this fashion significantly reduces the viscosity of the compositions, which allows the compositions to be proportioned more easily and more accurately than conventional AR-AFFF compositions.
- the novel polymers are branched polyamines containing a mixture of primary, secondary and tertiary amines in which the amine groups are substituted with at least two types of substituent: (a) a perfluoroalkyl moiety that is both oleophobic and hydrophobic and a (b) a hydrophilic group.
- the amine groups may further be substituted with (c) a siloxane moiety that acts as a foam rolling booster.
- the polyamine is a
- PEI polyethyleneimine
- other branched polyamines also could be used.
- the polyamine composition used to prepare the novel polymers is a highly branched polymer.
- Suitable polyamines are commercially available aliphatic polyamines prepared by polymerization of amines such as diethylenetriamine, triethylenetetramine,
- Suitable polyamines can be prepared from these and other amines by methods that are well known in the art.
- the polyamine is a PEI having a ratio of primary, secondary and tertiary amines that is about 1:2: 1, although the skilled artisan will recognize that this is not an absolute requirement, and that PEI compositions with differing ratios also can be used.
- the starting polyamine can have a molecular weight of from about 800 to about 25,000, advantageously 5000 to 25000, before it is derivitized, although, again, the skilled artisan will recognize that polymers with molecular weights outside this range may also be used if desired.
- “molecular weight” refers to the weight average molecular weight M w ).
- Suitable starting polyamine compositions are, for example, PEI polymers available commercially from, for example, SigmaAldrich (St. Louis, MO) and Nippon Shokubai (as Epomin®)
- novel polymers described herein comprise a highly branched substituted polyamine where the amino groups of the polyamine are substituted with (a) a perfluoroalkyl moiety having the structure -(CH 2 ) m (CF 2 ) n F,; and (b) a hydrophilic moiety, where the hydrophilic moiety is selected from the group consisting of -(CH 2 ) p CHOH(CH 2 ) q S0 3 ⁇ ,
- hydrophobic moiety (a) can be 1-12, advantageously 1-6 or 1-2 and n can be 4-16, advantageously 4-8 or 4-6.
- hydrophilic moiety (b) p and q independently can be 1-6, advantageously 1-3 or 1-2, and p+q is 2-8, advantageously 2-4.
- the starting polyamine has an average molecular weight M w of about 800 to 25,000, advantageously about 5000 to 25000, or 10,000 to 15,000, prior to substitution.
- the polymer advantageously has a fluorine content of between about 15% and about 25%, although a variation of 10% above and below these values also is acceptable.
- the fluorine content is determined by a calculation based on 100% conversion of perfluoroalkyl alkyl iodide starting material and by fluorine elemental analysis).
- the relative molar ratios of starting polymer, hydrophobic perfluoroalkyl moiety, hydrophilic moiety and siloxane moiety can vary as desired, but advantageously are in the ranges shown:
- Novel polyamine polymers containing the hydrophobic and hydrophilic substituents described above can be used as foam stabilizers without further substitution.
- a siloxane substituent can be added to the polymer.
- Suitable siloxane moieties include those having the formula (R 3 SiO) 2 Si(R)(CH 2 )30CH 2 CHOHCH 2 - or
- R 3 SiO[Si(R) 2 0] r Si(CH 2 ) 3 OCH 2 CHOHCH 2 _, where each R independently is lower alkyl, r l-9, and where the stabilizer has a silicon content of about 0.1 to about 10%.
- the term "lower alkyl” means C -C alkyl, advantageously C C 4 alkyl, and where the alkyl group can be straight chain or branched.
- the siloxane moiety can be (Me 3 SiO) 2 Si(Me)(CH 2 ) 3 OCH 2 CHOHCH 2 - or
- the polymers may conveniently be prepared by nucleophilic substitution of the amine groups of the polymer using suitable alkylating agents.
- suitable alkylating agents such as halogen atoms, tosylate, mesylate and triflate groups and the like.
- the perfluoroalkyl moiety is introduced by reacting the polymer with a perfluoroalkyl alkyl halide, more advantageously a perfluoroalkyl alkyl iodide.
- Suitable perfluoroalkyl reagents include those with the general structure X-(CH 2 ) m (CF 2 ) n F, where m is
- n is 4-16 and X is a leaving group that can be displaced by an amine, such as iodide.
- the hydrophilic moiety similarly is introduced by contacting the polymer with a reagent having a structure selected from X-(CH 2 ) p CHOH(CH 2 ) q S0 3 " , X-
- X is a leaving group that can be displaced by an amine.
- X in the hydrophilic reagent is chloride, bromide or iodide
- the siloxane moiety is advantageously introduced via the ring-opening reaction of an epoxide.
- the polymer can be reacted with a siloxane moiety selected from
- the alkylation reactions can be carried out simultaneously or sequentially.
- the reactions are carried out sequentially and conveniently in a single reaction vessel.
- the starting polyamine can first be reacted with a perfluoroalkyl alkyl iodide, followed by reaction with the hydrophilic reagent described above.
- the reaction is carried out in any suitable non-reactive solvent in which the reagents are soluble.
- isopropanol IP A
- IP A isopropanol
- the starting polymer and perfluoroalkyl alkyl halide are heated in IPA, for example at 70° C, for a period of time sufficient to consume all of the alkylating agent.
- the hydrophilic reagent is then introduced and the resulting mixture heated again to 70° C until the hydrophilic reagent is consumed.
- the order of reaction can be reversed, with the hydrophilic reagent added first, followed by the perfluoroalkyl alkyl halide.
- the siloxane epoxide reagent can be added in any order to the reaction mixture, but typically is added either last, or simultaneously with the reagent added second. Again the ring-opening of the epoxide can be carried out in the same solvent as the alkylation reactions used to introduce the perfluoroalkyl and hydrophilic moieties.
- the solvent can be removed in vacuo and/or by atmospheric distillation) and the resulting polymer typically is used without further purification.
- the polymer product may be further purified using methods well known in the art, for example, size exclusion chromatography, ion-exchange
- the polymers as described above can be used to prepare aqueous firefighting composition concentrates that are effective for preparing alcohol-resistant aqueous film- forming foams.
- the polymers can be used to prepare AR-AFFF concentrates using methods that are known in the art and the polymers described herein can be used to replace some or all of the high molecular weight polymers used in the concentrates known in the art. See for example, US Patent No. 5,750,043, the contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference in their entirety.
- Concentrates prepared from the polymers described herein are useful for extinguishing UL162 Class B polar (water soluble) and non-polar (water insoluble) liquid fuel fires.
- the concentrates also meet the standards set forth in EN 1568-3 an EN 1568-4. Methods for determining the effective amount of polymer for use in the concentrates are well known in the art.
- concentrates containing the polymers described above also contain an effective amount of a monomeric perfluoroalkyl surfactant, and an effective amount of at least one non-fluorinated surfactant.
- the concentrates also may contain one or more components such as a foam aid, a freeze protection composition, a composition comprising ion
- the AR-AFFF concentrates may be produced at any suitable strength, including, but not limited to, 1, 3 and 6% (w/w) foam concentrates, which are concentrations that are typical for commercial use. Concentrates that are less than 1% (w/w) or greater than 6% (w/w) also may be prepared. As used herein, the lowest numbered strength for the concentrate used indicates the most concentrated product, i.e., the percent designation refers to the proportioning rate of foam concentrate to water. Accordingly, one part of 1% concentrate used with 99 parts water gives 100 parts of use strength pre-mix; similarly, three parts 3% concentrate and 97 parts water gives 100 parts of pre-mix.
- water may include pure, deionized or distilled water, tap or fresh water, sea water, brine, or an aqueous or water- containing solution or mixture capable of serving as a water component for the fire-fighting composition.
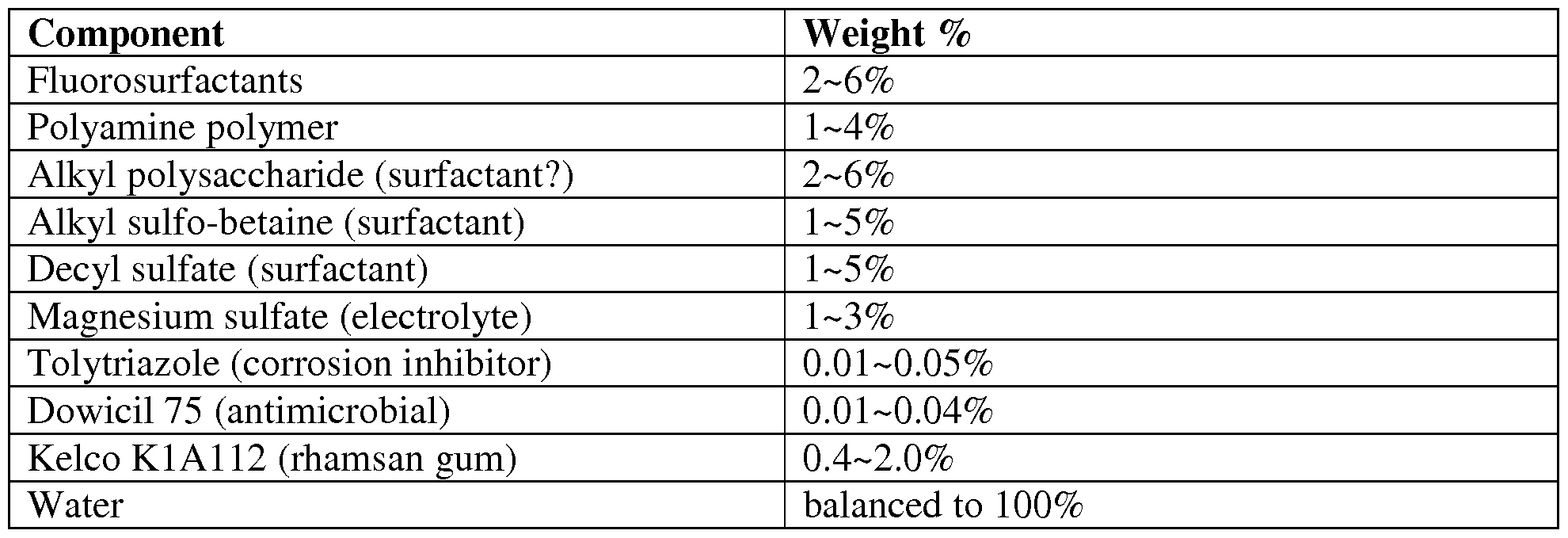
- Typical components used for preparing AR-AFFF concentrates are shown in the tables below, together with typical % concentrations (w/w).
- the above components would be reduced or increased accordingly relative to the 3% liquid concentrate to prepare 6% and 1% synthetic liquid foam concentrates, or other concentrate levels.
- the above amounts may be increased by a factor of 3
- the above amounts may be reduced by half.
- the high molecular weight fluoropolymers as described herein may be used in an amount to provide a foam concentrate that may have from about 0.005% or less to about 6% or more fluorine by weight of concentrate, more typically from about 0.01% to about 4.5% fluorine by weight of concentrate.
- the final fire-fighting foam or composition may have fluorine content of from about 0.0003% to about 0.065% fluorine by weight of solution, advantageously from about 0.0006% to about 0.05% by weight fluorine from the
- fluoropolymers being typical, or from 0.001% to about 0.035% by weight fluorine.
- a 3% concentrate may have from about 0.01% by weight fluorine to about 2% by weight fluorine from the fluoropolymer, advantageously from about 0.02% to about 1.5% by weight, or from about 0.05% to about 1% by weight.
- a 1% foam concentrate may have from about 0.03% to about 6% by weight fluorine from the fluoropolymer, advantageously from about 0.06% to about 4.5% by weight fluorine being typical, or from about 0.15% to about 3% by weight fluorine.
- a 6% concentrate may have from about 0.005% to about 1% by weight fluorine from the fluoropolymer, advantageously from about 0.01% to about 0.5% by weight fluorine, or from about 0.025% to about 0.4% by weight fluorine.
- Hydrocarbon (non-fluorinated) surfactants are non-fluorinated surfactants.
- Amphoteric hydrocarbon surfactants include, but are not limited to, those which contain in the same molecule, amino and carboxy, sulfonic, and sulfuric ester moieties and the like. Higher alkyl (C 6 -C 14 ) betaines and sulfobetaines are included in this category.
- Chembetaine CAS Librizol Inc.
- Mirataine CS Rhodia
- Deriphat 160C BASF
- C 12 amino-dicarboxylate a C 12 amino-dicarboxylate
- Anionic hydrocarbon surfactants include, but are not limited to, alkyl carboxylates, sulfates, sulfonates, and their ethoxylated derivatives. Alkali metal and ammonium salts are suitable. Cg-C 16 hydrocarbon surfactants are suitable, including, advantageously, Cg-Cio-
- Nonionic hydrocarbon surfactants help reduce interfacial tension and solubilize other components, especially in hard water, sea water or brine solutions. They also serve to control foam drainage, foam fluidity, and foam expansion.
- Suitable nonionic surfactants include, but are not limited to, polyoxyethylene derivatives of alkylphenols, linear or branched alcohols, fatty acids, alkylamines, alkylamides, and acetylenic glycols, alkyl glycosides and
- polyglycosides as defined in U.S. Pat. No. 5,207,932 (herein incorporated by reference) and others, and block polymers of polyoxyethylene and polyoxypropylene units.
- Fluorochemical surfactants are typically single perfluoro-tail molecules and may have multiple hydrophilic heads.
- the fluorochemical surfactant contains perfluoroalkyl groups no longer than C 6 , although Cg and longer fluorosurfactants can also be used.
- suitable fluorochemical surfactants include those described in
- the quantity of fluorochemical surfactant(s) may be added to increase extinguishing speed and burnback resistance.
- the presence of the fluoropolymers described herein permits the total fluorochemical surfactant content to be less than one-half of the typical workable levels required when the fluorinated polymers are absent while still meeting UL162 Class B and EN 1568 fire performance.
- the fluorosurfactant may provide less than about 0.2% or 0.1% fluorine in a 3% concentrate, or less than about 0.006% or 0.003% fluorine, respectively, at the working strength.
- Fluorine content provided by any fluorosurfactant in the final or working fire-fighting composition may be less than 0.002% or even 0.001% fluorine by weight of the working composition. Foam aids
- Foam aids may be used to enhance foam expansion and drain properties, while providing solubilization and anti-freeze action.
- Useful foam aids are well known in the art and are disclosed, for example, in U.S. Pat. Nos. 5,616,273, 3,457,172; 3,422,011 and 3,579,446, which are herein incorporated by reference.
- Typical foam aids include alcohols or ethers such as ethylene glycol monoalkyl ethers, diethylene glycol monoalkyl ethers, propylene glycol monoalkyl ethers, dipropylene glycol monoalkyl ethers, triethylene glycol monoalkyl ethers, l-butoxyethoxy-2-propanol, glycerine, and hexylene glycol.
- alcohols or ethers such as ethylene glycol monoalkyl ethers, diethylene glycol monoalkyl ethers, propylene glycol monoalkyl ethers, dipropylene glycol monoalkyl ethers, triethylene glycol monoalkyl ethers, l-butoxyethoxy-2-propanol, glycerine, and hexylene glycol.
- a freeze protection package is used to prevent the concentrate freezing or becoming unusably viscous at low temperatures.
- Typical components include glycerine, ethylene glycol, diethylene glycol, and propylene glycol.
- Other potential components include salts and other solids which reduce the freezing point of the concentrate, such as calcium, potassium, sodium and ammonium chloride and urea.
- the components of the sequestering, buffer, and corrosion package include agents that sequester and chelate metal ions.
- agents that sequester and chelate metal ions include polyaminopolycarboxylic acids, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, citric acid, tartaric acid, nitrilotriacetic acid,
- Sorensen's phosphate or Mcllvaine's citrate buffers The nature of the corrosion inhibitors is limited only by compatibility with other formula components. Typical corrosion inhibitors include ortho-phenylphenol, toluyl triazole, and many phosphate ester acids.
- water-soluble polymeric film formers precipitate from solution when the bubbles contact polar solvents and fuel, and form a vapor-repelling polymer film at the solvent/foam interface, preventing further foam collapse.
- suitable compounds include thixotropic polysaccharide gums as described in U.S. Pat. Nos. 3,957,657; 4,060,132; 4,060,489; 4,306,979; 4,387,032; 4,420,434; 4,424,133; 4,464,267, 5,218,021, and 5,750,043, which are herein incorporated by reference.
- Suitable commercially available compounds are marketed as Rhodopol, Kelco, Keltrol, Actigum, Cecal-gum, Calaxy, and Kalzan.
- Gums and resins useful as film formers include acidic gums such as xanthan gum, pectic acid, alginic acid, agar, carrageenan gum, rhamsam gum, welan gum, mannan gum, locust bean gum, galactomannan gum, pectin, starch, bacterial alginic acid, succinoglucan, gum arabic, carboxymethylcellulose, heparin, phosphoric acid polysaccharide gums, dextran sulfate, dermantan sulfate, fucan sulfate, gum karaya, gum tragacanth and sulfated locust bean gum.
- acidic gums such as xanthan gum, pectic acid, alginic acid, agar, carrageenan gum, rhamsam gum, welan gum, mannan gum, locust bean gum, galactomannan gum, pectin, starch, bacterial alginic acid, succino
- Neutral polysaccharides useful as film formers include: cellulose, hydroxyethyl cellulose, dextran and modified dextrans, neutral glucans, hydroxypropyl cellulose, as well, as other cellulose ethers and esters.
- Modified starches include starch esters, ethers, oxidized starches, and enzymatically digested starches.
- These components may be used to prevent biological decomposition of natural product based polymers incorporated as polymeric film formers.
- Examples include Kathon CG/ICP (Rohm & Haas Company)and Givgard G-4 40 (Givaudan, Inc.), and are disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 5,207,932, which is herein incorporated by reference. Additional preservatives are disclosed in U.S. Patents No. 3,957,657; 4,060,132; 4,060,489; 4,306,979; 4,387,032;
- Electrolytes may be added to AR-AFFF agents to balance the performance of such agents when proportioned with water ranging from soft to very hard, including sea water or brine, and to improve agent performance in very soft water.
- Typical electrolytes include salts of monovalent or polyvalent metals of Groups 1, 2, or 3, or organic bases.
- the alkali metals particularly useful are sodium, potassium, and lithium, or the alkaline earth metals, especially magnesium, calcium, strontium, and zinc or aluminum.
- Organic bases might include ammonium, trialkylammonium, bis-ammonium salts or the like.
- the anions of the electrolyte are not critical, except that halides may not be desirable due to metal corrosion. Sulfates, bisulfates, phosphates, nitrates and the like are commonly used. Examples of polyvalent salts include magnesium sulfate and magnesium nitrate.
- Concentrates containing fluoropolymers of the type described herein typically do not contain additional polymeric foam stabilizers and thickeners, but such components may be included if desired. These components can be optionally incorporated to enhance the foam stability and foam drainage properties.
- polymeric stabilizers and thickeners include partially hydrolyzed protein, starches, polyvinyl resins such as polyvinyl alcohol, polyacrylamides, carboxyvinyl polymers, polyvinyl polypyrrolidone, and poly(oxyethylene) glycol.
- High MW perfluorinated polymers of the type described herein may be used with commercially available synthetic surfactant concentrates to prepare foam concentrates.
- the commercially available surfactant concentrates are marketed worldwide and include those available from Chemguard, Kidde, and Tyco. These products include: Class A foams (CLASS A PLUS and SILVEX), excellent for extinguishing forest fires, structural fires, and tire fires; high expansion foams sold under the names HI-EX, EXTRA, C2, and VEE-FOAM; vapor suppressant foam sold by Chemguard as VRC foam; bomb foam, a 6% product sold by Chemguard as AFC-380.
- Class A foams CLASS A PLUS and SILVEX
- VRC foam high expansion foams sold under the names HI-EX, EXTRA, C2, and VEE-FOAM
- vapor suppressant foam sold by Chemguard as VRC foam
- bomb foam a 6% product sold by Chemguard as AFC-380.
- Synthetic surfactant concentrates listed as "wetting agents" by Underwriters Laboratory may also be included as base surfactant mixtures for preparing AR-AFFF concentrates.
- Products listed by UL as "wetting agents” are as follows: Fire Strike by Biocenter Inc.; Bio- Fire by Envirorenu Technologies LLC; Enviro-Skin 1% by Environmental Products Inc.; F-500 by Hazard Control Technologies Inc.; Knockdown by National Foam Inc.; Phos-Chek WD881 by Solutia Inc.; Flameout by Summit Environmental Corp. Inc. Micro-Blazeout by Verde Environmental Inc.; Bio-solve by Westford Chemical Corp.
- Concentrate prepared as described above may be mixed with water, typically as a 3% solution, and foamed using foaming devices well known in the art.
- water under pressure passes through a fire hose, typically 3 percent by volume of the concentrate composition is inducted into the hose line by the Venturi effect to form a foam solution of the concentrate diluted with water.
- the solution becomes aerated to produce finished foam by use of an air- aspirating nozzle located at the outlet end of the hose.
- a foam solution stored for any length of time prior to aeration is known as a foam premix and can likewise be aerated to produce a finished foam.
- Equipment which can be used to produce and apply these aqueous air-foams are known in the art and also are described in publications by the National Fire Protection Association.
- the concentrate upon dilution with water and aeration, produces an aqueous film- forming foam which is applied to a body of flammable liquid such as a spill or pool which is burning or subject to ignition.
- the foam extinguishes the burning liquid, and prevents further ignition by providing a blanket to cover the fuel surface and excluding air.
- the compositions are introduced into a fire or flame in an amount sufficient to extinguish the fire or flame.
- amount of extinguishing composition needed to extinguish a particular hazard will depend upon the nature and extent of the hazard.
- Example 1 Preparation of substituted highly branched polyamine containing
- a one-pot, two step conversion was used to prepare a highly substituted PEI. Briefly, a highly branched PEI was first reacted with a perfluoro alkyl iodide, and the resulting product was then reacted with 3-chloro-2-hydroxy-propanesulfonic acid without purification of the intermediate product to provide the final highly substituted PEI.
- Example 2 Use of highly branched poly amine in preparing foam concentrate
- a substituted PEI prepared according to Example 1 was tested in a firefighting concentrate and compared to two commercially available firefighting concentrates.
- Ansulite LV 3X3 and Ansulite lxl ARC are commercially available concentrates that contain a matched high molecular weight polymer as a foam stabilizer.
- Formulations were prepared that were identical to Ansulite LV 3X3 and Ansulite lxl ARC except that the high molecular weight polymer present in the commercial formulations was replaced with the same fluorine weight amount of the polymer from example 1. The resulting formulations achieved the same fire suppression performance and matched all the other desired physical properties of these commercial products).
- a polymer containing hydrophobic, hydrophilic and siloxane substituents was prepared via a two step conversion in a one pot reaction as summarized in the reaction scheme above. Briefly, to a 500ml three necked round bottom flask equipped with a thermometer, a magnetic stirrer and condenser was added a branched PEI ( M w ⁇ 1,800, 21.5g, 0.5 mol, monomer-based molarities), lH,lH,2H,2H-perfluorooctane iodide (2.82g, 0.00595mol), polydimethylsiloxane, diglycidyl ether terminated (M w ⁇ 980) ( 5.84g, 0.00595mol), H 2 0 (60ml) and isopropyl alcohol (IPA, 145 ml).
- PEI M w ⁇ 1,800, 21.5g, 0.5 mol, monomer-based molarities
- the calculated fluorine content -12.49% (wt%) and the calculated M w was -21,700, where both values were calculated based on assumed total conversion of reagents.
- Foam quality of the polymer was assessed on an aqueous solution at a concentration of 0.2g(F)/lL of H 2 0. Hexylene glycol (2g) was added and the resulting solution was agitated in a blender to make foam. Foam expansion was measured on 100ml of the solution against its foam volume and drainage time was also measured simultaneously at 50% of its drainage liquid.
- Foam quality of this sample with around 40% solid content was: FE(ml): 240ml;
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Emergency Management (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Emulsifying, Dispersing, Foam-Producing Or Wetting Agents (AREA)
- Fire-Extinguishing Compositions (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA2910174A CA2910174A1 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2014-03-14 | Poly-perfluoroalkyl substituted polyethyleneimine foam stabilizers and film formers |
| EP14721133.8A EP2967785B1 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2014-03-14 | Poly-perfluoroalkyl substituted polyethyleneimine foam stabilizers and film formers |
| AU2014236292A AU2014236292A1 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2014-03-14 | Poly-perfluoroalkyl substituted polyethyleneimine foam stabilizers and film formers |
| US14/775,558 US10173089B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2014-03-14 | Poly-perfluoroalkyl substituted polyethyleneimine foam stabilizers and film formers |
| AU2018220143A AU2018220143B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2018-08-24 | Poly-perfluoroalkyl substituted polyethyleneimine foam stabilizers and film formers |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201361785963P | 2013-03-14 | 2013-03-14 | |
| US61/785,963 | 2013-03-14 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2014153122A1 true WO2014153122A1 (en) | 2014-09-25 |
Family
ID=50631077
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US2014/029174 WO2014153122A1 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2014-03-14 | Poly-perfluoroalkyl substituted polyethyleneimine foam stabilizers and film formers |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10173089B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP2967785B1 (en) |
| AU (2) | AU2014236292A1 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2910174A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2014153122A1 (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018124968A1 (en) * | 2016-12-27 | 2018-07-05 | Agency For Science, Technology And Research | Water-based fire extinguisher formulation |
| EP3429699A4 (en) * | 2016-03-18 | 2019-10-30 | Tyco Fire Products LP | Polyorganosiloxane compounds as active ingredients in fluorine free fire suppression foams |
| US10780305B2 (en) | 2016-03-18 | 2020-09-22 | Tyco Fire Products Lp | Organosiloxane compounds as active ingredients in fluorine free fire suppression foams |
| WO2020212591A1 (en) | 2019-04-18 | 2020-10-22 | Incendin Nv | Polymeric compound for stabilizing fluorine-free fire extinguishing foam and method of making same |
| BE1027199A1 (en) | 2019-04-18 | 2020-11-13 | Incendin Nv | POLYMER COMPOUND AND USE THEREOF FOR STABILIZING FLUOR-FREE FIRE-EXTINGUISHING FOAM |
| BE1027198A1 (en) | 2019-04-18 | 2020-11-13 | Incendin Nv | POLYMER COMPOUND FOR STABILIZING FLUOR-FREE FIRE-EXTINGUISHING FOAM AND PROCEDURE FOR MAKING THIS |
Families Citing this family (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103237577B (en) | 2010-10-01 | 2016-11-30 | 泰科消防产品有限合伙公司 | There is the aqueous fire foam of the Oil repellent of attenuating |
| CA2910180A1 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2014-09-25 | Tyco Fire & Security Gmbh | Trimethylglycine as a freeze suppressant in fire fighting foams |
| CA2910185A1 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-09-18 | Tyco Fire Products Lp | Low molecular weight polyethylene glycol (peg) in fluorine containing fire fighting foam concentrates |
| EP3126015B1 (en) | 2014-04-02 | 2020-08-19 | Tyco Fire Products LP | Fire extinguishing compositions |
| MX2019001182A (en) | 2016-07-29 | 2019-06-12 | Tyco Fire Products Lp | Firefighting foam compositions containing deep eutectic solvents. |
| WO2018148632A1 (en) | 2017-02-13 | 2018-08-16 | Carbon, Inc. | Method of making composite objects by additive manufacturing |
| US11110311B2 (en) | 2017-05-31 | 2021-09-07 | Tyco Fire Products Lp | Antifreeze formulation and sprinkler systems comprising improved antifreezes |
| AU2017426443B2 (en) * | 2017-08-02 | 2023-03-16 | Perimeter Solutions Lp | Twin-tail hydrocarbon surfactants for foam compositions |
| US11065490B2 (en) | 2019-01-08 | 2021-07-20 | Tyco Fire Products Lp | Method for addition of fire suppression additive to base foam solutions |
| CN114269439A (en) | 2019-04-23 | 2022-04-01 | 泰科消防产品有限合伙公司 | Non-fluorinated agents for liquid vehicle systems |
| JP2022539343A (en) * | 2019-06-24 | 2022-09-08 | プロメガ コーポレイション | Modified polyamine polymers for delivery of biomolecules into cells |
| US11673011B2 (en) | 2021-05-14 | 2023-06-13 | Tyco Fire Products Lp | Firefighting foam composition |
| EP4337343A1 (en) | 2021-05-14 | 2024-03-20 | Tyco Fire Products LP | Fire-fighting foam composition |
| US11666791B2 (en) | 2021-05-14 | 2023-06-06 | Tyco Fire Products Lp | Fire-fighting foam composition |
| US11497952B1 (en) | 2021-05-14 | 2022-11-15 | Tyco Fire Products Lp | Fire-fighting foam concentrate |
| US11673010B2 (en) | 2021-05-14 | 2023-06-13 | Tyco Fire Products Lp | Fire-fighting foam concentrate |
| CA3218566A1 (en) | 2021-05-14 | 2022-11-17 | Joanna M. Monfils | Fire-fighting foam concentrate |
Citations (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3422011A (en) | 1966-05-03 | 1969-01-14 | Kidde & Co Walter | Foam producing material |
| US3457172A (en) | 1966-08-10 | 1969-07-22 | Flame Out Inc | Flame extinguishing composition |
| US3579446A (en) | 1968-04-29 | 1971-05-18 | Minimax Ag | Fire-extinguishing foam composition including a basic,nitrogenous compound |
| US3957657A (en) | 1971-04-06 | 1976-05-18 | Philadelphia Suburban Corporation | Fire fighting |
| US4060489A (en) | 1971-04-06 | 1977-11-29 | Philadelphia Suburban Corporation | Fire fighting with thixotropic foam |
| US4060132A (en) | 1974-11-19 | 1977-11-29 | Philadelphia Suburban Corporation | Fire fighting with thixotropic foam |
| US4306979A (en) | 1978-08-17 | 1981-12-22 | Hochiki Corporation | Foam type fire extinguishing agent for hydrophilic combustible liquids |
| US4387032A (en) | 1976-03-25 | 1983-06-07 | Enterra Corporation | Concentrates for fire-fighting foam |
| US4420434A (en) | 1981-01-09 | 1983-12-13 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Perfluoralkyl anion/perfluoroalkyl cation ion pair complexes |
| US4424133A (en) | 1980-09-30 | 1984-01-03 | Angus Fire Armour Limited | Fire-fighting compositions |
| US4464267A (en) | 1979-03-06 | 1984-08-07 | Enterra Corporation | Preparing fire-fighting concentrates |
| US4536298A (en) * | 1983-03-30 | 1985-08-20 | Dainippon Ink And Chemicals, Inc. | Aqueous foam fire extinguisher |
| US5207932A (en) | 1989-07-20 | 1993-05-04 | Chubb National Foam, Inc. | Alcohol resistant aqueous film forming firefighting foam |
| US5218021A (en) | 1991-06-27 | 1993-06-08 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Compositions for polar solvent fire fighting containing perfluoroalkyl terminated co-oligomer concentrates and polysaccharides |
| WO1996005889A1 (en) * | 1994-08-25 | 1996-02-29 | Dynax Corporation | Fluorochemical foam stabilizers and film formers |
| US5616273A (en) | 1994-08-11 | 1997-04-01 | Dynax Corporation | Synergistic surfactant compositions and fire fighting concentrates thereof |
| US6156222A (en) | 1998-05-08 | 2000-12-05 | Ciba Specialty Chemicals Corporation | Poly-perfluoroalkyl substituted polyamines as grease proofing agents for paper and foam stabilizers in aqueous fire-fighting foams |
| WO2012045080A1 (en) | 2010-10-01 | 2012-04-05 | Tyco Fire Products Lp | Aqueous fire-fighting foams with reduced fluorine content |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001314525A (en) * | 2000-05-02 | 2001-11-13 | Dainippon Ink & Chem Inc | Fire extinguishing chemical |
| WO2014052369A1 (en) | 2012-09-25 | 2014-04-03 | Tyco Fire & Security Gmbh | Perfluoroalkyl functionalized polyacrylamide for alcohol resistant-aqueous film-forming foam (ar-afff) formulation |
| KR20160010424A (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2016-01-27 | 타이코 파이어 앤 시큐리티 게엠베하 | Perfluoroalkyl composition with reduced chain length |
-
2014
- 2014-03-14 CA CA2910174A patent/CA2910174A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2014-03-14 WO PCT/US2014/029174 patent/WO2014153122A1/en active Application Filing
- 2014-03-14 US US14/775,558 patent/US10173089B2/en active Active
- 2014-03-14 AU AU2014236292A patent/AU2014236292A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2014-03-14 EP EP14721133.8A patent/EP2967785B1/en active Active
-
2018
- 2018-08-24 AU AU2018220143A patent/AU2018220143B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3422011A (en) | 1966-05-03 | 1969-01-14 | Kidde & Co Walter | Foam producing material |
| US3457172A (en) | 1966-08-10 | 1969-07-22 | Flame Out Inc | Flame extinguishing composition |
| US3579446A (en) | 1968-04-29 | 1971-05-18 | Minimax Ag | Fire-extinguishing foam composition including a basic,nitrogenous compound |
| US3957657A (en) | 1971-04-06 | 1976-05-18 | Philadelphia Suburban Corporation | Fire fighting |
| US4060489A (en) | 1971-04-06 | 1977-11-29 | Philadelphia Suburban Corporation | Fire fighting with thixotropic foam |
| US4060132A (en) | 1974-11-19 | 1977-11-29 | Philadelphia Suburban Corporation | Fire fighting with thixotropic foam |
| US4387032A (en) | 1976-03-25 | 1983-06-07 | Enterra Corporation | Concentrates for fire-fighting foam |
| US4306979A (en) | 1978-08-17 | 1981-12-22 | Hochiki Corporation | Foam type fire extinguishing agent for hydrophilic combustible liquids |
| US4464267A (en) | 1979-03-06 | 1984-08-07 | Enterra Corporation | Preparing fire-fighting concentrates |
| US4424133A (en) | 1980-09-30 | 1984-01-03 | Angus Fire Armour Limited | Fire-fighting compositions |
| US4420434A (en) | 1981-01-09 | 1983-12-13 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Perfluoralkyl anion/perfluoroalkyl cation ion pair complexes |
| US4536298A (en) * | 1983-03-30 | 1985-08-20 | Dainippon Ink And Chemicals, Inc. | Aqueous foam fire extinguisher |
| US5207932A (en) | 1989-07-20 | 1993-05-04 | Chubb National Foam, Inc. | Alcohol resistant aqueous film forming firefighting foam |
| US5218021A (en) | 1991-06-27 | 1993-06-08 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Compositions for polar solvent fire fighting containing perfluoroalkyl terminated co-oligomer concentrates and polysaccharides |
| US5616273A (en) | 1994-08-11 | 1997-04-01 | Dynax Corporation | Synergistic surfactant compositions and fire fighting concentrates thereof |
| WO1996005889A1 (en) * | 1994-08-25 | 1996-02-29 | Dynax Corporation | Fluorochemical foam stabilizers and film formers |
| US5750043A (en) | 1994-08-25 | 1998-05-12 | Dynax Corporation | Fluorochemical foam stabilizers and film formers |
| US6156222A (en) | 1998-05-08 | 2000-12-05 | Ciba Specialty Chemicals Corporation | Poly-perfluoroalkyl substituted polyamines as grease proofing agents for paper and foam stabilizers in aqueous fire-fighting foams |
| WO2012045080A1 (en) | 2010-10-01 | 2012-04-05 | Tyco Fire Products Lp | Aqueous fire-fighting foams with reduced fluorine content |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3429699A4 (en) * | 2016-03-18 | 2019-10-30 | Tyco Fire Products LP | Polyorganosiloxane compounds as active ingredients in fluorine free fire suppression foams |
| US10780305B2 (en) | 2016-03-18 | 2020-09-22 | Tyco Fire Products Lp | Organosiloxane compounds as active ingredients in fluorine free fire suppression foams |
| US11173334B2 (en) | 2016-03-18 | 2021-11-16 | Tyco Fire Products Lp | Polyorganosiloxane compounds as active ingredients in fluorine free fire suppression foams |
| WO2018124968A1 (en) * | 2016-12-27 | 2018-07-05 | Agency For Science, Technology And Research | Water-based fire extinguisher formulation |
| WO2020212591A1 (en) | 2019-04-18 | 2020-10-22 | Incendin Nv | Polymeric compound for stabilizing fluorine-free fire extinguishing foam and method of making same |
| BE1027199A1 (en) | 2019-04-18 | 2020-11-13 | Incendin Nv | POLYMER COMPOUND AND USE THEREOF FOR STABILIZING FLUOR-FREE FIRE-EXTINGUISHING FOAM |
| BE1027198A1 (en) | 2019-04-18 | 2020-11-13 | Incendin Nv | POLYMER COMPOUND FOR STABILIZING FLUOR-FREE FIRE-EXTINGUISHING FOAM AND PROCEDURE FOR MAKING THIS |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2967785A1 (en) | 2016-01-20 |
| US20160030793A1 (en) | 2016-02-04 |
| CA2910174A1 (en) | 2014-09-25 |
| AU2018220143B2 (en) | 2020-02-06 |
| EP2967785B1 (en) | 2018-10-03 |
| AU2018220143A1 (en) | 2018-09-13 |
| AU2014236292A1 (en) | 2015-11-05 |
| US10173089B2 (en) | 2019-01-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| AU2018220143B2 (en) | Poly-perfluoroalkyl substituted polyethyleneimine foam stabilizers and film formers | |
| EP2969055B1 (en) | Perfluoroalkyl composition with reduced chain length | |
| EP2904019B1 (en) | Perfluoroalkyl functionalized polyacrylamide for alcohol resistant-aqueous film-forming foam (ar-afff) formulation | |
| EP2969054B1 (en) | Trimethylglycine as a freeze suppressant in fire fighting foams | |
| US11338162B2 (en) | Low molecular weight polyethylene glycol (PEG) in fluorine containing fire fighting foam concentrates | |
| AU2014236241B2 (en) | Use of high molecular weight acrylic polymers in fire fighting foams | |
| EP3956382A1 (en) | Polymeric compound for stabilizing fluorine-free fire extinguishing foam and method of making same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14721133 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2014721133 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2910174 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2014236292 Country of ref document: AU Date of ref document: 20140314 Kind code of ref document: A |