WO2014054052A2 - Context based co-operative learning system and method for representing thematic relationships - Google Patents
Context based co-operative learning system and method for representing thematic relationships Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2014054052A2 WO2014054052A2 PCT/IN2013/000599 IN2013000599W WO2014054052A2 WO 2014054052 A2 WO2014054052 A2 WO 2014054052A2 IN 2013000599 W IN2013000599 W IN 2013000599W WO 2014054052 A2 WO2014054052 A2 WO 2014054052A2
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- context
- objects
- topic
- theme
- features
- Prior art date
Links
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N20/00—Machine learning
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/22—Indexing; Data structures therefor; Storage structures
- G06F16/2228—Indexing structures
- G06F16/2272—Management thereof
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/24—Querying
- G06F16/245—Query processing
- G06F16/2457—Query processing with adaptation to user needs
- G06F16/24578—Query processing with adaptation to user needs using ranking
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/28—Databases characterised by their database models, e.g. relational or object models
- G06F16/284—Relational databases
- G06F16/285—Clustering or classification
Definitions
- This invention relates to the field of information systems, computational systems, and databases.
- this invention relates to search systems, rankings systems, assessing systems, organizing systems, relational systems, and the like.
- this invention relates to machine learning systems, knowledge representation systems, data representation systems, and decision making systems.
- this invention relates, in general, to searching objects, ranking one or more objects and, in particular, to methods and apparatus for relating, assessing, ranking, organizing, and presenting object relationships associated with a theme and user context.
- this invention relates to context based co-operative learning system and method for representing thematic relationships.
- the Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite (often called TCP/IP, although not all applications use TCP) to serve billions of users worldwide. It is a network of networks that consists of millions of private, public, academic, business, and government networks, of local to global scope, that are linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless and optical networking technologies.
- the Internet carries an extensive range of information resources and services, such as the inter-linked hypertext documents of the World Wide Web (WWW) and the infrastructure to support email.
- WWW World Wide Web
- the World Wide Web (or Internet), is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet. With a web browser, one can view web pages that may contain text, images, videos, and other multimedia, and navigate between them via hyperlinks.
- the terms Internet and World Wide Web are often used in everyday speech without much distinction.
- the Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks and, in contrast, the Web is one of the services that runs on the Internet. It is a collection of text documents and other resources, linked by hyperlinks and URLs, usually accessed by web browsers from web servers. In short, the Web can be thought of as an application "running" on the Internet.
- Viewing a web page on the World Wide Web normally begins either by typing the URL of the page into a web browser or by following a hyperlink to that page or resource.
- the web browser then initiates a series of communication messages, behind the scenes, in order to fetch and display it.
- Searching on the Internet or through the web involves inputting a search parameter, and further involves the steps of processing the search parameters against the repository of web pages and their contents and the final step of showing those results through a web browser. Searching involves the use of search engines developed and deployed for the purpose mentioned above.
- a web search engine is designed to search for information on the World Wide Web.
- the search results are generally presented in a line of results often referred to as search engine results pages (SERPs).
- SERPs search engine results pages
- the information may be embedded in web pages, images, information and other types of files.
- Some search engines also mine data available in databases or open directories. Unlike web directories, which are maintained only by human editors, search engines also maintain real-time information by running an algorithm on a web crawler.
- a Web crawler is a computer program that browses the World Wide Web in a methodical, automated manner or in an orderly fashion.
- a search engine operates in the following order:
- Web search engines work by storing information about many web pages, which they retrieve from the HTML itself. These pages are retrieved by a Web crawler (sometimes also known as a spider)— an automated Web browser which follows every link on the site. The contents of each page are then analyzed to determine how it should be indexed (for example, words can be extracted from the titles,page content, headings, or special fields called meta tags). Data about web pages are stored i an index database for use in later queries. A query can be a single word. The purpose of an index is to allow information to be found as quickly as possible.
- Some search engines such as Google, store al l or part of the source page (referred to as a cache) as well as information about the web pages, whereas others, such as AltaVista, store every word of every page they find. This cached page always holds the actual search text since it is the one that was actually indexed, so it can be very useful when the content of the current page has been updated and the search terms are no longer in it.
- search engine When a user enters a query into a search engine (typically by using keywords), the engine examines its index and provides a listing of best-matching web pages according to its criteria, usually with a short summary containing the document's title and sometimes parts of the text.
- the index is built from the information stored with the data and the method by which the information is indexed.
- Most search engines support the use of the boolean operators AND, OR and NOT to further specify the search query. Boolean operators are for literal searches that allow the user to refine and extend the terms of the search.
- the engine looks for the words or phrases exactly as entered.
- Some search engines provide an advanced feature called proximity search which allows users to define the distance between keywords. There is also concept-based searching where the research involves using statistical analysis on pages containing the words or phrases you search for.
- natural language queries allow the user to type a question in the same form one would ask it to a human. A site like this would be ask.com or chacha.com
- search engine The usefulness of a search engine depends on the relevance of the result set it gives back. While there may be millions of web pages that include a particular word or phrase, some pages may be more relevant, popular, or authoritative than others. Most search engines employ methods to rank the results to provide the "best" results first. How a search engine decides which pages are the best matches, and what order the results should be shown in, varies widely from one engine to another. The methods also change over time as Internet usage changes and new techniques evolve. There are two main types of search engine that have evolved: one is a system of predefined and hierarchically ordered keywords that humans have programmed extensively. The other is a system that generates an "inverted index" by analyzing texts it locates. This second form relies much more heavily on the computer itself to do the bulk of the work.
- search engines do not produce search results that are driven, consolidated, and summarized by the major contextual uses based on the overall context and not just phrases. As a result, search results can be a disorganized sometimes not useful at all. This forces a user to surf through results without reaching to expected document, object. There were a few attempts to use simple key phrases for context determination. Without understanding perspective and in absence of ability to learn co-operatively this search becomes a mere extension to simple term frequency based searches.
- An object of the invention is to provide a system and method which provides iterative learning capability in a search engine.
- Another object of the invention is to provide a system and method which provides cooperative learning capability in a search engine.
- Yet another object of the invention is to provide a system and method which provides thematic relationship based search engine.
- Still another object of the invention is to provide a system and method which provides thematic relationship based learning capability in a search engine
- An additional object of the invention is to provide a system and method which provides establishment of contextual relationship in a search engine. Yet an additional object of the invention is to provide a system and method which provides a continuous learning search engine.
- Still an additional object of the invention is to provide a system and method which provides understanding of context based learning in a search engine.
- Another object is provide thematic association among one or more content documents to establish contextual ranking and enable user to search based on example
- object refers to documents, images, textual content, text files, videos, multimedia content, files, folders, and the like searchable content. Traditionally, all of these are searchable on the Internet through search engines.
- Context refers to user perspective or user inputs or learning from a user or any activity in relation to a user profile or user, directly. Context may be place, situation, meta data, and scenario along with association.
- the term, "theme” refers to database perspective which is pre-defined and pre-populated and probably classified.
- Theme is a perspective based association with reference to objective.
- Topic refers to a situation or event in relation to user perspective or system perspective. Topic is a perspective based associated with reference to objective.
- one context may have multiple themes or multiple topics.
- a system and method comprising the step(s) of data coming from various sources; with ability of co-operative learning allowing to build context; and has ability to search in repository of objects like documents (but not limited to documents) based on context with reference to theme. Further can able to represent thematic relationships and closeness among one or more objects.
- the system and method allows context driven co-operative methodology allows to determine the contextual relationships between features typically words and word phrases in case of documents building overall context for objects or documents and ranking them with reference to user context.
- the system and method allows to learn co-operatively with reference to more than one source of information and disambiguate to build systemic context.
- the system and method finds out contextual relationship between/among two or more objects and can rank them with reference to any predefined object.
- the system and method further ranks individual entities and extract them.
- the system and method helps in thematic representation of context and it allows searching with reference to user context.
- the system and method comprises context determination means which further comprises processor and memory coupled processor.
- the information is requested from client along with meta data with objects are used to determine the context.
- the context represented like a thematic relationship. It has ability to refine the existing object classes and evolve a new class if necessary with reference to context.
- a context based co-operative learning system comprising:
- - identifier means adapted to identify and index objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing
- - context determination mechanism adapted to define parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects;
- - information sources' gathering means adapted to gather sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects
- - searching means adapted to search for said objects, in response to at least a user query, within said determined context topic and / or said determined context theme;
- cluster data building mechanism adapted to build clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters;
- - context mapping means adapted to map at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined context topic and / or said determined context theme;
- - cooperative learning means adapted to allow multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme.
- said identifier means is adapted to identify and index objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, characterised, in that, said predetermined parameters comprises data, meta data, meta tags, and the like identifiable features of the objects.
- said identifier means is adapted to identify and index objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, characterised, in that, said identifier means comprises:
- - key features' identification mechanism adapted to identify key features in said objects, which key features relate to a topic
- - relationship identification mechanism adapted to identify relationships among identified key topic-based features per object.
- said identifier means is adapted to identify and index objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, characterised, in that, said identifier means comprises:
- - establishing means adapted to establish contextual / thematic features for said objects
- said co-operative learning means is a systemic and iterative machine learning means.
- said co-operative learning means comprises:
- cluster data building mechanism adapted to build clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters;
- - context mapping means adapted to map at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined topic;
- pre-defined parameters of clustering being associated with predetermined factors comprising likelihood factors, statistical factors, and closeness factors.
- said co-operative learning means comprises:
- cluster data building mechanism adapted to build clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters;
- - context mapping means adapted to map at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined topic;
- said co-operative learning means comprises:
- cluster data building mechanism adapted to build clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters;
- - context mapping means adapted to map at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined theme
- said co-operative learning means comprises:
- cluster data building mechanism adapted to build clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters;
- - context mapping means adapted to map at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined theme
- said co-operative learning means comprises:
- - context mapping means adapted to map the association of said query in terms of document context and / or user context and / or scenario context such that determination of document context and / or user context and / or scenario context being enabled by pre-determined factors such as likelihood factors, statistical factors, and closeness factors.
- said co-operative learning means comprises:
- said context determination means comprises semantic determination mechanism adapted to determine context (and content) based on semantic processing of said identified objects based on said identifiable features of said identified objects.
- said context determination means comprises syntactic determination mechanism adapted to determine context (and content) based on syntactic processing of said identified objects based on said identifiable features of said identified objects.
- said context determination means comprises topic determination mechanism adapted to determine context topic based on topic-based processing of said identified objects based on said identifiable features of said identified objects.
- said context determination mechanism comprises topic determination mechanism adapted to determine at least a topic that is a representative context of textual content of said identified objects.
- said context determination mechanism comprises topic determination mechanism adapted to determine at least a topic based on at least one of the following:
- said context determination mechanism comprises theme determination mechanism adapted to determine at least a theme based on at least one of the following:
- said context determination mechanism comprises topic determination mechanism adapted to determine at least a topic based on the following extracted parameters from a set of identified objects from at least one of the following:
- said context determination means comprises thematic determination mechanism adapted to determine context theme based on thematic processing of said identified objects based identifiable features of said identified objects.
- said context determination means comprises thematic determination mechanism adapted to determine at least a theme based on at least one of the following extracted parameters from a set of identified objects:
- sentence score that is computed, based on local score, global score, and normalization
- said context determination mechanism comprises contextual features inference mechanism adapted to infer contextual features for each of said objects, D;
- Di ⁇ Pi, Ti, Si, Oi ⁇ 0 ⁇ i ⁇ n
- said context determination mechanism comprises contextual features inference mechanism adapted to infer contextual features for each of said objects, D;
- Di ⁇ Pi, Ti, Si, Oi ⁇ ..0 ⁇ i ⁇ n
- n no. of doc in class
- said context determination further comprises clustering mechanism adapted to cluster said inferred features of said objects for a class in to at least the following the four situation vectors:
- Ti ⁇ tO, tl, t2, tn ⁇ for temporal features of the class i.
- Si ⁇ sO, si, s2, sn ⁇ for spatial features of the class i.
- Pi ⁇ p0, pi, p2, pn ⁇ for protagonist features of the class i.
- Oi ⁇ o0, ol, o2, n ⁇ for organisational features of the class i.
- said situation vectors which define a theme, are generated for each class, said situation vectors form at least a situation model / thematic model for that category:
- Tj ⁇ t0, tl, t2,...,tk ⁇
- said context determination mechanism comprises thematic relationship establishment means adapted to establish a theme during the use of said system for searching, said theme being established based on at least one of the parameters comprising user profile, scenario, and knowledge base.
- said context determination mechanism comprises thematic relationship determination means adapted to determine a thematic relationship between said objects.
- said system comprises a user input means or a user and information context defining means adapted to allow a user to input data for topic determination or identification, thereby allowing said system to form a cluster of objects, based on said topic, to be searched or retrieved.
- said system comprises a user input means or a user and information context defining means adapted to allow a user to input data for theme determination or identification, thereby allowing said system to form a cluster of objects, based on said theme, to be searched or retrieved.
- said system comprises classification means adapted to classify a user profile accessing said system and said searching means.
- said system comprises context based learning means adapted to allow said system to learn a context from said at least a user query and corresponding output search result, said context based learning means being an iterative learning mechanism and involving results based on pre-identified topic defined by said system.
- said system comprises context based learning means adapted to allow said system to learn a context from said at least a user query and corresponding output search result, said context based learning means being an iterative learning mechanism and involving results based on pre-identified themes defined by said system.
- said information sources' gathering means is a theme based information sources' gathering means.
- said information sources' gathering means is a topic based information sources' gathering means.
- said information sources' gathering means is a user generated information sources' gathering means.
- said information sources' gathering means is a machine based information sources' gathering means.
- said information sources' gathering means comprises mechanisms to gather information from at least the following three information resources: relation extractor, name entity recognizer, and situation builder; in order to help build a context.
- said system comprises searching means adapted to search for said objects within the theme clustered objects depending upon user query.
- said system comprises searching means adapted to search for said objects within the topic clustered objects depending upon user query.
- said system comprises display means adapted to display searched said objects from searching means.
- said system comprises ranking means adapted to rank searched said objects, said ranking being determined in accordance with reference to user context topic.
- said system comprises ranking means adapted to rank searched said objects, said ranking being determined in accordance with reference to user context theme.
- said step of identifying and indexing objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, characterised, in that, said pre-determined parameters comprising data, meta data, meta tags, and the like identifiable features of the objects.
- said step of identifying and indexing objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing characterised, in that, said step further comprises the steps of:
- said step of identifying and indexing objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing characterised, in that, said step further comprises the steps of:
- said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means comprising a step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other, systematically and iteratively, using a systemic and iterative machine learning means.
- said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means comprising the steps of:
- pre-defined parameters of clustering being associated with predetermined factors comprising likelihood factors, statistical factors, and closeness factors.
- said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means comprises the steps of:
- said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means comprises the steps of:
- said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means comprises the steps of:
- said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means comprises the steps of:
- said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means comprises the steps of:
- said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism comprises a step of determining context (and content) based on semantic processing of said identified objects based on said identifiable features of said identified objects, using a semantic determination mechanism.
- said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism comprises a step of determining context (and content) based on syntactic processing of said identified objects based on said identifiable features of said identified objects, using syntactic determination mechanism.
- said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism comprises a step of determining context topic based on topic-based processing of said identified objects based on said identifiable features of said identified objects, using topic determination mechanism.
- said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism comprises a step of determining at least a topic that is a representative context of textual content of said identified objects, using topic determination mechanism.
- said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism comprises a step of determining at least a topic, using topic determination mechanism, based on at least one of the following:
- said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects,' using a context determination mechanism comprises a step of determining at least a theme, using theme determination mechanism, based on at least one of the following:
- said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism comprises a step of determining at least a topic, using topic determination mechanism, based on at least one of the following:
- said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism comprises a step of determining context theme based on thematic processing of said identified objects based identifiable features of said identified objects, using theme determination mechanism.
- said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism comprises a step of determining at least a theme, using thematic determination mechanism, based on at least one of the following extracted parameters from a set of identified objects:
- sentence score that is computed, based on local score, global score, and normalization
- said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism comprises a step of inferring contextual features, using contextual features inference mechanism, for each of said objects, D;
- n no. of doc in class
- said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism comprises a step of inferring contextual features, using contextual features inference mechanism, for each of said objects, D;
- Di ⁇ Pi, Ti, Si, Oi ⁇ 0 ⁇ i ⁇ n
- n no. of doc in class
- step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism further comprises a step of clustering said inferred features of said objects for a class in to at least the following the four situation vectors, using clustering mechanism:
- Ti ⁇ to, ti, t 2 , t n ⁇ for temporal features of the class i.
- Si ⁇ so, si , s 2 , ........s n ⁇ for spatial features of the class i.
- Pi ⁇ po, pi , p 2 , p n ⁇ for protagonist features of the class i.
- Oi ⁇ oo, oi, o 2 , n ⁇ for organisational features of the class i.
- said situation vectors which define a theme, are generated for each class, said situation vectors form at least a situation model / thematic model for that category:
- T j ⁇ to, ti, t 2 ,...,t k ⁇
- said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism comprises a step of establishing a theme during the use of said method for searching said theme, using thematic relationship establishment means, being established based on at least one of the parameters comprising user profile, scenario, and knowledge base.
- said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism comprises a step of determining a thematic relationship between said objects, using thematic relationship determination means.
- said method comprises a step of allowing a user to input data for topic determination or identification, using user input means or a user and information context defining means, thereby allowing said system to form a cluster of objects, based on said topic* to be searched or retrieved.
- said method comprises a step of allowing a user to input data for theme determination or identification, using user input means or a user and information context defining means, thereby allowing said system to form a cluster of objects, based on said theme, to be searched or retrieved.
- said method comprises a step of classifying a user profile accessing said system and said searching means, using classification means.
- said method comprises a step of allowing said system to learn a context from said at least a user query and corresponding output search result, using context based learning means, said context based learning means being an iterative learning mechanism and involving results based on pre-identified topic defined by said method.
- said method comprises a step of allowing said system to learn a context from said at least a user query and corresponding output search result, using context based learning means, said context based learning means being an iterative learning mechanism and involving results based on pre-identified theme defined by said method.
- said step of gathering sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using information sources' gathering means comprises a step of gathering theme based sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using theme based information sources' gathering means.
- said step of gathering sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using information sources' gathering means comprises a step of gathering topic based sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using topic based information sources' gathering means.
- said step of gathering sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using information sources' gathering means comprises a step of gathering user generated based sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using user generated information sources' gathering means.
- said step of gathering sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using information sources' gathering means comprises a step of gathering machine based sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using machine based information sources' gathering means.
- said step of gathering sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using information sources' gathering means comprises a step of gathering information from at least the following three information resources: relation extractor, name entity recognizer, and situation builder; in order to help build a context.
- said method comprises a step of searching for said objects within the theme clustered objects depending upon user query, using searching means.
- said method comprises a step of searching for said objects within the topic clustered objects depending upon user query, using searching means.
- said method comprises a step of displaying searched said objects from searching means, using display means.
- said method comprises a step of ranking searched said objects, said ranking being determined in accordance with reference to user context topic, using ranking means.
- said method comprises a step of ranking searched said objects, said ranking being determined in accordance with reference to user context theme, using ranking means.
- Figures 1 and 2 illustrate a schematic of the system and method of this invention.
- Figure 3 illustrates mechanism for situation determination.
- Figure 4 illustrates context based learning mechanism which outputs topic as search results.
- Figure 5 illustrates context based learning mechanism which outputs theme as search results.
- Figure 6 illustrates relation extraction for theme.
- Figure 7 illustrates relation extraction for topic.
- an identifier means adapted to identify and index objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing.
- the identifier means comprises context determination mechanism(CDM) adapted to determine context (and content) of the objects based on data, meta data, meta tags, and the like identifiable features of the objects.
- the context determination means further comprises semantic determination mechanismadapted to determine context (and content) based on semantic processing of the objects based on data, meta data, meta tags, and the like identifiable features of the objects.
- the semantic processing is correlated with at least a lexical repository and at least a sense repository database.
- the context determination means further comprises syntactic determination mechanismadapted to determine context (and content) based on syntactic processing of the objects based on data, meta data, meta tags, and the like identifiable features of the objects.
- syntactic processing comprises the following steps, as seen in Figure 3 of the accompanying drawings:
- Search (input) (content) text (corpus) and at least a lexicon file are pre-processed to obtain tagged text with most-likely tag.
- the tagged text (contents) with most likely tag and at least a Lexicon rule file are processed by Bigram approach to obtain tagged text with lexical rule.
- the tagged text with lexical rulealong with at least a contextual rule file are processed with a rule based corrector to obtain final tagged text.
- the context determination means further comprises topic determination mechanismadapted to determine context topic based on topic-based processing of the objects based on data, meta data, meta tags, and the like identifiable features of the objects.
- This identifier means involves a establishing means adapted to perform astep of establishing contextual / topic- based features for the objects.
- the identifier means involves a key features' identification mechanism adapted to performfurther step of identifying key features in the objects, which key features relate to a topic.
- the identifier means involves a relationship identification mechanism adapted to involve still a further step of identifying relationships among identified key topic-based features per object.
- topics could be hierarchical topics, in that, a main topic can have sub-topics hierarchically linked to one another.
- Topic determination refers to determination of topic that is a representative context of the textual content of the objects.
- the relevant features of the documents/contents are determined in space of concepts.
- a topic is not a mere BOW (bag of words) and frequently occurring key phrases, it is an association among key phrases and that leads to a context.
- a topic is determined based on the occurrence of bigrams, trigrams, relationship and occurrence of key words and phrases. There is relation extraction between these occurrences.
- Situation model is used to determine the context with reference to situation parameters. This is shown in Figure 7 of the accompanying drawings.
- a theme is determined based on the occurrence of bigrams, trigrams, relationship and occurrence of key words and phrases. There is relation extraction between these occurrences.
- Situation model is used to determine the context with reference to situation parameters.This is shown in Figure 6 of the accompanying drawings.
- the topic determination mechanism determines a topic based on the following extracted parameters from a set of identified objects:
- topic determination deals with the construction of concept space i.e. confident single-value(unigram) words and confident multi-value( bigram, trigram) words.Consider documents to be bag of words (ordering of words is maintained). Upper case letters are used to represent sets and lower case letters are used for elements of the set.
- T ⁇ tl, t2, tp ⁇ is the concept space.
- C ⁇ cl, c2, ....,cm ⁇ is the class label.
- tf(di,w) denote the frequency of term feature w 6 W in the document di e D .
- F ⁇ fl , f2, .... , fm ⁇ be the set of names of files such that fi is the filename of document di € D.
- DH (dh l, dh2, ,dhm ⁇ be the set of document header of files fi € F.
- Topic Determination Mechanism is based on either determining topic based on association among key phrases, occurrence of bigram, trigram, and relationship between them or extracting relations between key phrases. Topic Detection is also based on extracted information (like bigram, trigram, and the like,)
- the context determination means further comprises thematic determination mechanismadapted to determine context theme based on thematic processing of the objects based on data, meta data, meta tags, and the likeidentifiable features of the objects.
- This identifier means involves a step of establishing contextual / thematic features for the objects.
- the identifier means involves a further step of identifying key features in the objects, which key features relate to a theme.
- the identifier means involves a still further step of identifying relationships among identified key thematic features per object.
- themes could be hierarchical themes, in that, a main theme can have sub-themes hierarchically linked to one another.
- the theme determination mechanism determines a theme based on the following extracted parameters from a set of identified objects:
- Sentence score that is computed, based on local score, global score, and normalization
- the relationship between the concepts and the topics are analyzed to identify context.
- the context is that information that describes the relationship between derived concepts and its associated topics.
- the relationship is analyzed by considering the documents that are processed using the TDR algorithm for finding topics along with the associated concepts. For each document, a topic and the set of associated concepts are discovered. These topics and their concepts are maintained.
- the procedure of identifying the relationship begins by grouping the identical topics together (by identical, it means if two strings match).
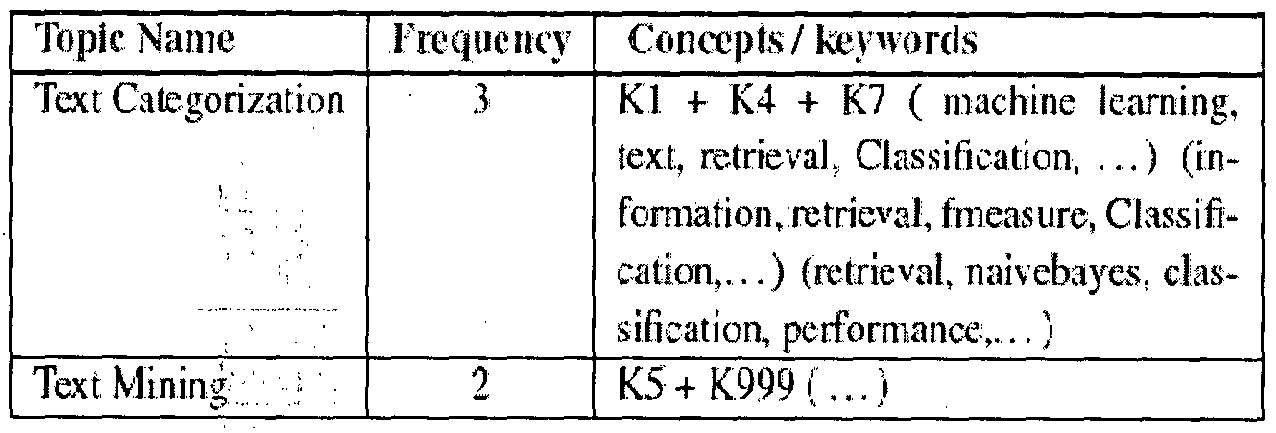
- Kl, K2,— , K1000 contains the list of keywords which are concepts identified during the word decomposition. Group identical topics.Tl, T4 and T7 are identical as all of them have topic "Text categorization”. Similarly T5 and T999 are identical. By grouping it means, add their concepts and maintain their occurrence frequency, and the like.
- the concepts Kl, K4 etc are actually replaced by their keyword list. Then , the system and method finds out term frequency of every keyword in the list of concepts for each topic. After that a list of keywords, is obtained, with their frequencies. Set a threshold limit for appropriate! concept selection considering accuracy. Set a threshold of 50% or 70% - dynamically based on relevance using gating algorithm. This algorithm dynamically changes the window based on relevance. Any keyword that has frequency that crosses the threshold is extracted to be related to the topic. Suppose the threshold is set to 50%, then : if (((frequency of the concept) / (frequency of the topic)) * 100 > threshold) then
- the frequency of the topic i.e., text categorization is 3.
- Frequency of the keyword depends upon the number of occurrence of the keyword within the set.
- Topic id Topic Name Concepts i keywords
- T4 Tex 1 C a tegorixati on K4 (information, retrieval, fmeasure.
- the related words help identify the context to which the topic belongs. if an index is created based on the process to extract the relationships , and then if the given keywords are as "text categorization", then the algorithm would return the related term that are associated with "text categorization ". Each topic is considered as a cluster with the related terms.
- the Situation Extractor basically aims at finding important components of text from the chunks of text. That is, it finds important sentences from chunks of text. For finding important sentences, it uses the score values determined for each sentences.
- the score values are calculated using the local and global score values of each word within the sentence.
- the local score (LS) of a word within a sentence is calculated by adding the score of the considered word with the score of the clause in which the word appears.
- the score of a word is the frequency of the word and the score of a clause is the addition of scores of all trigrams and bigrams containing the word.
- the score for bigrams or trigrams are calculated by adding the frequency of each word falling in bigram or trigram.
- global score (GS) for each word has to be calculated. It is calculated by first finding the similarity of each word with the set of all words in the document and summing the local score of all those words whose similarity value is greater than a predefined threshold. Wordnet path-similarity measure is used for finding similarity between two words.
- sentence score(SV) is determined. It is found by summing the square root of the product of local and global scores values of all words in the sentence.
- the sentence score is simply not calculated by adding the local and global score values of words in the sentence. If this is done, a long sentence will get higher importance value as it contains more words in it. To avoid selection of long sentences,the system and method normalize the score value using the sentence length as a parameter.
- the contextual features are inferred, using contextual features inference mechanism, for each object D;
- n no. of doc in class
- Tj set of temporal features
- Pi ⁇ po, pi , p 2 , p n ⁇ for protagonist features of the class i.
- Oj ⁇ oo, Oi , o 2 , n ⁇ for organisational features of the class i.
- Situation vectors which define a theme, are generated for each class. These situation vectors form the situation model / thematic model for that category.
- the context may be based on the following:
- Metadata closeness based on metadata
- a user input meansor a user and information context deflningmeans (UICM) adapted to allow a user (Ul, U2, U3, Un, Unevv) to input data for theme / context determination or identification.
- UICM user and information context deflningmeans
- This allows a user to establish a theme or a context with which the system and method of this invention will form a cluster of objects (Ol, O2,....0n)to be searched or retrieved. This involves a step of systemic context determination for user and for each of the search object.
- the system and method of this invention comprises a classification means adapted to classify a user profile. This can be determined based on the search query, user history, login preferences, cache history, IP history, or the like parameters related to a user.A profile library, a theme library, and the like may be built.
- a context based learning means adapted to allow the system and method of this invention to learn from user queries and output search results.
- This learning means is an iterative learning mechanism .
- nd involves results based on pre-identified themes or context defined by the system and- method of this invention or a user or both. This involves a step of building an overall search theme.
- context may be search context or user context or the like.
- an information sources' gathering means adapted to allow the system and method of this invention to gather sources of information (IS1, IS2,....ISn) in relation to or with reference to objects.
- TJiis information sources' gathering means comprises theme based or context based information sources' gathering means.
- This information sources' gathering means may be a user generated information sources' gathering means.
- this information sources' gathering means may be a machine based information sources' gathering means.
- a co- operative learning means (CPLM)adapted to allow multiple systems of this invention to cooperatively learn theme / context generation, theme / context identification, object theme / context identification, search analysis based on theme / context and the like means and mechanisms jn order to 'train' the system and method of this invention to output results based on identified ( pr determined themes / contexts.
- Co-operative learning is based on multi level association and it works on information coming from many sources. Co-operative learning
- co-operative learning involves identification of a correct profile, a correct context, correct theme, and / or the like. This is based on learning from various machines and eventually uses the concept of iterative learning to progressively or iteratively become more intelligent and accurate.
- the co-operative learning means is adapted to allow multi-level association so that more than one information sources work with each other. The information sources are associated with each other in order to build a higher level of cooperative learning.
- the co-operative learning means comprises sharing mechanism further adapted to share determined topic and determine theme in order to allow systems to learn with multiple perspectives.
- the co-operative learning means specifically, comprises a feature vectors' building mechanism adapted to allow intelligent systems to build feature vectors based on said pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing. These feature vectors are associated, by means of association mechanism, with probabilistic weight assignment in order to build representative feature vectors.
- Cooperative learning component comprising statistical mechanism, will statistically build weights using multi-level apriori and advanced bias based likelihood algorithm.
- a thematic relationship establishment means (TREM)adapted to establish a theme during the use of the system and method of this invention for searching.
- the theme may be established based on the. parameters involving user profile (UP), scenario (SC), knowledge base (KB) and the like.
- Learning user profile is imperative for the system and method of this invention.
- User profile can be learnt by the system of this invention using any techniques. These techniques may involve reinforcement learning techniques which further include heat maps, time maps, click maps, access to public data, access to private data, and the like.
- a thematic relationship determination means adapted to determine a thematic relationship between objects.
- a plurality of objects may be theme identifies and clustered based on the. theme which is common to the objects.
- An object may have multiple themes, and hence, an object can be a part of multiple clusters in which each cluster is a theme or a part of a theme. This involves a step of building an overall search theme.
- pre-determined factors such as likelihood factors, statistical ⁇ factors, and.closeness factors.
- clustering The process. of identifying which multiple series have similar behaviour and combining those series together is called as clustering.
- the system and method receives a set of series with a similar behavioural patterns, then these series are used to form a representative pattern.
- Thisrepresentative pattern can be referred as a cluster.
- Thecloseness of such patterns is measured and the system and method may decide to merge some of thesepatterns.
- All series that have a similar shape form a cluster.
- Clustering is based on thecloseness factor.
- An understanding of the C Value is necessary to comprehend why clustering works.
- a Closeness factor (C) can be calculated between two series. This C value quantifies thedifference in the shape of each series. The lower the C Value, the smaller the difference.
- a C value of 0 signifies an exact match of shapes even though the volumes might bedifferent.
- SM searchingmeans
- a displaymeans adapted to display searched objects from the searching means.
- a ranking means adapted to rank searched objects. This may involve user ranking or machine ranking or both. This involves a step of ranking the objects with reference to user context in overall themeV topic.Ranking (R) may take placealong with context based learning means (CBLM).User context (UC) can be added to as input to the ranking means (R) and context based learning means (CNLM). The user context is derived from context mapping means (CMM).
- the system and method of this invention provides searching, arranging and most importantly ranking objects with reference to context and representing the thematic relationship among objects. Further the results are arranged and presented with thematic relationship with reference to user or application context.
- the ability of co-operative, learning allows to correct wrong results, handle new contexts and scenarios without compromising accuracy.
- the system and method of this invention can be used for the following:
Abstract
A context based co-operative learning system comprises: identifier means adapted to identify and index objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing; context determination mechanism adapted to define parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects; information sources' gathering means adapted to gather sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects; searching means adapted to search for said objects, in response to at least a user query, within said determined context topic and / or said determined context theme; cluster data building mechanism adapted to build clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters; context mapping means adapted to map at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined context topic and / or said determined context theme; and co-operative learning means adapted to allow multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme.
Description
CONTEXT BASED CO-OPERATIVE LEARNING SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR REPRESENTING THEMATIC RELATIONSHIPS
Field of the Invention:
This invention relates to the field of information systems, computational systems, and databases.
Additionally, this invention relates to search systems, rankings systems, assessing systems, organizing systems, relational systems, and the like.
Additionally, this invention relates to machine learning systems, knowledge representation systems, data representation systems, and decision making systems.
Specifically, this invention relates, in general, to searching objects, ranking one or more objects and, in particular, to methods and apparatus for relating, assessing, ranking, organizing, and presenting object relationships associated with a theme and user context.
More specifically, this invention relates to context based co-operative learning system and method for representing thematic relationships.
Background of the Invention:
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite (often called TCP/IP, although not all applications use TCP) to serve billions of users worldwide. It is a network of networks that consists of millions of private, public, academic, business, and government networks, of local to global scope, that are linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries an extensive range of information resources and services, such as the inter-linked hypertext documents of the World Wide Web (WWW) and the infrastructure to support email.
The World Wide Web (or Internet), is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet. With a web browser, one can view web pages that may contain text, images, videos, and other multimedia, and navigate between them via hyperlinks.
The terms Internet and World Wide Web are often used in everyday speech without much distinction. However, the Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks and, in contrast, the Web is one of the services that runs on the Internet. It is a collection of text documents and other resources, linked by hyperlinks and URLs, usually accessed by web browsers from web servers. In short, the Web can be thought of as an application "running" on the Internet.
Viewing a web page on the World Wide Web normally begins either by typing the URL of the page into a web browser or by following a hyperlink to that page or resource. The web
browser then initiates a series of communication messages, behind the scenes, in order to fetch and display it.
'Searching' on the Internet or through the web involves inputting a search parameter, and further involves the steps of processing the search parameters against the repository of web pages and their contents and the final step of showing those results through a web browser. Searching involves the use of search engines developed and deployed for the purpose mentioned above.
A web search engine is designed to search for information on the World Wide Web. The search results are generally presented in a line of results often referred to as search engine results pages (SERPs). The information may be embedded in web pages, images, information and other types of files. Some search engines also mine data available in databases or open directories. Unlike web directories, which are maintained only by human editors, search engines also maintain real-time information by running an algorithm on a web crawler.
A Web crawler is a computer program that browses the World Wide Web in a methodical, automated manner or in an orderly fashion.
A search engine operates in the following order:
Web crawling
- Indexing
Searching
Web search engines work by storing information about many web pages, which they retrieve from the HTML itself. These pages are retrieved by a Web crawler (sometimes also known as a spider)— an automated Web browser which follows every link on the site. The contents of each page are then analyzed to determine how it should be indexed (for example, words can be extracted from the titles,page content, headings, or special fields called meta tags). Data about web pages are stored i an index database for use in later queries. A query can be a single word. The purpose of an index is to allow information to be found as quickly as possible. Some search engines, such as Google, store al l or part of the source page (referred to as a cache) as well as information about the web pages, whereas others, such as AltaVista, store every word of every page they find. This cached page always holds the actual search text since it is the one that was actually indexed, so it can be very useful when the content of the current page has been updated and the search terms are no longer in it.
When a user enters a query into a search engine (typically by using keywords), the engine examines its index and provides a listing of best-matching web pages according to its criteria, usually with a short summary containing the document's title and sometimes parts of the text. The index is built from the information stored with the data and the method by which the information is indexed. Most search engines support the use of the boolean operators AND, OR and NOT to further specify the search query. Boolean operators are for literal searches that allow the user to refine and extend the terms of the search. The engine looks for the
words or phrases exactly as entered. Some search engines provide an advanced feature called proximity search which allows users to define the distance between keywords. There is also concept-based searching where the research involves using statistical analysis on pages containing the words or phrases you search for. As well, natural language queries allow the user to type a question in the same form one would ask it to a human. A site like this would be ask.com or chacha.com
The usefulness of a search engine depends on the relevance of the result set it gives back. While there may be millions of web pages that include a particular word or phrase, some pages may be more relevant, popular, or authoritative than others. Most search engines employ methods to rank the results to provide the "best" results first. How a search engine decides which pages are the best matches, and what order the results should be shown in, varies widely from one engine to another. The methods also change over time as Internet usage changes and new techniques evolve. There are two main types of search engine that have evolved: one is a system of predefined and hierarchically ordered keywords that humans have programmed extensively. The other is a system that generates an "inverted index" by analyzing texts it locates. This second form relies much more heavily on the computer itself to do the bulk of the work.
Search techniques and techniques to find relationships among different objects based on keywords havetheir own limitations. There techniques give same results even if context is changed. The mere context based techniques without co-operative learning ability could not handle data coming from more than one source (with different contexts). Since the context is dynamic. It keeps changing with user, with scenario and even with place and position. Many times hen anyone starts a search the results are out of the context. There are typical issues like not providing context, failing to express own context, the inability of engine to process the context. Simple use of words and key phrases in absence of association cannot provide the context. Context obtained in absence of co-operative learning is typically not useful in complex scenarios.
Furthermore, there are no standard techniques available for defining context, modeling context, comparing contents across contexts and discovering contextual patterns from text. Learning context of the text would be of great help for analyzing the information contained in the text. For example, organizing the information according to context would help the search engines for fast and efficient retrieval of information, analyzing the search logs for contextual patterns can help a search engine developer to better serve its customers by re-organizing the search results according to the contexts of a new query. Analyzing the evolution of topics or decaying of topics in scientific literature would also help researchers to better organize and summarize the literature and to discover and predict new research trends. Also, analyzing the sentiments in customer reviews related to products and social events would help in summarizing the public opinion about them the products. Studying Author-topic patterns can also make easy the finding of experts and their perceptive of the research communities. Analyzing the text for knowledge building using information from multiple resources also helps in inferring a context.
Designing a context based learning system therefore becomes a great challenging task. In the process of learning context, several challenges related to text mining need to be addressed, which includes:
1. High dimensionality of the feature set
2. Feature Extraction and selection issues
3. High computational complexity issues
4. Parameter Estimation issues of Naive Bayesian Model
5. Context Identification
6. Context Modeling
Prior Art:
Today's search engines do not produce search results that are driven, consolidated, and summarized by the major contextual uses based on the overall context and not just phrases. As a result, search results can be a disorganized sometimes not useful at all. This forces a user to surf through results without reaching to expected document, object. There were a few attempts to use simple key phrases for context determination. Without understanding perspective and in absence of ability to learn co-operatively this search becomes a mere extension to simple term frequency based searches.
The major problem faced is not just search but learning, understanding context and establishing contextual relationship to search and keep learning to search in better way with additional learning. The techniques so far proposed failed to understand thematic relationship.
Hence, there is a need for context learning systems and methods, theme learning systems and methods, topic learning systems and methods, and correlational elements between these systems and methods, thereof.
Objects of the Invention:
An object of the invention is to provide a system and method which provides iterative learning capability in a search engine.
Another object of the invention is to provide a system and method which provides cooperative learning capability in a search engine.
Yet another object of the invention is to provide a system and method which provides thematic relationship based search engine.
Still another object of the invention is to provide a system and method which provides thematic relationship based learning capability in a search engine
An additional object of the invention is to provide a system and method which provides establishment of contextual relationship in a search engine.
Yet an additional object of the invention is to provide a system and method which provides a continuous learning search engine.
Still an additional object of the invention is to provide a system and method which provides understanding of context based learning in a search engine.
Another object is provide thematic association among one or more content documents to establish contextual ranking and enable user to search based on example
Summary of the Invention:
For the purposes of this invention, the term, "object" refers to documents, images, textual content, text files, videos, multimedia content, files, folders, and the like searchable content. Traditionally, all of these are searchable on the Internet through search engines.
For the purposes of this invention, the term, "context" refers to user perspective or user inputs or learning from a user or any activity in relation to a user profile or user, directly. Context may be place, situation, meta data, and scenario along with association.
For the purposes of this invention, the term, "theme" refers to database perspective which is pre-defined and pre-populated and probably classified. Theme is a perspective based association with reference to objective.
For the purposes of this invention, the term, "topic" refers to a situation or event in relation to user perspective or system perspective. Topic is a perspective based associated with reference to objective.
According to one embodiment, one context may have multiple themes or multiple topics.
According to this invention, there is provided a system and method comprising the step(s) of data coming from various sources; with ability of co-operative learning allowing to build context; and has ability to search in repository of objects like documents (but not limited to documents) based on context with reference to theme. Further can able to represent thematic relationships and closeness among one or more objects.
Typically, the system and method allows context driven co-operative methodology allows to determine the contextual relationships between features typically words and word phrases in case of documents building overall context for objects or documents and ranking them with reference to user context.
Typically, the system and method allows to learn co-operatively with reference to more than one source of information and disambiguate to build systemic context.
Typically, the system and method finds out contextual relationship between/among two or more objects and can rank them with reference to any predefined object.
Typically, the system and method further ranks individual entities and extract them.
Typically, the system and method helps in thematic representation of context and it allows searching with reference to user context.
Typically, the system and method comprises context determination means which further comprises processor and memory coupled processor. The information is requested from client along with meta data with objects are used to determine the context. The context represented like a thematic relationship. It has ability to refine the existing object classes and evolve a new class if necessary with reference to context.
According to this invention, there is provided a context based co-operative learning system comprising:
- identifier means adapted to identify and index objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing;
- context determination mechanism adapted to define parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects;
- information sources' gathering means adapted to gather sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects;
- searching means adapted to search for said objects, in response to at least a user query, within said determined context topic and / or said determined context theme;
- cluster data building mechanism adapted to build clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters;
- context mapping means adapted to map at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined context topic and / or said determined context theme; and
- cooperative learning means adapted to allow multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme.
Typically, said identifier means is adapted to identify and index objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, characterised, in that, said predetermined parameters comprises data, meta data, meta tags, and the like identifiable features of the objects.
Typically, said identifier means is adapted to identify and index objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, characterised, in that, said identifier means comprises:
- key features' identification mechanism adapted to identify key features in said objects, which key features relate to a topic; and
- relationship identification mechanism adapted to identify relationships among identified key topic-based features per object.
Additionally, said identifier means is adapted to identify and index objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, characterised, in that, said identifier means comprises:
- establishing means adapted to establish contextual / thematic features for said objects;
- key features' identification mechanism adapted to identify key features in said objects, which key features relate to a theme;
- relationship identification mechanism adapted to identify relationships among identified key thematic features per object.
Typically, said co-operative learning means is a systemic and iterative machine learning means.
Typically, said co-operative learning means comprises:
- cluster data building mechanism adapted to build clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters;
- context mapping means adapted to map at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined topic;
characterised, in that, said pre-defined parameters of clustering being associated with predetermined factors comprising likelihood factors, statistical factors, and closeness factors.
Additionally, said co-operative learning means comprises:
- cluster data building mechanism adapted to build clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters;
- context mapping means adapted to map at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined topic;
characterised, in that, said pre-defined parameters of clustering being associated with identification of multiple clusters having similar behaviour.
Additionally, said co-operative learning means comprises:
- cluster data building mechanism adapted to build clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters;
- context mapping means adapted to map at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined theme;
characterised, in that, said pre-defined parameters of clustering being associated with predetermined factors comprising likelihood factors, statistical factors, and closeness factors.
Additionally, said co-operative learning means comprises:
- cluster data building mechanism adapted to build clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters;
- context mapping means adapted to map at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined theme;
characterised, in that, said pre-defined parameters of clustering being associated with identification of multiple clusters having similar behaviour.
Additionally, said co-operative learning means comprises:
- context mapping means adapted to map the association of said query in terms of document context and / or user context and / or scenario context such that determination of document context and / or user context and / or scenario context being enabled by pre-determined factors such as likelihood factors, statistical factors, and closeness factors.
Additionally, said co-operative learning means comprises:
- sharing mechanism to share determined topic and determine theme in order to allow systems to learn with multiple perspectives;
- feature vectors' building mechanism to allow intelligent systems to build feature vectors based on said pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing;
- association mechanism adapted to associate said built feature vectors with probabilistic weight assignment in order to build representative feature vectors; and
- statistical mechanism adapted to statistically build weights using multi-level apriori and advanced bias based likelihood algorithm.
Typically, said context determination means comprises semantic determination mechanism adapted to determine context (and content) based on semantic processing of said identified objects based on said identifiable features of said identified objects.
Typically, said context determination means comprises syntactic determination mechanism adapted to determine context (and content) based on syntactic processing of said identified objects based on said identifiable features of said identified objects.
Typically, said context determination means comprises topic determination mechanism adapted to determine context topic based on topic-based processing of said identified objects based on said identifiable features of said identified objects.
Typically, said context determination mechanism comprises topic determination mechanism adapted to determine at least a topic that is a representative context of textual content of said identified objects.
Typically, said context determination mechanism comprises topic determination mechanism adapted to determine at least a topic based on at least one of the following:
- association among key phrases that leads to a context;
- occurrence of bigrams, trigrams, relationship and occurrence of key words and phrases; and
- relation extraction between said occurrences.
Typically, said context determination mechanism comprises theme determination mechanism adapted to determine at least a theme based on at least one of the following:
- association among key phrases that leads to a context;
- occurrence of bigrams, trigrams, relationship and occurrence of key words and phrases; and
- relation extraction between said occurrences.
Typically, said context determination mechanism comprises topic determination mechanism adapted to determine at least a topic based on the following extracted parameters from a set of identified objects from at least one of the following:
Top frequency unigrams;
Top frequency bigrams;
Longer key phrases;
Association among frequently occurring unigrams and frequently occurring bigrams; Corpus of frequent objects and their statistical association leading to most relevant pre-known topics;
Likelihood and reinforcement learning mechanisms in order to learn a new topic if there is no pre-known relevant topic;
Semi-supervised learning mechanisms in order to learn a new topic; and
Mapping of key phrases to a pre-known or learnt topic.
Typically, said context determination means comprises thematic determination mechanism adapted to determine context theme based on thematic processing of said identified objects based identifiable features of said identified objects.
Typically, said context determination means comprises thematic determination mechanism adapted to determine at least a theme based on at least one of the following extracted parameters from a set of identified objects:
local score of words that is computed;
global score of words, that is computed, based on similarity;
sentence score, that is computed, based on local score, global score, and normalization; and
situation representing primary context.
Typically, said context determination mechanism comprises contextual features inference mechanism adapted to infer contextual features for each of said objects, D;
Di = {Pi, Ti, Si, Oi} 0 <i< n
where,
n = no. of doc in class
Ti = set of temporal features
Si= set of spatial features
Pi= set of protagonist features
Oi= set of organisational features
Typically, said context determination mechanism comprises contextual features inference mechanism adapted to infer contextual features for each of said objects, D;
Di = {Pi, Ti, Si, Oi} ..0 <i< n
where,
n = no. of doc in class
Ti = set of temporal features
Si= set of spatial features
Pi= set of protagonist features
Oi= set of organisational features characterized, in that, said context determination further comprises clustering mechanism adapted to cluster said inferred features of said objects for a class in to at least the following the four situation vectors:
Ti = {tO, tl, t2, tn} for temporal features of the class i.
Si = {sO, si, s2, sn} for spatial features of the class i.
Pi = {p0, pi, p2, pn} for protagonist features of the class i.
Oi = {o0, ol, o2, n} for organisational features of the class i.
wherein, said situation vectors, which define a theme, are generated for each class, said situation vectors form at least a situation model / thematic model for that category:
CSj = {Tj, Sj, Pj, Oj } . . ., j=l to C
where,
C = no. of categories
Tj = {t0, tl, t2,...,tk}
Sj = {s0, si , s2,....,sk}
Pj = {p0, pl, p2, ...,pk}
Oj= {o0, ol , o2,...,ok}
Typically, said context determination mechanism comprises thematic relationship establishment means adapted to establish a theme during the use of said system for searching, said theme being established based on at least one of the parameters comprising user profile, scenario, and knowledge base.
Additionally, said context determination mechanism comprises thematic relationship determination means adapted to determine a thematic relationship between said objects.
Typically, said system comprises a user input means or a user and information context defining means adapted to allow a user to input data for topic determination or identification, thereby allowing said system to form a cluster of objects, based on said topic, to be searched or retrieved.
Typically, said system comprises a user input means or a user and information context defining means adapted to allow a user to input data for theme determination or identification, thereby allowing said system to form a cluster of objects, based on said theme, to be searched or retrieved.
Typically, said system comprises classification means adapted to classify a user profile accessing said system and said searching means.
Typically, said system comprises context based learning means adapted to allow said system to learn a context from said at least a user query and corresponding output search result, said context based learning means being an iterative learning mechanism and involving results based on pre-identified topic defined by said system.
Additionally, said system comprises context based learning means adapted to allow said system to learn a context from said at least a user query and corresponding output search result, said context based learning means being an iterative learning mechanism and involving results based on pre-identified themes defined by said system.
Typically, said information sources' gathering means is a theme based information sources' gathering means.
Additionally, said information sources' gathering means is a topic based information sources' gathering means.
Additionally, said information sources' gathering means is a user generated information sources' gathering means.
Additionally, said information sources' gathering means is a machine based information sources' gathering means.
Additionally, said information sources' gathering means comprises mechanisms to gather information from at least the following three information resources: relation extractor, name entity recognizer, and situation builder; in order to help build a context.
Typically, said system comprises searching means adapted to search for said objects within the theme clustered objects depending upon user query.
Additionally, said system comprises searching means adapted to search for said objects within the topic clustered objects depending upon user query.
Typically, said system comprises display means adapted to display searched said objects from searching means.
Typically, said system comprises ranking means adapted to rank searched said objects, said ranking being determined in accordance with reference to user context topic.
Additionally, said system comprises ranking means adapted to rank searched said objects, said ranking being determined in accordance with reference to user context theme.
According to this invention, there is also provided a method for context based co-operative learning method comprising the steps of:
- identifying and indexing objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, using an identifier means;
- defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism;
- gathering sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using information sources' gathering means;
- searching for said objects, in response to at least a user query, within said determined context topic and / or said determined context theme, using searching means;
- building clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters, using cluster data building mechanism;
- mapping at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined context topic and / or said determined context theme, using context mapping means; and
- allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means.
Typically, said step of identifying and indexing objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, characterised, in that, said pre-determined parameters comprising data, meta data, meta tags, and the like identifiable features of the objects.
Typically, said step of identifying and indexing objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, characterised, in that, said step further comprises the steps of:
- identifying key features in said objects, which key features relate to a topic, using key features' identification mechanism; and
- identifying relationships among identified key topic-based features per object, using relationship identification mechanism.
Additionally, said step of identifying and indexing objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, characterised, in that, said step further comprises the steps of:
- establishing contextual / thematic features for said objects, using establishing means;
- identifying key features in sad objects, which key features relate to a theme, using key features' identification mechanism;
- identifying relationships among identified key thematic features per object, using relationship identification mechanism.
Typically, said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means, comprising a step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other, systematically and iteratively, using a systemic and iterative machine learning means.
Typically, said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means, comprising the steps of:
- building clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters, using cluster data building mechanism;
- mapping at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined topic, using context mapping means;
characterised, in that, said pre-defined parameters of clustering being associated with predetermined factors comprising likelihood factors, statistical factors, and closeness factors.
Additionally, said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means, comprises the steps of:
- building clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters, using cluster data building mechanism;
- mapping at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and polj said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined topic, using context mapping means;
characterised, in that, said pre-defined parameters of clustering being associated with identification of multiple clusters having similar behaviour.
Additionally, said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means, comprises the steps of:
- building clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters, using cluster data building mechanism;
- mapping at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined theme, using context mapping means;
characterised, in that, said pre-defined parameters of clustering being associated with predetermined factors comprising likelihood factors, statistical factors, and closeness factors.
Additionally, said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means, comprises the steps of:
- building clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters, using cluster data building mechanism;
- mapping at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined theme, using context mapping means;
characterised, in that, said pre-defined parameters of clustering being associated with identification of multiple clusters having similar behaviour.
Additionally, said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means, comprises the steps of:
- mapping the association of said query in terms of document context and / or user context and / or scenario context such that determination of document context and / or user context and / or scenario context being enabled by pre-determined factors such as !ikelihood factors, statistical factors, and closeness factors, using context mapping means.
Additionally, said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means, comprises the steps of:
- sharing determined topic and determine theme in order to allow systems to learn with multiple perspectives, using a sharing mechanism;
- allowing intelligent systems to build feature vectors based on said pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, using a feature vectors' building mechanism;
- associating said built feature vectors with probabilistic weight assignment in order to build representative feature vectors, using an association mechanism; and
- statistical mechanism adapted to statistically build weights using multi-level apriori and advanced bias based likelihood algorithm.
Typically, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism, comprises a step of determining context (and content) based on semantic processing of said identified objects based on said identifiable features of said identified objects, using a semantic determination mechanism.
Typically, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism, comprises a step of determining context (and content) based on syntactic processing of said identified objects based on said identifiable features of said identified objects, using syntactic determination mechanism.
Typically, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism, comprises a step of determining context topic based on topic-based processing of said identified objects based on said identifiable features of said identified objects, using topic determination mechanism.
Typically, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism, comprises a step of determining at least a topic that is a representative context of textual content of said identified objects, using topic determination mechanism.
Typically, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism, comprises a step of determining at least a topic, using topic determination mechanism, based on at least one of the following:
- association among key phrases that leads to a context;
- occurrence of bigrams, trigrams, relationship and occurrence of key words and phrases; and
- relation extraction between said occurrences.
Typically, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects,' using a context determination mechanism, comprises a step of determining at least a theme, using theme determination mechanism, based on at least one of the following:
- association among key phrases that leads to a context;
- occurrence of bigrams, trigrams, relationship and occurrence of key words and phrases; and
- relation extraction between said occurrences.
Typically, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism, comprises a step of determining at least a topic, using topic determination mechanism, based on at least one of the following:
Top frequency unigrams;
- Top frequency bigrams;
Longer key phrases;
Association among frequently occurring unigrams and frequently occurring bigrams; Corpus of frequent objects and their statistical association leading to most relevant pre-known topics;
Likelihood and reinforcement learning mechanisms in order to learn a new topic if there is no pre-known relevant topic;
Semi-supervised learning mechanisms in order to learn a new topic; and
Mapping of key phrases to a pre-known or learnt topic.
Typically, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism, comprises a step of determining context theme based on thematic processing of said identified objects based identifiable features of said identified objects, using theme determination mechanism.
Typically, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism, comprises a step of determining at least a theme, using thematic determination mechanism, based on at least one of the following extracted parameters from a set of identified objects:
local score of words that is computed;
global score of words, that is computed, based on similarity;
sentence score, that is computed, based on local score, global score, and normalization; and
situation representing primary context.
Typically, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism, comprises a step of inferring contextual features, using contextual features inference mechanism, for each of said objects, D;
D, = {Pi, T„ S Oi} 0 <i< n
where,
n = no. of doc in class
Ti = set of temporal features
Sj= set of spatial features
Pj= set of protagonist features
Typically, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism, comprises a step of inferring contextual features, using contextual features inference mechanism, for each of said objects, D;
Di = {Pi, Ti, Si, Oi} 0 <i< n
where,
n = no. of doc in class
Ti = set of temporal features
Sj= set of spatial features
Pj= set of protagonist features
Oj= set of organisational features characterized, in that, step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism further comprises a step of clustering said inferred features of said objects for a class in to at least the following the four situation vectors, using clustering mechanism:
Ti = {to, ti, t2, tn} for temporal features of the class i.
Si = {so, si , s2, ........sn} for spatial features of the class i.
Pi = {po, pi , p2, pn} for protagonist features of the class i.
Oi = {oo, oi, o2, n} for organisational features of the class i.
wherein, said situation vectors, which define a theme, are generated for each class, said situation vectors form at least a situation model / thematic model for that category:
CSj = {Tj, Sj, Pj, Oj > ...J=l to C
where,
C = no. of categories
Tj = {to, ti, t2,...,tk}
Sj = {s0, Si, s2,....,sk}
Pj = (Po> Pi> P2, -,Pk}
Oj= {Oo, O], o2,...,ok}
Typically, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism, comprises a step of establishing a theme during the use of said method for searching said theme, using thematic relationship establishment means, being established based on at least one of the parameters comprising user profile, scenario, and knowledge base.
Additionally, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism, comprises a step of determining a thematic relationship between said objects, using thematic relationship determination means.
Typically, said method comprises a step of allowing a user to input data for topic determination or identification, using user input means or a user and information context defining means, thereby allowing said system to form a cluster of objects, based on said topic* to be searched or retrieved.
Additionally, said method comprises a step of allowing a user to input data for theme determination or identification, using user input means or a user and information context defining means, thereby allowing said system to form a cluster of objects, based on said theme, to be searched or retrieved.
Typically, said method comprises a step of classifying a user profile accessing said system and said searching means, using classification means.
Typically, said method comprises a step of allowing said system to learn a context from said at least a user query and corresponding output search result, using context based learning means, said context based learning means being an iterative learning mechanism and involving results based on pre-identified topic defined by said method.
Additionally, said method comprises a step of allowing said system to learn a context from said at least a user query and corresponding output search result, using context based learning means, said context based learning means being an iterative learning mechanism and involving results based on pre-identified theme defined by said method.
Typically, said step of gathering sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using information sources' gathering means, comprises a step of gathering theme based sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using theme based information sources' gathering means.
Additionally, said step of gathering sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using information sources' gathering means, comprises a step of gathering topic based sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using topic based information sources' gathering means.
Additionally, said step of gathering sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using information sources' gathering means, comprises a step of gathering user generated based sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using user generated information sources' gathering means.
Additionally, said step of gathering sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using information sources' gathering means, comprises a step of gathering machine based sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using machine based information sources' gathering means.
Additionally, said step of gathering sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using information sources' gathering means, comprises a step of gathering information from at least the following three information resources: relation extractor, name entity recognizer, and situation builder; in order to help build a context.
Typically, said method comprises a step of searching for said objects within the theme clustered objects depending upon user query, using searching means.
Additionally, said method comprises a step of searching for said objects within the topic clustered objects depending upon user query, using searching means.
Typically, said method comprises a step of displaying searched said objects from searching means, using display means.
Typically, said method comprises a step of ranking searched said objects, said ranking being determined in accordance with reference to user context topic, using ranking means.
Additionally, said method comprises a step of ranking searched said objects, said ranking being determined in accordance with reference to user context theme, using ranking means.
Detailed Description of the Invention:
According to this invention, there is provided a context based co-operative learning system and method for representing thematic relationships.
Figures 1 and 2 illustrate a schematic of the system and method of this invention. Figure 3 illustrates mechanism for situation determination.
Figure 4 illustrates context based learning mechanism which outputs topic as search results. Figure 5 illustrates context based learning mechanism which outputs theme as search results. Figure 6 illustrates relation extraction for theme. Figure 7 illustrates relation extraction for topic.
In accordance with an embodiment of this invention, there is provided anidentifier means adapted to identify and index objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing. The identifier means comprises context determination mechanism(CDM) adapted to determine context (and content) of the objects based on data, meta data, meta tags, and the like identifiable features of the objects. The context determination means further comprises semantic determination mechanismadapted to determine context (and content) based on semantic processing of the objects based on data, meta data, meta tags, and the like identifiable features of the objects. Typically, the semantic processing is correlated with at least a lexical repository and at least a sense repository database. The context determination means further comprises syntactic determination mechanismadapted to determine context (and content) based on syntactic processing of the objects based on data, meta data, meta tags, and the like identifiable features of the objects. Typically, the syntactic processing comprises the following steps, as seen in Figure 3 of the accompanying drawings:
1) Search (input) (content) text (corpus) and at least a lexicon file are pre-processed to obtain tagged text with most-likely tag.
2) The tagged text (contents) with most likely tag and at least a Lexicon rule file are processed by Bigram approach to obtain tagged text with lexical rule.
3) The tagged text with lexical rulealong with at least a contextual rule file are processed with a rule based corrector to obtain final tagged text.
The context determination means further comprises topic determination mechanismadapted to determine context topic based on topic-based processing of the objects based on data, meta data, meta tags, and the like identifiable features of the objects. This identifier means involves a establishing means adapted to perform astep of establishing contextual / topic- based features for the objects. The identifier means involves a key features' identification mechanism adapted to performfurther step of identifying key features in the objects, which key features relate to a topic. The identifier means involves a relationship identification mechanism adapted to involve still a further step of identifying relationships among identified key topic-based features per object. According to one embodiment, topics could be hierarchical topics, in that, a main topic can have sub-topics hierarchically linked to one another.
Topic determination refers to determination of topic that is a representative context of the textual content of the objects. The relevant features of the documents/contents are determined in space of concepts. Interestingly, a topic is not a mere BOW (bag of words) and frequently occurring key phrases, it is an association among key phrases and that leads to a context. Typically, a topic is determined based on the occurrence of bigrams, trigrams, relationship and occurrence of key words and phrases. There is relation extraction between these occurrences. Situation model is used to determine the context with reference to situation parameters. This is shown in Figure 7 of the accompanying drawings. Similarly, a theme is determined based on the occurrence of bigrams, trigrams, relationship and occurrence of key words and phrases. There is relation extraction between these occurrences. Situation model is used to determine the context with reference to situation parameters.This is shown in Figure 6 of the accompanying drawings.
Typically, the topic determination mechanism determines a topic based on the following extracted parameters from a set of identified objects:
- Top frequency unigrams
- Top frequency bigrams
Longer key phrases
- Association among frequently occurring unigrams and frequently occurring bigrams
- Corpus of frequent objects and their statistical association leading to most relevant pre-known topics
Likelihood and reinforcement learning mechanisms in order to learn a new topic if there is no pre-known relevant topic
Semi-supervised learning mechanisms in order to learn a new topic
Mapping of key phrases to apre-known or learnt topic
Typically, topic determination deals with the construction of concept space i.e. confident single-value(unigram) words and confident multi-value( bigram, trigram) words.Consider
documents to be bag of words (ordering of words is maintained). Upper case letters are used to represent sets and lower case letters are used for elements of the set. Let D = {dl, d2, ... ,dm } represent the document set of the input corpus. W={wl , w2, ... ,wn} represents the set of all the different term features in D. T={ tl, t2, tp} is the concept space. C={cl, c2, ....,cm} is the class label. Let tf(di,w) denote the frequency of term feature w 6 W in the document di e D . F = {fl , f2, .... , fm} be the set of names of files such that fi is the filename of document di€ D. Also, DH = (dh l, dh2, ,dhm} be the set of document header of files fi€ F.
Topic Determination Mechanism is based on either determining topic based on association among key phrases, occurrence of bigram, trigram, and relationship between them or extracting relations between key phrases. Topic Detection is also based on extracted information (like bigram, trigram, and the like,)
The context determination means further comprises thematic determination mechanismadapted to determine context theme based on thematic processing of the objects based on data, meta data, meta tags, and the likeidentifiable features of the objects. This identifier means involves a step of establishing contextual / thematic features for the objects. The identifier means involves a further step of identifying key features in the objects, which key features relate to a theme. The identifier means involves a still further step of identifying relationships among identified key thematic features per object. According to one embodiment, themes could be hierarchical themes, in that, a main theme can have sub-themes hierarchically linked to one another.
Typically, the theme determination mechanism determines a theme based on the following extracted parameters from a set of identified objects:
- Local score of words that is computed
Global score of words,that is computed, based on similarity across
Sentence score, that is computed, based on local score, global score, and normalization
- The situation represents primary context
The relationship between the concepts and the topics are analyzed to identify context. The context is that information that describes the relationship between derived concepts and its associated topics. The relationship is analyzed by considering the documents that are processed using the TDR algorithm for finding topics along with the associated concepts. For each document, a topic and the set of associated concepts are discovered. These topics and their concepts are maintained. The procedure of identifying the relationship begins by grouping the identical topics together (by identical, it means if two strings match).
For example, if for topics like :
Topic id Topic Name Concepts / keywords
Tl Text Categorization Kl
T2 Unsupervised text categorization K2
T3 Classification K3
T4 Text Categorization K4
T5 Text Mining K5
T6 Information Retrieval K6
T7 Text Categorization K7
T999 Text Mining K999
T1000 Machine Learning K IOOO
Kl, K2,— , K1000 contains the list of keywords which are concepts identified during the word decomposition. Group identical topics.Tl, T4 and T7 are identical as all of them have topic "Text categorization". Similarly T5 and T999 are identical. By grouping it means, add their concepts and maintain their occurrence frequency, and the like.
Topic Name. Frequency Concepts /' keywords list
Text Categorization 3 Kl + 4 + K7
Text Mining ,' ' '2 K5+ 99
The concepts Kl, K4 etc are actually replaced by their keyword list. Then ,the system and method finds out term frequency of every keyword in the list of concepts for each topic. After that a list of keywords, is obtained, with their frequencies. Set a threshold limit for appropriate! concept selection considering accuracy. Set a threshold of 50% or 70% - dynamically based on relevance using gating algorithm. This algorithm dynamically changes the window based on relevance. Any keyword that has frequency that crosses the threshold is extracted to be related to the topic. Suppose the threshold is set to 50%, then : if (((frequency of the concept) / (frequency of the topic)) * 100 > threshold) then
{concepts with frequencies greater than 50% threshold are identified as related to the topic}
In the above example, the frequency of the topic i.e., text categorization is 3. Frequency of the keyword depends upon the number of occurrence of the keyword within the set.
For example,
Consider the following, if the topics are:
Topic id Topic Name Concepts i keywords along with
Urclr list
Tl Tex 1 C 'a te go rizatio n Kl ( .machine learning, text, retrieval,
Classification,.. . )
T2 Unsuper ised TC K2
T3 Classification K3
T4 Tex 1 C a tegorixati on K4 (information, retrieval, fmeasure.
Classification, . .. }
T5 Test Mining KS
T6 Information Retrieval K6
Ί7 Text Categorization J 7(Fctiieval, naivebayes. classification, performance,. . . )
T 9 Text Mining 99
T1000 Machine Learnui KIOCO then after grouping identical topics it would become like :
Frequency of keyword becomes :
Applying the above formula for threshold = 50; for the above example, following is theresult.
For the concept: retrieval (3-freq) , the formula finds its relatedness as : 3/3 * 100 >
=50 then identified it as related. Thus, the related words help identify the context to which the topic belongs. if an index is created based on the process to extract the relationships , and then
if the given keywords are as "text categorization", then the algorithm would return the related term that are associated with "text categorization ". Each topic is considered as a cluster with the related terms.
The Situation Extractor basically aims at finding important components of text from the chunks of text. That is, it finds important sentences from chunks of text. For finding important sentences, it uses the score values determined for each sentences. The score values are calculated using the local and global score values of each word within the sentence. The local score (LS) of a word within a sentence is calculated by adding the score of the considered word with the score of the clause in which the word appears. The score of a word is the frequency of the word and the score of a clause is the addition of scores of all trigrams and bigrams containing the word. The score for bigrams or trigrams are calculated by adding the frequency of each word falling in bigram or trigram.
LS(w) = {the »core_giveii_to_w)+{the_score jjiven_tQj;he_Amse in u)hich w_a^mrs}
After local score calculation,global score (GS) for each word has to be calculated. It is calculated by first finding the similarity of each word with the set of all words in the document and summing the local score of all those words whose similarity value is greater than a predefined threshold. Wordnet path-similarity measure is used for finding similarity between two words.
GS(w) = ^{LS(vf) X Simtlarity(uh w'))
After finding Jocal and global score, sentence score(SV) is determined. It is found by summing the square root of the product of local and global scores values of all words in the sentence.
The sentence score is simply not calculated by adding the local and global score values of words in the sentence. If this is done, a long sentence will get higher importance value as it contains more words in it. To avoid selection of long sentences,the system and method normalize the score value using the sentence length as a parameter.
So now there are, in the chunk, sentences with higher score values. For building a situation, higher sentence score is not the only criteria for adding a sentence in a situation. Initially, the highest score sentence is added to a situation. Before adding the next higher score value sentence, a check is performed to find if this considered sentence is connected with the first highest score sentence by a connective like AND. If so, then the next higher score sentence is found unnecessary and not added to situation. This is because the words like "AND" may
speak about things already spoken about and may not add any new information to the situation. Also, if the next higher score sentence starts with an elaborating connective, it is found unnecessary and not added to situation by setting its score value to 0. Now, if the next higher score sentence is simple sentence then it is added to the situation. The procedure is repeated for all sentences in a chunk. Thus the system and method is able to determine situation(s) for every incoherent chunk which eventually builds a complete situation for the input text.
Typically, the contextual features are inferred, using contextual features inference mechanism, for each object D;
where,
n = no. of doc in class
Tj = set of temporal features
Sj= set of spatial features
Pj= set of protagonist features
' O'i = set of organization features
All the inferred features of the documents for a class are clustered, using clustering mechanism, into the four situation vectors like:
j = {to, ti , t2, tn} for temporal features of the class i.
Sj = {so, Si , s2, sn} for spatial features of the class i.
Pi = {po, pi , p2, pn} for protagonist features of the class i.
Oj = {oo, Oi , o2, n} for organisational features of the class i.
Situation vectors, which define a theme, are generated for each class. These situation vectors form the situation model / thematic model for that category.
CSj={Tj, Sj, Pj, Oj } .... j=l to C
where,
C = no. of categories
Sj = { So, S| , s^....^}
Pj = {Po» Pi, P2,—,Pk}
Oj= {Oo, 0 | , 02, . . ·, Ok}
According to a non-limiting exemplary embodiment, the context may be based on the following:
profile (profile based user clustering)
query (Bayesian query based likelihood)
metadata (closeness based on metadata)
- behavior (Behavior based analysis and learning to map behavior)
user classification
- User grouping
Co-operative search
In accordance with another embodiment of this invention, there is provided a user input meansor a user and information context deflningmeans (UICM) adapted to allow a user (Ul, U2, U3, Un, Unevv) to input data for theme / context determination or identification. This allows a user to establish a theme or a context with which the system and method of this invention will form a cluster of objects (Ol, O2,....0n)to be searched or retrieved. This involves a step of systemic context determination for user and for each of the search object.
The system and method of this invention comprises a classification means adapted to classify a user profile. This can be determined based on the search query, user history, login preferences, cache history, IP history, or the like parameters related to a user.A profile library, a theme library, and the like may be built.
In accordance with yet another embodiment of this invention, there is provided a context based learning means (CBLM) adapted to allow the system and method of this invention to learn from user queries and output search results. This learning means is an iterative learning mechanism . nd involves results based on pre-identified themes or context defined by the system and- method of this invention or a user or both. This involves a step of building an overall search theme. Typically, context may be search context or user context or the like.
In accordance with still another embodiment of this invention, there is provided an information sources' gathering means adapted to allow the system and method of this invention to gather sources of information (IS1, IS2,....ISn) in relation to or with reference to objects. TJiis information sources' gathering means comprises theme based or context based information sources' gathering means. This information sources' gathering means may be a user generated information sources' gathering means. Also or alternatively, this information sources' gathering means may be a machine based information sources' gathering means. Typically, there are at least the following three information resources: relation extractor, name entity recognizer, and situation builder.Knowledge from these information resources help to build a context. The relations extracted and extended help to add up to the knowledge. From all this information, the system was satisfactorily able to learn context specifically for medical abstract from aimed corpus. For any other text, the context learned was .the comprehension of the text.
In accordance with an additional embodiment of this invention, there is provided a co- operative learning means (CPLM)adapted to allow multiple systems of this invention to cooperatively learn theme / context generation, theme / context identification, object theme / context identification, search analysis based on theme / context and the like means and mechanisms jn order to 'train' the system and method of this invention to output results based on identified (pr determined themes / contexts.This involves systemic machine learning. This further involves a step of systemic theme / context determination for user and for each of the search object, through co-operative learning. Co-operative learning is based on multi level association and it works on information coming from many sources. Co-operative learning
"i 26
essentially relates to two or more machines or systems learning / teaching (from) each other. Further, co-operative learning involves identification of a correct profile, a correct context, correct theme, and / or the like. This is based on learning from various machines and eventually uses the concept of iterative learning to progressively or iteratively become more intelligent and accurate.The co-operative learning means is adapted to allow multi-level association so that more than one information sources work with each other. The information sources are associated with each other in order to build a higher level of cooperative learning. The co-operative learning meanscomprises sharing mechanism further adapted to share determined topic and determine theme in order to allow systems to learn with multiple perspectives. The co-operative learning means, specifically, comprises a feature vectors' building mechanism adapted to allow intelligent systems to build feature vectors based on said pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing.These feature vectors are associated, by means of association mechanism, with probabilistic weight assignment in order to build representative feature vectors. Cooperative learning component, comprising statistical mechanism, will statistically build weights using multi-level apriori and advanced bias based likelihood algorithm.
In accordance with yet an additional embodiment of this invention, there is provided a thematic relationship establishment means(TREM)adapted to establish a theme during the use of the system and method of this invention for searching. The theme may be established based on the. parameters involving user profile (UP), scenario (SC), knowledge base (KB) and the like.Learning user profile is imperative for the system and method of this invention. User profile can be learnt by the system of this invention using any techniques. These techniques may involve reinforcement learning techniques which further include heat maps, time maps, click maps, access to public data, access to private data, and the like.
In accordance with still an additional embodiment of this invention, there is provided a thematic relationship determination means (TRDM) adapted to determine a thematic relationship between objects. A plurality of objects may be theme identifies and clustered based on the. theme which is common to the objects. An object may have multiple themes, and hence, an object can be a part of multiple clusters in which each cluster is a theme or a part of a theme. This involves a step of building an overall search theme.
or scenario context is enabled by pre-determined factors such as likelihood factors, statistical · factors, and.closeness factors.
The process. of identifying which multiple series have similar behaviour and combining those series together is called as clustering. When the system and method receives a set of series with a similar behavioural patterns, then these series are used to form a representative pattern. Thisrepresentative pattern can be referred as a cluster. There can be many such patterns. Thecloseness of such patterns is measured and the system and method may decide to merge some of thesepatterns. All series that have a similar shape form a cluster. Clustering is based on thecloseness factor. An understanding of the C Value is necessary to comprehend why clustering works. A Closeness factor (C) can be calculated between two series. This C value quantifies thedifference in the shape of each series. The lower the C Value, the smaller the difference. A C value of 0 signifies an exact match of shapes even though the volumes might bedifferent.
In accordance with another additional embodiment of this invention, there is provided a searchingmeans (SM) adapted to search for objects within the theme clustered objects depending upon user query (Q).
In accordance .with yet another additional embodiment of this invention, there is provided a displaymeans (DM) adapted to display searched objects from the searching means.
In accordance ..with still another embodiment of this invention, there is provided a ranking means (R) adapted to rank searched objects. This may involve user ranking or machine ranking or both. This involves a step of ranking the objects with reference to user context in overall themeV topic.Ranking (R) may take placealong with context based learning means (CBLM).User context (UC) can be added to as input to the ranking means (R) and context based learning means (CNLM). The user context is derived from context mapping means (CMM).
The applications of the system and method of this invention are not limited to search but includes: L
- object association, ranking of objects, ranking of text documents, ranking of contents and establishing, systemic relationships
- Web based search
- Co-operative learning based search
- Document and content search
- Document collation
- Context based grouping
- Knowledge,building
- Information. based learning
- Document; and content representation
- WAN / LAN based systems
- Database management or polling systems
- Document management systems
The system and method of this invention provides searching, arranging and most importantly ranking objects with reference to context and representing the thematic relationship among objects. Further the results are arranged and presented with thematic relationship with reference to user or application context. The ability to build context - learn based on known context and co-operatively learn to refine context and further thematic relationships. As a result new search results are generated with reference to theme and the relationships among different objects are represented with reference to theme for decision-making. The ability of co-operative, learning allows to correct wrong results, handle new contexts and scenarios without compromising accuracy.
The system and method of this invention can be used for the following:
- Can find relationships among documents, contents and relevance based collation
Claims
Claims,
1. A context based co-operative learning system comprising:
- identifier means adapted to identify and index objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing;
- context determination mechanism adapted to define parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects;
- information sources' gathering means adapted to gather sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects;
- searching means adapted to search for said objects, in response to at least a user query, within said determined context topic and / or said determined context theme;
- cluster data building mechanism adapted to build clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters;
- context mapping means adapted to map at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined context topic and / or said determined context theme; and
- co-operative learning means adapted to allow multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other ,b,ased on determined context topic and / or determined context theme.
2. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said identifier , means adapted to identify and index objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, characterised, in that, said pre-determined parametei:S.:P.omprising data, meta data, meta tags, and the like identifiable features of the objects. . ;
3. A context) based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said identifier means adapted to identify and index objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, characterised, in that, said identifier means comprising: ,
- key features identification mechanism adapted to identify key features in said objects, which key features relate to a topic; and
- relationship identification mechanism adapted to identify relationships among identified key topic-based features per object.
4. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said identifier means adapted to identify and index objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, characterised, in that, said identifier means comprising:
- establishing means adapted to establish contextual / thematic features for said objects;
- key features' dentification mechanism adapted to identify key features in said objects, which key. eatures relate to a theme;
- relationship identification mechanism adapted to identify relationships among identified key thematic features per object.
5. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said cooperative learning means is a systemic and iterative machine learning means.
6. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said cooperative learning means comprising:
- cluster data building mechanism adapted to build clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters;
- context mapping means adapted to map at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined topic;
characterised, in that, said pre-defined parameters of clustering being associated with predetermined, factors comprising likelihood factors, statistical factors, and closeness factors.
7. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said cooperative learning means comprising:
- cluster data building mechanism adapted to build clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering
characterised^ Jtl„ that, said pre-defined parameters of clustering being associated
- context .mapping means adapted to map at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined theme;
characterised, in that, said pre-defined parameters of clustering being associated with identification of multiple clusters having similar behaviour.
10. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said cooperative learning means comprising:
- context mapping means adapted to map the association of said query in terms of document context and / or user context and / or scenario context such that determination of document context and / or user context and / or scenario context being enabled by pre-determined factors such as likelihood factors, statistical factors, and closeness factors.
1 1. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said cooperative learning means comprising:
16. A context Based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said context determination mechanism comprising topic determination mechanism adapted to determine at least a topic based on at least one of the following:
- association among key phrases that leads to a context;
- occurrence of bigrams, trigrams, relationship and occurrence of key words and phrases; and
- relation extraction between said occurrences.
17. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said context determination mechanism comprising theme determination mechanism adapted to determine at least a theme based on at least one of the following:
- association among key phrases that leads to a context;
- occurrence of bigrams, trigrams, relationship and occurrence of key words and phrases; and
- relation extraction between said occurrences.
situation representing primary context.
21. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said context determination mechanism comprising contextual features inference mechanism adapted to infer contextual features for each of said objects, D;
Di = {Pi, Ti, Si, Oi} 0 <i< n
where,
' ; n = no. of doc in class
Ti = set of temporal features
Pi= .set of protagonist features
Oi= set of organisational features in claim 1 wherein, said context inference mechanism adapted to
Oi= set of organisational features characterized, in that, said context determination further comprising clustering mechanism adapted to cluster said inferred features of said objects for a class in to at least the following the four situation vectors:
T, = .{fc, ,-ti.,J >,.-. t„} for temporal features of the class i.
Si = {so, , Si ..s2, sn} for spatial features of the class i.
Pi = ίφο,; PJ , P2, pn} for protagonist features of the class i.
Oi = {oo, oi , o2, ...n} for organisational features of the class i.
wherein, said situation vectors, which define a theme, are generated for each class, said situation vectors form at least a situation model / thematic model for that category:
where,
C = no. of categories
Tj = {to, t,, t2,...,tk}
23. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said context determination 'mechanism comprising thematic relationship establishment means adapted to establish a theme during the use of said system for searching, said theme being established based on at least one of the parameters comprising user profile, scenario, and knowledge base.
24. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said context determination mechanism comprising thematic relationship determination means adapted to determine a thematic relationship between said objects.
25. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said system comprising a user input means or a user and information context defining means adapted to allow a user to input data for topic determination or identification, thereby allowing said system to form a cluster of objects, based on said topic, to be searched or retrieved.
identified topic defined by said system.
29.
32. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said information sources' gathering means is a user generated information sources' gathering means.
33. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said information sources' gathering jneans is a machine based information sources' gathering means.
34. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said information sources' gathering means comprises mechanisms to gather information from at least the following three information resources: relation extractor, name entity recognizer, and situation builder; in order to help build a context.
35. A context based co-operative learning system as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said system comprising searching means adapted to search for said objects within
- building clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters, using cluster data building mechanism;
- mapping at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined context topic and / or said determined context theme, using context mapping means; and
- allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means.
41. A context based co-operative learning method as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said step of identifying and indexing objects in accordance with pre-determined parameters of identification and indexing, characterised, in that, said pre-determined parameters comprising data, meta data, meta tags, and the like identifiable features of the objects.
42. A context based co-operative learning method as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said
45. A content based, co-operative learning method as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context. topic, and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means, comprising the steps of:
- building clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster library based on pre-defined parameters of clustering said clusters, using cluster data building mechanism;
- mapping at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined topic, using context mapping means;
characterised, in that, said pre-defined parameters of clustering being associated with predetermined factors comprising likelihood factors, statistical factors, and closeness factors.
46. A context based co-operative learning method as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means, comprising the steps of:
- building clusters of relevant objects and further adapted to build at least a cluster
- mapping at least a context of said query for said searching means with said clusters from said cluster- library to segregate and poll said objects in response to said search query in line with at least a determined theme, using context mapping means;
characterised, in that, said pre-defined parameters of clustering being associated with identification of multiple clusters having similar behaviour.
49. A context based co-operative learning method as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said step of allowing multiple systems to co-operatively learn from each other based on determined context topic and / or determined context theme, using co-operative learning means, comprising the steps of:
- mapping the association of said query in terms of document context and / or user context and / or scenario context such that determination of document context and / or user context and / or scenario context being enabled by pre-determined factors such as likelihood factors, statistical factors, and closeness factors, using context mapping means. ,,,,
53. A context based co-operative learning method as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism, comprising a step of determining context topic based on topic- based processing of said identified objects based on said identifiable features of said identified objects, using topic determination mechanism.
54. A context based co-operative learning method as claimed in claim I wherein, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme o said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism, comprising a step of determining at least a topic that is a representative context of textual content of said identified objects, using topic determination mechanism.
- Likelihood and reinforcement learning mechanisms in order to learn a new topic if there is no prc-known relevant topic;
Semi-supervised learning mechanisms in order to learn a new topic; and
- Mapping of key phrases to a pre-known or learnt topic.
58. A context based co-operative learning method as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism, comprising a step of determining context theme based on thematic processing of said identified objects based identifiable features of said identified objects, using theme determination mechanism.
59. A context based co-operative learning method as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context
60.
theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context
T, = set of temporal features
S ~ set of spatial features
Pi= set of protagonist features
Oi= set of organisational features characterized, in that, step of defining parameters of identification in order to determine context topic and / or context theme of said objects based on identifiable features of said objects, using a context determination mechanism further comprising a step of clustering said inferred features of said objects for a class in to at least the following the four situation vectors, using clustering mechanism:
T, = {to, ti, t2,... tn} for temporal features of the class i.
Sj = {so, si, s , sn} for spatial features of the class i.
Pi = {po, pi, 2, pn} for protagonist features of the class i.
Oj = {oo, oi, o2, n} for organisational features of the class i.
wherein, said situation vectors, which define a theme, are generated for each class, said situation vectors form at least a situation model / thematic model for that category:
where,
C = no. of categories
65. A context based co-operative learning method as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said method comprising a step of allowing a user to input data for theme determination or identification, using user input means or a user and information context defining means, thereby allowing said system to form a cluster of objects, based on said theme, to be searched or retrieved.
66. A context based co-operative learning method as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said method comprising a step of classifying a user profile accessing said system and said searching means, using classification means.
67. A context based co-operative learning method as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said method comprising a step of allowing said system to learn a context from said at least a user query and corresponding output search result, using context based learning means, said context based learning means being an iterative learning mechanism and involving results based on pre-identified topic defined b said method.
ideptifl.e.drobjjects, using information sources' gathering means, comprises a
gathering machine based sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using machine based information sources' gathering means.
73. A context based co-operative learning method as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said step of gathering sources of information in relation to or with reference to said identified objects, using information sources' gathering means, comprises a step of gathering information from at least the following three information resources: relation extractor, name entity recognizer, and situation builder; in order to help build a context.
74. A context based co-operative learning method as claimed in claim 1 wherein, said method comprising a step of searching for said objects within the theme clustered objects depending upon user query, using searching means.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14/676,680 US10002330B2 (en) | 2012-10-01 | 2015-04-01 | Context based co-operative learning system and method for representing thematic relationships |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IN2893/MUM/2012 | 2012-10-01 | ||
| IN2893MU2012 | 2012-10-01 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14/676,680 Continuation US10002330B2 (en) | 2012-10-01 | 2015-04-01 | Context based co-operative learning system and method for representing thematic relationships |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2014054052A2 true WO2014054052A2 (en) | 2014-04-10 |
| WO2014054052A3 WO2014054052A3 (en) | 2014-05-30 |
Family
ID=50435532
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/IN2013/000599 WO2014054052A2 (en) | 2012-10-01 | 2013-10-01 | Context based co-operative learning system and method for representing thematic relationships |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10002330B2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2014054052A2 (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109074384A (en) * | 2016-04-25 | 2018-12-21 | 微软技术许可有限责任公司 | To context metadata ranking to generate related data opinion |
| US10810604B2 (en) | 2014-09-26 | 2020-10-20 | Bombora, Inc. | Content consumption monitor |
| US11589083B2 (en) | 2014-09-26 | 2023-02-21 | Bombora, Inc. | Machine learning techniques for detecting surges in content consumption |
| US11631015B2 (en) | 2019-09-10 | 2023-04-18 | Bombora, Inc. | Machine learning techniques for internet protocol address to domain name resolution systems |
Families Citing this family (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2014054052A2 (en) * | 2012-10-01 | 2014-04-10 | Parag Kulkarni | Context based co-operative learning system and method for representing thematic relationships |
| US9852188B2 (en) * | 2014-06-23 | 2017-12-26 | Google Llc | Contextual search on multimedia content |
| US9087090B1 (en) | 2014-07-31 | 2015-07-21 | Splunk Inc. | Facilitating execution of conceptual queries containing qualitative search terms |
| US9129041B1 (en) * | 2014-07-31 | 2015-09-08 | Splunk Inc. | Technique for updating a context that facilitates evaluating qualitative search terms |
| US10409912B2 (en) * | 2014-07-31 | 2019-09-10 | Oracle International Corporation | Method and system for implementing semantic technology |
| US10546030B2 (en) | 2016-02-01 | 2020-01-28 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Low latency pre-web classification |
| US9836188B2 (en) * | 2016-04-14 | 2017-12-05 | Qamar Hasan | Web button listing multiple descriptions in a single button |
| US10275444B2 (en) * | 2016-07-15 | 2019-04-30 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | Data analytics system and methods for text data |
| US10592568B2 (en) | 2016-10-27 | 2020-03-17 | International Business Machines Corporation | Returning search results utilizing topical user click data when search queries are dissimilar |
| US10558687B2 (en) * | 2016-10-27 | 2020-02-11 | International Business Machines Corporation | Returning search results utilizing topical user click data when search queries are dissimilar |
| US11205103B2 (en) | 2016-12-09 | 2021-12-21 | The Research Foundation for the State University | Semisupervised autoencoder for sentiment analysis |
| US10956627B1 (en) | 2017-07-10 | 2021-03-23 | The Auros Group, Inc. | Building performance assessment system and method |
| US11526565B2 (en) * | 2019-04-05 | 2022-12-13 | Ovh | Method of and system for clustering search queries |
| US11030257B2 (en) | 2019-05-20 | 2021-06-08 | Adobe Inc. | Automatically generating theme-based folders by clustering media items in a semantic space |
| US11604980B2 (en) | 2019-05-22 | 2023-03-14 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | Targeted crowd sourcing for metadata management across data sets |
| CN111401055B (en) * | 2020-04-07 | 2023-04-18 | 宁波深擎信息科技有限公司 | Method and apparatus for extracting context information from financial information |
| CN111695358B (en) * | 2020-06-12 | 2023-08-08 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Method and device for generating word vector, computer storage medium and electronic equipment |
| US11886827B1 (en) * | 2023-07-31 | 2024-01-30 | Intuit Inc. | General intelligence for tabular data |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20020194161A1 (en) * | 2001-04-12 | 2002-12-19 | Mcnamee J. Paul | Directed web crawler with machine learning |
| CN1766871A (en) * | 2004-10-29 | 2006-05-03 | 中国科学院研究生院 | The processing method of the semi-structured data extraction of semantics of based on the context |
| CN101395600A (en) * | 2006-02-28 | 2009-03-25 | 微软公司 | Adaptive semantic platform architecture |
| US20110252045A1 (en) * | 2010-04-07 | 2011-10-13 | Yahoo! Inc. | Large scale concept discovery for webpage augmentation using search engine indexers |
| CN102402539A (en) * | 2010-09-15 | 2012-04-04 | 倪毅 | Design technology for object-level personalized vertical search engine |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6182066B1 (en) * | 1997-11-26 | 2001-01-30 | International Business Machines Corp. | Category processing of query topics and electronic document content topics |
| US7529735B2 (en) * | 2005-02-11 | 2009-05-05 | Microsoft Corporation | Method and system for mining information based on relationships |
| WO2007050646A2 (en) * | 2005-10-24 | 2007-05-03 | Capsilon Fsg, Inc. | A business method using the automated processing of paper and unstructured electronic documents |
| US9461876B2 (en) * | 2012-08-29 | 2016-10-04 | Loci | System and method for fuzzy concept mapping, voting ontology crowd sourcing, and technology prediction |
| WO2014054052A2 (en) * | 2012-10-01 | 2014-04-10 | Parag Kulkarni | Context based co-operative learning system and method for representing thematic relationships |
| US10430806B2 (en) * | 2013-10-15 | 2019-10-01 | Adobe Inc. | Input/output interface for contextual analysis engine |
| US10235681B2 (en) * | 2013-10-15 | 2019-03-19 | Adobe Inc. | Text extraction module for contextual analysis engine |
| US9990422B2 (en) * | 2013-10-15 | 2018-06-05 | Adobe Systems Incorporated | Contextual analysis engine |
| US20150294220A1 (en) * | 2014-04-11 | 2015-10-15 | Khalid Ragaei Oreif | Structuring data around a topical matter and a.i./n.l.p./ machine learning knowledge system that enhances source content by identifying content topics and keywords and integrating associated/related contents |
| US9390086B2 (en) * | 2014-09-11 | 2016-07-12 | Palantir Technologies Inc. | Classification system with methodology for efficient verification |
-
2013
- 2013-10-01 WO PCT/IN2013/000599 patent/WO2014054052A2/en active Application Filing
-
2015
- 2015-04-01 US US14/676,680 patent/US10002330B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20020194161A1 (en) * | 2001-04-12 | 2002-12-19 | Mcnamee J. Paul | Directed web crawler with machine learning |
| CN1766871A (en) * | 2004-10-29 | 2006-05-03 | 中国科学院研究生院 | The processing method of the semi-structured data extraction of semantics of based on the context |
| CN101395600A (en) * | 2006-02-28 | 2009-03-25 | 微软公司 | Adaptive semantic platform architecture |
| US20110252045A1 (en) * | 2010-04-07 | 2011-10-13 | Yahoo! Inc. | Large scale concept discovery for webpage augmentation using search engine indexers |
| CN102402539A (en) * | 2010-09-15 | 2012-04-04 | 倪毅 | Design technology for object-level personalized vertical search engine |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10810604B2 (en) | 2014-09-26 | 2020-10-20 | Bombora, Inc. | Content consumption monitor |
| US11556942B2 (en) | 2014-09-26 | 2023-01-17 | Bombora, Inc. | Content consumption monitor |
| US11589083B2 (en) | 2014-09-26 | 2023-02-21 | Bombora, Inc. | Machine learning techniques for detecting surges in content consumption |
| CN109074384A (en) * | 2016-04-25 | 2018-12-21 | 微软技术许可有限责任公司 | To context metadata ranking to generate related data opinion |
| US11631015B2 (en) | 2019-09-10 | 2023-04-18 | Bombora, Inc. | Machine learning techniques for internet protocol address to domain name resolution systems |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20150206070A1 (en) | 2015-07-23 |
| US10002330B2 (en) | 2018-06-19 |
| WO2014054052A3 (en) | 2014-05-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10002330B2 (en) | Context based co-operative learning system and method for representing thematic relationships | |
| US9864808B2 (en) | Knowledge-based entity detection and disambiguation | |
| Wei et al. | A survey of faceted search | |
| US9715493B2 (en) | Method and system for monitoring social media and analyzing text to automate classification of user posts using a facet based relevance assessment model | |
| US8108405B2 (en) | Refining a search space in response to user input | |
| Zhang | Towards efficient and effective semantic table interpretation | |
| US20170212899A1 (en) | Method for searching related entities through entity co-occurrence | |
| JP2009093649A (en) | Recommendation for term specifying ontology space | |
| CN115563313A (en) | Knowledge graph-based document book semantic retrieval system | |
| WO2011022867A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for searching electronic documents | |
| Amer | Enhancing efficiency of web search engines through ontology learning from unstructured information sources | |
| Kubek et al. | Towards a librarian of the web | |
| Jannach et al. | Automated ontology instantiation from tabular web sources—the AllRight system | |
| Oo | Pattern discovery using association rule mining on clustered data | |
| Annadurai et al. | Architecture of personalized web search engine using suffix tree clustering | |
| Abramowicz et al. | Supporting topic map creation using data mining techniques | |
| Asa et al. | A comprehensive survey on extractive text summarization techniques | |
| Rajkumar et al. | Users’ click and bookmark based personalization using modified agglomerative clustering for web search engine | |
| Chahal et al. | An ontology based approach for finding semantic similarity between web documents | |
| Shah | Review of indexing techniques applied in information retrieval | |
| Peng et al. | Clustering-based topical web crawling for topic-specific information retrieval guided by incremental classifier | |
| Mohajeri et al. | BubbleNet: An innovative exploratory search and summarization interface with applicability in health social media | |
| Mukherjee et al. | Text classification using document-document semantic similarity | |
| Al-Akashi | Using Wikipedia Knowledge and Query Types in a New Indexing Approach for Web Search Engines | |
| Sharma et al. | Improved stemming approach used for text processing in information retrieval system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 13843551 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A2 |