WO2012154880A1 - Proteostasis regulators for treating cystic fibrosis and other protein misfolding diseases - Google Patents
Proteostasis regulators for treating cystic fibrosis and other protein misfolding diseases Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2012154880A1 WO2012154880A1 PCT/US2012/037159 US2012037159W WO2012154880A1 WO 2012154880 A1 WO2012154880 A1 WO 2012154880A1 US 2012037159 W US2012037159 W US 2012037159W WO 2012154880 A1 WO2012154880 A1 WO 2012154880A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- optionally substituted
- cycloalkyl
- heteroaryl
- cycloalkenyl
- group
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
- 0 *c1c(*)[n](*)nc1* Chemical compound *c1c(*)[n](*)nc1* 0.000 description 12
- YJGNDNDRLFLOCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)(C)N(C)c1cc(C)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O Chemical compound CC(C)(C)N(C)c1cc(C)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O YJGNDNDRLFLOCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CFEGSYNKNXUTJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCNc1cc(C)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O Chemical compound CCNc1cc(C)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O CFEGSYNKNXUTJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VJNUNKGFPPUJMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1NC2CCOCC2)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O Chemical compound Cc(cc1NC2CCOCC2)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O VJNUNKGFPPUJMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QNZRNJZSNFNUIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)(C)c1nc(C)n[s]1 Chemical compound CC(C)(C)c1nc(C)n[s]1 QNZRNJZSNFNUIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OBZDXOUIFWCLDA-SREVYHEPSA-N CC(C)=N/C(/C)=C(/C)\O Chemical compound CC(C)=N/C(/C)=C(/C)\O OBZDXOUIFWCLDA-SREVYHEPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VQGXEYUHQPYVCL-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)Nc1cc(C)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O Chemical compound CC(C)Nc1cc(C)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O VQGXEYUHQPYVCL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RGMJJJUPUDGJII-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)Nc1cc(C)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1O Chemical compound CC(C)Nc1cc(C)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1O RGMJJJUPUDGJII-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LDTVMYHINZSUPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)c1nc(C)n[nH]1 Chemical compound CC(C)c1nc(C)n[nH]1 LDTVMYHINZSUPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OAXIKEDMDGVZKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C1)NC(C=C)=NC1=O Chemical compound CC(C1)NC(C=C)=NC1=O OAXIKEDMDGVZKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PGGUCTMJFCEBPG-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C=C)c1n[s]c(C)n1 Chemical compound CC(C=C)c1n[s]c(C)n1 PGGUCTMJFCEBPG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WAMAFJZXJQNCDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCC(C)C(NCC1)=NC1=O Chemical compound CCC(C)C(NCC1)=NC1=O WAMAFJZXJQNCDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MKJKMINCWYQXLP-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCc([nH]1)nc(C)c1O Chemical compound CCc([nH]1)nc(C)c1O MKJKMINCWYQXLP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QQVLRUCDDBVQAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1NC2CCCC2)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O Chemical compound Cc(cc1NC2CCCC2)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O QQVLRUCDDBVQAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JDAOGJJYWILDNX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1NC2CCCCC2)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1O Chemical compound Cc(cc1NC2CCCCC2)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1O JDAOGJJYWILDNX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GCCSYYWROBUMGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1NCc2ccccc2)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O Chemical compound Cc(cc1NCc2ccccc2)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O GCCSYYWROBUMGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QQLSWLHZLJBXPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1Nc(cc2)ccc2C#N)n[n]1-c1nc(C)cc(C)n1 Chemical compound Cc(cc1Nc(cc2)ccc2C#N)n[n]1-c1nc(C)cc(C)n1 QQLSWLHZLJBXPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PHQOTYMPVQKUAF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1Nc(cc2)ccc2C#N)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O Chemical compound Cc(cc1Nc(cc2)ccc2C#N)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O PHQOTYMPVQKUAF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KYGFASYIJFHBQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1Nc(cc2)ccc2Cl)n[n]1-c1nc(C)cc(C)n1 Chemical compound Cc(cc1Nc(cc2)ccc2Cl)n[n]1-c1nc(C)cc(C)n1 KYGFASYIJFHBQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VWMBSJCYJQRUJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1Nc(cc2)ccc2Cl)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O Chemical compound Cc(cc1Nc(cc2)ccc2Cl)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O VWMBSJCYJQRUJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NMFUVXHZQPLZEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1Nc(cc2)ccc2F)n[n]1-c1nc(C)cc(C)n1 Chemical compound Cc(cc1Nc(cc2)ccc2F)n[n]1-c1nc(C)cc(C)n1 NMFUVXHZQPLZEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ULSVUTPAUHYKOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1Nc(cc2)ccc2F)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O Chemical compound Cc(cc1Nc(cc2)ccc2F)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O ULSVUTPAUHYKOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QNUQQRXTYCRXOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1Nc2c(C)cccc2)n[n]1-c1nc(C)cc(C)n1 Chemical compound Cc(cc1Nc2c(C)cccc2)n[n]1-c1nc(C)cc(C)n1 QNUQQRXTYCRXOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FHDQNKFSIBNVSZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1Nc2cc(C)ccc2)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O Chemical compound Cc(cc1Nc2cc(C)ccc2)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O FHDQNKFSIBNVSZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FMBYJURAMZMJQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1Nc2ccc(C)cc2)n[n]1-c1nc(C)cc(C)n1 Chemical compound Cc(cc1Nc2ccc(C)cc2)n[n]1-c1nc(C)cc(C)n1 FMBYJURAMZMJQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XIJOBJBWOPBBNG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1Nc2ccc(C)cc2)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O Chemical compound Cc(cc1Nc2ccc(C)cc2)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O XIJOBJBWOPBBNG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OBGQJTMJLUBXGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1Nc2cccc(C)c2)n[n]1-c1nc(C)cc(C)n1 Chemical compound Cc(cc1Nc2cccc(C)c2)n[n]1-c1nc(C)cc(C)n1 OBGQJTMJLUBXGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XOKVJPRXMFFLFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1Nc2ccccc2C)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O Chemical compound Cc(cc1Nc2ccccc2C)n[n]1C(NC(C)=C1)=NC1=O XOKVJPRXMFFLFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PSOZJOZKEVZLKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc1c[o]c(C)n1 Chemical compound Cc1c[o]c(C)n1 PSOZJOZKEVZLKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D403/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00
- C07D403/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings
- C07D403/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings directly linked by a ring-member-to-ring-member bond
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing three or more hetero rings
Definitions
- Protein homeostasis a balance between protein synthesis, folding, trafficking, aggregation, and degradation, referred to as protein homeostasis, utilizing sensors and networks of pathways [Sitia et al., Nature 426: 891-894, 2003; Ron et al, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 519-529, 2007].
- the cellular maintenance of protein homeostasis, or proteostasis refers to controlling the conformation, binding interactions, location and concentration of individual proteins making up the proteome. Protein folding in vivo is accomplished through interactions between the folding polypeptide chain and
- Cystic Fibrosis is caused by mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene 1 which encodes a multi-membrane spanning epithelial chloride channel.
- CFTR cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
- AF508 also impacts the normal function of additional organs (pancreas, intestine, gall bladder), suggesting that the loss-of- function impacts multiple downstream pathways that will require correction.
- CF and other maladies of protein misfolding arise as a result of an imbalance in the capacity of the protein homeostasis (proteostasis) environment to handle the reduced energetic stability of misfolded, mutated proteins that are critical for normal physiology 4"6 .
- proteostasis protein homeostasis
- the cellular proteomic and metabolic environment is highly adaptable, and responds to stress and disease through numerous signaling pathways that include, among others, the unfolded protein response (UPR) and heat shock response (HSR).
- URR unfolded protein response
- HSR heat shock response
- the present invention is directed to compounds having the Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila- lid), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb), compositions thereof and methods for the treatment of a condition associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis comprising an effective amount of these compounds.
- the invention is a compound having the Formula (la):
- G is a 3- to 7-membered optionally substituted heterocyclic or an optionally substituted heteroaryl
- Ai is N(R a ) 2 ;
- Each Ri is independently selected from the group consisting of hydi
- Ci-Cio alkyl optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n NR b
- Each R a is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)OR b , C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b and S(0) n R b; or the two R a groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl;
- Each R b is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two R b groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
- n 0, 1 or 2.
- the invention is directed to a compound having the Formula (lb):
- Gi is optionally substituted pyridyl or optionally substituted pyrimidyl
- Ai is N(R a ) 2 ;
- Each Ri is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b C(0)R b , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C(0)R
- Each R a is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)OR b , C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , and S(0) n R b ; or the two R a groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl;
- Each R b is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- Cio alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two R b groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
- n 0, 1 or 2.
- the invention additionally encompasses a method of treating cancer or a tumor comprising administering to a patient in need thereof an effective amount of a compound having the Formula (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (III), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) or (Xlla-XIIb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, clathrate or prodrug of any of thereof.
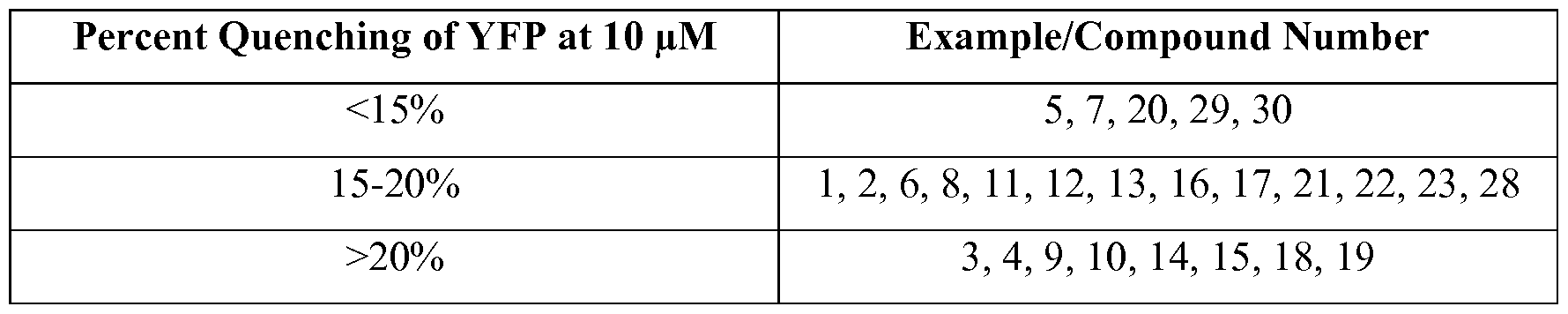
- the Figure is an immunoblot analysis showing enhanced levels of bands B and C when CFBE41o- lung cells were cultured in the presence and absence of DMSO (lane 1) and compound 1 (lane 2) in the assay described below in the Exemplification section.
- a cell encompasses both a single cell and a combination of two or more cells.
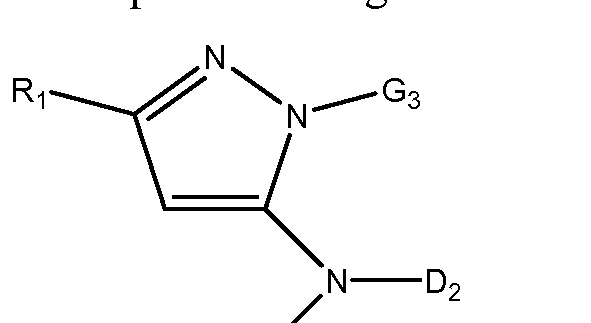
- G3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl, or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
- Ri is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b ,
- Di is phenyl substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b ,
- N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b S(0) n NR b R b , NR b S(0) n R b , S(0) n R b , S(0) n NR b R b , OC(0)OR b , and (C NR b )R b ;
- R a is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)OR b , C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b and S(0) n R b ;
- Each 3 ⁇ 4 is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C 2 - C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substitute
- n 0, 1 or 2.
- the invention is a compound having the Formula (lib).
- G3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 7-membered heterocyclic, aryl, or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
- R a is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)OR b , C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b and S(0) n R b ;
- Each R b is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two R b groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
- D 2 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted benzyl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, and C(Rs)3;
- Ri is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b ,
- Each R 5 is independently selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ),
- NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b S(0) n NR b R b , NR b S(0) n R b , S(0) n R b , S(0) n NR b R b , OC(0)OR b; and (C NR b )R b ; alternatively, two R5 groups can be taken together with the carbon to which they are attached to form a spiro C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl; and n is 0, 1 or 2.
- G 4 is a 6-membered heteroaryl containing one or more ring nitrogen atoms
- D 3 is optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl;
- Each Ri is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b
- Each R a is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)OR b , C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b and S(0) n R b ;
- Each R b is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- Cio alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl;or two R b groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
- n 0, 1 or 2.
- the invention is a compound having Formula (lid):
- D 4 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl;
- Ri is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b ,
- Each R a is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted
- Ci-Cio alkyl optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)OR b , C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b and S(0) n R b ;
- Each R c is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C(0)
- Each R b is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- Cio alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two R b groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
- n 0, 1 or 2.
- the invention is a compound having the Formula (Ilia):
- G3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 7-membered heterocyclic, aryl, or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
- Ri is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C 1 -C 10 alkyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b ,
- Each R 3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b S(0) n
- Re is phenyl substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C 1 -C 10 alkyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b ,
- N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)NR b , NR b S(0) n NR b R b , NR b S(0) n R b , S(0) n R b , S(0) n NR b R b , OC(0)OR b, and (C NR b )R b ;
- Each R b is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C 1 -C 10 alkyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C 2 - C 10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl;or two R b groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
- n 0, 1 or 2.
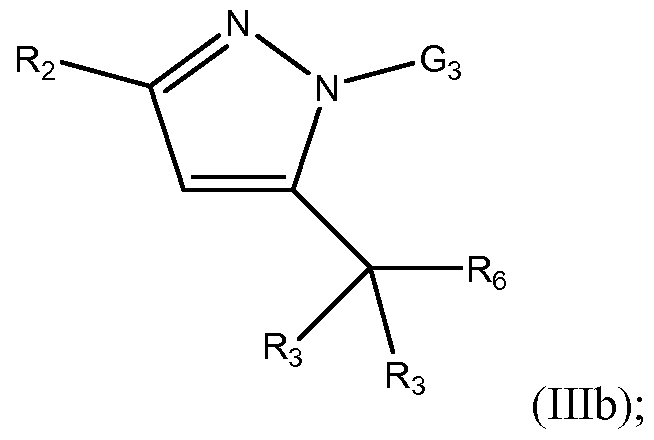
- the invention is a compound having the Formula (Illb):
- G3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 7-membered heterocyclic, aryl, or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
- R2 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, and optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl;
- Each R 3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C(0)R
- R6 is phenyl substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b ,
- Each 3 ⁇ 4 is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C 2 - C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl, or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8
- n 0, 1 or 2.
- the invention is a compound having the Formula (IV):
- G3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 7-membered heterocyclic, an aryl, or a heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
- Rs is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b ,
- R6 is phenyl substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, RbRb, C(0)ORb, N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b Rb, NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b ,
- Each 3 ⁇ 4 is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C 2 - C 10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl, wherein the two R b groups can be taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl
- n 0, 1 or 2.
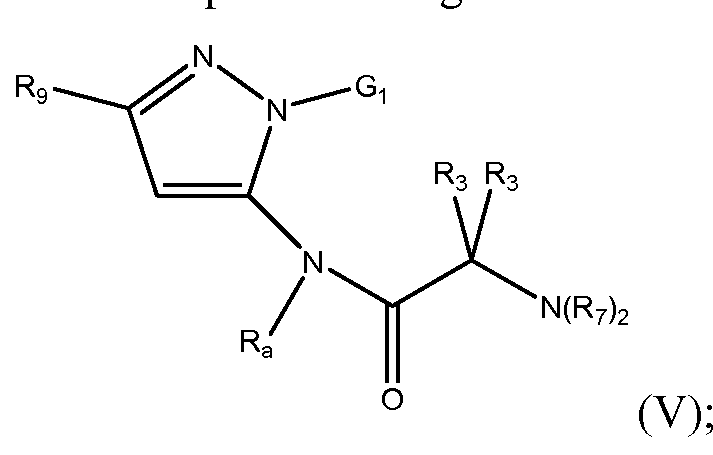
- Gi is an optionally pyridyl or an optionally substituted pyrimidyl
- R9 is selected from the group consisting of substituted methyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C 2 - Cio alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)Rb, NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ),
- Each R 3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C 1 -C 10 alkyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)Rb, NR b C(0)Rb,
- Each R a is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)OR b , C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b and S(0) n R b ;
- Each R 7 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)OR b , C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b and S(0) n R b ;
- the two R7 are taken together with the nitrogen atom to which they are attached to form a 3- to 7- membered heterocyclic or heteroaryl;
- Each R b is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two R b groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
- n 0, 1 or 2.
- e invention is a compound having the Formula (VI):
- B is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl;
- Rio is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci- C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b ,
- Each R a is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)OR b , C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b and S(0) n R b ;
- Each R c is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C(0)
- Each R b is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl, or two R b groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
- n 0, 1 or 2.
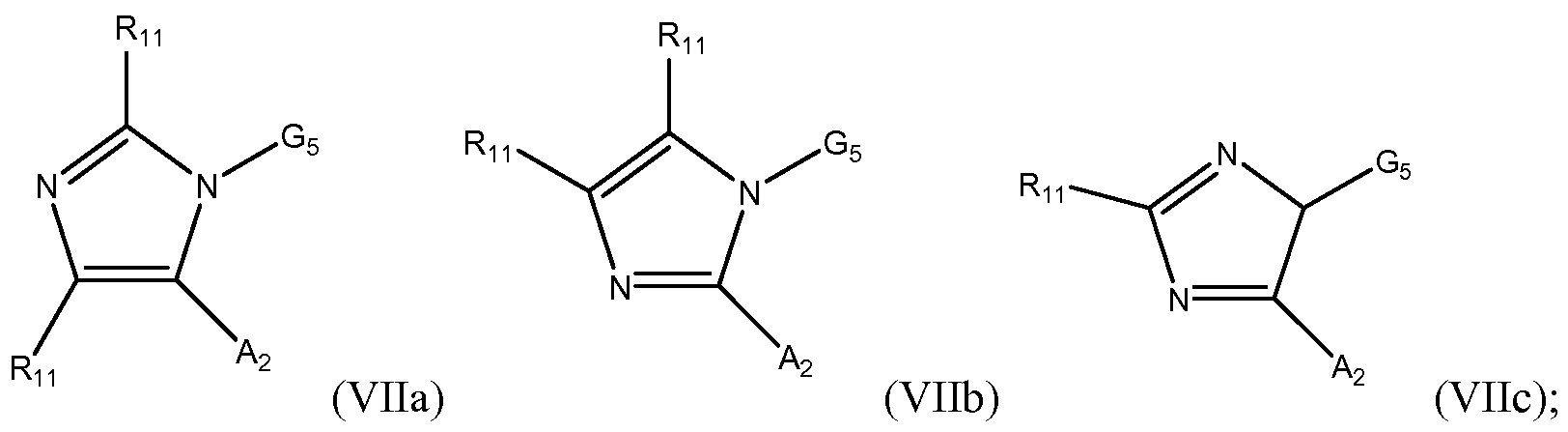
- the invention is a compound having the Formula (Vila), (Vllb) or (VIIc):
- G5 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl
- a 2 is N(R a ) 2 ;
- R 11 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci- C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b ,
- Each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C 1 -C 10 alkyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)OR b , C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b and S(0) n R b ; or the two R a groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl;
- Each R b is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C 1 -C 10 alkyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C 2 - C 10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two R b groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
- n 0, 1 or 2.
- the invention is a compound having the Formula
- Xi is selected from the group consisting of O and S;
- G5 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl
- a 2 is N(R a ) 2 ;
- R12 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci- C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b ,
- Each R a is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)OR b , C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b and S(0) n R b ; or the two R a groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl;
- Each R b is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- Cio alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two R b groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
- n 0, 1 or 2;
- the invention is a compound having the Formula (IXa) or
- G5 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl
- a 2 is N(R a ) 2 ;
- Each R 3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C(0)R
- Each R a is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)OR b , C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b and S(0) n R b , or the two R a groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl;
- Each R b is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two R b groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
- n 0, 1 or 2.
- the invention is additionally directed to a compound having the Formula (Xa) or
- G6 is nitrogen or C-H
- D5 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)OR b , C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , and S(0) n R b ;
- Each Ri is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C(0)R
- Both Ri can join with the carbon atoms to which they are attached to form an optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl;
- Each R 3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C
- Any two R3 can join to form an optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl;
- Each R b is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl;or two R b groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
- n 0, 1 or 2.
- Preferred compounds of Formula (Xa) and (Xb) are represented by Formulas (XIa) and (Xlb), respectively, which include all tautomeric forms, including those represented by Formulas (Xlla) and (Xllb), respectively.
- R g and R h independently have the meanings given for R3 in Formulas (Xa) and (Xb); R; and R j independently have the meanings given for Ri in Formulas (Xa) and (Xb) and D5 has the meaning given for this variable in Formulas (Xa) and (Xb).
- R g and R h are each independently hydrogen or Ci-C6-alkyl, or R g and R h are taken with the carbon atoms to which they are attached to form an optionally substituted benzo ring.
- R g and R h are each independently hydrogen or methyl.
- R g and R h are both hydrogen, R g and R h are both methyl, or R h is methyl and R g is hydrogen.
- Ri and R j are each independently selected from hydrogen and Ci-C6-alkyl.
- R j is hydrogen and R; is Ci-C6-alkyl, such as methyl.
- D 5 is preferably Ci- C6-alkyl, Cs-Cs-cycloalkyl, aryl-Ci-C6-alkyl, such as benzyl, or optionally substituted phenyl, such as phenyl substituted with up to three substituents independently selected from halogen, Ci-C6-alkyl and Ci-C6-alkoxy, such as methoxy.
- phenyl is unsubstituted or non-substituted, for example with chloro, CN, Ci-C4-alkyl or methoxy.
- the pharmaceutical composition comprises a compound of Formula (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (Xla- Xlb) or (Xlla-XIIb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
- the invention also includes a method of treating a patient suffering from a condition associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis comprising administering an effective amount of a compound of Formula (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) or (Xlla-XIIb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
- a compound of Formula Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) or (Xlla-XIIb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
- the invention further includes a method of treating a patient suffering from a condition associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis comprising administering to said patient an effective amount of a compound of Formula (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) or (Xlla-XIIb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
- a compound of Formula Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) or (Xlla-XIIb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
- the invention is a method of treating a patient suffering from a condition associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis comprising administering to said patient an effective amount of a compound having the Formula (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa- Illb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) or (Xlla-XIIb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
- the invention is directed to a pharmaceutical composition comprising:
- the present invention is directed to compounds of Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (III), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb), and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, prodrugs or solvates thereof, pharmaceutical compositions thereof and methods of use thereof in the treatment of conditions associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis.
- the invention is directed to a compound of Formula (la), pharmaceutical compositions thereof or methods of use thereof.
- the invention is a compound of Formula (lb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
- the compound has the Formula (lb), wherein Gi is an optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
- the invention is directed to a compound of Formula (Ila), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
- the compound has the Formula (Ila), wherein G3 is a 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or a heteroaryl, each optionally substituted.
- the compound has the Formula (Ila), wherein Di is phenyl substituted in its para position with a substituent selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R
- the compound has the Formula (Ila), wherein Di is phenyl substituted with a group selected from optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, and optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl.
- Di is phenyl substituted at its para position with a group selected from optionally substituted Ci- Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, and optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl.
- the compound has the Formula (Ila), wherein Ri is optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR
- the compound has the Formula (Ila), wherein R a is selected from the group consisting hydrogen, and optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl.
- the compound has the Formula (Ila), wherein G 3 is selected from the group consisting of, azetidinyl, azolidinyl, oxolanyl, thiophenyl, furanyl, pyrrolyl, pyrazolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, isoxazolinyl, thiazolyl, isothiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, piperidinyl, pyridyl, pyrimidyl, diazinyl, triazinyl, and
- the compound has the Formula (Ila), wherein G 3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted pyridyl and optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
- the invention additionally encompasses compounds having the Formula (lib), pharmaceutically acceptable salts, prodrugs or solvates thereof.
- the compound has the Formula (lib), wherein Ri is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n
- Ri is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- the compound has the Formula (lib), wherein D 2 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted benzyl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- the compound has the Formula (lib), wherein D 2 is C(Rs)3 and each R 5 is independently selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- the compound has the Formula (lib), wherein G 3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted heterocyclic and optionally substituted heteroaryl, such as optionally substituted pyridyl and optionally substituted pyrimidyl. In one embodiment, the compound has the Formula (lib), wherein G3 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
- the invention also encompasses compounds having the Formula (lie), and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, prodrugs and solvates thereof.
- the compound has the Formula (lie), wherein each Ri is independently selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR,, SR b , NR b R b , C(0)ORb, NO2, CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b
- optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- the compound has the Formula (lie), wherein G 4 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted pyridyl, optionally substituted pyrimidyl, optionally substituted diazinyl, and optionally substituted traizinyl. In an additional embodiment, G 4 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl. In another aspect, the compound has the Formula (lie), wherein D3 is optionally substituted phenyl.
- D 3 is phenyl substituted with one or more optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR
- the compound of the invention has the Formula (lid), or is a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
- the compound has the Formula (lid), wherein Ri is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b ,
- N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b S(0) n NR b R b , NR b S(0) n R b , S(0) n R b , S(0) n NR b R b , OC(0)OR b; and (C NR b )R b .
- Ri is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- the invention is a compound having the Formula (lid), wherein each R c is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C4 alkyl and OR b .
- R c is OH or O-C1-C4 alkyl, wherein the C1-C4 alkyl is optionally substituted.
- the invention is directed to a compound having the Formula
- the compound has the Formula (Ilia), wherein R 6 is phenyl substituted in its para position with a substituent selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C 2 -Ci 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b
- the compound has the Formula (Ilia), wherein Ri is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b ,
- the invention has the Formula (Ilia), wherein Ri is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- Ri is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- the compound has the Formula (Ilia), wherein G 3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted heterocyclic and optionally substituted heteroaryl. In another embodiment, G 3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted pyridyl and optionally substituted pyrimidyl. In a further aspect, the compound has the Formula (Ilia), wherein G 3 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
- the compound of the invention has the Formula (Illb).
- the compound has the Formula (Illb), wherein G 3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted heterocyclic and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- G 3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted pyridyl and optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
- the compound has the Formula (Illb) wherein G 3 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
- the invention is directed to a compound of Formula (IV), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
- the compound has the Formula (IV), wherein R 6 is phenyl substituted in its para position with a substituent selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b
- the compound has the Formula (IV), wherein R 8 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2- C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl.
- the compound has the Formula (IV), wherein G 3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted heterocyclic and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- G 3 can be optionally substituted pyridyl or optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
- the invention is directed to a compound of Formula
- the compound has the Formula (V), wherein R 9 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SR b , NRbRb, C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b S(0) n Rb, N(Rb)(COORb), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N
- R 9 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- the invention also encompasses a compound having the Formula (V), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein at least one R3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)
- the invention is directed to a compound havin the Formula (V), wherein Gi is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
- a non-limiting example of a compound having the Formula (V) is:
- the invention is directed to a compound having the Formula (VI).
- the compounds has the Formula (VI), Rio is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C4-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cyloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally sustituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , CO)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ),
- Rio is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C4-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b S(0) n NR b NR b b ), NR
- the compound has the Formula (VI), wherein B is
- each R 3 is as previously defined and each R f is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NRbRb, C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR
- the compound has the Formula (VI), wherein each R c is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci- C 4 alkyl and OR b .
- the compound has the Formula (VI), wherein R c is selected from the group consisting of hydroxyl and optionally substituted O- Ci-C 4 alkyl.
- Non-limiting examples of compounds having the Formula (VI) are selected from the group consistin
- the invention is a compound having the Formula (Vila), (Vllb), or (VIIc), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
- the invention is a compound having the Formula (Vila), (Vllb) or (VIIc), wherein R n is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b ,
- Rn is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- the compound has the Formula (Vila), (Vllb) or (VIIc), wherein A 2 is NR a Rg, wherein R g is optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2- C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)OR b , C(0)R b , and C(0)C(0)Rb.
- R g is optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- the invention also encompasses compounds having the Formula (VIII), and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, prodrugs and solvates thereof.
- the compound has the Formula (VIII), wherein Ri 2 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(CO
- R12 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- the compound has the Formula (VIII), wherein Xi is O. In a further aspect, the compound has the Formula (VIII), wherein Xi is S.
- the invention is also directed to compounds having the Formula (IXa) or (IXb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
- the compound has the Formula (IXa) or (IXb), wherein at least one R13 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , NO2, CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b S(0)
- At least one R1 3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C 3 -C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C 3 -C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- the compound has the Formula (IXa) or (IXb), wherein A2 is RaRg, wherein R g is optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, and C(0)C(0)Rb.
- A2 is RaRg
- R g is optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optional
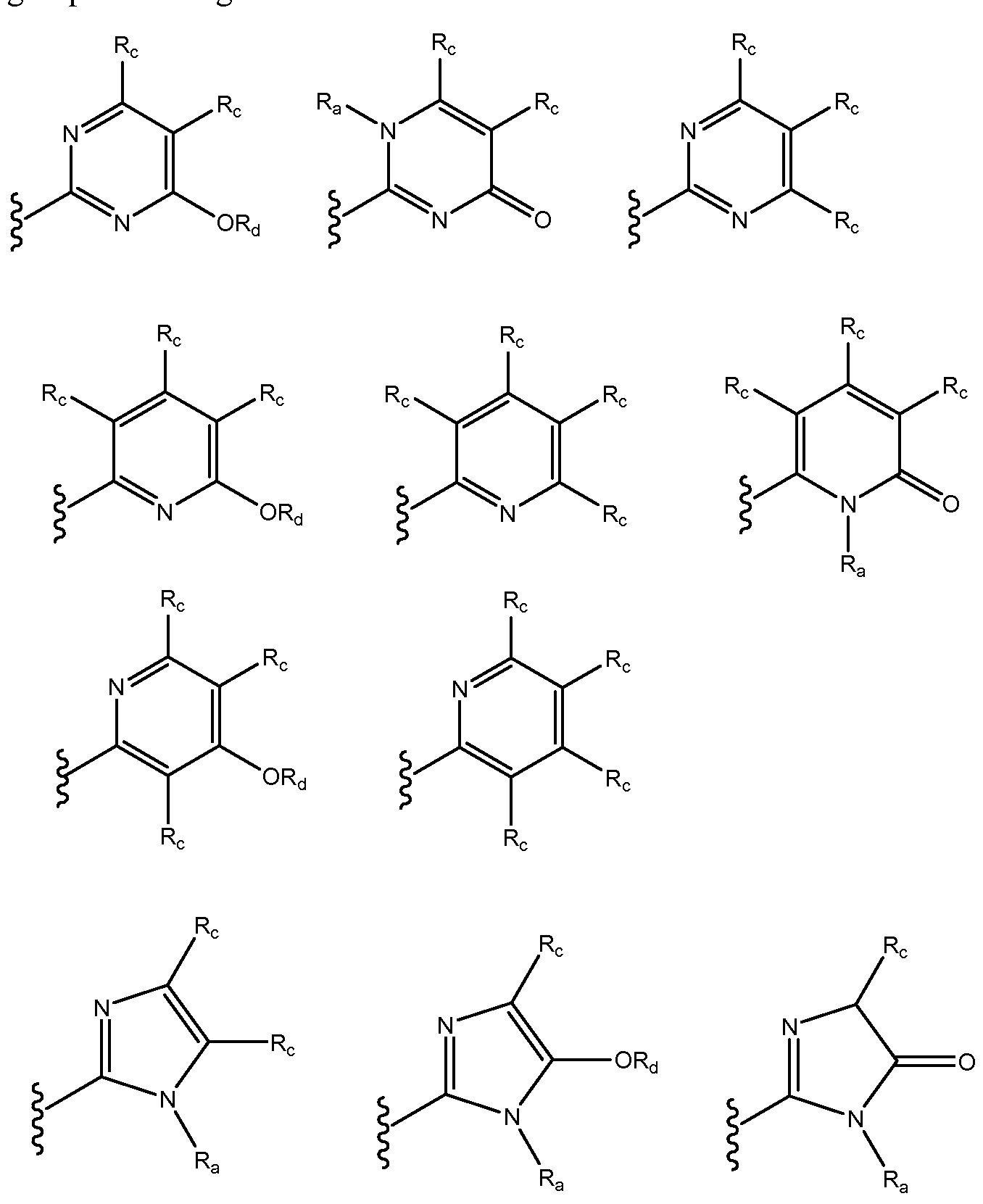
- the invention is directed to a compound of Formula (Ila), (lib), (Ilia), (Illb) or (IV), wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of:
- each R c is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b R b , C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C(0)
- Rd is hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C1 0 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl; and
- R e is (R a ), O, or S.
- the compound has the Formula (Ila), (lib), (III), or (IV) wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of:
- the invention is directed to a compound of Formula (V), wherein Gi is selected from the rou consistin
- each R a , R c and Ra are as defined above.
- the invention is a compound having the Formula (V), wherein Gi is selected from the group consisting of:
- the invention is a compound of Formula (la), (lb), (Vlla- VIIc), (VIII), or (IXa-Ixb), wherein each of Ai or A 2 is independently:
- p 0, 1, 2 or 3;
- Each R 3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR b , SR b , NR b Rb, C(0)OR b , N0 2 , CN, C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b , C(0)NR b R b , NR b C(0)R b , NR b C(0)N(R b ) 2 , NR b S(0) n R b , N(R b )(COOR b ), NR b C(0)C(0)R b , NR b C(0)R b
- Each R4 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C 1 -C 10 alkyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C 2 -C 10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C 12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)OR b , C(0)R b , C(0)C(0)R b and S(0) n R b ; or alternatively, the two R4 groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl.
- the compound is selected from those shown below in
- compositions comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of Formula (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xa), (XIa-XIb) or (Xlla- Xllb) are encompassed by the invention.
- a pharmaceutical compositions comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of Formula (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xa), (XIa-XIb) or (Xlla- Xllb) are encompassed by the invention.
- the pharmaceutical composition comprises an effective amount of a compound shown above in Table 1.
- Ri was defined as optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl and optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl and G3 was defined as optionally substituted pyrimidyl in an additional embodiment above.
- the invention thus, for example, encompasses compounds of Formula (Ila), wherein Ri is optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkenyl and optionally substituted C2-C1 0 alkynyl and G3 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
- alkyl refers to both branched and straight-chain saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon groups having the specified number of carbon atoms; for example, "C1-C1 0 alkyl” denotes alkyl having 1 to 10 carbon atoms.
- alkyl examples include, but are not limited to, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, i-propyl, n-butyl, i-butyl, sec -butyl, t-butyl, n-pentyl, n-hexyl, 2-methylbutyl, 2-methylpentyl, 2- ethylbutyl, 3-methylpentyl, and 4-methylpentyl.
- alkenyl refers to both straight and branched-chain moieties having the specified number of carbon atoms and having at least one carbon- carbon double bond.
- alkynyl refers to both straight and branched-chain moieties having the specified number or carbon atoms and having at least one carbon- carbon triple bond.
- cycloalkyl refers to cyclic alkyl moieties having 3 or more carbon atoms.
- examples of cycloalkyl include, but are not limited to, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl and adamantyl.
- cycloalkenyl refers to cyclic alkenyl moieties having 3 or more carbon atoms.
- cycloalkynyl refers to cyclic alkynyl moieties having 5 or more carbon atoms.
- heterocyclic encompasses heterocycloalkyl, heterocycloalkenyl, heterobicycloalkyl, heterobicycloalkenyl, heteropolycycloalkyl, heteropolycycloalkenyl and the like.
- Heterocycloalkyl refers to cycloalkyl groups containing one or more heteroatoms (O, S, or N) within the ring.
- Heterocycloalkenyl as used herein refers to cycloalkenyl groups containing one or more heteroatoms (O, S or N) within the ring.
- Heterobicycloalkyl refers to bicycloalkyl groups containing one or more heteroatoms (O,
- Heterobicycloalkenyl refers to bicycloalkenyl groups containing one or more heteroatoms (O, S or N) within a ring.
- Cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, groups also include groups similar to those described above for each of these respective categories, but which are substituted with one or more oxo moieties.
- aryl refers to mono- or polycyclic aromatic carbocyclic ring systems.
- a polycyclic aryl is a polycyclic ring system that comprises at least one aromatic ring.
- Polycyclic aryls can comprise fused rings, covalently attached rings or a combination thereof.
- aryl embraces aromatic radicals, such as, phenyl, naphthyl, indenyl, tetrahydronaphthyl, and indanyl.
- An aryl group may be substituted or unsubstituted.
- the aryl is a C4-C10 aryl.
- heteroaryl refers to aromatic carbocyclic groups containing one or more heteroatoms (O, S, or N) within a ring.
- a heteroaryl group can be monocyclic or polycyclic.
- a heteroaryl group may additionally be substituted or unsubstituted.
- the heteroaryl groups of this invention can also include ring systems substituted with one or more oxo moieties.
- a polycyclic heteroaryl can comprise fused rings, covalently attached rings or a combination thereof.
- heteroaryl groups include, but are not limited to, pyridinyl, pyridazinyl, imidazolyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazolyl, triazolyl, pyrazinyl, quinolyl, isoquinolyl, tetrazolyl, furyl, thienyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, oxazolyl, isothiazolyl, pyrrolyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl, indolyl, benzimidazolyl, benzofuranyl, cinnolinyl, indazolyl, indolizinyl, phthalazinyl, triazinyl, isoindolyl, purinyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, furazanyl, benzofurazanyl, benzothiophenyl, benzotriazolyl, benzothiazolyl, benzo
- heteroaryl groups may be C-attached or heteroatom-attached (where such is possible).
- a group derived from pyrrole may be pyrrol- 1-yl (N-attached) or pyrrol-3-yl (C- attached).
- the heteroaryl is 4- to 10-membered heteroaryl.
- substituted refers to substitution by independent replacement of one, two, or three or more of the hydrogen atoms with substituents including, but not limited to, -Ci-Ci 2 alkyl, -C 2 -C 12 alkenyl, -C 2 -C 12 alkynyl, -C 3 -C 12 cycloalkyl, -C 3 -C 12 cycloalkenyl, C 3 -Ci 2 cycloalkynyl, -heterocyclic, -F, -CI, -Br, -I, -OH, -N0 2 , -N 3 , -CN, -NH 2 , oxo, thioxo, -NHR X , -NR X R X , dialkylamino, -diarylamino, -diheteroarylamino, -OR x , -C(0)R y , - C
- haloalkyl refers to an alkyl group having 1 to (2n+l) subsistent(s) independently selected from F, CI, Br or I, where n is the maximum number of carbon atoms in the alkyl group.
- H is the symbol for hydrogen
- N is the symbol for nitrogen
- S is the symbol for sulfur
- O is the symbol for oxygen
- Me is an abbreviation for methyl.
- Non-limiting examples of optionally substituted aryl are phenyl, substituted phenyl, napthyl and substituted naphthyl.
- Enantiomers are a pair of stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
- a 1 : 1 mixture of a pair of enantiomers is a “racemic” mixture.
- the term “( ⁇ )” is used to designate a racemic mixture where appropriate.
- “Diastereoisomers” are stereoisomers that have at least two asymmetric atoms, but which are not mirror- images of each other. The absolute stereochemistry is specified according to the Cahn- Ingold-Prelog R— S system. When a compound is a pure enantiomer the stereochemistry at each chiral carbon may be specified by either R or S.
- Resolved compounds whose absolute configuration is unknown can be designated (+) or (-) depending on the direction (dextro- or levorotatory) which they rotate plane polarized light at the wavelength of the sodium D line.
- the compounds described herein contain olefinic double bonds or other centers of geometric asymmetry, and unless specified otherwise, it is intended that the compounds include both E and Z geometric isomers. Where a particular stereochemistry is described or depicted it is intended to mean that a particular enantiomer is present in excess relative to the other enantiomer.
- a compound has an R-configuration at a specific position when it is present in excess compared to the compound having an S-configuration at that position.
- a compound has an S-configuration at a specific position when it is present in excess compared to the compound having an R-configuration at that position.
- atoms making up the compounds of the present invention are intended to include isotopic forms of such atoms.
- Isotopes include those atoms having the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
- Isotopes of hydrogen include, for example, tritium and deuterium
- isotopes of carbon include, for example, 13 C and 14 C.
- the invention therefore encompasses embodiments in which one or more of the hydrogen atoms in Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (LXa-LXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb) are replaced with deuterium.
- the invention also encompasses embodiments wherein one or more of the carbon atoms in Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb) is replaced with silicon atoms.
- the invention additionally encompasses embodiment wherein one or more of the nitrogen atoms in Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb) are oxidized to N-oxide.
- 6-methyl-2-thioxo-2,3- dihydropyrimidin-4(lH)-one is treated with methyl iodide and potassium carbonate, in dimethyl sulfoxide, to afford 6-methyl-2-(methylthio)prymidin-4(lH)-one (CAS: 6328-58- l).
- the resulting 6-methyl-2-(methylthio)prymidin-4(lH)-one was treated with hydrazine and potassium carbonate in 2-propanol, at reflux, to afford 2-hydrazinyl-6- methylpryimidin-4(lH)-one (CAS: 37893-08-6).
- Scheme 2 depicts another potential method for the synthesis of compounds described in the invention from a substituted 2-chloropyrimidine.
- the preparation of Compound 6 from 2-chloro-4,6-dimethylpyrimidine is shown as an example.
- a solution of 2-chloro-4,6-dimethylpyrimidine in ethanol was treated with hydrazine hydrate and then heated at reflux to afford 2-hydrazinyl-4,6-dimethylpyrimidine.
- Scheme 3 illustrates an alternative route to the synthesis of 5-alkylamino
- the pyrrazole core is prepared as presented in Scheme 1 and 2. Then
- Scheme 4 is another alternative route to pyrazole heterocycles.
- the appropriate ⁇ -ketoamide is treated with hydrazine.
- 26 The resulting pyrazole is alkylated with the appropriate aromatic chloride to afford the desired product.
- the invention encompasses pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compounds described herein.
- the invention is directed to pharmaceutically acceptable salts of compounds of Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb).
- a "pharmaceutically acceptable salt” includes an ionic bond-containing product of the reaction between the disclosed compound with either an acid or a base, suitable for administering to a subject.
- compositions are well known in the art and are described, for example, in Berge et al. (1977), Pharmaceutical Salts, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 69(1): 1-19, the contents of which are herein incorporated by reference.
- a non-limiting example of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt is an acid salt of a compound containing an amine or other basic group which can be obtained by reacting the compound with a suitable organic or inorganic acid.
- Examples of pharmaceutically acceptable salts also can be metallic salts including, but not limited to, sodium, magnesium, calcium, lithium and aluminum salts.
- salts include hydrochlorides, hydrobromides, sulfates, methanesulfonates, nitrates, maleates, acetates, citrates, fumarates, tartrates (e.g. (+)-tartrates, (-)-tartrates or mixtures thereof including racemic mixtures), succinates, benzoates and salts with amino acids such as glutamic acid.
- Salts can also be formed with suitable organic bases when the compound comprises an acid functional group such as -COOH or -SO 3 H.
- bases suitable for the formation of a pharmaceutically acceptable base addition salts with compounds of the present invention include organic bases that are nontoxic and strong enough to react with the acid functional group.
- Such organic bases include amino acids such as arginine and lysine, mono-, di-, and triethanolamine, choline, mono-, di-, and trialkylamine, such as methylamine, dimethylamine, and trimethylamine, guanidine, N-benzylphenethylamine, N-methylglucosamine, N- methylpiperazine, morpholine, ethylendiamine, tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane and the like.
- amino acids such as arginine and lysine, mono-, di-, and triethanolamine, choline, mono-, di-, and trialkylamine, such as methylamine, dimethylamine, and trimethylamine, guanidine, N-benzylphenethylamine, N-methylglucosamine, N- methylpiperazine, morpholine, ethylendiamine, tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane and the like.
- the invention also includes hydrates of the compounds described herein, including for example solvates of the compounds described herein.
- the invention is to solvates of compounds of Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb).
- prodrugs of the compounds described herein for example, prodrugs of compounds of Formulae ((Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (TV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb).
- the invention additionally includes clathrates of the compounds described herein.
- the invention is directed to clathrates of compounds of Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (Xla- Xlb) and (Xlla-XIIb).
- the invention includes pharmaceutical compositions comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or excipient and a compound described herein.
- the excipient can be chosen based on the expected route of administration of the composition in therapeutic applications. The route of administration of the
- composition depends on the condition to be treated. For example, intravenous injection may be preferred for treatment of a systemic disorder and oral administration may be preferred to treat a gastrointestinal disorder.
- the route of administration and the dosage of the composition to be administered can be determined by the skilled artisan without undue experimentation in conjunction with standard dose-response studies. Relevant circumstances to be considered in making those determinations include the condition or conditions to be treated, the choice of composition to be administered, the age, weight, and response of the individual patient, and the severity of the patient's symptoms.
- compositions comprising compounds of Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla- Xllb), and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, clathrates or prodrugs of any of thereof, can be administered by a variety of routes including, but not limited to, parenteral, oral, pulmonary, ophthalmic, nasal, rectal, vaginal, aural, topical, buccal, transdermal, intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intradermal, intraocular, intracerebral, intralymphatic, intraarticular, intrathecal and intraperitoneal.
- compositions can also include, depending on the formulation desired, pharmaceutically-acceptable, non-toxic carriers or diluents, which are defined as vehicles commonly used to formulate pharmaceutical compositions for animal or human administration.
- diluent is selected so as not to affect the biological activity of the pharmacologic agent or composition. Examples of such diluents are distilled water, physiological phosphate-buffered saline, Ringer's solutions, dextrose solution, and Hank's solution.
- the pharmaceutical composition or formulation may also include other carriers, adjuvants, or nontoxic, nontherapeutic, nonimmunogenic stabilizers and the like.
- compositions can also include large, slowly metabolized macromolecules such as proteins, polysaccharides such as chitosan, polylactic acids, polyglycolic acids and copolymers (such as latex functionalized SEPHAROSETM, agarose, cellulose, and the like), polymeric amino acids, amino acid copolymers, and lipid aggregates (such as oil droplets or liposomes).
- macromolecules such as proteins, polysaccharides such as chitosan, polylactic acids, polyglycolic acids and copolymers (such as latex functionalized SEPHAROSETM, agarose, cellulose, and the like), polymeric amino acids, amino acid copolymers, and lipid aggregates (such as oil droplets or liposomes).
- compositions can be administered parenterally such as, for example, by intravenous, intramuscular, intrathecal or subcutaneous injection.
- parenteral such as, for example, by intravenous, intramuscular, intrathecal or subcutaneous injection.
- compositions can be accomplished by incorporating a composition into a solution or suspension.
- solutions or suspensions may also include sterile diluents such as water for injection, saline solution, fixed oils, polyethylene glycols, glycerine, propylene glycol or other synthetic solvents.
- Parenteral formulations may also include antibacterial agents such as, for example, benzyl alcohol or methyl parabens, antioxidants such as, for example, ascorbic acid or sodium bisulfite and chelating agents such as EDTA.
- Buffers such as acetates, citrates or phosphates and agents for the adjustment of tonicity such as sodium chloride or dextrose may also be added.
- the parenteral preparation can be enclosed in ampules, disposable syringes or multiple dose vials made of glass or plastic.
- auxiliary substances such as wetting or emulsifying agents, surfactants, pH buffering substances and the like can be present in compositions.
- Other components of pharmaceutical compositions are those of petroleum, animal, vegetable, or synthetic origin, for example, peanut oil, soybean oil, and mineral oil.
- glycols such as propylene glycol or polyethylene glycol are preferred liquid carriers, particularly for injectable solutions.
- Injectable formulations can be prepared either as liquid solutions or suspensions; solid forms suitable for solution in, or suspension in, liquid vehicles prior to injection can also be prepared.
- the preparation also can also be emulsified or encapsulated in liposomes or micro particles such as polylactide, polyglycolide, or copolymer for enhanced adjuvant effect, as discussed above. Langer, Science 249: 1527, 1990 and Hanes, Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 28: 97-1 19, 1997.
- the compositions and pharmacologic agents described herein can be administered in the form of a depot injection or implant preparation which can be formulated in such a manner as to permit a sustained or pulsatile release of the active ingredient.
- binders and carriers include, for example, polyalkylene glycols or triglycerides; such suppositories can be formed from mixtures containing the active ingredient in the range of about 0.5% to about 10%, preferably about 1%- to about 2%.
- Oral formulations include excipients, such as pharmaceutical grades of mannitol, lactose, starch, magnesium stearate, sodium saccharine, cellulose, and magnesium carbonate.
- Topical application can result in transdermal or intradermal delivery. Transdermal delivery can be achieved using a skin patch or using transferosomes.
- the pharmaceutical composition for the purpose of oral therapeutic administration, the pharmaceutical
- compositions can be incorporated with excipients and used in the form of tablets, troches, capsules, elixirs, suspensions, syrups, wafers, chewing gums and the like.
- Tablets, pills, capsules, troches and the like may also contain binders, excipients, disintegrating agent, lubricants, glidants, sweetening agents, and flavoring agents.
- binders include microcrystalline cellulose, gum tragacanth or gelatin.
- excipients include starch or lactose.
- disintegrating agents include alginic acid, corn starch and the like.
- lubricants include magnesium stearate or potassium stearate.
- An example of a glidant is colloidal silicon dioxide.
- sweetening agents include sucrose, saccharin and the like.
- flavoring agents include peppermint, methyl salicylate, orange flavoring and the like.
- Materials used in preparing these various compositions should be pharmaceutically pure and non-toxic in the amounts used.
- the composition is administered as a tablet or a capsule.
- tablets may be coated with shellac, sugar or both.
- a syrup or elixir may contain, in addition to the active ingredient, sucrose as a sweetening agent, methyl and propylparabens as preservatives, a dye and a flavoring such as cherry or orange flavor, and the like.
- a pharmaceutical composition may be presented as pessaries, tampons, creams, gels, pastes, foams or spray.
- nasally administering or nasal administration includes administering the composition to the mucus membranes of the nasal passage or nasal cavity of the patient.
- pharmaceutical compositions for nasal administration of a composition include therapeutically effective amounts of the compounds prepared by well-known methods to be administered, for example, as a nasal spray, nasal drop, suspension, gel, ointment, cream or powder. Administration of the composition may also take place using a nasal tampon or nasal sponge.
- suitable formulations may include biocompatible oil, wax, gel, powder, polymer, or other liquid or solid carriers. Such formulations may be administered by applying directly to affected tissues, for example, a liquid formulation to treat infection of conjunctival tissue can be administered dropwise to the subject's eye, or a cream formulation can be administered to the skin.
- Rectal administration includes administering the pharmaceutical compositions into the rectum or large intestine. This can be accomplished using suppositories or enemas.
- Suppository formulations can easily be made by methods known in the art. For example, suppository formulations can be prepared by heating glycerin to about 120°C, dissolving the pharmaceutical composition in the glycerin, mixing the heated glycerin after which purified water may be added, and pouring the hot mixture into a suppository mold.
- Transdermal administration includes percutaneous absorption of the composition through the skin.
- Transdermal formulations include patches, ointments, creams, gels, salves and the like.
- pulmonary will also mean to include a tissue or cavity that is contingent to the respiratory tract, in particular, the sinuses.
- an aerosol formulation containing the active agent a manual pump spray, nebulizer or pressurized metered-dose inhaler as well as dry powder formulations are contemplated.
- Suitable formulations of this type can also include other agents, such as antistatic agents, to maintain the disclosed compounds as effective aerosols.
- a drug delivery device for delivering aerosols comprises a suitable aerosol canister with a metering valve containing a pharmaceutical aerosol formulation as described and an actuator housing adapted to hold the canister and allow for drug delivery.
- the canister in the drug delivery device has a head space representing greater than about 15% of the total volume of the canister.
- the compound intended for pulmonary administration is dissolved, suspended or emulsified in a mixture of a solvent, surfactant and propellant. The mixture is maintained under pressure in a canister that has been sealed with a metering valve.
- Treating” or “treatment” includes preventing or delaying the onset of the symptoms, complications, or biochemical indicia of a disease, alleviating or ameliorating the symptoms or arresting or inhibiting further development of the disease, condition, or disorder.
- a “patient” is a human subject in need of treatment.
- an “effective amount” refers to that amount of the therapeutic agent that is sufficient to ameliorate of one or more symptoms of a disorder and/or prevent
- the term “inhibiting” or “decreasing” encompasses causing a net decrease by either direct or indirect means.
- the term “increasing” means to cause a net gain by either direct or indirect means.
- the invention encompasses the treatment of a condition associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis.
- Proteostasis refers to protein homeostasis.
- Dysfunction in protein homeostasis is a result of protein misfolding, protein aggregation, defective protein trafficking or protein degradation.
- Exemplary proteins of which there can be a dysfunction in proteostasis, for example that can exist in a misfolded state include, but are not limited to, glucocerebrosidase, hexosamine A, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator, aspartylglucsaminidase, a-galactosidase A, cysteine transporter, acid ceremidase, acid a-L-fucosidase, protective protein, cathepsin A, acid ⁇ -glucosidase, acid ⁇ -galactosidase, iduronate 2-sulfatase, a-L-iduronidase, galactocerebrosidase, acid a -mannosidase, acid ⁇ -mannosidase, arylsulfatase B, arylsulfatase A, N- acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate
- the protein is selected from the group consisting of huntingtin, tau, alpha-synuclein, a 1 anti-trypsin, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and superoxide dismutase.
- Protein conformational diseases encompass gain of function disorders and loss of function disorders.
- the protein conformational disease is a gain of function disorder.
- gain of function disorder is a disease characterized by increased aggregation- associated proteotoxicity. In these diseases, aggregation exceeds clearance inside and/or outside of the cell. Gain of function diseases include, but are not limited to
- Neurodegenerative diseases associated with aggregation of polyglutamine include, but are not limited to, Huntington's disease, dentatorubral and pallidoluysian atrophy, several forms of spino-cerebellar ataxia, and spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy.
- Alzheimer's disease is characterized by the formation of two types of aggregates: extracellular aggregates of ⁇ peptide and intracellular aggregates of the microtubule associated protein tau.
- Transthyretin-associated aggregation diseases include, for example, senile systemic amyloidoses and familial amyloidotic neuropathy.
- Lewy body diseases are characterized by an aggregation of a-synuclein protein and include, for example, Parkinson's disease.
- Prion diseases also known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathies or TSEs
- Exemplary human prion diseases are Creutzfeldt- Jakob Disease (CJD), Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker Syndrome, Fatal Familial Insomnia and Kuru.
- the protein conformation disease is a loss of function disorder.
- the terms "loss of function disease” and “loss of function disorder” are used interchangeably herein.
- Loss of function diseases are a group of diseases characterized by inefficient folding of a protein resulting in excessive degradation of the protein. Loss of function diseases include, for example, cystic fibrosis and lysosomal storage diseases. In cystic fibrosis, the mutated or defective enzyme is the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR).
- CFTR cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
- Lysosomal storage diseases are a group of diseases characterized by a specific lysosomal enzyme deficiency which may occur in a variety of tissues, resulting in the build-up of molecules normally degraded by the deficient enzyme.
- the lysosomal enzyme deficiency can be in a lysosomal hydrolase or a protein involved in the lysosomal trafficking.
- Lysosomal storage diseases include, but are not limited to, aspartylglucosaminuria, Fabry's disease, Batten disease, Cystinosis, Farber, Fucosidosis, Galactasidosialidosis, Gaucher' s disease (including Types 1, 2 and 3), Gml gangliosidosis, Hunter's disease, Hurler-Scheie's disease, Krabbe's disease, a-Mannosidosis, B-Mannosidosis, Maroteaux-Lamy's disease, Metachromatic Leukodystrophy, Morquio A syndrome, Morquio B syndrome, Mucolipidosis II,
- Mucolipidosis III Neimann-Pick Disease (including Types A, B and C), Pompe's disease, Sandhoff disease, Sanfilippo syndrome (including Types A, B, C and D), Schindler disease, Schindler-Kanzaki disease, Sialidosis, Sly syndrome, Tay-Sach's disease and Wolman disease.
- the disease associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis and/or in the heat shock response is a cardiovascular disease.
- Cardiovascular diseases include, but are not limited to coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, stroke, restenosis and arteriosclerosis.
- Conditions associated with a dysfunction of proteostasis also include ischemic conditions, such as, ischemia/reperfusion injury, myocardial ischemia, stable angina, unstable angina, stroke, ischemic heart disease and cerebral ischemia.
- the disease associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis is diabetes or diabetic retinopathy.
- the condition is selected from the group consisting of cystic fibrosis, Huntington's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, diabetic retinopathy, diabetes, and other retinal disorders. In one embodiment, the condition is cystic fibrosis.
- the invention is directed to a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of any one of Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (TV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (LXa-LXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb), and a second agent, wherein the second agent is selected from the group consisting of a pharmacologic chaperone and a proteostasis regulator.
- the invention also encompasses a method of treating a patient suffering from a condition associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the invention and a second agent, wherein the second agent is a pharmacologic chaperone.
- Pharmacologic chaperones or kinetic stabilizers refer to compounds that bind an existing steady state level of the folded mutant protein and chemically enhance the folding equilibrium by stabilizing the fold [Bouvier, Chem Biol 14: 241-242, 2007; Fan et al, Nat Med 5: 112-115, 1999; Sawkar et al, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99: 15428- 15433 , 2002; Johnson and Kelly, Accounts of Chemical Research 38: 911-921, 2005].
- the pharmacologic chaperone is administered in amount that in combination with a compound described herein in an amount that is sufficient to treat a patient suffering from a condition associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis.
- exemplary pharmacologic chaperones are described in U.S. Patent Publication No's. 20080056994, 20080009516, 20070281975, 20050130972, 20050137223, 20050203019, 20060264467 and 20060287358, the contents of which are incorporated by reference herein.
- the invention is a method of treating a patient suffering from a condition associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis comprising administering therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the invention and a second agent, wherein the second agent is a proteostasis regulator.
- proteostasis regulator refers to small molecules, siRNA and biologicals (including, for example, proteins) that enhance cellular protein homeostasis.
- proteostasis regulators can be agents that influence protein synthesis, folding, trafficking and degradation pathways.
- Proteostasis regulators encompass pharmacologic agents that stimulate the HSR signaling activity.
- Proteostasis regulators function by manipulating signaling pathways, including, but not limited to, the heat shock response or the unfolded protein response, or both, resulting in transcription and translation of proteostasis network components.
- Proteostasis regulators can enhance the folding, trafficking and function of proteins (for example, mutated proteins).
- Proteostasis regulators can also regulate protein chaperones by upregulating transcription or translation of the protein chaperone, or inhibiting degradation of the protein chaperone.
- Proteostasis regulators can influence the biology of folding, often by the coordinated increase in chaperone and folding enzyme levels and
- the proteostasis regulator is distinct from a chaperone in that the proteostasis regulator can enhance the homeostasis of a mutated protein but does not bind the mutated protein.
- proteostasis regulators can upregulate an aggregation pathway or a disaggregase activity.
- Exemplary proteostasis regulators are the celastrols, MG-132 and L-type Ca 2+ channel blockers (e.g., dilitiazem and verapamil).
- celastrol refers to celastrol and derivatives or analogs thereof, including, but not limited to, those celastrol derivatives described in Westerheide et al, J Biol Chem, 2004. 279(53): p. 56053-60, the contents of which are expressly incorporated by reference herein.
- Celastrol derivatives include, for example, celastrol methyl ester, dihydrocelastrol diacetate, celastrol butyl ether, dihydrocelastrol, celastrol benzyl ester, primesterol, primesterol diacetate and triacetate of celastrol.
- the proteostasis regulator is a heat shock response activator.
- a heat shock response activator is an agent that indirectly or directly activates the heat shock response, for example, by directly or indirectly activating heat shock transcription factor 1 (HSF1), inhibiting Hsp90, and/or activating chaperone expression (Westerheide et al, J Biol Chem, 2004. 279(53): p. 56053-60, the contents of which are expressly incorporated by reference herein).
- HSF1 heat shock transcription factor 1
- chaperone expression Westerheide et al, J Biol Chem, 2004. 279(53): p. 56053-60, the contents of which are expressly incorporated by reference herein.
- the terms “heat shock response activator,” “heat shock activator,” “heat shock response inducer,” and “heat shock inducer” are used interchangeably herein.
- Non- limiting examples of heat shock response activators are celastrols, non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs, ansamycin, geldenamycin, radiciol, glucuronic acid, and tributylin. Heat shock response activators have also been described, for example, in U.S. Patent Application Publication No's. 20070259820, 20070207992, 20070179087, 20060148767, the contents of each of which are expressly incorporated by reference herein. In some embodiments, the heat shock response activator is a small molecule heat shock response activator.
- the invention also encompasses a method of treating cancer or a tumor in a patient in need thereof comprising administering to said patient an effective amount of a compound described herein.
- Cancers that can be treated according to methods of the present invention include, but are not limited to, breast cancer, colon cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, multiple myeloma, basal cell carcinoma, neuroblastoma, hematologic cancer, rhabdomyosarcoma, liver cancer, skin cancer, leukemia, basal cell carcinoma, bladder cancer, endometrial cancer, glioma, lymphoma, and gastrointestinal cancer.
- the invention is a method of treating cancer or a tumor comprising administering an effective amount of a compound described herein in combination with the administration of a chemotherapeutic agent.
- Chemotherapeutic agents that can be utilized include, but are not limited to, alkylating agents such as cyclosphosphamide (CYTOXAN®); alkyl sulfonates such as busulfan, improsulfan and piposulfan; aziridines such as benzodopa, carboquone, meturedopa, and uredopa; ethylenimines and methylamelamines including altretamine, triethylenemelamine, trietylenephosphoramide, triethylenethiophosphaoramide and trimethylolomelamine; nitrogen mustards such as chlorambucil, chlornaphazine, cholophosphamide, estramustine, ifosfamide, mechlorethamine, mechlorethamine oxide hydrochloride,
- mycophenolic acid nogalamycin, olivomycins, peplomycin, potfiromycin, puromycin, quelamycin, rodorubicin, streptonigrin, streptozocin, tubercidin, ubenimex, zinostatin, zorubicin; anti-metabolites such as methotrexate and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU); folic acid analogues such as denopterin, methotrexate, pteropterin, trimetrexate; purine analogs such as fludarabine, 6-mercaptopurine, thiamiprine, thioguanine; pyrimidine analogs such as ancitabine, azacitidine, 6-azauridine, carmofur, cytarabine, dideoxyuridine, doxifluridine, enocitabine, floxuridine; androgens such as calusterone, dromostanolone propionate, epitiostanol, mepitiostane
- aldophosphamide glycoside aminolevulinic acid; amsacrine; bestrabucil; bisantrene; edatraxate; defofamine; demecolcine; diaziquone; elfornithine; elliptinium acetate;
- etoglucid gallium nitrate; hydroxyurea; lentinan; lonidamine; mitoguazone; mitoxantrone; mopidamol; nitracrine; pentostatin; phenamet; pirarubicin; podophyllinic acid; 2- ethylhydrazide; procarbazine; PSK®; razoxane; sizofiran; spirogermanium; tenuazonic acid; triaziquone; 2,2',2"-trichlorotriethylamine; urethan; vindesine; dacarbazine;
- ifosfamide mitomycin C; mitoxantrone; vincristine; vinorelbine; navelbine; novantrone; teniposide; daunomycin; aminopterin; xeloda; ibandronate; CPT-11 ; topoisomerase inhibitor RFS 2000; difluoromethylornithine (DMFO); retinoic acid; esperamicins;
- the invention is a method of treating cancer or a tumor comprising administering to a patient in need thereof an effective amount of a compound described herein in combination with radiation therapy.
- the HC1 salt can also be prepared.
- reaction mixture was concentrated in vacuo and the remaining residue was purified by column chromatography on silica using a mixture of dichloromethane/methanol as the eluant.
- the product obtained this way was further purified by preparative HPLC and then crystallization from a mixture of methanol and hexanes to afford 61 mg of l-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)-3-methyl-N-(p-tolyl)-lH- pyrazol-5 -amine as a pale yellow solid.
- the crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica using a mixture of dichloromethane/methanol as the eluant.
- the product obtained from this purification was further purified in another round of column chromatography on silica using a mixture of ethyl acetate/hexanes as the eluant to afford 130 mg of 2-(5-(isopropylamino)-3-methyl-lH-pyrazol-l-yl)-6-methylpyrimidin- 4(lH)-one as a white solid.
- the crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica using a mixture of hexanes/ethyl acetate as the eluant to afford 20 mg of 3 -methyl- l-(pyridin-2 - yl)-N-(/ tolyl)-lH-pyrazol-5 -amine as a yellow solid.
- CFTR transport assays AF508 expressing CFBE41° " lung cells were cultured in the presence of compound 1 in 12 well Sarstedt dishes, harvested, lysed and the processing of CFTR from the band B to the band C glycoform detected by SDS-PAGE and
- FluroChemSP Alpha Inotech densitometer/software package. Where band B and C were quantified from different exposures, an internal reference was used to normalize the signal intensity. This method has been described in detail in Hutt et al. (2010), 28 Reduced histone deacetylase 7 activity restores function to misfolded CFTR in cystic fibrosis, Nature Chemical Biology, 6(1), 25-33, the contents of which are expressly incorporated by reference herein.
- CFTR and halide-sensitive YFP were incubated at 27°C for 20 to 24 h. After incubation, cells were washed with PBS (containing 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KC1, 8.1 mM Na 2 HP04, 1.5 mMKH 2 P0 4 , lmMCaCl 2 , 0.5mMMgCl 2 ) and stimulated for 20 min with forskolin and test compounds. Microplates were read using a plate reader equipped with excitation (HQ500/20X: 500 nm) and emission (HQ535/30M: 535 nm) filters for yellow fluorescent protein.
- Each assay consisted of a continuous 30-s fluorescence reading (5 points per second) with 3 s before and 27 s after injection of 165 ul of an iodide-containing solution (PBS with CI " replaced by T). Final iodide concentration in the wells was 100 mM. These data were normalized to the initial background subtracted fluorescence.
- Table 6 shows percent quenching of yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) by select compounds described in the invention. Quenching values for the selected compounds were obtained at 10 ⁇ . Quenching of YFP signal is an indirect measure of CFTR function. Table 6: Activities for select compounds of the invention for the CFBE-YFP Quenching Assay
- Multigene Assay Monitoring of HSF-1 Activity via HSPA5 Transcript Levels in IMR 32 Human Neuroblastoma Cells
- This assay uses the QuantiGene Plex 2.0 Reagent System from Affymetrix. This assay combines the use of bDNA (branch DNA) and xMAP magnetic capture beads from Luminex Technologies to quantitatively and simultaneously detect multiple mRNA transcripts per well.
- Proteinase K should be used cold. Use lOul of Proteinase K per 1ml of Lysis mixture to make the lysis buffer. Add 50% v/v of the lysis mixture per well. Mix well to ensure proper lysing. Seal the plates with adhesive aluminum plate seals and incubate at 50°C for 30 minutes. Mix well again 10 times. Store plates at -80°C until assay is performed.
- a master mix pool without beads Prepare a master mix pool without beads. Distribute the master mix equally in 8 tubes and then add the respective bead mix to each tube. Vortex and add 20ul/well of the master mix to the 96-well plate. After transfer, add 80ul/well of the lysates to respective plates.
- the amount of cell lysate to be used in the assay should be determined either by performing an assay linearity test or by determining the sample input empirically for each cell line. In order to avoid signal saturation, sample input should be less than 400 cells/ul. Dilute cell lysates with DLM. Keep three wells in each plate as assay background (no cell lysates in these wells, only diluted lysis mixture as described previously and on the next page).
- DLM Dilute Lysis Mixture
- RNA Sample Prep 80 ul of DLM (33% lysis mixture) + 1 ul of RNA (250 ng/ul).
- Preamplifier Solution Add 7.5 ul of preamplifier to every 1ml of Amplifier Diluent.
- Amplifier Solution Add 7.5 ul of Amplifier to every 1ml of Amplifier Diluent.
- Label Probe Solution Add 7.5 ul of Label Probe to every 1ml of Label Probe Diluent.
- SAPE Solution Add 3.0 ul of SAPE to every 1ml of SAPE Diluent.
- PreAmplifier Hyb Step Soak compression plate for 2 min on Magnetic Separation device. Compression plate should make contact with the magnetic device at all time. Wash plate 4 times with 100 ul QGP 2.0 wash buffer, 60 second soak in between each wash required. Remove wash buffer from the final wash. Add 60 ul of Preamp solution per well. Incubate at 50°C for 1 hr with 300 RPM shaking (ThermoMaxQ plate shaker).
- Amplifier Hyb Step Soak compression plate for 2 min on Magnetic Separation Device. Compression plate should make contact with the magnetic device at all time. Wash plate 4 times with 100 ul QGP 2.0 wash buffer, 60 second soak in between each wash required. Remove wash buffer from the final wash. Add 60 ul of Amp solution per well. Incubate at 50°C for 1 hr with 300 RPM shaking (ThermoMaxQ plate shaker).
- Label Probe Hyb Step Soak compression plate for 2 min on Magnetic Separation Device. Compression plate should make contact with the magnetic device at all time. Wash plate 4 times with 100 ul QGP 2.0 wash buffer, 60 second soak in between each wash required. Remove wash buffer from the final wash. Add 60 ul of Label Probe solution per well. Incubate at 50°C for 1 hr with 300 RPM shaking (ThermoMaxQ plate shaker).
- SAPE Hyb Step Soak compression plate for 2 min on Magnetic Separation Device. Compression plate should make contact with the magnetic device at all time. Wash plate 4 times with 100 ul QGP 2.0 wash buffer, 60 second soak in between each wash required. Remove wash buffer from the final wash. Add 60 ul of SAPE solution per well. Incubate at room temperature for 30 min with 600 RPM shaking. The plate needs to be protected from light by wrapping in foil or by dimming the light.
- Control genes used to monitor general transcriptional effects include Tubl (alpha- tubulin) and TBP (TATA binding protein).
- Table 7 Activities for select compounds described in the invention for their ability to induce induction of the HSPA5 gene in IMR32 cells
- Acute ENaC stimulation by cAMP in a kidney cell line is mediated by exocytic insertion from a recycling channel pool. J Gen Physiol 125, 81-101 (2005).
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
The present invention is directed to compounds of Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa- Illb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb), pharmaceutical compositions thereof and methods of use thereof in the treatment of conditions associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis.
Description
PROTEOSTASIS REGULATORS FOR TREATING CYSTIC FIBROSIS AND OTHER
PROTEIN MISFOLDING DISEASES
RELATED APPLICATION
This application claims the benefit of U.S. Provisional Application No. 61/484,065 filed May 9, 2011. The entire teachings of the above application are incorporated herein by reference.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Cells normally maintain a balance between protein synthesis, folding, trafficking, aggregation, and degradation, referred to as protein homeostasis, utilizing sensors and networks of pathways [Sitia et al., Nature 426: 891-894, 2003; Ron et al, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 519-529, 2007]. The cellular maintenance of protein homeostasis, or proteostasis, refers to controlling the conformation, binding interactions, location and concentration of individual proteins making up the proteome. Protein folding in vivo is accomplished through interactions between the folding polypeptide chain and
macromolecular cellular components, including multiple classes of chaperones and folding enzymes, which minimize aggregation [Wiseman et al, Cell 131: 809-821, 2007].
Whether a given protein folds in a certain cell type depends on the distribution, concentration, and subcellular localization of chaperones, folding enzymes, metabolites and the like [Wiseman et al.]. Human loss of function diseases are often the result of a disruption of normal protein homeostasis, typically caused by a mutation in a given protein that compromises its cellular folding, leading to efficient degradation [Cohen et al, Nature 426: 905-909, 2003]. Human gain of function diseases are similarly the result of a disruption in protein homeostasis leading to protein aggregation [Balch et al. (2008), Science 219: 916-919].
Cystic Fibrosis (CF) is caused by mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene1 which encodes a multi-membrane spanning epithelial chloride channel. Ninety percent of patients have a deletion of phenylalanine (Phe) 508 (AF508) on at least one allele. This mutation results in disruption of the energetics of the protein fold2 leading to efficient degradation of CFTR in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The loss of a functional CFTR channel at the plasma membrane disrupts ionic homeostasis (CI", Na+, HCO3 ") and airway surface hydration leading to reduced lung function1.
Reduced periciliary liquid volume and increased mucus viscosity impede mucociliary clearance resulting in chronic infection and inflammation, phenotypic hallmarks of CF disease3. In addition to respiratory dysfunction, AF508 also impacts the normal function of additional organs (pancreas, intestine, gall bladder), suggesting that the loss-of- function impacts multiple downstream pathways that will require correction.
CF and other maladies of protein misfolding, including lysosomal storage diseases, type II diabetes, and cardiovascular and neurological diseases, arise as a result of an imbalance in the capacity of the protein homeostasis (proteostasis) environment to handle the reduced energetic stability of misfolded, mutated proteins that are critical for normal physiology4"6. The cellular proteomic and metabolic environment is highly adaptable, and responds to stress and disease through numerous signaling pathways that include, among others, the unfolded protein response (UPR) and heat shock response (HSR). The latter respond to misfolding and/or aggregation of proteins by altering the transcriptional and post-translational regulation of synthesis, folding and trafficking components to restore function to the protein fold as well as cell, tissue and host physiology4'7. There remains a need in the art for compounds and pharmaceutical compositions to treat conditions associated with proteostasis dysfunction.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention is directed to compounds having the Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila- lid), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb), compositions thereof and methods for the treatment of a condition associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis comprising an effective amount of these compounds.
In one embodiment, the invention is a compound having the Formula (la):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
G is a 3- to 7-membered optionally substituted heterocyclic or an optionally substituted heteroaryl;
Ai is N(Ra)2;
Each Ri is independently selected from the group consisting of hydi
optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally
substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb; or the two Ra groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl;
Each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
In another embodiment, the invention is directed to a compound having the Formula (lb):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
Gi is optionally substituted pyridyl or optionally substituted pyrimidyl;
Ai is N(Ra)2;
Each Ri is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted
C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, and S(0)nRb; or the two Ra groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl;
Each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- Cio alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
The invention additionally encompasses a method of treating cancer or a tumor comprising administering to a patient in need thereof an effective amount of a compound having the Formula (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (III), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) or (Xlla-XIIb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, clathrate or prodrug of any of thereof.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING
The Figure is an immunoblot analysis showing enhanced levels of bands B and C when CFBE41o- lung cells were cultured in the presence and absence of DMSO (lane 1) and compound 1 (lane 2) in the assay described below in the Exemplification section.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
A description of preferred embodiments of the invention follows.
As used herein, the words "a" and "an" are meant to include one or more unless otherwise specified. For example, the term "a cell" encompasses both a single cell and a combination of two or more cells.
provides compounds having the Formula (Ila):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
G3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl, or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
Ri is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Di is phenyl substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb,
N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Ra is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
Each ¾ is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
In an additional embodiment, the invention is a compound having the Formula (lib
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
G3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 7-membered heterocyclic, aryl, or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
Ra is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
Each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
D2 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted benzyl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, and C(Rs)3;
Ri is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each R5 is independently selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb; alternatively, two R5 groups can be taken together with the carbon to which they are attached to form a spiro C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl; and n is 0, 1 or 2.
lly directed to a compound having the Formula (lie):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
G4 is a 6-membered heteroaryl containing one or more ring nitrogen atoms;
D3 is optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl; Each Ri is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each Ra is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
Each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- Cio alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl;or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
In yet an additional aspect, the invention is a compound having Formula (lid):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein;
D4 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl;
Ri is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted
heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each Ra is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted
Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
Each Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- Cio alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
In a further aspect, the invention is a compound having the Formula (Ilia):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
G3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 7-membered heterocyclic, aryl, or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
Ri is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each R3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb; alternatively, the two R3 groups can be taken together with the carbon to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl;
Re is phenyl substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb,
N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)NRb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl;or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are
attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
In yet another embodiment, the invention is a compound having the Formula (Illb):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
G3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 7-membered heterocyclic, aryl, or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
R2 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, and optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl;
Each R3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb; alternatively, the two geminal R3 groups can be taken together with the carbon to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl; and
R6 is phenyl substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb,
N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each ¾ is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl, or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
In an additional aspect, the invention is a compound having the Formula (IV):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
G3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 7-membered heterocyclic, an aryl, or a heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
Rs is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
R6 is phenyl substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, RbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb,
N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each ¾ is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl, wherein the two Rb groups can be taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
on is a compound having the Formula (V):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
Gi is an optionally pyridyl or an optionally substituted pyrimidyl;
R9 is selected from the group consisting of substituted methyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- Cio alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each R3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb; alternatively, the two R3 groups can be taken together with
the carbon to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl;
Each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
Each R7 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
alternatively, the two R7 are taken together with the nitrogen atom to which they are attached to form a 3- to 7- membered heterocyclic or heteroaryl;
Each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
e invention is a compound having the Formula (VI):
(VI);
a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
B is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl;
Rio is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci- C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each Ra is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
Each Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl, or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
In a further embodiment, the invention is a compound having the Formula (Vila), (Vllb) or (VIIc):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof wherein:
G5 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl;
A2 is N(Ra)2;
R11 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci- C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb; or the two Ra groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl;
Each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
In yet another embodiment, the invention is a compound having the Formula
(VIII):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
Xi is selected from the group consisting of O and S;
G5 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl;
A2 is N(Ra)2;
R12 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci- C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb; or the two Ra groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl;
Each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- Cio alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2;
In yet a further aspect, the invention is a compound having the Formula (IXa) or
(Kb):
G5 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl;
A2 is N(Ra)2;
Each R 3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb, or the two Ra groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl;
Each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
The invention is additionally directed to a compound having the Formula (Xa) or
(Xb
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
G6 is nitrogen or C-H;
D5 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, and S(0)nRb;
Each Ri is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Both Ri can join with the carbon atoms to which they are attached to form an optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl;
Each R3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted
C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Any two R3 can join to form an optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl;
Each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl;or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
Preferred compounds of Formula (Xa) and (Xb) are represented by Formulas (XIa) and (Xlb), respectively, which include all tautomeric forms, including those represented by Formulas (Xlla) and (Xllb), respectively.
where in each of Formulas (XIa), (Xlb), (Xlla) and (Xllb), Rg and Rh independently have the meanings given for R3 in Formulas (Xa) and (Xb); R; and Rj independently have the meanings given for Ri in Formulas (Xa) and (Xb) and D5 has the meaning given for this variable in Formulas (Xa) and (Xb). Preferably, Rg and Rh are each independently hydrogen or Ci-C6-alkyl, or Rg and Rh are taken with the carbon atoms to which they are attached to form an optionally substituted benzo ring. Preferably, Rg and Rh are each independently hydrogen or methyl. In particularly preferred ambodiments, Rg and Rh are both hydrogen, Rg and Rh are both methyl, or Rh is methyl and Rg is hydrogen. Preferably, Ri and Rj are each independently selected from hydrogen and Ci-C6-alkyl. In certain embosiments, Rj is hydrogen and R; is Ci-C6-alkyl, such as methyl. D5 is preferably Ci- C6-alkyl, Cs-Cs-cycloalkyl, aryl-Ci-C6-alkyl, such as benzyl, or optionally substituted phenyl, such as phenyl substituted with up to three substituents independently selected from halogen, Ci-C6-alkyl and Ci-C6-alkoxy, such as methoxy. In preferred ambodiments, phenyl is unsubstituted or non-substituted, for example with chloro, CN, Ci-C4-alkyl or methoxy.
In one aspect, the pharmaceutical composition comprises a compound of Formula (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (Xla- Xlb) or (Xlla-XIIb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
The invention also includes a method of treating a patient suffering from a condition associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis comprising administering an effective amount of a compound of Formula (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) or (Xlla-XIIb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
The invention further includes a method of treating a patient suffering from a condition associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis comprising administering to said patient an effective amount of a compound of Formula (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) or (Xlla-XIIb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
In yet a further aspect, the invention is a method of treating a patient suffering from a condition associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis comprising administering to said patient an effective amount of a compound having the Formula (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa- Illb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) or (Xlla-XIIb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof.
In an additional aspect, the invention is directed to a pharmaceutical composition comprising:
a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or excipient;
an effective amount of a compound having the Formula (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa- Illb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) or (Xlla-XIIb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, clathrate or prodrug of any of thereof; and an effective amount of a second agent selected from the group consisting of a proteostasis regulator and a pharmacologic chaperone.
As discussed above, the present invention is directed to compounds of Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (III), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb), and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, prodrugs or solvates thereof, pharmaceutical compositions thereof and methods of use thereof in the treatment of conditions associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis.
In some embodiments, the invention is directed to a compound of Formula (la), pharmaceutical compositions thereof or methods of use thereof.
In certain additional aspects, the invention is a compound of Formula (lb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof. In some embodiments, the compound has the Formula (lb), wherein Gi is an optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
In yet an additional embodiment, the invention is directed to a compound of Formula (Ila), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof. In one embodiment, the compound has the Formula (Ila), wherein G3 is a 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or a heteroaryl, each optionally substituted.
In some embodiments, the compound has the Formula (Ila), wherein Di is phenyl substituted in its para position with a substituent selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbNRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb, and wherein the phenyl ring can optionally be further substituted. In further aspects, the compound has the Formula (Ila), wherein Di is phenyl substituted with a group selected from optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, and optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl. In yet additional embodiments, Di is
phenyl substituted at its para position with a group selected from optionally substituted Ci- Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, and optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl.
In certain embodiments, the compound has the Formula (Ila), wherein Ri is optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbNRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb. In certain additional embodiments, Ri is optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl.
In yet additional aspects, the compound has the Formula (Ila), wherein Ra is selected from the group consisting hydrogen, and optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl.
In a further embodiment, the compound has the Formula (Ila), wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of, azetidinyl, azolidinyl, oxolanyl, thiophenyl, furanyl, pyrrolyl, pyrazolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, isoxazolinyl, thiazolyl, isothiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, piperidinyl, pyridyl, pyrimidyl, diazinyl, triazinyl, and
tetrahydropyranyl, each optionally substituted. In yet an additional embodiment, the compound has the Formula (Ila), wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted pyridyl and optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
The invention additionally encompasses compounds having the Formula (lib), pharmaceutically acceptable salts, prodrugs or solvates thereof. In some embodiments, the compound has the Formula (lib), wherein Ri is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb,
OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb. In a further aspect, Ri is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted
C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
In an additional aspect, the compound has the Formula (lib), wherein D2 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted benzyl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl. In yet additional aspects, the compound has the Formula (lib), wherein D2 is C(Rs)3 and each R5 is independently selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl.
In certain additional embodiments, the compound has the Formula (lib), wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted heterocyclic and optionally substituted heteroaryl, such as optionally substituted pyridyl and optionally substituted pyrimidyl. In one embodiment, the compound has the Formula (lib), wherein G3 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
The invention also encompasses compounds having the Formula (lie), and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, prodrugs and solvates thereof. In one embodiment, the compound has the Formula (lie), wherein each Ri is independently selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR,, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, NO2, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb. In some embodiments, each Ri is
independently selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
In a further embodiment, the compound has the Formula (lie), wherein G4 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted pyridyl, optionally substituted pyrimidyl, optionally substituted diazinyl, and optionally substituted traizinyl. In an additional embodiment, G4 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
In another aspect, the compound has the Formula (lie), wherein D3 is optionally substituted phenyl. In some embodiments, D3 is phenyl substituted with one or more optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb.
In an additional embodiment, the compound of the invention has the Formula (lid), or is a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof. In some
embodiments, the compound has the Formula (lid), wherein Ri is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb,
N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb. In some embodiments, Ri is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
In an additional aspect, the invention is a compound having the Formula (lid), wherein each Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C4 alkyl and ORb. In an additional aspect, Rc is OH or O-C1-C4 alkyl, wherein the C1-C4 alkyl is optionally substituted.
Non-limiting examples of compounds encompassed by Formulae (Ila-IId) are shown below:
In some embodiments, the invention is directed to a compound having the Formula
(Ilia). In some embodiments, the compound has the Formula (Ilia), wherein R6 is phenyl substituted in its para position with a substituent selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-Ci0 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl,
optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb, and wherein the phenyl ring can optionally be further substituted.
In certain embodiments, the compound has the Formula (Ilia), wherein Ri is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb,
NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb,
NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb. In additional aspects, the invention has the Formula (Ilia), wherein Ri is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
In another embodiment, the compound has the Formula (Ilia), wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted heterocyclic and optionally substituted heteroaryl. In another embodiment, G3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted pyridyl and optionally substituted pyrimidyl. In a further aspect, the compound has the Formula (Ilia), wherein G3 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
In yet another embodiment, the compound of the invention has the Formula (Illb). In one aspect, the compound has the Formula (Illb), wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted heterocyclic and optionally substituted heteroaryl. In an additional embodiment, G3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted pyridyl and optionally substituted pyrimidyl. In certain embodiments, the compound has the Formula (Illb) wherein G3 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
In a further aspect, the invention is directed to a compound of Formula (IV), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof. In some embodiments, the compound has the Formula (IV), wherein R6 is phenyl substituted in its para position with a substituent selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally
substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb,
NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb, and wherein the phenyl ring can optionally be further substituted.
In some embodiments, the compound has the Formula (IV), wherein R8 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl.
In certain embodiments, the compound has the Formula (IV), wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted heterocyclic and optionally substituted heteroaryl. For example, G3 can be optionally substituted pyridyl or optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
In an additional embodiment, the invention is directed to a compound of Formula
(V), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof. In one embodiment, the compound has the Formula (V), wherein R9 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2,
NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb. In yet another aspect, R9 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
The invention also encompasses a compound having the Formula (V), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein at least one R3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb,
NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2,
NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb.
In additional embodiments, the invention is directed to a compound havin the Formula (V), wherein Gi is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
A non-limiting example of a compound having the Formula (V) is:
In additional embodiments, the invention is directed to a compound having the Formula (VI). In some embodiments, the compounds has the Formula (VI), Rio is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C4-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cyloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally sustituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, CO)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb. In yet an additional aspect, Rio is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C4-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbNRb,
NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb.
In additional aspects, the compound has the Formula (VI), wherein B is
C(R3)2N(Rf)2: wherein each R3 is as previously defined and each Rf is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb,
NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb,
NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb.
In another aspect, the compound has the Formula (VI), wherein each Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci- C4 alkyl and ORb. In yet another embodiment, the compound has the Formula (VI), wherein Rc is selected from the group consisting of hydroxyl and optionally substituted O- Ci-C4 alkyl.
Non-limiting examples of compounds having the Formula (VI) are selected from the group consistin
In an additional embodiment, the invention is a compound having the Formula (Vila), (Vllb), or (VIIc), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof. In some embodiments, the invention is a compound having the Formula (Vila), (Vllb) or (VIIc), wherein Rn is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb. In one embodiment, Rn is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
In certain aspects, the compound has the Formula (Vila), (Vllb) or (VIIc), wherein A2 is NRaRg, wherein Rg is optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, and
C(0)C(0)Rb. In certain embodiments, Rg is optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl.
The invention also encompasses compounds having the Formula (VIII), and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, prodrugs and solvates thereof. In some embodiments, the compound has the Formula (VIII), wherein Ri2 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb. In some embodiments, R12 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
In an additional embodiment, the compound has the Formula (VIII), wherein Xi is O. In a further aspect, the compound has the Formula (VIII), wherein Xi is S.
The invention is also directed to compounds having the Formula (IXa) or (IXb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof. In one embodiment, the compound has the Formula (IXa) or (IXb), wherein at least one R13 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, NO2, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb. In some embodiments, at least one R13 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
In a further aspect, the compound has the Formula (IXa) or (IXb), wherein A2 is RaRg, wherein Rg is optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10
alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, and C(0)C(0)Rb.
In certain additional aspects, the invention is directed to a compound of Formula (Ila), (lib), (Ilia), (Illb) or (IV), wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of:
wherein:
each Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Rd is hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl; and
Re is (Ra), O, or S.
In yet an additional aspect, the compound has the Formula (Ila), (lib), (III), or (IV) wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of:
In some embodiments, the invention is directed to a compound of Formula (V), wherein Gi is selected from the rou consistin
wherein:
each Ra, Rc and Ra are as defined above.
In another embodiment, the invention is a compound having the Formula (V), wherein Gi is selected from the group consisting of:
In one embodiment, the invention is a compound of Formula (la), (lb), (Vlla- VIIc), (VIII), or (IXa-Ixb), wherein each of Ai or A2 is independently:
wherein p is 0, 1, 2 or 3;
Each R3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb; alternatively, two geminal R3 groups can be taken together with the carbon to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl; or yet alternatively, two vicinal R3 groups can be taken together with the atoms to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl; and
Each R4 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl,
optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb; or alternatively, the two R4 groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl.
In additional embodiment, the compound is selected from those shown below in
Table 1:
TABLE 1
As discussed above, the invention additionally encompasses pharmaceutical compositions. For example, pharmaceutical compositions comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of Formula (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xa), (XIa-XIb) or (Xlla- Xllb) are encompassed by the invention.
In an additional embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition comprises an effective amount of a compound shown above in Table 1.
It is to be understood that the specific embodiments described herein can be taken in combination with other specific embodiments delineated herein. For example, for compounds of Formula (Ila), Ri was defined as optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl and optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl and G3 was defined as optionally substituted pyrimidyl in an additional embodiment above. The invention thus, for example, encompasses compounds of Formula (Ila), wherein Ri is
optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl and optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl and G3 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
The term "alkyl", as used herein, unless otherwise indicated, refers to both branched and straight-chain saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon groups having the specified number of carbon atoms; for example, "C1-C10 alkyl" denotes alkyl having 1 to 10 carbon atoms. Examples of alkyl include, but are not limited to, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, i-propyl, n-butyl, i-butyl, sec -butyl, t-butyl, n-pentyl, n-hexyl, 2-methylbutyl, 2-methylpentyl, 2- ethylbutyl, 3-methylpentyl, and 4-methylpentyl.
The term, "alkenyl", as used herein, refers to both straight and branched-chain moieties having the specified number of carbon atoms and having at least one carbon- carbon double bond.
The term, "alkynyl", as used herein, refers to both straight and branched-chain moieties having the specified number or carbon atoms and having at least one carbon- carbon triple bond.
The term "cycloalkyl," as used herein, refers to cyclic alkyl moieties having 3 or more carbon atoms. Examples of cycloalkyl include, but are not limited to, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl and adamantyl.
The term "cycloalkenyl," as used herein, refers to cyclic alkenyl moieties having 3 or more carbon atoms.
The term "cycloalkynyl," as used herein, refers to cyclic alkynyl moieties having 5 or more carbon atoms.
The term "heterocyclic" encompasses heterocycloalkyl, heterocycloalkenyl, heterobicycloalkyl, heterobicycloalkenyl, heteropolycycloalkyl, heteropolycycloalkenyl and the like. Heterocycloalkyl refers to cycloalkyl groups containing one or more heteroatoms (O, S, or N) within the ring. Heterocycloalkenyl as used herein refers to cycloalkenyl groups containing one or more heteroatoms (O, S or N) within the ring.
Heterobicycloalkyl refers to bicycloalkyl groups containing one or more heteroatoms (O,
S or N) within a ring. Heterobicycloalkenyl as used herein refers to bicycloalkenyl groups containing one or more heteroatoms (O, S or N) within a ring.
Cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, groups also include groups similar to those described above for each of these respective categories, but which are substituted with one or more oxo moieties.
The term "aryl", as used herein, refers to mono- or polycyclic aromatic carbocyclic ring systems. A polycyclic aryl is a polycyclic ring system that comprises at least one
aromatic ring. Polycyclic aryls can comprise fused rings, covalently attached rings or a combination thereof. The term "aryl" embraces aromatic radicals, such as, phenyl, naphthyl, indenyl, tetrahydronaphthyl, and indanyl. An aryl group may be substituted or unsubstituted. In some embodiments, the aryl is a C4-C10 aryl.
The term "heteroaryl", as used herein, refers to aromatic carbocyclic groups containing one or more heteroatoms (O, S, or N) within a ring. A heteroaryl group can be monocyclic or polycyclic. A heteroaryl group may additionally be substituted or unsubstituted. The heteroaryl groups of this invention can also include ring systems substituted with one or more oxo moieties. A polycyclic heteroaryl can comprise fused rings, covalently attached rings or a combination thereof. Examples of heteroaryl groups include, but are not limited to, pyridinyl, pyridazinyl, imidazolyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazolyl, triazolyl, pyrazinyl, quinolyl, isoquinolyl, tetrazolyl, furyl, thienyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, oxazolyl, isothiazolyl, pyrrolyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl, indolyl, benzimidazolyl, benzofuranyl, cinnolinyl, indazolyl, indolizinyl, phthalazinyl, triazinyl, isoindolyl, purinyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, furazanyl, benzofurazanyl, benzothiophenyl, benzotriazolyl, benzothiazolyl, benzoxazolyl, quinazolinyl, quinoxalinyl, naphthyridinyl, dihydroquinolyl, tetrahydroquinolyl, dihydroisoquinolyl, tetrahydroisoquinolyl, benzofuryl, furopyridinyl, pyrolopyrimidinyl, thiazolopyridinyl, oxazolopyridinyl and azaindolyl. The foregoing heteroaryl groups may be C-attached or heteroatom-attached (where such is possible). For instance, a group derived from pyrrole may be pyrrol- 1-yl (N-attached) or pyrrol-3-yl (C- attached). In some embodiments, the heteroaryl is 4- to 10-membered heteroaryl.
The term "substituted" refers to substitution by independent replacement of one, two, or three or more of the hydrogen atoms with substituents including, but not limited to, -Ci-Ci2 alkyl, -C2-C12 alkenyl, -C2-C12 alkynyl, -C3-C12 cycloalkyl, -C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, C3-Ci2 cycloalkynyl, -heterocyclic, -F, -CI, -Br, -I, -OH, -N02, -N3, -CN, -NH2, oxo, thioxo, -NHRX, -NRXRX, dialkylamino, -diarylamino, -diheteroarylamino, -ORx, -C(0)Ry, - C(0)C(0)Ry, -OC02Ry, -OC(0)Ry, OC(0)C(0)Ry, -NHC(0)Ry, -NHC02Ry, - NHC(0)C(0)Ry, NHC(S)NH2, -NHC(S)NHRX, -NHC(NH)NH2, -NHC(NH)NHRX, - NHC( H)RX, -C(NH)NHRX, and (C=NRX)RX; -NRxC(0)Rx, -NRxC(0)N(Rx)2, - NRxC02Ry, -NRxC(0)C(0)Ry, -NRXC(S)NH2, -NRXC(S)NHRX, -NRXC( H)NH2, - NRXC(NH)NHRX, -NRxC(NH)Rx, -C( Rx)NHRx -S(0)Ry, -NHS02Rx, -CH2NH2, - CH2S02CH3, -aryl, -arylalkyl, -heteroaryl, -heteroarylalkyl, -heterocycloalkyl, -C3-Ci2- cycloalkyl, -polyalkoxyalkyl, -polyalkoxy, -methoxymethoxy, -methoxyethoxy, -SH, -S- Rx, or -methylthiomethyl, wherein Rx is selected from the group consisting of -Ci-Ci2
alkyl, -C2-C12 alkenyl, -C2-C12 alkynyl, -C3-C12 cycloalkyl, -aryl, -heteroaryl and - heterocyclic and -Ry is selected from the group consisting of -C1-C12 alkyl, -C2-C12 alkenyl, -C2-C12 alkynyl, -C3-C12 cycloalkyl, -aryl, -heteroaryl, -heterocyclic, -NH2, -NH- C1-C12 alkyl, -NH-C2-C12 alkenyl, -NH-C2-Ci2-alkynyl, -NH-C3-Ci2 cycloalkyl, -NH-aryl, -NH-heteroaryl and -NH-heterocyclic. It is understood that the aryls, heteroaryls, alkyls, and the like can be further substituted.
The term "haloalkyl" as used herein refers to an alkyl group having 1 to (2n+l) subsistent(s) independently selected from F, CI, Br or I, where n is the maximum number of carbon atoms in the alkyl group.
As will be understood by the skilled artisan, "H" is the symbol for hydrogen, "N" is the symbol for nitrogen, "S" is the symbol for sulfur, "O" is the symbol for oxygen.
"Me" is an abbreviation for methyl.
Non-limiting examples of optionally substituted aryl are phenyl, substituted phenyl, napthyl and substituted naphthyl.
Certain of the compounds described herein contain one or more asymmetric centers and may thus give rise to enantiomers, diastereomers, and other stereoisomeric forms that may be defined, in terms of absolute stereochemistry, as (R)- or (S)-. The present invention is meant to include all such possible isomers, including racemic mixtures, optically pure forms and intermediate mixtures. Optically active (R)- and (S)- isomers may be prepared using chiral synthons or chiral reagents, or resolved using conventional techniques. "Isomers" are different compounds that have the same molecular formula. "Stereoisomers" are isomers that differ only in the way the atoms are arranged in space. "Enantiomers" are a pair of stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. A 1 : 1 mixture of a pair of enantiomers is a "racemic" mixture. The term "(±)" is used to designate a racemic mixture where appropriate. "Diastereoisomers" are stereoisomers that have at least two asymmetric atoms, but which are not mirror- images of each other. The absolute stereochemistry is specified according to the Cahn- Ingold-Prelog R— S system. When a compound is a pure enantiomer the stereochemistry at each chiral carbon may be specified by either R or S. Resolved compounds whose absolute configuration is unknown can be designated (+) or (-) depending on the direction (dextro- or levorotatory) which they rotate plane polarized light at the wavelength of the sodium D line. When the compounds described herein contain olefinic double bonds or other centers of geometric asymmetry, and unless specified otherwise, it is intended that the compounds include both E and Z geometric isomers.
Where a particular stereochemistry is described or depicted it is intended to mean that a particular enantiomer is present in excess relative to the other enantiomer. A compound has an R-configuration at a specific position when it is present in excess compared to the compound having an S-configuration at that position. A compound has an S-configuration at a specific position when it is present in excess compared to the compound having an R-configuration at that position.
Likewise, all tautomeric forms are also intended to be included. Where a particular compound is described or depicted it is intended to encompass that chemical structure as well as tautomers of that structure. For example the structures below are exemplary, but in no way limiting, of potential tautomers.
It is to be understood that atoms making up the compounds of the present invention are intended to include isotopic forms of such atoms. Isotopes, as used herein, include those atoms having the same atomic number but different mass numbers. Isotopes of hydrogen include, for example, tritium and deuterium, and isotopes of carbon include, for example, 13C and 14C. The invention therefore encompasses embodiments in which one or more of the hydrogen atoms in Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (LXa-LXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb) are replaced with deuterium. The invention also encompasses embodiments wherein one or more of the carbon atoms in Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb) is replaced with silicon atoms.
The invention additionally encompasses embodiment wherein one or more of the nitrogen atoms in Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb) are oxidized to N-oxide.
Exemplary synthetic routes for the preparation of compounds of the invention are shown below as Schemes 1-4 below. Methods for the synthesis that can be used to synthesize compounds of the invention have also been discussed in the literature, for example, in some of the references listed below. As will be understood by the skilled artisan, diastereomers can be separated from the reaction mixture using column chromatography.
The synthesis of Compound 1 was carried out by converting 6-methyl-2-thioxo- 2,3-dihydropyrimidin-4(lH)-one to Compound 1. Commercially 6-methyl-2-thioxo-2,3- dihydropyrimidin-4(lH)-one is treated with methyl iodide and potassium carbonate, in dimethyl sulfoxide, to afford 6-methyl-2-(methylthio)prymidin-4(lH)-one (CAS: 6328-58- l).19 The resulting 6-methyl-2-(methylthio)prymidin-4(lH)-one was treated with hydrazine and potassium carbonate in 2-propanol, at reflux, to afford 2-hydrazinyl-6- methylpryimidin-4(lH)-one (CAS: 37893-08-6).20 Treating a mixture of 2-hydrazinyl-6- methylpryimidin-4(lH)-one and 3-oxo-N-(p-tolyl)butanamide (CAS: 2415-85-2) in 1,4- dioxane with Lawesson's reagent and a sub-stoichiometric amount of pyridine affords the desired pyrazole (Compound l).21 The starting β-ketoamides can be purchased or synthesized as described in the literature.22 Compound 1 can be isolated as a free base or as a hydrochloride salt.
Scheme 2 depicts another potential method for the synthesis of compounds described in the invention from a substituted 2-chloropyrimidine. The preparation of Compound 6 from 2-chloro-4,6-dimethylpyrimidine is shown as an example. A solution of 2-chloro-4,6-dimethylpyrimidine in ethanol was treated with hydrazine hydrate and then heated at reflux to afford 2-hydrazinyl-4,6-dimethylpyrimidine. The 2-hydrazinyl-4,6- dimethylpyrimidine and (Z)-3-aminobut-2-enenitrile, in ethanol, were heated to reflux. The resulting l-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)-3 -methyl- lH-pyrazol-5-amine, in 1,4- dioxane, was heated to reflux in the presence of palladium(II) diacetate, cesium carbonate, l-iodo-4-methylbenzene, and Xantophos to afford compound 6. Reagents and aryl halides can be purchased or prepared as described in the literature.
Scheme 2
Compound 6
Scheme 3 illustrates an alternative route to the synthesis of 5-alkylamino
pyrrazoles. The pyrrazole core is prepared as presented in Scheme 1 and 2. Then
reductive amination with the complete pyrrazole core and an appropriate aldehyde, with suitable reducing agent, can afford compounds such as Compound 15.
Compound 15
Scheme 4 is another alternative route to pyrazole heterocycles. The appropriate β-ketoamide is treated with hydrazine.26 The resulting pyrazole is alkylated with the appropriate aromatic chloride to afford the desired product.27
Scheme 4
Compound 22
The invention encompasses pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compounds described herein. Thus, in certain aspects, the invention is directed to pharmaceutically acceptable salts of compounds of Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI),
(Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb). As used herein, a "pharmaceutically acceptable salt" includes an ionic bond-containing product of the reaction between the disclosed compound with either an acid or a base, suitable for administering to a subject. Pharmaceutically acceptable salts are well known in the art and are described, for example, in Berge et al. (1977), Pharmaceutical Salts, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 69(1): 1-19, the contents of which are herein incorporated by reference. A non-limiting example of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt is an acid salt of a compound containing an amine or other basic group which can be obtained by reacting the compound with a suitable organic or inorganic acid. Examples of pharmaceutically acceptable salts also can be metallic salts including, but not limited to, sodium, magnesium, calcium, lithium and aluminum salts. Further examples of pharmaceutically acceptable salts include hydrochlorides, hydrobromides, sulfates, methanesulfonates, nitrates, maleates, acetates, citrates, fumarates, tartrates (e.g. (+)-tartrates, (-)-tartrates or mixtures thereof including racemic mixtures), succinates, benzoates and salts with amino acids such as glutamic acid. Salts can also be formed with suitable organic bases when the compound comprises an acid functional group such as -COOH or -SO3H. Such bases suitable for the formation of a pharmaceutically acceptable base addition salts with compounds of the present invention include organic bases that are nontoxic and strong enough to react with the acid functional group. Such organic bases are well known in the art and include amino acids such as arginine and lysine, mono-, di-, and triethanolamine, choline, mono-, di-, and trialkylamine, such as methylamine, dimethylamine, and trimethylamine, guanidine, N-benzylphenethylamine, N-methylglucosamine, N- methylpiperazine, morpholine, ethylendiamine, tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane and the like.
The invention also includes hydrates of the compounds described herein, including for example solvates of the compounds described herein. In some embodiments, the invention is to solvates of compounds of Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb).
Also included in the present invention are prodrugs of the compounds described herein, for example, prodrugs of compounds of Formulae ((Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (TV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb).
The invention additionally includes clathrates of the compounds described herein. In some embodiments, the invention is directed to clathrates of compounds of Formulae
(Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (Xla- Xlb) and (Xlla-XIIb).
As discussed above, the invention includes pharmaceutical compositions comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or excipient and a compound described herein. The compound of any one of Formula (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) or (Xlla-XIIb), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, clathrate or prodrug of any of thereof, can be administered in pharmaceutical compositions comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or excipient. The excipient can be chosen based on the expected route of administration of the composition in therapeutic applications. The route of administration of the
composition depends on the condition to be treated. For example, intravenous injection may be preferred for treatment of a systemic disorder and oral administration may be preferred to treat a gastrointestinal disorder. The route of administration and the dosage of the composition to be administered can be determined by the skilled artisan without undue experimentation in conjunction with standard dose-response studies. Relevant circumstances to be considered in making those determinations include the condition or conditions to be treated, the choice of composition to be administered, the age, weight, and response of the individual patient, and the severity of the patient's symptoms.
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising compounds of Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (IV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (IXa-IXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla- Xllb), and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, clathrates or prodrugs of any of thereof, can be administered by a variety of routes including, but not limited to, parenteral, oral, pulmonary, ophthalmic, nasal, rectal, vaginal, aural, topical, buccal, transdermal, intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intradermal, intraocular, intracerebral, intralymphatic, intraarticular, intrathecal and intraperitoneal.
The compositions can also include, depending on the formulation desired, pharmaceutically-acceptable, non-toxic carriers or diluents, which are defined as vehicles commonly used to formulate pharmaceutical compositions for animal or human administration. The diluent is selected so as not to affect the biological activity of the pharmacologic agent or composition. Examples of such diluents are distilled water, physiological phosphate-buffered saline, Ringer's solutions, dextrose solution, and Hank's solution. In addition, the pharmaceutical composition or formulation may also include other carriers, adjuvants, or nontoxic, nontherapeutic, nonimmunogenic stabilizers and the like. Pharmaceutical compositions can also include large, slowly metabolized
macromolecules such as proteins, polysaccharides such as chitosan, polylactic acids, polyglycolic acids and copolymers (such as latex functionalized SEPHAROSE™, agarose, cellulose, and the like), polymeric amino acids, amino acid copolymers, and lipid aggregates (such as oil droplets or liposomes).
The compositions can be administered parenterally such as, for example, by intravenous, intramuscular, intrathecal or subcutaneous injection. Parenteral
administration can be accomplished by incorporating a composition into a solution or suspension. Such solutions or suspensions may also include sterile diluents such as water for injection, saline solution, fixed oils, polyethylene glycols, glycerine, propylene glycol or other synthetic solvents. Parenteral formulations may also include antibacterial agents such as, for example, benzyl alcohol or methyl parabens, antioxidants such as, for example, ascorbic acid or sodium bisulfite and chelating agents such as EDTA. Buffers such as acetates, citrates or phosphates and agents for the adjustment of tonicity such as sodium chloride or dextrose may also be added. The parenteral preparation can be enclosed in ampules, disposable syringes or multiple dose vials made of glass or plastic.
Additionally, auxiliary substances, such as wetting or emulsifying agents, surfactants, pH buffering substances and the like can be present in compositions. Other components of pharmaceutical compositions are those of petroleum, animal, vegetable, or synthetic origin, for example, peanut oil, soybean oil, and mineral oil. In general, glycols such as propylene glycol or polyethylene glycol are preferred liquid carriers, particularly for injectable solutions.
Injectable formulations can be prepared either as liquid solutions or suspensions; solid forms suitable for solution in, or suspension in, liquid vehicles prior to injection can also be prepared. The preparation also can also be emulsified or encapsulated in liposomes or micro particles such as polylactide, polyglycolide, or copolymer for enhanced adjuvant effect, as discussed above. Langer, Science 249: 1527, 1990 and Hanes, Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 28: 97-1 19, 1997. The compositions and pharmacologic agents described herein can be administered in the form of a depot injection or implant preparation which can be formulated in such a manner as to permit a sustained or pulsatile release of the active ingredient.
Additional formulations suitable for other modes of administration include oral, intranasal, and pulmonary formulations, suppositories, and transdermal applications. For suppositories, binders and carriers include, for example, polyalkylene glycols or triglycerides; such suppositories can be formed from mixtures containing the active
ingredient in the range of about 0.5% to about 10%, preferably about 1%- to about 2%. Oral formulations include excipients, such as pharmaceutical grades of mannitol, lactose, starch, magnesium stearate, sodium saccharine, cellulose, and magnesium carbonate. Topical application can result in transdermal or intradermal delivery. Transdermal delivery can be achieved using a skin patch or using transferosomes. [Paul et al., Eur. J. Immunol. 25: 3521-24, 1995; Cevc et al, Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1368: 201-15, 1998].
For the purpose of oral therapeutic administration, the pharmaceutical
compositions can be incorporated with excipients and used in the form of tablets, troches, capsules, elixirs, suspensions, syrups, wafers, chewing gums and the like. Tablets, pills, capsules, troches and the like may also contain binders, excipients, disintegrating agent, lubricants, glidants, sweetening agents, and flavoring agents. Some examples of binders include microcrystalline cellulose, gum tragacanth or gelatin. Examples of excipients include starch or lactose. Some examples of disintegrating agents include alginic acid, corn starch and the like. Examples of lubricants include magnesium stearate or potassium stearate. An example of a glidant is colloidal silicon dioxide. Some examples of sweetening agents include sucrose, saccharin and the like. Examples of flavoring agents include peppermint, methyl salicylate, orange flavoring and the like. Materials used in preparing these various compositions should be pharmaceutically pure and non-toxic in the amounts used. In another embodiment, the composition is administered as a tablet or a capsule.
Various other materials may be present as coatings or to modify the physical form of the dosage unit. For instance, tablets may be coated with shellac, sugar or both. A syrup or elixir may contain, in addition to the active ingredient, sucrose as a sweetening agent, methyl and propylparabens as preservatives, a dye and a flavoring such as cherry or orange flavor, and the like. For vaginal administration, a pharmaceutical composition may be presented as pessaries, tampons, creams, gels, pastes, foams or spray.
The pharmaceutical composition can also be administered by nasal administration. As used herein, nasally administering or nasal administration includes administering the composition to the mucus membranes of the nasal passage or nasal cavity of the patient. As used herein, pharmaceutical compositions for nasal administration of a composition include therapeutically effective amounts of the compounds prepared by well-known methods to be administered, for example, as a nasal spray, nasal drop, suspension, gel, ointment, cream or powder. Administration of the composition may also take place using a nasal tampon or nasal sponge.
For topical administration, suitable formulations may include biocompatible oil, wax, gel, powder, polymer, or other liquid or solid carriers. Such formulations may be administered by applying directly to affected tissues, for example, a liquid formulation to treat infection of conjunctival tissue can be administered dropwise to the subject's eye, or a cream formulation can be administered to the skin.
Rectal administration includes administering the pharmaceutical compositions into the rectum or large intestine. This can be accomplished using suppositories or enemas. Suppository formulations can easily be made by methods known in the art. For example, suppository formulations can be prepared by heating glycerin to about 120°C, dissolving the pharmaceutical composition in the glycerin, mixing the heated glycerin after which purified water may be added, and pouring the hot mixture into a suppository mold.
Transdermal administration includes percutaneous absorption of the composition through the skin. Transdermal formulations include patches, ointments, creams, gels, salves and the like.
In addition to the usual meaning of administering the formulations described herein to any part, tissue or organ whose primary function is gas exchange with the external environment, for purposes of the present invention, "pulmonary" will also mean to include a tissue or cavity that is contingent to the respiratory tract, in particular, the sinuses. For pulmonary administration, an aerosol formulation containing the active agent, a manual pump spray, nebulizer or pressurized metered-dose inhaler as well as dry powder formulations are contemplated. Suitable formulations of this type can also include other agents, such as antistatic agents, to maintain the disclosed compounds as effective aerosols.
A drug delivery device for delivering aerosols comprises a suitable aerosol canister with a metering valve containing a pharmaceutical aerosol formulation as described and an actuator housing adapted to hold the canister and allow for drug delivery. The canister in the drug delivery device has a head space representing greater than about 15% of the total volume of the canister. Often, the compound intended for pulmonary administration is dissolved, suspended or emulsified in a mixture of a solvent, surfactant and propellant. The mixture is maintained under pressure in a canister that has been sealed with a metering valve.
"Treating" or "treatment" includes preventing or delaying the onset of the symptoms, complications, or biochemical indicia of a disease, alleviating or ameliorating
the symptoms or arresting or inhibiting further development of the disease, condition, or disorder. A "patient" is a human subject in need of treatment.
An "effective amount" refers to that amount of the therapeutic agent that is sufficient to ameliorate of one or more symptoms of a disorder and/or prevent
advancement of a disorder, cause regression of the disorder and/or to achieve a desired effect.
As used herein, the term "inhibiting" or "decreasing" encompasses causing a net decrease by either direct or indirect means. The term "increasing" means to cause a net gain by either direct or indirect means.
The invention encompasses the treatment of a condition associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis. Proteostasis refers to protein homeostasis. Dysfunction in protein homeostasis is a result of protein misfolding, protein aggregation, defective protein trafficking or protein degradation. Exemplary proteins of which there can be a dysfunction in proteostasis, for example that can exist in a misfolded state, include, but are not limited to, glucocerebrosidase, hexosamine A, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator, aspartylglucsaminidase, a-galactosidase A, cysteine transporter, acid ceremidase, acid a-L-fucosidase, protective protein, cathepsin A, acid β-glucosidase, acid β-galactosidase, iduronate 2-sulfatase, a-L-iduronidase, galactocerebrosidase, acid a -mannosidase, acid β -mannosidase, arylsulfatase B, arylsulfatase A, N- acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase, acid β -galactosidase, N-acetylglucosamine-1- phosphotransferase, acid sphingmyelinase, NPC-1, acid a-glucosidase, β-hexosamine B, heparin N-sulfatase, a -N-acetylglucosaminidase, a -glucosaminide N-acetyltransferase, N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase, a -N-acetylgalactosaminidase, a -neuramidase, β -glucuronidase, β-hexosamine A and acid lipase, polyglutamine, a -synuclein, Αβ peptide, tau protein transthyretin and insulin.
In certain embodiments, the protein is selected from the group consisting of huntingtin, tau, alpha-synuclein, a 1 anti-trypsin, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and superoxide dismutase.
Protein conformational diseases encompass gain of function disorders and loss of function disorders. In one embodiment, the protein conformational disease is a gain of function disorder. The terms "gain of function disorder," "gain of function disease," "gain of toxic function disorder" and "gain of toxic function disease" are used interchangeably herein. A gain of function disorder is a disease characterized by increased aggregation-
associated proteotoxicity. In these diseases, aggregation exceeds clearance inside and/or outside of the cell. Gain of function diseases include, but are not limited to
neurodegenerative diseases associated with aggregation of polyglutamine, Lewy body diseases, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, transthyretin-associated aggregation diseases, Alzheimer's disease and prion diseases. Neurodegenerative diseases associated with aggregation of polyglutamine include, but are not limited to, Huntington's disease, dentatorubral and pallidoluysian atrophy, several forms of spino-cerebellar ataxia, and spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Alzheimer's disease is characterized by the formation of two types of aggregates: extracellular aggregates of Αβ peptide and intracellular aggregates of the microtubule associated protein tau. Transthyretin-associated aggregation diseases include, for example, senile systemic amyloidoses and familial amyloidotic neuropathy. Lewy body diseases are characterized by an aggregation of a-synuclein protein and include, for example, Parkinson's disease. Prion diseases (also known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathies or TSEs) are characterized by aggregation of prion proteins. Exemplary human prion diseases are Creutzfeldt- Jakob Disease (CJD), Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker Syndrome, Fatal Familial Insomnia and Kuru.
In a further embodiment, the protein conformation disease is a loss of function disorder. The terms "loss of function disease" and "loss of function disorder" are used interchangeably herein. Loss of function diseases are a group of diseases characterized by inefficient folding of a protein resulting in excessive degradation of the protein. Loss of function diseases include, for example, cystic fibrosis and lysosomal storage diseases. In cystic fibrosis, the mutated or defective enzyme is the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). One of the most common mutations of this protein is AF508 which is a deletion (Δ) of three nucleotides resulting in a loss of the amino acid phenylalanine (F) at the 508th (508) position on the protein. Lysosomal storage diseases are a group of diseases characterized by a specific lysosomal enzyme deficiency which may occur in a variety of tissues, resulting in the build-up of molecules normally degraded by the deficient enzyme. The lysosomal enzyme deficiency can be in a lysosomal hydrolase or a protein involved in the lysosomal trafficking. Lysosomal storage diseases include, but are not limited to, aspartylglucosaminuria, Fabry's disease, Batten disease, Cystinosis, Farber, Fucosidosis, Galactasidosialidosis, Gaucher' s disease (including Types 1, 2 and 3), Gml gangliosidosis, Hunter's disease, Hurler-Scheie's disease, Krabbe's
disease, a-Mannosidosis, B-Mannosidosis, Maroteaux-Lamy's disease, Metachromatic Leukodystrophy, Morquio A syndrome, Morquio B syndrome, Mucolipidosis II,
Mucolipidosis III, Neimann-Pick Disease (including Types A, B and C), Pompe's disease, Sandhoff disease, Sanfilippo syndrome (including Types A, B, C and D), Schindler disease, Schindler-Kanzaki disease, Sialidosis, Sly syndrome, Tay-Sach's disease and Wolman disease.
In another embodiment, the disease associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis and/or in the heat shock response is a cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular diseases include, but are not limited to coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, stroke, restenosis and arteriosclerosis. Conditions associated with a dysfunction of proteostasis also include ischemic conditions, such as, ischemia/reperfusion injury, myocardial ischemia, stable angina, unstable angina, stroke, ischemic heart disease and cerebral ischemia.
In yet another embodiment, the disease associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis is diabetes or diabetic retinopathy.
In some embodiments, the condition is selected from the group consisting of cystic fibrosis, Huntington's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, diabetic retinopathy, diabetes, and other retinal disorders. In one embodiment, the condition is cystic fibrosis.
In an additional embodiment, the invention is directed to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of any one of Formulae (Ia-Ib), (Ila-IId), (Illa-IIIb), (TV), (V), (VI), (Vlla-VIIc), (VIII), (LXa-LXb), (Xa-Xb), (XIa-XIb) and (Xlla-XIIb), and a second agent, wherein the second agent is selected from the group consisting of a pharmacologic chaperone and a proteostasis regulator. The invention also encompasses a method of treating a patient suffering from a condition associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the invention and a second agent, wherein the second agent is a pharmacologic chaperone. Pharmacologic chaperones or kinetic stabilizers refer to compounds that bind an existing steady state level of the folded mutant protein and chemically enhance the folding equilibrium by stabilizing the fold [Bouvier, Chem Biol 14: 241-242, 2007; Fan et al, Nat Med 5: 112-115, 1999; Sawkar et al, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99: 15428- 15433 , 2002; Johnson and Kelly, Accounts of Chemical Research 38: 911-921, 2005]. The pharmacologic chaperone is administered in amount that in combination with a compound described herein in an amount that is sufficient to treat a patient suffering from a condition
associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis. Exemplary pharmacologic chaperones are described in U.S. Patent Publication No's. 20080056994, 20080009516, 20070281975, 20050130972, 20050137223, 20050203019, 20060264467 and 20060287358, the contents of which are incorporated by reference herein.
In another embodiment, the invention is a method of treating a patient suffering from a condition associated with a dysfunction in proteostasis comprising administering therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the invention and a second agent, wherein the second agent is a proteostasis regulator. The term "proteostasis regulator" refers to small molecules, siRNA and biologicals (including, for example, proteins) that enhance cellular protein homeostasis. For example, proteostasis regulators can be agents that influence protein synthesis, folding, trafficking and degradation pathways.
Proteostasis regulators encompass pharmacologic agents that stimulate the HSR signaling activity. Proteostasis regulators function by manipulating signaling pathways, including, but not limited to, the heat shock response or the unfolded protein response, or both, resulting in transcription and translation of proteostasis network components. Proteostasis regulators can enhance the folding, trafficking and function of proteins (for example, mutated proteins). Proteostasis regulators can also regulate protein chaperones by upregulating transcription or translation of the protein chaperone, or inhibiting degradation of the protein chaperone. Proteostasis regulators can influence the biology of folding, often by the coordinated increase in chaperone and folding enzyme levels and
macromolecules that bind to partially folded conformational ensembles, thus enabling their progression to intermediates with more native structure and ultimately increasing the concentration of folded mutant protein for export. In one aspect, the proteostasis regulator is distinct from a chaperone in that the proteostasis regulator can enhance the homeostasis of a mutated protein but does not bind the mutated protein. In addition, proteostasis regulators can upregulate an aggregation pathway or a disaggregase activity. Exemplary proteostasis regulators are the celastrols, MG-132 and L-type Ca2+ channel blockers (e.g., dilitiazem and verapamil). The term "celastrols" refers to celastrol and derivatives or analogs thereof, including, but not limited to, those celastrol derivatives described in Westerheide et al, J Biol Chem, 2004. 279(53): p. 56053-60, the contents of which are expressly incorporated by reference herein. Celastrol derivatives include, for example, celastrol methyl ester, dihydrocelastrol diacetate, celastrol butyl ether, dihydrocelastrol, celastrol benzyl ester, primesterol, primesterol diacetate and triacetate of celastrol. In certain aspects, the proteostasis regulator is a heat shock response activator. A heat shock
response activator is an agent that indirectly or directly activates the heat shock response, for example, by directly or indirectly activating heat shock transcription factor 1 (HSF1), inhibiting Hsp90, and/or activating chaperone expression (Westerheide et al, J Biol Chem, 2004. 279(53): p. 56053-60, the contents of which are expressly incorporated by reference herein). The terms "heat shock response activator," "heat shock activator," "heat shock response inducer," and "heat shock inducer" are used interchangeably herein. Non- limiting examples of heat shock response activators are celastrols, non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs, ansamycin, geldenamycin, radiciol, glucuronic acid, and tributylin. Heat shock response activators have also been described, for example, in U.S. Patent Application Publication No's. 20070259820, 20070207992, 20070179087, 20060148767, the contents of each of which are expressly incorporated by reference herein. In some embodiments, the heat shock response activator is a small molecule heat shock response activator.
The invention also encompasses a method of treating cancer or a tumor in a patient in need thereof comprising administering to said patient an effective amount of a compound described herein. Cancers that can be treated according to methods of the present invention include, but are not limited to, breast cancer, colon cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, multiple myeloma, basal cell carcinoma, neuroblastoma, hematologic cancer, rhabdomyosarcoma, liver cancer, skin cancer, leukemia, basal cell carcinoma, bladder cancer, endometrial cancer, glioma, lymphoma, and gastrointestinal cancer. In another embodiment, the invention is a method of treating cancer or a tumor comprising administering an effective amount of a compound described herein in combination with the administration of a chemotherapeutic agent. Chemotherapeutic agents that can be utilized include, but are not limited to, alkylating agents such as cyclosphosphamide (CYTOXAN®); alkyl sulfonates such as busulfan, improsulfan and piposulfan; aziridines such as benzodopa, carboquone, meturedopa, and uredopa; ethylenimines and methylamelamines including altretamine, triethylenemelamine, trietylenephosphoramide, triethylenethiophosphaoramide and trimethylolomelamine; nitrogen mustards such as chlorambucil, chlornaphazine, cholophosphamide, estramustine, ifosfamide, mechlorethamine, mechlorethamine oxide hydrochloride, melphalan, novembichin, phenesterine, prednimustine, trofosfamide, uracil mustard; nitrosureas such as carmustine, chlorozotocin, fotemustine, lomustine, nimustine, ranimustine; antibiotics such as aclacinomysins, actinomycin, authramycin, azaserine, bleomycins, cactinomycin, calicheamicin, carabicin, carminomycin, carzinophilin,
chromomycins, dactinomycin, daunorubicin, detorubicin, 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine, doxorubicin, epirubicin, esorubicin, idarubicin, marcellomycin, mitomycins,
mycophenolic acid, nogalamycin, olivomycins, peplomycin, potfiromycin, puromycin, quelamycin, rodorubicin, streptonigrin, streptozocin, tubercidin, ubenimex, zinostatin, zorubicin; anti-metabolites such as methotrexate and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU); folic acid analogues such as denopterin, methotrexate, pteropterin, trimetrexate; purine analogs such as fludarabine, 6-mercaptopurine, thiamiprine, thioguanine; pyrimidine analogs such as ancitabine, azacitidine, 6-azauridine, carmofur, cytarabine, dideoxyuridine, doxifluridine, enocitabine, floxuridine; androgens such as calusterone, dromostanolone propionate, epitiostanol, mepitiostane, testolactone; anti-adrenals such as aminoglutethimide, mitotane, trilostane; folic acid replenisher such as frolinic acid; aceglatone;
aldophosphamide glycoside; aminolevulinic acid; amsacrine; bestrabucil; bisantrene; edatraxate; defofamine; demecolcine; diaziquone; elfornithine; elliptinium acetate;
etoglucid; gallium nitrate; hydroxyurea; lentinan; lonidamine; mitoguazone; mitoxantrone; mopidamol; nitracrine; pentostatin; phenamet; pirarubicin; podophyllinic acid; 2- ethylhydrazide; procarbazine; PSK®; razoxane; sizofiran; spirogermanium; tenuazonic acid; triaziquone; 2,2',2"-trichlorotriethylamine; urethan; vindesine; dacarbazine;
mannomustine; mitobronitol; mitolactol; pipobroman; gacytosine; arabinoside ("Ara-C"); cyclophosphamide; thiotepa; taxanes, e.g. paclitaxel (TAXOL®, Bristol-Myers Squibb Oncology, Princeton, N.J.) and docetaxel (TAXOTERE®; Aventis Antony, France); chlorambucil; gemcitabine; 6-thioguanine; mercaptopurine; methotrexate; platinum analogs such as cisplatin and carboplatin; vinblastine; platinum; etoposide (VP- 16);
ifosfamide; mitomycin C; mitoxantrone; vincristine; vinorelbine; navelbine; novantrone; teniposide; daunomycin; aminopterin; xeloda; ibandronate; CPT-11 ; topoisomerase inhibitor RFS 2000; difluoromethylornithine (DMFO); retinoic acid; esperamicins;
capecitabine; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, acids or derivatives of any of the above. Also included in this definition are anti-hormonal agents that act to regulate or inhibit hormone action on tumors such as anti-estrogens including for example tamoxifen, raloxifene, aromatase inhibiting 4(5)-imidazoles, 4-hydroxytamoxifen, trioxifene, keoxifene, LY 1 17018, onapristone, and toremifene (Fareston); and anti-androgens such as flutamide, nilutamide, bicalutamide, leuprolide, and goserelin; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, acids or derivatives of any of the above.
In a further embodiment, the invention is a method of treating cancer or a tumor comprising administering to a patient in need thereof an effective amount of a compound described herein in combination with radiation therapy.
The invention is illustrated by the following examples which are not meant to be limiting in any way.
EXEMPLIFICATION
'3-methyl-5-('p-tolylamino -lH-pyrazol-l-yl pyrimidin-4('lH -one
Example 1
To a solution of 6-methyl-2-thiouracil (30 g, 0.210 mole) in dimethylsulfoxide (300 mL) was added anhydrous potassium carbonate (32 g, 0.230 mol) and methyl iodide (14.2 mL, 0.230 mol). The reaction mixture was allowd to stir overnight followed by the addition of of water (740 mL). The precipitate was filtered, washed with water and dried on the air to give 21g of 6-methyl-2-(methylthio)prymidin-4(lH)-one as a white solid, m/z (ESI+)( 163 (MNa+). A mixture of 6-methyl-2-(methylthio)prymidin-4(lH)-one (21 g, 0.130 mol), hydrazine hydrate (63 mL, 1.30 mol), anhydrous potassium carbonate (1.4 g, 0.01 mol) and 2-propanol (150 mL) was heated at reflux for 4 hours and then stirred at 60 °C overnight. The precipitate was filtered, washed with methanol, washed with diethyl ether, and dried in air to give 6 g of 2-hydrazinyl-6-methylpryimidin-4(lH)-one as a white solid, m/z (ESI+)163 (MNa+).
To a mixture of 2-hydrazinyl-6-methylpryimidin-4(lH)-one (2 g, 0.0143 mol), N- acetoacetyl-p-toluidine (2.5g, 0.0130 mol) and Lawesson's reagent (5.8 g, 0.0143 mol) was added dry 1 ,4-dioxane/pyridine (95/5) solution (137 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 15 min., then heated at 55 °C (bath temperature) for 3 hours, and then stirred at room temperature overnight. The yellow solid, which precipitated, was filtered off and the filtrate was concentrated under vacuum (max. 55 °C bath temperature). The oily residue was triturated with diethyl ether/methanol (50/1) solution (50 mL). The yellow solid was precipitated and filtered to give 4 g of the crude product. The crude product was purified by flash chromatography on silica using a mixture of dichloromethane/methanol (100:0 to 100: 1) as the eluant to give a pale yellow solid. Crystallization from methanol (20 ml) gave 1.1 g of 6-methyl-2-(3-methyl-5-(p-
tolylamino)-lH-pyrazol-l-yl)pyrimidin-4(17i)-one as white needles, m/z (ESI )
295(MH+); XH NMR (500MHz,i/6-DMSO), δ 10.38 (bs, 1H), 7.16 (d, J= 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.1 1 (d, J= 8.5 Hz, 2H), 6.16 (bs, 1H), 5.98 (s, 1H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 2.20 (s, 3H).
The HC1 salt can also be prepared. A round bottom flask, equipped with a stir bar, was charged with 6-methyl-2-(3 -methyl-5-(p-tolylamino)- lH-pyrazol- 1 -yl)pyrimidin-
4(lH)-one (340 mg, 1.15 mmol) and dry 1,4-dioxane (10 mL). The flask was placed under a nitrogen atmosphere and the mixture was allowed to stir at room tempearture until all of the solids had dissolved to afford a homogeneous solution. A solution of hydrochloric acid (1 M in diethyl ether) (1.50 ml, 1.50 mmol) was added dropwise via syringe over 2 min to the flask. The mixture was allowed to stir for 15 min and was then condensed in vacuo to afford the salt as a white powder.
Table 2. Further Examples that were prepared according to the general method of Example 1.
Example 6: l-(4.6-Dimethylpyrimidin-2-y^
Example 6
Hydrazine monohydrate (1.02 mL, 21.0 mmol) was added to a solution of 2-chloro 4,6-dimethylpyrimidine (2 g, 14.0 mmol) in ethanol (5 mL). The mixture was allowed to stir at room temperature for 2 h. The precipitate that formed was collected by filtration and washed with methanol. The solid was allowed to dry in a stream of air to afford 1 g of 2- hydrazinyl-4,6-dimethylpyrimidine as a white solid (1 g). Yield: 52%; m/z (ESI+) 139 (MH+).
A mixture of 2-hydrazinyl-4,6-dimethylpyrimidine (500 mg, 3.62 mmol) and 3- aminocrotononitrile (312 mg, 3.80 mmol) in ethanol (10 mL) was heated at reflux for 3 h and was then concentrated in vacuo. The crude product was recrystallized from methanol to afford 800 mg of l-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)-3-methyl-lH-pyrazol-5-amine as a pale brown solid. Yield: 90%; m/z (ESI+) 226 (MNa+), 204 (MH+).
A mixture of cesium carbonate (1.45 g, 4.44 mmol), l-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2- yl)-3 -methyl- lH-pyrazol-5 -amine (350 mg, 1.48 mmol), and 4-iodotoluene (452 mg, 2.07 mmol) in 1,4-dioxane (10 mL) was heated at reflux, under argon athmosphere, for 15 min. Xantophos (342 mg, 0.592 mmol), followed by palladium(II) diacetate (83 mg, 0.370 mmol), was added to the reaction mixture at 100 °C. The reaction mixture was maintained at reflux, under argon atmosphere, for 12 h. The reaction mixture was concentrated in vacuo and the remaining residue was purified by column chromatography on silica using a mixture of dichloromethane/methanol as the eluant. The product obtained this way was further purified by preparative HPLC and then crystallization from a mixture of methanol and hexanes to afford 61 mg of l-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)-3-methyl-N-(p-tolyl)-lH- pyrazol-5 -amine as a pale yellow solid. Yield: 14%; m/z (ESI+) 294 (MH+); XH NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ 10.39 (bs, 1H), 7.19 (d, J= 8 Hz, 2H), 7.13 (d, J= 8 Hz, 2H), 6.93 (s, 1H), 5.84 (s, 1H), 2.56 (s, 6H), 2.39 (s, 3H), 2.37 (s, 3H). Table 3. Additional Example prepared according to the general method of Example 6.
Example 8: N-(3 -Methyl- l-(6-methyl-4-oxo- 1 ,4-dihydropyrimidin-2-yl)- !H-pyrazol-5- vDisobutyramide
Neat 3-aminobut-2-enenitrile (0.81 g, 7.4 mmol) was added in a ortionwise manner to a suspension of 2-hydrazinyl-6-methylpyrimidin-4(lH)-one (from example 1, 1 g, 7.1 mmol) in ethanol (10 mL) at room temperature. The reaction mixture was heated at reflux for 4 h and was then concentrated in vacuo. The crude product was purified by column chromatography using a mixture of dichloromethane/methanol as the eluant to afford 0.6 g of 2-(5-amino-3 -methyl- lH-pyrazol-l-yl)-6-methylpyrimidin-4(lH)-one as a white solid. Yield: 35%; m/z (ESI+) 206 (MH+).
A mixture of 2-(5-amino-3-methyl- lH-pyrazol- 1 -yl)-6-methylpyrimidin-4( lH)-one (0.15 g, 0.730 mmol) and pyridine (0.07 mL, 0.876 mmol) in dichloromethane (8 mL) was treated with a solution of isobutyryl chloride (0.091 mL, 0.876 mmol) in dichloromethane (2 mL). The reaction mixture was allowed to stir a room temperature for 24 h before it was diluted with dichloromethane (20 mL). The mixture was washed with 2M hydrochloric acid, a 5% aqueous solution of sodium bicarbonate, and brine. The organic phase was dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered, and condensed in vacuo to afford a solid. The solid was purified by column chromatography on silica using a dichloromethane/methanol gradient (0-10%) and then by preparative HPLC to afford 50 mg of N-(3 -Methyl- 1 -(6- methyl-4-oxo-l,4-dihydropyrimidin-2-yl)-lH-pyrazol-5-yl)isobutyramide as a pale yellow solid. Yield: 25%, m/z (ESI+) 298 (MNa+), 276 (MH+), XH NMR (500 MHz, d6-DMSQ) δ 1 1.80 (s, 1H), 6.62 (s, 1H), 6.24 (s, 1H), 2.64 (sept, J= 6.5 Hz, 1H), 2.34 (s, 3H), 2.21 (s, 3H), 1.19 (d, J= 6.5 Hz, 6H).
Example 14: 2-(5-(Isopropylamino)-3 -methyl- lH-pyrazol-l-yl)-6-methylpyrimidin-4(lH)- one
Example 14
A mixture of 2-(5-amino-3-methyl- lH-pyrazol- 1 -yl)-6-methylpyrimidin-4( lH)-one (from example 8, 400 mg, 1.95 mmol), acetone (272 μί, 3.70 mmol), acetic acid (670 μί, 1 1.7 mmol) and sodium triacetoxyborohydride (1.16 g, 5.46 mmol) in dichloroethane was allowed to stir at room temperature for 2 d. The reaction was quenched through the addition of an aqueous, saturated solution of sodium bicarbonate. The mixture was extracted with dichloromethane and the combined organic extracts were dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered, and condensed in vacuo. The crude product was purified by
column chromatography on silica using a mixture of dichloromethane/methanol as the eluant. The product obtained from this purification was further purified in another round of column chromatography on silica using a mixture of ethyl acetate/hexanes as the eluant to afford 130 mg of 2-(5-(isopropylamino)-3-methyl-lH-pyrazol-l-yl)-6-methylpyrimidin- 4(lH)-one as a white solid. Yield: 27%; m/z (ESI+) 270 (MNa+), 248 (MH+); ¾ NMR (200 MHz, d6-OMSO) δ 11.51 (bs, 1H), 7.62 (bs, 1H), 5.98 (bs, 1H), 5.33 (s, 1H), 3.42 (sept, J= 6.6 Hz, 1H), 2.20 (s, 3H), 2.11 (s, 3H), 1.19 (d, J= 6.6 Hz, 6H).
Table 4. Additional Example that was prepared according to the general method of Example 14.
A mixture of 3-oxo-N-(p-tolyl)butanamide (5 g, 26.1 mmol), hydrazine hydrochloride (3 g, 28.7 mmol), and Lawesson's reagent (1 1.6 g, 28.7 mmol) in a mixture of 1,4-dioxane/pyridine (190 mL/10 mL) was heated at 50 °C for 4 h. The reaction mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature and the solvent was decanted. The remaining solid residue was triturated with ethyl acetate and filtered. The filtrate and solvent from the reaction mixture were combined and condensed in vacuo. The crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica using a mixture of
dichloromethane/methanol as the eluant to afford 1 g of 3-methyl-N-(p-tolyl)-lH-pyrazol- 5-amine as a gray solid. Yield: 22%; m/z (ESI+) 188 (MNa+).
A mixture of 3-methyl-N-(p-tolyl)-lH-pyrazol-5-amine (300 mg, 1.60 mg), 2- fluoropyridine (128 μί, 1.76 mmol), and cesium carbonate (1.04 g, 3.2 mmol) in NN- dimethylformamide (5 mL) was heated at 120°C for 96 h. The reaction mixture was
allowed to cool to room temperature and the resulting suspension was filtered. The filtrate was evaporated under reduced pressure, dissolved in dichloromethane and washed with water. The organic phase was dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered, and condensed in vacuo. The crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica using a mixture of hexanes/ethyl acetate as the eluant to afford 20 mg of 3 -methyl- l-(pyridin-2 - yl)-N-(/ tolyl)-lH-pyrazol-5 -amine as a yellow solid. Yield: 5%; m/z (ESI+) 265 (MH+); XH NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ 10.42 (bs, 1H), 8.34 (d, J= 5 Hz, 1H), 8.00 (d, J= 9 Hz, 1H), 7.79 (t, J= 9 Hz, 1H), 7.13-7.07 (m, 5H), 5.83 (s, 1H), 2.32 (s, 3H), 2.29 (s, 3H).
Table 5. Further Examples that were prepared according to the general method of Example 17.
Example 33 : CFTR Folding and Trafficking Assay
CFTR transport assays. AF508 expressing CFBE41°" lung cells were cultured in the presence of compound 1 in 12 well Sarstedt dishes, harvested, lysed and the processing of CFTR from the band B to the band C glycoform detected by SDS-PAGE and
immunoblotting using either monoclonal 3G11 or M3A7.
Quantitation of CFTR glycoforms. Immunoblot exposures were selected to allow visualization of CFTR recovery under identical protein loads in same SDS-PAGE for all treatments. Given the dynamic range, quantitation of the band B and C glycoforms was made by analysis of band intensities that were in the linear range. The x-ray films were exposed for increasing time and the different exposures were quantified using a
FluroChemSP (Alpha Inotech) densitometer/software package. Where band B and C were
quantified from different exposures, an internal reference was used to normalize the signal intensity. This method has been described in detail in Hutt et al. (2010),28 Reduced histone deacetylase 7 activity restores function to misfolded CFTR in cystic fibrosis, Nature Chemical Biology, 6(1), 25-33, the contents of which are expressly incorporated by reference herein.
Immunoblot Analysis.
CFBE41°" lung cells were cultured in the presence and absence of compound 1 as described by Hutt et al. (2010).28 Immunoblot analysis shown in the Figure indicates enhanced levels of band B and C.
Compound 1
Example 34: CFTR Functional Assays
CFTR Iodide Flux Assay:
Ninety six well microplates containing CFBE41°" cells stably expressing AF508-
CFTR and halide-sensitive YFP were incubated at 27°C for 20 to 24 h. After incubation, cells were washed with PBS (containing 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KC1, 8.1 mM Na2HP04, 1.5 mMKH2P04, lmMCaCl2, 0.5mMMgCl2) and stimulated for 20 min with forskolin and test compounds. Microplates were read using a plate reader equipped with excitation (HQ500/20X: 500 nm) and emission (HQ535/30M: 535 nm) filters for yellow fluorescent protein. Each assay consisted of a continuous 30-s fluorescence reading (5 points per second) with 3 s before and 27 s after injection of 165 ul of an iodide-containing solution (PBS with CI" replaced by T). Final iodide concentration in the wells was 100 mM. These data were normalized to the initial background subtracted fluorescence.
Biological Activity of Select Compounds:
Iodide Flux Assay
Table 6 shows percent quenching of yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) by select compounds described in the invention. Quenching values for the selected compounds were obtained at 10 μΜ. Quenching of YFP signal is an indirect measure of CFTR function.
Table 6: Activities for select compounds of the invention for the CFBE-YFP Quenching Assay
Multigene Assay: Monitoring of HSF-1 Activity via HSPA5 Transcript Levels in IMR 32 Human Neuroblastoma Cells
This assay uses the QuantiGene Plex 2.0 Reagent System from Affymetrix. This assay combines the use of bDNA (branch DNA) and xMAP magnetic capture beads from Luminex Technologies to quantitatively and simultaneously detect multiple mRNA transcripts per well.
Procedure:
Warm up the Lysis mixture for 30 minutes at 37 °C prior to making the lysis buffer. Proteinase K should be used cold. Use lOul of Proteinase K per 1ml of Lysis mixture to make the lysis buffer. Add 50% v/v of the lysis mixture per well. Mix well to ensure proper lysing. Seal the plates with adhesive aluminum plate seals and incubate at 50°C for 30 minutes. Mix well again 10 times. Store plates at -80°C until assay is performed.
The overall procedure was performed according to the QuantiGene Plex 2.0
Reagent System instruction manual from Affymetrix.
Day 1 Procedure (for multiplex, 8-plates assay):
Prepare a master mix pool without beads. Distribute the master mix equally in 8 tubes and then add the respective bead mix to each tube. Vortex and add 20ul/well of the master mix to the 96-well plate. After transfer, add 80ul/well of the lysates to respective plates. The amount of cell lysate to be used in the assay should be determined either by performing an assay linearity test or by determining the sample input empirically for each cell line. In order to avoid signal saturation, sample input should be less than 400 cells/ul. Dilute cell lysates with DLM.
Keep three wells in each plate as assay background (no cell lysates in these wells, only diluted lysis mixture as described previously and on the next page).
1. Prepare the Hybridization Master Mix for for the 1st day hybridization
Total reaction per 96 well is 100 ul
Amount per 1 well, Lysis Mixture 6.7 ul; Proteinase K 0.2 u; Blocking Reagent 2.0 ul; Probe mix 5.0 ul; Bead mix 1.0 ul; Water 5.1 ul; TOTAL 20 ul (80 ul of lysate + 20 ul of master mix = 100 ul).
Master Mix for 8 Plex Sets
Amount per 1 well for 8 Plex Set (10 rxn)
Lysis Mixture 67 ul
Proteinase K 2 ul
Blocking Reagent 20 ul
Probe mix 50 ul
Bead mix O ul
Water 51 ul
TOTAL
19 ul 19 ul 19 ul
+1 ul (Plex 1) +1 ul (Plex 2)... +1 ul (Plex 8)
20 ul of master mix
+80 ul of sample
Dilute Lysis Mixture (DLM): 2: 1 ratio (2 parts water, one part lysis mixture).
For example: to make 3 ml of DLM, dilute 1 mL of lysis mixture into 2 mL of water.
Total RNA Sample Prep: 80 ul of DLM (33% lysis mixture) + 1 ul of RNA (250 ng/ul).
Cell lysate Sample Prep: Maximum cell lysate input is 80 ul per well.
Shake plates for 16-22 hours at 54°C ± 1°C and appropriate rpm. (I use 300rpm for
ThermoMax plate shakers).
Standard Operating Procedure FOR DAY 2 OF MGE ASSAY
(SIGNAL AMPLIFICATION AND TARGET RNA DETECTION)
General procedure:
1. Warm up the Amplifier Diluent, Label Probe Diluent, and SAPE Diluent at 37°C for 20 minutes to dissolve any precipitates. Mix Amplifier diluent well by inversion before use. Bring all diluents to room temperature before use.
For washing plates using the BioTek ELx-405 Magnetic plate washer, prepare Wash Buffer 2.0:
(Use 200 ml for priming the washer and 200 ml for the series of wash steps = 400ml total)
Wash Buffer (400ml'):
380ml water (can use Deionized water)
+ 1.2ml Wash Buffer Component 1
+ 20ml Wash Buffer Component 2
Be sure to mix each wash buffer component in the water before adding the next wash buffer component, otherwise they may precipitate and may take a long time to go back into solution. For other quantities, scale the ingredients accordingly. Do not store the
Wash Buffer. Make fresh for every use.
2. Transfer the overnight hybridization mixture to the Magnetic Separation Plate. a. Remove the overnight hybridization plate from the shaking incubation and centrifuge at 240 x g for one minute.
b. Pipet up and down 5 times using the Biomek FX robot and completely transfer the mixture to the magnetic separation plate (at this step, the plate should be kept on the magnet).
c. For multiplex plates, program the Biomek FX to mix and transfer each plate mixture to the magnetic separation plate on a magnet with 80 second incubation intervals between transfers.
3. Shake plate on room temperature plate shaker for two minutes and then wash the unbound sample away using the magnetic plate washer.
For Multiplex:
Prepare Working Solution for one 96 well PlexPlex format:
Warm up Amplifier diluents, Label Probe diluents and Sape diluents at 37°C for 30 mins. Preamplifier Solution: Add 7.5 ul of preamplifier to every 1ml of Amplifier Diluent. Amplifier Solution: Add 7.5 ul of Amplifier to every 1ml of Amplifier Diluent.
Label Probe Solution: Add 7.5 ul of Label Probe to every 1ml of Label Probe Diluent. SAPE Solution: Add 3.0 ul of SAPE to every 1ml of SAPE Diluent.
Procedure:
1. PreAmplifier Hyb Step: Soak compression plate for 2 min on Magnetic Separation device. Compression plate should make contact with the magnetic device at all time. Wash plate 4 times with 100 ul QGP 2.0 wash buffer, 60 second soak in between each wash required. Remove wash buffer from the final wash. Add 60 ul of Preamp solution per well. Incubate at 50°C for 1 hr with 300 RPM shaking (ThermoMaxQ plate shaker).
2. Amplifier Hyb Step: Soak compression plate for 2 min on Magnetic Separation Device. Compression plate should make contact with the magnetic device at all time. Wash plate 4 times with 100 ul QGP 2.0 wash buffer, 60 second soak in between each wash required. Remove wash buffer from the final wash. Add 60 ul of Amp solution per well. Incubate at 50°C for 1 hr with 300 RPM shaking (ThermoMaxQ plate shaker).
3. Label Probe Hyb Step: Soak compression plate for 2 min on Magnetic Separation Device. Compression plate should make contact with the magnetic device at all time. Wash plate 4 times with 100 ul QGP 2.0 wash buffer, 60 second soak in between each wash required. Remove wash buffer from the final wash. Add 60 ul of Label Probe solution per well. Incubate at 50°C for 1 hr with 300 RPM shaking (ThermoMaxQ plate shaker).
4. SAPE Hyb Step: Soak compression plate for 2 min on Magnetic Separation Device. Compression plate should make contact with the magnetic device at all time. Wash plate 4 times with 100 ul QGP 2.0 wash buffer, 60 second soak in between each wash required. Remove wash buffer from the final wash. Add 60 ul of SAPE solution per well. Incubate at room temperature for 30 min with 600 RPM shaking. The plate needs to be protected from light by wrapping in foil or by dimming the light.
5. Soak plate for 2 min on Magnetic Separation Device. Compression plate should make contact with the magnetic device at all time. Wash plate 4 times with 100 ul QGP 2.0 SAPE wash buffer, 60 second soak in between each wash required. Add 130 ul of SAPE wash buffer per well after the final wash. Shake plate at 400-500rpm for 2-3 minutes at room temperature. Plate is ready to read.
6. Use QGP2.0 96 well Luminex setting (Pick up 100 ul of sample, 100 beads/region and 45 second time out). I usually use "no timeout" as an optimal setting because some bead regions reach the 100 bead count slower than the other bead regions. With a no
timeout setting, one can be assured that every region will reach a minimum of 100 beads. The Luminex machine will move to the next sample if, a) All regions have reached 100+ beads, OR, b) Sample has run out.
Control genes used to monitor general transcriptional effects include Tubl (alpha- tubulin) and TBP (TATA binding protein).
Exemplary compounds with activity in the multigene assay described are described in the Table 7 below.
Table 7: Activities for select compounds described in the invention for their ability to induce induction of the HSPA5 gene in IMR32 cells
References:
1. Riordan, J.R. CFTR function and prospects for therapy. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008,
77, 701-26.
2. Qu, B.H., Strickland, E.H. and Thomas, P.J. Localization and suppression of a kinetic defect in cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator folding. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 15739-44.
3. Boucher, R.C. Evidence for airway surface dehydration as the initiating event in CF airway disease. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 261, 5-16.
4. Balch, W.E., Morimoto, R.I., Dillin, A. and Kelly, J.W. Adapting proteostasis for disease intervention. Science. 2008, 319, 916-9.
5. Powers, E.T., Morimoto, R.I., Dillin, A., Kelly, J.W. and Balch, W.E. Biological and chemical approaches to diseases of proteostasis deficiency. Annu. Rev. Biochem.2009,
78, 959-91.
6. Hutt, D.M., Powers, E.T. and Balch, W.E. The proteostasis boundary in misfolding diseases of membrane traffic. FEB S Lett. 2009, 583, 2639-46.
7. Gregersen, N. Protein misfolding disorders: pathogenesis and intervention. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2006, 29, 456-70.
8. Wang, X. et al. Hsp90 cochaperone Ahal down regulation rescues misfolding of CFTR in cystic fibrosis. Cell 127, 803-15 (2006).
9. Bruscia, E. et al. Isolation of CF cell lines corrected at DeltaF508-CFTR locus by SFHR-mediated targeting. Gene Ther 9, 683-5 (2002).
10. Bebok, Z. et al. Failure of cAMP agonists to activate rescued deltaF508 CFTR in CFBE410- airway epithelial monolayers. J Physiol 569, 601-15 (2005); Darren M Hutt, David Herman, Ana PC Rodrigues, Sabrina Noel, Joseph M Pilewski, Jeanne Matteson, Ben Hoch, Wendy Kellner, Jeffery W Kelly, Andre Schmidt, Philip J Thomas, Yoshihiro Matsumura, William RSkach, Martina Gentzsch, John RRiordan, Eric J Sorscher, Tsukasa Okiyoneda, John RYates III, Gergely L Lukacs, Raymond A Frizzell, Gerard Manning, Joel M Gottesfeld & William E Balch, Reduced histone deacetylase 7 activity restores function to misfolded CFTRin cystic fibrosis Nature Chemical Biology 6(1), 25-33, (2010).
1 1. Lei, D.C. et al. Episomal expression of wild-type CFTR corrects cAMP-dependent chloride transport in respiratory epithelial cells. Gene Ther 3, 427-36 (1996).
12. Devor, D.C, Bridges, R.J. & Pilewski, J.M. Pharmacological modulation of ion transport across wild-type and DeltaF508 CFTR-expressing human bronchial epithelia.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 279, C461-79 (2000).
13. Butterworth, M.B., Edinger, R.S., Johnson, J.P. & Frizzell, R.A. Acute ENaC stimulation by cAMP in a kidney cell line is mediated by exocytic insertion from a recycling channel pool. J Gen Physiol 125, 81-101 (2005).
14. Myerburg, M.M. et al. Airway surface liquid volume regulates ENaC by altering the serine protease-protease inhibitor balance: a mechanism for sodium hyperabsorption in cystic fibrosis. J Biol Chem 281, 27942-9 (2006).
15. Myerburg, M.M. et al. Prostasin expression is regulated by airway surface liquid volume and is increased in cystic fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294, L932- 41 (2008).
16. Gentzsch, M. et al. Endocytic trafficking routes of wild type and DeltaF508 cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. Mol Biol Cell 15, 2684-96 (2004).
17. Fulcher, M.L., Gabriel, S., Burns, K.A., Yankaskas, J.R. & Randell, S.H. Well differentiated human airway epithelial cell cultures. Methods Mol Med 107, 183- 206 (2005).
18. Coyne, C.B., Kelly, M.M., Boucher, R.C. & Johnson, L.G. Enhanced epithelial gene transfer by modulation of tight junctions with sodium caprate. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 23, 602-9 (2000).
19. David D. Davey, Marc Adler, Damian Arnaiz, Keith Eagen, Shawn Erickson, William Guilford, Margaret Kenrick, Michael M. Morrissey, Mike Ohlmeyer, Gonghua Pan, Vidyadhar M. Paradkar, John Parkinson, Mark Polokoff, Kurt Saionz, Cecile Santos, Babu Subramanyam, Ron Vergona, Robert G. Wei, Marc Whitlow, Bin Ye, Zuchun (Spring) Zhao, James J. Devlin, and Gary Phillips, Design, Synthesis, and Activity of 2- Imidazol-l-ylpyrimidine Derived Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Dimerization Inhibitors J. Med. Chem. 50, 1 146-1 157, (2007).
20. A. V. et al, Synthesis of 2-(Pyrazol-l-yl)pyrimidine Derivatives by
Cyclocondensation of Ethyl Acetoacetate (6-Methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2- yl)hydrazone with Aromatic Aldehydes Erkin, Russian Journal of General Chemistry (Translation ofZhurnal Obshchei Khimii), 74(3), 423-427; (2004).
21. Zoltan Kaleta, Gabor Tarkanyi, AAgnes Gomory, Ferenc Kalman, Tama's Nagy, and Tibor Soos, Synthesis and Application of a Fluorous Lawesson's Reagent: Convenient Chromatography-Free Product Purification, Organic Letters 8, 6, 1093-1095, (2006); One-pot synthesis of 5-(substituted-amino)pyrazoles Dharmpal S. Dodd, and Rogelio L. Martinez, Tetrahedron Letters 45, 4265^1267 (2004).
22. Arup Maiti, P. V. Narasimha Reddy, Megan Sturdy, Laura Marler, Scott D. Pegan, Andrew D. Mesecar, John M. Pezzuto, and Mark Cushman, Synthesis of Casimiroin and Optimization of Its Quinone Reductase 2 and Aromatase Inhibitory Activities J. Med. Chem. 52, 1873-1884, (2009).
23. A. M. Hussein, A. A. Harb, and I. A. Mousa Oxoanilides in Heterocyclic
Synthesis: An Expeditious Synthesis of New Polyfunctionally Substituted Pyridine and Pyrazole Derivatives J. Heterocyclic Chem., 45, 1819 (2008).
24. Khimiya Geterotsiklicheskikh Soedinenii, (7), 963-7; 1981; WO 2007027842; WO 2009031687; WO 2009099193 (Japanese).
25. James Schulte II, Scott R. Tweedie Palladium-Catalyzed Couplings of Heteroaryl Amines with Aryl Halides Using Sodium Phenolate as the Stoichiometric Base Synlett 2331, (2007); WO 2008042639; WO 2010020363.
26. Marion C. Lanier, Manisha Moorjani, Zhiyong Luo, Yongsheng Chen, Emily Lin, John E. Tellew, Xiaohu Zhang, John P. Williams, Raymond S. Gross, Sandra M. Lechner,
Stacy Markison, Tanya Joswig, William Kargo, Jaime Piercey, Mark Santos, Siobhan Malany, Marilyn Zhao, Robert Petroski, Man 'a I. Crespo, Jose '-Luis Di'az, John Saunders, Jenny Wen, Zhihong O'Brien, Kay von Jalali, Ajay Madan, and Deborah H. Slee, J Med Chem 52, 709 (2009); Thomas M. Stevenson, Thomas P. Selby, Gerard M.
Koether, Joseph E. Drumm, Xian J. Meng, M. P. Moon, Reed A. Coats, Tho V. Thieu, Albert E. Casalnuovo, and Rafael Shapiro 2-Azolyl-4-Benzylpyrimidine Herbicides: Novel Inhibitors of Carotenoid Biosynthesis Part II Chem of Agrochem 85 (2001).
27. David Font,a Anthony Linden, Montserrat Herasa, and Jose' M. Villalgordoa, A simple approach for the regioselective synthesis of imidazo[l,2-a]pyrimidiones and pyrimido[l,2-a]pyrimidinones Tetrahedron 62(7), 1433-144 (2006); Herman Gershon, Anthony Grefic, and Donald D. Clarke, Pyrimidines. 8. Chlorination of 6-methyluracil with Phosphorus Oxychloride in the Presence of Trialky amines, Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry 24(1), 205-9 (1987); Herman Gershon and Anthony Grefig, Primidines. 7. A study of the Chlorination of Pyrimidines with Phosphorus Oxychloride in the Presence of Ν,Ν-Dimethylaniline Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry 21(4), 1161-7 (1984).
28. Hutt, D.M., Herman. D., Rodrigues, A.P.C., Noel, S., Pilewski, J.M., Matteson, J., Hoch, B., Kellner, W., Kelly, J.W., Schmidt, A., Thomas, P.J., Matsumura, Y., Skach, W.R., Gentzsch, M., Riordan, J.R., Sorscher, E.J., Okiyoneda, T., Yates, J.R. Ill, Lukacs, G.L., Frizzell, R.A., Manning, G., Gottesfeld, and J.M., Balch, W.E. Reduced histone deacetylase 7 activity restores function to misfolded CFTR in cystic fibrosis. Nature: Chemical Biology . 2010, 6(1), 25-33.
While this invention has been particularly shown and described with references to preferred embodiments thereof, it will be understood by those skilled in the art that various changes in form and details may be made therein without departing from the scope of the invention encompassed by the appended claims.
Claims
What is claimed is:
1. A compound having the Formula (la):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
G is a 3- to 7-membered optionally substituted heterocyclic or an optionally substituted heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
Ai is N(Ra)2;
each Ri is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb; or the two Ra groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl; each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are
attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2. 2. The compound of claim 1, wherein Ai is:
each R3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb; alternatively, two geminal R3 groups can be taken together with the atom to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl; or yet alternatively, two vicinal R3 groups can be taken together with the atoms to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl; and each R4 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb; or alternatively, the two R4 groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl.
The compound of any one of claims 1 to 2, wherein G is selected from the group consisting of aziridinyl, azetidinyl, azolidinyl, oxolanyl, thiophenyl, furanyl, pyrrolyl,
pyrazolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, isoxazolinyl, thiazolyl, isothiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, piperidinyl, pyridyl, pyrimidyl, diazinyl, triazinyl,
tetrahydropyranyl each optionally substituted.
A compound having the Fo
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
Gi is optionally substituted pyridyl or optionally substituted pyrimidyl;
Ai is N(Ra)2;
each Ri is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb; or the two Ra groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl; each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl, or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are
attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
5. The compound of claim 4, wherein Ai is:
each R3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb,
C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb,
OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb; alternatively, two geminal R3 groups can be taken together with the carbon to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl; or yet alternatively, two vicinal R3 groups can be taken together with the atoms to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl; and each R4 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb; or alternatively, the two R4 groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl. 6. The compound of claim 5, wherein Gi is an optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
7. A compound having the Formula (Ila):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
G3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl, or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
Ri is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Di is phenyl substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Ra is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-
Cio alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
8. The compound of claim 7, wherein G3 is a 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or a
heteroaryl, each optionally substituted.
9. The compound of claim 8, wherein G3 is an optionally substituted, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic. 10. The compound of claim 8, wherein G3 is an optionally substituted heteroaryl.
11. The compound of any one of claims 7 to 10, wherein Ri is optionally substituted Ci- C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb.
12. The compound of any one of claims 7 to 10, wherein Ri is optionally substituted Ci- C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl.
13. The compound of any one of claims 7 to 12, wherein Di is phenyl substituted with one or more groups selected from optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, and optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl.
14. The compound of any one of claims 7 to 13, wherein Ra is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, and optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl.
15. The compound of any one of claims 7 to 14, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of aziridinyl, azetidinyl, azolidinyl, oxolanyl, thiophenyl, furanyl, pyrrolyl, pyrazolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, isoxazolinyl, thiazolyl, isothiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, triazolyl, tetrazolyl, piperidinyl, pyridyl, pyrimidyl, diazinyl, triazinyl,
tetrahydropyranyl, each optionally substituted.
16. The compound of claim 15, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted pyridyl and optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
17. The compound of any one of claims 7 and 1 1 to 14, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of:
wherein:
each Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Rd is hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl; and
Re is (Ra), O, or S.
18. The compound of any one of claims 7 and 11 to 14, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of:
19. The compound of claim 7, wherein the compound is selected from the
consisting of:
20. A compound having the Formula (lib):
G3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 7-membered heterocyclic, aryl, or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
Ri is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Ra is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
D2 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted benzyl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, and C(Rs)3;
each R5 is independently selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb; alternatively, two R5 groups can be taken together with the carbon to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
21. The compound of claim 20, wherein G3 is 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted. 22. The compound of claim 21, wherein G3 is an optionally substituted, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic.
23. The compound of claim 21, wherein G3 is optionally substituted heteroaryl. 24. The compound of any one of claims 20 to 23, wherein Ri is independently selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR,, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb,
NRbC(0)(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb,
NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb.
25. The compound of claim 24, wherein Ri is independently selected from the group
consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl. 26. The compound of any one of claims 20 to 25, wherein D2 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted benzyl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl. 27. The compound of any one of claims 20 to 25, wherein D2 is C(Rs)3, wherein each R5 is independently selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl,
optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl.
28. The compound of any one of claims 20 to 27, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted pyridyl and optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
29. The compound of claim 28, wherein G3 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
30. The compound of any one of claims 20 and 24 to 27, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of:
wherein:
each Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Rd is hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl; and
Re is (Ra), O, or S.
31. The compound of any one of claims 20 and 24 to 27, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of:
33. A compound having the Formula (lie):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
G4 is a 6-membered heteroaryl containing one or more ring nitrogen atoms;
D3 is optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl;
each Ri is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted
C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
each Ra is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)„Rb;
each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
34. The compound of claim 33, wherein Ri is independently selected from the group
consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb,
C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb. 35. The compound of claim 34, wherein Ri is independently selected from the group
consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
36. The compound of any one of claims 32 to 35, wherein G4 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted pyridyl, optionally substituted pyrimidyl, optionally substituted diazinyl, and optionally substituted traizinyl.
37. The compound of claim 36, wherein G4 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
38. The compound of any one of claims 32 to 37, wherein D3 is optionally substituted phenyl.
39. The compound of any one of claim 38, wherein D3 is phenyl substituted with one or more optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb,
C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb. 40. The compound of claim 32, wherein the compound is selected from the group
consisting of:
41. A compound having Formula (lid):
D4 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl;
Ri is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Ra is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)„Rb;
each Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- Cio alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
42. The compound of claim 41, wherein Rx is independently selected from the group
consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb,
NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb.
43. The compound of claim 42, wherein Ri is selected from the group consisting of
optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
44. The compound of any one of claims 41 to 43, wherein each Rc is independently
selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C4 alkyl and ORb.
45. The compound of claim 44, wherein each Rc is selected from the group consisting of hydroxyl and O-C1-C4 alkyl.
46. The compound of claim 41, wherein the compound is selected from the group consisting of:
47. A compound having the Formula (Ilia):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
G3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 7-membered heterocyclic, aryl, or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
Ri is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
each R3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb,
OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb; alternatively, the two geminal R3 groups can be taken together with the carbon atom to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3- C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl;
R6 is phenyl substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR,, SRb, NR,R,, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb,
N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
48. The compound of claim 47, wherein Rx is selected from the group consisting of
optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, OR,, SRb, RbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2,
NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb.
49. The compound of claim 48, wherein Ri is selected from the group consisting of
optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally
substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
50. The compound of any one of claims 47 to 49, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted heterocyclic and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
51. The compound of claim 50, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted pyridyl and optionally substituted pyrimidyl. 52. The compound of claim 51, wherein G3 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
53. The compound of claim 47, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of:
wherein:
each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
each Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Rd is hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl; and
Re is (Ra), O, or S.
54. The compound 7, wherein G is selected from the group consisting of:
55. A compound having the Formula (Illb):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
G3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 7-membered heterocyclic, aryl, or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
R2 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, and optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl;
each R3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb,
C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb; alternatively, the two geminal R3 groups are taken together with the carbon to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl;
R6 is phenyl substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb,
N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
56. The compound of claim 55, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of
optionally substituted heterocyclic and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
57. The compound of claim 56, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of
optionally substituted pyridyl and optionally substituted pyrimidyl. 58. The compound of claim 57, wherein G3 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
59. The compound of claim 54, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of:
wherein:
each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted
C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
each Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Rd is hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl; and
Re is (Ra), O, or S.
60. The compound of claim 54, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of:
61. A compound having the Formula (IV):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
G3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 7-membered heterocyclic, an aryl, or a heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
Rs is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
R6 is phenyl substituted with one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb,
N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
62. The compound of claim 61, wherein R8 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, and optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl.
63. The compound of any one of claims 61 to 62, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted heterocyclic and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
64. The compound of any one of claims 61 to 63, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted pyridyl and optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
65. The compound of claim 64, wherein G3 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
66. The compound of any one of claims 61 to 62, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of:
wherein:
each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
each Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
Rd is hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl;
Re is (Ra), O, or S.
67. The compound of any one of claims 61 to 62, wherein G3 is selected from the group consisting of:
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
Gi is an optionally pyridyl or an optionally substituted pyrimidyl;
R9 is selected from the group consisting of substituted methyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
each R3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted
C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb; alternatively, two geminal R3 groups can be taken together with the carbon to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl;
Ra is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
each R7 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
alternatively, the two R7 are taken together with the nitrogen atom to which they are attached to form a 3 - to 7- membered heterocyclic or a heteroaryl;
each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
and
n is 0, 1 or 2. 69. The compound of claim 68, wherein R9 is selected from the group consisting of
optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb,
NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb,
NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb. 70. The compound of claim 69, wherein R9 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
71. The compound of any one of claims 69 to 70, wherein at least one R3 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb,
SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb. 72. The compound of any one of claims 69 to 71, wherein Gi is optionally substituted pyrimidyl.
73. The compound of claim 69, wherein Gi is selected from the group consisting of:
wherein:
each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
each Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb; and
Rd is hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
74. The compound of claim 69, wherein Gi is selected from the group consisting of:
75. The compound of claim 69, wh
76. A compound having the Formula (VI):
(VI);
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
B is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl;
Rio is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-
C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl,
optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
each Ra is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
each Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; wherein the two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
77. The compound of claim 76, wherein Rio is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C4-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb,
NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb.
78. The compound of claim 77, wherein R10 is selected from the group consisting of
optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C4-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2,
NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb.
79. The compound of any one of claims 76 to 78, wherein B is C(R3)2N(Rf)2: wherein each R3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- Cio alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb; alternatively, the two geminal R3 groups can be taken together with the carbon to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8- membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl; and
each Rf is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb.
80. The compound of any one of claims 76 to 79, wherein each Rc is independently
selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C4 alkyl and ORb.
81. The compound of claim 80, wherein each Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of hydroxyl and optionally substituted O-C1-C4 alkyl. 82. The compound of claim 76, wherein the compound is selected from the group
consisting of:
83. A compound having the Formula (Vila), (Vllb) or (VIIc):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof wherein:
G5 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl;
A2 is N(Ra)2;
R11 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-
C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb,
OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted
C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb;
each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- Cio alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl, or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
84. The compound of claim 83, wherein the compound has the Formula (Vila).
85. The compound of claim 83, wherein the compound has the Formula (Vllb).
86. The compound of claim 83, wherein the compound has the Formula (VIIc).
87. The compound of any one of claims 83 to 86, wherein A2 is
wherein p is 0, 1, 2 or 3; and
each R3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb,
C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb; alternatively, two geminal R3 groups can be taken together with the carbon to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl; or yet alternatively, two vicinal R3 groups can be taken together with the atoms to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl.
88. The compound of any one of claims 83 to 87, wherein Rn is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb,
NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb,
NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb.
89. The compound of claim 88, wherein Rn is selected from the group consisting of
optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
90. The compound of any one of claims 83 to 89, wherein A2 is NRaRg, wherein Rg is optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, and
C(0)C(0)Rb.
91. The compound of claim 90, wherein each Rg is optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl.
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
Xi is selected from the group consisting of O and S;
G5 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl;
A2 is N(Ra)2;
R12 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci- C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb,
C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb; or the two Ra groups are taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl; each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
93. The compound of claim 92, wherein Ri2 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, RbRb, C(0)ORb,
N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb. 94. The compound of claim 93, wherein Ri2 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
95. The compound of any one of claims 91 to 93, wherein Xi is O.
96. The compound of any one of claims 91 to 93, wherein Xi is S. 97. The compound of any one of claims 91 to 96, wherein A2 is NRaRg, wherein Rg is optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, and
C(0)C(0)Rb.
98. A compound having the Formula (IXa) or (IXb):
G5 is optionally substituted pyrimidyl;
A2 is N(Ra)2;
each Ri3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
each Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb and S(0)nRb; or the two Ra groups can be taken together with the nitrogen atom which they are attached to form an optionally substituted 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic or optionally substituted heteroaryl; each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl; or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted;
n is 0, 1 or 2; and
p is 0, 1, 2 or 3.
each R3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally
substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb; and (C=NRb)Rb; alternatively, two geminal R3 groups can be taken together with the carbon to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl; or yet alternatively, two vicinal R3 groups can be taken together with the atoms to which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl.
100. The compound of any one of claims 98 to 99, wherein at least one R13 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb.
101. The compound of claim 100, wherein at least one R13 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl.
102. The compound of any one of claims 98 to 101, wherein A2 is NRaRg, wherein Rg is optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, and
C(0)C(0)Rb.
103. A compound represented by the Formula (Xa) or (Xb):
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or solvate thereof, wherein:
G6 is nitrogen or C-H;
D5 is selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted Ci-Cio alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, C(0)ORb, C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, and S(0)nRb;
each Ri is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb, C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb), NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb, OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
both Ri can join with the carbon atoms to which they are attached to form an optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl;
each R3 is independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, halo, ORb, SRb, NRbRb, C(0)ORb, N02, CN, C(0)Rb,
C(0)C(0)Rb, C(0)NRbRb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbC(0)N(Rb)2, NRbS(0)nRb, N(Rb)(COORb),
NRbC(0)C(0)Rb, NRbC(0)Rb, NRbS(0)nNRbRb, NRbS(0)nRb, S(0)nRb, S(0)nNRbRb,
OC(0)ORb, and (C=NRb)Rb;
alternatively, the two R3 be taken together with the carbon atoms to ahich they are attached to form an optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl;
each Rb is independently selected from the group consisting of H, optionally substituted C1-C10 alkyl, optionally substituted C2-C10 alkenyl, optionally substituted C2- Cio alkynyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted C3-C12 cycloalkenyl, optionally substituted heterocyclic, optionally substituted aryl and optionally substituted heteroaryl;or two Rb groups are taken together with the atom which they are attached to form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl, 3- to 8-membered heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl, each optionally substituted; and
n is 0, 1 or 2.
104. The compound of claim 103 represented by Formula (XIa) or (Xlb):
Rg and Rh are each independently hydrogen or Ci-C6-alkyl, or Rg and Rh are taken with the carbon atoms to which they are attached to form an optionally substituted benzo ring; Ri and Rj are each independently selected from hydrogen and Ci-C6-alkyl; and
D5 is Ci-C6-alkyl, Cs-Cs-cycloalkyl, aryl-Ci-C6-alkyl or optionally substituted phenyl.
105. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 1 to 104; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or prodrug of any of thereof.
106. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 1 to 3; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or prodrug of any of thereof.
107. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 4 to 6; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or prodrug of any of thereof. 108. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 7 to 19; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or prodrug of any of thereof.
109. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 20 to 32; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or prodrug of any of thereof.
1 10. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 33 to 40; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or prodrug of any of thereof.
1 11. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 41 to 46; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or prodrug of any of thereof.
1 12. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 47 to 54; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or prodrug of any of thereof. 1 13. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 55 to 60; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or prodrug of any of thereof.
1 14. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 61 to 67; or a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or prodrug of any of thereof. 1 15. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 68 to 75; or a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or prodrug of any of thereof.
1 16. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 76 to 82; or a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or prodrug of any of thereof.
1 17. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 83 to 91 ; or a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or prodrug of any of thereof.
1 18. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 92 to 97; or a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or prodrug of any of thereof.
1 19. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 98 to 102; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or prodrug of any of thereof. 120. A method of treating a patient suffering from a condition associated with a
dysfunction in proteostasis comprising administering an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 1 to 104.
121. A method of treating a patient suffering from a condition associated with a
dysfunction in proteostasis comprising administering to said patient a pharmaceutical composition of any one of claims 105 to 1 19.
122. The method of any one of claims 120 and 121, wherein the condition is associated with a dysfunction in the proteostasis of a protein selected from the group consisting of
hexosamine A, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator,
aspartylglucsaminidase, a-galactosidase A, cysteine transporter, acid ceremidase, acid a-L-fucosidase, protective protein, cathepsin A, acid β-glucosidase, acid β- galactosidase, iduronate 2-sulfatase, a-L-iduronidase, galactocerebrosidase, acid a - mannosidase, acid β -mannosidase, arylsulfatase B, arylsulfatase A, N- acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase, acid β -galactosidase, N-acetylglucosamine-1- phosphotransferase, acid sphingmyelinase, NPC-1, acid a-glucosidase, β-hexosamine B, heparin N-sulfatase, a -N-acetylglucosaminidase, a -glucosaminide N- acetyltransferase, N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase, al anti-trypsin, a -N- acetylgalactosaminidase, a -neuramidase, β -glucuronidase, β-hexosamine A and acid lipase, polyglutamine, a -synuclein, Αβ peptide, tau protein, hERG potassium channel, islet amyloid polypeptide, transthyretin Huntingtin, and superoxide dismutase.
123. The method of claim any one of claims 120 to 122, wherein the condition is
selected from the group consisting of Huntington's disease, Alzheimer's disease,
Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, cancer, diabetic retinopathy, diabetes, cancer and cystic fibrosis.
124. The method of claim 123, wherein the condition is cystic fibrosis.
125. The method of any one of claims 120 to 122, wherein an effective amount of a second agent is also administered, wherein the second agent is selected from the group consisting of a proteostasis regulator and a pharmacologic chaperone. 126. A pharmaceutical composition comprising:
a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or excipient;
an effective amount of a second agent selected from the group consisting of a proteostasis regulator and a pharmacologic chaperone; and
an effective amount of a compound of any one of claims 1 to 104.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201161484065P | 2011-05-09 | 2011-05-09 | |
| US61/484,065 | 2011-05-09 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2012154880A1 true WO2012154880A1 (en) | 2012-11-15 |
Family
ID=47139640
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US2012/037159 Ceased WO2012154880A1 (en) | 2011-05-09 | 2012-05-09 | Proteostasis regulators for treating cystic fibrosis and other protein misfolding diseases |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| WO (1) | WO2012154880A1 (en) |
Cited By (24)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103275010A (en) * | 2013-05-30 | 2013-09-04 | 上海皓元生物医药科技有限公司 | Preparation method of 1-(3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazolyl-5-yl)piperazine |
| WO2014146059A1 (en) * | 2013-03-15 | 2014-09-18 | Verseon, Inc. | Halogenopyrazoles as inhibitors of thrombin |
| US8916555B2 (en) | 2012-03-16 | 2014-12-23 | Axikin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 3,5-diaminopyrazole kinase inhibitors |
| WO2016057572A1 (en) | 2014-10-06 | 2016-04-14 | Mark Thomas Miller | Modulators of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator |
| WO2016154081A1 (en) | 2015-03-26 | 2016-09-29 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Pyrazolyl pyrimidinone compounds as pde2 inhibitors |
| US9533970B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2017-01-03 | Verseon Corporation | Multisubstituted aromatic compounds as serine protease inhibitors |
| US9540351B2 (en) | 2013-09-18 | 2017-01-10 | Axikin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pharmaceutically acceptable salts of 3,5-diaminopyrazole kinase inhibitors |
| US9546163B2 (en) | 2014-12-23 | 2017-01-17 | Axikin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 3,5-diaminopyrazole kinase inhibitors |
| US9951069B1 (en) | 2017-01-11 | 2018-04-24 | Rodin Therapeutics, Inc. | Bicyclic inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| US9975886B1 (en) | 2017-01-23 | 2018-05-22 | Cadent Therapeutics, Inc. | Potassium channel modulators |
| US10189810B2 (en) | 2014-09-17 | 2019-01-29 | Verseon Corporation | Pyrazolyl-substituted pyridone compounds as serine protease inhibitors |
| JP2019517455A (en) * | 2016-06-03 | 2019-06-24 | アッヴィ・エス・ア・エール・エル | Heteroaryl-substituted pyridines and methods of use |
| US10351532B2 (en) | 2014-12-29 | 2019-07-16 | The United States Of America, As Represented By The Secretary, Department Of Health And Human Services | Small molecule inhibitors of lactate dehydrogenase and methods of use thereof |
| US10421756B2 (en) | 2015-07-06 | 2019-09-24 | Rodin Therapeutics, Inc. | Heterobicyclic N-aminophenyl-amides as inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| US10532995B2 (en) | 2015-02-27 | 2020-01-14 | Verseon Corporation | Substituted pyrazole compounds as serine protease inhibitors |
| WO2020080960A1 (en) * | 2018-10-19 | 2020-04-23 | Auckland Uniservices Limited | Compounds for treating diabetes and/or related conditions |
| US10774064B2 (en) | 2016-06-02 | 2020-09-15 | Cadent Therapeutics, Inc. | Potassium channel modulators |
| US10919902B2 (en) | 2015-07-06 | 2021-02-16 | Alkermes, Inc. | Hetero-halo inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| US11191747B2 (en) | 2019-04-03 | 2021-12-07 | Aligos Therapeutics, Inc. | Pyrrole compounds |
| US11225475B2 (en) | 2017-08-07 | 2022-01-18 | Alkermes, Inc. | Substituted pyridines as inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| CN116162082A (en) * | 2023-02-16 | 2023-05-26 | 浙江大学 | Compound and composition for mycobacterium tuberculosis DprE1 enzyme inhibitor and application thereof |
| US11690844B2 (en) * | 2019-10-07 | 2023-07-04 | Purdue Research Foundation | Pyrazolyl pyrimidinone compounds and the uses thereof |
| US11746098B2 (en) | 2018-06-27 | 2023-09-05 | Proteostasis Therapeutics, Inc. | Proteasome activity enhancing compounds |
| US11993586B2 (en) | 2018-10-22 | 2024-05-28 | Novartis Ag | Crystalline forms of potassium channel modulators |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20100160324A1 (en) * | 2004-12-30 | 2010-06-24 | Astex Therapeutics Limited | Pyrazole derivatives as that modulate the activity of cdk, gsk and aurora kinases |
-
2012
- 2012-05-09 WO PCT/US2012/037159 patent/WO2012154880A1/en not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20100160324A1 (en) * | 2004-12-30 | 2010-06-24 | Astex Therapeutics Limited | Pyrazole derivatives as that modulate the activity of cdk, gsk and aurora kinases |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| IKUTA ET AL.: "Crystallographic Approach to Identification of Cyclin-dependent Kinase 4 (CDK4)-specific Inhibitors by Using CDK4 Mimic CDK2 Protein", J BIOL CHEM, vol. 276, no. 29, 2001, pages 27548 - 27554 * |
Cited By (52)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8916555B2 (en) | 2012-03-16 | 2014-12-23 | Axikin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 3,5-diaminopyrazole kinase inhibitors |
| US9346792B2 (en) | 2012-03-16 | 2016-05-24 | Axikin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 3,5-diaminopyrazole kinase inhibitors |
| US9365556B2 (en) | 2012-03-16 | 2016-06-14 | Axikin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 3,5-diaminopyrazole kinase inhibitors |
| US9382237B2 (en) | 2012-03-16 | 2016-07-05 | Axikin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 3,5-diaminopyrazole kinase inhibitors |
| US9687479B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2017-06-27 | Verseon Corporation | Multisubstituted aromatic compounds as serine protease inhibitors |
| WO2014146059A1 (en) * | 2013-03-15 | 2014-09-18 | Verseon, Inc. | Halogenopyrazoles as inhibitors of thrombin |
| US10251872B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2019-04-09 | Verseon Corporation | Multisubstituted aromatic compounds as serine protease inhibitors |
| US9533970B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2017-01-03 | Verseon Corporation | Multisubstituted aromatic compounds as serine protease inhibitors |
| US10058541B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2018-08-28 | Verseon Corporation | Multisubstituted aromatic compounds as serine protease inhibitors |
| CN103275010A (en) * | 2013-05-30 | 2013-09-04 | 上海皓元生物医药科技有限公司 | Preparation method of 1-(3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazolyl-5-yl)piperazine |
| US9540351B2 (en) | 2013-09-18 | 2017-01-10 | Axikin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pharmaceutically acceptable salts of 3,5-diaminopyrazole kinase inhibitors |
| US10189810B2 (en) | 2014-09-17 | 2019-01-29 | Verseon Corporation | Pyrazolyl-substituted pyridone compounds as serine protease inhibitors |
| WO2016057572A1 (en) | 2014-10-06 | 2016-04-14 | Mark Thomas Miller | Modulators of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator |
| US9730914B2 (en) | 2014-12-23 | 2017-08-15 | Axikin Pharmaceuticals | 3,5-diaminopyrazole kinase inhibitors |
| US9546163B2 (en) | 2014-12-23 | 2017-01-17 | Axikin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 3,5-diaminopyrazole kinase inhibitors |
| US10351532B2 (en) | 2014-12-29 | 2019-07-16 | The United States Of America, As Represented By The Secretary, Department Of Health And Human Services | Small molecule inhibitors of lactate dehydrogenase and methods of use thereof |
| US10961200B2 (en) | 2014-12-29 | 2021-03-30 | The United States Of America, As Represented By The Secretary, Department Of Health And Human Services | Small molecule inhibitors of lactate dehydrogenase and methods of use thereof |
| US11247971B2 (en) | 2014-12-29 | 2022-02-15 | The Trustees Of The University Of Pennsylvania | Small molecule inhibitors of lactate dehydrogenase and methods of use thereof |
| US10532995B2 (en) | 2015-02-27 | 2020-01-14 | Verseon Corporation | Substituted pyrazole compounds as serine protease inhibitors |
| WO2016154081A1 (en) | 2015-03-26 | 2016-09-29 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Pyrazolyl pyrimidinone compounds as pde2 inhibitors |
| US10287269B2 (en) | 2015-03-26 | 2019-05-14 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Pyrazolyl pyrimidinone compounds as PDE2 inhibitors |
| US10919902B2 (en) | 2015-07-06 | 2021-02-16 | Alkermes, Inc. | Hetero-halo inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| US11858939B2 (en) | 2015-07-06 | 2024-01-02 | Alkermes, Inc. | Hetero-halo inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| US10421756B2 (en) | 2015-07-06 | 2019-09-24 | Rodin Therapeutics, Inc. | Heterobicyclic N-aminophenyl-amides as inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| US10774064B2 (en) | 2016-06-02 | 2020-09-15 | Cadent Therapeutics, Inc. | Potassium channel modulators |
| JP7392211B2 (en) | 2016-06-03 | 2023-12-06 | アッヴィ・グローバル・エンタープライザズ・リミテッド | Heteroaryl-substituted pyridines and methods of use |
| JP2023172889A (en) * | 2016-06-03 | 2023-12-06 | アッヴィ・グローバル・エンタープライザズ・リミテッド | Heteroaryl-substituted pyridines and methods of use |
| JP2022009448A (en) * | 2016-06-03 | 2022-01-14 | アッヴィ・エス・ア・エール・エル | Heteroaryl-substituted pyridines and how to use |
| JP2019517455A (en) * | 2016-06-03 | 2019-06-24 | アッヴィ・エス・ア・エール・エル | Heteroaryl-substituted pyridines and methods of use |
| JP7622122B2 (en) | 2016-06-03 | 2025-01-27 | アッヴィ・グローバル・エンタープライザズ・リミテッド | Heteroaryl-substituted pyridines and methods of use |
| US10519149B2 (en) | 2017-01-11 | 2019-12-31 | Rodin Therapeutics, Inc. | Bicyclic inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| US10793567B2 (en) | 2017-01-11 | 2020-10-06 | Rodin Therapeutics, Inc. | Bicyclic inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| US10696673B2 (en) | 2017-01-11 | 2020-06-30 | Rodin Therapeutics, Inc. | Bicyclic inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| US11987580B2 (en) | 2017-01-11 | 2024-05-21 | Alkermes, Inc. | Bicyclic inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| US11286256B2 (en) | 2017-01-11 | 2022-03-29 | Alkermes, Inc. | Bicyclic inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| US11225479B2 (en) | 2017-01-11 | 2022-01-18 | Alkermes, Inc. | Bicyclic inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| US9951069B1 (en) | 2017-01-11 | 2018-04-24 | Rodin Therapeutics, Inc. | Bicyclic inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| US10717728B2 (en) | 2017-01-23 | 2020-07-21 | Cadent Therapeutics, Inc. | Potassium channel modulators |
| US9975886B1 (en) | 2017-01-23 | 2018-05-22 | Cadent Therapeutics, Inc. | Potassium channel modulators |
| US10351553B2 (en) | 2017-01-23 | 2019-07-16 | Cadent Therapeutics, Inc. | Potassium channel modulators |
| US11225475B2 (en) | 2017-08-07 | 2022-01-18 | Alkermes, Inc. | Substituted pyridines as inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| US11912702B2 (en) | 2017-08-07 | 2024-02-27 | Alkermes, Inc. | Substituted pyridines as inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| US11746098B2 (en) | 2018-06-27 | 2023-09-05 | Proteostasis Therapeutics, Inc. | Proteasome activity enhancing compounds |
| WO2020080960A1 (en) * | 2018-10-19 | 2020-04-23 | Auckland Uniservices Limited | Compounds for treating diabetes and/or related conditions |
| US11993586B2 (en) | 2018-10-22 | 2024-05-28 | Novartis Ag | Crystalline forms of potassium channel modulators |
| US11191747B2 (en) | 2019-04-03 | 2021-12-07 | Aligos Therapeutics, Inc. | Pyrrole compounds |
| US11771680B2 (en) | 2019-04-03 | 2023-10-03 | Aligos Therapeutics, Inc. | Pyrrole compounds |
| US20230293523A1 (en) * | 2019-10-07 | 2023-09-21 | Purdue Research Foundation | Pyrazolyl pyrimidinone compounds and the uses thereof |
| US11690844B2 (en) * | 2019-10-07 | 2023-07-04 | Purdue Research Foundation | Pyrazolyl pyrimidinone compounds and the uses thereof |
| US12414949B2 (en) | 2019-10-07 | 2025-09-16 | Purdue Research Foundation | Pyrazolyl pyrimidinone compounds and the uses thereof |
| CN116162082A (en) * | 2023-02-16 | 2023-05-26 | 浙江大学 | Compound and composition for mycobacterium tuberculosis DprE1 enzyme inhibitor and application thereof |
| CN116162082B (en) * | 2023-02-16 | 2025-07-11 | 浙江大学 | A compound, composition and application thereof for Mycobacterium tuberculosis DprE1 enzyme inhibitor |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2012154880A1 (en) | Proteostasis regulators for treating cystic fibrosis and other protein misfolding diseases | |
| US12180189B2 (en) | Proteostasis regulators | |
| AU2013202373B2 (en) | Proteasome activity enhancing compounds | |
| WO2012078902A2 (en) | Proteostasis regulators | |
| AU2013202373A1 (en) | Proteasome activity enhancing compounds | |
| US20130072473A1 (en) | Compounds for treating protein folding disorders | |
| EP2806875B1 (en) | Proteasome activity modulating compounds | |
| AU2013202368A1 (en) | Proteasome activity modulating compounds | |
| JP2024112835A (en) | Proteasome activity enhancing compounds | |
| WO2012078909A1 (en) | Thiazolpyrimidine proteostasis regulators | |
| ES2379242B1 (en) | CHROME DERIVATIVES | |
| CN106459041B (en) | Pyrimido [4,5-b] quinoline -4,5 (3H, 10H)-derovatives | |
| Zha et al. | Synthesis and in vitro anticancer evaluation of novel flavonoid-based amide derivatives as regulators of the PI3K/AKT signal pathway for TNBC treatment | |
| HK1195525B (en) | Proteostasis regulators | |
| HK1195525A (en) | Proteostasis regulators | |
| HK40049558A (en) | Proteasome activity enhancing compounds |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 12781996 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 12781996 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |