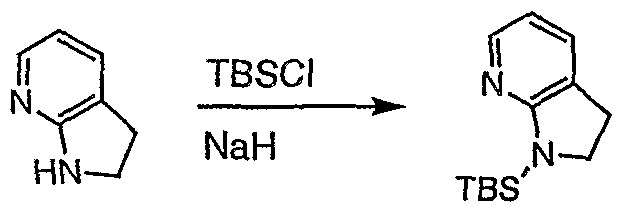WO2004078757A2 - Synthesis of 5-substituted 7-azaindoles and 7-azaidonines - Google Patents
Synthesis of 5-substituted 7-azaindoles and 7-azaidonines Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2004078757A2 WO2004078757A2 PCT/GB2004/000946 GB2004000946W WO2004078757A2 WO 2004078757 A2 WO2004078757 A2 WO 2004078757A2 GB 2004000946 W GB2004000946 W GB 2004000946W WO 2004078757 A2 WO2004078757 A2 WO 2004078757A2
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- compound
- formula
- alkyl
- palladium catalyst
- cor
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 CS(c1nc(*)c(*)nn1)(=O)=O Chemical compound CS(c1nc(*)c(*)nn1)(=O)=O 0.000 description 22
- UZGNFPCHQUHZAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Brc1cc(CCN2)c2nc1 Chemical compound Brc1cc(CCN2)c2nc1 UZGNFPCHQUHZAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BSANOBPMZHUQHD-UHFFFAOYSA-N BrC1=Cc(cc[nH]2)c2NC1 Chemical compound BrC1=Cc(cc[nH]2)c2NC1 BSANOBPMZHUQHD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZOYRFWSKOKZBNR-UHFFFAOYSA-N BrC1C=NC2NCCC2C1 Chemical compound BrC1C=NC2NCCC2C1 ZOYRFWSKOKZBNR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ILIJNWITJDWPLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N C(c1ccccc1)c1cc(CCN2)c2nc1 Chemical compound C(c1ccccc1)c1cc(CCN2)c2nc1 ILIJNWITJDWPLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CRVWXYRFTAXUKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C12)C1C(C(c1ccc(C)cc1)=O)=Cc1c2[nH]cc1 Chemical compound CC(C12)C1C(C(c1ccc(C)cc1)=O)=Cc1c2[nH]cc1 CRVWXYRFTAXUKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BVGCPFUVFNJWQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N CN(C)c(cc1)ccc1-c1cc(CCN2)c2nc1 Chemical compound CN(C)c(cc1)ccc1-c1cc(CCN2)c2nc1 BVGCPFUVFNJWQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UAPJZZOTKWZWBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N COc(ccc(C(c1cc(cc[nH]2)c2nc1)=O)c1)c1OC Chemical compound COc(ccc(C(c1cc(cc[nH]2)c2nc1)=O)c1)c1OC UAPJZZOTKWZWBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IGRJJGTUPFHARP-UHFFFAOYSA-N C[Si](C)(C)c1cc(cc[nH]2)c2nc1 Chemical compound C[Si](C)(C)c1cc(cc[nH]2)c2nc1 IGRJJGTUPFHARP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KUPDBTJKAHQIEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1)ccc1C(c1cc(cc[nH]2)c2nc1)=O Chemical compound Cc(cc1)ccc1C(c1cc(cc[nH]2)c2nc1)=O KUPDBTJKAHQIEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VPILNHNKECTYBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1)ccc1S([n](cc1)c(nc2N)c1c(N)c2C#N)(=O)=O Chemical compound Cc(cc1)ccc1S([n](cc1)c(nc2N)c1c(N)c2C#N)(=O)=O VPILNHNKECTYBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GSVRSNHGIUSRDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc1ccc(C(c2cc(CCN3)c3nc2)O)cc1 Chemical compound Cc1ccc(C(c2cc(CCN3)c3nc2)O)cc1 GSVRSNHGIUSRDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MQMZPMYZQSMLRE-OWOJBTEDSA-N FC(c1ccc(/C=C/c2cc(CCN3)c3nc2)cc1)(F)F Chemical compound FC(c1ccc(/C=C/c2cc(CCN3)c3nc2)cc1)(F)F MQMZPMYZQSMLRE-OWOJBTEDSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D471/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with one nitrogen atom, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D463/00
- C07D471/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with one nitrogen atom, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D463/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D471/04—Ortho-condensed systems
Definitions
- the present invention provides a novel substituted azaindoline intermediate and a method for its synthesis.
- the invention further provides the use of the intermediate in the manufacture of 5-substituted 7-azaindolines and 5- substituted 7-azaindoles.
- the 7-azaindole system forms the core structure of various pharmaceutically important substances such as antitumour agents, ligands of melatoninergic receptor, dopamine D 4 receptors, serotonin receptor, 5-HT6 receptor, p38 kinase inhibitors, renin inhibitors, thrombin inhibitors, and antitussive agents. Furthermore, antifungal activity of some 7-azaindoles in plant systems has recently been discovered.
- the production of 5-substituted-7-azaindoles therefore provides a number of problems in the art. There is therefore a need in the art for new methods of preparing such compounds.
- the present invention provides the use of functionalised 7-azaindoline derivatives as key intermediates. These intermediates can be rearomatized with DDQ to 7-azaindoles avoiding the use of heavy metal oxidants such as Mn(OAc) 3 or Mn0 2 (cf Scheme 2).
- the ability to avoid the use of heavy metal oxidants is particularly important when the resulting 5-functionalised-7- azaindoles are used in medicine.
- the present invention further provides a new, simple method to synthesise the starting unsubstituted 7-azaindoline, which avoids using harsh conditions described in the literature.
- the present invention therefore provides a significant advance in the production of 5-functionalised-7-azaindoles.
- the first aspect of the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
- X is an amino-protecting group, with the proviso that X is not benzyloxycarbonyl (Cbz).
- X is preferably selected from R 1 S(0) 2 , (R ⁇ Si, R 1 C(0), R I OCH 2 , R ⁇ NSOz, R ⁇ CCO)-, R 1 (R 1 0)CH-, R ⁇ HzCHz-, R 1 ⁇ -, PhC(0)CH 2 -,
- CH 2 CH-, C1CH 2 CH 2 -, Ph 3 C-, Ph 2 (4-pyridyl)C-, Me 2 N-, HO-CH 2 -, R ⁇ CH , (R 1 ) 3 SiOCH 2 -, (R 1 0) 2 CH-, t-BuOC(O)CH 2 -, Me 2 NCH 2 - and tetrahydropyr anylamine ;
- R 1 is C ⁇ - 6 alkyl, C 3-12 cycloalkyl, Ci- 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - 12 heterocyclyl or C 6 - n carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of - 6 alkyl, Si(R ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR i3 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R 3 is hydrogen or - 6 alkyl, preferably R 1 is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl, with the proviso that when X is R 1 OC(0)-, R 1 is not PhCH 2 .
- R 1 is preferably alkyl, more preferably methyl.
- R 1 is preferably alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl, more preferably CC1 3 CH 2 , Me 3 SiCH 2 CH 2 , t- butyl, 2,4-dimethyl ⁇ ent-3-yl, cyclohexyl, CCl 3 Me 2 COC(0), 1-adamantyl, 2- adamantyl or cyclohexyl.
- R 1 is preferably alkyl, more preferably Me or Et.
- R 1 is preferably aryl or heteroaryl, more preferably 2-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl or 4-nitrophenyl.
- R 1 is aryl or heteroaryl, more preferably Ph.-, p-methoxyphenyl-, 3,4- dimethoxyphenyl, 3-methoxyphenyl, 3,5-dimethoxyphenyl, 2-nitrophenyl or 2,4-dinitrophenyl.
- R I OCH 2 - N-alkoxymethylamine
- R 1 is alkyl, more preferably methyl, ethyl, C1CH 2 CH 2 -, Me 3 SiCH 2 CH 2 -, t-butyl or PhCH 2 -.
- R 1 is alkyl, more preferably methyl or t-butyl.
- R 1 is alkyl, more preferably methyl or ethyl.
- R 1 is preferably 2,4,6-trimethyl ⁇ henyl (mesityl), 4-methoxyphenyl, phenyl or toluyl.
- X is therefore most preferably a silyl group (especially t-butyldimethylsilyl (TBS), triisopropylsilyl (TIPS) or t-butyldimethylphenylsilyl (TBDPS)), N- alkoxymethylamine O ⁇ OQHb-) wherein R 1 is preferably methyl or a sulfonarnide R 1 S(0) 2 wherein R 1 is preferably phenyl, methoxymethyl (MOM) or ethoxymethyl.
- TSS t-butyldimethylsilyl
- TIPS triisopropylsilyl
- TDPS t-butyldimethylphenylsilyl
- N- alkoxymethylamine O ⁇ OQHb- wherein R 1 is preferably methyl or a sulfonarnide R 1 S(0) 2 wherein R 1 is preferably phenyl, methoxymethyl (MOM) or ethoxymethyl.
- Compound (I) of the present invention is a versatile intermediate and allows the production of many 5-substituted 7-azaindoles.
- the second aspect of the invention provides a method for synfhesising a compound of formula (I) comprising brominating a compound of formula (II);
- X is a amino-protecting group as defined in the first aspect of the invention.
- X is preferably selected from ( ⁇ Si or R ⁇ CH ⁇ wherein R 1 is C 1-6 alkyl or C 6- ⁇ 2 aryl, preferably methyl, ethyl, propyl n-butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- R 1 is C 1-6 alkyl or C 6- ⁇ 2 aryl, preferably methyl, ethyl, propyl n-butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- X is (R ⁇ Si and R 1 is independently Ci_ 6 alkyl or C 6- ⁇ 2 aryl, preferably methyl, ethyl, propyl, n-butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- Bromination can be carried out using reagents and conditions known in the art.
- the reagents are preferably Br 2 , dioxane dibromide, pyridinium perbromide or NBS.
- a compound of formula (II) can be provided from azaindoline using reagents and methods well known in the art.
- Protecting groups such as benzyl, acetamide, benzyl carbamate or p- toluenesulfonamide can be installed using standard methods known in the art, which are described in T. W. Greene and P. G. M. Wuts Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis 3 rd Edn., Wiley, New York 1999; pages 494-626.
- the protecting group X can be introduced prior to the formation of the azaindole skeleton, as illustrated below wherein the p-toluenesulfonyl group is linked to the nitrogen of the 7-azaindole system as a result of the reaction between N-tosylaziridine and malonodinitrile (Chemische Berichte 1985, 118, 4473).
- An alternative method of producing a compound of formula (I) involves the protection of a compound of formula (III) as illustrated.
- R 1 is C 1-6 alkyl, C 3 . 12 cycloalkyl, C ⁇ _ 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 - 12 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of - ⁇ alkyl, Si(R 3 ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , CO 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R 3 is hydrogen or C 1-6 alkyl, preferably R 1 is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- the compound of formula (III) can be produced from azaindoline using reagents and methods well known in the art. Examples of such brominations are indicated in Krasnokutskaya et al. Khim. Geterotsikl. Soed. 1977, 3, 380, WO00/26210, WO00/26211, WO00/64449, Taylor et al. Tetrahedron, 1987, 43, 5145.
- the third aspect of the invention provides a method for the production of a compound of formula (IV)
- each R 2 is independently OH, C 1-6 alkyl, Cj- 6 alkoxy, halo or C 6 - 12 carbocyclyl,
- X is selected from R X S(0) 2 , R 1 (R 1 0)CH-, C1CH 2 CH 2 -, Ph 3 C-, Ph 2 (4-pyridyl)C-, Me 2 N-, HO-CH 2 -, R ⁇ CHz-, (R l ) 3 SiOCH 2 -, (R 1 0) 2 CH-, t-BuOC(0)CH 2 -, Me 2 NCH 2 - and tetrahydropyranylamine;
- R 1 is C 1-6 alkyl, C 3 . 12 cycloalkyl, C 1-6 haloalkyl, C 6-12 heterocyclyl or C 6 - 12 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of Ci- 6 alkyl, Si(R 3 ) 3 ,
- R 3 is hydrogen or C 1-6 alkyl, preferably R 1 is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl n is 1, 2, 3 or 4, and M is Li, Sn, B, Mg, Zn, In, Cu, Zr, or Pd.
- the compound of formula (IV) may undergo one or more further transmetalation reactions for example by incubation with a metal halide such as ZnCl 2 , MgCl 2 , PdCl 2 , or (R 2 ) 3 SnW wherein R 2 is C ⁇ _ ⁇ 2 alkyl, preferably methyl or butyl and W is halogen preferably CI or I.
- a metal halide such as ZnCl 2 , MgCl 2 , PdCl 2 , or (R 2 ) 3 SnW
- R 2 is C ⁇ _ ⁇ 2 alkyl, preferably methyl or butyl and W is halogen preferably CI or I.
- Preferred examples of metal halides having the formula (R 2 ) 3 SnW include Bu 3 SnI or Me 3 SnCl.
- the fourth aspect of the invention provides a compound of formula (IV)
- each R 2 is independently -OH, C ⁇ - 6 alkyl, - 6 alkoxy, halo or C 6 - ⁇ 2 carbocyclyl, n is 1, 2, 3 or 4
- M is a metal preferably selected from Li, Sn, B, Mg, Zn, In, Cu, Zr, Pd or Zn
- R 1 is C 1-6 alkyl, C 3 - 12 cycloalkyl, - 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 - 12 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of Ci- 6 alkyl, Si(R 3 ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R is hydrogen or C ⁇ - 6 alkyl, preferably R is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- M can represent a metal such as Li, or metal alkyl group such as Sn(R ) 3 wherein R is a C ⁇ -12 alkyl.
- the fifth aspect of the invention provides a method for the production of a compound of formula (V)
- R 4 is a C ⁇ -6 alkyl, OH, or an C 6 - ⁇ 2 aryl group
- Z is a halide preferably chloride or bromide
- X is an amino-protecting group, preferably selected from R ⁇ O) ⁇ (R ⁇ Si, R 1 C(0), R'oCHa, R ⁇ NSOz, R 1 OC(0)-, R 1 (R 1 0)CH-, R 1 CH 2 CH 2 -, R !
- R 1 is Q. 6 alkyl, C 3 - 12 cycloalkyl, - 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 - 12 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of C 1-6 alkyl, Si(R ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R is hydrogen or Q, 6 alkyl, preferably R is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- the base is preferably t-BuLi.
- the sixth aspect of the invention provides a compound of formula (V)
- R 4 is a C 1-6 alkyl, OH, or an C 6 - ⁇ 2 aryl group
- R 1 is Q -6 alkyl, C 3-12 cycloalkyl, C 1-6 haloalkyl, C 6 - 12 heterocyclyl or C 6 - 12 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of Q- 6 alkyl, Si(R 3 ) 3 , OR 3 , NQ 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R 3 is hydrogen or C 1-6 alkyl, preferably R 1 is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- the seventh aspect of the invention provides a method of producing a compound of formula (VI)
- R 1 is Q- 6 alkyl, C 3 - 1 cycloalkyl, C ⁇ - 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 - 12 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of Q- 6 alkyl, Si(R ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R 3 is hydrogen or Q- 6 alkyl, preferably R 1 is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- boronate is selected from H-B(OR 15 ) 2 , (Me 2 C-0) 2 B-B(0- CMe 2 ) 2 and B(OR 15 ) 3 .
- the production of a compound of formula (VI) can be catalysed by the addition of a metal catalyst.
- the formation of a compound of formula (VI) can be catalysed by a palladium catalyst such as PdCl 2 or PdCl 2 (l,l'-bis(diphenylphosphino) ferrocene)
- the eighth aspect of the invention provides a compound of formula (VI)
- R 1 is Q -6 alkyl, C 3 - 12 cycloalkyl, Q- 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 - 12 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of Q- 6 alkyl, Si(R 3 ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R is hydrogen or Q- 6 alkyl, preferably R is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- B(R 5 ) 2 represents a pinacol ester
- the ninth aspect of the invention provides a method for the production of a compound of formula (VII)
- R is an optionally substituted Q -12 alkyl, C 2-12 alkenyl, COR carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl group;
- R 9 is optionally subsituted alkyl, carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl
- each substitutable carbon atom in R 8 or R 9 is optionally and independently substituted by one or more of Q- ⁇ 2 alkyl, C 2 - 12 alkenyl, carbocyclyl, or heterocyclyl, halogen, haloalkyl, OR 10 , SR 10 , N0 2 , CN, NR 10 R 10 , NR 10 COR 10 , NR 10 CONR 10 R 10 , NR 10 CO 2 R 10 , C0 2 R 10 , COR 10 ,
- each R 10 may be the same or different and is as defined below; wherein the Q- 12 alkyl optionally incorporates one or two insertions selected from the group consisting of -0-, -C(0)-, -N(R 10 )-, -S(O)- and -S(0 2 )- and wherein the Q -12 alkyl, carbocyclyl, or heterocyclyl group is optionally substituted by one or more of halogen, haloalkyl, OR 10 , SR, N0 2 , CN, NR 10 R 10 , NR 10 COR 10 , NR 10 CONR 10 R 10 , NR 10 COR 10 , NR 10 CO 2 R 10 , C0 2 R 10 , COR 10 , CONR 10 2 , S(0) 2 R 10 , SON
- each substitutable nitrogen atom in R 8 is optionally substituted by R 11 , COR 10 , SS00 22 RR 1100 oorr CC00 22 RR 1100 ,, v wherein each R 10 and R 11 may be the same or different and is as defined below;
- R 10 is hydrogen , Q- ⁇ 2 alkyl or aryl, optionally substituted by one or more of Q_ 4 alkyl, halogen, Q- 4 haloalkyl, OR 12 , SR 12 , N0 2 , CN, NR 12 R 12 , NR 12 COR 12 , NR 12 CONR 12 R 12 , NR 12 COR 12 , NR 12 C0 2 R 12 , C0 2 R 12 , COR 12 , CONR 12 2 ,
- R 11 is C ⁇ - 12 alkyl or aryl, opt tiioonnaallllyy ssuubbssttiittuuted by one or more of Q -4 alkyl, halogen, C ⁇ - 4 haloalkyl, OR 12 , SR 12 , N0 2 , CN, NR 12 R 12 , NR 12 COR 12 , NR 12 CONR 12 R 12 , NR 12 C0R 12 , NR 12 C0 2 R 12 , C0 2 R 12 , COR 12 , CONR 12 2 ,
- R 1 is Q- 6 alkyl, C 3 - 12 cycloalkyl, Q- 6 haloalkyl, C 6- ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 _ 12 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of Q- 6 alkyl, Si(R 3 ) 3 ,
- R 3 is hydrogen or Q- 6 alkyl, preferably R 1 is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- Q_ 12 alkyl wherein are independently selected from an optionally substituted Q_ 12 alkyl, C 2-12 alkenyl, COR 9 , carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl group and Z is a halogen preferably iodine, bromide or chlorine, or triflate.
- R 8 is preferably substituted with one or more of alkyl (e.g. methyl, ethyl or propyl), haloalkyl (preferably CF 3 ), halogen (e.g. F, CI or Br, preferably F), OR 13 , SR 13 , SOR 13 , N(R 13 ) 2 , wherein R is independently selected from hydrogen, Q- 4 alkyl or haloalkyl and is preferably phenyl or napthyl.
- R is preferably substituted in the 4-(para) position, by NR 14 R 14 , where R 14 is independently H or Q- 4 alkyl.
- a group as defined above contains two or more radicals, e.g. the radical R 10 , as for example in the groups SO 2 NR 10 R 10 and NR 10 COR 10 , the two or more radicals e.g. R 10 may be the same or different.
- reaction set out as option b) for the ninth aspect is a Stille reaction, which can be carried out according to Stille Angew. Chem., Int.ed, Engl. 1986, 25, 508; Mitchell Synthesis, 1992, 803, or Littke et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 6343.
- reaction set out as option c) for the ninth aspect is a Hiyama reaction which can be carried out according to Hatanaka et al. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 918, Hatanaka et al. Synlett, 1991, 845 or Tamao et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 6051, or Denmark et al. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 565, ibid. 2491.
- the reaction set out as option d) for the ninth aspect is a Suzuki reaction which can be carried out according to Suzuki Pure Appl. Chem. 1991, 63, 419, or Littke J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4020.
- a compound of formula (IV) is preferably incubated with an electrophile such as a Q_ ⁇ 2 alkyl halide for example methyl iodide, DMF, C0 2 , or a group R 10 -C(O)H wherein R 10 is Q- ⁇ 2 alkyl or C 6 - ⁇ 2 aryl.
- an electrophile such as a Q_ ⁇ 2 alkyl halide for example methyl iodide, DMF, C0 2 , or a group R 10 -C(O)H wherein R 10 is Q- ⁇ 2 alkyl or C 6 - ⁇ 2 aryl.
- a compound of formula (VII) is produced by the palladium-catalysed coupling reaction between a stannane of formula (VIII) and a group R -Y wherein R is a group as defined above and Y is a halogen,
- Compound (VIII) is formed by the transmetallation of a compound of formula (I) or (IV) as described in the third aspect of the invention.
- alkyl relates to both straight chain and branched alkyl radicals of 1 to 12 carbon atoms, preferably 1 to 8 carbon atoms and most preferably 1 to 4 carbon atoms including but not limited to methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, sec-butyl, isobutyl, tert-butyl n- pentyl, n-hexyl, n-heptyl, n-octyl.
- alkyl relates to a group having 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 or 12 carbon atoms.
- alkyl also encompasses cycloalkyl radicals including but not limited to cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, CH 2 -cyclopropyl, CH 2 -cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl.
- cycloalkyl relates to a group having 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 or 12 carbon atoms. Cycloalkyl groups may be optionally substituted or fused to one or more carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl group.
- Haloalkyl relates to an alkyl radical as defined above preferably having 1 to 8 carbon atoms, preferably 1 to 4 carbon atoms substituted with one or more halide atoms for example one or more of F, CI, Br or I, such as CH 2 CH 2 Br, CF 3 or CC1 3 .
- alkenyl means a straight chain or branched alkylenyl radical of 2 to 12 carbon atoms, preferably 2 to 6 carbon atoms and most preferably 2 to 4 carbon atoms, and containing one or more carbon-carbon double bonds and includes but is not limited to ethylene, n-propyl- 1-ene, n-propyl-2-ene, isopropylene, etc.
- alkenyl relates to a group having 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 or 12 carbon atoms.
- alkynyl means a straight chain or branched alkynyl radical of 2 to 12 carbon atoms, preferably 2 to 6 carbon atoms and most preferably 2 to 4 carbon atoms, and containing one or more carbon-carbon triple bonds and includes but is not limited to ethynyl, 2- methylethynyl etc.
- alkynyl relates to a group having 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 or 12 carbon atoms.
- Carbocyclyl relates to a saturated, partly unsaturated or unsaturated 3-12 membered hydrocarbon ring preferably a 6-12 membered hydrocarbon ring, including cycloalkyl and aryl.
- Aryl means an aromatic 3-12 membered hydrocarbon preferably a 6-12 membered hydrocarbon containing one ring or being fused to one or more saturated or unsaturated rings including but not limited to phenyl, napfhyl, anthracenyl or phenanthracenyl.
- Heteroaryl means an aromatic 3-12 membered aryl preferably a 6-12 membered aryl containing one or more heteroatoms selected from N, O or S and containing one ring or being fused to one or more saturated or unsaturated rings and;
- Heterocyclyl means a 3-12 membered ring system preferably a 6-12 membered ring system containing one or more heteroatoms selected from N, O or S and includes heteroaryl.
- the terms “carbocyclyl”, “aryl”, “heteroaryl” and “heterocyclyl” relate to a group having 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 or 12 carbon atoms.
- the heterocyclyl system can contain one ring or may be fused to one or more saturated or unsaturated rings; the heterocyclyl can be fully saturated, partially saturated or unsaturated and includes but is not limited to heteroaryl and heterocarbocyclyl.
- carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl groups include but are not limited to cyclohexyl, phenyl, acridine, benzimidazole, benzofuran, benzothiophene, benzoxazole, benzothiazole, carbazole, cinnoline, dioxin, dioxane, dioxolane, dithiane, dithiazine, dithiazole, dithiolane, furan, imidazole, imidazoline, imidazolidine, indole, indoline, indolizine, indazole, isoindole, isoquinoline, isoxazole, isothiazole, morpholine, napthyridine,
- fused includes a polycyclic compound in which one ring contains one or more atoms preferably one, two or three atoms in common with one or more other ring.
- Halogen means F, CI, Br or I, preferably F.
- Compounds of formula (VII) can be converted into alternative compounds of formula (VII) by conventional methods known in the art.
- a compound of formula (VII) may undergo oxidation, reduction, addition, elimination, substitution or transmetallation reactions in order to produce a further compound of formula (VII).
- the compounds of formula (VII) can be aromatised to 5-substituted 7- azaindoles (IX) using methods known in the art, in particular Mn(OAc) 3 /AcOH or Mn0 2 .
- the tenth aspect of the invention provides a method of producing a compound of formula (XI) by the aromatisation of a compound of formula (X) with DDQ wherein efficient oxidation of derivative (X) with DDQ to afford (XI) is promoted by the presence of electron-donating N-silyl group at nitrogen in (X).
- X' is a silyl group (R ⁇ Si R 1 is as defined in the first aspect
- X" is Br or R 8 and R 8 is as defined in the ninth aspect
- X' is t-butyldimethylsilyl (TBS), triisopropylsilyl (TIPS) or t- butyldimethyl ⁇ henylsilyl (TBDPS).
- TBS t-butyldimethylsilyl
- TIPS triisopropylsilyl
- TDPS t- butyldimethyl ⁇ henylsilyl
- This method allows the production of 5-substituted-7-azaindole moieties without the need for a high excess of oxidant and avoids the contamination of the product with heavy metal impurities (as can be seen for example with a Mn0 2 or Mn(OAc) 3 /AcOH medicated oxidation).
- Removal of the group X' can be carried out using method known in the art. Suitable methods for removing specific X' groups are set out in Greene and Wuts Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, 3 rd Edition, Wiley, New York, 1999. For example when X' is TBS, it can be removed by incubation with hydrochloric acid. Alternatively, when X' is PhS0 2 , removal can be afforded with KOH in EtOH.
- the eleventh aspect of the invention provides a compound of formula (XII)
- the twelfth aspect of the invention provides a method of producing a compound of formula (XII)
- (R 5 ) 3 B is selected from B(OR 15 ) 3 wherein R 15 is alkyl, cycloalkyl or two R 15 groups may together form a 4 to 7 membered ring
- R 1 is C 1-6 alkyl, C 3- ⁇ 2 cycloalkyl, Q- 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 - ⁇ 2 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of Q -6 alkyl, Si(R ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R 3 is hydrogen or Q- 6 alkyl, preferably R 1 is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- the thirteenth aspect of the invention provides a method for the production of a compound of formula (IX)
- R 8 is an optionally substituted Q_ ⁇ 2 alkyl, C 2 - ⁇ 2 alkenyl, COR 9 carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl group;
- R 9 is optionally substituted alkyl, carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl
- each substitutable carbon atom in R or R is optionally and independently substituted by one or more of Q- ⁇ 2 alkyl, C 2 - ⁇ 2 alkenyl, carbocyclyl, or heterocyclyl, halogen, haloalkyl, OR 10 , SR 10 , N0 2 , CN, NR 10 R 10 , NR 10 COR 10 , NR 10 CONR 10 R 10 , NR 10 COR 10 , NR 10 CO 2 R 10 , C0 2 R 10 , COR 10 , CONR 10 R 10 , S(0) 2 R 10 , SONH 2 , S(0)R 10 , SO 2 NR 10 R 10 , NR 10 S(O) 2 R 10 , wherein each R 10 may be the same or different and is as defined below; wherein the Q- ⁇ 2 alkyl optionally incorporates one or two insertions selected from the group consisting of -0-, -C(O)-, -NCR 10 )-, -S(O) 2
- R 10 is hydrogen, Q- ⁇ 2 alkyl or aryl, optionally substituted by one or more of Q -4 alkyl, halogen, Q- 4 haloalkyl, OR 12 , SR 12 , N0 2 , CN, NR 12 R 12 , NR 12 COR 12 , NR 12 CONR 12 R 12 , NR 12 COR 12 , NR 12 C0 2 R 12 , C0 2 R 12 , COR 12 , CONR 12 2 , S(0) 2 R 12 , SONH 2 , S(0)R 12 , S0 2 NR 12 R 12 , NR 12 S(0) 2 R 12 , wherein the Q- ]2 alkyl group optionally incorporates one or two insertions selected from the group consisting of -0-, -N(R 12 )-, -S(O)- and -S(0 2 )-, wherein each R 12 may be the same or different and is as defined below;
- R 11 is Q_ 12 alkyl or aryl, optionally substituted by one or more of C 1-4 alkyl, halogen, Q- 4 haloalkyl, OR 12 , SR 12 , N0 2 , CN, NR 12 R 12 , NR 12 COR 12 , NR 12 CONR 12 R 12 , NR 12 COR 12 , NR 12 C0 2 R 12 , C0 2 R 12 , COR 12 , CONR 12 2 , S(0) 2 R 12 , SONH 2 , S(0)R 12 , S0 2 NR 1 R 12 , NR 1 S(0) 2 R 12 , wherein the C 2 alkyl group optionally incorporates one or two insertions selected from the group consisting of -O-, -N(R 12 )-, -S(0)- and -S(0 2 )-, wherein each R 12 may be the same or different and is as defined below; R 12 is hydrogen, Q- 4 alkyl, or C ⁇ -4 hal
- R 1 is C ⁇ - 6 alkyl, C 3 - ⁇ 2 cycloalkyl, Q- 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 - 12 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of Q_ 6 alkyl, Si(R 3 ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R 3 is hydrogen or C ⁇ - 6 alkyl, preferably R 1 is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- R 7 is independently selected from an optionally substituted Q_ 12 alkyl, C 2- i 2 alkenyl, COR 9 , carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl group and Z is a halogen or inflate preferably iodine, bromine or chlorine.
- reaction set out is a Suzuki reaction which can be carried out according to Suzuki Pure Appl. Chem., 1991, 63, 419, or Littke J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4020.
- the fourteenth aspect of the invention provides a compound of formula
- R 4 is a Q- 6 alkyl, OH, or an C 6- ⁇ 2 aryl group
- R 1 is C ⁇ -6 alkyl, C 3 - ⁇ 2 cycloalkyl, Q- 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 - 12 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of Q- 6 alkyl, Si(R ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R 3 is hydrogen or Ci- 6 alkyl, preferably R 1 is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n-butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- the fifteenth aspect of the invention provides a method for the production of compound of formula (IX)
- R is an optionally substituted Q- ⁇ 2 alkyl, C 2 - ⁇ 2 alkenyl, COR carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl group;
- R 9 is optionally substituted alkyl, carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl; and wherein, each substitutable carbon atom in R 8 or R 9 is optionally and independently substituted by one or more of Q- ⁇ 2 alkyl, C 2 - ⁇ 2 alkenyl, carbocyclyl, or heterocyclyl, halogen, haloalkyl, OR 10 , SR 10 , N0 2 , CN, NR 10 R 10 , NR 10 COR 10 , NR 10 CONR 10 R 10 , NR 10 COR 10 , NR 10 CO 2 R 10 , C0 2 R 10 , COR 10 , CONR 10 R 10 , S(0) 2 R 10 , SONH 2 , S(0)R 10 , SO 2 NR 10 R 10 , NR 10 S(O) 2 R 10 , wherein each R 10 may be the same or different and is as defined below; whereinrthe Q- 12 alkyl optionally incorporates one or two insertions selected from the group consisting
- each substitutable nitrogen atom in R 8 is optionally substituted by R 11 , COR 10 , SS00 22 RR 1100 oorr CC00 22 RR 1100 ,, ⁇ wherein each R 10 and R 11 may be the same or different and is as defined below;
- R 10 is hydrogen , Q- ⁇ 2 alkyl or aryl, optionally substituted by one or more of Q- 4 alkyl, halogen, Q- 4 haloalkyl, OR 12 , SR 12 , N0 2 , CN, NR 12 R 12 , NR 12 COR 12 , NR 12 CONR 12 R 12 , NR 12 COR 12 , NR 12 C0 2 R 12 , C0 2 R 12 , COR 12 , CONR 12 2 , S(0) 2 R 12 , SONH 2 , S(0)R 12 , S0 2 NR 12 R 12 , NR 12 S(0) 2 R 12 , wherein the Q_ 12 alkyl group optionally incorporates one or two insertions selected from the group
- R 11 is Q- 12 alkyl or aryl, optionally substituted by one or more of Q- alkyl, halogen, Q -4 haloalkyl, OR 12 , SR 12 , N0 2 , CN, NR 12 R 12 , NR 12 COR 12 , NR 12 CONR 12 R 12 , NR 12 COR 12 , NR 12 C0 2 R 12 , C0 2 R 12 , COR 12 , CONR 1 2 , S(0) 2 R 12 , SONH 2 , S(0)R 12 , S0 2 NR 12 R 12 , NR 12 S(0) 2 R 12 , wherein the Q- ⁇ 2 alkyl group optionally incorporates one or two insertions selected from the group consisting of -0-, -N(R 12 )-, -S(O)- and -S(0 2 )-, wherein each R 12 may be the same or different and is as defined below; R 12 is hydrogen, Q- 4 alkyl, or Q- hal
- R 1 is Q- 6 alkyl, C 3 - ⁇ 2 cycloalkyl, Q, 6 haloalkyl, C 6- ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6- ⁇ 2 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of Q. 6 alkyl, Si(R ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R 3 is hydrogen or Q. 6 alkyl, preferably R 1 is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- R 7 is independently selected from an optionally substituted Q- ⁇ 2 alkyl, C 2 - ⁇ 2 alkenyl, COR 9 , carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl group and Z is a halogen or inflate preferably iodide, bromide or chloride.
- Z is a halogen or inflate preferably iodide, bromide or chloride.
- the sixteenth aspect of the invention provides a method of producing 7- azaindoline from 7-azaindole, comprising the reaction of 7-azaindole with a formic acid-triethylamine mixture in the presence of a palladium catalyst, followed by incubation with sodium hydroxide.
- This method avoids using high pressure, gaseous hydrogen, avoids concomitant formation of overreduced products and occurs at relatively low temperature.
- the seventeenth aspect provides a compound of formula (XV)
- R is substituted aryl, preferably substituted phenyl or optionally substituted five-membered heterocyclyl or aryl-C(O).
- the eighteenth aspect provides a method for the production of a compound of formula (XV)
- R 8 is as defined in the ninth aspect
- R is substituted aryl, preferably substituted phenyl or optionally substituted five-membered heterocyclyl;
- R 15 is hydrogen, Q -6 alkyl or C 6 - ⁇ 2 aryl and wherein two or more R 15 groups may together form a 4 to 7 membered ring;
- R 15 is hydrogen, -CMe 2 CMe 2 -, methyl, ethyl.
- R is as defined in the fifth aspect
- R 2 is Q_ 4 alkyl, most preferably methyl, ethyl, propyl and butyl.
- reaction set out in option a) for the eighteenth aspect is a Suzuki coupling reaction which can be earned out according to Suzuki Pure Appl. Chem. 1991, 63, 419; and Martin and Yang Acta Chem. Scand. 1993, 47, 221, or Littke J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4020.
- reaction set out in option b) for the eighteenth aspect is a Stille coupling reaction which can be carried out according to Stille Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1986, 25, 508; Mitchell, Synthesis 1992, 803, or Littke et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 6343.
- reaction set out in option c) for the eighteenth aspect is a Hiyama coupling reaction which can be carried out according to Hatanaka and Hiyama J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 918; Hatanaka and Hiyama Synlett. 1991, 845; Tamao et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 6051, or Denmark et al. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 565, ibid. 2491.
- a compound of formula (III) is incubated with an aryl boronic acid R -B(OH) 2 , heteroaryl boronic acid R - B(OH) 2 , aryltrialkyl stannane R 8 -Sn(R 2 ) , or heteroaryltrialkylstannane R 8 - R 9
- the nineteenth aspect provides a method for the production of a compound of formula (VII)
- R 8 is as defined in the ninth aspect
- R 8 is substituted aryl, preferably substituted phenyl or optionally substituted five-membered heterocyclyl;
- R 1 is Q_ 6 alkyl, C 3 - ⁇ 2 cycloalkyl, C ⁇ - 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 - ⁇ 2 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of Q- 6 alkyl, Si(R ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R is hydrogen or Q- 6 alkyl, preferably R is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- R 15 is hydrogen, Q- 6 alkyl or C 6 - ⁇ 2 aryl and wherein two or more R 15 groups may together form a 4 to 7 membered ring;
- R 15 is hydrogen, -CMe 2 CMe 2 -, methyl, ethyl.
- R 2 is as defined in the third aspect
- R 2 is Q- alkyl, most preferably methyl, ethyl, propyl and butyl.
- R 4 is as defined in the fifth aspect
- a group as defined above contains two or more radicals, e.g. the radical R 1 , as for example in NR ! R ⁇ the two or more radicals e.g. R 1 may be the same or different.
- reaction set out in option a) for the nineteenth aspect is a Suzuki coupling reaction which can be carried out according to Suzuki Pure Appl. Chem. 1991, 63, 419; and Martin and Yang Acta Chem. Scand.1993, 47, 221, or Littke J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4020.
- reaction set out in option b) for the nineteenth aspect is a Stille coupling reaction which can be carried out according to Stille Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1986 25, 508; Mitchell, Synthesis 1992, 803, or Littke et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 6343.
- reaction set out in option c) for the nineteenth aspect is a Hiyama coupling reaction which can be carried out according to Hatanaka and Hiyama /. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 918; Hatanaka and Hiyama Synlett. 1991, 845; Tamao et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 6051, or Denmark et al. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 565, ibid. 2491.
- a compound of formula (I) is incubated with an aryl boronic acid R 8 -B(OH) 2 , heteroaryl boronic acid R 8 - B(OH) 2 , aryltrialkyl stannane R 8 -Sn(R 2 ) 3 , or heteroaryltrialkylstannane R 8 - Sn(R 2 ) 3 where R 8 is as defined above and R 2 is Q- 4 alkyl.
- the twentieth aspect provides a compound of formula (XIII)
- the twenty first aspect provides a method for the production of a compound of formula (XVI)
- R 8 is as defined in the ninth aspect
- R 8 is substituted aryl, preferably substituted phenyl or optionally substituted five-membered heterocyclyl;
- R 2 is as defined in the third aspect
- R 2 is Q-- 4 alkyl, most preferably methyl, ethyl, propyl and butyl.
- R 4 is as defined in the fifth aspect
- R 15 is as defined in the seventh aspect
- R is hydrogen, -CMe 2 CMe 2 -, methyl, ethyl.
- reaction set out in option a) for the twenty first aspect is a Suzuki coupling reaction which can be earned out according to Suzuki Pure Appl. Chem. 1991, 63, 419; and Martin and Yang Acta Chem. Scand. 1993, 47, 221, or Littke J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4020.
- reaction set out in option b) for the twenty first aspect is a Stille coupling reaction which can be carried out according to Stille Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1986, 25, 508; Mitchell, Synthesis 1992, 803, or Littke et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 6343.
- reaction set out in option c) for the twenty first aspect is a Hiyama coupling reaction which can be earned out according to Hatanaka and Hiyama J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 918; Hatanaka and Hiyama Synlett. 1991, 845; Tamao et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 6051, or Denmark et al. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 565, ibid. 2491.
- a compound of formula (I) is incubated with an aryl boronic acid R -B(OH) 2 , heteroaryl boronic acid R - B(OH) 2 , aryltrialkyl stannane R 8 -Sn(R 2 ) 3 , or heteroaryltrialkylstannane R 8 - Sn(R 2 ) 3 where R 8 is as defined above and R 2 is Q- 4 alkyl.
- the twenty-second aspect provides a method for the production of a compound of formula (IX)
- R 2 is as defined in the third aspect wherein R 4 is as defined in the fifth aspect wherein R 8 is as defined in the ninth aspect
- R 1 is C ⁇ -6 alkyl, C 3- ⁇ 2 cycloalkyl, C ⁇ - 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 - i2 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of Q -6 alkyl, Si(R 3 ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R 3 is hydrogen or Q- 6 alkyl, preferably R 1 is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- R 15 is as defined in the seventh aspect
- R 15 is hydrogen, -CMe 2 CMe 2 -, methyl, ethyl.
- R is _ 4 alkyl, most preferably methyl, ethyl, propyl and butyl.
- R 4 is hydrogen, Q -4 alkyl, or Q -4 haloalkyl
- radicals e.g. the radical R , as for example in SnR R , the two or more
- radicals e.g. R may be the same or different.
- reaction set out in option a) for the twenty-second aspect is a Suzuki coupling reaction which can be earned out according to Suzuki Pure Appl. Chem. 1991, 63, 419; and Martin and Yang Acta Chem. Scand.1993, 47, 221, or Littke J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4020.
- reaction set out in option b) for the twenty-second aspect is a Stille coupling reaction which can be carried out according to Stille Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1986, 25, 508; Mitchell, Synthesis 1992, 803, or Littke et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 6343.
- reaction set out in option c) for the twenty-second aspect is a Hiyama coupling reaction which can be carried out according to Hatanaka and Hiyama /. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 918; Hatanaka and Hiyama Synlett. 1991, 845; Tamao et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 6051, or Denmark et al. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 565, ibid. 2491.
- a compound of formula (I) is incubated with an aryl boronic acid R -B(OH) 2 , heteroaryl boronic acid R - B(OH) 2 , aryltrialkyl stannane R 8 -Sn(R 2 ) 3 , or heteroaryltrialkylstannane R 8 - Sn(R 2 ) 3 where R 8 is as defined above and R 2 is Q- 4 alkyl.
- the twenty third aspect of the invention provides an alternative method for the production of a compound of formula (IX)
- R 1 is Ci- alkyl, C 3 - i2 cycloalkyl, Q- 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 - 12 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of C ⁇ - 6 alkyl, Si(R 3 ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R is hydrogen or Q- 6 alkyl, preferably R is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- reaction set out in the twenty third aspect is a Stille coupling reaction which can be carried out according to Stille Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1986, 25, 508; Mitchell, Synthesis 1992, 803, or Littke et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 6343.
- R 1 is C ⁇ -6 alkyl, C 3 - ⁇ 2 cycloalkyl, C ⁇ - 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 - 12 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of Q- 6 alkyl, Si(R 3 ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R 3 is hydrogen or Q- alkyl, preferably R 1 is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- the twenty fifth aspect of the invention provides a method of producing a compound of formula (XVIII)
- R 1 is C ⁇ - 6 alkyl, C 3 - ⁇ 2 cycloalkyl, C ⁇ - 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 _ 12 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of Q- 6 alkyl, Si(R 3 ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R 3 is hydrogen or Q. 6 alkyl, preferably R 1 is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- the twenty sixth aspect provides a compound of formula (Vila)
- R 9 is as defined in the ninth aspect wherein X is an amino-protecting group as defined in the first aspect, preferably selected from R 1 S(0) 2 , (R ⁇ Si, R ⁇ CO), R ⁇ CHa, R ⁇ NSOa, R 1 OC(0)-, R 1 (R 1 0)CH-, C1CH 2 CH 2 -, Ph 3 C-, Ph 2 (4-pyridyl)C-, Me 2 N-, HO-CH 2 -, R ⁇ CHz-, (R 1 ) 3 SiOCH 2 -, (R 1 0) 2 CH-, t-BuOC(0)CH 2 -, Me 2 NCH 2 - and tetrahydropyranylamine;
- R 1 is C ⁇ - 6 alkyl, C 3 - ⁇ 2 cycloalkyl, C ⁇ - 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 - 12 carbocyclyl; optionally substituted with one or more of Q- 6 alkyl, Si(R 3 ) 3 , OR 3 , N0 2 , C0 2 , C0 2 R 3 , halogen, haloalkyl, SR 3 , CN, NR 3 COR 3 , COR 13 CONR 3 R 3 , wherein R is hydrogen or Q- 6 alkyl, preferably R is methyl, ethyl, propyl, n- butyl, tert-butyl or phenyl.
- the twenty seventh aspect provides a compound of formula (IXa)
- R 1 is Q_ 6 alkyl, C 3 . 12 cycloalkyl, Ci- 6 haloalkyl, C 6 - ⁇ 2 heterocyclyl or C 6 -
- the twenty eighth aspect provides a compound of formula (XVIa)
- the present invention encompasses one or more compounds as defined in the first, fourth, fifth, sixth, seventh, ninth, twelfth, thirteenth, fourteenth, fifteenth, sixteenth, eighteenth, twentieth, twenty fourth, twenty sixth, twenty seventh and twenty eighth aspects of the invention and as set out below;
- the residual liquid was cooled (ice bath) and basified to pH 13 by slow addition of 50% aqueous NaOH (total of about 500 mL). Then, the mixture was refluxed for 2 h until TLC showed completion. Ice was added in amount sufficient to lower the temperature of the mixture to 20 °C. The two-phase system was then extracted with AcOEt (5x500 mL). Combined extracts were washed with brine, dried MgS0 4 , and concentrated in vacuum. The residual brown solid was separated by means of SGC with AcOEt:MeOH as eluent to afford recovered 1 (12.57 g, 25%) and desired 2 (36.05 g, 71%).
- DDQ (53 mg, 0.23 mmol) was added in three equal portions to a stirred solution of alcohol 14 (54 mg, 0.20 mmol) in a mixture of CH 2 C1 2 (15 mL) and 0.2 M pH 7 phosphate buffer (0.15 mL).
- the mixture was diluted with saturated aqueous NaHC0 3 (16 mL) and stirred vigorously for 1 h. Then the mixture was extracted with AcOEt (2x). The combined organic extracts were washed with saturated brine (lx), dried (MgS0 4 ) and concentrated. The residue was purified by PTLC with benzene as eluent to afford alcohol 15 (16 mg, 31 %).
- T ⁇ F (2.5 mL) was added dropwise 1.5 M solution of tert-butyllithium in pentane (1 mL, 1.51 mmol). After 35 min additional stining at -90 °C, tri-n- butyltin iodide (0.23 mL, 0.79 mmol) was added in one portion. The mixture was stirred at -90 °C for 10 min, -78 °C for 40 min, and then allowed to warm to r.t. The mixture was partitioned between AcOEt - brine. The aqueous layer was extracted with AcOEt (3x) and the combined organic solutions were dried (MgS0 4 ), and concentrated to afford the crude stannane 17, which was used in the next step without purification.
- DDQ (about 380 mg, 1.68 mmol) was added in portions to a solution of 4 (525 mg, 1.68 mmol) in a mixture of CH 2 C1 2 (90 mL) and 0.2 M phosphate buffer pH 7 solution (910 ⁇ L) until full consumption of the starting material (TLC). Then, saturated aqueous NaHC0 3 solution (22mL) was added, and the reaction mixture stined for 0.5 h. The organic layer was separated and the aqueous layer was extracted with CH 2 C1 2 (3x20 mL).
- Reaction was performed following the above protocol and using 31 (200 mg, 0.88 mmol), 36 (477 mg, 1.75 mmol), LiCl (112 mg, 2.63 mmol), PdCl 2 (PPh 3 ) 2 (62 mg, 0.088 mmol), 1.0 M aq. Na 2 C0 3 (2.19 mL, 2.19 mmol) in EtOH (5.2 mL) and toluene (5.2 mL) with refluxing overnight.
- the 5-bromo-7-azaindole 27 (0.5 g, 2.54 mmol), bis(pinacolato)diboron (0.968 g, 3.81 mmol), potassium acetate (0.748 g, 7.61 mmol), [1,1'- bis(diphenylphosphino)fenocene]dichloropalladium(II) complex with CH 2 C1 2 (1:1) (49 mg, 0.06 mmol) and DMF (11 mL) were heated in a sealed tube at 80 °C. After 44 h, the reaction mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature, diluted with EtOAc and saturated brine, and partitioned. The aqueous layer was extracted with EtOAc (3x).
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Nitrogen Condensed Heterocyclic Rings (AREA)
- Low-Molecular Organic Synthesis Reactions Using Catalysts (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
- Steroid Compounds (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10/548,162 US7652137B2 (en) | 2003-03-06 | 2004-03-05 | Synthesis of 5 substituted 7-azaindoles and 7-azaindolines |
| AT04717703T ATE490253T1 (en) | 2003-03-06 | 2004-03-05 | SYNTHESIS OF 5-SUBSTITUTED 7-AZAINDOLINES AND 7-AZAINDOLINES |
| EP04717703A EP1633750B1 (en) | 2003-03-06 | 2004-03-05 | Synthesis of 5-substituted 7-azaindoles and 7-azaindolines |
| DE602004030334T DE602004030334D1 (en) | 2003-03-06 | 2004-03-05 | SYNTHESIS OF 5-SUBSTITUTED 7-AZAINDOLES AND 7-AZAINDOLINES |
| JP2006505923A JP4711950B2 (en) | 2003-03-06 | 2004-03-05 | Synthesis of 5-substituted 7-azaindoles and 7-azaindolines |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| GB0305142.2 | 2003-03-06 | ||
| GBGB0305142.2A GB0305142D0 (en) | 2003-03-06 | 2003-03-06 | Synthesis |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2004078757A2 true WO2004078757A2 (en) | 2004-09-16 |
| WO2004078757A3 WO2004078757A3 (en) | 2005-09-01 |
Family
ID=9954241
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/GB2004/000946 WO2004078757A2 (en) | 2003-03-06 | 2004-03-05 | Synthesis of 5-substituted 7-azaindoles and 7-azaidonines |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7652137B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP1633750B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP4711950B2 (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE490253T1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE602004030334D1 (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2355726T3 (en) |
| GB (1) | GB0305142D0 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2004078757A2 (en) |
Cited By (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1749829A1 (en) | 2005-08-05 | 2007-02-07 | Eisai London Research Laboratories Limited | JNK inhibitors |
| WO2007135398A1 (en) * | 2006-05-22 | 2007-11-29 | Astrazeneca Ab | Indole derivatives |
| US7361763B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2008-04-22 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pyrrolo-pyridine kinase modulators |
| US7361764B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2008-04-22 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pyrrolo-pyridine kinase modulators |
| US7452993B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2008-11-18 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Fused ring heterocycle kinase modulators |
| US7626021B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2009-12-01 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Fused ring heterocycle kinase modulators |
| WO2011060216A1 (en) | 2009-11-12 | 2011-05-19 | Concert Pharmaceuticals Inc. | Substituted azaindoles |
| WO2011110479A1 (en) * | 2010-03-09 | 2011-09-15 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Process for the manufacture of 5-halogenated-7-azaindoles |
| WO2011090738A3 (en) * | 2009-12-29 | 2011-11-24 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Type ii raf kinase inhibitors |
| CN104478909A (en) * | 2014-11-19 | 2015-04-01 | 上海泰坦科技股份有限公司 | Synthetic process of heterocyclic boric acid compound |
| US9382239B2 (en) | 2011-11-17 | 2016-07-05 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) |
| US9505784B2 (en) | 2009-06-12 | 2016-11-29 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Fused 2-aminothiazole compounds |
| CN107001354A (en) * | 2014-04-11 | 2017-08-01 | 台北医学大学 | Inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| CN107033142A (en) * | 2017-05-15 | 2017-08-11 | 杭州科耀医药科技有限公司 | A kind of synthetic method of Venetoclax key intermediates |
| US9758522B2 (en) | 2012-10-19 | 2017-09-12 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Hydrophobically tagged small molecules as inducers of protein degradation |
| US9862688B2 (en) | 2014-04-23 | 2018-01-09 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Hydrophobically tagged janus kinase inhibitors and uses thereof |
| US10000483B2 (en) | 2012-10-19 | 2018-06-19 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Bone marrow on X chromosome kinase (BMX) inhibitors and uses thereof |
| US10017477B2 (en) | 2014-04-23 | 2018-07-10 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Janus kinase inhibitors and uses thereof |
| US10112927B2 (en) | 2012-10-18 | 2018-10-30 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) |
| CN110078726A (en) * | 2019-06-19 | 2019-08-02 | 陕西师范大学 | A kind of full synthetic method for replacing 2,3- dihydro -1H- pyrrolo- [2,3-b] pyridine derivate |
| US10450269B1 (en) | 2013-11-18 | 2019-10-22 | Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc. | Compounds and uses thereof for the modulation of hemoglobin |
| US10550121B2 (en) | 2015-03-27 | 2020-02-04 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases |
| US10647675B2 (en) | 2015-09-18 | 2020-05-12 | Kaken Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Biaryl derivative and medicine containing same |
| US10702527B2 (en) | 2015-06-12 | 2020-07-07 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Combination therapy of transcription inhibitors and kinase inhibitors |
| US10870651B2 (en) | 2014-12-23 | 2020-12-22 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) |
| US10906889B2 (en) | 2013-10-18 | 2021-02-02 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Polycyclic inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) |
| US11040957B2 (en) | 2013-10-18 | 2021-06-22 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Heteroaromatic compounds useful for the treatment of proliferative diseases |
| US11053195B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2021-07-06 | Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc. | Compounds and uses thereof for the modulation of hemoglobin |
| US11142507B2 (en) | 2015-09-09 | 2021-10-12 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101607958A (en) * | 2002-02-01 | 2009-12-23 | 阿斯特拉曾尼卡有限公司 | Quinazoline compound |
| CA2480317A1 (en) * | 2002-03-28 | 2003-10-09 | Eisai Co., Ltd. | 7-azaindoles as inhibitors of c-jun n-terminal kinases for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders |
| GB0305142D0 (en) | 2003-03-06 | 2003-04-09 | Eisai London Res Lab Ltd | Synthesis |
| EP1628975A2 (en) * | 2003-05-16 | 2006-03-01 | Eisai Co., Ltd. | Jnk inhibitors |
| GB0405055D0 (en) * | 2004-03-05 | 2004-04-07 | Eisai London Res Lab Ltd | JNK inhibitors |
| US8648192B2 (en) * | 2010-05-26 | 2014-02-11 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | 2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridin-4-ylboronic acid derivatives |
| CN105622605B (en) * | 2016-03-01 | 2017-10-13 | 苏州艾缇克药物化学有限公司 | A kind of synthetic method of the azaindole of 5 bromine 7 |
| CN106188050A (en) * | 2016-07-20 | 2016-12-07 | 南通雅本化学有限公司 | A kind of production technology of 5 bromine 7 azaindoles |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5705515A (en) * | 1994-04-26 | 1998-01-06 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Substituted sulfonamides as selective β-3 agonists for the treatment of diabetes and obesity |
| WO2003000688A1 (en) * | 2001-06-21 | 2003-01-03 | Aventis Pharma Limited | Azaindoles |
Family Cites Families (34)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4719218A (en) * | 1985-12-12 | 1988-01-12 | Smithkline Beckman Corporation | Pyrrolo[1,2-a]imidazole and pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyridine derivatives and their use as 5-lipoxygenase pathway inhibitor |
| JPH0830013B2 (en) * | 1989-07-28 | 1996-03-27 | 財団法人相模中央化学研究所 | Method for producing biaryl compound |
| GB9026926D0 (en) | 1990-12-12 | 1991-01-30 | Smith Kline French Lab | Novel process |
| ZA919797B (en) | 1990-12-13 | 1992-10-28 | Smithkline Beecham Corp | Bicyclo-5,6-dihydro-7h-pyrrolo-1,20-imidazol-7-ols and 7-ones |
| SE9100920D0 (en) * | 1991-03-27 | 1991-03-27 | Astra Ab | NEW ACTIVE COMPOUNDS |
| JP3119758B2 (en) | 1993-02-24 | 2000-12-25 | 日清製粉株式会社 | 7-Azaindole derivative and antiulcer drug containing the same as active ingredient |
| FR2732969B1 (en) | 1995-04-14 | 1997-05-16 | Adir | NOVEL PYRIDINIC COMPOUNDS, PROCESS FOR THEIR PREPARATION AND THE PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS CONTAINING THEM |
| WO1998047899A1 (en) | 1997-04-24 | 1998-10-29 | Ortho-Mcneil Corporation, Inc. | Substituted pyrrolopyridines useful in the treatment of inflammatory diseases |
| GB9721437D0 (en) | 1997-10-10 | 1997-12-10 | Glaxo Group Ltd | Heteroaromatic compounds and their use in medicine |
| CN1279682A (en) | 1997-10-20 | 2001-01-10 | 霍夫曼-拉罗奇有限公司 | bicyclic kinase inhibitors |
| CA2326185A1 (en) | 1998-04-02 | 1999-10-14 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone |
| US6610692B1 (en) | 1998-10-30 | 2003-08-26 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Thrombin inhibitors |
| AU752186B2 (en) * | 1998-10-30 | 2002-09-12 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Thrombin inhibitors |
| KR20010101266A (en) | 1998-12-17 | 2001-11-14 | 프리돌린 클라우스너, 롤란드 비. 보레르 | 4-aryloxindoles as inhibitors of jnk protein kinases |
| BR9916324A (en) | 1998-12-17 | 2001-10-02 | Hoffmann La Roche | 4,5-pyrazinoxindoles as protein kinase inhibitors |
| US6265403B1 (en) | 1999-01-20 | 2001-07-24 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Angiogenesis inhibitors |
| GB9904933D0 (en) | 1999-03-04 | 1999-04-28 | Glaxo Group Ltd | Compounds |
| US6239132B1 (en) | 1999-04-23 | 2001-05-29 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Thrombin inhibitors |
| ATE425142T1 (en) | 1999-04-23 | 2009-03-15 | Vertex Pharma | INHIBITORS OF C-JUN N-TERMINAL KINASES (JNK) |
| NZ517578A (en) | 1999-08-19 | 2004-02-27 | Signal Pharm Inc | Pyrazoloanthrone and derivatives thereof as JNK inhibitors and their compositions |
| EP1106621B1 (en) | 1999-12-07 | 2003-11-19 | Fuji Photo Film Co., Ltd. | Fluorescent substances |
| OA12514A (en) | 1999-12-24 | 2006-05-29 | Aventis Pharma Ltd | Azaindoles. |
| AU779855B2 (en) | 2000-01-06 | 2005-02-17 | Axys Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Novel compounds and compositions as protease inhibitors |
| US6897231B2 (en) | 2000-07-31 | 2005-05-24 | Signal Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Indazole derivatives as JNK inhibitors and compositions and methods related thereto |
| PE20020506A1 (en) | 2000-08-22 | 2002-07-09 | Glaxo Group Ltd | PIRAZOLE DERIVATIVES FUSED AS PROTEIN KINASE INHIBITORS |
| WO2002024648A2 (en) * | 2000-09-20 | 2002-03-28 | Abbott Laboratories | Process for the preparation of cell proliferation inhibitors |
| GB0108770D0 (en) * | 2001-04-06 | 2001-05-30 | Eisai London Res Lab Ltd | Inhibitors |
| WO2003028724A1 (en) | 2001-10-04 | 2003-04-10 | Smithkline Beecham Corporation | Chk1 kinase inhibitors |
| DE60331219D1 (en) | 2002-03-28 | 2010-03-25 | Eisai R&D Man Co Ltd | AZAINDOLE AS INHIBITORS FROM C-JUN N-TERMINAL KINASEN |
| CA2480317A1 (en) * | 2002-03-28 | 2003-10-09 | Eisai Co., Ltd. | 7-azaindoles as inhibitors of c-jun n-terminal kinases for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders |
| SE0202463D0 (en) | 2002-08-14 | 2002-08-14 | Astrazeneca Ab | Novel compounds |
| GB0305142D0 (en) | 2003-03-06 | 2003-04-09 | Eisai London Res Lab Ltd | Synthesis |
| EP1599475A2 (en) | 2003-03-06 | 2005-11-30 | Eisai Co., Ltd. | Jnk inhibitors |
| GB0516156D0 (en) * | 2005-08-05 | 2005-09-14 | Eisai London Res Lab Ltd | JNK inhibitors |
-
2003
- 2003-03-06 GB GBGB0305142.2A patent/GB0305142D0/en not_active Ceased
-
2004
- 2004-03-05 AT AT04717703T patent/ATE490253T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2004-03-05 US US10/548,162 patent/US7652137B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2004-03-05 ES ES04717703T patent/ES2355726T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2004-03-05 DE DE602004030334T patent/DE602004030334D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2004-03-05 EP EP04717703A patent/EP1633750B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2004-03-05 JP JP2006505923A patent/JP4711950B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2004-03-05 WO PCT/GB2004/000946 patent/WO2004078757A2/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5705515A (en) * | 1994-04-26 | 1998-01-06 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Substituted sulfonamides as selective β-3 agonists for the treatment of diabetes and obesity |
| WO2003000688A1 (en) * | 2001-06-21 | 2003-01-03 | Aventis Pharma Limited | Azaindoles |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| PI-TAI CHOU, ET AL.: "Excited-State Amine-Imine Double Proton Transfer in 7-Azaindoline" J. PHYS. CHEM. B, vol. 104, 2000, pages 7818-7829, XP002280766 * |
| SANDERSON, P. E. J.; ET AL.: "Azaindoles: Moderately Basic P1 Groups for Enhancing the Selectivity of Thrombin Inhibitors" BIOORGANIC AND MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY LETTERS, vol. 13, 2003, pages 795-798, XP002290822 * |
Cited By (50)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7601839B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2009-10-13 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals Inc. | Pyrrolo-pyridine kinase modulators |
| US7361763B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2008-04-22 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pyrrolo-pyridine kinase modulators |
| US7361764B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2008-04-22 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pyrrolo-pyridine kinase modulators |
| US7452993B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2008-11-18 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Fused ring heterocycle kinase modulators |
| US7582637B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2009-09-01 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pyrrolo-pyridine kinase modulators |
| US8268994B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2012-09-18 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Fused ring heterocycle kinase modulators |
| US7626021B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2009-12-01 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Fused ring heterocycle kinase modulators |
| US7829558B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2010-11-09 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Fused ring heterocycle kinase modulators |
| US7906648B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2011-03-15 | Sgx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Pyrrolo-pyridine kinase modulators |
| EP1749829A1 (en) | 2005-08-05 | 2007-02-07 | Eisai London Research Laboratories Limited | JNK inhibitors |
| WO2007135398A1 (en) * | 2006-05-22 | 2007-11-29 | Astrazeneca Ab | Indole derivatives |
| US9505784B2 (en) | 2009-06-12 | 2016-11-29 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Fused 2-aminothiazole compounds |
| WO2011060216A1 (en) | 2009-11-12 | 2011-05-19 | Concert Pharmaceuticals Inc. | Substituted azaindoles |
| WO2011090738A3 (en) * | 2009-12-29 | 2011-11-24 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Type ii raf kinase inhibitors |
| US20130040949A1 (en) * | 2009-12-29 | 2013-02-14 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Type ii raf kinase inhibitors |
| US11826365B2 (en) | 2009-12-29 | 2023-11-28 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Type II raf kinase inhibitors |
| US9180127B2 (en) | 2009-12-29 | 2015-11-10 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Type II Raf kinase inhibitors |
| AU2010343102B2 (en) * | 2009-12-29 | 2016-03-24 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Type II Raf kinase inhibitors |
| US9358231B2 (en) | 2009-12-29 | 2016-06-07 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Type II RAF kinase inhibitors |
| AU2016201096B2 (en) * | 2009-12-29 | 2017-08-31 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Type ii raf kinase inhibitors |
| WO2011110479A1 (en) * | 2010-03-09 | 2011-09-15 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Process for the manufacture of 5-halogenated-7-azaindoles |
| US9382239B2 (en) | 2011-11-17 | 2016-07-05 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) |
| US10981903B2 (en) | 2011-11-17 | 2021-04-20 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) |
| US10144730B2 (en) | 2011-11-17 | 2018-12-04 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) |
| US10112927B2 (en) | 2012-10-18 | 2018-10-30 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) |
| US10787436B2 (en) | 2012-10-18 | 2020-09-29 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) |
| US9758522B2 (en) | 2012-10-19 | 2017-09-12 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Hydrophobically tagged small molecules as inducers of protein degradation |
| US10000483B2 (en) | 2012-10-19 | 2018-06-19 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Bone marrow on X chromosome kinase (BMX) inhibitors and uses thereof |
| USRE48175E1 (en) | 2012-10-19 | 2020-08-25 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Hydrophobically tagged small molecules as inducers of protein degradation |
| US11053195B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2021-07-06 | Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc. | Compounds and uses thereof for the modulation of hemoglobin |
| US11040957B2 (en) | 2013-10-18 | 2021-06-22 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Heteroaromatic compounds useful for the treatment of proliferative diseases |
| US10906889B2 (en) | 2013-10-18 | 2021-02-02 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Polycyclic inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) |
| US10450269B1 (en) | 2013-11-18 | 2019-10-22 | Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc. | Compounds and uses thereof for the modulation of hemoglobin |
| CN107001354B (en) * | 2014-04-11 | 2021-06-22 | 台北医学大学 | Histone deacetylase inhibitors |
| CN107001354A (en) * | 2014-04-11 | 2017-08-01 | 台北医学大学 | Inhibitors of histone deacetylase |
| EP3129373A4 (en) * | 2014-04-11 | 2017-11-29 | Taipei Medical University | Histone deacetylase inhibitors |
| US10246455B2 (en) | 2014-04-11 | 2019-04-02 | Taipei Medical University | Histone deacetylase inhibitors |
| US10017477B2 (en) | 2014-04-23 | 2018-07-10 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Janus kinase inhibitors and uses thereof |
| US9862688B2 (en) | 2014-04-23 | 2018-01-09 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Hydrophobically tagged janus kinase inhibitors and uses thereof |
| CN104478909A (en) * | 2014-11-19 | 2015-04-01 | 上海泰坦科技股份有限公司 | Synthetic process of heterocyclic boric acid compound |
| US10870651B2 (en) | 2014-12-23 | 2020-12-22 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) |
| US11325910B2 (en) | 2015-03-27 | 2022-05-10 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases |
| US10550121B2 (en) | 2015-03-27 | 2020-02-04 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases |
| US12098154B2 (en) | 2015-03-27 | 2024-09-24 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases |
| US10702527B2 (en) | 2015-06-12 | 2020-07-07 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Combination therapy of transcription inhibitors and kinase inhibitors |
| US11142507B2 (en) | 2015-09-09 | 2021-10-12 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Inc. | Inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases |
| US10647675B2 (en) | 2015-09-18 | 2020-05-12 | Kaken Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Biaryl derivative and medicine containing same |
| CN107033142A (en) * | 2017-05-15 | 2017-08-11 | 杭州科耀医药科技有限公司 | A kind of synthetic method of Venetoclax key intermediates |
| CN110078726A (en) * | 2019-06-19 | 2019-08-02 | 陕西师范大学 | A kind of full synthetic method for replacing 2,3- dihydro -1H- pyrrolo- [2,3-b] pyridine derivate |
| CN110078726B (en) * | 2019-06-19 | 2022-05-17 | 陕西师范大学 | Synthetic method of fully-substituted 2, 3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolo [2,3-b ] pyridine derivative |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2004078757A3 (en) | 2005-09-01 |
| US7652137B2 (en) | 2010-01-26 |
| JP4711950B2 (en) | 2011-06-29 |
| EP1633750B1 (en) | 2010-12-01 |
| DE602004030334D1 (en) | 2011-01-13 |
| US20060235042A1 (en) | 2006-10-19 |
| EP1633750A2 (en) | 2006-03-15 |
| ES2355726T3 (en) | 2011-03-30 |
| JP2006520771A (en) | 2006-09-14 |
| GB0305142D0 (en) | 2003-04-09 |
| ATE490253T1 (en) | 2010-12-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1633750B1 (en) | Synthesis of 5-substituted 7-azaindoles and 7-azaindolines | |
| Kumar et al. | Synthesis of 7-azaindole and 7-azaoxindole derivatives through a palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction | |
| Pudlo et al. | First Suzuki–Miyaura type cross-coupling of ortho-azidobromobenzene with arylboronic acids and its application to the synthesis of fused aromatic indole-heterocycles | |
| MX2007009689A (en) | Process for preparing 2,3-disubstituted indoles. | |
| Ye et al. | Synthesis of 2-aminopyridines via ruthenium-catalyzed [2+ 2+ 2] cycloaddition of 1, 6-and 1, 7-diynes with cyanamides: scope and limitations | |
| WO2007014707A1 (en) | Heterocyclic benzylamino derivatives, their manufacture and use as pharmaceutical agents | |
| JP2008514710A (en) | Efficient synthesis of 4,5-dihydro-pyrazolo [3,4-c] pyrid-2-ones | |
| Franco et al. | Synthesis of 2-(pyrimidin-4-yl) indoles | |
| Malapel-Andrieu et al. | Synthesis and reactivity of substituted 3-([(Trifluoromethyl) sulfonyl] oxy)-1H-indole-2-carboxylate in palladium-catalyzed reactions | |
| Xie et al. | The synthesis of quinolines via denitrogenative palladium-catalyzed cascade reaction of o-aminocinnamonitriles with arylhydrazines | |
| Cooksey et al. | Oxidative Pictet-Spengler cyclisations through acceptorless iridium-catalysed dehydrogenation of tertiary amines | |
| Attia et al. | Synthesis, NMR conformational analysis and pharmacological evaluation of 7, 7a, 13, 14-tetrahydro-6 H-cyclobuta [b] pyrimido [1, 2-a: 3, 4-a′] diindole analogues as melatonin receptor ligands | |
| Molnár | Synthesis of condensed tetra-and polycyclic nitrogen heterocycles with a five-membered azacyclic core induced by ionic palladium catalysts | |
| Primas et al. | A new boronic-acid based strategy to synthesize 4 (5)-(het) aryl-1H-imidazoles | |
| Eskildsen et al. | Halogen dance in pyrazole 1-oxides: synthesis of pyrazolo [3, 4-c] quinoline 1-oxides | |
| US5374727A (en) | Asymmetric hydrogenation of dihydro-pyrido [1,2-a]indoles | |
| Krogsgaard-Larsen et al. | Syntheses of aza-analogous iso-ergoline scaffolds using carbene mediated C–H insertion | |
| CN114195703A (en) | Method for synthesizing difluoromethylene alkane-containing compound | |
| Oh et al. | Catalyst-free assembly of a polyfunctionalized 1, 2, 4-triazole-fused N-heterocycle, 6-acylated pyrrolo [1, 2-a][1, 2, 4] triazolo [5, 1-c] pyrazine | |
| Sayyed et al. | Selective reduction and functionalization of diethyl 1-alkyl-1H-indole-2, 3-dicarboxylates | |
| US7060830B2 (en) | Synthesized γ-carbolines | |
| CN116496151B (en) | Method for preparing fluorenone derivative by utilizing CATELLANI strategy | |
| WO2004013139A2 (en) | Process for preparing 7-azaindoles | |
| Parra et al. | Metalation and halogen‐metal exchange in the imidazo [1, 2‐a] quinoxaline series | |
| Aakermann et al. | Synthesis of tricyclic systems of biological interest |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AK | Designated states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AE AG AL AM AT AU AZ BA BB BG BR BW BY BZ CA CH CN CO CR CU CZ DE DK DM DZ EC EE EG ES FI GB GD GE GH GM HR HU ID IL IN IS JP KE KG KP KR KZ LC LK LR LS LT LU LV MA MD MG MK MN MW MX MZ NA NI NO NZ OM PG PH PL PT RO RU SC SD SE SG SK SL SY TJ TM TN TR TT TZ UA UG US UZ VC VN YU ZA ZM ZW |
|
| AL | Designated countries for regional patents |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): BW GH GM KE LS MW MZ SD SL SZ TZ UG ZM ZW AM AZ BY KG KZ MD RU TJ TM AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR BF BJ CF CG CI CM GA GN GQ GW ML MR NE SN TD TG |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | ||
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2006505923 Country of ref document: JP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2004717703 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2006235042 Country of ref document: US Ref document number: 10548162 Country of ref document: US |
|
| WWP | Wipo information: published in national office |
Ref document number: 2004717703 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWP | Wipo information: published in national office |
Ref document number: 10548162 Country of ref document: US |