WO2003020737A1 - O-pyrazole glucoside sglt2 inhibitors and method of use - Google Patents
O-pyrazole glucoside sglt2 inhibitors and method of use Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2003020737A1 WO2003020737A1 PCT/US2002/028480 US0228480W WO03020737A1 WO 2003020737 A1 WO2003020737 A1 WO 2003020737A1 US 0228480 W US0228480 W US 0228480W WO 03020737 A1 WO03020737 A1 WO 03020737A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- agent
- compound
- aryl
- inhibitor
- combination
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 *c1c(*c2ccccc2)c(O[C@@]([C@@]([C@]2O)O)O[C@@](CO)[C@@]2O)n[n]1* Chemical compound *c1c(*c2ccccc2)c(O[C@@]([C@@]([C@]2O)O)O[C@@](CO)[C@@]2O)n[n]1* 0.000 description 1
- YDUBQUANDNHHKO-QFXBJFAPSA-N Cc1c(Cc(cc2)ccc2SC)c(O[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]2O)O)O[C@H](CO)[C@H]2O)n[nH]1 Chemical compound Cc1c(Cc(cc2)ccc2SC)c(O[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]2O)O)O[C@H](CO)[C@H]2O)n[nH]1 YDUBQUANDNHHKO-QFXBJFAPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BWVBGVJIPCDCGT-VBTGVMJWSA-N OC[C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1O)O)O)O[C@H]1Oc1n[nH]c(C(F)(F)F)c1Cc1ccccc1 Chemical compound OC[C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1O)O)O)O[C@H]1Oc1n[nH]c(C(F)(F)F)c1Cc1ccccc1 BWVBGVJIPCDCGT-VBTGVMJWSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07H—SUGARS; DERIVATIVES THEREOF; NUCLEOSIDES; NUCLEOTIDES; NUCLEIC ACIDS
- C07H17/00—Compounds containing heterocyclic radicals directly attached to hetero atoms of saccharide radicals
- C07H17/02—Heterocyclic radicals containing only nitrogen as ring hetero atoms
Definitions
- the present invention relates to 0-pyrazole glucosides which are inhibitors of sodium dependent glucose transporters found in the intestine and kidney (SGLT2) and to a method for treating diabetes, especially type II diabetes, as well as hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, obesity, hypertriglyceridemia, Syndrome X, diabetic complications, atherosclerosis and related diseases, employing such 0-pyrazole glucosides alone or in combination with one, two or more other type antidiabetic agent and/or one, two or more other type therapeutic agents such as hypolipidemic agents.
- SGLT2 sodium dependent glucose transporters found in the intestine and kidney
- NIDDM type II diabetes
- NIDDM Normalization of plasma glucose in NIDDM patients would be predicted to improve insulin action, and to offset the development of diabetic complications.
- An inhibitor of the sodium-dependent glucose transporter SGLT2 in the kidney would be expected to aid in the normalization of plasma glucose levels, and perhaps body weight, by enhancing glucose excretion.
- novel, safe, and orally active antidiabetic agents is also desired in order to complement existing therapies, including the sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, metformin, and insulin, and to avoid the potential side effects associated with the use of these other agents.
- Hyperglycemia is a hallmark of type II diabetes (NIDDM) ; consistent control of plasma glucose levels in diabetes can offset the development of diabetic complications and beta cell failure seen in advanced disease.
- Plasma glucose is normally filtered in the kidney in the glomerulus and actively reabsorbed in the proximal tubule.
- SG T2 appears to be the major transporter responsible for the reuptake of glucose at this site.
- the SGLT2 specific inhibitor phlorizin or closely related analogs inhibit this reuptake process in diabetic rodents and dogs resulting in normalization of plasma glucose levels by promoting glucose excretion without hypoglycemic side effects.
- SGLT2 is a 672 amino acid protein containing 14 membrane-spanning segments that is predominantly expressed in the early SI segment of the renal proximal tubules.
- the substrate specificity, sodium dependence, and localization of SGLT2 are consistent with the properties of the high capacity, low affinity, sodium- dependent glucose transporter previously characterized in human cortical kidney proximal tubules.
- hybrid depletion studies implicate SGLT2 as the predominant Na + /glucose cotransporter in the SI segment of the proximal tubule, since virtually all Na-dependent glucose transport activity encoded in mRNA from rat kidney cortex is inhibited by an antisense oligonucleotide specific to rat SGLT2.
- SGLT2 is a candidate gene for some forms of familial glucosuria, a genetic abnormality in which renal glucose reabsorption is impaired to varying degrees. None of these syndromes investigated to date map to the SGLT2 locus on chromosome 16. However, the studies of highly homologous rodent
- SGLTs strongly implicate SGLT2 as the major renal sodium-dependent transporter of glucose and suggest that the glucosuria locus that has been mapped encodes an SGLT2 regulator. Inhibition of SGLT2 would be predicted to reduce plasma glucose levels via enhanced glucose excretion in diabetic patients.
- SGLTl another Na-dependent glucose cotransporter that is 60% identical to SGLT2 at the amino acid level, is expressed in the small intestine and in the more distal S3 segment of the renal proximal tubule.
- human SGLTl and SGLT2 are biochemically distinguishable.
- SGLTl the molar ratio of Na + to glucose transported is 2:1, whereas for SGLT2, the ratio is 1:1.
- the K m for Na + is 32 and 250- 300 mM for SGLTl and SGLT2 , respectively.
- K m values for uptake of glucose and the nonmetabolizable glucose analog ⁇ -methyl-D-glucopyranoside (AMG) are similar for SGLTl and SGLT2, i.e. 0.8 and 1.6 mM (glucose) and 0.4 and 1.6 mM (AMG) for SGLTl and SGLT2 transporters, respectively.
- the two transporters do vary in their substrate specificities for sugars such as galactose, which is a substrate for SGLTl only.
- phlorizin a specific inhibitor of SGLT2 activity, provided proof of concept in vivo by promoting glucose excretion, lowering fasting and fed plasma glucose, and promoting glucose utilization without hypoglycemic side effects in several diabetic rodent models and in one canine diabetes model .
- No adverse effects on plasma ion balance, renal function or renal morphology have been observed as a consequence of phlorizin treatment for as long as two weeks.
- no hypoglycemic or other adverse effects have been observed when phlorizin is administered to normal animals, despite the presence of glycosuria.
- Phlorizin itself is unattractive as an oral drug since it is a nonspecific SGLT1/SGLT2 inhibitor that is hydrolyzed in the gut to its aglycone phloretin, which is a potent inhibitor of facilitated glucose transport.
- Concurrent inhibition of facilitative glucose transporters (GLUTs) is undesirable since such inhibitors would be predicted to exacerbate peripheral insulin resistance as well as promote hypoglycemia in the CNS.
- Inhibition of SGLTl could also have serious adverse consequences as is illustrated by the hereditary syndrome glucose/galactose malabsorption (GGM) , in which mutations in the SGLTl cotransporter result in impaired glucose uptake in the intestine, and life-threatening diarrhea and dehydration.
- GGM hereditary syndrome glucose/galactose malabsorption
- the familial glycosuria syndromes are conditions in which intestinal glucose transport, and renal transport of other ions and amino acids, are normal. Familial glycosuria patients appear to develop normally, have normal plasma glucose levels, and appear to suffer no major health deficits as a consequence of their disorder, despite sometimes quite high (110-114 g/daily) levels of glucose excreted.
- the major symptoms evident in these patients include polyphagia, polyuria and polydipsia, and the kidneys appear to be normal in structure and function. Thus, from the evidence available thus far, defects in renal reuptake of glucose appear to have minimal long term negative consequences in otherwise normal individuals.
- EP 598359A1 (also JP 035988) (Tanabe Seiyaku) discloses compounds of the following structure A:
- EP 0850948A1 discloses structures of the following genus B:
- JP 09124684 discloses derivatives of structure B
- R 1 , R H, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl or together oxo
- JP 08027006-A discloses derivatives of structure A where various combinations of the glucose hydroxyl are acylated and appears to be similar to EP 598359A1.
- EP 0684254-Al appears to encompass derivatives of structure B disclosed in JP 09188625A.
- JP 10245391 discloses 500 structures as hypoglycemic agents for treatment of diabetes. These are O-glucosides of hydroxylated coumarins.
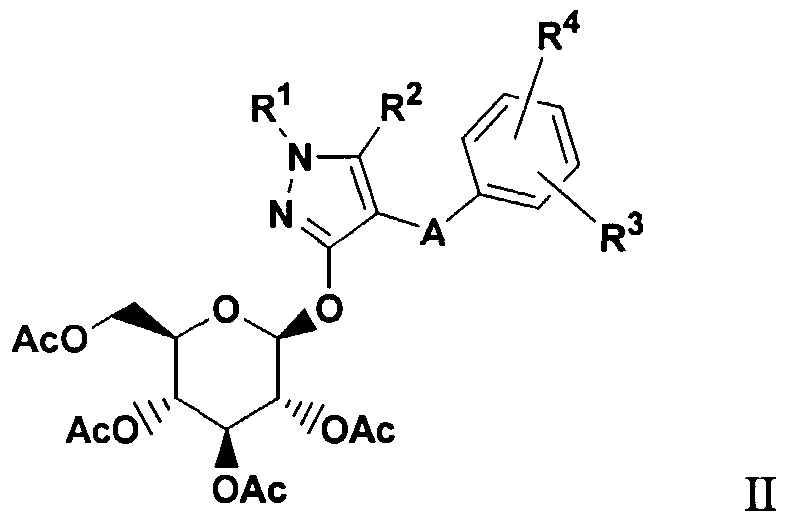
- 0- pyrazole glucoside compounds which have the formula I .
- R 1 is hydrogen, arylalkyl, alkenyl, or alkyl
- R 2 is alkyl or perfluoroalkyl ;
- R 3 and R 4 are each independently hydrogen, OH, OR 5 , OAryl, OCH 2 Aryl , alkyl, cycloalkyl, CF 3 , -OCHF 2 , -3,4- (OCH 2 0) , OCF 3 , halogen, -CN, -C0 2 R 5a , -C0 2 H, -COR 6 , -CH(OH)R 6a , -CH(OR 5b )R 6b , -CONR 6c R 6d , -NHCOR 5c , -NHS0 2 R 5d , -NHS0 2 Aryl, Aryl, -SR 5e , -SOR 5f , -S0 2 R 59 , -S0 2 Aryl, or a five, six or seven membered heterocycle which may contain 1 to 4 heteroatoms in the ring which are N, 0, S, SO, and/or S0 2 , or R 3 and R 4 together with
- R 5 , R 5a , R 5b , R 5C , R 5d , R 5e , R 5f , and R 59 are each independently alkyl; and R 6 , R 6a , R 6b , R 6c and R 6d are each independently hydrogen, alkyl, aryl, arylalkyl or cycloalkyl, or R 6c and R 6d together with the nitrogen to which they are attached form an annelated five, six or seven membered heterocycle which may contain 1 to 4 heteroatoms in the ring which are N, 0, S, SO, and/or S0 2
- the compounds of formula I possess activity as inhibitors of the sodium dependent glucose transporters found in the intestine and kidney of mammals and are useful in the treatment of diabetes and the micro- and macrovascular complications of diabetes such as retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy, and wound healing.
- the present invention provides for compounds of formula I, pharmaceutical compositions employing such compounds and for methods of using such compounds.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula I, alone or in combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
- a method for treating or delaying the progression or onset of diabetes, especially type I and type II diabetes, including complications of diabetes, including retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy and delayed wound healing, and related diseases such as insulin resistance (impaired glucose homeostasis) , hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, elevated blood levels of fatty acids or glycerol, obesity, hyperlipidemia including hypertriglyceridemia, Syndrome X, atherosclerosis and hypertension, and for increasing high density lipoprotein levels, wherein a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula I is administered to a mammalian, e.g., human, patient in need of treatment.
- a mammalian e.g., human
- the compounds of the invention can be used alone, in combination with other compounds of the present invention, or in combination with one or more other agent (s) active in the therapeutic areas described herein.
- a method for treating diabetes and related diseases as defined above and hereinafter wherein a therapeutically effective amount of a combination of a compound of formula I and at least one other type of therapeutic agent, such as an antidiabetic agent and/or a hypolipidemic agent, is administered to a human patient in need of treatment.
- a therapeutically effective amount of a combination of a compound of formula I and at least one other type of therapeutic agent such as an antidiabetic agent and/or a hypolipidemic agent
- A is CH 2 ;
- R 1 is hydrogen or benzyl
- R 3 and R 4 are independently hydrogen, OR 5 , OAryl , OCH 2 Aryl, -3 , 4- (OCH 2 0) , alkyl, cycloalkyl, CF 3 , -OCHF 2 , -OCF 3 , halogen, -C0 2 R 5a , -COR 6 , -CH(OH)R 6a , -CH (OR 5b ) R 6b ,
- R 3 is hydrogen
- R 4 is hydrogen, OR 5 , OAryl, OCH 2 Aryl , -3 , 4- (0CH 2 0) , alkyl, cycloalkyl, CF 3 , -OCHF 2 , -0CF 3 , halogen, -C0 2 R 5a ,
- YMC trademark of YMC Co, Ltd., Kyoto, Japan
- PBS phosphate buffered saline
- Ham's F-12 a cell growth medium commercially available from Life Technologies
- lower alkyl as employed herein alone or as part of another group includes both straight and branched chain hydrocarbons, containing 1 to 20 carbons, preferably 1 to 10 carbons, more preferably 1 to 8 carbons, in the normal chain, such as methyl, ethyl, propyl , isopropyl, butyl, t-butyl, isobutyl, pentyl, hexyl , isohexyl, heptyl , 4,4- dimethylpentyl , octyl, 2 , 2 , 4-trimethylpentyl , nonyl, decyl , undecyl , dodecyl , the various branched chain isomers thereof, and the like.
- any of such groups may be optionally substituted with one or more substituents such as halo, for example F, Br, Cl or I or CF 3 , alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, aryloxy, aryl (aryl) or diaryl, arylalkyl, arylalkyloxy, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl , cycloalkylalkyl, cycloalkylalkyloxy, optionally substituted amino, hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, acyl, oxo, alkanoyl, heteroaryl, heteroaryloxy, cycloheteroalkyl , arylheteroaryl , arylalkoxycarbonyl , heteroarylalkyl, heteroarylalkoxy, aryloxyalkyl , aryloxyaryl, alkylamido, alkanoylamino, arylcarbonylamino,
- cycloalkyl as employed herein alone or as part of another group includes saturated or partially unsaturated (containing 1 or more double bonds) cyclic hydrocarbon groups containing 1 to 3 rings, including monocyclicalkyl , bicyclicalkyl and tricyclicalkyl, containing a total of 3 to 20 carbons forming the rings, preferably 3 to 10 carbons , forming the ring and which may be fused to 1 or 2 aromatic rings as described for aryl, which include cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl, cyclooctyl, cyclodecyl and cyclododecyl, cyclohexenyl ,
- any of which groups may be optionally substituted with one or more substituents such as halogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, aryl, aryloxy, arylalkyl, cycloalkyl, alkylamido, alkanoylamino, oxo, acyl, arylcarbonylamino, amino, nitro, cyano, thiol and/or alkylthio and/or any of the alkyl substituents.
- substituents such as halogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, aryl, aryloxy, arylalkyl, cycloalkyl, alkylamido, alkanoylamino, oxo, acyl, arylcarbonylamino, amino, nitro, cyano, thiol and/or alkylthio and/or any of the alkyl substituents.
- alkenyl or “lower alkenyl” as used herein by itself or as part of another group refers to straight or branched chain radicals of 2 to 20 carbons, preferably 2 to 12 carbons, and more preferably 1 to 8 carbons in the normal chain, which include one or more double bonds in the normal chain, such as vinyl, 2-propenyl, 3-butenyl, 2-butenyl, 4-pentenyl, 3-pentenyl, 2-hexenyl, 3-hexenyl, 2-heptenyl, 3-heptenyl, 4-heptenyl, 3-octenyl, 3-nonenyl, 4-decenyl, 3-undecenyl, 4-dodecenyl, 4, 8, 12-tetradecatrienyl, and the like, and which may be optionally substituted with one or more substituents, namely, halogen, haloalkyl, alkyl, alkoxy, alkenyl, alkyny
- arylalkyl refers to alkyl, alkenyl and alkynyl groups as described above having an aryl substituent.
- Representative examples of arylalkyl include, but are not limited to, benzyl, 2- phenylethyl, 3-phenylpropyl, phenethyl, benzhydryl and naphthylmethyl and the like.
- alkyl groups as defined above have single bonds for attachment to other groups at two different carbon atoms, they are termed “alkylene” groups and may optionally be substituted as defined above for “alkyl”.
- halogen or "halo” as used herein alone or as part of another group refers to chlorine, bromine, fluorine, and iodine, with chlorine or fluorine being preferred.
- metal ion refers to alkali metal ions such as sodium, potassium or lithium and alkaline earth metal ions such as magnesium and calcium, as well as zinc and aluminum.
- aryl or “Aryl” as employed herein alone or as part of another group refers to monocyclic and bicyclic aromatic groups containing 6 to 10 carbons in the ring portion (such as phenyl or naphthyl including 1-naphthyl and 2-naphthyl) and may optionally include one to three additional rings fused to a carbocyclic ring or a heterocyclic ring (such as aryl, cycloalkyl, heteroaryl or cycloheteroalkyl rings for example
- substitutents such as halo, haloalkyl, alkyl, haloalkyl, alkoxy, haloalkoxy, alkenyl, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, alkynyl, cycloalkyl-alkyl , cycloheteroalkyl , cycloheteroalkylalkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, arylalkyl, aryloxy, aryloxyalkyl , arylalkoxy, alkoxycarbonyl , arylcarbonyl , arylalkenyl, aminocarbonylaryl, arylthio, arylsulfinyl, arylazo, heteroarylalkyl, heteroarylalkenyl, heteroarylheteroaryl, heteroaryloxy, hydroxy, nitro, cyano, amino, substituted amino wherein the amino includes 1 or
- heterocycle, hetero or heterocyclic ring represents an unsubstituted or substituted stable 5- to 7-membered monocyclic ring system which may be saturated or unsaturated, and which consists of carbon atoms and from one to four heteroatoms selected from N, 0 or S, and wherein the sulfur heteroatoms may optionally be oxidized.
- chain refers to cyclic groups in which the ring portion is composed solely of carbon atoms.
- prodrug esters as employed herein includes esters and carbonates formed by reacting one or more hydroxyls of compounds of formula I with alkyl, alkoxy, or aryl substituted acylating agents employing procedures known to those skilled in the art to generate acetates, pivalates, methylcarbonates, benzoates and the like.
- any compound that can be converted in vivo to provide the bioactive agent i.e., the compound of formula I
- a prodrug within the scope and spirit of the invention.
- Various forms of prodrugs are well known in the art. A comprehensive description of prodrugs and prodrug derivatives are described in: a.) The Practice of Medicinal Chemistry, Camille G.
- An administration of a therapeutic agent of the invention includes administration of a therapeutically effective amount of the agent of the invention.
- therapeutically effective amount refers to an amount of a therapeutic agent to treat or prevent a condition treatable by administration of a composition of the invention. That amount is the amount sufficient to exhibit a detectable therapeutic or preventative or ameliorative effect. The effect may include, for example, treatment or prevention of the conditions listed herein.
- the precise effective amount for a subject will depend upon the subject's size and health, the nature and extent of the condition being treated, recommendations of the treating physician, and the therapeutics or combination of therapeutics selected for administration. Thus, it is not useful to specify an exact effective amount in advance.
- other type of therapeutic agents includes, but is not limited to one or more antidiabetic agents (other than SGLT2 inhibitors of formula I), one or more anti-obesity agents, one or more anti-hypertensive agents, one or more anti-platelet agents, one or more anti-atherosclerotic agents and/or one or more lipid-lowering agents (including anti- atherosclerosis agents) .
- All stereoisomers of the compounds of the instant invention are contemplated, either in admixture or in pure or substantially pure form.
- the compounds of the present invention can have asymmetric centers at any of the carbon atoms including any one of the R substituents. Consequently, compounds of formula I can exist in enantiomeric or diastereomeric forms or in mixtures thereof.
- the processes for preparation can utilize racemates, enantiomers or diastereomers as starting materials . When diastereomeric or enantiomeric products are prepared, they can be separated by conventional methods for example, chromatographic or fractional crystallization.
- the compounds of formula I of the invention can be prepared as shown in the following reaction schemes and description thereof, as well as relevant published literature procedures that may be used by one skilled in the art . Exemplary reagents and procedures for these reactions appear hereinafter in the working Examples .
- R 1 is alkyl, alkenyl, or arylalkyl
- R 1 is hydrogen by sequential treatment with a base such as n-BuLi in a solvent such as THF followed by either commercially available or readily accessible alkylating agents such as compounds of formula VII, where A is either CH 2 , (CH 2 ) 2 , or allyl.
- the compounds of the present invention possess activity as inhibitors of the sodium dependent glucose transporters found in the intestine and kidney of mammals.
- the compounds of the invention are inhibitors of renal SGLT2 activity and therefore may be used in the treatment of diseases or disorders associated with SGLT2 activity.
- the compounds of the present invention can be administered to mammals, preferably humans, for the treatment of a variety of conditions and disorders, including, but not limited to, treating or delaying the progression or onset of diabetes (including Type I and Type II, impaired glucose tolerance, insulin resistance, and diabetic complications, such as nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy and cataracts) , hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, hypercholesterolemia, elevated blood levels of free fatty acids or glycerol, hyperlipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia, obesity, wound healing, tissue ischemia, atherosclerosis and hypertension.
- the compounds of the present invention may also be utilized to increase the blood levels of high density lipoprotein (HDL) .
- HDL high density lipoprotein
- compositions comprising, as an active ingredient, a therapeutically effective amount of at least one of the compounds of formula I, alone or in combination with a pharmaceutical carrier or diluent.
- compounds of the present invention can be used alone, in combination with other compounds of the invention, or in combination with one or more other therapeutic agent (s), e.g., an antidiabetic agent or other pharmaceutically active material.
- the compounds of the present invention may employed in combination with other inhibitors of SGLT2 activity or other suitable therapeutic agents useful in the treatment of the aforementioned disorders including: anti-diabetic agents; anti-hyperglycemic agents; hypolipidemic/lipid lowering agents; anti-obesity agents; anti-hypertensive agents and appetite supressants.
- Suitable anti-diabetic agents for use in combination with the compounds of the present invention include biguanides (e.g., metformin or phenformin) , glucosidase inhibitors (e.g,. acarbose or miglitol) , insulins (including insulin secretagogues or insulin sensitizers) , meglitinides (e.g., repaglinide) , sulfonylureas (e.g., glimepiride, glyburide, gliclazide, chlorpropamide and glipizide) , biguanide/glyburide combinations (e.g., Glucovance®) , thiazolidinediones (e.g., troglitazone, rosiglitazone and pioglitazone) , PPAR-alpha agonists, PPAR-gamma agonists, PPAR alpha/gamma dual agonists, glyco
- Glaxo-Welcome's GL-262570 englitazone (CP- 68722, Pfizer) or darglitazone (CP-86325, Pfizer, isaglitazone (MIT/J&J) , JTT-501 (JPNT/P&U) , L-895645 (Merck), R-119702 (Sankyo/WL) , NN-2344 (Dr. Reddy/NN) , or YM-440 (Yamanouchi) .
- Suitable PPAR alpha/gamma dual agonists include AR-H039242 (Astra/Zeneca) , GW-409544 (Glaxo-Wellcome) , KRP297 (Kyorin Merck) as well as those disclosed by Murakami et al, "A Novel Insulin Sensitizer Acts As a Coligand for Peroxisome Proliferation - Activated Receptor Alpha (PPAR alpha) and PPAR gamma. Effect on PPAR alpha Activation on Abnormal Lipid Metabolism in Liver of Zucker Fatty Rats", Diabetes 47, 1841-1847 (1998), and in U.S. application Serial No. 09/644,598, filed September 18, 2000, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein by reference, employing dosages as set out therein, which compounds designated as preferred are preferred for use herein.
- Suitable aP2 inhibitors include those disclosed in U.S. application Serial No. 09/391,053, filed September 7, 1999, and in U.S. application Serial No. 09/519,079, filed March 6, 2000, employing dosages as set out herein.
- Suitable DPP4 inhibitors include those disclosed in WO99/38501, W099/46272, W099/67279 (PROBIODRUG) , W099/67278 (PROBIODRUG), W099/61431 (PROBIODRUG), NVP- DPP728A (l-[ [ [2- [ (5-cyanopyridin-2- yl) amino] ethyl] amino] acetyl] -2-cyano- (S) -pyrrolidine) (Novartis) as disclosed by Hughes et al, Biochemistry, 38(36), 11597-11603, 1999, TSL-225 ( tryptophyl-1, 2 , 3 , 4- tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (disclosed by Yamada et al, Bioorg.
- Suitable meglitinides include nateglinide (Novartis) or KAD1229 (PF/Kissei) .
- glucagon-like peptide-1 such as GLP-K1-36) amide, GLP-K7-36) amide, GLP-l(7-37) (as disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 5,614,492 to Habener) , as well as AC2993 (Amylen) and LY-315902 (Lilly) .
- hypolipidemic/lipid lowering agents for use in combination with the compounds of the present invention include one or more MTP inhibitors, HMG CoA reductase inhibitors, squalene synthetase inhibitors, fibric acid derivatives, ACAT inhibitors, lipoxygenase inhibitors, cholesterol absorption inhibitors, ileal NaVbile acid cotransporter inhibitors, upregulators of LDL receptor activity, bile acid sequestrants, cholesterol ester transfer protein inhibitors (e.g., CP- 529414 (Pfizer) ) and/or nicotinic acid and derivatives thereof .
- MTP inhibitors HMG CoA reductase inhibitors
- squalene synthetase inhibitors fibric acid derivatives
- ACAT inhibitors lipoxygenase inhibitors
- cholesterol absorption inhibitors ileal NaVbile acid cotransporter inhibitors
- upregulators of LDL receptor activity e.g., CP- 529414 (Pfizer
- MTP inhibitors which may be employed as described above include those disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 5,595,872, U.S. Patent No. 5,739,135, U.S. Patent No. 5,712,279, U.S. Patent No. 5,760,246, U.S. Patent No. 5,827,875, U.S. Patent No. 5,885,983 and U.S. Patent No. 5,962,440.
- the HMG CoA reductase inhibitors which may be employed in combination with one or more compounds of formula I include mevastatin and related compounds, as disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 3,983,140, lovastatin (mevinolin) and related compounds, as disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 4,231,938, pravastatin and related compounds, such as disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 4,346,227, simvastatin and related compounds, as disclosed in U.S. Patent Nos. 4,448,784 and 4,450,171.
- Other HMG CoA reductase inhibitors which may be employed herein include, but are not limited to, fluvastatin, disclosed in U.S. Patent No.
- hypolipidemic agents are pravastatin, lovastatin, simvastatin, atorvastatin, fluvastatin, cerivastatin, atavastatin and ZD-4522.
- phosphinic acid compounds useful in inhibiting HMG CoA reductase such as those disclosed in GB 2205837, are suitable for use in combination with the compounds of the present invention.
- the squalene synthetase inhibitors suitable for use herein include, but are not limited to, ⁇ -phosphono- sulfonates disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 5,712,396, those disclosed by Biller et al, J. Med. Chem., 1988, Vol. 31, No. 10, pp 1869-1871, including isoprenoid (phosphinyl- methyl )phosphonates, as well as other known squalene synthetase inhibitors, for example, as disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 4,871,721 and 4,924,024 and in Biller, S.A., Neuenschwander , K. , Ponpipom, M.M. , and Poulter, CD., Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2, 1-40 (1996).
- squalene synthetase inhibitors suitable for use herein include the terpenoid pyrophosphates disclosed by P. Ortiz de Montellano et al , J. Med. Chem., 1977, 2 ⁇ , 243-249, the farnesyl diphosphate analog ⁇ and presqualene pyrophosphate (PSQ- PP) analogs as disclosed by Corey and Volante, J. Am. Chem. Soc, 1976, 98, 1291-1293, phosphinylphosphonates reported by McClard, R.W.
- fibric acid derivatives which may be employed in combination with one or more compounds of formula I include fenofibrate, gemfibrozil, clofibrate, bezafibrate, ciprofibrate, clinofibrate and the like, probucol, and related compounds, as disclosed in U.S. Patent No.
- bile acid sequestrants such as cholestyramine, colestipol and DEAE-Sephadex (Secholex®, policexide®) , as well as lipostabil (Rhone-Poulenc) , Eisai E-5050 (an N-substituted ethanolamine derivative) , imanixil (HOE-402), tetrahydrolipstatin (THL) , istigmastanylphos-phorylcholine (SPC, Roche) , aminocyclodextrin (Tanabe Seiyoku) , Ajinomoto AJ-814
- the ACAT inhibitor which may be employed in combination with one or more compounds of formula I include those disclosed in Drugs of the Future 24, 9-15 (1999), (Avasimibe); "The ACAT inhibitor, Cl-1011 is effective in the prevention and regression of aortic fatty streak area in hamsters", Nicolosi et al, Atherosclerosis (Shannon, Irel) . (1998), 137(1), 77-85; "The pharmacological profile of FCE 27677: a novel ACAT inhibitor with potent hypolipidemic activity mediated by selective suppression of the hepatic secretion of ApoBlOO-containing lipoprotein", Ghiselli, Giancarlo, Cardiovasc. Drug Rev.
- Inhibitors of acyl-CoA cholesterol O-acyl transferase (ACAT) as hypocholesterolemic agents. 6. The first water-soluble ACAT inhibitor with lipid-regulating activity. Inhibitors of acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT). 7. Development of a series of substituted N-phenyl-N' - [ (1- phenylcyclopentyl) methyl] ureas with enhanced hypocholesterolemic activity", Stout et al, Chemtracts: Org. Chem. (1995), 8(6), 359-62, or TS-962 (Taisho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd).
- the hypolipidemic agent may be an upregulator of LD2 receptor activity, such as MD-700 (Taisho
- Suitable cholesterol absorption inhibitor for use in combination with the compounds of the invention include SCH48461 (Schering-Plough) , as well as those disclosed in Atherosclerosis 115, 45-63 (1995) and J. Med. Chem. 41, 973 (1998).
- the lipoxygenase inhibitors which may be employed in combination with one or more compounds of formula I include 15-lipoxygenase (15-LO) inhibitors, such as benzimidazole derivatives, as disclosed in WO 97/12615, 15-LO inhibitors, as disclosed in WO 97/12613, isothiazolones, as disclosed in WO 96/38144, and 15-LO inhibitors, as disclosed by Sendobry et al "Attenuation of diet-induced atherosclerosis in rabbits with a highly selective 15-lipoxygenase inhibitor lacking significant antioxidant properties", Brit. J. Pharmacology (1997) 120, 1199-1206, and Cornicelli et al, "15-Lipoxygenase and its Inhibition: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Vascular Disease", Current Pharmaceutical Design, 1999
- Suitable anti-hypertensive agents for use in combination with the compounds of the present invention include beta adrenergic blockers, calcium channel blockers (L-type and T-type; e.g. diltiazem, verapamil, nifedipine, amlodipine and mybefradil) , diuretics (e.g., chlorothiazide, hydrochlorothiazide, flumethiazide, hydroflumethiazide, bendroflumethiazide, methylchlorothiazide, trichloromethiazide, polythiazide, benzthiazide, ethacrynic acid tricrynafen, chlorthalidone, furosemide, musolimine, bumetanide, triamtrenene, amiloride, spironolactone) , renin inhibitors, ACE inhibitors (e.g., captopril, zofenopril,
- Dual ET/AII antagonist e.g., compounds disclosed in WO 00/01389
- neutral endopeptidase (NEP) inhibitors neutral endopeptidase (NEP) inhibitors
- vasopepsidase inhibitors dual NEP-ACE inhibitors
- omapatrilat and gemopatrilat e.g., omapatrilat and gemopatrilat
- Suitable anti-obesity agents for use in combination with the compounds of the present invention include a beta 3 adrenergic agonist, a lipase inhibitor, a serotonin (and dopamine) reuptake inhibitor, a thyroid receptor beta drug and/or an anorectic agent.
- the beta 3 adrenergic agonists which may be optionally employed in combination with compounds of the present invention include AJ9677 (Takeda/Dainippon) , L750355 (Merck), or CP331648 (Pfizer,) or other known beta 3 agonists, as disclosed in U.S. Patent Nos.
- lipase inhibitors which may be optionally employed in combination with compounds of the present invention include orlistat or ATL-962 (Alizyme) , with orlistat being preferred.
- the serotonin (and dopoamine) reuptake inhibitor which may be optionally employed in combination with a compound of formula I may be sibutramine, topiramate (Johnson & Johnson) or axokine (Regeneron) , with sibutramine and topiramate being preferred.
- the anorectic agent which may be optionally employed in combination with compounds of the present invention include dexamphetamine, phentermine, phenylpropanolamine or mazindol, with dexamphetamine being preferred.
- the compounds of formula I will be employed in a weight ratio to biguanide within the range from about 0.01:1 to about 100:1, preferably from about 0.1:1 to about 5:1.
- the compounds of formula I will be employed in a weight ratio to the glucosidase inhibitor within the range from about 0.01:1 to about 100:1, preferably from about 0.5:1 to about 50:1.
- the compounds of formula I will be employed in a weight ratio to the sulfonyl urea in the range from about 0.01:1 to about 100:1, preferably from about 0.2:1 to about 10:1.
- the compounds of formula I will be employed in a weight ratio to the thiazolidinedione in an amount within the range from about 0.01:1 to about 100:1, preferably from about 0.2:1 to about 10:1.
- the thiazolidinedione anti-diabetic agent may be employed in amounts within the range from about 0.01 to about 2000 mg/day which may be administered in single or divided doses one to four times per day.
- the sulfonyl urea and thiazolidinedione may be incorporated in a single tablet with the compounds of formula I in amounts of less than about 150 mg.
- metformin or salt thereof may be employed in amounts within the range from about 500 to about 2000 mg per day which may be administered in single or divided doses one to four times daily.
- GLP-1 peptides may be administered in oral buccal formulations, by nasal administration or parenterally as described in U.S. Patent Nos. 5,346,701 (TheraTech) , 5,614,492 and 5,631,224 which are incorporated herein by reference.
- the SGLT2 inhibitor of formula I will be employed in a weight ratio to the meglitinide, PPAR-gamma agonist, PPAR-alpha/gamma dual agonist, aP2 inhibitor or DPP4 inhibitor within the range from about 0.01:1 to about 100:1, preferably from about 0.2:1 to about 10:1.
- the compounds of formula I of the invention will be generally be employed in a weight ratio to the hypolipidemic agent (were present) , within the range from about 500:1 to about 1:500, preferably from about 100:1 to about 1:100.
- the MTP inhibitor for oral administration, a satisfactory result may be obtained employing the MTP inhibitor in an amount within the range of from about 0.01 mg/kg to about 500 mg and preferably from about 0.1 mg to about 100 mg, one to four times daily.
- a preferred oral dosage form such as tablets or capsules, will contain the MTP inhibitor in an amount of from about 1 to about 500 mg, preferably from about 2 to about 400 mg, and more preferably from about 5 to about 250 mg, one to four times daily.
- an HMG CoA reductase inhibitor in an amount within the range of from about 1 to 2000 mg, and preferably from about 4 to about 200 mg.
- a preferred oral dosage form, such as tablets or capsules, will contain the HMG CoA reductase inhibitor in an amount from about 0.1 to about 100 mg, preferably from about 5 to about 80 mg, and more preferably from about 10 to about 40 mg.
- the squalene synthetase inhibitor may be employed in dosages in an amount within the range of from about 10 mg to about 2000 mg and preferably from about 25 mg to about 200 mg.
- a preferred oral dosage form, such as tablets or capsules will contain the squalene synthetase inhibitor in an amount of from about 10 to about 500 mg, preferably from about 25 to about 200 mg.
- the compounds of the formula I can be administered for any of the uses described herein by any suitable means, for example, orally, such as in the form of tablets, capsules, granules or powders; sublingually; bucally; parenterally, such as by subcutaneous, intravenous, intramuscular, or intrasternal injection or infusion techniques (e.g., as sterile injectable aqueous or non-aqueous solutions or suspensions) ; nasally, including administration to the nasal membranes, such as by inhalation spray; topically, such as in the form of a cream or ointment; or rectally such as in the form of suppositories; in dosage unit formulations containing non-toxic, pharmaceutically acceptable vehicles or diluents .
- suitable means for example, orally, such as in the form of tablets, capsules, granules or powders; sublingually; bucally; parenterally, such as by subcutaneous, intravenous, intramuscular, or intrasternal injection or infusion techniques
- a pharmaceutical composition will be employed containing one or more of the compounds of formula I, with or without other antidiabetic agent (s) and/or antihyperlipidemic agent (s) and/or other type therapeutic agents in association with a pharmaceutical vehicle or diluent.
- the pharmaceutical composition can be formulated employing conventional solid or liquid vehicles or diluents and pharmaceutical additives of a type appropriate to the mode of desired administration, such as pharmaceutically acceptable carriers, excipients, binders and the like.
- the compounds can be administered to mammalian species including humans, monkeys, dogs, etc.
- Typical solid formulations will contain from about 10 to about 500 mg of a compound of formula I.
- the dose for adults is preferably between 10 and 2,000 mg per day, which can be administered in a single dose or in the form of individual doses from 1-4 times per day.
- a typical injectable preparation may be produced by aseptically placing 250 mg of compounds of formula I into a vial, aseptically freeze-drying and sealing. For use, the contents of the vial are mixed with 2 mL of physiological saline, to produce an injectable preparation.
- the mRNA sequence for human SGLT2 (GenBank #M95549) was cloned by reverse-transcription and amplification from human kidney mRNA, using standard molecular biology techniques.
- the cDNA sequence was stably transfected into CHO cells, and clones were assayed for SGLT2 activity essentially as described in Ryan MJ, Johnson G, Kirk J, Fuerstenberg SM, Zager RA, Torok-Storb B, "HK-2 : an immortalized proximal tubule epithelial cell line from normal adult human kidney", Kidney International 45: 48-57 (1994) (hereinafter "Ryan et al.") Evaluation of inhibition of SGLT2 activity in a clonally selected cell line was performed essentially as described in Ryan et al., with the following modifications.
- Cells were grown in 96-well plates for 2- 4 days to 75,000 or 30,000 cells per well in F-12 nutrient mixture (Ham's F-12), 10% fetal bovine serum, 300 ug/ml Geneticin and penicillin-streptomycin. At confluence, cells were washed twice with 10 mM Hepes/Tris, pH 7.4, 137 mM N-methyl-D-glucamine, 5.4 mM KC1, 2.8 mM CaCl 2 , 1.2 mM MgS0 4 .
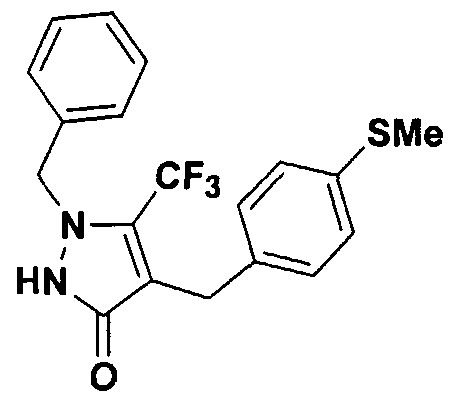
- ethyl 2- (4-phenylmethyl) -3-oxo-butanoate was prepared by condensation of ethyl acetoacetate and benzyl bromide and converted to 1, 2-dihydro-4- [ [4-phenyl] methyl ] -5-methyl- 3H-pyrazol-3-one which was subsequently converted to the title glucoside using the procedure as described in Example lc.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP02761586A EP1432720A1 (en) | 2001-09-05 | 2002-09-05 | O-pyrazole glucoside sglt2 inhibitors and method of use |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US31728001P | 2001-09-05 | 2001-09-05 | |
| US60/317,280 | 2001-09-05 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2003020737A1 true WO2003020737A1 (en) | 2003-03-13 |
Family
ID=23232943
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US2002/028480 WO2003020737A1 (en) | 2001-09-05 | 2002-09-05 | O-pyrazole glucoside sglt2 inhibitors and method of use |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20030087843A1 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP1432720A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2003020737A1 (en) |
Cited By (71)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2004031203A1 (en) * | 2002-10-04 | 2004-04-15 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Pyrazole derivative, medicinal composition containing the same, medicinal use thereof and intermediate in producing the same |
| WO2005012321A1 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2005-02-10 | Tanabe Seiyaku Co., Ltd. | Novel compounds |
| US6908905B2 (en) | 2001-04-27 | 2005-06-21 | Ajinomoto Co., Inc. | N-substituted pyrazole-O-glycoside derivatives and therapeutic agent for diabetes containing the same |
| WO2006054629A1 (en) * | 2004-11-18 | 2006-05-26 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | 1-SUBSTITUTED-3-β-D-GLUCOPYRANOSYLATED NITROGENOUS HETERO- CYCLIC COMPOUNDS AND MEDICINES CONTAINING THE SAME |
| US7056892B2 (en) | 1999-08-31 | 2006-06-06 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives, medicinal compositions containing the same and intermediates in the production thereof |
| US7084123B2 (en) | 2000-12-28 | 2006-08-01 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives and use thereof in medicines |
| US7084124B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2006-08-01 | Janssen Pharmaceutica, N.V. | Substituted indazole-O-glucosides |
| US7094764B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2006-08-22 | Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. | Substituted benzimidazole-, Benztriazole-, and benzimidazolone-O-glucosides |
| US7094763B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2006-08-22 | Janssen Pharaceutica, N.V. | Substituted fused heterocyclic C-glycosides |
| WO2006098413A1 (en) * | 2005-03-17 | 2006-09-21 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Process for production of glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivative |
| US7129220B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2006-10-31 | Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V | Substituted indole-O-glucosides |
| JP2007503413A (en) * | 2003-08-26 | 2007-02-22 | ベーリンガー インゲルハイム インターナショナル ゲゼルシャフト ミット ベシュレンクテル ハフツング | Glucopyranosyloxy-pyrazole, pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds, their use and methods for their preparation |
| WO2007128761A2 (en) | 2006-05-04 | 2007-11-15 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Uses of dpp-iv inhibitors |
| US7375090B2 (en) | 2003-08-26 | 2008-05-20 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Glucopyranosyloxy-pyrazoles, pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds, the use thereof and processed for the preparation thereof |
| WO2008087198A1 (en) * | 2007-01-19 | 2008-07-24 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition comprising a pyrazole-o-glucoside derivative |
| WO2008090209A2 (en) * | 2007-01-26 | 2008-07-31 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Use of glucopyranosyloxy- pyrazoles for preventing and treating neurodegenerative disorders |
| US7524822B2 (en) | 2006-01-11 | 2009-04-28 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Crystalline form of 1′-(1-methylethyl)-4′-[(2-fluoro-4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-5′-methyl-1H-pyrazol-3′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, a method for its preparation and the use thereof for preparing medicaments |
| WO2009138195A2 (en) * | 2008-05-16 | 2009-11-19 | Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland Gmbh | Use of thiophene glycoside derivatives for producing medicaments for treatment of hypertension |
| US7666845B2 (en) | 2006-12-04 | 2010-02-23 | Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. | Compounds having inhibitory activity against sodium-dependent glucose transporter |
| US7767651B2 (en) | 2005-01-28 | 2010-08-03 | Chugai Seiyaku Kabushiki Kaisha | Spiroketal derivatives and use thereof as diabetic medicine |
| US7838499B2 (en) | 2007-08-23 | 2010-11-23 | Theracos, Inc. | Benzylbenzene derivatives and methods of use |
| US7851617B2 (en) | 2006-07-27 | 2010-12-14 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Indole derivatives |
| EP2308841A2 (en) | 2006-09-29 | 2011-04-13 | Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Phlorizin analogs as SGLT2 inhibitors |
| WO2011048112A1 (en) | 2009-10-20 | 2011-04-28 | Novartis Ag | Glycoside derivatives and uses thereof |
| US7935674B2 (en) | 2005-01-31 | 2011-05-03 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Indole derivatives |
| US7943788B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2011-05-17 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Glucopyranoside compound |
| US7943748B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2011-05-17 | Chugai Seiyaku Kabushiki Kaisha | Glucitol derivative, prodrug thereof and salt thereof, and therapeutic agent containing the same for diabetes |
| US7943582B2 (en) | 2006-12-04 | 2011-05-17 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Crystalline form of 1-(β-D-glucopyransoyl)-4-methyl-3-[5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2- thienylmethyl]benzene hemihydrate |
| US7956041B2 (en) | 2002-04-26 | 2011-06-07 | Ajinomoto Co., Inc. | Prophylactic and therapeutic agent of diabetes mellitus |
| WO2011070592A2 (en) | 2009-12-09 | 2011-06-16 | Panacea Biotec Ltd. | Novel sugar derivatives |
| WO2011107494A1 (en) | 2010-03-03 | 2011-09-09 | Sanofi | Novel aromatic glycoside derivatives, medicaments containing said compounds, and the use thereof |
| US8048897B2 (en) | 2004-07-26 | 2011-11-01 | Chugai Seiyaku Kabushiki Kaisha | Cyclohexane derivative, prodrug thereof and salt thereof, and therapeutic agent containing the same for diabetes |
| JP4888840B2 (en) * | 2005-07-22 | 2012-02-29 | 味の素株式会社 | Process for the preparation of pyrazole-O-glycoside derivatives and novel intermediates of said process |
| WO2012025857A1 (en) | 2010-08-23 | 2012-03-01 | Hetero Research Foundation | Cycloalkyl methoxybenzyl phenyl pyran derivatives as sodium dependent glucose co transporter (sglt2) inhibitors |
| US8129434B2 (en) | 2007-12-13 | 2012-03-06 | Theracos, Inc. | Benzylphenyl cyclohexane derivatives and methods of use |
| US8283454B2 (en) | 2008-08-22 | 2012-10-09 | Theracos, Inc. | Processes for the preparation of SGLT2 inhibitors |
| WO2012140597A1 (en) | 2011-04-14 | 2012-10-18 | Novartis Ag | Glycoside derivatives and their uses for the treatment of diabetes |
| WO2012140596A1 (en) | 2011-04-14 | 2012-10-18 | Novartis Ag | Glycoside derivatives and uses thereof |
| US8551957B2 (en) | 2007-08-16 | 2013-10-08 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition comprising a glucopyranosyl-substituted benzene derivate |
| US8557782B2 (en) | 2006-05-03 | 2013-10-15 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Glucopyranosyl-substituted benzonitrile derivatives, pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds, their use and process for their manufacture |
| US8652527B1 (en) | 2013-03-13 | 2014-02-18 | Upsher-Smith Laboratories, Inc | Extended-release topiramate capsules |
| US8785403B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2014-07-22 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Glucopyranoside compound |
| US8802842B2 (en) | 2009-09-30 | 2014-08-12 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Method for the preparation of a crystalline form |
| EP2774619A1 (en) | 2013-03-04 | 2014-09-10 | BioActive Food GmbH | Composition for the treatment of hyperglycaemic diseases |
| US8853385B2 (en) | 2008-01-17 | 2014-10-07 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Combination therapy comprising SGLT inhibitors and DPP4 inhibitors |
| US8987323B2 (en) | 2010-06-12 | 2015-03-24 | Theracos, Inc. | Crystalline form of benzylbenzene SGLT2 inhibitor |
| US9024010B2 (en) | 2009-09-30 | 2015-05-05 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Processes for preparing of glucopyranosyl-substituted benzyl-benzene derivatives |
| US9024009B2 (en) | 2007-09-10 | 2015-05-05 | Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. | Process for the preparation of compounds useful as inhibitors of SGLT |
| US9035044B2 (en) | 2011-05-09 | 2015-05-19 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | L-proline and citric acid co-crystals of (2S, 3R, 4R, 5S,6R)-2-(3-((5-(4-fluorophenyl)thiopen-2-yl)methyl)4-methylphenyl)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol |
| US9056850B2 (en) | 2008-10-17 | 2015-06-16 | Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. | Process for the preparation of compounds useful as inhibitors of SGLT |
| US9101545B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2015-08-11 | Upsher-Smith Laboratories, Inc. | Extended-release topiramate capsules |
| US9127034B2 (en) | 2005-05-10 | 2015-09-08 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Processes for preparing of glucopyranosyl-substituted benzyl-benzene derivates and intermediates therein |
| US9174971B2 (en) | 2009-10-14 | 2015-11-03 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Process for the preparation of compounds useful as inhibitors of SGLT2 |
| EP2944311A1 (en) | 2014-05-16 | 2015-11-18 | BioActive Food GmbH | Combination of biologically active substances for treating hyperglycemic diseases |
| US9193751B2 (en) | 2012-04-10 | 2015-11-24 | Theracos, Inc. | Process for the preparation of benzylbenzene SGLT2 inhibitors |
| US9192617B2 (en) | 2012-03-20 | 2015-11-24 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| CN105403647A (en) * | 2015-10-09 | 2016-03-16 | 北京万全德众医药生物技术有限公司 | Method for separating and determining Clinofibrate intermediate and related substances by using liquid chromatography |
| US9308204B2 (en) | 2009-11-02 | 2016-04-12 | Pfizer Inc. | Dioxa-bicyclo[3.2.1]octane-2,3,4-triol derivatives |
| US9464043B2 (en) | 2013-10-12 | 2016-10-11 | Theracos Sub, Llc | Preparation of hydroxy-benzylbenzene derivatives |
| US9555001B2 (en) | 2012-03-07 | 2017-01-31 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition and uses thereof |
| US9949997B2 (en) | 2013-04-05 | 2018-04-24 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US9949998B2 (en) | 2013-04-05 | 2018-04-24 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US20180185291A1 (en) | 2011-03-07 | 2018-07-05 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical compositions |
| US10406172B2 (en) | 2009-02-13 | 2019-09-10 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US10544135B2 (en) | 2011-04-13 | 2020-01-28 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Process for the preparation of compounds useful as inhibitors of SGLT2 |
| US10610489B2 (en) | 2009-10-02 | 2020-04-07 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, pharmaceutical dosage form, process for their preparation, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US10617668B2 (en) | 2010-05-11 | 2020-04-14 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Pharmaceutical formulations |
| US11207337B2 (en) | 2015-09-15 | 2021-12-28 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Co-therapy comprising canagliflozin and phentermine for the treatment of obesity and obesity related disorders |
| US11576894B2 (en) | 2009-07-08 | 2023-02-14 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Combination therapy for the treatment of diabetes |
| US11666590B2 (en) | 2013-04-18 | 2023-06-06 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US11813275B2 (en) | 2013-04-05 | 2023-11-14 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7087579B2 (en) * | 2001-02-26 | 2006-08-08 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives and medicinal use thereof |
| ATE493973T1 (en) | 2004-06-04 | 2011-01-15 | Teva Pharma | PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION CONTAINING IRBESARTAN |
| JP2006100633A (en) * | 2004-09-30 | 2006-04-13 | Toyoda Gosei Co Ltd | Led lighting device |
| AR053329A1 (en) * | 2005-01-31 | 2007-05-02 | Tanabe Seiyaku Co | INDOL DERIVATIVES USEFUL AS INHIBITORS OF GLUCOSE CONVEYORS DEPENDENT ON SODIUM (SGLT) |
| UA91546C2 (en) * | 2005-05-03 | 2010-08-10 | Бьорінгер Інгельхайм Інтернаціональ Гмбх | Crystalline form of 1-chloro-4-(я-d-glucopyranos-1-yl)-2-[4-((s)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy)-benzyl]-benzene, a method for its preparation and the use thereof for preparing medicaments |
| WO2008109591A1 (en) * | 2007-03-08 | 2008-09-12 | Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Phlorizin analogs as inhibitors of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 |
| CN101445528B (en) * | 2008-12-25 | 2011-06-15 | 天津药物研究院 | Sulpho-glucosan derivative and preparation method and application thereof |
| KR101921934B1 (en) * | 2009-02-13 | 2018-11-26 | 베링거 인겔하임 인터내셔날 게엠베하 | Pharmaceutical composition comprising glucopyranosyl diphenylmethane derivatives, pharmaceutical dosage form thereof, process for their preparation and uses thereof for improved glycemic control in a patient |
| UY32427A (en) | 2009-02-13 | 2010-09-30 | Boheringer Ingelheim Internat Gmbh | PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION, PHARMACEUTICAL FORM, PROCEDURE FOR PREPARATION, METHODS OF TREATMENT AND USES OF THE SAME |
| PT2451797E (en) | 2009-07-10 | 2013-06-25 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Crystallisation process for 1-(ss-d-glucopyranosyl)-4-methyl-3-[5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-thienylmethyl]benzene |
| US20130035281A1 (en) | 2011-02-09 | 2013-02-07 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5264451A (en) * | 1992-04-07 | 1993-11-23 | American Home Products Corporation | Process for treating hyperglycemia using trifluoromethyl substituted 3H-pyrazol-3-ones |
| US5274111A (en) * | 1992-04-07 | 1993-12-28 | American Home Products Corporation | Trifluoromethyl substituted 1H-pyrazoles and derivatives thereof |
| WO2001016147A1 (en) * | 1999-08-31 | 2001-03-08 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives, medicinal compositions containing the same and intermediates in the production thereof |
| WO2002036602A1 (en) * | 2000-11-02 | 2002-05-10 | Ajinomoto Co., Inc. | Novel pyrazole derivatives and diabetes remedies containing the same |
| WO2002053573A1 (en) * | 2000-12-28 | 2002-07-11 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives and use thereof in medicines |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6515117B2 (en) * | 1999-10-12 | 2003-02-04 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | C-aryl glucoside SGLT2 inhibitors and method |
| US7087579B2 (en) * | 2001-02-26 | 2006-08-08 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives and medicinal use thereof |
-
2002
- 2002-09-05 EP EP02761586A patent/EP1432720A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2002-09-05 WO PCT/US2002/028480 patent/WO2003020737A1/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2002-09-05 US US10/235,336 patent/US20030087843A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5264451A (en) * | 1992-04-07 | 1993-11-23 | American Home Products Corporation | Process for treating hyperglycemia using trifluoromethyl substituted 3H-pyrazol-3-ones |
| US5274111A (en) * | 1992-04-07 | 1993-12-28 | American Home Products Corporation | Trifluoromethyl substituted 1H-pyrazoles and derivatives thereof |
| WO2001016147A1 (en) * | 1999-08-31 | 2001-03-08 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives, medicinal compositions containing the same and intermediates in the production thereof |
| EP1213296A1 (en) * | 1999-08-31 | 2002-06-12 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives, medicinal compositions containing the same and intermediates in the production thereof |
| WO2002036602A1 (en) * | 2000-11-02 | 2002-05-10 | Ajinomoto Co., Inc. | Novel pyrazole derivatives and diabetes remedies containing the same |
| WO2002053573A1 (en) * | 2000-12-28 | 2002-07-11 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives and use thereof in medicines |
Cited By (127)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7056892B2 (en) | 1999-08-31 | 2006-06-06 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives, medicinal compositions containing the same and intermediates in the production thereof |
| US7115575B2 (en) | 1999-08-31 | 2006-10-03 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives, medicinal compositions containing the same and intermediates in the production thereof |
| US7393838B2 (en) | 2000-12-28 | 2008-07-01 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives and use thereof in medicines |
| US7084123B2 (en) | 2000-12-28 | 2006-08-01 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives and use thereof in medicines |
| US7989424B2 (en) | 2000-12-28 | 2011-08-02 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives and use thereof in medicines |
| US7465713B2 (en) | 2000-12-28 | 2008-12-16 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives and use thereof in medicines |
| US7429568B2 (en) | 2000-12-28 | 2008-09-30 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivatives and use thereof in medicines |
| US6908905B2 (en) | 2001-04-27 | 2005-06-21 | Ajinomoto Co., Inc. | N-substituted pyrazole-O-glycoside derivatives and therapeutic agent for diabetes containing the same |
| US7956041B2 (en) | 2002-04-26 | 2011-06-07 | Ajinomoto Co., Inc. | Prophylactic and therapeutic agent of diabetes mellitus |
| US7888487B2 (en) | 2002-10-04 | 2011-02-15 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Pyrazole derivative, medicinal composition containing the same, medicinal use thereof and intermediate in producing the same |
| WO2004031203A1 (en) * | 2002-10-04 | 2004-04-15 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Pyrazole derivative, medicinal composition containing the same, medicinal use thereof and intermediate in producing the same |
| US7576063B2 (en) | 2002-10-04 | 2009-08-18 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Pyrazole derivative, medicinal composition containing the same, medicinal use thereof and intermediate in producing the same |
| US7521430B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2009-04-21 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | N-glucoside compounds having an inhibitory activity against sodium-dependent glucose transporter |
| US7511020B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2009-03-31 | Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. | Substituted benzimidazole-, benztriazole-, and benzimidazolone-O-glucosides |
| US7816331B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2010-10-19 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Substituted indazole-O-glucosides |
| US7816328B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2010-10-19 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Substituted fused heterocyclic C-glycosides |
| US7816330B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2010-10-19 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Substituted benzimidazole-, benztriazole-, and benzimidazolone-O-glucosides |
| US8222219B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2012-07-17 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Glucopyranoside compound |
| US8202984B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2012-06-19 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Glucopyranoside compound |
| US7129220B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2006-10-31 | Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V | Substituted indole-O-glucosides |
| WO2005012321A1 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2005-02-10 | Tanabe Seiyaku Co., Ltd. | Novel compounds |
| US7943788B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2011-05-17 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Glucopyranoside compound |
| EA011025B1 (en) * | 2003-08-01 | 2008-12-30 | Мицубиси Танабе Фарма Корпорейшн | Novel compounds |
| US7482330B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2009-01-27 | Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. | Substituted fused heterocyclic C-glycosides |
| US7511021B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2009-03-31 | Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. | Substituted indazole-O-glucosides |
| US8785403B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2014-07-22 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Glucopyranoside compound |
| US7511022B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2009-03-31 | Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. | Substituted indole-O-glucosides |
| US7820630B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2010-10-26 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Substituted indole-O-glucosides |
| US7094763B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2006-08-22 | Janssen Pharaceutica, N.V. | Substituted fused heterocyclic C-glycosides |
| US7094764B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2006-08-22 | Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. | Substituted benzimidazole-, Benztriazole-, and benzimidazolone-O-glucosides |
| US7084124B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2006-08-01 | Janssen Pharmaceutica, N.V. | Substituted indazole-O-glucosides |
| JP2007503413A (en) * | 2003-08-26 | 2007-02-22 | ベーリンガー インゲルハイム インターナショナル ゲゼルシャフト ミット ベシュレンクテル ハフツング | Glucopyranosyloxy-pyrazole, pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds, their use and methods for their preparation |
| US7375090B2 (en) | 2003-08-26 | 2008-05-20 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Glucopyranosyloxy-pyrazoles, pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds, the use thereof and processed for the preparation thereof |
| US8048897B2 (en) | 2004-07-26 | 2011-11-01 | Chugai Seiyaku Kabushiki Kaisha | Cyclohexane derivative, prodrug thereof and salt thereof, and therapeutic agent containing the same for diabetes |
| US7943748B2 (en) | 2004-07-27 | 2011-05-17 | Chugai Seiyaku Kabushiki Kaisha | Glucitol derivative, prodrug thereof and salt thereof, and therapeutic agent containing the same for diabetes |
| WO2006054629A1 (en) * | 2004-11-18 | 2006-05-26 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | 1-SUBSTITUTED-3-β-D-GLUCOPYRANOSYLATED NITROGENOUS HETERO- CYCLIC COMPOUNDS AND MEDICINES CONTAINING THE SAME |
| JP5086643B2 (en) * | 2004-11-18 | 2012-11-28 | キッセイ薬品工業株式会社 | 1-Substituted-3- (β-D-glycopyranosyl) nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound and medicament containing the same |
| US7750145B2 (en) | 2004-11-18 | 2010-07-06 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | 1-substituted-3-β-D-glucopyranosylated nitrogenous hetero-cyclic compounds and medicines containing the same |
| JPWO2006054629A1 (en) * | 2004-11-18 | 2008-05-29 | キッセイ薬品工業株式会社 | 1-Substituted-3- (β-D-glycopyranosyl) nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound and medicament containing the same |
| US7767651B2 (en) | 2005-01-28 | 2010-08-03 | Chugai Seiyaku Kabushiki Kaisha | Spiroketal derivatives and use thereof as diabetic medicine |
| US7935674B2 (en) | 2005-01-31 | 2011-05-03 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Indole derivatives |
| JP5122943B2 (en) * | 2005-03-17 | 2013-01-16 | キッセイ薬品工業株式会社 | Method for producing glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivative |
| US8022192B2 (en) | 2005-03-17 | 2011-09-20 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Process for production of glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivative |
| WO2006098413A1 (en) * | 2005-03-17 | 2006-09-21 | Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Process for production of glucopyranosyloxypyrazole derivative |
| US9127034B2 (en) | 2005-05-10 | 2015-09-08 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Processes for preparing of glucopyranosyl-substituted benzyl-benzene derivates and intermediates therein |
| US10442795B2 (en) | 2005-05-10 | 2019-10-15 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Processes for preparing of glucopyranosyl-substituted benzyl-benzene derivatives and intermediates therein |
| JP4888840B2 (en) * | 2005-07-22 | 2012-02-29 | 味の素株式会社 | Process for the preparation of pyrazole-O-glycoside derivatives and novel intermediates of said process |
| US7838500B2 (en) | 2006-01-11 | 2010-11-23 | Ajinomoto Co., Inc. | Crystalline form of 1′-(1-methylethyl)-4′-[(2-fluoro-4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-5′-methyl-1H-pyrazol-3′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, a method for its preparation and the use thereof for preparing medicaments |
| US7524822B2 (en) | 2006-01-11 | 2009-04-28 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Crystalline form of 1′-(1-methylethyl)-4′-[(2-fluoro-4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-5′-methyl-1H-pyrazol-3′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, a method for its preparation and the use thereof for preparing medicaments |
| US8557782B2 (en) | 2006-05-03 | 2013-10-15 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Glucopyranosyl-substituted benzonitrile derivatives, pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds, their use and process for their manufacture |
| EP2351568A2 (en) | 2006-05-04 | 2011-08-03 | Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH | Uses of dpp-iv inhibitors |
| WO2007128761A2 (en) | 2006-05-04 | 2007-11-15 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Uses of dpp-iv inhibitors |
| US7851617B2 (en) | 2006-07-27 | 2010-12-14 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Indole derivatives |
| EP2308841A2 (en) | 2006-09-29 | 2011-04-13 | Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Phlorizin analogs as SGLT2 inhibitors |
| US7943582B2 (en) | 2006-12-04 | 2011-05-17 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Crystalline form of 1-(β-D-glucopyransoyl)-4-methyl-3-[5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2- thienylmethyl]benzene hemihydrate |
| US7666845B2 (en) | 2006-12-04 | 2010-02-23 | Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. | Compounds having inhibitory activity against sodium-dependent glucose transporter |
| US8513202B2 (en) | 2006-12-04 | 2013-08-20 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Crystalline form of 1-(β-D-glucopyranosyl)-4-methyl-3-[5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-thienylmethyl]benzene hemihydrate |
| JP2010516655A (en) * | 2007-01-19 | 2010-05-20 | ベーリンガー インゲルハイム インターナショナル ゲゼルシャフト ミット ベシュレンクテル ハフツング | Pharmaceutical composition containing pyrazole-O-glucoside derivative |
| WO2008087198A1 (en) * | 2007-01-19 | 2008-07-24 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition comprising a pyrazole-o-glucoside derivative |
| WO2008090209A2 (en) * | 2007-01-26 | 2008-07-31 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Use of glucopyranosyloxy- pyrazoles for preventing and treating neurodegenerative disorders |
| WO2008090209A3 (en) * | 2007-01-26 | 2008-10-02 | Boehringer Ingelheim Int | Use of glucopyranosyloxy- pyrazoles for preventing and treating neurodegenerative disorders |
| US8551957B2 (en) | 2007-08-16 | 2013-10-08 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition comprising a glucopyranosyl-substituted benzene derivate |
| US8802637B2 (en) | 2007-08-23 | 2014-08-12 | Theracos, Inc. | Benzylbenzene derivatives and methods of use |
| US8106021B2 (en) | 2007-08-23 | 2012-01-31 | Theracos, Inc. | Benzylbenzene derivatives and methods of use |
| US8575321B2 (en) | 2007-08-23 | 2013-11-05 | Theracos, Inc. | Benzylbenzene derivatives and methods of use |
| US7838499B2 (en) | 2007-08-23 | 2010-11-23 | Theracos, Inc. | Benzylbenzene derivatives and methods of use |
| US9024009B2 (en) | 2007-09-10 | 2015-05-05 | Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. | Process for the preparation of compounds useful as inhibitors of SGLT |
| US8129434B2 (en) | 2007-12-13 | 2012-03-06 | Theracos, Inc. | Benzylphenyl cyclohexane derivatives and methods of use |
| US8853385B2 (en) | 2008-01-17 | 2014-10-07 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Combination therapy comprising SGLT inhibitors and DPP4 inhibitors |
| WO2009138195A2 (en) * | 2008-05-16 | 2009-11-19 | Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland Gmbh | Use of thiophene glycoside derivatives for producing medicaments for treatment of hypertension |
| WO2009138195A3 (en) * | 2008-05-16 | 2010-01-07 | Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland Gmbh | Use of thiophene glycoside derivatives for producing medicaments for treatment of hypertension |
| US9006403B2 (en) | 2008-08-22 | 2015-04-14 | Theracos, Inc. | Processes for the preparation of SGLT2 inhibitors |
| US8283454B2 (en) | 2008-08-22 | 2012-10-09 | Theracos, Inc. | Processes for the preparation of SGLT2 inhibitors |
| US9056850B2 (en) | 2008-10-17 | 2015-06-16 | Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. | Process for the preparation of compounds useful as inhibitors of SGLT |
| US12115179B2 (en) | 2009-02-13 | 2024-10-15 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US10406172B2 (en) | 2009-02-13 | 2019-09-10 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US11576894B2 (en) | 2009-07-08 | 2023-02-14 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Combination therapy for the treatment of diabetes |
| US8802842B2 (en) | 2009-09-30 | 2014-08-12 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Method for the preparation of a crystalline form |
| US9873714B2 (en) | 2009-09-30 | 2018-01-23 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Processes for preparing of glucopyranosyl-substituted benzyl-benzene derivatives |
| US9024010B2 (en) | 2009-09-30 | 2015-05-05 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Processes for preparing of glucopyranosyl-substituted benzyl-benzene derivatives |
| US10610489B2 (en) | 2009-10-02 | 2020-04-07 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, pharmaceutical dosage form, process for their preparation, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US9174971B2 (en) | 2009-10-14 | 2015-11-03 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Process for the preparation of compounds useful as inhibitors of SGLT2 |
| WO2011048112A1 (en) | 2009-10-20 | 2011-04-28 | Novartis Ag | Glycoside derivatives and uses thereof |
| US9439902B2 (en) | 2009-11-02 | 2016-09-13 | Pfizer Inc. | Dioxa-bicyclo[3.2.1]octane-2,3,4-triol derivatives |
| US9308204B2 (en) | 2009-11-02 | 2016-04-12 | Pfizer Inc. | Dioxa-bicyclo[3.2.1]octane-2,3,4-triol derivatives |
| US9439901B2 (en) | 2009-11-02 | 2016-09-13 | Pfizer Inc. | Dioxa-bicyclo[3.2.1]octane-2,3,4-triol derivatives |
| WO2011070592A2 (en) | 2009-12-09 | 2011-06-16 | Panacea Biotec Ltd. | Novel sugar derivatives |
| WO2011107494A1 (en) | 2010-03-03 | 2011-09-09 | Sanofi | Novel aromatic glycoside derivatives, medicaments containing said compounds, and the use thereof |
| US10617668B2 (en) | 2010-05-11 | 2020-04-14 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Pharmaceutical formulations |
| US10981942B2 (en) | 2010-06-12 | 2021-04-20 | Theracos Sub, Llc | Crystalline form of benzylbenzene SGLT2 inhibitor |
| US10533032B2 (en) | 2010-06-12 | 2020-01-14 | Theracos Sub, Llc | Crystalline form of benzylbenzene SGLT2 inhibitor |
| US8987323B2 (en) | 2010-06-12 | 2015-03-24 | Theracos, Inc. | Crystalline form of benzylbenzene SGLT2 inhibitor |
| US9834573B2 (en) | 2010-06-12 | 2017-12-05 | Theracos Sub, Llc | Crystalline form of benzylbenzene SGLT2 inhibitor |
| WO2012025857A1 (en) | 2010-08-23 | 2012-03-01 | Hetero Research Foundation | Cycloalkyl methoxybenzyl phenyl pyran derivatives as sodium dependent glucose co transporter (sglt2) inhibitors |
| US10596120B2 (en) | 2011-03-07 | 2020-03-24 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical compositions |
| US11564886B2 (en) | 2011-03-07 | 2023-01-31 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical compositions |
| US20180185291A1 (en) | 2011-03-07 | 2018-07-05 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical compositions |
| US10544135B2 (en) | 2011-04-13 | 2020-01-28 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Process for the preparation of compounds useful as inhibitors of SGLT2 |
| WO2012140596A1 (en) | 2011-04-14 | 2012-10-18 | Novartis Ag | Glycoside derivatives and uses thereof |
| WO2012140597A1 (en) | 2011-04-14 | 2012-10-18 | Novartis Ag | Glycoside derivatives and their uses for the treatment of diabetes |
| US9035044B2 (en) | 2011-05-09 | 2015-05-19 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | L-proline and citric acid co-crystals of (2S, 3R, 4R, 5S,6R)-2-(3-((5-(4-fluorophenyl)thiopen-2-yl)methyl)4-methylphenyl)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol |
| US9555001B2 (en) | 2012-03-07 | 2017-01-31 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition and uses thereof |
| US9192617B2 (en) | 2012-03-20 | 2015-11-24 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US9725478B2 (en) | 2012-04-10 | 2017-08-08 | Theracos Sub, Llc | Process for the preparation of benzylbenzene SGLT2 inhibitors |
| US9193751B2 (en) | 2012-04-10 | 2015-11-24 | Theracos, Inc. | Process for the preparation of benzylbenzene SGLT2 inhibitors |
| EP2774619A1 (en) | 2013-03-04 | 2014-09-10 | BioActive Food GmbH | Composition for the treatment of hyperglycaemic diseases |
| US8652527B1 (en) | 2013-03-13 | 2014-02-18 | Upsher-Smith Laboratories, Inc | Extended-release topiramate capsules |
| US8889190B2 (en) | 2013-03-13 | 2014-11-18 | Upsher-Smith Laboratories, Inc. | Extended-release topiramate capsules |
| US10363224B2 (en) | 2013-03-13 | 2019-07-30 | Upsher-Smith Laboratories, Llc | Extended-release topiramate capsules |
| US10172878B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2019-01-08 | Upsher-Smith Laboratories, Llc | Extended-release topiramate capsules |
| US9555005B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2017-01-31 | Upsher-Smith Laboratories, Inc. | Extended-release topiramate capsules |
| US9101545B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2015-08-11 | Upsher-Smith Laboratories, Inc. | Extended-release topiramate capsules |
| US10258637B2 (en) | 2013-04-05 | 2019-04-16 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US11833166B2 (en) | 2013-04-05 | 2023-12-05 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US9949997B2 (en) | 2013-04-05 | 2018-04-24 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US11090323B2 (en) | 2013-04-05 | 2021-08-17 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US11918596B2 (en) | 2013-04-05 | 2024-03-05 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US9949998B2 (en) | 2013-04-05 | 2018-04-24 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US11813275B2 (en) | 2013-04-05 | 2023-11-14 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US11666590B2 (en) | 2013-04-18 | 2023-06-06 | Boehringer Ingelheim International Gmbh | Pharmaceutical composition, methods for treating and uses thereof |
| US9464043B2 (en) | 2013-10-12 | 2016-10-11 | Theracos Sub, Llc | Preparation of hydroxy-benzylbenzene derivatives |
| US10093616B2 (en) | 2013-10-12 | 2018-10-09 | Theracos Sub, Llc | Preparation of hydroxy-benzylbenzene derivatives |
| WO2015173383A1 (en) | 2014-05-16 | 2015-11-19 | Bioactive Food Gmbh | Combination of biologically active substances for treatment of hyperglycaemic disorders |
| EP2944311A1 (en) | 2014-05-16 | 2015-11-18 | BioActive Food GmbH | Combination of biologically active substances for treating hyperglycemic diseases |
| US11207337B2 (en) | 2015-09-15 | 2021-12-28 | Janssen Pharmaceutica Nv | Co-therapy comprising canagliflozin and phentermine for the treatment of obesity and obesity related disorders |
| CN105403647A (en) * | 2015-10-09 | 2016-03-16 | 北京万全德众医药生物技术有限公司 | Method for separating and determining Clinofibrate intermediate and related substances by using liquid chromatography |
| CN105403647B (en) * | 2015-10-09 | 2020-09-01 | 北京万全德众医药生物技术有限公司 | Method for separating and measuring clinofibrate intermediate related substances by liquid chromatography |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1432720A1 (en) | 2004-06-30 |
| US20030087843A1 (en) | 2003-05-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20030087843A1 (en) | O-pyrazole glucoside SGLT2 inhibitors and method of use | |
| US6414126B1 (en) | C-aryl glucoside SGLT2 inhibitors and method | |
| US6515117B2 (en) | C-aryl glucoside SGLT2 inhibitors and method | |
| EP1268502B1 (en) | O-aryl glucoside sglt2 inhibitors and method | |
| US6555519B2 (en) | O-glucosylated benzamide SGLT2 inhibitors and method | |
| US6936590B2 (en) | C-aryl glucoside SGLT2 inhibitors and method | |
| EP1385856B1 (en) | Amino acid complexes of c-aryl glucosides for treatment of diabetes and method | |
| AU2001249598A1 (en) | O-aryl glucoside sglt2 inhibitors and method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AK | Designated states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AE AG AL AM AT AU AZ BA BB BG BY BZ CA CH CN CO CR CU CZ DE DM DZ EC EE ES FI GB GD GE GH HR HU ID IL IN IS JP KE KG KP KR LC LK LR LS LT LU LV MA MD MG MN MW MX MZ NO NZ OM PH PL PT RU SD SE SG SI SK SL TJ TM TN TR TZ UA UG US UZ VC VN YU ZA ZM Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AE AG AL AM AT AU AZ BA BB BG BR BY BZ CA CH CN CO CR CU CZ DE DK DM DZ EC EE ES FI GB GD GE GH GM HR HU ID IL IN IS JP KE KG KP KR KZ LC LK LR LS LT LU LV MA MD MG MK MN MW MX MZ NO NZ OM PH PL PT RO RU SD SE SG SI SK SL TJ TM TN TR TT TZ UA UG US UZ VC VN YU ZA ZM ZW |
|
| AL | Designated countries for regional patents |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): GH GM KE LS MW MZ SD SL SZ TZ UG ZM ZW AM AZ BY KG KZ MD RU TJ TM AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LU MC NL PT SE SK TR BF BJ CF CG CI CM GA GN GQ GW ML MR NE SN TD TG Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): GH GM KE LS MW MZ SD SL SZ UG ZM ZW AM AZ BY KG KZ RU TJ TM AT BE BG CH CY CZ DK EE ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LU MC PT SE SK TR BF BJ CF CG CI GA GN GQ GW ML MR NE SN TD TG |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | ||
| DFPE | Request for preliminary examination filed prior to expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed before 20040101) | ||
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2002761586 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWP | Wipo information: published in national office |
Ref document number: 2002761586 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWW | Wipo information: withdrawn in national office |
Ref document number: 2002761586 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: JP |
|
| WWW | Wipo information: withdrawn in national office |
Country of ref document: JP |