WO2002100857A1 - Quinuclidines-substituted-multi-cyclic-heteroaryls for the treatment of disease - Google Patents
Quinuclidines-substituted-multi-cyclic-heteroaryls for the treatment of disease Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2002100857A1 WO2002100857A1 PCT/US2002/016568 US0216568W WO02100857A1 WO 2002100857 A1 WO2002100857 A1 WO 2002100857A1 US 0216568 W US0216568 W US 0216568W WO 02100857 A1 WO02100857 A1 WO 02100857A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- oct
- pyridine
- carboxamide
- azabicyclo
- methyl
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 C**C1=C(*)I=C(C)N=*1 Chemical compound C**C1=C(*)I=C(C)N=*1 0.000 description 2
- MRQNFVPHYRFOSB-UHFFFAOYSA-N C=CC(NC1C(CC2)CCN2C1)=O Chemical compound C=CC(NC1C(CC2)CCN2C1)=O MRQNFVPHYRFOSB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RPAQKNMPMUTPBE-AWEZNQCLSA-N CC1(C)c(cc(C(N[C@@H]2C(CC3)CCN3C2)=O)nc2)c2OC1 Chemical compound CC1(C)c(cc(C(N[C@@H]2C(CC3)CCN3C2)=O)nc2)c2OC1 RPAQKNMPMUTPBE-AWEZNQCLSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VSFFJFOPGAUTNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc1c[o]c2c1cc(C(NC1C(CC3)CCN3C1)=O)nc2 Chemical compound Cc1c[o]c2c1cc(C(NC1C(CC3)CCN3C1)=O)nc2 VSFFJFOPGAUTNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FBEPJURSGQHOMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N O=C(CCCC1C(CC2)CCN2C1)c1cc2cccnc2[s]1 Chemical compound O=C(CCCC1C(CC2)CCN2C1)c1cc2cccnc2[s]1 FBEPJURSGQHOMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IPKZCLGGYKRDES-UHFFFAOYSA-N O=C(c(nc1)cc2c1[o]cc2)NC1C(CC2)CCN2C1 Chemical compound O=C(c(nc1)cc2c1[o]cc2)NC1C(CC2)CCN2C1 IPKZCLGGYKRDES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NJNIZJCRCANYGV-ZDUSSCGKSA-N O=C(c(nc1)cc2c1[s]cc2)N[C@@H]1C(CC2)CCN2C1 Chemical compound O=C(c(nc1)cc2c1[s]cc2)N[C@@H]1C(CC2)CCN2C1 NJNIZJCRCANYGV-ZDUSSCGKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GTPGKSNYGZTLQJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N O=C(c1cc(cncc2)c2[s]1)NC1C(CC2)CCN2C1 Chemical compound O=C(c1cc(cncc2)c2[s]1)NC1C(CC2)CCN2C1 GTPGKSNYGZTLQJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FSWJILNACZEMQN-AWEZNQCLSA-N O=C(c1cc2c[s]cc2cn1)N[C@@H]1C(CC2)CCN2C1 Chemical compound O=C(c1cc2c[s]cc2cn1)N[C@@H]1C(CC2)CCN2C1 FSWJILNACZEMQN-AWEZNQCLSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KYCAUWHYDUAAJT-INIZCTEOSA-N O=C(c1ncc2[s]c3ccccc3c2c1)N[C@@H]1C(CC2)CCN2C1 Chemical compound O=C(c1ncc2[s]c3ccccc3c2c1)N[C@@H]1C(CC2)CCN2C1 KYCAUWHYDUAAJT-INIZCTEOSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D519/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing more than one system of two or more relevant hetero rings condensed among themselves or condensed with a common carbocyclic ring system not provided for in groups C07D453/00 or C07D455/00
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D453/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing quinuclidine or iso-quinuclidine ring systems, e.g. quinine alkaloids
- C07D453/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing quinuclidine or iso-quinuclidine ring systems, e.g. quinine alkaloids containing not further condensed quinuclidine ring systems
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P1/00—Drugs for disorders of the alimentary tract or the digestive system
- A61P1/14—Prodigestives, e.g. acids, enzymes, appetite stimulants, antidyspeptics, tonics, antiflatulents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/02—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for peripheral neuropathies
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/04—Centrally acting analgesics, e.g. opioids
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/14—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for treating abnormal movements, e.g. chorea, dyskinesia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/14—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for treating abnormal movements, e.g. chorea, dyskinesia
- A61P25/16—Anti-Parkinson drugs
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/18—Antipsychotics, i.e. neuroleptics; Drugs for mania or schizophrenia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/22—Anxiolytics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/24—Antidepressants
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/28—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for treating neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system, e.g. nootropic agents, cognition enhancers, drugs for treating Alzheimer's disease or other forms of dementia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/30—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for treating abuse or dependence
- A61P25/34—Tobacco-abuse
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/30—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for treating abuse or dependence
- A61P25/36—Opioid-abuse
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P27/00—Drugs for disorders of the senses
- A61P27/02—Ophthalmic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P27/00—Drugs for disorders of the senses
- A61P27/02—Ophthalmic agents
- A61P27/06—Antiglaucoma agents or miotics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/04—Anorexiants; Antiobesity agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P31/00—Antiinfectives, i.e. antibiotics, antiseptics, chemotherapeutics
- A61P31/12—Antivirals
- A61P31/14—Antivirals for RNA viruses
- A61P31/18—Antivirals for RNA viruses for HIV
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P43/00—Drugs for specific purposes, not provided for in groups A61P1/00-A61P41/00
Definitions
- Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors play a large role in central nervous system (CNS) activity. Particularly, they are known to be involved in cognition, learning, mood, emotion, and neuroprotection. There are several types of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, and each one appears to have a different role in regulating CNS function. Nicotine affects all such receptors, and has a variety of activities. Unfortunately, not all of the activities are desirable. In fact, one of the least desirable properties of nicotine is its addictive nature and the low ratio between efficacy and safety.
- the present invention relates to molecules that have a greater effect upon the ⁇ 7 nAChRs as compared to other closely related members of this large ligand-gated receptor family. Thus, the invention provides compounds that are active drug molecules with fewer side effects.
- nAChRs comprise a large family of ligand-gated ion channels that control neuronal activity and brain function. These receptors have a pentameric structure. In mammals, this gene family is composed of nine alpha and four beta subunits that co- assemble to form multiple subtypes of receptors that have a distinctive pharmacology. Acetylcholine is the endogenous regulator of all of the subtypes, while nicotine non- selectively activates all nAChRs. The ⁇ 7 nAChR is one receptor system that has proved to be a difficult target for testing.
- Native 7 nAChR is not routinely able to be stably expressed in most mammalian cell lines (Cooper and Millar, Nature, 366(6454), p. 360-4, 1997).
- Another feature that makes functional assays of 7 nAChR challenging is that the receptor is rapidly (100 milliseconds) inactivated. This rapid inactivation greatly limits the functional assays that can be used to measure channel activity.
- Eisele et al. has indicated that a chimeric receptor formed between the N-terminal ligand binding domain of the 7 nAChR (Eisele et al., Nature, 366(6454), p 479-83, 1993), and the pore forming C-terminal domain of the 5-HT 3 receptor expressed well in Xenopus oocytes while retaining nicotinic agonist sensitivity.
- Eisele et al. used the N-terminus of the avian (chick) form of the ⁇ 7 nAChR receptor and the C-terminus of the mouse form of the 5-HT 3 gene.
- the al nAChR is a calcium channel while the 5-HT 3 R is a sodium and potassium channel.
- WO 00/73431 A2 discloses two binding assays to directly measure the affinity and selectivity of compounds at the ⁇ 7 nAChR and the 5-HT 3 R. The combined use of these functional and binding assays may be used to identify compounds that are selective agonists of the 7 nAChR.
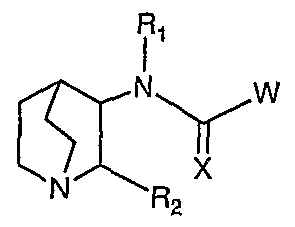
- the present invention discloses compounds of the Formula I:
- R f is H, alkyl, cycloalkyl, halogenated alkyl, substituted phenyl, or substituted naphthyl;
- R is H, alkyl, halogenated alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl;
- Each R is independently a bond to the core molecule provided that only one R 3 and no R 6 or R1 5 is also said bond, H, F, Br, Cl, I, alkyl, substituted alkyl, halogenated alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, halogenated alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, halogenated alkynyl, heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, lactam heterocycloalkyl, -CN, -NO 2 , -ORi, -C(O)N(R 10 ) 2 , -NR!COR 16 , -N(R 10 ) 2 , -SRi, -S(O) 2 R,, -C(O)R 16 , -CO 2 R ⁇ , aryl, R 7 , or R 9 ; J, L, M, and Q are N or C(R 6 ) provided that only one of J, L, M, or
- G and Y are C(R 6 ), provided that when the molecule is attached to the phenyl moiety at Y, G is CH;
- R 4 is H, alkyl, halogenated alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, halogenated cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, halogenated heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, R 7 , or R 9 ;
- Each R 5 is independently H, C 1-3 alkyl, or C 2-4 alkenyl;
- Each R 6 is independently H, F, Br, I, Cl, -CN, -CF 3 , -OR 5 , -SR 5 , or -N(R 5 ) 2 , or a bond to the core molecule provided that only one R 6 and no R 3 or R 15 is said bond,
- V is selected from O, S, or N(R t );
- E is O, S, or NR 19 ,
- E and G are independently selected from CR 18 , O, S, N, or NR 19 , and A is CR 18 or N, or
- E and G are independently selected from CR 18 , O, S, N, or NR 19 , and A is CR 18 or N, each 9-membered fused-ring moiety having 0-1 substituent selected from R 2 o and further having 0-3 substituent(s) independently selected from F, Cl, Br, or I, and having a bond directly or indirectly attached to the core molecule where valency allows in either the 6-membered or the 5-membered ring of the fused-ring moiety;
- Each R 8 is independently H, alkyl, halogenated alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, halogenated cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, halogenated heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, R 7 , R 9 , phenyl, or substituted phenyl;
- Each R 10 is independently H, alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, alkyl substituted with 1 substituent selected from R 13 , cycloalkyl substituted with 1 substituent selected from R 13 , heterocycloalkyl substituted with
- Each R ⁇ i is independently H, alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocyclo-alkyl, halogenated alkyl, halogenated cycloalkyl, or halogenated heterocycloalkyl;
- R 13 is -OR ⁇ , -SR n , -NR meaningR n , -C(O)R n , -C(O)NR n R ⁇ , -CN, -CF 3 , -NR u C(O)Rcliff, -S(O) 2 NRnR n , -NR ! ⁇ S(O) 2 R ⁇ , or -NO 2 ;
- Each R 15 is independently a bond to the core molecule provided that only one
- Ri 5 and no R 6 or R 3 is also said bond, H, F, Br, Cl, I, alkyl, substituted alkyl, halogenated alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, halogenated alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, halogenated alkynyl, heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, lactam heterocycloalkyl, -CN, -NO 2 , -OR1, -C(O)N(R 10 ) 2 , -NRiCORi ⁇ , -N(R ⁇ o) 2 , -SRi, -CO 2 R,, aryl, R 7 , or R 9 ;
- R 16 is H, alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, halogenated alkyl, heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, substituted phenyl, or substituted naphthyl;
- Each R 18 is independently H, alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, halogenated alkyl, halogenated cycloalkyl, halogenated heterocycloalkyl, substituted alkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, -OR ⁇ , -SR ⁇ , -NR ⁇ R ⁇ , -C(O)R ⁇ , -NO -C(O)NR ⁇ R ⁇ , -CN, - R n C(O)R n , -S(O) 2 NR ⁇ R ⁇ , -NR ⁇ S(O) 2 R ⁇ , F, Cl, Br, I, or a bond directly or indirectly attached to the core molecule, provided that there is only one said bond to the core molecule within the 9-membered fused- ring moiety, further provided that the fused-ring moiety has 0-1 substituent selected from alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, hal
- R 1 is H, alkyl, halogenated alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, halogenated cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, phenyl, -SO 2 R 8 , or phenyl having 1 substituent selected from R 20 and further having 0-3 substituents independently selected from F, Cl, Br, or I;
- R 2 o is alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, halogenated alkyl, halogenated cycloalkyl, halogenated heterocycloalkyl, -OR ⁇ , -SR ⁇ , -NR ⁇ R ⁇ , -C(O)R ⁇ , -C(O)NR meaningR ⁇ , -CN, -NR ⁇ C(O)R ⁇ , -S(O) 2 NR n Rn, -NR ⁇ S(O) 2 R ⁇ , -NO 2 , alkyl substituted with 1-4 substituent(s) independently selected from F, Cl, Br, I, or R 13 , cycloalkyl substituted with 1-4 substituent(s) independently selected from F, Cl, Br, I, or R 13 , or heterocycloalkyl substituted with 1-4 substituent(s) independently selected from F, Cl, Br, I, or R !3 ; or pharmaceutical composition, pharmaceutically acceptable salt, racemic mixture, or pure en
- the compounds of Formula I are use to treat any one or more than one, or combination of cognitive and attention deficit symptoms of Alzheimer's, neurodegeneration associated with diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, pre-senile dementia (mild cognitive impairment), senile dementia, schizophrenia, psychosis, attention deficit disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, mood and affective disorders, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, borderline personality disorder, traumatic brain injury, behavioral and cognitive problems associated with brain tumors, AIDS dementia complex, dementia associated with Down's syndrome, dementia associated with Lewy Bodies, Huntington's disease, depression, general anxiety disorder, age- related macular degeneration, Parkinson's disease, tardive dyskinesia, Pick's disease, post traumatic stress disorder, dysregulation of food intake including bulemia and anorexia nervosa, withdrawal symptoms associated with smoking cessation and dependant drug cessation, Gilles de la Tourette's Syndrome, glaucoma, neurodegeneration associated with glaucoma, or symptoms associated with pain.
- diseases such as
- X is O, or S;
- Each R ⁇ is H, alkyl, cycloalkyl, halogenated alkyl, substituted phenyl, or substituted naphthyl;
- Alkyl is both straight- and branched-chain moieties having from 1-6 carbon atoms;
- Halogenated alkyl is an alkyl moiety having from 1-6 carbon atoms and having 1 to (2n+l) substituent(s) independently selected from F, Cl, Br, or I where n is the maximum number of carbon atoms in the moiety; Cycloalkyl is a cyclic alkyl moiety having from 3-6 carbon atoms; Substituted phenyl is a phenyl either having 1-4 substituents independently selected from F, Cl, Br, or I, or having 1 substituent selected from R 12 and 0-3 substituents independently selected from F, Cl, Br, or I; Substituted naphthyl is a naphthalene moiety either having 1-4 substituents independently selected from F, Cl, Br, or I, or having 1 substituent selected from R 12 and 0-3 substituents independently selected from F, Cl, Br, or I, where the substitution can be independently on either only one ring or both rings of said naphthalene moiety; R 2 is H, alkyl,
- Aryl is phenyl, substituted phenyl, naphthyl, or substituted naphthyl;
- Each R 3 is independently a bond to the core molecule provided that only one R 3 and no R 6 or R 15 is also said bond, H, F, Br, Cl, I, alkyl, substituted alkyl, halogenated alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, halogenated alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, halogenated alkynyl, heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, lactam heterocycloalkyl, -CN, -NO 2 , -ORi, -C(O)N(R 10 ) 2 , -NR ⁇ COR 16 , -N(R 10 ) 2 , -SR 1; -S(O) 2 R,, -C(O)R 16 , -CO 2 R,, aryl, R 7 , or R 9 ;
- Halogenated alkenyl is an unsaturated alkenyl moiety having from 2-6 carbon atoms and having 1 to (2n-l) substituent(s) independently selected from F, Cl, Br, or I where n is the maximum number of carbon atoms in the moiety;
- Substituted alkenyl is an unsaturated alkenyl moiety having from 2-6 carbon atoms and having 0-3 substituents independently selected from -F, or -Cl, and further having 1 substituent selected from R 7 , R 9 , -OR 10 , -SR 10 , -NRioRio, -C(O)R ⁇ o, -C(O)NR 10 R ⁇ o, -NR 10 C(O)R 10 , -S(O) 2 NR 10 R ⁇ o, -NR 10 S(O) 2 R ⁇ o, -CN, phenyl, or phenyl having 1 substituent selected from R 20 and further having 0-3 substituents independently selected from F, Cl, Br, or I;
- Alkynyl is straight- and branched-chained moieties having from 2-6 carbon atoms and having at least one carbon-carbon triple bond;
- Halogenated alkynyl is an unsaturated alkynyl moiety having from 3-6 carbon atoms and having 1 to (2n-3) substituent(s) independently selected from F, Cl, Br, or I where n is the maximum number of carbon atoms in the moiety;
- Substituted alkynyl is an unsaturated alkynyl moiety having from 3-6 carbon atoms and having 0-3 substituents independently selected from -F, or -Cl, and further having 1 substituent selected from R 7 , R 9 , -OR 10 , -SRio, -NRioRio, -C(O)R JO , -C(O)NR 10 R 10 , -NR 10 C(O)R 10 , -S(O) 2 NR 10 R 10 , -NR 10 S(O) 2 R 10 , -CN, phenyl, or phenyl having 1 substituent selected from R 0 and further having 0-3 substituents independently selected from F, Cl, Br, or I;
- Halogenated cycloalkyl is a cyclic moiety having from 3-6 carbon atoms and having 1-4 substituents independently selected from F, or Cl; Substituted cycloalkyl is a cyclic moiety having from 3-6 carbon atoms and having 0-3 substituents independently selected from F, or Cl, and further having 1 substituent selected from -OR 10 , -SR 10 , -NRioRio.
- Heterocycloalkyl is a cyclic moiety having 4-7 atoms with 1-2 atoms within the ring being -S-, -N(R 19 )-, or -O-;
- Halogenated heterocycloalkyl is a cyclic moiety having from 4-7 atoms with 1-2 atoms within the ring being -S-, -N(R 19 )-, or -O-, and having 1-4 substituents independently selected from F, or Cl;
- Substituted heterocycloalkyl is a cyclic moiety having from 4-7 atoms with 1-2 atoms within the ring being -S-, -N(R 1 )-, or -O- and having 0-3 substituents independently selected from F, or Cl, and further having 1 substituent selected from -OR 10 , -SR 10 , -NRioRio, -C(O)R 10 , -C(O)NR 10 R 10 , -CN, -NR 10 C(O)R 10 , -NO 2 , -S(O) 2 NR ⁇ oR ⁇ o, -NR 1 oS(O) 2 R 1 o, phenyl, or phenyl having 1 substituent selected from R 2 o and further having 0-3 substituents independently selected from F, Cl, Br, or I; J, L, M, and Q are N or C(R 6 ) provided that only one of J, L, M, or Q, is N and the others
- G and Y are C(R 6 ), provided that when the molecule is attached to the phenyl moiety at Y, G is CH;
- R 4 is H, alkyl, halogenated alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, halogenated cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, halogenated heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, R 7 , or R 9 ;
- Each R 5 is independently H, C 1-3 alkyl, or C 2-4 alkenyl;
- C 1-3 alkyl is both straight- and branched-chain moieties having from 1-3 carbon atoms;
- Each R 6 is independently H, F, Br, I, Cl, -CN, -CF 3 , -OR 5 , -SR 5 , or -N(R 5 ) 2 , or a bond to the core molecule provided that only one R 6 and no R 3 or R 15 is said bond,
- V is selected from O, S, or N(R );
- E and G are independently selected from CR 18 , O, S, N, or NR 19 , and A is CR 18 or N, or
- E and G are independently selected from CR 18 , O, S, N, or NR 19 , and A is CR 18 or N, each 9-membered fused-ring moiety having 0-1 substituent selected from R 2 o and further having 0-3 substituent(s) independently selected from F, Cl, Br, or I, and having a bond directly or indirectly attached to the core molecule where valency allows in either the 6-membered or the 5-membered ring of the fused-ring moiety;
- Each R 8 is independently H, alkyl, halogenated alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, halogenated cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, halogenated heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, R 7 , R , phenyl, or substituted phenyl;
- Each Rii is independently H, alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocyclo-alkyl, halogenated alkyl, halogenated cycloalkyl, or halogenated heterocycloalkyl;
- R 12 is -OR ⁇ , -SR ⁇ , alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, halogenated alkyl, halogenated cycloalkyl, halogenated heterocycloalkyl, substituted alkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, -NR ⁇ R ⁇ , -C(O)R ⁇ , -NO 2 , -C(O)NR ⁇ R ⁇ , -CN, -NR ⁇ C(O)R ⁇ , -S(O) 2 NR ⁇ R ⁇ , or -NR n S(O) 2 R ⁇ ;
- R 13 is -OR ⁇ , -SR ⁇ , -NR ⁇ R ⁇ , -C(O)R
- R 1 is alkyl, substituted alkyl, halogenated alkyl, -OR ⁇ , -CN, -NO 2 , -NR1 0 R 10 ;
- Each R 15 is independently a bond to the core molecule provided that only one R1 5 and no R 6 or R 3 is also said bond, H, F, Br, Cl, I, alkyl, substituted alkyl, halogenated alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, halogenated alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, halogenated alkynyl, heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, lactam heterocycloalkyl, -CN, -NO 2 , -OR 1; -C(O)N(R ⁇ 0 ) 2 , -NR,COR 16 , -N(R 10 ) 2 , -SR1, -CO 2 R ⁇ , aryl, R 7 , or R 9 ;
- R 16 is H, alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, halogenated alkyl, heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, substituted phenyl, or substituted naphthyl;
- Each R 18 is independently H, alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, halogenated alkyl, halogenated cycloalkyl, halogenated heterocycloalkyl, substituted alkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, -OR ⁇ , -SR ⁇ , -NR ⁇ R ⁇ , -C(O)R ⁇ , -NO2, -C(O)NR ⁇ R ⁇ , -CN, -NR ⁇ C(O)R ⁇ , -S(O) 2 NR n Rn, -NR u S(O) 2 R ⁇ , F, Cl, Br, I, or a bond directly or indirectly attached to the core molecule, provided that there is only one said bond to the core molecule within the 9-membered fused- ring moiety, further provided that the fused-ring moiety has 0-1 substituent selected from alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, halogenated al
- R)9 is H, alkyl, halogenated alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, halogenated cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, phenyl, -SO 2 R 8 , or phenyl having 1 substituent selected from R 2 o and further having 0-3 substituents independently selected from F, Cl, Br, or I;
- R 20 is alkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, halogenated alkyl, halogenated cycloalkyl, halogenated heterocycloalkyl, -OR ⁇ , -SR lls -NR ⁇ R ⁇ , -C(O)R ⁇ , -C(O)NR ⁇ R ⁇ , -CN, -NR ⁇ C(O)R ⁇ , -S(O) 2 NR ⁇ R n , -NR ⁇ S(O) 2 R ⁇ , -NO 2 , alkyl substituted with 1-4 substituent(
- the invention includes methods of treating a mammal suffering from schizophrenia or psychosis by administering compounds of Formula I in conjunction with antipsychotic drugs.
- the compounds of Formula I and the antipsychotic drugs can be administered simultaneously or at separate intervals.
- the compounds of Formula I and the antipsychotic drugs can be incorporated into a single pharmaceutical composition.
- two separate compositions i.e., one containing compounds of Formula I and the other containing antipsychotic drugs, can be administered simultaneously.
- the present invention also includes the intermediates, the processes to make them and the compounds of the present invention, pharmaceutical compositions containing the active compounds, and methods to treat the identified diseases.
- a group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein X is O.
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein Ri is H.
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein Ri is alkyl, cycloalkyl, halogenated alkyl, or aryl.
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein the R configuration occurs at the C3 position of the quinuclidine ring.
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein the S configuration occurs at the C3 position of the quinuclidine ring.
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein R 2 is H. Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein R 2 is alkyl, halogenated alkyl, or substituted alkyl. Another group of compounds of
- Formula I includes compounds wherein R 2 is alkyl. Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein R 2 is methyl. Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein R 2 is alkyl, halogenated alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl. Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds where R 2 is other than H and wherein the stereochemistry is S at C2 and R at C3.
- R 3 is independently any one of the following: a bond to the core molecule provided that only one R and no R 6 or Rj 5 is also said bond, H, F, Br, Cl, I, alkyl, substituted alkyl, halogenated alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, halogenated alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, halogenated alkynyl, heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, lactam heterocycloalkyl, -CN, -NO 2 , -ORi, -C(O)N(R 10 ) 2 , -NRiCORie, -N(R 10 ) 2 , -SRi, -C(O)R 16 , -CO 2 R ⁇ , aryl, R 7 , or R 9 .
- R 2 is H
- Q is N with J, L, and M being CH
- the R 3 for Z" cannot be a bond to the core molecule when the R 3 for Z' is H.
- R 3 is a bond to the core molecule provided that only one R 3 and no R 6 or R 15 is also said bond, H F, Br, Cl, -CN, -NO 2 , alkyl, substituted alkyl, halogenated alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, halogenated alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, halogenated alkynyl, heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, lactam heterocycloalkyl, -ORi, -NRiCOR 16 , -N(R 10 ) 2 , -SR1, or aryl.
- R 3 is a bond to the core molecule provided that only one R 3 and no R 6 or R 15 is also said bond, H F, Br, Cl, -CN, -NO 2 , alkyl, substituted alkyl, halogenated alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, halogenated alkeny
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein R 4 is any one of the following: H, alkyl, halogenated alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, halogenated cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, halogenated heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, R , or R 9 .
- R is any one of the following: H, alkyl, halogenated alkyl, substituted alkyl, heterocycloalkyl, or substituted heterocycloalkyl.
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein each R 6 is independently any one of the following: a bond to the core molecule provided that only one R 6 and no R 3 or R 15 is said bond, H, F, Br, I, Cl, -CN, -CF 3 , -OR 5 , -SR 5 , or -N(R 5 ) 2 .
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein each R 6 is independently any one of the following: a bond to the core molecule provided that only one R 6 and no R 3 or R 15 is said bond, H, F, Br, Cl, -CN, -CF 3 , -OR 5 , -SR 5 , or -N(R 5 ) 2 .
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein each R 15 is independently selected from any one of the following: a bond to the core molecule provided that only one R 15 and no R 6 or R 3 is also said bond, H, F, Br, Cl, I, alkyl, substituted alkyl, halogenated alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, halogenated alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, halogenated alkynyl, heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, lactam heterocycloalkyl, -CN, -NO 2 , -ORi, -C(O)N(R ⁇ o) 2 , -NR ⁇ COR 16 , -N(R 10 ) 2 , -SRj, -CO2R1, aryl, R 7 , or R 9 .
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein each R 15 is independently selected from any one of the following: a bond to the
- R1 5 is independently selected from any one of the following: a bond to the core molecule provided that only one R ⁇ 5 and no R 6 or R 3 is also said bond, H, F, Br, Cl, -CN, -NO , alkyl, substituted alkyl, halogenated alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, halogenated alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, halogenated alkynyl, heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, lactam heterocycloalkyl, -OR 1; -NR ⁇ COR 16 , -N(R ⁇ o) 2 , -SRi, or aryl.
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein W is
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein W is
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein W is
- W includes any one or more or combination of the following: thieno[2,3-b]pyridin-2-yl, thieno[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yl, thieno[2,3-b]pyridin-6-yl, thieno[2,3-c]pyridin-2-yl, furo[3,2-c]pyridin-2-yl, thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-2-yl, furo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-yl, benzothieno[2,3-c]pyridin-3-yl, thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-5-yl, thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-6-yl, furo[2,3-c]pyridin-5-yl, benzothieno[3,2-c]pyridin-3-yl, thieno[3,2-c]pyridin-2-yl, 2,3- dihydrofuro
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes compounds wherein a carbon atom of sufficient valency of W is optionally substituted with any one or more or combination of the following: F, Br, Cl, I, alkyl, substituted alkyl, halogenated alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, halogenated alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, halogenated alkynyl, heterocycloalkyl, substituted heterocycloalkyl, lactam heterocycloalkyl, -CN, -CF 3 , -NO 2 , -ORi, -OR 5 , -C(O)N(R 10 ) 2 , -NR ⁇ COR 16 , -N(R ⁇ 0 ) 2 , -N(R 5 ) 2 , -SRi, -SR 5 , -S(O) 2 R ⁇ , -C(O)R 16 , -CO 2 Ri, aryl, R 7
- the compounds of Formula I have optically active center(s) on the quinuclidine ring. Although it is desirable that the stereochemical purity be as high as possible, absolute purity is not required.
- This invention involves racemic mixtures and compositions of varying degrees of streochemical purities. It is preferred to carry out stereoselective syntheses and/or to subject the reaction product to appropriate purification steps so as to produce substantially optically pure materials. Suitable stereoselective synthetic procedures for producing optically pure materials are well known in the art, as are procedures for purifying racemic mixtures into optically pure fractions.
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes any one or more or combination of the following: N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-2,3- dihydrofuro[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide; N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3- yl]furo[3,2-c]pyridine-2-carboxamide; N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-7- chlorofuro[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide; N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3- yl]furo[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide; N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yI]-3,3- dimethyl-2,3-dihydrofuro[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide;
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes any one or more or combination of the following: N-[(2S,3R)-2-methyl-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-2,3- dihydrofuro[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide; N-[(2S,3R)-2-methyl- 1 - azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]furo[3,2-c]pyridine-2-carboxamide; N-[(2S,3R)-2-methyl- l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-7-chlorofuro[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide; N-[(2S,3R)- 2-methyl- 1 -azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]furo[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide; N- [(2S,3R)-2-methyl-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes any one or more or combination of the following: N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]furo[3,2- c]pyridine-2-carboxamide; N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]furo[2,3-c]pyridine- 5-carboxamide; N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-2-methylfuro[2,3-c]pyridine-5- carboxamide; N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-3-methylfuro[2,3-c]pyridine-5- carboxamide; N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-3-ethylfuro[2,3-c]pyridine-5- carboxamide; N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes any one or more or combination of the following: N-[(3S)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-2,3- dihydrofuro[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide; N-[(3S)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3- yl]furo[3,2-c]pyridine-2-carboxamide; N-[(3S)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-7- chlorofuro[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide; N-[(3S)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3- yl]furo[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide; N-[(3S)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]furo[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide; N-[(3S)-l-azabicyclo
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes any one or more or combination of the following compounds: N-[(3S)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3- yl]furo[3,2-c] ⁇ yridine-2-carboxamide; N-[(3S)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]furo[2,3- c]pyridine-5-carboxamide; N-[(3S 1 -azabicyclo [2.2.2]oct-3- ⁇ yl]-2-methylfuro[2,3- c]pyridine-5-carboxamide; N-[(3S 1 -azabicyclo [2.2.2]oct-3- ⁇ yl]-3-methylfuro[2,3- c]pyridine-5-carboxamide; N-[(3S 1 -azabicyclo [2.2.2]oct-3- ⁇ yl]-3-methylfuro[2,3- c]pyridine-5-carboxamide; N-[(
- Another group of compounds of Formula I includes any one or more or combination of the following compounds: N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-2- vinylfuro[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxamide; 4-methyl-N-[(3R)- 1 -azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3- yl]furo[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxamide; 4-methylthio-N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct- 3-yl]furo[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxamide; 4-methoxy-N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct- 3-yl]furo[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxamide; 4-chloro-N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3- yl]furo[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxamide; N-[(3R
- Room temperature is within the range of 15-25 degrees Celsius.
- Pre-senile dementia is also known as mild cognitive impairment.
- AChR refers to acetylcholine receptor.
- nAChR refers to nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.
- 5HT 3 R refers to the serotonin-type 3 receptor.
- -btx refers to ⁇ -bungarotoxin.
- FLIPR refers to a device marketed by Molecular Devices, Inc. designed to precisely measure cellular fluorescence in a high throughput whole-cell assay. (Schroeder et. al, I. Biomolecular Screening, 1(2), p 75-80, 1996).
- TLC refers to thin-layer chromatography
- HPLC refers to high pressure liquid chromatography.
- MeOH refers to methanol.
- EtOH refers to ethanol.
- IPA refers to isopropyl alcohol.
- THF refers to tetrahydrofuran
- DMSO dimethylsulfoxide
- DMF dimethylformamide
- EtOAc refers to ethyl acetate.
- TMS refers to tetramethylsilane.
- TEA triethylamine
- DIEA diisopropylethylamine
- MLA refers to methyllycaconitine
- Ether refers to diethyl ether.
- HATU refers to O-(7-azabenzotriazol-l-yl)-N,N,N', N'-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate.
- DBU refers to l,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene.
- 50% saturated 1 : 1 NaCl/NaHCO 3 means a solution made by making a solution of 1 : 1 saturated NaCl/NaHCO 3 and adding an equal volume of water.
- Halogen is F, Cl, Br, or I.
- Cj_ j indicates a moiety of the integer 'i" to the integer "j" carbon atoms, inclusive.
- C 1-6 alkyl refers to alkyl of one to six carbon atoms.
- the core molecule is the quinuclidinyl-(carboxamide-type moiety):
- Mammal denotes human and other mammals.
- Brine refers to an aqueous saturated sodium chloride solution.
- Equ means molar equivalents.
- IR refers to infrared spectroscopy.
- Lv refers to leaving groups within a molecule, including Cl, OH, or mixed anhydride.
- Parr refers to the name of the company who sells the jars used for conducting reactions under pressure.
- PSI means pound per square inch.
- NMR nuclear (proton) magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- MS refers to mass spectrometry expressed as m/e or mass/charge unit.
- HRMS refers to high resolution mass spectrometry expressed as m/e or mass/charge unit.
- M+H + refers to the positive ion of a parent plus a hydrogen atom.
- M-H " refers to the negative ion of a parent minus a hydrogen atom.
- M+Na + refers to the positive ion of a parent plus a sodium atom.
- M+K + refers to the positive ion of a parent plus a potassium atom.
- El refers to electron impact.
- ESI refers to electrospray ionization.
- CI refers to chemical ionization.
- FAB refers to fast atom bombardment.
- compositions of the present invention may be in the form of pharmaceutically acceptable salts.
- pharmaceutically acceptable salts refers to salts prepared from pharmaceutically acceptable non-toxic bases including inorganic bases and organic bases, and salts prepared from inorganic acids, and organic acids. Salts derived from inorganic bases include aluminum, ammonium, calcium, ferric, ferrous, lithium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, zinc, and the like.
- Salts derived from pharmaceutically acceptable organic non-toxic bases include salts of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines, substituted amines including naturally occurring substituted amines, cyclic amines, such as arginine, betaine, caffeine, choline, N, N- dibenzylethylenediamine, diethylamine, 2-diethylaminoethanol, 2-dimethylamino- ethanol, ethanolamine, ethylenediamine, N-ethylmo ⁇ holine, N-ethylpiperidine, glucamine, glucosamine, histidine, hydrabamine, isopropylamine, lysine, methylglucamme, mo ⁇ holine, piperazine, piperidine, polyamine resins, procaine, purines, theobromine, triethylamine, trimethylamine, tripropylamine, and the like.
- cyclic amines such as arginine, betaine, caffeine, choline, N
- Salts derived from inorganic acids include salts of hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, hydroiodic acid, sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, phosphorous acid and the like.
- Salts derived from pharmaceutically acceptable organic non -toxic acids include salts of C ⁇ . 6 alkyl carboxylic acids, di-carboxylic acids, and tri-carboxylic acids such as acetic acid, propionic acid, fumaric acid, succinic acid, tartaric acid, maleic acid, adipic acid, and citric acid, and aryl and alkyl sulfonic acids such as toluene sulfonic acids and the like.
- an effective amount of a compound as provided herein is meant a non-toxic but sufficient amount of the compound(s) to provide the desired effect.
- the exact amount required will vary from subject to subject, depending on the species, age, and general condition of the subject, the severity of the disease that is being treated, the particular compound(s) used, the mode of administration, and the like. Thus, it is not possible to specify an exact “effective amount.” However, an appropriate effective amount may be determined by one of ordinary skill in the art using only routine experimentation.
- the amount of therapeutically effective compound(s) that is administered and the dosage regimen for treating a disease condition with the compounds and/or compositions of this invention depends on a variety of factors, including the age, weight, sex and medical condition of the subject, the severity of the disease, the route and frequency of administration, and the particular compound(s) employed, and thus may vary widely.
- the compositions contain well know carriers and excipients in addition to a therapeutically effective amount of compounds of Formula I.
- the pharmaceutical compositions may contain active ingredient in the range of about 0.001 to 100 mg/kg/day for an adult, preferably in the range of about 0.1 to 50 mg/kg/day for an adult. A total daily dose of about 1 to 1000 mg of active ingredient may be appropriate for an adult.
- the daily dose can be administered in one to four doses per day.
- the composition for therapeutic use may also comprise one or more non-toxic, pharmaceutically acceptable carrier materials or excipients.
- carrier material or excipient herein means any substance, not itself a therapeutic agent, used as a carrier and/or diluent and/or adjuvant, or vehicle for delivery of a therapeutic agent to a subject or added to a pharmaceutical composition to improve its handling or storage properties or to permit or facilitate formation of a dose unit of the composition into a discrete article such as a capsule or tablet suitable for oral administration.
- Excipients can include, by way of illustration and not limitation, diluents, disintegrants, binding agents, adhesives, wetting agents, polymers, lubricants, glidants, substances added to mask or counteract a disagreeable taste or odor, flavors, dyes, fragrances, and substances added to improve appearance of the composition.
- Acceptable excipients include lactose, sucrose, starch powder, cellulose esters of alkanoic acids, cellulose alkyl esters, talc, stearic acid, magnesium stearate, magnesium oxide, sodium and calcium salts of phosphoric and sulfuric acids, gelatin, acacia gum, sodium alginate, polyvinyl- pyrrolidone, and/or polyvinyl alcohol, and then tableted or encapsulated for convenient administration.
- Such capsules or tablets may contain a controlled-release formulation as may be provided in a dispersion of active compound in hydroxypropyl- methyl cellulose, or other methods known to those skilled in the art.
- the pharmaceutical composition may be in the form of, for example, a tablet, capsule, suspension or liquid. If desired, other active ingredients may be included in the composition.
- the compositions of the present invention may be administered by any suitable route, in the form of a pharmaceutical composition adapted to such a route, and in a dose effective for the treatment intended.
- the compositions may, for example, be administered parenterally, e.g., intravascularly, intraperitoneally, subcutaneously, or intramuscularly.
- saline solution, dextrose solution, or water may be used as a suitable carrier.
- Formulations for parenteral administration may be in the form of aqueous or non-aqueous isotonic sterile injection solutions or suspensions. These solutions and suspensions may be prepared from sterile powders or granules having one or more of the carriers or diluents mentioned for use in the formulations for oral administration.
- the compounds may be dissolved in water, polyethylene glycol, propylene glycol, EtOH, corn oil, cottonseed oil, peanut oil, sesame oil, benzyl alcohol, sodium chloride, and/or various buffers.
- Other adjuvants and modes of administration are well and widely known in the pharmaceutical art.
- the serotonin type 3 receptor is a member of a superfamily of ligand- gated ion channels, which includes the muscle and neuronal nAChR, the glycine receptor, and the ⁇ -aminobutyric acid type A receptor. Like the other members of this receptor superfamily, the 5HT R exhibits a large degree of sequence homology with 7 nAChR but functionally the two ligand-gated ion channels are very different. For example, al nAChR is rapidly inactivated, is highly permeable to calcium and is activated by acetylcholine and nicotine. On the other hand, 5HT 3 R is inactivated slowly, is relatively impermeable to calcium and is activated by serotonin.
- ⁇ 7 nAChR and 5HT 3 R proteins have some degree of homology, but function very differently. Indeed the pharmacology of the channels is very different.
- Ondansetron a highly selective 5HT 3 R antagonist, has little activity at the ⁇ 7 nAChR.
- GTS-21 a highly selective al nAChR agonist, has little activity at the 5HT 3 R.
- al nAChR is a ligand-gated Ca ++ channel formed by a homopentamer of al subunits.
- ⁇ -btx -bungarotoxin
- al nAChR has a high affinity binding site for both ⁇ -btx and methyllycaconitine (MLA).
- MVA methyllycaconitine
- ⁇ 7 nAChR is expressed at high levels in the hippocampus, ventral tegmental area and ascending cholinergic projections from nucleus basilis to thalamocortical areas.
- ⁇ 7 nAChR agonists increase neurotransmitter release, and increase cognition, arousal, attention, learning and memory.
- Schizophrenia is a complex multifactorial illness caused by genetic and non- genetic risk factors that produce a constellation of positive and negative symptoms.
- the positive symptoms include delusions and hallucinations and the negative symptoms include deficits in affect, attention, cognition and information processing. No single biological element has emerged as a dominant pathogenic factor in this disease. Indeed, it is likely that schizophrenia is a syndrome that is produced by the combination of many low penetrance risk factors.
- Pharmacological studies established that dopamine receptor antagonists are efficacious in treating the overt psychotic features (positive symptoms) of schizophrenia such as hallucinations and delusions.
- Clozapine an "atypical" antipsychotic drug, is novel because it is effective in treating both the positive and some of the negative symptoms of this disease.
- Clozapine's utility as a drug is greatly limited because continued use leads to an increased risk of agranulocytosis and seizure.
- No other antipsychotic drug is effective in treating the negative symptoms of schizophrenia. This is significant because the restoration of cognitive functioning is the best predictor of a successful clinical and functional outcome of schizophrenic patients (Green, M.F., Am J Psychiatry, 153:321- 30, 1996).
- it is clear that better drugs are needed to treat the cognitive disorders of schizophrenia in order to restore a better state of mental health to patients with this disorder.
- One aspect of the cognitive deficit of schizophrenia can be measured by using the auditory event-related potential (P50) test of sensory gating.
- P50 auditory event-related potential
- EEG electroencepholographic
- Normal individuals respond to the first click with greater degree than to the second click.
- schizophrenics and schizotypal patients respond to both clicks nearly the same (Cullum, CM. et. al., Schizophr. Res., 10:131-41, 1993).
- biochemical data indicate that schizophrenics have 50% fewer of ⁇ 7 nAChR receptors in the hippocampus, thus giving a rationale to partial loss of al nAChR functionality (Freedman, R. et. al., Biol. Psychiatry, 38:22-33, 1995).
- genetic data indicate that a polymo ⁇ hism in the promoter region of the al nAChR gene is strongly associated with the sensory gating deficit in schizophrenia (Freedman, R. et. al., Proc. Nat'lAcad. Sci. USA, 94(2):587-92, 1997; Myles-Worsley, M. et. al., Am. J. Med.
- schizophrenics express the same al nAChR as non-schizophrenics .
- Selective al nAChR agonists may be found using a functional assay on FLIPR (see WO 00/73431 A2).
- FLIPR is designed to read the fluorescent signal from each well of a 96 or 384 well plate as fast as twice a second for up to 30 minutes. This assay may be used to accurately measure the functional pharmacology of al nAChR and 5HT 3 R.
- To conduct such an assay one uses cell lines that expressed functional forms of the al nAChR using the ⁇ 7/5-HT 3 channel as the drug target and cell lines that expressed functional 5HT 3 R. In both cases, the ligand-gated ion channel was expressed in SH-EPl cells. Both ion channels can produce robust signal in the FLIPR assay.
- the compounds of the present invention are ⁇ 7 nAChR agonists and may be used to treat a wide variety of diseases. For example, they may be used in treating schizophrenia, or psychosis.
- Schizophrenia is a disease having multiple aspects.
- drugs are generally aimed at controlling the positive aspects of schizophrenia, such as delusions.
- One drug, Clozapine is aimed at a broader spectrum of symptoms associated with schizophrenia. This drug has many side effects and is thus not suitable for many patients.
- a drag to treat the cognitive and attention deficits associated with schizophrenia.
- Psychosis is a mental disorder characterized by gross impairment in the patient's perception of reality.
- the patient may suffer from delusions, and hallucinations, and may be incoherent in speech. His behavior may be agitated and is often incomprehensible to those around him.
- psychosis has been applied to many conditions that do not meet the stricter definition given above. For example, mood disorders were named as psychoses.
- antipsychotic drugs There are a variety of antipsychotic drugs.
- the conventional antipsychotic drugs include Chlo ⁇ romazine, Fluphenazine, Haloperidol, Loxapine, Mesoridazine, Molindone, Pe ⁇ henazine, Pimozide, Thioridazine, Thiothixene, and Trifluoperazine. These drugs all have an affinity for the dopamine 2 receptor.
- Atypical antipsychotic drags generally are able to alleviate positive symptoms of psychosis while also improving negative symptoms of the psychosis to a greater degree than conventional antipsychotics. These drugs may improve neurocognitive deficits. Extrapyramidal (motor) side effects are not as likely to occur with the atypical antipsychotic drugs, and thus, these atypical antipsychotic drugs have a lower risk of producing tardive dyskinesia. Finally these atypical antipsychotic drags cause little or no elevation of prolactin. Unfortunately, these drugs are not free of side effects.
- the side effects include: agranulocytosis; increased risk of seizures, weight gain, somnolence, dizziness, tachycardia, decreased ejaculatory volume, and mild prolongation of QTc interval.
- the compounds of Formula I and the anti-psychotic drugs can be administered simultaneously or at separate intervals.
- the compounds of Formula I and the anti-psychotic drugs can be inco ⁇ orated into a single pharmaceutical composition, e.g., a pharmaceutical combination therapy composition.
- two separate compositions i.e., one containing compounds of Formula I and the other containing anti-psychotic drugs, can be administered simultaneously.
- anti-psychotic drugs examples include, but are not limited to, Thorazine, Mellaril, Trilafon, Navane, Stelazine, Permitil, Prolixin, Risperdal, Zyprexa, Seroquel, ZELDOX, Acetophenazine, Ca ⁇ henazine, Chlo ⁇ rothixene, Droperidol, Loxapine, Mesoridazine, Molindone, Ondansetron, Pimozide, Prochlo ⁇ erazine, and Promazine.
- a pharmaceutical combination therapy composition can include therapeutically effective amounts of the compounds of Formula I, noted above, and a therapeutically effective amount of anti-psychotic drags.
- compositions may be formulated with common excipients, diluents or carriers, and compressed into tablets, or formulated elixirs or solutions for convenient oral administration or administered by intramuscular intravenous routes.
- the compounds can be administered rectally, topically, orally, sublingually, or parenterally and maybe formulated as sustained relief dosage forms and the like.
- therapeutically effective amounts of compositions containing compounds of Formula I and anti-psychotic drugs are administered on a different schedule. One may be administered before the other as long as the time between the two administrations falls within a therapeutically effective interval.
- a therapeutically effective interval is a period of time beginning when one of either (a) the compounds of Formula I, or (b) the anti-psychotic drugs is administered to a human and ending at the limit of the beneficial effect in the treatment of schizophrenia or psychosis of the combination of (a) and (b).
- the methods of administration of the compounds of Formula I and the anti-psychotic drags may vary. Thus, either agent or both agents may be administered rectally, topically, orally, sublingually, or parenterally.
- the compounds of the present invention are al nAChR agonists.
- the compounds of the present invention may be used to treat a variety of diseases including cognitive and attention deficit symptoms of Alzheimer's, neurodegeneration associated with diseases such as
- Alzheimer's disease pre-senile dementia (also known as mild cognitive impairment), and senile dementia.
- Alzheimer's disease has many aspects, including cognitive and attention deficits.
- these deficits are treated with cholinesterase inhibitors. These inhibitors slow the break down of acetylcholine, and thereby provide a general nonspecific increase in the activity of the cholinergic nervous system. Since the drags are nonspecific, they have a wide variety of side effects.
- Neurodegeneration is a common problem associated with diseases such as
- Alzheimer's disease While the current drags treat some of the symptoms of this disease, they do not control the underlying pathology of the disease. Accordingly, it would be desirable to provide a drug that can slow the progress of Alzheimer's disease.
- Pre-senile dementia mimild cognitive impairment
- Mild cognitive impairment is distinguished from senile dementia in that mild cognitive impairment involves a more persistent and troublesome problem of memory loss for the age of the patient.
- Senile dementia is not a single disease state. However, the conditions classified under this name frequently include cognitive and attention deficits.
- the compounds of the present invention are al nAChR agonists.
- yet other diseases to be treated with compounds of the present invention include treating the cognitive and attention deficits as well as the neurodegeneration associated with attention deficit disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, mood and affective disorders, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, borderline personality disorder, traumatic brain injury, behavioral and cognitive problems associated with brain tumors, AIDS dementia complex, dementia associated with Down's syndrome, dementia associated with Lewy Bodies, Huntington's disease, depression, general anxiety disorder, age-related macular degeneration, Parkinson's disease, tardive dyskinesia, Pick's disease, post traumatic stress disorder, dysregulation of food intake including bulemia and anorexia nervosa, withdrawal symptoms associated with smoking cessation and dependant drug cessation, Gilles de la Tourette's Syndrome, glaucoma, or symptoms associated with pain.
- the cognitive and attention deficits as well as the neurodegeneration associated with attention deficit disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, mood and affective disorders, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, borderline personality disorder, traumatic brain injury,
- Attention deficit disorder is generally treated with methylphenidate, an amphetamine-like molecule that has some potential for abuse. Accordingly, it would be desirable to provide a drag that treats attention deficit disorder while having fewer side effects than the currently used drug.
- ADHD Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- Treatment may include medications such as methylphenidate, dextroamphetamine, or pemoline, which act to decrease impulsivity and hyperactivity and to increase attention. No "cure" for ADHD currently exists. Children with the disorder seldom outgrow it; therefore, there is a need for appropriate medicaments.
- HCA's heterocyclic antidepressant
- MAOI's monoamine oxidase inhibitors
- Benign side effects from the use of lithium include, but are not limited to, weight gain, nausea, diarrhea, polyuria, polydipsia, and tremor.
- Toxic side effects from lithium can include persistent headache, mental confusion, and may reach seizures and cardiac arrhythmias. Therefore, agents with less side effects or interactions with food or other medications would be useful.
- HCA heterocyclic antidepressants
- MAOI's monoamine oxidase inhibitors
- Common side effects from HCA's are sedation and weight gain. In elderly patients with organic brain disease, the side effects from HCA's can also include seizures and behavioral symptoms. The main side effects from using MAOI's occur from dietary and drag interactions. Therefore, agents with fewer side effects would be useful.
- Borderline personality disorder although not as well known as bipolar disorder, is more common. People having borderline personality disorder suffer from a disorder of emotion regulation. Pharmaceutical agents are used to treat specific symptoms, such as depression or thinking distortions.
- HIV infection results from an infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). This virus attacks selected cells and impairs the proper function of the immune, nervous, and other systems. HIV infection can cause other problems such as, but not limited to, difficulties in thinking, otherwise known as AIDS dementia complex. Therefore, there is a need to drugs to relieve the confusion and mental decline of persons with AIDS.
- HIV human immunodeficiency virus
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis also known as Lou Gehrig's disease, belongs to a class of disorders known as motor neuron diseases wherein specific nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord gradually degenerate to negatively affect the control of voluntary movement.
- motor neuron diseases wherein specific nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord gradually degenerate to negatively affect the control of voluntary movement.
- amyotrophic lateral sclerosis although patients may receive treatment from some of their symptoms and although Riluzole has been shown to prolong the survival of patients. Therefore, there is a need for a pharmaceutical agent to treat this disease.
- Symptoms of brain tumors include behavioral and cognitive problems. Surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy are used to treat the tumor, but other agents are necessary to address associated symptoms. Therefore, there is a need to address the symptoms of behavioral and cognitive problems.
- Persons with Down's syndrome have in all or at least some of their cells an extra, critical portion of the number 21 chromosome.
- Adults who have Down's syndrome are known to be at risk for Alzheimer-type dementia.
- Genetically programmed degeneration of neurons in certain areas of the brain cause Huntington's disease. Early symptoms of Huntington's disease include mood swings, or trouble learning new things or remembering a fact.
- GAD General anxiety disorder
- Dementia with Lewy Bodies is a neurodegenerative disorder involving abnormal stractures known as Lewy bodies found in certain areas of the brain. Symptoms of dementia with Lewy bodies include, but are not limited to, fluctuating cognitive impairment with episodic delirium. Currently, treatment concerns addressing the parkinsonian and psychiatric symptoms. However, medicine to control tremors or loss of muscle movement may actually accentuate the underlying disease of dementia with Lewy bodies. Therefore, there is a need of a pharmaceutical agent to treat dementia with Lewy bodies.
- Age-related macular degeneration is a common eye disease of the macula which is a tiny area in the retina that helps produce sha ⁇ , central vision required for "straight ahead" activities that include reading and driving. Persons with AMD lose their clear, central vision. AMD takes two forms: wet and dry. In dry AMD, there is a slow breakdown of light-sensing cells in the macula. There currently is no cure for dry AMD. In wet AMD, new, fragile blood vessels growing beneath the macula as dry AMD worsens and these vessels often leak blood and fluid to cause rapid damage to the macula quickly leading to the loss of central vision. Laser surgery can treat some cases of wet AMD. Therefore, there is a need of a pharmaceutical agent to address AMD.
- Parkinson's disease is a neurological disorder characterized by tremor, hypokinesia, and muscular rigidity. Currently, there is no treatment to stop the progression of the disease. Therefore, there is a need of a pharmaceutical agent to address Parkinson's.
- Tardive dyskinesia is associated with the use of conventional antipsychotic drags. This disease is characterized by involuntary movements most often manifested by puckering of the lips and tongue and/or writhing of the arms or legs. The incidence of tardive dyskinesia is about 5% per year of drug exposure among patients taking conventional antipsychotic drags. In about 2% of persons with the disease, tardive dyskinesia is severely disfiguring. Currently, there is no generalized treatment for tardive dyskinesia. Furthermore, the removal of the effect-causing drags is not always an option due to underlying problems. Therefore, there is a need for a pharmaceutical agent to address the symptoms of tardive dyskinesia.
- Post-traumatic stress disorder is a form of anxiety triggered by memories of a traumatic event that directly affected the patient or that the patient may have witnessed.
- the disorder commonly affects survivors of traumatic events including sexual assault, physical assault, war, torture, natural disasters, an automobile accident, an ai ⁇ lane crash, a hostage situation, or a death camp.
- the affliction also can affect rescue workers at an ai ⁇ lane crash or a mass shooting, someone who witnessed a tragic accident or someone who has unexpectedly lost a loved one.
- Treatment for PTSD includes cognitive-behavioral therapy, group psychotherapy, and medications such as Clonazepam, Lorazepam and selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors such as Fluoxetine, Sertraline, Paroxetine, Citalopram and Fluvoxamine. These medications help control anxiety as well as depression.
- Various forms of exposure therapy (such as systemic desensitization and imaginal flooding) have all been used with PTSD patients. Exposure treatment for PTSD involves repeated reliving of the trauma, under controlled conditions, with the aim of facilitating the processing of the trauma. Therefore, there is a need for better pharmaceutical agents to treat Post traumatic stress disorder.
- Dysregulation of food intake associated with eating disease involve neurophysiological pathways.
- Anorexia nervosa is hard to treat due to patients not entering or remaining in after entering programs.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy has helped patients suffering from bulemia nervosa; however, the response rate is only about 50% and current treatment does not adequately address emotional regulation. Therefore, there is a need for pharmaceutical agents to address neurophysiological problems underlying diseases of dysregulation of food intake.
- Cigarette smoking has been recognized as a major public health problem for a long time. However, in spite of the public awareness of health hazard, the smoking habit remains extraordinarily persistent and difficult to break. There are many treatment methods available, and yet people continue to smoke. Administration of nicotine transdermally, or in a chewing gum base is common treatments. However, nicotine has a large number of actions in the body, and thus can have many side effects. It is clear that there is both a need and a demand of long standing for a convenient and relatively easy method for aiding smokers in reducing or eliminating cigarette consumption. A drag that could selectively stimulate only certain of the nicotinic receptors would be useful in smoke cessation programs.
- Smoke cessation programs may involve oral dosing of the drug of choice.
- the drag may be in the form of tablets. However, it is preferred to administer the daily dose over the waking hours, by administration of a series of incremental doses during the day.
- the preferred method of such administration is a slowly dissolving lozenge, troche, or chewing gum, in which the drug is dispersed.
- Another drug in treating nicotine addiction is Zyban. This is not a nicotine replacement, as are the gum and patch. Rather, this works on other areas of the brain, and its effectiveness is to help control nicotine craving or thoughts about cigarette use in people trying to quit.
- Zyban is not very effective and effective drugs are needed to assist smokers in their desire to stop smoking.
- These drags may be administered transdermally through the use of skin patches. In certain cases, the drugs may be administered by subcutaneous injection, especially if sustained release formulations are used.
- Drug use and dependence is a complex phenomenon, which cannot be encapsulated within a single definition. Different drugs have different effects, and therefore different types of dependence. Drug dependence has two basic causes, that is, tolerance and physical dependence. Tolerance exists when the user must take progressively larger doses to produce the effect originally achieved with smaller doses. Physical dependence exists when the user has developed a state of physiologic adaptation to a drag, and there is a withdrawal (abstinence) syndrome when the drag is no longer taken. A withdrawal syndrome can occur either when the drug is discontinued or when an antagonist displaces the drag from its binding site on cell receptors, thereby counteracting its effect. Drug dependence does not always require physical dependence.
- Drug dependence often involves psychological dependence, that is, a feeling of pleasure or satisfaction when taking the drug. These feelings lead the user to repeat the drug experience or to avoid the displeasure of being deprived of the drag.
- Drugs that produce strong physical dependence such as nicotine, heroin and alcohol are often abused, and the pattern of dependence is difficult to break. Drugs that produce dependence act on the CNS and generally reduce anxiety and tension; produce elation, euphoria, or other pleasurable mood changes; provide the user feelings of increased mental and physical ability; or alter sensory perception in some pleasurable manner.
- narcotic addiction is to switch the patient to a comparable drag that produces milder withdrawal symptoms, and then gradually taper off the substitute medication.
- the medication used most often is methadone, taken orally once a day. Patients are started on the lowest dose that prevents the more severe signs of withdrawal and then the dose is gradually reduced. Substitutes can be used also for withdrawal from sedatives. Patients can be switched to long-acting sedatives, such as diazepam or phenobarbital, which are then gradually reduced.
- Gilles de la Tourette's Syndrome is an inherited neurological disorder.
- the disorder is characterized by uncontrollable vocal sounds called tics and involuntary movements.
- the symptoms generally manifest in an individual before the person is 18 years of age.
- the movement disorder may begin with simple tics that progress to multiple complex tics, including respiratory and vocal ones.
- Vocal tics may begin as granting or barking noises and evolve into compulsive utterances.
- Coprolalia involuntary scatologic utterances
- Tics tend to be more complex than myoclonus, but less flowing than choreic movements, from which they must be differentiated. The patient may voluntarily suppress them for seconds or minutes.
- Clonidine may be used for simple and complex tics. Long-term use of Clonidine does not cause tardive dyskinesia; its limiting adverse effect is hypotension. In more severe cases, antipsychotics, such as Haloperidol may be required, but side effects of dysphoria, parkinsonism, akathisia, and tardive dyskinesia may limit use of such antipsychotics. There is a need for safe and effective methods for treating this syndrome. Glaucoma is within a group of diseases occurs from an increase in intraocular pressure causing pathological changes in the optical disk and negatively affects the field of vision.
- Medicaments to treat glaucoma either decrease the amount of fluid entering the eye or increase drainage of fluids from the eye in order to decrease intraocular pressure.
- current drags have drawbacks such as not working over time or causing side effects so the eye-care professional has to either prescribe other drags or modify the prescription of the drag being used.
- Alpha 7 nicotinic agonists may stimulate the release of inhibitory amino acids such as GAB A which will dampen hyperexcitablity.
- Alpha 7 nicotinic agonists are also directly neuroprotective on neuronal cell bodies. Thus alpha 7 nicotinic agonists have the potential to be neuroprotective in glaucoma. Persons afflicted with pain often have what is referred to as the "terrible triad" of suffering from the pain, resulting in sleeplessness and sadness, all of which are hard on the afflicted individual and that individual's family.
- the compounds of the present invention may be used in combination therapy with typical and atypical anti-psychotic drugs. All compounds within the present invention are useful for and may also be used in combination with each other to prepare pharmaceutical compositions. Such combination therapy lowers the effective dose of the anti-psychotic drag and thereby reduces the side effects of the anti-psychotic drugs.
- Some typical anti-psychotic drugs that may be used in the practice of the invention include Haldol.
- Some atypical anti-psychotic drugs include Ziprasidone, Olanzapine, Resperidone, and Quetiapine.
- the acid is converted into a mixed anhydride by treatment with bis (2-oxo-3-oxazolidinyl) phosphinic chloride in the presence of TEA with CH 2 C1 2 or CHC1 as the solvent.
- TEA bis (2-oxo-3-oxazolidinyl) phosphinic chloride
- the resulting anhydride solution is directly reacted with 3- aminoquinuclidine added neat or using DMF or aqueous DMF as solvent.
- HATU in the presence of an appropriate tertiary amine such as diisopropylethyl amine in a solvent such as DMF leads to the desired amides.
- a tertiary amine such as diisopropylethyl amine
- a solvent such as DMF
- condensation of 3-aminoquinuclidine with an ester W-C(O)-O-alkyl or W-C(O)-O-(electron-deficient aryl)
- an appropriate solvent such as ethanol
- the oximes can be prepared by treatment of the 3-quinuclidinones with hydroxylamine hydrochloride in the presence of a base.
- thioamides There are a variety of methods for constructing thioamides.
- a reagent such as Lawesson's reagent (2,4-bis(4- methoxyphenyl)-l,3-dithia-2,4-diphosphetane-2,4-disulfide). See Lawesson et. al. in Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg., 229 (1978)), or P 4 S 10 (see Chem. Rev., 45 (1961).
- a dithiocarboxylic ester with the corresponding quinuclidine to form the same thioamide.
- 2-Chloro-3-pyridinol (20.0 g, 0.154 mole), NaHCO 3 (19.5g, 0.232 mole, 1.5 equ), and 150 mL of water are placed in a flask.
- the flask is placed in an oil bath at 90°C, and after 5 min, 37% aqueous formaldehyde (40.5 mL, 0.541 mole, 3.5 equ) is added in six unequal doses in the following order: 12 mL, 3 x 8 mL, then 2.2 mL all at 90-minute intervals and then the final 2.3 mL after the reaction had stirred for 15 h at 90°C.
- the reaction is stirred at 90°C for another 4 h and then is cooled by placing the flask in an ice bath.
- the pH of the reaction is then adjusted to 1 using 6N HCI.
- the reaction is stirred for 1.5 h in an ice bath allowing an undesired solid to form.
- the undesired solid is removed by filtration, and the filtrate is extracted seven times with EtOAc.
- the combined organic extracts are concentrated in vacuo, toluene is added to the flask and removed in vacuo to azeotrope water, and then CH C1 2 is added and removed in vacuo to obtain 2-chloro-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-pyridinol (Cl) as a pale yellow solid (81% yield) sufficiently pure for subsequent reaction.
- Oxalyl chloride (3.1 mL, 35 mmol) is dissolved in 200 mL CH 2 C1 2 in dried flask under N 2 .
- the flask is placed in a dry-ice/acetone bath at -78°C, DMSO (4.95 mL, 70 mmol) in 10 mL CH 2 C1 2 is added drop-wise, and the mixture is stirred for 20 min.
- C4 (5.5 g, 30 mmol) in 10 mL CH 2 C1 2 is added, and the reaction is stirred 30 min at -78°C.
- TEA (21.3 mL, 153 mmol) is then added.
- the reaction is diluted with 10 mL saturated NaHCO 3 , is stirred vigorously for 1 h, the layers are separated, and the aqueous layer is extracted with 3 x 10 mL CH 2 C1 2 .
- the combined organic layer is concentrated to a pale oil which is dissolved in MeOH and passed over 15 mL Dowex 50W-X2 (hydrogen form) ion exchange resin eluting with MeOH followed by 5% TEA in MeOH.
- the fraction with the desired compound is concentrated in vacuo to give 150 mg of a pale oil.
- the crude oil is dissolved in 5 mL MeOH, 2 mL IN methanolic HCI is added, and the solution is concentrated to a pale yellow solid.
- Example 2 is obtained (31% yield) using acid C13 according to Method A with non-critical changes.
- Method B Acid C7 (435 mg, 2.2 mmol) and TEA (307 ⁇ L, 2.2 mmol) in CH 2 C1 2 (10 mL) are stirred until dissolved, diphenylphosphoryl azide (431 ⁇ L, 2.0 mmol) is added, and the reaction is stirred for 20 min at rt.
- R-(+)-3-aminoquinuclidine (252 mg, 2.0 mmol) in CH 2 C1 2 (3 mL) is added, and the reaction is stirred for 18 h at rt.
- the solution is diluted with MeOH and loaded onto a column of AG 50W-X2 resin (hydrogen form).
- the column is rinsed with MeOH, and the product eluted with a 5% TEA/MeOH solution onto a column of AMBERJET 4400 OH resin.
- the eluted material is concentrated to an oil.
- the crude material is chromatographed over 25 g slurry- packed silica gel, eluting with 0.3% ammonium hydroxide/4% MeOH/CH 2 Cl 2 followed by 0.5% ammonium hydroxide/5% MeOH/CH 2 Cl , and finally 0.5% ammonium hydroxide/8% MeOH/CH 2 Cl 2 .
- the fractions with the desired compound are collected and concentrated to an oil.
- the oil is dissolved in a minimum amount of MeOH and IN HCI in MeOH (5 mL) is added.
- Oxalyl chloride (685 ⁇ L, 7.8 mmol) is dissolved in 30 mL CH 2 C1 2 in a dry flask under N 2 .
- the flask is placed in a dry-ice/acetone bath, DMSO (1.11 mL, 15.6 mmol) in 5 mL CH 2 C1 2 is added drop-wise, and the mixture is stirred for 20 min.
- C16 (1.0 g, 6.1 mmol) in 10 mL CH C1 is added, and the reaction is stirred 30 min at - 78°C.
- Oxalyl chloride (869 ⁇ L, 9.9 mmol) is dissolved in 50 mL CH 2 C1 2 in a dry flask under N 2 .
- the flask is placed in a dry-ice/acetone bath at -78°C, DMSO (1.41 mL, 19.8 mmol) in 5 mL CH 2 C1 is added drop-wise, and the mixture is stirred for 20 min.
- 3,3-Dimethyl-2,3-dihydrofuro[2,3-c]pyridin-5-yl)methanol (C21) (1.53 g, 8.5 mmol) in 5 mL CH 2 C1 2 is then added, and the reaction is stirred 30 min at -78°C.
- Example 5 is obtained (21% yield) using acid C23 according to Method A with non-critical changes.
- Oxalyl chloride (784 ⁇ L, 8.9 mmol) is dissolved in 25 mL CH 2 C1 in a dry flask under N 2 .
- the flask is placed in a dry-ice/acetone bath at -78°C, and DMSO (1.26 mL, 17.8 mmol) in 5 mL CH 2 C1 2 is added.
- the mixture is stirred for 20 min and C25 (1.53 g, 8.5 mmol) in 5 mL CH 2 C1 2 is added.
- the reaction is stirred 1 h, TEA (5.9 mL, 42.5 mmol) is added, and the reaction is stirred 30 min at -78°C.
- Example 6 is obtained (54% yield) using acid C27 according to Method A with non-critical changes.
- Example 7 is obtained as a white solid with a yield of 18% using acid C34 according to Method A with non-critical changes.
- HRMS (FAB) calculated for C 15 H 17 N 3 O 2 +H: 272.1399, found 272.1402 (M+H) + .
- Ethyl glycolate (35.5 mL, 375 mmol) is slowly added (over 20 min) to a slurry of NaOH (15.8 g, 394 mmol) in 1 ,2-dimethoxyethane (400 mL) in a dry flask under N 2 with the flask being in an ice bath.
- the mixture is allowed to warm to rt, is stirred for 30 min, and ethyl 2-chloronicotinate (27.84 g, 150 mmol) in 1 ,2-dimethoxyethane (50 mL) is added over 10 min.
- the reaction is warmed to 65°C for 15 h in an oil bath.
- Example 8 is obtained as a white solid (29% yield) using acid C43 according to Method A with non-critical changes. MS (El) for C 15 Hi 7 N 3 O 2 , m/z: 271 (M) + .
- Oxalyl chloride (1.16 mL, 13.2 mmol) is added to CH 2 C1 2 (30 mL) in a dry flask under N 2 and in a dry-ice/acetone bath at -78°C.
- DMSO (18.80 mL, 26.5 mmol) is slowly added. The solution is stirred for 20 min, and C54 (1.88 g, 1 1.5 mmol) is added. The mixture is stirred for 1 h at -78°C, then 30 min at 0-5°C. The material is washed with saturated NaHCO 3 (75 mL), dried over K CO , filtered, and concentrated in vacuo to a yellow solid (3.23 g).
- the layers are separated and the residual aldehyde extracted with additional ether.
- the aqueous layer is acidified to pH 3 with concentrated HCI, then extracted with CH 2 C1 2 (4 X). Large amounts of acid remained in the aqueous layer, so the aqueous layer is concentrated to dryness.
- the solid is triturated with CHC1 3 (4 X), and then 10% MeOH/CH 2 Cl 2 (4 X) to extract much of the acid into the supernatant.
- the combined organic layer is dried over Na 2 SO 4 , filtered, and concentrated to a tan solid (1.69 g, greater than 100% isolated yield).
- the solid is diluted with CHC1 3 and refluxed for 3 h. The flask is removed from heat, allowed to cool slightly, then filtered.
- Example 9 is obtained as an off-white solid (64% yield ) using acid C56 according to Method A with non-critical changes.
- Example 10 is obtained as an off-white solid (49% yield) using acid C60 according to Method A with non-critical. HRMS (FAB) calculated for C 17 H 21 N 3 O 2 +H: 300.1712, found 300.1716 (M+H) + .
- Example 11 is obtained as an off-white solid (56% yield) using acid C70 according to Method A with non-critical changes.
- Example 3 (220 mg, 0.72 mmol) and sodium thiomethoxide (55 mg, 0.79 mmol) are added to DMF (3 mL) and stirred for 2 h at rt.
- the solution is diluted with MeOH and loaded onto a column of AG 50W-X2 resin (hydrogen form).
- the column is rinsed with MeOH, and the product eluted with a 5% TEA/MeOH solution onto a column of AMBERJET 4400 OH resin.
- the eluted material is concentrated to an oil (116 mg).
- the crude material is chromatographed over 5 g slurry-packed silica gel, eluting with 0.5% ammonium hydroxide/8% MeOH/CH 2 Cl 2 .
- Example 13 is obtained as a white salt (9% yield) using acid C102 according to Method A with non-critical changes.
- 2-Nitrothiophene (33.76 g, 261.4 mmol) is suspended in concentrated HCI (175 mL) and heated to 50°C.
- Stannous chloride (118.05 g, 523.2 mmol) is added portionwise, maintaining the reaction temperature between 45-50°C with an ice bath, that is removed after the addition.
- the solution is allowed to cool slowly to 30°C over an hour.
- the solution is then cooled in an ice bath and filtered.
- the cake is washed with concentrated HCI (20 mL), dried in a stream of air, and washed with ether (50 mL) to afford the hexachlorostannate salt of 2-aminothiophene as a brown solid (26% yield).
- 3,3-Dimethyl-2-formyl propionitrile sodium (3.33 g, 20.2 mmol) can readily be prepared from the method described by Bertz, S.H., et al., /. Org. Chem., 41, 2216- 2217 (1982).
- 3,3-Dimethyl-2-formyl propionitrile sodium is dissolved in MeOH (40 mL), and concentrated HCI (4 mL) and the hexachlorostannate salt of 2- aminothiophene (10.04 g, 19.1 mmol) in MeOH (130 mL) is slowly added drop-wise to the mixture.
- Example 14 is obgtained as a white salt (18% yield) using acid C106 according to Method A with non-critical changes. HRMS (FAB) calculated for C 15 H N 3 OS+H: 288.1170, found 288.1 180 (M+H) + .
- Example 15 N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]thieno[2,3-b]pyridine-6- carboxamide dihydrochloride:
- Example 15 is obtained as a yellow solid (43% yield) using acid C113 according to Method A with non-critical changes. MS (El) for Ci 5 H 17 N 3 OS, m/z: 287
- Example 17 is obtained as a white solid (8% yield) using acid C122 according to Method A with non-critical changes.
- Example 18 is obtained as a white solid (52% yield) using acid C129 according to Method A with non-critical changes.
- Example 19 is obtained as a white salt (37% yield) using thieno[3,2- b]pyridine-5-carboxylic acid according to Method A with non-critical changes.
- HRMS (FAB) calculated for C 15 H 17 N 3 OS+H: 288.1170, found 288.1180 (M+H) + .
- Methyl 3-aminothiophene-2-carboxylate (1.52 g, 9.68 mmol) is dissolved in 2M NaOH (10 mL, 20 mmol) and refluxed in a 115°C oil bath for 30 min. The mixture is cooled to rt, placed in an ice bath, and carefully acidified with concentrated HCI. The slurry is filtered and rinsed with water (25 mL). The cake is then dissolved in acetone (50 mL), dried over MgSO , filtered, and concentrated to a thick paste. The crude material is dissolved in 1-propanol (25 mL), and oxalic acid (0.90 g, 10.0 mmol) is added portionwise.
- 3,3-Dimethyl-2-formyl propionitrile sodium (5.38 g, 32.6 mmol) is dissolved in MeOH (60 mL) with concentrated HCI (6 mL).
- C135 (6.16 g, 32.6 mmol) is suspended in MeOH (200 mL) and added drop-wise to the acidic solution.
- the mixture is refluxed at 80°C for 5 h when an additional 20 mL concentrated HCI and 20 mL H 2 O are added; the mixture continued refluxing for another 12 h.
- the mixture is concentrated in vacuo, and the residue is dissolved with cold H 2 O (100 mL).
- Example 20 is obtained as a white salt (37% yield) using acid C 137 according to Method A with non-critical changes.
- 4-Chloropyridine hydrochloride (15 g, 99.9 mmol) is free-based by stirring in lOOOmL 1:1 saturated NaHCO 3 /ether for 1 h. The layers are allowed to separate, the aqueous layer is extracted with ether (2 x 175 mL), and the combined organic layer is dried over MgSO 4 , filtered, and concentrated to an oil. THF (300 mL) is chilled to - 70°C in a dry flask. N-butyllithium (105.1 mL, 168.2 mmol) is added drop-wise, and the mixture is placed in an ice bath. Diisopropylamine (23.6mL.
- Example 21 is obtained as a yellow salt (25% yield) using acid C142 according to Method A with non-critical changes.
- 2,3-Thiophene dicarboxaldehyde (1.40 g, 9.99 mmol) is dissolved in CH 2 C1 2 (100 mL) and the flask is placed in an ice bath.
- C153 (2.63 g, 11.0 mmol) is dissolved in CH 2 C1 2 (50 mL), DBU (1.65 mL, 11.0 mmol) is added, and this solution is added drop-wise to the chilled thiophene solution.
- the reaction mixture is stirred for 1 h while the flask is in an ice bath and then over night at rt.
- Example 22 is obtained as a white salt (32% yield) using acid C156 according to Method A with non-critical changes. MS (El) for C 15 H 17 N 3 OS, m/z: 287 (M) + .
- Methyl thieno[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylate (C155) (678 mg, 3.5 mmol) is dissolved in MeOH (16 mL) and water (2 mL). 2M NaOH (1.8 mL, 3.6 mmol) is added drop-wise, and the solution stirred at rt. After 2 days (complete disappearance of ester by TLC), the solution is concentrated in vacuo. The residue is dissolved in water (12 mL), and the pH is adjusted to 3.5 with 10% HCI.
- Example 23 is obtained as a white salt (31 % yield) using acid C160 according to Method A with non-critical changes. MS (El) for C ⁇ 5 H )7 N 3 OS, m/z: 287 (M) + .
- 2,4-Lutidine (51.4 mL, 0.445 mole) is added drop-wise to 250 mL fuming sulfuric acid in a flask under N 2 in an ice bath.
- the solution is treated portionwise with potassium nitrate (89.9 g, 0.889 mole) over a 15 min period.
- the reaction is stirred lh in an ice bath, 2 h at rt, is gradually warmed in a 100°C oil bath for 5 h, and then in a 130°C oil bath for 4 h.
- the mixture is cooled, is poured into 1000 mL ice, and the mixture is neutralized with NaHCO 3 (1,100 g, 13.1 mole).
- the precipitated Na 2 SO is removed by filtration, the solid is washed with 500 mL water and the filtrate is extracted with 4 x 500 mL ether. The combined organic layer is dried over anhydrous MgSO and is concentrated in vacuo to a yellow oil (50 g).
- the crude oil is distilled under vacuum to provide three fractions: 16 g recovered 2,4-lutidine (85°C), 16 g 2,4-dimethyl-3-nitro-pyridine (C169) contaminated with 25% 2,4-dimethyl-5- nitro-pyridine (135-145°C), and 16 g 2,4-dimethyl-5-nitro-pyridine (C170) contaminated with 2,4-dimethyl-3-nitropyridine (145-153°C).
- Example 24 is obtained as a white solid (40% yield) using acid C176 using Method C with non-critical changes.
- HRMS (FAB) calculated for Cj 5 H 18 N 4 O+H: 271.1559, found 271.1562 (M+H) + .
- Example 25 N-((3R)l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl)-l-methyl-lH-pyrrolo[2,3- c]pyridine-5-carboxamide dihydrochloride:
- Example 25 is obtained as a yellow solid (54% yield) using acid C178 according to Method C with non-critical changes.
- N-Butyl lithium (150.6 ml, 241 mmol) is added dropwise to ether (100 ml) at - 20°C under N 2 .
- 3-Bromotf ⁇ ianaphthene (10.5 ml, 80.3 mmol) is dissolved in ether (50 ml) and also added dropwise to the chilled solution, stirring cold for 0.5 h.
- DMF (16.3 ml, 210 mmol) is dissolved in ether (75 ml) and added dropwise, and the solution stirred an additional 15 h at -20°C.
- the reaction is quenched onto ice (300 g) in 10% H SO (200 ml) and stirred until both layers turned yellow in color.
- Example 26 is obtained as a white salt (62% yield) using acid C182 according to Method A with non critical changes.
- Example 27 is obtained using benzothieno[2,3-c]pyridine-3-carboxylic acid according to Method C making non-critical changes to afford 115 mg (86% yield) as a pale yellow solid.
- HRMS (FAB) calcd for C 19 H 19 N 3 OS+H: 338.1327, found 338.1325.
- Furo[2,3-c]pyridin-5-ylmethanol (7.70 g, 51.63 mmol) is dissolved in pyridine (45 mL), treated with acetic anhydride (14.36 mL, 154.9 mmol) and stirred for 18 h at rt. The pyridine is removed in vacuo and the resulting residue dissolved in EtOAc (200 mL), washed with 50% saturated sodium bicarbonate (4 x 90 mL), dried over MgSO and concentrated in vacuo to afford 9.32 g (94%) of furo[2,3-c]pyridin-5- ylmethyl acetate as a yellow oil.
- the solution is diluted with EtOH (35 mL), treated with K 2 CO 3 (4.09 g, 29.6 mmol) and stirred for 18 h at rt. Water (7 mL) is added and the mixture stirred for 2 days. The mixture is concentrated to dryness, partitioned between 50% saturated NaCl (50 mL) and CH C1 2 (4 x 50 mL), dried over K 2 CO 3 and concentrated in vacuo to a brown solid (833 mg). The crude material is chromatographed over a standard 40 g Biotage column, eluting with 50% EtOAc / hexane.
- 3-Chlorofuro[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carbaldehyde (317 mg, 1.74 mmol) is dissolved in THF (10 mL)/t-BuOH (5 mL)/H 2 O (5 mL), treated with a single portion of sodium chlorite (592 mg, 5.24 mmol) and KH 2 PO 4 (473 mg, 3.48 mmol) and stirred at rt for 18 h.
- the reaction mixture is concentrated in vacuo to dryness, suspended in water (10 mL), acidified to pH 3.5 with concentrated HCI and stirred at rt for 2 h.
- Example 28 is obtained using 3-chlorofuro[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxylic acid accoding to Method C making non-critical changes to afford 101 mg of a white solid. MS (El) m/z 305 (M + ).
- Furo[2,3-c]pyridin-5-ylmethyl acetate (5.17 g, 27.05 mmol) is dissolved in CH 2 C1 2 (130 mL), layered with saturated NaHCO 3 (220 mL), treated with Br 2 (8.36 mL, 162.3 mmol) and stirred very slowly for 4.5 h at rt. The mixture is stirred vigorously for 30 min, is diluted with CH 2 C1 2 (100 mL) and the layers separated. The aqueous layer is extracted with CH 2 C1 2 (2 x 100 mL) and the combined organics are concentrated to a small volume under a stream of nitrogen.
- the solution is diluted with EtOH (200 mL), treated with K 2 CO 3 (22.13 g, 160.1 mmol) and stirred for 2.5 days at rt.
- the mixture is concentrated to dryness, partitioned between 50% saturated NaCl (200 mL) and CH 2 C1 2 (5 x 200 mL), dried over Na 2 SO 4 and concentrated in vacuo to a yellow solid (6.07 g).
- the crude material is adsorbed onto silica gel (12 g) and chromatographed over 250 g slurry-packed silica gel, eluting with a gradient of 50% EtOAc / hexane to 100% EtOAc.
- Oxalyl chloride (1.77 mL, 20.1 mmol) is combined with CH 2 C1 2 (60 mL) in a dried flask under nitrogen, cooled to -78°C, treated dropwise with DMSO (2.86 mL, 40.25 mmol) and stirred for 20 min.
- the cooled solution is treated drop-wise with a solution of (3-bromofuro[2,3-c]pyridin-5-yl)methanol (4.0 mg, 17.5 mmol) in THF (50 mL), stirred for 1 h, then treated drop-wise with Et 3 N (12.2 mL, 87.5 mmol). The mixture is stirred for 30 min at -78°C, then 30 min at 0°C.
- Example 29 is obtained using 3-bromofuro[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxylic acid according to Method C making non-critical changes to afford 670 mg (96% yield) of a white solid.
- 3-Bromo-2-furaldehyde (14.22 g, 81.3 mmol) is combined with ethylene glycol (6.55 mL, 117.4 mmol) and /? ⁇ ra-toluene sulfonic acid monohydrate (772 mg, 4.06 mmol) in benzene (200 mL) and heated to reflux with a Dean-Stark trap for 5 h. Additional ethylene glycol (1.64 mL, 29.41 mmol) and benzene (150 mL) are added and the solution is heated for an additional 2 h. The mixture is cooled to rt, treated with saturated NaHCO 3 and stirred for 0.5 h. The layers are separated and the organics are dried over Na 2 SO 4 and concentrated to a brown oil (18.8 g). The crade material is chromatographed over 700 g slurry-packed silica gel, eluting with 15%
- the cooling bath is removed and the mixture allowed to warm to rt over 1 h.
- the mixture is diluted with water (20 mL) and EtOAc (20 mL), the layers are separated and the aqueous layer extracted with EtOAc (1 X 20 mL). The organics are dried over
- 2-(l,3-Dioxolan-2-yl)-3-furaldehyde (2.91 g, 17.31 mmol) is combined with formic acid (17 mL, 451 mmol) and water (4.25 mL) and stirred at rt for 18 h.
- the mixture is slowly transferred into a solution of NaHCO 3 (45 g, 541 mmol) in water (600 mL), then strirred for 0.5 h.
- EtOAc 200 mL
- the combined organics are dried over Na 2 SO 4 and concentrated to a yellow oil (3.28 g).
- Methyl furo[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylate (1.55 g, 8.74 mmol) is dissolved in MeOH (30 mL) and H 2 O ( 15 mL), treated with 3 N NaOH (6.4 mL) and stin-ed at rt for 7 h.
- the mixture is concentrated to dryness, dissolved in H 2 O (10 mL) and acidified to pH 2 with concentrated HCI.
- the solution is concentrated to dryness, suspended in a smaller amount of water (7 mL) and the resulting solid collected via filtration (lot A).
- the filtrate is concentrated, triturated with water (3 mL) and the resulting solid collected via filtration (lot B).
- Example 30 is obtained using furo[3,2-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid according to Method C to afford 163 mg (54%) of a pale yellow solid. MS (El) m/z: 271 (M + ).
- Methyl-3-bromothieno[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxylate (635 mg, 2.33 mmol) is combined with 25 ml MeOH.
- the mixture is treated with 2N NaOH (3 ml, 6 mmole) and 3 ml H 2 O and the reaction is stirred 4 h at rt.
- the volatiles are removed in vacuo and the residue is combined with 5 ml H 2 O.
- the pH of the mixture is adjusted to 3.5 with 10% aqueous HCI.
- Example 31 is obtained using 3-bromothieno[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxylic acid according to Method C to afford 240 mg (91%) of an off-white solid. MS (El) m/z: 365 (M + ).
- Benzofuran (11.02 ml, 100 mmol) and potassium acetate (1.96g, 200 mmol) are dissolved in CHC1 3 (50 ml).
- Bromine (10.3 ml, 200 mmol) is dissolved in CHC1 3 (20 ml) and added dropwise.
- the reaction is heated at 50°C for 5 h.
- the mixture is cooled to rt and quenched onto 5% sodium bisulfite solution (100 ml).
- the layers are allowed to separate, and the organic is washed with 5% NaHCO 3 (1 x 100 ml), dried over Na 2 SO , filtered, and concentrated to a green oil.
- 2,3-Dibromobenzofuran (1.37 g, 5.0 mmol) is dissolved in Et 2 O (20 ml) in a dry flask under nitrogen and cooled to -78°C.
- t-Butylithium (6.47 ml, 11.0 mmol) is added drop-wise, and the chilled solution is stirred 1 h.
- DMF (0.45 ml, 5.75 mmol) is dissolved in Et 2 O (5 ml) and also added dropwise, and the mixture is stirred at -78°C for another 4 h.
- the reaction is warmed to rt, whereby oxalic acid dihydrate (1.26 g, 10.0 mmol) and water (5 ml) are added.
- the reaction is warmed to rt, whereby oxalic acid dihydrate (6.18 g, 49.0 mmol) and water (25 ml) are added.
- the reaction continued stirring at rt overnight and is then diluted with water (125 ml) and EtOAc (175 ml).
- the layers are allowed to separate, and the aqueous is extracted with EtOAc (1 x 100 ml).
- the organics are combined, dried over sodium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated to a brown oil.
- the crade material is chromatographed over 350 g slurry-packed silica, eluting with 30% ethyl acetate/hexane.
- Example 32 is obtained using benzofuro [3 ,2-c]pyridine-3 -carboxylic acid according to Method C to afford 337 mg of a tan solid. MS (ESI+) for C ⁇ 9 H 19 N 3 O m/z 322.1 (M+H) + .
- 2-Methylenequinuclidin-3-one (17.8 g, 0.1296 mol, 1 eq) is dissolved in 40 mL MeOH in a Parr hydrogenation bottle. A THF slurry of 10% Pd/C (0.57 g) is added. The mixture is hydrogenated for 45 min at 45 psi, recharging as needed. The mixture is filtered through a pad of Celite. The Celite is washed with excess MeOH. The solution is concentrated to give a solid and a yellow oil. The mixture is taken up in ether, filtered and concentrated to provide 16.2g (90%) of 2-methylquinuclidin-3- one. MS (ESI) for C 8 H 13 NO m/z 140.2 (M + ).
- a solution of sodium n-propoxide (prepared from 5.5 g sodium (0.24mol) and lOOmL n-propanol) is added dropwise to a suspension of (3E/Z)-2-methyl-l- azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one oxime hydrochloride (45.8 g, 0.24 mol, 1 eq) in 150 mL «-propanol.
- 250 mL of n-propanol is added, and the mixture is heated under reflux.
- Sodium (55.2 g, 2.40 mol, 10 eq) is added in portions to the refluxing mixture. The mixture is heated under reflux overnight. After about 14 h, the mixture is cooled, water is added and the layers are separated.
- Example 33 is prepared using C18 according to Method C to afford 0.79g
- HCI Example 34 is obtained using (2S,3R)-2-methyl-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3- amine dihydrochloride and C56 according to Method C to afford 0.18g (49%) of the desired product.
- HRMS (FAB) calculated for 7 H 2 jN 3 O 2 +H 300.1712, found 300.1701.
- Example 35 is obtained using (2S,3R)-2-methyl-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3- amine dihydrochloride and C156 according to Method C to afford 0.209g (53%) of the desired product.
- HRMS (FAB) calculated for C 16 H 19 N 3 OS+H 302.1327, found 302.1347.
- Example 36 is obtained using thieno[2,3-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid and (2S,3R)-2-methyl-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-amine dihydrochloride according to Method C to provide 0.166g (44%) of the desired product.
- HRMS (FAB) calculated for C 16 H ⁇ 9 N 3 OS+H 302.1327, found 302.1323.
- Example 29 (350 mg, 1 mmol) is combined with dichlorobis(benzonitrile)palladium (TT) (57 mg, 0.15 mmol) and cuprous iodide (19 mg, 0.1 mmol) in a dry flask, and the flask is purged with N 2 .
- Anhydrous dioxane (3 mL) is added, followed by tri-t-butylphosphine (10% wt. in hexane, 658 ⁇ L, 0.325 mmol), trimethylsilylacetylene (170 ⁇ L, 1.2 mmol) and finally DIEA (168 ⁇ L, 1.2 mmol).
- the mixture is stirred at rt under N 2 for 24 h, then concentrated in vacuo.
- the residue is partitioned between CHC1 3 and 50% saturated NaCl, and the organics are dried over Na 2 SO 4 and concentrated in vacuo.
- the crade material is chromatographed over 17.5 g silica gel, eluting with 0.5% NH 4 OH / 8% MeOH / CHC1 3 .
- the appropriate fractions are combined and concentrated to an oil.
- the oil is layered with Et 2 O, capped and allowed to stand for 18 h.
- N-[(3R)-l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-3-[(trimethylsilyl)ethynyl]furo[2,3- c]pyridine-5-carboxamide (168 mg, 0.46 mmol) is dissolved in MeOH (10 mL), treated with ⁇ aHCO 3 (800 mg, 9.5 mmol) in H 2 O (10 mL) and stirred at rt for 3 h. The mixture is concentrated to dryness and partitioned between CHC1 3 and H 2 O. The organics are dried over Na 2 SO 4 and concentrated to a brown oil.
- Example 37 is chromatographed over 6 g silica gel, eluting with 1 % NH 4 OH / 6% MeOH / CHC1 3 . The appropriate fractions are combined and concentrated to afford 54 mg (40%) of Example 37 as a white solid.
- HRMS (FAB) calcd for C 17 H 17 N 3 O 2 +H ⁇ 296.1399, found 296.1388.
- Example 38 is obtained (92% yield) as the free base by coupling acid C18 with (S)-(-)-3-aminoquinuclidine according to Method C with omission of the HCI treatment.
- HRMS (FAB) calculated for C 15 H 17 N 3 O 2 +H: 272.1399, found 272.1404 (M+H) + .
- Example 39 N-[(+/-)l-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]furo[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide:
- Example 39 is obtained (43% yield) by coupling acid C18 with (+/-)-3- aminoquinuclidine according to Method C with non-critical changes. MS (ESI) m/z: 272.1 (M+H) + .
- 3,4-Dibromothiophene (12.5 ml, 113 mmol) is combined with CuCN (30.4 g, 339 mmol) in DMF (40 ml) in a dry flask under nitrogen utilizing an over-head stirrer. The reaction is allowed to reflux at 180°C for 5 h. The dark mixture is then poured into a solution of FeCl 3 (113.6 g, 700 mmol) in 1.7M HCI (200 ml) and heated at 65°C for 0.5 h, again using the over-head stirrer. The reaction is cooled to rt and extracted with CH 2 C1 (7 x 300 ml).
- 3,4-Dicyanothiophene (5.0 g, 37.2 mmol) is suspended in benzene (150 ml) in a dry flask under nitrogen utilizing an over-head stirrer.
- Diisobutyl aluminum hydride (1.0M in toluene) (82.0 ml, 82.0 mmol) is added dropwise, and the reaction stirred at rt for 2 h.
- the reaction is then carefully quenched with MeOH (5 ml) and poured onto 30% H 2 SO 4 (60 ml) with ice (200 g). The slurry is stirred until all lumps are dissolved, and the layers are allowed to separate.
- Methyl thieno[3,4-c]pyridine-6-carboxylate (250 mg, 1.3 mmol) is dissolved in MeOH (7 ml) and water (1 ml). 2M NaOH (0.72 ml, 1.43 mmol) is added drop- wise. The reaction is stirred overnight at rt and is monitored by TLC. The volatiles are removed in vacuo and the residue is dissolved in water (2 ml). 10% HCI is used to adjust the pH to 3, and the reaction again stirred overnight at rt. The aqueous solution is extracted repeatedly with EtOAc (20 x 10 ml). The combined organics are dried over MgSO , filtered, and concentrated to a yellow solid.
- the crude material is chromatographed over 25 g slurry-packed silica, eluting with 1% NH 4 OH/10% MeOH/CH 2 Cl 2 .
- the appropriate fractions are collected and concentrated to a dark oil.
- the oil is dissolved in IM HCI in MeOH (3 ml) and stirred overnight. A brown precipitate is formed, but upon isolation via filtration, the compound quickly degraded.
- the isolated salt is then free-based in MeOH with Amberjet 4400 OH Strongly Basic Anion Exchanger resin. The resin is filtered off, and the liquor concentrated to a glass.
- Binding Assay For saturation studies, 0.4 mL homogenate are added to test tubes containing buffer and various concentrations of radioligand, and are incubated in a final volume of 0.5 mL for 1 hour at 25 °C. Nonspecific binding was determined in tissues incubated in parallel in the presence of 1 ⁇ M MLA, added before the radioligand. In competition studies, drags are added in increasing concentrations to the test tubes before addition of approximately 3.0 to 4.0 nM [ 3 H]-MLA. The incubations are terminated by rapid vacuum filtration through Whatman GF/B glass filter paper mounted on a 48 well Brandel cell harvester. Filters are pre-soaked in 50 mM Tris HCI pH 7.0 - 0.05 % polyethylenimine. The filters are rapidly washed two times with 5 mL aliquots of cold 0.9% saline and then counted for radioactivity by liquid scintillation spectrometry.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- Addiction (AREA)
- Ophthalmology & Optometry (AREA)
- Pain & Pain Management (AREA)
- Virology (AREA)
- Psychology (AREA)
- Communicable Diseases (AREA)
- Hospice & Palliative Care (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- AIDS & HIV (AREA)
- Diabetes (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Tropical Medicine & Parasitology (AREA)
- Child & Adolescent Psychology (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Obesity (AREA)
- Nutrition Science (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Nitrogen Condensed Heterocyclic Rings (AREA)
- Heterocyclic Carbon Compounds Containing A Hetero Ring Having Oxygen Or Sulfur (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (9)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003503624A JP2004537532A (en) | 2001-06-12 | 2002-06-06 | Quinuclidine-substituted polycyclic heteroaryls for the treatment of disease |
| KR10-2003-7016210A KR20040018266A (en) | 2001-06-12 | 2002-06-06 | Quinuclidines-Substituted-Multi-Cyclic-Heteroaryls For The Treatment Of Disease |
| IL15934402A IL159344A0 (en) | 2001-06-12 | 2002-06-06 | Quinuclidines-substituted-multicyclic-heteroaryls for the treatment of disease |
| BR0210384-2A BR0210384A (en) | 2001-06-12 | 2002-06-06 | Multi-cyclic quinuclidine-substituted heteroaryl for the treatment of disease |
| MXPA03011484A MXPA03011484A (en) | 2001-06-12 | 2002-06-06 | Quinuclidines-substituted-multi-cyclic-heteroaryls for the treatment of disease. |
| EA200301216A EA200301216A1 (en) | 2001-06-12 | 2002-06-06 | MULTICYCLIC HETEROARYLS SUBSTITUTED WITH QUINUCLIDINES FOR THE DISEASE TREATMENT |
| CA002445467A CA2445467A1 (en) | 2001-06-12 | 2002-06-06 | Quinuclidines-substituted-multi-cyclic-heteroaryls for the treatment of disease |
| EP02778932A EP1406901A1 (en) | 2001-06-12 | 2002-06-06 | Quinuclidines-substituted-multi-cyclic-heteroaryls for the treatment of disease |
| NO20035522A NO20035522D0 (en) | 2001-06-12 | 2003-12-11 | Kinuclidine-substituted multicyclic heteroaryls for the treatment of disease |
Applications Claiming Priority (14)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US29771201P | 2001-06-12 | 2001-06-12 | |
| US29770901P | 2001-06-12 | 2001-06-12 | |
| US29771101P | 2001-06-12 | 2001-06-12 | |
| US29771001P | 2001-06-12 | 2001-06-12 | |
| US29770801P | 2001-06-12 | 2001-06-12 | |
| US60/297,710 | 2001-06-12 | ||
| US60/297,709 | 2001-06-12 | ||
| US60/297,712 | 2001-06-12 | ||
| US60/297,708 | 2001-06-12 | ||
| US60/297,711 | 2001-06-12 | ||
| US32859601P | 2001-10-11 | 2001-10-11 | |
| US60/328,596 | 2001-10-11 | ||
| US37349502P | 2002-04-18 | 2002-04-18 | |
| US60/373,495 | 2002-04-18 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2002100857A1 true WO2002100857A1 (en) | 2002-12-19 |
Family
ID=27569623
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US2002/016568 WO2002100857A1 (en) | 2001-06-12 | 2002-06-06 | Quinuclidines-substituted-multi-cyclic-heteroaryls for the treatment of disease |
Country Status (17)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7067515B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP1406901A1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2004537532A (en) |
| KR (1) | KR20040018266A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN1511154A (en) |
| AR (1) | AR036040A1 (en) |
| BR (1) | BR0210384A (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2445467A1 (en) |
| CO (1) | CO5540302A2 (en) |
| CZ (1) | CZ20033377A3 (en) |
| EA (1) | EA200301216A1 (en) |
| IL (1) | IL159344A0 (en) |
| MX (1) | MXPA03011484A (en) |
| NO (1) | NO20035522D0 (en) |
| PE (1) | PE20030431A1 (en) |
| PL (1) | PL367311A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2002100857A1 (en) |
Cited By (28)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2003055878A1 (en) * | 2001-12-27 | 2003-07-10 | Bayer Healthcare Ag | 2-heteroarylcarboxylic acid amides |
| WO2003104227A1 (en) * | 2002-01-20 | 2003-12-18 | Bayer Healthcare Ag | 2-heteroaryl carboxamides |
| WO2004039366A1 (en) * | 2002-11-01 | 2004-05-13 | Pharmacia & Upjohn Company Llc | Nicotinic acetylcholine agonists in the treatment of glaucoma and retinal neuropathy |
| WO2004039815A2 (en) * | 2002-11-01 | 2004-05-13 | Pharmacia & Upjohn Company Llc | Compounds having both alpha7 nachr agonist and 5ht antagonist activity for treatment of cns diseases |
| WO2004052894A1 (en) * | 2002-12-06 | 2004-06-24 | Pharmacia & Upjohn Company Llc | Crystalline fumarate salts of 1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct substituted furo[2,3-c]pyridinyl carboxamide and compositions and preparations thereof |
| WO2004064836A2 (en) * | 2003-01-22 | 2004-08-05 | Pharmacia & Upjohn Company Llc | Treatment of diseases with alpha-7 nach receptor full agonists |
| WO2005077899A2 (en) * | 2004-02-04 | 2005-08-25 | Abbott Laboratories | Amino-substituted tricyclic derivatives and methods of use |
| JPWO2004063201A1 (en) * | 2003-01-08 | 2006-05-18 | 三菱ウェルファーマ株式会社 | Schizophrenia treatment |
| JP2007500152A (en) * | 2003-07-30 | 2007-01-11 | バイエル・ヘルスケア・アクチェンゲゼルシャフト | N-biarylamide compounds |
| US7365193B2 (en) | 2004-02-04 | 2008-04-29 | Abbott Laboratories | Amino-substituted tricyclic derivatives and methods of use |
| US7396833B2 (en) | 2003-12-22 | 2008-07-08 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indoles, 1H-indazoles, 1,2-benzisoxazoles, and 1,2-benzisothiazoles, and preparation and uses thereof |
| US7429664B2 (en) | 2002-09-25 | 2008-09-30 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indazoles, benzothiazoles, and benzoisothiazoles, and preparation and uses thereof |
| US7488737B2 (en) | 2004-04-22 | 2009-02-10 | Memory Pharmaceutical Corporation | Indoles, 1H-indazoles, 1,2-benzisoxazoles, 1,2-benzoisothiazoles, and preparation and uses thereof |
| US7625924B2 (en) | 2004-12-22 | 2009-12-01 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Nicotinic alpha-7 receptor ligands and preparation and uses thereof |
| US7632831B2 (en) | 2004-05-07 | 2009-12-15 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | 1H-indazoles, benzothiazoles, 1,2-benzoisoxazoles, 1,2-benzoisothiazoles, and chromones and preparation and uses thereof |
| WO2011022692A2 (en) * | 2009-08-20 | 2011-02-24 | University Of Tennessee Research Foundation, The | Furanopyridine cannabinoid compounds and related methods of use |
| WO2011098776A1 (en) | 2010-02-15 | 2011-08-18 | Cambridge Enterprise Limited | 5-ht receptor modulators |
| US8048885B2 (en) | 2005-12-16 | 2011-11-01 | Novartis Ag | Organic compounds |
| US8173667B2 (en) | 2005-10-21 | 2012-05-08 | Novartis Ag | 1-aza-bicycloalkyl derivatives |
| US8236803B2 (en) | 2002-09-04 | 2012-08-07 | Novartis Ag | Aza-bicycloalkyl ethers and their use as alpha7-nAChR agonists |
| US8263619B2 (en) | 2004-03-25 | 2012-09-11 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indazoles, benzothiazoles, benzoisothiazoles, benzisoxazoles, and preparation and uses thereof |
| WO2013002365A1 (en) | 2011-06-30 | 2013-01-03 | 東レ株式会社 | Antipruritic agent |
| US8609662B2 (en) | 2004-07-14 | 2013-12-17 | Novartis Ag | 3-(heteroaryl-oxy)-2-alkyl-1-aza-bicycloalkyl derivatives as alpha. 7-nachr ligands for the treatment of CNS diseases |
| US8759346B2 (en) | 2005-12-16 | 2014-06-24 | Novartis Ag | Organic compounds |
| US8933090B2 (en) | 2004-06-18 | 2015-01-13 | Novartis Ag | 1-aza-bicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes |
| US9108961B2 (en) | 2010-05-17 | 2015-08-18 | Forum Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Crystalline form of (R)-7-chloro-N-(quinuclidin-3-yl)benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxamide hydrochloride |
| EP2876109A4 (en) * | 2012-07-23 | 2016-03-16 | Yuhan Corp | Fused ring compound containing furan or salt thereof and pharmaceutical composition comprising same |
| US9585877B2 (en) | 2012-05-08 | 2017-03-07 | Forum Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods of maintaining, treating or improving cognitive function |
Families Citing this family (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DK1432707T3 (en) * | 2001-10-02 | 2012-06-11 | Pharmacia & Upjohn Co Llc | AZABICYCLIC-SUBSTITUTED CONDENSED HETEROARYL COMPOUNDS FOR TREATMENT OF DISEASES |
| JP2007516275A (en) * | 2003-12-23 | 2007-06-21 | ファイザー・プロダクツ・インク | Therapeutic combinations for cognitive enhancement and psychotic disorders |
| GB0424564D0 (en) * | 2004-11-05 | 2004-12-08 | Novartis Ag | Organic compounds |
| CN101305010A (en) * | 2005-09-01 | 2008-11-12 | 阿雷生物药品公司 | Raf inhibitor compounds and methods of use thereof |
| AU2006295397A1 (en) * | 2005-09-23 | 2007-04-05 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indazoles, benzothiazoles, benzoisothiazoles, benzisoxazoles, pyrazolopyridines, isothiazolopyridines, and preparation and uses thereof |
| RU2008139599A (en) | 2006-03-07 | 2010-04-20 | Эррэй Биофарма Инк. (Us) | Heterobicyclic pyrazole derivatives and methods for their use |
| SA08290475B1 (en) | 2007-08-02 | 2013-06-22 | Targacept Inc | (2S,3R)-N-(2-((3-Pyridinyl)Methyl)-1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]Oct-3-yl)Benzofuran-2-Carboxamide, Novel Salt forms, and Methods of Use Thereof |
| US8697722B2 (en) * | 2007-11-02 | 2014-04-15 | Sri International | Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulators |
| MY159826A (en) | 2008-11-19 | 2017-02-15 | Forum Pharmaceuticals Inc | Treatment of cognitive disorders with (r)-7-chloro-n-(quinuclidin-3-yl)benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxamide and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof |
| TW201031664A (en) | 2009-01-26 | 2010-09-01 | Targacept Inc | Preparation and therapeutic applications of (2S,3R)-N-2-((3-pyridinyl)methyl)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl)-3,5-difluorobenzamide |
| JP5808319B2 (en) * | 2009-05-11 | 2015-11-10 | フォルム ファーマシューティカルズ、インコーポレイテッド | Treatment of cognitive impairment using specific α7 nicotinic acid receptors in combination with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors |
| WO2011020712A2 (en) * | 2009-08-18 | 2011-02-24 | Universite Libre De Bruxelles | Oligothiophenes derivatives |
| WO2011085389A1 (en) * | 2010-01-11 | 2011-07-14 | Astraea Therapeutics, Llc | Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulators |
| KR101928505B1 (en) * | 2011-01-28 | 2018-12-12 | 에스케이바이오팜 주식회사 | Pharmaceutical composition comprising pyridone derivatives |
| JP6359940B2 (en) * | 2014-10-14 | 2018-07-18 | 国立大学法人 名古屋工業大学 | Difluoromethylacetylene compounds and process for producing the same |
| CN106883270B (en) | 2015-11-26 | 2019-03-26 | 财团法人工业技术研究院 | Organometallic compound and organic light-emitting device including the same |
| JP7212781B2 (en) | 2018-12-19 | 2023-01-25 | ディスアーム セラピューティクス, インコーポレイテッド | Inhibitors of SARM1 in combination with neuroprotective agents |
| CN115974833B (en) * | 2022-12-28 | 2024-08-02 | 苏州汉德创宏生化科技有限公司 | Preparation method of 3-aminothiophene oxalate |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0030254A1 (en) * | 1979-08-29 | 1981-06-17 | Schering Aktiengesellschaft | Beta-carbolin-3-carboxylic acid derivatives, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their therapeutical use |
| EP0483836A1 (en) * | 1990-11-01 | 1992-05-06 | Asahi Kasei Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Pyrazolo [1,5-a] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid derivatives, their preparation process and their use |
| WO1993009116A1 (en) * | 1991-11-07 | 1993-05-13 | Yoshitomi Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. | Quinuclidine compound and medicinal use thereof |
| EP0560348A1 (en) * | 1992-03-12 | 1993-09-15 | Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation | Thieno 3,2-b pyridine derivatives for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders |
| US5260303A (en) * | 1991-03-07 | 1993-11-09 | G. D. Searle & Co. | Imidazopyridines as serotonergic 5-HT3 antagonists |
| EP0635508A1 (en) * | 1992-04-10 | 1995-01-25 | Asahi Kasei Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Tetrahydropyridine derivative having substituents on three rings |
| WO1997035860A1 (en) * | 1996-03-22 | 1997-10-02 | Universidad Complutense De Madrid Rectorado | Novel benzimidazol derivatives having an affinity for the serotoninergic 5-ht3/5 ht4 receptors |
| US5750536A (en) * | 1993-08-05 | 1998-05-12 | Dompe ' Spa | Tropyl 7-azaindol-3-ylcarboxyamides as antitussive agent |
Family Cites Families (70)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZA832549B (en) | 1982-04-14 | 1988-09-28 | Beecham Group Plc | Pharmaceutically active compounds |
| FR2531083B1 (en) | 1982-06-29 | 1986-11-28 | Sandoz Sa | NOVEL PIPERIDINE DERIVATIVES, THEIR PREPARATION AND THEIR USE AS MEDICINES |
| DE3429830A1 (en) | 1983-08-26 | 1985-03-07 | Sandoz-Patent-GmbH, 7850 Lörrach | AUTOMATIC CARBONIC ACID AND SULPHONIC ACID ESTERS OR AMIDES |
| US5175173A (en) | 1983-12-22 | 1992-12-29 | Sun Jung Hui | Carboxamides useful as antiemetic or antipsychotic agents |
| US4888353A (en) | 1986-02-28 | 1989-12-19 | Erbamont, Inc. | Carboxamides useful as antiemetic or antipsychotic agents |
| FR2557110B1 (en) | 1983-12-23 | 1989-11-24 | Sandoz Sa | NOVEL CYCLIC AMINE DERIVATIVES, THEIR PREPARATION AND THEIR USE AS MEDICAMENTS |
| DE3689974T2 (en) | 1985-03-14 | 1994-11-03 | Beecham Group Plc | Medicines to treat emesis. |
| US4937247A (en) | 1985-04-27 | 1990-06-26 | Beecham Group P.L.C. | 1-acyl indazoles |
| GB8520616D0 (en) | 1985-08-16 | 1985-09-25 | Beecham Group Plc | Compounds |
| US4910193A (en) | 1985-12-16 | 1990-03-20 | Sandoz Ltd. | Treatment of gastrointestinal disorders |
| DE3782107T2 (en) | 1986-07-25 | 1993-04-01 | Beecham Group Plc | AZABICYCLIC COMPOUNDS, METHOD FOR THEIR PRODUCTION AND THEIR PHARMACEUTICAL USE. |
| HU202108B (en) | 1986-07-30 | 1991-02-28 | Sandoz Ag | Process for producing pharmaceutical compositions containing serotonine antqgonistic derivatives of indol-carboxylic acid or imidazolyl-methyl-carbazol |
| EP0278173B1 (en) | 1986-12-17 | 1993-11-03 | Glaxo Group Limited | Use of heterocyclic derivatives in the treatment of depressions |
| EP0279990B1 (en) | 1986-12-17 | 1995-07-12 | Glaxo Group Limited | Use of heterocyclic derivatives in the treatment of cognitive disorders |
| GB8806990D0 (en) | 1988-03-23 | 1988-04-27 | Beecham Group Plc | Novel compounds |
| US5322951A (en) | 1987-01-05 | 1994-06-21 | Beecham Group, P.L.C. | Certain 1-(2,3-dihydro-indole)carbonyl intermediates |
| GB8701022D0 (en) | 1987-01-19 | 1987-02-18 | Beecham Group Plc | Treatment |
| US4835162A (en) | 1987-02-12 | 1989-05-30 | Abood Leo G | Agonists and antagonists to nicotine as smoking deterents |
| DE3852145T2 (en) | 1987-02-18 | 1995-04-06 | Beecham Group Plc | Indole derivatives, processes for their preparation and pharmaceutical preparations containing them. |
| DE3822792C2 (en) | 1987-07-11 | 1997-11-27 | Sandoz Ag | New use of 5HT¶3¶ antagonists |
| US4921982A (en) | 1988-07-21 | 1990-05-01 | Eli Lilly And Company | 5-halo-2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethylbenzofuran-7-carboxylic acids useful as intermediates for 5-HT3 antagonists |
| US4985420A (en) | 1987-12-10 | 1991-01-15 | Duphar International Research B.V. | 1,7-annelated indolecarboxylic acid esters and -amides |
| IE63474B1 (en) | 1987-12-24 | 1995-04-19 | Wyeth John & Brother Ltd | Heterocyclic compounds |
| US4863919A (en) | 1988-02-01 | 1989-09-05 | A. H. Robins Company, Incorporated | Method of enhancing memory or correcting memory deficiency with arylamido(and arylthiomido)-azabicycloalkanes |
| US4924010A (en) | 1988-02-04 | 1990-05-08 | Rorer Pharmaceutical Corporation | Benzoxepins as intermediates to 5HT3 antagonists |
| DE3810552A1 (en) | 1988-03-29 | 1989-10-19 | Sandoz Ag | Esters and amides of indole-, benzo[b]thiophene or benzo[b]furancarboxylic acids or 4-amino-2-methoxybenzoic acids with N-heterocyclic or N-heterobicyclic alcohols or amines, processes for their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and applicator for administration thereof |
| US5246942A (en) | 1988-04-27 | 1993-09-21 | Rhone-Poulenc Rorer Pharmaceuticals Inc. | Pharmaceutically useful dibenzofurancarboxamides of specific stereo-configuration |
| US4863921A (en) | 1988-04-27 | 1989-09-05 | Rorer Pharmaceutical Corporation | Dibenzofurancarboxamides and their pharmaceutical compositions and methods |
| US4920219A (en) | 1988-11-29 | 1990-04-24 | Rorer Pharmaceutical Corp. | Substituted saturated and unsaturated indole quinoline and benzazepine carboxamides and their use as pharmacological agents |
| US4933445A (en) | 1988-11-29 | 1990-06-12 | Rorer Pharmaceutical Corporation | Heteroazabenzobicyclic carboxamide 5-HT3 antagonists |
| US4920227A (en) | 1988-11-29 | 1990-04-24 | Rorer Pharmaceutical Corp. | Benzobicyclic carboxamide 5-HT3 antagonists |
| AU5650890A (en) | 1989-05-24 | 1990-12-18 | Nippon Shinyaku Co. Ltd. | Indole derivatives and medicine |
| EP0402056A3 (en) | 1989-06-06 | 1991-09-04 | Beecham Group p.l.c. | Azabicyclic compounds, process for their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them |
| US4935511A (en) | 1989-09-26 | 1990-06-19 | Rorer Pharmaceutical Corporation | Benzoxazine and benzoxazepine carboxamide 5-HT3 antagonists |
| GB2236751B (en) | 1989-10-14 | 1993-04-28 | Wyeth John & Brother Ltd | Heterocyclic compounds |
| GB8928837D0 (en) | 1989-12-21 | 1990-02-28 | Beecham Group Plc | Pharmaceuticals |
| EP0436245A1 (en) | 1989-12-27 | 1991-07-10 | Duphar International Research B.V | Substituted 3,4-annelated benzimidazol-2(1H)-ones |
| GB9009542D0 (en) | 1990-04-27 | 1990-06-20 | Beecham Group Plc | Novel compounds |
| AU7618991A (en) | 1990-05-14 | 1991-11-14 | Syntex (U.S.A.) Inc. | Novel tricyclic compounds |
| AU8405891A (en) | 1990-08-31 | 1992-03-30 | Nippon Shinyaku Co. Ltd. | Indole derivative and medicine |
| US5189041A (en) | 1990-11-16 | 1993-02-23 | Syntex (U.S.A.) Inc. | Tricyclic 5-ht3 receptor antagonists |
| GB9027098D0 (en) | 1990-12-13 | 1991-02-06 | Beecham Group Plc | Pharmaceuticals |
| HU211081B (en) | 1990-12-18 | 1995-10-30 | Sandoz Ag | Process for producing indole derivatives as serotonin antagonists and pharmaceutical compositions containing the same |
| US5114947A (en) | 1990-12-27 | 1992-05-19 | Erbamont Inc. | Method for alleviating anxiety using benzobicyclic carboxamides |
| IL100432A (en) | 1990-12-27 | 1996-01-19 | Erba Carlo Spa | Dihydrobenzofuran carboxamide derivatives their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them |
| GB9028105D0 (en) | 1990-12-27 | 1991-02-13 | Erba Carlo Spa | Process for the preparation of substituted benzofuran derivatives |
| DE4115215A1 (en) | 1991-05-10 | 1992-11-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | INDOLDER DERIVATIVES |
| GB9120628D0 (en) | 1991-09-27 | 1991-11-06 | Fujisawa Pharmaceutical Co | Pyrrolobenzoxazine derivatives and process for preparation thereof |
| JPH05310732A (en) | 1992-03-12 | 1993-11-22 | Mitsubishi Kasei Corp | Cinnoline-3-carboxylic acid derivative |
| US5273972A (en) | 1992-03-26 | 1993-12-28 | A. H. Robins Company, Incorporated | [(2-diakylaminomethyl)-3-quinuclidinyl]-benzamides and benzoates |
| SE9201478D0 (en) | 1992-05-11 | 1992-05-11 | Kabi Pharmacia Ab | HETEROAROMATIC QUINUCLIDINENES, THEIR USE AND PREPARATION |
| US5300512A (en) | 1992-06-24 | 1994-04-05 | G. D. Searle & Co. | Benzimidazole compounds |
| US5977144A (en) | 1992-08-31 | 1999-11-02 | University Of Florida | Methods of use and compositions for benzylidene- and cinnamylidene-anabaseines |
| GB9406857D0 (en) | 1994-04-07 | 1994-06-01 | Sandoz Ltd | Improvements in or relating to organic compounds |
| US5510478A (en) | 1994-11-30 | 1996-04-23 | American Home Products Corporation | 2-arylamidothiazole derivatives with CNS activity |
| GB9507882D0 (en) | 1995-04-18 | 1995-05-31 | Pharmacia Spa | Substituted dihydrobenzofuran derivatives as 5-ht4 agonists |
| SE9600683D0 (en) | 1996-02-23 | 1996-02-23 | Astra Ab | Azabicyclic esters of carbamic acids useful in therapy |
| FR2769915B1 (en) | 1997-10-21 | 2000-10-13 | Synthelabo | TRICYCLIC INDAZOLE DERIVATIVES, THEIR PREPARATION AND THEIR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATION |
| AU4980200A (en) | 1999-05-27 | 2000-12-18 | Pharmacia & Upjohn Company | Methods and compositions for measuring ion channel conductance |
| SE9904176D0 (en) | 1999-11-18 | 1999-11-18 | Astra Ab | New use |
| SE0000540D0 (en) | 2000-02-18 | 2000-02-18 | Astrazeneca Ab | New compounds |
| US20010036943A1 (en) | 2000-04-07 | 2001-11-01 | Coe Jotham W. | Pharmaceutical composition for treatment of acute, chronic pain and/or neuropathic pain and migraines |
| JP4616971B2 (en) | 2000-07-18 | 2011-01-19 | 田辺三菱製薬株式会社 | 1-azabicycloalkane compounds and pharmaceutical uses thereof |
| US20020016334A1 (en) | 2000-07-31 | 2002-02-07 | Coe Jotham Wadsworth | Pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) |
| DK1432707T3 (en) * | 2001-10-02 | 2012-06-11 | Pharmacia & Upjohn Co Llc | AZABICYCLIC-SUBSTITUTED CONDENSED HETEROARYL COMPOUNDS FOR TREATMENT OF DISEASES |
| DE10164139A1 (en) | 2001-12-27 | 2003-07-10 | Bayer Ag | 2-heteroaryl carboxamides |
| DE10211415A1 (en) | 2002-03-15 | 2003-09-25 | Bayer Ag | New azabicycloalkyl carboxylic acid N-biarylamides, are alpha-7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligands useful for improving attention, concentration, learning and/or memory performance |
| EP1499618B1 (en) | 2002-04-18 | 2010-10-13 | AstraZeneca AB | Furyl compounds |
| WO2003087103A1 (en) | 2002-04-18 | 2003-10-23 | Astrazeneca Ab | Thienyl compounds |
| NZ561993A (en) | 2002-04-18 | 2008-09-26 | Astrazeneca Ab | Spiroazabicyclic heterocyclic amines as potent ligands for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors |
-
2002
- 2002-05-30 AR ARP020102020A patent/AR036040A1/en unknown
- 2002-06-05 PE PE2002000470A patent/PE20030431A1/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2002-06-06 US US10/163,564 patent/US7067515B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2002-06-06 CZ CZ20033377A patent/CZ20033377A3/en unknown
- 2002-06-06 PL PL02367311A patent/PL367311A1/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2002-06-06 KR KR10-2003-7016210A patent/KR20040018266A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2002-06-06 CA CA002445467A patent/CA2445467A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2002-06-06 CN CNA028098145A patent/CN1511154A/en active Pending
- 2002-06-06 WO PCT/US2002/016568 patent/WO2002100857A1/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2002-06-06 IL IL15934402A patent/IL159344A0/en unknown
- 2002-06-06 EP EP02778932A patent/EP1406901A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2002-06-06 MX MXPA03011484A patent/MXPA03011484A/en unknown
- 2002-06-06 EA EA200301216A patent/EA200301216A1/en unknown
- 2002-06-06 BR BR0210384-2A patent/BR0210384A/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2002-06-06 JP JP2003503624A patent/JP2004537532A/en not_active Withdrawn
-
2003
- 2003-12-10 CO CO03108314A patent/CO5540302A2/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2003-12-11 NO NO20035522A patent/NO20035522D0/en not_active Application Discontinuation
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0030254A1 (en) * | 1979-08-29 | 1981-06-17 | Schering Aktiengesellschaft | Beta-carbolin-3-carboxylic acid derivatives, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their therapeutical use |
| EP0483836A1 (en) * | 1990-11-01 | 1992-05-06 | Asahi Kasei Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Pyrazolo [1,5-a] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid derivatives, their preparation process and their use |
| US5260303A (en) * | 1991-03-07 | 1993-11-09 | G. D. Searle & Co. | Imidazopyridines as serotonergic 5-HT3 antagonists |
| WO1993009116A1 (en) * | 1991-11-07 | 1993-05-13 | Yoshitomi Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. | Quinuclidine compound and medicinal use thereof |
| EP0560348A1 (en) * | 1992-03-12 | 1993-09-15 | Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation | Thieno 3,2-b pyridine derivatives for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders |
| EP0635508A1 (en) * | 1992-04-10 | 1995-01-25 | Asahi Kasei Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Tetrahydropyridine derivative having substituents on three rings |
| US5750536A (en) * | 1993-08-05 | 1998-05-12 | Dompe ' Spa | Tropyl 7-azaindol-3-ylcarboxyamides as antitussive agent |
| WO1997035860A1 (en) * | 1996-03-22 | 1997-10-02 | Universidad Complutense De Madrid Rectorado | Novel benzimidazol derivatives having an affinity for the serotoninergic 5-ht3/5 ht4 receptors |
Cited By (62)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8884017B2 (en) | 2001-12-27 | 2014-11-11 | Bayer Intellectual Property Gmbh | 2-heteroarylcarboxylic acid amides |
| US7732477B2 (en) | 2001-12-27 | 2010-06-08 | Bayer Schering Pharma Aktiengesellschaft | 2-heteroarylcarboxylic acid amides |
| WO2003055878A1 (en) * | 2001-12-27 | 2003-07-10 | Bayer Healthcare Ag | 2-heteroarylcarboxylic acid amides |
| US8076355B2 (en) | 2001-12-27 | 2011-12-13 | Bayer Schering Pharma Aktiengesellschaft | 2-heteroarylcarboxylic acid amides |
| WO2003104227A1 (en) * | 2002-01-20 | 2003-12-18 | Bayer Healthcare Ag | 2-heteroaryl carboxamides |
| US7977485B2 (en) | 2002-06-10 | 2011-07-12 | Bayer Schering Pharma Aktiengesellshaft | 2-heteroaryl carboxamides |
| US9067931B2 (en) | 2002-06-10 | 2015-06-30 | Bayer Intellectual Property Gmbh | 2-heteroaryl carboxamides |
| US10214524B2 (en) | 2002-06-10 | 2019-02-26 | Bayer Intellectual Property Gmbh | 2-heteroaryl carboxamides |
| US9012451B2 (en) | 2002-09-04 | 2015-04-21 | Novartis Ag | Aza-bicycloalkyl ethers and their use as ALPHA7-nachr agonists |
| US9567343B2 (en) | 2002-09-04 | 2017-02-14 | Novartis Ag | Aza-bicyloalkyl ethers and their use as alpha7-nachr agonists |
| US9849117B2 (en) | 2002-09-04 | 2017-12-26 | Novartis Ag | Aza-bicycloalkyl ethers and their use as alpha7-nachr agonists |
| US8236803B2 (en) | 2002-09-04 | 2012-08-07 | Novartis Ag | Aza-bicycloalkyl ethers and their use as alpha7-nAChR agonists |
| US8134003B2 (en) | 2002-09-25 | 2012-03-13 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indazoles, benzothiazoles, and benzoisothiazoles, and preparation and uses thereof |
| US7429664B2 (en) | 2002-09-25 | 2008-09-30 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indazoles, benzothiazoles, and benzoisothiazoles, and preparation and uses thereof |
| US8252811B2 (en) | 2002-09-25 | 2012-08-28 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indazoles, benzothiazoles, and benzoisothiazoles, and preparation and uses thereof |
| US7943773B2 (en) | 2002-09-25 | 2011-05-17 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indazoles, benzothiazoles, and benzoisothiazoles, and preparation and uses thereof |
| WO2004039815A3 (en) * | 2002-11-01 | 2004-07-22 | Upjohn Co | Compounds having both alpha7 nachr agonist and 5ht antagonist activity for treatment of cns diseases |
| WO2004039366A1 (en) * | 2002-11-01 | 2004-05-13 | Pharmacia & Upjohn Company Llc | Nicotinic acetylcholine agonists in the treatment of glaucoma and retinal neuropathy |
| WO2004039815A2 (en) * | 2002-11-01 | 2004-05-13 | Pharmacia & Upjohn Company Llc | Compounds having both alpha7 nachr agonist and 5ht antagonist activity for treatment of cns diseases |
| WO2004052894A1 (en) * | 2002-12-06 | 2004-06-24 | Pharmacia & Upjohn Company Llc | Crystalline fumarate salts of 1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct substituted furo[2,3-c]pyridinyl carboxamide and compositions and preparations thereof |
| JP4598674B2 (en) * | 2003-01-08 | 2010-12-15 | 田辺三菱製薬株式会社 | Schizophrenia treatment |
| JPWO2004063201A1 (en) * | 2003-01-08 | 2006-05-18 | 三菱ウェルファーマ株式会社 | Schizophrenia treatment |
| WO2004064836A2 (en) * | 2003-01-22 | 2004-08-05 | Pharmacia & Upjohn Company Llc | Treatment of diseases with alpha-7 nach receptor full agonists |
| WO2004064836A3 (en) * | 2003-01-22 | 2004-12-23 | Upjohn Co | Treatment of diseases with alpha-7 nach receptor full agonists |
| JP4813357B2 (en) * | 2003-07-30 | 2011-11-09 | バイエル・シェーリング・ファルマ・アクチェンゲゼルシャフト | N-biarylamide compounds |
| JP2007500152A (en) * | 2003-07-30 | 2007-01-11 | バイエル・ヘルスケア・アクチェンゲゼルシャフト | N-biarylamide compounds |
| US7964600B2 (en) | 2003-12-22 | 2011-06-21 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indoles, 1H-indazoles, 1,2-benzisoxazoles, and 1,2-benzisothiazoles, and preparation and uses thereof |
| US7790722B2 (en) | 2003-12-22 | 2010-09-07 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indoles, 1H-indazoles, 1,2-benzisoxazoles, and 1,2-benzisothiazoles, and preparation and uses thereof |
| US7396833B2 (en) | 2003-12-22 | 2008-07-08 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indoles, 1H-indazoles, 1,2-benzisoxazoles, and 1,2-benzisothiazoles, and preparation and uses thereof |
| US8158629B2 (en) | 2003-12-22 | 2012-04-17 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indoles, 1H-indazoles, 1,2-benzisoxazoles, and 1,2-benzisothiazoles, and preparation and uses thereof |
| US7951791B2 (en) | 2004-02-04 | 2011-05-31 | Abbott Laboratories | Amino-substituted tricyclic derivatives and methods of use |
| EP2258682A3 (en) * | 2004-02-04 | 2011-03-09 | Abbott Laboratories | Amino-substituted tricyclic derivatives and methods of use |
| US7365193B2 (en) | 2004-02-04 | 2008-04-29 | Abbott Laboratories | Amino-substituted tricyclic derivatives and methods of use |
| WO2005077899A3 (en) * | 2004-02-04 | 2005-12-01 | Abbott Lab | Amino-substituted tricyclic derivatives and methods of use |
| WO2005077899A2 (en) * | 2004-02-04 | 2005-08-25 | Abbott Laboratories | Amino-substituted tricyclic derivatives and methods of use |
| US8263619B2 (en) | 2004-03-25 | 2012-09-11 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indazoles, benzothiazoles, benzoisothiazoles, benzisoxazoles, and preparation and uses thereof |
| US8691841B2 (en) | 2004-03-25 | 2014-04-08 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indazoles, benzothiazoles, benzoisothiazoles, benzisoxazoles, and preparation and use thereof |
| US8486937B2 (en) | 2004-03-25 | 2013-07-16 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indazoles, benzothiazoles, benzoisothiazoles, benzisoxazoles, and preparation and use thereof |
| US7488737B2 (en) | 2004-04-22 | 2009-02-10 | Memory Pharmaceutical Corporation | Indoles, 1H-indazoles, 1,2-benzisoxazoles, 1,2-benzoisothiazoles, and preparation and uses thereof |
| US7902217B2 (en) | 2004-04-22 | 2011-03-08 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Indoles, 1H-indazoles, 1,2-benzisoxazoles, 1,2-benzoisothiazoles, and preparation and uses thereof |
| US7632831B2 (en) | 2004-05-07 | 2009-12-15 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | 1H-indazoles, benzothiazoles, 1,2-benzoisoxazoles, 1,2-benzoisothiazoles, and chromones and preparation and uses thereof |
| US9475811B2 (en) | 2004-06-18 | 2016-10-25 | Novartis Ag | 1-aza-bicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes |
| US8933090B2 (en) | 2004-06-18 | 2015-01-13 | Novartis Ag | 1-aza-bicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes |
| US9657010B2 (en) | 2004-07-14 | 2017-05-23 | Novartis Ag | Substituted quinuclidines as alpha 7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor activity modulators |
| US8609662B2 (en) | 2004-07-14 | 2013-12-17 | Novartis Ag | 3-(heteroaryl-oxy)-2-alkyl-1-aza-bicycloalkyl derivatives as alpha. 7-nachr ligands for the treatment of CNS diseases |
| US7625924B2 (en) | 2004-12-22 | 2009-12-01 | Memory Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Nicotinic alpha-7 receptor ligands and preparation and uses thereof |
| US8173667B2 (en) | 2005-10-21 | 2012-05-08 | Novartis Ag | 1-aza-bicycloalkyl derivatives |
| US9206181B2 (en) | 2005-12-16 | 2015-12-08 | Novartis Ag | 1-aza-bicyclo[3.3.1] non-4-yl)-[5-(1H-indol-5-yl)-heteroaryl]-amines as cholinergic ligands of the n-AChR for the treatment of psychotic and neurodegenerative disorders |
| US8637517B2 (en) | 2005-12-16 | 2014-01-28 | Novartis Ag | Organic compounds |
| US8048885B2 (en) | 2005-12-16 | 2011-11-01 | Novartis Ag | Organic compounds |
| US8759346B2 (en) | 2005-12-16 | 2014-06-24 | Novartis Ag | Organic compounds |
| WO2011022692A2 (en) * | 2009-08-20 | 2011-02-24 | University Of Tennessee Research Foundation, The | Furanopyridine cannabinoid compounds and related methods of use |
| WO2011022692A3 (en) * | 2009-08-20 | 2011-06-16 | University Of Tennessee Research Foundation, The | Furanopyridine cannabinoid compounds and related methods of use |
| US8431595B2 (en) | 2009-08-20 | 2013-04-30 | The University Of Tennessee Research Foundation | Furanopyridine cannabinoid compounds and related methods of use |
| WO2011098776A1 (en) | 2010-02-15 | 2011-08-18 | Cambridge Enterprise Limited | 5-ht receptor modulators |
| US9273044B2 (en) | 2010-05-17 | 2016-03-01 | Forum Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Crystalline form of (R)-7-chloro-N-(quinuclidin-3-yl)benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxamide hydrochloride monohydrate |
| US9550767B2 (en) | 2010-05-17 | 2017-01-24 | Forum Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Crystalline form of (R)-7-chloro-N-(quinuclidin-3-yl)benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxamide hydrochloride monohydrate |
| US9108961B2 (en) | 2010-05-17 | 2015-08-18 | Forum Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Crystalline form of (R)-7-chloro-N-(quinuclidin-3-yl)benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxamide hydrochloride |
| WO2013002365A1 (en) | 2011-06-30 | 2013-01-03 | 東レ株式会社 | Antipruritic agent |
| US9585877B2 (en) | 2012-05-08 | 2017-03-07 | Forum Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods of maintaining, treating or improving cognitive function |
| EP2876109A4 (en) * | 2012-07-23 | 2016-03-16 | Yuhan Corp | Fused ring compound containing furan or salt thereof and pharmaceutical composition comprising same |
| US9493478B2 (en) | 2012-07-23 | 2016-11-15 | Yuhan Corporation | Fused ring compound containing furan or salt thereof and pharmaceutical composition comprising same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| NO20035522D0 (en) | 2003-12-11 |
| AR036040A1 (en) | 2004-08-04 |
| KR20040018266A (en) | 2004-03-02 |
| US20030045540A1 (en) | 2003-03-06 |
| CN1511154A (en) | 2004-07-07 |
| PE20030431A1 (en) | 2003-05-26 |
| PL367311A1 (en) | 2005-02-21 |
| CO5540302A2 (en) | 2005-07-29 |
| MXPA03011484A (en) | 2004-03-18 |
| CZ20033377A3 (en) | 2004-11-10 |
| IL159344A0 (en) | 2004-06-01 |
| BR0210384A (en) | 2004-06-29 |
| CA2445467A1 (en) | 2002-12-19 |
| US7067515B2 (en) | 2006-06-27 |
| EP1406901A1 (en) | 2004-04-14 |
| JP2004537532A (en) | 2004-12-16 |
| EA200301216A1 (en) | 2004-06-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7067515B2 (en) | Quinuclidines-substituted-multi-cyclic-heteroaryls for the treatment of disease | |
| EP1432707B1 (en) | Azabicyclic-substituted fused-heteroaryl compounds for the treatment of disease | |
| EP1425286B1 (en) | Substituted 7-aza-[2.2.1]bicycloheptanes for the treatment of diseases | |
| US6828330B2 (en) | Quinuclidine-substituted hetero-bicyclic aromatic compounds for the treatment of disease | |
| US20030236264A1 (en) | Fused bicyclic-N-bridged-heteroaromatic carboxamides for the treatment of disease | |
| US20040147522A1 (en) | Compounds having both alpha7 nicotinic agonist activity and 5HT3 antagonist activity for the treatment of CNS diseases | |
| WO2004052894A1 (en) | Crystalline fumarate salts of 1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct substituted furo[2,3-c]pyridinyl carboxamide and compositions and preparations thereof | |
| AU2002348498A1 (en) | Quinuclidines-substituted-multi-cyclic-heteroaryls for the treatment of disease | |
| AU2002339957A1 (en) | Azabicyclic-substituted fused-heteroaryl compounds for the treatment of disease | |
| UA77447C2 (en) | Azabicyclic-substituted fused heteroaryls, a pharmaceutical composition based thereon |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AK | Designated states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AE AG AL AM AT AU AZ BA BB BG BR BY BZ CA CH CN CO CR CU CZ DE DK DM DZ EC EE ES FI GB GD GE GH GM HR HU ID IL IN IS JP KE KG KP KR KZ LC LK LR LS LT LU LV MA MD MG MK MN MW MX MZ NO NZ OM PH PL PT RO RU SD SE SG SI SK SL TJ TM TN TR TT TZ UA UG US UZ VN YU ZA ZM ZW |
|
| AL | Designated countries for regional patents |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): GH GM KE LS MW MZ SD SL SZ TZ UG ZM ZW AM AZ BY KG KZ MD RU TJ TM AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LU MC NL PT SE TR BF BJ CF CG CI CM GA GN GQ GW ML MR NE SN TD TG |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | ||
| DFPE | Request for preliminary examination filed prior to expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed before 20040101) | ||
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 1-2003-501280 Country of ref document: PH |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2002348498 Country of ref document: AU |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2445467 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2003/08844 Country of ref document: ZA Ref document number: 200308844 Country of ref document: ZA Ref document number: 028098145 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 1945/DELNP/2003 Country of ref document: IN |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 200301216 Country of ref document: EA |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 03108314 Country of ref document: CO |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: PA/a/2003/011484 Country of ref document: MX Ref document number: 159344 Country of ref document: IL Ref document number: PV2003-3377 Country of ref document: CZ Ref document number: 1020037016210 Country of ref document: KR |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 530143 Country of ref document: NZ Ref document number: 2003503624 Country of ref document: JP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2002778932 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWP | Wipo information: published in national office |
Ref document number: 2002778932 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: 8642 |
|
| WWP | Wipo information: published in national office |
Ref document number: PV2003-3377 Country of ref document: CZ |
|
| WWW | Wipo information: withdrawn in national office |
Ref document number: 2002778932 Country of ref document: EP |