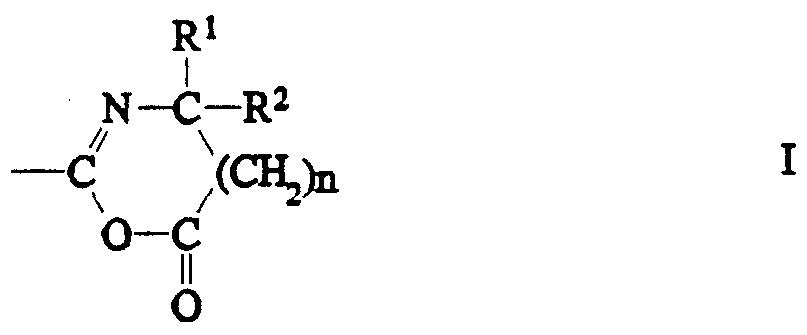WO1994000165A2 - Azlactone-functional substrates, corneal prostheses, and manufacture and use thereof - Google Patents
Azlactone-functional substrates, corneal prostheses, and manufacture and use thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO1994000165A2 WO1994000165A2 PCT/US1993/004554 US9304554W WO9400165A2 WO 1994000165 A2 WO1994000165 A2 WO 1994000165A2 US 9304554 W US9304554 W US 9304554W WO 9400165 A2 WO9400165 A2 WO 9400165A2
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- azlactone
- group
- functional
- nucleophilic
- carbon atoms
- Prior art date
Links
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08F—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING CARBON-TO-CARBON UNSATURATED BONDS
- C08F8/00—Chemical modification by after-treatment
- C08F8/30—Introducing nitrogen atoms or nitrogen-containing groups
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F2/00—Filters implantable into blood vessels; Prostheses, i.e. artificial substitutes or replacements for parts of the body; Appliances for connecting them with the body; Devices providing patency to, or preventing collapsing of, tubular structures of the body, e.g. stents
- A61F2/02—Prostheses implantable into the body
- A61F2/14—Eye parts, e.g. lenses, corneal implants; Implanting instruments specially adapted therefor; Artificial eyes
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F2/00—Filters implantable into blood vessels; Prostheses, i.e. artificial substitutes or replacements for parts of the body; Appliances for connecting them with the body; Devices providing patency to, or preventing collapsing of, tubular structures of the body, e.g. stents
- A61F2/02—Prostheses implantable into the body
- A61F2/14—Eye parts, e.g. lenses, corneal implants; Implanting instruments specially adapted therefor; Artificial eyes
- A61F2/142—Cornea, e.g. artificial corneae, keratoprostheses or corneal implants for repair of defective corneal tissue
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L27/00—Materials for grafts or prostheses or for coating grafts or prostheses
- A61L27/28—Materials for coating prostheses
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L27/00—Materials for grafts or prostheses or for coating grafts or prostheses
- A61L27/28—Materials for coating prostheses
- A61L27/34—Macromolecular materials
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L27/00—Materials for grafts or prostheses or for coating grafts or prostheses
- A61L27/50—Materials characterised by their function or physical properties, e.g. injectable or lubricating compositions, shape-memory materials, surface modified materials
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L27/00—Materials for grafts or prostheses or for coating grafts or prostheses
- A61L27/50—Materials characterised by their function or physical properties, e.g. injectable or lubricating compositions, shape-memory materials, surface modified materials
- A61L27/52—Hydrogels or hydrocolloids
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C45/00—Preparation of compounds having >C = O groups bound only to carbon or hydrogen atoms; Preparation of chelates of such compounds
- C07C45/61—Preparation of compounds having >C = O groups bound only to carbon or hydrogen atoms; Preparation of chelates of such compounds by reactions not involving the formation of >C = O groups
- C07C45/67—Preparation of compounds having >C = O groups bound only to carbon or hydrogen atoms; Preparation of chelates of such compounds by reactions not involving the formation of >C = O groups by isomerisation; by change of size of the carbon skeleton
- C07C45/68—Preparation of compounds having >C = O groups bound only to carbon or hydrogen atoms; Preparation of chelates of such compounds by reactions not involving the formation of >C = O groups by isomerisation; by change of size of the carbon skeleton by increase in the number of carbon atoms
- C07C45/70—Preparation of compounds having >C = O groups bound only to carbon or hydrogen atoms; Preparation of chelates of such compounds by reactions not involving the formation of >C = O groups by isomerisation; by change of size of the carbon skeleton by increase in the number of carbon atoms by reaction with functional groups containing oxygen only in singly bound form
- C07C45/71—Preparation of compounds having >C = O groups bound only to carbon or hydrogen atoms; Preparation of chelates of such compounds by reactions not involving the formation of >C = O groups by isomerisation; by change of size of the carbon skeleton by increase in the number of carbon atoms by reaction with functional groups containing oxygen only in singly bound form being hydroxy groups
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C49/00—Ketones; Ketenes; Dimeric ketenes; Ketonic chelates
- C07C49/76—Ketones containing a keto group bound to a six-membered aromatic ring
- C07C49/84—Ketones containing a keto group bound to a six-membered aromatic ring containing ether groups, groups, groups, or groups
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K5/00—Use of organic ingredients
- C08K5/04—Oxygen-containing compounds
- C08K5/15—Heterocyclic compounds having oxygen in the ring
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F2/00—Filters implantable into blood vessels; Prostheses, i.e. artificial substitutes or replacements for parts of the body; Appliances for connecting them with the body; Devices providing patency to, or preventing collapsing of, tubular structures of the body, e.g. stents
- A61F2/02—Prostheses implantable into the body
- A61F2/14—Eye parts, e.g. lenses, corneal implants; Implanting instruments specially adapted therefor; Artificial eyes
- A61F2/15—Implant having one or more holes, e.g. for nutrient transport, for facilitating handling
Definitions
- This invention relates to substrates, especially hydrogels, having azlactone-functional surfaces, mammalian body implants, (e.g., corneal prostheses), comprising such azlactone-functional hydrogels, and methods of making and using them.
- substrates especially hydrogels, having azlactone-functional surfaces, mammalian body implants, (e.g., corneal prostheses), comprising such azlactone-functional hydrogels, and methods of making and using them.
- Mammalian body implants such as corneal prostheses, (also known as keratoprostheses), are very useful to replace degenerated or injured mammalian tissue if the remainder of the mammalian body accepts the presence of such implant and if the biocompatible implant performs the function of the replaced tissue in an acceptable manner.
- Corneal prostheses are especially vital for the continued functioning of a mammal, especially a human being, because a degenerated or injured cornea obscures vision.
- the anterior surface of a keratoprosthesis should support the adherence and proliferation of corneal epithelial cells, resulting in an intact epithelial layer which is continuous with the surrounding host epithelium.
- a continuous layer of epithelium permits maintenance of the normal precorneal tear film, ensures a good optical surface and provides a barrier against microbial invasion.
- a prior effort has been to provide a corneal prosthesis using poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel as an optical element and a porous outer skirt secured to the periphery of the element.
- European Patent Publication 0 333 344 Capecchi et al.), the European counterpart to U.S. Pat. No.
- 5,108,428 discloses this corneal prosthesis and identifies the desire to coat or laminate the anterior surface with a basement membrane component(s) to facilitate growth of epithelial cells on it. Coating i ⁇ preferably performed by adsorption or chemical attachment or integration during polymerization with basement membrane component(s) prior to seeding of corneal epithelial cells on the anterior surface.
- Acceptable basement membrane components include laminin, fibronectin, Type I c&llagen, Type IV collagen, or a cell-free extract prepared from extracellular matrix of corneal epithelial cells.
- the present invention solves the problem of providing a biocompatible mammalian body implant, especially a corneal prosthesis, which is capable of providing surfaces for optimum mammalian cell growth, especially epithelial cell growth.
- One aspect of the present invention is a novel azlactone- functional substrate which is functional for reaction with nucleophilic compounds.
- Another aspect of the present invention is a novel azlactone-functional hydrogel which is useful as a component in a mammalian body implant.
- Another aspect of the present invention is a multi- functional azlactone composition useful for the preparation of an azlactone-functional substrate, especially an azlactone-functional hydrogel.
- Another aspect of the present invention is a mammalian body implant, especially a corneal prosthesis, which is prepared using an azlactone-functional hydrogel and a porous outer skirt of a nonwoven polyolefin web secured at the periphery of the hydrogel on its posterior surface.
- Another aspect of the present invention is a method of preparing an azlactone-functional substrate, especially an azlactone- functional hydrogel.
- Another aspect of the present invention is a method of preparing a mammalian body implant using an azlactone-functional hydrogel and the porous outer skirt of nonwoven polyolefin web.
- Another aspect of the present invention is a composition useful as an ultraviolet absorbing monomer employed with an azlactone- functional hydrogel.
- Substrate means a composition having nucleophilic surfaces and capable of reaction with an azlactone-functional composition.
- Hydrophilic composition regardless of its state of hydration, which is capable of swelling, but not dissolving, in water.
- Multi-functional azlactone composition means a composition having at least two azlactone moieties available for nucleophilic reaction.
- R 1 and R 2 independently can be an alkyl group having 1 to 14 carbon atoms, a cycloalkyl group having 3 to 14 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 5 to 12 ring atoms, an arenyl group having 6 to 26 carbon atoms and 0 to 3 S, N, and nonperoxidic 0 heteroatom ⁇ , or R' and R 2 taken together with the carbon to which they are joined can form a carbocyclic ring containing 4 to 12 ring atoms, and n is an integer 0 or 1.
- Azlactone-functional means that a reaction between a multi-functional azlactone composition and a substrate results in a covalent bond between nucleophilic surfaces of the substrate and at least one azlactone moiety of the multifunctional azlactone composition, such that at least one azlactone moiety remains available for further nucleophilic reaction with a biologically active material.
- Bioly active material means a chemical composition having azlactone-reactive, nucleophilic-functional groups and capable of reacting in a manner which affects biological processes, especially mammalian cells.
- biologically active materials are substances which are biologically, immunochemically, physiologically, or pharmaceutically active.
- biologically active materials include proteins, peptides, polypeptides, antibodies, antigenic substances, enzymes, cofactors, inhibitors, lectins, hormones, receptors, coagulation factors, amino acids, histones, vitamins, drugs, cell surface markers, and substances which interact with them.
- Activated substrate means an azlactone-functional substrate of Formula II:
- R 1 , R 2 , and n are as previously defined, wherein y i ⁇ at least one and is the number of azlactone moieties less at least one, wherein R 3 is a bridging group capable of covalently connecting a plurality of azlactone moieties, and wherein B is the substrate and A is the residue of the azlactone-reactive nucleophilic group on the substrate, such as O, S, or NR 4 , wherein R 4 is hydrogen or an alkyl group containing from 1 to 4 carbon atoms.
- “Bridging group” means a group comprising (a) an alkylene group having up to 14 carbon atoms; (b) an arylene group having up to 10 carbon atoms; (c) a cycloalkylene group having up to 6 carbon atoms; (d) a group resulting from the Michael reaction of a Michael donor nucleophilic compound with a plurality of 2-alkenyl azlactone Michael acceptors, where the Michael donor nucleophilic compound has at least two azlactone-reactive moieties; or (e) a combination of the above- listed bridging groups.
- Nonlimiting examples of alkylene, arylene, and cycloalkylene groups are disclosed in "Polyazlactones" by J. K.
- Nonlimiting examples of such Michael donor nucleophilic compounds include thiols and secondary amines as disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 4,485,236 (Rasmussen et al.), or combinations thereof; or carbon acids, enamine ⁇ , imides, and nitrogen heterocycles (as disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 5,149,806 (Moren et al.)) or combinations thereof.
- a feature of the present invention is that azlactone- functional substrates are capable of reacting with nucleophilic biologically active materials, such as extracellular matrix proteins, such as laminin, fibronectin, Type I collagen, Type IV collagen, or a cell-free extract prepared from extracellular matrix of corneal epithelial cells, in order to prepare a mammalian body implant for implantation and successful cell growth.
- nucleophilic biologically active materials such as extracellular matrix proteins, such as laminin, fibronectin, Type I collagen, Type IV collagen, or a cell-free extract prepared from extracellular matrix of corneal epithelial cells, in order to prepare a mammalian body implant for implantation and successful cell growth.
- azlactone-functional substrate couples biologically active materials in a manner which permit ⁇ further biochemical interaction with living cells.
- Another feature of the present invention is that coupling of biologically active materials to a hydrogel modifies surfaces of the hydrogel in a manner which permits biocompatible mammalian body implantation.
- the hydrogel can be any desired shape for mammalian body implantation.
- the surface modification enhances cell growth upon implantation, thus allowing articles of the present invention to be useful as a mammalian body implant.
- An advantage of the present invention is that the use of azlactone-functional hydrogels as elements of a corneal implant is superior to prior methods of enhancing cell growth.
- the invention provide ⁇ a mammalian body implant comprising a hydrogel having azlactone-reactive nucleophilic surfaces, a multi-functional azlactone composition covalently coupled to the azlactone-reactive nucleophilic surfaces, and a biologically active material coupled to the multi-functional azlactone composition.
- the invention also provides an azlactone-functional substrate comprising a substrate having azlactone-reactive nucleophilic surfaces and a multi-functional azlactone composition covalently coupled thereto in a manner such that at least one azlactone moiety remains available for further nucleophilic reaction.
- the invention also provides a biologically active substrate comprising the reaction product of an activated substrate described above and a biologically active material.
- the invention also provides a multi-functional azlactone composition selected from the group consisting of tris[ [2-[N-2-(4,4- dimethyl-2-oxazoline-5-one-2-yl)ethyl, N-isopropyl]-2-amino)ethyl]amine and N, ' , "-tris-2-(4,4-dimethyl-2-oxazoline-5-one-2-yl)ethyl-bis- (N,N"-isopropyl-2-aminoethyl)amine.
- the invention also provides a benzophenone ultraviolet light absorber selected from the group consisting of 2-allyloxy-4,4'- dimethoxy-2-hydroxy benzophenone and 3-allyl-2,2'-dihydroxy-4,4'- dimethoxy benzophenone.
- the invention also provides a method of making an azlactone-functional hydrogel comprising the steps of (a) forming a hydrogel in a dehydrated state comprising a composition having azlactone-reactive nucleophilic surfaces and reacting a multi ⁇ functional azlactone composition with the azlactone-reactive nucleophilic surfaces of the hydrogel in a dehydrated state in a manner that retains at least one azlactone moiety remaining available for further nucleophilic reaction.
- the invention also provides a method of forming a mammalian body implant comprising the steps of forming an azlactone-functional hydrogel according to the method described above and reacting a biologically active material with at least one azlactone moiety. Further description of embodiments of the invention follows with reference to the Drawings.
- FIG. 1 is a diagrammatic perspective view, partially broken away, of a corneal prosthesis according to the invention.
- Fig. 2 is a diagrammatic sectional view of a portion of the human eye incorporating a corneal prosthesis according to the invention.
- Fig. 3 is an enlarged view of a portion of Fig. 2 showing the anterior surface of the Fig. 1 prosthesis on which an epithelial layer has grown.
- Substrates useful for the present invention can be any natural or synthetic composition which has azlactone-reactive, nucleophilic surfaces due to the presence of azlactone-reactive, nucleophilic moieties such as hydroxyl, amine, or thiol moieties.
- Nonlimiting examples of substrates include naturally occurring compositions, such as cellulose (and modified cellulose derivatives), agarose, dextran, chitin and chitosan; synthetic compositions such as polymers derived from monomers such as hydroxyethyl methacrylate, hydroxypropyl aerylate, N-methylolacrylamide, allyl alcohol, allyl amine, and N-[3-(N'-isopropyl)aminopropyl] methacrylamide; and polymers derived by modification of polymers such as silica gel and glass particles reacted with ⁇ -triethoxysilylpropylamine, ⁇ - triethoxysilylpropane-1-thiol, or ⁇ -glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane (followed by hydroylsis of the epoxide), and hydrogels as defined herein.
- naturally occurring compositions such as cellulose (and modified cellulose derivatives), agarose, dextran,
- Hvdrooel Depending on the type of mammalian body implant, the selection of a useful hydrogel can vary according to desired physical and chemical characteristics.
- a hydrogel needs azlactone-reactive nucleophilic reaction sites for covalent coupling with an azlactone moiety.
- the azlactone-reactive nucleophilic reaction sites are hydroxyl groups.
- hydrogel compositions that are biocompatible with mammalian tissues are described in the art. Hydrogels that have been approved by governmental regulatory agencies for use with or in mammalian tissues are preferred.
- biocompatible hydrogels that have azlactone-reactive nucleophilic reaction sites for chemical interaction with a multi-functional azlactone composition include poly(vinyl alcohol) copolymer systems, and poly(vinylpyrrolidone) blends where the other polymer(s) of the blend contain azlactone-reactive nucleophilic surfaces.
- Ofstead European Published Patent Application No. 0137686A (“Ofstead '686A"), discloses desirable copolymer systems and blends.
- poly(vinyl alcohol) homopolymers and copolymers are preferred, either as bulk material or as coatings on the outer surfaces thereof.
- Preferred poly(vinyl alcohol) copolymers are described in U.S. Pat. No. 4,618,649 ("Ofstead '649") and U.S. Pat. No. 4,528,325 (“Ofstead '325").
- the presently most preferred material is poly(vinyl alcohol-co-vinyl acetate) prepared from a copolymer of vinyltrifluoroacetate (VTFA) "and vinyl acetate (VAc) and made according to the methods described in
- the weight ratio of VTFA to VAc can range from about 95:5 to about 99.9:0.1, and preferably between about 97:3 and 99:1.
- the presently preferred weight ratio is 98.5:1.5, which corresponds to a molar ratio of VTFA:VAc of 97.6:2.4.
- this poly(vinyl alcohol-co-vinyl acetate) material is a semi-crystalline hydrogel which has azlactone- reactive nucleophilic surfaces of hydroxyl moieties, has an equilibrium water content of 73% in normal saline, tensile strength of 110 kg/cm 2 , initial modulus of elasticity of 10-15 kg/cm 2 , and elongation of 436%. Tensile strength, elongation and modulus were all measured as described at col. 6, line 57 to col. 7, line 4 of Ofstead '649.
- biocompatible hydrogel materials can be used as optical elements of a corneal prosthesis so long as the water content is greater than 50% (preferably between 65% and 80%) and the tensile strength is greater than 20 kg/cm 2 (preferably greater than 40 kg/cm 2 ) . Further strength-related criteria that preferably are met are a modulus of elasticity between 3 and 115 kg/cm 2 (preferably 5-15 kg/cm 2 ), and elongation between 100-1000% (preferably greater than 150%).
- biocompatible hydrogel materials for use as an optical element include other pol (vinyl alcohol) copolymers, e.g., containing maleic anhydride (0-3%) (mole percent) as the comonomer, other hydrogel materials described in Ofstead '649 (see discussion at col. 3, lines 19-50 in particular), other hydrogel materials described in Ofstead '325, other hydrogel materials described in Ofstead '686A (including other blends with poly(vinylpyrrolidone) if the other polymers of the blends have azlactone-reactive nucleophilic moieties), and Hammar et al. U.S. Pat. No. 4,673,539.
- the water content and strength properties can be altered by varying the comonomer type and content in the polymer systems or the material ratios in the blends, permitting tailoring to meet physical and chemical characteristics needed for a mammalian body implant generally and a corneal prosthesis particularly.
- the presently most preferred poly(vinyl alcoholco-vinyl acetate) material for use in a corneal prosthesi ⁇ described above is made by molding of solvent cast discs of the precursor polymer as described in Ofstead '649, although lathe processing of thermally-molded buttons or bulk UV polymerized buttons can also be used.
- the technique disclosed in Example 14 of U.S. Pat. No. 4,673,539 can be employed for thermally-molded buttons.
- the VTFA/VAc precursor polymer is then converted to a poly(vinyl alcohol-co-vinyl acetate) hydrogel by a solvolysis reaction.
- the hydrogel is optically transparent, has a water content between about 50% and about 90%, has a tensile strength of greater than about 20 kg/cm 2 , and has an anterior surface capable of supporting a layer of epithelial cells.
- other materials can be added to the hydrogel to alter performance characteristics.
- an ultraviolet light absorbing monomer such as 2-allyloxy-4,4'-dimethoxy-2'-hydroxy benzophenone (2-allyloxy-BP) , 3-allyl-2,2'-dihydroxy-4,4'-dimethoxy benzophenone (3-allyl-BP) , 2,2'-dihydroxy-4-methoxy-4'-(2- methacryloyloxyethoxy) benzophenone (MEBP) disclosed in Japanese Kokai 020070711 published March 9, 1990, or 4-(2'-acryloyloxyethoxy)-2- hydroxy benzophenone (commercially available as "Cyasorb UV-2098" from American Cyanamid), can be copolymerized in weight percents ranging from about 0.1 to about 1 part by weight with vinyltrifluoroacetate to form a copolymer which in turn can be blended with preferred precursor polymers in weight ratios of from about 50:50 (precursor:uv-absorbing polymer) to 90:10 to form a uv
- the uv-absorbing monomer can be copolymerized with yinyltrifluoroacetate (VTFA) and maleic anhydride (MA) at a 98.5:1.5:0.25 (VTFA:MA:uv-absorbing monomer) weight ratio using thermal initiators such as Lupersol 225 (Pennwalt Corp.) sequentially heating at 40 ⁇ C for 12 hours and then at 60°C for 3 hours.
- thermal initiators such as Lupersol 225 (Pennwalt Corp.) sequentially heating at 40 ⁇ C for 12 hours and then at 60°C for 3 hours.
- 2-allyloxy-BP or 3-allyl-BP are presently preferred because they have the advantage of permanent, non-leachable ultraviolet protection and light absorbance which cuts off sharply at 380 run.
- any multi-functional azlactone composition can be useful in the present invention to provide a plurality of azlactones, defined in Formula I above, for reaction with the substrate to produce an azlactone-functional substrate, such as an activated substrate defined in Formula II above, and preferably an azlactone-functional hydrogel.
- an azlactone-functional substrate such as an activated substrate defined in Formula II above, and preferably an azlactone-functional hydrogel.
- the substrate has azlactone-reactive nucleophilic reaction sites, preferably hydroxyl groups, available for covalent reaction with an azlactone moiety
- the formation of the bond to covalently couple the multi-functional azlactone composition to the hydrogel uses at least one of the azlactone moieties and leaves at least one other azlactone moiety available for nucleophilic reaction with a biologically active material.
- Nonlimiting examples of multi-functional azlactone compositions include homopolymers, copolymers, and oligomers having at least two azlactones as defined in Formula I above.
- a multi-functional azlactone composition comprises at least two azlactones covalently connected to a bridging group, as defined above.
- Nonlimiting examples of suitable multi-functional azlactone compositions and their methods of preparation by Michael Addition are disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 4,485,236 (Rasmussen et al.), and in U.S. Pat. No. 5,149,806 (Moren et al.).
- multi-functional azlactone compositions are homopolymerB, copolymers, and oligomers prepared from the Michael Addition of 2-alkenyl azlactone monomers with nucleophilic group- substituted compounds having the formula (HX) n R 5 where R 5 is an organic group that has a valence of n and is the residue of a nucleophilic group-substituted compound, (HX) B R 5 , in which X is defined above and n is defined below, the residue having a molecular weight up to 20,000, preferably selected from mono-and polyvalent hydrocarbyl (i.e., aliphatic and aryl compounds having 2 to 20 carbon atoms and optionally one to four catenary heteroatoms of oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur, e.g., piperazine, furan, and thiophene), polyoxyalkylene, polyester, polyolefin, polyacrylate, and polysiloxane residues that can optionally all be further substitute
- Nonlimiting examples of 2-alkenyl azlactone monomers that can be polymerized to form multi-functional azlactone compositions and their synthesis are disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 4,304,705; 5,081,197; and 5,091,489 (all Heilmann et al.).
- Suitable 2-alkenyl azlactones include:
- the preferred 2-alkenyl azlactones include
- VDM 2-ethenyl-4,4-dimethyl-l,3-oxazolin-5-one
- IDM 2-isopropenyl-4,4-dimethyl-l,3-oxazolin-5-one
- VDM-based polymers and oligomers include vinyldimethylazlactone homopolymers and copolymers ("Poly-VDM”) , vinyldimethylazlactone oligomers (“Oligo-VDM”) prepared by the acid catalyzed polymerization of VDM according to U.S. Pat. No.
- Tris-VDM-T tris-Michael adduct of VDM and trie-(N'-isopropylaminoethyl)amine having the following formula III and named in this application as tris[ [2-[N-2-(4,4-dimethyl-2-oxazoline-5- one-2-yl)ethyl, N-isopropyl]-2-amino)ethyl]amine
- Tris-VDM-T tris[ [2-[N-2-(4,4-dimethyl-2-oxazoline-5- one-2-yl)ethyl, N-isopropyl]-2-amino)ethyl]amine
- Tris-VDM-B the tris-Michael adduct of VDM and bis-(N'- isopropylaminoethyl)amine having the following formula IV and named in this application as N,N' ,N"-tris-2-(4,4-dimethyl-2-oxazoline-5-one-2- yl)ethyl-bis-(N,N"-isopropyl-2-aminoethyl)amine
- Tris-VDM-T is presently preferred.
- Reaction of a multi-functional azlactone composition with a hydrogel preferably occurs with the hydrogel in a substantially dehydrated state and can occur at temperatures ranging from about 25°C to about 300°C for times ranging from about 1 min. to about 24 hours at ambient, elevated, or reduced pressures and under ambient or inert atmospheric conditions.
- the temperatures range from about 50°C to about 200°C.
- the reaction times range from about 30 min. to about 3 hours.
- the reaction vessel pressures are ambient.
- the reaction atmosphere is inert to azlactone functionality, using N 2 or another gas in anhydrous condition.
- Corneal ProstheBes A corneal prosthesis of the present invention includes an optical element having at least an anterior surface which is azlactone- functional and a porous outer skirt secured to the periphery of the element on the posterior surface thereof.
- a corneal prosthesis 10 including optical element 12 and porous outer skirt 14.
- Optical element 12 includes a full depth optically-transparent central portion 16 and a thinner outer portion 18 that overlies skirt 14 which extends around the periphery of prosthesiB 10.
- the anterior surface 17 of optical element 12 is azlactone-functional.
- the optical element 12 has an optically transparent central portion 16 and an anterior surface 17 that is capable of supporting a layer of epithelial cells
- the outer skirt 14 is used to secure the optical element 12 to the patient's surrounding tissue and is sufficiently porous to permit cell ingrowth and tissue attachment.
- the optical element 12 is made of a poly(vinyl alcohol) copolymer hydrogel described above with an anterior surface 17 having a multi-functional azlactone composition described above covalently coupled thereto.
- the prosthesis 10 also includes a layer of epithelial cells covering the anterior surface 17 of the optical element 12.
- such cells are attached to the anterior surface 17 via coupling of such cells to a biologically active material, such as a basement membrane component, after the biologically active material has been coupled to the azlactone-functional anterior surface 17 of optical element 12.
- a biologically active material such as a basement membrane component
- Optical element 12 is made of an optically transparent hydrogel material described above having a water content between 50% and 90%, a tensile strength of greater than 20 kg/cm 2 and an anterior surface capable of supporting a layer of epithelial cells.
- U.S. Pat. No 5,108,428 (Capecchi et al.), describes the desired properties of the optical element and the advantages of providing a layer of epithethial cells thereon.
- the use of an azlactone-functional anterior surface of the present invention to couple a biologically active material for enhancement of cell growth unexpectedly improves the ability of the anterior surface 17 to support a layer of epithelial cells thereon.
- the material of optical element 12 preferably is a hydrogel made from the hydrogel materials described above.
- Porous Skirt Porous outer skirt 14 is preferably made of a coherent mass of melt blown fibers having an interconnected network of pores substantially as described in U.S. Pat. No. 5,108,428 (Capecchi et al. ) ("Capecchi '428").
- the presently most preferred materials for porous skirt 14 are polybutylene (e.g., available under the trade designation Shell 8010) or a polybutylene/polypropylene blend (80%/20%).
- the polymeric material used to form the melt blown fibers also contain an antioxidant, such as Irganox 1010 branded antioxidant, commercially available from Ciba Geigy Corporation of Hawthorn, New York. The antioxidant is dry blended at about 1 percent by weight into the mixture of resins prior to feeding the re ⁇ in mix into the extruder.
- the skirt 14 is preferably made according the description contained in Capecchi '428 with reference to FIG. 4A thereof and Example 11 therein.
- U.S. Pat. No. 4,118,531 (Hauser), van Wente, "Superfine Thermoplastic Fibers", Industrial Engineering Chemistry, Vol. 48, pages 1342 et seq. (1956), and Report No. 4364 of the Naval Research Laboratories, published May 25, 1954 entitled “Manufacture of Superfine Organic Fibers" by van Wente et al., and Example 5 below describe methods of making melt blown microfiber web.
- Capecchi '428 generally describes the manufacture of the corneal prosthesis, except that in accordance with the present invention, the anterior surface 17 of the optical element 12 is azlactone-functional and has been reacted with a biologically active material suitable for enhancing epithethial cell growth.
- the optical element 12 (prior to the solvolysis step, described in Ofstead '649, which step causes water-swelling) is formed to shape in the presence of a ring of blown fiber web skirt 14. After preparing a film of the precursor polymer, at a thickness less than the specified central portion 16 thickness desired to accommodate swelling during solvolysis and hydration, using a spin casting drum, blown fiber web is cut to fit and placed in the drum next to the film.
- a solvent which is a solvent for the polymer of the optical element 12 and a nonsolvent for the skirt 14 (e.g., acetone) is injected to wet the blown fiber web and dissolve the surface of the film allowing the blown fibers to become embedded in the film.
- the solvent must be evaporated quickly to prevent total saturation of the blown fiber web and the complete dissolution of the film, which would occlude pores of the skirt 14.
- spinning continues in the spin casting drum, uncovered, for about 30 to about 60 minutes. After solvolyzing the precursor to form poly(vinyl alcohol- co-vinyl acetate) and hydrating to form the hydrogel, discs of the appropriate size are cut to form the corneal prosthesis 10.
- the precursor of optical element 12 (prior to the solvolysis step, described in Ofstead '649, which step causes water-swelling) is formed to shape (either by molding or by lathing of a preformed button) and solvent welded to the porous outer skirt 14 by dipping skirt 14 in a solvent (e.g., acetone) and pressing the two together. Just enough pressure is applied to make good contact between the two components 12 and 14.
- the precursor of element 12 is then taken through the solvolyBis stage attached to skirt 14, optical element 12 retaining its shape and optical clarity.
- Skirt 14 is sufficiently elastic to accommodate changes in the shape of optical element 12 during the solvolysis stage.
- a benefit of solvent welding is obtaining mechanical interlocking of the fibers in the hydrogel, avoiding the problem of delamination at an adhesive interface.
- ThiB is especially important with a material which is going to change in size on solvolysis and swelling. Also, by avoiding the use of adhesive to bond the two together, the different materials interfacing with the human eye are limited in number. This attachment method also avoids subjecting the hydrogel to processes that might potentially change its properties.
- optical element 12 and porous skirt 14 can be combined by using a biocompatible adhesive (e.g., cyanoacrylates) to form corneal prosthesis 10.
- a biocompatible adhesive e.g., cyanoacrylates
- Use of an adhesive introduces an additional material interfacing with a mammalian eye, but avoids processing techniques that can disrupt azlactone-functionality on anterior surface 17.
- both optical element 12 and porous skirt 14 are coated with a basement membrane component by chemical attachment reaction of the basement membrane component with the multi-functional azlactone composition covalently coupled to the anterior surface of the optical element 12.
- a basement membrane component by chemical attachment reaction of the basement membrane component with the multi-functional azlactone composition covalently coupled to the anterior surface of the optical element 12.
- one or more of the following basement membrane components could be used: laminin, fibronectin, Type I collagen, Type IV collagen or a cell-free extract prepared from the extracellular matrix of corneal epithelial cells.
- a holding device as seen in FIG. 5 of Capecchi '428 and in U.S. Pat. No. 5,032,131 (Aysta et al.), can be used to seed the basement membrane component on anterior surface 17 of optical element 12 with epithelial cells and porous skirt 14 with stromal keratocytes as described in Capecchi '428.
- the prosthesis 10 Prior to implantation of the prosthesis 10, it should be sterilized with ultraviolet or gamma radiation according to techniques according to those skilled in the art. Then, the prosthesis 10 is surgically implanted in the eye employing known keratectomy procedures and using fibrin adhesives generally described in Capecchi '428.
- the peripheral portion of prosthesis 10 including skirt 14 is sutured to cornea 50.
- Posterior surface 52 of prosthesis 10 seals anterior chamber 54, and the edge of overlying portion 18 is aligned with the epithelial layer of cornea 50, and skirt 14 is aligned with the stroma of the eye.
- Stromal tissue grows into the interconnected pores of porous skirt 14, serving to anchor prosthesis 10 in the patient's eye.
- Epithelial cells migrate from the epithelial layer of the surrounding tissue of cornea 50 to the anterior surface of optical element 12 and vice versa, forming a continuous epithelial layer 56 (see Fig. 3) on anterior surface 58 of element 12.
- Layer 56 desirably includes at least three cell layers and is about 50 to 100 ⁇ m thick.
- the preseeding of the anterior surface with epithelial cells and the preseeding of the skirt with stromal keratocytes facilitates re-epithelialization and tissue ingrowth.
- the complete covering of the anterior surface provides a normal precorneal tear film and a barrier against microbial invasion.
- Capecchi '428 also generally describes the procedures directed to laboratory experiments employed to determine useful cell growth.
- Nonlimiting examples of other mammalian body implants include partial thickness corneal implants, intralammelar implants, percutaneous implants, vascular grafts.
- the porous outer skirt could be taken through the solvolysis stage prior to bonding to the porous outer skirt.
- the optical element could be formed to its desired shape when in the hydrogel state.
- a curved optic shape for the optical element 12 can be imparted by placing the a disc of precursor polymer film of a desired thickness in a hot metal mold, preheated in an oven having a temperature of about 165°C, for about two minutes, followed by removal of the mold set and compression at about 50-100 psi during natural air cooling of the mold set. The curved optic is then solvolyzed and hydrolyzed. The optical element 12 so formed maintains curvature after hydration.
- the melt blown material also has application in other implant devices and can be used to anchor members made of material that is different from the melt blown material.
- the use of fibrin adhesive to inhibit epithelial downgrowth has application in other percutaneous type implants where epithelial downgrowth is a potential complication, e.g., peritoneal access devices, blood access devices, and periodontal surgery where there is a need to prevent the epithelium from migrating down the tooth-gingival interface.
- the examples describe preparation of epithelial cell cultures and their seeding in vitro and in vivo, preparation of stromal keratocytes and their ingrowth in vitro and in vivo, combinations of melt blown fiber and hydrogel in vitro, use of fibrin adhesive, preparation of polyvinyltrifluoroacetate-co-maleic anhydride and conversion to hydrogels containing ionic functional groups, and preparation of melt blown fiber webs.
- polyester release liner unprimed Polyester film, 2 7/8" x 8 1/2", washed with acetone
- the film was seated against the drum surface by squirting 1-2 ml acetone into the spinning drum. Nitrogen flowing through the tube purged air from the drum and then the flow was adjusted to a minimum detectable amount.
- Example 8 of Ofstead '649 was injected into the spinning drum. Then, a tube with a minimal, but detectable flow of nitrogen was inserted approximately halfway into the drum to maintain a low humidity, low oxygen, atmosphere. The drum was kept spinning, uninterrupted for 2 - 4 hours.
- the release film was carefully separated from the drum using a small metal spatula, and the film and the release liner. were pulled from the drum carefully to avoid cracking the pVTFA/VAc film.
- the release liner was removed from the film.
- the pVTFA/VAc film was cut at the seam using scissors.
- the spin casted film was protected from moisture by keeping the film in a nitrogen atmosphere, either inside a glove bag or sealed in a locking plastic bag. In some instances when longer storage times were required, pVTFA/VAc films were stored at temperature less than -20°C.
- the p(VTFA/VAc) was solvolyzed for 2 hours in 10% ammonium hydroxide/methanol solution in a beaker covered with a sealing film cover with the beaker placed in a chemical fume hood. Then the ammonium hydroxide/methanol solution was replaced with methanol and the film was soaked for an additional 2 hours in a chemical fume hood. After the methanol soaking, the film was rinsed by soaking at least four times in deionized water, with the film soaking in deionized water for minimum of 60 minutes between each rinse. After storage of the film for at least eight hours in deionized water, the PVA film was fully hydrated. Then, the hydrated PVA film was cut into desired sample configuration with a die or scissors.
- the films and discs samples were placed in a solution of 70% ethanol/water for 1-2 hours. Then, the 70% ethanol/water solution was replaced with absolute ethanol sufficient to cover the samples. The samples were soaked in absolute ethanol for 1-2 hours. In some instances, the samples were completely dried using six soakings in acetone for a minimum of 1 hr each. Because acetone is hygroscopic, the samples were soaked in a nitrogen-purged glove bag during the soakings. The hydrogel samples were then available in a dehydrated state, also known as a xerogel, for reaction with a multi-functional azlactone composition.
- Multi-functional azlactone compositions were prepared as follows:
- Poly-VDM Poly-Vinyldimethyl Azlactone
- Oligomeric-VDM (Oligo-VDM) was prepared as described in Example 1 of U.S. Pat. No. 5,081,197.
- Tris[ [ (2-[N-2-(4,4-dimethyl-2-oxazoline-5-one-2- yl)ethyl-N-isopropyl] - 2 - amino]ethyl]amine (Tris-VDM-T) was prepared in two steps. 1. Tris(N-isopropyl - 2 - aminoethyl)amine was prepared from a mixture of tris(2- aminoethyl)amine (W. R. Grace and Co., Lexington, MA) (50g), acetone (100 ml), ethanol 5 (25 ml) and platinum oxide (Aldrich, Milwaukee,
- Bis(N' ,N"-isopropyl-2-aminoethyl)amine was 5 prepared from bis(2-aminoethyl)amine and acetone as described in (C)(1) above.
- Tris-VDM-B was prepared by reaction of bis(N,N"- isopropy1-2-aminoethyl)amine and 3 molar equivalents of VDM (SNPE, Princeton, NJ) as 0 described in (C)(2) above.
- Example 3 Forming an azlactone-functional surface on a PVA hydrogel disc
- Multi-functional azlactone compositions were diluted in an 5 acetone solution to about five percent solids.
- Samples of PVA discs prepared and completely dried according to Example 12 were spread evenly in a glass petri dish. The discs were soaked in the multi ⁇ functional azlactone solution for 15 minutes, with gentle swirling of the solution in the petri dish to assure uniform coating of the PVA 0 discs. Then, excess solution was decanted and the discs were spread evenly in a single layer.
- the petri dish was placed in a locking plastic bag containing a small amount of dessicant (DrieriteTM) . Then, the azlactone coated PVA disc was cured at 100°C for 1 hour.
- DrieriteTM dessicant
- the azlactone-modified PVA discs were washed in three successive acetone 5 soaks for about 1 hour each.
- the azlactone-modified PVA discs were air ⁇ dried at room temperature (25°C) in a vacuum chamber or nitrogen purged glove bag.
- the dried azlactone modified PVA discs were stored in a small glass sample vial, inside a foil-laminate heat ⁇ ealed bag containing desiccant (DrieriteTM).
- Unhydrated azlactone modified PVA discs prepared according to Example 3 above were added to a concentrated solution of Bovine Serum Albumin ("BSA”) (Fraction V commercially available from Sigma Chemical of St. Louis, Missouri) at room temperature. After 45 minutes, the disca were removed from the protein solution and washed well in a phosphate buffered saline solution. The protein-modified PVA discs were hydrated overnight at 4°C in a phosphate buffered saline solution. Another set of unhydrated azlactone modified PVA discs prepared according to Example 3 above were reacted with Protein A (also from Sigma Chemical) according to the same techniques and conditions.
- BSA Bovine Serum Albumin
- Polybutylene (Shell 8510, Shell Chemical Company, Houston, Texas) and Polypropylene (Exxon 3505, Exxon Chemical Company, Houston, Texas) were dry blended in an 80:20 ratio with a 1% by weight of Irganox 1010 antioxidant (commercially available from Ciba Geigy Corporation of Hawthorn, New York) and fed to an extruder capable of melting the resins and delivering the molten resin as described in van Wente et al., "Manufacture of Superfine Organic Fibers", Naval Research Laboratory Report #4364, May 25, 1954 and in van Wente, "Superfine
- Thermoplastic Fibers " Industrial Engineering Chemistry. 48, 1342-1346, (1956) at a rate of 90-180 gr/cm die width/hr.
- the die had an orifice diameter of 0.033 cm (0.013 inch), an L/D ratio of 40:1 and there were 22.44 orifices per linear cm of die (57 orifices per linear inch of die).
- the molten polymer was extruded into a high velocity air stream created by two air knives with a u.025 cm (0.010 inch) air gap held at 1137 Torr (22 lbs/in 2 ) and 240°C.
- the attenuated fibers were collected on a rotating drum held 33 cm (13 inches) from the extruder.
- the resulting web had a basis weight of 45 g/m 2 , a thickness of 0.38 mm and average fiber diameters of 5 to 8 micrometers.
- the resulting web was washed in a 95% ethanol solution.
- Fiber diameter, basis weight and porosity can be controlled by controlling polymer feed rate, air flow rate and drum speed on the collector. Variations in the polymer blend composition or the base polymers used can also be made and processed in a similar manner.
- the web edges were cut after saturating the web in ethanol by placing the web in glass petri dish containing 95% ethanol and pressing out the air with rubber roller in order to wet the web.
- the web was transferred to a glass petri dish containing deionized water. Again the web was pressed with a rubber roller to assure wetting of the surface.
- Handling the web with long metal forceps the web was dipped into liquid nitrogen until frozen. The frozen web was removed and immediately cut with die punch to the desired shape. The web was refrozen between cuts if multiple cuts were necessary.
- a film of p(VTFA/VAc) having a composition of Example 1 was prepared using the spin casting method of Example 1.
- the sheet had a thickness of 0.05 to 0.10 mm less than the central optical element thickness ultimately desired to allow for a swell factor of 1.5 -1.6X p(VTFA/VAc) thickness when the film was to be solvolyzed and hydrated.
- the film was removed from the spin casting drum, and the p(VTFA/VAc) film was flattened on to a polyester release liner placed on glass. Using a knife coater, a thin coating of p(VTFA/VAc) (5%-15% solids) ⁇ solution dissolved in methyl ethyl ketone was spread on the spuncast p(VTFA/ Ac) film.
- Blown microfiber web prepared according to Example 5 was cut into sheets 7.3 cm X 21.6 cm (2 7/8 inches x 8 1/2 inches) and then cut again to form inner diameter holes of 4 mm diameter or rings having an 8 mm outer diameter with a 4 mm inner diameter. Then the cut blown microfiber web was positioned on the p(VTFA/VAc) film. The webs were held in position by sandwiching the composite of film and web between two glass .plates while the coating of p(VTFA/VAc) dried. After sufficient time for the adhesive coating to dry completely, the glass plate was removed. Then, the composite film was solvolyzed and hydrated using the conditions of Example 1. Then discs of the desired size were cut from the film after hydration.
- Example 7 Preparation of Corneal Prosthesis by Spin Casting Method
- a film of p(VTFA/VAc) of the composition of Example 1 was prepared using the spin caster drum of Example 1.
- the sheet had a thickness of 0.05 to 0.10 mm less than the central optical element thickness ultimately desired to allow for a swell factor of 1.5 -1.6X p(VTFA/VAc) thickness when the film was to be solvolyzed and hydrated.
- the film remained in the spin casting drum.
- the blown microfiber web prepared according to Example 5 was cut to fit in the spin ca ⁇ ting drum (7.3 cm X 21.6 cm) and inner diameter holes of 4 mm diameter were punched out. The web was positioned inside the spin casting drum next to p(VTFA/VAc) film.
- Example 12 While the drum was rotating, a small amount (2- 3 ml) of acetone was injected to wet the web and to aid in flattening the web against the drum. Nitrogen flow from the tube described in Example 12 was increased to hasten evaporation of the acetone. The email amount of the acetone dissolved the surface of the p(VTFA/VAc) film, allowing the web fibers to become embedded into the film. The acetone had to be evaporated quickly to prevent the total saturation of the web and the complete dissolution of the film, which would have otherwise resulted in the web having occluded pores. Then, the spin casting drum was spun at 3450 rpm for 30-60 mins. The drum was not covered during the spinning. Then, the composite film was solvolyzed and hydrated according to the procedures of Example 1. After hydration, the corneal prosthesis discs were cut from the composite film/web to the desired size.
- Example 8 Cyanoacrylate adhesion of web skirt to azlactone-functional hvdrooel optical element
- BSA modified PVA discs prepared according to Example 4 and blown microfiber web prepared according to Example 5 and punched to form rings according to Examples 6 and 7 were gathered for assembly into a corneal prosthesis.
- the BSA modified hydrated PVA disc was placed on a polyester relea ⁇ e liner, and cyanoacrylate (CA-4 commercially available from Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company of St. Paul, Minnesota) was brushed on to one side of the web ring.
- CA-4 commercially available from Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company of St. Paul, Minnesota
- the web ring surface having cyanoacrylate adhesive was positioned onto the BSA modified PVA disc, and a second polyester release liner was placed over the prosthesis assembly with hand pressure applied for 1-2 seconds. Then, the assembly was gently peeled from the release liners and placed in distilled water to prevent curling of the prosthesis assembly. The cyanoacrylate adhesive was allowed to cure undisturbed.
- Example 9 Use of azlactone-functional hydrogels to couple biologically active material
- Oligo-VDM 50% solids in methylethyl ketone (MEK) was coated onto p(VA/VAc) film (97.6:2.4 mole%) prepared according to Example 12 and heated for 1 hour at either 50°C, 100°C, or 150°C.
- a control sample was held at room temperature for the same period of time.
- the samples were analyzed by XPS (ESCA) using an Hewlett Packard 5950B ESCA instrument, using a monochromatic x-ray source, Al K- ⁇ radiation and a beam of 800 watts.
- Table 1 shows the distribution of carbon species as measured by XPS (ESCA) .
- p(VA/VAc) (97.6:2.4 mole%) films prepared according to Example 12 were coated with either poly-VDM or Oligo-VDM (30-50% in MEK), cured at 100°C for 1 hour and washed with acetone to remove unbound resin. These samples were tested for coupling of Protein A according to procedures described in U.S. Pat. No. 5,200,471. The results are shown in Table 2, where RA means radioactivity.
- Example 10 Use of biologically active hydrogels to enhance cell growth
- the discs were reacted with either fibronectin, laminin or type IV collagen in aqueous solution and, after washing, seeded with rabbit corneal epithelial cells which were then monitored for attachment and growth.
- the results showed that the cell growth on the VDM treated surfaces was improved relative to control surfaces.
- fibronectin with both Oligo-VDM and Poly-VDM cell growth numbered over 3000 per disc consistently over 10 days.
- cell growth rose from about 2000 cells per disc to about 4500 cells per disc at 10 days for both Oligo- VDM and Poly-VDM.
- Type IV collagen for the first 10 day ⁇ , cell growth numbered over 2000 cells per disc for Poly-VDM and rose from about 3000 cells per disc at 2 days to about 6000 cells per disc at 10 days for Oligo-VDM. By comparison, cell growth for controls of each of the three cell types declined to less than 1000 cells per disc after two days.
- Comparative Example 11 Inability to use carboxylate-functional hvdrooels to couple biologically active material
- Poly(vinyltrifluoroacetate-co-maleic anhydride (p(VTFA/MA) ) 99.9:0.1% (w/w) was prepared as follows: Methyltrifluoroacetate (Aldrich Chemical Co., 181.5g), vinyltrifluoroacetate (60 g) and maleic anhydride (Aldrich Chemical Co., 0.06g) were combined in a 500 ml roundbottom three-necked flask. The flask was fitted with a nitrogen bubbler and a dry ice/acetone condenser. Nitrogen was bubbled through the solution for 3 minutes and 3 drops Darocure 1173 initiator (E. M. Merck) were added.
- the reaction was stirred using a magnetic stirbar and.cooled in an ice bath. Polymerization was initiated by irradiating the reaction using a sun lamp (275 Watt) held approximately 5-10 cm from the reaction flask. After 5 hours, the reaction was stopped and the product was isolated by removing the solvent and residual monomer at___reduced pressure. The product was purified by dissolution in acetone and precipitation in heptane to yield p(VTFA/MA) (34.6g) having an intrinsic viscosity of 1.32.
- each of the p(VTFA/MA) films was dissolved in acetone to make a 10% solids solution and cast into film form under a stream of dry N : .
- the films were solvolyzed by soaking in 10% NH 4 OH/MeOH for 2 hours followed by soaking in MeOH for 2 hours and hydration in H : 0.
- the properties of the resulting hydrogels films are listed in Table 3 below.
- Cell growth on these samples increased from about 3000 cells after three days to a range of 6000 to 12,000 after five days for polymer compositions with three different MA mole percents: 0.07; 0.14; and 0.43. But cells died after five days to less than 3000 cells after seven days and less than about 2000 cells after 10 days. Further, subjective evaluation determined that the cells on the p(VA/MA) surface tended to "round up" and were not as adherent to the polymer surface as a surface employing azlactone functionality to couple biologically active material for enhancing cell growth.
- Example 12 Use of azlactone-functional materials on a cellulose substrate
- the samples were then analyzed by Diffuse Reflectance Infra-red Fourier Transfer (DRIFT) spectroscopy (using a Perkin Elmer Model 1750 spectrophotometer) using as the background spectra a sample of unmodified Whatman #4 paper (i.e., this results in a difference spectra between the test sample and the unmodified paper).
- DRIFT Diffuse Reflectance Infra-red Fourier Transfer
- the Poly- VDM treated samples showed a weak 1820 cm' 1 peak for all heated samples. (The 1820 cm' 1 peak is characteristic of the azlactone moiety.)
- the Oligo-VDM treated (samples Bl to B4) and the Tris-VDM-T (samples Cl to C4) samples showed trace absorption of 1820 cm '1 . In samples Dl to D4 the azlactone absorption could not be detected by this method.
- Whatman #4 filter paper was coated with Poly-VDM by soaking in a 33% solids solution for 15 minutes, draining excess solution, heating for 1 hour at 100°C, washing extensively with MEK, and air drying under dry N 2 . Samples were then reacted in aqueous solution at pH 9.0, 1.5M in K j S0 4 containing either 0.1M Cl(CH 2 ) 3 NH 2 HC1 or CH 3 CH 2 SCH 2 CH,NH 2 HC1 (reacted at room temperature for 2 hours).
- 2-allyloxy-4,4'-dimethoxy-2-hydroxy benzophenone (2- allyloxy-BP) , and 3-ally1-2,2'-dihydroxy-4,4'-dimethoxy benzophenone (3-allyl-BP) are prepared according to the following process.
- 2,2'-dihydroxy-4,4'-dimethoxy benzophenone is added 39 grams allylbromide, 165 grams of potassium carbonate and 400 ml of acetone.
- the mixture was refluxed for three hours, cooled to room temperature and the resulting salt was filtered out from the solution.
- the filtrate was concentrated to a re ⁇ idual oil, water and methylene chloride were added, and the organic layer was extracted.
- the extract was washed several additional times with water.
- the methylene chloride was dried with magnesium sulfate and the solvent was evaporated under vacuum to produce about 94 grams of brown-colored oil comprising 2- allyloxy-BP.
- the 3-allyl-BP was synthesized by placing 10 grams of the brown-colored oil in a round bottom flask. The flask was placed in an oil bath at 240°C. After 30 minute ⁇ of heating with stirring, the material is cooled to room temperature and 20 ml of methanol was added. As the solution cooled, a yellow solid precipitated. Recrystallization twice from methanol produced 2.5 grams of 3-allyl-BP having a melting point of about 70-71°C.
- Poly(VTFA/3-allyl-BP) was then dissolved in acetone (30 weight percent) and then was blended with 30 weight percent solids of p(VFTA/VAc) in acetone solution prepared according to Example 8 of Ofstead '649 in blend ratios ranging from 50:50 to 90:10 (p(VTFA/VAc) :p(VTFA/3-allyl-BP) ) .
- the solution was well mixed and cast on a glass plate.
- water uptake in percent ranged from 59.2% for the 50:50 blend to 63.1% for the 90:10 blend.
- an unblended p(VA/VAc) film had a water uptake of 68.2%.
- VTFA prepared according to Example 1 of PCT Publication WO 92/07899
- 3-allyl-BP prepared according to Example 13 above
- MA maleic anhydride
- the reaction ve ⁇ sel was heated at 40°C for 12 hours and then at 60°C for 3 hours to yield poly(VTFA/3-allyl-BP/MA) .
- the yield was 98.3%.
- the reaction vessel charged with twice the amount of 3- allyl-BP reduced the yield to 48.4%.
- the resulting copolymer was dissolved in acetone (30% by weight of solids) and prepared into a film in the same manner as described for blended compositions of Example 14 above. After solvolysis and hydration, the water uptake was 57.2% for the copolymer prepared from 0.25 weight percent of 3-allyl-BP and 78.5% for the copolymer prepared from 0.50 weight percent of 3-allyl-BP.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Transplantation (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Dermatology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Ophthalmology & Optometry (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Dispersion Chemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Materials For Medical Uses (AREA)
- Addition Polymer Or Copolymer, Post-Treatments, Or Chemical Modifications (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP6502338A JPH07508196A (en) | 1992-06-24 | 1993-05-13 | Azlactone functional base material, prosthetic cornea, and its production and utilization |
| DE69316751T DE69316751T2 (en) | 1992-06-24 | 1993-05-13 | AZLAKTON FUNCTIONAL SUBSTRATES, CORNEAL PROSTHESES AND THEIR USE |
| EP93913870A EP0647143B1 (en) | 1992-06-24 | 1993-05-13 | Azlactone-functional substrates, corneal prostheses, and manufacture and use thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US07/903,367 US5292514A (en) | 1992-06-24 | 1992-06-24 | Azlactone-functional substrates, corneal prostheses, and manufacture and use thereof |
| US07/903,367 | 1992-06-24 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO1994000165A2 true WO1994000165A2 (en) | 1994-01-06 |
| WO1994000165A3 WO1994000165A3 (en) | 1994-02-17 |
Family
ID=25417387
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US1993/004554 WO1994000165A2 (en) | 1992-06-24 | 1993-05-13 | Azlactone-functional substrates, corneal prostheses, and manufacture and use thereof |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US5292514A (en) |
| EP (1) | EP0647143B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPH07508196A (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2136728A1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE69316751T2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO1994000165A2 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1998028026A1 (en) * | 1996-12-23 | 1998-07-02 | Novartis Ag | Reactive coatings |
| WO2000045174A1 (en) * | 1999-02-01 | 2000-08-03 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Whole cell selection utilizing azlactone-functional supports |
| CN104830135A (en) * | 2015-05-04 | 2015-08-12 | 中国科学院长春应用化学研究所 | Antibacterial coating and preparation method thereof |
Families Citing this family (91)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5344701A (en) * | 1992-06-09 | 1994-09-06 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Porous supports having azlactone-functional surfaces |
| US6197056B1 (en) * | 1992-07-15 | 2001-03-06 | Ras Holding Corp. | Segmented scleral band for treatment of presbyopia and other eye disorders |
| US5709854A (en) * | 1993-04-30 | 1998-01-20 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Tissue formation by injecting a cell-polymeric solution that gels in vivo |
| GB9310241D0 (en) * | 1993-05-18 | 1993-06-30 | Unilever Plc | Cosmetic treatment of substrates |
| US5408002A (en) * | 1993-09-09 | 1995-04-18 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Azlactone-functional polymer blends, articles produced therefrom and methods for preparing both |
| US5420197A (en) * | 1994-01-13 | 1995-05-30 | Hydromer, Inc. | Gels formed by the interaction of polyvinylpyrrolidone with chitosan derivatives |
| US5476665A (en) * | 1994-04-13 | 1995-12-19 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Azlactone functional particles incorporated in a membrane formed by solvent phase inversion |
| US5561097A (en) * | 1994-04-28 | 1996-10-01 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Method of controlling density of ligand coupled onto supports and products produced therefrom |
| US5510421A (en) * | 1994-05-26 | 1996-04-23 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Azlactone-functional membranes and methods of preparing and using same |
| US5840106A (en) * | 1995-11-13 | 1998-11-24 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Water-based pigmented inks |
| US5714632A (en) * | 1995-11-13 | 1998-02-03 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Azlactone-based surfactants |
| JP4330268B2 (en) * | 1997-09-03 | 2009-09-16 | ザ リージェンツ オブ ザ ユニバーシティ オブ カリフォルニア | Novel biomimetic hydrogel materials |
| JP4111546B2 (en) * | 1997-12-15 | 2008-07-02 | ウルトラデント プロダクツ インコーポレイテッド | Polymerizable isolation barrier and method of forming and using such a barrier |
| ATE514729T1 (en) * | 1999-02-01 | 2011-07-15 | Eidgenoess Tech Hochschule | BIOMATERIALS ADDED BY NUCLEOPHILIC REACTION ON CONJUGATE UNSATURATED GROUPS |
| US6958212B1 (en) * | 1999-02-01 | 2005-10-25 | Eidgenossische Technische Hochschule Zurich | Conjugate addition reactions for the controlled delivery of pharmaceutically active compounds |
| EP1173790A2 (en) * | 1999-03-01 | 2002-01-23 | Boston Innovative Optics, Inc. | System and method for increasing the depth of focus of the human eye |
| US6630243B2 (en) * | 1999-05-20 | 2003-10-07 | Bausch & Lomb Incorporated | Surface treatment of silicone hydrogel contact lenses comprising hydrophilic polymer chains attached to an intermediate carbon coating |
| US6440571B1 (en) * | 1999-05-20 | 2002-08-27 | Bausch & Lomb Incorporated | Surface treatment of silicone medical devices with reactive hydrophilic polymers |
| AUPQ197799A0 (en) | 1999-08-02 | 1999-08-26 | Commonwealth Scientific And Industrial Research Organisation | Hydrophilic biomedical compositions |
| GB0002626D0 (en) | 2000-02-05 | 2000-03-29 | Eastman Kodak Co | Nonionic oligomeric surfactants and their use as dispersants and stabilisers |
| US7291673B2 (en) * | 2000-06-02 | 2007-11-06 | Eidgenossiche Technische Hochschule Zurich | Conjugate addition reactions for the controlled delivery of pharmaceutically active compounds |
| US6787635B2 (en) * | 2001-04-05 | 2004-09-07 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Solid phase synthesis supports and methods |
| US7147661B2 (en) * | 2001-12-20 | 2006-12-12 | Boston Scientific Santa Rosa Corp. | Radially expandable stent |
| US8282912B2 (en) * | 2002-03-22 | 2012-10-09 | Kuros Biosurgery, AG | Compositions for tissue augmentation |
| MXPA05002669A (en) * | 2002-09-13 | 2005-08-19 | Ocular Sciences Inc | Devices and methods for improving vision. |
| US7628810B2 (en) * | 2003-05-28 | 2009-12-08 | Acufocus, Inc. | Mask configured to maintain nutrient transport without producing visible diffraction patterns |
| US20050046794A1 (en) * | 2003-06-17 | 2005-03-03 | Silvestrini Thomas A. | Method and apparatus for aligning a mask with the visual axis of an eye |
| CN1318463C (en) * | 2003-09-24 | 2007-05-30 | 天津工业大学 | Environment responding aquogel copolymer and its prepn |
| CA2558573A1 (en) * | 2004-03-11 | 2005-09-22 | Trivascular, Inc. | Modular endovascular graft |
| WO2005116729A2 (en) | 2004-05-20 | 2005-12-08 | Coopervision, Inc., | Corneal onlays and wavefront aberration correction to enhance vision |
| EP4023240A1 (en) * | 2004-07-06 | 2022-07-06 | 3D Matrix, Inc. | Purified amphiphilic peptide compositions and uses thereof |
| CN101018513B (en) * | 2004-08-13 | 2011-11-16 | 渥太华健康研究所 | Vision enhancing ophthalmic devices and related methods and compositions |
| US7556858B2 (en) * | 2004-09-30 | 2009-07-07 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Substrate with attached dendrimers |
| US9999497B2 (en) * | 2005-01-31 | 2018-06-19 | Yichieh Shiuey | Corneal implants and methods and systems for placement |
| US7976577B2 (en) | 2005-04-14 | 2011-07-12 | Acufocus, Inc. | Corneal optic formed of degradation resistant polymer |
| WO2007092550A2 (en) * | 2006-02-08 | 2007-08-16 | Coopervision Inc. | Corneal onlays and related methods |
| US7883520B2 (en) * | 2006-04-10 | 2011-02-08 | Forsight Labs, Llc | Corneal epithelial pocket formation systems, components and methods |
| US8911496B2 (en) | 2006-07-11 | 2014-12-16 | Refocus Group, Inc. | Scleral prosthesis for treating presbyopia and other eye disorders and related devices and methods |
| WO2008008366A2 (en) | 2006-07-11 | 2008-01-17 | Refocus Group, Inc. | Scleral prosthesis for treating presbyopia and other eye disorders and related devices and methods |
| CN100512889C (en) * | 2006-12-08 | 2009-07-15 | 华南理工大学 | Process of making cornea histoengineering support in bionic structure |
| US20080255663A1 (en) * | 2007-04-13 | 2008-10-16 | Akpek Esen K | Artificial Cornea and Method of Making Same |
| MX2009011005A (en) | 2007-04-13 | 2009-11-02 | Kuros Biosurgery Ag | Polymeric tissue sealant. |
| CA2706135C (en) * | 2007-08-02 | 2014-10-21 | Refocus Group, Inc. | Scleral prosthesis having crossbars for treating presbyopia and other eye disorders |
| US8480638B2 (en) * | 2007-10-04 | 2013-07-09 | Aciont, Inc. | Intraocular iontophoretic device and associated methods |
| US9943401B2 (en) | 2008-04-04 | 2018-04-17 | Eugene de Juan, Jr. | Therapeutic device for pain management and vision |
| WO2009158071A2 (en) * | 2008-06-26 | 2009-12-30 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Solid support with a grafted chain |
| EP3238749B1 (en) | 2008-10-06 | 2018-09-19 | 3-D Matrix Ltd. | Tissue plug |
| US20100087920A1 (en) * | 2008-10-07 | 2010-04-08 | Forsight Labs, Llc | Corneal Onlay Lenses and Related Methods for Improving Vision of Presbyopic Patients |
| MX2011005311A (en) * | 2008-11-19 | 2011-07-29 | Refocus Group Inc | Artificial intraocular lens, altered natural crystalline lens, or refilled natural crystalline lens capsule with one or more scleral prostheses for improved performance. |
| US20100198348A1 (en) * | 2009-01-30 | 2010-08-05 | Hiles Michael C | Biomaterials with modified optical character and methods for preparing and using same |
| US10004593B2 (en) | 2009-08-13 | 2018-06-26 | Acufocus, Inc. | Intraocular lens with elastic mask |
| AU2010282311B2 (en) | 2009-08-13 | 2015-08-13 | Acufocus, Inc. | Masked intraocular implants and lenses |
| BR112012008079A2 (en) | 2009-08-13 | 2016-03-01 | Acufocus Inc | corneal graft with nutrient transport structures |
| NO2490635T3 (en) | 2009-10-23 | 2018-02-03 | ||
| EP2490620A4 (en) | 2009-10-23 | 2017-03-22 | Forsight Labs, Llc | Conformable therapeutic shield for vision and pain |
| EP2496987B1 (en) * | 2009-11-04 | 2020-04-29 | Alcon Inc. | A silicone hydrogel lens with a grafted hydrophilic coating |
| CN107033368A (en) | 2009-11-09 | 2017-08-11 | 聚光灯技术合伙有限责任公司 | fragmentation hydrogel |
| CN106913902A (en) | 2009-11-09 | 2017-07-04 | 聚光灯技术合伙有限责任公司 | Polysaccharide based aquagel |
| USD656526S1 (en) | 2009-11-10 | 2012-03-27 | Acufocus, Inc. | Ocular mask |
| US20120245683A1 (en) * | 2009-12-04 | 2012-09-27 | Acufocus, Inc. | Corneal implant for refractive correction |
| TWI483996B (en) * | 2009-12-08 | 2015-05-11 | Novartis Ag | A silicone hydrogel lens with a covalently attached coating |
| US8480227B2 (en) | 2010-07-30 | 2013-07-09 | Novartis Ag | Silicone hydrogel lenses with water-rich surfaces |
| EP3730093B1 (en) | 2010-09-30 | 2022-12-21 | KeraMed, Inc. | Reversibly deformable artificial cornea |
| US12044905B2 (en) | 2011-04-28 | 2024-07-23 | Journey1 Inc | Contact lenses for refractive correction |
| WO2013055746A1 (en) | 2011-10-12 | 2013-04-18 | Novartis Ag | Method for making uv-absorbing ophthalmic lenses by coating |
| WO2013082545A1 (en) | 2011-12-02 | 2013-06-06 | Acufocus, Inc. | Ocular mask having selective spectral transmission |
| EP3466964A1 (en) | 2012-07-06 | 2019-04-10 | 3-D Matrix Ltd. | Fill-finish process for peptide solutions |
| US9974646B2 (en) | 2012-09-05 | 2018-05-22 | University Of Miami | Keratoprosthesis, and system and method of corneal repair using same |
| EP2932314B1 (en) | 2012-12-17 | 2017-02-01 | Novartis AG | Method for making improved uv-absorbing ophthalmic lenses |
| US9204962B2 (en) | 2013-03-13 | 2015-12-08 | Acufocus, Inc. | In situ adjustable optical mask |
| US9427922B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2016-08-30 | Acufocus, Inc. | Process for manufacturing an intraocular lens with an embedded mask |
| EP3014345A2 (en) | 2013-06-26 | 2016-05-04 | Nexisvision, Inc. | Contact lenses for refractive correction |
| SG11201603699SA (en) | 2013-12-17 | 2016-07-28 | Novartis Ag | A silicone hydrogel lens with a crosslinked hydrophilic coating |
| EP3116551B1 (en) | 2014-03-10 | 2022-09-07 | 3-D Matrix Ltd. | Sterilization of peptide compositions |
| WO2015138514A1 (en) | 2014-03-10 | 2015-09-17 | 3-D Matrix, Ltd. | Self-assembling peptide compositions |
| JP6545727B2 (en) | 2014-03-10 | 2019-07-17 | 株式会社スリー・ディー・マトリックス | Spontaneous organization peptides for treating lung air vesicles |
| HUE046948T2 (en) | 2014-08-26 | 2020-03-30 | Novartis Ag | Method for applying stable coating on silicone hydrogel contact lenses |
| US9943403B2 (en) | 2014-11-19 | 2018-04-17 | Acufocus, Inc. | Fracturable mask for treating presbyopia |
| USD844145S1 (en) * | 2014-12-22 | 2019-03-26 | Henry Ford Health System | Vision assessment chart |
| US10687935B2 (en) | 2015-10-05 | 2020-06-23 | Acufocus, Inc. | Methods of molding intraocular lenses |
| CA3005891C (en) | 2015-11-24 | 2023-12-12 | Acufocus, Inc. | Toric small aperture intraocular lens with extended depth of focus |
| MY184638A (en) | 2015-12-15 | 2021-04-13 | Alcon Inc | Method for applying stable coating on silicone hydrogel contact lenses |
| WO2017120092A1 (en) | 2016-01-06 | 2017-07-13 | 3-D Matrix, Ltd. | Combination compositions |
| US20170342211A1 (en) | 2016-05-31 | 2017-11-30 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Azlactone functionalized substrates for conjugation of biomolecules |
| CN117492231A (en) | 2017-12-13 | 2024-02-02 | 爱尔康公司 | Zhou Pao and month polishing gradient contact lens |
| CN117085140A (en) | 2017-12-15 | 2023-11-21 | 立美基股份有限公司 | Surfactant peptide nanostructures and their use in drug delivery |
| EP3790508A4 (en) | 2018-05-09 | 2022-02-09 | AcuFocus, Inc. | Intraocular implant with removable optic |
| DE102018129478B4 (en) * | 2018-11-22 | 2021-05-27 | Carl Zeiss Meditec Ag | Ophthalmic implant with an active substance delivery system and method for producing such an ophthalmic implant |
| USD948724S1 (en) | 2019-04-16 | 2022-04-12 | Henry Ford Health System | Vision assessment chart |
| US11950997B2 (en) * | 2019-05-20 | 2024-04-09 | The Trustees Of The Stevens Institute Of Technology | Artificial cornea with double-side microtextured pHEMA hydrogel |
| JP7472470B2 (en) * | 2019-11-11 | 2024-04-23 | artience株式会社 | Ultraviolet absorbing monomer, ultraviolet absorbing polymer, molding resin composition, and molded article |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0105665A1 (en) * | 1982-09-27 | 1984-04-18 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Azlactone-functional compounds and curable compositions containing same |
| EP0333344A2 (en) * | 1988-03-02 | 1989-09-20 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Corneal implants and manufacture and use thereof |
| EP0392735A2 (en) * | 1989-04-10 | 1990-10-17 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Polymeric supports |
| US5081197A (en) * | 1990-10-23 | 1992-01-14 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Oligo(2-alkenyl azlactones) |
| WO1992007879A1 (en) * | 1990-11-05 | 1992-05-14 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Biological active material covalently immobilized on to azlactone-functional polymeric supports and method for preparing it |
Family Cites Families (32)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2714721A (en) * | 1953-01-23 | 1955-08-09 | Jr William Stone | Artificial corneal implants |
| CA1073648A (en) * | 1976-08-02 | 1980-03-18 | Edward R. Hauser | Web of blended microfibers and crimped bulking fibers |
| US4304705A (en) * | 1980-01-02 | 1981-12-08 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Radiation-curable polymers containing pendant unsaturated peptide groups derived from azlactone polymers |
| US4914223A (en) * | 1981-10-29 | 1990-04-03 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Acrylamidoacylated oligomers |
| SE8200751L (en) * | 1982-02-09 | 1983-08-10 | Olle Larm | PROCEDURE FOR COVALENT COUPLING FOR MANUFACTURE OF CONJUGATE AND REQUIRED PRODUCTS |
| US4612012A (en) * | 1982-07-28 | 1986-09-16 | White Thomas C | Corneal implant |
| US4451619A (en) * | 1982-09-30 | 1984-05-29 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Method of hydrophilizing or hydrophobizing polymers |
| US5059654A (en) * | 1983-02-14 | 1991-10-22 | Cuno Inc. | Affinity matrices of modified polysaccharide supports |
| US4673539A (en) * | 1983-06-03 | 1987-06-16 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Process for thermoformed articles |
| US4528325A (en) * | 1983-06-03 | 1985-07-09 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Co. | Copolymers of poly(vinyl trifluoroacetate) or poly(vinyl alcohol) |
| US4618649A (en) * | 1983-06-03 | 1986-10-21 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Copolymers of poly(vinyl trifluoroacetate) or poly(vinyl alcohol) |
| IE56908B1 (en) * | 1983-09-08 | 1992-01-29 | Minnesota Mining & Mfg | Polymer blends with high water absorption |
| US4655770A (en) * | 1985-06-06 | 1987-04-07 | Ioptex, Inc. | Surface passivated intraocular lens |
| DE3521684A1 (en) * | 1985-06-18 | 1986-12-18 | Dr. Müller-Lierheim KG, Biologische Laboratorien, 8033 Planegg | METHOD FOR COATING POLYMERS |
| AU593010B2 (en) * | 1985-08-23 | 1990-02-01 | Washington Research Foundation | Polymeric intraocular lens material |
| JPS6283885A (en) * | 1985-10-08 | 1987-04-17 | Nitto Electric Ind Co Ltd | Immobilized enzyme membrane and production thereof |
| US4757014A (en) * | 1985-11-08 | 1988-07-12 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Immobilization of biologically active protein on a polymeric fibrous support |
| US4772283A (en) * | 1986-05-16 | 1988-09-20 | White Thomas C | Corneal implant |
| US4715858A (en) * | 1986-07-25 | 1987-12-29 | Lindstrom Richard L | Epicorneal lens |
| US4979959A (en) * | 1986-10-17 | 1990-12-25 | Bio-Metric Systems, Inc. | Biocompatible coating for solid surfaces |
| US4865601A (en) * | 1987-07-07 | 1989-09-12 | Caldwell Delmar R | Intraocular prostheses |
| US4910277A (en) * | 1988-02-09 | 1990-03-20 | Bambury Ronald E | Hydrophilic oxygen permeable polymers |
| FR2627078B1 (en) * | 1988-02-16 | 1994-03-18 | Allergan Inc | EYE DEVICE |
| US5032131A (en) * | 1988-03-02 | 1991-07-16 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Prosthesis holding device |
| US4852969A (en) * | 1988-03-17 | 1989-08-01 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Silyl 2-amidoacetate and silyl 3-amidopropionate compositions and optical fiber made therefrom |
| JP2561309B2 (en) * | 1988-03-28 | 1996-12-04 | テルモ株式会社 | Medical material and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP2855224B2 (en) * | 1988-07-22 | 1999-02-10 | バイオ―メトリック システムズ,アイエヌシー. | Preparation of polymer surface |
| CA2001720C (en) * | 1988-10-31 | 2001-10-02 | Randal A. Goffe | Membrane affinity apparatus and purification methods related thereto |
| US5013795A (en) * | 1989-04-10 | 1991-05-07 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Azlactone graft copolymers |
| US5064578A (en) * | 1989-04-21 | 1991-11-12 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Method for making a high wet-strength polyolefin blown microfiber web |
| US5149806A (en) * | 1990-03-28 | 1992-09-22 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Azlactone michael adducts |
| DE69120284T2 (en) * | 1990-10-30 | 1997-03-06 | Minnesota Mining & Mfg | OBJECTS WITH A HYDROPHILIC POLYMER SHELL AND METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF |
-
1992
- 1992-06-24 US US07/903,367 patent/US5292514A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1993
- 1993-05-13 JP JP6502338A patent/JPH07508196A/en active Pending
- 1993-05-13 WO PCT/US1993/004554 patent/WO1994000165A2/en active IP Right Grant
- 1993-05-13 EP EP93913870A patent/EP0647143B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1993-05-13 CA CA002136728A patent/CA2136728A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 1993-05-13 DE DE69316751T patent/DE69316751T2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0105665A1 (en) * | 1982-09-27 | 1984-04-18 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Azlactone-functional compounds and curable compositions containing same |
| EP0333344A2 (en) * | 1988-03-02 | 1989-09-20 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Corneal implants and manufacture and use thereof |
| EP0392735A2 (en) * | 1989-04-10 | 1990-10-17 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Polymeric supports |
| US5081197A (en) * | 1990-10-23 | 1992-01-14 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Oligo(2-alkenyl azlactones) |
| WO1992007879A1 (en) * | 1990-11-05 | 1992-05-14 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Biological active material covalently immobilized on to azlactone-functional polymeric supports and method for preparing it |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| US,E,RE33477 (S. LOSHAEK) 4 December 1990 * |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1998028026A1 (en) * | 1996-12-23 | 1998-07-02 | Novartis Ag | Reactive coatings |
| US6436481B1 (en) | 1996-12-23 | 2002-08-20 | Novartis Ag | Method of producing a reactive coating by after-glow plasma polymerization |
| WO2000045174A1 (en) * | 1999-02-01 | 2000-08-03 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Whole cell selection utilizing azlactone-functional supports |
| US6379952B1 (en) | 1999-02-01 | 2002-04-30 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Method for cell selection utilizing azlactone-functional supports |
| CN104830135A (en) * | 2015-05-04 | 2015-08-12 | 中国科学院长春应用化学研究所 | Antibacterial coating and preparation method thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0647143B1 (en) | 1998-01-28 |
| CA2136728A1 (en) | 1994-01-06 |
| WO1994000165A3 (en) | 1994-02-17 |
| US5292514A (en) | 1994-03-08 |
| JPH07508196A (en) | 1995-09-14 |
| DE69316751T2 (en) | 1998-09-10 |
| DE69316751D1 (en) | 1998-03-05 |
| EP0647143A1 (en) | 1995-04-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0647143B1 (en) | Azlactone-functional substrates, corneal prostheses, and manufacture and use thereof | |
| EP0333344B1 (en) | Corneal implants and manufacture and use thereof | |
| US5836313A (en) | Methods for making composite hydrogels for corneal prostheses | |
| US5433745A (en) | Corneal implants and methods for producing same | |
| EP0946220B1 (en) | Reactive coatings | |
| Tamada et al. | Fibroblast growth on polymer surfaces and biosynthesis of collagen | |
| US5401508A (en) | Hydrogel compositions and structures made from same | |
| EP0714417B1 (en) | Polymer surface coatings | |
| US20060147501A1 (en) | Collagen compositions and biomaterials | |
| JPH02191629A (en) | Graft peptide copolymer | |
| Latkany et al. | Plasma surface modification of artificial corneas for optimal epithelialization | |
| EP0585436A1 (en) | Immobilization of chemical species in crosslinked matrices | |
| WO2002096978A1 (en) | Crosslinked elastin and process for producing the same | |
| WO1994017851A1 (en) | Bilayer composite hydrogels for corneal prostheses | |
| Bots et al. | Small diameter blood vessel prostheses from blends of polyethylene oxide and polypropylene oxide | |
| Yang et al. | Preparation of poly (acrylic acid) modified polyurethane membrane for biomaterial by UV radiation without degassing | |
| EP3500313B1 (en) | Wound dressing comprising polymer fibers | |
| JP3626195B2 (en) | Azlactone functional membrane | |
| Hsiue et al. | Platelet adhesion and cellular interaction with poly (ethylene oxide) immobilized onto silicone rubber membrane surfaces | |
| EP0534014A1 (en) | Non-adhesive biocompatible surface | |
| JPH08266615A (en) | Cell nonadhesive/nonproliferation medical supplies | |
| Bots et al. | Small diameter blood vessel prostheses from polyethers | |
| JPH04129561A (en) | Wound covering material | |
| MXPA99005936A (en) | Reactive coatings | |
| JPS6023624B2 (en) | antithrombotic material |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AK | Designated states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): CA CZ JP |
|
| AL | Designated countries for regional patents |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK ES FR GB GR IE IT LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AK | Designated states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): CA CZ JP |
|
| AL | Designated countries for regional patents |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK ES FR GB GR IE IT LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| DFPE | Request for preliminary examination filed prior to expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed before 20040101) | ||
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | ||
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2136728 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 1993913870 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWP | Wipo information: published in national office |
Ref document number: 1993913870 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWG | Wipo information: grant in national office |
Ref document number: 1993913870 Country of ref document: EP |