KR100965719B1 - Method for renovating random access effectively in a mobile telecommunication system - Google Patents
Method for renovating random access effectively in a mobile telecommunication system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR100965719B1 KR100965719B1 KR1020030023788A KR20030023788A KR100965719B1 KR 100965719 B1 KR100965719 B1 KR 100965719B1 KR 1020030023788 A KR1020030023788 A KR 1020030023788A KR 20030023788 A KR20030023788 A KR 20030023788A KR 100965719 B1 KR100965719 B1 KR 100965719B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- mbms
- value
- base station
- duration value
- terminals
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B7/00—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field
- H04B7/24—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts
- H04B7/26—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field for communication between two or more posts at least one of which is mobile
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/06—Selective distribution of broadcast services, e.g. multimedia broadcast multicast service [MBMS]; Services to user groups; One-way selective calling services
Abstract
본 발명은 이동통신시스템에서 기지국 제어기가 단말기들에게 억세스 프리앰블을 전송할 구간을 제공하는 방법에 있어서, 미리 설정되어 있는 시간 단위로 기지국에 의해 사용이 허락되는 역방향 채널들의 수를 측정하는 과정과, 상기 시간 단위로 상기 단말기들에 의한 역방향 채널의 할당 요구 시도 횟수를 상기 측정한 역방향 채널들의 수로 결정하는 과정을 포함한다.
그룹 시그널링 메시지, 역방향 채널, 백-오프 윈도우, 무선 프레임, 전송구간 갱신
According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method in which a base station controller transmits an access preamble to terminals in a mobile communication system, the method comprising: measuring a number of reverse channels allowed by a base station on a predetermined time basis; And determining the number of attempts to allocate the reverse channel by the terminals on a time basis as the measured number of reverse channels.
Group signaling message, reverse channel, back-off window, radio frame, transmission section update
Description
도 1은 종래 이동통신시스템에서 MBMS를 제공하기 위한 네트워크 구조를 개략적으로 도시한 도면.1 is a diagram schematically illustrating a network structure for providing MBMS in a conventional mobile communication system.
도 2는 종래 임의의 MBMS가 이뤄지기 위해서 사용자와 네트워크 사이에 이루어져야 하는 동작들을 개괄적으로 도시한 도면.2 is a diagram schematically illustrating operations that must be performed between a user and a network in order for any conventional MBMS to be performed.
도 3은 도 2에서 교시되고 있는 절차 중 일부 절차에 대한 구체적인 시그널링을 도시한 도면.3 illustrates specific signaling for some of the procedures taught in FIG.
도 4는 종래 기술에 따른 다수의 사용자가 RACH의 사용을 시도하는 경우를 나타내는 도면.4 is a diagram illustrating a case where a plurality of users according to the prior art attempts to use a RACH.
도 5는 종래 기술에 따른 RACH의 동작을 나타내는 흐름도.5 is a flow chart showing operation of the RACH according to the prior art.
도 6은 본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 RACH의 동작을 보이고 있는 도면.6 is a view illustrating operation of a RACH according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 7은 본 발명의 실시 예에 따라 Pmbms가 지속적으로 갱신되는 경우 UE MAC에서의 RACH 동작을 수행되는 제어 흐름을 보이고 있는 도면.7 is a diagram illustrating a control flow of performing an RACH operation in a UE MAC when P mbms is continuously updated according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 8은 본 발명의 실시 예에 따라 UE가 Pmbms를 갱신하기 위한 제어 흐름을 보이고 있는 도면.8 is a diagram illustrating a control flow for a UE to update P mbms according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 9는 본 발명의 실시 예에 따라 UE가 RNC로부터의 MBMS 제어 메시지에 대응하여 그룹 응답 메시지를 전송하기 위한 제어 흐름을 보이고 있는 도면.9 is a diagram illustrating a control flow for a UE to transmit a group response message in response to an MBMS control message from an RNC according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 10은 본 발명의 실시 예에 따라 RNC가 Pmbms를 결정하고 갱신하기 위한 제어 흐름을 보이고 있는 도면.
10 illustrates a control flow for the RNC to determine and update P mbms according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명은 이동통신시스템에 관한 것으로서, 보다 상세하게는 다수의 단말기들이 소정의 역방향 메시지를 랜덤접근채널을 통하여 동시에 전송함으로 인해 발생되는 충돌을 방지하는 역방향 메시지의 전송 구간을 제공하는 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a mobile communication system, and more particularly, to a method of providing a reverse message transmission interval for preventing a collision caused by a plurality of terminals simultaneously transmit a predetermined reverse message through a random access channel. .
오늘날 통신산업의 발달로 인해 부호분할다중접속(CDMA: Code Division Multiple Access, 이하 "CDMA"라 칭하기로 한다) 이동통신시스템에서 제공하는 서비스는 음성 서비스뿐만이 아니라 패킷 데이터, 서킷 데이터 등과 같은 큰 용량의 데이터를 전송하는 멀티캐스팅 멀티미디어 통신으로 발전해 나가고 있다. 따라서, 상기 멀티캐스팅 멀티미디어 통신을 지원하기 위해 하나의 데이터 소스에서 다수의 이동단말들(User Equipment, 이하 "UE"라 칭함)로 서비스를 제공하는 방송/멀티캐스트 서비스(Broadcast/Multicast Service)가 제안되었다. 상기 방송/멀티캐스트 서비스는 메시지 위주의 서비스인 셀 방송 서비스(Cell Broadcast Service, 이하 "CBS 서비스"라 칭함)와 실시간 영상 및 음성, 정지 영상, 문자 등 멀티미디어 형태를 지원하는 멀티캐스트 멀티미디어 방송 서비스(Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service, 이하 "MBMS"라 칭함)로 구분할 수 있다.Today, due to the development of the telecommunications industry, the services provided by the code division multiple access (CDMA) mobile communication system are not only voice services but also large capacity such as packet data and circuit data. It is evolving into a multicasting multimedia communication that transmits data. Accordingly, in order to support the multicasting multimedia communication, a broadcast / multicast service which provides a service from a data source to a plurality of mobile terminals (hereinafter referred to as UE) is proposed. It became. The broadcast / multicast service is a cell broadcast service (hereinafter, referred to as a "CBS service"), a message-oriented service, and a multicast multimedia broadcast service supporting multimedia forms such as real-time video, voice, still image, and text ( Multimedia Broadcast / Multicast Service, hereinafter referred to as "MBMS".
통상적으로 MBMS란 무선 네트워크를 통하여 동일한 멀티미디어 데이터를 다수의 수신자들에게 전송하는 서비스를 통칭한다. 상기 MBMS는 한 Node B내에서 동시에 다량의 서비스가 전개될 가능성이 있다는 측면에서, 방송채널을 통해서 서비스된다. 즉, 다수의 UE들이 하나의 무선 채널을 공유하도록 함으로써 무선 자원을 절약할 수 있도록 한다.Typically, MBMS refers to a service for transmitting the same multimedia data to multiple receivers through a wireless network. The MBMS is serviced through a broadcast channel in that there is a possibility that a large number of services can be simultaneously deployed in one Node B. That is, by allowing a plurality of UEs to share one radio channel, it is possible to save radio resources.
도 1은 이동통신시스템에서 MBMS를 제공하기 위한 네트워크 구조를 개략적으로 도시한 도면이다.1 is a diagram schematically illustrating a network structure for providing an MBMS in a mobile communication system.
상기 도 1을 참조하면, 멀티캐스트/방송-서비스 센터(MB-SC: Multicast/Broadcast- Service Center, 이하 "MB-SC"라 칭하기로 한다)(110)는 MBMS 스트림(stream)을 제공하는 소스(source)이다. 상기 MB-SC(110)는 MBMS에 따른 MBMS 데이터 스트림을 스케줄링(scheduling)하여 전송 네트워크(transit N/W)(120)로 전달한다. 상기 전송 네트워크(120)는 상기 MB-SC(110)와 서비스 패킷 무선 서비스 지원 노드(SGSN: Serving GPRS Support Node, 이하 "SGSN"이라 칭하기로 한다)(130) 사이에 존재하는 네트워크(network)를 의미한다. 상기 전송 네트워크(120)는 상기 MB-SC(110)로부터 전달받은 MBMS 데이터 스트림을 상기 SGSN(130)으로 전달한다. 여기서, 상기 전송 네트워크(120)는 게이트웨이 패킷 무선 서비스 지원 노드(GGSN: Gateway GPRS Support Node, 이하 "GGSN"이라 칭하기로 한다)와 외부 네트워크 등으로 구성 가능하다. 임의의 시점에서 상기 MBMS 데이터를 수신하고자 하는 다수의 UE들, 일 예로 제1기지국(제1Node B), 즉 제1셀(cell 1)(160)에 속하는 UE 1(161), UE 2(162), UE 3(163)과, 제2기지국, 즉 제2셀(170)에 속하는 UE 4(171), UE 5(172)가 존재하고 있다고 가정하기로 한다. 상기 전송 네트워크(120)에서 MBMS 데이터 스트림을 전달받은 SGSN(130)은 MBMS를 제공받고자 하는 가입자들, 즉 UE들의 MBMS 관련 서비스를 제어하는 역할을 수행한다. 일 예로 UE들 각각의 MBMS 과금 관련 데이터를 관리하거나 MBMS 데이터를 특정 무선 네트워크 제어기(RNC: Radio Network Controller, 이하 "RNC"라 칭하기로 한다)(140)에게 선별적으로 전송하는 역할 등의 MBMS 관련 서비스를 제어한다. 상기와 같이 RNC에 대해 선별적인 전송을 수행하기 위해 상기 SGSN(130)은 특정 NMBMS를 제공할 RNC들의 명단을 알고 있어야 한다. 상기 도 1에서는 나타나고 있지 않으나 하나의 MBMS에 대해서 다수의 SGSN들과, 각 SGSN에 대해서 다수의 RNC들이 존재할 수 있다. Referring to FIG. 1, a multicast / broadcast-service center (MB-SC) hereinafter referred to as a "MB-SC" 110 is a source for providing an MBMS stream. (source). The MB-SC 110 schedules and transmits the MBMS data stream according to the MBMS to the
상기 RNC(140)는 상기 SGSN(130)로부터 전달되는 MBMS 데이터를 연결된 기지국들의 셀들에 대해 선별적으로 전송하는 기능을 제공한다. 즉, 상기 RNC(140)는 다수의 셀들을 제어하며, 자신이 관리하고 있는 셀들 중 특정 MBMS를 요구하는 UE가 존재하는 특정 셀로 MBMS 데이터를 전송한다. 이를 위해서 상기 RNC(140)는 특정 MBMS를 제공할 셀들의 명단을 알고 있어야만 한다. 또한 상기 RNC(140)는 상기 MBMS를 제공하기 위해 설정되는 무선 채널(radio channel)을 제어하고, 상기 SGSN(130)으로부터 전달받은 MBMS 데이터 스트림을 가지고 상기 MBMS에 관한 정보 를 관리한다. 이하 설명의 편의상 "기지국"과 "셀"을 동일한 개념으로 사용하기로 한다. 상기 기지국은 한 개의 셀만을 관리하거나 다수의 셀들을 관리할 수도 있음은 물론이다.The
상기 도 1에 도시하지는 않았지만 홈위치 등록기(HLR: Home Location Register)는 상기 SGSN(130)과 연결되어, MBMS 서비스를 위한 가입자 인증을 수행한다.Although not shown in FIG. 1, a Home Location Register (HLR) is connected to the SGSN 130 to perform subscriber authentication for an MBMS service.
상기 각 셀들(160, 170)은 특정 MBMS의 제공을 요청한 UE들과 하나의 무선 채널을 통해 연결하고, 상기 무선 채널을 통해 상기 UE들에게 MBMS 관련 데이터를 전송한다. 상기 UE들(161, 162, 163)은 상기 제1셀(160)과 하나의 무선 채널을 통해 연결되면, 상기 무선 채널을 통해 MBMS를 제공받을 수 있는 단말장치 또는 가입자를 의미한다. 상기 UE들(171, 172)은 상기 제2셀(170)과 하나의 무선 채널을 통해 연결되면, 상기 무선 채널을 통해 MBMS를 제공받을 수 있는 단말장치 또는 가입자를 의미한다.Each of the
상기 도 1에서 보여지고 있는 네트워크 구조에 있어 임의의 MBMS를 제공하는 과정을 고려하면 다음과 같다.Considering the process of providing an arbitrary MBMS in the network structure shown in FIG. 1 as follows.
임의의 MBMS를 제공하기 위해서는 먼저 상기 MBMS에 대한 기본 정보들이 UE들에게 전달되어야 하고, 상기 MBMS에 대한 기본 정보들을 수신한 UE들이 상기 임의의 MBMS를 제공받고자 할 경우 그 UE들 명단이 네트워크로 전달되어야 한다. 이렇게 네트워크에서 상기 임의의 MBMS를 제공받기를 원하는 UE들 명단을 수신하면, 상기 네트워크는 상기 UE들을 호출(paging)하여 상기 MBMS를 제공하기 위한 무선 베어러(Radio Bearer)를 설정해야 한다. 상기 UE들과 무선 베어러가 설정된 후, 상기 설정된 무선 베어러를 통해 상기 임의의 MBMS를 제공한다. 한편, 상기 MBMS가 종료되면 그 종료 사실이 모든 UE들에게 통보되어야만하고, 이에 따라 모든 UE들은 상기 MBMS를 위해 할당하였었던 모든 자원(resource)들을 해제(release)해야 정상적인 MBMS가 가능하다.In order to provide an arbitrary MBMS, basic information on the MBMS must first be delivered to UEs, and when the UEs receiving the basic information on the MBMS wish to receive the arbitrary MBMS, the list of UEs is delivered to the network. Should be. When receiving a list of UEs that want to receive the arbitrary MBMS in the network, the network should set up a radio bearer for providing the MBMS by paging the UEs. After the radio bearer is set up with the UEs, the random MBMS is provided through the set radio bearer. On the other hand, when the MBMS is terminated, it must be notified to all UEs, and thus, all UEs must release all resources allocated for the MBMS so that normal MBMS is possible.
도 2에서는 임의의 MBMS가 이뤄지기 위해서 사용자와 네트워크 사이에 이루어져야 하는 동작들을 개괄적으로 도시하고 있다. 상기 도 2에서 도시된 핵심 망(Core Network; 이하 'CN'이라 한다)은 SGSN(130), Transit N/W(120), MB-SC(110)를 모두 포괄한다.2 schematically illustrates operations that must be performed between a user and a network in order for an arbitrary MBMS to be performed. The core network (hereinafter referred to as 'CN') illustrated in FIG. 2 includes the SGSN 130, the Transit N /
상기 도 2를 참조하면, 예약 단계(SUBSCRIPTION STEP)(201)는 임의의 MBMS를 받고자 하는 UE를 서비스 제공자에게 등록하는 과정이다. 이때, 서비스 제공자와 UE는 과금이나 서비스 수신에 관련된 기본적인 정보를 교환하게 된다. 고지 단계(ANNOUNCEMENT STEP)(202)는 임의의 MBMS에 대한 서비스 고지(SERVICE ANNOUNCEMENT)가 이루어지는 단계이다. 상기 고지 단계(ANNOUNCEMENT STEP)(202)를 통해, 임의의 MBMS 서비스를 받고자 하는 UE들은 해당 서비스에 대한 기본적인 정보들을 인지할 수 있다. 예를 들어 상기 기본적인 정보들은 상기 MBMS의 식별자(MBMS ID), 서비스 개시 시간과 지속 시간 등이 될 수 있다. BM-SC는 상기 서비스 관련된 기본 정보들을 UE들에게 전달하기 위해서, 서비스 고지 메시지(service announcement message) 등을 CBS(Cell Broadcast Service) 등을 이용해 방송할 수 있다.
Referring to FIG. 2, a reservation step (SUBSCRIPTION STEP) 201 is a process of registering a UE to receive a certain MBMS with a service provider. At this time, the service provider and the UE exchange basic information related to charging or service reception.
상기 고지 단계(ANNOUNCEMENT STEP)(202)를 통해 특정 서비스에 대한 기본 정보를 습득한 UE들(161 내지 172)은, 만약 그 서비스를 수신하고자 한다면, 연결 단계(JOINING STEP)(203)를 수행한다. 상기 연결 단계(203)에서 상기 UE들은 수신하고자 하는 서비스 식별자(MBMS ID)를 임의의 메시지에 담아 네트워크로 전달한다. BM-SC(110)와 상기 UE들 사이에 위치하고 있는 장치들, 즉 SGSN(130), Transit NW(120) 등은 임의의 MBMS에 따른 MBMS 데이터를 수신하고자 하는 UE들과 그 UE들이 위치하고 있는 장치를 인지할 수 있다. 예를 들어 SGSN(130)은 UE들의 명단과 그 UE들이 위치하고 있는 RNC(140)의 명단을 파악할 수 있으며, 추후 상기 UE들이 위치하고 있는 RNC(140)로만 MBMS 데이터를 전송할 것이다.UEs 161 to 172 that have acquired basic information about a specific service through the
방송모드 베어러 설정 단계(MULTICAST MODE BEARER SETUP STEP)(204)에서는 SGSN(130)과 Transit NW(120) 상에 상기 MBMS를 제공하기 위한 전송 베어러(transport bearer)가 미리 설정될 수 있다. 예를 들어 SGSN(130)과 GGSN(미도시) 사이에 상기 MBMS를 위한 GTP-U/UDP/IP/L2/L1 bearer(3GPP TS 23.060 참조)가 미리 설정될 수 도 있다.In the broadcast mode
통지 단계(NOTIFICATION STEP)(205)는 상기 MBMS가 곧 시작될 것이므로, 서비스를 수신하고자 하는 UE들을 호출하는 단계이다. 상기 통지 단계(205)에는 기존의 호출 방식이 사용되거나 MBMS에 최적화된 호출 방식이 사용될 수 있다. 상기 통지 단계(NOTIFICATION STEP)(205)에 대해서는 도 3을 통해 자세히 설명될 것이다.
무선자원 할당 단계(RADIO RESOURCE ALLOCATION STEP)(206)는 상기 MBMS를 제공하기 위한 무선자원을 실제 할당하고, 그 정보를 관련 장치들에 공지하는 단계 이다. RADIO
현재 표준회의에서는 MBMS를 제공할 때, 포인트 투 포인트(Point to Point, 이하 "PTP"라 칭함) 방식과 포인트 투 멀티포인트(Point to Multi-point, 이하 "PTM"이라 칭함) 방식 중 효율적인 방식을 선택하도록 하는 방안이 논의되고 있다. 상기 PTM 방식은 하나의 공통 채널을 통해 전송되는 스트림을 다수의 UE들이 공유하는 방식이다. 상기 PTP 방식은 전용 채널들을 이용해서, UE별로 스트림을 각각 전송하는 방식이다. 일반적으로 PTM 방식이 PTP 방식보다 효율적이다. 하지만, 상기 PTM 방식에서는 전력제어가 수행되지 않기 때문에, UE의 수가 일정 수 보다 적을 경우에는, PTP 방식이 오히려 효율적일 수 있다. 극단적인 예로, 한 셀에 단 1명의 UE만이 특정 MBMS를 제공받기를 원한다면, PTP 방식을 이용하는 것이 보다 효율적일 것이다. 따라서, 상기 PTP 방식과 상기 PTM 방식의 선택기준으로는 UE의 수가 고려되어야 할 것이다. 상기 특정 셀에서 PTP 방식과 PTM 방식의 선택 기준이 되는 UE의 수(이하 "MBMS 임계 값"이라 칭함)는 셀별로 결정되는 변수이며, 상황에 따라 달라질 수 있다. 현재 표준회의 논의 상황을 참고하면, MBMS 임계 값은 10이하가 될 것으로 보인다. In the current standard meeting, when providing MBMS, an efficient method between point to point (PTP) and point to multi-point (PTM) method is provided. How to choose is discussed. The PTM scheme is a scheme in which a plurality of UEs share a stream transmitted through one common channel. The PTP scheme uses a dedicated channel to transmit a stream for each UE. In general, the PTM method is more efficient than the PTP method. However, since the power control is not performed in the PTM scheme, when the number of UEs is smaller than a certain number, the PTP scheme may be more efficient. In an extreme example, if only one UE wants to receive a particular MBMS in a cell, it would be more efficient to use the PTP scheme. Therefore, the number of UEs should be considered as the selection criteria of the PTP scheme and the PTM scheme. The number of UEs (hereinafter, referred to as “MBMS thresholds”) that are the selection criteria of the PTP scheme and the PTM scheme in the specific cell is a variable determined for each cell and may vary depending on a situation. Referring to the current discussion of the standards meeting, the MBMS threshold is expected to be less than 10.
전술한 바를 참고할 때, 상기 무선자원 할당 단계(RADIO RESOURCE ALLOCATION STEP)(206)에서 무선 자원을 할당하기 위해 RNC는 셀별로 해당 MBMS를 제공받고자 하는 UE의 수가 MBMS 임계 값보다 큰지 작은지를 알아야 한다. 즉, MBMS 임계 값보다 클 경우, PTM 방식을 설정하고, MBMS 임계 값보다 적을 경우, PTP 방식으로 설정한다. 특정 셀에 대해 특정 MBMS를 제공하기 위한 무선 자원을 할당함에 있어 UE의 수가 MBMS 임계 값보다 큰지 여부를 판단하는 과정을 카운팅(counting)이라고 한다. 필요시 특정 셀에서 UE의 수가 MBMS 임계 값보다 큰지 여부를 다시 판단하는 과정을 재 카운팅(recounting)이라고 한다. 상기 카운팅(counting)과 재 카운팅(recounting)에 대해서는 도 3을 참조하여 보다 구체적으로 설명한다. 상기 무선자원 할당 단계(RADIO RESOURCE ALLOCATION STEP)(206)에서는, 상기 PTP 방식과 상기 PTM 방식 중 결정된 방식에 대응하여 무선자원을 할당하게 될 것이다.Referring to the foregoing, in order to allocate radio resources in the RADIO
상기 무선자원 할당 단계(RADIO RESOURCE ALLOCATION STEP)(206)까지 진행된 뒤, 데이터 전송 단계(DATA TRANSFER STEP)(207)에서 실제 MBMS 데이터가 UE들에게 전송된다. 이 때, 암호 키(ciphering key) 갱신 등이 진행될 수도 있다. 예를 들어 임의의 MBMS에 대한 암호 키(ciphering key)를 변경해야 할 필요성이 발생할 경우, RNC(140)는 새로운 암호 키(ciphering key)를 상기 MBMS를 수신하고 있는 모든 UE들에게 전달한다.After the RADIO
이 후, 상기 MBMS가 종료되면, 무선자원 해제 단계(RADIO RESOURCE RELEASE STEP)(208)에서 앞서 설정한 무선자원을 해제하고, MBMS RB RELEASE 등의 메시지를 상기 MBMS를 수신하고 있는 모든 UE들에게 전송한다.Thereafter, when the MBMS is terminated, the radio resource set in the radio resource release step RADIO
도 3에서는 임의의 MBMS가 이뤄지기 위해서 사용자와 네트워크 사이에 이루어져야 하는 동작들에서 일부 동작에 따른 구체적인 시그널링을 도시하고 있다. 상기 도 2에서 도시된 핵심 망(Core Network; 이하 'CN'이라 한다)은 SGSN(130), Transit N/W(120), MB-SC(110)를 모두 포괄하지만, 도 3에서는 상기 CN 중 SGSN만 을 고려하였다. 상기 도 3에서 구체적으로 보이고 있는 단계들은 상기 도 2에서의 연결 단계(JOINING STEP)(203), 통지 단계(NOTIFICATION STEP)(205), 무선자원 할당 단계(RADIO RESOURCE ALLOCATION STEP)(206) 및 무선자원 해제 단계(RADIO RESOURCE RELEASE STEP)(208)이다. 3 illustrates specific signaling according to some operations in operations that must be performed between a user and a network in order for an arbitrary MBMS to be performed. The core network illustrated in FIG. 2 includes the
상기 도 3을 참조하면, 고지 단계(ANNOUNCEMENT STEP)(202)를 통해 임의의 MBMS에 대한 기본 정보, 즉 MBMS ID 등을 인지한 UE는 ACTIVATE MBMS PDP CONTEXT REQUEST 메시지를 SGSN으로 전송한다(301단계). 상기 메시지를 수신한 SGSN은, 만약 UE가 해당 서비스를 요청한 첫 번째 UE라면 MBMS PDP CONTEXT를 구성하여 상기 UE를 상기 CONTEXT에 저장하고, GGSN과 필요한 동작을 수행한다. 상기 필요한 동작은 GTP 터널 셋업(tunnel setup) 과정이 될 수 있으며, SGSN이 상기 서비스 관련 정보들을 GGSN에게 통보하고, 상호간에 사용할 논리적 식별자를 교환하는 과정 등이 포함될 수 있다. 보다 자세한 사항은 3GPP TS 23.060에 기술되어 있다. 상기 MBMS PDP CONTEXT는 임의의 MBMS 서비스에 대한 관련 정보가 저장되어 있는 변수들의 집합이며, 상기 ACTIVATE MBMS PDP CONTEXT REQUEST 메시지를 전송한 UE들의 명단 및 위치 등과 해당 MBMS 데이터를 전송할 전송 베어러 관련 정보 등을 저장하고 있을 수 있다. 상기 SGSN은 상기 UE에게 ACTIVATE MBMS PDP CONTEXT ACCEPT 메시지를 전송하여, 연결 단계의 수행이 완료되었음을 통보한다(302단계). 전술한 301단계와 상기 302단계는 상기 도 2에서의 연결 단계(JOINING STEP)(203)에 해당한다.Referring to FIG. 3, the UE, upon recognizing basic information about an arbitrary MBMS, that is, an MBMS ID, through an
해당 MBMS의 개시에 임박하여 상기 연결 단계(JOINING STEP)(203)가 수행된 UE들을 호출하는 통지 단계(NOTIFICATION STEP)(205)는 303단계와 304단계에서 수 행된다. 즉, 상기 SGSN은 상기 MBMS의 개시에 임박해서 또는 첫 번째 MBMS 데이터를 수신한 뒤, 상기 서비스를 받고자 하는 UE들을 상기 통지 단계(NOTIFICATION STEP)(205)를 통해 깨운다. 상기 서비스를 받고자 하는 UE들은 상기 301단계에서 ACTIVATE MBMS PDP CONTEXT REQUEST 메시지를 전송한 UE들이 될 것이다. 먼저, 상기 SGSN은 상기 303단계에서 상기 연결 단계(JOINING STEP)를 수행한 UE들이 위치하고 있는 RNC들로 NOTIFICATION 메시지를 전송한다. 상기 SGSN으로부터 NOTIFICATION 메시지를 수신한 상기 RNC들은 상기 304단계에서 상기 연결 단계(JOINING STEP)를 수행한 UE들이 위치하는 셀들을 통해 해당 UE들로 NOTIFICATION 메시지를 전송한다. 따라서 상기 NOTIFICATION 메시지는 해당 MBMS에 대한 연결 단계를 수행한 모든 UE들이 수신하게 된다. 즉, 아이들 모드(idle mode)를 포함한 모든 상태의 UE들이 상기 NOTIFICATION 메시지를 수신할 수 있어야 한다. 이를 위해서 상기 NOTIFICATION 메시지는 호출 메시지(PAGING MESSAGE)를 통해 전송될 수 있다. 이에 대해서는 기 출원된 P2002-0068597에서 자세히 기술되어 있다. The
305단계, 306 단계, 307 단계에서는 특정 셀에 대한 MBMS를 PTP 방식에 의해 제공할지, PTM 방식에 의해 제공할지를 결정한다.In
UE는 아이들 모드(idle mode), URA_PCH, CELL_PCH, CELL_FACH, CELL_DCH 등의 상태에 있을 수 있다. 상기 아이들 모드(idle mode)를 제외한 나머지 상태를 RRC 연결 모드(connected mode)로 통칭한다. 임의의 UE가 상기 RRC 연결 모드(connected mode)에 있을 경우, RNC는 해당 UE들에 대한 정보를 계속 저장하고 있어야 하는 부담이 있다. 그러므로, 다수의 UE들이 특정 MBMS를 제공받을 때, 최소한의 UE들(셀 별로 MBMS 임계 값만큼의 UE들)만 RRC 연결 모드(connected mode)에 있도록 해주기 위해서, 상기 305단계 내지 상기 307 단계가 제안되었다. 다시 말해서, 특정 셀에 MBMS 임계 값 이상의 UE들이 특정 MBMS의 제공을 원할 경우, 상기 MBMS 임계 값만큼의 UE들만 RRC 연결을 유지하도록 한다. 이 경우에는 해당 셀에 대해 PTM 방식이 설정될 것이다. 하지만, 특정 셀에서 MBMS 임계 값 이하의 UE들이 특정 MBMS의 제공을 원하는 경우, 모든 UE들이 RRC 연결을 유지하도록 한다. 이 경우 해당 셀에 대해 PTP 방식이 설정될 수도 있다.The UE may be in an idle mode, URA_PCH, CELL_PCH, CELL_FACH, CELL_DCH, or the like. The other states except for the idle mode are collectively referred to as an RRC connected mode. If any UE is in the RRC connected mode, the RNC is burdened to keep storing information about the UEs. Therefore, when a plurality of UEs are provided with a particular MBMS, steps 305 to 307 are proposed in order to ensure that only a minimum number of UEs (UEs per MBMS threshold per cell) are in the RRC connected mode. It became. In other words, when UEs having an MBMS threshold or higher in a specific cell want to provide a specific MBMS, only UEs corresponding to the MBMS threshold maintain RRC connection. In this case, the PTM method will be set for the cell. However, if UEs below the MBMS threshold in a specific cell want to provide a particular MBMS, all the UEs maintain the RRC connection. In this case, a PTP scheme may be set for the corresponding cell.
전술한 바에 의해 RRC 연결 모드로 상태 천이한 UE들은 이 후 셀 단위로 위치가 추적되며, 상기 추적된 위치정보는 RNC가 관리한다.As described above, UEs which have transitioned to the RRC connected mode are tracked in cell units, and the tracked location information is managed by the RNC.
이를 보다 자세히 살펴보면, NOTIFICATION 메시지를 수신한 아이들 모드(idle mode)의 UE들은 305단계에서 RRC CONNECTION SETUP 절차를 수행한다. 상기 절차는 UE가 RRC CONNECTION REQUEST 메시지를 RNC로 전송하고, 상기 RNC가 RRC CONNECTION SETUP 메시지를 상기 UE로 전송한 뒤, 상기 UE가 RRC CONNECTION SETUP COMPLETE 메시지를 상기 RNC로 전송함으로써 완료된다. 상기 UE는 상기 RRC CONNECTION REQUEST 메시지에 MBMS ID를 삽입하여 전송하며, 상기 RNC는 306단계에서 상기 RRC CONNECTION REQUEST 메시지에 포함된 MBMS별로의 수신을 카운팅 한다. 상기 RNC는 특정 MBMS ID를 포함하는 RRC CONNECTION REQUEST 메시지의 수가 MBMS 임계 값에 도달하면, 더 이상의 응답 메시지를 수신할 필요가 없게 된다. 이와 같은 상황이 발생하면 상기 RNC는 307단계에서 상기 특정 MBMS ID를 포함하는 응답 메시지를 더 이상 전송하지 말 것을 요청하는 STOP 메시지를 전송한다. 상기 STOP 메시지를 수신한 UE들은 상기 304단계에서 수신한 NOTIFICATION 메시지에 대한 응답 메시지의 전송 시도를 중단한다. 상기 RRC CONNECTION REQUEST 메시지는 랜덤접근채널(Random Access CHannel, 이하 "RACH"라 칭함)을 통해 전송되므로, 상기 응답 메시지의 전송 시도를 중단하는 것은 RACH 이용 시도를 중지한다는 의미와 동일하다.Looking at this in more detail, UEs in the idle mode having received the NOTIFICATION message perform an RRC CONNECTION SETUP procedure in
상기 SGSN은 308단계에서 상기 RNC로 MBMS RAB ASSIGNMENT REQUEST 메시지를 송신한다. 상기 MBMS RAB ASSIGNMENT REQUEST 메시지에는 MBMS 서비스를 제공하기 위해 요구되는 QoS(Quality of Service) 정보가 포함될 수 있다. 상기 RNC는 전달받은 QoS 정보와 상기 306단계에서의 카운팅 값을 바탕으로 각 셀별로 MBMS RB 정보를 결정한다. 상기 MBMS RB 정보는 Layer 2(이하 "L2"라 칭함) 정보와 Layer 1(이하 "L1"라 칭함) 정보를 포괄한다. 상기 L2 정보로는 RLC/PDCP 관련 정보 등이 포함될 수 있으며, 상기 L1 정보로는 TFS 정보, TFCS 정보, 채널화 코드 정보, 전송 출력 관련 정보 등이 포함될 수 있다. 상기 RNC는 PTM 방식에 따른 무선채널이 설정될 셀에는 상기 정보들을 셀별로 결정하며, PTP 방식에 따른 무선채널이 설정될 셀에 대해서는 UE별로 상기 정보들을 결정한다.The SGSN transmits an MBMS RAB ASSIGNMENT REQUEST message to the RNC in
상기 RNC는 309단계에서 상기 MBMS RB 정보들을 UE들에게 전달한다. 만약, 상기 PTM 방식에 따른 무선채널의 설정이 결정되었다면, MBMS RB SETUP 메시지에는 PTM 방식에 따른 무선채널 정보가 삽입될 것이며, 상기 PTP 방식에 따른 무선채널의 설정이 결정되었다면 상기 PTP 방식에 따른 무선채널 정보가 삽입될 것이다.
The RNC delivers the MBMS RB information to UEs in
상기 SGSN과 상기 MBMS RB SETUP 메시지를 수신한 UE들간에는 207단계에서 설정된 무선채널을 통해 MBMS 데이터를 전송하는 데이터 전송 단계가 수행된다. A data transmission step of transmitting MBMS data through the wireless channel established in
UE들은 상기 207단계에서 MBMS에 따른 MBMS 데이터를 제공받으면서, 다른 셀로 이동할 수 있다. 이러한 UE들의 이동성으로 인해, 하나의 셀내에서 특정 MBMS를 제공받는 UE들의 수는 가변될 수 있다. 보다 효율적인 MBMS를 제공하기 위해서는 이와 같이 가변되는 UE들의 수를 주기적으로 갱신할 필요가 있다. 예를 들어 특정 MBMS에 대한 초기 제공 시에 임의의 셀에는 상기 특정 MBMS를 제공받기 위한 MBMS 임계 값만큼의 UE들이 있었을 것이다. 하지만, 일정 시간이 흐른 후 일부 UE들이 다른 셀로 이동하였다고 가정할 시 RNC는 상기 이동한 수만큼의 아이들 모드에 있는 UE들에 대해 추가로 상기 특정 MBMS를 제공할 수 있어야 한다. 하지만 많은 수의 UE들이 다른 셀로 이동하였으나 상기 특정 MBMS를 제공받기를 기다리는 아이들 모드의 UE들이 존재하지 않는 경우에는 해당 셀에 대한 무선채널의 종류를 PTP 방식에 따른 무선채널로 변경할 수 있다.UEs may move to another cell while receiving MBMS data according to MBMS in
이를 위해 상기 RNC는 310단계에서 RECOUNTING 메시지를 상기 아이들 모드의 UE들에게 전송한다. 상기 RECOUNTING 메시지에는 해당 MBMS ID가 포함될 수 있다. 상기 RECOUNTING 메시지를 수신하면, 아이들 모드(idle mode)의 UE들은 310단계에서 RRC CONNECTION SETUP 절차를 수행한다. 상기 RNC는 상기 아이들 모드의 UE들로부터의 응답 메시지를 카운트한다. 상기 카운트 값과 기존에 특정 MBMS를 계속하여 제공받고 있는 UE들의 수의 합이 MBMS 임계 값에 도달할 시 상기 RNC는 311단계에서 STOP 메시지를 전송함으로써 더 이상의 응답 메시지가 전송되는 것을 차단한다.
To this end, the RNC transmits a RECOUNTING message to the UEs in the idle mode in
살펴본 바와 같이, 하나의 메시지를 이용해서 다수의 UE들에게 동일한 정보를 제공하는 그룹 시그널링 메시지(예컨대, Notification message 또는 RECOUNTING 메시지)는, UE들로부터 동일한 시점에 다수의 응답 메시지들이 전송되는 상황을 초래할 수 있다. 그 이유로 상기 응답 메시지들은 모든 UE들이 공유할 수 있는 RACH를 통해 전송되기 때문에 동시에 많은 UE들이 사용하고자 하는 경우에는 한정된 용량을 가지는 RACH의 성능이 저하될 우려가 있다.As described above, a group signaling message (eg, a notification message or a RECOUNTING message) that provides the same information to multiple UEs using one message may result in a situation in which multiple response messages are transmitted at the same time from the UEs. Can be. For this reason, since the response messages are transmitted through a RACH that can be shared by all UEs, when many UEs intend to use them at the same time, the performance of the RACH having a limited capacity may be degraded.
통상적으로 RACH는 전용채널을 가지고 있지 않은 UE들이 역방향으로 데이터를 전송하기 위해서 사용하는 채널이다. 상기 전용채널을 가지고 있지 않은 UE들은 Cell_FACH, Cell_PCH, URA_PCH 또는 아이들 모드(idle mode)에 있는 UE들로써 대표된다. PRACH는 RACH 전송에 사용되는 무선 자원들의 집합으로 규정할 수 있으며, 상기 무선 자원들은 하기의 것들로써 구성된다.Typically, the RACH is a channel used by UEs not having a dedicated channel to transmit data in the reverse direction. UEs that do not have the dedicated channel are represented by UEs in Cell_FACH, Cell_PCH, URA_PCH, or idle mode. The PRACH may be defined as a set of radio resources used for RACH transmission, and the radio resources are configured as follows.
1. 프리앰블 스크램블링 코드(Preamble scrambling code) : 특정 PRACH 당 하나씩 대응하는 스크램블링 코드를 의미한다. 상기 PRACH의 사용을 위해 역방향으로 전송되는 프리앰블(preamble)과 RACH 데이터는 상기 프리앰블 스크램블링 코드(preamble scrambling code)에 의해 스크램블링되어 전송된다.1. Preamble scrambling code: Preamble scrambling code: One scrambling code corresponding to one specific PRACH. Preamble and RACH data transmitted in the reverse direction for use of the PRACH is scrambled by the preamble scrambling code and transmitted.
2. 시그네쳐 셋(signature set) : 하나의 PRACH 당 16개까지 할당될 수 있는 확산률(SF)이 16인 OVSF 코드들로써, 프리앰블과 RACH 데이터를 코딩하는데 사용된다.2. Signature set: OVSF codes with a spread factor (SF) of 16, which can be assigned up to 16 per PRACH, are used to code preamble and RACH data.
3. 액세스 슬롯 셋(access slot set) : 2개의 타임 슬롯들로 구성되며, 각 액세스 슬롯(access slot)의 시작점에서 프리앰블(preamble) 전송이 시작된다. 3. Access slot set: Composed of two time slots, preamble transmission is started at the start of each access slot.
도 5는 RACH를 통해 데이터를 전송하기 위한 UE의 통상적인 제어 흐름을 보이고 있는 도면이다. 상기 도 5에서 보이고 있는 제어 흐름은 아이들 모드(idle mode)의 UE 또는 Cell_PCH/URA_PCH/Cell_FACH 상태의 UE를 대상으로 한다.5 is a diagram illustrating a typical control flow of a UE for transmitting data on the RACH. The control flow shown in FIG. 5 is for a UE in idle mode or a UE in Cell_PCH / URA_PCH / Cell_FACH state.
상기 도 5를 참조하면, 501단계에서 역방향으로 전송할 데이터가 발생할 경우 UE는 502단계로 진행한다. 상기 역방향으로 전송할 데이터가 발생할 경우는 해당 UE가 호출 메시지를 수신하거나 위치정보 갱신 메시지를 전송할 필요가 있을 경우에 해당한다.Referring to FIG. 5, if data to be transmitted in the reverse direction occurs in
상기 도 5에서 502단계 내지 507단계는 RACH 신호 전송 동작에 해당한다. UE는 상기 502단계에서 지속값 검사(persistence value test)라는 것을 수행한다. 이를 위해서는 지속값(persistence value)을 결정하여야 한다.In FIG. 5,
이를 위해 각 UE들은, 특정 시점에 RACH를 통해 전송하고자 하는 데이터의 종류에 따라 액세스 서비스 클래스(ASC : Access Service Class)라는 것을 할당받는다. 상기 ASC는 ASC #0에서 ASC #7까지 총 8개가 존재한다. 상기 ASC들 각각에 대해서는 지속값(persistence value), 가용한 시그네쳐 셋(signature set) 및 가용한 액세스 슬롯(access slot)들이 결정되어 있다. 상기 정보는 시스템 정보로 UE들에게 전달된다. 각 UE는 여러 종류의 데이터 스트림들을 가질 수 있으며, 이들을 무선 베어러(radio bearer)라고 한다. 상기 무선 베어러는 제어 메시지를 전달하기 위한 무선 베어러(radio bearer)와 음성통화를 위한 무선 베어러(radio bearer)가 각각 존재할 수 있다. 상기 무선 베어러(radio bearer)들은 RADIO BEARER SETUP 과정 등을 통해 설정된다. 이 때 각 무선 베어러(radio bearer)들에는 ASC가 할당된 다. 그러므로 상기 501단계에서 역방향으로 전송할 데이터가 발생하였다는 것은 이미 UE가 상기 데이터를 전송할 무선 베어러(radio bearer)에 대응되는 ASC를 인지하고 있음을 의미한다.To this end, each UE is assigned an Access Service Class (ASC) according to the type of data to be transmitted through the RACH at a specific time. There are a total of eight ASCs from
상기 502단계에서 상기 UE는 해당 ASC에 해당하는 지속값(persistence value)을 이용해서 지속값 검사(persistence value test)를 실시한다. 상기 지속값(Persistence value)은 0에서 1사이의 실수 값으로써, 본질적으로 상기 지속값 검사(persistence value test)를 성공할 확률을 의미한다. 예컨대, 상기 지속값(persistence value)이 0.5라 가정하면, 상기 지속값 검사(persistence value test)에 의해 성공할 확률이 50%임을 의미한다. 상기 UE는 상기 지속값 검사(Persistence value test)가 성공할 경우 503단계로 진행하고, 실패할 경우 10ms 동안 대기하였다가 전술한 지속값 검사(persistence value test)를 다시 시도한다. In
상기 503단계에서 상기 UE는 프리앰블(preamble)을 전송한다. 이 때 상기 UE는 상기 ASC에 대응되는 가용한 시그네쳐(signature)들 중 하나를 무작위로 선택하고, 상기 선택한 시그네쳐(signature)를 이용하여 상기 프리앰블(preamble)을 코딩한 후 초기 전력을 설정하여 전송한다. 상기 초기 전력의 설정에 대해서는 3GPP TS 25.331에서 자세히 기술하고 있음에 따라 구체적인 설명은 생략한다.In
504단계에서 상기 UE는 상기 전송한 프리앰블에 대응하여 Node B로부터 AICH(Acquisition Indication Channel) 신호가 수신되는 지를 감시한다. 상기 AICH 신호는 특정 시그네쳐(signature)를 송신한 UE에게 상기 프리앰블(Preamble) 신호 를 성공적으로 수신하였음을 알려줌과 동시에 RACH를 통한 메시지 전송을 허가하는 의미를 가진다. In
상기 UE는 상기 504단계에서 상기 AICH 신호가 자신이 송신한 시그네쳐를 포함하고 있지 않다고 판단하면 506단계로 진행한다. 상기 AICH 신호가 자신이 송신한 시그네쳐를 포함하고 있지 않는 다는 것은 자신이 송신한 시그네쳐(signature)에 대한 ACK 신호 또는 NACK 신호가 감지되지 않을 경우(no response 상황)임을 의미한다.If the UE determines in
상기 UE는 상기 506단계에서 가용한 시그네쳐(signature)들 중 하나를 다시 선택하고, 전송 전력을 스텝 사이즈(step size) 만큼 증가시킨 후 상기 503단계로 진행하여 상기 다시 선택한 시그네쳐를 포함하는 프리앰블을 상기 증가된 전력에 의해 전송한다. 상기 전송 전력을 증가시키는 것은 상기 Node B가 상기 UE에 의해 전송되는 프리앰블을 인지할 확률을 높이기 위함이다.In
상기 UE는 상기 504단계에서 상기 AICH 신호에 의해 ACK 신호를 수신하게 되면 505단계로 진행하여 RACH 데이터를 전송한다. 이 때 상기 UE는 상기 ACK 신호를 수신한 뒤 3 또는 4 타임슬롯(time slot)을 대기한 후 상기 RACH 데이터를 전송한다. 상기 RACH 데이터는 상기 ACK 신호의 수신을 야기한 프리앰블(preamble)에 포함된 시그네쳐(signature)와 동일한 OVSF 코드 트리 상에 위치한 OVSF 코드를 이용하여 전송한다.If the UE receives the ACK signal by the AICH signal in
상기 UE는 상기 504단계에서 상기 AICH 신호에 의해 NACK 신호를 수신하게 되면, 507 단계로 진행한다. 상기 UE는 507단계에서 NBO1 ×10 ms 동안 대기한 후 상기 502단계로 진행한다. 상기 NBO1은 시스템 정보로 주어지는 값이다.If the UE receives the NACK signal by the AICH signal in
전술한 바에 의해 UE들이 동시에 RACH의 사용을 시도하는 경우에 있어 발생할 수 있는 문제점을 도 4를 참조하여 구체적으로 살펴보면 다음과 같다. 상기 도 4에서는 UE 1(410)과 UE 2(420)가 동일한 PRACH를 사용하며, 동일한 시그네쳐 셋(signature set)과 액세스 슬롯(access slot)들을 공유하는 상황을 가정한다. 또한, 본 발명의 효과적인 설명을 위하여 UE 1(410)과 UE 2(420)가 속한 ASC에 대응되는 시그네쳐(signature)들이 [S1,..,S9]의 9개라고 가정하며, 액세스 슬롯(access slot)들에 대한 고려는 생략하기로 한다.As described above, a problem that may occur when UEs attempt to use the RACH at the same time will be described in detail with reference to FIG. 4. In FIG. 4, it is assumed that
상기 도 4를 참조하면, UE 1(410)이 S1을 선택한 뒤 프리앰블(preamble)(411)을 전송하였으나, 이에 대응한 AICH를 통해서는 상기 S1에 대응한 ACK 또는 NACK이 전송되지 않았다. 이 경우, 상기 UE 1(410)은 새로운 시그네쳐(signature)로써 S2를 선택하고, 전송 출력을 스텝 사이즈(step size)만큼 증가시킨 뒤 두 번째 프리앰블(preamble)(412)을 전송한다. 상기 두 번째 프리앰블(412)에 대응하여서도 ACK 또는 NAC을 수신하지 못한 상기 UE 1(410)은 새로운 시그네쳐로써 S4를 선택한 후 스텝 사이즈만큼 증가된 전송 전력에 의해 세 번째 프리앰블(413)을 전송한다. 이에 대응하여서도 ACK 또는 NACK를 수신하지 못한 상기 UE 1(410)은 또 다시 새로운 시그네쳐로써 S9를 선택한 후 상기 스텝 사이즈만큼 증가된 전송 전력에 의해 네 번째 프리앰블(414)을 전송한다. Node B는 상 기 UE 1(410)로부터 전송된 네 번째 프리앰블을 수신한 후 이에 응답하여 AICH를 통해 시그네쳐 S9를 포함하는 ACK(441)를 전송한다. 따라서 상기 UE 1(410)은 상기 네 번째 프리앰블(414)에 대응하여 상기 ACK(441)을 수신하게 된다. 상기 ACK(441)을 수신한 상기 UE 1(410)은 소정 시간이 경과한 후 할당된 PRACH를 통해 RACH 데이터(415)를 전송한다.Referring to FIG. 4, the
한편, UE 2(420)는 상기 UE 1(410)에 의해 두 번째 프리앰블(412)이 전송되는 시점에서 시그네쳐 S3에 의해 첫 번째 프리앰블(421)을 전송한다. 상기 UE 2(420)는 상기 첫 번째 프리앰블(421)에 대응하여 ACK 또는 NACK을 수신하지 못함에 따라 새로운 시그네쳐로써 S1을 선택하고, 전송 전력을 스텝 사이즈만큼 증가시켜 두 번째 프리앰블(422)을 전송한다. 이에 대응하여서도 ACK 또는 NACK를 수신하지 못한 상기 UE 2(420)는 또 다시 새로운 시그네쳐로써 S9를 선택한 후 상기 스텝 사이즈만큼 증가된 전송 전력에 의해 세 번째 프리앰블(423)을 전송한다. 이때 상기 세 번째 프리앰블(423)은 상기 UE 1(410)에 의해 네 번째 전송된 프리앰블(414)과 동일한 시점에서 동일한 시그네쳐에 의해 전송되었다. 따라서 상기 UE 2(420) 또한 상기 Node B로부터 상기 세 번째 프리앰블(423)에 대응하여 상기 ACK(441)을 수신하게 된다. 상기 ACK(441)을 수신한 상기 UE 2(420)는 소정 시간이 경과한 후 할당된 PRACH를 통해 RACH 데이터(424)를 전송한다.Meanwhile, the
전술한 바와 같이 동일한 시점에 둘 이상의 UE들이 동일한 시그네쳐를 선택하여 프리앰블을 전송한 경우, 상기 둘 이상의 UE들은 수신되는 ACK 신호를 자신이 송신한 프리앰블에 대한 ACK 신호로 이해하게 되어 RACH 데이터의 전송을 시작한 다. 이때, 상기 복수의 UE들로부터 전송되는 RACH 데이터들은 ACK에 대응되는 시그네쳐와 동일한 OVSF 코드 트리 상의 OVSF 코드를 사용하므로, 상기 RACH 데이터들간에는 직교성이 존재하지 않는다. 즉, Node B는 상기 복수의 UE들로부터 전송되는 어떠한 RACH 데이터들도 제대로 수신할 수 없다.As described above, when two or more UEs select the same signature and transmit the preamble at the same time, the two or more UEs understand the received ACK signal as an ACK signal for the preamble transmitted by the UE. Start. In this case, since the RACH data transmitted from the plurality of UEs use the same OVSF code on the same OVSF code tree as the signature corresponding to the ACK, there is no orthogonality between the RACH data. That is, the Node B cannot properly receive any RACH data transmitted from the plurality of UEs.
이와 같이 동일한 시점에 다수의 UE들이 동일한 시그네쳐를 선택할 경우, RACH 데이터의 전송에 실패할 가능성이 증가하며, 아울러 둘 이상의 UE들이 전송함으로써 역방향 간섭(interference)이 증가할 수 있다. 즉, 상기 RACH 데이터의 전송에서와 같이 일반적인 역방향 메시지가 다수의 UE들에 의해 동시에 전송되는 경우, 상기와 같은 문제점이 발생될 가능성이 항상 내재되어 있다.As such, when a plurality of UEs select the same signature at the same time point, the possibility of failing to transmit the RACH data increases, and in addition, backward interference may increase by transmitting two or more UEs. That is, when a general reverse message is simultaneously transmitted by a plurality of UEs as in the transmission of the RACH data, there is always a possibility that such a problem may occur.
한편, 상기와 같은 상황은 하나의 그룹 시그널링(group signaling) 메시지에 의해서 많은 수의 UE들이 RACH 데이터 전송을 동시에 시도할 수 있는 MBMS의 수행에 있어서 더욱 심각한 문제를 초래할 수 있다.
On the other hand, such a situation may cause a more serious problem in the performance of the MBMS that a large number of UEs can attempt to transmit RACH data simultaneously by one group signaling message.
상기한 바와 같은 문제점을 해결하기 위한 본 발명의 목적은 이동통신시스템에서 그룹 시그널링 메시지에 대응한 응답 메시지의 전송 확률을 증가시키는 방법을 제공함에 있다.An object of the present invention for solving the above problems is to provide a method for increasing the transmission probability of a response message corresponding to a group signaling message in a mobile communication system.
본 발명의 다른 목적은 이동통신시스템에서 그룹 시그널링 메시지에 대응하여 응답 메시지가 전송될 확률을 실시간으로 조정하는 방법을 제공함에 있다.Another object of the present invention is to provide a method for adjusting in real time the probability that a response message is transmitted in response to a group signaling message in a mobile communication system.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은 이동통신시스템에서 그룹 시그널링 메시지에 대응 한 응답 메시지를 실시간으로 조정되는 전송 확률에 의해 효율적으로 전송하는 방법을 제공함에 있다.Another object of the present invention is to provide a method for efficiently transmitting a response message corresponding to a group signaling message in a mobile communication system based on a transmission probability adjusted in real time.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은 이동통신시스템에서 복수의 단말들로부터 동시에 전송될 수 있는 응답 메시지들이 스케줄링에 의해 전송될 수 있도록 하는 방법에 제공함에 있다.It is still another object of the present invention to provide a method for allowing response messages that can be simultaneously transmitted from a plurality of terminals in a mobile communication system to be transmitted by scheduling.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은 이동통신시스템에서 복수의 단말들로부터의 응답 메시지들을 전송하기 위한 랜덤접근채널들의 성능을 최적화시키는 방법을 제공함에 있다.Another object of the present invention is to provide a method for optimizing the performance of random access channels for transmitting response messages from a plurality of terminals in a mobile communication system.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은 MBMS 응답 메시지를 전송하고자 하는 단말들에 대해 전송 확률을 주기적으로 갱신시켜주는 방법을 제공함에 있다.Another object of the present invention is to provide a method for periodically updating a transmission probability for terminals to which an MBMS response message is to be transmitted.
본 발명에서 제안하는 방법은; 이동통신시스템에서 기지국 제어기가 단말기들에게 억세스 프리앰블을 전송할 구간을 제공하는 방법에 있어서, 미리 설정되어 있는 시간 단위로 기지국에 의해 사용이 허락되는 역방향 채널들의 수를 측정하는 과정과, 상기 시간 단위로 상기 단말기들에 의한 역방향 채널의 할당 요구 시도 횟수를 결정하는 과정을 포함하며, 상기 할당 요구 시도 횟수는 상기 측정한 역방향 채널들의 수임을 특징으로 한다.
본 발명에서 제안하는 다른 방법은; 이동통신시스템에서 단말기들이 기지국 제어기에 의해 지속적으로 갱신되는 지속 값에 의해 억세스 프리앰블을 전송하는 방법에 있어서, 상기 지속 값을 수신하고, 이전 지속 값을 상기 지속 값으로 변경하는 과정과, 0에서 1사이의 실수 값을 임의로 결정하고, 상기 실수 값이 상기 변경한 지속 값보다 작으면 상기 억세스 프리앰블을 기지국으로 전송하는 과정을 포함한다.The method proposed in the present invention; A method for providing a section in which a base station controller transmits an access preamble to terminals in a mobile communication system, the method comprising: measuring a number of reverse channels allowed to be used by a base station in a predetermined time unit; And determining the number of attempts to allocate the reverse channel by the terminals, wherein the number of attempts to allocate the reverse channel is the number of the measured reverse channels.
Another method proposed by the present invention; Claims [1] A method of transmitting an access preamble by a terminal in which a terminal continuously updates by a base station controller in a mobile communication system, the method comprising: receiving the duration value and changing a previous duration value to the duration value; And arbitrarily determine a real value between and transmitting the access preamble to a base station if the real value is less than the changed duration value.
본 발명에서 제안하는 또 다른 방법은; 이동통신시스템에서 기지국 제어기가 단말기들에게 억세스 프리앰블을 전송할 구간을 제공하는 방법에 있어서, 상기 기지국 제어기가 미리 설정되어 있는 시간 단위로 기지국에 의해 사용이 허락되는 역방향 채널들의 수를 측정하고, 상기 측정한 역방향 채널들의 수를 지속 값으로 갱신하여 상기 단말기들로 전송하는 과정과, 상기 단말기들은 상기 갱신된 지속 값을 수신하고, 상기 갱신된 지속값을 이전 지속 값으로 변경하고, 0에서 1사이에서 임의로 결정한 실수 값이 상기 변경된 이전 지속 값보다 작으면 상기 억세스 프리앰블을 상기 기지국으로 전송하는 과정을 포함한다.Another method proposed by the present invention is; A method for providing a section in which a base station controller transmits an access preamble to terminals in a mobile communication system, the method comprising: measuring a number of reverse channels permitted by a base station in a predetermined time unit, and measuring Updating the number of reverse channels to a duration value and transmitting the updated duration value to the terminals, and the terminals receive the updated duration value, change the updated duration value to a previous duration value, and range from 0 to 1 And transmitting the access preamble to the base station when the randomly determined real value is smaller than the changed previous sustain value.
본 발명에서 제안하는 또 다른 방법은; 이동통신시스템에서 기지국 제어기가 단말기들에게 억세스 프리앰블을 전송할 구간을 제공하는 방법에 있어서, 상기 단말기들로부터 요청된 멀티미디어 방송 멀티캐스트 서비스(MBMS: Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service)가 제공될 것임을 통지하기 위해 상기 단말기들을 호출할 시, 초기 지속 값을 상기 단말기들에게 전송함으로써, 상기 단말기들이 상기 초기 지속 값을 사용하여 상기 억세스 프리앰블을 전송하도록 하는 과정과, 미리 설정되어 있는 시간 단위로 상기 억세스 프리앰블들에 대응하여 기지국이 역방향 채널들의 사용을 허락한 허락 횟수를 측정하는 과정과, 상기 측정한 허락 횟수를 상기 초기 지속 값으로 갱신하고, 상기 갱신한 지속 값을 포함하는 엑세스 컨트롤 메시지를 MBMS 제어채널을 통해 상기 단말기들에게 전송하는 과정을 포함한다.Another method proposed by the present invention is; A method for providing a section in which a base station controller transmits an access preamble to a mobile station in a mobile communication system, the terminal to notify that a multimedia broadcast multicast service (MBMS) requested from the terminals will be provided. Calling the terminal to transmit an initial persistence value to the terminals, thereby causing the terminals to transmit the access preamble using the initial persistence value, and corresponding to the access preambles in predetermined time units. Measuring a number of grants for which the base station permits the use of reverse channels, updating the measured number of grants to the initial duration value, and accessing an access control message including the updated duration value through the MBMS control channel; The process of transmitting to them.
본 발명에서 제안하는 또 다른 방법은; 이동통신시스템에서 단말기들이 기지국 제어기에 의해 제공되는 지속 값에 의해 억세스 프리앰블을 전송하는 방법에 있어서, 상기 기지국 제어기로부터 요청된 멀티미디어 방송 멀티캐스트 서비스(MBMS: Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service)가 제공될 것임을 통지함과 함께 상기 기지국 제어기로부터 제공되는 초기 지속 값을 사용하여 랜덤접근채널의 할당을 요청하는 상기 억세스 프리앰블을 전송하는 과정과, 상기 초기 지속 값을 사용하여 상기 억세스 프리앰블을 전송하는 중 상기 기지국 제어기에 의해 갱신된 지속 값을 수신하면, 상기 초기 지속 값 또는 이전 지속 값을 상기 갱신된 지속 값으로 변경하는 과정과, 0에서 1사이의 실수 값을 임의로 결정하고, 상기 실수 값이 상기 변경한 지속 값보다 작으면 상기 억세스 프리앰블을 기지국으로 전송하는 과정을 포함한다.Another method proposed by the present invention is; A method for transmitting terminals an access preamble by a persistence value provided by a base station controller in a mobile communication system, wherein the multimedia broadcast multicast service (MBMS) requested from the base station controller is provided. And transmitting the access preamble requesting allocation of a random access channel using an initial sustain value provided from the base station controller, and transmitting the access preamble using the initial sustain value. Receiving an updated persistence value, changing the initial persistence value or the previous persistence value to the updated persistence value, randomly determining a real value between 0 and 1, wherein the real value is greater than the changed persistence value If small, transmitting the access preamble to a base station It includes forward.
본 발명에서 제안하는 또 다른 방법은; 이동통신시스템에서 기지국 제어기가 단말기들에게 억세스 프리앰블을 전송할 구간을 제공하는 방법에 있어서, 상기 단말기들에 의해 요청된 멀티미디어 방송 멀티캐스트 서비스(MBMS: Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service)가 제공될 것임을 통지하기 위해 상기 단말기들을 호출 시 초기 지속 값을 상기 단말기들에게 전송하는 과정과, 상기 단말기들이 상기 기지국 제어기로부터 상기 MBMS가 제공될 것임을 통지하는 호출과 함께 수신한 초기 지속 값을 사용하여 상기 호출에 대응하는 응답 메시지를 전송하기 위해 랜덤접근채널의 할당을 요청하는 상기 억세스 프리앰블을 상기 기지국 제어기로 전송하는 과정과, 상기 기지국 제어기가 미리 설정되어 있는 시간 단위로 상기 억세스 프리앰블들에 대응하여 기지국이 역방향 채널들의 사용을 허락한 허락 횟수를 측정하는 과정과, 상기 기지국 제어기가 상기 측정한 허락 횟수를 상기 초기 지속 값으로 갱신하고, 상기 갱신한 지속 값을 포함하는 MBMS 제어채널을 제2공통제어물리채널을 통해 상기 단말기들에게 전송하는 과정과, 상기 단말기들이 상기 초기 지속 값을 사용하여 상기 억세스 프리앰블을 전송하는 도중 상기 갱신된 지속 값을 수신하면, 상기 초기 지속 값 또는 이전 지속 값을 상기 수신한 지속 값으로 변경하는 과정과, 상기 단말기들이 상기 변경된 지속 값을 사용하여 상기 호출에 대응하는 응답 메시지를 상기 기지국 제어기로 전송하기 위해 랜덤접근채널의 할당을 요청하는 상기 억세스 프리앰블을 전송하는 과정을 포함한다.Another method proposed by the present invention is; In a method for providing a section in which a base station controller transmits an access preamble to a mobile communication system, the base station controller provides a multimedia broadcast multicast service (MBMS) requested by the terminals. Sending an initial persistence value to the terminals when calling the terminals, and a response message corresponding to the call using the initial persistence value received by the terminals from the base station controller indicating that the MBMS will be provided; Transmitting the access preamble to the base station controller for requesting allocation of a random access channel to transmit a message; and using the reverse channels in response to the access preambles in predetermined time units. The number of permits allowed Determining, and updating, by the base station controller, the measured number of permits to the initial duration value, and transmitting an MBMS control channel including the updated duration value to the terminals through a second common control physical channel. When the terminals receive the updated duration value while transmitting the access preamble using the initial duration value, changing the initial duration value or the previous duration value to the received duration value; And transmitting the access preamble requesting allocation of a random access channel to transmit a response message corresponding to the call to the base station controller using the changed duration value.
삭제delete
이하 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예의 상세한 설명이 첨부된 도면들을 참조하여 설명될 것이다. 하기에서 각 도면의 구성요소들에 참조부호를 부가함에 있어 동일한 구성요소들에 대해서는 비록 다른 도면상에 표시되더라도 가능한 한 동일한 부호를 가지도록 하고 있음에 유의해야 한다. 또한, 본 발명을 설명함에 있어 관련된 공지 기능 또는 구성에 대한 구체적인 설명이 본 발명의 요지를 불필요하게 흐릴 수 있다고 판단되는 경우에는 그 상세한 설명은 생략할 것이다. 그리고, 후술되는 용어들은 본 발명에서의 기능을 고려하여 정의 내려진 용어들로서 이는 사용자 또는 칩 설계자의 의도 또는 관례 등에 따라 달라질 수 있으며, 그 정의는 본 명세서 전반에 걸친 내용을 토대로 내려져야 할 것이다.DETAILED DESCRIPTION A detailed description of preferred embodiments of the present invention will now be described with reference to the accompanying drawings. In the following description of the reference numerals to the components of the drawings it should be noted that the same reference numerals as possible even if displayed on different drawings. In addition, in describing the present invention, when it is determined that a detailed description of a related known function or configuration may unnecessarily obscure the subject matter of the present invention, the detailed description thereof will be omitted. In addition, terms to be described below are terms defined in consideration of functions in the present invention, which may vary according to the intention or custom of a user or a chip designer, and the definitions should be made based on the contents throughout the present specification.
후술될 본 발명에서는, 특정 MBMS의 제공을 요구하는 복수의 UE들로부터의 MBMS 응답메시지들이 도착하는 상황에 따라 지속값(이하 "Pmbms"로 칭함)을 조절하고, 상기 복수의 UE들이 상기 조절된 Pmbms에 의해 RACH의 할당 요청을 제어하는 방안을 제안할 것이다. 즉, 하나의 MBMS 제어 메시지가 다수의 응답메시지들을 촉발하는 상황에서, UE들이 상기 MBMS 제어 메시지에 대해 응답메시지를 전송 시 이용할 Pmbms를 제시하고, 이 후 상기 UE들의 응답 메시지 전송 성공율 등을 고려하여 상기 Pmbms를 지속적으로 갱신시켜 주는 것이다. 상기 Pmbms를 지속적으로 갱신하는 것은 상기 UE들의 응답 메시지 전송 성공율 등을 고려하여 Pmbms를 변경하고, 상기 변경된 Pmbms를 UE들에게 알려주는 과정을 반복하는 것에 의해 수행된다.In the present invention to be described later, the duration value (hereinafter referred to as "P mbms ") is adjusted according to the situation in which the MBMS response messages from the plurality of UEs requesting the provision of a specific MBMS arrives, and the plurality of UEs adjust the adjustment. We will propose a method of controlling the allocation request of the RACH by the P mbms . That is, in a situation where one MBMS control message triggers a plurality of response messages, the UE presents P mbms to be used when transmitting a response message to the MBMS control message, and then considers the success rate of response messages of the UEs. This is to continuously update the P mbms . It is continually updated as the P mbms is performed by changing the P mbms in consideration of the response message transmission success rate of the UE, and the process is repeated indicating the changed P mbms to the UE.
이하 본 발명의 실시 예를 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 상세히 설명하면 다음과 같다.Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
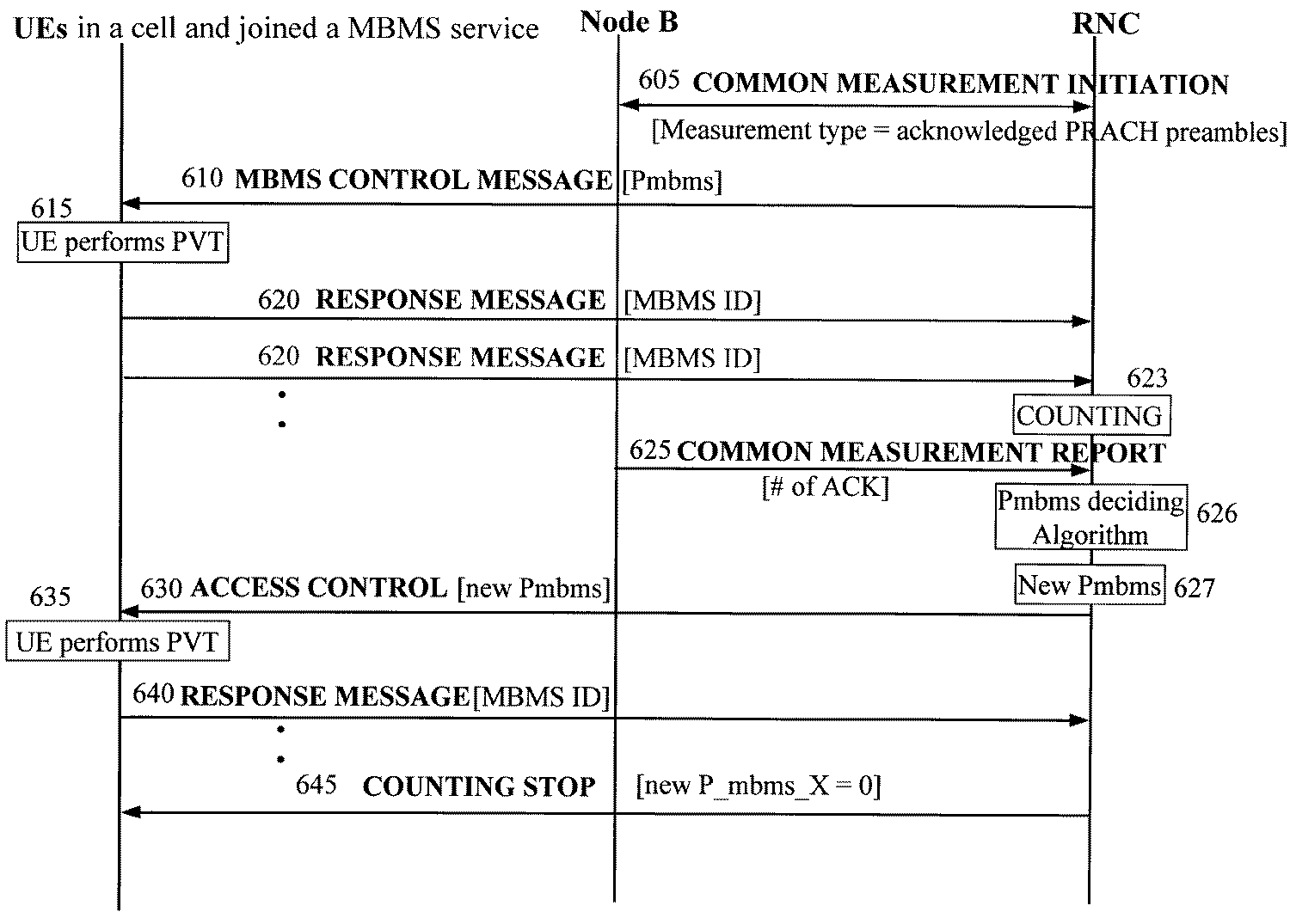
도 6은 본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 이동통신시스템에서의 시그널링 절차를 보이고 있는 도면이다. 상기 도 6에서의 시그널링은 특정 셀에 위치하고 있으면서 특 정 MBMS를 제공받고 있거나 제공받고자 하는 UE들을 대상으로 한다. 6 is a diagram illustrating a signaling procedure in a mobile communication system according to an embodiment of the present invention. The signaling in FIG. 6 targets UEs that are located in a specific cell and are provided or want to receive a specific MBMS.
상기 도 6을 참조하면, 605단계에서 RNC와 Node B간에 COMMON MEASUREMENT INITIATION 절차가 이루어진다. 상기 COMMON MEASUREMENT INITIATION 절차는 상기 RNC가 상기 Node B로 COMMON MEASUREMENT INITIATION REQUEST 메시지를 보냄으로써 시작되며, 상기 Node B가 상기 RNC로 COMMON MEASUREMENT INITIATION RESPONSE 메시지를 전송함으로써 완료된다. 상기 COMMON MEASUREMENT INITIATION 절차를 위해 전송되는 메시지들은 3GPP TS 25.433에 자세히 기술되어 있으므로 설명은 생략한다. 상기 COMMON MEASUREMENT INITIATION 절차를 통해 상기 RNC는 MBMS가 제공될 셀에 대해 "acknowledged PRACH preambles"라는 측정을 구성한다. 이는 특정 셀에서 20 msec 단위로, acknowledged PRACH preamble의 개수를 측정해서 보고하도록 요청하는 것이다. 상기 보고과정은 625단계의 COMMON MEASUREMENT REPORT라는 메시지를 통해 이루어진다. 상기 acknowledged PRACH preamble은 향후 RNC가 Pmbms를 변경할 때, 참고 데이터로 사용할 수 있다. 상기 COMMON MEASUREMENT에 대해서는 625단계에서 다시 설명한다.Referring to FIG. 6, a common measurement initialization procedure is performed between the RNC and the Node B in
상기 RNC는 610단계에서 특정 MBMS의 제공을 원하는 복수의 UE들로부터의 응답메시지들을 촉발하는 MBMS CONTROL 메시지를 전송한다. 상기 MBMS CONTROL 메시지에는 Pmbms의 초기 값이 포함된다. 상기 Pmbms의 초기 값은 해당 셀에서 응답 메시지를 전송할 것이 예산되는 UE들의 수와 해당 셀의 PRACH 자원 상황을 고려해서 결정하는 것이 바람직할 것이다. 일 예로써 상기 Pmbms의 초기 값은 BOW_X_Y의 역수로 결정할 수 있다. 이에 대해 부연 설명하자면, 상기 BOW_X_Y는 특정 셀에서 MBMS 제어 메시지에 대한 응답 메시지를 전송할 UE들의 수와 해당 셀의 PRACH 자원 상황을 고려했을 때, 가장 적절한 Back-off window의 크기를 의미한다. 상기 BOW_X_Y는 10 msec 단위를 가지는 정수이다. 상기 UE는 0에서 BOW_X_Y 사이의 값들 중 하나의 값을 동일한 확률로 선택하고, 상기 선택된 값만큼 대기한 후 RACH 동작을 시작한다. 다시 말해서 상기 BOW_X_Y의 역수는 임의의 UE가 가장 효율적으로 동작하고 있다고 가정할 경우, 상기 UE가 특정 시점에서 RACH 동작을 시작할 확률을 의미할 수 있다. 물론 상기 Pmbms의 초기 값을 일률적으로 특정 값으로 설정할 수도 있다. 그 이유로는, 상기 Pmbms의 초기 값이 너무 큰 값으로 설정되어, RACH 혼잡 상황이 발생하더라도, 추후 RNC가 Pmbms를 조정함으로써 혼잡 상황을 해소할 것이다. 한편, 상기 Pmbms의 초기 값이 너무 작은 값으로 설정되어 응답 메시지의 전송이 더디게 진행되더라도, 추후 RNC가 Pmbms를 조정함으로써 그 상황을 개선할 것이기 때문이다. 다만 Pmbms의 초기 값을 적절한 값으로 설정할 경우, 상기 조정의 정도가 작으므로 RACH 성능 개선의 정도가 더욱 커질 수 있다는 장점이 있다.In
상기 MBMS CONTROL 메시지를 수신한 UE들은 응답메시지를 전송하기에 앞서 수신한 Pmbms의 초기 값을 이용해서 PVT를 수행한다(615단계). 상기 UE들은 상기 Pmbms를 이용해서 수행한 PVT를 통과할 시 620단계에서 응답메시지를 전송한다. 상기 PVT는 UE별로 수행됨에 따라 상기 응답 메시지의 전송 또한 UE별로 수행하게 된다. 상기 응답메시지는 RRC CONNECTION REQUEST 등의 메시지가 될 수 있으며, 상기 메시지에는 MBMS ID가 포함된다. UEs receiving the MBMS CONTROL message perform PVT using the initial value of the received P mbms prior to transmitting the response message (step 615). The UEs transmit a response message in
상기 RNC는 623단계에서 상기 UE별로 수신되는 응답메시지에 포함된 MBMS ID를 이용해서 카운팅 동작을 수행한다. 상기 카운팅 동작은 특정 MBMS 제어 메시지에 대하여 상기 UE별로 전송하는 응답 메시지의 수를 세다가, 일정 조건이 충족되면 UE들로부터의 응답메시지 전송을 중지시키는 동작을 의미한다. 상기 일정 조건은, 상기 MBMS를 제공받고자 하는 UE들 중 RRC 연결을 가지는 UE의 수가 MBMS 임계 값과 같아지는 경우가 될 수 있다.The RNC performs a counting operation using the MBMS ID included in the response message received for each UE in
상기 Node B는 625단계에서 COMMON MEASUREMENT REPORT 메시지를 통해, 최근 20 msec 동안 특정 MBMS를 제공받고자 프리앰블을 전송한 UE들에게 보내진 acknowledgement의 수(이하 "# of ACK"이라 칭함)를 보고한다. 상기 COMMON MEASUREMENT REPORT 메시지를 통해 # of ACK가 보고되는 것은 상기 605단계에서 구성된 "acknowledged PRACH preambles"라는 측정에 대응한 것이다. 상기 acknowledgement는 AICH를 통해 전송되는 순방향 신호이다. 일반적으로 t라는 시점에 n개의 acknowledgement가 보내졌다는 것은, t보다 조금 이후 시점에 n 명의 UE들이 RACH를 이용해서 메시지를 전송함을 의미한다. 그러나 다수의 UE들이 동일한 시그네쳐를 사용하였다면, 상기 UE들은 메시지 전송에 실패할 것으로 상기 # of ACK은 RNC가 수신할 응답메시지의 수와 관련된다. 또한 상기 # of ACK은 해당 셀에서 RACH가 사용되고 있는 정도를 나타낸다. 즉, 상기 # of ACK의 크기가 클수록, 해당 셀에서 많은 UE들이 RACH 사용을 시도함을 의미한다. 이 경우는 그만큼 RACH 혼잡 상황이 발생할 확률이 높아진다. 한편 상기 # of ACK이 작을수록, 해당 셀에서 소수의 UE들이 RACH 사용을 시도함을 의미하며, 이 경우는 주어진 RACH 자원의 효율적인 사용이 이루어지고 있지 못하다는 것이다.The Node B reports the number of acknowledgments (hereinafter referred to as "# of ACK") sent to UEs that transmit a preamble for a specific MBMS for the last 20 msec through a COMMON MEASUREMENT REPORT message in
상기 RNC는 626단계에서 상기 Pmbms의 조정 여부와 조정이 필요할 시 상기 Pmbms를 조정하여 새로운 Pmbms를 결정하는 Pmbms deciding algorithm을 실행한다. 상기 도면에는 편의상 상기 Pmbms deciding algorithm의 실행을 상기 625단계 이후로 표시하였지만, 실제로는 상기 610단계에서 특정 MBMS에 대한 제어메시지를 전송하면서 시작된다.The RNC adjusts the P mbms when adjustments are required and whether the adjustment of the P mbms at
[ Pmbms deciding algorithm ][P mbms deciding algorithm]
먼저 RNC는 Pmbms 갱신 주기가 시작되면, 상기 Pmbms 갱신 주기동안 COMMON MEASUREMENT REPORT 메시지들을 통해 수신한 # of ACK들을 모두 합하고, 상기 합에 의해 얻어진 값을 total # of ACK으로 갱신한다. 상기 Pmbms 갱신 주기는 Pmbms 갱신을 결정하는 시간 단위이다. 상기 RNC는 매 Pmbms 갱신 주기가 끝나는 시점에서 Pmbms의 조정 여부와 조정 크기를 결정한다. 상기 Pmbms 갱신 주기의 시작 시점은 상기 Pmbms deciding algorithm의 시작을 촉발한 MBMS 제어 메시지의 전송이 완료된 시점이다. 상기 RNC는 상기 Pmbms 갱신 주기가 끝나는 시점마다 상기 Pmbms의 조정 여부를 결정한다. 즉, 상기 RNC는 상기 total # of ACK이 congestion threshold_up보다 작 을 경우, 기존의 Pmbms를 PV STEP SIZE만큼 높여 새로운 Pmbms로 결정하고, 상기 새로이 결정된 Pmbms를 UE들에게 전달한다. 앞에서 살펴보았듯이 상기 total # of ACK은 일정 기간 동안 AICH를 통해 전송된 ACK의 개수를 의미한다. 상기 파라미터는 Pmbms의 갱신 주기동안 UE들의 RACH 사용 시도 빈도 수와 연관이 있다. 즉, 상기 total # of ACK이 크다면 많은 UE들이 RACH를 사용하고자 시도하였음을 의미하며, 상기 total # of ACK이 작다면 소수의 UE들이 RACH를 사용하고자 시도하였음을 의미한다. 그러므로 상기 total # of ACK이 지나치게 작을 경우, 상기 Pmbms를 높여서, UE들의 RACH 사용 시도를 늘리는 것이 바람직하다. 하지만, 상기 total # of ACK이 congestion threshold_down보다 클 경우, 상기 Pmbms를 PB STEP SIZE 만큼 낮춤으로써 UE들의 RACH 사용 시도 빈도를 줄이는 것이 바람직할 것이다. 마지막으로 상기 RNC는 상기 total # of ACK이 congestion threshold_down과 congestion threshold_up 사이의 값일 경우, 기존의 Pmbms를 그대로 유지한다. 상기 Pmbms 갱신 주기, congestion threshold_up, congestion threshold_down, STEP SIZE는 RNC가 상황에 따라 결정하는 내부 파라미터이다. 상기 값들은 필드 테스트 등을 통해 적절한 값이 정해질 수 있을 것이다.First, when the RNC starts updating period mbms P, the P mbms update period for COMMON MEASUREMENT REPORT combined and all of the # ACK of the message received on, and updates the value obtained by the sum total # of the ACK. The P mbms update period is a unit of time for determining P mbms update. The RNC determines whether to adjust P mbms and the size of adjustment at the end of every P mbms update period. The start time of the P mbms update period is a time when the transmission of the MBMS control message that triggered the start of the P mbms deciding algorithm is completed. The RNC determines whether to adjust the P mbms every time the P mbms update period ends. That is, when the total # of ACK is smaller than the congestion threshold_up, the RNC increases the existing P mbms by PV STEP SIZE to determine a new P mbms and delivers the newly determined P mbms to the UEs. As described above, the total # of ACK means the number of ACKs transmitted through the AICH for a certain period of time. The parameter is related to the frequency of RACH usage attempts of UEs during an update period of P mbms . That is, if the total # of ACK is large, this means that many UEs have attempted to use the RACH. If the total # of ACK is small, it means that a small number of UEs have attempted to use the RACH. Therefore, when the total # of ACK is too small, it is desirable to increase the P mbms, to increase the attempt to use the RACH of the UEs. However, if the total # of ACK is greater than the congestion threshold_down, it may be desirable to reduce the frequency of UE attempts to use RACH by lowering the P mbms by PB STEP SIZE. Finally, the RNC maintains the existing P mbms when the total # of ACK is a value between the congestion threshold_down and the congestion threshold_up. The P mbms update period, the congestion threshold_up, the congestion threshold_down, and the STEP SIZE are internal parameters determined by the RNC according to the situation. The values may be determined appropriately through field tests.
상기 Pmbms 갱신 주기의 크기는 20msec의 배수로 결정될 수 있다. 상기 Pmbms 갱신 주기의 크기가 클 수록 Pmbms 갱신 동작이 더디게 진행되지만 상기 Pmbms의 결정 이 신중하게 이루어진다. 이에 반하여 상기 Pmbms 갱신 주기의 크기가 작을수록 Pmbms 갱신 동작은 빠르게 진행되지만 Pmbms 결정에 오차가 개입할 소지가 크다.The size of the P mbms update period may be determined in multiples of 20 msec. The larger the size of the P mbms update period is, the slower the P mbms update operation is, but the determination of the P mbms is made more carefully. On the other hand, the smaller the size of the P mbms update period is, the faster the P mbms update operation proceeds, but there is a greater possibility of error in P mbms determination.
상기 RNC는 627단계에서 Pmbms가 변경되었다면, 630단계에서 상기 변경에 의해 새로이 결정된 Pmbms를 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지에 담아서 UE들에게 전송한다. 상기 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지는 셀 내에 있는 모든 UE들이 수신할 수 있는 방송 채널로써, 논리채널로는 MBMS 제어채널(이하 "MCCH"라 칭함)을 통해 물리계층으로 제공된다. 상기 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지를 포함하는 MCCH는 물리채널을 통해 셀 내의 UE들에게 전송된다. 이때, 상기 물리채널로는 제2공통제어물리채널(S-CCPCH : Secondary Common Control Physical Channel)이 될 수 있다. 상기 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지 포맷의 일 예는 하기 <표 1>과 같다.If in
상기 <표 1>에서 보이고 있는 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지는 Message Type, MBMS ID, Pmbms로 구성된다. 상기 Message Type은 해당 메시지가 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지임을 나타내는 Information Element(이하 "IE"로 칭함)이다. 상기 MBMS ID는 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지가 영향을 미치는 MBMS의 식별자이다. 상기 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지를 수신한 UE들은 상기 IE를 이용해서, 자신의 Pmbms 갱신 여부를 판단한다. 즉, 임 의의 UE가 특정 MBMS에 연결된 상황에서, 상기 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지를 수신하였으며, 상기 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지의 MBMS ID가 상기 특정 MBMS라면 상기 메시지에 포함된 정보가 유효한 것으로 판단한다. 하지만 상기 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지의 MBMS ID가 상기 특정 MBMS가 아닌 다른 값이라면, 상기 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지에 포함된 정보를 무시한다. 상기 Pmbms는 UE들이 MBMS와 관련된 응답 메시지를 RACH를 통해 전송 시 사용할 Persistence value이다. 상기 MBMS와 관련이 없는 역방향 데이터 전송에는 상기 Persistence Value를 사용하지 않는다.The ACCESS CONTROL message shown in Table 1 is composed of Message Type, MBMS ID, and P mbms . The Message Type is an information element (hereinafter referred to as "IE") indicating that the message is an ACCESS CONTROL message. The MBMS ID is an identifier of the MBMS to which the ACCESS CONTROL message affects. UEs receiving the ACCESS CONTROL message use the IE to determine whether to update their P mbms . That is, when an arbitrary UE is connected to a specific MBMS, if the ACCESS CONTROL message is received, and the MBMS ID of the ACCESS CONTROL message is the specific MBMS, it is determined that the information included in the message is valid. However, if the MBMS ID of the ACCESS CONTROL message is a value other than the specific MBMS, the information included in the ACCESS CONTROL message is ignored. The P mbms is a Persistence value that UEs will use when transmitting a response message related to MBMS through the RACH. The Persistence Value is not used for reverse data transmission that is not related to the MBMS.
상기 특정 MBMS의 제공받기를 원하는 UE들 중 RACH 사용에 성공하지 못한 UE들은 635단계에서 새로운 Pmbms로 갱신한 뒤, 그 값을 이용해서 PVT를 시도한다. 상기 새로운 Pmbms를 이용해서 수행한 PVT가 성공한 UE들은 640단계에서 RRC CONNECTION REQUEST 메시지와 같은 응답 메시지를 RACH를 통해 전송한다.UEs that do not succeed in using RACH among UEs that want to be provided with the specific MBMS update to a new P mbms in
상기 RNC는 상기 UE별로 수신되는 응답메시지에 대한 카운팅 동작을 지속하다가, MBMS 임계 값만큼의 UE들에 대한 응답 메시지들을 수신하였다면, 645단계로 진행하여 COUNTING STOP 메시지를 전송한다. 상기 COUNTING STOP 메시지는 Pmbms을 0으로 설정한 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지로 대체할 수도 있다.The RNC continues the counting operation for the response message received for each UE. If the RNC receives response messages for UEs corresponding to MBMS thresholds, the RNC proceeds to step 645 and transmits a COUNTING STOP message. The COUNTING STOP message may be replaced with an ACCESS CONTROL message in which P mbms is set to zero.
전술한 바와 같이 본 발명의 실시 예에서는 RNC가 특정 MBMS에 대한 제어 메시지를 전송하고, 상기 MBMS 제어 메시지가 다수의 응답 메시지들을 촉발하며, 상기 다수의 응답 메시지들이 RACH를 통해 전송될 때, 상기 응답 메시지들을 전송하는 UE들이 RACH 사용에 성공할 확률인 Persistence Value를 RACH 상황에 맞춰 조절 함으로써, RACH에 발생할 수 있는 혼잡상황을 회피하는 방식이다. 이 때, RNC는 임의시점에서 RACH의 상태를 판단하기 위해, Node B가 보고하는 COMMON MEASUREMENT REPORT의 acknowledged PRACH preamble 값을 이용할 수 있다.As described above, in the embodiment of the present invention, when the RNC transmits a control message for a specific MBMS, the MBMS control message triggers a plurality of response messages, and the plurality of response messages are transmitted through the RACH, the response The UE transmitting the messages adjusts the Persistence Value, which is a probability of success in using the RACH, according to the RACH situation, thereby avoiding congestion that may occur in the RACH. At this time, the RNC may use the acknowledged PRACH preamble value of the COMMON MEASUREMENT REPORT reported by the Node B to determine the state of the RACH at any time.
도 7은 본 발명의 실시 예에 따라 Pmbms가 지속적으로 갱신되는 경우 UE MAC에서의 RACH 동작을 수행되는 제어 흐름을 보이고 있는 도면이다. 하기에서의 MAC, RRC, RLC, 물리계층 등은 3GPP TS 25.301에 기술되어 있는 프로토콜 엔터티들을 지시한다.7 is a diagram illustrating a control flow of performing a RACH operation in a UE MAC when P mbms is continuously updated according to an embodiment of the present invention. The MAC, RRC, RLC, physical layer, etc. below indicate protocol entities described in 3GPP TS 25.301.
상기 도 7을 참조하면, UE의 RRC는 705단계에서 RACH 전송 제어 정보를 상기 UE의 MAC으로 전달한다. 상기 RACH 전송 제어 정보로는 아래와 같은 것들이 있으며, 이 중 Pmbms는 본 발명을 위해 제안된 파라미터이다.Referring to FIG. 7, the RRC of the UE transmits RACH transmission control information to the MAC of the UE in
RACH 전송 제어 정보 = M_max, N_BO1min, N_BO1max, ASC parameters, Pmbms RACH transmission control information = M_max, N_BO1min, N_BO1max, ASC parameters, Pmbms
상기 파라미터들 중, M_max, N_BO1min, N_BO1max, ASC parameters는 시스템 정보를 통해 취득하는 정보들이다. 상기 UE의 RRC는 상기 정보를 최초 취득하거나, 갱신된 정보를 취득할 경우 CMAC-CONFIG-Req라는 프리미티브를 통해 상기 UE의 MAC에게 전달한다. 상기 파라미터들의 용도에 대해서는 하기 해당 부분에서 다시 설명하도록 한다.Among the parameters, M_max, N_BO1min, N_BO1max, and ASC parameters are information obtained through system information. When the RRC of the UE acquires the information for the first time or obtains the updated information, the RRC of the UE transmits the information to the MAC of the UE through a primitive called CMAC-CONFIG-Req. The use of these parameters will be described later in the relevant section.
상기 파라미터들 중, Pmbms는 본 발명을 위해 제안된 파라미터로써, 그룹 응답을 요구하는 MBMS 제어 메시지를 통해 수신하거나, 시스템 정보를 통해 취득할 수 있다. 예를 들어 상기 도 6에서 보이고 있는 MBMS CONTROL 메시지의 Pmbms 필드를 통해 RNC가 UE에게 전달할 수 있다. 다른 예로써 기존 시스템 정보에 Pmbms 필드를 추가해서 UE에게 전달할 수 있다. 상기 UE의 RRC는 상기 Pmbms를 최초 취득하거나, 갱신된 Pmbms를 취득할 경우 CMAC-CONFIG-Req라는 프리미티브를 통해 상기 UE의 MAC으로 전달한다. Among the parameters, P mbms is a parameter proposed for the present invention, and can be received through an MBMS control message requesting a group response or acquired through system information. For example, the RNC can deliver to the UE through the P mbms field of the MBMS CONTROL message shown in FIG. As another example, the P mbms field may be added to the existing system information and transmitted to the UE. Of the UE RRC transmits the first case to obtain the acquired or updated P mbms the P mbms through the primitive called CMAC-CONFIG-Req to the MAC of the UE.
상기에서 프리미티브란 계층들간 전달되는 정보의 묶음을 명명한 것이다. 현재 3GPP 규격에서는 RRC와 MAC 사이에 다양한 종류의 프리미티브를 규정하고 있다. 상기 CMAC-CONFIG-Req는 RRC가 MAC으로 제어정보를 전달할 때 주로 사용하는 프리미티브이다. 상기 Pmbms는 UE가 관리하는 P_mbms 변수에 저장되어 있다.In the above description, a primitive refers to a bundle of information transmitted between layers. The 3GPP specification currently defines various kinds of primitives between RRC and MAC. The CMAC-CONFIG-Req is a primitive mainly used when the RRC transfers control information to the MAC. The P mbms is stored in a P_mbms variable managed by the UE.
상기 UE는 710단계에서 그룹 응답이 필요하다고 판단될 때까지 대기하며, 상기 그룹 응답이 필요하다고 판단될 시 715단계로 진행한다. 상기 그룹 응답은 임의의 응답메시지를 전송할 때, 다른 UE들도 동일한 목적의 응답메시지를 전송할 가능성이 높은 응답메시지를 의미한다. 상기 UE는 특정 역방향 메시지의 그룹 응답 여부를 아래 기준으로 판단한다. The UE waits until it is determined that a group response is necessary in
[ 그룹 응답 판단 기준 ][Group Response Criteria]
1. 역방향 메시지가 MBMS 관련 메시지일 것.1. Reverse message is MBMS related message.
2. Pmbms가 P_mbms 변수에 저장되어 있을 것.2. P mbms should be stored in the P_mbms variable.
상기 MBMS 관련 메시지에는 MBMS ID를 포함하는 RRC CONNECTION REQUEST 메시지 등도 포함된다. The MBMS related message also includes an RRC CONNECTION REQUEST message including an MBMS ID.
상기 그룹 응답의 필요로 인해 상기 715단계로 진행할 시 상기 UE는 ASC 선택을 한 후 상기 선택한 ASC의 PRACH partition을 확인하고, P_mbms 변수에서 Pmbms를 확인한다. 상기 ASC 선택 방식에 대해서는 3GPP TS 25.321에 잘 기술되어 있다. 이를 간단히 설명하자면, 상기 ASC 선택은 RACH로 전송할 데이터의 우선순위에 따라 RACH 동작에 사용될 ASC를 선택하는 것을 의미한다. 상기 데이터의 우선순위는 상기 데이터가 전송되는 논리 채널(logical channel)의 우선순위(MLP: MAC Logical Channel Priority)에 의해서 결정되며, 상기 우선순위는 RRC connection setup 과정 등을 통해 논리 채널별로 UE에게 통보된다. 상기 ASC는 8개의 등급으로 구성되며, 각 등급별로 사용될 PRACH 자원이 결정되어 있다. 이를 PRACH partition이라고 한다. 상기 715단계에서 PRACH partition i는 UE가 ASC 선택 과정을 통해 ASC i를 선택하였을 경우 ASC i에 할당되어 있는 PRACH 자원을 의미한다. 상기 PRACH partition i는 시그네쳐(signature)들과 액세스 슬롯(access slot)들을 포함한다. When the UE proceeds to step 715 due to the necessity of the group response, the UE selects the ASC, checks the PRACH partition of the selected ASC, and checks P mbms in the P_mbms variable. The ASC selection scheme is well described in 3GPP TS 25.321. In brief, the ASC selection means selecting an ASC to be used for the RACH operation according to the priority of data to be transmitted to the RACH. The priority of the data is determined by the priority (MLP: MAC Logical Channel Priority) of the logical channel through which the data is transmitted, and the priority is notified to the UE for each logical channel through an RRC connection setup process. do. The ASC is composed of eight classes, and the PRACH resources to be used for each class are determined. This is called a PRACH partition. In
상기 UE는 720단계에서는, RACH 동작(725단계 내지 775단계)의 시도 회수를 제어하는 변수인 M을 0으로 설정한다. 상기 M은 상기 RACH 동작이 반복될 때마다 725단계에서 1씩 증가하며, 730단계에서 상기 M이 M_ max보다 크거나 같아지면, 735단계로 진행한다. 상기 75단계로 진행할 시 상기 UE는 RACH를 통한 데이터 전송이 실패하였음을 통보하고, RACH 과정을 종료한다. 도면에서 preamble cycle은 745단계에서 775단계사이의 동작을 의미하는 것으로써, RACH 전송제어정보를 갱신하면서 시작하여 물리계층으로부터 L1 억세스 정보(access info)를 전달받으면서 완료 되는 주기이다. 상기 변수 M_max는 시스템 정보를 통해 UE에게 통보되며, 네트워크는 상기 M_max를 적절히 조정함으로써, UE가 RACH 전송 시도를 필요이상으로 반복하는 것을 막을 수 있다. In
상기 UE는 745단계에서 RACH 전송제어정보를 갱신한다. 상기 RACH 전송제어정보의 갱신은, RRC가 갱신된 시스템 정보를 수신한 뒤, CMAC-CONFIG-Req 프리미티브를 MAC으로 전달함으로써 이루어진다. 또는 Pmbms의 경우, RRC가 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지를 수신하고, 새로운 Pmbms를 포함하는 CMAC-CONFIG-Req 프리미티브를 MAC으로 전달함으로써 이루어진다. The UE updates RACH transmission control information in
상기 UE는 750단계에서 T2 타이머를 설정한다. 상기 T2 타이머의 용법에 대해서는 767단계에서 설명한다.The UE sets a T2 timer in
상기 UE는 760단계에서 0에서 1사이의 실수인 R1을 무작위로 선택한다. 상기 765단계에서는 상기 R1과 Pmbms의 크기를 비교해서, 상기 Pmbms가 크거나 같은 경우 770단계로 진행한다. 그렇지 않고 R1이 클 경우에는 767단계로 진행한다. 상기 760단계와 상기 765단계를 Persistence Value Test라고 명명한다. In
상기 UE는 상기 767단계에서 새로운 PVT를 수행하기에 앞서, 상기 설정한 T2 만큼 대기한 후 상기 745단계로 진행한다. 상기 767단계를 두는 이유는, 상기 UE가 새로운 PVT를 시도하기 전에 일정시간 대기하도록 하는 것이다. 만약 상기 767단계가 없다면, 상기 UE는 PVT가 실패하는 즉시 새로운 PVT를 시도하는 동작을 PVT가 성공할 때까지 반복할 것이므로, PVT의 의미가 없어지기 때문이다. 상기 T2 값은 예를 들어 10msec 정도로 설정될 수 있을 것이다.Before the UE performs the new PVT in
상기 760단계와 상기 765단계의 PVT를 통과한 UE는 770단계에서 PHY-ACCESS-REQ 프리미티브를 물리계층으로 전달한다. 상기 PHY-ACCESS-REQ 프리미티브에는 상기 715에서 선택된 ASC의 PRACH partition의 식별자가 포함된다.The UE, which has passed the PVT of
상기 PHY-ACCESS-REQ 프리미티브를 전달받은 물리계층은, 상기 PHY-ACCESS-REQ 프리미티브에 포함된 PRACH partition 식별자에 대응되는 PRACH partition을 이용해서, 프리앰블 전송 과정을 실행한다. 상기 과정에 대해서는 3GPP TS 25.214에 자세히 기술되어 있다. 이를 간략하게 설명하면, 물리계층은 해당하는 PRACH partition에 할당된, 시그네쳐들 중 하나의 시그네쳐와 액세스 슬롯들 중 하나의 액세스 슬롯을 무작위로 선택하고, 상기 선택된 시그네쳐와 액세스 슬롯을 통해 프리앰블을 전송하고, AICH를 감시한다. 만약 AICH를 통해 ACK 신호를 수신하면, 이를 PHY-ACCESS-CNF라는 프리미티브의 L1 access info를 통해 MAC에 보고한다. 상기 ACK 신호가 아닌 NACK 신호를 수신하면, 마찬가지로 PHY-ACCESS-CNF의 L1 access info를 통해 MAC에 보고한다. 하지만, AICH를 통해 아무런 신호도 감지되지 않는다면, 전송 전력을 스텝 사이즈만큼 증가시켜서 프리앰블을 재 전송한다. 이 과정을 ACK 또는 NACK 신호를 수신하거나, 프리앰블의 전송 전력이 일정 값 이상이 될 때까지 반복한다. 상기 프리앰블의 전송 전력이 일정 값 이상이 될 경우, no ack 상황으로 인지하고, 이를 PHY-ACCESS-CNF의 L1 access info를 통해 MAC에 보고한다.The physical layer receiving the PHY-ACCESS-REQ primitive executes a preamble transmission process using a PRACH partition corresponding to a PRACH partition identifier included in the PHY-ACCESS-REQ primitive. This process is described in detail in 3GPP TS 25.214. In brief, the physical layer randomly selects a signature of one of the signatures and an access slot of one of the access slots assigned to the corresponding PRACH partition, and transmits a preamble through the selected signature and the access slot. , Monitor the AICH. If the ACK signal is received through the AICH, it is reported to the MAC through the L1 access info of the PHY-ACCESS-CNF primitive. When the NACK signal is received instead of the ACK signal, it is reported to the MAC through the L1 access info of the PHY-ACCESS-CNF. However, if no signal is detected through the AICH, the preamble is retransmitted by increasing the transmit power by the step size. This process is repeated until the ACK or NACK signal is received or the transmit power of the preamble is greater than or equal to a predetermined value. When the transmission power of the preamble is greater than or equal to a predetermined value, the preamble is recognized as a no ack situation and reported to the MAC through the L1 access info of the PHY-ACCESS-CNF.
775단계에서 MAC은 물리계층이 전송한 PHY-ACCESS-CNF의 L1 access info의 값을 해석해서, 다음 행동을 결정한다. 만약 L1 access info가 no Ack일 경우 755 단계로 진행하고, ACK일 경우에는 780단계로 진행하며, NACK일 경우에는 777단계로 진행한다.In
상기 L1 access info가 'No Ack'인 경우 데이터를 전송할 수 없으므로, 상기 725단계부터 RACH 과정을 다시 수행한다. 이 때 상기 RACH 과정 재 시작 전에 755단계에서 T2만큼 대기한 후 상기 725단계로 진행한다.If the L1 access info is 'No Ack', data cannot be transmitted. Therefore, the RACH process is performed again from
상기 L1 access info가 'Nack'인 경우 마찬가지로 데이터를 전송할 수 없으므로, 상기 725단계부터 RACH 과정을 다시 수행한다. 이 때 상기 RACH 과정을 재 시작 전에 777단계에서 T2만큼 대기하고, 779단계에서 다시 TBO1만큼 대기한 후 상기 725단계로 진행한다. 상기 TBO1은 NBP1 ×10 msec이며, 상기 NBO1은 NBO1max
와 NBO1min 사이에서 무작위로 추출된 임의의 값이다. 상기 과정은 NACK 신호를 수신한 UE들이 RACH 동작을 재 시도하기 전 대기 시간을 무작위로 선택하는 효과를 제공한다. When the L1 access info is 'Nack', data cannot be transmitted in the same manner, so the RACH process is performed again from
상기 L1 access info가 'ACK' 인 경우, MAC은 780단계에서 전송할 데이터를 PHY-DATA-REQ라는 프리미티브에 담아서, 물리계층으로 전달한다. 상기 물리계층은 상기 프리미티브에 담겨있는 데이터를 PRACH를 통해 전송한다. If the L1 access info is 'ACK', the MAC transmits the data to be transmitted to the physical layer in a primitive called PHY-DATA-REQ in
전술한 도 7에서 제시하고 있는 본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 UE의 RACH 동작은 통상적인 RACH 동작과 아래에서 제안한 바에 의해 차별화될 수 있을 것이다.The RACH operation of the UE according to the embodiment of the present invention shown in FIG. 7 described above may be differentiated from the conventional RACH operation by the following proposal.
첫 번째로, 705단계에서 UE의 MAC은 RACH 전송 제어 정보로 Pmbms를 추가로 취득한다.First, in
두 번째로, 710단계에서 UE의 MAC은 그룹 응답을 RACH를 통해 전송할 필요가 있을 때 상기 과정을 진행한다. 통상적인 RACH 동작은 RACH를 통해 역방향 데이터를 전송할 필요가 있을 때 RACH동작을 실행한다.Secondly, in
세 번째로, 715단계에서 UE의 MAC은 선택된 ASC의 persistence value를 사용하지 않고 Pmbms를 사용한다.Thirdly, in
네 번째로, 745단계에서 UE의 MAC은 RACH 전송 제어 정보 갱신 과정에서 Pmbms 갱신도 함께 수행한다.Fourth, in
다섯 번째로, 765단계에서 UE의 MAC은 715단계에서 선택된 ASC의 persistence value를 사용하지 않고 Pmbms를 사용한다.Fifth, in
도 8은 본 발명의 실시 예에 따라 UE가 Pmbms를 갱신하기 위한 제어 흐름을 보이고 있는 도면이다.8 is a diagram illustrating a control flow for updating a UE P mbms according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 8을 참조하면, UE은 805단계에서 RNC로부터 Pmbms를 포함하는 임의의 메시지를 수신할 시 810단계로 진행한다. 예를 들어 상기 Pmbms는 상기 도 6에서의 MBMS CONTROL 메시지와 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지를 통해 수신할 수 있다. 상기 UE는 상기 810단계로 진행할 시 상기 수신한 임의의 메시지에 포함된 MBMS ID와, 자신이 연결 단계(JOINING STEP)를 수행한 MBMS의 MBMS ID를 비교한다. 상기 두 MBMS ID들이 일치한다면 상기 UE는 815단계로 진행하고, 일치하지 않는다면 상기 805단계로 진행하여 다른 Pmbms가 도착하기를 기다린다.Referring to FIG. 8, the UE proceeds to step 810 when receiving an arbitrary message including P mbms from the RNC in
상기 815단계로 진행하면 상기 UE의 RRC는 상기 수신한 Pmbms를 CMAC-CONFIG- Req 프리미티브에 포함시켜 MAC으로 전달한다. 상기 UE의 MAC은 820단계에서 상기 전달받은 Pmbms를 P_mbms 변수에 저장한 후 Pmbms를 갱신하기 위한 절차를 종료한다. 상기 UE의 MAC은 상기 P_mbms 변수에 이미 다른 값이 저장되어 있으면, 저장되어 있는 값을 새로운 값으로 갱신한다. 상기 P_mbms 변수는 특정 UE가 Pmbms 값을 저장해두는 변수로, 상기 전술한 절차를 통해 갱신된다. 한편, 상기 UE의 MAC은 그룹 응답 메시지의 전송을 위한 RACH 과정이 종료되면, 상기 P_mbms 변수를 지운다.In
도 9는 본 발명의 실시 예에 따라 UE가 RNC로부터의 MBMS 제어 메시지에 대응하여 그룹 응답 메시지를 전송하기 위한 제어 흐름을 보이고 있는 도면이다.9 is a diagram illustrating a control flow for a UE to transmit a group response message in response to an MBMS control message from an RNC according to an embodiment of the present invention.
상기 도 9를 참조하면, UE는 900단계에서 RNC로 전송할 그룹 응답 메시지가 발생하는 지를 감시하고, 상기 그룹 응답 메시지가 발생하면 905단계로 진행한다. 상기 그룹 응답 메시지의 발생은 상기 RNC로부터 그룹 응답이 요구되는 MBMS 제어 메시지가 수신됨으로써 야기된다.Referring to FIG. 9, the UE monitors whether a group response message to be transmitted to the RNC is generated in
임의의 RRC 메시지의 그룹 응답 여부는 아래와 같이 판별된다.Whether or not a group responds to any RRC message is determined as follows.
[ 그룹 응답 판단 기준 ][Group Response Criteria]
1. 역방향 메시지가 MBMS 관련 메시지일 것1. Reverse message must be MBMS related message
2. Pmbms가 P_mbms 변수에 저장되어 있을 것.2. P mbms should be stored in the P_mbms variable.
상기 UE의 RRC는 905단계에서 전송할 그룹 응답 메시지를 RLC-DATA-Req 프리미티브로 만들어 RLC로 전달한다. 이 때 상기 프리미티브에는 그룹 응답 식별자(Group response indicator)가 포함된다. 상기 RLC-DATA-Req는 RLC-AM-DATA- Req, RLC-UM-DATA-Req, RLC-TM-DATA-Req를 모두 포괄한다. 상기 그룹 응답 식별자(Group response indicator)는 해당 프리미티브를 통해 전달되는 데이터가 그룹 응답인지 아닌지를 나타내는 1 비트의 플래그이다. 편의상 0은 그룹 응답을 나타내며, 1은 그룹 응답이 아님을 나타낸다고 가정할 수 있다.In
상기 UE의 RLC는 910단계에서 상기 RRC로부터 전달받은 상기 RLC-DATA-Req의 데이터를 RLC 버퍼에 저장하고, 전송해야할 데이터가 있음을 알리기 위해 MAC-STATUS-Response 프리미티브를 MAC으로 전달한다. 이 때 상기 프리미티브에는 그룹 응답 식별자(Group response indicator)가 포함되며, 그 값은 상기 RRC로부터 전달받은 값을 그대로 사용한다. 상기 프리미티브를 통해서는 상기 RLC 버퍼의 상황을 나타내는 버퍼 점유률(BO : Buffer Occupancy) 등의 파라미터도 함께 전달된다. The RLC of the UE stores the data of the RLC-DATA-Req received from the RRC in an RLC buffer in
상기 UE의 MAC은 915단계에서 상기 RLC로부터의 MAC-STATUS-Response를 전달받으며, 920단계에서 상기 프리미티브의 그룹 응답 식별자(Group response indicator)를 검사한다. 상기 검사에 의해 그룹 응답이 요구된다고 판단되면 상기 도 7을 참조하여 살펴본 동작을 수행한다. 하지만, 상기 검사 결과 그룹 응답이 아니라고 판단되면 930단계로 진행하여 통상적인 RACH 동작을 수행한다. 상기 통상적인 RACH 동작은 3GPP TS 25.321의 chapter 11.2.2에 기술되고 있다.The MAC of the UE receives the MAC-STATUS-Response from the RLC in
상기 RLC 버퍼에 저장된 그룹 응답 메시지는 상기 도 7에 도시된 RACH 동작의 성공에 의해 물리계층이 Ack신호를 받을 경우, PHY-DATA_REQ를 통해 전송된다.The group response message stored in the RLC buffer is transmitted through PHY-DATA_REQ when the physical layer receives an Ack signal due to the success of the RACH operation shown in FIG.
도 10은 본 발명의 실시 예에 따라 RNC가 Pmbms를 결정하고 갱신하기 위한 제 어 흐름을 보이고 있는 도면이다. 10 is a diagram illustrating a control flow for the RNC to determine and update P mbms according to an embodiment of the present invention.
상기 도 10을 참조하면, RNC는 1000단계에서 그룹 응답을 초래할 MBMS 제어 메시지가 발생하는 지를 감시하고, 이와 같은 MBMS 제어 메시지가 발생하면 1005단계로 진행한다. 상기 그룹 응답을 초래할 수 있는 MBMS 제어 메시지의 예로는, Notification 메시지이나 RECOUNTING 메시지 등이 있다. 상기 RNC는 상기 1005단계에서 Pmbms의 초기 값을 결정한다. 상기 Pmbms의 초기 값을 설정하는 방안에 대해서는 이미 도 6을 참조하여 설명하였다. 상기 RNC는 1010단계에서 상기 발생한 MBMS 제어 메시지를 전송한다. 상기 MBMS 제어 메시지에는 앞에서 결정한 Pmbms의 초기 값이 포함된다. 상기 MBMS 제어 메시지는 한 셀 내의 모든 UE들이 수신할 수 있도록 S-CCPCH와 같은 방송 채널을 통해 전송될 것이다.Referring to FIG. 10, the RNC monitors whether an MBMS control message is generated to cause a group response in
상기 RNC는 상기 MBMS 제어 메시지를 전송한 후 1015단계에서 상기 Pmbms의 갱신을 위한 알고리즘으로써 "Pmbms deciding algorithm"을 실행한다. 상기 Pmbms
deciding algorithm은 상기 Pmbms의 변경 필요성 여부와, 변경이 필요할 시 새로운 Pmbms를 결정하는 알고리즘을 의미한다. 이에 대한 일 예는 이미 도 6을 참조하여 설명하였다. 상기 도 6을 참조하여 제안한 예를 따를 경우, 상기 Pmbms deciding algorithm은 해당 Node B에게 적절한 COMMON MEASUREMENT 설정을 요구하는 단계와, 상기 Node B가 보고하는 COMMON MEASUREMENT에 의해 Pmbms의 재 설정 여부를 판단한 후 새로운 Pmbms를 설정하는 단계를 포괄한다.The RNC executes the "P mbms deciding algorithm" as an algorithm for updating the P mbms in
상기 RNC는 1020단계에서 상기 Pmbms deciding algorithm에 의해 새로운 Pmbms가 설정되었다고 판단하면 1025단계로 진행하나 새로운 Pmbms가 설정되지 않으면 상기 1015단계로 리턴하여 상기 Pmbms deciding algorithm을 계속 실행한다.If the RNC determines that the new P mbms is set by the P mbms deciding algorithm in
상기 RNC는 상기 1025단계로 진행하면 상기 새로운 Pmbms를 담은 ACCESS CONTROL 메시지를 해당 셀의 방송 채널을 통해 UE들에게 전송하고, 상기 1015단계로 리턴한다.When the RNC proceeds to step 1025, the RNC transmits an ACCESS CONTROL message containing the new P mbms to UEs through a broadcast channel of the corresponding cell, and returns to step 1015.
전술한 RNC의 동작은 그룹 응답(Group response)이 완료되면 종료된다. 예를 들어 상기 도 10에 의한 상기 RNC의 동작이 Notification 메시지를 전송하면서 시작되었다면, 응답 메시지의 전송을 중지시키는 STOP 메시지를 전송함으로써 종료될 것이다.The operation of the above-described RNC ends when the group response is completed. For example, if the operation of the RNC according to FIG. 10 was started while sending a notification message, the operation of the RNC would be terminated by sending a STOP message that stops sending a response message.
전술한 바와 같이 본 발명에서는 응답 메시지가 전송될 확률을 셀 상황 등을 고려하여 지속적으로 갱신함으로써 응답 메시지의 전송 성공률을 향상시킬 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 RACH의 성능을 최적화할 수 있는 효과를 가진다. 즉, 다수의 단말기들로부터의 데이터 전송이 동일한 시점에서 빈번하게 이루어지는 멀티캐스트 멀티미디어 방송 서비스의 경우 다수의 역방향 메시지들이 동시에 전송됨으로서 유발되는 랜덤접근채널 상의 혼잡과 충돌을 완화시킬 수 있다는 장점이 있다.As described above, in the present invention, by continuously updating the probability that the response message is transmitted in consideration of the cell situation, the transmission success rate of the response message can be improved and the performance of the RACH can be optimized. That is, in the case of a multicast multimedia broadcasting service in which data transmission from multiple terminals is frequently performed at the same time, congestion and collision on a random access channel caused by multiple reverse messages are simultaneously transmitted can be alleviated.
Claims (21)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020030023788A KR100965719B1 (en) | 2003-04-15 | 2003-04-15 | Method for renovating random access effectively in a mobile telecommunication system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020030023788A KR100965719B1 (en) | 2003-04-15 | 2003-04-15 | Method for renovating random access effectively in a mobile telecommunication system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20040089937A KR20040089937A (en) | 2004-10-22 |
| KR100965719B1 true KR100965719B1 (en) | 2010-06-24 |
Family
ID=37441398
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020030023788A KR100965719B1 (en) | 2003-04-15 | 2003-04-15 | Method for renovating random access effectively in a mobile telecommunication system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR100965719B1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100662408B1 (en) * | 2005-05-24 | 2007-01-02 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | method for allocating channel for random access |
| CN100429956C (en) * | 2005-07-11 | 2008-10-29 | 大唐移动通信设备有限公司 | Method for realizing public-measurement in multi-frequency point system |
| US7904055B2 (en) | 2005-08-23 | 2011-03-08 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Communicating message in mobile communication system |
| KR101333918B1 (en) | 2006-01-05 | 2013-11-27 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Point-to-multipoint service communication of mobile communication system |
| WO2007078171A2 (en) | 2006-01-05 | 2007-07-12 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method of transmitting feedback information in a wireless communication system |
| JP4806030B2 (en) | 2006-01-05 | 2011-11-02 | エルジー エレクトロニクス インコーポレイティド | Method for transferring signals in a mobile communication system |
| ES2459371T3 (en) | 2006-01-05 | 2014-05-09 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Transmission of information in a mobile communications system |
| KR20070080552A (en) | 2006-02-07 | 2007-08-10 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method for transmitting response information in the mobile communication system |
| KR100912784B1 (en) | 2006-01-05 | 2009-08-18 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Data transmission method and data retransmission method |
| KR101211807B1 (en) | 2006-01-05 | 2012-12-12 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method for managing synchronization state for mobile terminal in mobile communication system |
| KR101358469B1 (en) | 2006-02-07 | 2014-02-06 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method for selection and signaling of downlink and uplink bandwidth in wireless networks |
| KR101216751B1 (en) | 2006-02-07 | 2012-12-28 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Method for avoiding collision using identifier in mobile network |
| KR101387475B1 (en) | 2006-03-22 | 2014-04-22 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | method of processing data in mobile communication system having a plurality of network entities |
| EP2030359B1 (en) | 2006-06-21 | 2017-12-20 | LG Electronics Inc. -1- | Method of supporting data retransmission in a mobile communication system |
| WO2007148946A2 (en) * | 2006-06-23 | 2007-12-27 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Methods of efficiently utilizing resources in a wireless communication system |
| KR101570812B1 (en) | 2007-09-28 | 2015-11-20 | 시그널 트러스트 포 와이어리스 이노베이션 | Method and apparatus for terminating transmission of a message in an enhanced random access channel |
| DK2208383T3 (en) | 2007-10-25 | 2020-12-14 | Signal Trust For Wireless Innovation | Method, devices and system for handling and setting up enhanced MAC-E / ES resources |
| WO2009088877A2 (en) | 2008-01-02 | 2009-07-16 | Interdigital Patent Holdings, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for cell reselection |
| KR101417058B1 (en) * | 2008-02-05 | 2014-07-09 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method and apparatus for the configuration of reception/transmission timing for enhanced uplink service in cell_fach state in mobile communication system |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20040064867A (en) * | 2003-01-10 | 2004-07-21 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method for providing random access effectively in mobile telecommunication system |
-
2003
- 2003-04-15 KR KR1020030023788A patent/KR100965719B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20040064867A (en) * | 2003-01-10 | 2004-07-21 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method for providing random access effectively in mobile telecommunication system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20040089937A (en) | 2004-10-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR100965719B1 (en) | Method for renovating random access effectively in a mobile telecommunication system | |
| KR100827137B1 (en) | Method for serving multimedia broadcast/multicast service in mobile communication system | |
| EP1561293B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for establishing feedback in a broadcast or multicast service | |
| KR20040064867A (en) | Method for providing random access effectively in mobile telecommunication system | |
| KR100548344B1 (en) | Rrc connection method in mobile communication system | |
| KR101189945B1 (en) | Method for transmitting mbms service in mobile communication system | |
| KR100976475B1 (en) | Method of securing quality of communication service | |
| EP1561292B1 (en) | Rrc group reject methods and apparatuses for mobile communications | |
| US7821979B2 (en) | Communicating control messages for point-to-multipoint service in wireless communication system | |
| EP1609330B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for controlling access to network in wireless communication system | |
| KR100888426B1 (en) | Method for transmitting/receiving control message of mbms in mobile communication system | |
| KR101114175B1 (en) | Method for transmitting and receiving point-to-multipoint service in mobile communication system | |
| KR101120759B1 (en) | Referencing of downlink channels in wireless communication system | |
| US8068843B2 (en) | Method for increasing system capacity by transmitting control Signal for MBMS data by combining RLC and PDCP messages | |
| KR20050014984A (en) | Methoed for retransmitting rrc connection request in a mobile communication system which support mbms | |
| EP1420551A2 (en) | Method for transmitting and receiving control messages in a mobile communication system providing MBMS service | |
| KR20040098394A (en) | Method for transmitting paging information to a mbms service in mobile communication system | |
| CN101156479B (en) | Method and system for ascending link establishment in wireless honeycomb communication | |
| KR20040014706A (en) | Method for transmitting/receiving control message in mobile communication system serving multimedia broadcast/multicast service | |
| KR20060016292A (en) | Methoed for retransmitting rrc connection request in a mobile communication system which support mbms | |
| KR100871216B1 (en) | Method for transmitting/receiving control message in mobile communication system serving multimedia broadcast/multicast service | |
| CN102655687A (en) | Method and system for establishing uplink for wireless cellular communication |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E90F | Notification of reason for final refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20130530 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20140529 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20150528 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20160530 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| LAPS | Lapse due to unpaid annual fee |