JP4250231B2 - File management apparatus, file management method, and storage medium - Google Patents
File management apparatus, file management method, and storage medium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4250231B2 JP4250231B2 JP26734798A JP26734798A JP4250231B2 JP 4250231 B2 JP4250231 B2 JP 4250231B2 JP 26734798 A JP26734798 A JP 26734798A JP 26734798 A JP26734798 A JP 26734798A JP 4250231 B2 JP4250231 B2 JP 4250231B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- record
- file
- image information
- image
- list
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、ファイル管理装置、ファイル管理方法、及び記憶媒体に関し、詳しくは、複数ファイルを保存すると共に、ファイルを検索することができるファイル管理装置、当該ファイル管理装置に適用されるファイル管理方法、及び当該ファイル管理方法を実行するプログラムを記憶した記憶媒体に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来、文書や図面等の原稿画像を読み取って適宜編集し、その画像を磁気ディスク、光磁気ディスク等に記録して管理する画像管理システムが知られている。
【0003】
一般に、このような画像管理システムでは、原稿画像を読み取って得られた画像情報を圧縮してハードディスクあるいは光ディスクに記録する。また、画像の検索を行なうためのインデックス情報を画像情報と関連づけて記録している。このインデックス情報から必要な画像を検索して、検索結果を基に画像情報を読み出してディスプレイに表示し、あるいはその画像をプリンタによって記録紙に出力する。また、必要に応じて画像の追加、編集や加工など各種画像処理を行う。
【0004】
図27A及び図27Bに一般的な画像ファイリングシステムの従来例を示す。
【0005】
図27Aは、スキャナを用いて原稿をスキャンし、文書データベースにその画像を保存するときの画像ファイリングシステムの構成を示すブロック図である。120は、原稿を光学的に読み取って光電変換素子等により、読み取った画像をデジタル信号に変換するスキャナである。121はスキャナ120の動作を制御するためのスキャナ制御手段、123は読み取った画像についてのインデックスを入力するためのインデックス入力手段、122はインデックスと画像を対応させて管理するデータベース管理手段、124は画像やインデックスの情報を保存する文書データベースである。矢印は情報の流れを示す。
【0006】
まず、スキャナ120で原稿から読み取られた画像はスキャナ制御手段121を介してデータベース管理手段122に送られる。また、インデックス入力手段123から入力されたインデックス情報がデータベース管理手段122に送られる。データベース管理手段122ではスキャナ制御手段121から送られてきた画像に、インデックス入力手段123から入力されたインデックス情報を付加して文書データベース124に保存する。
【0007】
図27Bは、文書データベースにおいて検索手段を用いて所望の画像を検索するときの画像ファイリングシステムの構成を示すブロック図である。130は、画像及び該画像に対応するインデックスが保存されている文書データベースであり、131は文書データベース130を管理するためのデータベース管理手段である。132は文書データベース130から所望の画像を検索するための検索手段であり、検索条件入力手段133により入力された検索条件をもとにして画像を検索する。134は、検索した結果を管理するための検索結果リスト管理手段であり、135はその検索結果リストである。矢印は情報の流れを示す。
【0008】
まず、検索条件入力手段133から、検索したい画像の条件が入力されると、検索手段132が、文書データベース管理手段131を介して文書データベース130から条件に適合した画像を検索し、得られた検索結果を、検索結果リスト管理手段134を介して検索結果リスト135に出力する。
【0009】
検索結果リスト管理手段134は、検索結果リスト135に基づき、検索された文書の画像情報を、画像表示部制御手段140を介して画像表示部141に送り画像を表示させたり、またプリンタ制御手段142を介してプリンタ143に送って画像をプリントさせたりすることができる。
【0010】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、上記従来の画像ファイリングシステムでは、文書の記録操作と検索操作とが分離した構成となっており、さらに、記録操作においても、画像のスキャンとインデックスの入力操作は固定した手順で行われていた。
【0011】
また、記録操作において、文書の記録とインデックスの入力は個々の文書ごとに行われていた。
【0012】
このために、複数の文書の記録操作において、操作者はスキャンとインデックス入力とを交互に行う必要があり、従って操作が煩雑となり、生産性も低かった。
【0013】
また、記録操作と検索操作とが分離した構成となっていたので、誤操作により入力された誤ったデータは、いったん記録操作を終了し、その後に検索操作を行って修正操作を行う必要があり、多くの操作ステップと操作時間を必要とした。
【0014】
また、複数の画像に対して一括した操作を行うために、複数の画像に対して同一の識別マークを付しておき、識別マークの付いた画像だけを探して一括した操作を行うことが可能であるが、こうした方法において、一度記録操作を終了してから、検索操作に移行して、所望の画像を検索して確認した後に、再度画像スキャンやインデックス入力の操作に移行する必要があるなど、操作が非常に煩雑であった。
【0015】
本発明はこのような問題点に鑑みてなされたものであって、操作性を改善したファイル管理装置、ファイル管理方法、及び記憶媒体を提供することを目的とする。
【0016】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記目的を達成するために、請求項1記載のファイル管理装置によれば、画像情報とインデックスデータとをレコードに関連付け、複数のレコードを一覧表示したリストを用いて、画像を管理するリスト管理手段と、所定の画像情報が既に関連付けられているレコードと、所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコードと、画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードとを前記リストに一覧表示する表示手段と、前記表示手段により表示されたリストにおいて、新たな画像の保存を行いたい複数のレコードに、同一の標識マークを付加するマーク付加手段と、前記リストにおいて前記標識マークの付加されたレコードを順番に選択する選択手段と、前記選択手段で選択中のレコードが、所定の画像情報が既に関連付けられているレコードであるか、所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコードであるか、画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードであるか、を判定する判定手段と、前記選択手段で選択中のレコードが、前記判定手段によって、前記所定の画像情報が既に関連づけられているレコードであると判定された場合に、新たに入力された画像情報を当該選択中のレコードにおける最終ページの後に追加し、前記所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコード又は画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードであると判定された場合に、新たに入力された画像情報を当該選択中のレコードに追加する処理を実行する処理実行手段と、を有することを特徴とする。
【0017】
また、請求項5記載のファイル管理方法によれば、リスト管理手段が、画像情報とインデックスデータとをレコードに関連付け、複数のレコードを一覧表示したリストを用いて、画像を管理するリスト管理ステップと、表示手段が、所定の画像情報が既に関連付けられているレコードと、所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコードと、画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードとを前記リストに一覧表示する表示ステップと、マーク付加手段が、前記表示されたリストにおいて、新たな画像の保存を行いたい複数のレコードに、同一の標識マークを付加するマーク付加ステップと、選択手段が、前記リストにおいて前記標識マークの付加されたレコードを順番に選択する選択ステップと、判定手段が、前記選択ステップで選択中のレコードが、所定の画像情報が既に関連付けられているレコードであるか、所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコードであるか、画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードであるかを判定する判定ステップと、処理実行手段が、前記判定ステップで、前記選択中のレコードが、前記所定の画像情報が既に関連づけられているレコードであると判定された場合に、新たに入力された画像情報を当該選択中のレコードにおける最終ページの後に追加し、前記所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコード又は画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードであると判定された場合に、新たに入力された画像情報を当該選択中のレコードに追加する処理を実行する処理実行ステップと、を有することを特徴とする。
【0018】
さらに、請求項6記載の記憶媒体は、コンピュータ読み取り可能であり、コンピュータを、画像情報とインデックスデータとをレコードに関連付け、複数のレコードを一覧表示したリストを用いて、画像を管理するリスト管理手段、所定の画像情報が既に関連付けられているレコードと、所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコードと、画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードを前記リストに一覧表示する表示手段、前記表示手段により表示されたリストにおいて、新たな画像の保存を行いたい複数のレコードに、同一の標識マークを付加するマーク付加手段、前記リストにおいて前記標識マークの付加されたレコードを順番に選択する選択手段、前記選択手段で選択中のレコードが、前記所定の画像情報が既に関連付けられているレコードであるか、前記所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコードであるか、画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードであるかを判定する判定手段、前記選択手段で選択中のレコードが、前記判定手段によって、前記所定の画像情報が既に関連づけられているレコードであると判定された場合に、新たに入力された画像情報を当該選択中のレコードにおける最終ページの後に追加し、前記所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコード又は画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードであると判定された場合に、新たに入力された画像情報を当該選択中のレコードに追加する処理を実行する処理実行手段、として機能させるためのプログラムを格納していることを特徴とする。
【0019】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の実施の形態を、図面を参照して説明する。
【0020】
(第1の実施の形態)
本発明の第1の実施形態を、図1〜図14を参照して説明する。
【0021】
(ハードウエア構成)
図1は、第1の実施形態に係るファイル管理装置のハードウエアの構成を示すブロック図である。
【0022】
1は、ファイル管理装置の全体の制御を行なうCPU(中央処理装置)であり、画像情報、各操作の指示情報を伝達する情報伝達手段としてのバス18に接続されている。3は、使用者に画像情報のイメージや、文書リスト等を表示するためのCRTディスプレイであり、ディスプレイインターフェース回路2を通じてバス18に接続されている。5は、使用者がファイル管理装置に各種動作を指示するためのキーボードであり、ポインティングデバイスを含み、キーボードインターフェース回路4を通じて、バス18に接続されている。7は、被写体から画像情報を読み取るスキャナであり、スキャナインターフェース回路6を通じて、バス18に接続されている。9は、画像情報とそれぞれの画像情報を管理するための識別情報とを保存するメモリであり、磁気ディスクあるいは光磁気ディスクから構成され、メモリインターフェース回路8を通して、バス18に接続されている。11は、使用者が入力したさまざまなインデックス情報と画像識別情報とが関連づけて保存されたデータベースを格納するメモリであり、メモリインターフェース回路10を通じて、バス18に接続されている。13は、ファイル管理装置のプログラムを実行する際に使用するメモリであり、RAMからなり、メモリインターフェース回路12を通じて、バス18に接続される。15は、ファイル管理装置のプログラムを保存するためのメモリであり、磁気ディスクあるいは光磁気ディスクからなり、メモリインターフェース回路14を通じて、バス18に接続されている。17は、ファイル管理装置のプログラムが保存されているフロッピーディスク等を本システムに接続するための外部ディスク接続装置(ディスクドライブ)であり、外部ディスクインターフェース回路16を通じて、バス18に接続される。201は、保存されている文書の画像情報や文書リストなどをプリントするためのプリンタであり、プリンタインターフェース回路200を介してバス18に接続されている。
【0023】
ファイル管理装置で実行されるプログラムはフロッピーディスク等により外部からファイル管理装置に提供される。フロッピーディスク上のプログラムはプログラムの実行に先立ち、外部ディスク接続装置17から読込まれ、メモリ15に保存される。ついで、プログラムはメモリ13にロードされ、CPU1により実行される。
【0024】
(ソフトウエア処理の構成)
図2は、ファイル管理装置でファイル管理処理が行われることによって実現する諸機能の構成を示す図である。
【0025】
20は文書の画像を記録する画像記録部、21は画像記録部20内のデータを、整合性を維持して管理する画像記録部管理手段、22は文書を検索するためのインデックスデータを記録するインデックスデータ記録部、23はインデックスデータ記録部22内のデータを、整合性を維持して管理するインデックスデータ記録部管理手段、24は所望の文書を検索するための検索条件を入力する検索条件入力手段、25はデータベースから所望の文書を検索するための検索手段である。検索条件入力手段24はキーボードと検索条件入力画面で構成される。26は原稿から画像データを読み込むスキャナ、27はスキャナ26の制御を行うスキャナ制御手段、28はインデックスデータの入力を行うインデックス入力手段である。30は、文書のリストを表示する文書リスト表示手段31の管理制御を行う文書リスト制御手段である。
【0026】
32は文書の画像の制御を行う画像制御手段、40は画像表示部41を制御して文書の画像表示を行う画像表示部制御手段である。
【0027】
文書リスト制御手段30は、文書リスト表示手段31を制御するとともに、インデックスデータ記録部管理手段23、画像制御手段32、インデックス入力手段28に接続されている。
【0028】
画像制御手段32は画像記録部管理手段21、文書リスト制御手段30、スキャナ制御手段27、画像表示部制御手段40に接続されている。
【0029】
42はプリンタ43を制御して文書の画像情報を記録紙に出力させるプリンタ制御手段であり、画像制御手段32に接続されている。
【0030】
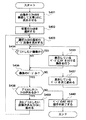
次に、上記構成における文書の検索、文書の新規記録、インデックスの入力について、図3を適宜参照して説明する。図3は文書リスト制御手段30の制御動作を示すフローチャートである。
【0031】
(検索動作)
使用者が検索条件入力手段24から、所望の文書を検索するための検索条件を入力する。検索条件は、例えばキーワード等からなる。
【0032】
入力された検索条件は検索手段25(一般に検索エンジンともいわれる)に渡され、検索手段25はインデックスデータ記録部管理手段23を経由して、インデックスデータ記録部22内の文書データベースから、検索条件に一致する文書を探し出し、その結果を文書リスト制御手段30に出力する(S10でYES)。文書リスト制御手段30はその結果を文書リスト化する(S11)と共に、文書管理リスト表示手段31(一般にCRTおよびCRTの制御回路で構成される)上に表示する(S12)。
【0033】
(新規記録)
使用者はスキャナ制御手段27を起動し、スキャナ26から新規の文書を読み込む(S20でYES)。スキャナ26は所定の枚数の原稿を読み込み、画像データを画像制御手段32に出力する。画像制御手段32は画像データを、画像記録部管理手段21を経由して画像記録部20に記録すると共に、文書リスト制御手段30に新規文書生成情報を通知する。
【0034】
文書リスト制御手段30は新規文書生成情報に基づき、既に表示している文書リストに新規の文書を追加して新規のレコードを作成し、表示する(S21,S22)。このレコード内には、作成日付、ページ数等のスキャン時に確定された文書属性が含まれる。更新された文書属性は、インデックスデータ記録部管理手段23を経てインデックスデータ記録部22に記録される(S23)。
【0035】
(インデックス後付け)
使用者は文書リスト制御手段30へインデックス入力を開始する指示を行う(S30でYES)。この指示により、文書リスト制御手段30はインデックス入力手段28からの出力を受け取るモードとなる。ついで使用者はインデックス入力手段28からインデックスを入力する(S31)。ここでは、前述の新規にスキャンした文書に対応するインデックスを入力する。入力されたインデックスは文書リスト制御手段30により文書リスト上の所定の場所に表示される(S32)。入力されたインデックスデータは自動で、あるいは文書リスト制御手段30への使用者の指示により、インデックスデータ記録部管理手段23を経てインデックスデータ記録部22へ送られ記録される(S33)。
【0036】
(インデックス先付け)
なお、インデックス情報を文書の入力に先立ちインデックスを入力するインデックス先付けも可能である。以下に、インデックス先付けの動作を説明する。
【0037】
使用者は文書リスト制御手段30へインデックス先付けの指示を行う(S40でYES)。この指示により、文書リスト制御手段30は、文書リストの最下端の新規レコードにインデックスを入力できるようにする(S41)。この新規レコードは現時点では画像データと関連を持たない。つぎに、使用者はインデックス入力手段28から新規のインデックスデータを入力する(S42)。このデータは文書リスト制御手段30により、文書リスト上に表示される(S43)と共に、必要に応じて、インデックスデータ記録部管理手段23を経由してインデックスデータ記録部22へ記録される(S44)。
【0038】
(インデックス先付けレコードへの画像の記録)
使用者は、前述したインデックス先付けレコードに対応させて画像データの入力を行うことができる(S50でYES)。使用者はまず、文書リスト制御手段30に対し、入力画像データに対応するインデックス先付けの行われたレコードを選択する(S51)。ついでスキャナ制御手段27によりスキャナ26から画像データを読み込む。画像データは画像制御手段32により、画像表示部制御手段40を経て画像表示部41へ送られるとともに、画像記録部管理手段21へ送られ、画像記録部20に記録される。画像記録部20は記録した画像のアドレス情報を、画像制御手段32を経て、あるいは直接に文書リスト制御手段30へ渡す。また画像制御手段32から文書リスト制御手段30へ文書ページ数等の読込み情報が送られる。文書リスト制御手段30は該情報を、インデックスデータ記録部管理手段23を経てインデックスデータ記録部22へ記録すると共に、文書リスト上の該当するレコードのステータスをインデックス先付けから通常の文書へ変更する。さらに文書リスト制御手段30は文書リストの表示を更新する(S52,S53)。
【0039】
なお、記録画像のアドレス情報は、画像記録部管理手段21からインデックスデータ記録部管理手段23に直接渡すように構成することも可能である。
【0040】
(画像情報の表示、印刷)
使用者は、文書リストから任意のファイルを選択して、その画像情報の表示、印刷を行なうことができる。
【0041】
使用者が文書リストの任意のファイルを選択して画像の表示をキーボード5などで指示すると、文書リスト制御手段30は、インデックスデータ記録部管理手段23を経由してインデックスデータ記録部22から、選択されたファイルの画像の検索情報を得る。続いて文書リスト制御手段30は、画像の検索情報と画像表示の指示を画像制御手段32に送る。画像制御手段32は、受け取った画像の検索情報を基に、画像記録部管理手段21を経由して画像記録部20から画像情報を得て、画像情報を画像表示部制御手段40に送る。画像表示部制御手段40は画像表示部41に、受け取った画像情報を表示させる。
【0042】
画像情報の印刷も同様に、使用者が選択した画像情報を受け取った文書リスト制御手段30は、検索情報と画像の印刷の指示を画像制御手段32に送る。画像制御手段32は、受け取った画像の検索情報を基に、画像記録部管理手段21を経由して画像記録部20から画像情報を得て、画像情報をプリンタ制御手段42に送る。プリンタ制御手段42はプリンタ43に、受け取った画像情報を印刷させる。
【0043】
次に、以上の動作を文書リスト上で、さらに詳細に説明する。
【0044】
(文番リストの構成)
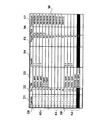
図4は、文書リストWを示す図である。文書リストWは文書リスト制御手段30により生成され、ディスプレイ3上に表示される。この文書リストWには検索結果のファイルと、スキャナ26から入力された新規ファイルとが表示されている。51はファイルの状態を示すプロパティ列、52はリスト上の番号を示すファイルナンバ列、53,54,56は各文書のインデックス項目であり、55は各ファイルのページ数、57はスキャナ26で被写体の画像を記録した作成日付を示す作成日付である。インデックス項目は、図示しないデータベース構造設定手段を用いて使用者が文書の種類に応じて自由に設計することができる。図4の例では、文書管理のためのインデックス情報として、文書のタイトルを示すタイトル53、文書の章の区切りを示す章54、文書の評価をあらわすランク56を加えている。また、これらの列の順番は、任意に入れ替えることができる。
【0045】
また、図4に示した文書リストWでは、画像記録済みファイルと、インデックスのみを先に入力したインデックス先付けファイルとを、同一画面上に、明確に区別がつくようにして表示している。すなわち、プロパティ列51内に示すアイコン58、59は、各ファイルの状態を示すアイコンであり、アイコン58はファイルに画像情報がすでに記録されていることを示し、アイコン59はファイルに画像情報がまだ記録されておらず、インデックス先付けファイルであることを示す。図4の文書リストWでは、範囲60,61で示すファイルナンバが1から10のファイルは画像記録済みのファイルであり、範囲62で示すファイルナンバが11から15のファイルはインデックス先付けファイルであることが容易に判別できる。
【0046】
なお、範囲60のファイルは、画像情報とインデックス情報とが記録されている既存ファイルであり、範囲61のファイルは、画像情報が保存されているがインデックス情報が入力されていない新規ファイルであり、範囲62のファイルは、インデックス情報のみが記録されているインデックス先付けファイルである。
【0047】
(検索動作)
図5A及び図5Bは、検索動作を行なった場合の文書リストWを示す図である。図5Aの文書リストWは、保存されている文書の全件を含んでおり、検索動作を行う前の初期状態の一例である。ここで使用者が、検索条件入力手段24に検索条件として、例えばランク“A”を入力すると、検索手段25は、インデックスデータ記録部管理手段23を経由してインデックスデータ記録部22から検索条件に一致するレコード(ファイル)を探し出し、その結果を文書リスト制御手段30に出力する。文書リスト制御手段30では、その結果を基に文書リストを作成して、文書リスト表示手段31上に表示する。上記のような検索動作によって作成されて表示された文書リストWは、図5Bのようになる。
【0048】
(新規記録)
図6A及び図6Bは、新規記録を行なった場合の文書リストWを示す図である。図6Aは、新規記録前の文書リストを示している。ここで、スキャナ26を用いて新規の文書を読み込み、文書リスト制御手段30に新規文書生成情報を通知する。文書リスト制御手段30は新規文書生成情報に基づき、既に表示している文書リストに追加して、新規のレコードを作成して表示する。作成、更新された文書属性はインデックスデータ記録部管理手段23を経てインデックスデータ記録部22に記録される。
【0049】
上記のような新規文書の記録動作によって作成されて表示された文書リストWを図6Bで示す。図6Bに示すファイルナンバ4、5、6番のレコード(ファイル)が作成され、画像情報のスキャンに対応したページ数、作成日付が表示され、またファイルの属性を示すアイコンがプロパティ列に表示されている。
【0050】
(インデックス後付け)
図7A及び図7Bは、インデックス情報の後付けを行なった場合の文書リストWを示す図である。
【0051】
使用者が文書リスト制御手段30へインデックス入力を開始する指示を行う。この指示により、図7Aに示すように、文書リスト制御手段30はインデックス入力手段28からの出力を受け取るモードとなる。ついで使用者はインデックス入力手段28から所定のインデックスを入力する。入力されたインデックスは文書リスト制御手段30によりリスト上の所定の場所に表示される。入力されたインデックスデータは自動で、あるいは文書リスト制御手段30への使用者の指示により、インデックスデータ記録部管理手段23を経てインデックスデータ記録部22へ記録される。
【0052】
1つのインデックス項目への入力動作を終了すると、次のインデックス項目(例えば図の右隣のインデックス項目)への入力動作へ移ることもできる。同様に1つのレコード(ファイル)へのインデックス入力動作を終了すると、次のレコード(ファイル)(例えば図の下側のレコード)へのインデックス入力動作に移ることもできる。例えば、図7Aの例ではファイルナンバ4番のタイトル列からインデックス入力を開始して、図7Bに示すようにファイルナンバ6番のランク列まで連続してインデックス入力を行う。
【0053】
さらに、入力する列を指定して(例えばChapterとRankのみ)指定した列のみへの連続入力を行うこともできる。
【0054】
(インデックス先付け)
図8A及び図8Bは、インデックス情報の先付けを行なった場合の文書リストWを示す図である。
【0055】
使用者が文書リスト制御手段30へインデックス先付けの指示を行う。この指示により、図8Aに示すように、文書リスト制御手段30は、文書リストの最下端の新規レコードへインデックス入力を可能にする。つぎに、使用者はインデックス入力手段28から新規のインデックスデータを入力する。このデータは文書リスト制御手段30により、文書リスト上に表示されると共に、必要に応じて、インデックスデータ記録部管理手段23を経由してインデックスデータ記録部22へ記録される。
【0056】
1つのインデックス項目への入力動作を終了すると、次のインデックス項目への入力動作へ移ることもできる。同様に1つのレコード(ファイル)へのインデックス入力動作を終了すると、別のレコード(ファイル)へのインデックス入力動作に移ることもでき、この時に画像データと関連を持たないファイルがインデックス先付けファイルとして作成される。例えば、図8Aの例では新規ファイルのタイトル列からインデックス入力を開始して、図8Bに示すようにファイルナンバ9番の章列まで連続してインデックス入力を行なった。この例では、ファイルナンバ7、8、9番のインデックス先付けファイルが作成された。
【0057】
(インデックス先付けレコードへの画像の記録)
図9A及び図9Bは、インデックス情報の先付けファイルに対して画像の記録を行なった場合の文書リストWを示す図である。
【0058】
使用者はまず、文書リスト制御手段30に対し、インデックス先付けの行われたレコードを選択する操作を行う。つまり、入力される画像データが対応するレコードを選択する。ついでスキャナ制御手段27によりスキャナ26から画像データを読み込む。画像データは画像制御手段32により、画像表示部制御手段40を経て画像表示部41へ送られるとともに、画像記録部管理手段21へ送られ、画像記録部20に記録される。画像記録部20は記録した画像のアドレス情報を、画像制御手段32を経て、あるいは直接に文書リスト制御手段30へ渡す。また画像制御手段32から文書リスト制御手段30へ文書ページ数等の読込み情報が送られる。文書リスト制御手段30は該情報を、インデックスデータ記録部管理手段23を経てインデックスデータ記録部22へ送り記録すると共に、文書リスト上の該当するレコードのステータスを、インデックス先付けから通常の文書へと変更する。さらに文書リスト制御手段30は文書リストの表示を更新する。
【0059】
上記のような新規文書の記録動作によって作成されて表示された文書リストWを図9Bで示す。図9Bに示すファイルナンバ7、8、9番のファイルに画像情報が入力され、リスト上でページ数、作成日付が更新され、またプロパティ列でファイルの属性を示すアイコンの表示がアイコン59からアイコン58へ変更されている。
【0060】
これらの文書リスト例を基にして、この文書リスト上でそれぞれの所望のファイルに識別マークを付けておき、識別マークが付けられたファイルに対して一括した操作を行う例を以下に示す。なお、以下、この識別マークをタグと呼ぶことにする。ファイルに付けられたタグをファイルタグ、そのファイルに含まれるページに付けられたタグをページタグとする。
【0061】
図10は、インデックスデータが入力されていないファイルに対してファイルタグが付けられた文書リストWの例を示す図である。図10の文書リストでは、それぞれのファイルにはすでに各ページ数に相当した枚数の画像が保存されているが、ファイル番号1、2、3、5、12、14の各ファイルではタイトル列や章列のインデックスデータがまだ入力されていない。プロパティ列にあるアイコン71は、そのファイルにタグが付けられていることを表すファイルタグである。図10では、このファイルタグを、インデックスデータがまだ入力されていないファイルを選んで付けるようにしている。
【0062】
図11は、ファイルタグが付けられたファイルに対してインデックスデータを入力した後の文書リストWの例を示す図である。ファイルタグが付けられたファイルの各々におけるインデックス列、章列に対して順次、インデックスデータを入力していった結果得られる文書リストWが示されている。
【0063】
図12は、保存された画像に対して各ファイル単位でファイルタグが付され、画像記録部20に記録されている画像の例を示す図である。図12において、ファイル1は201から223までの画像が保存されているが、ファイルタグ71が付けられている。ファイル2、3、5も同様にそれぞれ231、271、301から始まる画像が保存されているが、ファイルタグ71が付けられている。ファイル4については291から293までの画像が保存されているが、ファイルタグ71は付けられていない。
【0064】
次に、第1の実施形態において使用者が行う操作の手順を、図13及び図14を参照して説明する。
【0065】
図13は、画像がすでに保存されている所望のファイルに対してインデックス後付けのためのファイルタグ71を付ける操作の手順を示すフローチャートである。
【0066】
まず、ステップS401で、画像がすでに保存されているファイルを検索して文書リストWに表示させる。ステップS402で、文書リストW上の最初のファイルを選択し、ステップS403で、選択されたファイルのタイトル列にインデックスデータが入力されているかを確認する。ステップS404で、タイトル列にインデックスデータが入力されていないときには、ステップS405に進み、この選択ファイルに対してファイルタグ71を付ける操作をする。この操作によつて、図10のようにファイルタグ71が選択ファイルに対して表示されるようになる。
【0067】
選択ファイルに対してファイルタグ71を付ける操作が完了した場合、あるいはすでにインデックスデータ入力済みのときは、ステップS406で、ファイル選択を文書リストW上の次のファイルに進める。ステップS407によって、この操作を順次、次のファイルに対して行うためにステップS404からステップS406を繰り返し、すべてのファイルに対してファイルタグ付けの確認が終了したら、ステップS408でファイルタグ付けを終了する。
【0068】
図14は、ファイルタグ71が付けられたファイルに対してインデックスデータを順次入力していく操作の手順を示すフローチャートである。
【0069】
まず、ステップS411で、文書リストW上でファイルタグ71が付けられた最初のファイルを選択し、ステップS412で、選択ファイルの1ページ目の画像(図12の画像201、231・・など)を表示させる。ステップS413では、文書リストW上で選択しているファイルのインデックス項目をインデックスデータ入力モードにする。ステップS414では、表示されている画像(図12の画像201、231、・・など)の内容をもとにして各インデックス項目にインデックスデータを入力する。たとえば、図12に示す例ではファイル1のタイトル列に対して“menuspec”というインデックスデータを入力する。1つのインデックス項目の入力が終了したら、ステップS415を経由してステップS416で次のインデックス項目へ入力モードを移動し、ステップS417でインデックスデータを入力する。ファイルタグ71が付いているファイルのすべてのインデックス項目にインデックスデータの入力が終了したら(S415でYES)ステップS418に進み、ファイルタグ71の付いたファイルがまだ残っていれば(S418でNO)ステップS419に進み、ファイルタグ71の付いた次のファイルへ移動し、ステップS412からステップS417を繰り返す。ファイルタグ71の付いたすべてのファイルに対してインデックス後付け操作が終了したら(S418でYES)、ステップS420で、ファイルタグ71の付いたファイルへのインデックスデータ入力を終了する。
【0070】
以上説明したように、ファイルの記録や検索を行うことができるファイル管理装置において、記録ファイルの属性情報とファイル検索結果情報が一体になった文書リストWを使用して、インデックスの入力が必要なファイルに対してファイルタグ71を付けておく。そして、そのファイルタグ71が付いた複数のファイルだけを対象にしてインデックス後付け操作を行うことができる。従って、複数のファイルに対してインデックスデータの入力を連続して一括行えるので、非常に効率がよい。
【0071】
上記の第1の実施形態では、文書リストWに表示されたファイルに対して1ファイルずつファイルタグを付けるようにしているが、これに代わって、複数のファイルをまとめて選択してファイルタグを付けるようにしてもよい。
【0072】
また、ファイルの番号を指定してファイルタグを付けるようにしてもよい。
【0073】
上記の第1の実施形態では、ファイルタグが付いているファイルに対して一括してインデックス後付け操作をするときに、1つのファイルに対する操作が終了したら次のファイルタグを捜して移動するようにしているが、これに代わって、ファイルタグ付きファイルに関しては1つのファイルに対する1操作が終了したら自動的に次のファイルタグ付きファイルに移動するようにしてもよい。
【0074】
さらに上記の第1の実施形態では、インデックスデータを入力する操作手順として、1画像ずつ表示させて確認しながらインデックスデータを入力するようにしているが、これに代わって、すでに公知であるところのバーコードやOCRなどの解析手法を用いて文書画像の内容から自動的にインデックスを生成し、インデックス項目にデータを自動的に入力するようにしてもよい。
【0075】
(第2の実施の形態)
次に、本発明の第2の実施形態として、文書リストWにおいて、ファイルタグが付いたファイルあるいは画像をすべて一括して印刷する方式を説明する。
【0076】
なお、第2の実施形態の構成は、基本的に第1の実施形態の構成と同じであるので、第2の実施形態の説明では第1の実施形態の構成を流用する。
【0077】
図15は、印刷したいファイルあるいは画像に対してファイルタグを付けたときの文書リストWの例を示す図である。
【0078】
それぞれのファイルには表示されているページ数に相当した画像が保存されているが、ファイル1、2、3、5、12、14にはファイルタグ71が付けられている。アイコン72は、そのファイルの中に含まれているページにファイルタグが付けられていることを示すページタグである。
【0079】
図16は、画像が保存されているファイル1からファイル5について、ファイルタグ71とページタグ72とが付いている様子を示す図である。ファイル1には画像201から画像223までのページが保存されているが、図16では最初の5ページだけを示してあり、そのうちの画像201,203,204にページタグ72が付けられている。ファイル2にはファイルタグ71が付けられている。ファイル3には画像271から画像283までのページが存在するが、図16では最初の5ページだけを示してあり、そのうちの画像273と画像275にページタグ72が付けられている。ファイル4にはファイルタグが付けられていない。ファイル5にはファイルタグ71が付けられている。
【0080】
図17は、図16においてファイルタグ71及びページタグ72が付けられているファイル及び画像のプリント出力の様子を示す図である。
【0081】
ファイル1においては、ページタグ72が付けられていた画像201、203、204が印刷され、ペーパP201、P203、P204が出力される。ファイル2では、ファイルタグ71が付けられていたのですべての画像が印刷され、ペーパP231〜P265,・・が出力される。ファイル3では、ページタグ72が付けられていた画像273,275が印刷され、ペーパP273,P275が出力される。ファイル4ではタグが付けられていないので印刷されない。ファイル5では、ファイルタグ71が付けられているのですべての画像が印刷され、ペーパP301〜P305,・・が出力される。
【0082】
次に、第2の実施形態において使用者が行う操作の手順を、図18及び図19を参照して説明する。
【0083】
図18は、ファイルの中に保存されているページに対してページタグを付ける操作の手順を示すフローチャートである。
【0084】
まず、ステップS431で、画像のあるファイルを文書リストWに表示させる。ステップS432で所望のファイルを選択し、ステップS433では、選択ファイルの最初のページ画像を表示させてプリントしたい画像かどうかを確認する。この画像がプリントを取りたい画像であれば(S434でYES)、ステップS435で、現在表示中のページ画像に対してページタグ72を付ける操作を行う。ページタグ72を付ける操作が終了したらステップS436で、そのファイルの最終ページになったことを確認する。最終ページでなければステップS437で、表示しているページを次のページに進めて、ステップS434からステップS437を繰り返す。ファイルの最終ページに到達したならば(S436でYES)、ステップS438で、まだプリントしたいファイルが残っているかを確認する。残っていればステップS439で、次にプリントしたい画像が存在するファイルを選択して、ステップS433からステップS439を繰り返す。プリントしたいファイルが無ければ(S438でNO)、ステップS440でページタグ付け操作を終了する。
【0085】
図19は、文書リストW上でファイルタグ71が付けられたファイルあるいはページタグ72が付けられたページをプリントするときの操作の手順を示すフローチャートである。
【0086】
ステップS451で、ファイルタグ付きファイルとページタグ付きページのプリントを開始すると、まず最初のファイルを選択する(S452)。ステップS453で、選択されたファイルがファイルタグ付きファイルかどうかを判断し、ファイルタグ付きファイルであればステップS454で、このファイルのすべてのページをプリントする。ファイルにファイルタグ71が付いていなければステップS455で当該ファイルの最初のページをチェツクし、ページタグ付きページと判断したら(S456でYES)ステップS457で、このページの画像をプリントする。次に、ステップS458で最終ページになっていなければ、ステップS459で次のページに進んで、ステップS456からステップS459を繰り返す。最終ページに到達していたときにはステップS460で、文書リストWの最後のファイルになつているかを判断する。最終ファイルでなければステップS461で次のファイルに進み、ステップS453からステップS461を繰り返す。最終ファイルになっていればステップS462で、ファイルタグ71が付けられたファイルあるいはページタグ72が付けられたページのプリントを終了する。
【0087】
なお、文書を保存、管理する管理手段においては、保存している画像に対してその画像を新しいものに差し替えることがある。この操作を画像の改訂と言うが、このときに以前の画像を削除しないで改訂画像(改訂ページ)として保存できるようにしたものがある。本発明におけるページタグはこの改訂ページに対して付けられたとしても前述と同様の効果を奏する。この改訂ページにページタグを付けて一括プリントを行う手順を、図20から図22を参照して説明する。
【0088】
図20は、改訂ページが存在するファイルにおいてページタグ72を付けたときの画像の様子を示す図である。
【0089】
画像204の改訂ページが画像204aであり、画像271の改訂ページが画像271aであり、どちらもページタグ72が付けられている。
【0090】
図21は、図20においてファイルタグ71及びページタグ72が付けられているファイル及び画像のプリント出力の様子を示す図である。
【0091】
画像204に対してはペーパP204がプリント出力され、改訂ページ204aに対してはペーパP204aがプリント出力される。また、改訂ページ271aに対してはペーパP271aがプリント出力される。
【0092】
図22は、改訂ページにページタグ72を付けるときの操作の手順を示すフローチャートである。
【0093】
ステップS471で、画像のあるファイルを文書リストWに表示させ、ステップS472で所望のファイルを選択し、ステップS473では、選択ファイルの最初のページ画像を開く。ステップS474では、そのページ画像が改訂されているかどうかを判断し、改訂されていなければステップS475で、プリントする画像かどうかを判定する。プリントが必要な画像であればステップS476で、表示している画像にページタグ72を付ける。
【0094】
ページ画像が改訂されていれば(S474でYES)ステップS477で、その改訂ページを表示してステップS478で、プリントする画像かどうかを判定する。プリントが必要な画像であれば(S478でYES)ステップS479で、表示している改訂ページにページタグ72を付ける。
【0095】
次にステップS480で、当該ファイルの最終ページが選択対象になっているかどうかを確認し、最終ページでなければステップS481で、選択表示しているページを次のページに進めてから、ステップS474からステップS481までを繰り返す。ファイルの最終ページに到達したならば(S480でYES)ステップS482で、まだプリントしたいファイルが残っているかを確認し、残っていればステップS483で、次にプリントしたい画像が存在するファイルを選択して、ステップS473からステップS482までを繰り返す。プリントしたいファイルが無ければステップS484でページタグ付け操作を終了する。
【0096】
ここで説明した改訂ページには、1ページの画像に対して複数回の改訂が行われた結果、複数の改訂ページが存在する場合があるが、この場合も同様の操作でページタグ72を付けて一括操作することができる。
【0097】
以上説明したように、ファイルの記録や検索を行うことができるファイル管理装置において、記録ファイルの属性情報とファイル検索結果情報が一体になった文書リストWを使用して、その文書リストW上のファイルにファイルタグを付加すると共に、ファイルに含まれるページに対してページタグを付ける。そして、ファイルタグが付加されているファイル及びページタグが付加されているページを探し、それらを対象にプリント処理を行う。これにより、一括したプリント処理が容易に行える。
【0098】
(第3の実施の形態)
次に、本発明の第3の実施形態として、文書リストW上でファイルタグが付いたファイルに対して画像をスキャンして新しい画像を一括して保存する方式を説明する。
【0099】
文書リストWには、新規ファイルやインデックス先付けファイルや画像ありファイルが混在しているが、これらのファイルにおいて新たな画像をスキャンして保存するときは、保存先のファイルの種類に応じて保存動作を変える必要がある。例えば、画像ありファイルに対しての新たな画像の保存は追加スキャンとなるが、インデックス先付けファイルに対しての新たな画像の保存は新規スキャンとなる。こうした保存先ファイルの種類に応じて異なる保存動作をすることを避けるために、第3の実施の形態では、同一の文書リストW上で、新たな画像保存の対象ファイルに対してファイルタグを付け、これによって、保存先ファイルの種類に拘わらず一括してこれらの画像の保存を行うようにする。
【0100】
図23は、新たな画像保存の対象ファイルにファイルタグを付けたときの文書リストWの例を示す図である。
【0101】
ファイル1からファイル10までのファイルは、アイコン58が付き、画像がすでに保存されているファイルであり、ファイル11からファイル15までのファイルは、アイコン59が付き、画像が保存されていないインデックス先付けファイルである。ファイル1、2、3、8、12、13のプロパテイ列にはファイルタグ71がそれぞれ付けられている。
【0102】
第3の実施形態では、ファイルタグ71が付けられているファイルに対して順次新たな1ページの画像の保存を行った例を説明する。
【0103】
図24は、図23の文書リストWにおいてファイルタグ71が付けられているファイルに対して、新らたな画像を追加スキャンあるいは新規スキャンによって保存した様子を示す図である。
【0104】
ファイル1にはファイルタグ71が付けれられているので、最終画像223の次に新規画像224が追加されている。ファイル2に対しても同様に新規画像266が追加されている。ファイル12は、画像が保存されていないインデックス先付けファイルなので、画像は追加されないで新規画像339がファイル12に保存される。ファイル13についても同様に新規画像340が保存される。
【0105】
図25は、画像のあるファイル、インデックス先付けファイル、新規ファイルに対してファイルタグを付ける操作の手順を示すフローチャートである。
【0106】
ステップS501で、検索したファイルを文書リストWに表示させ、ステップS502で、その文書リストWの最初のファイルを選択する。ステップS503で、選択されたファイルが画像のあるファイルであるかどうかを判別し、画像のあるファイルであると判別した場合、まずそのファイルの最初のページを表示して画像の内容を確認する(S504)。その結果、画像の追加スキャンが必要であると判断した場合(S505でYES)ステップS510で、そのファイルにファイルタグ71を付ける操作を行う。
【0107】
選択されたファイルが画像のあるファイルでなければ(S503でNO)ステップS506で、選択されたファイルがインデックス先付けファイルであるかを判断し、インデックス先付けファイルならばステップS507で、先付けされているインデックスの内容を確認する。その結果、画像の新規スキャンが必要であると判断した場合(S508でYES)ステップS510で、そのファイルにファイルタグ71を付ける操作を行う。
【0108】
選択されたファイルがインデックス先付けファイルでないならば(S506でNO)ステップS509で、新規ファイルであるか否かを判断し、新規ファイルであると判断したときはステップS510で、ファイルタグを付けて画像の新規スキャンを行うようにする。
【0109】
ステップS511で、選択ファイルが文書リストWの最後のファイルであるか否かを判断し、最後のファイルではないと判断したときにはステップS512で、文書リストWで次のファイルを選択し、ステップS503へ戻る。最後のファイルであったときにはステップS513でファイルタグ付け操作を終了する。
【0110】
図26は、文書リストW上のファイルタグ付きファイルにおいて1ページずつ画像をスキャンして保存していくときの動作を示すフローチャートである。
【0111】
ステップS521で、ファイルタグ付きファイルに対してスキャン処理を開始するとまずステップS522で、文書リストWの最初のファイルを選択する。ステップS523で、選択されたファイルがファイルタグ71の付いたファイルであるか否かを判断する。ファイルタグ71の付いたファイルならば、ステップS524で、選択されたファイルが画像のあるファイルであるか否かを判断する。画像のあるファイルであると判断した場合、ステップS524で、そのファイルの中の最終ページの後ろにスキャンした画像を追加する。
【0112】
選択されたファイルが画像のあるファイルではないと判断した場合(S524でNO)ステップS526で、選択されたファイルがインデックス先付けファイルであるか否かを判断する。インデックス先付けファイルであると判断した場合、ステップS527で画像の新規スキャンを行う。
【0113】
選択されたファイルがインデックス先付けファイルでないと判断した場合(S526でNO)ステップS528で、新規ファイルであるか否かを判断する。新規ファイルであったときステップS527で画像の新規スキャンを行う。
【0114】
ステップS529で、選択したファイルが文書リストW上で最終ファイルであるか否かを判断し、最終ファイルになっていなければ、ステップS530で次のファイルに進み、ステップS523からステップS529を繰り返す。最終ファイルになっていれば、ステップS531でファイルタグ付きファイルへのスキャン動作を終了する。
【0115】
文書リストWのファイルに対して画像をスキャンして保存する方法としては1ファイルずつ確認しながらスキャンしてもよいが、本実施形態のように1ファイルに対して1ページずつファイル送りしながら順次記録していく方法や、決められた複数ページを記録しながら順次ファイル送りをする方法など、自動的にファイルタグの付けられたファイルを順送りしながら画像をスキャンして記録していく方法をとることもできる。
【0116】
第3の実施形態ではスキャンによって画像を保存するようにしているが、これに代わって、例えば画像のコピーやインポートなどの方法を用いて新たに画像を追加保存させるようにしたときにも同様の効果が得られる。
【0117】
以上のように、文書リストWを用いて、対象となるファイルに対してファイルタグを付けて画像のスキャンを行うときに、その文書リストに含まれるファイルの種別、属性などを判断しながら連続してスキャンを行うので、複数のファイルに対するスキャンを効率よく行うことができる。
【0118】
以上の各実施の形態では、文書リストWの対象となるファイルタグ付きファイルあるいはページタグ付きページに対して、インデックス後付け、プリント、スキャンをするときの方式について述べた。しかしながら、この方式は、ファイルの削除、ファイルのコピー、ファイルのエクスポート、ファイルの統合、インデックス先付け、ファイルの移動、表示ページの移動、表示ファイルの移動、インデックス修正ファイルの移動など、文書リストWにおいて任意の複数のファイルあるいはページを一括して操作する際に、すべて同様の効果があることはもちろんである。
【0119】
なお、本発明を、複数の機器から構成されるシステムに適用しても、あるいは1つの機器からなる装置に適用してもよい。
【0120】
また、前述した各実施形態の機能を実現するソフトウェアのプログラムコードを記憶した記憶媒体を、システムあるいは装置に供給し、そのシステムあるいは装置のコンピュータ(またはCPUやMPU)が記憶媒体に格納されたプログラムコードを読み出して実行することによっても、本発明が達成されることは言うまでもない。
【0121】
この場合、記憶媒体から読み出されたプログラムコード自体が、前述の各実施形態の機能を実現することになり、そのプログラムコードを記憶した記憶媒体が本発明を構成することになる。
【0122】
プログラムコードを供給するための記憶媒体として、例えば、フロッピィディスク、ハードディスク、光ディスク、光磁気ディスク、CD−ROM、CD−R、磁気テープ、不揮発性のメモリカード、ROMなどを用いることができる。
【0123】
また、コンピュータが読み出したプログラムコードを実行することにより、前述した各実施形態の機能が実現されるだけでなく、そのプログラムコードの指示に基づき、コンピュータ上で稼働しているOSなどが実際の処理の一部または全部を行い、その処理によって前述した各実施形態の機能が実現される場合も、本発明に含まれることは言うまでもない。
【0124】
さらに、記憶媒体から読み出されたプログラムコードが、コンピュータに挿入された機能拡張ボードやコンピュータに接続された機能拡張ユニットに備わるメモリに書き込まれた後、そのプログラムコードの指示に基づき、その機能拡張ボードや機能拡張ユニットに備わるCPUなどが実際の処理の一部または全部を行い、その処理によって前述した各実施形態の機能が実現される場合も、本発明に含まれることは言うまでもない。
【0125】
【発明の効果】
以上詳述したように請求項1、請求項5、または請求項6記載の発明によれば、画像情報とインデックスデータとをレコードに関連付けて管理するリストにおいて、新たな画像の保存処理を施したい複数のレコードに同一の標識マークを付加しておく。後刻、前記リストにおいて標識マークの付加されたレコードを探し、発見されたレコードに応じた保存処理を行う。
【0126】
これによって、ファイルを新規に記録する操作と追加して記録する操作や、検索操作と記録操作とが一括して行うことができ、操作性が改善される。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】第1の実施形態に係るファイル管理装置のハードウエアの構成を示すブロック図である。
【図2】ファイル管理装置でファイル管理処理が行われることによって実現する諸機能の構成を示す図である。
【図3】文書リスト制御手段の制御動作を示すフローチャート(2/2)である。
【図4】文書リストを示す図である。
【図5】Aは検索動作を行なった場合の検索前の文書リストを示す図である。Bは検索動作を行なった場合の検索後の文書リストを示す図である。
【図6】Aは新規記録を行なった場合の新規記録前の文書リストを示す図である。Bは新規記録を行なった場合の新規記録後の文書リストを示す図である。
【図7】Aはインデックス情報の後付けを行なった場合の処理前の文書リストを示す図である。Bはインデックス情報の後付けを行なった場合の処理後の文書リストを示す図である。
【図8】Aはインデックス情報の先付けを行なった場合の処理前の文書リストを示す図である。Bはインデックス情報の先付けを行なった場合の処理後の文書リストを示す図である。
【図9】Aはインデックス情報の先付けファイルに対して画像の記録を行なった場合の画像記録前の文書リストを示す図である。Bはインデックス情報の先付けファイルに対して画像の記録を行なった場合の画像記録後の文書リストを示す図である。
【図10】インデックスデータが入力されていないファイルに対してファイルタグが付けられた文書リストの例を示す図である。
【図11】ファイルタグが付けられたファイルに対してインデックスデータを入力した後の文書リストの例を示す図である。
【図12】保存された画像に対して各ファイル単位でファイルタグが付され、画像記録部に記録されている画像の例を示す図である。
【図13】画像がすでに保存されている所望のファイルに対してインデックス後付けのためのファイルタグを付ける操作の手順を示すフローチャートである。
【図14】ファイルタグが付けられたファイルに対してインデックスデータを順次入力していく操作の手順を示すフローチャートである。
【図15】印刷したいファイルあるいは画像に対してファイルタグを付けたときの文書リストの例を示す図である。
【図16】画像が保存されているファイルにおいて、ファイルタグとページタグとが付いている様子を示す図である。
【図17】図16においてファイルタグ及びページタグが付けられているファイル及び画像のプリント出力の様子を示す図である。
【図18】ファイルの中に保存されているページに対してページタグを付ける操作の手順を示すフローチャートである。
【図19】文書リスト上でファイルタグが付けられたファイルあるいはページタグが付けられたページをプリントするときの操作の手順を示すフローチャートである。
【図20】改訂ページが存在するファイルにおいてページタグを付けたときの画像の様子を示す図である。
【図21】図20においてファイルタグ及びページタグが付けられているファイル及び画像のプリント出力の様子を示す図である。
【図22】改訂ページにページタグを付けるときの操作の手順を示すフローチャートである。
【図23】新たな画像保存の対象ファイルにファイルタグを付けたときの文書リストの例を示す図である。
【図24】図23の文書リストにおいてファイルタグが付けられているファイルに対して、新らたな画像を追加スキャンあるいは新規スキャンによって保存した様子を示す図である。
【図25】画像のあるファイル、インデックス先付けファイル、新規ファイルに対してファイルタグを付ける操作の手順を示すフローチャートである。
【図26】文書リスト上のファイルタグ付きファイルにおいて1ページずつ画像をスキャンしていくときのスキャン動作を示すフローチャートである。
【図27】Aはスキャナを用いて原稿をスキャンし、文書データベースにその画像を保存するときの従来における画像ファイリングシステムの構成を示すブロック図である。Bは文書データベースにおいて検索手段を用いて所望の画像を検索するときの従来における画像ファイリングシステムの構成を示すブロック図である。
【符号の説明】
1 CPU
3 ディスプレイ
5 キーボード
7 スキャナ
9 メモリ(画像データ用)
11 メモリ(インデックスデータベース用)
13 メモリ(プログラム動作用)
15 メモリ(プログラム保存用)
17 外部ディスク接続装置
23 インデックスデータ記録部管理手段
24 検索条件入力手段
25 検索手段
26 スキャナ
28 インデックス入力手段
30 文書リスト制御手段
31 文書リスト表示手段
32 画像制御手段
41 画像表示部
71 ファイルタグ
72 ページタグ
201 プリンタ
W 文書リスト[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a file management apparatus, a file management method, and a storage medium, and more specifically, a file management apparatus capable of storing a plurality of files and searching for a file, a file management method applied to the file management apparatus, And a storage medium storing a program for executing the file management method.
[0002]
[Prior art]
2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, there has been known an image management system that reads a document image such as a document or a drawing, edits it as appropriate, and records and manages the image on a magnetic disk, a magneto-optical disk, or the like.
[0003]
In general, in such an image management system, image information obtained by reading a document image is compressed and recorded on a hard disk or an optical disk. In addition, index information for searching for an image is recorded in association with the image information. A necessary image is retrieved from the index information, and the image information is read out based on the retrieval result and displayed on a display, or the image is output to a recording sheet by a printer. Also, various image processing such as image addition, editing and processing is performed as necessary.
[0004]
27A and 27B show a conventional example of a general image filing system.
[0005]
FIG. 27A is a block diagram showing a configuration of an image filing system when a document is scanned using a scanner and the image is stored in a document database. A
[0006]
First, an image read from a document by the
[0007]
FIG. 27B is a block diagram illustrating a configuration of an image filing system when a desired image is searched using a search unit in a document database.
[0008]
First, when the condition of an image to be searched is input from the search
[0009]
Based on the
[0010]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, the conventional image filing system has a configuration in which the document recording operation and the search operation are separated from each other. Further, in the recording operation, image scanning and index input operations are performed in a fixed procedure. It was.
[0011]
In the recording operation, document recording and index input are performed for each individual document.
[0012]
For this reason, in the recording operation of a plurality of documents, the operator needs to perform scanning and index input alternately, so that the operation becomes complicated and the productivity is low.
[0013]
In addition, since the recording operation and the search operation were separated, it is necessary to correct the correct data by performing the search operation after the recording operation is ended for the erroneous data entered by the erroneous operation. It required many operation steps and operation time.
[0014]
In addition, in order to perform batch operations on multiple images, it is possible to attach the same identification mark to multiple images and perform batch operations by searching only for images with identification marks. However, in such a method, after the recording operation is finished, it is necessary to shift to a search operation, search for a desired image, confirm it, and then shift to an image scan or index input operation again. The operation was very complicated.
[0015]
The present invention has been made in view of such problems, and an object thereof is to provide a file management apparatus, a file management method, and a storage medium with improved operability.
[0016]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to achieve the above object, according to the file management device of
[0017]
[0018]
And claims 6 Storage medium described Is a computer-readable list management means for associating a computer with image information and index data and associating the record with a list and displaying a list of a plurality of records, and predetermined image information is already associated with the computer. Display means for displaying a list of records in which the predetermined index data is associated first and the image information is not associated, and a new record in which both the image information and the index data are not associated, In the list displayed by the display means, a mark adding means for adding the same mark mark to a plurality of records for which a new image is to be stored, and a selection for sequentially selecting the record to which the mark mark is added in the list Means, the record being selected by the selection means is Is a record in which certain image information is already associated, or is a record in which the predetermined index data is associated in advance and image information is not associated, or both image information and index data are not associated A determination unit that determines whether the record is a new record, and a record that is being selected by the selection unit is newly input when the determination unit determines that the predetermined image information is already associated with the record. The added image information is added after the last page in the selected record, and the predetermined index data is associated first and the image information is not associated, or both the image information and the index data are not associated. Newly entered image if it is determined to be a new record It stores a program to function as the processing execution means for executing a process of adding the records in the selected a broadcast It is characterized by that.
[0019]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
[0020]
(First embodiment)
A first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS.
[0021]
(Hardware configuration)
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a hardware configuration of the file management apparatus according to the first embodiment.
[0022]
[0023]
A program executed by the file management apparatus is provided to the file management apparatus from the outside by a floppy disk or the like. The program on the floppy disk is read from the external
[0024]
(Configuration of software processing)
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of various functions realized by performing file management processing in the file management apparatus.
[0025]
[0026]
[0027]
The document
[0028]
The
[0029]
[0030]
Next, document search, new document recording, and index input in the above configuration will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing the control operation of the document list control means 30.
[0031]
(Search operation)
The user inputs a search condition for searching for a desired document from the search condition input means 24. The search condition includes, for example, a keyword.
[0032]
The input search condition is passed to the search means 25 (generally also called a search engine), and the search means 25 passes through the index data recording section management means 23 to search conditions from the document database in the index
[0033]
(New record)
The user activates the scanner control means 27 and reads a new document from the scanner 26 (YES in S20). The
[0034]
The document list control means 30 creates a new record by adding a new document to the already displayed document list based on the new document generation information, and displays it (S21, S22). This record includes document attributes determined at the time of scanning, such as the creation date and the number of pages. The updated document attribute is recorded in the index
[0035]
(Index added)
The user instructs the document list control means 30 to start index input (YES in S30). By this instruction, the document
[0036]
(Index assignment)
Note that index indexing can be performed in which index information is input prior to document input. Hereinafter, the index assignment operation will be described.
[0037]
The user instructs the document list control means 30 to assign an index (YES in S40). In response to this instruction, the document list control means 30 enables an index to be input to the newest record at the bottom of the document list (S41). This new record is not related to the image data at this time. Next, the user inputs new index data from the index input means 28 (S42). This data is displayed on the document list by the document list control means 30 (S43) and, if necessary, recorded in the index
[0038]
(Recording an image to an index record)
The user can input image data in association with the above-described index assignment record (YES in S50). First, the user selects the index-assigned record corresponding to the input image data to the document list control means 30 (S51). Next, image data is read from the
[0039]
The address information of the recorded image may be directly transferred from the image recording
[0040]
(Display and print image information)
The user can select an arbitrary file from the document list and display and print the image information.
[0041]
When the user selects an arbitrary file in the document list and instructs display of an image with the
[0042]
Similarly, in the printing of image information, the document
[0043]
Next, the above operation will be described in more detail on the document list.
[0044]
(Structure of sentence number list)
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the document list W. As shown in FIG. The document list W is generated by the document list control means 30 and displayed on the
[0045]
Further, in the document list W shown in FIG. 4, the image-recorded file and the index-attached file in which only the index is input first are displayed on the same screen so as to be clearly distinguished. That is, the
[0046]
The file in the
[0047]
(Search operation)
5A and 5B are diagrams showing a document list W when a search operation is performed. The document list W in FIG. 5A includes all cases of stored documents, and is an example of an initial state before performing a search operation. Here, when the user inputs, for example, rank “A” as a search condition to the search
[0048]
(New record)
6A and 6B are diagrams showing a document list W when new recording is performed. FIG. 6A shows a document list before new recording. Here, a new document is read using the
[0049]
FIG. 6B shows a document list W created and displayed by the new document recording operation as described above. The records (files) of
[0050]
(Index added)
7A and 7B are diagrams showing a document list W when index information is retrofitted.
[0051]
The user instructs the document list control means 30 to start index input. By this instruction, as shown in FIG. 7A, the document
[0052]
When the input operation to one index item is finished, the operation can be shifted to the input operation to the next index item (for example, the index item on the right side of the figure). Similarly, when the index input operation for one record (file) is finished, the operation can be shifted to the index input operation for the next record (file) (for example, the lower record in the figure). For example, in the example of FIG. 7A, the index input is started from the title column of the
[0053]
Furthermore, it is also possible to specify a column to be input (for example, only Chapter and Rank) and perform continuous input only to the specified column.
[0054]
(Index assignment)
8A and 8B are diagrams showing a document list W when index information is pre-attached.
[0055]
The user instructs the document list control means 30 to assign an index. By this instruction, as shown in FIG. 8A, the document list control means 30 enables an index input to the newest record at the bottom end of the document list. Next, the user inputs new index data from the index input means 28. This data is displayed on the document list by the document
[0056]
When the input operation to one index item is completed, the operation can be shifted to the input operation to the next index item. Similarly, when the index input operation for one record (file) is completed, it is possible to move to the index input operation for another record (file). At this time, a file that is not related to the image data is created as an index assignment file. Is done. For example, in the example of FIG. 8A, the index input is started from the title column of the new file, and the index input is continuously performed up to the chapter column of the
[0057]
(Recording an image to an index record)
FIG. 9A and FIG. 9B are diagrams showing a document list W when an image is recorded on the index information prior file.
[0058]
First, the user performs an operation for selecting the index-assigned record to the document
[0059]
FIG. 9B shows a document list W created and displayed by the new document recording operation as described above. Image information is input to the files of
[0060]
Based on these document list examples, an example in which an identification mark is attached to each desired file on the document list and a batch operation is performed on the file with the identification mark is shown below. Hereinafter, this identification mark is referred to as a tag. A tag attached to a file is a file tag, and a tag attached to a page included in the file is a page tag.
[0061]
FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating an example of a document list W in which file tags are attached to files for which no index data is input. In the document list of FIG. 10, each file already stores a number of images corresponding to the number of pages. In each file with
[0062]
FIG. 11 is a diagram illustrating an example of the document list W after the index data is input to the file with the file tag attached. A document list W obtained as a result of sequentially inputting index data to the index column and chapter column in each file tag is shown.
[0063]
FIG. 12 is a diagram illustrating an example of an image recorded in the
[0064]
Next, an operation procedure performed by the user in the first embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 13 and 14.
[0065]
FIG. 13 is a flowchart showing an operation procedure for attaching a
[0066]
First, in step S401, a file in which an image is already stored is searched and displayed on the document list W. In step S402, the first file on the document list W is selected, and in step S403, it is confirmed whether index data is input to the title column of the selected file. If no index data is input to the title column in step S404, the process proceeds to step S405, and an operation for attaching the
[0067]
When the operation of attaching the
[0068]
FIG. 14 is a flowchart showing a procedure of operations for sequentially inputting index data to a file to which a
[0069]
First, in step S411, the first file with the
[0070]
As described above, in a file management apparatus capable of recording and searching for a file, it is necessary to input an index using the document list W in which the attribute information of the recording file and the file search result information are integrated. A
[0071]
In the first embodiment described above, file tags are attached to the files displayed in the document list W one by one, but instead, a plurality of files are selected together to select file tags. You may make it attach.
[0072]
Further, a file tag may be attached by designating a file number.
[0073]
In the first embodiment described above, when performing a post-indexing operation on a file with a file tag at once, when the operation on one file is completed, the next file tag is searched for and moved. However, instead of this, regarding a file tagged file, it may be automatically moved to the next file tagged file when one operation for one file is completed.
[0074]
Furthermore, in the first embodiment, as an operation procedure for inputting the index data, the index data is input while displaying and confirming the images one by one. An index may be automatically generated from the contents of the document image using an analysis method such as barcode or OCR, and data may be automatically input to the index item.
[0075]
(Second Embodiment)
Next, as a second embodiment of the present invention, a method for collectively printing all files or images with file tags in the document list W will be described.
[0076]
Since the configuration of the second embodiment is basically the same as the configuration of the first embodiment, the configuration of the first embodiment is used in the description of the second embodiment.
[0077]
FIG. 15 is a diagram showing an example of the document list W when a file tag is attached to a file or image to be printed.
[0078]
Each file stores images corresponding to the number of displayed pages, but files 1, 2, 3, 5, 12, and 14 have
[0079]
FIG. 16 is a diagram illustrating a state in which a
[0080]
FIG. 17 is a diagram showing a state of print output of files and images to which the
[0081]
In the
[0082]
Next, an operation procedure performed by the user in the second embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 18 and 19.
[0083]
FIG. 18 is a flowchart showing a procedure of an operation for attaching a page tag to a page stored in a file.
[0084]
First, a file with an image is displayed on the document list W in step S431. In step S432, a desired file is selected, and in step S433, the first page image of the selected file is displayed to check whether the image is to be printed. If this image is an image to be printed (YES in S434), an operation of attaching a
[0085]
FIG. 19 is a flowchart showing an operation procedure when printing a file with a
[0086]
In step S451, when printing of a file with a file tag and a page with a page tag is started, the first file is selected (S452). In step S453, it is determined whether the selected file is a file-tagged file. If it is a file-tagged file, all pages of this file are printed in step S454. If the
[0087]
In the management means for storing and managing the document, the stored image may be replaced with a new one. This operation is called image revision. At this time, there is an image that can be saved as a revised image (revision page) without deleting the previous image. Even if the page tag in the present invention is attached to the revised page, the same effect as described above can be obtained. A procedure for performing batch printing with a page tag attached to the revised page will be described with reference to FIGS.
[0088]
FIG. 20 is a diagram illustrating a state of an image when a
[0089]
The revised page of the
[0090]
FIG. 21 is a diagram showing a state of print output of files and images to which the
[0091]
Paper P204 is printed out for the
[0092]
FIG. 22 is a flowchart showing an operation procedure when the
[0093]
In step S471, a file with an image is displayed on the document list W. In step S472, a desired file is selected. In step S473, the first page image of the selected file is opened. In step S474, it is determined whether the page image has been revised. If it has not been revised, it is determined in step S475 whether it is an image to be printed. If the image requires printing, the
[0094]
If the page image has been revised (YES in S474), the revised page is displayed in step S477, and it is determined in step S478 whether the image is to be printed. If the image needs to be printed (YES in S478), the
[0095]
Next, in step S480, it is confirmed whether or not the last page of the file is a selection target. If it is not the last page, the page currently selected and displayed is advanced to the next page in step S481, and from step S474. Steps up to step S481 are repeated. If the last page of the file has been reached (YES in S480), in step S482, it is confirmed whether there is still a file to be printed. If it remains, in step S483, the file containing the next image to be printed is selected. Steps S473 to S482 are repeated. If there is no file to be printed, the page tagging operation is terminated in step S484.
[0096]
In the revised page described here, there may be a plurality of revised pages as a result of a plurality of revisions to the image of one page. In this case, the
[0097]
As described above, in a file management apparatus capable of recording and searching for a file, the document list W in which the attribute information of the recording file and the file search result information are integrated is used on the document list W. A file tag is added to the file, and a page tag is attached to a page included in the file. Then, a file to which a file tag is added and a page to which a page tag is added are searched, and print processing is performed on them. Thereby, batch print processing can be easily performed.
[0098]
(Third embodiment)
Next, as a third embodiment of the present invention, a method for scanning a file with a file tag on the document list W and saving new images all together will be described.
[0099]
The document list W contains a mixture of new files, indexed files, and files with images. When a new image is scanned and saved in these files, the save operation depends on the type of the save destination file. Need to change. For example, saving a new image for a file with an image is an additional scan, but saving a new image for an index-attached file is a new scan. In order to avoid different saving operations depending on the type of the save destination file, in the third embodiment, a file tag is attached to a new file to be saved on the same document list W. As a result, these images are collectively saved regardless of the type of the save destination file.
[0100]
FIG. 23 is a diagram showing an example of the document list W when a file tag is attached to a new image storage target file.
[0101]
The files from
[0102]
In the third embodiment, an example will be described in which a new one-page image is sequentially stored in a file to which a
[0103]
FIG. 24 is a diagram illustrating a state in which a new image is saved by an additional scan or a new scan for a file to which a
[0104]
Since a
[0105]
FIG. 25 is a flowchart showing a procedure of an operation for attaching a file tag to a file with an image, an index file, and a new file.
[0106]
In step S501, the searched file is displayed in the document list W, and the first file in the document list W is selected in step S502. In step S503, it is determined whether or not the selected file is a file with an image. If it is determined that the selected file is a file with an image, the first page of the file is first displayed to confirm the contents of the image ( S504). As a result, if it is determined that an additional scan of the image is necessary (YES in S505), an operation of attaching the
[0107]
If the selected file is not a file with an image (NO in step S503), it is determined in step S506 whether the selected file is an index-priority file. If the selected file is an index-priority file, the index that has been prioritized is determined in step S507. Check the contents of. As a result, when it is determined that a new scan of the image is necessary (YES in S508), an operation of attaching the
[0108]
If the selected file is not an index pre-attached file (NO in S506), it is determined whether or not it is a new file in step S509. If it is determined that the file is a new file, in step S510, a file tag is attached to the image. To perform a new scan.
[0109]
In step S511, it is determined whether or not the selected file is the last file in the document list W. If it is determined that the selected file is not the last file, the next file is selected in the document list W in step S512, and the process advances to step S503. Return. If it is the last file, the file tagging operation is terminated in step S513.
[0110]
FIG. 26 is a flowchart showing an operation when scanning and saving an image page by page in a file-tagged file on the document list W.
[0111]
When the scanning process is started for the file tagged file in step S521, the first file in the document list W is first selected in step S522. In step S523, it is determined whether or not the selected file is a file with a
[0112]
If it is determined that the selected file is not a file with an image (NO in S524), it is determined in step S526 whether the selected file is an index file. If it is determined that the file is an index-attached file, a new image is scanned in step S527.
[0113]
If it is determined that the selected file is not an index file (NO in S526), it is determined in step S528 whether or not it is a new file. If it is a new file, a new scan of the image is performed in step S527.
[0114]
In step S529, it is determined whether or not the selected file is the last file on the document list W. If it is not the last file, the process proceeds to the next file in step S530, and steps S523 to S529 are repeated. If it is the final file, the scanning operation for the file-tagged file ends in step S531.
[0115]
As a method of scanning and saving an image with respect to a file in the document list W, scanning may be performed while checking one file at a time. However, as in this embodiment, the files are sequentially sent one page at a time for each file. A method of scanning and recording images while sequentially feeding files with file tags automatically, such as a method of recording or sequentially sending files while recording a predetermined number of pages You can also.
[0116]
In the third embodiment, an image is stored by scanning. However, instead of this, for example, when a new image is additionally stored by using a method such as copy or import of an image, the same applies. An effect is obtained.
[0117]
As described above, when an image is scanned with a file tag attached to a target file using the document list W, it is continuously determined while determining the type and attribute of the file included in the document list. Therefore, it is possible to efficiently scan a plurality of files.
[0118]
In each of the above-described embodiments, the method for performing post-indexing, printing, and scanning on a file-tagged file or a page-tagged page that is the target of the document list W has been described. However, this method is used in the document list W such as file deletion, file copy, file export, file integration, index assignment, file movement, display page movement, display file movement, index correction file movement, etc. Needless to say, all the same effects can be obtained when manipulating a plurality of arbitrary files or pages.
[0119]
The present invention may be applied to a system composed of a plurality of devices or an apparatus composed of a single device.
[0120]
Further, a storage medium storing software program codes for realizing the functions of the above-described embodiments is supplied to a system or apparatus, and a computer (or CPU or MPU) of the system or apparatus is stored in the storage medium. It goes without saying that the present invention can also be achieved by reading and executing the code.
[0121]
In this case, the program code itself read from the storage medium realizes the functions of the above-described embodiments, and the storage medium storing the program code constitutes the present invention.
[0122]
As a storage medium for supplying the program code, for example, a floppy disk, hard disk, optical disk, magneto-optical disk, CD-ROM, CD-R, magnetic tape, nonvolatile memory card, ROM, or the like can be used.
[0123]
Further, by executing the program code read by the computer, not only the functions of the above-described embodiments are realized, but the OS running on the computer based on the instruction of the program code performs the actual processing. Needless to say, the present invention also includes a case where the functions of the above-described embodiments are realized by performing part or all of the above-described processing.
[0124]
Further, after the program code read from the storage medium is written to a memory provided in a function expansion board inserted into the computer or a function expansion unit connected to the computer, the function expansion is performed based on the instruction of the program code. Needless to say, the present invention also includes the case where the CPU or the like provided in the board or the function expansion unit performs part or all of the actual processing and the functions of the above-described embodiments are realized by the processing.
[0125]
【The invention's effect】
[0126]
As a result, an operation for newly recording a file, an operation for additionally recording a file, and a search operation and a recording operation can be performed in a lump, thereby improving operability.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a hardware configuration of a file management apparatus according to a first embodiment.
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of various functions realized by performing file management processing in a file management apparatus.
FIG. 3 is a flowchart (2/2) illustrating a control operation of a document list control unit.
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a document list.
FIG. 5A is a diagram showing a document list before search when a search operation is performed. B is a diagram showing a document list after retrieval when a retrieval operation is performed.
FIG. 6A is a diagram showing a document list before new recording when new recording is performed. B is a diagram showing a document list after new recording when new recording is performed.
FIG. 7A is a diagram showing a document list before processing when index information is retrofitted. B is a diagram showing a processed document list when index information is retrofitted.
FIG. 8A is a diagram showing a document list before processing when index information is assigned in advance. B is a diagram showing a processed document list when index information is pre-attached.
FIG. 9A is a diagram showing a document list before image recording when an image is recorded on an index information prior file. B is a diagram showing a document list after image recording in a case where an image is recorded on an index information prior file.
FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating an example of a document list in which a file tag is attached to a file for which index data has not been input.
FIG. 11 is a diagram showing an example of a document list after index data is input to a file with a file tag attached thereto.
FIG. 12 is a diagram illustrating an example of an image recorded in an image recording unit with a file tag attached to each stored file for each file.
FIG. 13 is a flowchart showing a procedure of an operation for attaching a file tag for index addition to a desired file in which an image has already been stored.
FIG. 14 is a flowchart showing an operation procedure for sequentially inputting index data to a file with a file tag attached thereto.
FIG. 15 is a diagram illustrating an example of a document list when a file tag is attached to a file or image to be printed.
FIG. 16 is a diagram illustrating a state in which a file tag and a page tag are attached to a file in which an image is stored.
FIG. 17 is a diagram showing a state of print output of files and images to which file tags and page tags are attached in FIG. 16;
FIG. 18 is a flowchart showing a procedure of an operation for attaching a page tag to a page stored in a file.
FIG. 19 is a flowchart showing an operation procedure when printing a file tag or a file with a page tag on a document list.
FIG. 20 is a diagram illustrating an image when a page tag is attached to a file in which a revised page exists.
FIG. 21 is a diagram illustrating a state of print output of files and images to which file tags and page tags are attached in FIG. 20;
FIG. 22 is a flowchart showing an operation procedure when a page tag is attached to a revised page.
FIG. 23 is a diagram illustrating an example of a document list when a file tag is attached to a new image storage target file.
FIG. 24 is a diagram illustrating a state in which a new image is stored by additional scanning or new scanning with respect to a file to which a file tag is attached in the document list of FIG.
FIG. 25 is a flowchart illustrating a procedure of an operation for attaching a file tag to a file with an image, an index assignment file, and a new file.
FIG. 26 is a flowchart showing a scanning operation when an image is scanned page by page in a file-tagged file on a document list.
FIG. 27A is a block diagram showing the configuration of a conventional image filing system when a document is scanned using a scanner and the image is stored in a document database. B is a block diagram showing a configuration of a conventional image filing system when a desired image is searched using a search means in a document database.
[Explanation of symbols]
1 CPU
3 Display
5 Keyboard
7 Scanner
9 Memory (for image data)
11 Memory (for index database)
13 Memory (for program operation)
15 Memory (for saving programs)
17 External disk connection device
23 Index data recording unit management means
24 Search condition input means
25 Search means
26 Scanner
28 Index input means
30 Document list control means
31 Document list display means
32 Image control means
41 Image display
71 File tag
72 page tags
201 Printer
W Document list
Claims (6)
所定の画像情報が既に関連付けられているレコードと、所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコードと、画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードとを前記リストに一覧表示する表示手段と、
前記表示手段により表示されたリストにおいて、新たな画像の保存を行いたい複数のレコードに、同一の標識マークを付加するマーク付加手段と、
前記リストにおいて前記標識マークの付加されたレコードを順番に選択する選択手段と、
前記選択手段で選択中のレコードが、所定の画像情報が既に関連付けられているレコードであるか、所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコードであるか、画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードであるか、を判定する判定手段と、
前記選択手段で選択中のレコードが、前記判定手段によって、前記所定の画像情報が既に関連づけられているレコードであると判定された場合に、新たに入力された画像情報を当該選択中のレコードにおける最終ページの後に追加し、前記所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコード又は画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードであると判定された場合に、新たに入力された画像情報を当該選択中のレコードに追加する処理を実行する処理実行手段と、を有することを特徴とするファイル管理装置。A list management means for associating image information and index data with a record, and managing images using a list in which a plurality of records are displayed ;
A record in which predetermined image information is already associated, a record in which predetermined index data is associated first and image information is not associated, and a new record in which both image information and index data are not associated Display means for displaying a list in a list;
In list displayed by the display means, a plurality of records you want to save the new image, a mark adding means for adding the same label mark,
A selection means for sequentially selecting the records to which the mark marks are added in the list ;
Whether the record being selected by the selection means is a record in which predetermined image information is already associated, a record in which predetermined index data is associated in advance and image information is not associated, A determination means for determining whether the index data is a new record not associated with both;
When the record being selected by the selection means is determined by the determination means to be a record in which the predetermined image information has already been associated, the newly input image information in the record being selected When it is determined that the record is added after the last page and the predetermined index data is associated with the image information and the image information is not associated with each other, or the image information and the index data are not associated with each other, A file management apparatus comprising: processing execution means for executing processing for adding newly input image information to the selected record .
前記マーク付加手段は、前記検索手段で検索されて一覧表示されたリストにおいて、前記新たな画像の保存を行いたい複数のレコードに、同一の標識マークを付加することを特徴とする請求項1から請求項3のいずれか1項に記載のファイル管理装置。 It further has a search means for searching for a record satisfying the input search condition and displaying a list of the searched records on the display means,
The mark adding means, in the list displayed list is searched by the searching means, wherein the plurality of records you want to save the new image, claim 1, characterized in that for adding the same label mark the file management apparatus according to any one of claims 3.
表示手段が、所定の画像情報が既に関連付けられているレコードと、所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコードと、画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードとを前記リストに一覧表示する表示ステップと、
マーク付加手段が、前記表示されたリストにおいて、新たな画像の保存を行いたい複数のレコードに、同一の標識マークを付加するマーク付加ステップと、
選択手段が、前記リストにおいて前記標識マークの付加されたレコードを順番に選択する選択ステップと、
判定手段が、前記選択ステップで選択中のレコードが、所定の画像情報が既に関連付けられているレコードであるか、所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコードであるか、画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードであるかを判定する判定ステップと、
処理実行手段が、前記判定ステップで、前記選択中のレコードが、前記所定の画像情報が既に関連づけられているレコードであると判定された場合に、新たに入力された画像情報を当該選択中のレコードにおける最終ページの後に追加し、前記所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコード又は画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードであると判定された場合に、新たに入力された画像情報を当該選択中のレコードに追加する処理を実行する処理実行ステップと、を有することを特徴とするファイル管理方法。 A list management step in which the list management means associates the image information and the index data with the record, and manages the image using a list in which a plurality of records are displayed in a list;
The display means includes a record in which the predetermined image information is already associated, a record in which the predetermined index data is associated in advance and the image information is not associated, and a new in which both the image information and the index data are not associated. A display step for displaying records in the list;
Mark adding means, in the displayed list, a plurality of records you want to save the new image, a mark adding step of adding the same label mark,
A selection step in which the selection means sequentially selects the records to which the mark marks are added in the list ;
Whether the record being selected in the selection step is a record in which the predetermined image information is already associated, or whether the predetermined index data is associated in advance and the image information is not associated. A determination step of determining whether the image information and the index data are new records that are not associated with each other;
When it is determined in the determination step that the record being selected is a record to which the predetermined image information has already been associated, the process execution unit selects the newly input image information. When it is determined that the record is added after the last page in the record and the predetermined index data is associated with the image and the image information is not associated, or the image information and the index data are not associated with each other. , the file management method, characterized by having a process execution step of executing a process of adding a new input image information to record in the selected.
画像情報とインデックスデータとをレコードに関連付け、複数のレコードを一覧表示したリストを用いて、画像を管理するリスト管理手段、
所定の画像情報が既に関連付けられているレコードと、所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコードと、画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードを前記リストに一覧表示する表示手段、
前記表示手段により表示されたリストにおいて、新たな画像の保存を行いたい複数のレコードに、同一の標識マークを付加するマーク付加手段、
前記リストにおいて前記標識マークの付加されたレコードを順番に選択する選択手段、
前記選択手段で選択中のレコードが、前記所定の画像情報が既に関連付けられているレコードであるか、前記所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコードであるか、画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードであるかを判定する判定手段、
前記選択手段で選択中のレコードが、前記判定手段によって、前記所定の画像情報が既に関連づけられているレコードであると判定された場合に、新たに入力された画像情報を当該選択中のレコードにおける最終ページの後に追加し、前記所定のインデックスデータが先に関連付けられ且つ画像情報が関連付けられていないレコード又は画像情報とインデックスデータの両方が関連付けられていない新規レコードであると判定された場合に、新たに入力された画像情報を当該選択中のレコードに追加する処理を実行する処理実行手段、として機能させるためのプログラムを格納した、コンピュータ読み取り可能な記憶媒体。 Computer
A list management means for associating image information and index data with a record, and managing images using a list in which a plurality of records are displayed as a list;
The list includes a record in which predetermined image information is already associated, a record in which predetermined index data is associated in advance and image information is not associated, and a new record in which both image information and index data are not associated Display means to list
In the list displayed by the display means, mark adding means for adding the same mark mark to a plurality of records for which a new image is to be stored;
Selection means for sequentially selecting the records with the mark marks added thereto in the list;
Whether the record being selected by the selection means is a record in which the predetermined image information is already associated, a record in which the predetermined index data is associated in advance and image information is not associated, Determining means for determining whether the information and index data are new records that are not associated with each other;
When the record selected by the selection means is determined by the determination means to be a record in which the predetermined image information has already been associated, the newly input image information in the record being selected When it is determined that the record is added after the last page and the predetermined index data is associated with the image information and the image information is not associated with each other or the image information and the index data are not associated with each other, A computer-readable storage medium storing a program for functioning as processing execution means for executing processing for adding newly input image information to the selected record .
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP26734798A JP4250231B2 (en) | 1998-09-04 | 1998-09-04 | File management apparatus, file management method, and storage medium |
| US09/390,282 US6633893B2 (en) | 1998-09-04 | 1999-09-03 | File management system and method, and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP26734798A JP4250231B2 (en) | 1998-09-04 | 1998-09-04 | File management apparatus, file management method, and storage medium |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2000082070A JP2000082070A (en) | 2000-03-21 |
| JP2000082070A5 JP2000082070A5 (en) | 2005-10-27 |
| JP4250231B2 true JP4250231B2 (en) | 2009-04-08 |
Family
ID=17443558
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP26734798A Expired - Fee Related JP4250231B2 (en) | 1998-09-04 | 1998-09-04 | File management apparatus, file management method, and storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4250231B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4378063B2 (en) | 2000-05-22 | 2009-12-02 | 株式会社リコー | Image forming apparatus |
| US8510270B2 (en) * | 2010-07-27 | 2013-08-13 | Oracle International Corporation | MYSQL database heterogeneous log based replication |
| US9298878B2 (en) | 2010-07-29 | 2016-03-29 | Oracle International Corporation | System and method for real-time transactional data obfuscation |
| US11645261B2 (en) | 2018-04-27 | 2023-05-09 | Oracle International Corporation | System and method for heterogeneous database replication from a remote server |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH05274204A (en) * | 1992-01-30 | 1993-10-22 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | File managing device |
| JPH08305747A (en) * | 1995-04-28 | 1996-11-22 | Hitachi Ltd | Method and device for selecting insurance commodity |
| JPH10162126A (en) * | 1996-12-02 | 1998-06-19 | Planet Computer:Kk | Electronization device for document |
-
1998
- 1998-09-04 JP JP26734798A patent/JP4250231B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2000082070A (en) | 2000-03-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US6594650B2 (en) | File management system and its method and storage medium | |
| US9135230B2 (en) | Digital document editing method, digital document editing program and digital document editing apparatus | |
| US20050289447A1 (en) | Systems and methods for generating and storing referential links in a database | |
| US7103837B2 (en) | Information processing system and display method | |
| US6633893B2 (en) | File management system and method, and storage medium | |
| JPH04205659A (en) | Electronic filing device | |
| US8040564B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus, image reading apparatus, and control method thereof | |
| JP4250231B2 (en) | File management apparatus, file management method, and storage medium | |
| JP2003127473A (en) | Imaging apparatus | |
| US6862603B1 (en) | File management system, file management method, and storage medium | |
| JPH0793336A (en) | Image storage device and image storage and retrieval device | |
| US11269496B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus, control method, and storage medium | |
| JP4026955B2 (en) | File management apparatus, file management method, and storage medium | |
| JPH0981585A (en) | Electronic filing device | |
| US7197704B1 (en) | Document management method, system, and storage medium thereof with priority assignment indicative of processing order | |
| JP2004259031A (en) | Document management device | |
| JPH06231183A (en) | Document filing device | |
| US20060203258A1 (en) | File management apparatus | |
| US11039023B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus, control method, and storage medium thereof | |
| JP4011756B2 (en) | Management apparatus, management method, and storage medium | |
| JP2004001280A (en) | Printer and method for displaying image | |
| JP4250232B2 (en) | File management apparatus, method, and storage medium | |
| JP2003317076A (en) | Apparatus and method for image management, and control program | |
| JPH08263512A (en) | Document retrieval device | |
| JPH0991300A (en) | File management method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050905 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20050905 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20060209 |
|
| RD05 | Notification of revocation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7425 Effective date: 20070626 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080930 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20081201 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20090106 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20090119 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120123 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130123 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140123 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |