EP0802509A2 - Automatic road use charging method - Google Patents
Automatic road use charging method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0802509A2 EP0802509A2 EP97100575A EP97100575A EP0802509A2 EP 0802509 A2 EP0802509 A2 EP 0802509A2 EP 97100575 A EP97100575 A EP 97100575A EP 97100575 A EP97100575 A EP 97100575A EP 0802509 A2 EP0802509 A2 EP 0802509A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- beacon
- data
- vehicle
- payment
- tariff
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07B—TICKET-ISSUING APPARATUS; FARE-REGISTERING APPARATUS; FRANKING APPARATUS
- G07B15/00—Arrangements or apparatus for collecting fares, tolls or entrance fees at one or more control points
- G07B15/06—Arrangements for road pricing or congestion charging of vehicles or vehicle users, e.g. automatic toll systems
- G07B15/063—Arrangements for road pricing or congestion charging of vehicles or vehicle users, e.g. automatic toll systems using wireless information transmission between the vehicle and a fixed station
Definitions
- the invention is based on a method for automatically collecting road user fees according to the preamble of claim 1 and an apparatus for carrying out this method according to the preamble of claim 10.
- beacon-based and autonomous systems consist of on-board equipment and beacons mounted on the street.
- the vehicle-side device contains an electronic means of payment with which the road user fee is paid, a microwave transponder for communication with the beacons and a data memory with parameters which influence the fee to be paid.
- the beacon contains the tariff structure, that is, it determines it the fee to be paid based on the data reported by the vehicle and the operator's specifications.
- a communication link is established between the device in the vehicle and the beacon as a vehicle drives past. In a first step, data is transmitted from the vehicle device to the beacon and in a second step, the beacon notifies the device of the fee to be paid.
- the fee is paid using the electronic means of payment in the vehicle.
- the device then transmits a payment guarantee to the beacon.
- the fee collection process is thus triggered by the passage of the beacon through the vehicle.
- the location of the beacon defines a position in the road network at which the payment process must take place.
- signals, which are transmitted to the device at an entry station not only the current position of the vehicle, but also the origin and the length of stay within certain road sections can be included in the determination of the fee.
- the disadvantage of these beacon-based systems can be seen in the large number of beacons to be installed, which is necessary for a differentiated and comprehensive collection of road user fees.
- the autonomous systems do not use beacons. Instead, the vehicle devices have satellite navigation systems (for example GPS, Global Positioning System) so that the vehicle can autonomously determine its position on the earth's surface. Since no beacons are provided, the vehicle devices contain a digital map and information about corresponding paying agents on this card and the entire tariff structure. If the vehicle device determines that it is located at a payment point, the fee to be paid is determined on the basis of the data in the memory, the electronic means of payment also present in the device are accessed and a payment is initiated. In contrast to the beacon-based system, the operator has no payment guarantee immediately after the payment process. This payment guarantee can be transmitted, for example, by means of possibly uneconomical mobile radio.
- satellite navigation systems for example GPS, Global Positioning System
- the method according to the invention with the features mentioned in the main claim combines the advantages of beacon-based systems with the advantages of autonomous systems. It is particularly advantageous that the tariff structure is permanently under the control of the operator, since it is not stored in the individual vehicles but, as in the beacon-based system, in the beacons. Since the beacons advantageously have a connection to central computer systems, uniformity of tariffs and thus equal treatment of all drivers is guaranteed. It is also possible to change the tariff structure quickly and in accordance with the changing framework conditions without having to refer to the individual vehicles. Another important advantage of the method according to the invention is that, because the payment guarantees are transferred directly to the beacon, and thus the operator, it is not possible for the operator to withdraw from the payment or to subsequently produce authentic receipts.
- the method according to the invention therefore has a high level of reliability and security. Since the satellite-based permanent position determination and storage can also be used to record the past of a vehicle movement profile, the method according to the invention uses in a particularly advantageous manner only comparatively few beacons which are not used for determining the position but only for determining and collecting fees.
- the vehicle-side devices according to the invention in addition to the above-mentioned ones, also have the particular advantage that they can be comparatively inexpensive, since memories for accommodating the road network and the tariff structures and a higher computing power capacity are eliminated. Accordingly, the devices according to the invention are also smaller and are lighter.
- FIG. 1 shows a device 1 arranged in a vehicle, not shown here Beacon 2 and a satellite 3 arranged on the street side.
- the device 1 contains a microwave transponder 4 which is connected via a connection 5 to an electronic payment means 6, in particular a chip card.
- the device 1 also contains a satellite navigation module 7, in particular a global positioning system, GPS.
- the device 1 has a data memory 8 which is connected to the other components of the device 1 via the connections 5, 9, 10 and 11.
- the signal S emitted by the satellite 3 is recorded by the satellite navigation module 7.
- the microwave transponder 4 transmits a data flow D1 consisting of tariff-relevant parameters and position data to the beacon 2, which, after receiving it, notifies the microwave transponder 4 of the amount of the fee D2 to be paid.
- the microwave transponder 4 transmits a payment guarantee Z to the beacon 2.
- the beacon 2 transmits a receipt Q to the chip card.
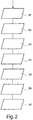
- FIG. 2 explains in detail the functioning of the device according to FIG. 1.
- the vehicle equipped with a device 1 continuously determines its position with the aid of its satellite navigation module 7 and the signal S thus received by the satellite 3 (position determination, 101).
- the time S is also transmitted with the signal S, so that the position determination in method step 101 takes place at defined times.
- the current time together with the respective position of the device 1 are stored in the data memory 8 (method step 102). If the vehicle now passes a beacon 2, the last stored position or the last stored positions are transmitted to the beacon 2 by means of the microwave transponder 4 as data flow D1.
- the data memory 8 also contains other tariff-relevant parameters such as, for example, vehicle class, pollutant emissions or other vehicle or driver-related data, which are likewise transmitted to the beacon 2 together with the position data in the data flow D1 (method step 103) .
- Beacon 2 contains the tariff structure and a digital map network and is therefore able to determine the fee to be paid from data D1.
- the amount of the fee to be paid is communicated to the microwave transponder 4 by the beacon 2 via a data flow D2 (method step 104).
- the fee to be paid is paid in the vehicle by means of the electronic payment means 6, that is to say debited from the chip card (method step 105).
- the microwave transponder 4 then transmits a payment guarantee Z to the beacon 2 (method step 106), which the operator can hand over to a clearing house in order to ultimately receive the fee. If the payment guarantee Z is in order, the beacon 2 sends a receipt Q to the transponder 4 for storage in the chip card 6 (method step 107).
- the position data can be stored in method step 101 in two ways.
- the position data can thus be stored at periodic intervals, and the frequency of the storage can be changed by signals transmitted by number beacons 2.
- the device 1 only stores certain positions. A list of these specific positions is accordingly transferred from the beacon 2 to the vehicle passing through this beacon 2 and thus from the device 1. If the device 1 uses the satellite navigation module 7 to determine a correspondence between its own position and one of the positions contained in the list during the course of the journey, a corresponding note is stored in the data memory 8. If the vehicle passes another beacon, the stored memo is transmitted from the microwave transponder 4 in the data flow D1 to the beacon 2. The beacon 2 can now calculate the fee to be paid on the basis of the tariff structure stored in it and the digital road map and request the device 1 to pay.
- the device 1 can be provided to store a plurality of positions in the data memory 8, so that the device 1 records a movement profile of the vehicle, which can then be settled on only a few payment beacons 2.
Abstract
Description
Die Erfindung geht aus von einem Verfahren zur automatischen Erhebung von Straßenbenutzungsgebühren gemäß Oberbegriff des Anspruchs 1 sowie einer Vorrichtung zur Durchführung dieses Verfahrens gemäß Oberbegriff des Anspruchs 10.The invention is based on a method for automatically collecting road user fees according to the preamble of claim 1 and an apparatus for carrying out this method according to the preamble of
Die gegenwärtig zur automatischen Erhebung von Straßenbenutzungsgebühren verwendeten Systeme lassen sich in bakengestützte und autonome Systeme untergliedern. Bakengestütze Systeme setzen sich aus fahrzeugseitigen Geräten und straßenseitig montierten Baken zusammen. Das fahrzeugseitige Gerät enthält ein elektronisches Zahlungsmittel, mit welchem die Straßenbenutzungsgebühr entrichtet wird, einen Mikrowellen-Transponder zur Kommunikation mit den Baken sowie einen Datenspeicher mit Parametern, welche die zu zahlende Gebühr beeinflussen. Die Bake enthält die Tarifstruktur, das heißt, sie bestimmt aufgrund der vom Fahrzeug gemeldeten Daten und aufgrund der Vorgaben des Betreibers die zu entrichtende Gebühr. Während der Vorbeifahrt eines Fahrzeuges wird eine Kommunikationsverbindung zwischen dem im Fahrzeug befindlichen Gerät und der Bake aufgebaut. In einem ersten Schritt werden Daten von dem fahrzeugseitigen Gerät zur Bake übertragen und in einem zweiten Schritt teilt die Bake dem Gerät die zu entrichtende Gebühr mit. Mit Hilfe des im Fahrzeug befindlichen elektronischen Zahlungsmittels wird die Gebühr entrichtet. Das Gerät übermittelt dann eine Zahlungsgarantie an die Bake. Der Gebührenerhebungsvorgang wird also durch die Passage der Bake durch das Fahrzeug ausgelöst. Durch den Ort der Bake wird eine Position im Straßennetz definiert, an welchem der Bezahlvorgang zu erfolgen hat. Zudem kann durch die Speicherung von Signalen, welche dem Gerät an einer Einfahrtstation übermittelt werden, nicht nur die aktuelle Position des Fahrzeugs, sondern auch die Herkunft und die Verweildauer innerhalb bestimmter Straßenabschnitte in die Ermittlung der Gebühr miteinbezogen werden. Der Nachteil dieser bakengestützten Systeme ist allerdings in der großen Anzahl von zu installierenden Baken zu sehen, die für eine differenzierte und umfassende Erhebung von Straßenbenutzungsgebühren notwendig ist.The systems currently used to automatically collect road tolls can be broken down into beacon-based and autonomous systems. Beacon-supported systems consist of on-board equipment and beacons mounted on the street. The vehicle-side device contains an electronic means of payment with which the road user fee is paid, a microwave transponder for communication with the beacons and a data memory with parameters which influence the fee to be paid. The beacon contains the tariff structure, that is, it determines it the fee to be paid based on the data reported by the vehicle and the operator's specifications. A communication link is established between the device in the vehicle and the beacon as a vehicle drives past. In a first step, data is transmitted from the vehicle device to the beacon and in a second step, the beacon notifies the device of the fee to be paid. The fee is paid using the electronic means of payment in the vehicle. The device then transmits a payment guarantee to the beacon. The fee collection process is thus triggered by the passage of the beacon through the vehicle. The location of the beacon defines a position in the road network at which the payment process must take place. In addition, by storing signals, which are transmitted to the device at an entry station, not only the current position of the vehicle, but also the origin and the length of stay within certain road sections can be included in the determination of the fee. The disadvantage of these beacon-based systems, however, can be seen in the large number of beacons to be installed, which is necessary for a differentiated and comprehensive collection of road user fees.
Die autonomen Systeme verwenden keine Baken. Statt dessen weisen die Fahrzeuggeräte Satellitennavigationssysteme (zum Beispiel GPS, Global Positioning System) auf, so daß das Fahrzeug seine Position auf der Erdoberfläche autonom bestimmen kann. Da keine Baken vorgesehen sind, enthalten die Fahrzeuggeräte eine digitale Landkarte sowie Informationen über entsprechende Zahlstellen auf dieser Karte und die gesamte Tarifstruktur. Stellt das Fahrzeuggerät fest, daß es sich an einer Zahlstelle befindet, so wird aufgrund der Daten im Speicher die zu entrichtende Gebühr ermittelt, auf das ebenfalls im Gerät vorhandene elektronische Zahlungsmittel zugegriffen und eine Zahlung veranlaßt. Im Unterschied zum bakengestützten System hat der Betreiber unmittelbar nach dem Bezahlvorgang noch keine Zahlungsgarantie vorliegen. Diese Zahlungsgarantie kann beispielsweise mittels unter Umständen unwirtschaftlichem Mobilfunk übermittelt werden. Andere Systeme speichern die Zahlungsgarantien auf dem Zahlungsmittel (Chipkarte) und übermitteln diese erst beim nächsten Kontakt mit einer geeigneten Infrastruktur, zum Beispiel beim Wiederaufladen der Karten. Beim Verlust dieser Karte verliert der Betreiber alle darauf gespeicherten Zahlungsgarantien. Die bisher bekannten autonomen Systeme weisen den Nachteil auf, daß schnell veränderliche Tarifstrukturen, zum Beispiel Tarife, die von Verkehrs- oder Umweltdaten abhängen, nur unter größerem technischen Aufwand den einzelnen Fahrzeuggeräten gemeldet werden können. Zudem kann nicht garantiert werden, daß alle Fahrzeuge immer im Besitz der jeweils aktuellen Tarifstrukturen sind. Von Nachteil ist auch, daß im nachhinein eine authentische Quittung für einen Bezahlvorgang in der Vergangenheit erzeugt werden kann, indem das Gerät gefälschten GPS-Signalen ausgesetzt wird. Schließlich zeichnen sich die autonomen Systeme durch einen hohen Preis aus, der insbesondere auf dem notwendigerweise großen Speicher zur Aufnahme des Straßennetzes und der Tarifstrukturen sowie der erforderlichen hohen Rechenleistung beruht.The autonomous systems do not use beacons. Instead, the vehicle devices have satellite navigation systems (for example GPS, Global Positioning System) so that the vehicle can autonomously determine its position on the earth's surface. Since no beacons are provided, the vehicle devices contain a digital map and information about corresponding paying agents on this card and the entire tariff structure. If the vehicle device determines that it is located at a payment point, the fee to be paid is determined on the basis of the data in the memory, the electronic means of payment also present in the device are accessed and a payment is initiated. In contrast to the beacon-based system, the operator has no payment guarantee immediately after the payment process. This payment guarantee can be transmitted, for example, by means of possibly uneconomical mobile radio. Other systems save the payment guarantees on the means of payment (chip card) and only transmit them the next time they contact a suitable infrastructure, for example when reloading the cards. If this card is lost, the operator loses all payment guarantees stored on it. The previously known autonomous systems have the disadvantage that rapidly changing tariff structures, for example tariffs that depend on traffic or environmental data, can be reported to the individual vehicle devices only with greater technical outlay. In addition, it cannot be guaranteed that all vehicles are always in possession of the current tariff structures. Another disadvantage is that afterwards an authentic receipt for a payment process in the past can be generated by exposing the device to fake GPS signals. Finally, the autonomous systems are characterized by a high price, which is based in particular on the necessary large memory for accommodating the road network and the tariff structures as well as the high computing power required.
Das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren mit den im Hauptanspruch genannten Merkmalen verbindet die Vorteile bakengestützter Systeme mit den Vorteilen autonomer Systeme. Von besonderem Vorteil ist, daß die Tarifstruktur permanent unter der Kontrolle des Betreibers steht, da diese nicht in den einzelnen Fahrzeugen, sondern, wie beim bakengestützten System, in den Baken gespeichert ist. Da die Baken in vorteilhafter Weise eine Anbindung an zentrale Rechnersysteme aufweisen, ist eine Einheitlichkeit der Tarife und damit die Gleichbehandlung aller Autofahrer gewährleistet. Zudem ist es möglich, die Tarifstruktur schnell und den wechselnden Rahmenbedingungen entsprechend zu ändern, ohne auf die einzelnen Fahrzeuge rückgreifen zu müssen. Ein weiterer wesentlicher Vorteil des erfindungsgemäßen Verfahrens liegt darin, daß es aufgrund der erfindungsgemäß ermöglichten unmittelbaren Übergabe der Zahlungsgarantien an die Bake und damit den Betreiber nicht möglich ist, sich der Zahlung zu entziehen oder nachträglich authentische Quittungen herzustellen. Das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren weist also eine hohe Zuverlässigkeit und Sicherheit auf. Da durch die satellitengestützte permanente Positionsermittlung und -speicherung auch die Vergangenheit eines Fahrzeugbewegungsprofils erfaßt werden kann, verwendet das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren in besonders vorteilhafter Weise nur vergleichsweise wenige Baken, die nicht der Positionsermittlung, sondern nur noch der Gebührenermittlung und -erhebung dienen. Dabei kann auf den Einsatz von sogenannten Einfahrtstationen, das heißt, Stationen, ab denen eine gebührenpflichtige Fahrt beginnt, ganz verzichtet werden kann, da die jeweiligen erfindungsgemäß verwendeten Zahlungsbaken Tarifstruktur und digitale Karten enthalten, so daß, zusammen mit dem fahrzeugseitig gespeicherten Positionsdaten, auch eine Gebührenerhebung für die Vergangenheit möglich ist.The method according to the invention with the features mentioned in the main claim combines the advantages of beacon-based systems with the advantages of autonomous systems. It is particularly advantageous that the tariff structure is permanently under the control of the operator, since it is not stored in the individual vehicles but, as in the beacon-based system, in the beacons. Since the beacons advantageously have a connection to central computer systems, uniformity of tariffs and thus equal treatment of all drivers is guaranteed. It is also possible to change the tariff structure quickly and in accordance with the changing framework conditions without having to refer to the individual vehicles. Another important advantage of the method according to the invention is that, because the payment guarantees are transferred directly to the beacon, and thus the operator, it is not possible for the operator to withdraw from the payment or to subsequently produce authentic receipts. The method according to the invention therefore has a high level of reliability and security. Since the satellite-based permanent position determination and storage can also be used to record the past of a vehicle movement profile, the method according to the invention uses in a particularly advantageous manner only comparatively few beacons which are not used for determining the position but only for determining and collecting fees. The use of so-called entrance stations, i.e. stations from which a chargeable journey begins, can be used entirely can be dispensed with, since the respective payment beacons used according to the invention contain tariff structure and digital cards, so that, together with the position data stored on the vehicle side, it is also possible to charge for the past.
Die erfindungsgemäßen fahrzeugseitigen Vorrichtungen weisen neben den genannten insbesondere auch den Vorteil auf, daß sie vergleichsweise preiswert sein können, da Speicher zur Aufnahme des Straßennetzes und der Tarifstrukturen sowie eine höhere Rechenleistungskapazität entfallen. Demgemäß bauen die erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtungen auch kleiner und sind leichter.The vehicle-side devices according to the invention, in addition to the above-mentioned ones, also have the particular advantage that they can be comparatively inexpensive, since memories for accommodating the road network and the tariff structures and a higher computing power capacity are eliminated. Accordingly, the devices according to the invention are also smaller and are lighter.
Weitere vorteilhafte Ausgestaltungen der Erfindung sind den weiteren Ansprüchen zu entnehmen.Further advantageous embodiments of the invention can be found in the further claims.
Die Erfindung wird anhand eines Ausführungsbeispiels und dazugehöriger Figuren näher erläutert.The invention is explained in more detail using an exemplary embodiment and associated figures.
Die Figuren zeigen:
- Figur 1
- eine schematische Darstellung einer Vorrichtung zur automatischen Ermittlung und Erhebung von Straßenbenutzungsgebühren sowie deren Peripherie und
Figur 2- ein das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren illustrierendes Flußdiagramm.
- Figure 1
- is a schematic representation of a device for the automatic determination and collection of road use fees and their periphery and
- Figure 2
- a flowchart illustrating the inventive method.
Die Figur 1 zeigt eine in einem hier nicht dargestellten Fahrzeug angeordnete Vorrichtung 1, eine straßenseitig angeordnete Bake 2 und einen Satelliten 3. Die Vorrichtung 1 enthält einen Mikrowellen-Transponder 4 der über einen Anschluß 5 mit einem elektronischen Zahlungsmittel 6, insbesondere einer Chipkarte, verbunden ist. Die Vorrichtung 1 enthält zudem ein Satellitennavigationsmodul 7, insbesondere ein Global Positioning System, GPS. Schließlich weist die Vorrichtung 1 einen Datenspeicher 8 auf, der über die Anschlüsse 5, 9, 10 und 11 mit den anderen Komponenten der Vorrichtung 1 verbunden ist. Das vom Satelliten 3 ausgestrahlte Signal S wird vom Satellitennavigationsmodul 7 aufgenommen. Der Mikrowellen-Transponder 4 übermittelt einen aus Tarif-relevanten Parametern und Positionsdaten bestehenden Datenfluß D1 an die Bake 2, die im Anschluß an deren Empfang den Betrag der zu entrichtenden Gebühr D2 an den Mikrowellen-Transponder 4 mitteilt. Nach Zahlung übermittelt der Mikrowellen-Transponder 4 eine Zahlungsgarantie Z an die Bake 2. Nach Prüfung der Zahlungsgarantie übermittelt die Bake 2 eine Quittung Q an die Chipkarte.FIG. 1 shows a device 1 arranged in a vehicle, not shown here Beacon 2 and a
Die Figur 2 erläutert detailliert die Funktionsweise der Vorrichtung nach Figur 1.FIG. 2 explains in detail the functioning of the device according to FIG. 1.
Das mit einer Vorrichtung 1 ausgestattete Fahrzeug ermittelt ständig mit Hilfe seines Satellitennavigationsmoduls 7 und des damit vom Satelliten 3 empfangenen Signals S seine Position (Positionsermittlung, 101). Mit dem Signal S wird außerdem die Uhrzeit übermittelt, so daß die im Verfahrensschritt 101 erfolgende Positionsermittlung zu definierten Zeitpunkten erfolgt. Die jeweils aktuelle Uhrzeit zusammen mit der jeweiligen Position der Vorrichtung 1 werden im Datenspeicher 8 gespeichert (Verfahrensschritt 102). Passiert das Fahrzeug nun eine Bake 2 werden die letzte gespeicherte Position oder die letzten gespeicherten Positionen mittels des Mikrowellen-Transponders 4 als Datenfluß D1 an die Bake 2 übertragen. Der Datenspeicher 8 enthält neben den Positions- und Uhrzeitdaten auch andere Tarif-relevante Parameter wie beispielsweise Fahrzeugklasse, Schadstoffausstoß oder weitere Fahrzeug- beziehungsweise Fahrer-bezogene Daten, die zusammen mit den Positionsdaten im Datenfluß D1 ebenfalls an die Bake 2 übermittelt werden (Verfahrensschritt 103). Die Bake 2 enthält die Tarifstruktur sowie ein digitales Kartennetz und ist daher in der Lage, aus den Daten D1 die zu entrichtende Gebühr zu ermitteln. Der Betrag der zu entrichtenden Gebühr wird von der Bake 2 über einen Datenfluß D2 dem Mikrowellen-Transponder 4 mitgeteilt (Verfahrensschritt 104). Während der Verfahrensschritte 103 und 104 kann in vorteilhafter Weise vorgesehen werden, eine gegenseitige Authentifizierung der Kommunikationspartner vorzunehmen, so daß durch die Feststellung, daß der jeweilige Partner auch zur Teilnahme an der Gebührenerhebung berechtigt beziehungsweise verpflichtet ist, ein Maximum an Sicherheit gewährleistet ist. Die zu entrichtende Gebühr wird mittels des elektronischen Zahlungsmittels 6 im Fahrzeug entrichtet, das heißt von der Chipkarte abgebucht (Verfahrensschritt 105). Anschließend übermittelt der Mikrowellen-Transponder 4 der Bake 2 eine Zahlungsgarantie Z (Verfahrensschritt 106), welche der Betreiber an eine Verrechnungsstelle überreichen kann, um so die Gebühr letztendlich zu erhalten. Ist die Zahlungsgarantie Z in Ordnung, sendet die Bake 2 eine Quittung Q an den Transponder 4, zur Ablage in die Chipkarte 6. (Verfahrensschritt 107).The vehicle equipped with a device 1 continuously determines its position with the aid of its
Die in Verfahrenschritt 101 erfolgende Speicherung der Positionsdaten kann in zwei Weisen erfolgen. So kann die Speicherung der Positionsdaten in periodischen Abständen erfolgen, wobei die Häufigkeit der Speicherung durch von Zahlbaken 2 ausgesendeten Signalen geändert werden kann. In besonders bevorzugter Ausführungsform speichert die Vorrichtung 1 nur bestimmte Positionen. Eine Liste dieser bestimmten Positionen wird demgemäß von der Bake 2 dem diese Bake 2 passierenden Fahrzeug und damit der Vorrichtung 1 übergeben. Stellt die Vorrichtung 1 mittels des Satellitennavigationsmoduls 7 im weiteren Verlauf der Fahrt eine Übereinstimmung zwischen der eigenen Position und einer der in der Liste enthaltenen Positionen fest, so wird ein entsprechender Vermerk im Datenspeicher 8 gespeichert. Passiert das Fahrzeug eine weitere Bake, so wird der gespeicherte Vermerk vom Mikrowellen-Transponder 4 im Datenfluß D1 auf die Bake 2 übertragen. Die Bake 2 kann nun anhand der in ihr gespeicherten Tarifstruktur und der digitalen Straßenkarte eine Berechnung der zu entrichtenden Gebühr vornehmen und die Vorrichtung 1 zur Zahlung auffordern.The position data can be stored in
In besonders vorteilhafter Weise kann vorgesehen sein, mehrere Positionen im Datenspeicher 8 zu speichern, so daß die Vorrichtung 1 ein Bewegungsprofil des Fahrzeugs aufnimmt, welches dann an nur wenigen Zahlbaken 2 abgerechnet werden kann.In a particularly advantageous manner, it can be provided to store a plurality of positions in the
Claims (16)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19615733A DE19615733A1 (en) | 1996-04-20 | 1996-04-20 | Procedure for the automatic collection of road tolls |
| DE19615733 | 1996-04-20 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0802509A2 true EP0802509A2 (en) | 1997-10-22 |
| EP0802509A3 EP0802509A3 (en) | 2000-01-26 |
| EP0802509B1 EP0802509B1 (en) | 2003-05-07 |
Family
ID=7791903
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP97100575A Expired - Lifetime EP0802509B1 (en) | 1996-04-20 | 1997-01-16 | Automatic road use charging method |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0802509B1 (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE239952T1 (en) |
| DE (2) | DE19615733A1 (en) |
Cited By (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2001003073A1 (en) * | 1999-07-06 | 2001-01-11 | Gsi Gesellschaft Für Systemtechnik Und Informatik Mbh | Flexible charge collection system |
| WO2001011572A1 (en) * | 1999-08-04 | 2001-02-15 | Vodafone Ag | Control unit for verifying proper functioning of toll devices installed in vehicles |
| EP1089088A2 (en) * | 1999-09-30 | 2001-04-04 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Position detecting apparatus with DSRC feature and its control method |
| WO2001075807A1 (en) * | 2000-03-31 | 2001-10-11 | Steven Daniels | Vehicle tracking system |
| EP1197925A2 (en) * | 2000-09-19 | 2002-04-17 | Siemens AG | Assembly for the payment of fees for the use of tollroads |
| WO2002035477A1 (en) * | 2000-10-27 | 2002-05-02 | Vodafone Holding Gmbh | Method for charging tolls |
| WO2003034346A1 (en) * | 2001-10-11 | 2003-04-24 | Vodafone Ag | Detection system for vehicles equipped with gps |
| US6580978B1 (en) * | 2002-04-15 | 2003-06-17 | United Defense, Lp | Path following using bounded beacon-aided inertial navigation |
| EP1630747A2 (en) * | 2004-08-31 | 2006-03-01 | Fela Management AG | Toll collection system and method |
| EP2280287A1 (en) | 2009-07-28 | 2011-02-02 | Nxp B.V. | Integration of positioning and road charging data |
| EP2325807A1 (en) * | 2009-11-23 | 2011-05-25 | Kapsch TrafficCom AG | Method and device for generating toll information in a road toll system |
| EP2541502A1 (en) * | 2011-06-29 | 2013-01-02 | Kapsch TrafficCom AG | Method for acquiring toll fees in a road toll system |
| EP2581882A1 (en) * | 2011-10-12 | 2013-04-17 | Kapsch TrafficCom AG | Method for levying charges on vehicles in an open road toll system |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19935277A1 (en) * | 1999-07-27 | 2001-02-15 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | Automatic fee collection method and apparatus therefor |
| DE10103552A1 (en) * | 2001-01-26 | 2002-08-01 | Volkswagen Ag | Device for locating objects has data memory with object-specific data, position sensor, mobile radio device for sending object-specific data, position sensor data to central unit |
| DE10131841A1 (en) * | 2001-06-30 | 2003-01-16 | Wissenschaftliche Werkstatt Fu | Road usage model for charging road users according to emissions they cause with special low emission zones where it is very expensive for high emission vehicles to enter |
| DE10224466B4 (en) * | 2002-06-03 | 2007-06-14 | Fendt, Günter | Method and system for influencing road users with regard to the selection behavior of the route selection on recommended roads and / or toll roads |
| DE102006024729A1 (en) * | 2006-05-26 | 2007-11-29 | Siemens Ag | Method for checking the function of a mobile detection unit |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5101200A (en) * | 1989-06-09 | 1992-03-31 | Swett Paul H | Fast lane credit card |
| DE4344433B4 (en) * | 1993-12-24 | 2004-09-30 | T-Mobile Deutschland Gmbh | Registration system and method for motorway tolls using an electronic vignette |
| DE4402614A1 (en) * | 1994-01-28 | 1995-08-03 | Deutsche Telekom Mobil | Procedure for determining fees for the use of traffic routes by vehicles |
| SE502406C2 (en) * | 1994-02-02 | 1995-10-16 | Rolf Rising | Vehicle control information system |
| DE4427392A1 (en) * | 1994-08-03 | 1996-02-08 | Wolfgang Neifer | Road use charge levying apparatus |
| US5490079A (en) * | 1994-08-19 | 1996-02-06 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | System for automated toll collection assisted by GPS technology |
-
1996
- 1996-04-20 DE DE19615733A patent/DE19615733A1/en not_active Withdrawn
-
1997
- 1997-01-16 AT AT97100575T patent/ATE239952T1/en active
- 1997-01-16 DE DE59710013T patent/DE59710013D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-01-16 EP EP97100575A patent/EP0802509B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| None |
Cited By (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2001003073A1 (en) * | 1999-07-06 | 2001-01-11 | Gsi Gesellschaft Für Systemtechnik Und Informatik Mbh | Flexible charge collection system |
| WO2001011572A1 (en) * | 1999-08-04 | 2001-02-15 | Vodafone Ag | Control unit for verifying proper functioning of toll devices installed in vehicles |
| EP1089088A2 (en) * | 1999-09-30 | 2001-04-04 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Position detecting apparatus with DSRC feature and its control method |
| EP1089088A3 (en) * | 1999-09-30 | 2003-11-26 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Position detecting apparatus with DSRC feature and its control method |
| WO2001075807A1 (en) * | 2000-03-31 | 2001-10-11 | Steven Daniels | Vehicle tracking system |
| EP1197925A2 (en) * | 2000-09-19 | 2002-04-17 | Siemens AG | Assembly for the payment of fees for the use of tollroads |
| EP1197925A3 (en) * | 2000-09-19 | 2004-03-31 | Siemens AG | Assembly for the payment of fees for the use of tollroads |
| WO2002035477A1 (en) * | 2000-10-27 | 2002-05-02 | Vodafone Holding Gmbh | Method for charging tolls |
| WO2003034346A1 (en) * | 2001-10-11 | 2003-04-24 | Vodafone Ag | Detection system for vehicles equipped with gps |
| US6580978B1 (en) * | 2002-04-15 | 2003-06-17 | United Defense, Lp | Path following using bounded beacon-aided inertial navigation |
| EP1630747A2 (en) * | 2004-08-31 | 2006-03-01 | Fela Management AG | Toll collection system and method |
| EP2280287A1 (en) | 2009-07-28 | 2011-02-02 | Nxp B.V. | Integration of positioning and road charging data |
| WO2011013076A1 (en) * | 2009-07-28 | 2011-02-03 | Nxp B.V. | Integration of position and road charging data |
| CN102472820A (en) * | 2009-07-28 | 2012-05-23 | Nxp股份有限公司 | Integration of position and road charging data |
| US9159171B2 (en) | 2009-07-28 | 2015-10-13 | Telit Automotive Solutions Nv | Integration of position and road charging data |
| EP2325807A1 (en) * | 2009-11-23 | 2011-05-25 | Kapsch TrafficCom AG | Method and device for generating toll information in a road toll system |
| EP2407935A1 (en) * | 2009-11-23 | 2012-01-18 | Kapsch TrafficCom AG | Control device for a road toll system |
| US9269197B2 (en) | 2009-11-23 | 2016-02-23 | Kapsch Trafficcom Ag | Method and device for generating toll information in a road-toll system |
| EP2541502A1 (en) * | 2011-06-29 | 2013-01-02 | Kapsch TrafficCom AG | Method for acquiring toll fees in a road toll system |
| US8732000B2 (en) | 2011-06-29 | 2014-05-20 | Kapsch Trafficcom Ag | Method for determining toll fees in a road toll system |
| EP2581882A1 (en) * | 2011-10-12 | 2013-04-17 | Kapsch TrafficCom AG | Method for levying charges on vehicles in an open road toll system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0802509A3 (en) | 2000-01-26 |
| EP0802509B1 (en) | 2003-05-07 |
| ATE239952T1 (en) | 2003-05-15 |
| DE59710013D1 (en) | 2003-06-12 |
| DE19615733A1 (en) | 1997-10-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0741891B2 (en) | Method and system for determining toll charges for traffic routes and/or areas | |
| DE4344433B4 (en) | Registration system and method for motorway tolls using an electronic vignette | |
| EP1088286B1 (en) | Roadside control device for a toll apparatus installed in a motor vehicle | |
| DE102004013807B4 (en) | Electronic toll system for traffic routes and method of operation thereof | |
| DE69831096T2 (en) | METHOD FOR AUTOMATICALLY CHARGING TOLLS FOR VEHICLES | |
| EP0802509B1 (en) | Automatic road use charging method | |
| EP0752688A2 (en) | Road distances identifying device | |
| AT507031B1 (en) | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR HOLDING TOLL | |
| EP1101201B1 (en) | Method and system for monitoring the proper operation of a debiting device | |
| EP1449174B1 (en) | Detection system for surface areas for detecting vehicles with a gps | |
| EP1630747A2 (en) | Toll collection system and method | |
| EP1192600A1 (en) | Flexible charge collection system | |
| DE102005058033A1 (en) | Vehicle usage authorization verification method, involves exchanging information about presence of authorization between two vehicles, and displaying presence of authorization with vehicle identification on output unit of other vehicle | |
| DE102005027765A1 (en) | Method for updating software in a vehicle device of an electronic toll collection system and toll system for carrying out the method | |
| CH695585A5 (en) | Method and apparatus for automatic toll collection. | |
| DE10015069A1 (en) | Electronic road toll collection system has arrangement for transferring payments, especially debit arrangement for pre-paid chip card, conventional vehicle-to-vehicle communications device | |
| EP1475752A2 (en) | Electronic toll collection system and method | |
| EP1943627A1 (en) | Tollgate detection device and a tollgate detection method | |
| DE4322188C1 (en) | Arrangement for the exchange of data between moving objects and base stations | |
| WO2007073748A1 (en) | System and method for determining the tolls for road sections and/or regions which are subject to a toll | |
| EP1203354B2 (en) | Method for automatically charging tolls and device therefor | |
| EP1657683A2 (en) | Method and system for detecting a vehicle | |
| DE10258653A1 (en) | Arrangement for calculation of tolls accrued by a vehicle travelling within a road network, whereby use of short-range vehicle to vehicle communications technology reduces the cost of an associated data network implementation | |
| EP1170702B1 (en) | Device and method for charging usage fees | |
| DE102004033124A1 (en) | Navigation and congestion charging system for road vehicle being driven through city streets has mobile telephone onboard vehicle noting which cell it is in and sending out position signal |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT CH DE GB LI SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT CH DE GB LI SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20000726 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20011116 |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT CH DE GB LI SE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: SCINTILLA AG, DIREKTION Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59710013 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20030612 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20030807 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20040210 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20130122 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20140124 Year of fee payment: 18 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20140325 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20140122 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20140116 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20140116 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 59710013 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 239952 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20150116 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150801 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150131 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150116 |