EP0482687A1 - Concentrated, liquid, pourable composition - Google Patents
Concentrated, liquid, pourable composition Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0482687A1 EP0482687A1 EP91202510A EP91202510A EP0482687A1 EP 0482687 A1 EP0482687 A1 EP 0482687A1 EP 91202510 A EP91202510 A EP 91202510A EP 91202510 A EP91202510 A EP 91202510A EP 0482687 A1 EP0482687 A1 EP 0482687A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- composition
- weight
- salt
- internal olefin
- sulphonates
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 44
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 10
- JRZJOMJEPLMPRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N olefin Natural products CCCCCCCC=C JRZJOMJEPLMPRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 22
- 239000002736 nonionic surfactant Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 150000001336 alkenes Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 239000003945 anionic surfactant Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 150000007530 organic bases Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 229920001223 polyethylene glycol Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 229920001451 polypropylene glycol Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 239000002202 Polyethylene glycol Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 150000001340 alkali metals Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 150000003863 ammonium salts Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- BDHFUVZGWQCTTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N sulfonic acid Chemical compound OS(=O)=O BDHFUVZGWQCTTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylene glycol Chemical compound OCCO LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propylene glycol Chemical compound CC(O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylene oxide Chemical compound C1CO1 IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Butanol Chemical compound CCCCO LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- AMQJEAYHLZJPGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Pentanol Chemical compound CCCCCO AMQJEAYHLZJPGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- GOOHAUXETOMSMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propylene oxide Chemical compound CC1CO1 GOOHAUXETOMSMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000001346 alkyl aryl ethers Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- -1 carboxylate salt Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- ZSIAUFGUXNUGDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexan-1-ol Chemical compound CCCCCCO ZSIAUFGUXNUGDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- ZXEKIIBDNHEJCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N isobutanol Chemical compound CC(C)CO ZXEKIIBDNHEJCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- DUFKCOQISQKSAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Polypropylene glycol (m w 1,200-3,000) Chemical compound CC(O)COC(C)CO DUFKCOQISQKSAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- DKGAVHZHDRPRBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tert-Butanol Chemical compound CC(C)(C)O DKGAVHZHDRPRBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000001931 aliphatic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- JXLHNMVSKXFWAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N azane;7-fluoro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole-4-sulfonic acid Chemical compound N.OS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(F)C2=NON=C12 JXLHNMVSKXFWAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000000837 carbohydrate group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethylene glycol Chemical compound OCCOCCO MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- BDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-1-ol Chemical compound CCCO BDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims 1
- GLDOVTGHNKAZLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecan-1-ol Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCO GLDOVTGHNKAZLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 238000006386 neutralization reaction Methods 0.000 description 13
- 230000007062 hydrolysis Effects 0.000 description 12
- 238000006460 hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 12
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 9
- AKEJUJNQAAGONA-UHFFFAOYSA-N sulfur trioxide Chemical compound O=S(=O)=O AKEJUJNQAAGONA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- GGQQNYXPYWCUHG-RMTFUQJTSA-N (3e,6e)-deca-3,6-diene Chemical compound CCC\C=C\C\C=C\CC GGQQNYXPYWCUHG-RMTFUQJTSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000007795 chemical reaction product Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000003599 detergent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 3
- RAHZWNYVWXNFOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulphur dioxide Chemical compound O=S=O RAHZWNYVWXNFOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 125000000129 anionic group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 239000007844 bleaching agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 2
- GNTDGMZSJNCJKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N divanadium pentaoxide Chemical compound O=[V](=O)O[V](=O)=O GNTDGMZSJNCJKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011552 falling film Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910001220 stainless steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010935 stainless steel Substances 0.000 description 2
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O Ammonium Chemical compound [NH4+] QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 1
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 1
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 1
- ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Potassium Chemical compound [K] ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfur Chemical compound [S] NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005864 Sulphur Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012190 activator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000032683 aging Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000002091 cationic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000012459 cleaning agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910017053 inorganic salt Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229960004592 isopropanol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002304 perfume Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011591 potassium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004064 recycling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009991 scouring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002453 shampoo Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000344 soap Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002689 soil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010269 sulphur dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004291 sulphur dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D3/00—Other compounding ingredients of detergent compositions covered in group C11D1/00
- C11D3/16—Organic compounds
- C11D3/20—Organic compounds containing oxygen
- C11D3/2003—Alcohols; Phenols
- C11D3/2006—Monohydric alcohols
- C11D3/201—Monohydric alcohols linear
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/02—Anionic compounds
- C11D1/12—Sulfonic acids or sulfuric acid esters; Salts thereof
- C11D1/14—Sulfonic acids or sulfuric acid esters; Salts thereof derived from aliphatic hydrocarbons or mono-alcohols
- C11D1/143—Sulfonic acid esters
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/02—Anionic compounds
- C11D1/37—Mixtures of compounds all of which are anionic
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/66—Non-ionic compounds
- C11D1/83—Mixtures of non-ionic with anionic compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D3/00—Other compounding ingredients of detergent compositions covered in group C11D1/00
- C11D3/16—Organic compounds
- C11D3/20—Organic compounds containing oxygen
- C11D3/2003—Alcohols; Phenols
- C11D3/2006—Monohydric alcohols
- C11D3/2017—Monohydric alcohols branched
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D3/00—Other compounding ingredients of detergent compositions covered in group C11D1/00
- C11D3/16—Organic compounds
- C11D3/20—Organic compounds containing oxygen
- C11D3/2003—Alcohols; Phenols
- C11D3/2041—Dihydric alcohols
- C11D3/2044—Dihydric alcohols linear
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/02—Anionic compounds
- C11D1/04—Carboxylic acids or salts thereof
- C11D1/06—Ether- or thioether carboxylic acids
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/02—Anionic compounds
- C11D1/12—Sulfonic acids or sulfuric acid esters; Salts thereof
- C11D1/22—Sulfonic acids or sulfuric acid esters; Salts thereof derived from aromatic compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/66—Non-ionic compounds
- C11D1/662—Carbohydrates or derivatives
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/66—Non-ionic compounds
- C11D1/72—Ethers of polyoxyalkylene glycols
Definitions
- the invention relates to a concentrated, liquid, pourable composition
- a concentrated, liquid, pourable composition comprising an alkali or earth alkali metal or ammonium salt or a salt of an organic base of an internal olefin sulphonic acid, having 8 to 26 carbon atoms.
- a detergent composition comprising an alkali or earth alkali metal or ammonium salt or a salt of an organic base of an internal olefin sulphonic acid, having from 8 to 26 carbon atoms, and containing at least 25% by weight of beta-hydroxysulphonate, calculated on the total amount of sulphonate.
- compositions with 50 to 90% by weight of beta-hydroxysulphonate are used.
- compositions may contain other surfactants of anionic, nonionic, amphoteric or cationic type and depending upon the formulations to be used the compositions may contain builders, sequestring agents, bleaching agents, bleach activators, greyness-preventing agents, soil release polymers, foam control agents, fluorescent whiteners, enzymes and perfumes.
- the compositions are thus suitable for a number of applications such as solid and liquid laundry detergents, dishwash detergents, cleaning agents, liquid soaps, shampoos and liquid scouring agents.
- the invention relates to a concentrated liquid, pourable composition
- a concentrated liquid, pourable composition comprising:
- inventive compositions are easily storageable, handlable and transportable. Furthermore, they may be easily spray-dried or converted into less concentrated compositions.
- the internal olefin sulphonate contains at least 25% by weight of beta-hydroxy sulphonate, preferably at least 50%, more preferably more than 70% by weight of beta-hydroxy sulphonate.
- Preferred internal olefin sulphonic acids contain from 13 to 24 carbon atoms.
- the sulphonic acids may be present in the form of their salts with sodium, potassium, ammonium or an organic base.
- the internal olefin sulphonates are generally prepared by reacting in a film reactor an internal olefin having from 8 to 26 carbon atoms with a sulphonating agent, in a mol ratio of sulphonating agent to internal olefin of 1.3 to 0.9, preferably 1.15 to 0.95, while cooling the reactor with a cooling means having a temperature not exceeding 35 °C and allowing the reaction product of the sulphonating step to neutralize and hydrolyze.
- the internal olefins used as starting material are those having 8 to 26 carbon atoms, preferably 13 to 24 carbon atoms.
- Examples of the internal olefins are those having the general formula: wherein each of R1, R2, R3 and R4 independently are linear or branched alkyl groups or hydrogen and the total carbon number of R1, R2, R3 and R4 is from 6 to 24, and wherein at least one of R1 and R2 and one of R3 and R4 is an alkyl group.
- the neutralization/hydrolysis step is carried out directly after the sulphonating step. An ageing step is consequently avoided or minimized.
- the sulphonation may be carried out batchwise, semi-continuously or continuously, preferably continuously.
- the neutralization/hydrolysis is preferably carried out continuously and at a temperature of 20 to 50 °C, preferably 30 to 45 °C.
- Hydrolysis is preferably carried out continuously and at temperatures of 140-190 °C.
- aqueous base For the neutralization/hydrolysis an aqueous base is generally used. To prepare concentrated products, the amount of water is regulated accordingly.
- Component c) may be included in the composition at the same time when water is added.
- This third component is a lower alcohol, a nonionic surfactant, a polyethylene glycol, a polypropylene glycol, a salt-tolerant anionic surfactant or a mixture thereof.
- lower alcohols examples include methanol, ethanol, propanol, iso-propanol, butanol, iso-butanol, tert.butanol, a pentanol or a hexanol, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, a linear or branched C1 to C6 mono-alkylether of mono- or di-ethylene glycol, a linear or branched C1 to C6 mono-alkylether of mono- or di-propylene glycol, or a mixture thereof.
- nonionic surfactants are C7 to C18-alcohols that are alkoxylated with ethylene oxide and/or propylene oxide with a minimum degree of alkoxylation of 2.
- nonionic surfactants are C6 to C12-alkylphenols, alkoxylated with ethylene oxide and/or propylene oxide with a minimum degree of alkoxylation of 2.
- nonionic surfactants are hydrophilic C8 to C18-alkyl polyglycosides with 1 to 4 carbohydrate units.
- Polyethylene glycols may have a molecular weight from 300 to 5000, preferably from 800 to 4000.
- Polypropylene glycols may have a molecular weight from 250 to 4000, preferably from 400 to 2500.
- salt-tolerant anionic surfactants are a C8 to C18-alcoholalkoxy carboxylate salt with a degree of alkoxylation of 1 to 10, or C6 to C10 aliphatic or aromatic sulphonates.
- a preferred composition according to the invention comprises from 60 to 90% by weight of component a), from 8 to 38% by weight of water and from 2 to 32% by weight of component c).
- composition according to the invention may comprise some impurities, such as unreacted olefin and inorganic salt.
- impurities such as unreacted olefin and inorganic salt.
- the amounts of them generally do not exceed about 5% by weight each, calculated on the internal olefin sulphonate.
- the sulphur trioxide was prepared by burning sulphur in dry air followed by conversion of the sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide over a vanadium pentoxide catalyst at about 450 °C.
- the reactor was cooled by flowing water of a temperature of 8 to 11 °C along the outside of the stainless steel reactor tube.
- the internal olefin mixture (either A, or B or C) flowed along the inner part of the reactor wall as a flowing film in downward direction and was allowed to react cocurrently with the sulphur trioxide, which was introduced at the same time in the top of the reactor, diluted with air. The reaction proceeded continuously.
- the reaction mixture coming out of the falling film sulphonation reactor was conducted into a continuous neutralization loop, provided with a combined pump/high sheer mixer and two heat exchangers, and having a volume of about 26 litres; in that continuous neutralization loop the reaction mixture coming from the sulphonation reactor was subjected to neutralization/hydrolysis at 30-45 °C by, at the same time, continuously introducing into the loop streams of i) a concentrated (50% by weight) aqueous sodium hydroxide solution, ii) water, and iii) water plus nonionic surfactant and intimately mixing these streams by means of the combined pump/high sheer mixer and recycling in the neutralization loop.
- the recycle rate in the loop was about 20 times greater than the intake rate of the reaction mixture coming from the film reactor.
- the average residence time of the neutralization/hydrolysis mixture in the continuous neutralization loop was dependent on the precise composition of a particular product and of the initial olefin feed rate, and amounted to 40-55 min.
- the intake rate of the concentrated aqueous sodium hydroxide stream was adjusted on the basis of alkalinity measurements in the end-product (i.e. after the continuous hydrolysis step), which was aimed to be slightly basic.
- the amounts of water (total) and nonionic surfactant were calculated on the basis of the desired composition.
- the anionic active matter concentration was actually measured in the end-product (i.e. after the continuous hydrolysis step) during the production.
- the product mixture exited continuously into a continuous laminar tubular hydrolysis reactor that was heated externally with oil having a temperature of 170-190 °C, the reactor being provided with a preheater section heated with steam at 6 bar, a cooler, and a constant pressure valve; the volume of the hydrolysis reactor was about 40 litres from which the average residence time for each specific product could be estimated.
- the product flowing out of the constant pressure valve was analysed and, if necessary, adjustments were made in, for instance, the SO3/olefin ratio, the feed rate of concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, water, etc. on the basis of these analyses. After these adjustments sufficient time was allowed to obtain representative samples which were then collected and analyzed.
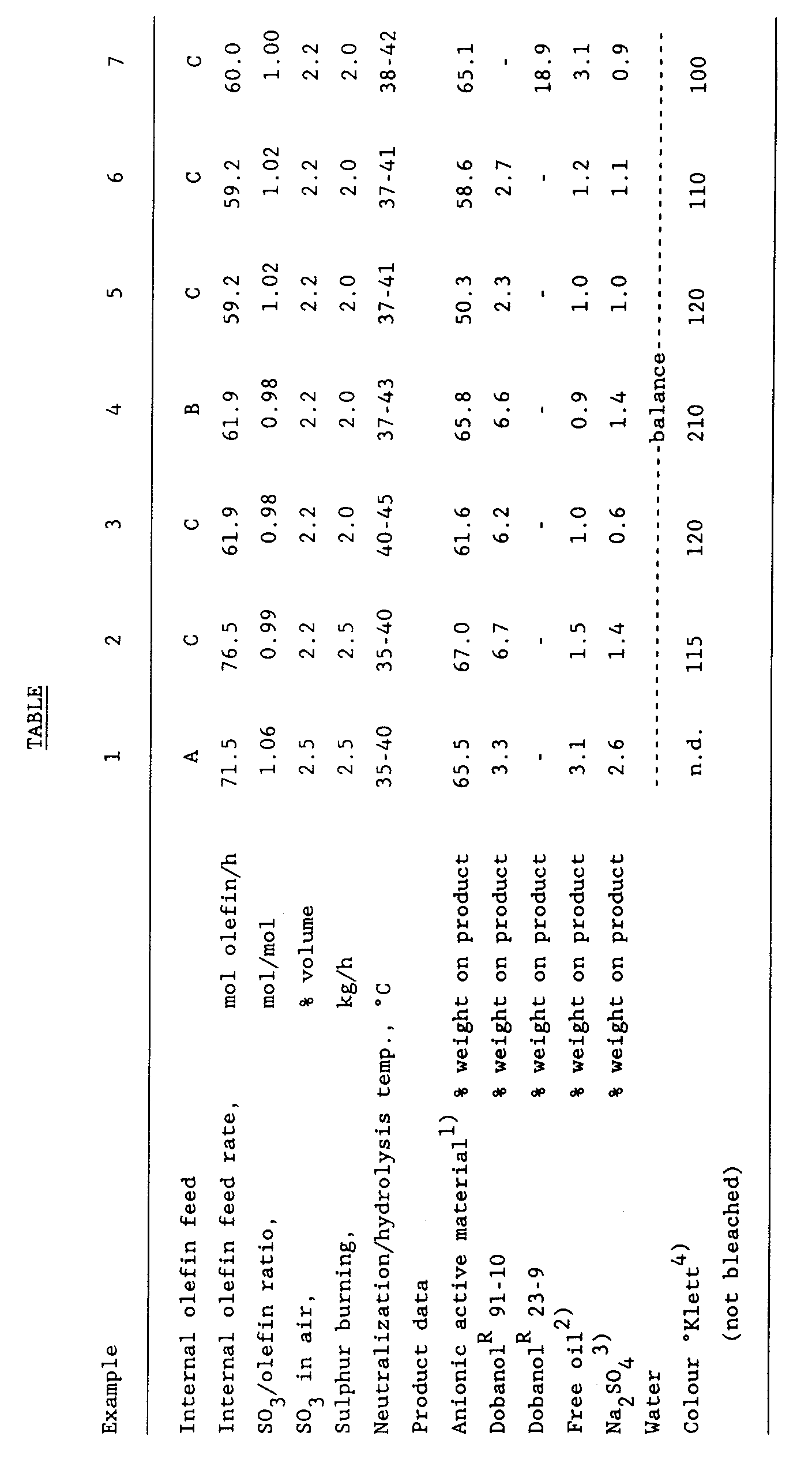
- the specific reaction conditions and analytical data of the products are given in the Table.
- compositions given in the Table are all liquid and pourable at 20 °C and can be pumped at that temperature, whilst this holds also for the materials during production in the continuous neutralization loop and the continuous hydrolysis reactor. Reducing during production the amount of nonionic surfactant in Examples 1 and 7 to zero leads to products that can not be pumped through the neutralization/hydrolysis reactor even in spite of the higher temperature in the neutralization loop.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Emergency Medicine (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
- Detergent Compositions (AREA)
Abstract
- a) from 50 to 95% by weight of an alkali or earth alkali metal or ammonium salt or a salt of an organic base of an internal olefin sulphonic acid, having from 8 to 26 carbon atoms, these internal olefin sulphonates having at least 25% by weight of beta-hydroxy sulphonates;
- b) from 4 to 49% by weight of water; and
- c) from 1 to 46% by weight of a lower alcohol, a nonionic surfactant, a polyethylene glycol, a polypropylene glycol, a salt-tolerant anionic surfactant, or a mixture thereof.
Description
- The invention relates to a concentrated, liquid, pourable composition comprising an alkali or earth alkali metal or ammonium salt or a salt of an organic base of an internal olefin sulphonic acid, having 8 to 26 carbon atoms.
- In the European patent application No. 89203337 has been described a detergent composition comprising an alkali or earth alkali metal or ammonium salt or a salt of an organic base of an internal olefin sulphonic acid, having from 8 to 26 carbon atoms, and containing at least 25% by weight of beta-hydroxysulphonate, calculated on the total amount of sulphonate. Especially compositions with 50 to 90% by weight of beta-hydroxysulphonate are used.
- There is further described that the compositions may contain other surfactants of anionic, nonionic, amphoteric or cationic type and depending upon the formulations to be used the compositions may contain builders, sequestring agents, bleaching agents, bleach activators, greyness-preventing agents, soil release polymers, foam control agents, fluorescent whiteners, enzymes and perfumes. The compositions are thus suitable for a number of applications such as solid and liquid laundry detergents, dishwash detergents, cleaning agents, liquid soaps, shampoos and liquid scouring agents.
- There have now been found concentrated, liquid and pourable compositions which have advantages over the compositions, disclosed in European patent application No. 89203337.
- The invention relates to a concentrated liquid, pourable composition comprising:
- a) from 50 to 95% by weight of an alkali or earth alkali metal or ammonium salt or a salt of an organic base of an internal olefin sulphonic acid, having from 8 to 26 carbon atoms, these internal olefin sulphonates having at least 25% by weight of beta-hydroxy sulphonates;
- b) from 4 to 49% by weight of water; and
- c) from 1 to 46% by weight of a lower alcohol, a nonionic surfactant, a polyethylene glycol, a polypropylene glycol, a salt-tolerant anionic surfactant, or a mixture thereof.
- The inventive compositions are easily storageable, handlable and transportable. Furthermore, they may be easily spray-dried or converted into less concentrated compositions.
- Component a), the internal olefin sulphonate, contains at least 25% by weight of beta-hydroxy sulphonate, preferably at least 50%, more preferably more than 70% by weight of beta-hydroxy sulphonate. Preferred internal olefin sulphonic acids contain from 13 to 24 carbon atoms. The sulphonic acids may be present in the form of their salts with sodium, potassium, ammonium or an organic base.
- The internal olefin sulphonates, containing beta-hydroxy sulphonates, are generally prepared by reacting in a film reactor an internal olefin having from 8 to 26 carbon atoms with a sulphonating agent, in a mol ratio of sulphonating agent to internal olefin of 1.3 to 0.9, preferably 1.15 to 0.95, while cooling the reactor with a cooling means having a temperature not exceeding 35 °C and allowing the reaction product of the sulphonating step to neutralize and hydrolyze.
- The internal olefins used as starting material are those having 8 to 26 carbon atoms, preferably 13 to 24 carbon atoms. Examples of the internal olefins are those having the general formula:
wherein each of R₁, R₂, R₃ and R₄ independently are linear or branched alkyl groups or hydrogen and the total carbon number of R₁, R₂, R₃ and R₄ is from 6 to 24, and wherein at least one of R₁ and R₂ and one of R₃ and R₄ is an alkyl group. - In the process for preparing internal olefin sulphonates the neutralization/hydrolysis step is carried out directly after the sulphonating step. An ageing step is consequently avoided or minimized.
- The sulphonation may be carried out batchwise, semi-continuously or continuously, preferably continuously.
- The neutralization/hydrolysis is preferably carried out continuously and at a temperature of 20 to 50 °C, preferably 30 to 45 °C. Hydrolysis is preferably carried out continuously and at temperatures of 140-190 °C.
- For the neutralization/hydrolysis an aqueous base is generally used. To prepare concentrated products, the amount of water is regulated accordingly.
- Component c) may be included in the composition at the same time when water is added. This third component is a lower alcohol, a nonionic surfactant, a polyethylene glycol, a polypropylene glycol, a salt-tolerant anionic surfactant or a mixture thereof.
- Examples of lower alcohols are methanol, ethanol, propanol, iso-propanol, butanol, iso-butanol, tert.butanol, a pentanol or a hexanol, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, a linear or branched C₁ to C₆ mono-alkylether of mono- or di-ethylene glycol, a linear or branched C₁ to C₆ mono-alkylether of mono- or di-propylene glycol, or a mixture thereof.
- Examples of nonionic surfactants are C₇ to C₁₈-alcohols that are alkoxylated with ethylene oxide and/or propylene oxide with a minimum degree of alkoxylation of 2.
- Further examples of nonionic surfactants are C₆ to C₁₂-alkylphenols, alkoxylated with ethylene oxide and/or propylene oxide with a minimum degree of alkoxylation of 2.
- Other examples of nonionic surfactants are hydrophilic C₈ to C₁₈-alkyl polyglycosides with 1 to 4 carbohydrate units.
- Polyethylene glycols may have a molecular weight from 300 to 5000, preferably from 800 to 4000.
- Polypropylene glycols may have a molecular weight from 250 to 4000, preferably from 400 to 2500.
- Examples of salt-tolerant anionic surfactants are a C₈ to C₁₈-alcoholalkoxy carboxylate salt with a degree of alkoxylation of 1 to 10, or C₆ to C₁₀ aliphatic or aromatic sulphonates.
- A preferred composition according to the invention comprises from 60 to 90% by weight of component a), from 8 to 38% by weight of water and from 2 to 32% by weight of component c).
- The composition according to the invention may comprise some impurities, such as unreacted olefin and inorganic salt. The amounts of them generally do not exceed about 5% by weight each, calculated on the internal olefin sulphonate.
- In a falling film reactor of stainless steel, having a length of 6 m and a diameter of 2,54 cm, were introduced internal olefins of different compositions:
- A. a mixture of internal olefins in the range of from C₁₄ to C₂₀, average molecular weight 230 and a purity of 97%;
- B. a mixture of C₁₄ internal olefins and C₁₆ internal olefins, in a weight ratio of 1:2, average molecular weight 214 and a purity of more than 99%; and
- C. a mixture of C₁₄-, C₁₆- and C₁₈ internal olefins, in a weight ratio of 1:1:1, average molecular weight 222 and a purity of more than 99%.
- The sulphur trioxide was prepared by burning sulphur in dry air followed by conversion of the sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide over a vanadium pentoxide catalyst at about 450 °C.
- The reactor was cooled by flowing water of a temperature of 8 to 11 °C along the outside of the stainless steel reactor tube. The internal olefin mixture (either A, or B or C) flowed along the inner part of the reactor wall as a flowing film in downward direction and was allowed to react cocurrently with the sulphur trioxide, which was introduced at the same time in the top of the reactor, diluted with air. The reaction proceeded continuously.
- The reaction mixture coming out of the falling film sulphonation reactor was conducted into a continuous neutralization loop, provided with a combined pump/high sheer mixer and two heat exchangers, and having a volume of about 26 litres; in that continuous neutralization loop the reaction mixture coming from the sulphonation reactor was subjected to neutralization/hydrolysis at 30-45 °C by, at the same time, continuously introducing into the loop streams of i) a concentrated (50% by weight) aqueous sodium hydroxide solution, ii) water, and iii) water plus nonionic surfactant and intimately mixing these streams by means of the combined pump/high sheer mixer and recycling in the neutralization loop. The recycle rate in the loop was about 20 times greater than the intake rate of the reaction mixture coming from the film reactor. The average residence time of the neutralization/hydrolysis mixture in the continuous neutralization loop was dependent on the precise composition of a particular product and of the initial olefin feed rate, and amounted to 40-55 min. The intake rate of the concentrated aqueous sodium hydroxide stream was adjusted on the basis of alkalinity measurements in the end-product (i.e. after the continuous hydrolysis step), which was aimed to be slightly basic. The amounts of water (total) and nonionic surfactant were calculated on the basis of the desired composition. The anionic active matter concentration was actually measured in the end-product (i.e. after the continuous hydrolysis step) during the production.
- From the continuous neutralization loop the product mixture exited continuously into a continuous laminar tubular hydrolysis reactor that was heated externally with oil having a temperature of 170-190 °C, the reactor being provided with a preheater section heated with steam at 6 bar, a cooler, and a constant pressure valve; the volume of the hydrolysis reactor was about 40 litres from which the average residence time for each specific product could be estimated. The product flowing out of the constant pressure valve was analysed and, if necessary, adjustments were made in, for instance, the SO₃/olefin ratio, the feed rate of concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, water, etc. on the basis of these analyses. After these adjustments sufficient time was allowed to obtain representative samples which were then collected and analyzed. The specific reaction conditions and analytical data of the products are given in the Table.
- It is further observed that the compositions given in the Table are all liquid and pourable at 20 °C and can be pumped at that temperature, whilst this holds also for the materials during production in the continuous neutralization loop and the continuous hydrolysis reactor. Reducing during production the amount of nonionic surfactant in Examples 1 and 7 to zero leads to products that can not be pumped through the neutralization/hydrolysis reactor even in spite of the higher temperature in the neutralization loop.
Claims (11)
- A concentrated, liquid, pourable composition comprising:a) from 50 to 95% by weight of an alkali or earth alkali metal or ammonium salt or a salt of an organic base of an internal olefin sulphonic acid, having from 8 to 26 carbon atoms, these internal olefin sulphonates having at least 25% by weight of beta-hydroxy sulphonates;b) from 4 to 49% by weight of water; andc) from 1 to 46% by weight of a lower alcohol, a nonionic surfactant, a polyethylene glycol, a polypropylene glycol, a salt-tolerant anionic surfactant, or a mixture thereof.
- A composition as claimed in claim 1 wherein the internal olefin sulphonates comprise at least 50% by weight of beta-hydroxy sulphonates.
- A composition as claimed in claim 1 or 2 wherein the internal olefin sulphonates comprise at least 70% by weight of beta-hydroxy sulphonates.
- A composition as claimed in one or more of the claims 1-3, wherein the internal olefin sulphonic acid moiety comprises from 13 to 24 carbon atoms.
- A composition as claimed in one or more of the claims 1-4 wherein the lower alcohol is methanol, ethanol, propanol, isopropanol, butanol, iso-butanol, tert.butanol, pentanol or hexanol, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, a linear or branched C₁ to C₆ mono-alkylether of mono- or di-ethylene glycol, a linear or branched C₁ to C₆ mono-alkylether of mono- or di-propylene glycol, or a mixture thereof.
- A composition as claimed in one or more of the claims 1-4 wherein the nonionic surfactant is a C₇ to C₁₈-alcohol that is alkoxylated with ethylene oxide and/or propylene oxide with a minimum degree of alkoxylation of 2.
- A composition as claimed in one or more of the claims 1-4 wherein the nonionic surfactant comprises a C₆ to C₁₂-alkylphenol, alkoxylated with ethylene oxide and/or propylene oxide with a minimum degree of alkoxylation of 2.
- A composition as claimed in one or more of the claims 1-4 wherein the nonionic surfactant comprises a hydrophilic C₈ to C₁₈-alkylpolyglycoside with 1 to 4 carbohydrate units.
- A composition as claimed in one or more of the claims 1-4 comprising polyethylene glycol with a molecular weight from 300 to 5000, preferably from 800 to 4000.
- A composition as claimed in one or more of the claims 1-4 comprising polypropylene glycol with a molecular weight from 250 to 4000, preferably from 400 to 2500.
- A composition as claimed in one or more of the claims 1-4 wherein the salt-tolerant anionic surfactant comprises a C₈ to C₁₈-alcoholalkoxy carboxylate salt with a degree of alkoxylation of 1 to 10, or a C₆ to C₁₀ aliphatic or aromatic sulphonate.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| GB909023366A GB9023366D0 (en) | 1990-10-26 | 1990-10-26 | Concentrated,liquid,pourable composition |
| GB9023366 | 1990-10-26 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0482687A1 true EP0482687A1 (en) | 1992-04-29 |
| EP0482687B1 EP0482687B1 (en) | 1996-06-12 |
Family
ID=10684426
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP91202510A Expired - Lifetime EP0482687B1 (en) | 1990-10-26 | 1991-09-26 | Concentrated, liquid, pourable composition |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0482687B1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE69120205T2 (en) |
| GB (1) | GB9023366D0 (en) |
Cited By (24)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2186783A2 (en) | 2010-01-27 | 2010-05-19 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Process for the preparation of olefins |
| EP2186784A2 (en) | 2010-01-27 | 2010-05-19 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Process for the preparation and recovery of olefins |
| EP2186785A2 (en) | 2010-01-27 | 2010-05-19 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Process for the separation of olefins from paraffins |
| EP2261298A1 (en) | 2009-06-10 | 2010-12-15 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Method for enhanced hydrocarbon recovery |
| WO2012163852A1 (en) | 2011-05-27 | 2012-12-06 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Composition and method for enhanced hydrocarbon recovery |
| US8403044B2 (en) | 2009-05-05 | 2013-03-26 | Stepan Company | Sulfonated internal olefin surfactant for enhanced oil recovery |
| WO2013167646A1 (en) | 2012-05-09 | 2013-11-14 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Method for enhanced hydrocarbon recovery |
| JP2014076988A (en) * | 2012-09-20 | 2014-05-01 | Kao Corp | Internal olefin sulfonate composition and detergent composition containing the same |
| JP2014167106A (en) * | 2013-02-01 | 2014-09-11 | Kao Corp | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| JP2014167107A (en) * | 2013-02-01 | 2014-09-11 | Kao Corp | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| WO2014137974A1 (en) * | 2013-03-06 | 2014-09-12 | Shell Oil Company | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| WO2015141699A1 (en) * | 2014-03-19 | 2015-09-24 | L'oreal | Foaming composition containing internal olefin sulfonates and one foam-enhancing agent or foam booster |
| JP2015178466A (en) * | 2014-03-19 | 2015-10-08 | ロレアル | Foamable composition containing an internal olefin sulfonate and one polymer suspending agent |
| EP2952567A4 (en) * | 2013-02-01 | 2016-09-07 | Kao Corp | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| EP3162872A1 (en) * | 2016-06-24 | 2017-05-03 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Internal olefin sulfonate composition and use thereof in enhanced oil recovery |
| JP2017214568A (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2017-12-07 | 花王株式会社 | Liquid detergent composition for fiber products |
| JP2017214567A (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2017-12-07 | 花王株式会社 | Detergent composition for fiber |
| WO2018030328A1 (en) * | 2016-08-09 | 2018-02-15 | 花王株式会社 | Surfactant composition |
| WO2018123942A1 (en) * | 2016-12-26 | 2018-07-05 | 花王株式会社 | Method for processing fiber product |
| CN109154129A (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2019-01-04 | 花王株式会社 | The clean method of clothing |
| CN109196081A (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2019-01-11 | 花王株式会社 | Fibre cleanser compositions |
| EP3467082A4 (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2019-12-18 | Kao Corporation | LIQUID DETERGENT COMPOSITION FOR TEXTILE PRODUCTS |
| US10815164B2 (en) | 2015-10-19 | 2020-10-27 | Shell Oil Company | Process for producing styrene |
| US11584881B2 (en) * | 2017-06-30 | 2023-02-21 | Dow Global Technologies Llc | Low-temperature stabilized surfactant blend for enhanced oil recovery |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4309317A (en) * | 1979-02-20 | 1982-01-05 | Lion Corporation | Clear aqueous olefin sulfonate solution |
| US4715991A (en) * | 1985-04-26 | 1987-12-29 | Lion Corporation | Aqueous high concentration surfactant slurry containing an olefin sulfonate |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB8817293D0 (en) * | 1988-07-20 | 1988-08-24 | Shell Int Research | Process for preparation of internal olefin sulphonates |
-
1990
- 1990-10-26 GB GB909023366A patent/GB9023366D0/en active Pending
-
1991
- 1991-09-26 DE DE1991620205 patent/DE69120205T2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1991-09-26 EP EP91202510A patent/EP0482687B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4309317A (en) * | 1979-02-20 | 1982-01-05 | Lion Corporation | Clear aqueous olefin sulfonate solution |
| US4715991A (en) * | 1985-04-26 | 1987-12-29 | Lion Corporation | Aqueous high concentration surfactant slurry containing an olefin sulfonate |
Cited By (53)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8403044B2 (en) | 2009-05-05 | 2013-03-26 | Stepan Company | Sulfonated internal olefin surfactant for enhanced oil recovery |
| EP2261298A1 (en) | 2009-06-10 | 2010-12-15 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Method for enhanced hydrocarbon recovery |
| EP2186783A2 (en) | 2010-01-27 | 2010-05-19 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Process for the preparation of olefins |
| EP2186784A2 (en) | 2010-01-27 | 2010-05-19 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Process for the preparation and recovery of olefins |
| EP2186785A2 (en) | 2010-01-27 | 2010-05-19 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Process for the separation of olefins from paraffins |
| WO2012163852A1 (en) | 2011-05-27 | 2012-12-06 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Composition and method for enhanced hydrocarbon recovery |
| US10000688B2 (en) | 2011-05-27 | 2018-06-19 | Shell Oil Company | Composition and method for enhanced hydrocarbon recovery |
| WO2013167646A1 (en) | 2012-05-09 | 2013-11-14 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Method for enhanced hydrocarbon recovery |
| US20150129227A1 (en) * | 2012-05-09 | 2015-05-14 | Julian Richard BARNES | Method for enhanced hydrocarbon recovery |
| US10030194B2 (en) * | 2012-05-09 | 2018-07-24 | Shell Oil Company | Method for enhanced hydrocarbon recovery |
| JP2014076988A (en) * | 2012-09-20 | 2014-05-01 | Kao Corp | Internal olefin sulfonate composition and detergent composition containing the same |
| EP3741834A1 (en) * | 2013-02-01 | 2020-11-25 | Kao Corporation | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| US9861566B2 (en) | 2013-02-01 | 2018-01-09 | Kao Corporation | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| CN104955933A (en) * | 2013-02-01 | 2015-09-30 | 花王株式会社 | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| JP2014167107A (en) * | 2013-02-01 | 2014-09-11 | Kao Corp | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| US10328008B2 (en) | 2013-02-01 | 2019-06-25 | Kao Corporation | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| JP2014167106A (en) * | 2013-02-01 | 2014-09-11 | Kao Corp | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| EP2952566A4 (en) * | 2013-02-01 | 2016-09-07 | Kao Corp | OLEFIN SULFONATE COMPOSITION |
| EP2952567A4 (en) * | 2013-02-01 | 2016-09-07 | Kao Corp | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| EP2952568A4 (en) * | 2013-02-01 | 2016-10-26 | Kao Corp | OLEFIN SULFONATE COMPOSITION |
| US9861567B2 (en) | 2013-02-01 | 2018-01-09 | Kao Corporation | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| US9789045B2 (en) | 2013-02-01 | 2017-10-17 | Kao Corporation | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| CN105026514A (en) * | 2013-03-06 | 2015-11-04 | 国际壳牌研究有限公司 | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| US10184076B2 (en) | 2013-03-06 | 2019-01-22 | Shell Oil Company | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| WO2014137974A1 (en) * | 2013-03-06 | 2014-09-12 | Shell Oil Company | Internal olefin sulfonate composition |
| WO2015141699A1 (en) * | 2014-03-19 | 2015-09-24 | L'oreal | Foaming composition containing internal olefin sulfonates and one foam-enhancing agent or foam booster |
| JP2015178467A (en) * | 2014-03-19 | 2015-10-08 | ロレアル | Foamable composition containing an internal olefin sulfonate and one foam enhancer or foam enhancer |
| JP2015178466A (en) * | 2014-03-19 | 2015-10-08 | ロレアル | Foamable composition containing an internal olefin sulfonate and one polymer suspending agent |
| US10815164B2 (en) | 2015-10-19 | 2020-10-27 | Shell Oil Company | Process for producing styrene |
| US10947479B2 (en) | 2016-05-31 | 2021-03-16 | Kao Corporation | Method for washing clothing |
| RU2747642C2 (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2021-05-11 | Као Корпорейшн | Detergent composition for textile products |
| CN109196081A (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2019-01-11 | 花王株式会社 | Fibre cleanser compositions |
| US11248195B2 (en) | 2016-05-31 | 2022-02-15 | Kao Corporation | Liquid detergent composition for textile products comprising an internal olefin sulfonate/organic solvent mixture |
| US11124743B2 (en) | 2016-05-31 | 2021-09-21 | Kao Corporation | Liquid detergent composition for textile products |
| JP2017214568A (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2017-12-07 | 花王株式会社 | Liquid detergent composition for fiber products |
| EP3467082A4 (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2019-12-18 | Kao Corporation | LIQUID DETERGENT COMPOSITION FOR TEXTILE PRODUCTS |
| EP3467080A4 (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2019-12-18 | Kao Corporation | DETERGENT COMPOSITION FOR TEXTILE PRODUCT |
| EP3467083A4 (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2019-12-18 | Kao Corporation | LIQUID CLEANING AGENT COMPOSITION FOR FIBER ARTICLE |
| EP3467196A4 (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2019-12-18 | Kao Corporation | METHOD OF CLEANING CLOTHES |
| EP3467081A4 (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2019-12-18 | Kao Corporation | CLEANING AGENT COMPOSITION FOR FIBERS |
| CN109154129B (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2021-09-14 | 花王株式会社 | Method for cleaning clothes |
| JP2017214567A (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2017-12-07 | 花王株式会社 | Detergent composition for fiber |
| US11053456B2 (en) | 2016-05-31 | 2021-07-06 | Kao Corporation | Detergent composition for textile products |
| CN109154129A (en) * | 2016-05-31 | 2019-01-04 | 花王株式会社 | The clean method of clothing |
| EP3162872A1 (en) * | 2016-06-24 | 2017-05-03 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | Internal olefin sulfonate composition and use thereof in enhanced oil recovery |
| WO2018030328A1 (en) * | 2016-08-09 | 2018-02-15 | 花王株式会社 | Surfactant composition |
| US10941369B2 (en) | 2016-08-09 | 2021-03-09 | Kao Corporation | Surfactant composition |
| RU2742374C2 (en) * | 2016-08-09 | 2021-02-05 | Као Корпорейшн | Surfactant composition |
| AU2017310702B2 (en) * | 2016-08-09 | 2021-09-09 | Kao Corporation | Surfactant composition |
| JPWO2018030328A1 (en) * | 2016-08-09 | 2019-06-13 | 花王株式会社 | Surfactant composition |
| JP7051685B2 (en) | 2016-08-09 | 2022-04-11 | 花王株式会社 | Surfactant composition |
| WO2018123942A1 (en) * | 2016-12-26 | 2018-07-05 | 花王株式会社 | Method for processing fiber product |
| US11584881B2 (en) * | 2017-06-30 | 2023-02-21 | Dow Global Technologies Llc | Low-temperature stabilized surfactant blend for enhanced oil recovery |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE69120205D1 (en) | 1996-07-18 |
| DE69120205T2 (en) | 1997-02-06 |
| EP0482687B1 (en) | 1996-06-12 |
| GB9023366D0 (en) | 1990-12-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0482687B1 (en) | Concentrated, liquid, pourable composition | |
| US5922670A (en) | Dimeric alcohol-bis and trimeric alcohol-tris-sulphates and ether sulphates thereof | |
| EP0351928B1 (en) | A process for the preparation of internal olefin sulphonates | |
| US5691299A (en) | Anionic detergent mixtures | |
| US5382677A (en) | Process for the production of highly concentrated pastes of α-sulfofatty acid alkyl ester alkali metal salts | |
| CA1072976A (en) | Sulphonation process and apparatus | |
| US5117032A (en) | Process for making glycerol ether sulfates | |
| US5446188A (en) | Process for the production of highly concentrated fatty alcohol sulfate pastes | |
| US3957671A (en) | Acid mix compositions containing benzoic acid | |
| US3376333A (en) | Sulfuric acid esters of linear secondary alcohol ethoxylates and salts thereof and method of producing same | |
| US5514368A (en) | Process for the production of hydrophilicized triglycerides | |
| US3492239A (en) | Light-colored sulfonation products | |
| US5847229A (en) | Process for the production of end-capped nonionic surfactants | |
| JP7649380B2 (en) | Method for producing internal olefin, method for producing internal olefin sulfonate, and method for low-temperature stabilization | |
| US5847183A (en) | Fatty alcohol (ether) sulfates with improved low-temperature behavior | |
| US3337601A (en) | Process for the production of alcohol sulfates | |
| EP0399581A2 (en) | Surface active compositions | |
| EP0431653A2 (en) | Liquid surface active compositions | |
| JP4744120B2 (en) | Method for producing anionic surfactant composition | |
| JPH01317546A (en) | Ethoxylation or propoxylation catalyst | |
| US20080020962A1 (en) | Production of High Active to Super High Active Surfactants in a Vacuum Neutralizer | |
| EP0506308B1 (en) | Method for sulfonating acyloxybenzenes and neutralization of resulting product | |
| US4943393A (en) | Process for the manufacture of ester sulfonate pastes of low viscosity | |
| US4692551A (en) | Preparation of carboxypropylated non-ionic surfactants | |
| Roberts | Manufacture of anionic surfactants |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): DE FR GB IT NL |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19920818 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19941207 |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE FR GB IT NL |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 69120205 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19960718 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19970725 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19970827 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19970929 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19971010 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19980926 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19990401 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19980926 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19990531 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 19990401 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19990701 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20050926 |